Page 1
Appendix B
BIOS revision
(AP5T-1)
48.87901.011
Frequently Asked Question
Note: FAQ may be updated without notice. If you
cannot find the information that you need in this
appendix, visit our WWW home page, (address:
http://www.aopen.com.tw) and check the FAQ
area and other new information.
Q: How can I identify the mainboard BIOS version?
A: The AOpen mainboard BIOS version appears on the upper-left corner of the
POST (Power-On Self Test) screen. Normally, it starts with R and is found in
between the model name and the date. For example:
AP53/AX53 R3.80 Oct.22.1996
Q: How can I identify version of the mainboard?
A: The AOpen mainboard version appears as ppppp-x on the PCB, near the PCI
slot and is enclosed in a white bordered box. The ppppp is the project code
used byAOpeninternallyand-xistheversioncode.Forexample, for AP5T with
95152 project code and -1 version code, the mainboard version appears on the
PCB as follows:
MB verison -1
95152-1
AP5T MB
B-1
Page 2

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why do AOpen MBs use many Electrolytic Capacitors instead of
Tantalum Capacitor?
A: The quality of Electrolytic capacitor has huge difference depends on model and
vendor. Normally, Tantalum capacitor is better than Electrolytic capacitor, but
good quality and high price Electrolytic capacitor is even better than Tantalum
capacitor. Originally, AOpen motherboards use 100uF Tantalum capacitor
nears CPU to reduce voltage ripple, but the technology improvement has
introduced an 1000uF very low ESR (Equivalent Serial Resistor) of Electrolytic
capacitor with only 0.15 ohm comparing with 0.7 ohm of Tantalum capacitor.
The lower the ESR and higher the capacitance value, the smaller the CPU
voltage ripple.
Following are the specifications of capacitors that AOpen is currently using:
Tantalum: SPRAGUE 100uF,
Part number 595D107X06R3C2T,
Max ESR is 0.7 at 25 degree 100KHz.
Electrolytic: SANYO 1000uF,
Part number 16MV1000CG,
Max ESR is 0.15 at 20 degree 100KHz.
Also, more capacitors are not exactly equal to better CPU voltage, it depends
on where you put your capacitor (the layout). The most accurate way is to use
storage scope to measure the CPU voltage directly, but of course, it is difficult
for end user to do so. AOpen design team follows Intel, AMD and Cyrix'sdesign
specification strictly, it is approved by Intel, AMD and Cyrix..
Q: Why the AOpen mainboards (MB) do not have cache module expansion
slot?
A: Faster CPU speed requires more difficult and complex MB timing design. Every
trace and components delay must be taken into consideration. The expansion
cache slot design will cause 2 or 3ns delay in PBSRAM timing, and the
extended trace length to the cache module through the golden finger will further
delay the timing by 1 or 2ns. This may result in unreliable system once the
cache module and slot becomes worn. All AOpen MBs support 512KB
PBSRAM onboard. For better performance (around 3% higher than 256KB),
we strongly recommend you to use 512KB onboard. Otherwise, reliable 256KB
is better than unreliable 512KB with cache module. AOpen is the first company
to promote this concept since the fourth quarter of 1995.
B-2
Page 3

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is MMX?
A: MMX is the new single-line multiple-instruction technology of the new Intel
Pentium PP/MT (P55C) CPU. A new Pentium Pro CPU (Klamath) with MMX
technology is also expected to be released soon. The MMX instructions are
specifically useful for multimedia applications (such as 3D video, 3D sound,
video conference). The performance can be improved if applications use these
instructions. All AOpen MBs have at least dual power onboard to support
PP/MT, it is not necessary to have special chipset for MMX CPU.
Q: What is USB (Universal Serial Bus)?
A: USB is a new 4-pin serial peripheral bus that is capable of cascading
low/medium speed peripherals (less than 10Mbit/s) such as keyboard, mouse,
joystick, scanner, printer and modem/ISDN. With USB, the traditional complex
cables from back panel of your PC can be eliminated.
You need the USB driver to support USB device(s). AOpen MBs are all USB
ready, you may get latest BIOS from AOpen web site
(http://www.aopen.com.tw). Our latest BIOS includes the keyboard driver
(called Legacy mode), that simulates USB keyboard to act as AT or PS/2
keyboard and makes it possible to use USB keyboard if you don't have driver in
your OS. For other USB devices, you may get the drivers from your device
vendor or from OS (such as Win95). Be sure to turn off "USB Legacy Support"
in BIOS "Chipset Setup" if you have another driver in your OS.
Q: What is P1394?
A: P1394 (IEEE 1394) is another standard of high-speed serial peripheral bus.
Unlike lowor medium speed USB, P1394 supports 50 to 1000Mbit/s and can be
used for video camera, disk and LAN. Since P1394 is still under development, ,
there is no P1394 device currently available in the PC market. Also, there is no
chipset that can support P1394. Probably in the near future, a card will be
developed to support P1394 device.
Q: What is SMBus (System Management Bus, also called I2C bus)?
A: SMBus is a two-wire bus developed for component communication (especially
for semiconductor IC). It is most useful for notebook to detect component
status and replace hardware configuration pin (pull-high or pull-low). For
example, disabling clock of DIMM that does not exist, or detecting battery low
condition. The data transfer rate of SMBus is only 100Kbit/s, it allows one host
to communicate with CPU and many masters and slaves to send/receive
message. The SMBus may be used for jumpless mainboard, the components
which support SMbus are not ready yet, we will keep eyes on it.
Q: What is FCC DoC (Declaration of Conformity)?
B-3
Page 4
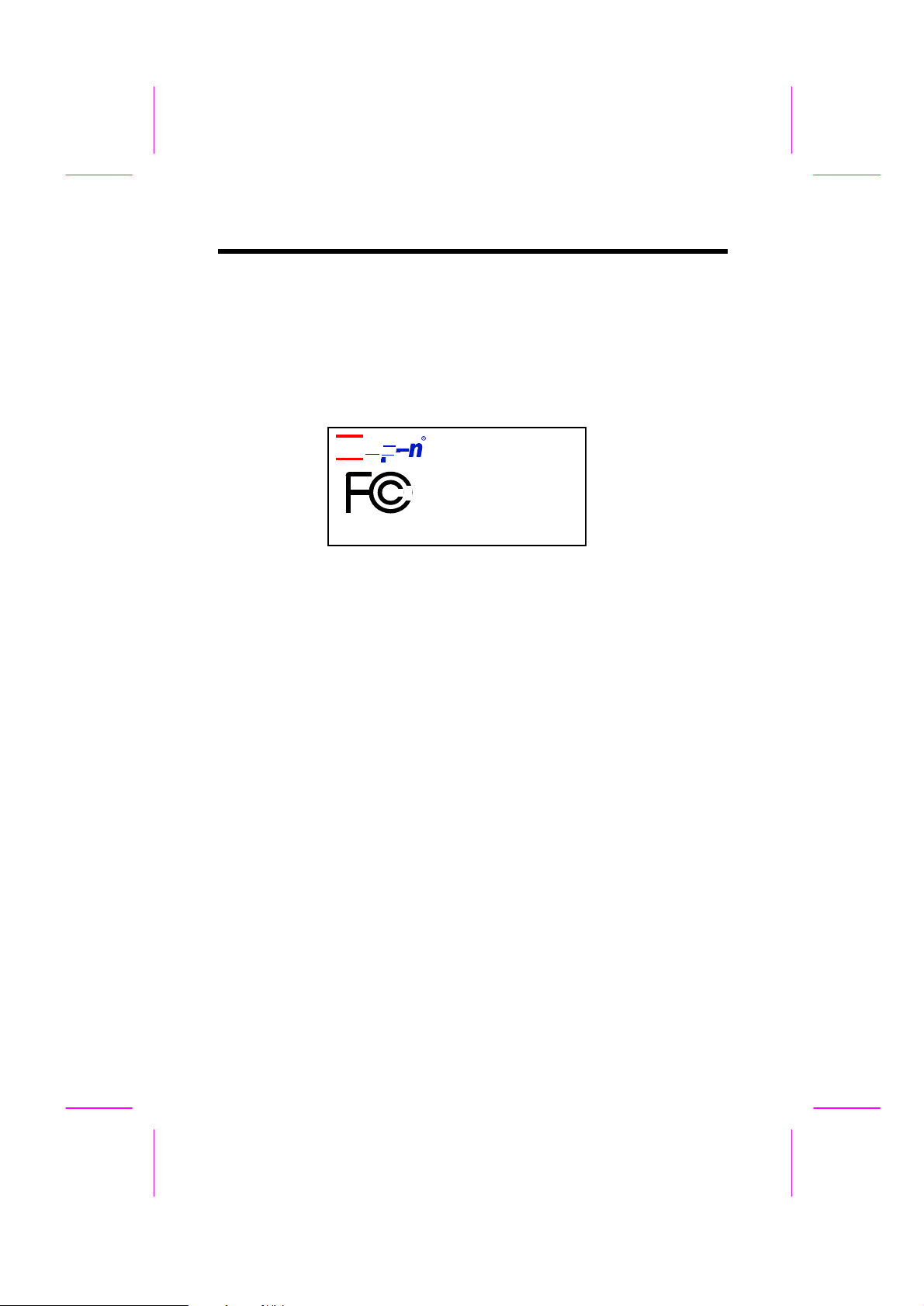
Frequently Asked Questions
A: The DoC is new certification standard of FCC regulations. This new standard
allows DIY component (such as mainboard) to apply DoC label separately
without a shielding of housing. The rule to test mainboard for DoC is to remove
housing and test it with regulation 47 CFR 15.31. The DoC test of mainboard is
more difficult than traditional FCC test. If the mainboard passes DoC test, that
means it has very low EMI radiation and you can use any kind of housing (even
paper housing). Following is an example of DoC label. Currently, AOpen
AX65/AP57/AP5T/AX5T had passed DoC test.
AX5T
Test To Comply
With FCC Standards
FOR HOME OR OFFICE USE
Q: What is PBSRAM (Pipelined Burst SRAM)?
A: For Pentium CPU, the Burst means reading four QWord (Quad-word,4x16= 64
bits) continuously with only the first address decoded by SRAM. The PBSRAM
will automatically send the remaining three QWord to CPU according to
predefined sequence. The normal address decoding time for SRAM is 2 to 3
clocks. This makes the CPU data read timing of four QWord to be at least 32-2-2 and a total of 9 clocks if traditional asynchronous SRAM is used.
However, with PBSRAM, there is no need to decode address for rest three
Qword. Therefore, data read timing can be 3-1-1-1, that is equivalent to 6
clocks and is faster than asynchronous SRAM.
Q: What is EDO (Extended Data Output) memory?
A: The EDO DRAM technology of EDO is actually very similar to FPM (Fast Page
Mode). Unlike traditional FPM that tri-states thememoryoutputdatatostartthe
pre-charge activity, EDO DRAM holds the memory data valid until the next
memory access cycle, that is similar to pipeline effect and reduces one clock
state.
Q: What is SDRAM (Synchronous DRAM)?
A: The SDRAM is a new generation DRAM technology that allows DRAM to use
the same clock as the CPU host bus (EDO and FPM are asynchronous and do
not have clock signal). The idea is the same as "Burst" (refer to the previous Q
& A). It requires only one clock for the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th QWord (for example,
5-1-1-1 compares with EDO 5-2-2-2). The SDRAM comes in 64-bit 168-pin
DIMM (Dual-in-line Memory Module) and operates at 3.3V. Note that some old
DIMMs are made by FPM/EDO and only operate at 5V. Do not confuse them
B-4
Page 5
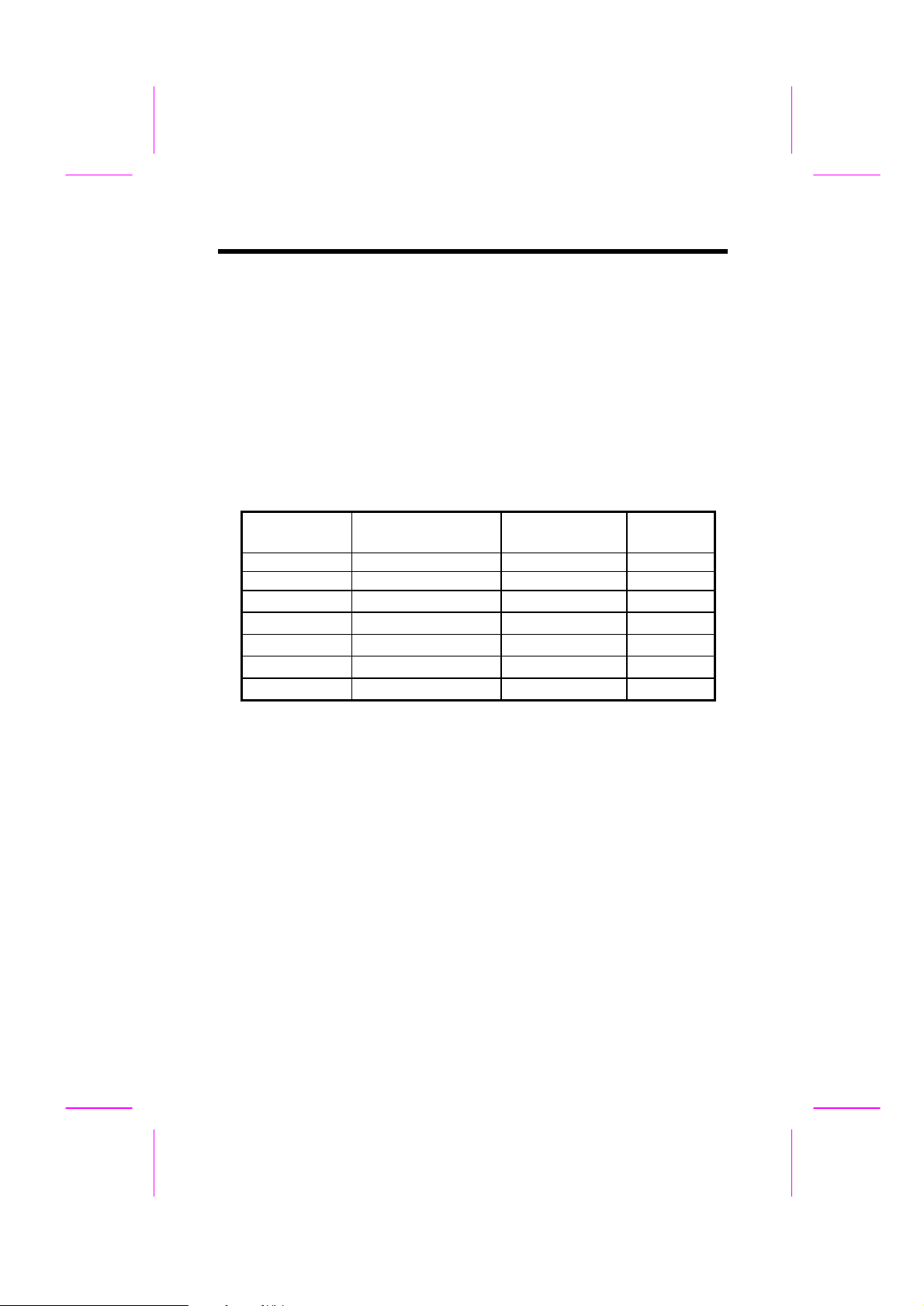
Frequently Asked Questions
with SDRAM DIMM. AOpen is the first company to support dual-SDRAM
DIMMs onboard (AP5V), from Q1 1996.
Q: Can SDRAM DIMM work together with FPM/EDO SIMM?
A: The FPM/EDO operate at 5V while SDRAM operates at 3.3V. The current MB
design provides different power to DIMM and SIMM but connects the data bus
together. If you combine SIMM and DIMM, the system will still work fine;
however, only temporarily. After a few months, the SDRAM 3.3V data input will
be damaged by 5V FPM/EDO data output line. Therefore, we strongly NOT
recommend DIMM and SIMM combined together. There is one exception, if
yourSDRAMsupports5Vtolerance(suchasTIorSamsung),whichaccepts 5V
signal at 3.3V operating power, you can combine them.
Manufacturer Model Suggested CAS
Latency Time
Samsung KM416511220AT-G12 2 Yes
NEC D4S16162G5-A12-7JF 2 No
Hitachi HM5216805TT10
TI
TI
TI
TI
TMX626812DGE-12
TMS626812DGE-15
TMS626162DGE-15
TMS626162DGE-M67
2 No
2 Yes
3 Yes
3 Yes
3 Yes
5V
Tolerance
Q: What is Bus Master IDE (DMA mode)?
A: The traditional PIO (Programmable I/O) IDE requires the CPU to involve in all
the activities of the IDE access including waiting for the mechanical events. To
reduce the workload of the CPU, the bus master IDE device transfers data
from/to memory without interrupting CPU, and releases CPU to operate
concurrently while data is transferring between memory and IDE device. You
need the bus master IDE driver and the bus master IDE HDD to support bus
master IDE mode. Note that it is different with master/slave mode of the IDE
device connection. For more details, refer to section 2.3 "Connectors".
B-5
Page 6

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the Ultra DMA/33?
A: This is the new specification to improve IDE HDD data transfer rate. Unlike
traditional PIO mode, which only uses the rising edge of IDE command signalto
transfer data, the DMA/33 uses both rising edge and falling edge. Hence, the
data transfer rate is double of the PIO mode 4 or DMA mode 2. (16.6MB/s x2 =
33MB/s).
The following table lists the transfer rate of IDE PIO and DMA modes. The IDE
bus is 16-bit, which means every transfer is two bytes.
Mode Clock per
33MHz
PCI
PIO mode 0 30ns 20 600ns (1/600ns) x 2byte = 3.3MB/s
PIO mode 1 30ns 13 383ns (1/383ns) x 2byte = 5.2MB/s
PIO mode 2 30ns 8 240ns (1/240ns) x 2byte = 8.3MB/s
PIO mode 3 30ns 6 180ns (1/180ns) x 2byte = 11.1MB/s
PIO mode 4 30ns 4 120ns (1/120ns) x 2byte = 16.6MB/s
DMA mode 0 30ns 16 480ns (1/480ns) x 2byte = 4.16MB/s
DMA mode 1 30ns 5 150ns (1/150ns) x 2byte = 13.3MB/s
DMA mode 2 30ns 4 120ns (1/120ns) x 2byte = 16.6MB/s
DMA/33
Q: What is the performance of Ultra DMA/33? Do we need special driver?
A: You need driver to activate DMA/33, there are now driver from INTEL or you
can use driver in the Windows 95 Memphis, which can recognize South Bridge
PIIX4.
We got the mass productionsampleQuantumFireballST1.6A,followingare the
test result.
MB : AOpen AP5T
CPU : P54C-200 Mhz
DRAM : 16MB * 2 (FP-7)
VGA : AOpen PV60
CDROM : AOpen CD-920E (20X)
OS : Win95 OSR2
30ns 4 120ns (1/120ns) x 2byte x2 = 33MB/s
Clock
count
Cycle
time
Data Transfer rate
B-6
Page 7

Frequently Asked Questions
Model OS/Driver Mode Winbench97
Quantum
Fireball 1.2G
Quantum
Fireball 1.2G
Quantum
ST1.6A
Quantum
ST1.6A
Windows 95 OSR2 PIO
Windows 95 OSR2 +
INTEL PIIX4 driver
Windows 95 OSR2 PIO
Windows 95 OSR2 +
INTEL PIIX4 driver
mode 4
DMA
mode 2
mode 4
DMA/33 1040 4020
Disk Winmark
(Business)
717 2150
822 3050
853 2630
Winbench97
Disk Winmark
(High End)
Q: What is PnP (Plug and Play)?
A: In the past, the IRQ/DMA and memory or I/O space of add-on cards are
normally set manually, i.e., by jumper or by proprietary utility. The user has to
check the user's guide for the correct setting. Sometimes, resource conflict
occurs and this leads to unstable system. The PnP specification suggests a
standard register interface for both BIOS and OS (such as Win95). These
registers are used by BIOS and OS to configure system resource and prevent
any conflicts. The IRQ/DMA/Memory will be automatically allocated by PnP
BIOS or OS.
Currently, almost all the PCI cards and most ISA cards are PnP compliant. If
you are still using a Legacy ISA card that cannot support PnP, set the
corresponding resource (IRQ/DMA/memory) to ISA in the BIOS "PCI/PnP
Setup".
Q: What is ACPI (Advanced Configuration & Power Interface) and OnNow?
A: The ACPI is new powermanagementspecificationof1997(PC97). It intends to
save more power by taking full control of power management to operating
system and not through BIOS. Because of this, the chipset or super I/O chip
needs to provide standard register interface to OS (such as Win97) and
provides the ability for OS to shutdown and resume power of different part of
chip. The idea is a bit similar to the PnP register interface.
ACPI defines momentary soft power switch to control the powerstate transition.
Most likely, it uses the ATX form factor with momentary soft power switch. The
most attractive part of ACPI for desktop user is probably the "OnNow" feature,
an idea from notebook. This feature allows you to immediately resume to your
original work without the long time waiting from bootup, entering Win95 and
running Winword. The AX5T with Intel TX chipset can support ACPI.
Q: What is ATX Soft Power On/Off and Momentary Switch?
B-7
Page 8

Frequently Asked Questions
A: The Soft Power On of the ATX specification means to provide a standby current
for special circuit to wait for wakeup event when main power is off. For
example, Infrared wakeup, modem wakeup, or voice wakeup. Currently, the
most simple usage is to provide standby current for power switch circuit so that
powerswitchcanturnon/offthemainpowerthroughsoftpowercontrolpin. The
ATX power specification does not mention anything about the power switch
type. You can use toggle or momentary switch, note that ACPI specification
requires momentary switch for power state control. All the AOpen ATX MBs
support momentary switch and AX5T/AX58/AX6L support modem wakeup
(Modem Ring-On).
Soft Power Off means to turn off system through software, Windows 95
Shutdown function can be used to verify if your mainboard supports soft power
off. AOpen AX5T/AX58/AX6F/AX6L support soft power off.
Q: What is the AGP (Accelerated Graphic Port)?
A: AGP is a PCI-like bus interface targeted for high-performance 3D graphic. AGP
supports only memory read/write operation and single-master single-slave
one-to-one only. The AGP uses both rising and falling edge of the 66MHz clock
and produces 66MHz x 4byte x 2 = 528MB/s data transfer rate. The AOpen
AX6L MB are designed to support AGP via the new Intel Klamath LX chipset.
Q: Which Pentium chipset has the best performance?
A: The performance difference of chipset depends on whatkindofDRAM they use
and the DRAM timing they support. (They all use PBSRAM, so that the
difference is very little at 2nd level cache.)
The following table lists the read timing of current available chipsets. The four
digital represents the clocks needed for 1st-2nd-3rd-4th QWord. Notice that the
Intel HX + EDO or SIS 5571+ EDO are almost the same as VX + SDRAM and
the TX + SDRAM has the best performance among Pentium chipsets. Please
note AP57 does not support SDRAM.
B-8
Page 9

Frequently Asked Questions
P5 Chipset Model PBSRAM FPM EDO SDRAM
Intel 430FX AP5C/P 3-1-1-1 7-3-3-3 7-2-2-2 NA
Intel 430VX AP5VM/
AP5V
Intel 430HX AP53/
AP5K/
AX53
Intel 430TX AP5T/
AX5T
SIS 5571 AP57 3-1-1-1 5-3-3-3 4/5-2-2-2 (6/7-1-1-1)
SIS 5582 AP58/
AX58
Q: What is the memory performance improvement of TX chipset?
A: Following is the compare table of TX+SDRAM, VX+SDRAM, TX+EDO,
HX+EDO and VX+EDO.
CPU : Pentium PP/MT (P55C) 200MHz
DRAM :16MB EDO or SDRAM
HDD : Quantum Fireball 1280AT
VGA : AOpen PV60 S3 Trio64V+ 800x600x256 Small font
OS : Windows 95 OSR2
3-1-1-1 6-3-3-3 6-2-2-2 6-1-1-1
3-1-1-1 6-3-3-3 5-2-2-2 NA
3-1-1-1 6-3-3-3 5-2-2-2
3-1-1-1 5-3-3-3 4/5-2-2-2 6/7-1-1-1
5-1-1-1
Chipset Model DRAM Timing Winstone96
Intel 430VX AP5VM EDO 6-2-2-2 86.1
Intel 430HX AP53/AP5K EDO 5-2-2-2 86.8
Intel 430TX AP5T/AX5T EDO 5-2-2-2 87.3
Intel 430VX AP5VM/AP5V SDRAM 6-1-1-1 86.6
Intel 430TX AP5T/AX5T SDRAM 5-1-1-1 87.7
Q: Does Pentium or Pentium Pro MB support Deturbo mode?
A: The Deturbo mode was originally designed to slow down CPU speed for old
applications (especially old games). It uses programming loop to wait or delay
special event. This programming method is considered very bad since the
delay of loop highly depends on the CPU speed and the application fails at
high-speed CPU. Almost all new applications (including games) use RTC or
interrupt to wait event. There is no need for Deturbo mode now. The Turbo
B-9
Page 10

Frequently Asked Questions
switch is now used as Suspend switch. However, some MBs still support
Turbo/Deturbo function via keyboard. You can set the system to Deturbo by
pressing <Ctrl> <Alt> <->. To back to Turbo mode, press <Ctrl> <Alt> <+>.
Note that the Deturbo mode has been removed in new MBs since these require
more code space in Flash ROM.
Q: Power Management Icon does not appear in the Windows 95 Control Panel
even though the APM under BIOS Setup is enabled.
A: This problem occurs if you did not enable the APM function before you install
Windows 95. If you have already installed Windows 95, re-install it after the
BIOS APM function is enabled.
Q: Why does the system fail to go into suspend mode under Win95?
A: This problem may be caused by your CDROM settings. The CDROM Auto
Insert Notification of Win95 is default enabled, the system will continue to
monitor your CDROM, auto-execute application when a CD diskette is loaded,
and prevents the system from entering into suspend mode. To resolve this, go
into Control Panel è System è Device Manager è CDROM è Setting, and
disable the "Auto Insert Notification" function.
Q: What is Windows 95 Registry?
A: The functions of Windows 95 Registry and the Windows 3.1 INI files are almost
the same. Both store the hardware and software configurations. The only
difference is that Registry is a database while INI is text file. You can run
REGEDIT.EXE to further understand the Registry structure. Checking and
studying the structure of this file will help you solve some configuration
problems.
Q: Why are there question marks or "standard IDE controller" presented
under Device Manager after installing Win'95 on AP5T/AX5T based
system?
A: Intel has introduced 430TX chipsetwithlatestfeatureof"ACPI", "USB" & "Ultra
DMA/33". Since these devices are so new that Win'95 did not anticipate to
support them on Aug. of '95 which Win'95 initially is being released. Under
Win'95 Device Manager, you may see following devices installed:
B-10
Page 11

Frequently Asked Questions
-Other Devices
? PCI Bridge
? PCI Card (or PCI Universal Serial Devices)
-Hard Disk Controllers
Standard Dual PCI IDE Controller
Primary IDE Controller
Secondary IDE Controller
PCI Bridge:
This device stands for the "ACPI" feature which implemented within
PIIX4(82371AB) chipset. This new feature is expected to be fully utilized under
Windows'97(Memphis). Please look for more details on ACPI from FAQ "What
is ACPI?".
Even though the limitation of above, you can eliminate this question mark by
simply install the utility (TX.EXE) provided by AOpen on any of Intel 430TX
based mainboard. Please download this utility from AOpen homepage. After
installation, the following devices will be created & recognized under Device
Manager:
-Hard Disk Controllers
Intel 82371AB PCI Bus Master IDE Controller Primary IDE Controller
Secondary IDE Controller
-System Devices
Intel 82371AB PCI to ISA Bridge
Intel 82371AB Power Management Controller
Intel 82439TX Pentium(r) Processor to PCI Bridge
PCI Card (or PCI Universal Serial Devices) :
If you are Win'95 OSR 2.0 user (shows "PCI Universal Serial Devices"), you
may obtain USBSUPP.EXE from Microsoft or your OEM system provider for
installing Microsoft USB supplement which will create "USB Supplement to
OSR2" in the list of Add/Remove program tool under Control Panel. After above
installation, please run TX.EXE provided by AOpen so that OSR 2.0 will newly
create following device under Device Manager.
-Universal Serial Bus Controller
Intel 824371AB PCI to USB Universal Host Controller USB Root Hub
B-11
Page 12

Frequently Asked Questions
If you are Win'95 OSR 2.1 user, only TX.EXE installation is necessary. If you
are Win'95 retail(.950 or .950A, shows "PCI Card") user, there is no direct
upgradepathavailablefromMicrosoftatthismoment.Allofaboveareexpected
to be implemented under Windows'97.
Standard Dual PCI IDE Controller:
The IDE controller chipset -- PIIX4 -- will be fully recognized under Windows'97
also. In the mean while, you may download the driver for Win'95 from AOpen
homepage at "http://www.aopen.com.tw" which supports both Bus Mastering &
Ultra DMA/33. After installation, you should be able to see Win'95 recognize it
under Device Manager as below:
-Hard Disk Controllers
Intel 82371AB PCI Bus Master IDE Controller
Primary Bus Master IDE Controller
Secondary Bus Master IDE Controller
Even though all of above are the current limitations of Win'95 on Intel 430TX
chipset which are expected to implement on Win'97, your system still can enjoy
the best performance of AP5T/AX5T without any problem.
Q: How can I eliminate the "?" marks presented under Device Manager after
installing Win'95 on TX based system?
A: Although your system will still work fine with this "?" exist. We received many
requests about how to eliminate it. AOpen driver team spends few weeks to
develop an utility (TX.EXE) for convenience of Win95 users. It is very user
friendly and can be used on any TX mainboard, not limited to AOpen
AP5T/AX5T. You are welcome to distribute it, simply say thanks to our driver
team.
Q: Which version of the Windows '95 that I am using?
A: You may determine the version of Windows '95 by following steps.
1. Double click "System" in "Control Panel".
2. Click "General".
3. Look for "System" heading & refer to following,
4.00.950 Windows 95
4.00.950A Windows 95 + Service Pack or OEM Service Release 1
4.00.950B OEM Service Release 2 or OEM Service Release 2.1
B-12
Page 13

Frequently Asked Questions
If you are running OSR 2.1, you may tell it from by checking "USB Supplement
to OSR2" in the list of installed program of Add/Remove program tool under
Control Panel, and checking for version 4.03.1212 of the Ntkern.vxd file in the
Windows\System\Vmm32 folder.
Q: What is the performance improvement of AMD K6 and Cyrix M2?
A: Following is the compare table of the new generation CPU.
DRAM: 64MB EDO
HDD : Quantum Fireball 1280AT
VGA : Matrox Millennium VGA, 4MB, 1024x768 24bit, 85Hz.
OS : Windows 95 4.00.950
CPU MB Chipset Winstone97
Business
M2- 150
(60MHz x 2.5)
PP/MT-200 AP5T/AX5T Intel 430TX 48.3 21.9
PP/MT-233 AP5T/AX5T Intel 430TX 50.5 23.6
K6 PR2-200 AP5T/AX5T Intel 430TX 50.3 22
* K6 PR2-210
(83.3MHz x 2.5)
K6 PR2-233 AP5T/AX5T Intel 430TX 51.7 23.6
* K6 PR2-250
(83.3MHz x 3)
You can see that K6-233 is better than PP/MT-233 on Business Winstone97,
but the High-End graphic Winstone97 is almost the same.
Note that, if you over-clock K6 to 250M (83.3MHz*3), it could be the fastest
socket -7 system among all. But please be reminded, it is your own risk to
over-clock, it may cause system unstable.
Q: When can we have real jumperless mainboard?
A: PnP had achieved the goal of jumperless add-on card, but true jumperless
mainboard still has some technical concerns. For example, CPU clock and
voltage do not have standard interface. Currently, the so called jumperless
mainboard is actually depends on the BIOS to detect or manually set the CPU
clock and voltage. If the setting is wrong, it will cause system unstable or
damage after long time use. The other disadvantage is, because some of the
AP5T/AX5T Intel 430TX 48 20.1
AP5T Intel 430TX 51.2 23
AP5T Intel 430TX 54 24.8
Winstone97
High-End
B-13
Page 14

Frequently Asked Questions
jumper setting information is stored in CMOS, if the battery is lost or BIOS setup
is accidentally changed, end user (or distributor) may need to open the housing
and check the CPU again.
Most of all, you need a start voltage to boot CPU and go into BIOS for
jumperless setting. 2.85V may be OK for P55C and K6-166, but minimum
voltage of K6-233MHz is 3.1V, it can not boot if user plugs K6-233 onto current
jumperless mainboard.
We probably need to wait after the mature of SMbus, if CPU and clock
generator and other ICs are all SMbus compliance. Chipset can then detect and
report the system configuration right after power on. Then we can have true
jumperless mainboard.
Q: What is the difference of Synchronous and Asynchronous Switching
Regulator?
A: Switching regulator turns on/off Power FET with very high frequency and uses
L/C charge and discharge circuit to do voltage drop. Most of the current
switching designs are Asynchronous mode, which from the technical point of
view, uses Schottky diode for current loop back when power FET is off, and still
consumes very high power as well as heat. AOpen AP5T-3/AX5T-3 implement
high efficient Synchronous switching design that uses MOS FET for the current
loop back and synchronous with the major Power FET (One is on, the other will
be off.). The temperature is less than 36 degree C compared with 57 degree of
Asynchronous design.
Q: What is RTC Wake Up Timer (Alarm)?
A: RTC (Real Time Clock) is adevicelikeelectronic watch,andkeepthe date/time
of the computer system running. The Wake Up Timer is more like an alarm,
which wakes up and powers on your system at a pre-defined time for specific
application.It canbesettowakeupeverydayoronspecificdatewithinamonth.
The date/time accurate is second. To set the date/time, go into BIOS setup,
Power Management RTC Wake Up Timer, select Enable. RTC is a standard
device of all the mainboard, but Wake Up Timer is not a standard design,
AOpen AX5T/AX58 support RTC Wake Up Timer.
B-14
Page 15

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is LDCM (LAN Desktop Client Manager)?
A: This is a software of Intel. The major goal is to provide an easy way for
corporate network administrator to monitor the status of all the clients
(workstation). You need at least DMI BIOS for LDCM. AOpen BIOS is also DMI
readybutunfortunately,IntelLDCMneedsIntelnetworkcardtoworkproperly.It
is obviously not suitable for home user to pay LDCM extra cost.
Q: What is ADM (Advanced Desktop Manager)?
A: This is a desktop clientand server management software developed by AOpen.
It is similar as Intel LDCM with some improvement. ADM is not only for
corporate network management, it can also be used as system status
monitoring utility, for example, CPU fan, thermal and system voltage
monitoring.
Features ADM2.0 LDCM 3.0
VGA card
Network card
Support DMI BIOS 2.0
Support Win95
Support Win NT
Real-Time CPU/Memory
Utilization Monitoring
Multi-Machine
Monitoring on One Screen
Remote Management
Protocol
Standard SNMP Trap
Remote File Transfer
No limitation Only ATI
No limitation Only Intel
Yes Yes
Yes Yes
No (will besupportedon
ADM 2.1)
Yes No
Yes No
Standard SNMP
protocol
Yes (so that can work
with standard software
such as HP Open View)
No Yes
Yes
Intel proprietary RAP
protocol
No
B-15
Page 16

Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Does AOpen mainboard support Fan/Voltage/Thermal monitoring and
protection?
A: Yes, please check following table.
Features AP5T-3 AX6F-1 AX5T-3 AX5T-3.1
Synchronous Switching
Regulator
3.3V and CPU Vcore
Over-current protection
CPU Thermal Protection Yes Yes Yes Yes
CPU Fan Monitoring No No No Yes
System Voltage
Monitoring
Q: What is the difference between AX5T-1, AX5T-2 and AX5T-3?
A: AX5T-2 fixes the ATX power supply to off state when you first time install your
AX5T mainboard. AX5T-3 Implements switching regulator and many other
features.
Note that they all have 75MHz and AX5T-3 has 83.3MHz jumper setting. The
user set clock to 75MHz/83.3MHz is taking his own risk, and is probably to have
system unstable behavior.
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes No Yes Yes
No No Yes Yes
Item AX5T-3.1 AX5T-3 AX5T-2 AX5T-1
75MHz jumper setting Yes Yes Yes Yes
83.3MHz jumper setting Yes Yes No No
ATX Power Supply initial
state
Onboard Power Regulator Synchronous
3.3V and CPU Vcore
Over-current protection
CPU Thermal Protection Yes Yes No No
CPU Fan monitoring Yes No No No
System Voltage
Monitoring
B-16
Off Off Off Random
Synchronous
Switching
Yes Yes No No
Yes Yes No No
Switching
Linear Linear
 Loading...
Loading...