Circuit Note
High Common-Mode Voltage Difference
Amplifier
Precision, Low Noise, CMOS, Dual, Rail-toRail Output Op Amp
Precision, Selectable Gain, Fully Differential
Funnel Amplifier
Quad-Channel Isolator with Integrated
5 V, Low Noise, High Accuracy, XFET
Voltage Reference
Σ-Δ ADC
Rev. 0
Circuits from the Lab™ circuits from Analog Devices have been designed and built by Analog Devices
g practices have been employed in the design and construction of
each circuit, and their function and performance have been tested and verified in a lab environment at
suitability and applicability for your use and application. Accordingly, in no event shall Analog Devices
be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, consequential or punitive damages due to any cause
whatsoever connected to the use of any Circuits from the Lab circuits. (Continued on last page)
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
5V_REF
2.5V_CM
5V
V
SHUNT
= 0V TO 100mV
NOTE: SIGNAL VOLTAGES
SHOWN FOR POSITIVE SOURCE
0V TO
−1V
0V TO 10V
2.5V TO
4.5V
15V
5V
15V
15V
−15V
LOAD
+
−
2.5V TO
0.5V
1kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
1kΩ
10kΩ
10kΩ
+
−
REF+
REF−
+
−
+
–
−15V
+IN 0.4×
–IN 0.4×
+
–
VOCM
AD629
1/2
AD8622
1/2
AD8622
ADR435
AD8475 AD7170
AIN+
REFIN+
AIN−
REFIN−
GND
VDD
SCLK
PDSTR
DOUT
V
OA
V
OB
V
IC
V
IA
V
IB
V
OC
VDD1V
ISO
GND
1
GND
ISO
5V
1
0V TO
100mV
V
SHUNT
V
SOURCE
R
SHUNT
ADuM5402
10154-001
CN-0240
Devices Connected/Referenced
AD629
AD8622
AD8475
ADuM5402
DC-to-DC Converter
Circuits from the Lab™ reference circuits are engineered and
tested for quick and easy system integration to help solve today’s
analog, mixed-signal, and RF design challenges. For more
information and/or support, visit www.analog.com/CN0240.
ADR435
AD7170
12-Bit, Low Power
Bidirectional Isolated High-Side Current Sense with 270 V Common-Mode Rejection
EVALUATION AND DESIGN SUPPORT
Circuit Evaluation Boards
CN-0240 Circuit Evaluation Board (EVAL-CN0240-SDPZ)
System Demonstration Platform (EVAL-SDP-CB1Z)
Design and Integration Files
Schematics, Layout Files, Bill of Materials
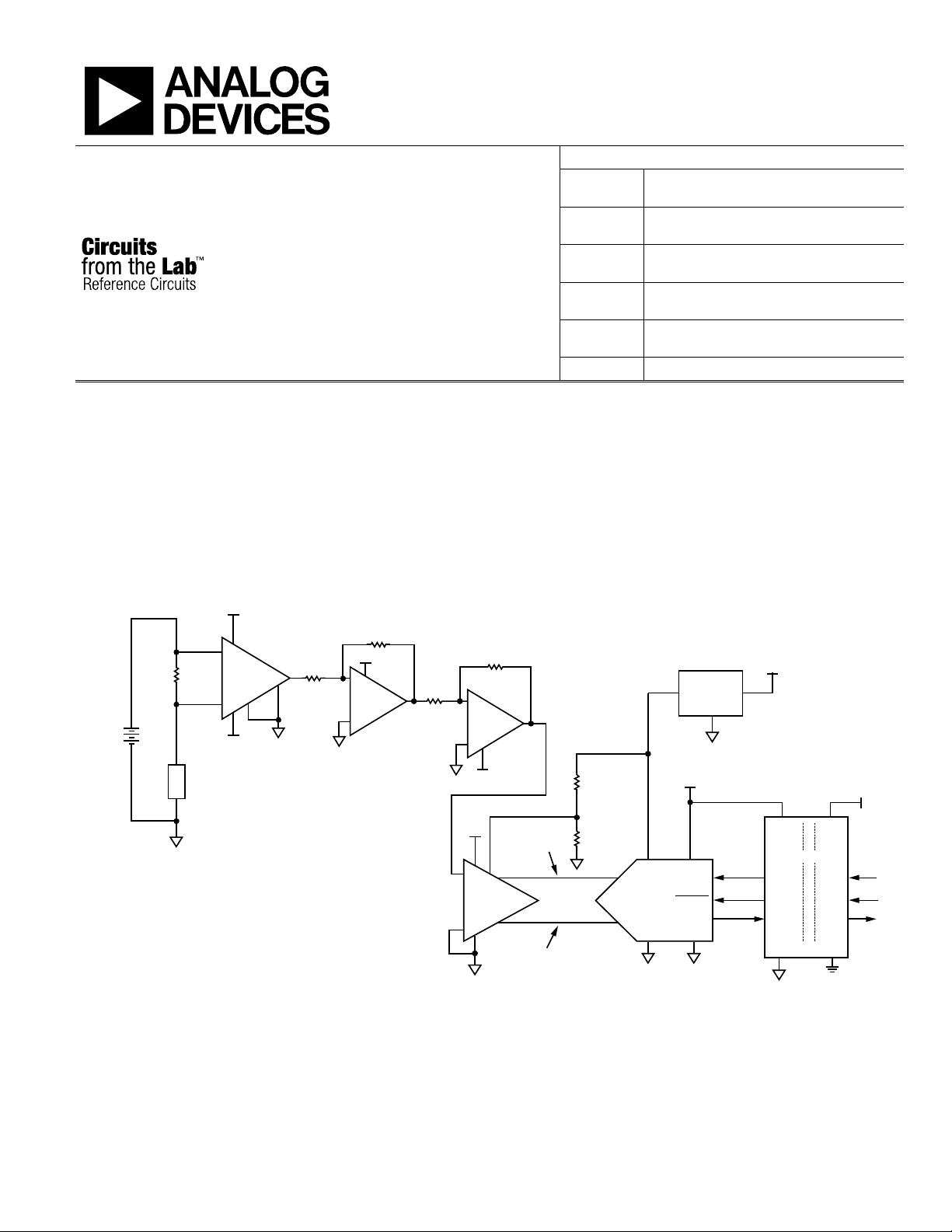
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
This circuit, shown in Figure 1, monitors bidirectional current
from sources with dc voltages of up to ±270 V with less than 1%
linearity error. The load current passes through a shunt resistor,
which is external to the circuit. The shunt resistor value is
chosen so that the shunt voltage is approximately 100 mV at
maximum load current.
engineers. Standard engineerin
room temperature. However, you are solely responsible for testing the circuit and determining its
Figure 1. High Common-Mode Voltage Bidirectional Isolated Current Monitor (All Connections and Decoupling Not Shown)
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
www.analog.com
CN-0240 Circuit Note
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
21.1kΩ
380kΩ
380kΩ
380kΩ
20kΩ
REF(–)
–IN
+IN
–V
S
NC
+V
S
OUTPUT
REF(+)
AD629
NC = NO CONNECT
10154-002
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE (±V)
COMMON-MODE VOLTAGE (±V)
400
360
320
280
240
200
160
120
80
40
0
0 2 6 104 8 12 14 1816 20
TA = +25°C
TA = +85°C
TA = –40°C
10154-003
The AD629 amplifier accurately measures and buffers (G = 1) a
small differential input voltage and rejects large positive
common-mode voltages up to 270 V.
The dual AD8622 is used to amplify the output of the AD629 by
a factor of 100. The AD8475 funnel amplifier attenuates the
signal (G = 0.4), converts it from single-ended to differential,
and level shifts the signal to satisfy the analog input voltage
range of the AD7170 sigma-delta ADC.
Galvanic isolation is provided by the ADuM5402 quad channel
isolator. This is not only for protection but also to isolate the
downstream circuitry from the high common-mode voltage. In
addition to isolating the output data, the ADuM5402 digital
isolator can supply isolated +5.0 V for the circuit.
The measurement result from the AD7170 is provided as a
digital code utilizing a simple 2-wire, SPI-compatible serial
interface.
This combination of parts provides an accurate high voltage
positive and negative rail current sense solution with a small
component count, low cost, and low power.
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The circuit is designed for a full-scale shunt voltage of 100 mV
at maximum load current I
resistor is R
= (500 mV)/(I
SHUNT
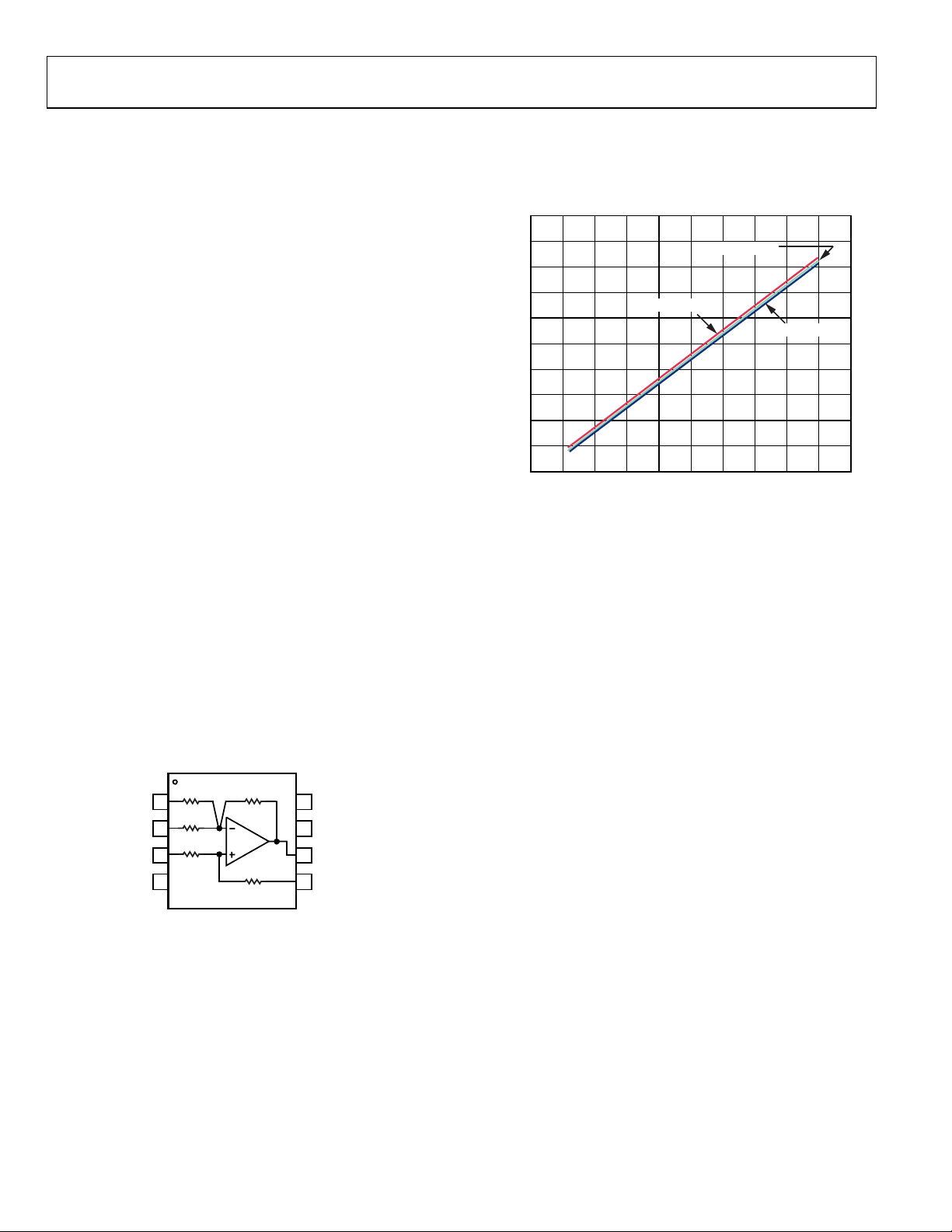
The AD629, shown in Figure 2, is a difference amplifier
designed with internal thin film resistors allowing continuous
common-mode signals up to ±270 V with transient protection
to ±500 V. For REF(+) and REF(−) grounded, the signal on the
+IN terminal is attenuated by a factor of 20. The signal is then
amplified by a noise gain of 20, restoring the original amplitude
at the output.
Figure 2. AD629 High Common-Mode Voltage Difference Amplifier
The CMRR is 77 dB minimum @ 500 Hz for the AD629A, and
86 dB minimum @ 500 Hz for the AD629B.
In order to maintain the desired common-mode rejection, there
are several important conditions to meet. First, the ability of
. Therefore, the value of the shunt
MAX
).
MAX
the part to reject these common-mode signals is determined by
the power supply voltage as shown in Figure 3. Failure to
implement dual supplies of a sufficient voltage will reduce the
common-mode rejection.
Figure 3. AD629 Common-Mode Voltage Range vs. Power Supply Voltage
Secondly, the AD629 should only be operated in the unity gain
mode using the internal matched thin film resistors. Changing
the gain with external resistors will degrade the common-mode
rejection due to mismatch errors.
The AD8622 is a CMOS low power, precision, dual, rail-to-rail
output op amp used primarily for amplifying the signal of
interest.
By cascading two inverting gain stages with a gain of –10, the
100 mV full-scale output of the AD629 is amplified by a factor
of 100 yielding a 10 V full-scale signal. These values can be
either positive or negative, depending on the direction of the
current.
The dual supplies of the AD8622 allow both the input and
output signals to swing above and below ground as required to
measure bidirectional input currents.
In the final stage of the signal chain before conversion into a
digital word, the AD8622 output voltage is conditioned to fit the
analog input voltage range of the ADC.
The AD8475 "funnel amplifier," shown in Figure 4, provides two
optional attenuation factors (0.4 and 0.8). In addition, the signal
is converted into a differential one, and the common-mode
voltage at the output is determined by the voltage on the VOCM
pin. With a single 5 V supply, the analog input voltage range is
±12.5 V (for a single-ended input).
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 5
 Loading...
Loading...