Circuit Note
engineers. Standard engineering practices have been employed in the design and construction of
each circuit, and their function and performance have been tested and verified in a lab environment at
ever, you are solely responsible for testing the circuit and determining its
suitability and applicability for your use and application. Accordingly, in no event shall Analog Devices
12.288MHz
ADAU1761 SLAVE
ADAU1761 MASTER
ADAV801/ADAV803
DIGITAL
INPUT/OUTPUT
SWITCHING MATRIX
(DATAPATH)
PLAYBACK
DATA INPUT
ILRCLK
IBCLK
ISDATA
DIRIN
MCLKI
SYSCLK3
DIR
DITOUT
OSDATA
OBCLK
OLRCLK
DAC_SDATA
ADC_SDATA
ADAU1761
BCLK
SERIAL DAT A
INPUT/OUTPUT
LRCLK
MCLK
DIT
AUX DATA
INPUT
TORX173S/PDIF IN
I
2
S IN
I
2
S OUT
S/PDIF OUTTOTX173
AUX DATA
OUTPUT
RECORD
DATA
OUTPUT
PLL
PLL
09970-001
Circuits from the Lab™ reference circuits are engineered and
tested for quick and easy system integration to help solve today’s
analog, mixed-signal, and RF design challenges. For more
information and/or support, visit www.analog.com/CN0219.
S/PDIF and I2S Interface for a SigmaDSP Codec
Using the ADAV801/ADAV803 Audio Codec
EVALUATION AND DESIGN SUPPORT
Circuit Evaluation Boards
ADAU1761 Evaluation Board (EVAL-ADAU1761Z)
USBi USB Interface Board (EVAL-ADUSB2EBZ)
(Included with EVAL-ADAU1761Z Board)
ADAV801 Evaluation Board (EVAL-ADAV801EBZ) or
ADAV803 Evaluation Board (EVAL-ADAV803EBZ)
Design and Integration Files
Schematics, Layout Files, Bill of Materials
CN-0219
Devices Connected/Referenced
ADAU1761
ADAV801/
ADAV803
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) is a high quality digital
audio format that is commonly used in consumer electronics
and is used to interconnect audio equipment. Many audio
codecs/DSPs only support I
which is a problem when using these parts in circuits that need
to support both S/PDIF or the AES (Audio Engineering Society)
professional standard.
SigmaDSP® Stereo, Low Power, 96 kHz,
24-Bit Audio Codec with Integrated PLL
Audio Codec for Recordable DVD
2
(SPI/I
C Control Interface)
2
S as digital audio input/output,
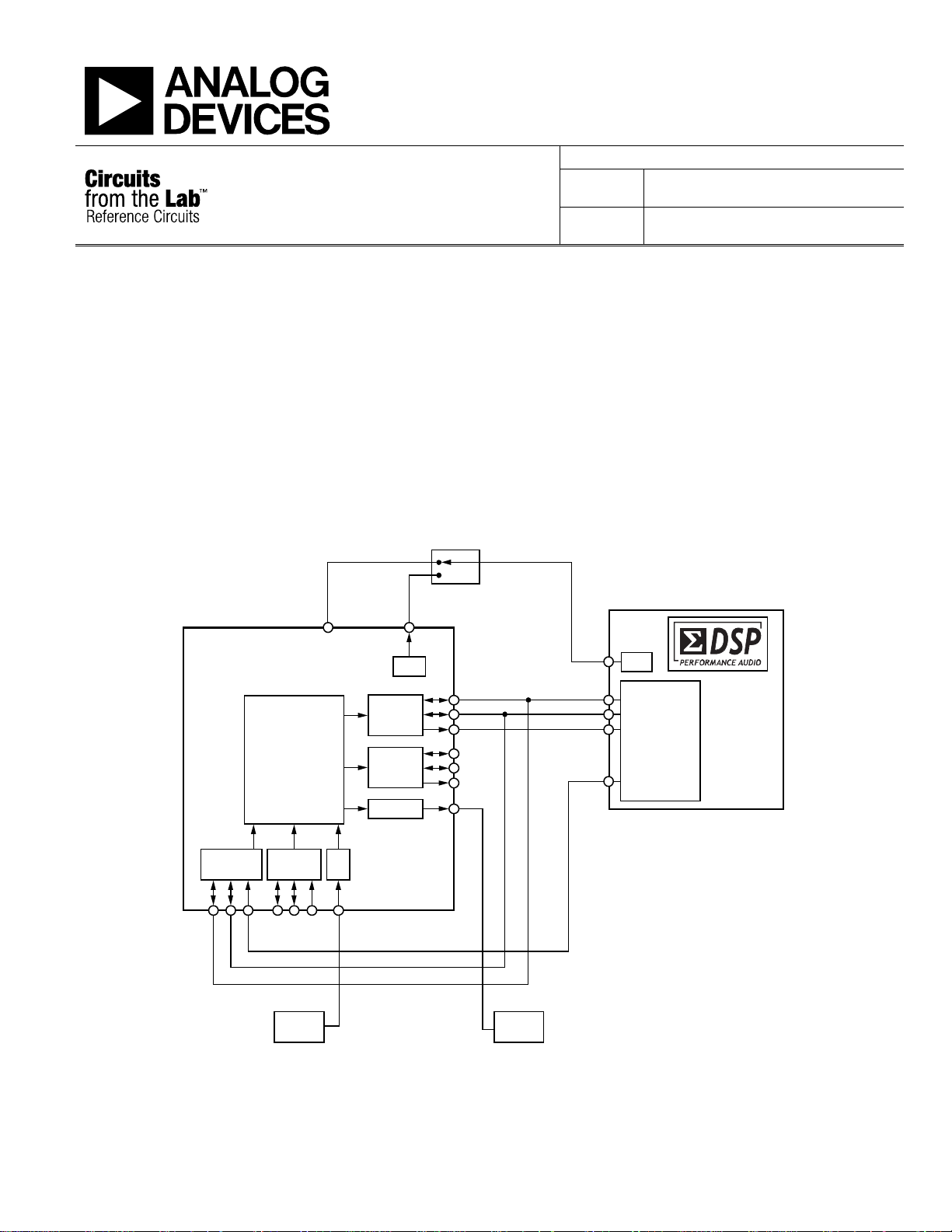
Figure 1. ADAV801/ADAV803 Connections for S/PDIF In/Out to ADAU1761 SigmaDSP (Sim plified Schematic: Power Supply Decoupling and All Connections Not Shown)
Rev.0
Circuits from the Lab™ circuits from Analog Devices have been designed and built by Analog Devices
room temperature. How
be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, consequential or punitive damages due to any cause
whatsoever connected to the use of any Circuits from the Lab circuits. (Continued on last page)
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com

CN-0219 Circuit Note
The circuit, in Figure 1, shows how to overcome this problem
by connecting the ADAV801 or the ADAV803 audio codec to a
SigmaDSP® device, such as the ADAU1761.
The audio input in S/PDIF format is converted to I
2
S before
processing by the ADAU1761, and the processed audio output
2
in I
S format is converted back to S/PDIF by the ADAV801/
ADAV803. The ADAV801/ ADAV803 has a flexible digital
input/output routing matrix that allows it to process audio in
2
either I
S or S/PDIF format and output it in either format as a
master or slave with the use of an onboard SRC (sample rate
converter). The ADAV801/ ADAV803 support the consumer
audio standard, and channel status data can be embedded in the
audio stream by writing to the relevant registers in the
ADAV801/ ADAV803. This is a useful feature for passing
configuration information between devices. The ADAV801/
ADAV803 has a stereo DAC/ADC that can also be used to
process audio as needed.
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The ADAV801/ ADAV803 has two sets of input/output I2S
ports, either of which can be used. In the configuration shown
in Figure 1, the playback port ILRCLK and record port
OLRCLK pins are connected to the LRCLK pin of the
ADAU1761. The IBCLK and OBCLK pins are connected to the
BCLK pin of the ADAU1761. The ISDATA pin is connected to
the ADC_SDATA pin of the ADAU1761, and the OSDATA is
connected to the DAC_SDATA pin of the ADAU1761.
The S/PDIF input comes from the TORX173 fiber optic
receiver module into the DIRIN pin and is then output to the
ADAU1761 on the record port in I
processed by the ADAU1761 SigmaDSP® device it is output on
the ADC_SDATA pin to the playback port of the ADAV801/
ADAV803 in I
2
S format. It is then converted to S/PDIF format
on the DITOUT pin and fed to the TOTX173 fiber optical
transmitter module.
The circuit is powered from a 3.3 V AVDD supply. The master
clock for the circuit is generated either by the ADAV801/
ADAV803 or by an external oscillator, depending on whether
the ADAU1761 is to be configured as master or slave. In the
case where the ADAU1761 is a slave, i.e. the BLCK and LRCLK
are driven by the ADAV801/ ADAV803, the MCLK is 256× the
recovered audio clock from the S/PDIF stream. It can also be
configured to be 512× the recovered clock. This clock is
accessed on the SYSCLK3 pin of the ADAV801/ ADAV803 and
connected to the MCLK pin of the ADAU1761.
When the ADAU1761 is master, the MCLK is generated by an
onboard oscillator and is supplied to the ADAV801/ADAV803
on the MCLKI pin. In this case, the ADAU1761 drives the
LRCLK and BCLK lines, and the SRC on the ADAV801/
2
S format. Once the audio is
Rev. 0| Page 2 of 4
ADAV803 is used to synchronize the audio between the I
and the S/PDIF port.
Register Settings
A complete design support documentation package for this circuit
note can be found at www.analog.com/CN0219-DesignSupport.
This includes register setting files for both master and slave
configuration for the ADAV801/ADAV803 and ADAU1761.
These register settings files can be loaded using the relevant
evaluation board software.
COMMON VARIATIONS
This circuit can also be set up with any part that has a
SigmaDSP processor core and requires an S/PDIF/AES audio
interface, including the ADAU1401A, ADAU1701, and
ADAU1781. Although not described in this circuit note, the
above circuit can be modified to work with the AES audio
format. Instead of optical connectors, XLR connectors would be
used, and transformers would be required to convert from
differential to single-ended signals and vice versa.
CIRCUIT EVALUATION AND TEST
This circuit is tested using the ADAV801/ ADAV803
(E VA L-ADAV801EBZ or E VA L-ADAV803EBZ) and
ADAU1761 (E VAL -ADAU1761Z) evaluation boards.
The necessary connections between the two boards and
link configurations are contained in the design support
documentation. Figure 2 shows the full test setup using both
evaluation boards.
Equipment Needed
The ADAU1761 evaluation board is programmed using
SigmaStudio thru a USBI board (EVA L-ADUSB2EBZ). The
SigmaStudio GUI software requires a PC with the following:
Windows® 7, Windows Vista, or Windows XP Professional or
Home Edition with SP2, 128 MB of RAM (256 MB recommended), 50 MB of available hard disk space, 1024 × 768 screen
resolution, and USB 1.1/2.0 data port. The ADAV801/
ADAV803 board is controlled using the printer port of a PC
with its own software that can be downloaded from the ADI
website. Two optical connectors are needed to connect the
S/PDIF input/output to the ADAV801/ ADAV803 board. Eight
single pin jumper cables are needed to make the necessary
connections between the two evaluation boards.
Getting Started
From this point, follow the documentation for the
EVA L-ADAU1761Z and EVA L -ADAV801/ EVA L-ADV803EBZ
regarding software installation, setup, and operation of the
system.
2
S port

Circuit Note CN-0219
+12V
USB
TO PC
EVAL-ADUSB2EBZ
I
2
C
−12V
GND
EVAL-ADAV80xEBZ
EVAL-ADAU1761Z
FIBER OPTIC OUTPUT
FIBER OPTIC INPUT
PARALLEL
PORT
TO PC
09970-002
POWER
SUPPLY
+12V
−12V
GND
EVAL-ADAV80xEBZ
EVAL-ADAU1761Z
I
2
S AND MCLK
CONNECTIONS
(SEE DESIGN SUPPORT DOCUMENTS)
EVAL-ADUSB2EBZ
I
2
C/SPI
AUDIO PRECISION
APx585
OPTICAL
S/PDIF IN
OPTICAL
S/PDIF OUT
PC
USB
USBi
PARALLEL
09970-003
The SigmaStudio software is used to program and tune the
registers and SigmaDSP core in the ADAU1761. SigmaStudio
can be downloaded from www.analog.com/sigmastudio.
The software for the ADAV801/ ADAV803 can also be
downloaded from the ADI website. Once the software is
installed, the register setting files in the design documentation
can be loaded to program both boards depending on whether
you want the ADAU1761 device to be master or slave. The
ADAU1761 SigmaStudio project has just a simple audio pass-
thru with volume control for the purposes of testing the circuit
of Figure 1.
Figure 2. Test Setup for Connecting the ADAV801/ADAV803 Board to the ADAU1761 Board
Figure 3. Functional Diagram of Test Setup
Rev. 0| Page 3 of 4

CN-0219 Circuit Note
Setup and Test
An Audio Precision APx585 multichannel audio analyzer can be
used to generate the S/PDIF input and capture the S/PDIF
output. With the ADAU1761 as master and a full-scale 1 kHz
input tone, the THD + N should be ~130 dB at the S/PDIF
output. In slave mode, the THD + N should be ~142 dB, since
there is no SRC needed to synchronize the S/PDIF stream to the
ADAU1761 I
LEARN MORE
CN0219 Design Support Package:
www.analog.com/CN0219-DesignSupport
Gildersleeve, Brett, Using the EVAL-ADUSB2EBZ, Application
Note AN-1006, Analog Devices.
SigmaStudio™ Graphical Development Tool:
www.analog.com/sigmastudio
Data Sheets and Evaluation Boards
ADAU1761 Data Sheet
ADAU1761 Evaluation Board
ADAV801 Data Sheet
ADAV803 Data Sheet
ADAV801/ADAV803 Evaluation Board and Software
2
S stream.
REVISION HISTORY
10/11—Revision 0: Initial Version
(Continue d from first page) Circuits from the Lab circuits are intended only for use with Analog Devices products and are the intellectual property of Analog Devices or its licensors. While you
may use the Circuits from the Lab circuits in the design of your product, no other license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patents or other intellectual property by
application or use of the Circuits from the Lab circuits. Informati on furnished by Analo g Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, "Circuits from the Lab" are supplied "as is"
and without warranties of any kind, express, implied, or statutory including, but not limited to, any implied warranty of merchantability, noninfringement or fitness for a particular
purpose and no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for their use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from their use. Analog Devices
reserves the right to change any Circuits fro m the Lab circuits at any time without notice but is under no obligation to do so.
©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
CN09970-0-10/11(0)
Rev. 0| Page 4 of 4
 Loading...
Loading...