1 GSPS Quadrature Digital Upconverter
with 18-Bit I/Q Data Path and 14-Bit DAC
AD9957
Rev. C
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the prop erty of their respective owner s.
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2007–2012 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
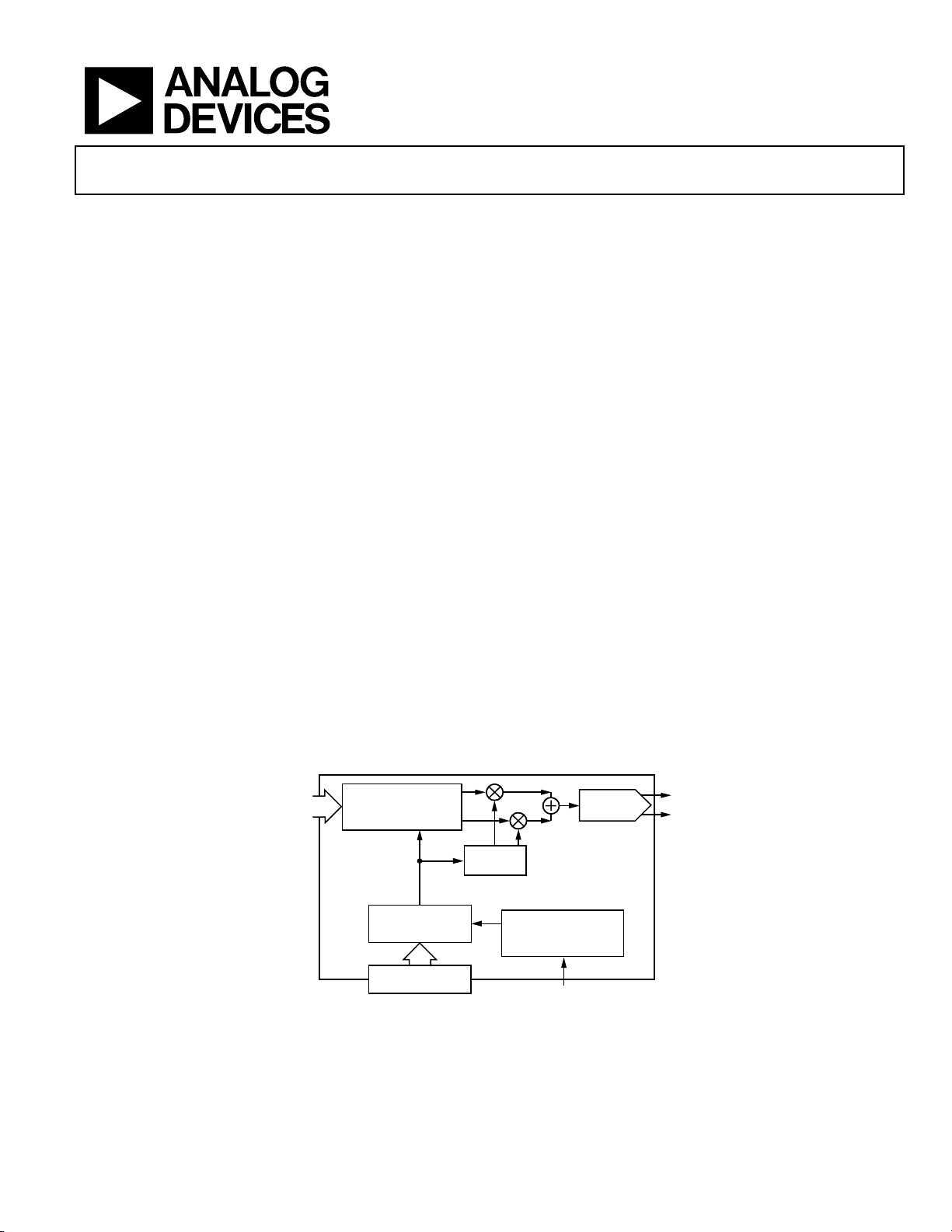
FORMAT AND
INTERPOLATE
NCO
I
Q
REFERENCE CL OCK INPUT
I/Q DATA
DATA
FOR
XMIT
REFERENCE CL OCK
INPUT CIRCUITRY
TIMING
AND
CONTROL
14-BIT DAC
USER INTER FACE
06384-001
AD9957
Data Sheet
FEATURES
1 GSPS internal clock speed (up to 400 MHz analog output)
Integrated 1 GSPS 14-bit DAC
250 MSPS input data rate
Phase noise ≤ −125 dBc/Hz (400 MHz carrier @ 1 kHz offset)
Excellent dynamic performance >80 dB narrow-band SFDR
8 programmable profiles for shift keying
Sin(x)/(x) correction (inverse sinc filter)
Reference clock multiplier
Internal oscillator for a single crystal operation
Software and hardware controlled power-down
Integrated RAM
Phase modulation capability
Multichip synchronization
Easy interface to Blackfin SPORT
Interpolation factors from 4× to 252×
Interpolation DAC mode
Gain control DAC
Internal divider allows references up to 2 GHz
1.8 V and 3.3 V power supplies
100-lead TQFP_EP package
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9957 functions as a universal I/Q modulator and agile
upconverter for communications systems where cost, size, power
consumption, and dynamic performance are critical. The AD9957
integrates a high speed, direct digital synthesizer (DDS), a high
performance, high speed, 14-bit digital-to-analog converter (DAC),
clock multiplier circuitry, digital filters, and other DSP functions
onto a single chip. It provides baseband upconversion for data
transmission in a wired or wireless communications system.
The AD9957 is the third offering in a family of quadrature
digital upconverters (QDUCs) that includes the AD9857 and
AD9856. It offers performance gains in operating speed, power
consumption, and spectral performance. Unlike its predecessors,
it supports a 16-bit serial input mode for I/Q baseband data.
The device can alternatively be programmed to operate either as
a single tone, sinusoidal source or as an interpolating DAC.
The reference clock input circuitry includes a crystal oscillator,
a high speed, divide-by-two input, and a low noise PLL for
multiplication of the reference clock frequency.
APPLICATIONS
HFC data, telephony, and video modems
Wireless base station transmissions
Broadband communications transmissions
Internet telephony
The user interface to the control functions includes a serial port
easily configured to interface to the SPORT of the Blackfin®
DSP and profile pins to enable fast and easy shift keying of any
signal parameter (phase, freq u e nc y, o r amplitude).
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
Figure 1.
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com

AD9957 Data Sheet
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
RAM Control .................................................................................. 27
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 4
Specifications ..................................................................................... 5
Electrical Specifications ............................................................... 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 8
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 8
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ............................. 9
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 12
Modes of Operation ....................................................................... 16
Overview ...................................................................................... 16
Quadrature Modulation Mode ................................................. 17
BlackFin Interface (BFI) Mode ................................................. 18
Interpolating DAC Mode .......................................................... 19
RAM Overview ........................................................................... 27
RAM Segment Registers ............................................................ 27
RAM State Machine ................................................................... 27
RAM Trigger (RT) Pin ............................................................... 27
Load/Retrieve RAM Operation ................................................ 28
RAM Playback Operation ......................................................... 28
Overview of RAM Playback Modes ......................................... 29
RAM Ramp-Up Mode ........................................................... 29
RAM Bidirectional Ramp Mode .......................................... 30
RAM Continuous Bidirectional Ramp Mode .................... 32
RAM Continuous Recirculate Mode ................................... 33
Clock Input (REF_CLK) ................................................................ 34
REFCLK Overview ..................................................................... 34
Crystal Driven REF_CLK ......................................................... 34
Direct Driven REF_CLK ........................................................... 34
Single Tone Mode ....................................................................... 20
Signal Processing ............................................................................ 21
Parallel Data Clock (PDCLK) ................................................... 21
Transmit Enable Pin (TxEnable) .............................................. 21
Input Data Assembler ................................................................ 22
Inverse CCI Filter ....................................................................... 23
Fixed Interpolator (4×) .............................................................. 23
Programmable Interpolating Filter .......................................... 24
QDUC Mode ........................................................................... 24
BFI Mode ................................................................................. 24
Quadrature Modulator .............................................................. 25
DDS Core ..................................................................................... 25
Inverse Sinc Filter ....................................................................... 25
Output Scale Factor (OSF) ........................................................ 26
14-Bit DAC .................................................................................. 26
Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) Multiplier ...................................... 35
PLL Charge Pump ...................................................................... 36
External PLL Loop Filter Components ................................... 36
PLL Lock Indication .................................................................. 36
Additional Features ........................................................................ 37
Output Shift Keying (OSK) ....................................................... 37
Manual OSK ............................................................................ 37
Automatic OSK ....................................................................... 37
Profiles ......................................................................................... 38
I/O_UPDATE Pin ...................................................................... 38
Automatic I/O Update ............................................................... 38
Power-Down Control ................................................................ 39
General-Purpose I/O (GPIO) Port .......................................... 39
Synchronization of Multiple Devices ........................................... 40
Overview ..................................................................................... 40
Auxiliary DAC ........................................................................ 26
Rev. C | Page 2 of 64
Clock Generator ......................................................................... 40

Data Sheet AD9957
Sync Generator ............................................................................ 40
I/O_RESET—Input/Output Reset ........................................ 48
Sync Receiver ............................................................................... 41
Setup/Hold Validation ................................................................ 42
Synchronization Example .......................................................... 44
I/Q Path Latency ......................................................................... 45
Example .................................................................................... 45
Power Supply Partitioning ............................................................. 46
3.3 V Supplies .............................................................................. 46
DVDD_I/O (Pin 11, Pin 15, Pin 21, Pin 28, Pin 45, Pin 56,
Pin 66) ...................................................................................... 46
AVDD (Pin 74 to Pin 77 and Pin 83) ................................... 46
1.8 V Supplies .............................................................................. 46
DVDD (Pin 17, Pin 23, Pin 30, Pin 47, Pin 57, Pin 64) ..... 46
AVDD ( Pi n 3 ) .......................................................................... 46
AVDD ( Pi n 6 ) .......................................................................... 46
AVDD (Pin 89 and Pin 92) .................................................... 46
I/O_UPDATE—Input/Output Update ................................ 48
Serial I/O Timing Diagrams ...................................................... 48
MSB/LSB Transfers ..................................................................... 48
I/O_UPDATE, SYNC_CLK, and System Clock
Relationships ................................................................................ 49
Register Map and Bit Descriptions ............................................... 50
Register Map ................................................................................ 50
Register Bit Descriptions............................................................ 55
Control Function Register 1 (CFR1) .................................... 55
Control Function Register 2 (CFR2) .................................... 56
Control Function Register 3 (CFR3) .................................... 58
Auxiliary DAC Control Register ........................................... 58
I/O Update Rate Register ....................................................... 58
RAM Segment Register 0 ....................................................... 58
RAM Segment Register 1 ....................................................... 59
Serial Programming ........................................................................ 47
Control Interface—Serial I/O .................................................... 47
General Serial I/O Operation .................................................... 47
Instruction Byte ........................................................................... 47
Instruction Byte Information Bit Map ................................. 47
Serial I/O Port Pin Descriptions ............................................... 47
SCLK—Serial Clock................................................................ 47
CS
—Chip Select Bar ............................................................... 47
SDIO—Serial Data Input/Output ......................................... 47
SDO—Serial Data Out ........................................................... 48
Amplitude Scale Factor (ASF) Register ............................... 59
Multichip Sync Register ......................................................... 59
Profile Registers ........................................................................... 60
Profile<7:0> Register—Sing le To n e ...................................... 60
Profile<7:0> Register—QDUC ............................................. 60
RAM Register .......................................................................... 60
GPIO Configuration Register ............................................... 60
GPIO Data Register ................................................................ 60
Outline Dimensions ........................................................................ 61
Ordering Guide ........................................................................... 61
Rev. C | Page 3 of 64

AD9957 Data Sheet
REVISION HISTORY
4/12—Rev. B to R e v. C
Changes to Table 1 ............................................................................ 7
Changes to Table 3 .......................................................................... 11
Change to Sync Generator Section ............................................... 41
Changes to Sync Receiver Section and Setup/Hold Validation
Section .............................................................................................. 42
Changes to Table 13 ........................................................................ 50
Changes to Table 19 ........................................................................ 57
Changes to Table 26 ........................................................................ 59
10/10—Rev. A t o R e v. B
Changes to Data Rate in Features Section ..................................... 1
Changes to Specifications Section .................................................. 6
Added EPAD Notation to Figure 4 and Table 3 ........................... 9
Changes to XTAL_SEL Pin Description ...................................... 11
Changes to BlackFin Interface (BFI) Mode Section .................. 18
Changes to Figure 30 and Figure 31 ............................................. 22
Changes to Programmable Interpolating Filter Section ............ 24
Changes to Fifth Paragraph of Quadrature Modulator Section...... 25
Changes to RAM Segment Registers Section ............................. 27
Changes to RAM Playback Operation Section ........................... 28
Changes to Control Interface—Serial I/O Section ..................... 47
Added to I/O_UPDATE, SYNC_CLK, and System Clock
Relationships Section and Figure 64 ............................................ 49
Changes to Default Values of Profile 0 Register—Single Tone
(0x0E) and Profile 0 Register—QDUC (0x0E) in Table 14 ....... 51
Changes to Default Values in Table 15 ......................................... 52
Changes to Default Values in Table 16 ......................................... 53
Changes to Default Values in Table 17 ......................................... 54
Updated Outline Dimensions ....................................................... 61
1/08—Rev. 0 to R e v. A
Changes to REFCLK Multiplier Specification ............................... 3
Changes to I/O_Update/Profile<2:0>/RT Timing
Characteristics and I/Q Input Timing Characteristics ................. 5
Replaced Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions
Section ................................................................................................. 8
Changes to Figure 25 Through Figure 29.................................... 15
Deleted Table 4, Renumbered Sequentially ................................ 20
Changes to DDS Core Section ...................................................... 24
Changes to Figure 47 and Table 6................................................. 33
Replaced Synchronization of Multiple Devices Section ............ 39
Added I/Q Path Latency Section .................................................. 44
Added Power Supply Partitioning Section .................................. 45
Changes to General Serial I/O Operation Section ..................... 46
Changes to Table 13 ....................................................................... 48
Changes to Table 14 ....................................................................... 49
Changes to Table 19 ....................................................................... 54
Changes to Table 20 ....................................................................... 56
Changes to GPIO Configuration Register and
GPIO Data Register Sections ........................................................ 58
5/07—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. C | Page 4 of 64
Data Sheet AD9957
REFCLK Multiplier
Disabled
60 10001
MHz
Input Impedance (Differential)
2.8 kΩ
Differential
100 2000
mV p-p
VCO1 range setting
500 MHz/V
Output Offset
2.3
µA
Enabled @ 20×
−140
dBc/Hz
SPECIFICATIONS
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD (1.8V) and DVDD (1.8V) = 1.8 V ± 5%, AVDD (3.3V) = 3.3 V ± 5%, DVDD_I/O (3.3V) = 3.3 V ± 5%, T = 25°C, R
I
= 20 mA, external reference clock frequency = 1000 MHz with REFCLK multiplier disabled, unless otherwise noted.
OUT
Table 1.
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
REF_CLK INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Frequency Range
Enabled 3.2 60 MHz
Maximum REFCLK Input Divider Frequency Full temperature range 1500 1900 MHz
Minimum REFCLK Input Divider Frequency Full temperature range 25 35 MHz
External Crystal 25 MHz
Input Capacitance 3 pF
Input Impedance (Single-Ended) 1.4 kΩ
Duty Cycle REFCLK multiplier disabled 45 55 %
REFCLK multiplier enabled 40 60 %
REF_CLK Input Level Single-ended 50 1000 mV p-p
= 10 kΩ,
SET
REFCLK MULTIPLIER VCO GAIN CHARACTERISTICS
VCO Gain (KV) @ Center Frequency VCO0 range setting 429 MHz/V
VCO2 range setting 555 MHz/V
VCO3 range setting 750 MHz/V
VCO4 range setting 789 MHz/V
VCO5 range setting2 850 MHz/V
REFCLK_OUT CHARACTERISTICS
Maximum Capacitive Load 20 pF
Maximum Frequency 25 MHz
DAC OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Full-Scale Output Current 8.6 20 31.6 mA
Gain Error −10 +10 %FS
Differential Nonlinearity 0.8 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity 1.5 LSB
Output Capacitance 5 pF
Residual Phase Noise @ 1 kHz Offset, 20 MHz A
OUT
REFCLK Multiplier Disabled −152 dBc/Hz
Enabled @ 100× −140 dBc/Hz
AC Voltage Compliance Range −0.5 +0.5 V
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR SINGLE TONE)
f
= 20.1 MHz −70 dBc
OUT
f
= 98.6 MHz −69 dBc
OUT
f
= 201.1 MHz −61 dBc
OUT
f
= 397.8 MHz −54 dBc
OUT
Rev. C | Page 5 of 64
AD9957 Data Sheet
f
= 201.1 MHz
−157
dBm/Hz
f
= 25 MHz
−82 dBc
MODULATOR CHARACTERISTICS
Carrier Feedthrough
−78 dBc
Maximum SCLK Frequency
70 Mbps
Minimum Pulse Width
High 1
SYNC_CLK
Minimum TxEnable Hold Time to PDCLK
0 ns
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
NOISE SPECTRAL DENSITY (NSD)
Single Tone
f
= 20.1 MHz −167 dBm/Hz
OUT
f
= 98.6 MHz −162 dBm/Hz
OUT
OUT
f
= 397.8 MHz −151 dBm/Hz
OUT
TWO-TONE INTERMODULATION DISTORTION (IMD) I/Q rate = 62.5 MSPS; 16× interpolation
OUT
f
= 50 MHz −78 dBc
OUT
f
= 100 MHz −73 dBc
OUT
Input Data
Error Vector Magnitude 2.5 Msymbols/s, QPSK, 4× oversampled 0.53 %
270.8333 ksymbols/s, GMSK, 32×
oversampled
2.5 Msymbols/s, 256-QAM, 4×
oversampled
WCDMA—FDD (TM1), 3.84 MHz Bandwidth,
5 MHz Channel Spacing
Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio (ACLR) IF = 143.88 MHz −78 dBc
0.77 %
0.35 %
SERIAL PORT TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Minimum SCLK Pulse Width Low 4 ns
High 4 ns
Maximum SCLK Rise/Fall Time 2 ns
Minimum Data Setup Time to SCLK 5 ns
Minimum Data Hold Time to SCLK 0 ns
Maximum Data Valid Time in Read Mode 11 ns
I/O_UPDATE/PROFILE<2:0>/RT TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
cycle
Minimum Setup Time to SYNC_CLK 1.75 ns
Minimum Hold Time to SYNC_CLK 0 ns
I/Q INPUT TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Maximum PDCLK Frequency 250 MHz
Minimum I/Q Data Setup Time to PDCLK 1.75 ns
Minimum I/Q Data Hold Time to PDCLK 0 ns
Minimum TxEnable Setup Time to PDCLK 1.75 ns
MISCELLANEOUS TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
Wake-Up Time3 1
Fast Recovery Mode 8 SYSCLK cycles4
Full Sleep Mode 150 μs
Minimum Reset Pulse Width High 5 SYSCLK cycles4
DATA LATENCY (PIPELINE DELAY)
Data Latency Single Tone Mode
Frequency, Phase-to-DAC Output 79 SYSCLK cycles4
Rev. C | Page 6 of 64
Data Sheet AD9957
Current
DVDD (1.8V) Pin Current Consumption
QDUC mode
610 mA
POWER CONSUMPTION
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
CMOS LOGIC INPUTS
Voltage
Logic 1 2.0 V
Logic 0 0.8 V
Logic 1 90 150 µA
Logic 0 90 150 µA
Input Capacitance 2 pF
XTAL_SEL INPUT
Logic 1 Voltage 1.25 V
Logic 0 Voltage 0.6 V
Input Capacitance 2 pF
CMOS LOGIC OUTPUTS 1 mA load
Voltage
Logic 1 2.8 V
Logic 0 0.4 V
POWER SUPPLY CURRENT
DVDD_I/O (3.3V) Pin Current Consumption QDUC mode 16 mA
AVDD (3.3V) Pin Current Consumption QDUC mode 28 mA
AVDD (1.8V) Pin Current Consumption QDUC mode 105 mA
Single Tone Mode 800 mW
Continuous Modulation 8× interpolation 1400 1800 mW
Inverse Sinc Filter Power Consumption 150 200 mW
Full Sleep Mode 12 40 mW
1
The system clock is limited to 750 MHz maximum in BFI mode.
2
The gain value for VCO range Setting 5 is measured at 1000 MHz.
3
Wake-up time refers to the recovery from analog power-down modes. The longest time required is for the Reference Clock Multiplier PLL to relock to the reference.
4
SYSCLK cycle refers to the actual clock frequency used on-chip by the DDS. If the reference clock multiplier is used to multiply the external reference clock frequency,
the SYSCLK frequency is the external frequency multiplied by the reference clock multiplication factor. If the reference clock multiplier and divider are not used, the
SYSCLK frequency is the same as the external reference clock frequency.
Rev. C | Page 7 of 64
AD9957 Data Sheet
AVDD (3.3V), DVDD_I/O (3.3V) Supplies
4 V
06384-003
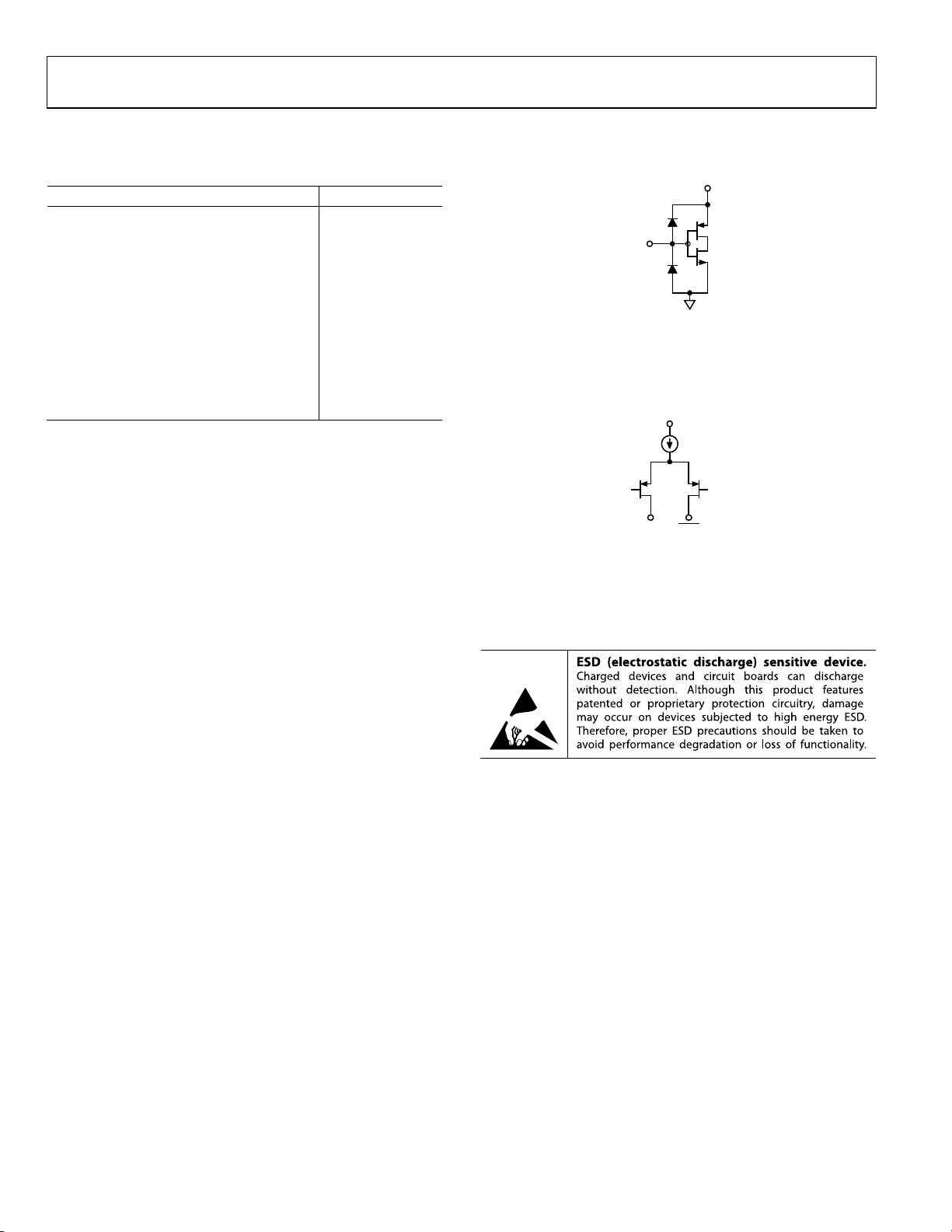
AVOID OVERDRIVING DIGITAL INPUTS.
FORWARD BIASING ESD DIODES M AY
COUPLE DIGITAL NOISE ONTO POWER
PINS.
DIGITAL INPUTS
INPUT
DVDD_I/O
06384-055
MUST TERMINATE OUTPUTSTO AGND
FOR CURRENT FLOW. DO NOT EXCEED
THE OUTPUT VOLTAGE COMPLIANCE
RATING.
IOUT IOUT
DAC OUTPUTS
AVDD
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
AVDD (1.8V), DVDD (1.8V) Supplies 2 V
Digital Input Voltage −0.7 V to +4 V
XTAL_SEL −0.7 V to +2.2 V
Digital Output Current 5 mA
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
θJA 22°C/W
θJC 2.8°C/W
Maximum Junction Temperature 150°C
Lead Temperature, Soldering (10 sec) 300°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
Figure 2. Equivalent Input Circuit
ESD CAUTION
Figure 3. Equivalent Output Circuit
Rev. C | Page 8 of 64
Data Sheet AD9957
26
27
28
29
30
55
54
53
52
51
TQFP-100 ( E _PAD)
TOP VIEW
(Not to S cal e)
AD9957
D16
D15
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
DGND
DVDD (1.8V)
5
4
3
2
7
6
9
8
1
11
10
16
15
14
13
18
17
20
19
22
21
12
24
23
25
32
33
343536
38
39
40
414243
4445464748
49
50
31
37
D14
D13
D12
D11
D10
D9D8D7
D6
PDCLK
TxENABLE/FS
DGND
D5/SPORT I-DATA
D4/SPORT Q-DATA
D3
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
DVDD (1.8V)
D2D1D0
80
IOUT79AGND78AGND77AVDD (3.3V)76AVDD (3.3V)
75
AVDD (3.3V)
74
AVDD (3.3V)
73
AGND
72
NC
71
I/O_RESET
70
CS
69
SCLK
68
SDO
67
SDIO
66
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
65
DGND
64
DVDD (1.8V)
63
DGND
62
DGND
61
NC
60
OSK
59
I/O_UPDATE
58
DGND
57
DVDD (1.8V)
56
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
SYNC_CLK
PROFILE0
PROFILE1
PROFILE2
RT
100
99989796959493
929190
89
88
8786858483
82
81
NCNCNCNCAGND
XTAL_SEL
REFCLK_OUTNCAVDD (1.8V)
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
AVDD (1.8V)
AGNDNCNC
AGND
DAC_RSET
AVDD (3.3V)
AGND
IOUT
NC
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
AVDD (1.8V)
AGND
AGND
AVDD (1.8V)
SYNC_IN+
SYNC_IN–
SYNC_OUT+
SYNC_OUT–
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
SYNC_SMP_ERR
DGND
MASTER_RESET
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
DGND
DVDD (1.8V)
EXT_PWR_DWN
PLL_LOCK
CCI_OVFL
DVDD_I/O ( 3.3V)
DGND
DVDD (1.8V)
NC
D17
06384-004
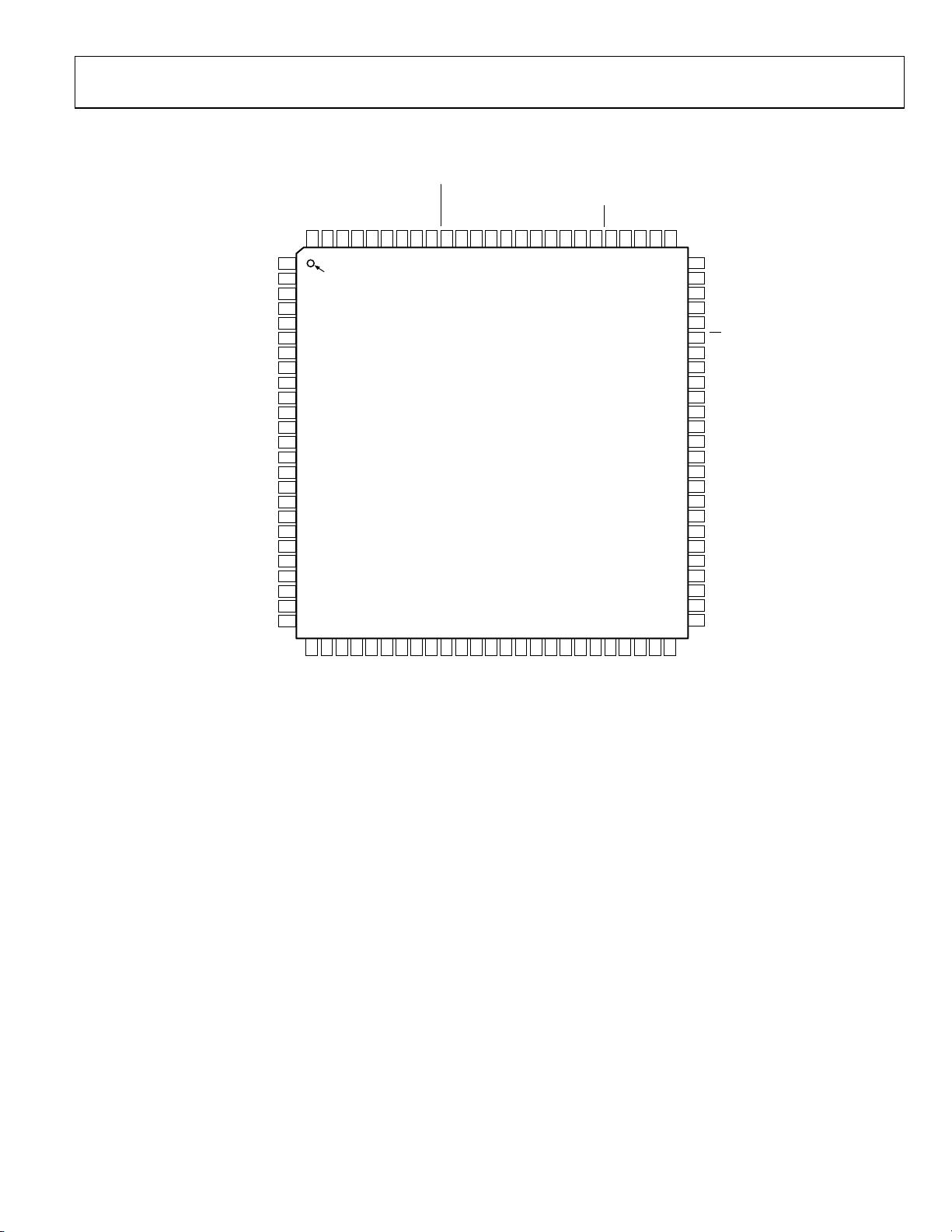
PIN 1
INDICATOR
NOTES
1. NC = NO CONNECT.
2. EXPOSED PAD S HOUL D BE S OL DE RE D TO GROUND.
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Figure 4. Pin Configuration
Rev. C | Page 9 of 64
AD9957 Data Sheet
4, 5, 73, 78, 79,
AGND
I
Analog Ground.
25 to 27, 31 to
D<17:0>
I/O
Parallel Data Input Bus (Active High). These pins provide the interleaved, 18-bit, digital, I
41
TxENABLE/FS
I
Transmit Enable, Digital Input (Active High). See the Signal Processing section for details.
55
SYNC_CLK
O
Table 3. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic I/O1 Description
1, 24, 61, 72, 86,
87, 93, 97 to 100
2 PLL_LOOP_FILTER I PLL-Loop Filter Compensation. See External PLL Loop Filter Components section.
3, 6, 89, 92 AVDD (1.8V) I Analog Core VDD. 1.8 V analog supplies.
74 to 77, 83 AVDD (3.3V) I Analog DAC VDD. 3.3 V analog supplies.
17, 23, 30, 47, 57,
64
11, 15, 21, 28, 45,
56, 66
82, 85, 88, 96
13, 16, 22, 29, 46,
58, 62, 63, 65
7 SYNC_IN+ I
8 SYNC_IN− I
9 SYNC_OUT+ O
10 SYNC_OUT− O
12 SYNC_SMP_ERR O
14 MASTER_RESET I
18 EXT_PWR_DWN I
19 PLL_LOCK O
20 CCI_OVFL O
NC Not Connected. Allow device pin to float.
DVDD (1.8V) I Digital Core VDD. 1.8 V digital supplies.
DVDD_I/O (3.3V) I Digital Input/Output VDD. 3.3 V digital supplies.
DGND I Digital Ground.
Synchronization Signal, Digital Input (Rising Edge Active). Synchronization signal from
external master to synchronize internal subclocks. See the Synchronization of Multiple
Devices section.
Synchronization Signal, Digital Input (Falling Edge Active). Synchronization signal from
external master to synchronize internal subclocks. See the Synchronization of Multiple
Devices section.
Synchronization Signal, Digital Output (Rising Edge Active). Synchronization signal from
internal device subclocks to synchronize external slave devices. See the Synchronization of
Multiple Devices section.
Synchronization Signal, Digital Output (Falling Edge Active). Synchronization signal from
internal device subclocks to synchronize external slave devices. See the Synchronization of
Multiple Devices section.
Synchronization Sample Error, Digital Output (Active High). A high on this pin indicates
that the AD9957 did not receive a valid sync signal on SYNC_IN+/SYNC_IN−. See the
Synchronization of Multiple Devices section.
Master Reset, Digital Input (Active High). This pin clears all memory elements and sets
registers to default values.
External Power-Down, Digital Input (Active High). A high level on this pin initiates the
currently programmed power-down mode. See the Power-Down Control section for
further details. If unused, tie to ground.
PLL Lock, Digital Output (Active High). A high on this pin indicates that the clock multiplier
PLL has acquired lock to the reference clock input.
CCI Overflow Digital Output, Active High. A high on this pin indicates a CCI filter overflow.
This pin remains high until the CCI overflow condition is cleared.
39, 42 to 44, 48
to 50
42 SPORT I-DATA I In Blackfin interface mode, this pin serves as the I-data serial input.
43 SPORT Q-DATA I In Blackfin interface mode, this pin serves as the Q-data serial input.
40 PDCLK O Parallel Data Clock, Digital Output (Clock). See the Signal Processing section for details.
51 RT I
52 to 54 PROFILE<2:0> I
and Q vectors for the modulator to upconvert. Also used for a GPIO port in Blackfin
interface mode.
In Blackfin interface mode, this pin serves as the FS input to receive the RFS output signal
from the Blackfin.
RA M Trigger, Digital Input (Active High). This pin provides control for the RAM amplitude
scaling function. When this function is engaged, a high sweeps the amplitude from the
beginning RAM address to the end. A low sweeps the amplitude from the end RAM
address to the beginning. If unused, connect to ground or supply.
Profile Select Pins, Digital Inputs (Active High). These pins select one of eight
phase/frequency profiles for the DDS core (single tone or carrier tone). Changing the state
of one of these pins transfers the current contents of all I/O buffers to the corresponding
registers. State changes should be set up to the SYNC_CLK pin.
Output System Clock/4, Digital Output (Clock). The I/O_UPDATE and PROFILE<2:0> pins
should be set up to the rising edge of this signal.
Rev. C | Page 10 of 64
Data Sheet AD9957
68
SDO
O
Serial Data Output, Digital Output (Active High). This pin is only active in unidirectional
84
DAC_RSET
O
94
REFCLK_OUT
O
Reference Clock Output. Analog output. See the REFCLK Overview section for more
Pin No. Mnemonic I/O1 Description
59 I/O_UPDATE I/O
60 OSK I
67 SDIO I/O
69 SCLK I
70
CS
71 I/O_RESET I
80
IOUT
81 IOUT O
90 REF_CLK I Reference Clock Input. Analog input. See the REFCLK Overview section for more details.
91
REF_CLK
Input/Output Update; Digital Input Or Output (Active High) Depending on the Internal I/O
Update Active Bit. A high on this pin indicates a transfer of the contents of the I/O buffers
to the corresponding internal registers.
Output Shift Keying, Digital Input (Active High). When using OSK (manual or automatic),
this pin controls the OSK function. See the Output Shift Keying (OSK) section of the data
sheet for details. When not using OSK, tie this pin high.
Serial Data Input/Output, Digital Input/Output (Active High). This pin can be either
unidirectional or bidirectional (default), depending on configuration settings. In
bidirectional serial port mode, this pin acts as the serial data input and output. In
unidirectional, it is an input only.
serial data mode. In this mode, it functions as the output. In bidirectional mode, this pin is
not operational and should be left floating.
Serial Data Clock. Digital clock (rising edge on write, falling edge on read). This pin
provides the serial data clock for the control data path. Write operations to the AD9957
use the rising edge. Readback operations from the AD9957 use the falling edge.
I
Chip Select, Digital Input (Active Low). Bringing this pin low enables the AD9957 to detect
serial clock rising/falling edges. Bringing this pin high causes the AD9957 to ignore input
on the serial data pins.
Input/Output Reset, Digital Input (Active High). Rather than resetting the entire device
during a failed communication cycle, when brought high, this pin resets the state machine
of the serial port controller and clears any I/O buffers that have been written since the last
I/O update. When unused, tie this pin to ground to avoid accidental resets.
O
Open-Source DAC Complementary Output Source. Analog output, current mode. Connect
through 50 Ω to AGND.
Open-Source DAC Output Source. Analog output, current mode. Connect through 50 Ω to
AGND.
Analog Reference Pin. This pin programs the DAC output full-scale reference current.
Attach a 10 kΩ resistor to AGND.
I
Complementary Reference Clock Input. Analog input. See the REFCLK Overview section
for more details.
95 XTAL_SEL I
(EPAD)
Exposed Pad
(EPAD)
1
I = input, O = output.
details.
Crystal Select (1.8 V Logic). Analog input (active high). Driving the XTAL_SEL pin high enables
the internal oscillator to be used with a crystal resonator. If unused, connect it to AGND.
The EPAD should be soldered to ground.
Rev. C | Page 11 of 64
AD9957 Data Sheet
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
START 0Hz 50MHz/DIV STOP 500MHz
06384-048
1
1
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
START 0MHz 50MHz/DIV STOP 500MHz
06384-050
1
1
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
START 0Hz 50MHz/DIV STOP 500MHz
06384-052
1
1
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
CENTER 102MHz 5kHz/DIV SP AN 50kHz
06384-049
1
1
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
CENTER 222MHz 5kHz/DIV SP AN 50kHz
06384-051
1
1
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
CENTER 372MHz 5kHz/DIV SP AN 50kHz
06384-053
1
1
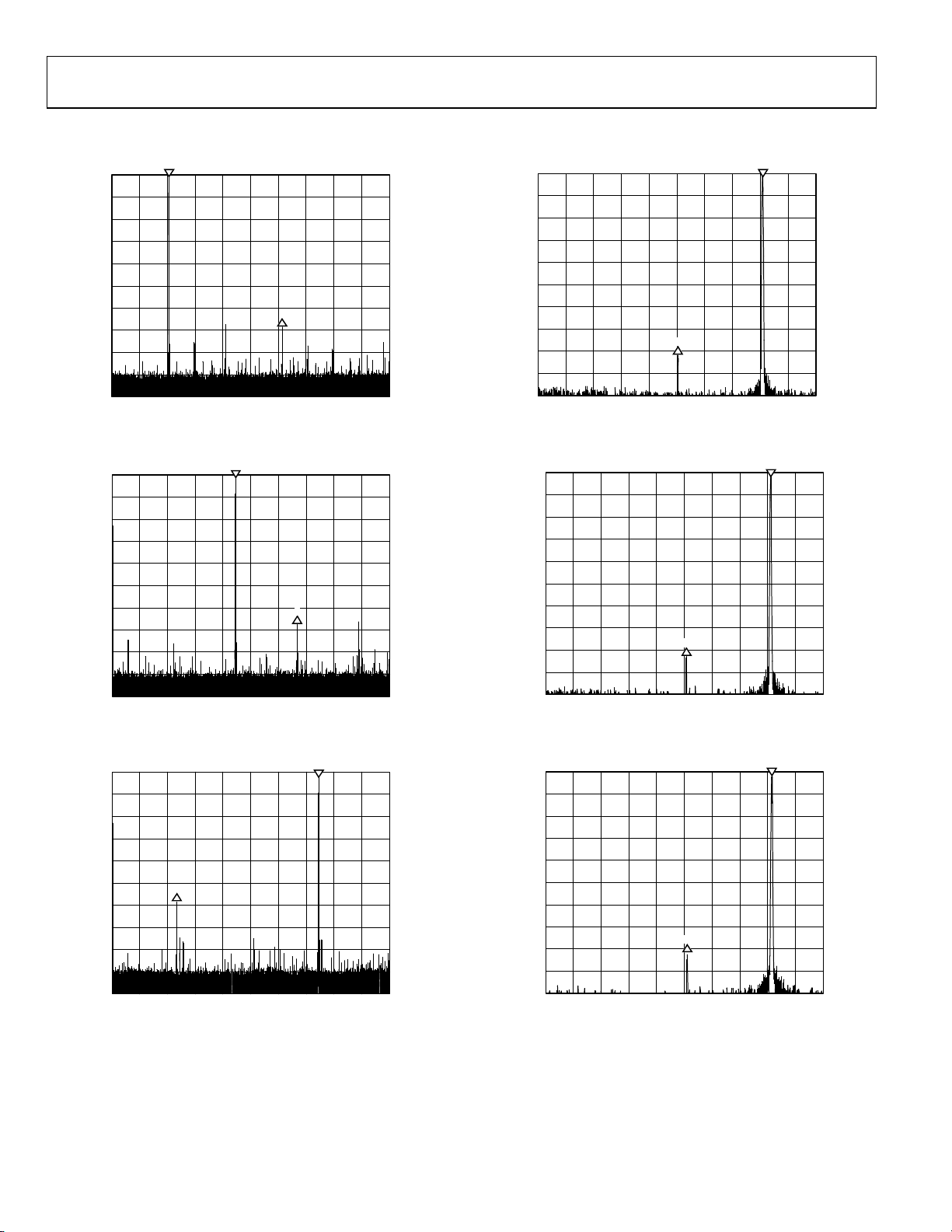
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
Figure 5. 15.625 kHz Quadrature Tone, Carrier = 102 MHz,
CCI = 16, f
= 1 GHz
S
Figure 6. 15.625 kHz Quadrature Tone, Carrier = 222 MHz,
CCI = 16, f
= 1 GHz
S
Figure 8. Narrow-Band View of Figure 5
(with Carrier and Lower Sideband Suppression)
Figure 9. Narrow-Band View of Figure 6
(with Carrier And Lower Sideband Suppression)
Figure 7. 15.625 kHz Quadrature Tone, Carrier = 372 MHz,
CCI = 16, f
= 1 GHz
S
Figure 10. Narrow-Band View of Figure 7
(with Carrier and Lower Sideband Suppression)
Rev. C | Page 12 of 64
Data Sheet AD9957
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
START 0Hz 50MHz/DIV STOP 500MHz
06384-044
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
START 0MHz 50MHz/DIV STOP 500MHz
06384-045
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
START 0Hz 50MHz/DIV STOP 500MHz
06384-046
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
CENTER 102MHz 2MHz/DIV SPAN 20MHz
06384-041
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
CENTER 222MHz 2MHz/DIV SPAN 20MHz
06384-042
0
–20
–10
–50
–40
–30
–80
–70
–60
–90
–100
CENTER 372MHz 2MHz/DIV SPAN 20MHz
06384-043
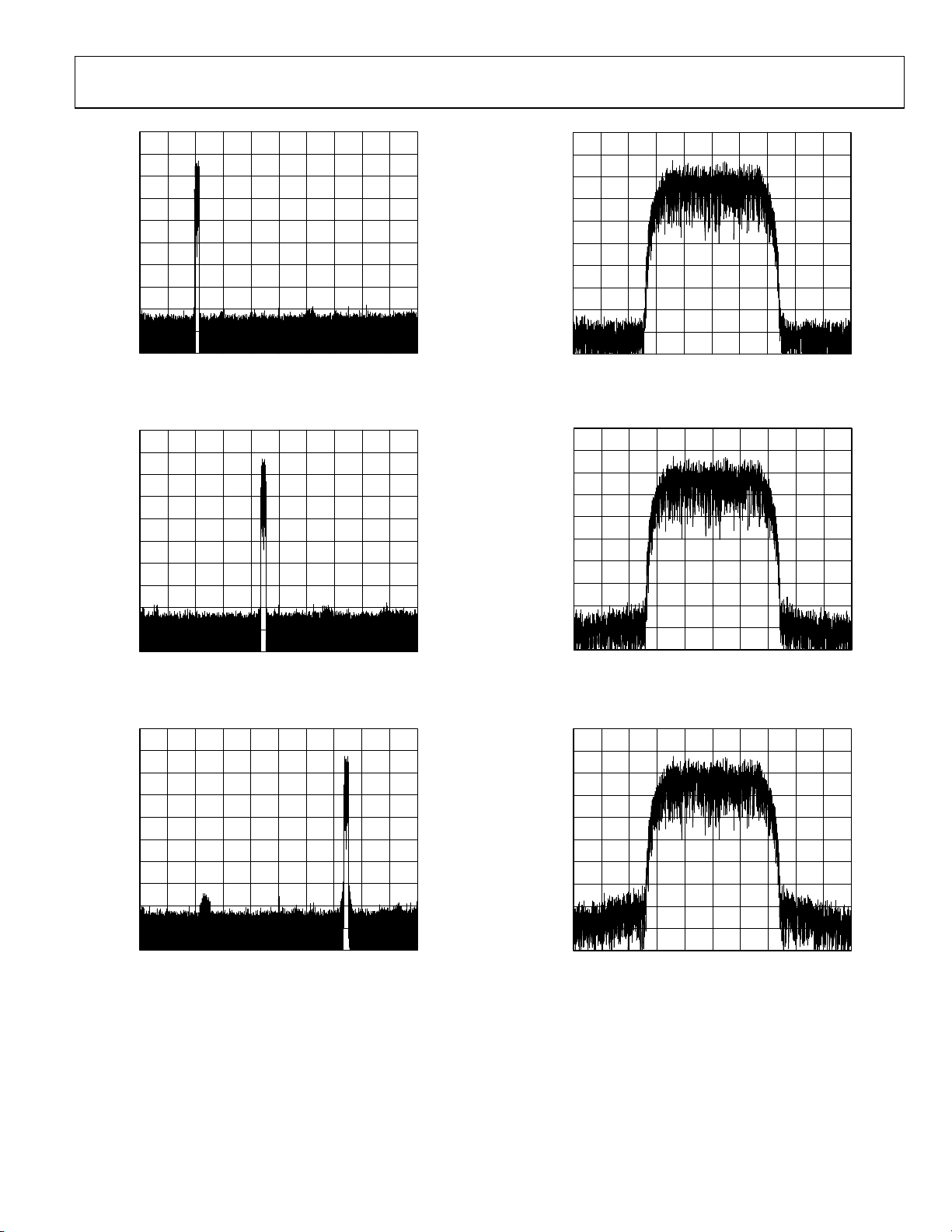
Figure 11. QPSK, 7.8125 Msymbols/s, 4x Oversampled Raised Cosine,
α = 0.25, CCI = 8, Carrier = 102 MHz, f
= 1 GHz
S
Figure 12. QPSK, 7.8125 Msymbols/s, 4x Oversampled Raised Cosine,
α = 0.25, CCI = 8, Carrier = 222 MHz, f
= 1 GHz
S
Figure 14. Narrow-Band View of Figure 11
Figure 15. Narrow-Band View of Figure 12
Figure 13. QPSK, 7.8125 Msymbols/s, 4x Oversampled Raised Cosine,
α = 0.25, CCI = 8, Carrier = 372 MHz, f
Figure 16. Narrow-Band View of Figure 13
= 1 GHz
S
Rev. C | Page 13 of 64
AD9957 Data Sheet
–50
–55
–60
–65
–75
–70
06384-058
SFDR (dBc)
FREQUENCY OUT (MHz)
SFDR WITHOUT PLL
SFDR WITH PLL
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400
400 450300250 350200150100500
06384-059
SFDR (dBc)
FREQUENCY OUT (MHz)
–75
–70
–65
–60
–55
–45
–50
LOW SUPPLY
HIGH SUPPLY
400 450300250 350200150100500
06384-060
SFDR (dBc)
FREQUENCY OUT (MHz)
–75
–70
–65
–60
–55
–50
–40°C
+85°C
–90
–100
–120
–110
–140
–150
–130
–170
–160
10 100 1k
10k 100k 100M1M 10M
06384-061
MAGNITUDE ( dBc/Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
f
OUT
= 20.1MHz
f
OUT
= 98.6MHz
f
OUT
= 201.1MHz
f
OUT
= 397.8MHz
–90
–100
–110
–120
–130
–140
–150
–160
10 100 1k 10k 100k 1M 10M 100M
06384-054
MAGNITUDE ( dBc/ Hz)
FREQUENCY OFFSET (Hz)
f
OUT
= 20.1MHz
f
OUT
= 397.8MHz
f
OUT
= 98.6MHz
f
OUT
= 201.1MHz
1200
200
400
600
800
1000
0
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
06384-062
POWER DISSIPATION (mW)
SYSTEM CLOCK FREQUENCY (MHz)
DVDD 3.3V
AVDD 3.3V
AVDD 1.8V
DVDD 1.8V
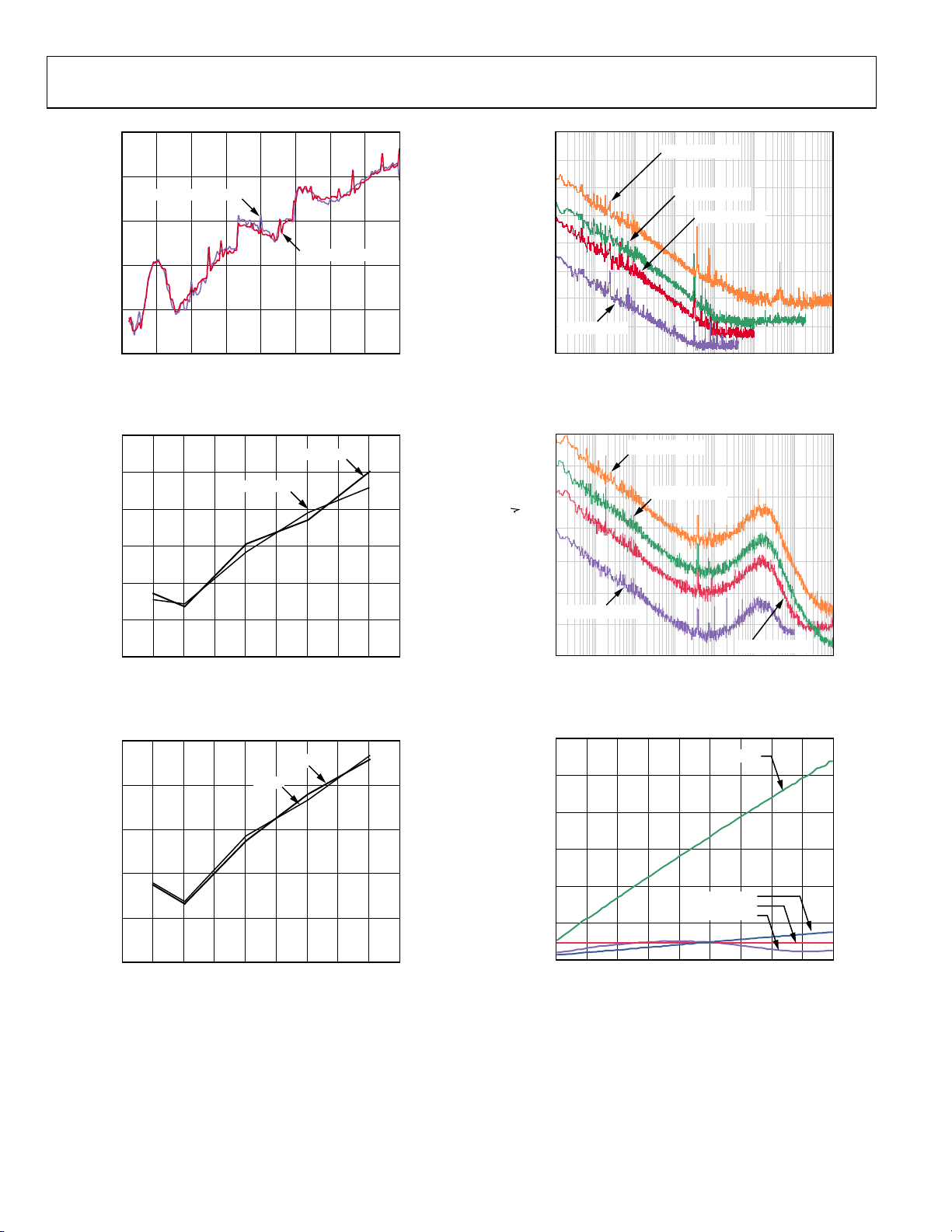
Figure 17. Wideband SFDR vs. Output Frequency in Single Tone Mode,
PLL with REFCLK = 15.625 MHz × 64
Figure 18. SFDR vs. Output Frequency and Supply (±5%) in Single Tone
Mode, REFCLK = 1 GHz
Figure 20. Residual Phase Noise, System Clock = 1 GHz
Figure 21. Residual Phase Noise Using the REFCLK Multiplier,
REFCLK = 50 MHz with 20x Multiplication, System Clock = 1 GHz
Figure 19. SFDR vs. Frequency and Temperature in Single Tone Mode,
REFCLK = 1 GHz
Figure 22. Power Dissipation vs. System Clock (PLL Disabled)
Rev. C | Page 14 of 64
Data Sheet AD9957
1200
200
400
600
800
1000
0
400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
06384-063
POWER DISSIPATION (mW)
SYSTEM CLOCK FREQUENCY (MHz)
DVDD 1.8V
AVDD 1.8V
AVDD 3.3V
DVDD 3.3V
06384-064
–110
–100
–90
–80
–70
–60
–50
–40
–30
–20
CENTER 143.86MHz SPAN 25.5MHz2.55MHz/DIV
Tx CHANNEL
BANDWIDTH: 3.84MHz
ADJACENT CHANNEL
BANDWIDTH: 3.84MHz
SPACING: 3M Hz
ADJACENT CHANNEL
BANDWIDTH: 3.84MHz
SPACING: 10M Hz
POWER: –11.88dBm
LOWER: –78.27dB
UPPER: –78.50d B
LOWER: –81.42dB
UPPER: –81.87d B
W-CDMA SGFF FWD
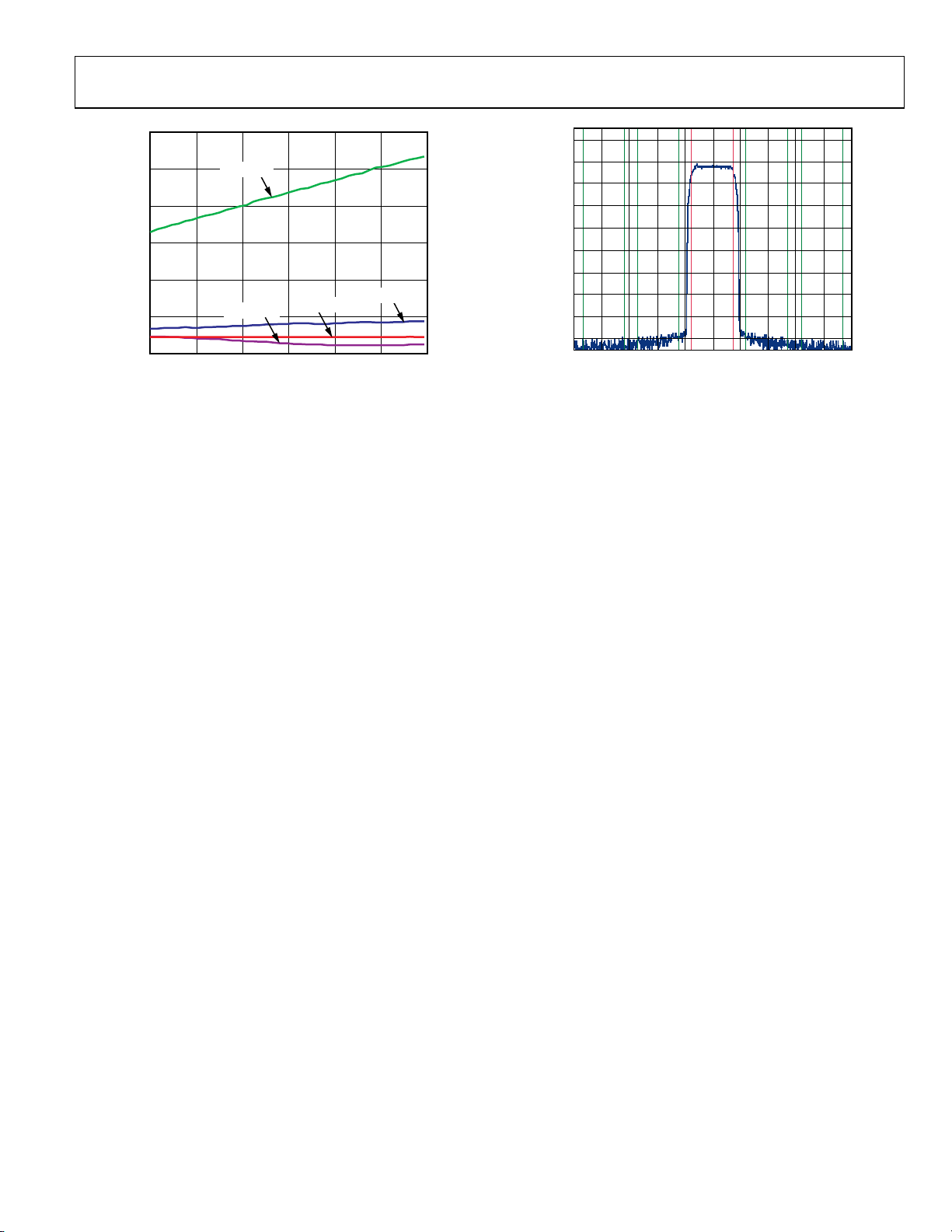
Figure 24. Typical ACLR for Wideband CDMA
Figure 23. Power Dissipation vs. System Clock (PLL Enabled)
Rev. C | Page 15 of 64
AD9957 Data Sheet
06384-005
PDCLK
I/Q IN
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
TxENABLE
FTW
PW
DAC GAIN
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
FTW
PW
8
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SEL
PARALLEL DATA
TIMING AND CONTROL
AD9957
ω
cos (ωt+θ)
sin (ωt+θ)
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
CCI_OVFL
OSK
DDS
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
POWER
DOWN
CONTROL
RT
RAM
PROFILE
SERIAL I/O
PORT
I/O_UPDATE
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
3
I Q ISQS
18
DATA ASSEMBL E R AND FORMATTE R
I
Q
IS
QS
BLACKFIN I NTERFACE
18
18
16
16
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
INVERSE
CCI
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
INVERSE
CCI
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
OSK
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING AND CONTROL
DAC
14-BIT
OUTPUT
SCALE
FACTOR
SDIO
CS
I/O_RESET
SCLK
SDO
MODES OF OPERATION
OVERVIEW
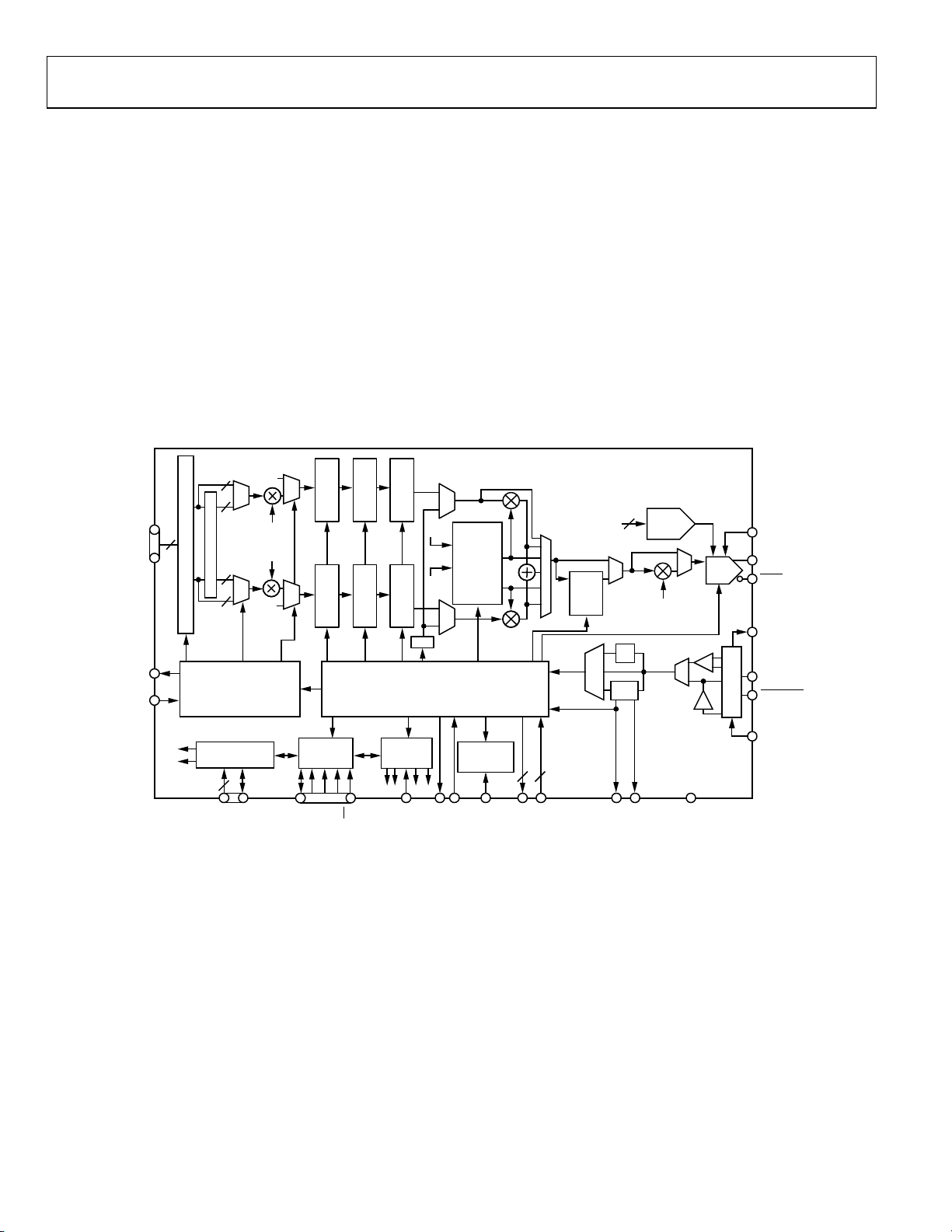
The AD9957 has three basic operating modes.
• Quadrature modulation (QDUC) mode (default)
• Interpolating DAC mode
• Single tone mode
The active mode is selected via the operating mode bits in
Control Function Register 1 (CFR1). Single tone mode allows
the device to operate as a sinusoidal generator with the DDS
driving the DAC directly.
than that of the DAC. An internal chain of rate interpolation
filters the user data and upsamples to the DAC sample rate.
Combined, the filters provide for programmable rate interpolation while suppressing spectral images and retaining the original
baseband spectrum.
QDUC mode employs both the DDS and the rate interpolation
filters. In this case, two parallel banks of rate interpolation
filters allow baseband processing of in-phase and quadrature
(I/Q) signals with the DDS providing the carrier signal to be
modulated by the baseband signals. A detailed block diagram of
the AD9957 is shown in Figure 25.
Interpolating DAC mode bypasses the DDS, allowing the user
to deliver baseband data to the device at a sample rate lower
Figure 25. Detailed Block Diagram
The inverse sinc filter is available in all three modes.
Rev. C | Page 16 of 64
Data Sheet AD9957
06384-006
PDCLK
I/Q IN
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
TxENABLE
DAC GAIN
OUTPUT
SCALE
FACTOR
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
FTW
PW
8
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SE
L
AD9957
ω
cos (ωt+θ)
sin (ωt+θ)
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
OSK
DDS
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
POWER
DOWN
CONTROL
18
DATAASSEMBLER AND FO RMATTER
I
Q
IS
QS
BLACKFIN I NTERFACE
18
18
16
16
INVERSE
CCI
INVERSE
CCI
OSK
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING AND CONTROL
DAC
14-BIT
CCI_OVFL
FTW
PW
PARALLEL DATA
TIMING AND CONTROL
RT
RAM
PROFILE
SERIAL I/O
PORT
I/O_UPDATE
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
3
I Q ISQS
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
SDIO
CS
I/O_RESET
SCLK
SDO
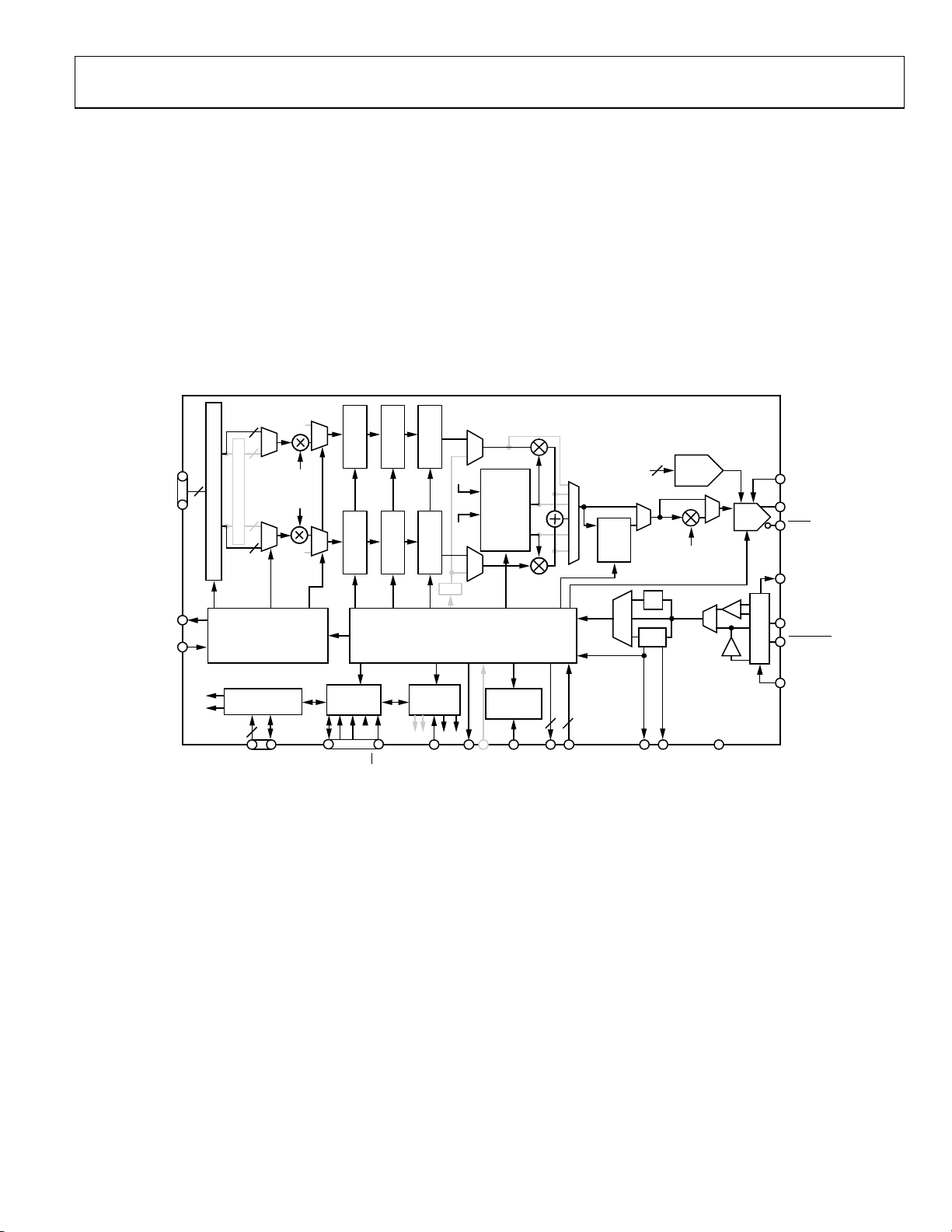
QUADRATURE MODULATION MODE
A block diagram of the AD9957 operating in QDUC mode is
shown in Figure 26; grayed items are inactive. The parallel input
accepts 18-bit I- and Q-words in time-interleaved fashion. That
is, an 18-bit I-word is followed by an 18-bit Q-word, then the
next 18-bit I-word, and so on. One 18-bit I-word and one 18-bit
Q-word together comprise one internal sample. The data assembler and formatter de-interleave the I- and Q-words so that each
sample propagates along the internal data pathway in parallel
fashion. Both I and Q data paths are active; the parallel data
clock (PDCLK) serves to synchronize the input of I/Q data to
the AD9957.
The PROFILE and I/O_UPDATE pins are also synchronous to
the PDCLK.
The DDS core provides a quadrature (sine and cosine) local
oscillator signal to the quadrature modulator, where the
interpolated I and Q samples are multiplied by the respective
phase of the carrier and summed together, producing a
quadrature modulated data stream. This data stream is routed
through the inverse sinc filter (optionally), and the output
scaling multiplier. Then it is applied to the 14-bit DAC to
produce the quadrature modulated analog output signal.
Figure 26. Quadrature Modulation Mode
Rev. C | Page 17 of 64
AD9957 Data Sheet
06384-007
PDCLK
I/Q IN
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
TxENABLE
DAC GAIN
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
FTW
PW
8
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SEL
AD9957
ω
cos (ωt+θ)
sin (ωt+θ)
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
OSK
DDS
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
POWER
DOWN
CONTROL
2
DATAASSEMBLER AND FO RMATTER
I
Q
IS
QS
BLACKFIN I NTERFACE
18
18
16
16
INVERSE
CCI
INVERSE
CCI
OSK
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING AND CONTROL
DAC
14-BIT
CCI_OVFL
OSK
FTW
PW
PARALLEL DATA
TIMING AND CONTROL
RT
RAM
PROFILE
SERIAL I/O
PORT
I/O_UPDATE
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
3
I Q ISQS
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
OUTPUT
SCALE
FACTOR
SDIO
CS
I/O_RESET
SCLK
SDO
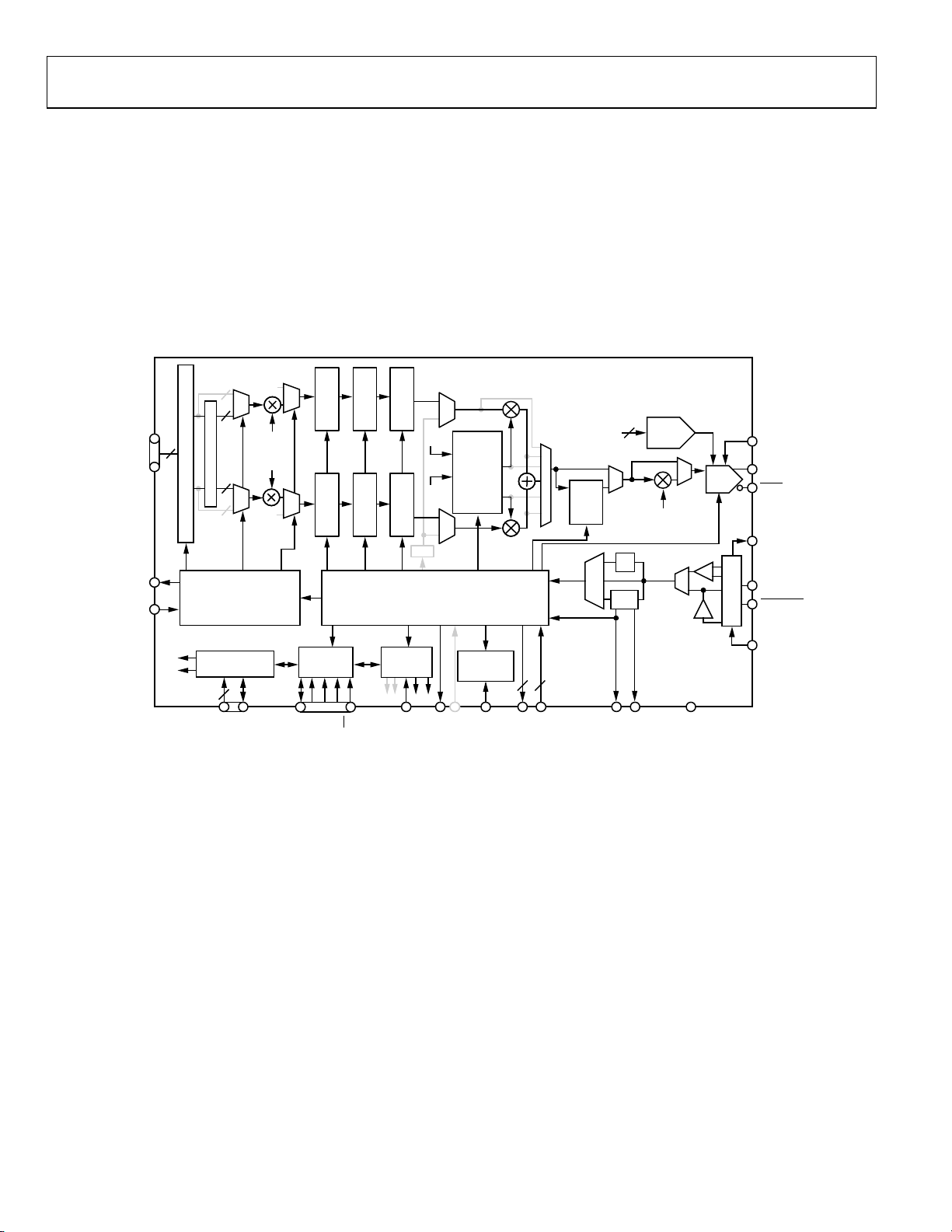
BLACKFIN INTERFACE (BFI) MODE
A subset of the QDUC mode is the Blackfin interface (BFI)
mode, shown in Figure 27; grayed items are inactive. In this
mode, a separate I and Q serial bit stream is applied to the
baseband data port instead of parallel data-words. The two
serial inputs provide for 16-bit I- and Q-words (unlike the
18-bit words in normal QDUC mode). The serial bit streams
are delivered to the Blackfin interface. The Blackfin interface
converts the 16-bit serial data into 16-bit parallel data to
propagate down the signal processing chain.
The Blackfin interface includes an additional pair of half-band
filters in both I and Q signal paths (not shown explicitly in the
diagram). The two half-band filters increase the interpolation
of the baseband data by a factor of four, relative to the normal
QDUC mode.
The synchronization of the serial data occurs through the
PDCLK signal. In BFI mode, the PDCLK signal is effectively
the bit clock for the serial data.
Note that the system clock is limited to 750 MHz in BFI mode.
Figure 27. Quadrature Modulation Mode, Blackfin Interface
Rev. C | Page 18 of 64
Data Sheet AD9957
06384-008
PDCLK
I/Q IN
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
TxENABLE
DAC GAIN
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
FTW
PW
8
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
XTAL_SEL
PARALLEL DATA
TIMING AND CONTROL
AD9957
ω
cos (ωt+θ)
sin (ωt+θ)
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
DDS
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
POWER
DOWN
CONTROL
18
DATAASSEMBLER AND FO RMATTER
I
Q
IS
QS
BLACKFIN I NTERFACE
18
18
16
16
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
INVERSE
CCI
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
INVERSE
CCI
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
OSK
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING AND CONTROL
DAC
14-BIT
FTW
PW
OSK
RT
RAM
PROFILE
SERIAL I/O
PORT
I/O_UPDATE
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
3
I Q IS QS
OUTPUT
SCALE
FACTOR
CCI_OVFL
SDIO
CS
I/O_RESET
SCLK
SDO
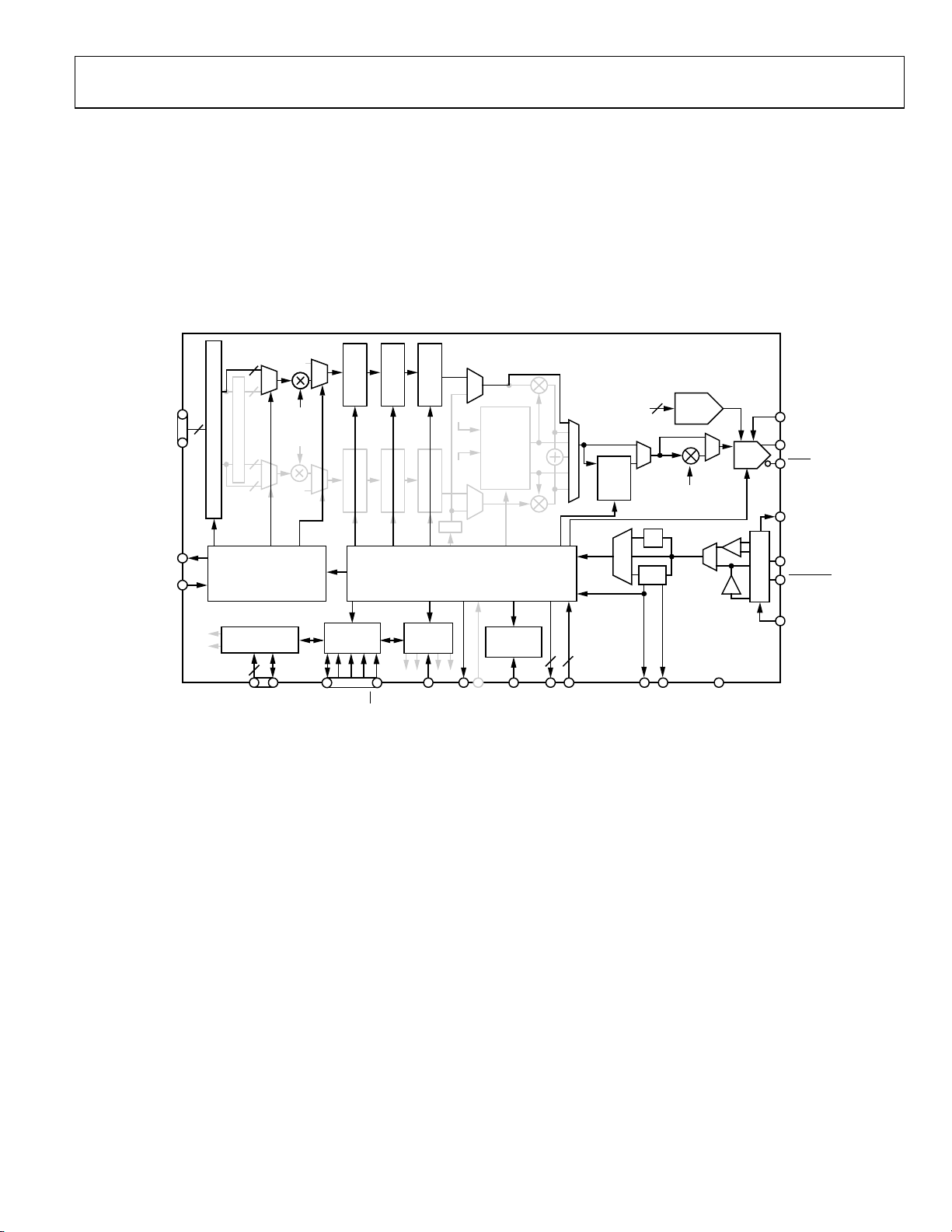
INTERPOLATING DAC MODE
A block diagram of the AD9957 operating in interpolating DAC
mode is shown in Figure 28; grayed items are inactive. In this
mode, the Q data path, DDS, and modulator are all disabled; only
the I data path is active.
As in quadrature modulation mode, the PDCLK pin functions
as a clock, synchronizing the input of data to the AD9957.
No modulation takes place in the interpolating DAC mode;
therefore, the spectrum of the data supplied at the parallel port
remains at baseband. However, a sample rate conversion takes
place based on the programmed interpolation rate. The interpolation hardware processes the signal, effectively performing
an oversample with a zero-stuffing operation. The original
input spectrum remains intact and the images that otherwise
would occur from the sample rate conversion process are
suppressed by the interpolation signal chain.
Figure 28. Interpolating DAC Mode
Rev. C | Page 19 of 64
AD9957 Data Sheet
06384-009
PDCLK
I/Q IN
EXT_PWR_DWN
DAC_RSET
IOUT
IOUT
TxENABLE
FTW
PW
DAC GAIN
θ
INVERSE
SINC
FILTER
CLOCK
FTW
PW
8
SYSCLK
PLL
÷2
CLOCK MODE
REF_CLK
REF_CLK
REFCLK_OUT
X
TAL_SEL
PARALLEL DATA
TIMING AND CONTROL
AD9957
ω
cos (ωt+θ)
sin (ωt+θ)
SYNC_OUT
SYNC_IN
PLL_LOCK
PLL_LOOP_FILTER
MASTER_RESET
2
2
CCI_OVFL
OSK
DDS
AUX
DAC
8-BIT
POWER
DOWN
CONTROL
RT
RAM
PROFILE
SERIAL I/O
PORT
I/O_UPDATE
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
3
I Q IS QS
10
DATAASSEMBLER AND FO RMATTER
I
Q
IS
QS
BLACKFIN I NTERFACE
18
18
16
16
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
INVERSE
CCI
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
HALF-BAND
FILTERS (4×)
INVERSE
CCI
CCI
(1× TO 63×)
OSK
INTERNAL CLOCK TIMING AND CONTROL
DAC
14-BIT
OUTPUT
SCALE
FACTOR
SDIO
CS
I/O_RESET
SCLK
SDO
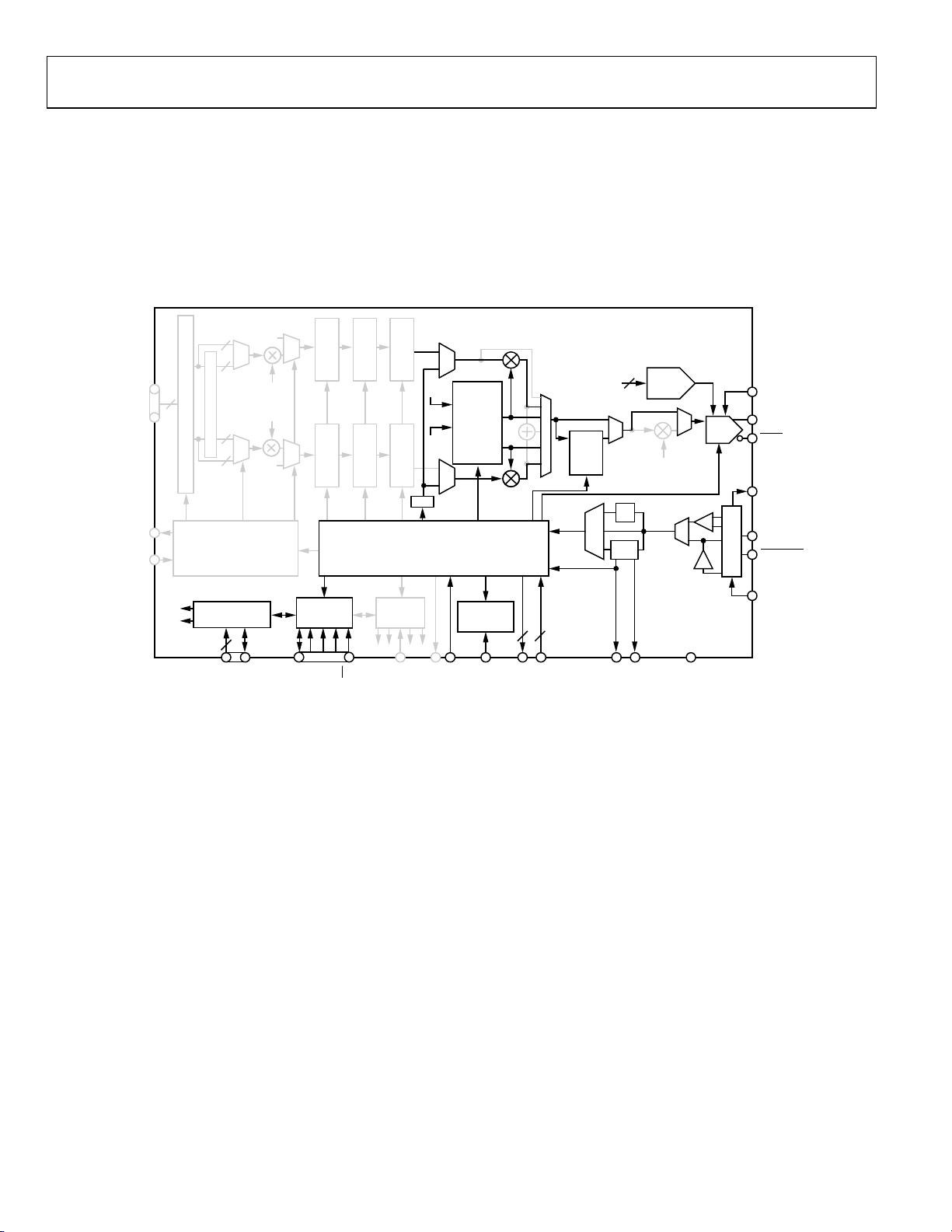
SINGLE TONE MODE
A block diagram of the AD9957 operating in single tone mode
is shown in Figure 29; grayed items are inactive. In this mode,
both I and Q data paths are disabled from the 18-bit parallel
data port up to, and including, the modulator. The internal
DDS core produces a single frequency signal based on the
programmed tuning word. The user may select either the
cosine or sine output of the DDS. The sinusoid at the DDS
output can be scaled using a 14-bit amplitude scale factor (ASF)
and optionally routed through the inverse sinc filter.
Single tone mode offers the output shift keying (OSK) function.
It provides the ability to ramp the amplitude scale factor between
zero and an arbitrary preset value over a programmable time
interval.
Figure 29. Single Tone Mode
Rev. C | Page 20 of 64
 Loading...
Loading...