Circuit Note
Devices Connected/Referenced
Circuits from the Lab™ reference circuits are engineered and
tested for quick and easy system integration to help solve today’s
analog, mixed-signal, and RF design challenges. For more
information and/or support, visit www.analog.com/CN0208.
ADAU1446
ADMP441 Digital MEMS Microphone
High Performance Digital MEMS Microphone's Simple Interface to SigmaDSP
Audio Processor with I
2
S Output
SigmaDSP® Digital Audio Processor with
Flexible Audio Routing Matrix
CN-0208
EVALUATION AND DESIGN SUPPORT
Circuit Evaluation Boards
ADAU1446 Evaluation Board (EVAL-ADAU1446EBZ)
ADMP441 Evaluation Board (EVAL-ADMP441Z-FLEX)
Design and Integration Files
Schematics, Layout Files, Bill of Materials
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
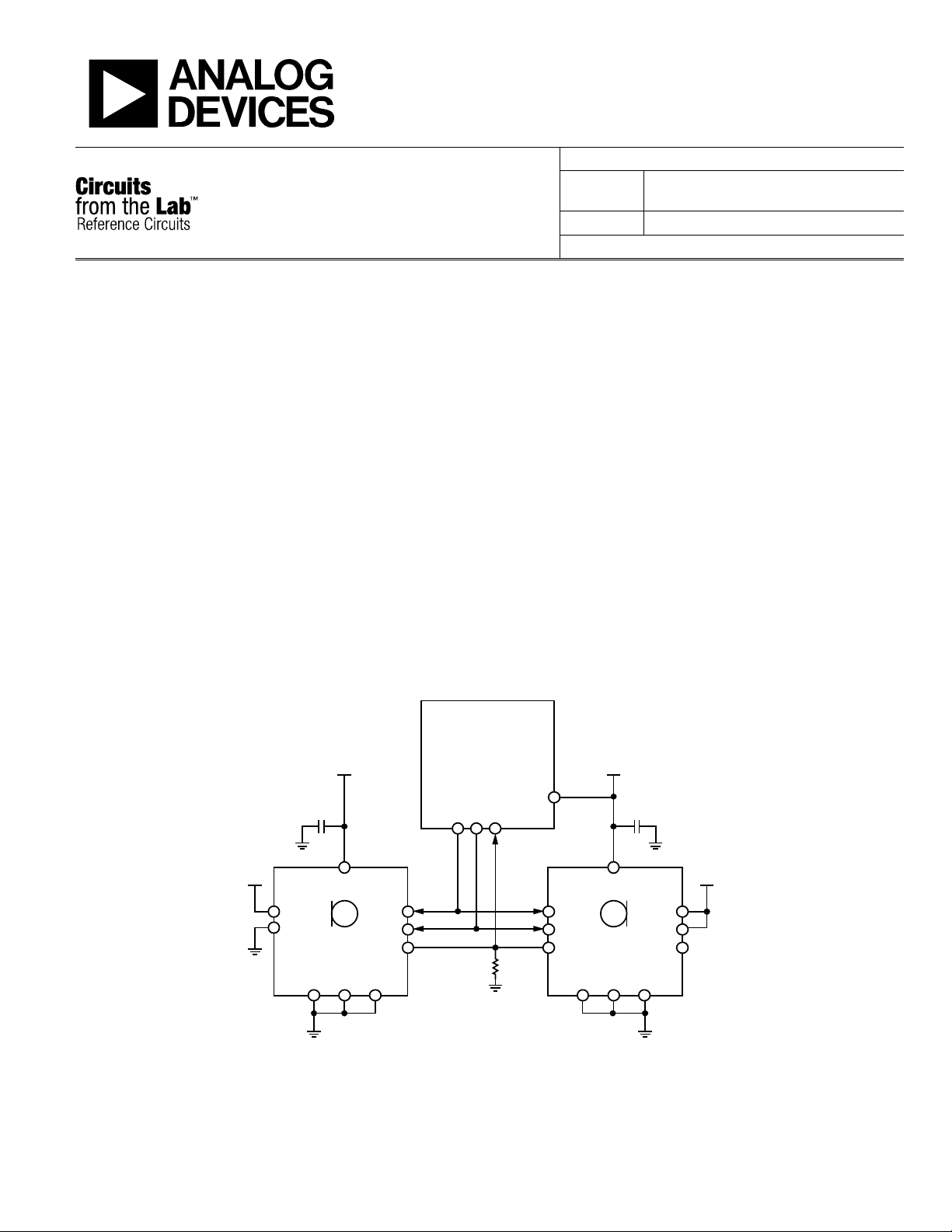
The circuit, shown in Figure 1, allows up to two digital MEMS
microphones to be interfaced to an audio processor on a single
data line. The ADMP441 consists of a MEMS microphone
element and an ASIC with I
microphones to be used in an audio system without the need
for a codec between the MEMS microphones and the processor.
Analog Devices’ MEMS microphones have a high signal-tonoise ratio (SNR) and a flat wideband frequency response,
2
S output. This allows stereo
FROM VOLTAGE
REGULATOR (3.3V)
3.3V
0.1µF
ADAU1446
BCLK0
LRCLK0
SDATA_IN0
making them an excellent choice for high performance, low
power applications.
Up to two ADMP441 MEMS microphones can be input to a single
data line on th
DAU1446 SigmaDSP® audio processor. The
e A
ADAU1446 can be set up with up to nine serial data inputs, so
up to eighteen ADMP441’s can input to a single audio processor.
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The ADMP441 digital MEMS microphones are connected to the
ADAU1446’s SDATA_IN pins. The only necessary passive components
in this circuit are a
and a large p
discharge it while the ADMP441’s output drivers are tri-stated.
The bypass capacitors should be placed as close to the
ADMP441 VDD pin (Pin 7) as possible.
IOVDD
single 0.1 μF bypass capacitor for each ADMP441
ull-down resistor (100 kΩ) on the SD line to
3.3V
0.1µF
3.3V
CHIPEN
L/R
Figure 1. %JHJUBM.&.4Microphone Connection to SigmaDSP Audio Processor (Simplified Schematic: Power Supply Decoupling and All Connections Not Shown)
Rev.A
Circuits from the Lab™ circuits from Analog Devices have been designed and built by Analog Devices
engineers. Standard engineering practices have been employed in the desi
each circuit, and their function and performance have been tested and verified in a lab environment at
room temperature. However, you are solely responsible for testing the circuit and determining its
suitability and applicability for your use and application. Accordingly, in no event shall Analog Devices
be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, consequential or punitive damages due to any cause
whatsoever connected to the use of any Circuits from the Lab circuits. (Continued on last page)
VDD
LEFT
ADMP441
GND GND
SCK
WS
SD
GND
gn and construction of
100kΩ
VDD
SCK
WS
SD
GND GND
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
CHIPEN
RIGHT
ADMP441
GND
L/R
3.3V
09838-001
www.analog.com
CN-0208 Circuit Note
Figure 2. SigmaStudio Serial Input Port Configuration for ADMP441 Microphone Input to ADAU1446
The MEMS microphone’s VDD sh
source as
the ADAU1446’s 3.3 V IOVDD. Even though the
ould be supplied from the same
ADMP441 can operate with VDD between 1.8 V and 3.3 V,
IOVDD on the ADAU1446 must be 3.3 V.
There are three signals that need to be connected between the
ADMP441 and ADAU1446 for the I
2
S data stream: frame clock,
bit clock, and data. Table 1 shows the connections when using
the ADAU1446’s serial data input port 0.
Table 1. Hardware Signal Connections
Signal ADMP441 ADAU1446
Frame clock WS (pin 3) LRCLK0 (pin 15)
Bit clock SCK (pin 1) BCLK0 (pin 12)
Serial Data SD (pin 2) SDATA_IN0 (pin 11)
The L/R pin on the two ADMP441’s should be set to opposite
settings—one pulled to VDD, and the other to ground. When
pulled to GND, the microphone will output its data on the left
2
channel of the I
S stream, and when pulled to VDD, it will
output its data on the right channel.
The ADMP441 is enabled by pulling the CHIPEN pin high.
This pin can either be tied directly to the microphone’s VDD,
which will keep it always enabled while it is powered, or it could
be connected to a GPIO on the ADAU1446, allowing the
SigmaDSP to enable and disable the microphone.
The ADMP441 has a sensitivity of −26 dBFS. In most
applications, the microphone output needs to have some gain
added in the ADAU1446’s signal flow. The SigmaDSP core can
add up to 24 dB of gain to the input signal before a full-scale
signal at 120 dB SPL is clipped. If gain is added to the signal in
the SigmaDSP, then the processor’s output must still be limited
to 0 dBFS.
• LRCLK polarity set for left channel low, right channel
high.
• 24-bit, I
2
S data format.
A screenshot of the SigmaStudio register controls for the serial
input port is shown in Figure 2.
The register settings described here are for using serial input
port 0 with clock input 0, but they could be applied to any of the
nine serial input ports. Serial inputs 1–8 are controlled with
registers 0xE001 to 0xE008. If any of these serial input ports
are connected to additional ADMP441 MEMS microphones, the
corre
nding registers should be set in the same way as serial
spo
input port 0 described above.
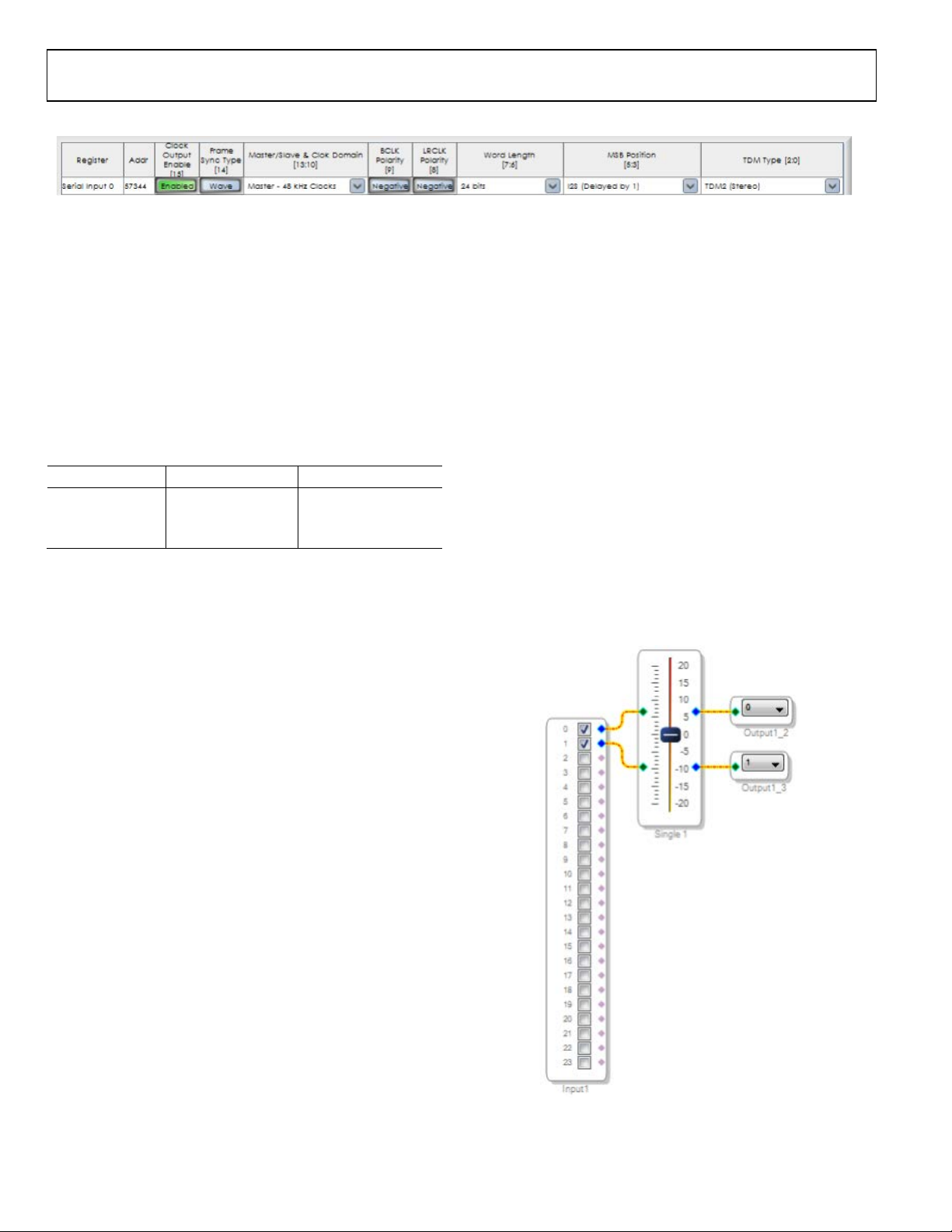
In the SigmaStudio schematic, the data from serial input port 0
is on pins 0 and 1 of the Input cell. The left channel is on pin 0
and the right channel on pin 1. Figure 3 shows a simple
SigmaStudio schematic with two audio channels going through
a volume control to the outputs.
09838-002
Register Settings
Register 0xE000 must be set in the ADAU1446 to enable its
2
serial input port for I
S input. When this register is set to 0xA4
0x00, Serial Input Port 0 will be configured for:
• Enabling the clock outputs.
• 50% duty cycle clock.
• 48 kHz clock master.
• Data changes on the falling edge of BCLK, clocked on
the BCLK rising edge.
Rev. A | Page 2 of 4
09838-003
Figure 3. SigmaStudio Schematic with Stereo Input on Serial Input Port 0
 Loading...
Loading...