Page 1
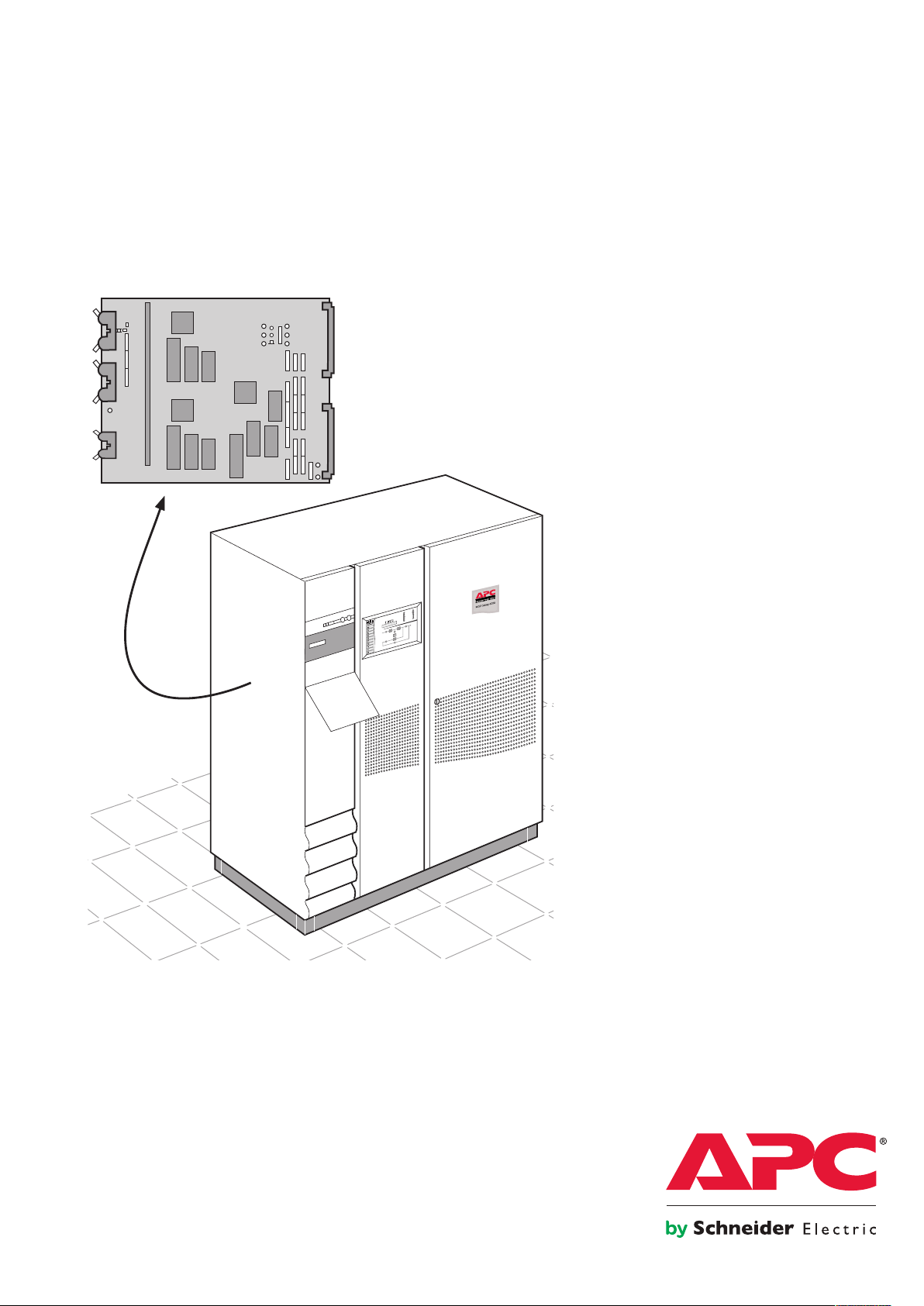
MGETM GalaxyTM 6000
50, 60 Hz
250 - 600 kVA
"GTC link"
communication
interface
User manual
5 kVA
120%
12
100%
100%
0 Hour 50 Min.
80%
0%
5
0%
5
0
vel
d le
GALAXY 6000 400 kVA
oa
L
0
e
SALLE IQ
Tim
kup
Bac
le
ilab
ted
Ava
rotec
ad p
5N
Lo
oad
Q
L
ent
quipm
e
e
Hom
larms
A
1
Q
QF1
line
On
Trend
s
Normal AC
Statistic
tifier
Rec
Q4S
05
Battery
30/05/20
5:24:32
1
AC
ass
Inverter
Byp
3BP
Q
s
pas
By
Output
Set up
6739389EN/FB - Page 1
Page 2

Page 2 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 3

Contents
Presentation ...................................................................................................... 4
Introduction ................................................................................................................ 4
"GTCZ" and "GT2Z" boards features ......................................................................... 4
Communication settings ........................................................................... 5
JBUS protocol.................................................................................................. 6
Introduction ................................................................................................................ 6
Principle ..................................................................................................................... 7
Synchronizing data exchanges .................................................................................. 7
Description of request and response frames ............................................................. 7
Checking received messages on the slave-side ........................................................ 8
Functions.................................................................................................................... 9
CRC 16 algorithm .................................................................................................... 14
UPS theory of operation .......................................................................... 18
Unitary UPS ............................................................................................................. 18
Parallel connected UPS with "Static Switch" cubicle ............................................... 19
UPS without Mains 2 ................................................................................................ 19
Unitary UPS ..................................................................................................... 21
Block diagram .......................................................................................................... 21
Measured quantities ................................................................................................. 21
Main status bits ........................................................................................................ 22
Operating modes ..................................................................................................... 22
Parallel connected UPS ........................................................................... 24
Block diagram .......................................................................................................... 24
Measured quantities ................................................................................................. 24
Main status bits of system operations ...................................................................... 25
Operating modes ..................................................................................................... 25
Static switch cubicle .................................................................................. 26
Block diagram .......................................................................................................... 26
Measured quantities ................................................................................................. 26
Main status bits of system operations ...................................................................... 27
Operating modes ..................................................................................................... 27
System information .................................................................................... 28
Message format ....................................................................................................... 28
Example of read data ............................................................................................... 28
Sample commands .................................................................................................. 28
List of variable fields ................................................................................................ 28
General definitions ................................................................................................... 29
Signaling field ........................................................................................................... 29
Tables measured data .............................................................................................. 29
Tables of binary data ................................................................................................ 31
Table of control devices ........................................................................................... 33
Telemonitoring information ....................................................................................... 33
Glossary of information descriptors ......................................................................... 34
Glossary of telemonitoring information descriptors .................................................. 37
TM
All MGE
GalaxyTM 6000 products are protected by patents. They implement original APC by Schneider Electric technology
not available to other manufacturers.
This document may be copied only with the written consent of APC by Schneider Electric.
Authorized copies must be marked "APC by Schneider Electric GTC link communication interface user manual No.
6739389EN".
6739389EN/FB - Page 3
Page 4

Presentation
Introduction
The "GTC link" communication
interface is designed to transmit
TM
MGE
operating information and remote
"on/off" commands (if available) to
an external computer.
The JBUS hexadecimal
communication protocol is used
(the JBUS ASCII mode is not used
in this application).
The "GTC link" features two
symmetrical communication
channels, both with a simplified
V24 (RXD and TXD only) and an
RS485 interface.
It consists of a "GTCZ"
communication board (central unit)
and a "RAUZ 1" (communication
network management and
interconnection board).
In option, two additional
communication ports can be added:
"GT2Z" board (central unit) and
"RAUZ 2" board (communication
network management and
interconnection board).
Refer to the "communication
options connection manual" of
MGE
6739388XU, for all informations
about connections.
GalaxyTM 6000 UPS
TM
GalaxyTM 6000 nr
"GTCZ" and "GT2Z"
boards features
The "GTCZ" and "GT2Z" boards
are functionally divided into two
main modules:
The ACQ module
◗ performs data acquisition;
◗ monitors the status bus of the
monitor/control boards;
◗ computes physical quantities and
battery backup time;
◗ processes alarms;
◗ sends commands to monitor/
control boards;
◗ stores configurable parameters
and communicates with the "Soft
Tunor" software, used by APC by
Schneider Electric after-sales
service;
◗ transfers data using the on-board
communication channels.
The COM module
The COM communication module
is designed for external devices
(e.g. "AMUZ" type board of a
"Monitor" or "Tele-Monitor") to:
◗ retrieve information and
parameters processed by the ACQ;
◗ send commands to monitor/
control boards;
◗ be integrated into other systems
(remote indications and
supervision).
Each "GTCZ" or "GT2Z" board is
equipped with two symmetrical
communication ports, COM1 and
COM2:
◗ on the "GTCZ" board:
◗ ◗ COM1 for a "display devices"
network consisting of "AMUZ"
boards in a unitary or parallel
connected UPS configurations,
◗ ◗ COM2 for a supervisory system;
◗ on the "GT2Z" board:
◗ ◗ COM1 and COM2 for a
supervisory system.
The "GTCZ" and "GT2Z" boards
are configured with the APC by
Schneider Electric after-sales
customization software called "Soft
Tunor".
The computer link is via the test
connector located on the front
panel of the cubicles and performs:
◗ configuration, calibration and
control of the ACQ module;
◗ configuration of COM1 and
COM2 ports.
Page 4 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 5
Communication settings
The COM1 and COM2
communication ports can be
configured as follows:
◗ data rate: 1200, 2400, 4800,
9600 Baud;
◗ data bits: 8 (always);
◗ parity: none, odd, even;
◗ stop bits: 1 or 2;
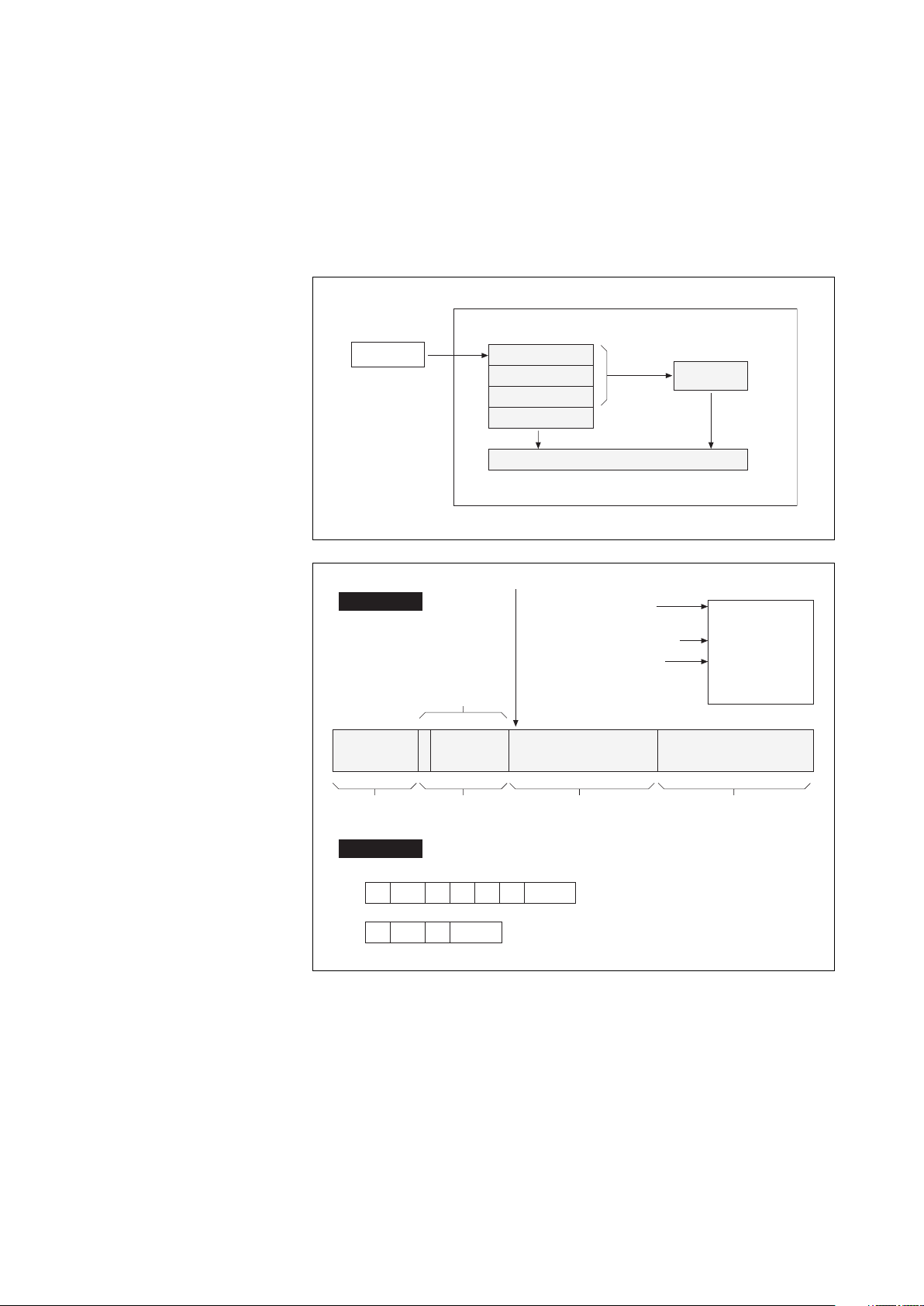
Location of the "GTCZ" and "GT2Z" boards in the cubicle electronics
◗ slave address: 20H to F8H in
increments of 8H;
◗ interface:
◗ ◗ 0 = RS232 simplified,
◗ ◗ 1 = RS232 complete
(not implemented),
◗ ◗ 2 = RS485;
◗ command masks;
◗ other parameters (modem type,
telephone number, handshaking,
modem protocol, password)
reserved for later use.
INTERNAL BUS
SRIZ
Test channel
Status
Acquisition
Status
Test channel
Acquisition
Status
Test channel
Acquisition
Status
Test channel
Acquisition
Status
Test channel
Commands
CRIZ
CROZ
AROZ
GTCZ
(only in rectifier-inverter cubicle)
(only in rectifier-inverter cubicle)
(in all cubicles)
COM1
RAUZ 1
COM2
Soft Tunor
Acquisition
Status
Test channel
Commands
GT2Z
COM1
RAUZ 2
COM2
6739389EN/FB - Page 5
Page 6
JBUS protocol
Introduction
JBUS protocol can be used to read
or write one or more bits or words.
In the interest of simplicity, this
document describes only the
procedures necessary for operation
and monitoring of the APC by
Schneider Electric unit.
Communications are initiated by
the master and include a request
from the master and a response
from the slave.
Master requests must be
addressed to one specific slave
(identified by its address in the first
byte of the request frame) as
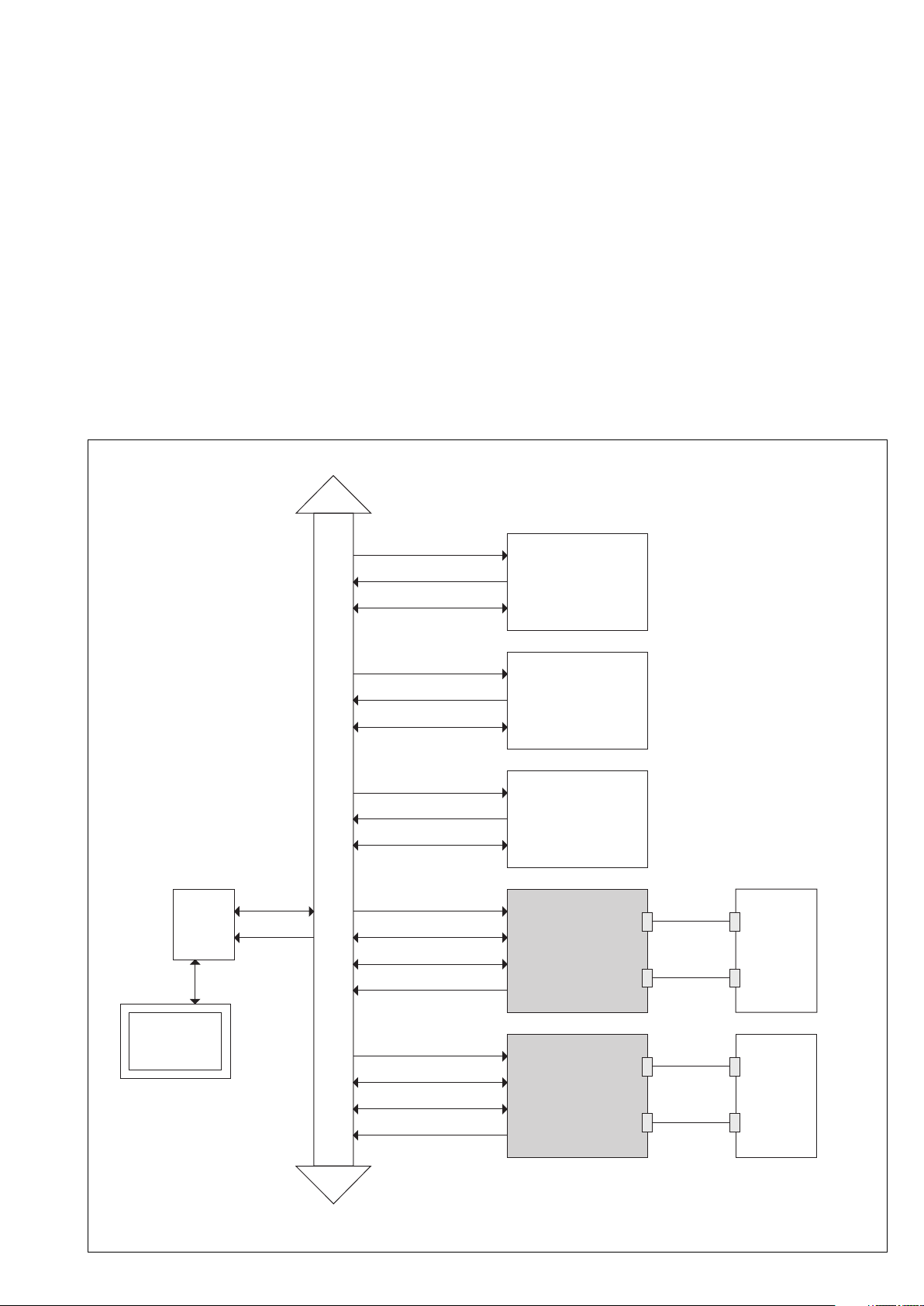
shown in the diagram opposite:
MASTER
Slave
request
request
response
Wait
Master
Slave Slave
Response analysis
and preparation
of next exchange
request
Wait
SLAVE 1
SLAVE N
PHYSICAL
MEDIA
to slave 1 to slave N
response
request processing
Exchange i
response
Exchange i+1
Page 6 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 7
JBUS protocol (continued)
Principle
A full understanding of the protocol
is only required if the master is a
computer that must be
programmed.
All communications include 2
messages: a request from the
master and a response from the
slave.
Each message or frame containes
4 types of information:
◗ slave address (1 byte)
The slave address specifies the
destination station (see address
list):
◗ ◗ unitary rectifier-inverter cubicle,
◗ ◗ parallel rectifier-inverter cubicle,
◗ ◗ Static Switch cubicle.
If zero, the request addresses all
slaves and there is no response
message (in which case it is a
broadcast message, a function not
used in this application);
◗ function code (1 byte)
Selects a command (e.g. read or
write a bit or a word) and checks
that the response is correct.
The JBUS protocol comprises 10
functions of which 3 may be used in
this application: function 3 (read n
output or internal words), or
function 4 (read n input words), or
function 16 (write n words);
◗ information field (n bytes)
The information field contains the
parameters related to the functions:
bit address, word address, bit
value, word value, number of bits,
number of words;
◗ check word (2 bytes)
A word used to detect transmission
errors.
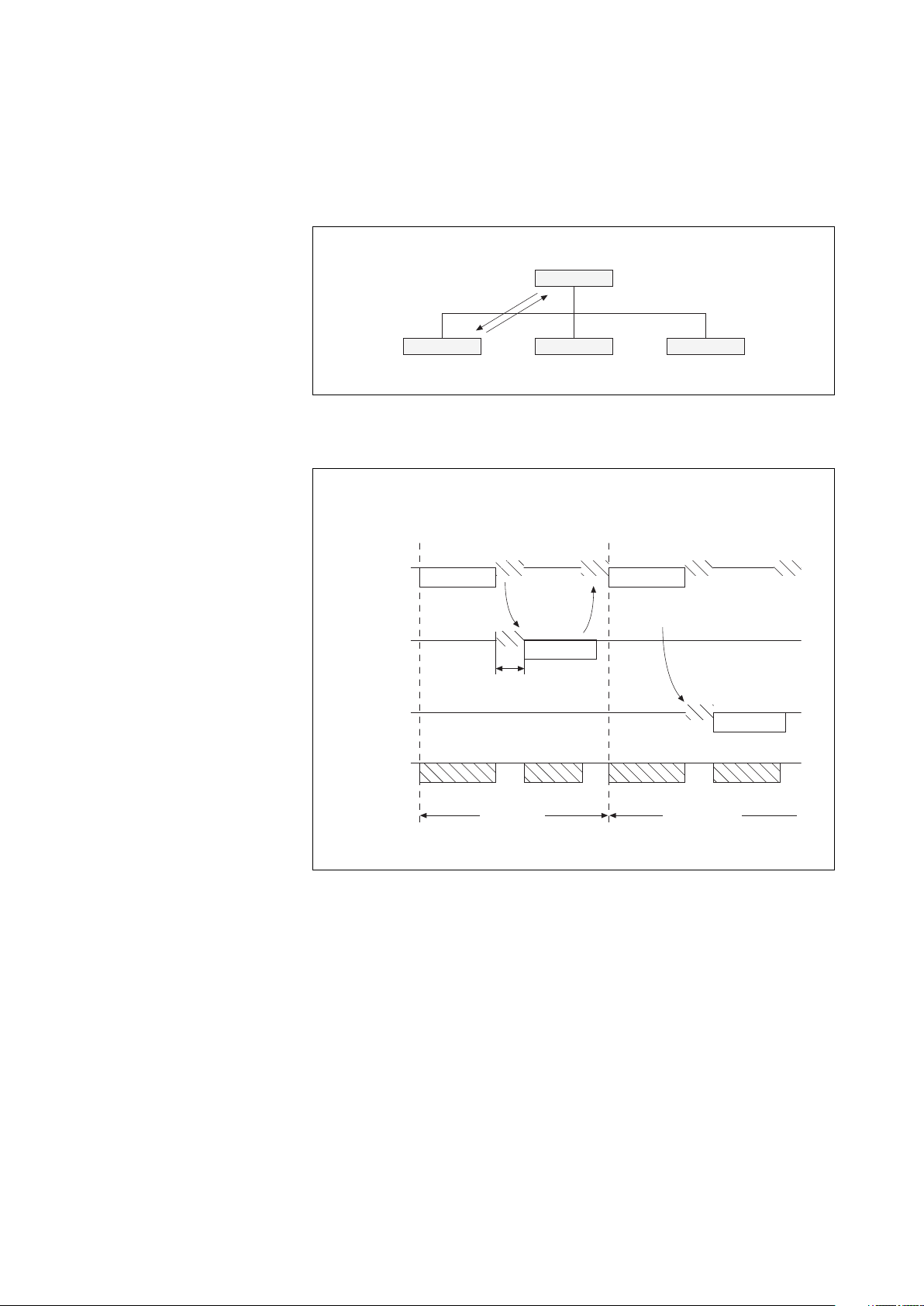
Synchronizing data
exchanges
Any character received after 3 or
more character lengths of silence is
interpreted as the start of a frame.
Therefore, a minimum silence of 3
character lengths between frames
must be respected.
Description of request and response frames
request
1 byte
slave adress
(1 à FF)
This function code selects one of
10 possible commands:
- Function 1 : read n output or internal bits
- Function 2 : read n input bits
- Function 3 : read n output or internal words
- Function 4 : read n input words
- Function 5 : write one bit
- Function 6 : write one word
- Function 8 : data exchange diagnostics
- Function 11 : read event counter
- Function 15 : write n bits
- Function 16 : write n words
response
slave adress
(1 à FF)
1 byte
function
code
function
code
information requested: bit/word address,
bit/word value, bit/word number.
information
n bytes
values of bits or words read
values of bits or words written
number of bits or words
data
check word
When the message is
received, the slave reads
the check word and accepts
or refuses the message
CRC
check word
2 bytes
1 byte1 byte
◗ bytes
2 bytes
6739389EN/FB - Page 7
Page 8
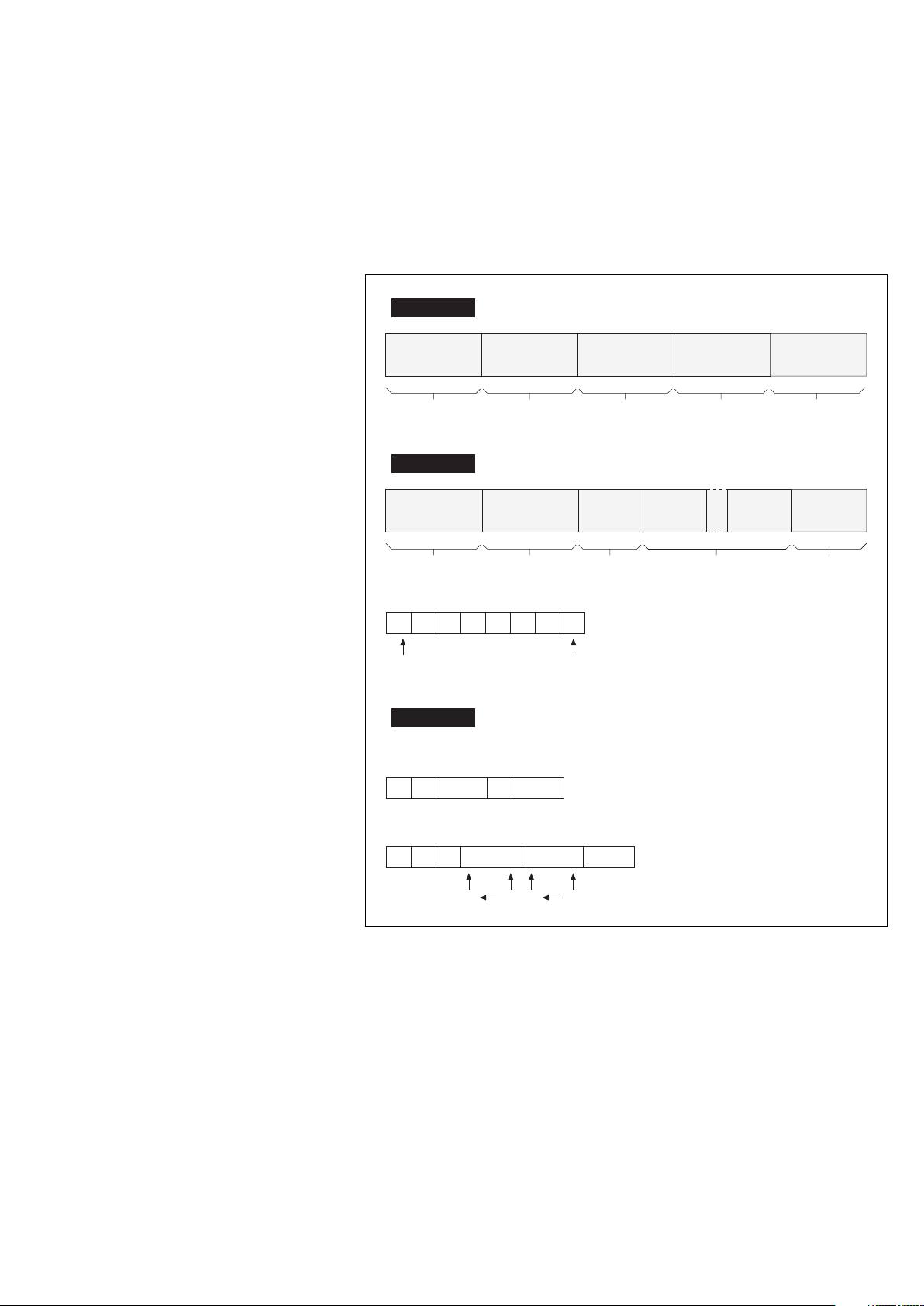
JBUS protocol (continued)
Checking received
messages on the slave
side
After the master sends a request
containing the slave address, the
function code and data, it computes
the CRC and sends it as the check
word (CRC 16).
When the slave receives the
request, it stores the message in
memory and calculates the CRC 16
to compare it to the received CRC
16.
master
slave
slave address
function
data
CRC 16
CRC 16 comparison
CRC 16
computation
If the message is incorrect (unequal
CRC 16 values), the slave does
not respond.
If the message received is correct
but the slave is unable to process it
(incorrect address, incorrect data,
etc.), the slave returns an error
message with the following
contents (see opposite):
response
function code
received and
MS bit = 1
slave
address
(1 à FF)
1 byte 1 byte 1 byte
example
01
01
1
09
00 0000 00 DD CB
H
89 H01 86 50
Error codes:
1. Unknown function code
2. Incorrect address
3. Incorrect data
4. Station not ready
8. Write error
9. Field overlap
request
response
errors handled
by the
communication
port
CRC 16
2 bytes
Page 8 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 9
Functions
Function 1 and 2: read N bits
◗ function 1: read output or internal
bits;
◗ function 4: read input bits.
The number of bits must be less
than or equal to the bit field size
(see memory board).
request
slave address 1 or 2
JBUS protocol (continued)
address of
first bit
MSB LSB
number of bits
to read
CRC 16
1 byte
response
slave address 1 or 2
1 byte
byte detail:
last bit transmitted first bit transmitted
Unused bits are set to zero
example
Reading bits at location 404 to 411 of slave at address 20H (charger signals)
request:
20 01 0404 66 FE
response:
20 01 02
1 byte 2 bytes 2 bytes 2 bytes
number of
bytes
read
1 byte 1 byte ✷ bytes 2 bytes
0E
10101001
00101110
FB B7
first
byte
read
last
byte
read
CRC 16
40440B
411
(binary values)
40C
6739389EN/FB - Page 9
Page 10

JBUS protocol (continued)
Function 3 and 4: read N words
The number of words must be less
than or equal to the word field size
(see memory board).
◗ function 3: read output or internal
words;
◗ function 4: read input words.
request
slave address
3 or 4
adress of
first bit
MSB LSB
number of
words
MSB LSB
CRC 16
Function 5: writing a bit
1 byte
response
slave address
1 byte
example
Reading words at location 146 to 14B of slave at address 28H (voltage fields)
request:
03 0146 06 A7 E0
28
response:
03 0C XXXX YYYY CRC 16
28
1 byte 2 bytes
3 or 4
1 byte 1 byte
word 0146
number of
bytes read
word 014B
2 bytes 2 bytes
first word
PF pf
2 bytes 2 bytes
last word
PF pf
2 bytes
CRC 16
Page 10 - 6739389EN/FB
request
slave address 5
1 byte 2 bytes 2 bytes1 byte 1 byte
response
slave address 5
In function 5 the response and request frames are identical.
example
Setting bit location C05 to 1 of slave at address 40H (inverter on)
request:
05 0C05 FF 0040
1 byte
bit address
bit address
90 7A
bit set to 0
bit set to 1
bit value 0 CRC 16
bit value 0 CRC 16
write 0
write FF
Page 11

Function 6: writing a word
JBUS protocol (continued)
request
slave address
1 byte 1 byte 2 bytes2 bytes 2 bytes
response
slave address
The response is echoed acknowledging that the word sent has been received.
example
Writing the value 1000 into the word location 810H of slave at address 50H
06 08 10 10 00
50
Function 8: reading error diagnosis counters
Each slave manages a set of nine
16 bit counters for error diagnosis
(see opposite):
- request / response:
slave address
6
6
8
word address
word address
8A 2E
sub-function
code
data
CRC 16word
CRC 16word
CRC 16
1 byte
- the slave must echo 00 XYZT
the request
- reset error 0A 0000
diagnosis counter
- read the total number of:
received frames with CRC error (CNT 1) 0B XXXX
received frames with CRC error (CNT 2) 0C XXXX
number of exception responses (CNT 3) 0D XXXX
frames addressed to the station (CNT 4) 0E XXXX
(not including broadcast)
broadcast requests received (CNT 5) 0F XXXX
number of NACK responses (CNT 6) 10 XXXX
unit not ready responses (CNT 7) 11 XXXX
illegal characters (CNT 8) 12 XXXX
1 byte 2 bytes 2 bytes 2 bytes
X, Y, Z, T are user
defined (transmission
parameters)
requests:
XXXX equals 0000
response:
XXXX is the counter
value
6739389EN/FB - Page 11
Page 12
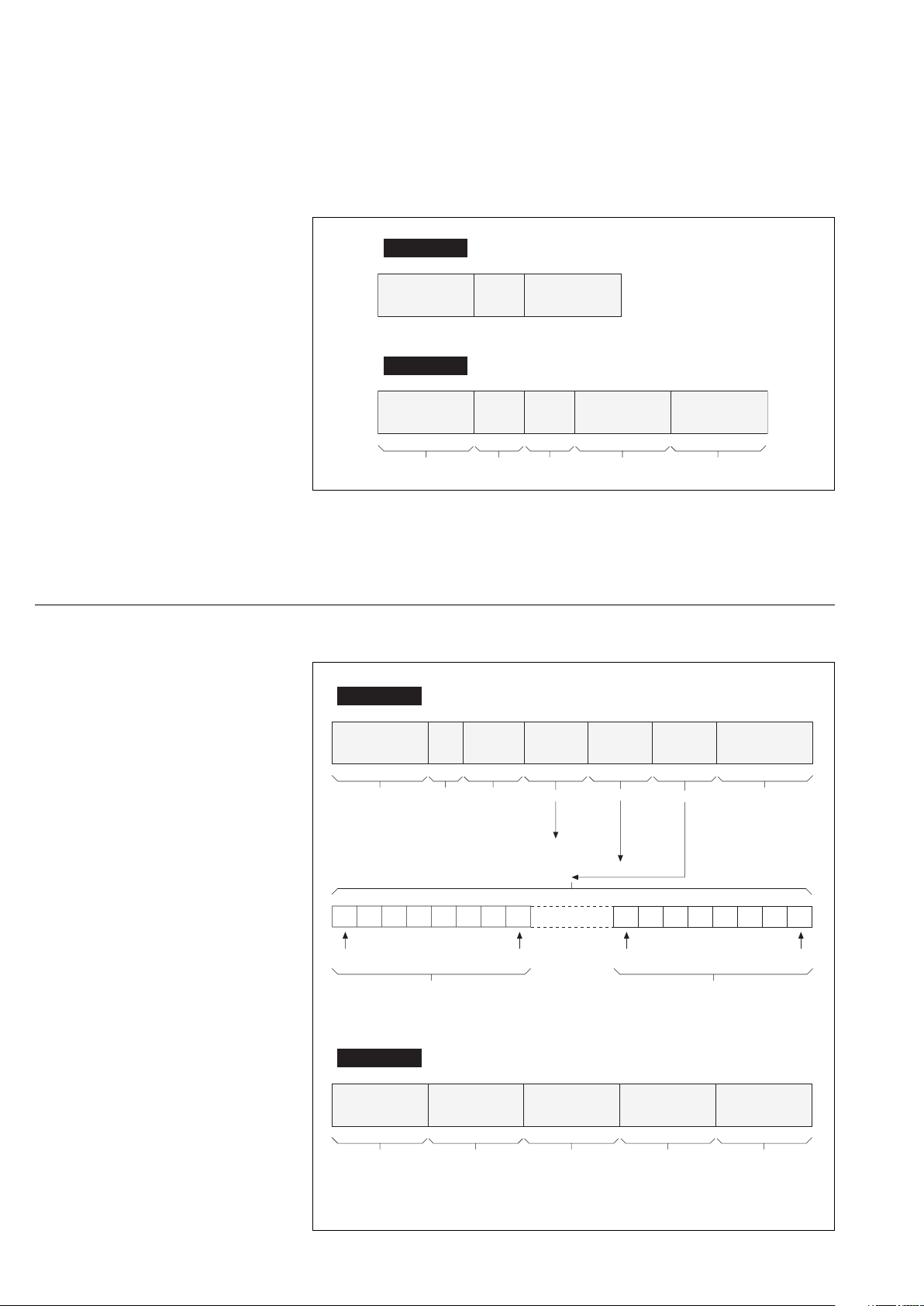
JBUS protocol (continued)
Function 11: reading event counters
The master and each slave have
one event counter.
This counter is incremented each
time a frame is received and
interpreted correctly by the slave
(except for function 11 itself).
A correctly transmitted message
increments the counter. If the slave
sends an exception response, the
counter is not incremented.
The master can read the counter to
determine whether or not the slave
correctly interpreted the command
(incremented the counter or not).
request
slave address 0B
response
slave address
1 byte
1 byte 2 bytes 2 bytes 2 bytes
CRC 16
0
slave
counter word
CRC 160B
These functions can be used to
diagnose the data exchange taking
place between master and slaves.
If the master counter equals the
slave counter, the slave executed
the command sent by the master.
Function 15: writing n consecutive bits
request
slave adress
1 byte
réponse
last bit of
first byte
0F
1 byte
first byte
address of
the first bit
2 bytes
first bit of
first byte
number
of bits
2 bytes
2 X 1968
If the master counter is one higher
than the slave counter, the slave
did not execute the command sent
by the master.
number
of bytes
1 byte n bytes 2 bytes
1 N 246
last bit of
byte N
bit data
N bytes
CRC 16
first bit of
byte N
Page 12 - 6739389EN/FB
response
slave address
1 byte
Note: if the slave address is 0, all units execute the write command without sending a
response.
0F CRC 16
address of
the first bit
number of bits
2 bytes1 byte 2 bytes 2 bytes
1 X 1968
Page 13

Function 16: writing n consecutive words
request
JBUS protocol (continued)
1 byte
LSB
first word
response
slave address
1 byte 2 bytes1 byte
1 byte
LSB LSBMSBMSBMSBMSB
10
(*)
address of
first word
2 bytes
10
(*)
number
of words
2 bytes
2 X 123
address of
first word
2 bytes
number
of bytes N
1 byte 2 bytes
4 N 246
data bytesslave address
n bytes
number of
words written
2 bytes
CRC 16
CRC 16
last word
Note: if the slave address is 0, all units execute the write command without sending a
response
example
Writing words 00 and 01 of slave at address 20 (synchronization counter)
(00) = 0000
(01) = 0000
request
10
20
response
20
(*)
0000 0002 0000 0000 0000 000004 5C 93
(*)
10
0000
(*)
0002 47 79
6739389EN/FB - Page 13
Page 14

JBUS protocol (continued)
CRC 16 algorithm
If the CRC 16 is calculated using
the above algorithm, the least
significant byte is transmitted first.
Hex FFFF --> CRC 16
CRC 16
CRC 16 shift to the right
no
no
remainder
BYTE --> CRC 16
n = 0
n = n+1
n > 7
no
following byte
yes
CRC 16
yes
end of message
poly --> CRC 16
yes
= exclusive or
n = number of data bits
poly = CRC 16 polynomial = 2
15
+ 213 + 20 = $ A001
END
Page 14 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 15

Example of CRC computation
JBUS protocol (continued)
CRC register initialization Shift 1 1111 1111 1111 1111
of 1st character 0000 0010
Set flag to 1,
Set flag to 1,
Set flag to 0 Shift 4 0011 0011 1111 1111 1
2nd character 0000 0111
polynomial 1010 0000 0000 0001
polynomial 1010 0001
Shift 1 0111 1111 1111 1110 1
Shift 2 0110 1111 1111 1111 1
Shift 3 0110 0111 1111 1111 0
Shift 5 0100 1001 1111 1111 0
Shift 6 0010 0100 1111 1111 1
Shift 7 0100 0010 0111 1111 0
Shift 8 0010 0001 0011 1111 1
Shift 1 0100 0000 1001 1101 1
Shift 2 0111 0000 0100 1110 1
Shift 3 0110 1000 0010 0111 1
Shift 4 0110 0100 0001 0011 0
Shift 5 0011 0010 0000 1001 1
Shift 6 0100 1001 0000 0100 0
Shift 7 0010 0100 1000 0010 0
Shift 8 0001 0010 0100 0001 0
1111 1111 1111 1101
1101 1111 1111 1111
1100 1111 1111 1110
101 1
1001 0011 1111 1110
101 1
1000 0100 1111 1110
101 1
1000 0001 0011 1110
1000 0001 0011 1001
101 1
1110 0000 1001 1101
101 1
1101 0000 0100 1111
101 1
1100 1000 0010 0110
101 1
1001 0010 0000 1000
byte
byte
6739389EN/FB - Page 15
Page 16

JBUS protocol (continued)
Example of CRC 16 computation in "C" using table lookup
#define CPH 0 /* most significant bytes */
#define CPL 1 /* least significant bytes */
/* TABLE OF MOST SIGNIFICANT BYTES FOR CRC16 COMPUTATION */
char tbcrch [ ] =
{
0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,
1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,
1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,
0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,
1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,
0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,
0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,
1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,
1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,
0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,
0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,
1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,
0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,
1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,
1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,
0,193,129,64,1,192,128,65,1,192,128,65,0,193,129,64,
};
/* TABLE OF LEAST SIGNIFICANT BYTES FOR CRC16 COMPUTATION */
char tbcrcl [ ] =
{
0,192,193,1,195,3,2,194,198,6,7,199,5,197,196,4,
204,12,13,205,15,207,206,14,10,202,203,11,201,9,8,200,
216,24,25,217,27,219,218,26,30,222,223,31,221,29,28,220,
20,212,213,21,215,23,22,214,210,18,19,211,17,209,208,16,
240,48,49,241,51,243,242,50,54,246,247,55,245,53,52,244,
60,252,253,61,255,63,62,254,250,58,59,251,57,249,248,56,
40,232,233,41,235,43,42,234,238,46,47,239,45,237,236,44,
228,36,37,229,39,231,230,38,34,226,227,35,225,33,32,224,
160,96,97,161,99,163,162,98,102,166,167,103,165,101,100,164,
108,172,173,109,175,111,110,174,170,106,107,171,105,169,168,104,
120,184,185,121,187,123,122,186,190,126,127,191,125,189,188,124,
180,116,117,181,119,183,182,118,114,178,179,115,177,113,112,176,
80,144,145,81,147,83,82,146,150,86,87,151,85,149,148,84,
156,92,93,157,95,159,158,94,90,154,155,91,153,89,88,152,
136,72,73,137,75,139,138,74,78,142,143,79,141,77,76,140,
68,132,133,69,135,71,70,134,130,66,67,131,65,129,128,64,
};
Page 16 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 17

JBUS protocol (continued)
/***************************************************************************************************** */
/* FUNCTION CALL: crc = crc16 (message, length); */
/* with char *message; message = address of message */
/* */
/* int length; length of received message (including CRC) */
/* expressed in number of bytes */
/* int crc; = CRC16 calculated from the "address", "code" and */
/* "information" fields. */
/* */
/* RETURN VALUE: calculated crc 16 (int crc) */
/******************************************************************************************************/
int crc16 (message, length)
unsigned char message [ ]; /* buffer containing message */
/* for which the crc16 is to be calculated. */
int length; /* length of message to be checked */
/* (including crc16) */
{ /* beginning of the function */
int i ; /* loop variable */
int j ; /* calculation and displacement variable */
union { /* calculated crc16: */
int ival ; /* - whole */
unsigned char cval [ 2 ]; /* - table of 2 characters */
/* unsigned is important since otherwise the sign */
/* extension causes negative displacements with */
/* respect to the beginning of the table */
} crcal;
/*$ initialization of calculated crc */
crcal.ival = 0XFFFF;
i = 0;
/*$ correction of the length to be checked: remove the */
/*$ received crc16 from the length to be checked */
length = length - 2;
/*$ WHILE there are bytes to be checked DO */
while ( i < length )
{
/*$ calculate the table index */
j = (int) ( message [ i ] ^ crcal.cval [ CPH ] );
/*$ most significant byte */
crcal.cval [ CPH ] = tbcrch [ j ] ^ crcal.cval [ CPL ];
/*$ least significant byte */
crcal.cval [ CPL ] = tbcrcl [ j ];
/*$ next byte */
i++;
}; /*$ END WHILE there are bytes to be checked */
/*$ return the calculated crc */
return ( crcal.ival );
} /* end of function */
Note: if the CRC16 is computed
using table lookup, the most
significant byte is transmitted first.
6739389EN/FB - Page 17
Page 18

UPS theory of operation
Unitary UPS
The unitary MGE
TM
GalaxyTM 6000
UPSs are made up of five modular
sub-assemblies:
Mains 1 power up
◗ the inverter receives power from
the rectifier-charger and supplies
power to the load. There is no
direct connection between Mains
and load;
◗ the battery is charged or the
charge maintained.
Mains 1 power down
◗ the inverter receives power from
the battery and supplies power to
the load;
◗ the battery discharges.
◗ rectifier-charger;
◗ battery;
◗ three-phase inverter;
◗ static switch;
◗ maintenance bypass.
Mains 2
Mains 1
Mains 2
Mains 1
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
The load and Mains 2 operate at 50
or 60 Hz.
static by-pass switch
inverter
load
battery
static by-pass switch
inverter
load
Major overload
◗ Mains 2 supplies power to the
load via the static switch;
◗ the inverter is shut down;
◗ the inverter starts-up
automatically as soon as overload
is removed;
◗ power is transferred without
affecting the load.
Maintenance
◗ Mains 2 supplies power to the
load via the maintenance bypass;
◗ the rectifier-charger and inverter
are shut down and disconnected
from all sources of power.
Mains 2
Mains 1
Mains 2
Mains 1
Q1
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
battery
static by-pass switch
inverter
battery
static by-pass switch
Q4S
inverter
QF1
battery
Q3BP
Q5N
load
load
Page 18 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 19

UPS theory of operation (continued)
Parallel connected UPS with "Static Switch"
Up to six parallel connected
rectifier-inverter cubicles can be
combined with one "Static Switch"
cubicle to form a system that
operates like a unitary UPS system.
Each parallel connected rectifierinverter cubicle houses a:
◗ rectifier-charger;
◗ battery;
◗ three-phase inverter.
The "Static Switch" cubicle
contains:
◗ static by-pass switch;
◗ maintenance bypass.
The units have separate batteries:
Mains 2
rectifiercharger
Mains 1
rectifiercharger
Mains 1
UPS without Mains 2
All UPSs without Mains 2 contain
the same sub-assemblies:
◗ rectifier-charger;
◗ battery (option);
◗ three-phase inverter.
They may or may not be parallel
connected depending on type and
may or may not contain a battery.
The output voltage has a frequency
of 50 or 60 Hz.
cubicle
static by-pass switch
inverter
battery
inverter
load
battery
Operation without battery
Mains 1 power up:
◗ the inverter receives power from
the rectifier-charger and supplies
power to the load. There is no
direct connection between Mains 1
and the load.
Mains 1 power down:
◗ no power to the load.
Maintenance position
(disconnected):
◗ no power to the load (except in
parallel connected systems, where
other units supply power).
Mains 1
Mains 1
Mains 1
Q1
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
inverter
load
inverter
load
inverter
Q5N
load
6739389EN/FB - Page 19
Page 20

UPS theory of operation (continued)
Operation with battery
Mains 1 power up:
◗ the inverter receives power from
the rectifier-charger and supplies
power to the load. There is no
direct connection between Mains 1
and the load.
Mains 1 power down:
◗ the inverter runs on battery power
and supplies power to the load;
◗ the battery discharges.
Maintenance position
Mains 1
Mains 1
rectifiercharger
rectifiercharger
inverter
load
battery
inverter
load
battery
(disconnected):
◗ no power to the load (except in
parallel connected systems, where
other units supply power).
Mains 1
Q1
rectifiercharger
inverter
Q5N
load
QF1
battery
Page 20 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 21

This chapter presents the specific
operating aspects and system data
provided by the "GTCZ" and
"GT2Z" boards in unitary UPSs.
For more detailed information,
please refer to the "system
information" section.
Block diagram
Mains 2
Q4S
a
Unitary UPS
Q3BP
static by-pass switch
Measured quantities
Mains 1
Q1
rectifiercharger
inverter
K3N
b e c d
QF1
battery
F Mains 2 <1A2> U Mains 2 <149 to 14E>
a
b
F Mains 1 <1A0> U Mains 1 <140 to 142>
I Mains 2 <109 to 10B>
I Mains 1 <100 to 102>
c
F inverter <1A1> U inverter <143 to 148>
I inverter <106 to 108>
d
F load <1A3> U load <14F to 154>
Apparent and active
power <180 to 187>
I load <10C to 10E>
e
I battery or I dc <115 or 1C1> U battery or U dc <155 or 1C0>
Battery backup time <1C2> Battery temperature <1C3>
Q5N
load
The numbers enclosed by <> are the addresses in the data array.
6739389EN/FB - Page 21
Page 22

Unitary UPS (continued)
Main status bits (UPS operating information)
Operating modes
The following section describes the
different states of a
TM
MGE
the addresses of the bits in the
system data array.
Normal operation
GalaxyTM 6000 UPS and
Normal : inverter powers load and full backup bit 4C4 = 1
time available
Danger : inverter does not power load bit 4C6 = 1
Downgraded : malfunction or environment fault bit 4C5 = 1
Load on battery : fonctionnement en autonomie bit 4C7 = 1
Normal: bit 4C4 = 1
Danger: bit 4C6 = 0
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = malfunction dependent
Load on battery: bit 4C7 = 0
Q1 closed: bit 40E = 1
Rectifier/charger on: bit 408 = 1
QF1 closed: bit 400 = 1
Inverter connected: bit 484 = 1
Q5N closed: bit 498 = 1
Q3BP open: bit 497 = 0
Q4S closed: bit 496 = 1
SS open: bit 499 = 0
K2S open (if available): bit 494 = 0
Load on battery
Normal: bit 4C4 = 1
Danger: bit 4C6 = 0
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = malfunction dependent
Load on battery: bit 4C7 = 1
Q1 indifferent: bit 40E = X (N/A)
Rectifier/charger off: bit 408 = 0
QF1 closed: bit 400 = 1
Inverter connected: bit 484 = 1
Q5N closed: bit 498 = 1
Q3BP open: bit 497 = 0
Q4S closed: bit 496 = 1
SS open: bit 499 = 0
K2S open (if available): bit 494 = 0
Page 22 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 23

Unitary UPS (continued)
Load on Mains 2
Load on bypass
Normal: bit 4C4 = 0
Danger: bit 4C6 = 1
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = X (N/A)
Load on battery: bit 4C7 = X (N/A)
Q1 indifferent: bit 40E = X (N/A)
Rectifier/charger indifferent: bit 408 = X (N/A)
QF1 indifferent: bit 400 = X (N/A)
Inverter disconnected: bit 484 = 0
Q5N closed: bit 498 = 1
Q3BP open: bit 497 = 0
Q4S closed: bit 496 = 1
SS closed: bit 499 = 1
K2S closed (if available): bit 494 = 1
Normal: bit 4C4 = 0
Danger: bit 4C6 = 1
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = X (N/A)
Load on battery: bit 4C7 = X (N/A)
Q1 indifferent: bit 40E = X (N/A)
Rectifier/charger indifferent: bit 408 = X (N/A)
QF1 indifferent: bit 400 = X (N/A)
Inverter connected indifferent: bit 484 = X (N/A)
Q5N open: bit 498 = 0
Q3BP closed: bit 497 = 1
Q4S indifferent: bit 496 = X (N/A)
SS indifferent: bit 499 = X (N/A)
K2S indifferent: bit 494 = X (N/A)
6739389EN/FB - Page 23
Page 24

Parallel connected UPS
This chapter presents the specific
operating aspects and system data
provided by the "GTCZ" and
"GT2Z" boards in parallel
connected UPSs.
For more detailed information,
please refer to the "system
information" section.
Block diagram
Measured quantities
Mains 1
Q1
rectifiercharger
inverter
K3N
b e c d
QF1
battery
F Mains 1 <1A0> U Mains 1 <140 to 142>
b
F inverter <1A1> U inverter <143 to 148>
c
F load <1A3> U load <14F to 154>
d
Apparent and active
power <180 to 187>
I battery or I dc <115 or 1C1> U battery or U dc <155 or 1C0>
e
Battery backup time <1C2> Battery temperature <1C3>
I Mains 1 <100 to 102>
I inverter <106 to 108>
I load <10C to 10E>
Q5N
load
Page 24 - 6739389EN/FB
The numbers enclosed by <> are the addresses in the data array.
Page 25

Parallel connected UPS (continued)
Main status bits of system operations
Operating modes
The following section describes the
different states of a
TM
MGE
the addresses of the bits in the
system data array.
Normal operation
GalaxyTM 6000 UPS and
Normal : inverter powers load and maximum bit 4C4 = 1
backup time available
Danger : inverter does not power load bit 4C6 = 1
Downgraded : malfunction or environment fault bit 4C5 = 1
Load on battery : load on battery power bit 4C7 = 1
Normal: bit 4C4 = 1
Danger: bit 4C6 = 0
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = malfunction dependent
Load on battery: bit 4C7 = 0
Q1 closed: bit 40E = 1
Rectifier/charger on: bit 408 = 1
QF1 closed: bit 400 = 1
Inverter connected: bit 484 = 1
Q5N closed: bit 498 = 1
Load on battery
Disconnected
Normal: bit 4C4 = 1
Danger: bit 4C6 = 0
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = malfunction dependent
Load on battery: bit 4C7 = 1
Q1 indifferent: bit 40E = X (N/A)
Rectifier/charger off: bit 408 = 0
QF1 closed: bit 400 = 1
Inverter connected: bit 484 = 1
Q5N closed: bit 498 = 1
Normal: bit 4C4 = 0
Danger: bit 4C6 = 1
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = X (N/A)
Load on battery: bit 4C7 = X (N/A)
Q1 indifferent: bit 40E = X (N/A)
Rectifier/charger indifferent: bit 408 = X (N/A)
QF1 indifferent: bit 400 = X (N/A)
Inverter not connected: bit 484 = X (N/A)
Q5N open: bit 498 = 0
6739389EN/FB - Page 25
Page 26

Static Switch cubicle
This chapter presents the specific
operating aspects and system data
provided by the "GTCZ" and
"GT2Z" boards for
TM
MGE
Switch" cubicles.
For more detailed information,
please refer to the "system
information" section.
Block diagram
GalaxyTM 6000 "Static
Mains 2
Q4S
Q3BP
static by-pass switch (SS and K2S*)
a
Measured quantities
inverter 1
inverter 2
inverter n
* : K2S is the contactor that is parallel-mounted with the static switch on devices with an output
greater than 800 kVA.
F Mains 2 <1A2> U Mains 2 <149 to 14E>
a
b
F load <1A3> U load <14F to 154>
Apparent and
active power <180 to 187>
The numbers enclosed by <> are the addresses in the data array.
I Mains 2 <109 to 10B>
I load <10C to 10E>
b
Q5N
load
Page 26 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 27

Main indicators of system operations
Normal : charge alimentée par l'onduleur bit 4C4 = 1
Danger : charge non alimentée par l'onduleur bit 4C6 = 1
Downgraded : anomalie de fonctionnement bit 4C5 = 1
Operating modes
The following section describes the
different states of a Static Switch
cubicle and the addresses of the
bits in the system data array.
Static Switch (continued)
ou défaut d'environnement
Normal operation
Load on Mains 2
Load on bypass
Normal: bit 4C4 = 1
Danger: bit 4C6 = 0
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = malfunction dependent
Q5N closed: bit 498 = 1
Q3BP open: bit 497 = 0
Q4S closed: bit 496 = 1
SS open: bit 499 = 0
K2S open (if available): bit 494 = 0
Inverters connected to load: bit 4AE = 1
Normal: bit 4C4 = 0
Danger: bit 4C6 = 1
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = X (N/A)
Q5N closed: bit 498 = 1
Q3BP open: bit 497 = 0
Q4S closed: bit 496 = 1
SS closed (if K2S not available): bit 499 = 1
K2S closed (if available): bit 494 = 1
Inverters not connected to load: bit 4AE = 0
Normal: bit 4C4 = 0
Danger: bit 4C6 = 1
Downgraded: bit 4C5 = X (N/A)
Q5N open: bit 498 = 0
Q3BP closed: bit 497 = 1
Q4S indifferent: bit 496 = X (N/A)
CS indifférent: bit 499 = X (N/A)
SS indifferent: bit 494 = X (N/A)
Inverter connected indifferent: bit 4AE = X (N/A)
6739389EN/FB - Page 27
Page 28

System information
Message format
This section describes the
messages exchanged between the
"GTC link" communication interface
Data rate 1200 Baud 2400 Baud 4800 Baud 9600 Baud
status information only 0,5 s 0,25 s 0,12 s 0,06 s
all measurements 2 s 1 s 0,5 s 0,25 s
and the external computer based
on the JBUS protocol.
The length of time after which a
message must be interpreted as
"not understood" depends on the
type of command sent.
Response time of event (independent of data rate)
- inverter start-up and connect : 30 s
- rectifier-charger startup : 30 s
- rectifier-charger or inverter stop : 30 s
The table opposite lists maximum
response times:
Example of read data array commands sent by the terminal
(address: 20H)
For the "responses", refer to the
"JBUS protocol" section function 1
and 3.
request station function data length CRC 16
code address
read voltage 20 03 0140 0015 82 9C
array
(21 values)
read current 20 03 0100 000F 28 03
array
(15 values)
read global 20 01 04C0 000B 7A 70
state bits
(11 bits)
Sample commands
List of variable fields
(same for all cubicle types)
The binary data and binary
commands can be accessed bit or
word-wise.
The word address and position of
the bit in the word can be
determined from the bit address:
◗ hundreds and tens digit of bit
address = word address;
◗ least significant digit of bit
address = bit position.
command station function bit data not CRC 16
code address used
charger on 20 05 0C00 FF 00 89 DB
charger off 20 05 0C01 FF 00 D8 1B
inverter on 20 05 0C04 FF 00 C8 1A
inverter off 20 05 0C05 FF 00 99 DA
JBUS fields address in hexadecimal access
start end
signaling 0 5 read / write
signaling 6 F read
binary data 40 BF read
commands C0 DF read / write
counters E0 FF read
currents 100 13 read
voltages 140 17 read
powers 180 19F read
frequencies 1A0 1BF read
battery 1C0 1DF read
adjustments 200 2FF read
maintenance 300 3FF read
Page 28 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 29

General definitions
Signaling field
(same for all cubicle types)
System information (continued)
object 0 1
switch open closed
unit off on
fault no fault fault
control device not activated activated
signaling units data JBUS address
hex. word
synchronisation counter 0
(MSB)
synchronisation counter ms 0 4294967295 1
(LSB)
binary times N/A 2
binary times N/A 3
binary times N/A 4
binary times N/A 5
manufacturer's ID without 1 MSB 6
model ID (MSB) without 102 LSB 6
model ID (LSB) without 54380 7
configuration 1 without N/A MSB 8
inverter type, LSB 8
same as 200
configuration 2 without hardware version MSB 9
software version LSB 9
not used A
not used B
state of equipment without same as 4E C
state of processing without same as 4C D
not used E
not used F
Tables of measured data
Current fields
Legend:
◗ yes: available in this cubicle;
◗ bat: available in this cubicle if
battery installed;
◗ no entry: not available.
measured current units JBUS address type
hex. word unitary parallel Static Switch
I1 (I phase 1) Mains 1 A 100 yes yes
I2 (I phase 2) Mains 1 A 101 yes yes
I3 (I phase 3) Mains 1 A 102 yes yes
I1 (I phase 1) inverter A 106 yes yes
I2 (I phase 2) inverter A 107 yes yes
I3 (I phase 3) inverter A 108 yes yes
I1 (I phase 1) Mains 2 A 109 yes yes
I2 (I phase 2) Mains 2 A 10A yes yes
I3 (I phase 3) Mains 2 A 10B yes yes
I1 (I phase 1) load A 10C yes yes yes
I2 (I phase 2) load A 10D yes yes yes
I3 (I phase 3) load A 10E yes yes yes
I battery A 115 bat bat
% load - 120 yes yes yes
% peak load (Ph1) - 121 yes yes yes
% peak load (Ph2) - 122 yes yes yes
% peak load (Ph3) - 123 yes yes yes
6739389EN/FB - Page 29
Page 30

System information (continued)
Voltage fields
Legend:
◗ yes: available in this cubicle;
◗ no entry: not available.
measured voltage units JBUS address type
hex. word unitary parallel SS
U12 Mains 1 V 140 yes yes
U23 Mains 1 V 141 yes yes
U31 Mains 1 V 142 yes yes
U1N inverter V 143 yes yes
U2N inverter V 144 yes yes
U3N inverter V 145 yes yes
U12 inverter V 146 yes yes
U23 inverter V 147 yes yes
U31 inverter V 148 yes yes
U1N Mains 2 V 149 yes yes
U2N Mains 2 V 14A yes yes
U3N Mains 2 V 14B yes yes
U12 Mains 2 V 14C yes yes
U23 Mains 2 V 14D yes yes
U31 Mains 2 V 14E yes yes
U1N load V 14F yes yes yes
U2N load V 150 yes yes yes
U3N load V 151 yes yes yes
U12 load V 152 yes yes yes
U23 load V 153 yes yes yes
U31 load V 154 yes yes yes
U battery V 155 yes yes
Power fields
Frequency fields
Legend:
◗ yes: available in this cubicle;
◗ no entry: not available.
power measurements units JBUS address type
hex. word unitary parallel SS
P1 (load active power) kW 180 yes yes yes
P2 (load active power) kW 181 yes yes yes
P3 (load active power) kW 182 yes yes yes
S1 (load apparent power) kVA 183 yes yes yes
S2 (load apparent power) kVA 184 yes yes yes
S3 (load apparent power) kVA 185 yes yes yes
P (load active power) kW 186 yes yes yes
S1 (load apparent power) kVA 187 yes yes yes
% inverter load - 188 yes yes yes
power factor - 189 yes yes yes
frequencies units JBUS address type
measurements hex. word unitary parallel SS
F Mains 1 dHz 1A0 yes yes
F inverter dHz 1A1 yes yes
FMains 2 dHz 1A2 yes yes
F load dHz 1A3 yes yes yes
Page 30 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 31

System information (continued)
Battery and adjustments
fields
Legend:
◗ no entry: not available;
◗ yes: available in this cubicle;
◗ bat: available in this cubicle if
battery installed;
◗ bat/opt: available if option
installed.
Inverter type:
◗ 0: unitary;
◗ 1: parallel without static switch;
◗ 2: parallel with static switch;
◗ 3: Static Switch cubicle.
Battery installed:
◗ 0 = no;
◗ 1 = yes.
Sensor installed:
◗ 0 = no;
◗ 1 = yes.
battery measurements units JBUS address type
hex. word unitary parallel SS
U battery V 1C0 yes yes
I battery A 1C1 bat bat
battery backup time mn 1C2 bat/opt bat/opt
battery room temperature °C 1C3 bat/opt bat/opt
battery adjustments units JBUS address type
hex. word unitary parallel SS
inverter type - 200 yes yes yes
battery installed - 201 yes yes
battery temperat. sensor - 202 yes yes
In (I rated load) A 208 yes yes yes
Pn (P rated load) kW 209 yes yes yes
Tables of binary data
Rectifier-charger
Legend:
◗ no entry: not available;
◗ yes: available in this cubicle;
◗ bat: available in this cubicle if
battery installed.
rectifier-charger bit meaning JBUS type
information address
hex.
bit=0 bit=1 bit word unit. para. SS
B_Etat_QF1 open closed 400 40 bat bat
B_Etat_Dech_Bat not discharging discharging 401 bat bat
B_Etat_Ubat_Min not reached min. volt. fault 402 bat bat
B_Etat_Ubat_Aut not reached warning 403 bat bat
B_Etat_Tempe_Ht normal outside toleran. 404 bat bat
B_Etat_Res1_Ht not reached outside toleran. 405 bat bat
B_Etat_Vent_Bat no fault fault 406 yes yes
B_Etat_Cha_Bat not charging charging 407 bat bat
B_Etat_Pont off on 408 bat bat
B_Etat_Def_Maj_Cha no fault fault 409 yes yes
B_Etat_Q1 open closed 40E yes yes
B_Etat_Arr_Urg not activated activated 411 41 yes yes
B_Etat_U_Res1 normal outside toleran. 412 yes yes
B_Etat_F_Res1 normal outside toleran. 413 yes yes
B_Etat_Arr_Prog not activated activated 417 bat bat
B_Etat_Lim_Groupe not activated activated 419 bat bat
B_Etat_IBat_Aux not activated activated 41A bat bat
B_Etat_Egal_Bat not active active 41B bat bat
B_Etat_Groupe not activated activated 41E yes yes
6739389EN/FB - Page 31
Page 32

System information (continued)
Inverter
Legend:
◗ no entry: not available;
◗ yes: available in this cubicle.
Connectivity
Legend:
◗ no entry: not available;
◗ yes: available in this cubicle;
◗ >800k: on static switch cubicles
higher than 800 kVA.
inverter bit meaning JBUS type
information address
hex.
bit=0 bit=1 bit word unit. para. SS
B_Etat_Su_Mut no overload overload 440 44 yes yes
B_Etat_Def_Maj_Ond no fault fault 441 yes yes
B_Etat_Lim_Ond no limitation limitation 445 yes yes
B_Etat_Suth_Mut no overload overload 446 yes yes
B_Etat_Aux_Libre not activated activated 44C yes yes
B_Etat_Arr_Urg not activated activated 44D yes yes
B_Etat_Arr_Forc_Cext not activated activated 454 46 yes yes
B_Etat_Inv_Fréq not activated activated 465 yes yes
B_Etat_Arr_Prot_Cext not activated activated 467 yes yes
connectivity bit meaning JBUS type
information address
hex.
bit=0 bit=1 bit word unit. par. SS
B_Etat_Su_Ond no overload overload 480 48 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Vent no fault ventilation fault 482 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Ond_Coup not connected connected 484 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Arr_Inter enable disable 485 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Cde_Pilote not synchro. synchro. 486 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Def_Coup no fault fault 487 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Res2_Ht normal outside toleran. 48A yes yes
B_Etat_Arr_Urg not activated activated 48D yes yes yes
B_Etat_K2S open closed 494 49 >800k
B_Etat_Q4S open closed 496 yes yes
B_Etat_Q3BP open closed 497 yes yes
B_Etat_Q5N open closed 498 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Cde_Cs_Res2 open closed 499 yes yes
B_Etat_F_Res2 normal outside toleran. 49C yes yes
B_Etat_U_Res2 normal outside toleran.49D yes yes
B_Etat_Freq_Auto not activated activated 49F yes yes
B_Etat_Su_Res2 no overload overload 4A0 4A yes yes
B_Etat_Suth_Res2 no overload overload 4A1 yes yes
B_Etat_Suth_Ond no overload overload 4A2 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Arm_Aux no fault fault 4A3 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Sans_Trou not activated activated 4A4 yes yes
B_Etat_Ver_Sec not activated activated 4A5 yes yes
B_Etat_Nb_Ond_Suff insufficient sufficient 4AF yes
Page 32 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 33

System information (continued)
Global information
Legend:
◗ no entry: not available;
◗ yes: available in this cubicle;
Table of control
devices
Legend:
◗ no entry: not available;
◗ yes: available in this cubicle.
global bit meaning JBUS type
information address
hex.
bit=0 bit=1 bit word unit. par. SS
B_Etat_Arr_Acq no fault fault 4C0 4C yes yes yes
B_Etat_Cde_Batt_Fin no fault backup time 4C1 yes yes
end
B_Etat_Fin_Vie_Batt no fault battery 4C2 yes yes
obsolete
B_Etat_Cde_Sys_Nor no fault normal 4C4 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Cde_Sys_Deg not downgraded downgraded 4C5 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Cde_Sys_Dan safe unsafe 4C6 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Cde_Bat_Deg not on batteries on batteries 4C7 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Arr_Urg not activated activated 4C8 yes yes yes
B_Etat_CS_K2S open closed 4C9 yes yes yes
B_Etat_Coup_ASI disconnected connected 4CA yes yes yes
B_Etat_Vent_US no fault fault 4DD yes yes yes
B_Num_Test_Com no error error 4E9 4E yes yes yes
B_Reg_Autres not configurated configurated 4EA yes yes yes
B_Reg_Voie not configurated configurated 4EB yes yes yes
B_Mes_Invalides valid invalid 4EC yes yes yes
B_Etat_Modifié no change change 4EF yes yes yes
commands bit meaning JBUS type
address
hex.
bit=0 bit=1 bit word unit. par. SS
B_Ope_Mar_Cha not activated activated C00 C0 yes yes
B_Ope_Arr_Cha not activated activated C01 yes yes
B_Ope_Arr_Ond not activated activated C04 yes yes
B_Ope_Mar_Ond not activated activated C05 yes yes
Telemonitoring
information
Legend:
◗ no entry: not available;
◗ yes: available in this cubicle.
information bit meaning JBUS address type
hexadecimal
bit=0 bit=1 bit word unit. par. SS
reason for call no transition transition
(high transitions) structure
reason for call no transition transition (same 51 yes yes yes
(low transitions) structure
main number valid invalid 520 52 yes yes yes
invalid
secondary number valid invalid 528 yes yes yes
invalid
(same 50 yes yes yes
as word 4C)
as word 4C)
6739389EN/FB - Page 33
Page 34

System information (continued)
Glossary of information
descriptors
(data words at address 40 to 4E)
Every bit is listed according to the
following format:
bit address: description
(bit = 0 / bit = 1).
Word address: 40
400: battery circuit breaker
(0=open/1=closed)
Battery protection circuit breaker
"QF1" is located near the battery
and is "on" (closed) during normal
operation. When it either trips or is
turned "off" (open) the load is no
longer protected since battery
power is no longer available if
Mains 1 fails.
401: battery discharging (0=not
discharging/1=discharging)
The inverter powers the load.
Mains 1 is either not available or
outside tolerances and the inverter
is battery powered.
402: minimum battery voltage
(0=not reached/1=min. volt. fault)
A fault indicates that the minimum
battery voltage has been reached
during Load on battery and the
inverters it supplies are stopped. If
Mains 2 is not available, which is
generally the case, the load not
longer receives power.
403: low battery shutdown
warning (0=not reached/
1=warning)
The warning indicates that the end
of backup time is imminent. It is
only applicable when the inverters
operate on battery power.
404: battery temperature
(0=normal/1=outside tolerances)
This information only exists if the
system is equipped with the
"Temperature Monitor" option. It
tells the user that the temperature
of the battery is outside the
allowable range. The rectifiercharger circuit is switched so that
the battery charging current
becomes zero. The battery is no
longer being recharged (battery
protection).
405 : Mains 1 voltage (0=normal/
1=outside tolerances)
Indicates that the Mains 1 power
supply voltage is outside tolerances
and the inverter on battery power.
406 : battery room ventilation
(0=no fault/1=fault)
Informs the user of a battery room
ventilation fault. The rectifiercharger circuit is switched so that
the battery charging current
becomes zero. The battery is no
longer being recharged. It prevents
vented led-acid batteries from
giving off hydrogen gas The user
must remedy the ventilation
problem.
407: battery charging (0=not
charging/1=charging)
Informs the user whether the
battery is currently being recharged
(only valid for vented lead-acid
batteries).
408: rectifier-charger status
(0=off/1=on)
Gives the status of the rectifiercharger circuit. It stops every time
Mains 1 power fails. In this case the
load is battery powered via the
inverter.
409: major rectifier-charger fault
(0=no fault/1=fault)
Informs the user of a major rectifiercharger fault requiring after-sales
servicing.
40E: Mains 1 input switch
(0=open/1=closed)
"Q1" Mains 1 input switch which
powers the rectifier-charger.
Normally the switch is closed or
"on". The switch can be opened to
disconnect the unit from Mains 1 for
servicing.
Word address: 41
411: emergency off switch (0=not
activated/1=activated)
Normally-closed switch connected
to the units. When activated, the
rectifier-charger circuits and the
inverters stop operating. The "QF1"
battery circuit breaker is also
opened.
If the "emergency off" also tripped
the protection devices to
disconnect the units from Mains 1
and Mains 2, the load no longer
receives power and the units are
completely disconnected.
412: rectifier-charger input
voltage (0=normal/1=outside
tolerances)
The rectifier-charger stops
operating when the Mains 1 phaseto-phase voltage is outside
tolerances.
413: rectifier-charger input
frequency (0=normal/1=outside
tolerances)
The rectifier-charger stops
operating when the Mains 1
frequency is outside tolerances.
417: gradual rectifier-charger
shutdown (0=not activated/
1=activated)
Indicates that the rectifier-charger
received an external command to
gradually stop operating (e.g.
gradual load-shedding when using
power from engine generator sets).
419: engine generator set current
limiting (0=not activated/
1=activated)
Informs the user that the rectifiercharger has received an external
command to limit the current drawn
from Mains 1. The additional power
required by the inverter is supplied
by the battery (which discharges).
Example: operating from a
generator that delivers insufficient
power.
41A: battery current limiting
(0=not activated/1=activated)
The rectifier-charger received an
external command to limit the
current that charges the battery.
Normal battery charging is resumed
when Mains 1 returns.
Example: operating from a
generator that delivers insufficient
power to supply load and charge
batteries.
Note: the current limit is
programmable.
Page 34 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 35

System information (continued)
41B: battery equalization (0=not
active/1=active)
The rectifier-charger has been
manually switched to equalization
mode, to equalize battery cell
voltages. This action stops all
inverters powered by the battery (if
they were not already stopped).
41E: operation on enginegenerator set (0=not activated /
1=activated)
Indicates that the rectifier-charger
is supplied by an engine-generator
set and not by the normal Mains 1
power supply.
Word address: 44
440: inverter stack overload
(0=no/1=overload)
Indicates an overload condition due
to a load power factor exceeding 0.9.
441: major inverter fault (0=no/
1=fault)
Informs the user of an inverter fault
requiring after-sales servicing.
445: inverter output current
limiting (0=no/1=active)
Informs the user that an overload
exceeding 1.6 In has occurred at
the output: the inverter stops
operating.
446: inverter thermal overload
(0=no/1=overload)
Informs the user that the output is
overloaded by a factor between 1
and 1.6 In: the inverter stops
operating.
44C: outside contact (0=not
activated/1=activated)
Normally open switch. Initiates the
actions that have been configured
using the after-sales "Soft Tunor"
computer software. Possible
actions when activated:
◗ no action;
◗ inverter off;
◗ forced inverter shutdown;
◗ conditional inverter shutdown;
◗ frequency change (when
powering on the unit) with respect
to the frequency configured by the
after-sales "Soft Tunor" computer
software (i.e. 50Hz to 60Hz or vice
versa).
44D: emergency off switch
(0=not activated/1=activated)
Normally-closed switch connected
to the units. When activated, the
rectifier-charger circuits and the
inverters stop operating. The "QF1"
battery circuit breaker is also
opened. If the "emergency off" also
trips the protection devices to
disconnect the units from Mains 1
and Mains 2, the load no longer
receives power and the units are
completely disconnected.
Word address: 46
464: forced inverter shutdown
(0=not activated / 1=activated)
Indicates to the user that a
shutdown of the inverter will result
in transfer of the load to Mains 2
with the risk of a 0.8 second
interruption in the supply of power
to the load.
465: frequency conversion
(0=not activated / 1=activated)
Indicates that the
TM
MGE
GalaxyTM 6000 UPS is
operating as a frequency converter
between the input and the output
(50 Hz / 60 Hz).
466: conditional inverter
shutdown (0=not activated /
1=activated)
Indicates to the user that a
shutdown of the inverter will take
place only if the load transfer
conditions to Mains 2 are correct to
avoid an interruption in the supply
of power to the load.
Word address: 48
480: inverter overload (0=no/
1=overload)
Informs the user that the load is
drawing more than the rated UPS
output.
482: ventilation of the battery
cabinets (0=no fault / 1=fault)
Indicates to the user that ventilation
in a battery cabinet is incorrect due
to a fan fault or shutdown. This fault
does not result in UPS shutdown.
This information is available only on
European versions of the
TM
MGE
GalaxyTM 6000 UPS.
484: inverter connected to the
load (0=not connected/
1=connected)
The inverter is operating and
powers the load.
485: inverter off disable
(0=enabled/1=disabled)
The inverter off command is
disabled.
486: synch with Mains 2 (0=not
synch/1=synch)
The inverter may operate without
its frequency synchronized to that
of Mains 2 (i.e. free-running
operation); in this case, it operates
at an accurate (within 0.05 Hz)
fixed frequency. Alternatively, the
inverter may be operated with its
frequency synchronized to that of
Mains 2.
487: transfer fault (0=no fault/
1=fault)
Informs the user of a fault on the
static switch, used to transfer the
load between Mains 2 and inverter
output. After-sales servicing is
required.
48A: Mains 2 voltage outside
tolerances (0=normal / 1=outside
tolerances)
Indicates to the user that the Mains
2 backup power supply voltage is
outside tolerances. A transfer of the
load to the Mains 2 backup power
supply will result in a 0.8 second
interruption in the supply of power
to the load or may not take place.
48D: emergency off switch
(0=not activated/1=activated)
Normally-closed switch connected
to the units. When activated, the
rectifier-charger circuits and the
inverters stop operating. The "QF1"
battery circuit breaker is also
opened.
If the "emergency off" also tripped
the protection devices to
disconnect the units from Mains 1
and Mains 2, the load no longer
receives power and the units are
completely disconnected.
6739389EN/FB - Page 35
Page 36

System information (continued)
Word address: 49
494: contactor K2S (0=open/
1=closed)
Indicates the position of contactor
K2S . Contactor K2S is connected
in parallel with the static switch on
the Mains 2 line on certain high
output units. It is installed in staticswitch cubicles with power ratings
over 400 kVA.
496: Mains 2 input switch
(0=open/1=closed)
Switch "Q4S" is located on the
Mains 2 phases at the input of the
static switch (on the bypass line).
The switch is normally closed.
497: maintenance bypass switch
(0=open/1=closed)
Switch "Q3BP" bypasses the static
switch and connects Mains 2
directly to the load. This switch is
normally open. When closed (with
"Q4S" and "Q5N" open), the load
can continue to be powered while
the UPS is isolated for servicing.
498: inverter output switch
(0=open/1=closed)
Switch "Q5N" is located at the
output of the inverter and is used to
disconnect the load from the
inverter (or from the output busbars
when several units are connected
in parallel).
This switch is normally closed.
499: static switch status
(0=open/1=closed)
The static switch on Mains 2 is
normally open (inverter powers the
load). The load is transferred to
Mains 2 by closing the static switch
when the inverters are no longer
capable of delivering the required
power (overload, end of backup
time or internal error).
49C: Mains 2 frequency
(0=normal/1=outside tolerances)
When the frequency of Mains 2 is
outside tolerances, load transfer
from inverter to Mains 2 will include
an interruption of 0.8 s or will not
take place.
49D: Mains 2 voltage (0=normal/
1=outside tolerances)
When the phase-to-phase Mains 2
input voltage is outside tolerances,
load transfer from inverter to Mains
2 will include an interruption of 0.8
second.
49F: free-running frequency
request (0=not activated/
1=activated)
Indicates that the inverter received
an external command to
desynchronize its output frequency
from the frequency of Mains 2.
Word address: 4A
4A0: static bypass (Mains 2)
overload (0=no/1=overload)
The load, supplied via the static
bypass line (Mains 2), is drawing
more than the rated current but
continues to be supplied by Mains 2.
4A1: static bypass (Mains 2)
thermal overload (0=no/
1=overload)
Informs the user that the load is no
longer powered by Mains 2 due to
an extended overload condition.
4A2: inverter thermal overload
(0=no/1=overload)
Informs the user that the load is
overloaded by a factor between 1
and 1.6 In: the inverter stops
operating.
4A3: auxiliary cubicle fault (0=no
fault / 1=fault)
Indicates to the user that the fault
auxiliary contact connected to the
cubicle has been activated. This
information is available only on
U.S. versions of the
TM
MGE
4A4: transfer to Mains 2 with
interrupt prohibited (0=not
activated/1=activated)
An auxiliary command prohibits
transfer to Mains 2 with power
interruption.
4A5: transfer lockout (0=not
activated/1=activated)
The inverter received an auxiliary
command prohibiting transfer to
Mains 2. The load is totally
dependent on inverter power. If the
inverter stops (internal fault), the
load will no longer receive power.
GalaxyTM 6000 UPS.
4AF: inverter quantity
(0=insufficient/1=sufficient)
This only concerns systems with
parallel connected inverters and a
static switch cubicle. It informs the
user that the number of inverters to
be connected to the load is
insufficient to supply the necessary
power. Additional inverter(s) must
be turned on so that the inverters
can start supplying the power to the
load. If this is not the case, Mains 2
continues to supply the power.
Word address: 4C
(summary of operating
information)
4C0: acquisition fault (0=no fault
/ 1=fault)
Indicates an acquisition fault for the
internal analogue or logic values of
the "GTCZ" or "GT2Z"
communication board.
4C1: battery backup time (0=no
fault/1=backup time end)
The computed "remaining backup
time" is less than the amount
configured in the unit.
4C2: end of battery life (0=no
fault / 1=end of battery life)
Indicates that the battery has
reached its maximum service life
and should be replaced.
4C4: system normal, load
protected (0=not normal/
1=normal)
Indicates that the inverter powers
the load and that the full battery
backup time is available if Mains 1
fail. The unit is operating normally.
Note: for parallel connected inverter
cubicles, this only refers to the
output power supplied by that
specific unit. The load may be
unprotected if more than one inverter
is required to supply the load power.
All required inverters in the system
or the static switch cubicle if it exists
must therefore be checked.
4C5: system downgraded due to
malfunction (0=not downgraded/
1=downgraded)
Indicates a malfunction or
environment fault; nevertheless the
inverter can still power the load.
Page 36 - 6739389EN/FB
Page 37

System information (continued)
◗ malfunctions:
◗ ◗ static switch cubicle ventilation
fault,
◗ ◗ static switch control fault,
◗ ◗ environment faults:
◗ ◗ battery temperature outside
tolerances,
◗ ◗ overload exceeding 5%,
◗ ◗ Mains 2 voltage, frequency or
phase outside tolerances with
respect to inverter.
4C6: unsafe operation, load
unprotected (0=safe/1=unsafe)
Indicates that:
◗ Mains 2 powers the load due to
inverter shutdown (manual or due
to an overload or internal fault) or
due to opening "Q5N" at the
inverter output;
◗ not able to rely on battery backup
because circuit breaker "QF1" is
open.
Note: for parallel connected
inverters this only refers to the
specific unit. The load may still be
protected because more than one
inverter is supplying power.
4C7: operating on battery power
(0=no/1=on battery power)
Indicates that the unit is operating
on battery power because:
◗ Mains 1 voltage failure or dip;
◗ insufficient Mains 1 power (e.g.
engine generator set) with extra
energy required supplied by the
battery.
4C8: emergency off switch
(0=not activated/1=activated)
Normally-closed switch connected
to the units. When activated, the
rectifier-charger circuits and the
inverters stop operating. The "QF1"
battery circuit breaker is also
opened.
If the "emergency stop" also tripped
the protection devices to
disconnect the units from Mains 1
and Mains 2, the load no longer
receives power and the units are
completely disconnected.
4C9: power supplied via SS or
K2S (0=open/1=closed)
Indicates that the static switch or
the mechanical switch on the Mains
2 backup line is closed. The load is
supplied by Mains 2.
4CA: inverter connected
(0=disconnected/1=connected)
Indicates that the inverter is in
operation and supplying the load.
Word address: 4D
4DD: cubicle ventilation (0=no
fault / 1=fault)
Indicates to the user that ventilation
in a cubicle is incorrect due to a fan
fault or shutdown. This fault does
not result in UPS shutdown. This
information is available only on
U.S. versions of the
TM
MGE
GalaxyTM 6000 UPS.
Word address: 4E (summary
of communication interface
information)
4E9: communication interface
test error (0=no error/1=error)
Error free communications can no
longer be guaranteed.
4EA: unit in configuration mode
(0=no config./1=config)
The after-sales "Soft Tunor"
computer software is connected to
the cubicle, blocking all remote
commands.
4EB: remote setting (0=no
setting / 1=setting)
Indicates to the user that the Soft
Tunor after-sales-support computer
tool has been connected to the
communication channel.
4EC: invalid measurements
(0=valid/1=invalid)
The communication interface
receives invalid measurement data
and status information from the
cubicle.
4EF: change in status (0=no
change / 1=change)
Indicates a change in status of at
least one indicator between two
reads of logical data. This
information can be reset by the
device connected to the
communication channel.
Glossary of
telemonitoring
information descriptors
(data words at address 50 to D4)
Word address: 50
The causes of high transition
alarms followed by a call from the
UPS site to the central monitoring
site are logged in this word.
Word structure is similar to that of
word 4C.
Word address: 51
The causes of low transition alarms
followed by a call from the UPS site
to the central monitoring site are
logged in this word.
Word structure is similar to that of
word 4C.
Word address: 52
520: invalid telephone number
for main telemonitoring site
(0=valid / 1=invalid)
Indicates that calls from the UPS
site to the central telemonitoring
site consistently fail. The number of
the telemonitoring site is therefore
declared invalid and no longer
used. A second set of calls is then
undertaken using the backup
number.
The telephone number is
reinstated:
◗ on reception of a new
communication configuration using
the Soft Tunor after-sales-support
computer tool,
◗ when the "GTCZ" or "GT2Z"
communication board is deenergised.
528: invalid telephone number
for secondary telemonitoring site
(0=valid / 1=invalid)
Indicates that calls from the UPS
site to the secondary telemonitoring
site consistently fail. The number of
the telemonitoring site is therefore
declared invalid and no longer
used.
6739389EN/FB - Page 37
Page 38

System information (continued)
The telephone number is
reinstated:
◗ on reception of a new
communication configuration using
the Soft Tunor after-sales-support
computer tool,
◗ when the "GTCZ" or "GT2Z"
communication board is deenergised.
Word address: C1
C10: call reset (0= not activated /
1=activated)
Call reset command issued by the
central telemonitoring site. The
information bits that provoked the
call to the central telemonitoring
site are reset.
C11: return call (0= not activated
/ 1=activated)
Return call command issued by the
central telemonitoring site. The
UPS site recalls the central
telemonitoring site following a time
delay of approximately 30 seconds.
C14: status change reset (0= not
activated / 1=activated)
Indicates that the central
telemonitoring site issues a reset
command for the status change bit
at address 4EF.
Page 38 - 6739389EN/FB
 Loading...
Loading...