Page 1

Copyright
This Product, Including Any Software And Documentation, May Not, In
Whole Or In Part, Be Copied, Photocopied, Translated Or Reduced To
Any Electronic Or Machine-Readable Form Without Prior Written Consent
From ASUSTek Computer Inc., Except For Copies Retained By The
Purchaser For Backup Purposes.
No Warranty Or Representation, Either Expressed Or Implied, Is Made
With Respect To This Documentation, Its Quality, Performance, Merchant
ability, Or Fitness For A Particular Purpose. As A Result, The Documenta
tion Is Licensed ''As Is," And The Licensee Will Assume The Entire Risk
As To Its Quality And Performance. This Work's Content Is Copyrighted
And Licensed To ASUSTek By Its Documentation Vendor And All Rights
Are Reserved. ASUSTek Reserves The Right To Revise This Work And
Any Accompanying Software And Documentation And To Make Changes
In The Content Without Obligation To Notify Any Person Or Organization
Of The Revision Or Change.
In No Event Will ASUSTek Be Liable For Direct, Indirect, Special, Inciden
tal, Or Consequential Damages Arising Out Of The Use Or Inability To
Use This Product Or Documentation Even If Advised Of The Possibility
Of Such Damages. In Particular, ASUSTek Shall Not Have Liability For
Any Hardware, Software, Or Data Stored Or Used With The Product,
Including The Costs Of Repairing, Replacing, Or Recovering Such
Hardware, Software Or Data.
Products Mentioned In This Manual Are Mentioned For Identification
Purposes Only. Product Names Appearing In This Manual May Or May
Not Be Registered Trademarks Or Copyrights Of Their Respective
Companies.
© Copyright 1995
User's Manual Rev 1.01
Related Mainboard: P/I-P55SP4 P.C.B. Rev 1.2 and up
Related BIOS: #401AO-0201 or up (# appears in upper left-hand
corner of screen at beginning of Power-On Boot-up)
Date: November 1995 ASUSTek Computer Inc.
Page 2

Table of Contents
Chapter 1: Feature Guide............................................1-1
The P/I-P55SP3AV Package.................................................................1-2
Bundled Software......................................................................... 1-3
Main Features........................................................................................1-4
Static Electricity Precautions...............................................................1-5
Mainboard Layout................................................................................ 1-6
Using Your Mainboard
Hardware Settings..........................................................................1-8
The System Configuration Record
System IRQs.................................................................................. 1-11
BIOS-Supported Enhanced ГОЕ Features.................................1-12
Other IDE Devices..................................................................1-13
Faster Data Transfer...............................................................1-13
Power Conservation.....................................................................1-13
Audio Features..............................................................................1-13
On-Board Video Display..............................................................1-14
SCSI BIOS Firmware & The SC-200 Controller Card
........................................................................
.............................................
...............
1-8
1-10
1-14
Chapter 2: Upgrade Guide
Installing Expansion Cards..................................................................2-2
Installation Procedure....................................................................2-2
Assigning System IRQs for Expansion Cards.............................2-4
Upgrading System Memory................................................................2-6
Configuring System Memory........................................................2-7
Installing SIMMs.............................................................................2-8
Updating the Flash BIOS....................................................................2-10
.........................................
2-1
Chapter 3: Software Guide.........................................3-1
Award BIOS Setup................................................................................3-1
Standard CMOS Setup
BIOS Features Setup..................................................................... 3-8
Chipset Features Setup.................................................................3-12
Power Management Setup...........................................................3-14
PCI/PNP & Onboard I/O Setup
Load BIOS Defaults
Load Setup Defaults
Setting Supervisor & User Passwords
...................................................................
..................................................
......................................................................
.....................................................................
.......................................
3-3
3-18
3-23
3-24
3-25
Page 3

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
IDE HDD Auto Detection
Save And Exit Setup
Exit Without Saving......................................................................3-28
NCR SCSI BIOS & Drivers.................................................................3-29
Flash Memory Writer Utility.............................................................3-30
Chapter 4: Technical Summary
Jumper Setting Summary.....................................................................4-1
Level 2 Cache Size: JP6 & JP8
PS/2 Mouse Port Selector: JP12..................................................... 4-2
Onboard Audio Selector: JP13.......................................................4-2
CPU Internal Clock Ext. Mulitple Selector: JP14 & JP15.... 4-3
Voltage Regulator Output Selector: JP19 & JP21
Flash EPROM Boot Block Write Selector: JP24
CPU External Clock Speed Selector: JP26& JP27
UART2/IR Selection: JP35 & JP36..................................................4-7
SMC I/O Selector: JP37....................................................................4-7
Level 2 Cache Options..........................................................................4-8
External Connections..........................................................................4-10
Port & Controller Cables..............................................................4-12
Connecting A Power Supply.......................................................4-13
The PCI-SC200 SCSI Interface Card
Setting Up the PCI-SC200
SCSI ID Numbers
..........................................................................
............................................................
.....................................................................
................................
.........................................................
........................
...........................
........................
.................................................
............................................................
3-26
3-28
4-1
4-1
4-4
4-5
4-6
4-15
4-15
4-17
IV
Page 4

Feature Guide
This manual explains how to use this system mainboard and in
stall upgrades. It has an overview of the design and features of the
board and provides useful information if you want to change the
configuration of the board, or a system it is installed in.
How The Manual Is Organized
This manual is divided into four chapters:
Feature Guide - an overview of the board features
Upgrade Guide - upgrades for the board or system
Software Guide - the Setup Utility and other software & firmware
Technical Summary - technical reference
The manual assumes that your mainboard is already installed in
a computer system, so we've organized the contents to reflect this.
The first chapter introduces the mainboard's features and shows
where things are on the board in case you want to install an upgrade.
Chapter 2 explains how to install upgrades.
Chapter 3 explains the Award BIOS Setup Utility, SCSI BIOS and
the Flash Memory Writer BIOS update utility.
Chapter 4 lists settings and specifications and has instructions for
adding cache memory and the optional SCSI interface card.
1-1
Page 5

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
Since we are assuming that your mainboard is already installed
in a system, it was most likely set up by your system dealer accord
ing to the design specifications of your computer. This could mean
that your mainboard's current settings are not the same as the de
faults shown in this manual. Your system manual may have addi
tional information on how the mainboard should be set up.
If you want to change the existing configuration, consult all of
your system documentation. Also be certain that opening up and
working on the system yourself won't violate your system warranty.
Most system vendors do allow you to open the system to install ex
pansion cards or additional peripheral equipment.
This manual provides all the information you need to upgrade
or change the setup of the board. If you don't feel confident of your
ability to work on the computer yourself, ask your dealer or a quali
fied technician to do it for you.
The P/I-P55SP3AV Package
Your mainboard package comes with the following:
• The P/I-P55SP3AV Mainboard & User's Manual
• AV689 Audio/VGA port card (optional VGA-only card)
• 1 IDE Device & 1 Floppy Disk Drive ribbon cable
• External Parallel port with cable
• External Serial port with cable
• External Game port with cable
1-2
• Support, Driver and bundled software
• Optional External PS/2 mouse port with cable
• Optional External Infrared Module
Page 6

Feature Guide
If you purchased your mainboard as an upgrade, make sure
all of the items listed are present and undamaged. If you dis
cover a problem, contact your vendor immediately.
If the mainboard came installed in a system, you should have
received the support floppy disks and this manual. In this case, the
drivers needed to support your particular system configuration may
already be installed on the system hard disk drive. If not, you should
install the ones you need.
Bundled Software
This mainboard comes with a variety of software, including Sup
port software to update the BIOS, SIS PCI Enhanced IDE device driv
ers for multiple operating systems and SIS VGA display drivers and
utilities. In addition, there is software for the ESS audio hardware.
The PCI IDE driver disk has 'readme' files that explain how to install
and use the drivers.
The software includes:
Support:
• PFlash Flash Memory Writer — updates the system BIOS with
a new BIOS file.
• SIS 5513 PCI ГОЕ Drivers for various operating systems (for on
board PCI IDE).
Video & Audio:
• SIS Video Display Drivers & Utilities with printable User's
*
Manual file
• ESS Audio Package with User's Manual
1-3
Page 7

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Main Features
The P/I-P55SP3AV has many performance and system features
integrated onto the mainboard, including the following:
• Supports 75, 90,100,120,133,150 or 166MHz P54C/CS/CQS
Pentium CPUs in a ZIP (Zero Insertion Force) Socket 7.
• SIS 551X chipset
• Uses 72-pin SIMM DRAM modules of 1MB to 128MB in mul
tiple configurations up to 512MB, with support for both Fast
Page Mode and Extended Data Output (EDO) SIMMs.
• Write-back "Level 2" external static RAM cache with two cache
options, SRAM DIP sockets and a cache module socket. Sock
eted SRAM allows installation of 256KB, 512KB or 1MB of
Asynchronous 15ns SRAM.
With a cache module in the cache socket, the SRAM DIP sock
ets are disabled. Cache module options include 256KB or
512KB Pipelined SRAM.
• On-board SIS 6205 Super VGA video display chip supports
mulitple resolutions and color depths using system DRAM.
• On-board ESS 1788 AudioDrive audio chip supports 16-bit
soimd card features.
• AV689 Audio/Display port card with audio jacks, volume con
trol, Wave Table daughter-card connector and CD-ROM drive
audio connectors. Standard 15-pin VGA display card port.
• Four 16-bit ISA, three 32-bit PCI expansion slots, with one
shared PCI/ISA slot position. The PCI slots are Bus Master
capable. Additional connector for the AV689 Audio/Display
port card.
1-4
Page 8

Feature Guide
• BIOS support for Power management, "Plug and Play" fea
tures and Enhanced IDE, including support for up to four IDE
hard disks or other IDE devices and hard disks larger than
528MB, up to 8.4GB. Auto detection of installed ГОЕ hard disk
drives via BIOS Setup Utility.
• On-board "Multi-I/O' with: 2 serial ports - 16550 Fast UART
compatible - the second UART can support an IrDA-compatible infrared port module via the 5-pin onboard connector, in
stead of the COM2 port; 1 parallel port with EPP and ECP ca
pabilities; one standard Game port; floppy disk drive controller
with 2.88MB support.
• On-board PCI Bus Master IDE controller with two connectors
supports four IDE devices in two channels, faster data trans
fer rates and supports Enhanced IDE devices such as Tape
Backup and CD-ROM drives. The controller supports PIO
Modes 3 and 4 at a maximum transfer rate of ITMB/second
and Bus Master ГОЕ DMA Mode 2 at maximum ITMB/second.
• Optional IrDA-compatible infrared port module and external
PS/2 port/cable.
• On-board NCR SCSI BIOS firmware supports the optional PCI
SC-200 SCSI controller card.
Static Electricity Precautions
Under the right conditions, static electricity will build up. If you
touch the mainboard or other sensitive components, the buHd-up will
discharge into the components and circuitry. Computer components
are sensitive to damage from static electric discharge. They can be
damaged or destroyed if the discharge is powerful enough. Static
build-up is most likely to occur in dryer and cooler conditions, but
it is always important to be cautious.
1-5
Page 9

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
To protect the mainboard and other components against damage
from static electric discharge, you should follow some basic precau
tions whenever you handle them:
1. Use a grounding wrist strap. The strap will have an 'alligator'
'dip at the end of a shielded wire lead. Clip it to a grounded
object. Any static electricity will then harmlessly discharge
through the strap. Put on and connect the strap before you
handle the components.
2. Use an anti-static pad. Put any components on the pad when
ever you work on them outside the computer. If you don't have
a pad, put the components on the anti-static bag they came in.
Both the wrist strap and pad are inexpensive and are generally
available from computer supply companies.
Mainboard Layout
The diagram on the next page shows the location of important
components on the mainboard. There are other small diagrams later
in the manual that point out the location of the topic being explained.
1. Pentium in ZIP Socket?
2. L2 Cache module socket & chip sockets
3. External Feature connectors & Battery
4. ISA expansion slots
5. VGA Feature (L), AV689 Port Card (R) connectors
6. PCI expansion slots
7. I/O, Floppy & IDE connectors
1-6
8. SIMM memory banks
9. PS/2 Mouse connector (or port option)
10. Keyboard connector
11. Power Supply connector
Page 10
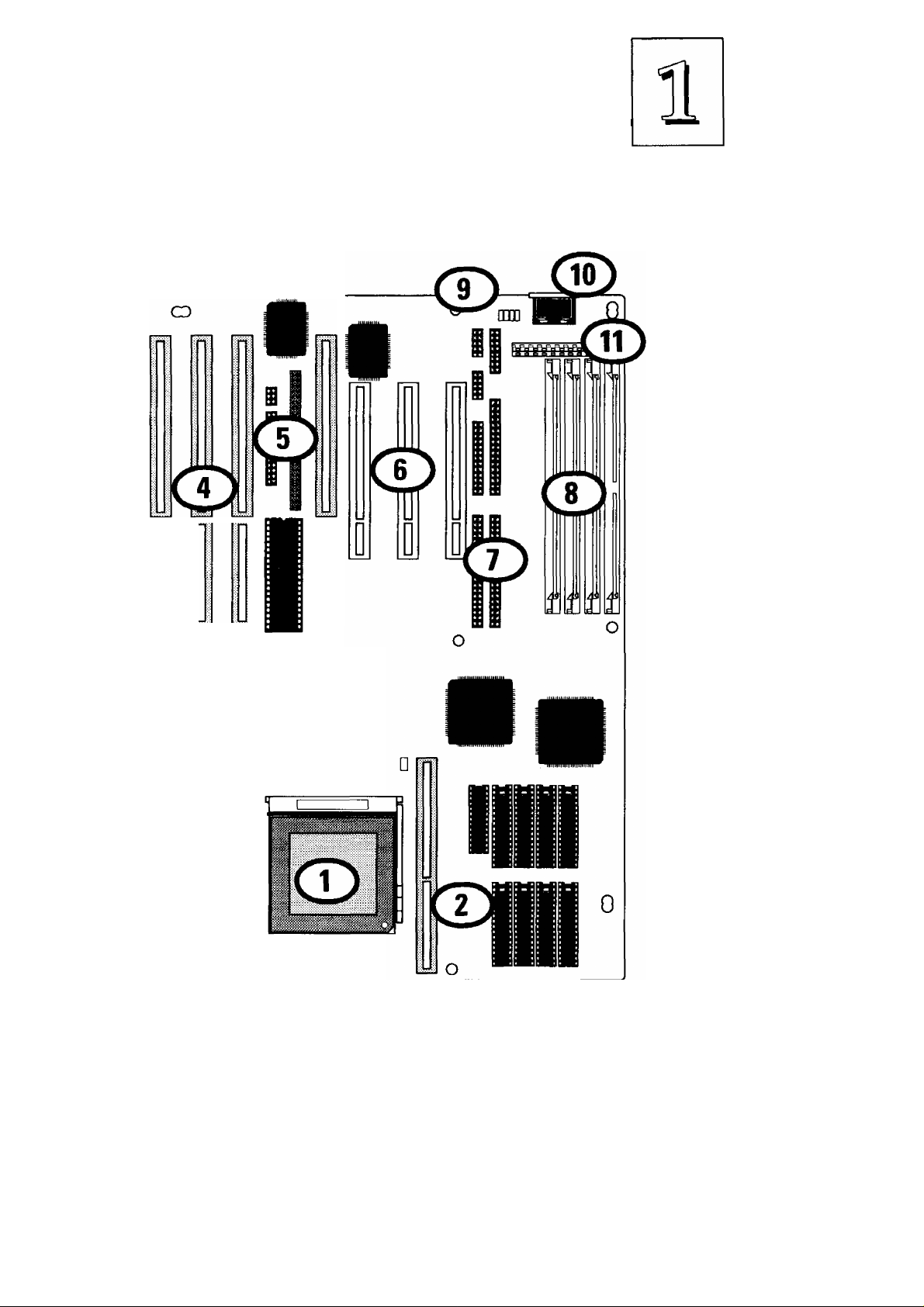
P/I-P55SP3AV Layout
Feature Guide
o
■ ■
™
.........
WKm
1-7
Page 11
P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Using Your Mainboard
In addition to the operating instructions in your system manual,
there are a few additional things specific to the mainboard you will
need to know. These have to do with the hardware settings on the
mainboard and the system configuration record.
Hardware Settings
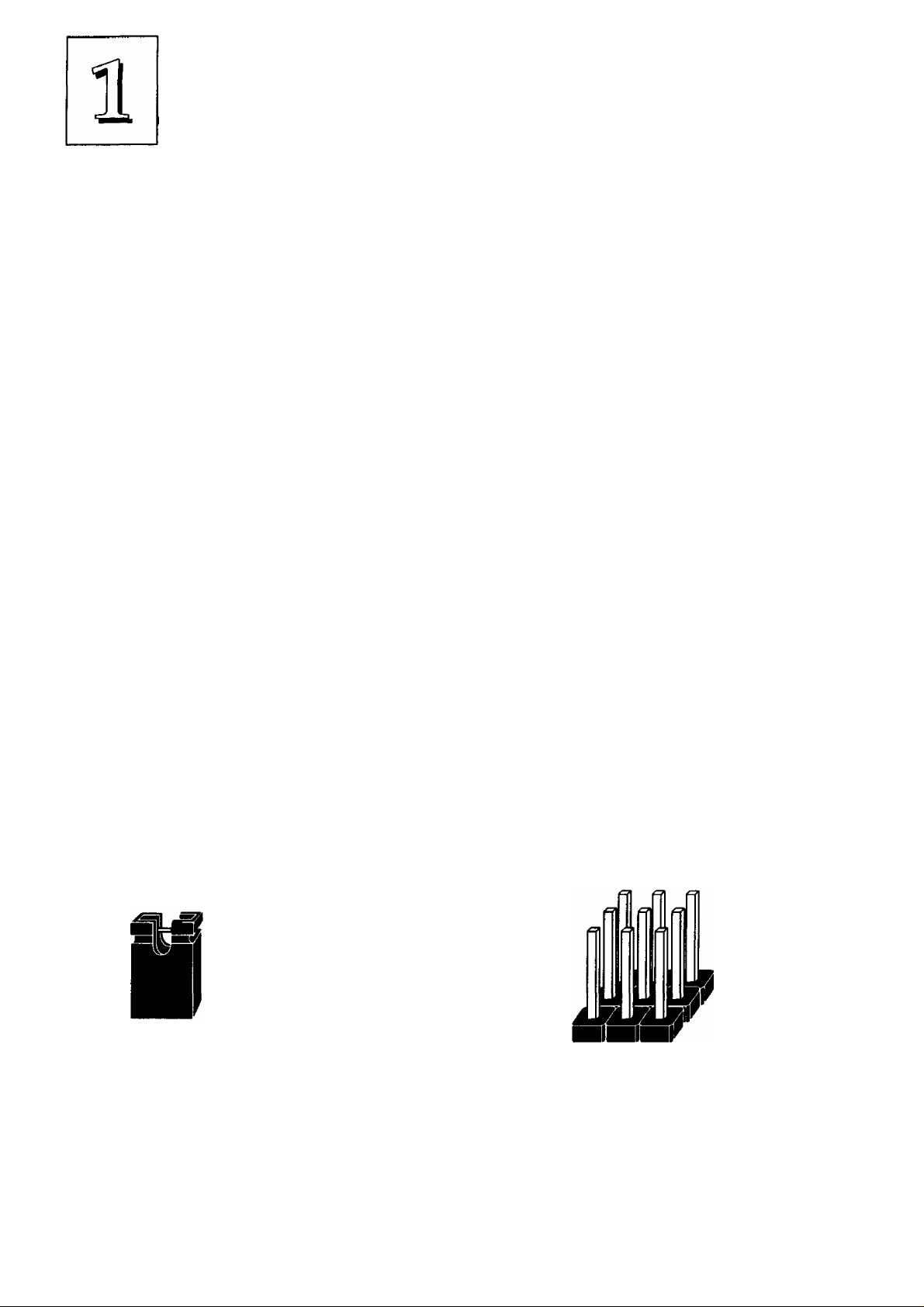
There are a number of hardware settings on the board. They
specify configuration options for various features. The settings are
made using something called a 'jumper'. A jumper is a set of two or
more metal pins in a plastic base attached to the mainboard. A plas
tic jumper 'cap' with a metal plate inside fits over two pins to create
an electrical contact between them. The contact establishes a hard
ware setting.
Some jumpers have two pins, others have three or more. The
jumpers are sometimes combined into sets called jumper 'blocks',
where all the jumpers in the block must be set together to establish a
hardware setting. The next figures show how this looks.
Jumpers and caps
1-8
Jumper cap 3-pin jumper 2-pin jumper Jumper block
Page 12

Feature Guide
Setting options for most jumpers are printed on the board in a
stylized bird's-eye view, with which pins to connect for each setting
marked by a bar connecting two pins. For example, if a jumper has
three pins, connecting, or 'shorting', the first and second pins creates
one setting and shorting the second and third pins creates another.
The same type of diagrams are used in this manual. The jumpers are
always shown from the scime point of view as shown in the whole-
board diagram in this chapter. The next figures show what the
manual diagrams look like and what they represent.
Jumper diagrams
Jumpers are shown like this
O O
Jumper caps like this Jumper settings like this
O O O
O 0-0
O 0-0
O 0-0
0-0 o
Jumpers in
a 'block'
Some jumpers are oriented
9
vertically; if the pin
4
position needs to be
o
shown. Pin 1 is marked.
1-9
Page 13

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
The System Configuration Record
All personal computers use a BIOS (Basic Input Output System)
as the basic software that tells the computer how to function. In or
der for the BIOS to function, there has to be a record of the computer's
hardware and configuration settings for it to refer to. This record is
created by using a software program that is permanently stored in
the BIOS ROM chip on the mainboard. The program is called the
Setup Utility.
The system configuration record the utility creates is also stored
on the mainboard. Unlike the utility program, the record is not re
corded permanently. The memory it gets stored in must be main
tained by battery power when the computer is turned off. If battery
support fails, the record will be lost and you will have to recreate it.
When you buy your computer, the system configuration record
will already be set. The settings will be optimized for your computer
hardware and may vary from the basic defaults. You should run the
Setup Utility when you first use your computer. Write down the set
tings. The Setup Utility is explained in Chapter 3.
Important:
In some circumstances it is possible the configuration record may
be corrupted or lost. If this happens, your computer will not work
properly the next time you turn it on. This is not a serious problem.
To fix it, run the Setup Utility and re-enter your configuration from
your written record. Many of the entries will be set automatically
using defaults. Check your record against the defaults and make any
changes needed. You can use the IDE HDD Auto Detection feature
to enter IDE hard disk information. When you restart the computer,
it should work normally.
1-10
Page 14

Feature Guide
System IRQs
In this manual you'll see something called an "IRQ" mentioned.
If you're not familiar with these, this is a short explanation of what
they are and why you may need to know about them if you upgrade
your system. If you are running Windows 95, your system should,
in principle, be able to deal with any IRQ requirements that occur in
the process of changing or upgrading your system configuration and
you will probably not need to concern yourself with them. Windows
3.x or other users, will need to be aware of IRQ use in the system
configuration.
An IRQ, or interrupt request, is the process whereby an input or
output device tells the CPU to temporarily interrupt whatever it is
doing and immediately process something from the source of the
interrupt. When finished the CPU goes back to what it was already
processing. This happens very quickly. There are 16 IRQs, IRQ 0
through IRQ 15. Devices that need an IRQ line to operate sometimes
must have the use of that line exclusively Some IRQs are already in
use by parts of your system. This is a design standard common to
IBM-compatible personal computer.
Some expansion cards require the use of an IRQ line, for example,
network interface cards and sound cards. When you install a card that
uses an IRQ, it probably will have a default IRQ setting that you
might need to change if that IRQ is already in use and cannot be
shared. There are different ways of setting an IRQ assignment in hard
ware, with jumpers being the most common.
"Plug and Play" expansion cards have their IRQ assigned by the
system under Windows 95, or, without Windows 95, can be config
ured using an ISA configuration utility.
There is some IRQ setup to do in the BIOS Setup utility. This is
explained in detail in Chapter 3.
1-11
Page 15

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
BIOS-Supported Enhanced IDE Features
The BIOS has several feature enhancements for IDE hard disk
drives and support for other IDE devices.
The original IDE implementation was limited to two hard disk
drives with relatively slower data transfer rates. While this solution
is simple and reliable, it has some limitations that have become more
significant as the performance level of other system components and
overall system performance have increased dramatically with the
advent of new microprocessor, expansion bus and operating system
technologies.
In response to these demands, the IDE specification has been
updated to increase its capabilities and provide improved perfor
mance. Together these are referred to as 'Enhanced IDE'. Enhanced
IDE features comprise the following:
• Support for IDE hard disk drives larger than the former 528MB
limit imposed by various technical factors. Both Large and LBA
modes are supported.
• Support for IDE devices other than hard disk drives, includ
ing IDE Tape Backup and CD-ROM drives.
• Support for two IDE channels with two devices per channel,
allowing the use of four IDE devices in one system.
• Support for faster data transfer rates, particularly with IDE
controllers that have a PCI local bus interface.
This mainboard supports the use of these new features. The fea
tures work with the on-board PCI EIDE controller which has two con
nectors built onto the board. With this controller you can use one or
both connectors to connect up to four IDE devices.
1-12
Page 16

Feature Guide
Other IDE Devices
Enhanced IDE allows the use of IDE devices other than hard
disks. Two devices such devices are Tape Backup and CD-ROM
drives. To use ГОЕ devices other than hard disks with this mainboard
you may need to install a device driver in your system software con
figuration. Under Windows 95, you may only need to use the stan
dard procedure to add a device to the system. Refer to the documen
tation that comes with any device you will install for instructions
about this and any other installation requirements.
Faster Data Transfer
Enhanced IDE includes a scheme to support a significant increase
in the rate of data transfer from the ГОЕ device to the rest of the sys
tem compared to the previous standard. One aspect of this scheme
is support for fast PIO timing modes. If you use both the on-board
controller and hard disks that support fast timing, you can increase
the data transfer rate significantly.
Power Conservation
This mainboard incorporates the power conservation technology,
which you can set up in the BIOS Setup Utility, where the Power
Management Setup section controls the board's power management
scheme. The power management features include hard disk and
video controls. For more information see the section on Power Man
agement Setup in Chapter 3.
Audio Features
This mainboard includes full 16-bit sound card capabilities and
comes with a suite of Windows audio utilities. Refer to the documen
tation that comes with the software for further information.
1-13
Page 17

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
There are external Speaker, Microphone and Line-in jacks as well
as the volume control in the mounting bracket of the AV689 audio/
display port card that comes with the mainboard. CD-ROM audio
and Wave Table daughter-card connectors are moxmted on the AV689.
The,ESS AudioDrive chip supports third-party Wave Table cards from
several vendors, including Turtle Beach and Creative Labs.
On-Board Video Display
The onboard SIS video display uses a either 1MB or 2MB of sys
tem DRAM as display memory to support multiple resolutions and
color depths. You set the display memory size from the ChipSet Fea
tures section of the BIOS Setup utility. See that section in Chapter 3
for more information. A standard 15-pin VGA port is mounted on the
AV689 audio/display port card that comes with the mainboard. The
port card plugs into the connector between ISA slots Slotl and Slot2.
An optional VGA port-only card is also available.
SCSI BIOS Firmware & The Optional SC-200 Controller Card
This mainboard has on-board NCR SCSI firmware recorded in the
BIOS flash ROM chip that supports the NCR 53C810 PCI Fast SCSI2 controller. There is an optional SCSI controller card, the SC-200 that
uses this firmware. The NCR SCSI controller is a full 32-bit PCI DMA
bus master and supports the ASPI and CAM standards.
You can connect a chain of up to seven devices to the SCSI inter
face. The SC-200 SCSI interface card provides both internal and ex
ternal connectors. There are details on this card and how to connect
SCSI devices to it at the end of Chapter 4.
Two floppy disks with support drivers come with the SC-200
card. There is detailed information about the drivers in "ReadMe"
files on the disks. There is more information about these disks in the
section on "SCSI BIOS & Drivers" in Chapter 3.
1-14
Page 18

Upgrade Guide
This section explains how to install options on your mainboard.
It covers the most likely and technically accessible upgrades you
might want to do, including adding expansion cards, increasing sys
tem memory and upgrading the BIOS.
Installing upgrades will either improve the performance of your
computer, or add some additional capabilities to it. You can install
upgrades yourself, or have your dealer or a qualified computer tech
nician do it for you.
It is also possible to increase the size of the Level 2 cache, but since
this is a much more technically demanding upgrade that you are both
less likely to undertake, and in most cases would probably require
at least partially disassembling your system, the technical reference
information about this is in Chapter 4. It is probably best to have a
qualified technician perform the upgrade for you if you want to up
grade the socketed cache.
2-1
Page 19

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
InstalUng Expansion Cards
There are many ISA and PCI expansion cards you can install in
your system to expand its capabilities. Any card you get will come
with instructions on how to configure and install it. For your refer
ence, we have included a brief decsription here of how to install a card
in your system case. This is followed by an explanation of some is
sues regarding the installation of expansion cards that use an IRQ.
If you are running Windows 95, which supports Tlug and Play'
configuration, the Windows 95 configuration process will handle the
assignment of available system resources during the installation pro
cess. Refer to your Windows 95 documentation for more information
about this. If you are running previous version of Windows, you will
need to configure any new expansion cards yourself.
Installation Procedure
Expansion cards often require pre-installation configuration and
sometimes post-installation software setup. Check your card docu
mentation for instructions on this. Once you have configured an ex
pansion card you want to install, the installation procedure is fairly
simple. Your system manual should have instructions for installing
expansion cards specific to the design of your system housing. The
procedure here covers the basics for your reference.
Before you start, always make sure the computer is turned off.
You should also make sure to carefully observe static electricity dis
charge precautions. You can damage your expansion card, the
mainboard, or both by not being careful about this.
The basic procedure for instaUing expansion cards is the same for
both ISA and PCI cards. Please note that the PCI Slot3 and ISA Slot
1 share the same mounting bracket position, so you can only use
one of these slots at a time.
2-2
Page 20
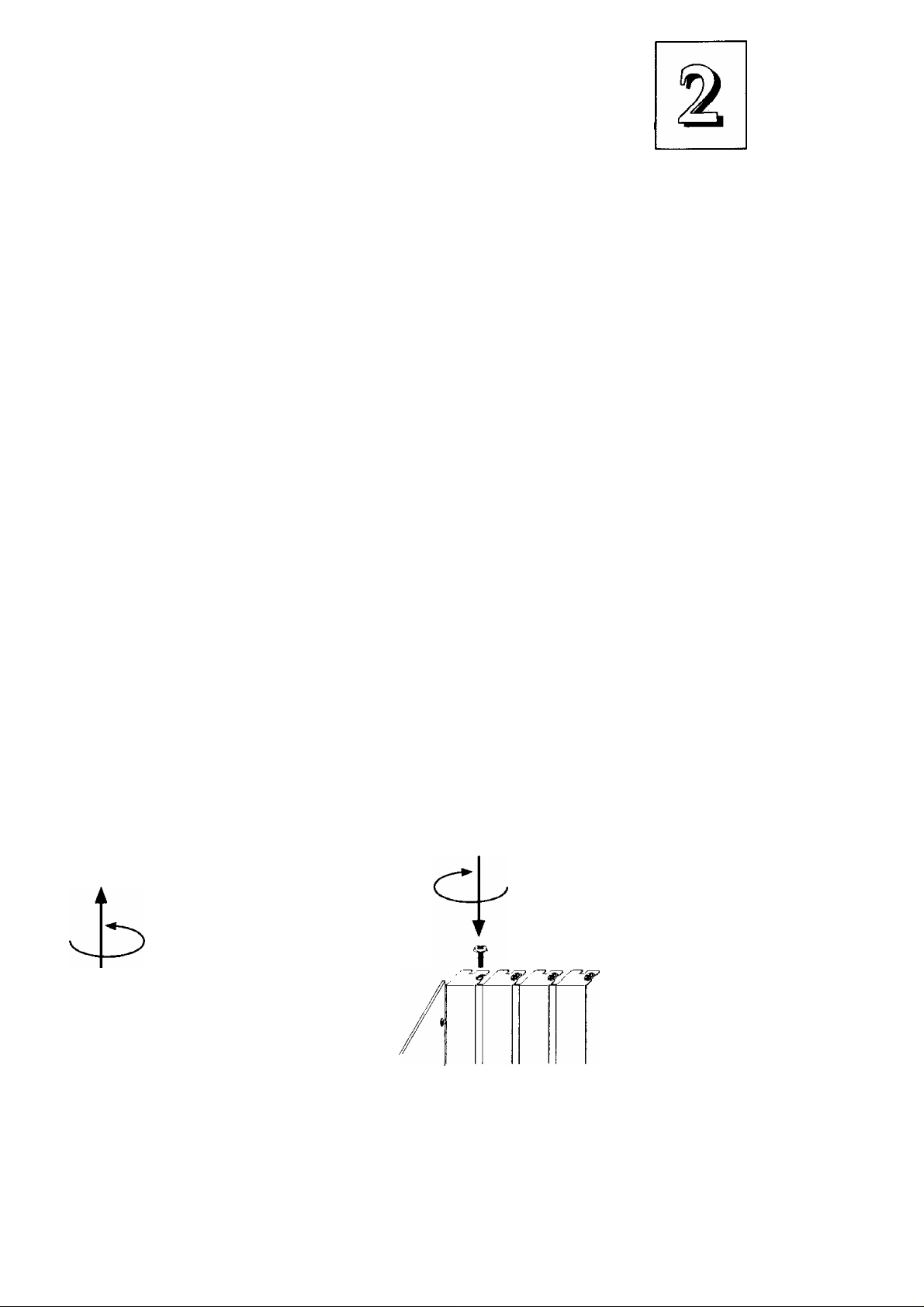
upgrade Guide
The basic procedure is as follows:
1. Open the system case to gain access to the expansion slots.
2. Remove the slot-cover corresponding to the slot you want plan
to use. Put the slot-cover retaining screw aside and store the
slot cover in case you need it later.
3. Remove the card from its protective packaging if you haven't
already.
4. Align the card's slot connectors to the slot. Keep the card at a
90° angle to the mainboard. Insert the card into the slot by
pressing it firmly downward. If there is a lot of resistance, make
sure the slot connectors are lined up correctly. PCI cards require
little pressure to insert. ISA cards may need a bit more force.
5. Attach the card's mounting bracket to the case using the slot
cover screw you put aside in Step 2.
6. Close the case, reconnect aU devices, turn on the computer and
check to see if the card is working properly, as well as do any
software set up required. If rurming Windows 95, follow the
configuration procedure.
Use the screw to
secure the card to
Remove the slot
retaining screw
& slot cover
the case
The component side of the card should face right (or
up) for an ISA card and left (or down) for a PCI card
2-3
Page 21

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Assigning System IRQs for Expansion Cards
Some expansion cards need to use an IRQ to operate. Generally
an IRQ must be exclusively assigned to one use. As mentioned in
Chapter 1, there are 16 IRQs available. In a normal system design,
some' of them are already in use. Expansion cards that need to use
an IRQ then draw from the unused group of System IRQs.
Both ISA and PCI expansion cards may need to use IRQs. Sys
tem IRQs are available to cards installed in the ISA expansion bus
first, and any remaining can be used by cards installed on the PCI bus.
Currently, there are two types of ISA cards. The original ISA expan
sion card design, now referred to as "Legacy" ISA cards, requires that
you configure the card hardware manually and then install it in any
available slot on the ISA bus. Under this scheme, you must ensure
that the installed cards do not conflict with each other by using the
same IRQ. This process requires careful manual system configuration
to avoid conflicts that prevent the system from working properly.
To address this problem, the Plug and Play specification was
developed to allow automatic system configuration whenever a Plug
and Play-compliant card is added to the system. For Plug and Play
(PNP) cards, IRQs are assigned automatcally from those available.
If the system has both Legacy and PNP ISA cards installed, IRQs
are assigned to PNP cards from the IRQs not already hardware as
signed to the Legacy cards. In this case, you can establish the system
confguration in one of two ways. If you have an ISA Configuration
Utility, you can use it to indicate which IRQs are in use by Legacy
cards. If you do not have an ICU program, you can use the "PCI/PNP
& Onboard I/O Setup" section of the BIOS Setup utility to indicate
which IRQs are being used by Legacy cards. Refer to Chapter 3 for
information on how to do this.
2-4
Page 22

upgrade Guide
Any PCI expansion cards that need to use an IRQ have one au
tomatically assigned from the IRQs remaining after Legacy and PNP
ISA cards have had theirs assigned. In the PCI bus design, the BIOS
automatically assigns an IRQ to a PCI slot that has a card installed
which requires an IRQ. When installing a PCI card, you need to set
something called the "INT" assignment. Since all the PCI slots on this
mainboard use "INTA#", you only need to make sure that any PCI
card you install is set to INT A.
Assigning DMA Channels For ISA Cards
Some ISA cards, both Legacy and PNP may also need to use a
DMA (Direct Memory Access) channel. DMA assignments for this
mainboard are handled the same way as the IRQ assignment process
described above. If you don't use an ICU program, you can select a
DMA channel in the "PCI/PNP & Onboard I/O Setup" section of
the BIOS Setup utility.
2-5
Page 23

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
Upgrading System Memory
This section explains how to install system memory. There are
instructions on how to configure and install memory and an expla
nation of the technical specifications required.
System DRAM is the main source of data for the CPU. Data re
mains stored in DRAM as long as the system is turned on, and is lost
when you turn it off. The Level 2 cache memory is Static RAM
(SRAM), which is faster than DRAM memory. When the CPU looks
for data, it first searches the cache. If the information is not there, the
search continues in the DRAM. With this design, the CPU looks in
the fastest source of data first, which lets it operate as fast as possible.
The DRAM subsystem uses memory chips permanently mounted
on small circuit boards to form "SIMMs"' (Single In-line Memory
Modules). The memory chips have a speed rating that is measured
in nanoseconds (ns). This mainboard requires either Fast Page Mode
(FPM) DRAM or Extended Data Output (EDO) DRAM with a speed
of at least 70ns.
This mainboard can use 72-pin SIMMs in four sizes from 1MB up
to 128MB (megabytes). Depending on the combination of modules
you use, you can install between 2MB and512MB. The 32-bit mod
ules used for this board come with memory chips on either one or
both sides of the module.
IMPORTANT: Do not use SIMM modules with more than 24 chips
per module with this mainboard. Modules with more than 24 chips
exceed the design specifications of the memory subsystem and will
cause unreliable operation. DO NOT use 32 or 36-chip modules with
this mainboard.
2-6
Page 24

upgrade Guide
Configuring System Memory
If you want to add system memory, you should use the configu
ration options and specifications shown in this section.
Memory Combinations
You can configure the system memory in a variety of ways, us
ing different combinations of SIMM modules. Using the 4 SIMM
sockets there are many configuration options.
Please note:
• Modules must be installed in pairs, in sequence, i.e. SIMM 1
& 2, SIMM 3 & 4, or all four sockets.
• Modules pairs must be the same size.
• Required Specifications:
Module Size:
Single-sided SIMMS: 1MB, 4MB, 16MB, 64MB
Double-sided SIMMS: 2MB, 8MB, 32MB, 128MB
DRAM Type: Fast Page Mode, Asymmetric or EDO (Extended
Data Output)
DRAM Speed: 70ns or faster for 50, 60 or 66MHz external
clock. EDO DRAM requires 60ns or faster for a 66MHz exter
nal clock setting.
RAS access time [Trac]: 60ns - 70ns
CAS access time [Tcac]: 10ns - 25ns
Parity: Either parity or non-parity
2-7
Page 25
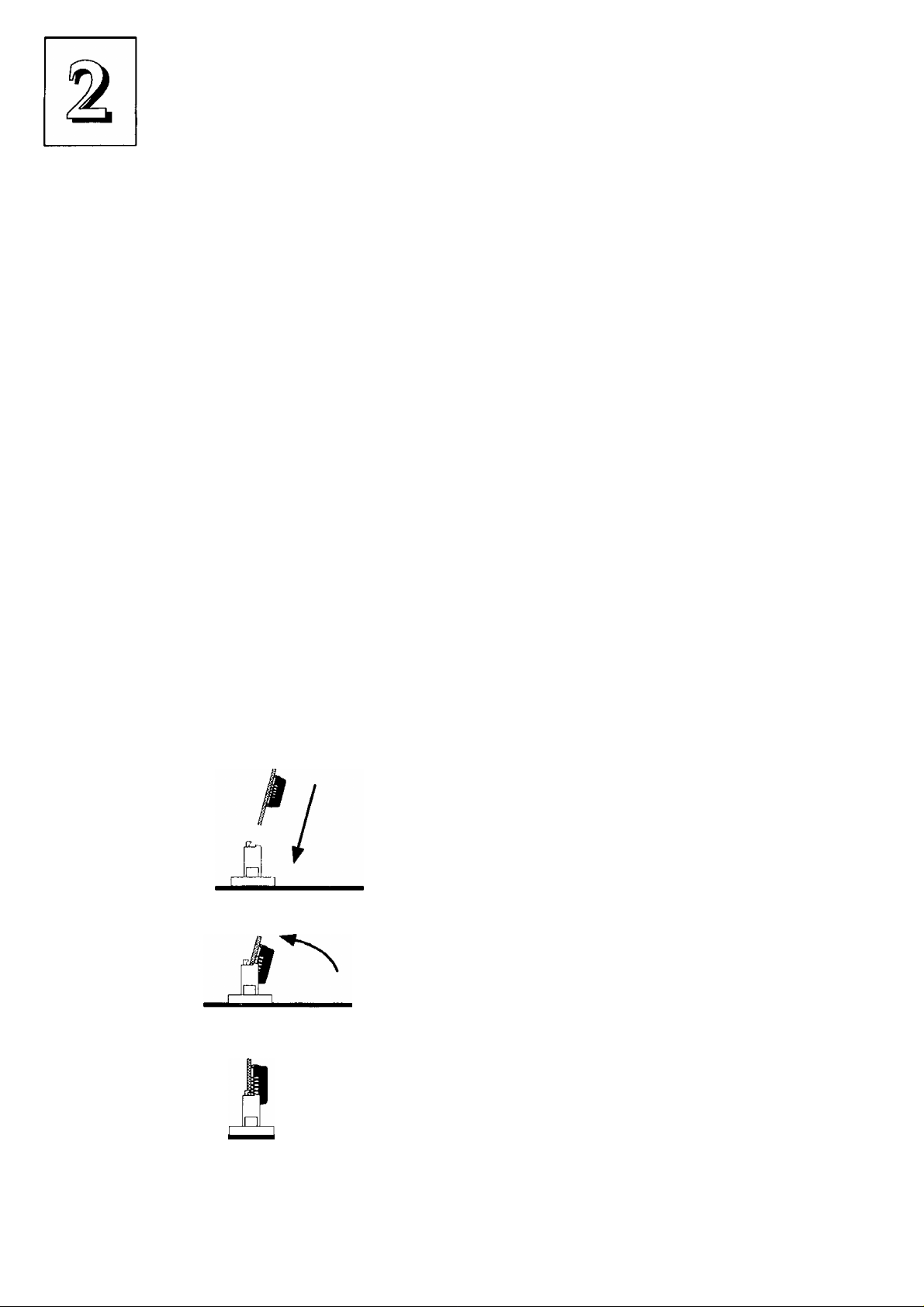
P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
Installing SIMMs
To install SIMMs follow these instructions:
1. The modules will only insert in a socket in one orientation. An
orientation cut-out will prevent you from inserting them the
wrong way See the figures at right.
2. Press the module edge connector into the socket at a moder
ate angle to the board. See the figures below.
3. Press the module forward onto the socket's vertical posts, so
that the alignment pins at the top of each post go into the cir
cular holes at each end of the module.
4. The module should click into place, as the retaining clips at
each end of the socket grip the module to secure it.
5. Repeat this procedure for each module you install.
Installing a Memory Module
Insert the SIMM
into the socket at
an angle.
Press it forward
onto the position
ing pins.
2-8
The retaining clips
should fit over the
edge and hold the
SIMM in place.
Page 26
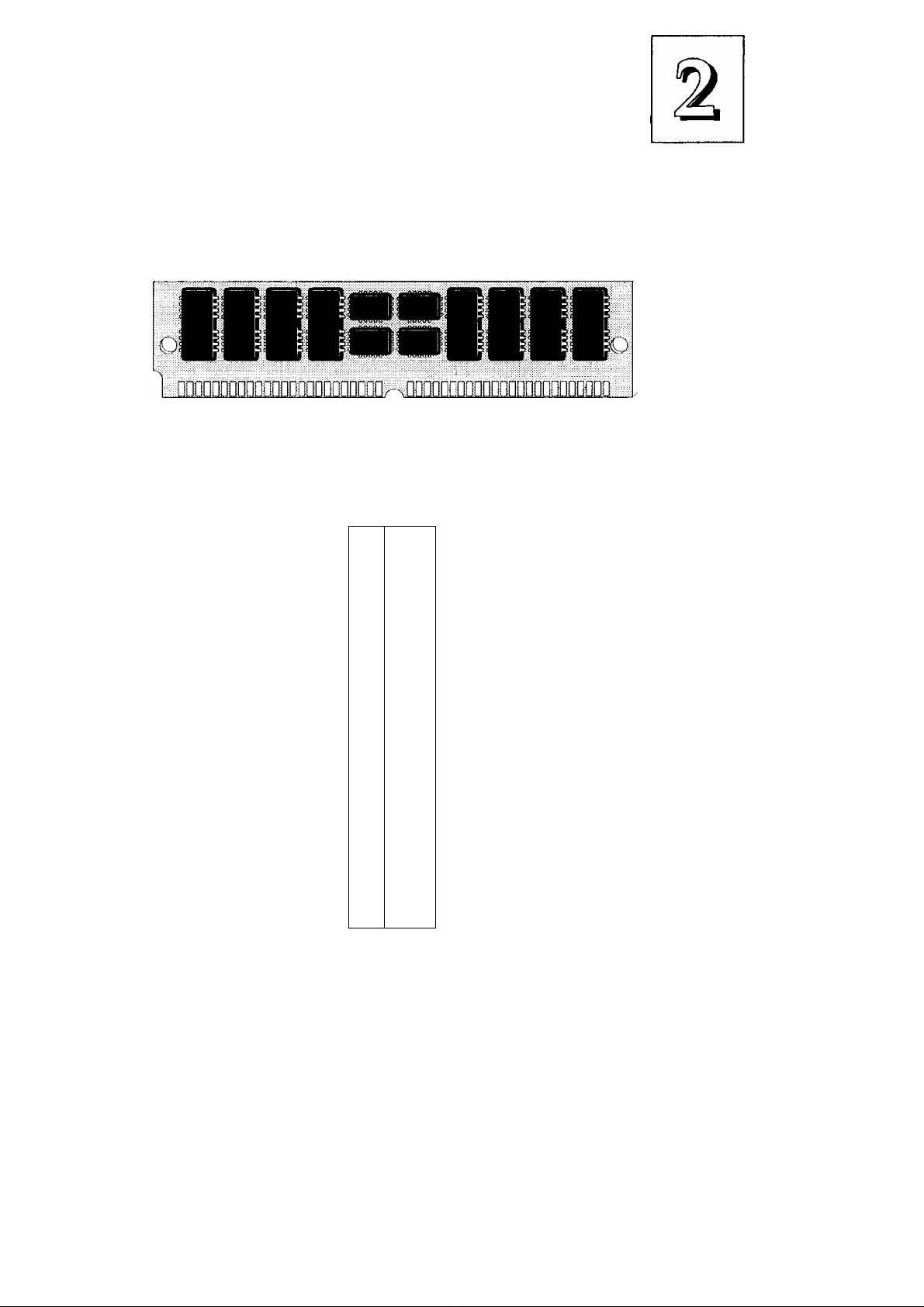
Module Sockets & Orientation
Cut-out
SIMMs have a cut-out at one end that matches an
extension on one of the vertical posts of each socket.
Upgrade Guide
SIMM# 4 3
I
2 1
r? 1^
!'
1
1
■
t
I
rli
Put orientation cut-out at this end.
Remember: Modules must be installed in pairs, in sequence and
must meet all the required specifications and be the same speed,
2-9
Page 27

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
Updating the Flash BIOS
This mainboard has two programmable BIOS Flash EPROM op
tions. One has a "boot block" feature, the other doesn't. You can up
date either of them when BIOS upgrades are available.
Jumper JP24 enables programming for the BIOS EPROM boot
block. There are two settings. The default setting. Boot Block Protect,
with pins 1&2 shorted, prevents boot block programming. The other
setting. Boot Block Programmable, with pins 2&3 shorted, allows pro
gramming to install a new BIOS including a boot block area.
Note: The Flash EPROM with no boot block area does not require
the use of jumper JP24 to allow programming the Flash BIOS.
BIOS With Boot Block Update Procedure
1. Set JP24 to the Boot Block
Programmable setting.
2. Refer to Chapter 3 for instruc
tions on using the Flash Memory
Writer Utility to install a new
BIOS file in the flash chip.
3. When you have successfully
installed the new BIOS, set JP24
back to the Boot Block Protect
setting.
2-10
Page 28

Software Guide
This chapter explains the Setup Utility for the Award BIOS, the
SCSI BIOS and drivers, and the system BIOS flash memory update
utility.
Award BIOS Setup
All computer mainboards of this type have a 'Setup' utility pro
gram stored in the BIOS ROM that is used to create a record of the
system configuration and settings. If you received your mainboard
installed as part of a system, the proper entries have probably already
been made. If so, you might want to call up the Setup Utility, as de
scribed later, to take a look at them, and perhaps record them for fu
ture reference, particularly the hard disk specifications.
If you are installing the board or reconfiguring your system,
you'll need to enter new setup information. This section explains how
to use the program and make the appropriate entries.
The Setup Utility is stored in the BIOS ROM. When you turn the
computer on, a screen message appears to give you an opportunity
to call up the Setup Utility. It displays during the POST (Power On
Self Test). If you don't have a chance to respond, reset the system by
simultaneously typing the <Ctrl>, <Alt> and <Delete> keys, or by
pushing the 'Reset' button on the system cabinet. You can also restart
by turning the system OFF then ON.
This message will then reappear:
TO ENTER SETUP BEFORE BOOT PRESS CTRL - ALT - ESC OR DEL KEY
3-1
Page 29

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
After you press the <Del> key the main program screen will ap
pear, displaying the following choices.
Main Program Screen
ROM PCI/rSA BIOS(PI-55SP3AV)
CMOS SETUP UTILITY
AWARD SOFTWARE,INC.
STANDARD CMOS SETUP
BIOS FEATURES SETUP
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP
POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP
PCI/PNP & ONBOARD I/O SETUP
LOAD BIOS DEFAULTS
LOAD SETUP DEFAULTS
ESC : Quit
FIO : Save & Exit Setup
Time, Date, Hard Disk Type...
SUPERVISOR PASSWORD
USER PASSWORD
IDE HDD AUTO DETECTION
SAVE Sl EXIT SETUP
EXIT WITHOUT SAVING
: Select Item
(SHIFT}F2 : Change Color
This screen provides access to the utility's various functions.
Note: The 'BIOS Defaults' are minimized settings for trou
bleshooting. Use the 'Setup Defaults' to load optimized defaults for
regular use. If you choose defaults at this level, it modifies all appli
cable settings.
A section at the bottom of the screen explains the controls for this
screen. Use the arrow keys to move between items, <Shift>+<F2> to
change the color scheme of the display and <Esc> to exit the utility.
If you want to save changes, press the <F10> key to save the changes
you made and exit the utility. Another section at the bottom of the
screen displays a brief explanation of the item highlighted in the list.
3-2
Page 30

Software Guide
Standard CMOS Setup
"STANDARD CMOS SETUP" records some basic system hard
ware information and sets the system clock and error handling. If
your mainboard is already installed in a working system you will not
need to do this. If the configuration record which gets stored in the
CMOS memory on the board is lost or corrupted, or if you change
your system hardware configuration, you will need to recreate the
record. The configuration record can be lost or corrupted if the on
board battery that maintains it weakens or fails.
Standard CMOS Setup Screen
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS(PI-55SP3AV)
AWARD SOFTWARE, INC.
Date (mm:dd:yy) : Tue, Sep 26 1995
Time (hh:mm:ss) : 10: 00: 00
HARD DISKS
Primary Master : User
Primary Slave : None
Secondary Master
Secondary Slave
Drive A : 1.44M,
Drive B
Video
Halt On
ESC : Quit
FI :Help
None
EGA/VGA
All Errors
TYPE SIZE
547 530
: None
: None
3.5 in.
(SHIFT)F2
STANDARD CMOS SETUP
HEADS PRECOMP
CYLS
32 0 1059
0
0 0
0
0
0
Select Item
Change Color
0 0
0 0
0
Extended Memory: 15360K
LANDZ SECTOR
0 0
0
0
Base Memory: 640K
Other Memory: 384K
Total Memory: 16384K
0 0
PU/PD/+/- : Modify
63
LBA
0
3-3
Page 31

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
"STANDARD CMOS SETUP" displays a screen with a list of en
tries. Follow the on-screen instructions to move around the screen.
Instructions at the bottom of the screen list the controls for this screen.
Use the arrow keys to move between fields, and the <Page Up>
(TU')/ <Page Down> (TD') or plus and minus keys to change the op
tion shown in the selected field. Pressing <Shift>+<F2> changes the
color scheme of the display, and <Esc> exits this level and returns to
the main screen.
Modifiable fields appear in a different color. If you need infor
mation about what changes to make, press the <F1> key. The help
menu will then give you information on the item highlighted. The
display of available memory at the lower right-hand side of the screen
functions automatically.
Date & Time
The first two lines on the screen are the date and time settings for
the system clock.
Hard Drive Type
You must enter the specifications of aU non-SCSI hard disk drives
installed in your system. MFM, ESDI and IDE hard disks all need to
have their specifications recorded here. The on-board PCI IDE con
nectors provide two channels. Primary and Secondary for connect
ing up to four IDE hard disks or other IDE devices, two to each chan
nel. Only hard disks need to be entered here.
If you have any SCSI hard disks installed in your system, do not
enter their specifications here. SCSI drives are not supported directly
by the PC BIOS. If your mainboard has the SCSI controller card op
tion, and you will use it, see the SCSI instructions that follow later in
this section. If you have some other SCSI controller, follow the instruc
tions that came with it on how to install any required SCSI drivers.
3-4
Page 32

Software Guide
The are four hard disks listed "Primary Master", "Primary Slave"
"Secondary Master" and "Secondary Slave". For each IDE channel,
the first device is the 'master' and the second device the 'slave'.
To enter the specifications for an MFM or ESDI hard disk drive,
you must first select a 'type'. You can select the "User" option and
enter the specifications yourself manually or there are 45 pre-defined
drive specifications which you can look through to see if the specifi
cations for your drive are assigned a type number. Do this by using
the <Page Up> or <Page Down> key to change the option listed af
ter the drive letter.
For an IDE hard drive, you should set the entry to "Auto" and
the BIOS will automatically detect all drive information needed. You
can use the IDE HDD Auto Detection utility described later to super
vise the auto-detection process. If you want to do this, leave the drive
set to "None". You can also enter specifications manually by using
the "User" option.
There are six categories of information you must enter: "Cyls"
(number of cylinders), "Heads" (number of read/write heads),
"Precomp" (write precompensation), "LandZ" (landing zone), "Sec
tor" (number of sectors) and "Mode". The "Size" entry is automati
cally determined by the other specifications. Your hard disk vendor's
or system manufacturer's documentation should provide you with
the drive specifications. If you have an IDE drive, unless your drive
is already formatted with specifications different from those autodetected, the easiest thing to do is use the "Auto" setting to autodetect the drive specifications.
3-5
Page 33

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Mode Setting For Hard Disk Drives Larger Than 528MB
The last of the specification entries. Mode, requires additional
explanation. The Mode settings are for IDE hard disks only. You can
ignore this item for MEM and ESDI drives. There are three entries you
can select from in the Mode field, "Normal", "Large" and "LBA".
Set Mode to the Normal setting for IDE hard disk drives smaller
than 528MB. Use the LBA setting for drives over 528MB that use Logi
cal Block Addressing mode to allow larger IDE hard disks. The Large
setting is for drives over 528MB that do not use the LBA mode. This
type of drive can only be used with MS-DOS and is uncommon. The
majority of IDE drives over 528MB use the LBA mode.
Note: Entering incorrect drive specifications will result in a hard
disk drive functioning improperly or not at all.
Floppy Disk Drives
The next two lines record the types of floppy disk drive present.
The options for drives A and B are:
360KB, 5.25 in.
1.2MB, 5.25 in.
720KB, 3.5 in.
1.44MB, 3.5 in.
2.88MB, 3.5 in.
None
priate entry.
3-6
Highlight the listing after each drive name and select the appro
Page 34

Software Guide
Video Display Types
"Video" refers to the type of video display card your system has.
The options are:
EGA/VGA
Mono (for Hercules or MDA)
CGA 40
CGA 80
You should select the setting that matches your video display
card. If you have a VGA or any higher resolution card, choose the
EGA/VGA setting.
Error Handling
The last line "Halt On" controls whether the system stops in case
of an error. The options are:
All Errors
No Errors
All, But Keyboard
All, But Diskette
All, But Disk/Key
For most purposes, we suggest that you leave the setting on the
default, "All Errors", unless you know why you want to use a. dif
ferent setting.
When you have made your selections, exit to the main program
screen by pressing the <Esc> key.
3-7
Page 35

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
BIOS Features Setup
"BIOS FEATURES SETUP" is a list of system configuration op
tions. Some entries are defaults required by the mainboard's design.
Others will improve your system's performance if enabled, or let you
set Up some system features according to your preference.
BIOS Features Setup Screen
ROM PCI/ISA BIOSÌPI-55SP3AV)
BIOS FEATURES SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE INC.
virus Warning
CPU Internal Cache Enabled
External Cache
Quick Power On Self Test
Boot Sequence
Swap Floppy Drive Disabled
Boot Up Floppy seek Disabled DCOOO-DFFFF Shadow
Boot Up NuinLock Status
Boot Up System Speed
IDE HDD Block Mode Enabled
TVpanatic Rate Setting Disabled
TVpaiiatic Rate (Chars/Sec)
lypertatic Delay (Msec) 250
Security Option
PS/2 mouse function control
Disabled Video BIOS Shadow Enabled
C8000-CBFFF Shadow Disabled
Enabled CCOOO-CFFFF Shadow Disabled
Disabled DOOOO-D3FFF Shadow Disabled
C,A D4000-D7FFF Shadow Disabled
D8000-DBFFF Shadow
On
High
6
System
Enabled
ESC : Quit : Select Item
FI : Help PU/PD/ + /- ; Modify
F5 : Old Values (SHIFT)F2 : Color
F6 : Load BIOS Defaults
F7 ; Load Setup Defaults
Disabled
Disabled
A section at the lower right of the screen explains how to navi
gate and make changes. The controls are the same as for the Standard
CMOS Setup.
If you need information about what changes to make, highlight
an entry and press the <F1> key. A pop-up help menu will display
information about the highlighted item. Press the <F5> key to recall
the last set of values saved for this page. Pressing the <F6> key loads
the BIOS default values for this page and <F7> loads the Setup de
fault values.
The following explains the options for each entry and indicates
the default settings (Setup Defaults) for this screen.
3-8
Page 36

Software Guide
Virus Protection
The "Virus Warning" default setting is "Disabled". This feature
protects the boot sector and partition table of your hard disk. Any
attempt to write to them will halt the system and cause a warning
message to appear. If this happens, you can either allow the opera
tion to continue or stop it and use an anti-virus utility on a virus-free
bootable floppy disk to reboot and investigate your system.
Cache Control
The "CPU Internal Cache" and "External Cache" default settings
are "Enabled". These settings enable CPU's 'Level V built-in cache
and the 'Level 2' secondary cache. The BIOS Default settings will dis
able the L2 cache. Leave both enabled unless you are troubleshoot
ing a problem.
Boot Up Features
The "Quick Power On Self Test" default setting is "Disabled".
This feature speeds up the Power On Self Test (POST) by skipping
some items that are normally checked during the full POST If your
system is functioning normally, you can use this feature to speed the
boot up process.
The "Boot Sequence" default setting is "C:, A:"; the other option
is "A:, C:", The setting determines where the computer looks first for
an operating system, the hard disk or the floppy drive.
The "Swap Floppy Drive" default setting is "Disabled". When
enabled, the BIOS will swap floppy drive assignments so that Drive
A will function as Drive B: and Drive B: as Drive A: under DOS.
The "Boot Up Floppy Seek" default setting is "Disabled". When
enabled, the BIOS will check if there is a 360KB floppy disk drive
installed. Don't change this unless there is a 360KB drive installed.
I
L
3-9
Page 37

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
The default "Boot Up NumLock Status" setting is "On". When
the computer boots, the numbers on the numeric keypad of an IBMcompatible extended keyboard will be active. If you turn this off the
keypad cursor controls will be active.
' "Boot Up System Speed" sets the CPU speed at boot up. The de
fault setting is "High".
IDE Block Mode
The "IDE HDD Block Mode" default setting is "Enabled". This
feature enhances hard disk performance by making multi-sector
transfers instead of one sector per transfer. Most IDE drives, except
very early designs, can use this feature.
Keyboard Interface
The "Typematic Rate Setting" default setting is "Disabled'
enabled, you can set the typematic controls that follow.
The "Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec)" controls the speed at which
the system registers repeated keystrokes. The choices range from 6
to 30 characters per second (default is 6).
The "Typematic Delay (Msec)" controls the time between the
display of the first and second characters. There are four delay rate
choices: 250ms, 500ms, 750ms and 1000ms (default is 250ms).
Security Option Password Control
The "Security Option" controls the Password Setting in the main
If
screen. The default setting, "System", uses the User Password feature
every time you boot up. The other setting is "Setup". This uses the
Supervisor Password only to protect the Setup Utility settings. You
create a password by using the Supervisor or User Password com
mand from the main screen as explained later in this chapter.
3-10
Page 38

Software Guide
PS/2 Mouse
The "PS/2 mouse function control" default setting is "Enabled".
When enabled and a device is connected to it, the PS/2 port uses IRQ
12. If no device is attached to the port, IRQ 12 is not used.
Shadow Controls
The default setting for the "Video BIOS Shadow" is "Enabled".
This copies the video display card BIOS into system DRAM to im
prove performance.
The next lines, "C8000-CBFFF Shadow" to "DCOOO-DFFFF
Shadow" are for shadowing other expansion card ROMs. The default
setting for these areas is "Disabled". If you have other expansion
cards with ROMs on them, you will need to know which addresses
the ROMs use to shadow them specifically. When you shadow a ROM
it reduces the memory available between 640KB and 1024KB by the
amount used for shadowing.
After you have made your selections in BIOS Features Setup,
press the <Esc> key to go back to the main screen. The next item is
Chipset Features Setup.
3-11
Page 39

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Chipset Features Setup
This screen controls the settings for the board's chip set. Naviga
tion and controls for this screen are the same as for the previous
screen.
Chipset Features Screen
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS(PI-55SP3AV)
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE INC.
Auto Configuration
L2 (WB) Tag Bit Length
Async SRAM Leadoff
Async SRAM Burst Timing
FP CAS Precharge IT Video BIOS Cacheable Enabled
RAS To CAS delay time
FP RAS Precharge time
RAS active when refresh
CAS delay in post-write
EDO CAS pulse Width
EIX) CAS Precharge time
EDO RAS Precharge time
L2 Cache Update Mode
Next Address (NA#)
CPU to PCI Burst Write
CPU to PCI Post Write
CPU-PCl Post Write Rate
Snoop PCI Master Write
Snoop PCI Master Read
Slow Refresh (1:4)
Enabled ISA Bus Clock Frequency PCICLK/3
7bits 16-bit ISA Wait State 1 Wait
3/4
2T
4T
4T
5T
IT
R1/W2 Hole Start Address OFCOOOOH
IT
4T
WB
Disabled
Enabled
Enabled
4T
Enabled
Enabled
Disabled
16-bit I/O Recory Time
8-bit I/O Recory Time 8 BUSCLK
Onboard VGA Mem Size
Onboard VGA Mem Frequency Normal
Allocate Memory Hole
Hole Size
ESC Quit Ti—><— : Select
Fl
Help
F5 Old Values (SHIFT)F2 : Color
F6 Load BIOS Defaults
F7
Load Setup Defaults
PU/PD/+/- : Modi fy
5 BUSCLK
1MB
Disabled
256KB
Item
3-12
Page 40

Software Guide
The first eleven lines after "Auto Configuration", which should
be set to "Enabled", are optimal settings for this mainboard that are
defined by the Auto Configuration feature, which configures the set
tings based on the CPU clock speed. All the other settings up to "Al
locate Memory Hole", with the exception of "Slow DRAM Refresh
(1:4)", are the recommended settings for this mainboard. You should
not change them unless you know what you are doing.
If you install SIMMs that use Slow Refresh DRAM, you should
set "Slow DRAM Refresh (1:4)" to "Enabled ".
There are two settings for "Onboard VGA Mem Size", "1MB"
and "2MB". With 2MB of display memory, higher resolutions and
with more colors can be displayed. See the documentation file for the
SIS 6205 Super VGA for more information on this.
The settings for "Onboard VGA Mem Frequency" are "Normal"
"Fast" and "Fastest". You must have 60ns or EDO system DRAM to
use the "Fastest" setting. The default setting is "Fast"
You can enable "Allocate Memory Hole" if you need it for an
expansion card that requires this feature. The documentation for the
card should have instructions regarding the required Hole Start Ad
dress and Hole Size settings.
When you are done with this section, press the <Esc> key to go
back to the main screen. The next section covers Power Management
Setup.
3-13
Page 41

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
Power Management Setup
Power Management Setup controls the mainboard's "green" fea
tures. The features shut down the video display and hard disk to save
energy.
The Power Management Setup Screen
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS (PI-55SP3AV)
POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE INC.
Power Management
Video Off Option
Video Off Method
Suspend Switch
Doze Speed (div by)
Stdby Speed(div by)
** PM Timers **
HDD Power Down
Doze Mode
Standby Mode
Suspend Mode
** PM Events **
COM Ports Activity
LPT Ports Activity
HDD Ports Activity
PCI/ISA Master Act.
IRQl-15 Activity
VGA Activity
User Define
Susp,Stdby->Off
V/H SYNC+Blank
Enable
8
32
Disable
Disable
Disable
Disable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Disable
IRQ3
IRQ4
IRQ5
IRQ 6
IRQ7
IRQS
IRQ 9
IRQ 10
IRQll
1RQ12
IRQ13
IRQ14
IRQ15
(COM 2)
(COM 1)
(LPT 2)
(Floppy Disk)
(LPT 1)
(RTC Alarm)
(IRQ2 Redir)
(Reserved)
(Reserved)
(PS/2 Mouse)
(Coprocessor)
(Hard Disk 1)
(Hard Disk 2)
ESC
Quit Ti ^ :Select Item
FI
Help PU/PD/+/- : Modify
F5
Old Values (SHIFT)F2 : Color
F6
Load BIOS Defaults
F7
Load Setup Defaults
Enable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Disable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Enable
Power Management
"Power Management" is the master control for the power sav
ing modes. Display Turn off and HDD Power Down that together
form the hardware power conservation scheme. There are four set
tings:
Max Saving
Sets the power conservation options to maxi
mize power saving by putting the system into
power saving mode after a brief period of sys
tem inactivity
3-14
Page 42

Software Guide
Min Saving
Disable
User Defined
Max Saving
The "Max Saving" defaults are "1 Min" and "20 Sec".
Min Saving
The "Min Saving" defaults are "20Min" and "40 Min".
t^ideo Off
Another set of power saving assignments
which activate each after a moderate period
of system inactivity.
Turns off all power saving
Allows you to set power saving options ac
cording to your requirements.
The "Video Off Option" default is "Susp,Stby-> Off". This line
defines when the video off features activate. The next line sets how.
The "Video Off Method" default is "V/H SYNC+Blank". The
other options are "DPMS"and "Blank Only". When power manage
ment blanks the monitor screen, the default setting blanks the screen
and turns off vertical and horizontal scanning. The DPMS (Display
Power Management System) setting allows the BIOS to control the
video display card if it has the DPMS feature. If you don't have a
"Green" monitor, use the Blank Only option.
Note: "Screen Saver" software does not work with this feature.
Screen savers are to prevent burning in a static image on the CRT
while the monitor is on. A screen saver cannot display while the
monitor is shut down to save both electricity and the screen.
3-15
Page 43

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Suspend Switch
The "Suspend Switch" default is "Enable". This enables the SMI
connector on the mainboard. The SMI connector connects to the lead
from a Suspend switch mounted on the system case.
Doze & Standby Speeds
The next two lines set the speed the CPU will operate at during
each mode. The number indicates what the normal CPU speed is di
vided by.
PM Timers
The next lines control the time-out settings for the Power Man
agement scheme. The features are "HDD Power Down", which puts
the hard disk into its lowest power consumption mode, and the Doze,
Standby and Suspend system inactivation modes.
The system automatically recovers from any power saving mode
when there is system activity, as, for example, when you type any key,
or when there is an IRQ wake-up event such as moving the mouse
or a modem ring.
"HDD Power Down" shuts down any IDE hard disk drives in
the system if they are not accessed for the specified period. The time
settings range from "1 Min" to "20 Min", or "Disable".
HDD Power Down does not affect SCSI hard disks.
The "Doze Mode", "Standby Mode" and "Suspend Mode" lines
set the period of time after which each of these modes activate. At
'Max Saving' they activate sequentially after one minute each, at 'Min
Saving' after one hour.
3-16
Page 44

Software Guide
PM Events
If there is any activity from any part of the the system listed in
this group while the system is suspended, the system will wake up
if that item is Enabled. You can set IRQs 3-15 individually in the list
at the right of the screen.
Note: Normally, a Microsoft serial mouse or compatible will use
either COMl (IRQ4) or COM2 (IRQ3) and a PS/2-type mouse will
use IRQ12. If you know which IRQ your mouse is using, you can
make sure the Wake-up Event for that IRQ is turned on here and the
system will wake up when you move the mouse or click a button.
IRQ3 to IRQ1S Individual Settings
You can set IRQs 3-15 individually. Activity on any enabled IRQ
will wake up the system.
When you are done here, press the <Esc> key to go back to the
main screen.
3-17
Page 45

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
PCVPNP & Onboard I/O Setup
This screeivconfigures the PCI Bus slots. Plug and Play, and the
onboard I/O features.
PCI/PNP & Onboard I/O Setup Screen
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS(PI-55SP3AV)
PCI/PNP & ONBOARD I/O SETUP
AWARD SOFTWARE INC.
SLOT 1 (RIGHT) IRQ
SLOT 2 IRQ
SLOT 3 (LEFT) IRQ
PCI Latency Timer
IRQ 3 Used By ISA
IRQ 4 Used By ISA
IRQ 5 Used By ISA
IRQ 9 Used By ISA
IRQ 10 Used By ISA
IRQ 11 Used By ISA
IRQ 15 Used By ISA
Auto
Auto
Auto
80 PCI Clock
No/lCU
No/ICU
No/ICU
No/ICU
No/ICU
No/ICU
No/ICU
Onboard FDC Controller
Onboard FDC Swap A & B
Onboard Serial Port 1
Onboard Serial Port 2
Onboard Parallel Port
Parallel Port Mode
ECP DMA Select
UART2 Use Infrared
Internal PCI/IDE
IDE Primary Master PIO
IDE Primary Slave PIO
IDE Secondary Master PIO
IDE Secondary Slave PIO
Enabled
No Swap
COMI,3F8H
COM2,2F8H
378H/IRQ7
Normal
Disabled
Disabled
Enabled
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
DMA 1 Used By ISA
DMA 3 Used By ISA
DMA 5 Used By ISA
ISA MEM Block BASE
No/ICU
No/ICU
No/ICU
No/ICU
ESC : Quit
FI : Help PU/PD/+/F5 : Old Values (SHIFT)F2
F6 ; Load BIOS Defaults
F7 : Load Setup Defaults
: Select Item
Modify
Color
The first three lines on the screen set how PCI slot IRQ use is de
termined. All the PCI slots use INTA#, so any cards you install should
be set to INTA#. The default setting for each line is "Auto", which
will use auto-routing to detemine IRQ use. Use the options "14" or
"14&15" if you install a separate Enhanced IDE controller card. A onechannel card uses the "14" setting and a two-channel card the
"14&15" setting. If you use one or both of these IRQs here, they are
not available to the on-board PCI IDE controller, which uses IRQ 14
for the Primary and IRQ 15 for the Secondary channel.
The next line is the "PCI Latency Timer" setting. Do not change
the "80 PCI Clock" setting. This default setting enables maximum PCI
performance for this mainboard.
3-18
Page 46

Software Guide
PNP (Plug And Play)
The seven "IRQ ... Used By ISA" lines indicate whether or not
the IRQ indicated for each line is being used by a 'legacy'(non-PNP)
ISA card. The default setting "No/ICU" indicates either that the IRQ
is not in use by the ISA Bus or that ctn ISA Configuration Utility (ICU)
is being used to determine if an ISA card is using that IRQ. If you
install a legacy ISA card that needs a specific IRQ, and you are not
using an ICU, you must set the line for that IRQ to "Yes".
For example, if you install a PNP ISA card that needs to use IRQ
3, you would set the "IRQ 3 Used By ISA" line to "No/ICU". If, how
ever, you install a legacy ISA card that needs to use IRQ 3, and you
are not using an ICU, set the "IRQ 3 Used By ISA" line to "Yes".
The three "DMA ... Used By ISA" lines indicate whether or not
the DMA chanel listed is being used by a legacy ISA card. The de
fault setting "No/ICU" indicates either that the DMA channel is not
in use by the ISA Bus or that an ICU is being used to determine if an
ISA card is using that IRQ. If you install a legacy ISA card that needs
to use a specific DMA channel, and you are not using an ICU, you
must set the line for that charmel to "Yes".
If you have a legacy ISA card that uses ciny memory segment in
the C800h to DFFFh address range and you have not used an ICU to
specify the range it uses, you should set the base address and block
size by using the "ISA MEM Block BASE" line. When you select a
base address from the six options, the "ISA MEM Block SIZE" line
will appear and you can select a block size from the four options. If
you use an ICU to accomplish the same thing, leave "ISA MEM
Block BASE" on the default "No/ICU" setting. If you have more than
one legacy ISA card that needs to use this address range, you can
increase the block size as necessary.
3-19
Page 47

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Controller Settings
The default setting for the "Onboard FDC Controller" is "En
abled". This setting activates the onboard floppy disk controller and
connector. Choose the "Disabled" setting if you want to use a sepa
rate controller card.
The default setting for the "Onboard FDC Swap A: B:" is "No
Swap". If you want to reverse the drive letter assignments of two
floppy disk drives you can set this to "Swap AB" and the swap will
be controlled in hardware. This feature is the same as physically
changing the floppy disk drive cable connector positions. It is sepa
rate from the BIOS Features Setup "Swap Floppy Drive" feature.
Serial Ports
The "Onboard Serial Port 1" and "Onboard Serial Port 2" lines
control the assignments for the mainboard's two onboard serial con
nectors. They can be assigned as follows:
COMl address is 3F8H (Onboard Serial Port 1 default)
COM2 address is 2F8H (Onboard Serial Port 2 default)
COM3 default address is 3E8H
COM4 default address is 2E8H
Disabled turns off the on-board port
Make sure both ports have different COM assignments. It should
be unnecessary to change the default settings.
3-20
Page 48

Software Guide
Parallel Port
The options for "Onboard Parallel Port" are:
3BCH/IRQ7
378H/IRQ7
278H/IRQ5
Disabled
This line controls the on-board parallel port and connector, set
ting the port address and IRQ assignment or disabling the port. It
should be unnecessary to change the default setting.
Parallel Port Mode
The options for "Parallel Port Mode" are:
Normal
EPP
ECP
ECP&EPP
If you want to use one of the parallel port enhancements listed,
set this line for the enhanced mode your peripheral supports. "ECP"
Default setting
Default setting
default DMA 3
automatically sets the "ECP DMA Select" line to "3", where it is oth
erwise set to "Disabled", and cannot be set independently.
3-21
Page 49

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
UART2 Use Infrared
The default setting for the "UART2 Use Infrared " is "Disabled".
The default setting leaves the second serial port UART set to support
the Serial Port 2 connector. The "Enabled" setting activates the
onboard infrared IrDA feature and sets the second serial UART to
support the JP31 infrared module connector on the mainboard in
stead. Choose this if you want to connect an infrared control mod
ule to the mainboard. If your system already has a second serial port
connected to the onboard COM2 connector, it will no longer work if
you enable the infrared feature.
Internal PCI/IDE, IDE PIO
The default setting for the "Internal PCI/IDE" is "Enabled". This
activates both onboard IDE channels and connectors. The "Disabled"
setting disables the onboard controller and removes the PIO lines that
follow it. The PIO timing mode settings are best left set on "Auto",
which will auto-select the PIO mode for each device. The BIOS will
select the best IDE timing for the device. If the timing selected is too
fast for the device and it doesn't operate properly, you can manually
select from Mode 0 to Mode 4 to find a usable timing speed. Mode 0
is the slowest and Mode 4 is the fastest timing.
When you're finished making settings for this screen, press the
<Esc> key to go back to the main screen.
3-22
Page 50

Software Guide
Load BIOS Defaults
"LOAD BIOS DEFAULTS" loads the troubleshooting default
values permanently recorded in the BIOS ROM. These settings are
non-optimal and turn off all high performance features.
The Standard CMOS Setup screen is not affected. To use this fea
ture, highlight it on the main screen and press <Enter>. A line will
appear asking if you want to load the BIOS default values. Press the
<Y> key and then <Enter>. The default settings will load. Press <N>
if you don't want to proceed.
Load BIOS Defaults Screen
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS(PI-55SP3AV)
STANDARD CMOS SETUP
BIOS FEATURES SETUP
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP
POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP
PCI/PNP & ONBOTUIE
LOAD BIOS DEFADLl
LOAD SETUP DEFAUI
ESC ; Quit
FIO : Save & Exit Setup
Load BIOS Defaults except Standard CMOS SETUP
CMOS SETUP UTILITY
AWARD SOFTWARE,INC.
SUPERVISOR PASSWORD
USER PASSWORD
IDE HDD AUTO DETECTION
SAVE & EXIT SETUP
SAVING
Ti—; Select Item
(SHIFT)F2 : Change Color
3-23
Page 51

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Load Setup Defaults
The "LOAD SETUP DEFAULTS" option loads optimized set
tings from the BIOS ROM. Use this option to load default settings for
normal use.
The Setup Defaults default settings do not affect the Standard
CMOS Setup screen. To use the Setup Defaults, highlight the entry
on the main screen and press <Enter>. A line will appear asking if
you want to load the Setup default values. Press the <Y> key and then
press <Enter>. The Setup Defaults will load. Press <N> if you don't
want to proceed.
Load Setup Defaults Screen
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS(PI-55SP3AV)
STANDARD CMOS SETUP
BIOS FEATURES SETUP
CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP
POWER MANAGEMENT SETUP
PCI/PNP & ONBOARI
LOAD BIOS DEFAULT
LOAD SBTUP DEFADl
ESC ; Quit
FIO : Save & Exit Setup
Load SETUP Defaults except Standard CMOS SETUP
CMOS SETUP UTILITY
AWARD SOFTWARE,INC,
SUPERVISOR PASSWORD
USER PASSWORD
IDE HDD AUTO DETECTION
SAVE St EXIT SETUP
SAVING
Ti-M-: Select Item
(SHIFT)F2 : Change Color
3-24
Page 52

Software Guide
Setting Supervisor & User Passwords
The "SUPERVISOR PASSWORD" and "USER PASSWORD"
options set passwords. The Supervisor Password is for system and
Setup Utility access. The User Password is for the system only The
mainboard ships with no passwords. To create a password, highlight
the type you want and press the <Enter> key. At the prompt, type
your password. The password is case sensitive, and can be up to 8
alphanumeric characters. Press <Enter> after you have finished typ
ing in the password. At the next prompt, confirm the new password
by re-typing it and pressing <Enter> again. When you're done, the
screen automatically reverts to the main screen. Remember, when you
use this feature, the ""Security Option"" line in BIOS FEATURES
SETUP will determine when entering the password will be required.
To disable either password, press the <Enter> key instead of en
tering a new password when the "Enter Password" dialog box ap
pears. A message confirms the password has been disabled.
Password Setting
3-25
Page 53

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
IDE HDD Auto Detection
If your system has an IDE hard drive, you can use this utility to
detect its parameters and enter them into the Standard CMOS Setup
automatically.
Tliis utility will detect as many as four IDE drives if your system
configuration supports that many In sequence, a set of parameters
for each drive will appear in the box. To accept the entries displayed
press the Y key, to skip to the next drive, press the N key. If you ac
cept the values, the parameters will appear listed beside the drive
letter on the screen and the next letter, without parameters will ap
pear and the program will attempt to detect parameters for the next
drive. If you press the N key to skip rather than accept a set of pa
rameters, zeros are entered after that drive letter.
Remember, if you use another IDE controller that does not have
Enhanced IDE support for four devices, you can only install two IDE
hard disk drives. Your IDE controller must support Enhanced IDE
features in order to use Drive E: and Drive F:. The on-board PCI IDE
controller supports Enhanced IDE and has two connectors that sup
port a total of four IDE devices. If you want to use another PCI IDE
controller, you must disable the onboard PCI IDE controller by set
ting the "Internal PCI/IDE" line in the PCI/PNP & Onboard I/O
Setup screen to "Disabled".
When you are finished, any entries you accepted are automati
cally entered on the line for that drive in the Standard CMOS Setup.
Any entries you skipped are ignored and nothing is entered for that
drive in Standard CMOS Setup.
3-26
Page 54

Software Guide
IDE HDD Auto Detection Screen
ROM PCI/ISA BIOS(PI-55SP3AV)
CMOS SETUP UTILITY
AWARD SOFTWARE,INC.
HARD DISKS
Primary Master:
OPTIONS SIZE CYLS. HEADS PRECOMP LANDZONE SECTORS MODE
liY)
547
TYPE SIZE CYLS HEADS PRECOMP LANDZ SECTOR MODE
Select Primary Master Option (N=Skip)? N
530
32
1059
63
LBA
Note: If you are setting up a hard disk that supports LBA mode,
three lines will appear in the parameter box. Choose the line that lists
LBA for an LBA drive. Do not choose Large or Normal
Important!: This utility will only detect one set of parameters for
an IDE hard drive. Some IDE drives can use more than one set. This
is not a problem if the drive is new and there is nothing on it. If the
hard disk drive is already fully formatted when you install it, and dif
ferent parameters than those detected here were used, you will have
to enter them manually.
If the parameters listed don't match the ones used when the drive
was formatted, the drive won't be readable. If the auto-detected pa
rameters displayed do not match the ones that should be used for
your drive, do not accept them. Press the <N> key to reject the val
ues and enter the correct ones manually from the Standard CMOS
Setup screen.
3-27
Page 55

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
Save And Exit Setup
The next selection on the Utilities menu is "SAVE AND EXIT
SETUP". If you select this and press the <Enter> key the values en
tered during the current session will be recorded in the CMOS
memory on the mainboard. The system will check it every time you
turn your system on and compare it to what it finds as it checks the
system. This record is required for the system to operate.
Exit Without Saving
The last selection on the main screen is "EXIT WITHOUT SAV
ING". Selecting this option and pressing the <Enter> key lets you exit
the Setup Utility without recording any new values or changing old
ones. If you want to save a new configuration, do not use this option.
If you use it, any new setting information will be lost.
You can now use your system without further reference to this
utility unless you change the system hardware configuration. Re
member, if the system configuration information stored in CMOS
memory gets corrupted, you will have to reenter it.
3-28
Page 56

Software Guide
NCR SCSI BIOS & Drivers
The NCR 53C810 SCSI BIOS is recorded on the same flash
memory chip as the system BIOS. To use the on-board NCR SCSI
BIOS, the optional SC-200 SCSI controller card must be installed in
your system.
All SCSI devices you connect to your system require driver soft
ware. The NCR SCSI BIOS directly supports SCSI hard disks under
DOS, Windows and OS/2. It also uses device drivers that are on the
DOS-format support floppy disk that comes with the SC-200 control
ler card to support hard disks and other SCSI devices used with DOS,
Windows, Windows 95, Windows NT, Novell NetWare and OS/2.
These drivers provide higher performance than the direct BIOS sup
port. To use these device drivers you must install them on your sys
tem hard disk drive and add them to your system configuration
files.There is also driver support for SCSI devices used with SCO
Unix. A second, SCO Unix-format, support floppy disk has the Unix
drivers on it.
See the "Readme" files that come with the drivers for instructions
on what they are and how to use them. You can print out the Readme
files with any text editor.
3-29
Page 57

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
Flash Memory Writer Utility
Your mainboard comes with a utility to upgrade the BIOS. The
BIOS is stored on a 'flash' EPROM BIOS ROM chip on the mainboard
that can be erased and reprogrammed. This is what the Flash Memory
Writer (FMW) utility does. The utility is in the "Flash" directory on
the DOS-formatted support floppy disk that comes with the
mainboard. You will find three files in the directory:
PFLASH.EXE
README
SS5IXXXX.AWD
(xxxx = a 4-digit version number)
Flash Memory Writer records (or "programs") a new BIOS file
onto the flash memory chip. The BIOS file on the support disk may
be newer than the BIOS on the mainboard, so you may want to up
date your BIOS right away. Compare the four numbers after "SS5I"
in the new BIOS file name to the last four numbers of the code that
displays in the upper left-hand comer of your screen while the PowerOn Self-Test is running. If the number from the support disk file is
larger, then you should reprogram the System BIOS. If they are the
same, don't bother. To reprogram the System BIOS, you must first do
the following:
- the Flash Memory Writer utility
- a text file of instructions
- a BIOS file for this mainboard
1. Set jumper JP24 to the Boot Block Programmable setting. When
you finish updating the BIOS, set JP24 back to the default Boot
Block Protect setting. See Chapter 4 for jumper setting infor
mation.
3-30
Page 58

Software Guide
2. Make sure the CPU is running in 'real mode'.
FMW will not run if the CPU is operating in protected or vir
tual mode. This means that you can not run it with Windows
rurming or with any memory manager software (including
HIMEM.SYS). You must disable any memory manager soft
ware first. The easiest way to do this is to:
a. Boot your system from a bootable floppy disk with no
config.sys or autoexec.bat files and then run Flash Memory
Writer from a backup copy of your support disk. You can make
your back-up floppy bootable when you format it, and use one
disk for both purposes.
b. If you are using MS-DOS 6.x, you can use the feature that
allows you to confirm or abort each line of these files. You do
this by pressing <F8> while the "Starting MS-DOS..." line is on
the screen. If you are running Windows 95, shut down and
select the shut-down option to restart your computer in MSDOS mode. You will still need to disable the autoexec.bat and
config.sys files if you have any set to run in DOS-only mode.
There are other ways to accomplish the same result. The main
point is to make sure no memory managers are running. If you aren't
sure, try running FMW. If it runs, you've succeeded. If it displays a
warning message about the CPU mode, you'll have to try again.
Once you've satisfied the two requirements mentioned above,
you can run FMW. You can copy the contents of the "Flash" directory
to your hard disk drive, or you can rim the utility from a backup of
the support floppy disk. Make sure the new BIOS file is in the same
directory as the FMW utility. To run FMW, switch to the "Flash" di
rectory if you're not already in it. Type 'PFLASH' at the DOS prompt
and press the <Enter> key. The following screen will appear;
3-31
Page 59

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
The Flash Memory Writer Utility Screen
ASUSTek PNP BIOS
FLASH MEMORY WRITER VI.0
Copyright (C) 1995, ASUSTek COMPUTER Inc
FAash Type -- SST 29EE010
Current BIOS Revision: #401A0-0201
Choose one of the following:
1. Save Current BIOS To File
2. update BIOS Main Block From File
3. Advanced Features
Enter Choice; [1]
Press ESC To Exit
There are three command options which you invoke by typing
the number of the command and pressing the "Enter" key:
1. Save Current BIOS To File
This command reads the system BIOS already installed on the
mainboard and writes a copy of it to a file in the 'Flash' di
rectory. This leaves you with a backup of your original BIOS
in case you need to re-install it. This option is highly recom
mended.
2. Update BIOS Main Block From File
This updates the BIOS, but not the boot block and ESCD, from
a file on disk. This can be either a new file or the backup file
created by the "Save Current BIOS To File " command.
3. Advanced Features
Selecting this option brings up the Advanced Features screen.
3-32
Page 60

Software Guide
There is a line at the bottom of the screen "Press ESC To Exit".
If you press the Escape key the program will terminate and re
turn you to the DOS prompt.
If you type a "3" and then press the "Enter" key the Advanced
Features screen will appear.
The Advanced Features Screen
Advanced Features
Flash Type -- SST 29EE010
Current BIOS Revision: #40lA0-0301
Choose one of the following:
1. Clear PNP ESCD Parameter Block
2. Update BIOS Including Boot Block and ESCD
Enter Choice: [2]
Press BSC To Exit
There are two command options which you invoke by typing the
number of the command and pressing the "Enter" key:
1, Clear PNP ESCD Parameter Block
This command erases the Plug and Play configuration record.
2. Update BIOS Including Boot Block and ESCD.
This updates the Boot Block, the BIOS and the Plug and Play
ESCD Parameter Block from a new file in the FLASH directory.
Operation and controls are the same as for the main screen.
3-33
Page 61

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Follow this procedure to update Plug and Play system BIOS ver
sion 0103 or later:
1. Back up your existing system BIOS by using the "Save Current
BIOS To File" command. Type "1" and press "Enter" to execute
-the command. A second screen will appear.
Type the BIOS file name, e.g. SS5I0201.AWD, press "Enter" and
the program will write a file containing the current BIOS to the
directory you are running FMW from.
2. Install the new BIOS using the "Update BIOS Main Block From
File" command. Type a "2" and press "Enter".
When you type this command a second screen will pop up
instructing you to type in the name of the new BIOS file. Type
in the whole file name, e.g. SS5I0202. AWD and press the "En
ter" key to confirm that you want to program the BIOS. The
utility will then install the new BIOS file.
DO NOT TURN OFF THE SYSTEM IF THERE IS A PROBLEM!
If you have a problem installing the new BIOS file, choose com
mand "2" again and try again. If you can not successfully pro
gram the new BIOS file for whatever reason, press "2" again
and re-install your original BIOS from the backup file you cre
ated in Step 1 above.
3. Once you have successfully installed a new BIOS, exit FMW
and turn your system OFF. Set jumper JP24 to the Boot Block
Protect setting and turn the system ON again. The system
should come on using the new BIOS.
Warning: If you do not successfully install a complete BIOS file,
your system may not be able to boot. If this happens it will require
service by your system vendor. Follow the requirements and instruc
tions in this section precisely to avoid this inconvenience.
3-34
Page 62

Technical Summary
The first part of this section summarizes the mainboard's speci
fications and explains the L2 external cache. The second part explains
how to set up the optional PCI-SC200 SCSI Interface card.
Jumper Setting Summary
The settings for jumpers JP7 and JP9 are fixed. You can note what they are for
reference, but you should not change them.
Level 2 Cache Size; JP6 & JP8
Set these according to the size of the installed cache.
JP6 JP8
256K
512K
1MB
~o
oo
1 1
O
256KB Cache 512KB Cache 1MB Cache
c_ c_
-D ~0
05 OO
o
1&2 1&2
1&2 2&3
2&3 2&3
o
1
c_ c_
"D ~0
CT» Oft
W 0 ^^0
o
o
o
$ $
"U
05
4-1
Page 63

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
PS/2 Mouse Port Selector: JP12
This jumper controls the on-board PS/2 Mouse lead connector. When set to
Enable, the port is active and uses IRQ12.
JP12
c_
T3
ro
Default
o
(D
Disable
Enable
C12
ro
1&2
28.3
0
o
Disable
PS/2 Mouse
Onboard Audio Selector: JP13
This jumper controls the onboard audio. When set to Enable, the onboard audio is
active.
JP13
Enable
PS/2 Mouse
Enable
Disable Short
-©O
Enable
Audio
For the Open setting, place jumper cap over one pin
Open Default
JP13 JP13
Disable
Audio
4-2
Page 64

Technical Summary
CPU Internal Clock External Mulitple Selector: JP14& JP15
These set the factor by which the external bus clock is multiplied to establish the
internal CPU clock speed.
CPU Internal Clock
Int. Clock = 1.5 X Ext. Clock
Int. Clock = 2 X Ext. Clock Short
Int. Clock = 2.5 X Ext. Clock Short Short
Int. Clock = 3 X Ext. Clock
C—
O
O
C—
C—
O
tn
O
1.5xExtClk ZxExtClk
CXI
3
(p
0
o
o
c_
~X)
•PM»
JP14 JP15
Open Open 75/90/100
Open 120/133MHZ
Open Short
C—
“O
0 o
C—
$
CXI
0
2.5 X Ext Clk 3 X Ext Clk
150/166MHZ
“D
o
C-
(7)
3
CXI
0
4-3
Page 65

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Voltage Regulator Output Selector: JP19 & JP21
Set these jumpers according to the voltage type of the installed CPU.
JP19 JP21
STP/VR
VRE
IMPORTANT: You must set these jumpers correctly for the CPU's voltage type or
your system will operate improperly. An incorrect setting can damage the CPU.
Open Short
Short
"O
ro
O
O
"D
CO
3.3V+5%
STD/VR
Open
"O
ro
o
o
"O
CD
3.45V-3.6V
VRE
4-4
Page 66

Technical Summary
Flash EPROM Boot Block Write Selector: JP24
This jumper prevents or allows writing to the BIOS flash EPROM boot block.
JP24
Boot Block Protect
Boot Block Programmable
I
O
~o
ro
Boot Block
Protected
1&2 Default
2&3
O
1
~U
ro
Programming
Enabled
4-5
Page 67

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
CPU External Clock Speed Selector: JP26& JP27
Set these as shown, according to the CPU's internal clock speed.
Int. Clk
166MHz 66Mhz 2&3
150MHz
133MHz
120MHz
100MHz 66Mhz 2&3 1&2
90MHz 60Mhz 1&2 2&3
75MHz
Important CPUs are normally listed by their internal dock speed, as
shown above. You MUST also set JP14 & JP15 for the correct multiple of
the external clock speed.
Ext. Clock JP26
60Mhz 1&2 2&3
66Mhz 2&3 1&2
60Mhz 1&2 2&3
SOMhz
40Mhz 1&2 1&2
o
2&3
o
JP27
1&2
2&3
Int. Clk Multiple
2.5 X Ext. Clock
2.5 X Ext. Clock
2 X Ext. Clock
2 X Ext. Clock
1.5 X Ext. Clock
1.5 X Ext. Clock
1.5 X Ext. Clock
1.5 X Ext. Clock
o o
O
-O "O
ISJ N3
^ 03
66MHz Ext. 60MHz Ext. 50MHz Ext.
o
■ n “D
ro N3
03
C- C—
"O "O
PO PO
03
o o
c_ c_
“D -D
ro ISO
03
40MHz Ext.
4-6
Page 68

Technical Summary
UARTг/IR Selection: JP35 & JP36
These set UART2 to support either the second serial port and COM 2 connector or
the IR (InfraRed) port and JP31 connector.
JP35
COM2 1&2
IR 2&3
“D
Ca3
CD
■ a
CO
cn
C.
"T?
CO
cn
JP36
1&2
2&3
c_
“O
CO
CJl
o o
i
I
o
o
Enable
COM2
SMC I/O Selector: JP37
This Enables/Disables the onboard SMC Multi-I/O features.
i
Enable
IR
JP37
Enable 1&2
Disabled
C_
"O
CO
2&3
o
Enable
SMC I/O
S3
o
Disable
SMC I/O
4-7
Page 69

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Level 2 Cache Options
Cache Type & Size: See jumper section for settings, and below for other
specifications. Cache RAM required speed is 15ns,
This mainboard supports standard Asynchronous SRAM in the sockets, or Burst or
PipeTine Burst SRAM on a cache module installed in the cache socket. Refer to
the chart below for specifications. You can upgrade either cache.
Cache Specifications
Cache Type
SRAM Sockets
Cache Module
Size
256KB
512KB 64K8x8pcs
1MB 128K8x8pcs 32K8x1 pc
256KB
512KB
Data Chip Size
32K8x8pcs
Tag Chip Size
8K8,16K8or32K8x1pc
16K8or 32K8x1pc
Important:
Data SRAM mustbe either Mixed Mode or 3.3V SRAM.
Tag SRAM must be either Mixed Mode or -I-5V SRAM.
Note that jumpers JPG and JP8 select the cache size for both types of
cache, so you must set them for the size of the installed cache.
L2 Cache Size
256KB 32MB
Cacheable Memory Size
4-8
512KB 64MB
1MB
This chart shows the maximum amount of
system memory each size option can cache.
128MB
Page 70

L2 Cache Options
Socketed SRAM cache options
Technical Summary
111
32-pin
64K8
or
128KB
MÎ!":
r
28-pin
8K8 or
32K8
Tag
chip
Cache module installation
28-pin
32K8
Note: 28-pin chips use the 32-in sockets
256KB
cache
32K8x8
Chip
installed
Socket
empty
■
512KB
cache
64K8x8
or
The cache modulesocket is
designed so that the cache module
can only be inserted one way,
preventing incorrect orientation
1MB
cache
128K8x8
4-9
Page 71

P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
External Connections
There are several connectors on the board for switches and indicator lights from
the system case. The connectors are made of the same components as the
jumper switches. There are also connectors for the on-board I/O ports and a
system power supply.
Connector Block:
SMI Switch Connector for a Suspend switch lead.
Reset Switch Connector for a Reset switch lead.
Speaker Connector for a system case speaker lead.
Keylock Connector for a keyboard lock and Power-On LED.
Turbo Switch Connector for a Turbo Switch. No function on this mainboard.
Turbo LED Connector for a Turbo LED.
[Note: The Turbo feature is not supported on this mainboard. A Turbo LED will
light all the time if connected, but a switch will have no effect.]
PS/2 Mouse Connector for a PS/2 mouse port lead.
JP10 SM Out Connector for a power management lead from a green device.
JP17 Fan Power Connector for cooling fan +12V power lead.
JP29 IDE LED
JP30VOI Control
JP31 IR
Fan Power, volt Lithium cell. It has a life expectancy
IDE LEO, M ""I I of approximately 7 years. Replace it by
Case, IR &
Volume Control ^ battery out. Insert a new battery
connectors CMOS Battery with the writing side face up.
Connector for an IDE activity LED.
Connector for a digital volume control module
Connector for an IrDA-compliant infrared port module
PS/2 Mouse
connector (or port)
Please Note:
The battery that supports the onboard
CMOS memory (where the system
configuration record is stored) is a 3-
--------
1 lifting up the retaining clip and pulling
4-10
Page 72

Technical Summary
Case Feature Connectors
Turbo LED + Eo
SMI Suspend Switch
I o
CO
o
oo
oo
oo
oo
Tv
5
o
O
7^
Keylock
Turbo Switch ^
Reset
Other Feature Connectors
Off-board PS/2 Mouse
port lead connector (some
models have an on-board
PS/2 mouse port instead)
O
o ^
o
c_
m JP29
oo
■ o
CO
ooooo
Fan power lead
connector (+12V)
IDE LED activity
light connector
Infrared port
connector
IRCON
3D
m
CO
o
oo
o
oo
oo
CO
-D
Speaker
feature connector
<
o
r”
o O
o
—1
3D
O
i“
Volume Control
connector
O
O
00
o
c:
SM Out green
Pin Out
- GND
o
o
UP
MUTE
o DOWN
o GND
P30
4-11
Page 73

PA-P55SP3AV User's Manual
I/O Port Connectors
Serial Port cable connectors,
C0M1 (upper), COM2 (lower)
Game port
cable connector
Floppy Disk Drive
Parallel Port
cable connector
When you connect a ribbon cable, you must orient the cable connector so
that the Pin 1 edge of the cable is at the Pin 1 end of the on-board connec
tor. The Pin 1 edge of the ribbon cable is colored to indentify it.
Port & Controller Cables
The mainboard comes with the following cables. External ports attach to the
cable connector
IDE Hard Disk Drive
cable connectors.
Primary (left),
Secondary (right)
mainboard with ribbon cables that are attched to the port mounting bracket.
External ports:
• 2 serial ports with ribbon cables attached to one mounting bracket
• 1 parallel port
• 1 game port
Internal Controller Cables
• 1 IDE ribbon connector cable
• 1 floppy disk drive ribbon connector cable
4-12
Page 74

Technical Summary
Connector and Port Cables
Floppy Drive ribbon cable
IDE ribbon cable
Game port & cable
Important Note: IDE ribbon cables must be < 18 in. (46cm), with the
Parallel port & cable
Serial ports & cable
second drive connector no more than 6 in. (15cm) from the first
connector. Any second IDE cable used to attach devices to the
second IDE channel, must meet these required specifications.
Connecting A Power Supply
The system power supply connector on the mainboard is for a standard power
supply. To connect the leads from the power supply, you should first make sure
the power supply is unplugged. Most power supplies have two leads. Each lead
has six wires, two of which are black. Orient the lead plugs so the black wires' are
in the middle when attached to the mainboard.
Align the plastic guide pins on the lead plug to its receptacles on the connector.
You may need to hold the plug at an angle to align the guide pins. Once you have
the guide pins aligned, press the plug onto the connector so that the plastic clips
on the plug snap into place and secure it to the connector.
4-13
Page 75

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Audio/Display & Display Port Cards
Audio/Display Port Card
CD-ROM -
Wave Table Audio
Connector Connectors
t———1—i—
SONY
Mitsumi
Panasonic
v'-'”' •” ..
■ -.i-; ■ -■ ■vi '' -
lilEiiiiMlIllilllllllpllilillllllll
;
___
Display Port Card
............
.
...
■ ■ ' v
Microphone
Line - In
Volume Control
External Speaker
15-pin Display
Monitor Port
To install, plug either
card into the connector
on the mainboard. The
4-14
VGA-only card only
uses a section of the
connector.
15-pin Display
Monitor Port
Page 76

Technical Summary
The PCI-SC200 SCSI Interface Card
Your mainboard may have come with an optional SCSI (Small
Computer System Interface) controller card, the PCI-SC200. The card
is also available separately. This card works with the SCSI BIOS on
the mainboard. Together, they provide a complete PCI Fast SCSI-2 in
terface. With the card installed in your system you can connect SCSI
devices installed in your system case to the internal connector on the
card. You also have the additional option of connecting external SCSI
devices to the external SCSI-2 connector on the card.
If you get the PCI-SC200 later on as an option, you will need to
install it yourself. The setup procedure is explained here. The basic
card installation procedure is explained at the end of Chapter 2.
The PCTSC200 SCSI Interface Card
Internal SCSI ribbon cable connector
External SCSI 2 cable connector
PCI edge connector
Setting Up the PCI-SC200
There are two jumper settings you may need to make on the card
to set it up. One setting assigns the PCI INT interrupt, the other sets
the card's termination.
4-15
Page 77

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Setting the INT Assignment
As explained in Chapter 2, any PCI card you install must use PCI
INT A. On the PCI-SC200, you assign the INT by setting jumper JPl
or JP2. The default setting for the card already is INT A, so you do
not need to change the setting to use the SC-200 with this mainboard.
The INT assignment jumper settings are illustrated below. The
settings are printed on the card for your convenience.
JPl & 2: Interrupt settings
CP
Q_ Q_
“5 —>
C)
CM »—
6
o
o
INT A
(default)
Terminator Settings
SCSI devices are connected together in a "chain" by cables. In
ternal devices connect to the PCI-SC200 with a fifty-pin flat ribbon
cable. External devices connect to the external port with a SCSI-2
cable. If there is more than one internal or external device, additional
devices are connected with cables to form a "daisy chain". The SCSI
chain must be "terminated" at both ends, or the devices in the chain
will not work properly.
1
INTB INTO
o
O'
CM «—
O- Q_
—> —i
o
o
C)
i)
(...)
CM »—
O- O-
—3 “3
n
o
CC)
s
INTD
CM
O-
4-16
Page 78

Technical Summary
Many SCSI devices use a set of terminating resistors to terminate
the device. The PCTSC200 has "active" termination that you set us
ing jumper JP5. If you need to terminate the PCI-SC200, you do it by
setting the jumper. The are two settings, terminated and
unterminated, as shown below.
JP5: Terminator setting
%
LO
Q_
Termination
Disabled
in
Termination
Enabled
(default)
Decide whether or not you need to terminate the PCI-SC200
based on its position in the SCSI chain. Only the devices at each end
of the chain need to be terminated. If you have only internal or only
external devices connected to the PCI-SC200, then you must termi
nate the PCI-SC200. If you have both internal and external devices
connected, you must not terminate the card. The figures on the next
page illustrate these requirements.
SCSI ID Numbers
All SCSI devices, including the PCI-SC200 interface card must
have a SCSI identification number that is not in use by any other SCSI
O-
( )
L
device. There are eight possible ID numbers, 0 through 7. The PCISC200 has a fixed SCSI ID of 7.
You can connect up to seven SCSI devices to the interface card.
You must set a SCSI ID number for each device. SCSI devices vary
in how they set the ID number. Some use jumpers, others have some
kind of selector switch. Refer to the manual for any device you in
stall for details on how to set its ID number.
4-17
Page 79

P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Example 1: Only internal or only external devices connected
Internal SCSI Cable
SCSI
Device 1
(Termination
Disabled)
SCSI
Device 2
End Device
(Termination
Enabled)
Note: SCSI controller
Beginning Device
(Termination Enabled)
card ID# is "7".
Example 2: Both internal and external devices connected
Internal SCSI Cable
SCSI
Device 3
SCSI
Device 4
(Card Termination Disabled)
4-18
External SCSI Cable
SCSI
Device 2
(Termination
Disabled)
(Termination
Disabled)
Note: SCSI interface
card ID# is still "7 ".
SCSI
Device 1
Beginning Device
(Termination
Enabled)
End Device
(Termination
Enabled)
Page 80

TECHNICAL UPDATE
Product Number:
Motherboard Revision:
Manual Revision:
P/I-P55SP3AV
1.2 and later
1.02
On page 1-4, the forth feature item should read:
• Write-back "Level 2" external static RAM cache with two cache
options, SRAM sockets and a cache module slot. The SRAM
socket allows installation of 256KB, 512KB, or 1MB of SRAM
cache chips. When a pipeline burst cache module is installed you
must remove the SRAM chips to prevent conflicts.
On page 1-5, the third feature item second sentence should read:
...The controller supports PIO Modes 3 and 4 at a maximum trans
fer rate of 17MB/second and Bus Master IDE DMA Mode 2 at
maximum transfer rate of 22MB/second.
On page 4-6, remove all references to 40MHz Ext Clock
On page 4-11, the Fan power connector in detail:
jp
17
B-
G-
CPU Fan Power Connector
GND
+ 12V
GND
P/I-P55SP3AV User's Manual
Page 81

TECHNICAL UPDATE
Product Number:
Motherboard Version:
Manual Version:
P/I-P55SP3AV
1.2 and later
1.1
On Page 2~7, the two sentences:
DRAM Speed: 70ns or faster for 50,60 or 66MHz external clock. EDO
DRAM requires 60ns or faster for a 66MHz external clock setting.
Change to:_______________________________
DRAM speed requirements for both FP DRAM & EDO DRAM:
CPU internal clock (speed of the CPU): 75,90,120, 150MHz
CPU external clock: 50 or 60MHz
>Use 70ns or faster (the lower the number, the faster)
CPU internal clock (speed of the CPU) 100,133,167MHz
CPU external clock: 66MHz
>Use 60ns or faster (the lower the number, the faster)
On Page 4~7:
If you have a UMC Super MuIti-I/0, the jumper settings for JP35, JP36,
and JP37 are not used. The default settings for JP35 and JP36 are fixed
on position 1-2 and JP37 is removed.
The Infrared function on the UMC super multi-I/0 chip is enabled
through BIOS setup only, no hardware settings are necessary.
Check to see whether you have a
SMC Super Multi-I/0 or a UMC
Super Multi-I/0. The above ap
plies to UMC only, otherwise re
fer to page 4-7 for UART2/IR Se
lection.
P/I-P55SP3AV User’s Manual
Page 82

Declaration of Conformity
We, Manufacturer/Importer
(fuil address)
ASUS COMPUTER GmbH
HARKORT STR. 25
40880 RATINGEN, BRD. GERMANY
declare that the product
(description of the apparatus, system,, installation to which it refers)
MOTHERBOARD & AV CARD
P/I-P55SP3AV WITH AV689
is in confirmity with
(reference to the specification under which confirmity is declared)
in accordance with 89/336 EEC-EMC Directive
DECLARE.DOC
n EN 55011 Limits and methods of measurement
of radio disturbance characteristics of
industrial, scientific and medical (ISM)
high frequency equipment
n EN55013 Limits and methods of measurement
of radio disturbance characteristics of
broadcast receivers and associated
equipment
□ EN 55014 Limits and methods of measurement
of radio distrubance characteristics of
household electrical applicances,
portable tools and similar electrical
apparatus
□ EN 55015 Limits and methods of measurement
of radio disturbance characteristics of
fluorescent lamps and luminaires
□ EN 55020 Immunity from radio interference of
broadcast receivers and associated
equipment
m EN 55022 Limits and methods of measurement
of radio disturbance characteristics of
information technology equipment
□ DIN V VDE 0855 Cabled distribution systems: Equipment
EN 61000-3-2^
EN60555-2
□ EN61000-3-3*
EN60555-3
m EN 50081-1
@ EN 50082-1
m prEN 55024-2
EN61000-4-2
@ prEN 55024-3
EN61000-4-3
m prEN 55024-4
EN61000-4-4
□ prENV 50142
□ ENV 50141
□
electrical equipment "Harmonics"
electrical equipment "Voltage fluctuations’
Generic emission standard
Generic immunity standard
“ESD" (lEC 801-2) (IEC1000-4-2)
Radiated, radio frequency electromagnetic
field (lEC 801-3) (IEC1000-4-3)
Electrical fast transient requirements
Surge immunity requirements
(lEC 801-5)
Immunity to conducted disturbances
□ part 10 for receiving and/or distrubution from
G part 12 sound and television signals
11 CE marking (EC conformity marking)
The manufacturer also declares the conformity of above mentioned product
with the actual required safety standards in accordance with LVD 73/23 EEC
Disturbances in supply systems caused
by household appliances and similar
Disturbances in supply systems cause
by household appliances and similar
Electrostatic discharge requirements
■Burst" (lEC 801-4) (IEC1000-4-4)
* Replacement of
EN60555-2/-3
Ref. No. 9511185E
 Loading...
Loading...