Page 1

Voice Gateway &
Pocket Voice Gateway
H.323 and MGCP Protocols
User’s Manual
Page 2
USER'S NOTICE
No part of this manual, including the products and software described in it, may be
reproduced, transmitted, transcribed, stored in a retrieval system, or translated into
any language in any form or by any means, except documentation kept by the purchaser
for backup purposes, without the express written permission of THE MANUF ACTURER.
THE MANUFACTURER PROVIDES THIS MANUAL “AS IS” WITHOUT WARRANTY
OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED
TO THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
MANUFACTURER, ITS DIRECTORS, OFFICERS, EMPLOYEES OR AGENTS BE
LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
DAMAGES (INCLUDING DAMAGES FOR LOSS OF PROFITS, LOSS OF BUSINESS,
LOSS OF USE OR DATA, INTERRUPTION OF BUSINESS AND THE LIKE), EVEN
IF THE MANUFACTURER HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES ARISING FROM ANY DEFECT OR ERROR IN THIS MANUAL OR
PRODUCT.
Product warranty or service will not be extended if: (1) the product is repaired, modified
or altered, unless such repair, modification of alteration is authorized in writing by THE
MANUFACTURER; or (2) the serial number of the product is defaced or missing.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered
trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for
identification or explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
The product name and revision number are both printed on the product itself. Manual
revisions are released for each product design represented by the digit before and
after the period of the manual revision number. Manual updates are represented by
the third digit in the manual revision number.
For previous or updated manuals, BIOS, drivers, or product release information, contact
THE MANUFACTURER.
SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION CONTAINED IN THIS MANUAL ARE
FURNISHED FOR INFORMA TIONAL USE ONLY, AND ARE SUBJECT T O CHANGE
AT ANY TIME WITHOUT NOTICE, AND SHOULD NOT BE CONSTRUED AS A
COMMITMENT BY THE MANUFACTURER. THE MANUFACTURER ASSUMES NO
RESPONSIBILITY OR LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS OR INACCURACIES THAT
MAY APPEAR IN THIS MANUAL, INCLUDING THE PRODUCTS AND SOFTWARE
DESCRIBED IN IT.
Copyright © 2001 All Rights Reserved.
Product Name: Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Manual Revision: 1.00 E790
Release Date: Aug 2001
2 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 3

CONTACT INFORMATION
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 3
Page 4

CONTENTS
1. Introduction .............................................................................. 7
1.1. How to make calls to Internet phones................................ 7
1.2. How to make calls to PSTN phones .................................. 7
1.3. Item Checklist .................................................................... 7
2. Features .................................................................................... 8
2.1. Voice Gateway Features.................................................... 8
2.2. Pocket Voice Gateway Features........................................ 9
3. Specifications......................................................................... 10
3.1. Model Specifications and Comparison ............................ 10
4. Installation .............................................................................. 11
4.1. Understanding the Voice Gateway ...................................11
4.1.1 Front Panel LED Descriptions ................................11
4.1.2. Rear Panel Descriptions ....................................... 12
4.2. Connecting the Voice Gateway........................................ 14
5. System Configuration............................................................ 15
5.1. Console Control ............................................................... 15
5.1.1 PIN Definition of RJ-45 type UART........................ 15
5.1.2. COM Port Configurations...................................... 16
5.1.3. Access Console Control........................................ 17
5.1.4. Console Command Set......................................... 18
5.2. Telnet Control.................................................................. 27
5.2.1. Establish Connection ............................................ 27
5.3. Web (HTTP) Console....................................................... 27
5.3.1. System Info (VoIP MISC) ...................................... 28
5.3.2. H.323 Info ............................................................. 30
5.3.3. MGCP Info ............................................................ 32
5.4. Keypad Control ................................................................ 34
5.4.1. Basic Commands.................................................. 34
5.4.2. Supplemental Services Commands...................... 36
4 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 5

CONTENTS
6. Software Upgrade .................................................................. 37
6.1. Through the User Console Interface................................ 37
6.2. Through the HTTP Web Console..................................... 40
7. System Operation .................................................................. 44
7.1 H.323 Notes...................................................................... 44
7.2 MGCP Notes..................................................................... 45
7.3 Application Examples........................................................ 45
7.4 VoIP Voice Gateway to VoIP Networks............................. 48
7.5 VoIP Voice Gateway to VoIP Networks with PSTN line .... 49
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 5
Page 6

FCC & DOC COMPLIANCE
This device complies with FCC Rules Part 15. Operation is subject to the
following two conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference, and
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits
are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate
radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
manufacturer's instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment to an outlet on a circuit different from that
to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
WARNING! Any changes or modifications to this product not expressly approved by the manufacturer could void any assurances
of safety or performance and could result in violation of Part 15 of
the FCC Rules.
6 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 7

1. Introduction
Thank you for purchasing an Voice Gateway / Pocket V oice Gateway . The Voice
Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway, like the rest of the VoIP voice gateway products offers the highest performance and interoperability capabilities in a Voice
over Internet Protocol (VoIP) environment for residential and small business
users. With VoIP technology, users can dial with a VoIP phone to all over the
world at a very low cost or even no cost.
This new “VoIP voice gateway” not only provides a compact integration of
technology but also opens the gate to the Internet for traditional Plain Old
T elephone Service (POTS). By connecting the Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice
Gateway to a broadband data network, such as a cable modem or xDSL
modem, high quality telephony service though the Internet can easily be
attained.
With high compression rates and well-engineered VoIP voice gateway jitter
control system, the Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway can also provide smooth and high quality telephone service even on an original
narrowband network, such as ISDN.
1.1. How to make calls to Internet phones
If you have already an Internet Service account from your local ISP , you can use
this service to provide VoIP Telephone Service by VoIP voice gateway. Make
sure that your ISP’ s firewall allows VoIP services (H.323 or MGCP).
1.2. How to make calls to PSTN phones
As well as free telephony service by VoIP technology of VoIP products, you
can subscribe to an Internet Telephony Service Account from your ITSP,
then you can let your Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway to provide
telephony service to PSTN.
NOTES: The Media Access Control (MAC) address (printed on a label on the bottom of the voice gateway) is needed for your local ISP/
ITSP to configure your subscription. Have this number ready before
you contact your local ITSP.
1.3. Item Checklist
Check that your package is complete. If you discover damaged or missing
items, please contact your retailer.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
AC Power adapter
Ethernet cable (RJ-45, Catagory 5)
UART RJ-45 Console Cable
This User’s Manual
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 7
Page 8

2. Features
2.1. Voice Gateway Features
Supports
• G.711/G.723.1/G.729A voice compression algorithm
• Multiple VoIP protocols: H.323, H.225.0, Q.931, H.245, R TP/R TCP,
H.450*, H.235*, MGCP 1.0: MGCP, SDP, RTP/RTCP
• Multiple UI/GUI for management and configuration: Web Console,
Telnet, Console, Phone Set, SNMP.
• Voice: DTMF detection and generation, G.168 compliant echo canceller, silence detection (VAD) and CNG, Call Progress and User
Tone Generation, Caller ID (optional), FoIP supporting T.30 & T.38
Fax Relay (optional)
• T elephony Supplemental services: Inner Conference Call, Speed Dial,
Redial, Call Back, Distinct Ring, Call waiting*, Call Holding*, and
Call Forwarding*
• Supports multiple languages for phone set configuration (phone number report & speed dial), voice record & playback*, and voice mail*
Provides
• T wo 10/100 Base-T Fast Ethernet RJ-45 interfaces — WAN & LAN
• One UART RJ-45 connector console interface
• One or four RJ-11 POTS interfaces, FXS and FXO available
FXS only: 2 or 4 FXS port
FXO/FXS: 1 FXO i/f and 1 or 3 FXS port
FXO only: 2 or 4 FXO port
8 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 9

2. Features
2.2. Pocket Voice Gateway Features
Support
• G.711/G.723.1/G.729A# voice compression algorithm
• Multiple VoIP protocols: H.323, H.225.0, Q.931, H.245, R TP/R TCP,
H.450*, H.235*, MGCP 1.0: MGCP, SDP, RTP/RTCP
• Multiple UI/GUI for management and configuration: Web Console,
Telnet, Console, Phone Set, SNMP.
• Voice: DTMF detection and generation, G.168 compliant echo canceller, silence detection (VAD) and CNG, Call Progress and User
Tone Generation, Caller ID (optional), FoIP supporting T.30 & T.38
Fax Relay (optional)
• T elephony Supplemental services: Inner Conference Call, Speed Dial,
Redial, Call Back, Distinct Ring, Call waiting*, Call Holding*, and
Call Forwarding*
• Supports multiple languages for phone set configuration (phone number report & speed dial), voice record & playback*, and voice mail*
Provides
• Provide one 10/100 Base-T Fast Ethernet RJ-45 interface
• Provide one UART RJ-45 connector console interface
• Provide one RJ-11 POTS interfaces, FXS and FXO available
FXS: 1 FXS port
FXO: 1 FXO port
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 9
Page 10
3. Specifications
3.1. Model Specifications and Comparison
Description
Models:
Tel Interface:
FxS Ports:
FxO Ports:
CPE Interface:
Console:
VoIP Protocols:
Voice Compression:
Voice Features:
Tel Supp Services:
Voice Gateway Pocket Voice Gateway
FXS only FXO/FSX FXO only FXS FXO
2 or 4 RJ-11 POTS interface 1 RJ-11 POTS Interface
2 or 4 1 or 3 0 1 0
0 1 2 or 4 0 1
LAN: 10/100 Base-T Ethernet (RJ45) WAN: 10/100 Base-T Ethernet Crossover
WAN: 10/100 Base-T Ethernet Crossover USB*
UART RJ45 Serial Interface
MGCP or H.323 Selectable with RTP/FTCP Transmission
G.711 (a-law / µ-law), G.723.1 (5.3kbps / 6.3kbps), G729A
DTMF Detect / Generate, G.168 Compliant DTMF Detect / Generate, Echo
Echo Canceller, Silence Detection, (VAD) Cancellation, Silence Detection (VAD),
and CNG, CAll Progress Tone Generation, Call Progress, Tone Generation
User Defined Tone Generation, Caller ID*,
T.38 Fax Relay*
Inner Conference Call, Speed Dial, Redial, Call Back,
Configuration:
Power Adapter:
Distinctive Ring, Call Waiting*, Call Holding*, and Call Forwarding*
Console Telnet Web Console, Keypad, SNMP
+5V, -24V, -56V, -5V +12V 2.5A
*optional features
10 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 11
4. Installation
4.1. Understanding the Voice Gateway
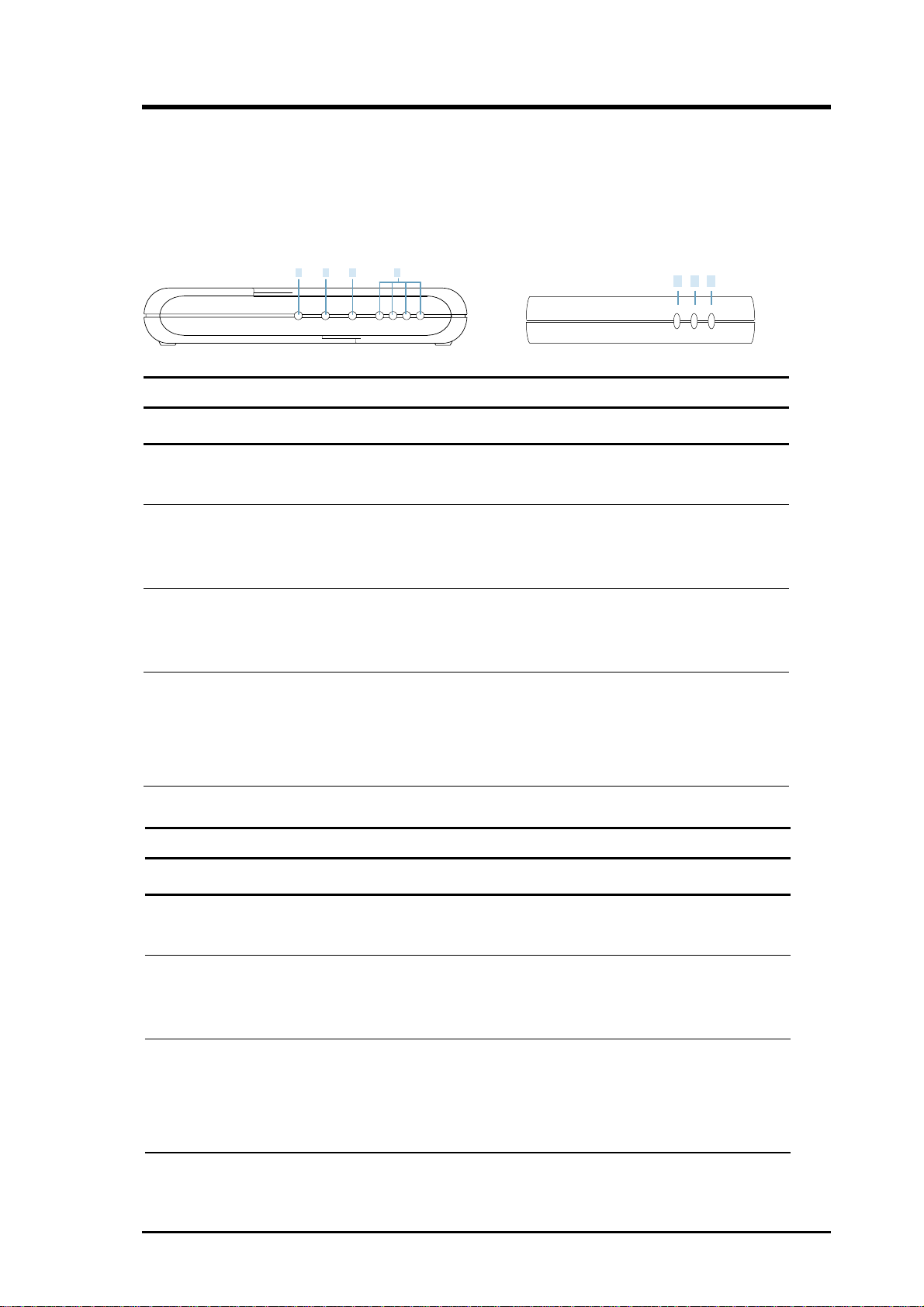
4.1.1 Front Panel LED Descriptions
Voice Gateway
1 2 3 4
PWR LAN WAN P4 P3 P2 P1
Pocket Voice Gateway
1 2 3
POWER
WAN
TEST
Voice Gateway
LED State Description
1. PWR On Voice Gateway is power ON
Off Voice Gateway is power Off
2. LAN On LAN port is linked with other device
Flashing Data is transmitting
Off No network connectivity on this port
3. WAN On WAN port is linked with other device
Flashing Data is transmitting
Off No network connectivity on this port
4. P4–P1 Off T elephone Set is On-Hook or Line is not enabled
On Telephone Set is Off-Hook
Flashing Ring Indication
NOTE: System initialization will turn the LED ON for a few sec.
Pocket Voice Gateway
LED State Description
1. PWR On Voice Gateway is power ON
Off Voice Gateway is power Off
2. LAN On LAN port is linked with other device
Flashing Data is transmitting
Off No network connectivity on this port
3. LINE/ Off Telephone Set is On-Hook or Line is not enabled
PHONE On Telephone Set is Off-Hook
Flashing Ring Indication
NOTE: System initialization will turn the LED ON for a few sec.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 11
Page 12
4. Installation
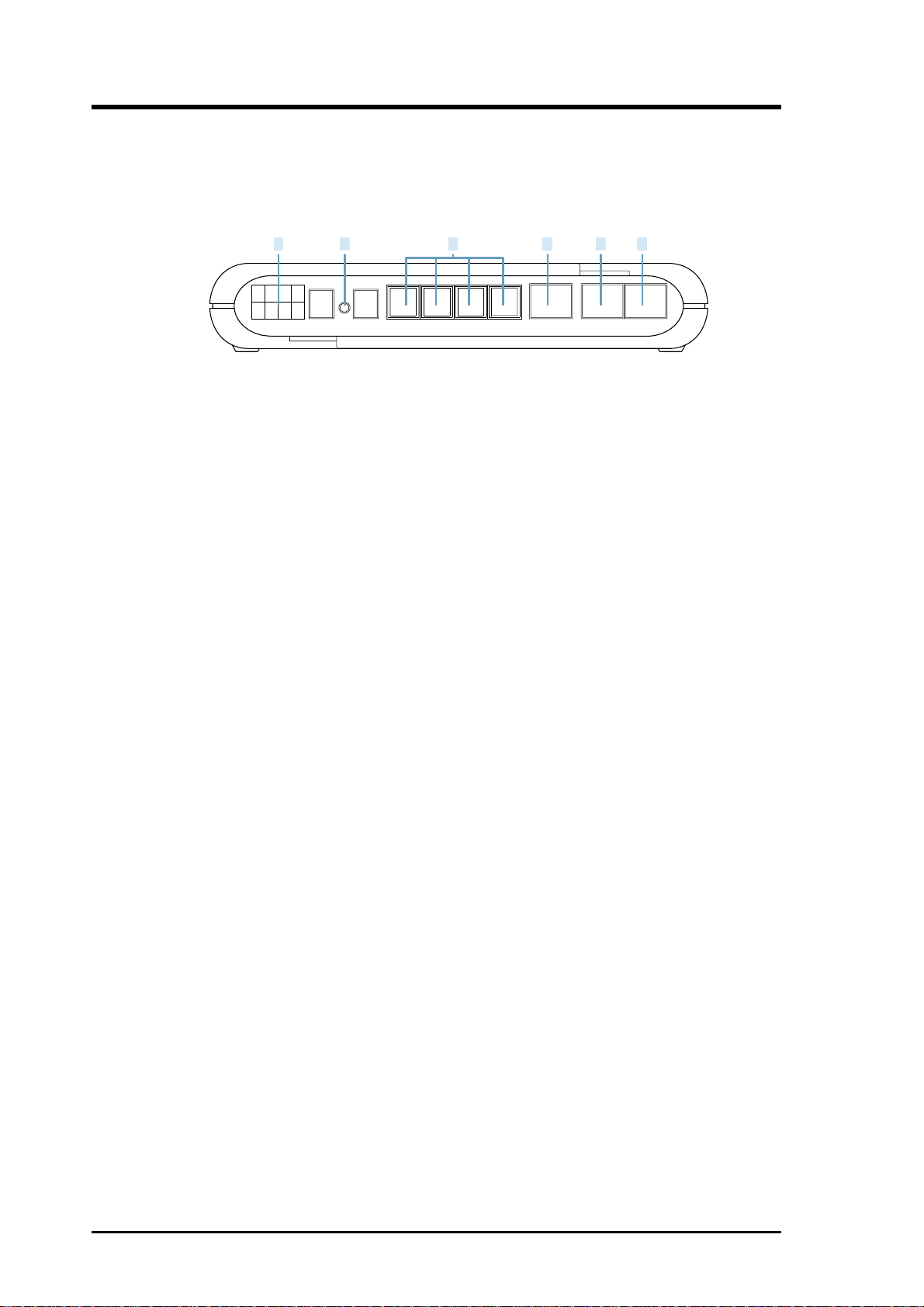
4.1.2. Rear Panel Descriptions
Voice Gateway
1 3 4 652
DC POWER Reset
Console
LAN WANP1 P2 P3 P4
1. DC Multiple-voltage Power Input Jack
The provided power adapter converts AC power to multiple-voltage DC
power for use with this jack. Power supplied through this jack will supply power to the voice gateway
2. Reset
The reset button, when pressed, resets the voice gateway without the
need to unplug the power cord.
3. P1 - P4 (Phone Lines)
These ports are connected to either telephone sets or telco’s telephone
line depending to different models:
FXS only model: P1-P4 are connecting to telephone sets
FXO/FXS model: Line is connecting to telco’s telephone line while P2-
P4 are connecting to telephone sets.
FXO only model: L1-L4 are connecting to telco’s telephone line.
4. CONSOLE
The RJ45 port supports the RS232 terminal interface for voice gateway
management
5. LAN (optional)
The LAN port supports 10/100Base-T networks. This port allows your
PC to be connected to the voice gateway through a CAT.5 twisted pair
Ethernet cable.
6. WAN
The WAN port supports 10/100Base-T networks. This port (built with
crossover) allows your voice gateway to be connected to an Internet
Access device, e.g. router, cable modem, ADSL modem, through a CA T .5
twisted pair Ethernet cable.
12 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 13
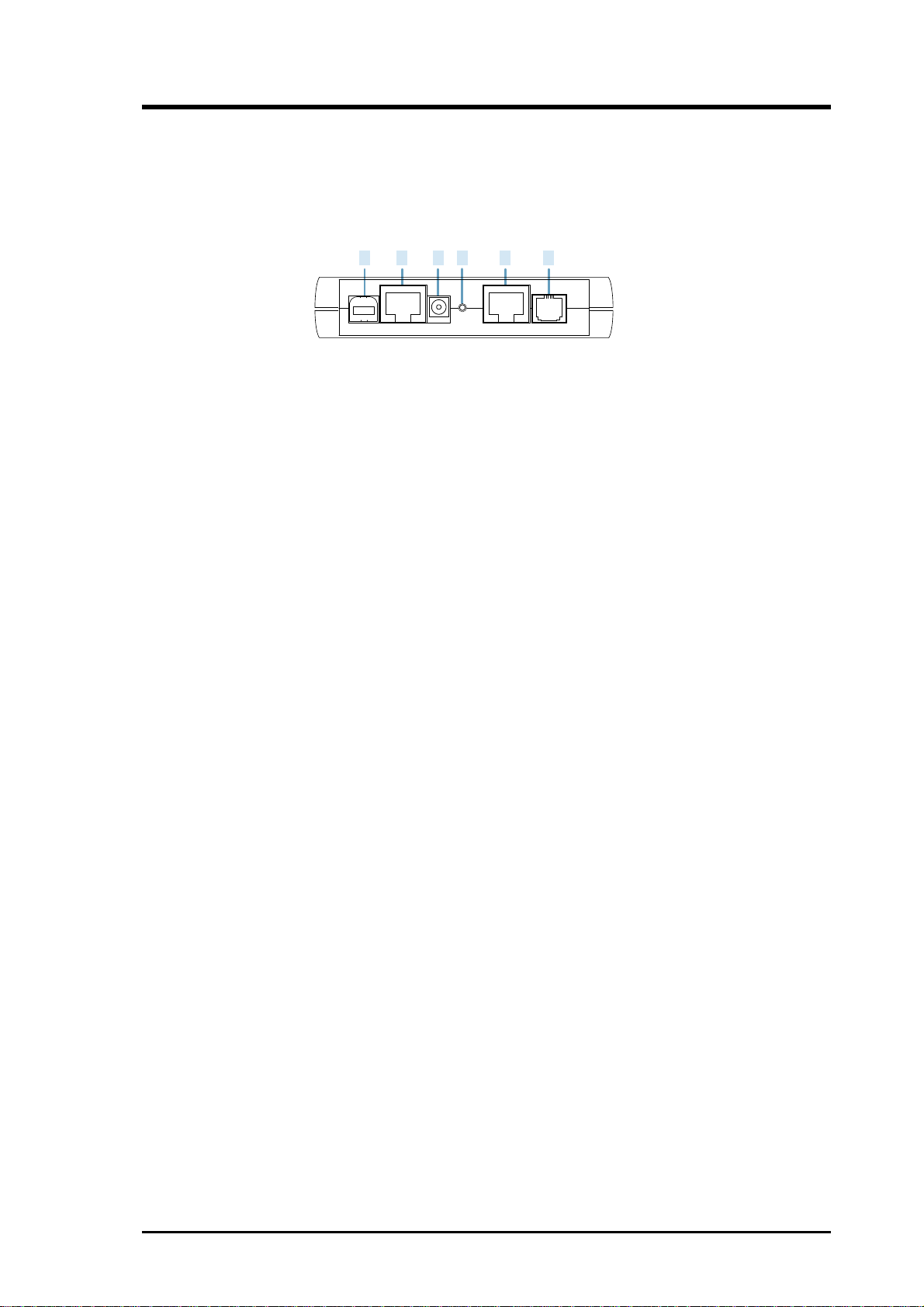
Pocket Voice Gateway
4. Installation
1 2 3 5 6
USB PWR PHONELANResetCONSOLE
4
1. USB (optional)
The oprtional USB port allows the pocket voice gateway to be connected
to your computer through the USB interface
2. CONSOLE
The RJ45 port supports the RS232 terminal interface for voice gateway
management
3. DC +12V/1.25A Power Input Jack
The provided power adapter converts AC power to DC power for use
with this jack. Power supplied through this jack will supply power to the
pocket voice gateway.
4. Reset
The reset button, when pressed, resets the voice gateway without the
need to unplug the power cord.
5. LAN
The LAN port supports 10/100Base-T networks. This port allows your
PC to be connected to the voice gateway through a CAT.5 twisted pair
Ethernet cable. The RJ45 port supports the RS232 terminal interface for
pocket voice gateway management
6. PHONE (LINE)
This port is connected to either a telephone set or telco’s telephone line
depending to different models:
FXS model: connecting to telephone sets (PHONE)
FXO model: connecting to telco’s telephone line (LINE)
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 13
Page 14

4. Installation
4.2. Connecting the Voice Gateway
T o avoid overheating problems, allow at least 3 centimeters (one inch) spacing between the ventilation holes and any object to either side of the unit.
Avoid any obstructions on the top of the unit. The top of the unit should be
at least 5 centimeters (two inches) from any obstruction. Connect the voice
gateway using the following steps:
1. Connect the Ethernet Cable from the WAN port of voice gateway to
the Internet access port. This Internet access port is a 10/100 BaseT
connection on a router, switch, or broadband devices, such as cable
modem or ADSL modem.
2. Connect the 10/100BaseT cable (RJ-45) from your computer to the
LAN port connector on the voice gateway rear panel (optional).
3. Connect the telephone line from your telephone to the P1–P4 (RJ-
11) connector on the rear panel.
4. Connect the AC adapter to multi-voltage input jack on the voice gateway rear panel. Then plug the AC adapter to a wall electrical outlet.
Pocket Voice Gateway
USB PWR PHONELANResetCONSOLE
POWER
Internet
Access
Device
TELEPHONE
DC POWER Reset
POWER
Voice Gateway
TELEPHONES
PC
Console
LAN WANP1 P2 P3 P4
Internet
Access
Device
PC
14 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 15
5. System Configuration
The Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway can be configured in many
ways such as using telnet, Web browser, telephone keypad, or SNMP control. Although there are many VoIP protocols, Voice Gateway currently supports H.323 protocol and MGCP protocol.
For H.323 protocol, it can support both version 2 and version 3.
For MGCP protocol, Voice Gateway can support most major profiles to
achieve maximum interoperability . This includes RFC standard profile (RFC
2705, MGCP 1.0), NCS standard profile (for Packet Cable, NCS 1.0), and
some proprietary profile (MGCP 0.1, NCS 1.0).
The following sections describe all methods for controlling Voice Gateway.
5.1. Console Control
This section describes how to set up the different operation modes or monitor
the performance of the Voice Gateway using the User Mode Console.
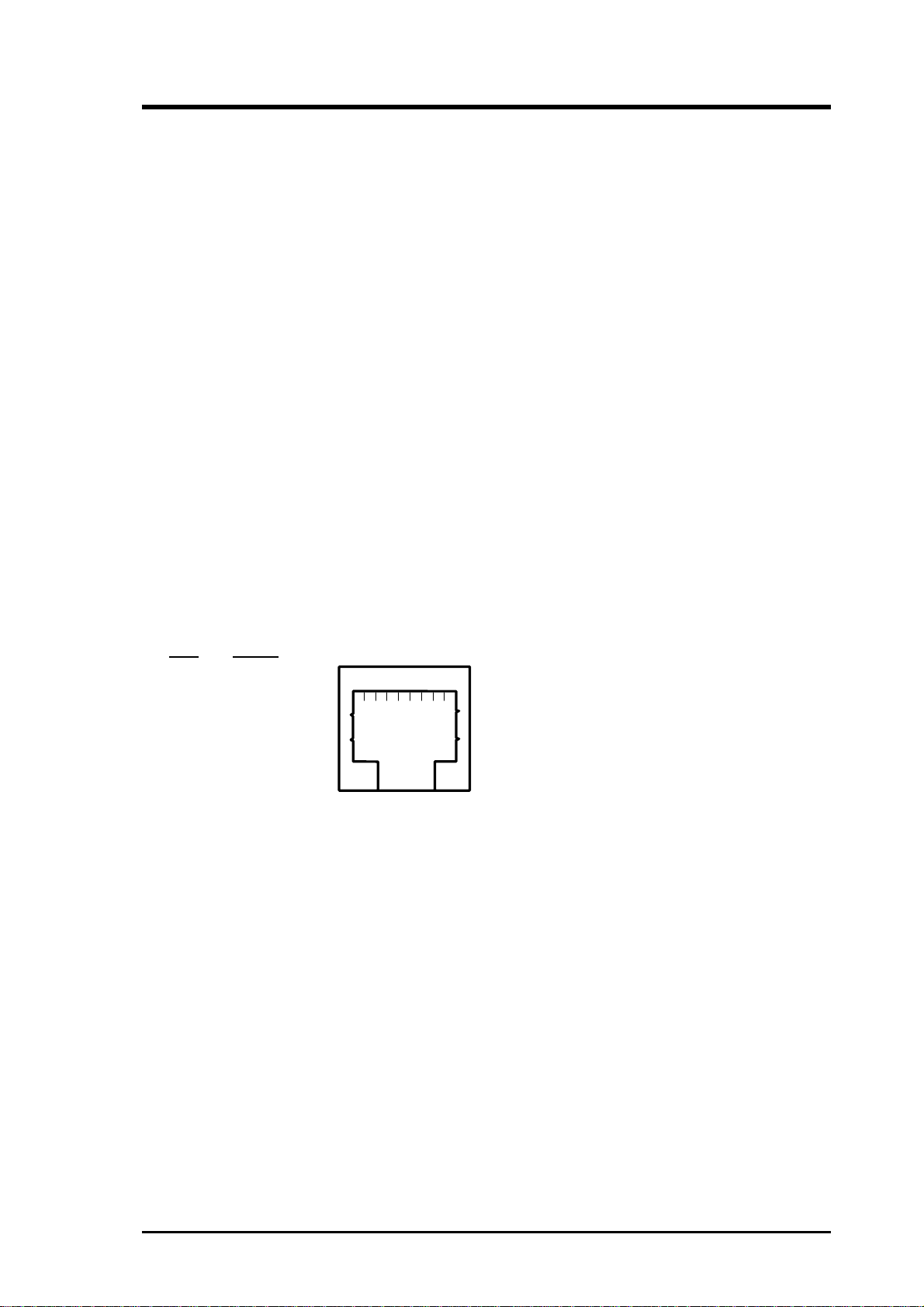
5.1.1 PIN Definition of RJ-45 type UART
PIN Signal
1NC
2NC
3 TXD
4 GND
5 GND
6 RXD
7NC
8NC
HUB RJ45 Connector
18234567
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 15
Page 16

5. System Configuration
5.1.2. COM Port Configurations
To access the user console, use the console cable to connect the Console
port on the Voice Gateway to your PC’s empty COM port. Open a VT100
terminal emulation program such as Windows’ HyperTerminal to configure the COM port. (The setup under HyperT erminal is given as an example
below.)
In Windows, click Start, Programs, Accessories, Communications, and
then select HyperTerminaI. When the HyperTerminal window appears,
double click the HyperT erminal icon to run it. If you cannot find it, add the
program using Add/Remove Programs in Control Panel.
1. When HyperTerminal is started, you
will be prompted to establish a new
connection. Follow the on-screen
instruction.
2. A user console connection do not
require dial-up information. Simply
choose the COM port that you are
using and then click OK.
3. Configure the COM port as shown
below. You are now ready to
configure the operation mode.
Recommended COM Port Settings:
Bit Rate: 9600 bps
Data Bits: 8
Parity Check: None
Stop Bit: 1
Flow Control: None
16 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 17

5. System Configuration
5.1.3. Access Console Control
In order to configure the voice gateway, press [CTRL D] to enter the console control mode. To protect the system settings, a username “voip” and a
password is required. The factory password is the last 6 digits of the Ethernet MAC address. For example, if the MAC address of the voice gateway is
00:E0:18:F0:00:36, then the default password is f00036. (The default password is in lower case) Use the command “passwd” to change the password.
To reset the Voice Gateway to the above default values, press [CTRL O R]
during system bootup while attached using the console cable.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 17
Page 18

5. System Configuration
5.1.4. Console Command Set
1. System Commands
h323 (valid only on H.323 Client)
Enter H.323 Client [H323] Command Group.
help
Display the help menu. It lists all available commands in the current command group.
ip
Enter TCP/IP [IP] Command Group.
info
Display all information. It shows all information about the Voice Gateway/Pocket Voice Gateway, including hardware and software version, Internet configuration, and run-time status.
mg (valid only on MGCP Client)
Enter MGCP Client [MG] Command Group.
ping
Send ICMP echo request. Use this command to detect the connectivity with other Internet devices.
quit
Quit console command mode.
reboot
Reboot the system.
tel
Enter Telephony [TEL] Command Group.
2. Telephony Commands [TEL]
back
Return Root Command Group.
help
Display help menu. It lists all available commands in the current command group.
info
Display Telephony information.
set_sd_line
<Usage>: set_sd_line [line]
Input up to 8 Speed Dial entries SD(2~9) of a line.
line: Specify the line number of configuration.
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
speed dial phone: max. 19 digits
18 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 19

5. System Configuration
speed dial Ring: [0] normal / [1] fast / [2] slow
[example]
set_sd_line 1
Input all SD(2~9) entries of Line 1.
Follow the prompt to fill in the phone number and select the ring type.
[Tips]
If you want to clear any SD entries, type “NULL” in [speed dial phone].
If you skip the rest of the SD entries, type “s” in [speed dial phone].
set_sd
<Usage>: set_sd [line] [SetNum] [phone] [ring]
Input one Speed Dial entry to a line.
line: Specify the line number of configuration.
SetNum: Specify the entry number of SD(2~9)
phone: Max. 19 digits
ring: [0] normal / [1] fast / [2] slow
[example]
set_sd 1 2 12345678 0
set up Line 1, SD(2), phone: 12345678, ring: normal
set_sd 1 2 NULL 0
clear SD(2) entry of Line 1.
show_sd
<Usage>: show_sd [option]
Show all Speed Dial entries in all lines
[option]
? Display this help.
set_country
<Usage> : set_country [option]
Select the country of location to generate a suitable tone signal.
[option]
? Display this help
set_ring
<Usage> : set_ring
Set up the ring cadence.
Follow the prompt to assign the ring on/off duration
[option]
? Display this help
[prompt]
on_duration - assign the on duration (unit : ms)
off_duration - assign the off duration (unit : ms)
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 19
Page 20

5. System Configuration
show_ring
<Usage> : show_ring
Show the ring cadence.
[option]
? Display this help
set_buffer
<Usage> : set_buffer [option]
Set jitter buffer size.
[option]
? Display this help
set_gain
<Usage> : set_gain
Use this command to set gain control
[option]
? Display this help.
set_idt
<Usage> : set_idt
Use this command to set inter-digit time
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
inter-digit time - assign the inter-digit time.
set_rbt
<Usage> : set_rbt
Use this command to enable/disable pseudo ring back tone
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
Enable/Disable pseudo ring back tone
set_echocncl
<Usage> : set_echocncl
Use this command to enable/disable echo cancellation
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
Enable/Disable echo cancellation
3. Internet Protocols Commands [IP]
help
Display help menu. It lists all available commands in the current command group.
20 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 21

5. System Configuration
back
Return root command group.
info
Display TCP/IP information.
set_ip
<Usage> : set_ip [option] [IP] [Netmask] [Default Gateway]
Set up the IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway of the voice gateway.
Type “set_ip” command, then, follow the prompt to complete the setting.
Type “set_ip” command and the parameters of IP address, subnet mask, and default gateway in
one command line
[option]
? Display this help
This command is only valid in Disable DHCP status, and you can use “show_dhcpc” command
to read current DHCP status.
show_ip
<Usage> : show_ip [option]
Show current IP , Netmask , Default Gateway
[option]
? Display this help
set_dhcpc
<Usage> : set_dhcpc [option] | [0|1]
Disable/enable the DHCP client
Disable DHCP client – use assigned static IP
Enable DHCP client – obtain IP automatically from DHCP server
[option]
? Display this help.
show_dhcpc
<Usage:> show_dhcpc [option]
Show the current status of DHCP client
Enabled -> obtain IP automatically from DHCP server
Disabled -> use assigned static IP
[option]
? Display this help.
set_time
<Usage> : set_time [option] | [yy-mm-dd] [hh:mm:ss]
Set up current time of day.
yy-mm-dd Year (A.D.), month (1-12), and day (1-31).
hh:mm:ss Hour (0-23), minute (0-59), and second (0-59).
[option]
? Display this help.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 21
Page 22

5. System Configuration
set_snmp_comm
<Usage> : set_snmp_comm [option]
Set up SNMP community for SNMP Get(Read)/Set(Write).
[option]
? Display this help
show_snmp_comm
<Usage> : show_snmp_comm [option]
Show SNMP Get(Read)/Set(Write) community .
[option]
? Display this help
dload
<Usage> : dload [option]
Download image file from TFTP Server.
Follow the prompt to assign the TFTP Server IP and download image file name then start to
download the image file.
[option]
? Display this help
[prompt]
TFTP Server IP - assign the TFTP Server IP
Download image file name - assign the download image file name
4. H.323 Commands [H323]
(Valid only on H.323 client)
help
Display help menu. It lists all available commands in the current command group.
back
Return root command group.
info
Display H.323 protocol information
set_codec
<Usage> : set_codec
Use this command to set the preferred audio codec
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
codec choose the preferred audio codec
silence choose to enable/disable the silence suppression function.
set_phno
<Usage> : set_phno
22 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 23

5. System Configuration
Use this command to set up the phone number for each line
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
phone number - enter the phone number for each line
set_h323id
<Usage> : set_h323id
Use this command to setup the h323 id
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
h323_id enter the h323 id
set_gk
<Usage> : set_gk
Use this command to enable/disable gatekeeper functionality
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
Gatekeeper Enable this function to register with a gatekeeper
DNS Enable this only if your DNS server provides gatekeeper information.
Auto Discovery Enable this to auto-discovery the gatekeeper.
H.323 GK IPInput static gatekeeper IP address if AutoDiscovery is turned off.
set_altgk
<Usage> : set_altgk
Use this command to setup alternate gatekeeper
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
No use this number to index the table.
IP define the IP address corresponding to this gatekeeper.
set_fs
<Usage> : set_fs
Use this command to enable/disable fast start functionality
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
fast-start enable this to use the fast start function defined in H.323.
set_gw
<Usage> : set_gw
Use this command to enable/disable gateway support
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 23
Page 24

5. System Configuration
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
Enter a Gateway IP if an H.323 Gateway is present to support phone number/IP translation.
set_maptab
<Usage> : set_maptab
Use this command to setup the mapping table content
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
No use this number to index the table.
Phone assign a phone number.
IP define the IP address corresponding to the phone number.
set_ac
<Usage> : set_ac
Use this command to enable/disable the function of auto insertion of the area code
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
Area-Code enter the area code here to enable auto insertion.
set_nat
<Usage> : set_nat
Use this command to set no answer time
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
nat set no answer time
set_shp
<Usage> : set_shp
Use this command to enable/disable sharp flag ‘#’ support (end of phone no)
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
shp Enable/Disable sharp flag ‘#’ support
set_autoswitch
<Usage> : set_autoswitch
Use this command to enable/disable auto-switch support
[option]
? Display this help.
[prompt]
Enable/Disable auto-switch support
24 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 25

5. System Configuration
set_dtmfrelay
<Usage> : set_dtmfrelay
Use this command to select a DTMF rely protocol
5. MGCP Commands [MG]
(Valid only on MGCP client)
info
This will show all information of MGCP gateway setting. It includes Profile ID, Call agent
information, Endpoint information..
restart
This will restart the MGCP gateway. It will re-activate using the parameter stored in the system
help
Display help menu.
back
Return root command group.
set_profile
<Usage> : set_profile [number] | [option]
number Set up MGCP profile, there are three basic profiles :
RFC 2705
NCS
MGCP 0.1 NCS 1.0 (CLARENT)
[option]
? Display this help.
After changing MGCP profile MG will automatically restart.
show_profile
<Usage> : show_profile [option]
Show MGCP profile detail.
[option]
? Display this help.
all Show all profile.
set_ca
<Usage> : set_ca [option]
Set up Call Agent (CA) information of MG.
Follow the prompt to complete the setting.
[option]
? Display this help
[prompt]
localname The local name of CA, max 32 characters allowed. This value is optional. e.g. CA1.
Type “NULL” to clear.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 25
Page 26

5. System Configuration
Domain | IP The Domain name or IP of the CA. e.g. “1.2.3.4” or “yourCA.company.com”.
If Domain name is used, use “set_dns” to set up DNS. Type “NULL” to clear the entry. Max
100 characters.
Port The port number of CA, 1024 ~ 65535, usually 2427 or 2727.
After setting CA information, MG will automatically restart.
show_ca
<Usage> : show_ca [option]
Show the CA information of MG and current NotifiedEntity of all endpoints.
[option]
? Display this help
set_gwname
<Usage> : set_gwname [option]
Set MG’s DomainName. epX@DomainName is name of endpoint X of this MGCP Gateway
Follow the prompt to complete the setting.
[option]
? Display this help
[prompt]
DomainName Max 50 characters allowed.
Type “NULL” to use default domain name ‘V’+MAC.
After setting Domain Name, MG will automatically restart.
show_gwname
<Usage> : show_gwname [option]
Show MG’s Domain Name
[option]
? Display this help
set_dns
<Usage> : set_dns [option]
Set a DNS Server IP of MG.
If CA is given in Domain Name, this value must be set.
Follow the prompt to complete the setting.
[option]
? Display this help
[prompt]
DNS Server IP Type “NULL” to clear DNS Server IP.
show_dns
<Usage> : show_dns [option]
Show DNS Server IP of MG
[option]
? Display this help
26 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 27

5. System Configuration
5.2. Telnet Control
The Voice Gateway can be controlled by Telnet applications. This capability is disabled when the voice gateway is already controlled from the console. Users may access all console commands using Telnet.
5.2.1. Establish Connection
T elnet can be used to enter the console control mode. The parameters of the
factory default are shown below. The default values using Telnet are:
IP Address = 192.168.100.100
Netmask = 255.255.255.0
Default Gateway = 192.168.100.254
You have to also enter a username (default “voip”) and password while you
use T elnet to connect to the system. The default password using T elnet is the
same as the console control input (last 6 lowercase characters of the Ethernet MAC address). The console mode using the console cable has a higher
priority than using Telnet. Therefore, the Telnet user cannot enter control
mode while another computer has control through the console port. If a
currect T elnet session is active, it will be disconnected when a connection is
started through the console port. Except priority levels, there are no differences in commands when accessing through Telnet or the console port.
5.3. Web (HTTP) Console
Users can use browsers to setup or
show the information of the voice
gateway . For example, they can use
Internet Explorer to configure the
telephone number of VoIP phone.
The IP address of the Web console
is the same as the IP address used
by Telnet.
The web page is divided into several frames, each of which is related to a
VoIP module. It includes system settings, H.323 or MGCP settings, and
About. Users can follow the procedures listed below to set up Voice Gateway.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 27
Page 28

5. System Configuration
5.3.1. System Info (VoIP MISC)
5.3.1.1. System Status
28 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 29

5. System Configuration
5.3.1.2. System Configuration
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 29
Page 30

5. System Configuration
5.3.2. H.323 Info
5.3.2.1. H.323 Status
30 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 31

6. System Configuration
5.3.2.1. H.323 Configuration
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 31
Page 32

6. System Configuration
5.3.3. MGCP Info
5.3.3.1 MGCP Status
32 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 33

6. System Configuration
5.3.3.2 MGCP Configuration
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 33
Page 34

5. System Configuration
5.4. Keypad Control
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway can be controlled using the keypad
on the telephone set. Users can press special codes to set up the gateway.
The control codes are listed below:
5.4.1. Basic Commands
1. Set Speed Dial
## (Do) [1] (Do) [2–9 phone ID] (Do) [phone NO./IP][#] (Do) [0–2 :Ring Type] (Do----)
• When input IP, use * key to identify . (dot).
• Ring Type : 0 (Normal), 1(Fast), 2(Slow)
• Each phone can set 8 speed dial numbers
2. Read Speed Dial
## (Do) [2] (Do) [2–9 phone ID] (phone number will be spoken) (Do)
• You can repeat this operation to hear all telephone setting.
3. DHCP
Enable: ## (Do) [3] (Do) [1 to enable] (Do----)
Disable: ## (Do) [3] (Do) [0 to disable] (Do) then
[1] (Do) [ press IP][#], or
[2] (Do) [ press netmask][#], or
[3] (Do) [ press default gateway][#], or
[# ](Do----)
• If you make an entry error , press # to finish, and repeat any DHCP entry.
• If the parameter is changed, system will reboot (Voice Gateway Reboots Automatically)
(Do): Short Tone Sound
(Do----): Long Tone Sound
34 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 35

5. System Configuration
4. MGCP
## (Do) [4] (Do) then
[1] (Do) [press CAIP] [#] (Do), or
[2] (Do) [press CAPort] [#] (Do), or
[3] (Do) [press dnsIP] [#] (Do), or
[4] (Do) [1–3 to set ProfileID] (Do), or
[#] (Do——) (# indicate finish setting)
• CAIP = Call Agent IP address
• If the IP or Port parameter is changed, MG module will be restarted.
• Supported Profile ID: 1=MGCP 1.0 (RFC2705), 2=NCS 1.0 (Packet Cable),
3=Clarent (NCS1.0 MGCP 0.1)
5. H323
## (Do) [5] (Do) then
[1] (Do) [1] (Do) [press phone] [#] (Do), or [2] [phone number will be spoken] (Do ), or
[2] (Do) [0 , set GK not exist] (Do), or [1, set GK exist] (Do) [press GKIP] [#] (Do)
[3] (Do) [0/1 to set fastStart] (Do), or
[4] (Do) [press dnsIP] [#] (Do), or
[5] (Do) [0/1 to set AutoDiscovery] (Do), or
[6] (Do) [0, set GW not exist] (Do), or [1, set GW exist] (Do) [press GWIP] [#] (Do)
[#] (Do----)( # indicate finish setting )
6. Restore Factory Defaults
##*9 [1 to confirm]
(Do): Short Tone Sound
(Do----): Long Tone Sound
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 35
Page 36

5. System Configuration
5.4.2. Supplemental Services Commands
Currently, the VoIP products of support the following basic supplemental
services.
Automatic Callback (**66)
Automatic Callback allows a subscriber to initiate a call set up to the last
directory number that was dialed from the subscriber’s line so that the number is dialed automatically without the subscriber having to redial.
Automatic Redial (**69)
Automatic Recall allows a subscriber to automatically call back the last
number that called the subscriber’s directory number , whether the subscriber
answered the call or not. To activate the AR feature, the subscriber needs to
go off hook, waits for a dial tone, and dials a feature activation code (**69).
Speed Calling (**74 + one digit (2 – 9))
Speed calling permits the subscriber to dial selected directory numbers using fewer digits than normally required. This is accomplished through the
assignment of one-digit code to frequently called directory number. Subscribers are allowed to assign eight directory numbers to the Speed Calling
List (2 through 9).
Distinctive Ringing (**61)
Distinctive Ringing allows the subscriber to manage incoming calls by designating special directory numbers that may be identified using distinctive
ringing patterns. Currently the VoIP gateway supports Fast/Normal/Slow
Ringing. The Ring On/Off Patterns are On-1s, Off-1s (Fast mode)/On-2s,
Off-1s (Normal Mode)/On-1s, Off-2s (Slot Mode).
Inner Conference Call (***1-4)
The VoIP products of with multiple phones can support an extra service for
inner phones conference. Each user under the same Voice Gateway can call
each other without any Internet connectivity. For example, the user in the
phone 1 can dial ***3 to the user in the phone 3 directly.
36 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 37

6. Software Upgrade
Voice Gateway / Pocket V oice Gateway are software upgradable. Users may
download the latest software from our web site and upgrade the voice gateway . Besides, users may switch between H.323 protocol and MGCP protocol by using different software image files.
Voice Gateways provide two interfaces for software upgrades, RS232 User
Console Interface and HTTP Web Console Interface. This section will describe the step-by-step software upgrade procedures of both interfaces.
6.1. Through the User Console Interface
VGW
Ethernet
RS232 (console)
Computer
HyperTerminal
TFTP Server
Download Image File
1. Save the upgrade software image file to your hard drive.
2. Make sure the modem is connected to your computer through the Ethernet interface and the Console port on the modem is connected to your
computer’s COM port.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 37
Page 38

6. Software Upgrade
3. Run a TFTP server program. Example: Cisco TftpServer (TFTPServer11-980730.exe) from:
http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/tftp
4. Turn on the hyperterminal user console. Refer to 5.1.2 “COM Port Configuration”.
5. Type “ip” under the “User >>” prompt to enter the IP directory.
6. Type “dload” command under the IP directory to upgrade the voice gate-
way. The IP address of the TFTP Server and the file name of the new
software are required.
7. Voice gateway will reboot automatically after image downloaded, and
the new user console will be launched.
38 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 39

6. Software Upgrade
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 39
Page 40

6. Software Upgrade
6.2. Through the HTTP Web Console
VGW
Ethernet
Computer
Web Browser
TFTP Server
Download Image File
1. Save the upgrade software image file to your hard drive.
2. Make sure the modem is connected to your computer through the Ethernet .
3. Run a TFTP server program. Example: Cisco TftpServer (TFTPServer11-980730.exe) from:
http://www.cisco.com/pcgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/tftp
40 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 41

6. Software Upgrade
4. Power ON the voice gateway.
5. Run a web browser program. Example: Microsoft IE 5.0. The factory
default network settings are:
IP: 192.168.100.100
Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
Default gateway: 192.168.100.254
Type:
http://192.168.100.100/ to enter the web console
6. User need to login to access the web console. The factory default user
name and password are:
Login name: voip
Password: The last 6 digits of the MAC address
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 41
Page 42

6. Software Upgrade
7. In the web console, click on <VoIP MISC> in the left column, then select <Configuration> on the top command bar.
8. Click on the “Download” button to start downloading the new software. You can click “See the download result” to see the real time downloading status.
42 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 43

6. Software Upgrade
9. After downloading the new software successfully, the voice gateway
will reboot automatically and the link will be disconnected. User may
refresh the display and find the upgraded web console interface.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 43
Page 44

7. System Operation
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway products can be operated in two
modes: H.323 voice gateway and MGCP voice gateway. The system requirements are different in H.323 and MGCP environments.
7.1 H.323 Notes
Yes?
Dial IP or E.164
through GK
Yes?
Dial IP or E.164
through GW
H.323 is a peer-to-peer connection protocol for VoIP . In an H.323 environment,
you can make a phone call to the destination directly, or though an H.323
gatekeeper and/or a trunk gateway . Then,
you can make a phone call by either an
IP address or a telephone number (E.164
number). Therefore, in our configuration,
users have to setup the strategy to make
a phone call. The criterion follows the
rule:
GK?
No?
GW?
No?
Dial IP only
Make an H.323 phone call to other H.323 VoIP terminal (if H.323 firmware
exists)
1. Call to pure VoIP (non-E.164 telephone) terminal
a. Pick up phone. After hearing a dial tone, dial the IP address of the
peer terminal. Here you have to use star (*) as dot (.), and then press
hash (#) to end. For example, if the IP address of the peer terminal is
192.168.100.2 then you have to press 192*168*100*2#
2. Call to E.164-addressed telephone terminal
a. In this environment, you have to connect to an H.323 Gatekeeper or
Gateway to support E.164 address or IP Address.
b. You can use one of the user interfaces to configure the IP address of
the H.323 Gatekeeper or Gateway. Refer to Chapter 5 for the configuration interface.
After you setup the IP address of the Gatekeeper and phone number of each
line, you can dial to the peer terminal as in a standard telephone. For example, if you want to dial to 7123456 then you just press 7123456# to make
this phone call.
44 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 45

7. System Operation
7.2 MGCP Notes
MGCP is a client-server connection protocol of V oIP technology . In an MGCP
environment, it is compulsory for a server (named Call Agent or Call Manager) to manage and control all MGCP clients. Different Call Agents may
employ different MGCP profiles, which define the procedures and parameters of a VoIP phone call.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway can support RFC standard profiles
(RFC2705, MGCP 1.0), NCS standard profile (Packet Cable), and some
proprietary profile (MGCP 0.1, NCS 1.0).
While the operator will set up the call agent with IP phone information,
users have to set up the Voice Gateway with a valid IP address, the IP address (or domain name) of the Call Agents, and the corresponding MGCP
profile.
In an MGCP environment, all clients need to use E.164 number to start the
connection. The mapping of an E.164 number and IP address is handled by
the MGCP Call Agent, then a user can call a peer VoIP terminal by the
E.164 number . You can simply make a phone call as in standard telephones.
For example, if you want to dial to 7123456 , you press 7123456 to make
the phone call.
7.3 Application Examples
The voice gateways can be configured to perform many roles to support
various demands from customers. Here, it presents some application examples for customer to know how to configure the voice gateway.
7.3.1 VoIP Voice Gateway to VoIP Networks using IP address
The first simple example shows the use of the Ethernet WAN port to connect to a VoIP network. The other LAN port connects to another computer.
One or more telephone directly connects to the FXS interfaces (P1, P2 …
or Phone). This example provides you simple VoIP phone to another VoIP
phone (VoIP to VoIP).
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 45
Page 46

7. System Operation
192.168.100.101
DC POWER Reset
POWER
PHONE 1
PHONE 2
Console
PC
192.168.100.102
LAN WANP1 P2 P3 P4
VoIP
Networks
You can check the following items to make sure your configuration setting
is correct. If you cannot have the correct result, please check the User Menu
to see more details about system setting. Or you can connect to our customers support to inquire the setting.
a. Use inner conference call to make phone call between each phones on
the voice gateway:
- Pick up one of telephone set, you will hear the dial tone.
- Then dial ***1 to ***4 (for 4 ports) to make phone call to another one.
- If the one is on-hook, voice gateway will ring the telephone. Pick up
the phone, then the phone call establish well.
- If the one is already in use then you will hear busy tone.
b. Make the VoIP phone to VoIP Networks
- Pick up one of telephone set, you will hear the dial tone.
- Then the IP address of called party. For example, if you want to dial
VoIP phone to 192.168.100.102, you have to dial 192*168*100*102#.
- If called party is available then you will hear ring back tone. And if
he accept the call, the phone call establish well.
- If the one is already in use then you will hear busy tone.
c. For H.323 phone in this case, you cannot dial E.164 telephone number
(the traditional telephone number, like the one as your cell phone). And
for multiple ports voice gateway , you cannot make VoIP phone to specified port. For example, you cannot dial to P2 directly without any setting. The P2 will receive the call only when P1 is already in use. But you
can use other port (P2, P3, P4) to dial out without any limitations.
d. For MGCP phone, you need Call Agent to control the MGCP phone.
Therefore, you cannot dial IP address in this example.
46 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 47

7. System Operation
7.3.2 V oIP V oice Gateway to V oIP Networks using E.164 telephone number without VoIP Server
Since there are some limitations in the first example, our Voice Gateway
supports another features to provide E.164 numbers’ call without server. If
another party (caller/called) of VoIP phone can support this feature also,
then the both parties can use this function to dial the VoIP phone as the
traditional telephone servers. Please refer to user menu to setup the H.323
telephone number mapping (show_maptab and set_map_tab commands in
H.323 command directory)
192.168.100.101
DC POWER Reset
POWER
PHONE 1
Tel#: 1011
PHONE 2
Tel#: 1012
Console
PC
192.168.100.102
Tel#: 1021
LAN WANP1 P2 P3 P4
VoIP
Networks
a. This example can support all features in the previous example. It means
you can dial VoIP phone using IP address and E.164 number co-existed.
b. Y ou have to configure the mapping table according above in both caller/
called parties. For example, you have already setup the following mapping table:
Index Telephone IP Address
0 1011 192.168.100.101
1 1012 192.168.100.101
2 1013 192.168.100.101
3 1014 192.168.100.101
4 1021 192.168.100.102
c. From another VoIP phone, you can dial 1012# to make the phone call to
the second port of Voice Gateway. You can dial to second port directly
even port one is also available for the call.
d. Here, we mention again. For MGCP phone, it needs Call Agent to control
it. Therefore, you cannot dial VoIP phone to others. The voice gateway
can support inner conference call only without controlling from Call Agent.
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 47
Page 48

7. System Operation
7.3.3 VoIP Voice Gateway to VoIP Networks
controlled by VoIP Server
Call Agent
Gatekeeper
VoIP
Networks
LAN WANP1 P2 P3 P4
Tel#: 234-5678
DC POWER Reset
POWER
PHONE 1
Tel#: 1011
PSTN
Trunk
Gateway
PHONE 2
Tel#: 1012
Console
PC
192.168.100.102
Tel#: 1021
In order to dial out to PSTN world, the VoIP system has to connect to trunk
gateway to PSTN controlled by VoIP Server . For example, you have to connect to Call Agent or Gatekeeper. Then you can dial to PSTN using VoIP
phone.
a. You have to setup the VoIP phone is controlled by Sever first in this
example.
b. For H.323, you have to enable Gatekeeper function in the H.323 com-
mand directory . And setup the IP address of Gatekeeper. Some vendor’s
trunk gateway supports E.164 numbering function but does not support
Gatekeeper functionality, please enable trunk gateway and disable
Gatekeeper in H.323 command directory.
c. For H.323, the voice gateway has to setup the telephone number itself.
Please use the set_phno command in H.323 command directory to set
them.
d. For MGCP, you have to setup the IP address of Call Agent. Then you
have to setup the DNS name of the voice gateway. The similar setting
have to support in setting of Call Agent. Then the voice gateway can
make phone call well.
e. If the voice gateway cannot connect to server well, you still can use the
function of inner conference call. So, you can hear the dial tone also
while you pick up the phone. By the way, if you want to dial out, you
will hear busy tone since it cannot connect to VoIP server.
f. For H.323, you can also dial to VoIP phone using IP address without
connecting to VoIP server.
48 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
Page 49

7. System Operation
7.3.4 VoIP Voice Gateway to VoIP Networks with PSTN line
The voice gateway of also support FXO interface to PSTN world directly.
Three models of voice gateway support this function. AVG6001BA and
AVG6001BD support one FXO interface. AVG6004BA support four FXO
interfaces. Here is the example to support PSTN line and you can dial to
traditional phone using our VoIP voice gateway.
Due to the variety of telephony specification, the FXO interface of voice
gateway has to commit the specification very well. For example, you have
to setup the call progressive tone of the PSTN line from Telephone companies or PBX. Please contact to our Technical Service to inquire the details
specification of PSTN line in different countries and different PBX.
a. The function of P2 (or P3 and P4 in 4 ports model) is as same as all the
examples above.
b. To provide PSTN backup functionality, you can use inner conference
call to make a PSTN phone out. Just dial ***1, you can hear the second
tone. Then you can dial the E.164 telephone number to real PSTN world.
User can also configure the PSTN line port using E.164 number, for
example 1011. Then after all other VoIP phone dial to 1011, the second
tone can be hear . Then user can also dial the telephone number to PSTN
world. Here, this voice gateway can be treated as a translation (so called
gateway) between VoIP phone and PSTN phone.
c. Vice verse, the user at PSTN world can dial to this PSTN line. After
second ring, the voice gateway will pick up the phone and send the second dial tone again. Then user can also dial to VoIP phone using IP
address or E.164 telephone number that is described in previous section.
PSTN
DC POWER Reset
POWER
Splitter
PHONE 2
PHONE 3
Console
PC
LAN WANLine P2 P3 P4
VoIP
Networks
Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway 49
Page 50

(This page was intentionally left blank.)
50 Voice Gateway / Pocket Voice Gateway
 Loading...
Loading...