Page 1

P4S55FX+
P4S55FX
User Manual
Version 1.01
Published March 2004
Copyright©2004 ASRock INC. All rights reserved.
1
Page 2

Copyright Notice:
No part of this manual may be reproduced, transcribed, transmitted, or translated in
any language, in any form or by any means, except duplication of documentation by
the purchaser for backup purpose, without written consent of ASRock Inc.
Products and corporate names appearing in this manual may or may not be registered trademarks or copyrights of their respective companies, and are used only for
identification or explanation and to the owners’ benefit, without intent to infringe.
Disclaimer:
Specifications and information contained in this manual are furnished for informational use only and subject to change without notice, and should not be constructed
as a commitment by ASRock. ASRock assumes no responsibility for any errors or
omissions that may appear in this manual.
With respect to the contents of this manual, ASRock does not provide warranty of
any kind, either expressed or implied, including but not limited to the implied warranties or conditions of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose.
In no event shall ASRock, its directors, officers, employees, or agents be liable for
any indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages (including damages for
loss of profits, loss of business, loss of data, interruption of business and the like),
even if ASRock has been advised of the possibility of such damages arising from any
defect or error in the manual or product.
ASRock Website: http://www.asrock.com
2
Page 3

Contents
1 Introduction ................................................... 4
1.1 Package Contents .......................................................... 4
1.2 Specifications ................................................................ 5
1.3 Motherboard Layout (P4S55FX+) ................................. 7
1.4 Motherboard Layout (P4S55FX) .................................. 8
1.5 ASRock I/O PlusTM (P4S55FX+/ P4S55FX) ................... 9
2 Installation...................................................... 10
Pre-installation Precautions ................................................... 10
2.1 CPU Installation .............................................................. 11
2.2 Installation of CPU Fan and Heatsink ............................ 11
2.3 Installation of Memory Modules (DIMM)......................... 12
2.4 Expansion Slots (PCI and AGP Slots) ........................... 14
2.5 Jumpers Setup .............................................................. 15
2.6 Onboard Headers and Connectors .............................. 16
2.7 Serial ATA (SATA) Hard Disks Installation ..................... 19
2.8 Making An SATA Driver Diskette................................... 20
3 BIOS Setup ...................................................... 21
3.1 BIOS Setup Utility ........................................................... 21
3.1.1 BIOS Menu Bar ....................................................... 21
3.1.2 Legend Bar ............................................................. 21
3.2 Main Menu...................................................................... 22
3.3 Advanced, Security, Power, Boot, and Exit Menus ..... 24
4 Software Support ........................................... 25
4.1 Install Operating System ............................................... 25
4.2 Support CD Information ................................................. 25
4.2.1 Running Support CD ............................................... 25
4.2.2 Drivers Menu .......................................................... 25
4.2.3 Utilities Menu ........................................................... 25
4.2.4 ASRock “PC-DIY Live Demo” Program .................. 25
4.2.5 Contact Information ................................................ 25
Appendix ............................................................ 26
1. Advanced BIOS Setup Menu .......................................... 26
2. Security Setup Menu ....................................................... 31
3. Power Setup Menu .......................................................... 32
4. Boot Setup Menu ............................................................. 33
5. Exit Menu ......................................................................... 34
3
Page 4

Chapter 1 Introduction
Thank you for purchasing ASRock P4S55FX+ / P4S55FX motherboard, a reliable
motherboard produced under ASRock’s consistently stringent quality control. It delivers excellent performance with robust design conforming to ASRock’s commitment to quality and endurance.
In this manual, chapter 1 and 2 contain introduction of the motherboard and step-bystep guide to the hardware installation. Chapter 3 and 4 contain the configuration
guide to BIOS setup and information of the Support CD. More information of advanced BIOS setup is offered on page 26 for advanced users’ reference.
Because the motherboard specifications and the BIOS software might be
updated, the content of this manual will be subject to change without
notice. In case any modifications of this manual occur, the updated
version will be available on ASRock website without further notice. You
may find the latest memory and CPU support lists on ASRock website as
well. ASRock website
1.1 Package Contents
ASRock P4S55FX+ or P4S55FX Motherboard
(ATX Form Factor: 12.0-in x 8.6-in, 30.5 cm x 21.8 cm)
ASRock P4S55FX+ / P4S55FX Quick Installation Guide
ASRock P4S55FX+ / P4S55FX Support CD
One 80-conductor Ultra ATA 66/100/133 IDE Ribbon Cable
One Ribbon Cable for a 3.5-in Floppy Drive
One Serial ATA (SATA) Cable (For P4S55FX+ Only)
One Serial ATA (SATA) HDD Power Cable (For P4S55FX+ Only)(Optional)
One ASRock I/O PlusTM Shield
http://www.asrock.com
4
Page 5

1.2 Specifications
Platform: ATX Form Factor: 12.0-in x 8.6-in, 30.5 cm x 21.8 cm
CPU: Socket 478, supports Intel® Pentium® 4 (Prescott, Northwood,
Willimate) / Celeron® processor
Chipsets: North Bridge:
SiS 655FX, FSB @ 800/533/400 MHz,
with Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology ready
South Bridge:
P4S55FX+:
SiS 964, supports USB 2.0, ATA 133, SATA 1.5Gb/s
P4S55FX:
SiS 964L, supports USB 2.0, ATA 133
Memory: 4 DDR DIMM Slots: DDR1, DDR2, DDR3, and DDR4
Supports PC3200 (DDR400) / PC2700 (DDR333) /
PC2100 (DDR266) , Max. 3.5GB
Dual Channel Memory Technology support (see CAUTION 1)
IDE: IDE1: ATA 133 / Ultra DMA Mode 6
IDE2: ATA 133 / Ultra DMA Mode 6
Supports up to 4 IDE devices
Serial ATA: 2 SATA connectors
Supports up to 1.5Gb/s data transfer rate
(SATA is only available on P4S55FX+ Motherboard)
Floppy Port: Supports up to 2 floppy disk drives
Audio: 5.1 channels AC’97 Audio
LAN: Speed: 802.3u (10/100 Ethernet), supports Wake-On-LAN
Hardware Monitor: CPU temperature sensing
Chassis temperature sensing
CPU overheat shutdown to protect CPU life
(ASRock U-COP)(see CAUTION 2)
CPU fan tachometer
Chassis fan tachometer
Voltage monitoring: +12V, +5V, +3V, Vcore
PCI slots: 5 slots with PCI Specification 2.2
AGP slot: 1 AGP slot, supports 1.5V, 8X/4X AGP card (see CAUTION 3)
USB 2.0: 8 USB 2.0 ports:
includes 6 default USB 2.0 ports on the rear panel,
plus one header to support 2 additional USB 2.0 ports
(see CAUTION 4)
5
Page 6

ASRock I/O PlusTM: 1 PS/2 mouse port, 1 PS/2 keyboard port,
1 serial port: COM1,
1 parallel port: ECP/EPP support,
6 default USB 2.0 ports,
1 RJ 45 port,
Audio Jack: Line In / Line Out / Microphone
BIOS: AMI BIOS
Supports “Plug and Play”
ACPI 1.1 compliance wake up events
Supports jumperfree
SMBIOS 2.3.1 support
CPU frequency stepless control
(only for advanced users’ reference, see CAUTION 5)
OS: Microsoft® Windows® 98SE / ME / 2000 / XP compliant
CAUTION!
1. This motherboard supports Dual Channel Memory Technology. Before you
implement Dual Channel Memory Technology, make sure to read the
installation guide of memory modules on page 12 for proper installation.
2. If the CPU is overheated, please check if the CPU fan on the motherboard
functions properly before you resume the system. To improve heat
dissipation, remember to spray thermal grease between the CPU and the
heatsink when you install the PC system.
3. Do NOT use a 3.3V AGP card on the AGP slot of this motherboard!
It may cause permanent damage!
4. Power Management for USB 2.0 works fine under Microsoft
SP1 / 2000 SP4. It may not work properly under Microsoft
ME. Please refer to Microsoft
http://www.microsoft.com/whdc/hwdev/bus/USB/USB2support.mspx
5. Although this motherboard offers stepless control, it is not recommended
to perform over-clocking. Frequencies other than the recommended CPU
bus frequencies may cause the instability of the system or damage the
CPU.
®
official document at
®
Windows® XP
®
Windows® 98 /
6
Page 7
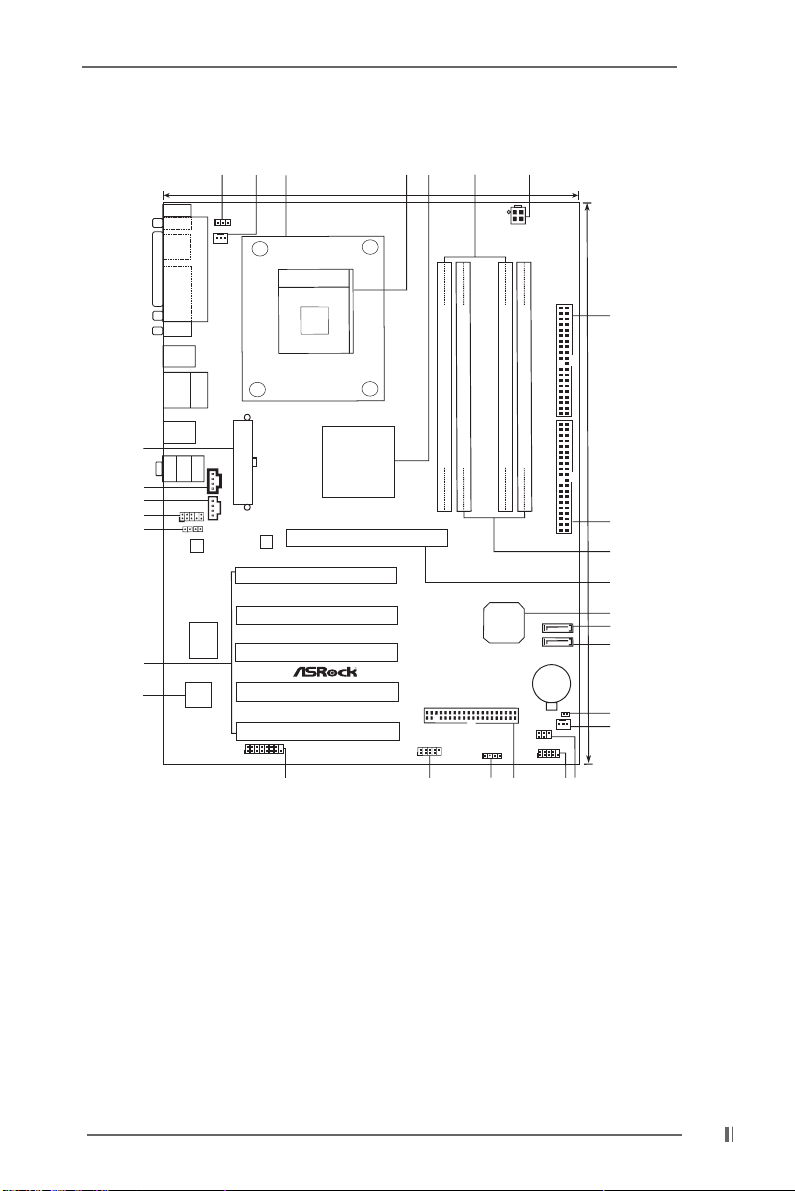
1.3 Motherboard Layout (P4S55FX+)
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
PS2
Mouse
PS2
Keyboard
COM1
USB2.0
T: US B2
B:USB3
USB2.0
T: US B0
B:USB1
USB2.0
T: US B4
B:USB5
Bottom:
MicIn
1
3457
2
6
21.8cm (8.6 in)
1
PARALLEL PORT
PS2_USB_PWR1
CPU_FAN1
ATX12V1
PGA478
IDE2
8
Top:
RJ-45
Center:
LineOut
Top:
LineIn
CD1
ATXPWR1
AUDIO1
1
AUX1
JR1 JL1
Audio
CODEC
LAN
PHY
SiS
655FX
1.5V_AGP1
DDR1 (64/72bit, 184-pin module)
PCI 1
PCI 2
SATA
ATA133
FSB800
USB2.0
5.1 CH
FLOPPY1
USB67
1
21 20
2MB
BIOS
Super
GAME1
AGP 8X
DDR400
P4S55FX+
PCI 3
PCI 4
PCI 5
I/O
22
DDR2 (64/72bit, 184-pin module)
SPEAKER1
1
SiS
964
DDR3 (64/72bit, 184-pin module)
19
DDR4 (64/72bit, 184-pin module)
CMOS
Battery
CLRCMOS1
CHA_FAN1
1
PANEL 1
PLED PWRBTN
1
HDLED RESET
IDE1
SATA2
SATA1
IR1
18 17
30.5cm (12.0 in)
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
1 PS2_USB_PWR1 Jumper 15 Clear CMOS Solder Points (CLRCMOS1)
2 CPU Fan Connector (CPU_FAN1) 16 Chassis Fan Connector (CHA_FAN1)
3 CPU Heatsink Retention Module 17 Infrared Module Header (IR1)
4 CPU Socket 18 System Panel Header (PANEL1)
5 North Bridge Controller 19 Floppy Connector (FLOPPY1)
6 184-pin DDR DIMM Slots 20 Chassis Speaker Header (SPEAKER 1)
(Dual Channel A: DDR1, DDR3; Blue) 21 USB 2.0 Header (USB67, Blue)
7 ATX 12V Connector (ATX12V1) 22 Game Connector (GAME1)
8 Secondary IDE Connector (IDE2, Black) 23 Flash Memory
9 Primary IDE Connector (IDE1, Blue) 24 PCI Slots (PCI1- 5)
10 184-pin DDR DIMM Slots 25 JR1 Jumper / JL1 Jumper
(Dual Channel B: DDR2, DDR4; Black) 26 Front Panel Audio Header (AUDIO1)
11 AGP Slot (1.5V_AGP1) 27 Internal Audio Connector: AUX1 (White)
12 South Bridge Controller 28 Internal Audio Connector: CD1 (Black)
13 Secondary Serial ATA Connector (SATA2) 29 ATX Power Connector (ATXPWR1)
14 Primary Serial ATA Connector (SATA1)
7
Page 8
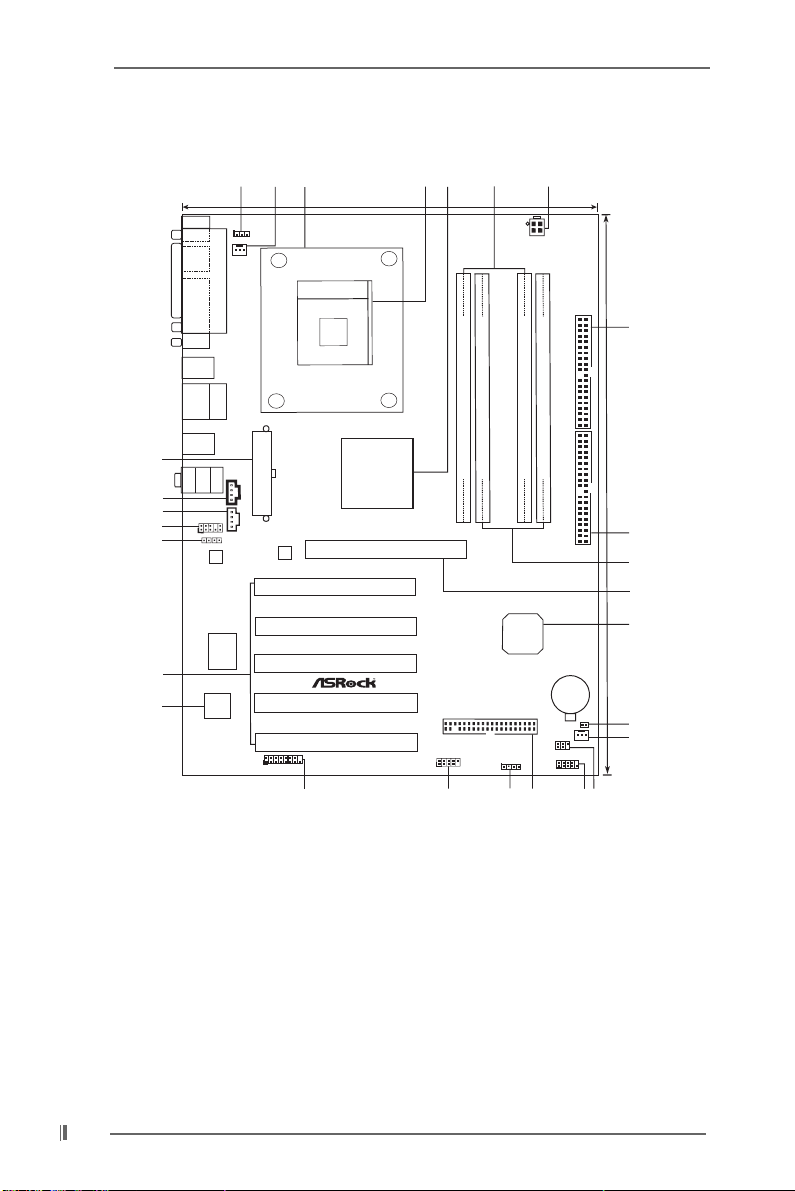
1.4 Motherboard Layout (P4S55FX)
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
PS2
Mouse
PS2
Keyboard
COM1
USB2.0
T: US B2
B:USB3
USB2.0
T: US B0
B:USB1
USB2.0
T: US B4
B:USB5
Bottom:
MicIn
1
1
3457
2
6
21.8cm (8.6 in)
1
PARALLEL PORT
CPU_FAN1
PS2_USB_PWR1
ATX12V1
PGA478
IDE2
8
Top:
RJ-45
Center:
LineOut
Top:
LineIn
CD1
ATXPWR1
AUDIO1
AUX1
JR1 JL1
Audio
CODEC
LAN
PHY
SiS
655FX
1.5V_AGP1
DDR1 (64/72bit, 184-pin module)
PCI 1
PCI 2
GAME1
P4S55FX
PCI 3
PCI 4
AGP 8X
DDR400
PCI 5
20
ATA133
FSB800
USB2.0
5.1 CH
FLOPPY1
USB67
1
19 18
2MB
BIOS
Super
I/O
DDR2 (64/72bit, 184-pin module)
964L
SPEAKER1
1
SiS
DDR3 (64/72bit, 184-pin module)
17
DDR4 (64/72bit, 184-pin module)
CMOS
Battery
CLRCMOS1
CHA_FAN1
1
PANEL 1
PLED PWRBTN
1
HDLED RESET
IDE1
IR1
16 15
30.5cm (12.0 in)
9
10
11
12
13
14
1 PS2_USB_PWR1 Jumper 14 Chassis Fan Connector (CHA_FAN1)
2 CPU Fan Connector (CPU_FAN1) 15 Infrared Module Header (IR1)
3 CPU Heatsink Retention Module 16 System Panel Header (PANEL1)
4 CPU Socket 17 Floppy Connector (FLOPPY1)
5 North Bridge Controller 18 Chassis Speaker Header (SPEAKER 1)
6 184-pin DDR DIMM Slots 19 USB 2.0 Header (USB67, Blue)
(Dual Channel A: DDR1, DDR3; Blue) 20 Game Connector (GAME1)
7 ATX 12V Connector (ATX12V1) 21 Flash Memory
8 Secondary IDE Connector (IDE2, Black) 22 PCI Slots (PCI1- 5)
9 Primary IDE Connector (IDE1, Blue) 23 JR1 Jumper / JL1 Jumper
10 184-pin DDR DIMM Slots 24 Front Panel Audio Header (AUDIO1)
(Dual Channel B: DDR2, DDR4; Black) 25 Internal Audio Connector: AUX1 (White)
11 AGP Slot (1.5V_AGP1) 26 Internal Audio Connector: CD1 (Black)
12 South Bridge Controller 27 ATX Power Connector (ATXPWR1)
13 Clear CMOS Solder Points (CLRCMOS1)
8
Page 9
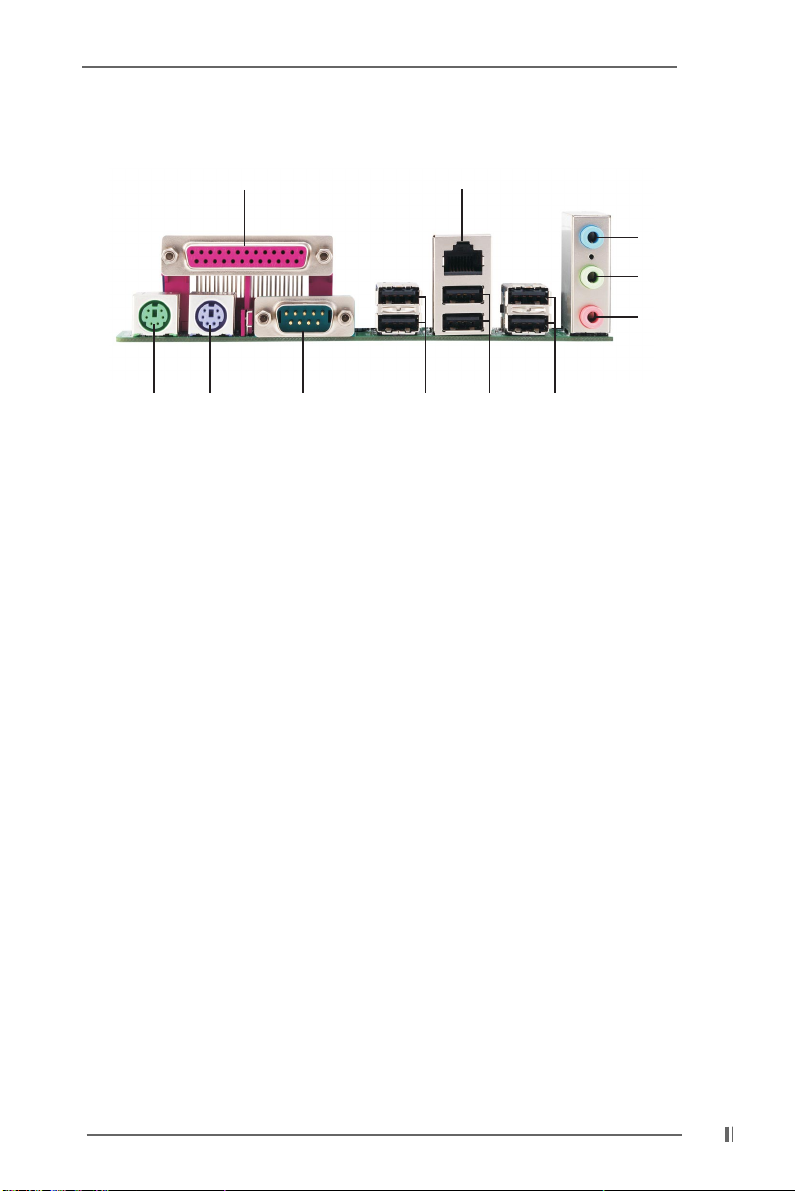
1.5 ASRock I/O Plus
TM
(P4S55FX+ / P4S55FX)
1
11
1 Parallel Port 7 USB 2.0 Ports (USB0, USB1)
2 RJ-45 Port 8 USB 2.0 Ports (USB2, USB3)
3 Line In (Light Blue) 9 Serial Port: COM1
4 Line Out (Lime) 10 PS/2 Keyboard Port (Purple)
5 Microphone (Pink) 11 PS/2 Mouse Port (Green)
6 USB 2.0 Ports (USB4, USB5)
2
8910
7
6
3
4
5
9
Page 10

Chapter 2 Installation
P4S55FX+ / P4S55FX is an ATX form factor (12.0-in x 8.6-in, 30.5 cm x 21.8 cm)
motherboard. Before you install the motherboard, study the configuration of your
chassis to ensure that the motherboard fits into it.
Pre-installation Precautions
Take note of the following precautions before you install motherboard components
or change any motherboard settings.
1. Unplug the power cord from the wall socket before touching any component.
2. To avoid damaging the motherboard components due to static electricity, NEVER
place your motherboard directly on the carpet or the like. Also remember to use
a grounded wrist strap or touch a safety grounded object before you handle
components.
3. Hold components by the edges and do not touch the ICs.
4. Whenever you uninstall any component, place it on a grounded antistatic pad or
in the bag that comes with the component.
Before you install or remove any component, ensure
that the power is switched off or the power cord is
detached from the power supply. Failure to do so may
cause severe damage to the motherboard, peripherals,
and/or components.
10
Page 11

2.1 CPU Installation
Step 1. Unlock the socket by lifting the lever up to a 90o angle.
Step 2. Position the CPU directly above the socket such that its marked corner
matches the base of the socket lever.
Step 3. Carefully insert the CPU into the socket until it fits in place.
The CPU fits only in one correct orientation. DO NOT force the
CPU into the socket to avoid bending of the pins.
Step 4. When the CPU is in place, press it firmly on the socket while you push
down the socket lever to secure the CPU. The lever clicks on the side tab
to indicate that it is locked.
Step 1 Step 2, 3 Step 4
2.2 Installation of CPU Fan and Heatsink
This motherboard adopts 478-pin CPU socket to support Intel® Pentium® 4 /
Celeron® CPU. It requires larger heatsink and cooling fan to dissipate heat.
You also need to spray thermal grease between the CPU and the heatsink to
improve heat dissipation. Make sure that the CPU and the heatsink are securely fastened and in good contact with each other. Then connect the CPU
fan to the CPU_FAN connector (CPU_FAN1, see p.7 No. 2 / p.8 No. 2). For
proper installation, please kindly refer to the instruction manuals of the CPU
fan and the heatsink.
11
Page 12

2.3 Installation of Memory Modules (DIMM)
P4S55FX+ / P4S55FX motherboard provides four 184-pin DDR (Double Data
Rate) DIMM slots, and supports Dual Channel Memory Technology. For dual
channel configuration, you always need to install identical (the same brand,
speed, size and chip-type) DDR DIMM pair in the slots of the same color. In other
words, you have to install identical DDR DIMM pair in Dual Channel A (DDR1
and DDR3; Blue slots; see p.7 No. 6 / p.8 No.6) or identical DDR DIMM pair in Dual
Channel B (DDR2 and DDR4; Black slots; see p.7 No. 10 / p.8 No.10), so that
Dual Channel Memory Technology can be activated. This motherboard also
allows you to install four DDR DIMMs for dual channel configuration. In that case,
it is not necessary to install identical DDR DIMMs in all four slots; however, it
always requires identical DDR DIMM pair to be installed in the slots of the same
color. Please refer to the Dual Channel Memory Configuration Table below.
Dual Channel Memory Configurations
DDR1 DDR2 DDR3 DDR4
(Blue Slot) (Black Slot) (Blue Slot) (Black Slot)
(1) Populated - Populated (2) - Populated - Populated
(3)* Populated Populated Populated Populated
* For the configuration (3), you may:
install identical DDR DIMMs in all four slots or
install identical DDR DIMM pair in DDR1 (Blue Slot) and DDR3 (Blue Slot)
and identical DDR DIMM pair in DDR2 (Black Slot) and DDR4 (Black Slot)
12
1. If you want to install two memory modules, for optimal compatibility
and reliability, it is recommended to install them in the slots of the
same color. In other words, install them either in the set of blue slots
(DDR1 and DDR3), or in the set of black slots (DDR2 and DDR4).
2. If only one memory module or three memory modules are installed
in the DDR DIMM slots on this motherboard, it is unable to activate
the Dual Channel Memory Technology.
3. If a pair of memory modules is NOT installed in the same Dual
Channel, for example, installing a pair of memory modules in DDR1
and DDR2, it is unable to activate the Dual Channel Memory Technology .
Page 13

Installing a DIMM
Please make sure to disconnect power supply before adding or
removing DIMMs or the system components.
Step 1. Unlock a DIMM slot by pressing the retaining clips outward.
Step 2. Align a DIMM on the slot such that the notch on the DIMM matches the break
on the slot.
notch
break
notch
break
The DIMM only fits in one correct orientation. It will cause permanent
damage to the motherboard and the DIMM if you force the DIMM into the
slot at incorrect orientation.
Step 3. Firmly insert the DIMM into the slot until the retaining clips at both ends fully
snap back in place and the DIMM is properly seated.
13
Page 14

2.4 Expansion Slots (PCI and AGP Slots)
There are 5 PCI slots and 1 AGP slot on P4S55FX+ / P4S55FX motherboard.
PCI slots: PCI slots are used to install expansion cards that have the 32-bit PCI
interface.
AGP slot: The AGP slot is used to install a graphics card. The ASRock AGP slot has
a special locking mechanism which can securely fasten the graphics
card inserted.
Please do NOT use a 3.3V AGP card on the AGP slot of this motherboard!
It may cause permanent damage! For the voltage information of your
AGP card, please check with the AGP card vendors.
Installing an expansion card
Step 1. Before installing the expansion card, please make sure that the power
supply is switched off or the power cord is unplugged. Please read the
documentation of the expansion card and make necessary hardware
settings for the card before you start the installation.
Step 2. Remove the system unit cover (if your motherboard is already installed in a
chassis).
Step 3. Remove the bracket facing the slot that you intend to use. Keep the screws
for later use.
Step 4. Align the card connector with the slot and press firmly until the card is
completely seated on the slot.
Step 5. Fasten the card to the chassis with screws.
Step 6. Replace the system cover.
14
Page 15

2.5 Jumpers Setup
The illustration shows how jumpers are
setup. When the jumper cap is placed on
pins, the jumper is “Short”. If no jumper cap
is placed on pins, the jumper is “Open”. The
illustration shows a 3-pin jumper whose pin1
and pin2 are “Short” when jumper cap is
Short
placed on these 2 pins.
Jumper Setting
PS2_USB_PWR1 Short pin2, pin3 to enable
(see p.7 No. 1 / p.8, No. 1) +5VSB (standby) for PS/2
1_2
+5V
2_3
+5VSB
or USB wake up events.
Note: To select +5VSB, it requires 2 Amp and higher standby current provided
by power supply.
JR1/JL1 Jumpers
(see p.7 No. 25 / p.8 No. 23)
JR1 JL1
Note: If the jumpers JL1 and JR1 are short, both the front panel and the rear panel
audio connectors can work.
Clear CMOS
(CLRCMOS1, 2 solder points)
(see p.7 No. 15 / p.8 No. 13)
solder points
Open
Note: CLRCMOS1 allows you to clear the data in CMOS. The data in CMOS includes
system setup information such as system password, date, time, and system
setup parameters. To clear and reset the system parameters to default setup,
please turn off the computer and unplug the power cord, then short the solder
points for more than 3 seconds by using metal material, e.g., a paper clip. If you
need to clear the CMOS when you just finish updating the BIOS, you must boot
up the system first, and then shut it down before you do the clear-CMOS
action.
15
Page 16

2.6 Onboard Headers and Connectors
Onboard headers and connectors are NOT jumpers. Do NOT place jumper
caps over these headers and connectors. Placing jumper caps over the
headers and connectors will cause permanent damage of the motherboard!
FDD Connector
(33-pin FLOPPY1)
(see p.7 No. 19 / p.8 No. 17)
Note: Make sure the red-striped side of the cable is plugged into Pin1 side of the
connector.
Primary IDE Connector (Blue) Secondary IDE Connector (Black)
(39-pin IDE1, see p.7 No. 9 / p.8, No. 9) (39-pin IDE2, see p.7 No. 8 / p.8, No. 8)
Pin1
FLOPPY1
the red-striped side to Pin1
PIN1
IDE1
connect the blue end
to the motherboard
PIN1
80-conductor ATA 66/100/133 cable
IDE2
connect the black end
to the IDE devices
Note: If you use only one IDE device on this motherboard, please set the IDE
device as “Master”. Please refer to the instruction of your IDE device vendor
for the details. Besides, to optimize compatibility and performance, please
connect your hard disk drive to the primary IDE connector (IDE1, blue) and
CD-ROM to the secondary IDE connector (IDE2, black).
Serial ATA Connectors Serial ATA (SATA) connectors
(Only on P4S55FX+ motherboard) are only available on P4S55FX+
(SATA2: see p.7 No. 13) motherboard. These two Serial
(SATA1: see p.7 No. 14) ATA (SATA) connectors support
SATA2
SATA1
SATA data cables for internal
storage devices. The current
SATA interface allows up to
1.5 Gb/s data transfer rate.
Serial ATA (SATA) Either end of the SATA data cable
Data Cable can be connected to the SATA
(Only for P4S55FX+ motherboard) hard disk or the SATA connector
on the motherboard.
16
Page 17

Serial ATA (SATA) Please connect the black end of
Power Cable SATA power cable to the power
(Only for P4S55FX+ motherboard) connector on each drive. Then
(Optional) connect the white end of SATA
connect to the SATA
HDD power connector
connect to the
power supply
power cable to the power
connector of the power supply.
1
USB_PWR
USB_PWR
1
CD-R
GND
GND
CD-L
AUX-R
GND
GND
AUX-L
1
P-7
P+7
P+6
P-6
IRTX
+5V
GND
IRRX
GND
+5VA
MIC-POWER
MIC
GND
DUMMY
GND
DUMMY
CD1
AUX1
BACKOUT-R
BACKOUT-L
AUD-OUT-L
GND
AUD-OUT-R
are not sufficient, this USB 2.0
header is available to support 2
additional USB 2.0 ports.
tuner card, or MPEG card.
control of audio devices.
USB 2.0 Header ASRock I/O PlusTM provides you
(9-pin USB67) 6 default USB 2.0 ports on the
(see p.7 No. 21 / p.8 No. 19) rear panel. If the rear USB ports
Infrared Module Header This header supports an optional
(5-pin IR1) wireless transmitting and
(see p.7 No. 17 / p.8 No. 15) receiving infrared module.
Internal Audio Connectors These connectors allow you
(4-pin CD1, 4-pin AUX1) to receive stereo audio input
(CD1: see p.7 No.28 / p.8 No. 26) from sound sources such as
(AUX1: see p.7 No.27 / p.8 No. 25) a CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, TV
Front Panel Audio Header This is an interface for the front
(9-pin AUDIO1) panel audio cable that allows
(see p.7 No.26 / p.8 No. 24) convenient connection and
1
PLED+
HDLED+
1
+5V
PLED-
PWRBTN#
GND
HDLED-
DUMMY
DUMMY
GND
DUMMY
RESET#
SPEAKER
System Panel Header This header accommodates
(9-pin PANEL1) several system front panel
(see p.7 No.18 / p.8 No. 16) functions.
Chassis Speaker Header Please connect the chassis
(4-pin SPEAKER 1) speaker to this header.
(see p.7 No.20 / p.8 No. 18)
17
Page 18

Chassis Fan Connector Please connect the chassis fan
(3-pin CHA_FAN1) cable to this connector and
(see p.7 No. 16 / p.8, No. 15) match the black wire to the
GND
+12V
CHA_FAN_SPEED
ground pin.
CPU Fan Connector Please connect the CPU fan
(3-pin CPU_FAN1) cable to this connector and
(see p.7 No. 2 / p.8, No. 2) match the black wire to the
GND
+12V
CPU_FAN_SPEED
ground pin.
Game Connector Connect a Game cable to this
(15-pin GAME1) connector if the Game port
(see p.7 No. 22 / p.8, No. 20) bracket is installed.
+5V
JBB1
JBX
MIDI_OUT
JBY
JBB2
MIDI_IN
1
JAX
JAB1
+5V
GND
GND
+5V
JAB2
JAY
ATX Power Connector Please connect an ATX power
(20-pin ATXPWR1) supply to this connector.
(see p.7 No. 29 / p.8, No. 27)
ATX 12V Connector Please connect an ATX 12V
(4-pin ATX12V1) power supply to this connector.
(see p.7 No. 7 / p.8, No. 7)
18
Page 19

2.7 Serial ATA (SATA) Hard Disks Installation
This motherboard adopts SiS 964 southbridge chipset that supports Serial
ATA (SATA) hard disks and RAID functions. You may install SATA hard disks
on this motherboard for internal storage devices. This section will guide you
to install the SATA hard disks.
STEP 1: I nstall the SATA hard disks into the drive bays of your chassis.
STEP 2: Connect one end of the SATA data cable to the motherboard’s
primary SATA connector (SATA1).
STEP 3: Connect the other end of the SATA data cable to the primary SATA
hard disk.
STEP 4: C onnect the SATA power cable to the SATA hard disk. If you just want
to install only one SATA HDD, the installation process is complete at
this step. If you want to install two SATA HDDs or you want to use
RAID function, please continue to do the following steps.
STEP 5: C onnect one end of the second SATA data cable to the
motherboard’s secondary SATA connector (SATA2).
STEP 6: C onnect the other end of the SATA data cable to the secondary SATA
hard disk.
STEP 7: C onnect the SATA power cable to the SATA hard disk.
2.8 Hot Plug and Hot Swap Functions for SATA HDDs
P4S55FX+ motherboard supports Hot Plug function for SATA Devices. Usually,
each power wire will provide 2 power connectors for HDDs. We suggest you
to connect SATA HDDs to different power wires to prevent intervention.
As to Hot Swap support, please refer to the updates of later version driver that
supports Hot Swap function on our website www.asrock.com
NOTE
What is Hot Plug Function?
If the SATA HDDs are NOT set for RAID configuration, it is called “Hot
Plug” for the action to insert and remove the SATA HDDs while the system
is still power-on and in working condition.
However, please note that it cannot perform Hot Plug if the OS has been
installed into the SATA HDD.
What is Hot Swap Function?
If SATA HDDs are built as RAID1 then it is called “Hot Swap” for the action
to insert and remove the SATA HDDs while the system is still power-on
and in working condition.
19
Page 20

2.9 Making An SATA Driver Diskette
If you want to install Windows 2000 or Windows XP on your SATA HDDs, you
will need to make an SATA driver diskette before you start the OS installation.
STEP 1: I nsert the ASRock Support CD into your optical drive to boot your
system. (Do NOT insert any floppy diskette into the floppy drive at
this moment!)
STEP 2: D uring POST at the beginning of system boot-up, press <F11> key,
and then a window for boot devices selection appears. Please
select CD-ROM as the boot device.
STEP 3: W hen you see the message on the screen, “Do you want to
generate Serial ATA driver diskette [YN]?”, press <Y>.
STEP 4: Then you will see these messages,
Please insert a diskette into the floppy drive.
WARNING! Formatting the floppy diskette will
lose ALL data in it!
Start to format and copy files [YN]?
Please insert a floppy diskette into the floppy drive, and press <Y>.
STEP 5: The system will start to format the floppy diskette and copy SATA
drivers into the floppy diskette.
Once you have the SATA driver diskette ready, you may start to install Windows
2000 / Windows XP on your system directly without setting the RAID configuration on your system, or you may start to use “SiS RAID BIOS Setting Utility” to set
RAID 0 / RAID 1 / JBOD configuration before you install the OS. Before you start
to configure the RAID function, you need to check the installation guide in the
Support CD for proper configuration. Please refer to the document in the Support
CD, “Guide to SATA Hard Disks Installation and RAID Configuration”, which is
located in the folder at the following path:
.. \ RAID BIOS Setting Utility
You may also set the RAID configuration by using “SiS RAID Utility for Windows”
in Windows environment. Please refer to the document in the Support CD,
“Guide to SiS RAID Utility for Windows”, which is located in the folder at the
following path:
.. \ RAID Utility for Windows
20
Page 21

Chapter 3 BIOS Setup
3.1 BIOS Setup Utility
This section explains how to use the BIOS Setup Utility to configure your system.
The Flash Memory on the motherboard stores the BIOS Setup Utility. You may run the
BIOS Setup Utility when you start up the computer. Please press <F2> during the
Power-On-Self-Test (POST) to enter the BIOS Setup Utility, otherwise, POST
continues with its test routines.
If you wish to enter the BIOS Setup after POST, restart the system by pressing
<Ctl> + <Alt> + <Delete>, or by pressing the reset button on the system chassis.
You may also restart by turning the system off and then back on.
The BIOS Setup Utility is designed to be user-friendly. It is a menu-driven program,
which allows you to scroll through its various sub-menus and select among the
predetermined choices.
Because the BIOS software is constantly being updated, the
following BIOS setup screens and descriptions are for reference
purpose only, and may not exactly match what you see on your
screen.
3.1.1 BIOS Menu Bar
The top of the screen has a menu bar with the following selections:
MAIN Sets up the basic system configuration
ADVANCED Sets up the advanced features
SECURITY Sets up the security features
POWER Configures Power Management features
BOOT Configures the default system device that is used
to locate and load the Operating System
EXIT Exits the current menu or the BIOS Setup
To access the menu bar items, press the right or left arrow key on the keyboard
until the desired item is highlighted.
3.1.2 Legend Bar
At the bottom of the Setup Screen is a legend bar. The following table lists the keys
in the legend bar with their corresponding functions.
21
Page 22

Navigation Key(s) Function Description
<F1> Displays the General Help Screen
<ESC> Jumps to the Exit menu or returns to the upper menu
from the current menu
/ Moves cursor up or down between fields
/ Selects menu to the left or right
+ / - Increases or decreases values
<Enter> Brings up a selected menu for a highlighted field
<F9> Loads all the setup items to default value
<F10> Saves changes and exits Setup
3.2 Main Menu
When you enter the BIOS Setup Utility, the following screen appears.
Advanced
Main
System Date
System Time
Floppy Drives
IDE Devices
BIOS Version
Processor Type
Processor Speed
Cache Size
Microcode Update
TotalMemory
DDR1
DDR2
DDR3
DDR4
F1:Help
Esc:Exit
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY -VERSION 3.31a
Security
Jan
10:07:40
P4S55FX+ BIOS P1.00
Pentium(R)4CPU
2400 MHz
512 KB
F27/33
256 MB (Single Channel)
256 MB / 166 MHz (DDR 333)
None
None
None
:Select Item
:Select Menu
Power
2 2004 Fri
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Boot
Exit
Sub-Menu
[ Setup Help ]
Month: Jan -Dec
Day: 01-31
Year:1980-2099
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
System Date [Month/Day/Year]
Set the system date that you specify. Valid values for month, day, and year are
Month: (Jan to Dec), Day: (1 to 31), Year: (up to 2099). Use keys to move
between the Month, Day and Year fields.
System Time [Hour:Minute:Second]
Set the system to the time that you specify. Use keys to move between
the Hour, Minute and Second fields.
Floppy Drives
Use this to set the type of floppy drives installed.
IDE Devices
Use this to configure IDE devices.
22
Page 23

TYPE
To set the type of the IDE device, first, please select “IDE Devices” on Main
menu and press <Enter> to get into the sub-menu. Then, select among
“Primary IDE Master”, “Primary IDE Slave”, “Secondary IDE Master”, and
“Secondary IDE Slave” to make configuration of its type. After making your
selections on this sub-menu, press <ESC> key to return to the upper menu,
in whcih the hard disk drive field will display the size of the hard disk drive
that you configured. Below are the configuration options.
Main
Primary IDE Master:
Type
Cylinders
Heads
Write Precompensation
Sectors
Maximum Capacity
LBA Mode
Block Mode
Fast Programmed I/O Modes
32 Bit Transfer Mode
Ultra DMA Mode
F1:Help
Esc:Previous Menu
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY - VERSION3.31a
Auto
Off
Off
Auto
On
Auto
:Select Item
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Sub-Menu
[ SetupHelp ]
Select how to set the
parameters of drive,
Or
Select [AUTO] to set
all HDD parameters
automatically.
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
[USER]: It allows user to manually enter the number of cylinders, heads,
and sectors per track for the drive.
Before attempting to configure a hard disk drive, make sure you
have the correct configuration information supplied by the drive
manufacturer. Incorrect settings may cause the system to fail
to recognize the installed hard disk.
[Auto]: Select [Auto] to automatically detect hard disk drive. If auto-
detection is successful, the BIOS Setup automatically fills in the
correct values for the remaining fields on this sub-menu. If the autodetection fails, it may due to that the hard disk is too old or too new.
If the hard disk was already formatted on an older system, the BIOS
Setup may detect incorrect parameters. In these cases, select [User]
to manually enter the IDE hard disk drive parameters.
After entering the hard disk information into BIOS, use a disk utility,
such as FDISK, to partition and format new IDE hard disk drives.
This is necessary so that you can write or read data from the hard
disk. Make sure to set the partition of the Primary IDE hard disk
drives to active.
23
Page 24

[CD/DVD]: This is used for IDE CD/DVD drives.
[ARMD]: This is used for IDE ARMD (ATAPI Removable Media Device),
such as MO.
Cylinders
This is used to configure the number of cylinders. Refer to the drive
documentation to determine the correct value.
Heads
This is used to configure the number of read/write heads. Refer to
the drive documentation to determine the correct values.
Write Pre-compensation
Enter Write Pre-compensation sector. Refer to the drive documentation to
determine the correct value.
Sectors
This is used to configure the number of sectors per track. Refer to the
drive documentation to determine the correct value.
Maximum Capacity
This field shows the drive’s maximum capacity as calculated by the BIOS
based on the drive information you entered.
LBA Mode
This allows user to select the LBA mode for a hard disk > 512 MB under
DOS and Windows; for Netware and UNIX user, select [Off] to disable the
LBA mode.
Block Mode
Set the block mode to [On] will enhance hard disk performance by reading
or writing more data during each transfer.
Fast Programmed I/O Modes
This allows user to set the PIO mode to enhance hard disk performance by
optimizing the hard disk timing.
32 Bit Transfer Mode
It allows user to enable 32-bit access to maximize the IDE hard disk data
transfer rate.
Ultra DMA Mode
Ultra DMA capability allows improved transfer speeds and data integrity
for compatible IDE devices. Set to [Disabled] to suppress Ultra DMA
capability.
3.3 Advanced, Security, Power, Boot, and Exit Menus
Detailed descriptions of these menus are listed in the Appendix. See page 26.
24
Page 25

Chapter 4 Software Support
4.1 Install Operating System
This motherboard supports various Microsoft® Windows® operating systems:
98 SE / ME / 2000 / XP. Because motherboard settings and hardware options vary,
use the setup procedures in this chapter for general reference only. Refer to your
OS documentation for more information.
4.2 Support CD Information
The Support CD that came with the motherboard contains necessary drivers and
useful utilities that enhance the motherboard features.
4.2.1 Running The Support CD
To begin using the support CD, insert the CD into your CD-ROM drive. The CD
automatically displays the Main Menu if “AUTORUN” is enabled in your computer.
If the Main Menu did not appear automatically, locate and double click on the file
ASSETUP.EXE from the BIN folder in the Support CD to display the menus.
4.2.2 Drivers Menu
The Drivers Menu shows the available devices drivers if the system detects
installed devices. Install the necessary drivers to activate the devices.
4.2.3 Utilities Menu
The Utilities Menu shows the applications software that the motherboard
supports. Click on a specific item then follow the installation wizard to install it.
4.2.4 ASRock PC-DIY Live Demo Program
ASRock presents you a multimedia PC-DIY live demo, which shows you how to
install your own PC system step by step. You can find the file through the
following path:
..\ MPEGAV \ AVSEQ01.DAT
To see this demo program, you can run Microsoft® Media Player® to play the file.
4.2.5 Contact Information
If you need to contact ASRock or want to know more about ASRock, welcome
to visit ASRock’s website at http://www.asrock.com; or you may contact your
dealer for further information.
25
Page 26

Appendix: Advanced BIOS Setup
This section will introduce you the following BIOS Setup menus: “Advanced,”
“Security,” “Power,” “Boot,” and “Exit.”
1. Advanced BIOS Setup Menu
Advanced
Main
CPU Host Frequency
Actual Frequency
DRAM Frequency
CPU Ratio Selection
Spread Spectrum
Hyper ThreadingTechnology
Flexibility
Chipset Configuration
Resource
Configuration
Peripheral
Configuration
System Hardware Monitor
F1:Help
Esc:Exit
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY - VERSION3.31a
Security
:Select Item
:Select Menu
Power
Auto
133MHz
Auto
Locked
Disabled
Auto
Disabled
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Boot
Exit
Sub-Menu
[ Setup Help ]
<Enter> to enable how
to set the CPU host
frequency.
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
CPU Host Frequency:
This shows current CPU host frequency of the installed motherboard.
DRAM Frequency:
If [Auto] is selected, the motherboard will detect the memory module(s) inserted
and assigns appropriate frequency automatically. You may also select other
value as operating frequency: [100MHz (DDR 200)], [133MHz (DDR 266)],
[166MHz (DDR 333)], [200MHz (DDR 400)]. If the installed CPU is an FSB-800MHz
CPU, the option [100MHz (DDR 200)] will not be available.
CPU Ratio Selection:
CPU Ratio is the multiple that times the frontside bus frequency will equal
the core speed of the installed processor. Whether the option is open or locked
is determined by the installed processor.
Spread Spectrum:
This field should always be set to [Disabled] for better system stability.
Hyper-Threading Technology:
To enable this feature, it requires a computer system with an Intel Pentium®4
processor that supports Hyper-Threading technology and an operating system
that includes optimization for this technology, such as Microsoft® Windows
XP. Set to [Auto] if using Microsoft® Windows® XP, or Linux kernel version
2.4.18 or higher. This option will be hidden if the current CPU does not support
Hyper-Threading technology.
®
26
Page 27

Flexibility:
The default value of this option is [Disabled]. It will allow better tolerance for
memory compatibility when it is set to [Enabled].
Chipset Configuration:
Advanced
Chipset Configuration
AGP Data Rate
AGP Fast Write
AGP Aperture Size
USB Controller
USB 2.0 Support
USB Device Legacy Support
VDDQ Voltage
VCCM Volatge
IDE Driving Strength
ZCLK /AGP /PCI Frequency mode
DRAM Access Mode
F1:Help
Esc:Previous Menu
Advanced
Chipset Configuration
VDDQ Voltage
VCCM Volatge
IDE Driving Strength
ZCLK /AGP /PCI Frequency mode
DRAM Access Mode
DRAM CAS Latency
DRAM Precharge Time
DRAM RAS to CAS Delay
DRAM ACT to Precharge Delay
DIMM1, 2 Address /Command Rate
DIMM3, 4 Address /Command Rate
DIMM1, 2 FWDSDCLK Delay
DIMM3, 4 FWDSDCLK Delay
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY -VERSION 3.31a
:Select Item
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY -VERSION 3.31a
Auto
Disabled
64M
Enabled
Enabled
Disabled
1.66V
2.62V
Normal
Sync. Mode
Auto
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
1.66V
2.62V
Normal
Sync. Mode
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
Auto
2T
2T
Auto
Auto
Sub-Menu
[ Setup Help ]
<Enter> to select the
AGP data transfer rate.
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
[ Setup Help ]
<Enter> to select the
AGP data transfer rate.
F1:Help
Esc:Previous Menu
:Select Item
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Sub-Menu
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
AGP Data Rate: This allows you to select the AGP data transfer rate between
[8X] or [4X] for an AGP 3.0 card. For AGP 2.0 card, you may select
between [4X], [2X], and [1X]. The default value is [Auto].
AGP Fast Write: This allows you to enable or disable the feature of AGP fast
write protocol support.
AGP Aperture Size: It refers to a section of the PCI memory address range
used for graphics memory. It is recommended to leave this field at the
default value unless the installed AGP card’s specifications requires other
sizes.
27
Page 28

USB Controller: Use this to enable or disable the use of USB controller.
USB 2.0 Support: Use this to enable or disable the use of USB 2.0 support.
USB Device Legacy Support: Use this to enable or disable the support to
emulate legacy I/O devices such as mouse, keyboard,... etc.
VDDQ Voltage: Use this to select VDDQ voltage between [1.66V] and [1.57V].
VCCM Voltage: Use this to select VCCM voltage between [2.62V] and [2.55V].
IDE Driving Strength: Select [Normal] or [Strong] for IDE driving strength.
ZCLK/AGP/PCI Frequency mode: If the item CPU Host Frequency is set to
[Manual], it allows you to set the value for this item. You may set this item to
synchronize with CPU Host Frequency or fix it at 132/66/33 MHz.
DRAM Access Mode: The default value is [Auto], which will automatically
select the proper access mode for the system. You may select between
[Single Channel] and [Dual Channel] if you have properly set the dual
channel memory configuration.
DRAM CAS Latency: This is used to adjust the means of memory accessing.
Configuration options: [Auto], [2T], [2.5T], [3T]. Please note that not all the
DDR DIMMs can support CAS latency=3T.
DRAM Precharge Time: Use this to select among [Auto], [3T], [2T], [4T], and
[5T] for DRAM Precharge Time <tRP>.
DRAM RAS to CAS Delay: Use this to select among [Auto], [3T], [2T], [4T], and
[5T] for DRAM RAS to CAS Delay <tRCD>.
DRAM ACT to Precharge Delay: Use this to select among [Auto], [6T], [7T],
[5T], [4T], [8T] and [9T] for DRAM ACT to Precharge Delay <tRAS>.
DIMM1, 2 Address/Command Rate: Use this to select among [Auto], [2T],
and [1T] for DIMM1, 2 Address/Command Rate <MA>.
DIMM3, 4 Address/Command Rate: Use this to select among [Auto], [2T],
and [1T] for DIMM3, 4 Address/Command Rate <MA>.
DIMM1, 2 FWDSDCLK Delay: Use this to select [Auto] or other values for
DIMM1, 2 FWDSDCLK delay.
DIMM3, 4 FWDSDCLK Delay: Use this to select [Auto] or other values for
DIMM3, 4 FWDSDCLK delay.
28
Page 29

Resource Configuration:
Advanced
Resource Configuration
PCI Latency Timer (PCI Clocks)
Primary Graphics Adapter
F1:Help
Esc:Previous Menu
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY -VERSION 3.31a
32
PCI
:Select Item
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Sub-Menu
[ Setup Help ]
<Enter> to select PCI
clocks. Leave on
default setting for the
best PCI performance.
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
PCI Latency Timer (PCI Clocks): The default is 32. It is recommended to keep
the default value unless the inserted PCI expansion cards’ specifications
require other settings.
Primary Graphics Adapter: This allows you to select [AGP] or [PCI] as the
primary graphics adapter.
Peripheral Configuration:
Advanced
Peripheral Configuration
OnBoard FDC
OnBoard Serial Port
OnBoard Infrared Port
OnBoard Parallel Port
Parallel Port Mode
EPP Version
Parallel Port IRQ
Parallel Port DMA Channel
OnBoard Midi Port
Midi IRQ Select
OnBoard Game Port
OnBoard IDE
OnBoard SATA
OnBoard LAN
OnBoard AC' 97 Audio
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY -VERSION 3.31a
Auto
Auto
Disabled
Auto
ECP + EPP
1.9
Auto
Auto
Disabled
5
200H
Both
Enabled
Enabled
Auto
[ Setup Help ]
<Enter> to enable or
disable the floppy
drive controller.
F1:Help
Esc:Previous Menu
:Select Item
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Sub-Menu
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
OnBoard FDC: Use this to enable or disable floppy drive controller.
OnBoard Serial Port: Use this to set the address for the serial port COM1.
Configuration options: [Auto], [Disabled], [3F8 / IRQ4 / COM1],
[2F8 / IRQ3 / COM2], [3E8 / IRQ4 / COM3], [2E8 / IRQ3 / COM4].
29
Page 30

OnBoard Serial Port
Use this to set addresses for the on-board serial ports or disable serial
ports. Configuration options: [Auto], [Disabled], [3F8 / IRQ4 / COM1],
[2F8 / IRQ3 / COM2], [3E8 / IRQ4 / COM3], [2E8 / IRQ3 / COM4].
OnBoard Infrared Port
You may select [Auto] for the on-board infrared port feature, which will
enable this feature if the infrared module is installed. Or you may disable
the feature by selecting [Disabled].
OnBoard Parallel Port: Select Parallel Port address or disable Parallel Port.
Configuration options: [Auto], [Disabled], [378], [278].
Parallel Port Mode: Set the operation mode of the parallel port. The
default value is [ECP+CPP]. If this option is set to [ECP+EPP], it will
show the EPP version in the following item, “EPP Version”.
OnBoard Midi Port: Select address for Midi Port or disable Midi Port.
Configuration options: [Disabled], [330], [300].
Midi IRQ Select: Use this to select Midi IRQ.
OnBoard Game Port: Select address for Game Port or disable Game Port.
Configuration options: [Disabled], [200], [208].
OnBoard IDE: This allows you to enable or disable the onboard IDE controller.
OnBoard SATA: This allows you to enable or disable the onboard SATA
controller. This option is available only for P4S55FX+ motherboard.
OnBoard LAN: This allows you to enable or disable the onboard LAN feature.
OnBoard AC’97 Audio: Select [Disabled], [Auto] or [Enabled] for the onboard
AC’97 Audio feature.
System Hardware Monitor: You can check the status of the hardware on your
system. It allows you to monitor the parameters for CPU temperature,
Motherboard temperature, CPU fan speed, and critical voltage.
Advanced
System Hardware Monitor
CPU Temperature
M/B
Temperature
CPU FanSpeed
Chassis FanSpeed
Vcore
+ 3.30V
+ 5.00V
+ 12.00V
F1:Help
Esc:Previous Menu
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY -VERSION 3.31a
35C/ 95F
27C/ 82F
3110 RPM
N/A
1.601 V
3.312 V
4.972 V
12.161 V
:Select Item
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Sub-Menu
[ Setup Help ]
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
30
Page 31

2. Security Setup Menu
Advanced
Main
Supervisor Password
User Password
Set SupervisorPassword
Set UserPassword
Password Check
F1:Help
Esc:Exit
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY -VERSION 3.31a
Security
Clear
Clear
[ Enter ]
[ Enter ]
Setup
:Select Item
:Select Menu
Power
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Boot
Exit
Sub-Menu
[ Setup Help ]
<Enter> to set the
supervisor password.
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
Supervisor Password: This field shows the status of the Supervisor Password.
[Clear]: No password has been set.
[Set]: Supervisor password has been set.
User Password: This field shows the status of the User Password.
[Clear]: No password has been set.
[Set]: User password has been set.
Set Supervisor Password: Press <Enter> to set Supervisor Password. Valid
password can be a 1 to 6 alphanumeric characters combination. If you already
have a password, you must enter your current password first in order to
create a new password.
Set User Password: Press <Enter> to set User Password. Valid password can
be a 1 to 6 alphanumeric characters combination. If you already have a
password, you must enter your current password first in order to create a new
password.
Password Check: Select the check point for “Password Check”. Configuration
options: [Setup], [Always]. If [Setup] option is selected, the “Password Check”
is performed before BIOS setup. If [Always] option is selected, the “Password
Check” is performed before both boot-up and BIOS setup.
31
Page 32

3. Power Setup Menu
Advanced
Main
Suspend To RAM (S3)
Repost Video on S3 Resume
Restore on AC / Power Loss
Ring-In Power On
PCI Devices Power On
PS/2 Keyboard Power On
RTC Alarm Power On
RTC Alarm Date
RTC Alarm Hour
RTCAlarmMinute
RTC Alarm Second
F1:Help
Esc:Exit
:Select Item
:Select Menu
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY - VERSION3.31a
Security
Power
Disabled
Disabled
Power Off
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Disabled
Everyday
12
30
00
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Boot
Exit
Sub-Menu
[ Setup Help ]
<Enter> to select
auto-detect or disable
theACPIS3feature.
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
Suspend to RAM (S3): This field allows you to select whether to auto-detect or
disable the Suspend-to-RAM (S3) feature. Select [Auto] will enable this feature
if the system supports it.
Repost Video on S3 Resume: This feature allows you to repost video on S3
resume. It is recommended to enable this feature under Microsoft® Windows
98 / ME.
Restore on AC/Power Loss: This allows you to set the power state after an
unexpected AC/power loss. If [Power Off] is selected, the AC/power remains
off when the power recovers. If [Power On] is selected, the AC/power
resumes and the system starts to boot up when the power recovers.
Ring-In Power On: Use this to enable or disable Ring-in signals to turn on the
system from the power-soft-off mode.
PCI Devices Power On: Use this to enable or disable PCI devices to turn on the
system from the power-soft-off mode.
PS/2 Keyboard Power On: Use this to enable or disable PS/2 keyboard to turn on
the system from the power-soft-off mode.
RTC Alarm Power On: Use this to enable or disable RTC (Real Time Clock) to
power on the system. If [Enable] is selected, you will need to fill the RTC Alarm
Date / Hour / Minute / Second sub-fields with the actual wake up time you desire.
®
32
Page 33

4. Boot Setup Menu
Advanced
Main
Quick Boot Mode
Boot Up Num-Lock
Boot To OS/2
Boot From Network
Boot Device Priority
F1:Help
Esc:Exit
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY -VERSION 3.31a
Security
Enabled
On
No
Disabled
:Select Item
:Select Menu
Power
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Boot
Exit
Sub-Menu
[ Setup Help ]
<Enter> to enable or
disable the quick boot
mode.
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
Quick Boot Mode: Enable this mode will speed up the boot-up routine by skipping
memory retestings. The default value is [Enabled].
Boot Up Num-Lock: If this is enabled, it will automatically activate the Numeric Lock
function after boot-up. The default value is [On].
Boot To OS/2: This enables boot-up to OS/2 operating system.
The default value is [No].
Boot From Network: Use this to enable or disable “boot from network” feature.
The default value is [Disabled].
Boot Device Priority: This allows you to set the boot device priority.
33
Page 34

5. Exit Menu
Advanced
Main
Exit Saving Changes
Exit Discarding Changes
Load Default Settings
Discard Changes
F1:Help
Esc:Exit
AMIBIOS SETUPUTILITY -VERSION 3.31a
Security
[ Enter ]
[ Enter ]
[ Enter ]
[ Enter ]
:Select Item
:Select Menu
Power
+/-:Change Values
Enter:Select
Boot
Exit
Sub-Menu
[ Setup Help ]
Exits and saves the
changesinCMOSRAM.
F9:Setup Defaults
F10:Save &Exit
Exit Saving Changes: After you enter the sub-menu, the message “Save current
settings and exit” will appear. If you press <ENTER>, it will save the current
settings and exit the BIOS SETUP Utility.
Exit Discarding Changes: After you enter the submenu, the message “Quit
without saving changes” will appear. If you press <ENTER>, you will exit the
BIOS Setup Utility without making any changes to the settings.
Load Default Settings: After you enter the submenu, the message “Load default
settings” will appear. If you press <Enter>, it will load the default values for all
the setup configurations.
Discard Changes: After you enter the sub-menu, the message “Load setup
original values” will appear. If you press <ENTER>, the original values will be
restored and all changes are discarded.
34
 Loading...
Loading...