Analog Devices ADSP 21363 pra Datasheet
a
SHARC® Processor
Preliminary Technical Data
SUMMARY
High performance 32-bit/40-bit floating point processor
optimized for professional audio processing
At 333 MHz/2 GFLOPs, with unique audio centric peripherals
such as the Digital Audio Interface the ADSP-21363 SHARC
processor is ideal for applications that require industry
leading equalization, reverberation and other effects
processing
Single-Instruction Multiple-Data (SIMD) computational
architecture
Two 32-bit IEEE floating-point/32-bit fixed-point/40-bit
extended precision floating-point computational units,
each with a multiplier, ALU, shifter, and register file
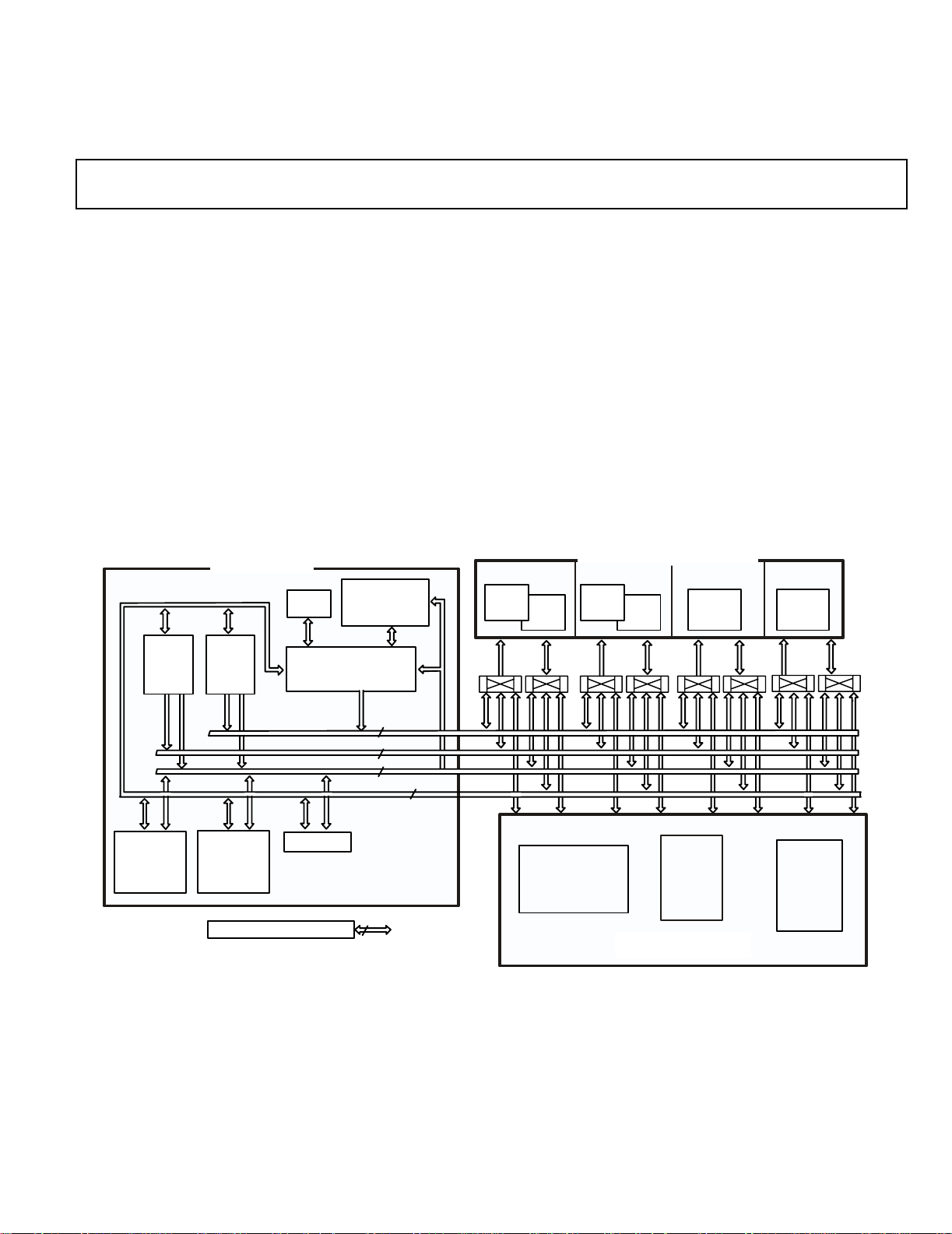
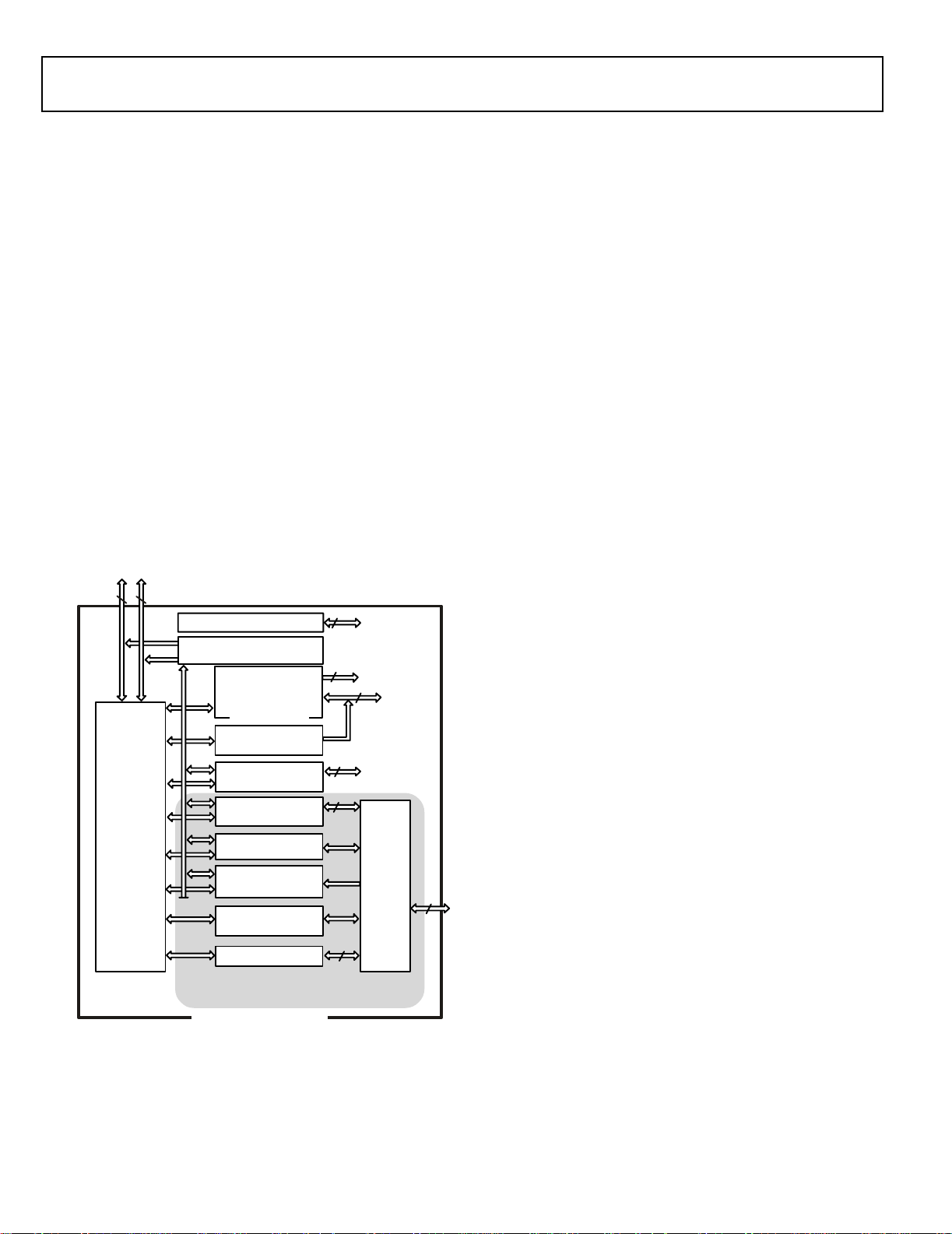
CORE PROCESSOR
INSTRUCTION
TIMER
CACHE
32 X 48-BIT
ADSP-21363
On-chip memory—3M bit of on-chip SRAM and a dedicated
4M bit of on-chip mask-programmable ROM
Code compatible with all other members of the SHARC family
The ADSP-21363 is available with a 333 MHz core instruction
rate. For complete ordering information, see Ordering
Guide on Page 44
BLOCK 0 BLOCK 1 BLOCK 2 BLOCK 3
SRAM
1M BIT ROM
2M BIT
4 BLOCKS OF ON-CHIP MEMORY
SRAM
1M BI T ROM
2M BIT
SRAM
0.5M BIT
SRAM
0.5M BIT
DAG1
8X4X32
PROCESSING
ELEME NT
(PEX)
DAG2
8X4X32
PM ADDRESS BUS
DM ADDRESS BUS
PM DATA BUS
PROCESSING
ELEMENT
(PEY)
JTAG TE ST & EMULA TION
PX REGISTER
PROGRAM
SEQUENCER
DM DATA BUS
32
32
64
64
6
S
Figure 1. Functional Block Diagram – Processor Core
SHARC and the SHARC logo are registered trademarks of Analog Devices, Inc.
Rev. PrA
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies.
ADDR DATA
IOA
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106 U.S.A.
Tel:781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax:781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
ADDR DATA
IOD
IOP REGISTERS
(MEMORY MAPPED)
IOA
ADDR DATA
IOD IOA IOD IOD
SPI
SPORTS
IDP
PCG
TIMERS
I/O PROCESSOR
AND PERIPHERALS
SEE “ADSP-21363 MEMORY
AND I/O INTERFACE FEATURES”
SECTION FOR DETAILS
ADDR DATA
IOA
SIGNAL
ROUTING
UNIT

ADSP-21363 Preliminary Technical Data
KEY FEATURES – PROCESSOR CORE
At 333 MHz (3.0 ns) core instruction rate, the ADSP-21363
performs 2 GFLOPS/666 MMACS
3M bit on-chip single-ported SRAM (1M Bit in blocks 0 and 1,
and 0.50M Bit in blocks 2 and 3) for simultaneous access by
the core processor and DMA
4M bit on-chip mask-programmable ROM (2M bit in block 0
and 2M bit in block 1)
Dual Data Address Generators (DAGs) with modulo and bit-
reverse addressing
Zero-overhead looping with single-cycle loop setup, provid-
ing efficient program sequencing
Single Instruction Multiple Data (SIMD) architecture
provides:
Two computational processing elements
Concurrent execution
Code compatibility with other SHARC family members at
the assembly level
Parallelism in busses and computational units allows sin-
gle cycle executions (with or without SIMD) of a multiply
operation, an ALU operation, a dual memory read or
write, and an instruction fetch
Transfers between memory and core at a sustained 5.4G
bytes/s bandwidth at 333 MHz core instruction rate
INPUT/OUTPUT FEATURES
DMA Controller supports:
25 DMA channels for transfers between ADSP-21363 internal
memory and a variety of peripherals
32-bit DMA transfers at core clock speed, in parallel with full-
speed processor execution
Asynchronous parallel port provides access to asynchronous
external memory
16 multiplexed address/data lines support 24-bit address
external address range with 8-bit data or 16-bit address
external address range with 16-bit data
55M byte per sec transfer rate
External memory access in a dedicated DMA channel
8- to 32- bit and 16- to 32-bit packing options
Programmable data cycle duration options: 2 to 31 CCLK
Digital audio interface (DAI) includes six serial ports, two Pre-
cision Clock Generators, an Input Data Port, three timers,
and a Signal routing unit
Six dual data line serial ports that operate at up to 50M bit/s
on each data line—each has a clock, frame sync and two
data lines that can be configured as either a receiver or
transmitter pair
Left-justified Sample Pair and I
direction for up to 24 simultaneous receive or transmit
channels using two I
port
TDM support for telecommunications interfaces including
128 TDM channel support for newer telephony interfaces
such as H.100/H.110
2
2
S Support, programmable
S compatible stereo devices per serial
Up to 12 TDM stream support, each with 128 channels per
frame
Companding selection on a per channel basis in TDM mode
Input data port provides an additional input path to the
SHARC core, configurable as eight channels of serial data
or seven channels of serial data and a single channel of up
to 20-bit wide parallel data
Signal routing unit provides configurable and flexible con-
nections between all DAI components–six serial ports, two
precision clock generators, an input data port with a data
acquisition port, one SPI port, three timers, 10 interrupts,
six flag inputs, six flag outputs, and 20 SRU I/O pins
(DAI_P20-1)
Two Serial Peripheral Interfaces (SPI): primary on dedicated
pins, secondary on DAI pins provide:
Master or slave serial boot through primary SPI
Full-duplex operation
Master-Slave mode multi-master support
Open drain outputs
Programmable baud rates, clock polarities and phases
3 Muxed Flag/IRQ lines
1 Muxed Flag/Timer expired line
Pulse Width Modulation provides:
16 PWM outputs configured as four groups of four outputs
Supports center-aligned or edge-aligned PWM waveforms
Can generate complementary signals on two outputs in
paired mode or independent signals in non paired mode
PLL has a wide variety of software and hardware multi-
plier/divider ratios
Dual voltage: 3.3 V I/O, 1.2 V core
Available in 136-ball Mini-BGA and 144-lead INT–HS LQFP
Packages (see Ordering Guide on Page 44)
Rev. PrA | Page 2 of 44 | September 2004
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
ADSP-21363Preliminary Technical Data
The ADSP-21363 SHARC processor is a member of the SIMD
SHARC family of DSPs that feature Analog Devices' Super Harvard Architecture. The ADSP-21363 is source code compatible
with the ADSP-2126x, and ADSP-2116x DSPs as well as with
first generation ADSP-2106x SHARC processors in SISD (Single-Instruction, Single-Data) mode. The ADSP-21363 is a 32bit/40-bit floating point processor optimized for professional
audio applications with a large on-chip SRAM, multiple internal
buses to eliminate I/O bottlenecks, and an innovative Digital
Audio Interface (DAI).
As shown in the functional block diagram on Page 1, the
ADSP-21363 uses two computational units to deliver a significant performance increase over previous SHARC processors on
a range of signal processing algorithms. Fabricated in a state-ofthe-art, high speed, CMOS process, the ADSP-21363 processor
achieves an instruction cycle time of 3.0 ns at 333 MHz. With its
SIMD computational hardware, the ADSP-21363 can perform 2
GFLOPS running at 333 MHz.
Table 1 shows performance benchmarks for the ADSP-21363.
Table 1. ADSP-21363 Benchmarks (at 333 MHz)
Benchmark Algorithm Speed
(at 333 MHz)
1024 Point Complex FFT (Radix 4, with reversal) 27.9 µs
FIR Filter (per tap)
IIR Filter (per biquad)
Matrix Multiply (pipelined)
[3x3] × [3x1]
[4x4] × [4x1]
Divide (y/×) 10.5 ns
Inverse Square Root 16.3 ns
1
Assumes two files in multichannel SIMD mode
1
1
1.5 ns
6.0 ns
13.5 ns
23.9 ns
The ADSP-21363 continues SHARC’s industry leading standards of integration for DSPs, combining a high performance
32-bit DSP core with integrated, on-chip system features.
The block diagram of the ADSP-21363 on Page 1, illustrates the
following architectural features:
• Two processing elements, each of which comprises an
ALU, Multiplier, Shifter and Data Register File
• Data Address Generators (DAG1, DAG2)
• Program sequencer with instruction cache
• PM and DM buses capable of supporting four 32-bit data
transfers between memory and the core at every core processor cycle
• Three Programmable Interval Timers with PWM Generation, PWM Capture/Pulse width Measurement, and
External Event Counter Capabilities
•On-Chip SRAM (3M bit)
• On-Chip mask-programmable ROM (4M bit)
• 8- or 16-bit Parallel port that supports interfaces to off-chip
memory peripherals
• JTAG test access port
The block diagram of the ADSP-21363 on Page 6, illustrates the
following architectural features:
• DMA controller
• Six full duplex serial ports
• Two SPI-compatible interface ports—primary on dedicated pins, secondary on DAI pins
• Digital Audio Interface that includes two precision clock
generators (PCG), an input data port (IDP), six serial ports,
eight serial interfaces, a 20-bit parallel input port, 10 interrupts, six flag outputs, six flag inputs, three timers, and a
flexible signal routing unit (SRU) and an SPI port
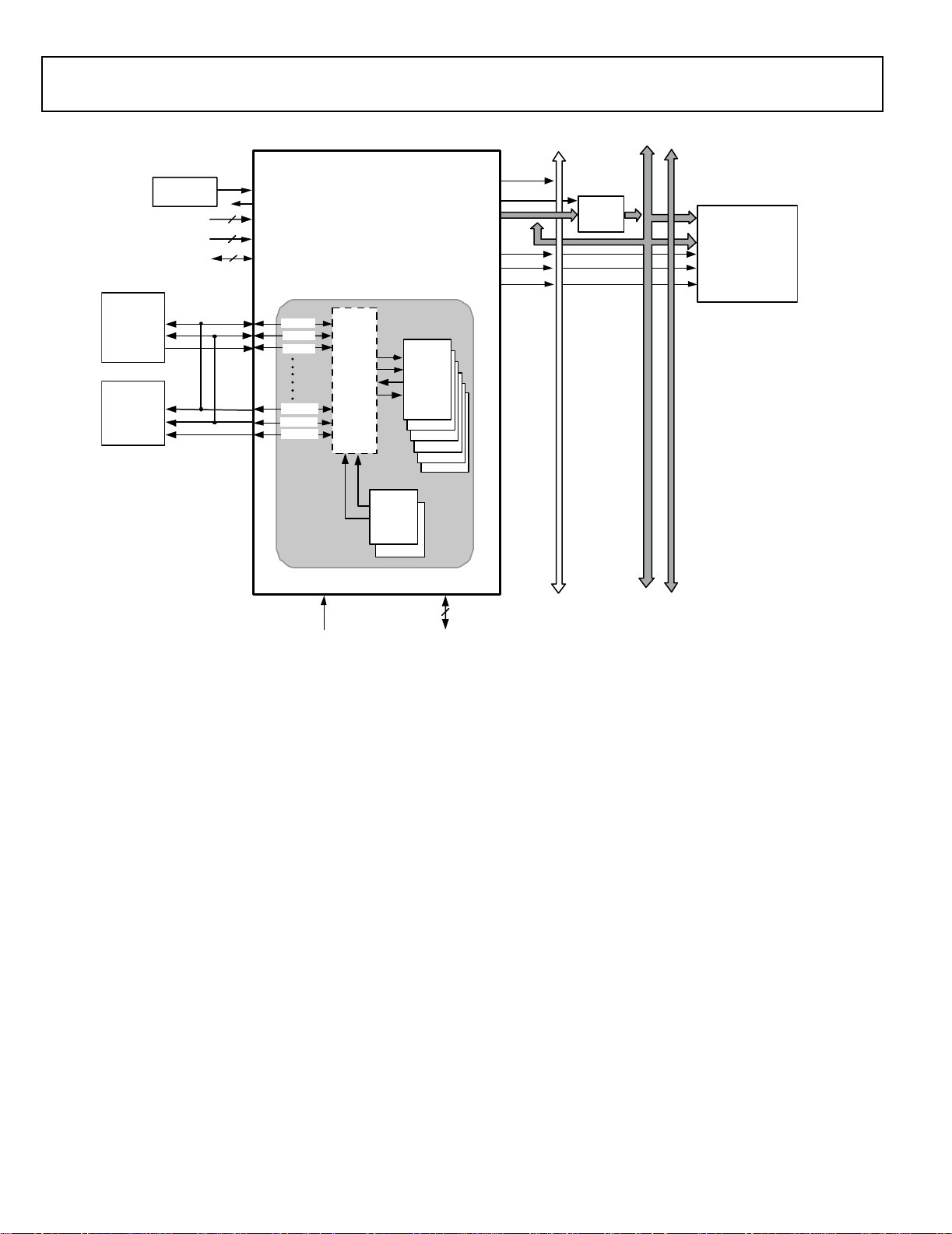
Figure 2 on Page 4 shows one sample configuration of a SPORT
using the precision clock generators to interface with an I
ADC and an I
2
S DAC with a much lower jitter clock than the
2
S
serial port would generate itself. Many other SRU configurations are possible.
ADSP-21363 FAMILY CORE ARCHITECTURE
The ADSP-21363 is code compatible at the assembly level with
the ADSP-2126x, ADSP-21160 and ADSP-21161, and with the
first generation ADSP-2106x SHARC processors. The ADSP21363 shares architectural features with the ADSP-2126x and
ADSP-2116x SIMD SHARC processors, as detailed in the following sections.
SIMD Computational Engine
The ADSP-21363 contains two computational processing elements that operate as a Single-Instruction Multiple-Data
(SIMD) engine. The processing elements are referred to as PEX
and PEY and each contains an ALU, multiplier, shifter and register file. PEX is always active, and PEY may be enabled by
setting the PEYEN mode bit in the MODE1 register. When this
mode is enabled, the same instruction is executed in both processing elements, but each processing element operates on
different data. This architecture is efficient at executing math
intensive signal processing algorithms.
Entering SIMD mode also has an effect on the way data is transferred between memory and the processing elements. When in
SIMD mode, twice the data bandwidth is required to sustain
computational operation in the processing elements. Because of
this requirement, entering SIMD mode also doubles the bandwidth between memory and the processing elements. When
using the DAGs to transfer data in SIMD mode, two data values
are transferred with each access of memory or the register file.
Independent, Parallel Computation Units
Within each processing element is a set of computational units.
The computational units consist of an arithmetic/logic unit
(ALU), multiplier, and shifter. These units perform all operations in a single cycle. The three units within each processing
Rev. PrA | Page 3 of 44 | September 2004
ADSP-21363 Preliminary Technical Data
ADC
(OPTIONAL)
CLK
SDAT
DAC
(OPTIONAL)
CLK
SDAT
FS
FS
CLOCK
2
2
3
CLKI N
XTAL
CLK_ CFG1-0
BOOTC FG1-0
FLAG3-1
DA I_ P1
DAI_P2
DAI_P3
DA I_ P1 8
DA I_ P1 9
DA I_ P20
ADSP-21363
SCL K0
CLK
FS
PCGA
PCGB
SFS 0
SD0 A
SD0 B
SPO RT0
SP ORT 1
SPO RT2
SPO RT3
SPORT 4
SPO RT5
SRU
DAI
RESET JTAG
CLKOUT
AD15-0
6
ALE
RD
WR
CO NT R O L
LATCH
ADDR
PARALLEL
DATA
OE
WE
CSFLAG0
DATA
ADDRESS
PO RT
RAM
BOOT ROM
I/O D EVICE
Figure 2. ADSP-21363 System Sample Configuration
element are arranged in parallel, maximizing computational
throughput. Single multifunction instructions execute parallel
ALU and multiplier operations. In SIMD mode, the parallel
ALU and multiplier operations occur in both processing elements. These computation units support IEEE 32-bit singleprecision floating-point, 40-bit extended precision floatingpoint, and 32-bit fixed-point data formats.
Data Register File
A general-purpose data register file is contained in each
processing element. The register files transfer data between the
computation units and the data buses, and store intermediate
results. These 10-port, 32-register (16 primary, 16 secondary)
register files, combined with the ADSP-2136x enhanced Harvard architecture, allow unconstrained data flow between
computation units and internal memory. The registers in PEX
are referred to as R0-R15 and in PEY as S0-S15.
Single-Cycle Fetch of Instruction and Four Operands
The ADSP-21363 features an enhanced Harvard architecture in
which the data memory (DM) bus transfers data and the program memory (PM) bus transfers both instructions and data
(see Figure 1 on Page 1). With the ADSP-21363’s separate program and data memory buses and on-chip instruction cache,
the processor can simultaneously fetch four operands (two over
each data bus) and one instruction (from the cache), all in a single cycle.
Instruction Cache
The ADSP-21363 includes an on-chip instruction cache that
enables three-bus operation for fetching an instruction and four
data values. The cache is selective—only the instructions whose
fetches conflict with PM bus data accesses are cached. This
cache allows full-speed execution of core, looped operations
such as digital filter multiply-accumulates, and FFT butterfly
processing.
Data Address Generators With Zero-Overhead Hardware Circular Buffer Support
The ADSP-21363’s two data address generators (DAGs) are
used for indirect addressing and implementing circular data
buffers in hardware. Circular buffers allow efficient programming of delay lines and other data structures required in digital
signal processing, and are commonly used in digital filters and
Fourier transforms. The two DAGs of the ADSP-21363 contain
sufficient registers to allow the creation of up to 32 circular buffers (16 primary register sets, 16 secondary). The DAGs
automatically handle address pointer wraparound, reduce overhead, increase performance, and simplify implementation.
Circular buffers can start and end at any memory location.
Rev. PrA | Page 4 of 44 | September 2004
ADSP-21363Preliminary Technical Data
Flexible Instruction Set
The 48-bit instruction word accommodates a variety of parallel
operations, for concise programming. For example, the
ADSP-21363 can conditionally execute a multiply, an add, and a
subtract in both processing elements while branching and fetching up to four 32-bit values from memory—all in a single
instruction.
ADSP-21363 MEMORY AND I/O INTERFACE FEATURES
The ADSP-21363 adds the following architectural features to
the SIMD SHARC family core.
On-Chip Memory
The ADSP-21363 contains three megabits of internal SRAM
and four megabits of internal mask-programmable ROM. Each
block can be configured for different combinations of code and
data storage (see Table 2). Each memory block supports single-
Table 2. ADSP-21363 Internal Memory Space
IOP Registers 0x0000 0000 - 0003 FFFF
Long Word (64 bits) Extended Precision Normal or
Instruction Word (48 bits)
BLOCK 0 ROM
0x0004 0000–0x0004 7FFF
Reserved
0x0004 8000–0x0004 BFFF
BLOCK 0 RAM
0x0004 C000–0x0004 FFFF
BLOCK 1 ROM
0x0005 0000–0x0005 7FFF
Reserved
0x0005 8000–0x0005 BFFF
BLOCK 1 RAM
0x0005 C000–0x0005 FFFF
BLOCK 2 RAM
0x0006 0000–0x0006 1FFF
Reserved
0x0006 2000– 0x0006 FFFF
BLOCK 3 RAM
0x0007 0000–0x0007 1FFF
Reserved
0x0007 2000– 0x0007 FFFF
BLOCK 0 ROM
0x0008 0000–0x0008 AAAA
BLOCK 0 RAM
0x0009 0000–0x0009 5555
BLOCK 1 ROM
0x000A 0000–0x000A AAAA
BLOCK 1 RAM
0x000B 0000–0x000B 5555
BLOCK 2 RAM
0x000C 0000–0x000C 2AAA
BLOCK 3 RAM
0x000E 0000–0x000E 2AAA
cycle, independent accesses by the core processor and I/O processor. The ADSP-21363 memory architecture, in combination
with its separate on-chip buses, allow two data transfers from
the core and one from the I/O processor, in a single cycle.
The ADSP-21363’s, SRAM can be configured as a maximum of
96K words of 32-bit data, 192K words of 16-bit data, 64K words
of 48-bit instructions (or 40-bit data), or combinations of different word sizes up to three megabits. All of the memory can be
accessed as 16-bit, 32-bit, 48-bit, or 64-bit words. A 16-bit floating-point storage format is supported that effectively doubles
the amount of data that may be stored on-chip. Conversion
between the 32-bit floating-point and 16-bit floating-point formats is performed in a single instruction. While each memory
block can store combinations of code and data, accesses are
most efficient when one block stores data using the DM bus for
transfers, and the other block stores instructions and data using
the PM bus for transfers.
Normal Word (32 bits) Short Word (16 bits)
BLOCK 0 ROM
0x0008 0000–0x0008 FFFF
Reserved
0x0009 0000–0x0009 7FFF
BLOCK 0 RAM
0x0009 8000–0x0009 FFFF
BLOCK 1 ROM
0x000A 0000– 0x000A FFFF
Reserved
0x000B 0000– 0x000B 7FFF
BLOCK 1 RAM
0x000B 8000–0x000B FFFF
BLOCK 2 RAM
0x000C 0000–0x000C 3FFF
Reserved
0x000C 4000– 0x000D FFFF
BLOCK 3 RAM
0x000E 0000–0x000E 3FFF
Reserved
0x000E 4000–0x000F FFFF
BLOCK 0 ROM
0x0010 0000–0x0011 FFFF
Reserved
0x0012 0000–0x0012 FFFF
BLOCK 0 RAM
0x0013 0000–0x0013 FFFF
BLOCK 1 ROM
0x0014 0000–0x0015 FFFF
Reserved
0x0016 0000–0x0016 FFFF
BLOCK 1 RAM
0x0017 0000–0x0017 FFFF
BLOCK 2 RAM
0x0018 0000–0x0018 7FFF
Reserved
0x0018 8000–0x001B FFFF
BLOCK 3 RAM
0x001C 0000–0x001C 7FFF
Reserved
0x001C 8000–0x001F FFFF
Reserved
0x0020 0000–0xFFFF FFFF
Rev. PrA | Page 5 of 44 | September 2004
ADSP-21363 Preliminary Technical Data
Using the DM bus and PM buses, with one bus dedicated to
each memory block, assures single-cycle execution with two
data transfers. In this case, the instruction must be available in
the cache.
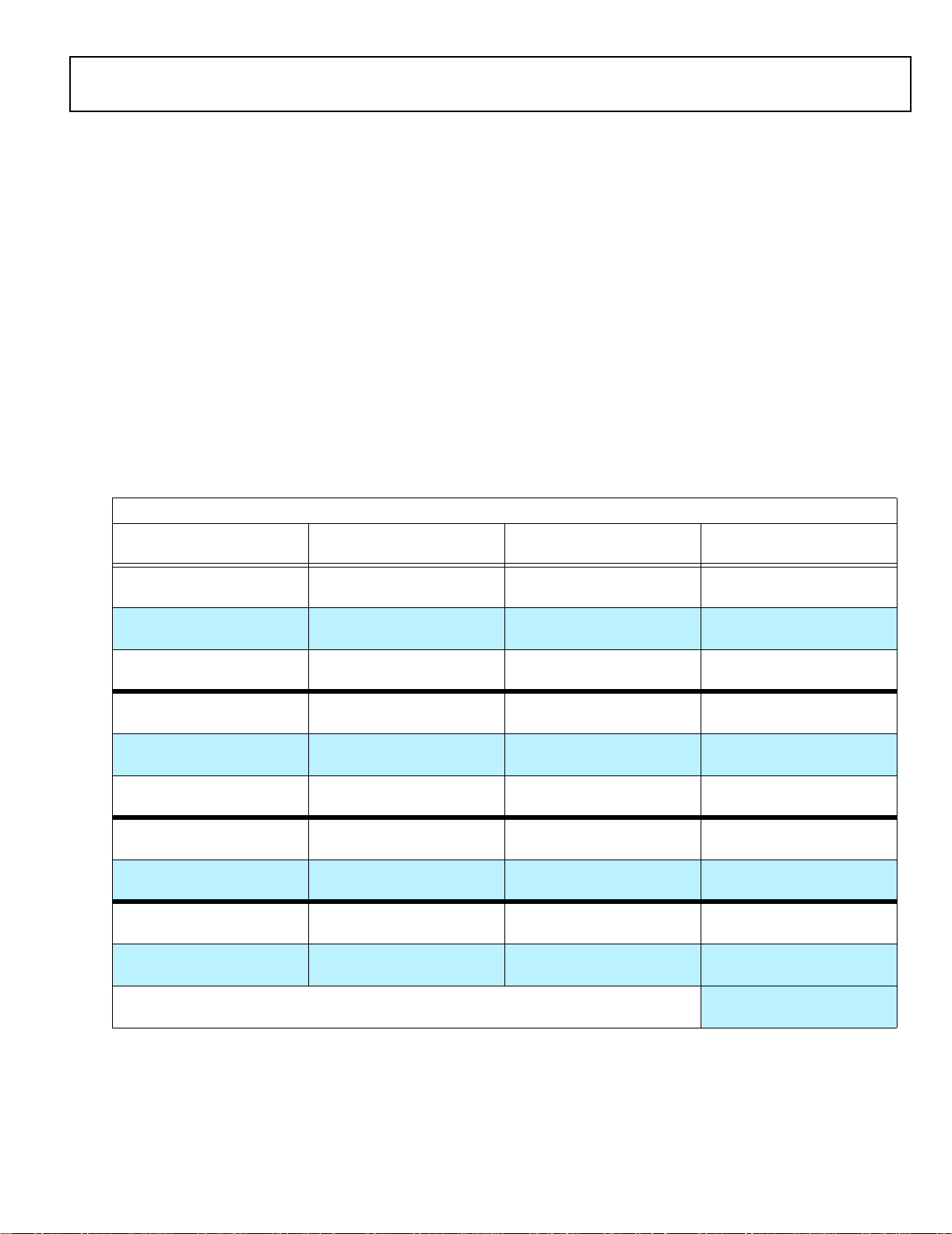
DMA Controller
The ADSP-21363’s on-chip DMA controller allows data transfers without processor intervention. The DMA controller
operates independently and invisibly to the processor core,
allowing DMA operations to occur while the core is simultaneously executing its program instructions. DMA transfers can
occur between the ADSP-21363’s internal memory and its serial
ports, the SPI-compatible (Serial Peripheral Interface) ports, the
IDP (Input Data Port), the Parallel Data Acquisition Port
(PDAP), or the parallel port. Twenty-five channels of DMA are
available on the ADSP-21363—two for the SPI interface, two for
memory-to-memory transfers, twelve via the serial ports, eight
via the Input Data Port, and one via the processor’s parallel
port. Programs can be downloaded to the ADSP-21363 using
DMA transfers. Other DMA features include interrupt generation upon completion of DMA transfers, and DMA chaining for
automatic linked DMA transfers.
TO PROCESSOR BUSSES AND
SYSTEM MEMORY
IO DATA
BUS ( 32)
Figure 3. ADSP-21363 I/O Processor and Peripherals Block Diagram
CONTROL, STATUS, & DAT A BUFFERS
IO ADDRESS
(MEMORY MAPPED)
IOP REGISTERS
BUS (18)
GPIO FLAGS/IRQ/TIMEXP
DMA CONTROLLER
25 CHANNELS
CONTROL/GPIO
ADDRESS/DATA BUS/ GPIO
PARALLEL PORT
PWM (16)
SPI PORT (1)
SPI PORT (1)
SERIAL PORTS (6)
INPUT
DATA PORTS (8)
PRECISION CL OCK
GENERATORS (2)
TIMERS (3)
DIGITAL AUDIO INTERFACE
I/O PROCESSOR
4
3
16
4
4
SIGNAL ROUTING UNIT
3
Digital Audio Interface (DAI)
The Digital Audio Interface (DAI) provides the ability to connect various peripherals to any of the SHARCs DAI pins
(DAI_P20–1).
Programs make these connections using the Signal Routing
Unit (SRU, shown in Figure 3).
The SRU is a matrix routing unit (or group of multiplexers) that
enables the peripherals provided by the DAI to be interconnected under software control. This allows easy use of the DAI
associated peripherals for a much wider variety of applications
by using a larger set of algorithms than is possible with nonconfigurable signal paths.
The DAI also includes six serial ports, two precision clock generators (PCGs), an input data port (IDP), an SPI port, six flag
outputs and six flag inputs, and three timers. The IDP provides
an additional input path to the ADSP-21363 core, configurable
as either eight channels of I
2
S serial data or as seven channels
plus a single 20-bit wide synchronous parallel data acquisition
port. Each data channel has its own DMA channel that is independent from the ADSP-21363's serial ports.
For complete information on using the DAI, see the ADSP-
2136x SHARC Processor Hardware Reference.
Serial Ports
The ADSP-21363 features six synchronous serial ports that provide an inexpensive interface to a wide variety of digital and
mixed-signal peripheral devices such as Analog Devices’
AD183x family of audio codecs, ADCs, and DACs. The serial
ports are made up of two data lines, a clock and frame sync. The
data lines can be programmed to either transmit or receive and
each data line has a dedicated DMA channel.
Serial ports are enabled via 12 programmable and simultaneous
receive or transmit pins that support up to 24 transmit or 24
receive channels of audio data when all six SPORTS are enabled,
or six full duplex TDM streams of 128 channels per frame.
The serial ports operate at a maximum data rate of 50M bits/s.
Serial port data can be automatically transferred to and from
on-chip memory via dedicated DMA channels. Each of the
serial ports can work in conjunction with another serial port to
provide TDM support. One SPORT provides two transmit signals while the other SPORT provides the two receive signals.
The frame sync and clock are shared.
20
Serial ports operate in four modes:
• Standard DSP serial mode
•Multichannel (TDM) mode
2
S mode
•I
• Left-justified sample pair mode
Left-justified sample pair mode is a mode where in each frame
sync cycle two samples of data are transmitted/received—one
sample on the high segment of the frame sync, the other on the
low segment of the frame sync. Programs have control over various attributes of this mode.
Rev. PrA | Page 6 of 44 | September 2004

ADSP-21363Preliminary Technical Data
Each of the serial ports supports the left-justified sample pair
2
S protocols (I2S is an industry standard interface com-
and I
monly used by audio codecs, ADCs and DACs such as the
Analog Devices AD183x family), with two data pins, allowing
four left-justified sample pair or I
devices) per serial port, with a maximum of up to 24 I
2
S channels (using two stereo
2
S channels. The serial ports permit little-endian or big-endian
transmission formats and word lengths selectable from 3 bits to
32 bits. For the left-justified sample pair and I
2
S modes, dataword lengths are selectable between 8 bits and 32 bits. Serial
ports offer selectable synchronization and transmit modes as
well as optional µ-law or A-law companding selection on a per
channel basis. Serial port clocks and frame syncs can be internally or externally generated.
Parallel Port
The Parallel Port provides interfaces to SRAM and peripheral
devices. The multiplexed address and data pins (AD15–0) can
access 8-bit devices with up to 24 bits of address, or 16-bit
devices with up to 16 bits of address. In either mode, 8- or 16bit, the maximum data transfer rate is 55M bytes/sec.
DMA transfers are used to move data to and from internal
memory. Access to the core is also facilitated through the parallel port register read/write functions. The RD
, WR, and ALE
(Address Latch Enable) pins are the control pins for the parallel
port.
Serial Peripheral (Compatible) Interface
The ADSP-21363 SHARC processor contains two Serial Peripheral Interface ports (SPIs). The SPI is an industry standard
synchronous serial link, enabling the ADSP-21363 SPI compatible port to communicate with other SPI compatible devices. The
SPI consists of two data pins, one device select pin, and one
clock pin. It is a full-duplex synchronous serial interface, supporting both master and slave modes. The SPI port can operate
in a multimaster environment by interfacing with up to four
other SPI compatible devices, either acting as a master or slave
device. The ADSP-21363 SPI compatible peripheral implementation also features programmable baud rate and clock phase
and polarities. The ADSP-21363 SPI compatible port uses open
drain drivers to support a multimaster configuration and to
avoid data contention.
Pulse Width Modulation
The PWM module is a flexible, programmable, PWM waveform
generator that can be programmed to generate the required
switching patterns for various applications related to motor and
engine control or audio power control. The PWM generator can
generate either center-aligned or edge-aligned PWM waveforms. In addition, it can generate complementary signals on
two outputs in paired mode or independent signals in non
paired mode (applicable to a single group of four PWM
waveforms).
The entire PWM module has four groups of four PWM outputs
each. Therefore this module generates 16 PWM outputs in total.
Each PWM group produces two pairs of PWM signals on the
four PWM outputs.
The PWM generator is capable of operating in two distinct
modes while generating center-aligned PWM waveforms: single
update mode, or double update mode. In single update mode
the duty cycle values are programmable only once per PWM
period. This results in PWM patterns that are symmetrical
around the mid-point of the PWM period. In double update
mode, a second updating of the PWM registers is implemented
at the mid-point of the PWM period. In this mode, it is possible
to produce asymmetrical PWM patterns that produce lower
harmonic distortion in three-phase PWM inverters.
Timers
The ADSP-21363 has a total of four timers: a core timer able to
generate periodic software interrupts and three general purpose
timers that can generate periodic interrupts and be independently set to operate in one of three modes:
• Pulse Waveform Generation mode
• Pulse Width Count /Capture mode
• External Event Watchdog mode
The core timer can be configured to use FLAG3 as a Timer
Expired signal, and each general-purpose timer has one bidirectional pin and four registers that implement its mode of
operation: a 6-bit configuration register, a 32-bit count register,
a 32-bit period register, and a 32-bit pulse width register. A single control and status register enables or disables all three
general purpose timers independently.
Program Booting
The internal memory of the ADSP-21363 boots at system
power-up from an 8-bit EPROM via the parallel port, an SPI
master, an SPI slave or an internal boot. Booting is determined
by the Boot Configuration (BOOTCFG1–0) pins. Selection of
the boot source is controlled via the SPI as either a master or
slave device.
Phase-Locked Loop
The ADSP-21363 uses an on-chip Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) to
generate the internal clock for the core. On power up, the
CLKCFG1–0 pins are used to select ratios of 32:1, 16:1, and 6:1.
After booting, numerous other ratios can be selected via software control. The ratios are made up of software configurable
numerator values from 1 to 32 and software configurable divisor values of 1, 2, 4, 8, and 16.
Power Supplies
The ADSP-21363 has separate power supply connections for the
internal (V
DDINT
), external (V
), and analog (A
DDEXT
VDD/AVSS
power supplies. The internal and analog supplies must meet the
1.2 V requirement. The external supply must meet the 3.3 V
requirement. All external supply pins must be connected to the
same power supply.
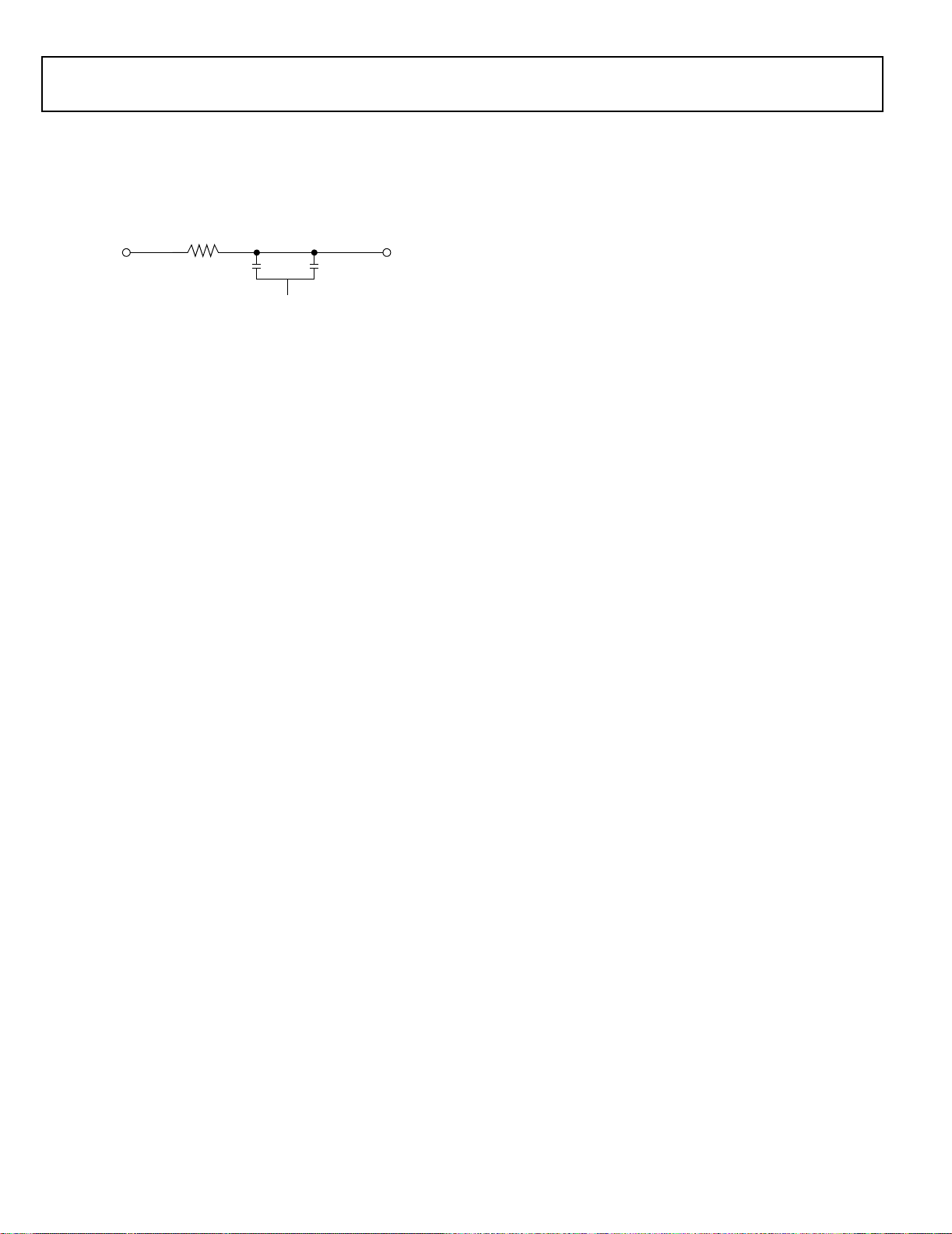
Note that the analog supply (A
) powers the ADSP-21363’s
VDD
clock generator PLL. To produce a stable clock, programs
should provide an external circuit to filter the power input to
the A
pin. Place the filter as close as possible to the pin. For
VDD
an example circuit, see Figure 4. To prevent noise coupling, use
)
Rev. PrA | Page 7 of 44 | September 2004
ADSP-21363 Preliminary Technical Data
a wide trace for the analog ground (A
) signal and install a
VSS
decoupling capacitor as close as possible to the pin. Note that
the A
VSS
and A
pins specified in Figure 4 are inputs to the
VDD
processor and not the analog ground plane on the board.
10⍀
V
DDINT
Figure 4. Analog Power (A
A
VSS
) Filter Circuit
VDD
0.01F0.1F
A
VDD
Target Board JTAG Emulator Connector
Analog Devices DSP Tools product line of JTAG emulators uses
the IEEE 1149.1 JTAG test access port of the ADSP-21363 processor to monitor and control the target board processor during
emulation. Analog Devices DSP Tools product line of JTAG
emulators provides emulation at full processor speed, allowing
inspection and modification of memory, registers, and processor stacks. The processor's JTAG interface ensures that the
emulator will not affect target system loading or timing.
For complete information on Analog Devices’ SHARC DSP
Tools product line of JTAG emulator operation, see the appropriate “Emulator Hardware User's Guide”.
DEVELOPMENT TOOLS
The ADSP-21363 is supported with a complete set of
CROSSCORE® software and hardware development tools,
including Analog Devices emulators and VisualDSP++® devel-
opment environment. The same emulator hardware that
supports other SHARC processors also fully emulates the
ADSP-21363.
The VisualDSP++ project management environment lets programmers develop and debug an application. This environment
includes an easy to use assembler (which is based on an algebraic syntax), an archiver (librarian/library builder), a linker, a
loader, a cycle-accurate instruction-level simulator, a C/C++
compiler, and a C/C++ runtime library that includes DSP and
mathematical functions. A key point for these tools is C/C++
code efficiency. The compiler has been developed for efficient
translation of C/C++ code to DSP assembly. The SHARC has
architectural features that improve the efficiency of compiled
C/C++ code.
The VisualDSP++ debugger has a number of important features. Data visualization is enhanced by a plotting package that
offers a significant level of flexibility. This graphical representation of user data enables the programmer to quickly determine
the performance of an algorithm. As algorithms grow in complexity, this capability can have increasing significance on the
designer’s development schedule, increasing productivity. Statistical profiling enables the programmer to non intrusively poll
the processor as it is running the program. This feature, unique
to VisualDSP++, enables the software developer to passively
gather important code execution metrics without interrupting
the real-time characteristics of the program. Essentially, the
developer can identify bottlenecks in software quickly and efficiently. By using the profiler, the programmer can focus on
those areas in the program that impact performance and take
corrective action.
Debugging both C/C++ and assembly programs with the
VisualDSP++ debugger, programmers can:
• View mixed C/C++ and assembly code (interleaved source
and object information)
• Insert breakpoints
• Set conditional breakpoints on registers, memory,
and stacks
• Trace instruction execution
• Perform linear or statistical profiling of program execution
• Fill, dump, and graphically plot the contents of memory
• Perform source level debugging
• Create custom debugger windows
The VisualDSP++ IDDE lets programmers define and manage
DSP software development. Its dialog boxes and property pages
let programmers configure and manage all of the SHARC development tools, including the color syntax highlighting in the
VisualDSP++ editor. This capability permits programmers to:
• Control how the development tools process inputs and
generate outputs
• Maintain a one-to-one correspondence with the tool’s
command line switches
The VisualDSP++ Kernel (VDK) incorporates scheduling and
resource management tailored specifically to address the memory and timing constraints of DSP programming. These
capabilities enable engineers to develop code more effectively,
eliminating the need to start from the very beginning, when
developing new application code. The VDK features include
Threads, Critical and Unscheduled regions, Semaphores,
Events, and Device flags. The VDK also supports Priority-based,
Preemptive, Cooperative, and Time-Sliced scheduling
approaches. In addition, the VDK was designed to be scalable. If
the application does not use a specific feature, the support code
for that feature is excluded from the target system.
Because the VDK is a library, a developer can decide whether to
use it or not. The VDK is integrated into the VisualDSP++
development environment, but can also be used via standard
command line tools. When the VDK is used, the development
environment assists the developer with many error-prone tasks
and assists in managing system resources, automating the generation of various VDK based objects, and visualizing the
system state, when debugging an application that uses the VDK.
VisualDSP++ Component Software Engineering (VCSE) is
Analog Devices’ technology for creating, using, and reusing
software components (independent modules of substantial
functionality) to quickly and reliably assemble software applications. Download components from the Web and drop them into
Rev. PrA | Page 8 of 44 | September 2004

ADSP-21363Preliminary Technical Data
the application. Publish component archives from within VisualDSP++. VCSE supports component implementation in
C/C++ or assembly language.
Use the Expert Linker to visually manipulate the placement of
code and data on the embedded system. View memory utilization in a color-coded graphical form, easily move code and data
to different areas of the processor or external memory with the
drag of the mouse, examine run time stack and heap usage. The
Expert Linker is fully compatible with the existing Linker Definition File (LDF), allowing the developer to move between the
graphical and textual environments.
In addition to the software and hardware development tools
available from Analog Devices, third parties provide a wide
range of tools supporting the SHARC processor family. Hardware tools include SHARC processor PC plug-in cards. Third
party software tools include DSP libraries, real-time operating
systems, and block diagram design tools.
Designing an Emulator-Compatible DSP Board (Target)
The Analog Devices family of emulators are tools that every
DSP developer needs to test and debug hardware and software
systems. Analog Devices has supplied an IEEE 1149.1 JTAG
Test Access Port (TAP) on each JTAG DSP. Nonintrusive incircuit emulation is assured by the use of the processor’s JTAG
interface—the emulator does not affect target system loading or
timing. The emulator uses the TAP to access the internal features of the processor, allowing the developer to load code, set
breakpoints, observe variables, observe memory, and examine
registers. The processor must be halted to send data and commands, but once an operation has been completed by the
emulator, the processor system is set running at full speed with
no impact on system timing.
To use these emulators, the target board must include a header
that connects the processor’s JTAG port to the emulator.
For details on target board design issues including mechanical
layout, single processor connections, multiprocessor scan
chains, signal buffering, signal termination, and emulator pod
logic, see the EE-68: Analog Devices JTAG Emulation Technical
Reference on the Analog Devices website (www.analog.com)—
use site search on “EE-68.” This document is updated regularly
to keep pace with improvements to emulator support.
debug programs for the EZ-KIT Lite system. It also allows incircuit programming of the on-board Flash device to store userspecific boot code, enabling the board to run as a standalone
unit without being connected to the PC.
With a full version of VisualDSP++ installed (sold separately),
engineers can develop software for the EZ-KIT Lite or any custom defined system. Connecting one of Analog Devices JTAG
emulators to the EZ-KIT Lite board enables high-speed, nonintrusive emulation.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
This data sheet provides a general overview of the ADSP-21363
architecture and functionality. For detailed information on the
ADSP-2136x Family core architecture and instruction set, refer
to the ADSP-2136x SHARC Processor Hardware Reference and
the ADSP-2136x SHARC Processor Programming Reference.
Evaluation Kit
Analog Devices offers a range of EZ-KIT Lite evaluation platforms to use as a cost effective method to learn more about
developing or prototyping applications with Analog Devices
processors, platforms, and software tools. Each EZ-KIT Lite
includes an evaluation board along with an evaluation suite of
the VisualDSP++ development and debugging environment
with the C/C++ compiler, assembler, and linker. Also included
are sample application programs, power supply, and a USB
cable. All evaluation versions of the software tools are limited
for use only with the EZ-KIT Lite product.
The USB controller on the EZ-KIT Lite board connects the
board to the USB port of the user’s PC, enabling the VisualDSP++ evaluation suite to emulate the on-board processor incircuit. This permits the customer to download, execute, and
Rev. PrA | Page 9 of 44 | September 2004
ADSP-21363 Preliminary Technical Data
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
ADSP-21363 pin definitions are listed below. Inputs identified
as synchronous (S) must meet timing requirements with respect
to CLKIN (or with respect to TCK for TMS and TDI). Inputs
identified as asynchronous (A) can be asserted asynchronously
to CLKIN (or to TCK for TRST
V
or GND, except for the following:
DDEXT
). Tie or pull unused inputs to
• DAI_Px, SPICLK, MISO, MOSI, EMU
, TMS, TRST, TDI,
and AD15–0 (NOTE: These pins have pullup resistors.)
The following symbols appear in the Type column of Table 3:
A = Asynchronous, G = Ground, I = Input, O = Output,
P = Power Supply, S = Synchronous, (A/D) = Active Drive,
(O/D) = Open Drain, and T = Three-State , (pd) = pulldown
resistor, (pu) = pullup resistor.
Table 3. Pin Descriptions
Pin Type State During &
After Reset
AD15–0 I/O/T
(pu)
RD
WR
ALE O
FLAG3–0 I/O/A Three-state Flag Pins. Each flag pin is configured via control bits as either an input or output. As
O
(pu)
O
(pu)
(pd)
Three-state with
pullup enabled
Three-state, driven
1
high
Three-state, driven
1
high
Three-state, driven
1
low
Function
Parallel Port Address/Data. The ADSP-21363 parallel port and its corresponding
DMA unit output addresses and data for peripherals on these multiplexed pins. The
multiplex state is determined by the ALE pin. The parallel port can operate in either
8-bit or 16-bit mode. Each AD pin has a 22.5 kΩ internal pullup resistor. See Address
Data Modes on Page 13 for details of the AD pin operation.
For 8-bit mode: ALE is automatically asserted whenever a change occurs in the upper
16 external address bits, A23–8; ALE is used in conjunction with an external latch to
retain the values of the A23–8.
For 16-bit mode: ALE is automatically asserted whenever a change occurs in the
address bits, A15–0; ALE is used in conjunction with an external latch to retain the
values of the A15–0. To use these pins as flags (FLAGS15–0) or PWMs (PWM15–0), 1)
set (=1) bit 20 of the SYSCTL register to disable the parallel port, 2) set (=1) bits 22–25
of the SYSCTL register to enable FLAGS in groups of four (bit 22 for FLAGS3–0, bit 23
for FLAGS7–4 etc.) or, set (=1) bits 26–29 of the SYSCTL register to enable PWMs in
groups of four (bit 26 for PWM0–3, bit 27 for PWM4–7, and so on). When used as an
input, the IDP Channel 0 can use these pins for parallel input data.
Parallel Port Read Enable. RD is asserted low whenever the processor reads 8-bit or
16 -bi t da ta fr om a n ex tern al m emor y dev ice . Wh en A D15– 0 ar e fl ags , th is pi n re mai ns
deasserted. RD has a 22.5 kΩ internal pullup resistor.
Parallel Port Write Enable. WR is asserted low whenever the processor writes 8-bit or
16-bit data to an external memory device. When AD15–0 are flags, this pin remains
deasserted. WR
Parallel Port Address Latch enable. ALE is asserted whenever the processor drives
a new address on the parallel port address pins. On reset, ALE is active high. However,
it can be reconfigured using software to be active low. When AD15–0 are flags, this
pin remains deasserted. ALE has a 20 kΩ internal pulldown resistor.
an inp ut, it ca n be test ed a s a c ond itio n. A s an o utp ut, it ca n be us ed t o si gna l ex ter nal
peripherals. These pins can be used as an SPI interface slave select output during SPI
mastering. These pins are also multiplexed with the IRQx
In SPI master boot mode, FLAG0 is the slave select pin that must be connected to an
SPI EPROM. FLAG0 is configured as a slave select during SPI master boot. When bit 16
is set (=1) in the SYSCTL register, FLAG0 is configured as IRQ0.
When bit 17 is set (=1) in the SYSCTL register, FLAG1 is configured as IRQ1
When bit 18 is set (=1) in the SYSCTL register, FLAG2 is configured as IRQ2
When bit 19 is set (=1) in the SYSCTL register, FLAG3 is configured as TIMEXP which
indicates that the system timer has expired.
has a 22.5 kΩ internal pullup resistor.
and the TIMEXP signals.
.
.
Rev. PrA | Page 10 of 44 | September 2004
Table 3. Pin Descriptions (Continued)
ADSP-21363Preliminary Technical Data
Pin Type State During &
After Reset
DAI_P20–1 I/O/T
(pu)
SPICLK I/O
(pu)
SPIDS
MOSI I/O (O/D)
MISO I/O (O/D)
BOOTCFG1–0 I Input only Boot Configuration Select. This pin is used to selec t the boot mode for the processor.
I Input only Serial Peripheral Interface Slave Device Select. An active low signal used to select
(pu)
(pu)
Three-state with
programmable
pullup
Three-state with
pullup enabled
Three-state with
pullup enabled
Three-state with
pullup enabled
Function
Digital Audio Interface Pins. These pins provide the physical interface to the SRU.
The SRU configuration registers define the combination of on-chip peripheral inputs
or outputs connected to the pin and to the pin’s output enable. The configuration
registers of these peripherals then determines the exact behavior of the pin. Any input
or output signal present in the SRU may be routed to any of these pins. The SRU
provides the connection from the Serial ports, Input data port, precision clock generators and timers, and SPI to the DAI_P20–1 pins These pins have internal 22.5 kΩ
pullup resistors which are enabled on reset. These pullups can be disabled in the
DAI_PIN_PULLUP register.
Serial Peripheral Interface Clock Signal. Driven by the master, this signal controls
the rate at which data is transferred. The master may transmit data at a variety of baud
rates. SPICLK cycles once for each bit transmitted. SPICLK is a gated clock that is active
during data transfers, only for the length of the t ransferred word. Sla ve devices ignore
the serial clock if the slave select input is driven inactive (HIGH). SPICLK is used to shift
out and shift in the data driven on the MISO and MOSI lines. The data is always shifted
out on one clock edge and sampled on the opposite edge of the clock. Clock polarity
and clock phase relative to data are programmable into the SPICTL control register
and define the transfer format. SPICLK has a 22.5 kΩ internal pullup resistor.
the processor as an SPI slave device. This input signal behaves like a chip select, and
is provided by the master device for the slave devices. In multimaster mode the DSPs
signal can be driven by a slave device to signal to the processor (as SPI master)
SPIDS
that an error has occurred, as some other device i s al so t ry ing to b e th e ma ste r de vice .
If asserted low when the device is in master mode, it is considered a multimaster error.
For a single-master, multiple-slave configuration where flag pins are used, this pin
must be tied or pulled high to V
ADSP-21363 SPI interaction, any of the master ADSP-21363's flag pins can be used to
drive the SPIDS signal on the ADSP-21363 SPI slave device.
SPI Master Out Slave In. If the ADSP-21363 is configured as a master, the MOSI pin
becomes a data transmit (output) pin, transmitting output data. If the ADSP-21363 is
configured as a slave, the MOSI pin becomes a data receive (input) pin, receiving input
data. In an ADSP-21363 SPI interconnection, the data is shifted out from the MOSI
output pin of the master and shifted into the MOSI input(s) of the slave(s). MOSI has a
22.5 kΩ internal pullup resistor.
SPI Master In Slave Out. If the ADSP-21363 is configured as a master, the MISO pin
becomes a data receive (input) pin, receiving input data. If the ADSP-21363 is
configured as a slave, the MISO pin becomes a data transmit (output) pin, transmitting
output data. In an ADSP-21363 SPI interconnection, the data is shifted out from the
MISO output pin of the slave and shifted into the MISO input pin of the master. MISO
has a 22.5 kΩ internal pullup resistor. MISO can be configured as O/D by setting the
OPD bit in the SPICTL register.
Note: Only one slave is allowed to transmit data at any given time. To enable broadcast
transmission to multiple SPI-slaves, the processor's MISO pin may be disabled by
setting (=1) bit 5 (DMISO) of the SPICTL register.
The BOOTCFG pins must be valid before reset is asserted. See Table 5 for a description
of the boot modes.
on the master device. For ADSP-21363 to
DDEXT
Rev. PrA | Page 11 of 44 | September 2004
ADSP-21363 Preliminary Technical Data
Table 3. Pin Descriptions (Continued)
Pin Type State During &
Function
After Reset
CLKIN I Input only Local Clock In. Used in conjunction with XTAL. CLKIN is the ADSP-21363 clock input.
It configures the ADSP-21363 to use either its internal clock generator or an external
clock source. Connecting the necessary components to CLKIN and XTAL enables the
internal clock generator. Connecting the external clock to CLKIN while leaving XTAL
unconnected configures the ADSP-21363 to use the external clock source such as an
external clock oscillator. The core is clocked either by the PLL output or this clock input
depending on the CLKCFG1–0 pin settings. CLKIN may not be halted, changed, or
operated below the specified frequency.
XTAL O Output only
2
Crystal Oscillator Terminal. Used in conjunction with CLKIN to drive an external
crystal.
CLKCFG1–0 I Input only Core/CLKIN Ratio Control. These pins set the start up clock frequency. See Table 6
for a description of the clock configuration modes.
Note that the operating frequency can be changed by programming the PLL multiplier
and divider in the PMCTL register at any time after the core comes out of reset.
RSTOUT
/CLKOUT O Output only Local Clock Out/ Reset Out. Drives out the core reset signal to an external device.
CLKOUT can also be configured as a reset out pin.The functionality can be switched
between the PLL output clock and reset out by setting bit 12 of the PMCTREG register.
The default is reset out.
RESET I/A Input only Processor Reset. Resets the ADSP-21363 to a known state. Upon deassertion, there
is a 4096 CLKIN cycle latency for the PLL to lock. After this time, the core begins
program execution from the hardware reset vector address. The RESET
input must be
asserted (low) at power-up.
TCK I Input only
3
Test Clock (JTAG). Provides a clock for JTAG boundary scan. TCK must be asserted
(pulsed low) after power-up or held low for proper operation of the ADSP-21363.
TMS I/S
(pu)
TDI I/S
(pu)
TDO O Three-state
TRST
I/A
(pu)
Three-state with
pullup enabled
Three-state with
pullup enabled
4
Three-state with
pullup enabled
Test Mode Select (JTAG). Used to control the test state machine. TMS has a 22.5 kΩ
internal pullup resistor.
Test Data Input (JTAG). Provides serial data for the boundary scan logic. TDI has a
22.5 kΩ internal pullup resistor.
Test Data Output (JTAG). Serial scan output of the boundary scan path.
Test Reset (JTAG). Resets the test state machine. TRST must be asserted (pulsed low)
after power-up or held low for proper operation of the ADSP-21363. TRST
has a
22.5 kΩ internal pullup resistor.
EMU
O (O/D)
(pu)
Three-state with
pullup enabled
Emulation Status. Must be connected to the ADSP-21363 Analog Devices DSP Tools
product line of JTAG emulators target board connector only. EMU
has a 22.5 kΩ
internal pullup resistor.
V
DDINT
P Core Power Supply. Nominally +1.2 V dc and supplies the processor’s core
(13 pins on the Mini-BGA package, 32 pins on the LQFP package).
V
DDEXT
P I/O Power Supply. Nominally +3.3 V dc. (6 pins on the Mini-BGA package, 10 pins on
the LQFP package).
A
VDD
P Analog Power Supply. Nominally +1.2 V dc and supplies the processor’s internal PLL
(clock generator). This pin has the same specifications as V
, except that added
DDINT
filtering circuitry is required. For more information, see Power Supplies on Page 7.
A
VSS
G Analog Power Supply Return.
GND G Power Supply Return. (54 pins on the Mini-BGA package, 39 pins on the LQFP
package).
1
RD, WR, and ALE are three-stated (and not driven) only when RESET is active.
2
Output only is a three-state driver with its output path always enabled.
3
Input only is a three-state driver with both output path and pullup disabled.
4
Three-state is a three-state driver with pullup disabled.
Rev. PrA | Page 12 of 44 | September 2004
ADSP-21363Preliminary Technical Data
ADDRESS DATA PINS AS FLAGS
To use these pins as flags (FLAGS15–0) set (=1) bit 20 of the
SYSCTL register to disable the parallel port. Then set (=1) bits
22 to 25 in the SYSCTL register accordingly.
Table 4. AD15–0 to Flag Pin Mapping
AD Pin Flag Pin
AD0 FLAG8
AD1 FLAG9
AD2 FLAG10
AD3 FLAG11
AD4 FLAG12
AD5 FLAG13
AD6 FLAG14
AD7 FLAG15
AD8 FLAG0
AD9 FLAG1
AD10 FLAG2
AD11 FLAG3
AD12 FLAG4
AD13 FLAG5
AD14 FLAG6
AD15 FLAG7
BOOT MODES
CORE INSTRUCTION RATE TO CLKIN RATIO MODES
For details on processor timing, see Timing Specifications and
Figure 5 on Page 16.
Table 6. Core Instruction Rate/ CLKIN Ratio Selection
CLKCFG1–0 Core to CLKIN Ratio
00 6:1
01 32:1
10 16:1
ADDRESS DATA MODES
The following table shows the functionality of the AD pins for
8-bit and 16-bit transfers to the parallel port. For 8-bit data
transfers, ALE latches address bits A23–A8 when asserted, followed by address bits A7–A0 and data bits D7–D0 when
deasserted. For 16-bit data transfers, ALE latches address bits
A15–A0 when asserted, followed by data bits D15–D0 when
deasserted.
Table 7. Address/ Data Mode Selection
EP Data
Mode
8-bit Asserted A15–8 A23–16
8-bit Deasserted D7–0 A7–0
16-bit Asserted A7–0 A15–8
16-bit Deasserted D7–0 D15–8
ALE AD7–0
Function
AD15–8
Function
Table 5. Boot Mode Selection
BOOTCFG1–0 Booting Mode
00 SPI Slave Boot
01 SPI Master Boot
10 Parallel Port boot via EPROM
Rev. PrA | Page 13 of 44 | September 2004
ADSP-21363 Preliminary Technical Data
ADSP-21363 SPECIFICATIONS
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter
1
K Grade B Grade C Grade
Min Max Min Max Min Max Unit
V
DDINT
A
VDD
V
DDEXT
2
V
IH
2
Low Level Input Voltage @ V
V
IL
V
IH_CLKIN
V
IL_CLKIN
4, 5
T
AMB
1
Specifications subject to change without notice.
2
Applies to input and bidirectional pins: AD15–0, FLAG3–0, DAI_Px, SPICLK, MOSI, MISO, SPIDS, BOOTCFGx, CLKCFGx, RESET, TCK, TMS, TDI, TRST.
3
Applies to input pin CLKIN.
4
See Thermal Characteristics on Page 37 for information on thermal specifications.
5
See Engineer-to-Engineer Note (No. TBD) for further information.
Internal (Core) Supply Voltage 1.14 1.26 1.14 1.26 0.95 1.05 V
Analog (PLL) Supply Voltage 1.14 1.26 1.14 1.26 0.95 1.05 V
External (I/O) Supply Voltage 3.13 3.47 3.13 3.47 3.13 3.47 V
High Level Input Voltage @ V
3
High Level Input Voltage @ V
Low Level Input Voltage @ V
= max 2.0 V
DDEXT
= min –0.5 +0.8 –0.5 +0.8 –0.5 +0.8 V
DDEXT
= max 1.74 V
DDEXT
= min –0.5 +1.19 –0.5 +1.19 –0.5 +1.19 V
DDEXT
+ 0.5 2.0 V
DDEXT
+ 0.5 1.74 V
DDEXT
+ 0.5 2.0 V
DDEXT
+ 0.5 1.74 V
DDEXT
DDEXT
DDEXT
+ 0.5 V
+ 0.5 V
Ambient Operating Temperature 0 +70 –40 +85 –40 +105 °C
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
Parameter
V
OH
V
OL
4, 5
I
IH
4
I
IL
I
ILPU
I
OZH
I
OZL
I
OZLPU
I
DD-INTYP
AI
DD
11, 12
C
IN
1
Specifications subject to change without notice.
2
Applies to output and bidirectional pins: AD15–0, RD, WR, ALE, FLAG3–0, DAI_Px, SPICLK, MOSI, MISO, EMU, TDO, CLKOUT, XTAL.
3
See Output Drive Currents on Page 36 for typical drive current capabilities.
4
Applies to input pins: SPIDS, BOOTCFGx, CLKCFGx, TCK, RESET, CLKIN.
5
Applies to input pins with 22.5 kΩ internal pullups: TRST, TMS, TDI.
6
Applies to three-statable pins: FLAG3–0.
7
Applies to three-statable pins with 22.5 kΩ pullups: AD15–0, DAI_Px, SPICLK, EMU, MISO, MOSI.
8
Typical internal current data reflects nominal operating conditions.
9
See Engineer-to-Engineer Note (No. TBD) for further information.
10
Characterized, but not tested.
11
Applies to all signal pins.
12
Guaranteed, but not tested.
1
2
2
High Level Output Voltage @ V
Low Level Output Voltage @ V
High Level Input Current @ V
Low Level Input Current @ V
5
6, 7
6
7
8, 9
10
Low Level Input Current Pullup @ V
Three-State Leakage Current @ V
Three-State Leakage Current @ V
Three-State Leakage Current Pullup @ V
Supply Current (Internal) t
Supply Current (Analog) A
Input Capacitance fIN=1 MHz, T
Test Conditions Min Max Unit
= min, IOH = –1.0 mA
DDEXT
= min, IOL = 1.0 mA
DDEXT
= max, VIN = V
DDEXT
= max, VIN = 0 V 10 µA
DDEXT
= max, VIN = 0 V 200 µA
DDEXT
= max, VIN = V
DDEXT
= max, VIN = 0 V 10 µA
DDEXT
= max, VIN = 0 V 200 µA
DDEXT
= min, V
CCLK
= max 10 mA
VDD
= nom 500 mA
DDINT
=25°C, VIN=1.2V 4.7 pF
CASE
3
3
max 10 µA
DDEXT
max 10 µA
DDEXT
2.4 V
0.4 V
Rev. PrA | Page 14 of 44 | September 2004
 Loading...
Loading...