Page 1

a
Getting Started With
SHARC
Revision 3.0, April 2010
®
Processors
Part Number
82-003536-01
Analog Devices, Inc.
One Technology Way
Norwood, Mass. 02062-9106
Page 2

Copyright Information
©2010 Analog Devices, Inc., ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. This document
may not be reproduced in any form without prior, express written consent
from Analog Devices, Inc.
Printed in the USA.
Disclaimer
Analog Devices, Inc. reserves the right to change this product without
prior notice. Information furnished by Analog Devices, Inc. is believed to
be accurate and reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog
Devices, Inc. for its use; nor for any infringement of patents or other rights
of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by
implication or otherwise under the patent rights of Analog Devices, Inc.
Trademark and Service Mark Notice
The Analog Devices logo, Blackfin, CROSSCORE, EZ-Extender,
EZ-KIT Lite, SHARC, the SHARC logo, TigerSHARC, and
VisualDSP++ are registered trademarks of Analog Devices, Inc.
EZ-Board is a trademark of Analog Devices, Inc.
All other brand and product names are trademarks or service marks of their
respective owners.
Page 3

CONTENTS
PREFACE
Purpose of This Manual .................................................................. ix
Intended Audience .......................................................................... ix
Manual Contents ............................................................................. x
What’s New in This Manual ............................................................. x
Technical or Customer Support ........................................................ x
Supported SHARC Processors ......................................................... xi
Product Information ...................................................................... xii
Analog Devices Web Site .......................................................... xii
VisualDSP++ Online Documentation ...................................... xiii
Technical Library CD .............................................................. xiii
INTRODUCTION TO SHARC PROCESSORS
What are SHARC Processors? ........................................................ 1-1
SHARC Applications ............................................................... 1-2
Architecture Overview ............................................................. 1-3
Super Harvard Architecture ................................................. 1-3
Common Architectural Features .......................................... 1-4
Four Generations of SHARC Processors ................................... 1-5
Getting Started With SHARC Processors iii
Page 4

Contents
Processor Peripherals and Performance .......................................... 1-8
Performance ............................................................................ 1-8
THE EVALUATION PROCESS
Evaluation Tools ........................................................................... 2-1
Selecting Software Development Tools ..................................... 2-2
VisualDSP++ From Analog Devices ..................................... 2-2
Platform and Processor Support ...................................... 2-4
Getting Help and Staying Up to Date ............................. 2-9
Analog Devices Tools Product Line ............................... 2-10
Embedded Processors and DSPs .................................... 2-11
Software Modules ............................................................. 2-12
Selecting Hardware Development Tools ................................. 2-12
Evaluation Systems ........................................................... 2-12
EZ-KIT Lite ................................................................. 2-12
EZ-Board ..................................................................... 2-13
ADSP-21489 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices .......... 2-14
ADSP-21479 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices .......... 2-16
ADSP-21469 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices .......... 2-18
ADSP-21375 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices .......... 2-21
ADSP-21371 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices .......... 2-24
ADSP-21369 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices .......... 2-27
ADSP-21364 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices .......... 2-30
ADSP-21262 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices .......... 2-33
iv Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 5

Contents
EZ-Boards ........................................................................ 2-36
ADSP-21489 EZ-Board From Analog Devices ............... 2-37
ADSP-21479 EZ-Board From Analog Devices ............... 2-40
ADSP-21469 EZ-Board From Analog Devices ............... 2-43
Debug Agent ................................................................. 2-46
EZ-Extender Daughter Boards ....................................... 2-47
SHARC USB EZ-Extender ............................................ 2-47
SHARC EZ-Extender .................................................... 2-49
SHARC Audio EZ-Extender .......................................... 2-51
USB EZ-Extender for Blackfin and SHARC .................. 2-53
JTAG Emulators ............................................................... 2-54
High Performance USB 2.0 JTAG Emulator .................. 2-55
USB 1.1 JTAG Emulator ............................................... 2-58
Selecting the Right Combination of Tools .............................. 2-60
Scenario 1 ......................................................................... 2-60
Scenario 2 ......................................................................... 2-61
Software Development on SHARC Processors ........................ 2-61
SUPPORT OPTIONS
Available Support .......................................................................... 3-1
Analog Devices Web Site ......................................................... 3-1
Processor and Development Tools Selection Information ...... 3-2
Getting Started Information ................................................ 3-2
Applications Notes, EE-Notes, and Other Articles ............... 3-3
Communities-Related Information ...................................... 3-3
Getting Started With SHARC Processors v
Page 6

Contents
Platform-Related Information ............................................. 3-3
Visual Learning and Development (VLD) ........................... 3-4
Workshops and Seminars ......................................................... 3-4
SHARC Processor Workshops ............................................. 3-4
SHARC Processor Seminars ................................................ 3-5
Processor Documentation ........................................................ 3-5
SHARC Processor Manuals ................................................. 3-5
Hardware Reference Manuals .......................................... 3-6
Programming Reference .................................................. 3-6
Data Sheets ........................................................................ 3-7
Anomalies Lists for Processors and Tools ............................ 3-7
BSDL Files ......................................................................... 3-8
IBIS Models ....................................................................... 3-8
CROSSCORE Tools Documentation ...................................... 3-8
VisualDSP++ Documentation ............................................. 3-9
VisualDSP++ Getting Started Guide ............................... 3-9
VisualDSP++ User’s Guide ............................................ 3-10
VisualDSP++ C/C++ Compiler Library Manual for
SHARC Processors ..................................................... 3-10
VisualDSP++ Runtime Library Manual for SHARC
Processors .................................................................. 3-10
VisualDSP++ Assembler and Preprocessor Manual ......... 3-10
VisualDSP++ Linker and Utilities Manual ..................... 3-11
VisualDSP++ Kernel (VDK) User’s Guide ..................... 3-11
vi Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 7

Contents
VisualDSP++ Loader and Utilities Manual ..................... 3-11
VisualDSP++ Example Programs ................................... 3-12
Hardware Tools Documentation ........................................ 3-13
SHARC EZ-KIT Lite Evaluation System Manual ........... 3-13
SHARC EZ-Board Evaluation System Manual ............... 3-14
SHARC EZ-Extender Manual ....................................... 3-14
VisualDSP++ Help ............................................................ 3-14
Find a Third Party—Faster Time to Market ........................... 3-15
EngineerZone ........................................................................ 3-15
Social Networking Web Sites ................................................. 3-16
MyAnalog.com ...................................................................... 3-16
INDEX
Getting Started With SHARC Processors vii
Page 8

Contents
viii Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 9

PREFACE
Thank you for your interest in the SHARC® family of processors from
Analog Devices, Inc.
Purpose of This Manual
Getting Started With SHARC Processors provides you with information
about the evaluation process, Analog Devices tools, training, documentation, and other informational resources to assist you in the evaluation of
SHARC processors. This manual describes the resources available to help
you evaluate and design the SHARC processors into your final system.
For engineers already using SHARC processors in their designs, this guide
provides resources and pointers to help transition your system to take
advantage of the newest generation of processors. For detailed descriptions
of processor internal architectures, refer to the applicable hardware reference manual. For detailed descriptions of processor software, refer to the
applicable programming reference manual. A complete list of documents
that support your product can be found at the Analog Devices Web site at:
http://www.analog.com/processors/technical_library
Intended Audience
The primary audiences for this guide are system designers, programmers,
and hardware engineers who want to learn whether a specific SHARC
processor matches design requirements for new applications.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors ix
Page 10

Manual Contents
Manual Contents
This manual consists of:
• Chapter 1, “Introduction to SHARC Processors”
This chapter briefly describes the processor architecture, available
models, and processor features.
• Chapter 2, “The Evaluation Process”
This chapter focuses on available software and hardware tools.
• Chapter 3, “Support Options”
This chapter describes support (documentation, training, and
more) available during the evaluation and development processes.
What’s New in This Manual
This is Revision 3.0 of Getting Started With SHARC Processors. Changes to
this book from Revision 2.0 include:
• Addition of fourth generation SHARC products
• Corrections of typographic errors and reported document errata
Technical or Customer Support
You can reach Analog Devices, Inc. Customer Support in the following
ways:
• Visit the Embedded Processing and DSP products Web site at:
http://www.analog.com/processors/technical_support
• E-mail tools questions to:
processor.tools.support@analog.com
x Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 11

Preface
• E-mail processor questions to:
processor.support@analog.com (World wide support)
processor.europe@analog.com (Europe support)
processor.china@analog.com (China support)
• Phone questions to 1-800-ANALOGD
• Contact your Analog Devices, Inc. local sales office or authorized
distributor
Supported SHARC Processors
The name “SHARC” refers to a family of high performance, 32-bit,
floating-point processors that can be used in speech, sound, graphics, and
imaging applications. VisualDSP++® currently supports the following
SHARC processors:
ADSP-21020 ADSP-21060 ADSP-21061 ADSP-21062
ADSP-21065L ADSP-21160 ADSP-21161 ADSP-21261
ADSP-21262 ADSP-21266 ADSP-21362 ADSP-21363
ADSP-21364 ADSP-21365 ADSP-21366 ADSP-21367
ADSP-21368 ADSP-21369 ADSP-21371 ADSP-21375
ADSP-21462 ADSP-21465 ADSP-21467 ADSP-21469
ADSP-21478 ADSP-21479 ADSP-21483 ADSP-21486
ADSP-21487 ADSP-21488 ADSP-21489
The list of supported SHARC processors is subject to change. For a complete and up-to-date listing of SHARC processors refer to:
http://www.analog.com/sharc
Getting Started With SHARC Processors xi
Page 12

Product Information
Product Information
Product information can be obtained from the Analog Devices Web site,
VisualDSP++ online Help system, and a technical library CD.
Analog Devices Web Site
The Analog Devices Web site, www.analog.com, provides information
about a broad range of products—analog integrated circuits, amplifiers,
converters, and digital signal processors.
To access a complete technical library for each processor family, go to
http://www.analog.com/processors/technical_library. The manuals
selection opens a list of current manuals related to the product as well as a
link to the previous revisions of the manuals. When locating your manual
title, note a possible errata check mark next to the title that leads to the
current correction report against the manual.
Also note, MyAnalog.com is a free feature of the Analog Devices Web site
that allows customization of a Web page to display only the latest information about products you are interested in. You can choose to receive
weekly e-mail notifications containing updates to the Web pages that meet
your interests, including documentation errata against all manuals.
MyAnalog.com provides access to books, application notes, data sheets,
code examples, and more.
MyAnalog.com to sign up. If you are a registered user, just log on.
Visit
Your user name is your e-mail address.
xii Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 13
Preface
VisualDSP++ Online Documentation
Online documentation comprises the VisualDSP++ Help system, software
tools manuals, hardware tools manuals, processor manuals, Dinkum
Abridged C++ library, and FLEXnet License Tools software documentation. You can search easily across the entire VisualDSP++ documentation
set for any topic of interest.
For easy printing, supplementary Portable Documentation Format (.pdf)
files for all manuals are provided on the VisualDSP++ installation CD.
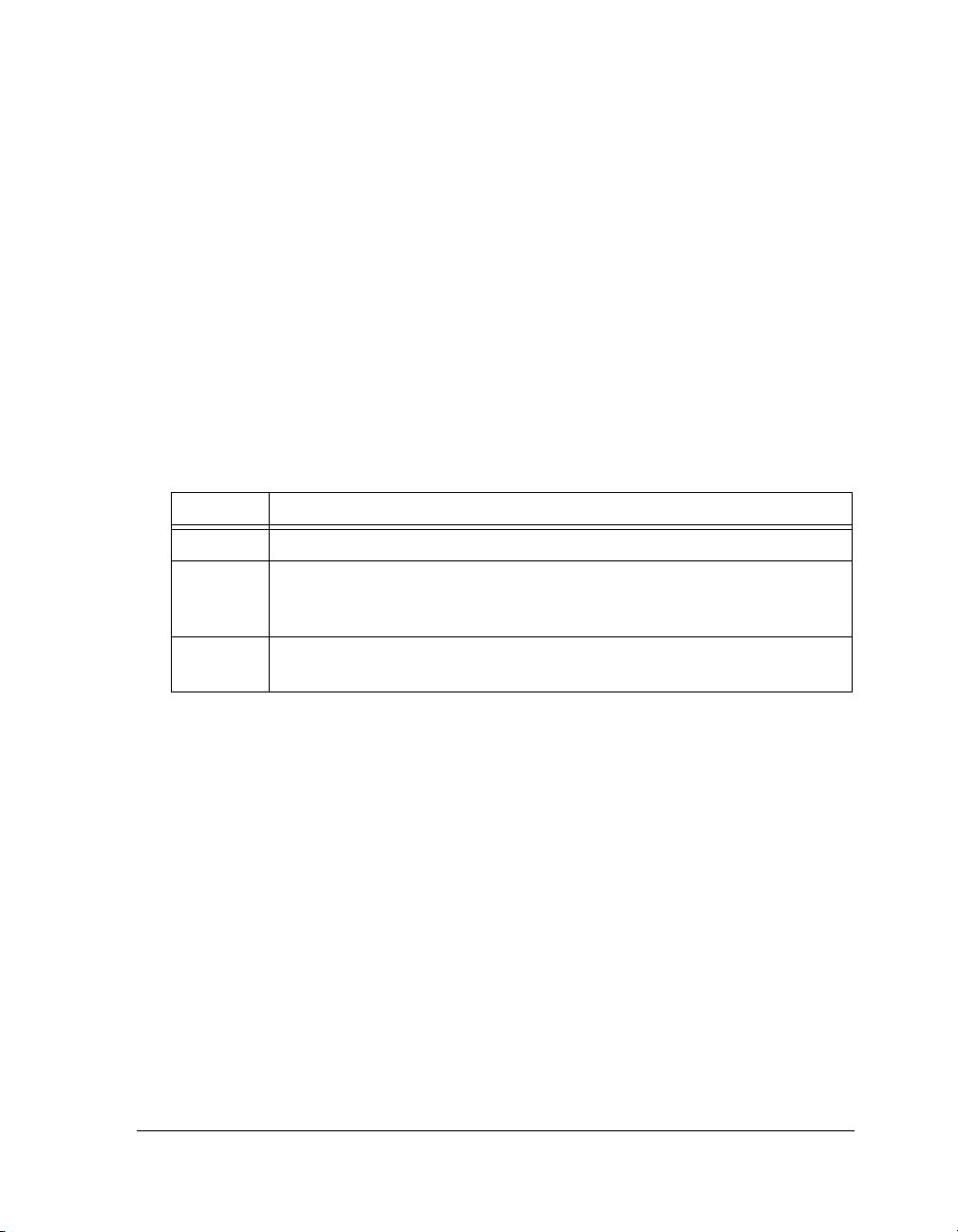
Each documentation file type is described as follows.
File Description
.chm Help system files and manuals in Microsoft® help format
.htm or
.html
.pdf VisualDSP++ and processor manuals in PDF format. Viewing and printing the
Dinkum Abridged C++ library and FLEXnet License Tools software documentation. Viewing and printing the .html files requires a browser, such as Internet
Explorer 6.0 (or higher).
.pdf files requires a PDF reader, such as Adobe Acrobat Reader (4.0 or higher).
Technical Library CD
The technical library CD contains seminar materials, product highlights, a
selection guide, and documentation files of processor manuals,
VisualDSP++ software manuals, and hardware tools manuals for the following processor families: Blackfin®, SHARC, TigerSHARC®,
ADSP-218x, and ADSP-219x.
To order the technical library CD, go to http://www.analog.com/proces-
sors/technical_library
processor, click the request CD check mark, and fill out the order form.
, navigate to the manuals page for your
Getting Started With SHARC Processors xiii
Page 14

Product Information
Data sheets, which can be downloaded from the Analog Devices Web site,
change rapidly, and therefore are not included on the technical library
CD. Technical manuals change periodically. Check the Web site for the
latest manual revisions and associated documentation errata.
xiv Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 15

1 INTRODUCTION TO SHARC
PROCESSORS
This chapter briefly describes the SHARC processor’s architecture and key
features and compares available models.
Topics include:
• “What are SHARC Processors?” on page 1-1
• “Four Generations of SHARC Processors” on page 1-5
What are SHARC Processors?
SHARC is the name of a family of high performance 32-bit floating-point
processors based on a Super Harvard Architecture. SHARC processors
dominate the floating-point digital signal processing market, delivering
exceptional core and memory performance complemented by outstanding
I/O throughput. The industry standard SHARC family makes floating-point processing economical for applications where performance and
dynamic range are key considerations such as home, professional, and
automotive audio, medical, and industrial and instrumentation products.
The SHARC processor portfolio currently consists of four generations of
products providing code-compatible solutions, ranging from entry-level
products priced at less than $10 to the highest performance products
offering fixed- and floating-point computational power to 450 MHz/2700
MFLOPs. Regardless of the specific product choice, all SHARC processors
provide a common set of features and functionality usable across many
signal processing markets and applications. This baseline functionality
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 1-1
Page 16

What are SHARC Processors?
enables the SHARC user to leverage legacy code and design experience,
while transitioning to higher-performance, more highly-integrated
SHARC products.
By integrating on-chip, single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD) processing elements, SDRAM, and I/O peripherals, SHARC processors deliver
breakthrough signal processing performance.
SHARC Applications
The combination of a high performance core surrounded by appropriate
peripherals, a large software library, and award-winning development tools
makes SHARC processors the ideal choice for audio and broad market
processor applications. Here are some applications:
• Home theater/digital home applications. The ADSP-21266,
ADSP-21365, ADSP-21366, ADSP-21367, ADSP-21467,
ADSP-21483, ADSP-21486, and ADSP-21487 processors enable
highly efficient software implementations of audio decode and
postprocessing algorithms, such as Dolby® Digital, Dolby Digital
EX, DTS-ES Discrete 6.1, DTS-ES Matrix 6.1, DTS 96/24™ 5.1,
DTS-HD, DTS Express, MPEG-2 AAC LC, MPEG-2 BC 2ch,
Dolby Pro Logic II, Dolby Pro Logic 2x, Dolby True HD, DTS
Neo:6, DDPlus DCV, Neural Audio, Audyssey room equalization,
and WMA Pro. Libraries of all standard—and many proprietary—
audio algorithms reside in on-chip ROM, eliminating the need for
external ROM.
• Professional audio applications. A number of third generation
(ADSP-2136x) and fourth generation (ADSP-2146x) SHARC processors are well-suited for professional audio applications requiring
high processing power and advanced on-chip peripherals such as
sample rate conversion, S/PDIF transmitter/receiver, and BGA and
LQFP package options.
1-2 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 17

• Automotive audio applications. The ADSP-21362, ADSP-21365,
ADSP-21369, ADSP-21371, ADSP-21462, ADSP-21465,
ADSP-21469, ADSP-21472, ADSP-21475, and ADSP-21479
processors, with integration of sample-rate conversion, DTCP
cipher, precision clock generators, and serial ports, are ideal choices
for new multichannel automotive audio designs.
• Broad market use. SHARC processors are available in commercial,
industrial, and automotive temperature grade packages. They are
used in a wide variety of signal processing applications, providing
up to 450 MHz performance in a single-instruction, multiple-data
architecture (SIMD). Applications include imaging, medical
devices, communications, military, test equipment, 3-D graphics,
speech recognition, and motor control.
Architecture Overview
Introduction to SHARC Processors
This section describes architectural features of the SHARC processor.
Super Harvard Architecture
The 32-bit floating-point SHARC processors from Analog Devices are
based on a Super Harvard Architecture that balances exceptional core and
memory performance with outstanding I/O throughput capabilities. This
architecture extends the original concepts of separate program and data
memory buses by adding an I/O processor with its associated dedicated
buses.
In addition to satisfying the demands of the most computationally-intensive, real-time signal processing applications, SHARC processors integrate
large memory arrays and application-specific peripherals designed to simplify product development and reduce time to market.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 1-3
Page 18

What are SHARC Processors?
Common Architectural Features
SHARC processors share the following architectural features.
• 32/40-bit IEEE floating-point math
• 32-bit fixed-point multipliers with 64-bit product and 80-bit accumulation
• No arithmetic pipeline. All computations are single cycle.
• Circular buffer addressing supported in hardware
• Sixteen address pointers supporting 16 circular buffers
• Six nested levels of zero-overhead looping in hardware
• Rich algebraic assembly language syntax
• Conditional arithmetic, bit manipulation, divide and square root,
bit field deposit and extract supported by instruction set
• Zero-overhead background transfers at full clock rate without processor intervention
In the core, every instruction can execute in a single cycle. The buses and
instruction cache provide rapid unimpeded data flow to the core to maintain the execution rate.
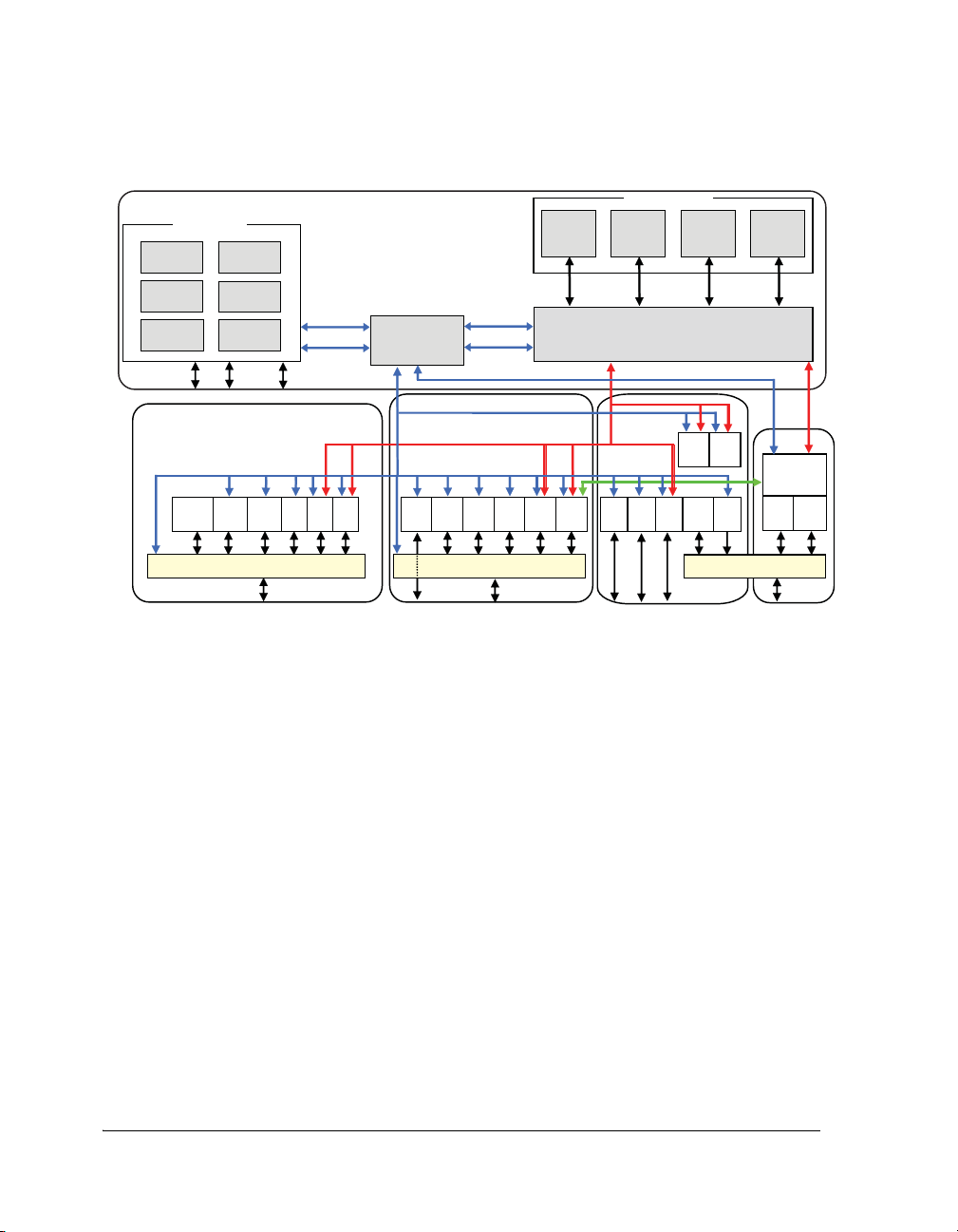
Figure 1-1 shows a detailed block diagram of a single core SHARC 32-bit
processor and the I/O processor (IOP). It illustrates the following architectural features:
• Two processing elements (PEx and PEy), each containing 32-bit
IEEE floating-point computation units—multiplier, arithmetic
logic unit (ALU), shifter, and data register file
• Program sequencer with related instruction cache, interval timer,
and data address generators (DAG1 and DAG2)
1-4 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 19

Introduction to SHARC Processors
• An SDRAM controller that provides an interface to as many as four
separate banks of industry-standard SDRAM devices
• Up to a maximum of 5M bits of on-chip SRAM and up to 4M bits
of on-chip, mask-programmable ROM
• Input/output processor (IOP) with integrated direct memory
access (DMA) controller, serial peripheral interface (SPI) compatible port, and serial ports (SPORTs) for point-to-point
multiprocessor communications
• A variety of audio-centric peripheral modules including a
Sony/Philips digital interface (S/PDIF), sample rate converter
(SRC), and pulse width modulation (PWM)
• JTAG test access port for emulation
Figure 1-1 also shows the three on-chip buses of the
ADSP-21472/21475/21479 processors: the PM bus, DM bus, and I/O
bus. The PM bus provides access to instructions or data. During a single
cycle, these buses let the processor access two data operands from memory,
access an instruction (from cache), and perform a DMA transfer. In addition, Figure 1-1 shows the asychronous memory interface available on the
ADSP-2147x processors.
Four Generations of SHARC Processors
The SHARC architecture has a long history in the floating-point processor market. While architectural enhancements have been made with each
successive processor generation, the common traits of exceptional floating-point performance, matched to high-bandwidth memory and I/O
transfers, remains. All four generations of SHARC processors are still in
production, offering a variety of code-compatible options to meet a wide
array of price, performance, and footprint requirements.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 1-5
Page 20
What are SHARC Processors?
Internal Memory I/F
Block 0
RAM/ROM
B0D
64-BIT
Instruction
Cache
5Stage
Sequencer
PEx PEy
PMD
64-BIT
IOD0 32-BIT
EPD BUS 64-BIT
Core Bus
Cross Bar
S/PDIF
Tx/Rx
PCG
A
-
D
DPI Routing/Pins
SPI/B UART
Block 1
RAM/ROM
Block 2
RAM
Block 3
RAM
AMI
SDRAM
CTL
EP
External Port Pin MUX
TIMER
1
-
0
SPORT
7
-
0
ASRC
3-0
PWM
3
-
0
DAG1/2
Core
Timer
PDAP/
IDP
7
-
0
TWI
IOD0 BUS
DTCP/
MTM
PCG
C
-
D
PERIPHERAL BUS
32-BIT
CORE
FLAGS/
PWM3
-
1
JTAG
Internal Memory
DMD
64-BIT
PMD 64-BIT
CORE
FLAGS
IOD1
32-BIT
PERIPHERAL BUS
B1D
64-BIT
B2D
64-BIT
B3D
64-BIT
DPI Peripherals
DAI Peripherals
Peripherals
External
Port
SIMD Core
S
THERMAL
DIODE
FFT
FIR
IIR
MLB
SPEP BUS
DMD
64-BIT
FLAGx/IRQx/
TMREXP
WDT
RTC
SHIFT
REG
DAI Routing/Pins
Figure 1-1. ADSP-2147x Processor Block Diagram
First generation SHARC products offer performance of up to
66 MHz/198 MFLOPS and form the cornerstone of the SHARC processor family. Their easy-to-use instruction set architecture that supports
both 32-bit fixed-point and 32/40-bit floating-point data formats, combined with large memory arrays and sophisticated communications ports,
make them suitable for a wide array of parallel processing applications
including consumer audio, medical imaging, military, industrial, and
instrumentation.
Second generation SHARC products double the level of signal processing
performance (100 MHz/600 MFLOPS) by utilizing a single-instruction,
multiple-data (SIMD) architecture. This hardware extension doubles the
number of computational resources available to the system programmer.
Second generation products contain dual multipliers, ALUs, shifters, and
data register files, significantly increasing overall system performance in a
1-6 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 21

Introduction to SHARC Processors
variety of applications. This capability is especially relevant in consumer,
automotive, and professional audio where the algorithms related to stereo
channel processing can effectively utilize the SIMD architecture.
Third generation SHARC products employ an enhanced SIMD architecture that extends CPU performance to an impressive 400 MHz/2.4
GFLOPS. These products also integrate a variety of ROM configurations
and audio-centric peripherals designed to decrease time to market and
reduce the overall bill of materials costs. Third generation SHARC audio
processors feature a high level of integrated on-chip peripherals, such as
multichannel audio surround sound decoders and postprocessing algorithms, S/PDIF transmitter/receiver, high performance asynchronous
sample rate conversion, PWM channels, code security, and DTCP cipher
for protection of digital data in automobiles. A number of third generation processors are also pin compatible for use with a single hardware
platform. This increased level of performance and peripheral integration
allow third generation SHARC processors to be considered as single chip
solutions for a variety of audio markets.
Fourth generation SHARC products not only increase the core performance to an industry-leading 450 MHz/2.7 GFLOPS but also boost the
performance with the addition of accelerator blocks implementing the
FIR, IIR, and FFT functions to off-load core activities from being consumed by filter processing. Fourth generation SHARC processors
integrate some of the highest memory on-chip RAM with a capacity of
5M bits. Extra memory capacity is further enhanced with the innovative
VISA (variable instruction set architecture) mode where programs can save
up to 30% of code size by reducing the opcodes for many instructions. For
industrial and automotive applications, fourth generation processors also
incorporate a thermal diode to allow customers the flexibility to operate in
higher ambient operating temperature conditions without sacrificing on
overall performance. DTCP cipher for protection of digital data in automotive applications is also integrated in automotive parts.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 1-7
Page 22

Processor Peripherals and Performance
Integration of peripherals continue with serial ports, SPI ports, S/PDIF
Tx/Rx, and an 8-channel asynchronous sample rate converter block. The
fourth generation SHARC allows data from the serial ports to be directly
transferred to external memory by the DMA controller, again preserving
internal memory space for code and data. The fourth generation processor
also incorporates link ports that allow processor-to-processor communication for data movement. Some fourth generation SHARC processors also
integrate real-time clock (RTC) and watchdog timer functionality. In
addition, a number of fourth generation processors are also pin compatible for use with a single hardware platform.
Each SHARC processor provides unique capabilities, while being code
compatible with previous generations of SHARC devices, so legacy code is
easily ported to the newer products. Table 1-1, Table 1-2, Table 1-3,
Table 1-4, and Table 1-5 list key SHARC processor specifications.
more information, view the SHARC processor selection table online at the
Analog Devices Web site at:
For
http://www.analog.com/sharc
Processor Peripherals and Performance
SHARC processors represent a class of devices that combine an extremely
capable single-instruction, multiple-data (SIMD) processor engine with
features like core timers, general-purpose timers, UARTs, and SPI ports.
In addition to advanced peripherals, SHARC processors use a software
programmable, on-chip phase lock loop (PLL) that allows software control
during runtime of core and peripheral clock of the SHARC processors.
Performance
Real-time signal processing tasks are I/O and computationally intensive.
In addition to high speed math units and single cycle instruction
1-8 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 23

Introduction to SHARC Processors
execution (including single cycle multiply accumulates [MACs]), SHARC
processors are designed for maximum I/O and memory access bandwidth.
This balance of core speed, memory integration, and I/O bandwidth
achieves the sustained performance critical to real-time applications.
Table 1-1. ADSP-2126x SHARC Processor Specifications
ADSP-21261 ADSP-21262 ADSP-21266
Frequency (MHz) 150 200 200
On-Chip RAM 1M bit 2M bit 2M bit
On-Chip ROM 3M bit 4M bit 4M bit
SRC 0 0 0
PWM 0 0 0
UART 0 0 0
SPI 1 1 1
SPDIF 0 0 0
TWI 0 0 0
Timer 3 3 3
SPORT 4 6 6
SRU 1 1 1
DTCP 0 0 0
PCG 2 2 2
Temp. Grade –40°C to +85°C –40°C to +85°C –40°C to +105°C
Execution from Ext. Memory? No No No
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 1-9
Page 24
Processor Peripherals and Performance
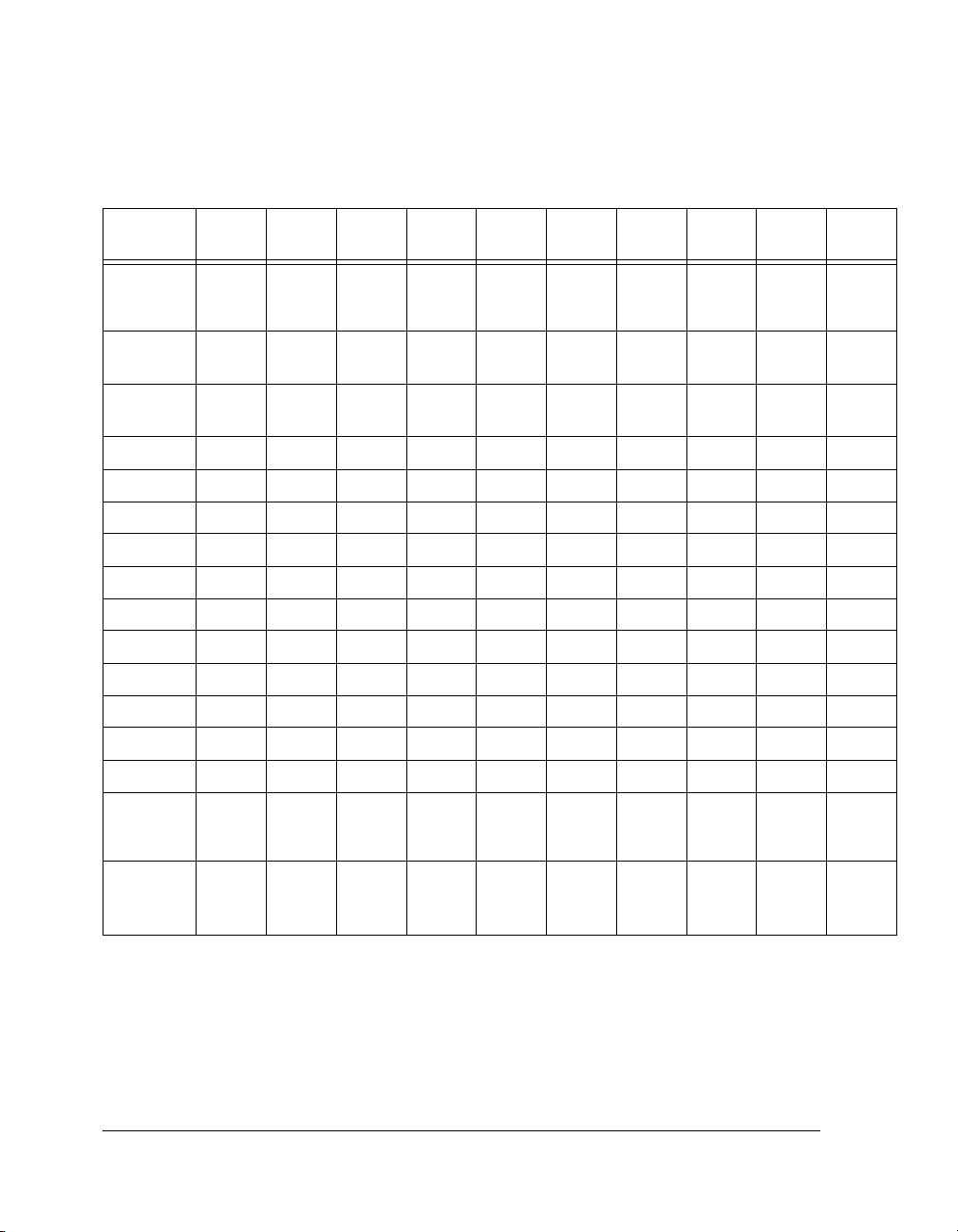
Table 1-2. ADSP-2136x/ADSP-2137x SHARC Processor Specifications
Frequency
(MHz)
On-Chip
RAM
On-Chip
ROM
SRC
PWM
UART
SPI
SPDIF
TWI
Timer
SPORT
SRU
DTCP
PCG
Te m p.
Grade
Execution
from Ext.
Memory?
ADSP21362
333 333 333 333 333 266,
3M bit 3M bit 3M bit 3M bit 3M bit 2M bit 2M bit 2M bit 1M bit 0.5M bit
4M bit 4M bit 4M bit 4M bit 4M bit 6M bit 6M bit 6M bit 4M bit 2M bit
–128dB 0 –140dB –128dB –128dB –128dB –140dB –128dB 0 0
1111111111
1111122211
2221122222
1111111110
0000011111
3333333322
6666688884
1111111111
1001100000
2222244444
–40°C
to
+85°C
No No No No No No No No Yes Yes
ADSP21363
–40°C
to
+105°C
ADSP21364
–40°C
to
+105°C
ADSP21365
–40°C
to
+85°C
ADSP21366
–40°C
to
+85°C
ADSP21367
333,
400
–40°C
to
+85°C
ADSP21368
333,
400
–40°C
to
+85°C
ADSP21369
266,
333,
400
–40°C
to
+85°C
ADSP21371
266 266
0°C to
+70°C
ADSP21375
0°C to
+70°C
1-10 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 25
Introduction to SHARC Processors
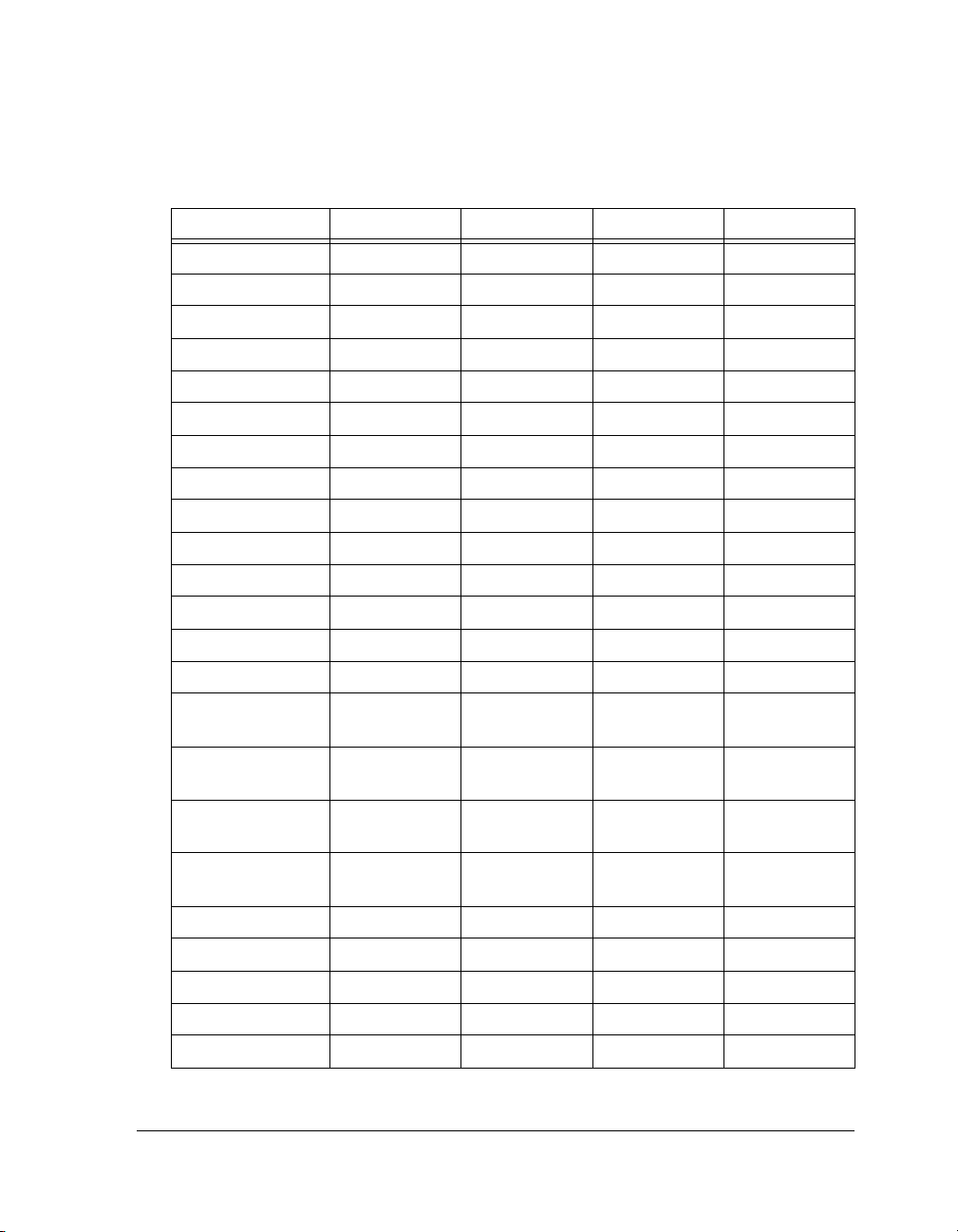
Table 1-3. ADSP-2146x SHARC Processor Specifications
ADSP-21462 ADSP-21465 ADSP-21467 ADSP-21469
Frequency (MHz) 400 400 450 450
On-Chip RAM 5M bit 5M bit 5M bit 5M bit
On-Chip ROM 0M bit 4M bit 4M bit 0M bit
SRC –128dB –128dB –128dB –128dB
PWM1111
UART1111
SPI 2222
SPDIF1111
TWI1111
Timer2222
SPORT8888
SRU 1111
DTCP1100
PCG4444
Tem p. Gr ade at
450 MHz
Tem p. Gr ade at
400 MHz
Execution from Ext.
Memory?
MLB
(Media Local Bus)
FIR Accelerators Yes Yes Yes Yes
IIR Accelerators Yes Yes Yes Yes
FFT Accelerators Yes Yes Yes Yes
Link Ports2222
Thermal Diode Yes Yes Yes Yes
— — 0°C to +70°C 0°C to +70°C
–40°C to +85°C –40°C to +85°C –40°C to +85°C –40°C to +85°C
Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes No No
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 1-11
Page 26

Processor Peripherals and Performance
Table 1-3. ADSP-2146x SHARC Processor Specifications (Cont’d)
ADSP-21462 ADSP-21465 ADSP-21467 ADSP-21469
DDR2 Interface Yes Yes Yes Yes
VISA Yes Yes Yes Yes
1-12 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 27
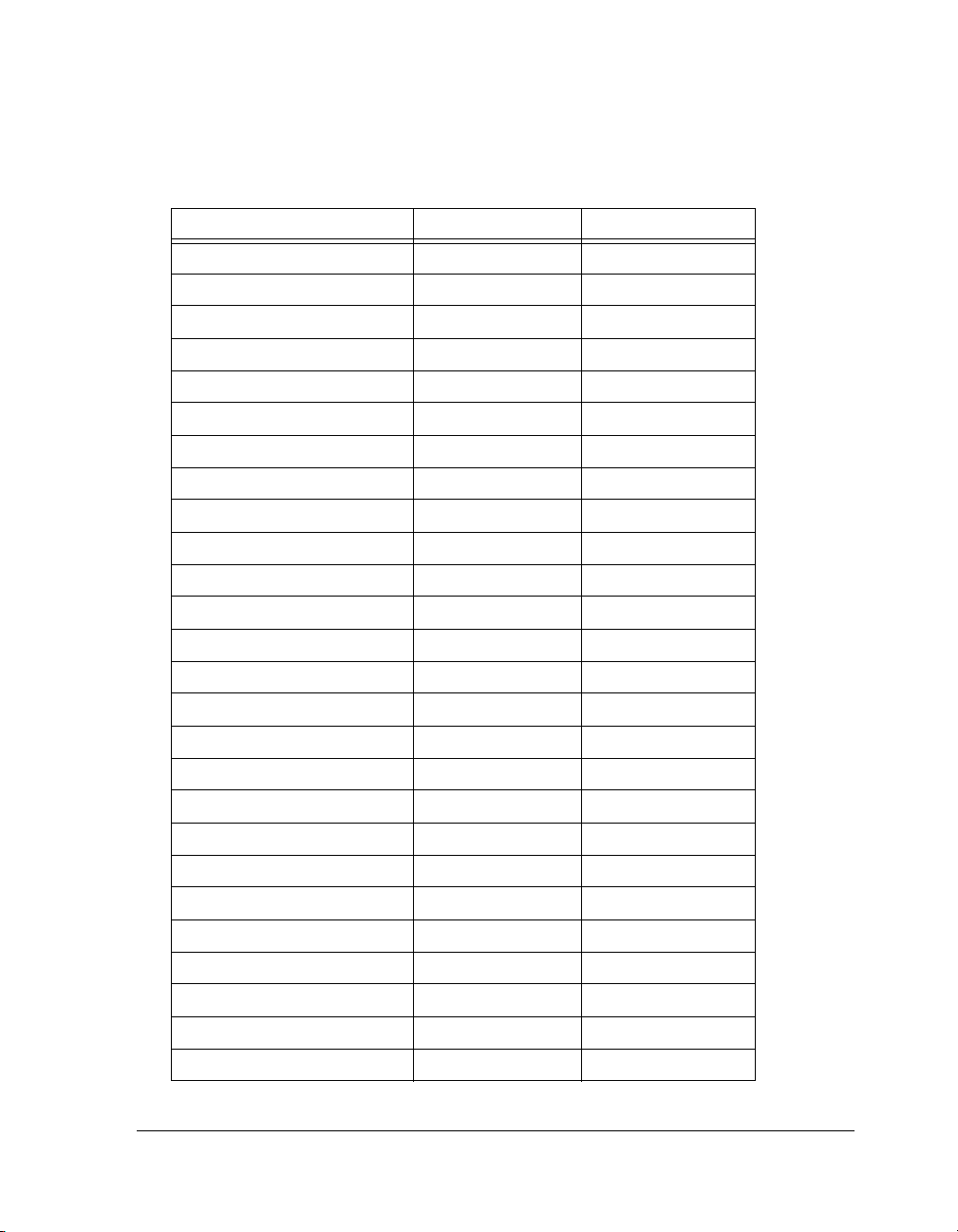
Introduction to SHARC Processors
Table 1-4. ADSP-2147x SHARC Processor Specifications
ADSP-21478 ADSP-21479
Frequency (MHz) 266 266
On-Chip RAM 3M bit 5M bit
On-Chip ROM 0M bit 0M bit
SRC –128dB –128dB
PWM 4 4
UART 1 1
SPI 2 2
SPDIF 1 1
TWI 1 1
Timer 2 2
SPORT 8 8
SRU 1 1
DTCP 0 0
PCG 4 4
Temp. Grade 0°C to +70°C –40°C to +105°C
Execution from Ext. Memory? Yes Yes
MLB (Media Local Bus) No No
FIR Accelerators Yes Yes
IIR Accelerators Yes Yes
FFT Accelerators Yes Yes
Thermal Diode No No
SDRAM Interface Yes Yes
VISA Yes Yes
WDT Yes Yes
RTC Yes Yes
Shift Register Yes Yes
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 1-13
Page 28

Processor Peripherals and Performance
Table 1-4. ADSP-2147x SHARC Processor Specifications (Cont’d)
ADSP-21478 ADSP-21479
AMI Interface 16 bit Yes Yes
SDRAM Bus Width 16 bit 16 bit
IDP/PDAP Yes Yes
1-14 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 29

Introduction to SHARC Processors
Table 1-5. ADSP-2148x SHARC Processor Specifications
ADSP-21483 ADSP-21486 ADSP-21487 ADSP-21488 ADSP-21489
Frequency (MHz)
On-Chip RAM
On-Chip ROM
SRC
PWM
UART
SPI
SPDIF
TWI
Timer
SPORT
SRU
PCG
Tem p. Gr ade
Execution from Ext.
Memory?
MLB (Media Local Bus)
FIR Accelerators
IIR Accelerators
FFT Accelerators
WDT
AMI Interface 16 bit
SDRAM Bus Width
IDP/PDAP
400 400 400 400 400
3M bit 5M bit 5M bit 3M bit 5M bit
4M bit 4M bit 4M bit 0M bit 0M bit
–140dB –128dB –128dB –128dB –128dB
44444
11111
22222
11111
11111
33333
88888
11111
44444
–40°C to
+85°C
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
16 bit 16 bit 16 bit 16 bit 16 bit
Yes Yes Yes Yes Yes
–40°C to
+105°C
–40°C to
+85°C
–40°C to
+85°C
–40°C to
+85°C
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 1-15
Page 30

Processor Peripherals and Performance
1-16 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 31

2 THE EVALUATION PROCESS
This chapter describes the available software and hardware tools needed to
evaluate SHARC processors and develop application programs.
This chapter introduces the software and hardware evaluation tools that
are currently available, including:
• “Selecting Software Development Tools” on page 2-2
• “Selecting the Right Combination of Tools” on page 2-60
Evaluation Tools
This section examines the process through which SHARC processor applications are developed. Various tools are used at each stage. Typical
application development occurs over multiple stages.
Most users acquire a set of software development tools first. The software
development tools run on a PC and provide code generation and debug
utilities such as a compiler, assembler, linker, simulator, debugger, and
libraries. For information on selecting appropriate software, see “Selecting
Software Development Tools” on page 2-2.
Optionally, users acquire a hardware tool to begin testing the application
on a SHARC processor. Development boards typically provide expansion
headers, allowing you to prototype basic hardware without customized
user hardware.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-1
Page 32

Evaluation Tools
“Selecting Software Development Tools” provides a summary of the avail-
able software development tools for SHARC processors. Most
development tools available for SHARC processors provide a cycle-accurate simulator which can be used to develop initial algorithms and
applications without the actual hardware.
Selecting Software Development Tools
Because SHARC processors are programmable, software development
tools are required to author software applications. Typical software development tools include a C/C++ compiler, runtime libraries, assembler, and
linker. Emulation, simulation, debugging, and project management capabilities vary, based on the tools vendor. The process of selecting tools is
shown in Figure 2-1.
Currently, one set of software development tools is available for the
SHARC processor architecture: VisualDSP++ 5.0 from Analog Devices.
VisualDSP++ From Analog Devices
VisualDSP++ is an easy-to-install and easy-to-use integrated software
development and debugging environment (IDDE) that enables efficient
management of projects from start to finish from within a single interface.
Because project development and debugging is integrated, you can move
quickly and easily between editing, building, and debugging activities.
Key features include the native C/C++ compiler, advanced graphical plotting tools, statistical profiling, and the VisualDSP++ Kernel (VDK),
which allows a user’s code to be implemented in a more structured and
easier to scale manner. Other features include assembler, linker, libraries,
loader, splitter, cycle-accurate and functional-accurate compiled simulators, emulator support, and more. VisualDSP++ offers programmers a
powerful yet easy-to-use programming tool with flexibility that significantly reduces the time to market.
2-2 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 33

Decide to evaluate SHARC
Build custom hardware
Validate design concept
Purchase EZ-KIT Lite
license (part of VisualDSP++
evaluation license)
Download VisualDSP++
Test Drive
Purchase ADI extender
cards or A/D eval cards
Purchase a full VisualDSP++
license
Design/test/debug system
Emulation
Optional
Evaluation
Simulation
EZ-KIT Lite allows VisualDSP++
tools to work with either JTAG
emulator pod or with included
USB cable directly connected to PC.
Test Drive version of VisualDSP++
- Free
- Simulation only
- 90-day license
- Design and build custom
hardware/firmware/software.
- Purchase JTAG emulator pod.
An evaluation license limits a
user’s programming space.
The Evaluation Process
Figure 2-1. Tool Selection Workflow
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-3
Page 34

Evaluation Tools
Platform and Processor Support
VisualDSP++ supports SHARC processors from Analog Devices. Windows® System 7 (as of VisualDSP++ 5.0 Update 7), Windows® Vista,
Windows® XP, and Windows® 2000 hosts are supported.
Develop High Performance Applications Quickly
At the heart of VisualDSP++ is a robust and powerful C/C++ compiler.
The compiler consistently delivers industry-leading performance on standard benchmarks, ensuring that all but the most performance-demanding
applications can be written entirely in the C language, accelerating development time while maintaining a portable code base. The compiler is
backed by a rich library of signal processing routines, allowing easy access
to hand-coded, optimized implementations of FFTs, FIRs, and so forth.
The ANSI-C compiler is also augmented with popular language extensions and enhancements to make it more amiable to existing code bases.
Examples include GNU GCC extensions and multiple heap support.
A compiler’s mission is to produce correct code, so there are occasions
when the compiler must take a conservative approach to a code sequence
when a more aggressive approach could have been taken if certain constraints could be guaranteed by the programmer. The VisualDSP++
compiler supports a broad range of pragmas that allow the programmer to
better exploit the compiler while maintaining C language neutrality. Just
as important, the compiler has the ability to feed back advisory information to the programmer, offering further improvements to a code
sequence, should the programmer be able to make certain guarantees
about it. This information is displayed seamlessly in the VisualDSP++
main editor window. This removes the black box label that compilers
sometimes have.
Backing the compiler is a powerful assembler and linker technology. Processors from Analog Devices are noted for their intuitive algebraic
assembly language syntax, and the VisualDSP++ assembler extends that
2-4 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 35

The Evaluation Process
ease of use with the ability to import C header files, allowing for symbolic
references into arbitrarily complex C data structures. Binary data can be
included directly into assembly source files, creating an easy way to add
blocks of static data (such as audio samples and bitmaps) to an application. The VisualDSP++ linker is fully multicore and multiprocessor (MP)
aware, allowing for the creation of cross-linked, multi-executable applications in a single pass. Other powerful capabilities of the linker include
dead code and data elimination, code and data overlays, and section spilling (for example, automatic overflow from internal to external memory).
VisualDSP++, when used in combination with ADSP-2146x SHARC processors, is designed to take advantage of the VISA (Variable Instruction
Set Architecture) feature. The code generation tools provide the option to
turn on or off the use of the VISA feature. The user must place code to be
compressed into the correct segment in the linker definition file. Compressed or uncompressed code is then generated by the VisualDSP++ tool
chain without further user effort.
Leverage-Proven Application Infrastructure
VisualDSP++ goes beyond robust code generation tools, providing considerable application infrastructure and middleware out of the box to speed
application development.
The VisualDSP++ kernel (VDK) is a robust, royalty-free, real-time operating system (RTOS) kernel. This pre-emptive multitasking kernel
incorporates state-of-the-art scheduling and resource allocation techniques
tailored specifically for the memory and timing constraints of DSP programming. The kernel facilitates development of performance-structured
applications using frameworks of template files. It provides essential kernel features in a minimal footprint. Features include a fully pre-emptive
scheduler (time slicing and cooperative scheduling are also supported),
thread creation, semaphores, interrupt management, inter-thread messaging, events, and memory management (memory pools and multiple
heaps). In MP environments, MP messaging is also provided.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-5
Page 36

Evaluation Tools
Configuration of these elements is done graphically, with code wizards to
speed the creation of new threads and interrupt handlers. VDK has been
available for multiple releases of VisualDSP++ and is now a key component of products shipping from a number of high-volume vendors.
As embedded applications become increasingly part of the connected
world, the ability to rapidly add reliable USB connectivity to an application can often make or break a development schedule. For SHARC
processors, USB 2.0 device connectivity is provided via an EZ-Extender®
daughter board for the EZ-KIT Lite®/EZ-Board™. (See “SHARC USB
EZ-Extender” on page 2-47.) USB data is sent using the SHARC external
port. Bulk and asynchronous transfer modes are supported out of the box,
with USB-IF logo-certified embedded and host applications provided with
full source code.
VisualDSP++ uses incremental builds, multiple build configurations
(“Debug” and “Release,” for example), a syntax-coloring editor, and many
other code editing features. Makefiles can be imported and exported
freely.
Debug and Tune Your Application With Ease
The ability to develop a high performance application is often gated by
the visibility into your running system that your debugger provides. VisualDSP++ excels in this regard, with best-in-class debugging and inspection
support. Robust fundamental C language source debugging (source-level
stepping and breakpoints, stack unwinds, local variable and C expression
support, memory and register windows) serves as a foundation upon
which multiple innovative and unique tools rest.
VisualDSP++ supports a variety of debugging targets. Most common is a
JTAG connection to an EZ-KIT Lite/EZ-Board or to a custom target
board by means of Analog Devices emulator products. However, there will
be occasions where closer inspection in a simulated environment may be
2-6 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 37

The Evaluation Process
required. VisualDSP++ provides core cycle-accurate simulators, allowing
inspection of every nuance of activity within the processor, including visualization of the processor’s pipeline and cache.
As many of the most performance-demanding applications process a signal
of some sort, comprehensive memory plotting is a corner stone of VisualDSP++ debugger support. VisualDSP++ provides multiple views, from
basic (line plots) to sophisticated (eye diagrams and waterfalls) to pinpoint
anomalous data sequences in your application. Image viewing in a number
of data formats is also available.
VDK users get unparalleled visibility into the internals of the kernel. Status on a per-thread basis is available, as is a comprehensive pictorial
history of kernel events and CPU loading. Thread changes, posted and
pended semaphores, and other kernel events are captured in this display.
Inspection, or even application stimulation, from the debugger at runtime
is possible through the use of the processor’s background telemetry channels (BTCs). BTC allows for an arbitrary number of communication
channels to be established between the host debugger and the application.
Channels may go in either direction, so BTC can be used to read and
write data as the processor runs. Scalar values or entire arrays may be serviced by a channel. Arrays read from the target can even be plotted in real
time.
Multiprocessor users get the same compelling set of debugging features
across all processors, unified into a single debugging interface. Individual
windows can be made to “float” their focus to whichever processor currently is the debugger’s focus, or they can be “pinned” to a specific
processor so their contents do not follow the debugger’s focus. To further
aid MP debug, synchronous run, step, halt, and reset are also provided.
The patented statistical profiler from Analog Devices offers unprecedented
and unique visibility into a running application. Operating completely
non-intrusively to the application, the application is polled thousands of
times per second and a statistical view of where an application is spending
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-7
Page 38

Evaluation Tools
the majority of its time is quickly assembled. This tool can be used to easily inspect an application for unexpected hotspots (for example, suggesting
the need to move a key routine from external to internal memory). Simulator targets provide a completely linear profiling view.
Going even further, the VisualDSP++ compiler is able to act upon profiling information. Profile-guided optimization (PGO) is a technique that
allows the compiler to instrument an application, run the application, and
then make a second pass compilation, exploiting the information that was
gathered during the previous run of the application. This gives the compiler unique insight on a block-by-block basis, allowing it to optimize
with a level of granularity that is not possible with a tool that operates
only on a file-by-file basis.
Integrate Into Your Existing Environment
A development tool suite is always a part of an organization’s larger software engineering environment. VisualDSP++ has been designed to operate
in a larger environment.
Since an embedded systems engineer is often developing on a new platform while maintaining existing products that were likely developed with
an earlier version of the tools, VisualDSP++ can be installed discretely an
arbitrary number of times at a variety of release levels, allowing engineering to easily switch between current and legacy versions of VisualDSP++.
To better integrate to source code control (SCC) systems, VisualDSP++ is
able to connect to any SCC provider that supports the Microsoft® common source code control (MCSCC) interface. This interface is supported
by all leading SCC vendors. VisualDSP++ goes one step further by supporting the control of VisualDSP++ itself within a source code control
system.
The ability to robustly test an embedded application is enabled through a
comprehensive automation application programming interface (API).
Using language-neutral automation technology from Microsoft®, nearly
2-8 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 39

The Evaluation Process
every feature of the graphical environment is available to script authors.
Applications can be rebuilt, downloaded, and run from a simple script
executed from the command line or from within a custom test harness
framework. The automation API is supported by C++ and VBScript examples for all API calls, though any automation-aware language can be used.
For prototype runs and/or small volume deployment, an Analog Devices
emulator can be used to program the flash memory in your custom system. Accessible through the automation API, the flash programmer can be
scripted, making it possible to develop a turnkey user interface for use by a
production floor technician or other individual not familiar with VisualDSP++. Device drivers are provided for all flash devices found on
EZ-KIT Lite products, and these drivers can be easily adjusted to support
an arbitrary flash device.
Getting Help and Staying Up to Date
VisualDSP++ includes a comprehensive, indexed, searchable online Help
system. In addition to information concerning VisualDSP++, manuals for
Analog Devices processors, application notes, and more are included in
the Help system. Versions of these documents (in
.pdf format) are also
available on the installation CD or online at:
http://www.analog.com/processors/technical_library
Licensed users of VisualDSP++ are entitled to free technical support. The
support staff is dedicated to VisualDSP++ and has specific expertise
regarding it. There is never a per-incident or maintenance fee; support
remains free regardless of how long you have owned your software.
Major and minor upgrades and updates to VisualDSP++ are also free and
are released through the Analog Devices Web site.
Use Third Parties
Use the independent network of third-party developers. For more information, see “Find a Third Party—Faster Time to Market” on page 3-15.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-9
Page 40

Evaluation Tools
Take a VisualDSP++ Test Drive!
Take a free 90-day Test Drive of VisualDSP++. To take a Test Drive, you
can download a Test Drive or request a CD from the Analog Devices DSP
Tools Web site at:
http://www.analog.com/processors/tools/testdrive
or contact your local Analog Devices sales representative/distributor.
Analog Devices Tools Product Line
CROSSCORE®, the development tools product line from Analog
Devices, provides easier and more robust methods for engineers to develop
and optimize systems by shortening product development cycles for faster
time to market. The CROSSCORE components include the VisualDSP++
software development environment, EZ-KIT Lite evaluation systems,
EZ-Board evaluation boards, EZ-Extender daughter boards, and emulators for rapid on-chip debugging. For more information on development
tools, visit the Analog Devices Web site:
http://www.analog.com/processors/tools
Table 2-1 provides information about SHARC processor evaluation kits.
For additional information, visit the following Analog Web site:
http://www.analog.com/sharc/ezkits
Table 2-1. SHARC Processor Evaluation Kits
Processor Evaluation Kit/Reference Board Daughter Board
ADSP-21261
ADSP-21262
ADSP-21266
ADSP-21363
ADSP-21364
ADSP-21365
ADSP-21366
- 21262 EZ-KIT Lite
Desktop Evaluation Board
- 21364 EZ-KIT Lite
Desktop Evaluation Board
- EZ-Extender Daughter Board
- USB EZ-Extender Daughter Board
- EZ-Extender Daughter Board
- USB EZ-Extender Daughter Board
2-10 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 41

The Evaluation Process
Table 2-1. SHARC Processor Evaluation Kits (Cont’d)
Processor Evaluation Kit/Reference Board Daughter Board
ADSP-21367
ADSP-21368
ADSP-21369
ADSP-21371
ADSP-21375
ADSP-21467
ADSP-21469
ADSP-21478
ADSP-21479
ADSP-21483
ADSP-21486
ADSP-21487
ADSP-21488
ADSP-21489
For current information, go to:
- 21369 EZ-KIT Lite
Desktop Evaluation Board
- 21371 EZ-KIT Lite
Desktop Evaluation Board
- 21375 EZ-KIT Lite
Desktop Evaluation Board
- 21469 EZ-Board
Evaluation Board
- 21469 EZ-KIT Lite
Desktop Evaluation Board
- 21479 EZ-Board
Evaluation Board
- 21479 EZ-KIT Lite
Desktop Evaluation Board
- 21489 EZ-Board
Evaluation Board
- 21489 EZ-KIT Lite
Desktop Evaluation Board
http://www.analog.com/sharc/ezkits.
Embedded Processors and DSPs
- USB EZ-Extender Daughter Board
- USB EZ-Extender Daughter Board
(supports the ADSP-21375 EZ-KIT Lite
only)
- Debug Agent Board
- Audio EZ-Extender Daughter Board
- Blackfin/SHARC USB EZ-Extender
Daughter Board
- Debug Agent Board
- Audio EZ-Extender Daughter Board
- Blackfin/SHARC USB EZ-Extender
Daughter Board
- Debug Agent Board
- Audio EZ-Extender Daughter Board
- Blackfin/SHARC USB EZ-Extender
Daughter Board
Analog Devices is a leading supplier of embedded and digital signal processing solutions, and its low cost SHARC processors and integrated
mixed-signal processors are ideal for an ever-increasing spectrum of applications. Advances in design by Analog Devices provide faster processing,
more memory, lower power consumption, and simplified system
integration. Analog Devices products and technology provide a competitive edge complete with expert technical support, comprehensive
development tools, and third-party developers.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-11
Page 42

Evaluation Tools
Software Modules
Analog Devices has a wide range of tested and optimized software modules
available, including decoders, encoders, codecs and other algorithms that
provide multimedia functions for the SHARC family. The software modules allow engineers to quickly and easily incorporate these functions,
providing a faster development path to the end product. In addition, the
highly optimized software modules feature a consistent API and framework to ensure rapid development of multiple functions.
Selecting Hardware Development Tools
Hardware development tools include development and evaluation boards
(such as EZ-KIT Lite or EZ-Board), daughter boards, and JTAG
emulators.
Evaluation Systems
Typically, development and evaluation boards are standalone printed circuit boards (PCBs) that contain a SHARC processor with other devices.
Analog Devices offers two evaluation systems: EZ-KIT Lite and
EZ-Board.
EZ-KIT Lite
The EZ-KIT Lite board is a low cost hardware platform that includes a
SHARC processor surrounded by several other devices such as audio
codecs, video encoders, video decoders, flash, SDRAM, and so on. Each
EZ-KIT Lite includes a board, cable, power supply, documentation, software, and a license key.
Each EZ-KIT Lite board also includes an on-board JTAG emulator with a
USB 2.0 connector and a standard 14-pin, 100-mil, JTAG header for use
with high performance JTAG emulators available from Analog Devices.
Using the processor’s JTAG port and the VisualDSP++ software, you can
2-12 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 43

The Evaluation Process
set breakpoints, single-step through code, view memory, fill/dump memory, perform real-time data manipulation, profile execution and memory
access, plot data, and use standard I/O.
EZ-KIT Lite evaluation systems include a serial number, that when registered, yields full VisualDSP++ license status for 90 days from the date of
installation. After 90 days, the license changes to restricted status, which
limits the size of the application that can be built and supports debug
agent connectivity only. Refer to “Software Development on SHARC Pro-
cessors” on page 2-61 to see where the EZ-KIT Lite fits into the phases of
program development.
Most EZ-KIT Lite boards include three expansion connectors configured
in the shape of a U. Several third-party expansion boards connect to the
EZ-KIT Lite board via these connectors. See the “EZ-Boards” on page
2-36 for details.
EZ-Board
SHARC EZ-Board evaluation boards provide developers with a low cost
platform for initial evaluation of SHARC processors via an external JTAG
emulator or standalone debug agent board.
To debug, you must have a debug agent board or an emulator.
The EZ-Board has an expansion interface that allows for modularity with
different EZ-Extender boards.
The following sections briefly describe EZ-KIT Lite and EZ-Board development systems that are currently available for SHARC processors.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-13
Page 44

Evaluation Tools
ADSP-21489 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21489-EZLITE
Figure 2-2. ADSP-21489 EZ-KIT Lite Evaluation System
2-14 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 45

The Evaluation Process
The ADSP-21489 EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system, as shown in
Figure 2-2, provides developers with a cost-effective method for initial
evaluation of the ADSP-21483/21486/21487/21489 SHARC processors
via a USB-based, PC-hosted tool set.
The EZ-KIT Lite includes an ADSP-21489 SHARC processor desktop
evaluation board along with an evaluation suite of the VisualDSP++ development and debugging environment, including the C/C++ compiler,
assembler, and linker. The evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ is designed to
be used with the EZ-KIT Lite only.
The EZ-KIT Lite also comes with a standalone debug agent board that is
removable to allow a user to plug in an external emulator.
Features
The ADSP-21483/21486/21487/21489 SHARC processors, which
are pin-compatible, have similar memory maps. Software development for any of these devices can be performed on the
ADSP-21489 processor. Thus the EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system
may be used for any of these devices.
• ADSP-21489 EZ-Board (see “ADSP-21489 EZ-Board From Ana-
log Devices” on page 2-37 for board features)
• Evaluation version of VisualDSP++
• Debug agent board
• Audio, USB cables
• Accessories
• Power supply
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-15
Page 46

Evaluation Tools
ADSP-21479 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21479-EZLITE
Figure 2-3. ADSP-21479 EZ-KIT Lite Evaluation System
The ADSP-21479 EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system, as shown in
Figure 2-3, provides developers with a cost-effective method for initial
evaluation of the ADSP-21478/21479 SHARC processors via a
2-16 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 47

The Evaluation Process
USB-based, PC-hosted tool set. With this EZ-KIT Lite, users can learn
more about Analog Devices ADSP-21479 hardware and software development, and quickly prototype a wide range of applications.
The EZ-KIT Lite includes an ADSP-21479 SHARC processor desktop
evaluation board along with an evaluation suite of the VisualDSP++ development and debugging environment, including the C/C++ compiler,
assembler, and linker. The evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ is designed to
be used with the EZ-KIT Lite only.
The EZ-KIT Lite also comes with a standalone debug agent board that is
removable to allow a user to plug in an external emulator.
Features
The ADSP-21478/21479 SHARC processors, which are pin-compatible, have similar memory maps. Software development for any
of these devices can be performed on the ADSP-21479 processor.
Thus the EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system may be used for any of
these devices.
• ADSP-21479 EZ-Board (see “ADSP-21479 EZ-Board From Ana-
log Devices” on page 2-40 for board features)
• Evaluation version of VisualDSP++
• Debug agent board
• Audio, USB cables
• Accessories
• Power supply
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-17
Page 48

Evaluation Tools
ADSP-21469 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21469-EZLITE
Figure 2-4. ADSP-21469 EZ-KIT Lite Evaluation System
2-18 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 49

The Evaluation Process
The ADSP-21469 EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system, as shown in
Figure 2-4, provides a cost-effective method for initial evaluation of the
ADSP-21462/21465/21467/21469 SHARC processors via a USB-based
PC-hosted tool set.
The EZ-KIT Lite includes an ADSP-21469 SHARC processor desktop
evaluation board along with an evaluation suite of the VisualDSP++ development and debugging environment with the C/C++ compiler, assembler,
and linker. The evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ is designed to be used
with the EZ-KIT Lite only.
The EZ-KIT Lite also comes with a standalone debug agent board that is
removable to allow a user to plug in an external emulator. It also includes
sample processor application programs, a CE-approved power supply, and
a USB cable.
Features
The ADSP-21462/21465/21467/21469 SHARC processors, which
are pin-compatible, have similar memory maps. Software development for any of these devices can be performed on the
ADSP-21469 processor. Thus the EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system
may be used for any of these devices.
• ADSP-21469 SHARC processor
• 4M x 8-bit flash memory
• 64M x 16-bit DDR2 memory
• 16M bit SPI flash memory
• AD1939 high performance, multibit sigma-delta codec
• 4 x 2 RCA jack for 4 channels of stereo audio output
• 2 x 2 RCA jack for 2 channels of stereo audio input
• 2 DB25 connectors for differential inputs/outputs
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-19
Page 50

Evaluation Tools
• Headphone jack (connected to one of the stereo outputs)
• SPDIF In RCA jack
• SPDIF Out RCA jack
• ADM1032 two-wire sensor
• ADM3202 RS-232 line driver/receiver
• USB standalone debug agent
• USB 2.0 interface
• JTAG ICE 14-pin header
• Evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ development tools
• Flash programmer utility for downloading boot code to on-board
flash memory
• SHARC expansion interface II with connectors supporting EBIU,
Flags/IRQs, DAI, DPI, PWR_IN, 3.3 V, GND
• 8 LEDs: 1 power (green), 1 board reset (red), and 6 general-purpose (amber)
• 5 push buttons: 1 reset, 2 connected to DAI, 2 connected to
IRQ/Flag
• 2 link port connectors
• DMAX connector for probing
• USB cable
• CE certified
2-20 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 51

The Evaluation Process
ADSP-21375 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21375-EZLITE
Figure 2-5. ADSP-21375 EZ-KIT Lite Evaluation System
The ADSP-21375 EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system, as shown in
Figure 2-5, provides developers with a cost-effective method for initial
evaluation of the ADSP-21375 SHARC processors.
The EZ-KIT Lite includes an ADSP-21375 SHARC processor desktop
evaluation board and fundamental debugging software to facilitate architecture evaluations via a USB-based PC-hosted tool set. With this EZ-KIT
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-21
Page 52

Evaluation Tools
Lite, users can learn more about Analog Devices ADSP-21375 SHARC
processor hardware and software development and prototype applications.
The ADSP-21375 EZ-KIT Lite provides an evaluation suite of the VisualDSP++ development environment with the C/C++ compiler, assembler,
loader, and linker. All software tools are limited to use with the EZ-KIT
Lite.
Features
• ADSP-21375 SHARC processor
• 2M x 16-bit x 4 banks
• 1M x 8-bit flash memory
• 2M bit SPI flash
• AD1835 codec
• ADM3202 RS-232 line driver/receiver
• Parallel port, SDRAM control, flags, DAI, DPI
• ELVIS interface
• Stereo in/stereo out RCA jack
• USB interface
• JTAG ICE 14-pin header
• Evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ development tools
• Flash programmer utility for downloading boot code to on-board
flash memory
• Type A expansion interface with three connectors supporting external port, FLAG, SPI, and DAI interfaces
• 20-pin DPI header
2-22 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 53

The Evaluation Process
• 26-pin DAI header
• 11 LEDs: 1 power (green), 1 board reset (red), 1 USB monitor
(amber), and 8 general-purpose (amber)
• 5 push buttons: 1 reset, 2 connected to DAI, 2 connected to the
FLAG pins of the processor
• CE certified
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-23
Page 54

Evaluation Tools
ADSP-21371 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21371-EZLITE
Figure 2-6. ADSP-21371 EZ-KIT Lite Evaluation System
The ADSP-21371 EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system, as shown in
Figure 2-6, provides developers with a cost-effective method for initial
evaluation of the ADSP-21371 SHARC processors. With this EZ-KIT
Lite, users can learn more about the Analog Devices ADSP-21371 hardware and software development tools, and quickly prototype a wide range
of applications.
2-24 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 55

The Evaluation Process
The EZ-KIT Lite includes an ADSP-21371 SHARC processor desktop
evaluation board along with an evaluation suite of the VisualDSP++ development and debugging environment, including the C/C++ compiler,
assembler, and linker. The evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ is designed to
be used with the EZ-KIT Lite only.
Additionally, the ADSP-21371 EZ-KIT Lite contains the National Instruments Educational Laboratory Virtual Instrumentation Suite (ELVIS)
interface. This interface allows usage of DC voltage and current measurement modules, oscilloscope and bode analyzer modules, function
generator, arbitrary waveform generator, and digital I/O. NI ELVIS is a
LabVIEW™-based design and prototype environment for university science and engineering laboratories curriculum. For more details, go to
www.ni.com.
Features
• ADSP-21371 SHARC processor
• 208-pin MQFP package
• 266 MHz core clock speed
• 128M bit (1M x 32-bit x 4 banks) SDRAM
• 1M x 8-bit flash memory
• 2M bit SPI flash memory
• AD1835A audio codec
• 4 x 2 RCA phono jack for 4 channels of stereo output
• 2 x 1 RCA phono jack for 1 channel of stereo input
• 3.5 mm headphone jack for 1 channel stereo output
• ADM3202 RS-232 line driver/receiver
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-25
Page 56

Evaluation Tools
• National Instruments Educational Laboratory Virtual Instrumentation Suite (ELVIS) Interface
• JTAG ICE 14-pin header
• Evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ development tools
• Type A expansion interface with three connectors supporting parallel port, FLAG, DPI, and DAI interfaces
• 26-pin DPI header
• 20-pin DAI header
• 11 LEDs: 1 power (green), 1 board reset (red), 1 USB monitor
(amber), and 8 general-purpose (amber)
• 5 push buttons: 1 reset, 2 connected to DAI, 2 connected to the
FLAG pins of the processor
• CE certified
2-26 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 57

The Evaluation Process
ADSP-21369 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21369-EZLITE
Figure 2-7. ADSP-21369 EZ-KIT Lite Evaluation System
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-27
Page 58

Evaluation Tools
The ADSP-21369 EZ-KIT Lite, as shown in as shown in Figure 2-7, provides a cost-effective method for initial evaluation of the
ADSP-21367/21368/21369 SHARC processors via a USB-based
PC-hosted tool set.
The EZ-KIT Lite includes an ADSP-21369 SHARC processor desktop
evaluation board along with an evaluation suite of the VisualDSP++ development and debugging environment with the C/C++ compiler, assembler,
loader, and linker. It also includes sample processor application programs,
a CE-approved power supply, and a USB cable.
Features
The ADSP-21367/21368/21369 SHARC processors, which are
pin-compatible, have similar memory maps. Software development
for any of these devices can be performed on the ADSP-21369 processor. Thus the EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system may be used for
any of these devices.
• ADSP-21369 SHARC processor
• 1M x 8-bit flash memory
• 1M 32-bit 4 banks SDRAM
• 512K x 8-bit SRAM
• 2M SPI flash memory
• AD1835 stereo, 96-kHz, 24-bit codec
• 4 x 2 RCA jack for 4 channels of stereo audio output
• 1 x 2 RCA jack for 1 channel of stereo audio input
• Headphone jack (connected to one of the stereo outputs)
• SPDIF In RCA jack
2-28 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 59

The Evaluation Process
• SPDIF Out RCA jack
• ADM3202 RS-232 driver/receiver
• USB interface
• JTAG ICE 14-pin header
• Evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ development tools
• Flash programmer utility for downloading boot code to on-board
flash memory
• Type A expansion interface with three connectors supporting external port, FLAG, SPI, and DAI interfaces
• 20-pin DPI header
• 26-pin DAI header
• 12 LEDs: 1 power (green), 1 board reset (red), 1 USB reset (red), 1
USB monitor (amber), and 8 general-purpose (amber)
• 5 push buttons: 1 reset, 2 connected to DAI, 2 connected to the
FLAG pins of the processor
• ELVIS interface
• USB cable
• 3.5-mm stereo headphones
• 6-foot RCA audio cable
• 6-foot 3.5-mm/RCA x 2 Y-cable
• CE certified
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-29
Page 60

Evaluation Tools
ADSP-21364 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21364-EZLITE
Figure 2-8. ADSP-21364 EZ-KIT Lite Board
2-30 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 61

The Evaluation Process
The ADSP-21364 EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system, as shown in
Figure 2-8, provides developers with a cost-effective method for initial
evaluation of ADSP-21363/21364/21365/21366 SHARC processors.
The EZ-KIT Lite includes an ADSP-21364 SHARC processor desktop
evaluation board and fundamental debugging software to facilitate architecture evaluations via a USB-based PC-hosted tool set. With this EZ-KIT
Lite, users can learn more about ADSP-21363/21364/21365/21366
SHARC processor hardware and software development and prototype
applications. The ADSP-21364 EZ-KIT Lite provides an evaluation suite
of the VisualDSP++ development environment with the C/C++ compiler,
assembler, loader, and linker. All software tools are limited to use with the
EZ-KIT Lite.
Features
The ADSP-21363/21364/21365/21366 SHARC processors, which
are pin-compatible, have similar memory maps. Software development for any of these devices can be performed on the
ADSP-21364 SHARC processor. Thus, this EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system may be used for any of these devices.
• ADSP-21364 SHARC processor
• 1M x 8-bit flash memory
• 512K x 8-bit SRAM
• 2M bit SPI flash memory
• AD1835 stereo, 96-kHz, 24-bit codec
• 4 x 2 RCA jack for 4 channels of stereo audio output
• 1 x 2 RCA jack for 1 channel of stereo audio input
• Headphone jack (connected to one of the stereo outputs)
• SPDIF In RCA jack
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-31
Page 62

Evaluation Tools
• SPDIF Out RCA jack
• USB interface
• JTAG ICE 14-pin header
• Evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ development tools
• Flash programmer utility for downloading boot code to on-board
flash memory
• Type A expansion interface with three connectors supporting parallel port, FLAG, SPI, and DAI interfaces
• 4 programmable flags
• 11 LEDs: 1 power (green), 1 board reset (red), 1 USB monitor
(amber), and 8 general-purpose (amber)
• 5 push buttons: 1 reset, 2 connected to DAI, 2 connected to the
FLAG pins of the processor
• USB cable
• CE certified
2-32 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 63

The Evaluation Process
ADSP-21262 EZ-KIT Lite From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21262-EZLITE
Figure 2-9. ADSP-21262 EZ-KIT Lite Evaluation System
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-33
Page 64

Evaluation Tools
The ADSP-21262 EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system, as shown in
Figure 2-9, provides developers with a cost-effective method for initial
evaluation of the ADSP-21261/21262/21266 SHARC processors for a
wide range of applications.
The ADSP-21262 EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system includes an
ADSP-21262 SHARC processor desktop evaluation board and fundamental debugging software to facilitate architecture evaluations via a
USB-based PC-hosted tool set. With this EZ-KIT Lite, you can learn
more about Analog Devices ADSP-21262 SHARC processor hardware
and software development and prototype applications. The EZ-KIT Lite
provides an evaluation suite of the VisualDSP++ integrated development
and debug environment (IDDE) with the C/C++ compiler, advanced
plotting tools, statistical profiling, and the VisualDSP++ kernel (VDK).
Other features include: assembler, linker, libraries, loader, and splitter.
VisualDSP++ offers programmers a powerful programming tool with flexibility that shortens time to market.
Features
The ADSP-21261/21262/21266 SHARC processors, which are
pin-compatible, have similar memory maps. Software development
for any of these devices can be performed on the ADSP-21262
SHARC processor. Thus, this EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system may
be used for any of these devices.
• ADSP-21262 SHARC processor
• 1M x 8-bit flash memory
• 512K x 8-bit SRAM
• 2M bit SPI flash memory
• AD1835 stereo, 96-kHz, 24-bit codec
• 4 x 2 RCA jack for 4 channels of stereo audio output
2-34 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 65

The Evaluation Process
• 1 x 2 RCA jack for 1 channel of stereo audio input
• Headphone jack (connected to one of the stereo outputs)
• SPDIF receiver with RCA jack
• USB interface
• JTAG ICE 14-pin header
• Evaluation suite of VisualDSP++ development tools
• 0-ohm resistor for current measurement
• Flash programmer utility for downloading boot code to on-board
flash memory
• Type A expansion interface with three connectors supporting parallel port, FLAG, SPI, and DAI interfaces
• 12 LEDs: 1 power (green), 1 board reset (red), S/PDIF (amber),
1 USB monitor (amber), and 8 general-purpose (amber)
• 5 push buttons: 1 reset, 2 general-purpose input (connected to
DAI), and 2 IRQs (connected to flag pins)
• USB cable
• CE certified
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-35
Page 66

Evaluation Tools
EZ-Boards
SHARC EZ-Board evaluation boards provide developers with a low cost
platform for initial evaluation of SHARC processors via an external JTAG
emulator or standalone debug agent board.
To debug, you must have a debug agent board or an emulator.
The EZ-Board has an expansion interface that allows for modularity with
different EZ-Extender boards.
2-36 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 67

The Evaluation Process
ADSP-21489 EZ-Board From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21489-EZBRD
Figure 2-10. ADSP-21489 EZ-Board
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-37
Page 68

Evaluation Tools
The ADSP-21489 EZ-Board evaluation board, as shown in Figure 2-10,
provides developers with a low cost platform for initial evaluation of the
ADSP-2148x SHARC processors via an external JTAG emulator or standalone debug agent board.
Features
To debug, you must have a debug agent board or emulator. The
EZ-Board has an expansion interface that allows for modularity
with different EZ-Extender boards.
• ADSP-21489 SHARC processor
• 176-pin LQFP package
• 25 MHz CLKIN oscillator
• 4M x 8-bit flash memory, ST Micro M29W320EB
• 16M bit x 16-bit, Micron MT48LC16M16A2P-6A
• 1M x 16-bit, ISSI IS61WV102416BLL-10TLI
• 16M bit SPI flash memory
• AD1939 audio codec
• SPDIF receiver with RCA phone jacks
• ADM1032 two wire sensor
• ADM3202 RS-232 line driver/receiver
• 5 V at 3.6 amps
• 11 LEDs: 1 power (green), 1 board reset (red),
1 temperature limit (amber), and 8 general-purpose (amber)
• 5 push buttons: 1 reset, 2 general-purpose input (connected to
DAI), and 2 IRQs (connected to flag pins)
2-38 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 69

The Evaluation Process
• Expansion interface: AMI, flags/IRQs, DAI, DPI, PWR_IN,
3.3 V, GND
• Standalone debug agent interface
• WDT (watch dog timer) system reset implementation
• MP JTAG IN and OUT connectors
• 0-ohm resistors for DSP current measurement
• CE certified
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-39
Page 70

Evaluation Tools
ADSP-21479 EZ-Board From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21479-EZBRD
Figure 2-11. ADSP-21479 EZ-Board
2-40 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 71

The Evaluation Process
The ADSP-21479 EZ-Board evaluation board, as shown in Figure 2-11,
provides developers with a low cost platform for initial evaluation of the
ADSP-2147x SHARC processors via an external JTAG emulator or standalone debug agent board.
Features
To debug, you must have a debug agent board or emulator. The
EZ-Board has an expansion interface that allows for modularity
with different EZ-Extender boards.
• ADSP-21479 SHARC processor
• 196-pin BGA package
• 16.625 MHz CLKIN oscillator
• 4M x 8-bit flash memory, ST Micro M29W320EB
• 16M bit x 16-bit, Micron MT48LC16M16A2P
• 1M x 16-bit, ISSI IS61WV102416BLL-10TLI
• 16M bit SPI flash memory
• AD1939 audio codec
• SPDIF receiver with RCA phone jacks
• ADM3202 RS-232 line driver/receiver
• 5 V at 3.6 amps
• 11 LEDs: 1 power (green), 1 board reset (red),
1 temperature limit (amber), and 8 general-purpose (amber)
• 5 push buttons: 1 reset, 2 general-purpose input (connected to
DAI), and 2 IRQs (connected to flag pins)
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-41
Page 72

Evaluation Tools
• Expansion interface: AMI, flags/IRQs, DAI, DPI, PWR_IN,
3.3 V, GND
• Standalone debug agent interface
• RTC (real time clock) implementation
• Shift register interface
• MP JTAG IN and OUT connectors
• 0-ohm resistors for DSP current measurement
• CE certified
2-42 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 73

The Evaluation Process
ADSP-21469 EZ-Board From Analog Devices
Part Number: ADZS-21469-EZBRD
Figure 2-12. ADSP-21469 EZ-Board
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-43
Page 74

Evaluation Tools
The ADSP-21469 EZ-Board evaluation board, as shown in Figure 2-12,
provides developers with a low cost platform for initial evaluation of the
ADSP-2146x SHARC processors via an external JTAG emulator or standalone debug agent board.
Features
To debug, you must have a debug agent board or emulator. The
EZ-Board has an expansion interface that allows for modularity
with different EZ-Extender boards.
• ADSP-21469 SHARC processor
• 324-pin PBGA package
• 25 MHz CLKIN oscillator
• 4M x 8-bit flash memory, ST Micro M29W320EB
• 64M x 16-bit, Micron MT47H64M16HR-3
• 16M bit SPI flash memory
• AD1939 audio codec
• SPDIF receiver with RCA phono jacks connected to DAI pin for
input/output
• ADM1032 two wire sensor
• ADM3202 RS-232 line driver/receiver 5 V
• 5 V at 3.6 amps
• 11 LEDs: 1 power (green), 1 board reset (red),
1 temperature limit (amber), and 8 general-purpose (amber)
• 5 push buttons: 1 reset, 2 general-purpose input (connected to
DAI), and 2 IRQs (connected to flag pins)
2-44 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 75

The Evaluation Process
• Expansion interface: EBIU, flags/IRQs, DAI, DPI, PWR_IN
(5 V), 3.3 V, GND
• Standalone debug agent interface
• USB cable
• Link port connectors
• DMAX connector for probing
• 0-ohm resistors for DSP current measurement
• CE certified
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-45
Page 76

Evaluation Tools
Debug Agent
Part Number: ADZS-DBGAGENT-BRD
Figure 2-13. Debug Agent Board
The standalone debug agent is intended to provide a modular low cost
emulation solution for EZ-Boards as well as evaluation boards designed by
third parties. The standalone debug agent is very similar to the debug
agent that is on existing EZ-KIT Lites but has the flexibility to move from
one board to another board.
2-46 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
The standalone debug agent board (Figure 2-13) only works on
EZ-Boards or approved third-party boards.
Page 77

The Evaluation Process
EZ-Extender Daughter Boards
EZ-Extender daughter boards enhance and extend EZ-Board and EZ-KIT
Lite features and functionalities. This section describes the EZ-Extender
daughter boards that are currently available.
SHARC USB EZ-Extender
Part Number: ADZS-SHRCUSB-EZEXT
Figure 2-14. SHARC USB EZ-Extender
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-47
Page 78

Evaluation Tools
The SHARC USB EZ-Extender daughter board, as shown in Figure 2-14,
provides a solution for users to evaluate different peripherals on SHARC
processors.
The SHARC USB EZ-Extender daughter board allows developers to connect to the parallel port on the ADSP-21262 and ADSP-21364 EZ-KIT
Lite and to the asynchronous memory bus on the ADSP-21369 EZ-KIT
Lite and the ADSP-21375 EZ-KIT Lite. The EZ-Extender has peripherals
that support USB 2.0.
The SHARC USB EZ-Extender daughter board features:
• USB 2.0 interface. No power supply required, derives power from
EZ-KIT Lite.
• CE certified
• Dimensions: 3.13 in (H) x 3.6 in (W)
2-48 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 79

SHARC EZ-Extender
Part Number: ADZS-21262-1-EZEXT
The Evaluation Process
Figure 2-15. SHARC EZ-Extender
The SHARC EZ-Extender daughter board, as shown in Figure 2-15, is a
separately sold assembly that plugs into a SHARC EZ-KIT Lite evaluation
system’s expansion interface. The extender aids the design and prototyping phases of SHARC processor-targeted applications.
The SHARC EZ-Extender allows developers to connect a number of Analog Devices analog-to-digital (ADC) high-speed converter (HSC)
evaluation boards to the ADSP-21262 EZ-KIT Lite and the ADSP-21364
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-49
Page 80

Evaluation Tools
EZ-KIT Lite. The SHARC EZ-Extender also provides developers a breadboard area and the ability to access all of the pins on the ADSP-21262 and
ADSP-21364 EZ-KIT Lite’s expansion interface.
The SHARC EZ-Extender features:
• Expansion interface for connecting to the ADSP-21262 and
ADSP-21364 EZ-KIT Lites
• Analog Devices high-speed converter (HSC) interface for connecting analog-to-digital (ADC) HSC evaluation boards such as the
AD9244-40PCB and the AD9244-65PCB
• 40-pin, 0.1-in. spacing, right angle, female socket connector
• RJ45 connector for providing SPI signals for configuring converter
registers
• SMA connector for connecting to an external clock source
• Unpopulated socket for inserting of an optional oscillator
• SMT footprint area; 1206 and 805 footprints
• SOIC24 and SOIC20 footprints
• Dimensions: 5 in. x 5 in.
2-50 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 81

SHARC Audio EZ-Extender
Part Number: ADZS-SHAUDIO-EZEXT
The Evaluation Process
Figure 2-16. SHARC Audio EZ-Extender
The SHARC audio EZ-Extender daughter board, as shown in
Figure 2-16, provides a solution for users to evaluate audio applications
on the ADSP-214xx EZ-Board/EZ-KIT Lite. Software examples are provided in the latest update of VisualDSP++.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-51
Page 82

Evaluation Tools
The EZ-Extender consists of three Analog Devices AD1939 audio codecs
and provides 24 channels of analog audio out, 12 channels of analog audio
in. The primary codec operates in both in I
run at sample rates of 48, 96, or 192 kHz. The other two codecs are configured to operate in dual line TDM mode. The three codecs together can
operate in dual line TDM mode for 24 analog channels out and 12 analog
channels in at a sample rate of 192 kHz.
The audio input and output is available via multiple RCA connectors. A
group of switches is available if a user should decide to evaluate the audio
codec inputs and outputs in a differential mode.
2
S and TDM mode and can
DB25 to XLR cables are not supplied with the EZ-Extender.
The SHARC audio EZ-Extender daughter board features:
• Analog codecs – AD1939 (3): ADI 192 kHz audio codec, 24 channels audio out (12 stereo channels), 12 channels audio in (6 stereo
channels)
• Single-ended input/output – RCA 4 x 1 inputs (3), RCA 4 x 2
outputs (3)
• Differential input/output – DB25 connector inputs (2), DB25
connector outputs (3)
2-52 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 83

USB EZ-Extender for Blackfin and SHARC
Part Number: ADZS-BFSHUSB-EZEXT
The Evaluation Process
Figure 2-17. Blackfin/SHARC USB EZ-Extender
The Blackfin/SHARC USB EZ-Extender daughter board, as shown in
Figure 2-17, plugs onto the expansion interface of the ADSP-BF518F,
ADSP-BF526, and ADSP-21469 EZ-Board and EZ-KIT Lite. The
EZ-Extender aids the design and prototyping phases of the processor
targeted applications and extends the capabilities of the evaluation system
by providing a connection between the asynchronous memory bus of the
Blackfin/SHARC processor and a USB 2.0 device.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-53
Page 84

Evaluation Tools
The Blackfin/SHARC USB EZ-Extender daughter board features:
• USB 2.0 interface – PLX Technology NET2272 device
• USB driver and application code
• CE certified
JTAG Emulators
JTAG (Joint Test Action Group) is defined by the IEEE 1149.1 standard
for a test access port for testing electronic devices. This standard defines a
method for serially scanning the I/O status of each pin on the device as
well as controlling internal operation of the device.
Boundary-scan testing was developed in the mid 1980s as the JTAG interface to solve physical access problems on PCBs caused by increasingly
crowded assemblies due to novel packaging technologies. Boundary-scan
embeds test circuitry at chip level to form a complete board-level test protocol. With boundary-scan—industry standard IEEE 1149.1 since
1990—you can access the most complex assemblies for testing, debugging,
in-system device programming, and diagnosing hardware problems.
SHARC processors are equipped with a JTAG port and thus support the
IEEE 1149.1 standard for system test.
Through the JTAG port, you can run and halt the processor remotely.
The internal and external processor memory can be read or written, and
breakpoints can be set.
Most development boards include some built-in JTAG emulation circuitry. Your own hardware, most likely, does not contain this circuitry.
2-54 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 85

High Performance USB 2.0 JTAG Emulator
Part Number: ADZS-HPUSB-ICE
The Evaluation Process
Figure 2-18. High Performance USB 2.0 JTAG Emulator
The Analog Devices high-speed, high performance, universal serial
bus-based emulator (HP-USB), as shown in Figure 2-18, provides a portable, non-intrusive, target-based debugging solution for Analog Devices
JTAG processors.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-55
Page 86

Evaluation Tools
These easy-to-use USB-based emulators perform a wide range of emulation functions, including single-step and full-speed execution with
predefined breakpoints, and viewing and/or altering of register and
memory contents. With the ability to automatically detect and support
multiple I/O voltages, the HP-USB emulator enables you to communicate
with all of the Analog Devices JTAG processors using a full-speed
USB 1.0 or high-speed USB 2.0 port on the host PC.
Applications and data can be tested and transferred easily (and rapidly,
when the HP-USB emulator is connected to a high-speed USB 2.0 port on
your host PC) between the emulators and the separately available VisualDSP++ development and debugging environment.
The plug-and-play architecture of USB allows the emulators to be automatically detected and configured by the host operating system. It can also
be connected to (and disconnected from) the host without opening the PC
or turning off the power to the PC. A 3-meter (9-foot) cable is included to
connect the emulators to the host PC, thus providing abundant
accessibility.
As a bonus, customers in an environment that does not allow them to
open their PCs without IS support will find that both emulators eliminate
the need to obtain that help and thus can be easily moved from the lab to
the local desktop to the laptop.
Features
• High-speed USB 2.0 (backward compatible with full-speed USB
1.1) interface and connector
• JTAG clock operation from 10 MHz to 50 MHz
• Support for all ADI JTAG processors
• Multiple processor I/O voltage support with automatic detection
• 1.8 V, 2.5 V, and 3.3 V compliant and tolerant
2-56 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 87

The Evaluation Process
• 5 V tolerant and 3.3 V compliant for 5 V processors
• Multiprocessor support
• 14-pin JTAG connector
• 3-meter USB cable for-difficult-to-reach targets
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-57
Page 88

Evaluation Tools
USB 1.1 JTAG Emulator
Part Number: ADZS-USB-ICE
Figure 2-19. USB 1.1 JTAG Emulator
The cost-effective universal serial bus (USB)-based emulator, as shown in
Figure 2-19, from Analog Devices provides a portable, non-intrusive, tar-
get-based debugging solution for Analog Devices JTAG processors.
2-58 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 89

The Evaluation Process
This USB-based emulator performs a wide range of emulation functions,
including single-step and full-speed execution with predefined breakpoints, and viewing and/or altering of register and memory contents.
With the ability to automatically detect and support multiple I/O voltages, the USB emulator enables users to communicate with all of the
Analog Devices JTAG processors using a full-speed USB 1.1 or high-speed
USB 2.0 port on the host PC. Applications and data can easily be tested
and transferred between the emulator and the separately available VisualDSP++ development and debugging environment.
The plug-and-play architecture of USB allows the emulators to be
detected automatically and configured by the host operating system. The
USB can also be connected to (and disconnected from) the host without
opening the PC or turning off the power to the PC. A 3-meter (9-foot)
cable is included to connect the emulators to the host PC, thus providing
abundant accessibility.
As a bonus, customers in an environment that does not allow them to
open their PCs without IS support will find that the USB emulator eliminates the need to obtain that help and thus can be easily moved from the
lab to the local desktop to the laptop.
Features
• Full-speed USB 1.1 compliant (forward compatible with
high-speed USB 2.0 interface and connector)
• Support for all ADI JTAG processors
• Multiple processor I/O voltage support with automatic detection
• 1.8 V, 2.5 V, and 3.3 V compliant and tolerant
• 5 V tolerant and 3.3 V compliant for 5 V processors
• Multiprocessor support
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-59
Page 90

Evaluation Tools
• 14-pin JTAG connector
• 3-meter USB cable for difficult to reach targets
Selecting the Right Combination of Tools
Knowing which tools to use is critical to ensuring a quick development
cycle. There are many options for software and hardware development
tools. Two of the most common scenarios described in this section contain circumstances encountered by other developers along with
recommended solutions. Your needs may be similar to one of the following scenarios.
Scenario 1
Question. We are a small design house with one software engineer and one
hardware engineer for this project. We cannot afford a substantial initial
investment in tools. What do you recommend?
Answer. Purchase a SHARC EZ-KIT Lite evaluation system (for example,
p/n: ADZS-21364-EZLITE).
This hardware platform allows you to begin software development.
By interfacing components to the board’s expansion headers, the platform
can serve as the basis for a hardware prototype. The EZ-KIT Lite
evaluation system includes VisualDSP++, but the software license restricts
various capabilities (debug agent connectivity only and reduced program
size allowance).
Obtain a TestDrive serial number on the Analog Devices Web site at:
http://www.analog.com/processors/tools/testdrive
When the TestDrive license expires, consider purchasing a full seat of
VisualDSP++ (p/n: VDSP-SHARC-PC-FULL).
2-60 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 91

The Evaluation Process
After you have finished constructing your hardware, purchase a low cost
USB emulator (p/n: ADZS-USB-ICE) from Analog Devices.
Scenario 2
Question. We have a team of five software engineers who are developing code
for the SHARC processor, but no more than three are likely to be using the
tools at any given time. How do we handle licensing? Does each engineer need
a license?
Answer. A floating license may be right for you. VisualDSP++ may be
installed on many machines. A developer checks out a floating license
from a license server onto any machine. With three floating licenses, up to
three people can use VisualDSP++ at the same time. A strong network
connection to the floating license server is recommended.
Order a floating license (p/n: VDSP-SHARC-PCFLOAT).
Software Development on SHARC Processors
Once the development tools are installed, begin working with application
software development. Figure 2-1 on page 2-3 shows a typical development flow.
Some users modify a development board in parallel with software application development. The modified board serves as a prototype until their
own hardware is built and ready.
Eventually, your custom hardware becomes available and you then move
development to that platform. This custom hardware will include a 14-pin
header called a JTAG port that connects to the SHARC processor. To
debug this custom board, Analog Devices recommends that you purchase
a JTAG emulator. Emulators enable you to perform the debug operations
that you may have performed previously on a development board on your
own custom hardware.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 2-61
Page 92

Evaluation Tools
2-62 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 93

3 SUPPORT OPTIONS
This chapter addresses the support options available for users both during
the evaluation process and development phases of SHARC processor processor design.
Available Support
Analog Devices provides a wide variety of processor support options.
Material is available online. Live training is also available. This information is available to evaluators of software and hardware solutions at the
beginning of the evaluation process, to design engineers while they are
developing a system, and to support engineers as they resolve compatibility and usability issues after product release.
Since information about its processor products is updated continuously
and new material is added constantly, Analog Devices encourages you to
keep up to date with new developments through our online resources.
Analog Devices Web Site
Your first point of reference for the most recent information is always the
Analog Devices Web site. The following kinds of information are
available:
• Processor and development tools selection guides
• Additional getting started information
• Applications notes, EE-notes, and other articles
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 3-1
Page 94

Available Support
• Communities-related information
• Platform-related information
Visit the SHARC processor home page at:
http://www.analog.com/sharc.
The Analog Devices Embedded Processing and DSP page, which offers
access to other processor families, is located at:
http://www.analog.com/processors
To visit the knowledge base, use your browser to access this site:
http://www.analog.com/processors/knowledgebase. This information is
available to all classes of users, Analog Devices customers, and interested
parties.
Processor and Development Tools Selection Information
For processor-specific information start at the Web site’s SHARC processor page (http://www.analog.com/sharc), and then check SHARC
processor offerings with regards to package, speed, or temperature specifications. Links provide access to additional processor selection information
(such as peripherals and memory), development tools selection information, and other materials.
Getting Started Information
The SHARC processor page (http://www.analog.com/sharc) provides
links that introduce the SHARC processor architecture and targeted
applications. To find out about the processor’s core and peripherals, refer
to this Web site topic at the Analog Devices Web site. You may also want
to check the benchmark data available from independent testers. A link to
training and events provides an up-to-date list of local training seminars
and upcoming events where you can learn more about all SHARC processor products.
3-2 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 95

Support Options
Applications Notes, EE-Notes, and Other Articles
The most useful documents available to users are the Application or EE(Engineer-to-Engineer) Notes, since they offer detailed technical information about using the SHARC processor. These materials may be
downloaded from the Web site.
These documents supplement the standard documentation for processors
and tools. EE-Notes focus on a very narrow or specific topic. Note that
you can also use VisualDSP++ Help to search, locate, and view this collection of articles, as well as the entire list of all EE-Notes.
Additional links are provided to recently published articles, many of
which have been featured in trade magazines. Please point your browser
to:
http://www.analog.com/ee-notes
Communities-Related Information
For information about application-specific development types, refer to the
“Communities” topic at the SHARC processor Web site. Here you can
find information about a particular application theme, such as audio,
automotive telematics, or video and imaging.
Platform-Related Information
“Platform-related information” refers to the SHARC processor and its use
with other hardware or software solutions.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 3-3
Page 96

Available Support
Visual Learning and Development (VLD)
The Analog Devices Web site offers free on-demand video tutorials. Subjects include:
• SHARC Processors Overview
• SHARC ADSP-2146x Processor Overview
• SHARC ADSP-21469 EZ-KIT Overview
Please go to
http://www.analog.com/vld for additional video modules.
Workshops and Seminars
The most efficient way to learn about the SHARC processor architecture
is by attending a 3½-day (or 1-day) SHARC seminar. These seminars
provide a mixture of lectures and demonstrations. The 3½-day workshop
provides hands-on exercises and serves as an excellent starting point for
both hardware and software development.
A variety of training options are available, both online and in a classroom
setting. For users who prefer live training sessions, a variety of venues is
available.
SHARC Processor Workshops
SHARC processor workshops are designed to develop a strong working
knowledge of Analog Devices processors through lecture and hands-on
exercises in a classroom setting.
These practical courses teach how to use the latest software development
tools. First, the core elements of the processor, which includes the computational units, the data address generators, and the program sequencer, are
examined along with the relevant assembly code instructions. A number of
simulator labs help in understanding operation of the individual elements.
Memory configuration (both internal and external) is discussed next.
3-4 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 97

Support Options
Advanced instructions are presented with a follow on lab session about
code optimization. The I/O peripherals, which include the SPORTS, link
ports, and external port, are discussed in detail along with DMA operation
between these peripherals and internal memory.
Workshops are offered through Kaztek Engineering throughout the world.
Visit the Kaztek Web site for the schedule of upcoming workshops and
pricing information at:
http://www.kaztek.com
SHARC Processor Seminars
The SHARC processor seminar is a subset of the SHARC Processor
Workshop slide set and does not include hands-on exercises. A SHARC
seminar is often accompanied by tools and software demonstrations running on hardware (sometimes by key Analog Devices third party partners).
Contact your local Analog Devices sales office or distribution partner for
information on SHARC seminars or refer to:
http://www.analog.com/processors/learning/index.html
Processor Documentation
Three documents accompany each SHARC processor: a data sheet,
a hardware reference, and a programming reference. These documents
enable you to design software and hardware.
SHARC Processor Manuals
Two kinds of manuals provide detailed information about the SHARC
processor: the hardware reference manual and the programming reference.
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 3-5
Page 98

Available Support
Hardware Reference Manuals
Each processor’s hardware reference manual provides architectural information about that particular SHARC processor. The descriptions cover
functional blocks, buses, and ports, including all features and processes
that they support.
The VisualDSP++ Help system also includes a copy of each hardware reference manual and provides powerful search facilities to help you locate
information.
You can find SHARC processor hardware reference manuals at:
http://www.analog.com/processors/manuals
Programming Reference
The programming reference contains information about the processor
architecture and assembly language for SHARC processors. The manual
provides information on how assembly instructions execute on the
SHARC processor’s architecture, along with reference information about
processor operations.
The VisualDSP++ Help system also includes a searchable version of the
programming reference so you can locate information quickly.
The processor core and instruction set, which is common to all SHARC
processors, is documented in the programming reference manual.
You can find the SHARC processor programming reference at:
http://www.analog.com/processors/manuals
3-6 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
Page 99

Support Options
Data Sheets
Data sheets are created for each SHARC processor and for each revision of
a single product. Each SHARC processor data sheet provides:
• A high-level overview of the processor
• A description of processor pins
• Electrical, power, and timing characteristics/requirements
• Device package dimensions
• Environmental (temperature) information
To obtain data sheets for SHARC processors, open your browser and
access:
http://www.analog.com/sharc
Anomalies Lists for Processors and Tools
Analog Devices maintains an anomalies list for each subfamily of SHARC
processors and also maintains an anomalies list for tools. These documents
are updated as new information becomes available.
Processor anomalies represent the currently-known differences between
revisions of SHARC devices and the functionality specified in the SHARC
processor data sheets and hardware manuals. A revision number with the
form “-x.x” is branded on all parts to identify them according to silicon
revisions.
For processor anomalies, refer to:
http://www.analog.com/processors/ic/anomalies
For tools anomalies, refer to:
http://www.analog.com/processors/tools/anomalies
Getting Started With SHARC Processors 3-7
Page 100

Available Support
BSDL Files
Boundary scan description language (BSDL) files are necessary for the
application of boundary scan for board and system-level testing and
in-system programming. BSDL files are the electronic data sheets that
describe the IEEE 1149.1 or JTAG design within an IC, and are provided
by the IC vendors as part of their device specifications. Use BSDL files to
describe the test logic and generate a test for a loaded board.
IBIS Models
I/O buffer information specification (IBIS) models are used with various
IBIS-based simulators for transmission line simulation of digital systems.
These models accurately simulate I/O buffers, termination, and circuit
board traces. The simulation time is much faster than SPICE simulations,
because it is a behavioral model that relies on tabulated current versus
voltage characteristics. For more information about IBIS models, see the
main ANSI/EIA IBIS home page at:
http://www.eigroup.org/IBIS
CROSSCORE Tools Documentation
This documentation describes the various components of the
CROSSCORE software and hardware tools. Analog Devices offers a software tools environment (VisualDSP++) and an assortment of hardware
development tools.
For software tools, each release of VisualDSP++ includes a complete set of
online manuals, describing the entire software development tool chain.
“Hardware Tools Documentation” on page 3-13 describes EZ-KIT Lite
evaluation systems, EZ-Board evaluation systems, extender boards, and
emulators.
3-8 Getting Started With SHARC Processors
 Loading...
Loading...