ANALOG DEVICES AD9889B Service Manual
High Performance
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
FEATURES
HDMI/DVI transmitter compatible with HDMI 1.1 and
HDCP 1.1
Single 1.8 V power supply
Video/audio inputs are 3.3 V tolerant
80-lead, Pb-free LQFP
Digital video
80 MHz operation supports all video formats from 480i to
1080i and 720p
Programmable 2-way color space converter
Supports RGB, YCbCr, DDR, ITU656 formats
Auto input video format detection
Digital audio
Supports standard S/PDIF for stereo or compressed audio
up to 192 kHz
8-channel LPCM I2S audio up to 192 kHz
Special features for easy system design
On-chip MPU to perform HDCP operations
On-chip I
5 V tolerant I
No audio master clock needed for S/PDIF support
2
C master to handle EDID reading
2
C and MPD I/Os, no extra device needed
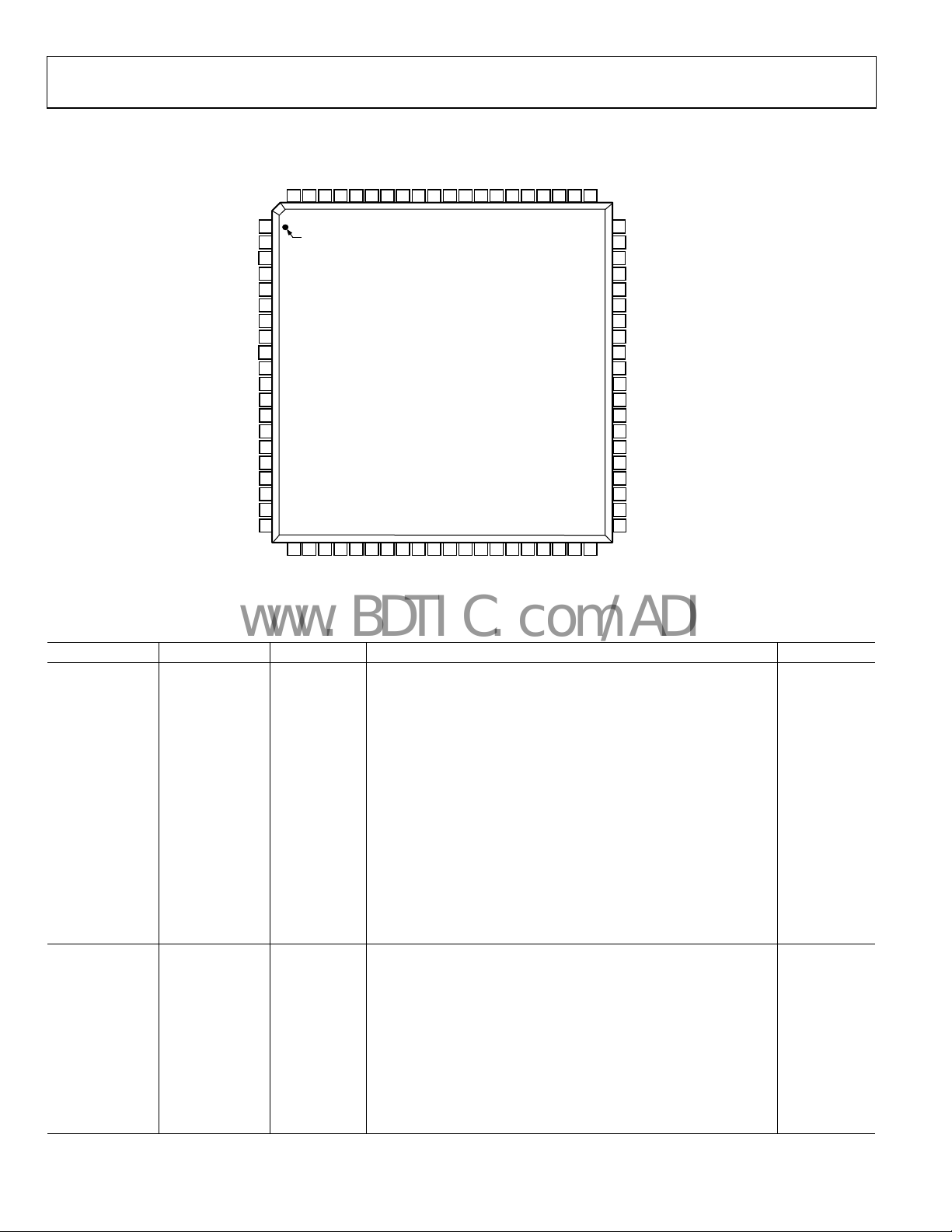
CLK
VSYNC
HSYNC
D[23:0]
S/PDIF
MCLK
I2S[3:0]
DE
HDMI™/DVI Transmitter
AD9889
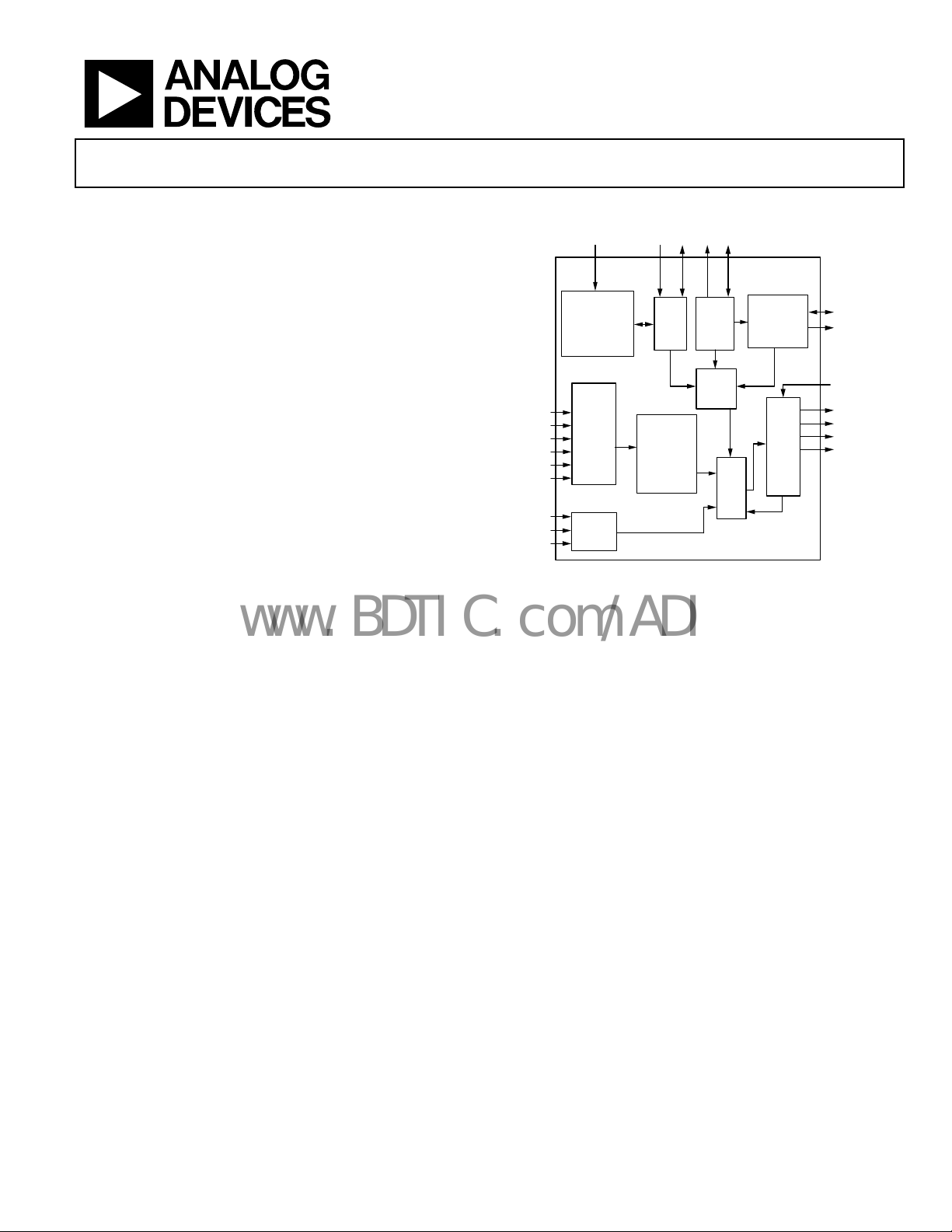
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
MDAMCL
HTPG SCL
REGISTER
CONFIGURATION
LOGIC
VIDEO
DATA
CAPTURE
AUDIO
DATA
CAPTURE
SDA
I2C
SLAVE
COLOR
SPACE
CONVERSION
4:2:2
TO
4:4:4
CONVERSION
2
C
I
MASTER
HDCP
CIPHER
MASK
Figure 1.
XOR
HDCP
CONTROLLER
HDM
ITX
CORE
AD9889
DDSDA
DDCSCL
SWING_ADJ
Tx0[1:0]
Tx1[1:0]
Tx2[1:0]
TxC[1:0]
1
0
0
-
5
7
6
5
0
APPLICATIONS
DVD players and recorders
Digital set-top boxes
AV receivers
Digital cameras and camcorders
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9889 is an 80 MHz, high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI
to 1080i and 720p, and graphic resolutions up to XGA (1024 ×
768 @ 75 Hz). With the inclusion of HDCP, the AD9889 allows
the secure transmission of protected content as specified by the
HDCP 1.1 protocol.
The AD9889 supports both S/PDIF and 8-channel I
Its high fidelity 8-channel I
7.1 surround audio at 192 kHz. The S/PDIF can carry stereo
LPCM (linear pulse code modulation) audio or compressed
audio including Dolby® Digital, DTS®, and THX®.
TM
1.1) transmitter. It supports HDTV formats up
2
2
S can transmit either stereo or
S audio.
The AD9889 helps to reduce system design complexity and cost
by incorporating such features as HDCP master, I
2
C master for
EDID reading, a single 1.8 V power supply, and 5 V tolerance
2
C and hot plug detect pins.
on I
Fabricated in an advanced CMOS process, the AD9889 is provided in a space-saving, 80-lead, surface-mount, Pb-free plastic
LQFP and is specified over the 0°C to 70°C temperature range.
EVALUATION KITS AND OTHER RESOURCES
Evaluation kits, reference design schematics, software quick
start guide, and codes are available from Analog Devices local
sales and marketing personnel.
Rev. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Anal og Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or ot her
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 © 2005 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features.............................................................................................. 1
2
I
S Audio...................................................................................... 17
Applications....................................................................................... 1
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Evaluation Kits and Other Resources ............................................ 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 2
Electrical Specifications ................................................................... 3
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 5
Explanation of Test Levels ........................................................... 5
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 5
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions............................. 6
2
I
C Addresses ................................................................................ 8
List of Reference Documents...................................................... 8
Format Standards ......................................................................... 8
Design Guide..................................................................................... 9
General Description..................................................................... 9
S/PDIF Audio.............................................................................. 17
CTS Generation.......................................................................... 17
N Parameter................................................................................ 18
CTS Parameter............................................................................ 18
Packet Configuration................................................................. 19
Pixel Repetition .......................................................................... 19
HDCP Handling......................................................................... 20
EDID Reading............................................................................. 20
Interrupts..................................................................................... 20
Power Management ................................................................... 20
2-Wire Serial Register Map........................................................... 21
2-Wire Serial Control Register Detail Chip Identification ....... 33
Source Product Description (SPD) Infoframe....................... 37
2-Wire Serial Control Port ............................................................ 40
Data Transfer via Serial Interface............................................. 40
Video Data Capture...................................................................... 9
Input Formats................................................................................ 9
4:2:2 to 4:4:4 Data Conversion.................................................. 14
Horizontal Sync, Vertical Sync, and Degeneration................ 14
Degeneration............................................................................... 14
HSYNC and VSYNC Generation............................................. 14
Color Space Conversion Matrix (CSC) ................................... 16
Audio Data Capture ....................................................................... 17
REVISION HISTORY
10/05—Revision 0: Initial Version
Serial Interface Read/Write Examples..................................... 41
PCB Layout Recommendations.................................................... 42
Power Supply Bypassing............................................................ 42
Digital Inputs .............................................................................. 42
Color Space Converter (CSC) Common Settings...................... 43
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 45
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 45
Rev. 0 | Page 2 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ELECTRICAL SPECIFICATIONS
Table 1.
AD9889KSTZ-80
Parameter Temp Test Level Min Typ Max Unit
DIGITAL INPUTS
Input Voltage, High (VIH) Full VI 1.4 V
Input Voltage, Low (VIL) Full VI 0.7 V
Input Current, High (VIH) Full V −1.0 mA
Input Current, Low (VIL) Full V +1.0 mA
Input Capacitance 25°C V 3 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Output Voltage, High (VOH) Full VI AVDD − 0.1 V
Output Voltage, Low (VOL) Full VI 0.4 V
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
θJC Junction-to-Case
Thermal Resistance V 25 °C/W
θJA Junction-to-Ambient
Thermal Resistance V 30 °C/W
Ambient Temperature Full V 0 25 70 °C
DC SPECIFICATIONS
Input Leakage Current, IIL 25°C VI −10 +10 µA
Input Clamp Voltage (−16 mA) 25°C V −0.8 V
Input Clamp Voltage (+16 mA) 25°C V +0.8
Differential High Level Output Voltage V AVCC V
Differential Output Short-Circuit Current V 10 µA
POWER SUPPLY
VDD (All) Supply Voltage Full IV 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
VDD Supply Voltage Noise Full V 50 mV p-p
Complete Power-Down Current
(Everything Except I
Quiet Power Down Current
(Monitor Detect On)
Transmitter Supply Current
(27 MHz Typical Random Pattern)
Transmitter Supply Current
(80 MHz Typical Random Pattern)
Transmitter Total Power
(80 MHz Single Pixel Stripe Pattern; Worst Case
Operating Conditions)
AC SPECIFICATIONS
CLK Frequency 25°C IV 13.5 80 MHz
CLK Duty Cycle 25°C VI 40% 60%
Worst Case CLK Input Jitter Full VI 1.0 ns
Setup Time to CLK Falling Edge VI TBD TBD ns
Hold Time to CLK Falling Edge VI TBD TBD ns
TMDS Differential Swing VII 800 1000 1200 mV
VSYNC and HSYNC Delay from DE Falling Edge VI 1 UI
VSYNC and HSYNC Delay to DE Rising Edge VI 1 UI
DE High Time 25°C VI 8191 UI
DE Low Time 25°C VI 138 UI
Differential Output Swing Low-to-High
Transition Time
Differential Swing Output High-to-Low
Transition Time
2
C)
25°C IV 6 13 mA
25°C VI 7 mA
25°C VI 165 mA
25°C IV 185 205 mA
Full VI 430 mW
25°C VII 75
25°C VII 75
490 ps
490 ps
Rev. 0 | Page 3 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
AD9889KSTZ-80
Parameter Temp Test Level Min Typ Max Unit
AUDIO AC TIMING
Sample Rate (I2S and S/PDIF) Full IV 32 192 kHz
I2S Cycle Time 25°C IV 1 UI
I2S Setup Time 25°C IV 15 ns
I2S Hold Time 25°C IV 0 ns
Audio Pipeline Delay 25°C IV 75 us
Rev. 0 | Page 4 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 2.
Parameter Rating
Digital Inputs 5 V to 0.0 V
Digital Output Current 20 mA
Operating Temperature Range −40°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature 150°C
Maximum Case Temperature 150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
Table 3.
Level Test
I 100% production tested.
II
III Sample tested only.
IV
V Parameter is a typical value only.
VI
VII Limits defined by HDMI specification.
100% production tested at 25°C and sample tested at
specified temperatures.
Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization
testing.
100% production tested at 25°C; guaranteed by design
and characterization testing.
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate on
the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy
electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance
degradation or loss of functionality.
Rev. 0 | Page 5 of 48
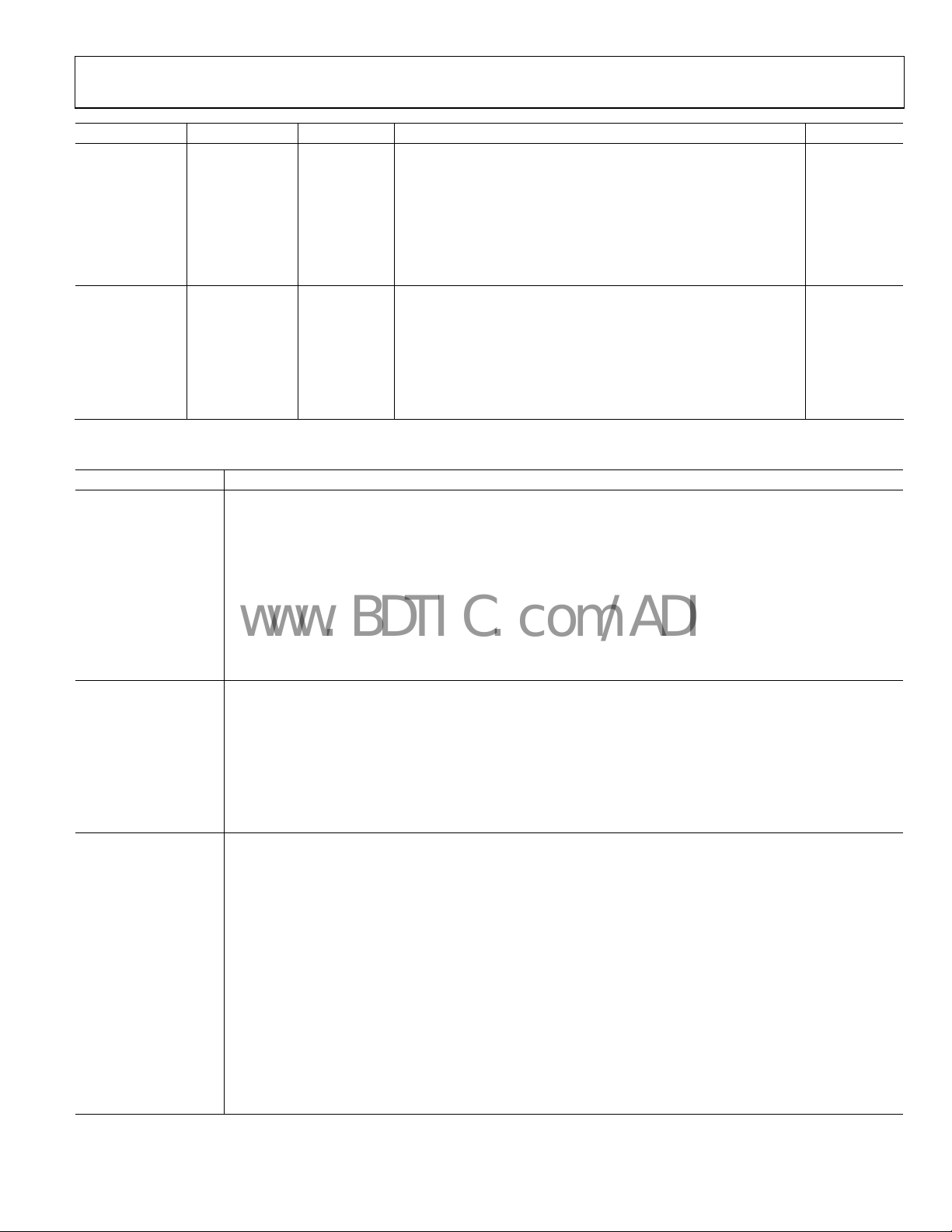
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
DD
DD
DD
GND79GND78D177D276D375D474D573D672D771D870D969D1068D1167D1266D1365D1464DV
80
DD
DV
DV
DV
63
62
61
DV
DE
HSYNC
VSYNC
CLK
S/PDIF
MCLK
I2S0
I2S1
I2S2
I2S3
SCLK
LRCLK
GND
PV
GND
GND
PV
PV
1
DD
D0
DD
DD
DD
PIN 1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
DD
DD
EXT_SW
HPD
AV
PV
GND
AD9889
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
GND
DD
GND
Tx0–
TxC–
TxC+
Tx0+
AV
Figure 2. Pin Configuration
34
35
36
37
38
DD
Tx1–
PD/A0
Tx1+
Tx2–
Tx2+
AV
60
GND
59
GND
58
D15
57
D16
56
D17
55
D18
54
D19
53
D20
52
D21
51
D22
50
D23
49
MCL
48
MDA
47
SDA
46
SCL
45
DDSDA
44
DDCSCL
43
GND
42
GND
41
AV
DD
39
40
INT
GND
05675-002
Table 4. Complete Pinout List
Pin Type Pin No. Mnemonic Description Value
INPUTS
50 to 58,
65 to 78, 2 D[23:0] Video Data Input 1.8 V CMOS
6 CLK Video Clock Input 1.8 V CMOS
3 DE Data Enable Bit for Digital Video 1.8 V CMOS
4 HSYNC Horizontal SYNC Input 1.8 V CMOS
5 VSYNC Vertical SYNC Input 1.8 V CMOS
23 EXT_SW Differential Output Swing Adjustment 1.8 V CMOS
25 HPD Hot Plug Detect Signal 1.8 V CMOS
7 S/PDIF S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) Audio Input Pin 1.8 V CMOS
8 MCLK Audio Reference Clock, 128 × fs or 256 × fs 1.8 V CMOS
12 to 9 I2S[3:0] I2S Audio Data Inputs 1.8 V CMOS
13 SCLK I2S Audio Clock 1.8 V CMOS
14 LRCLK Left/Right Channel Selection 1.8 V CMOS
33 PD/A0 Power-Down Control 1.8 V CMOS
OUTPUTS
28, 27 TxC+ Differential Clock Output TMDS
TxC− Differential Clock Output Complement
38, 37 Tx2+ Differential Output Channel 2 TMDS
Tx2− Differential Output Channel 2 Complement
35, 34 Tx1+ Differential Output Channel 1 TMDS
Tx1− Differential Output Channel 1 Complement
31, 30 Tx0+ Differential Output Channel 0 TMDS
Tx0− Differential Output Channel 0 Complement
40 INT Monitor Sense Connection Status 1.8 V CMOS
Rev. 0 | Page 6 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pin Type Pin No. Mnemonic Description Value
POWER SUPPLY
24, 29, 36, 41 AVDD Output Power Supply 1.8 V
1, 61, 62, 63, 64 DVDD Digital and I/O Power Supply 1.8 V
16, 19, 20, 21 PVDD PLL Power Supply 1.8 V
CONTROL
47 SDA Serial Port Data I/O 3.3 V CMOS
46 SCL Serial Port Data Clock (100 kHz Maximum) 3.3 V CMOS
48 MDA Serial Port Data I/O to HDCP Keys 3.3 V CMOS
49 MCL Serial Port Data Clock to HDCP Keys 3.3 V CMOS
45 DDSDA Serial Port Data I/O to Receiver 3.3 V CMOS
44 DDCSCL Serial Port Data Clock to Receiver 3.3 V CMOS
Table 5. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin Mnemonic Description
OUTPUTS
TxC+ Differential Clock Output at Pixel Clock Rate; Transition Minimized Differential Signaling (TMDS).
TxC− Differential Clock Output Complement.
Tx2+ Differential Output of the Red Data at 10× the Pixel Clock Rate; TMDS.
Tx2− Differential Red Output Complement.
Tx1+ Differential Output of the Green Data at 10× the Pixel Clock Rate; TMDS.
Tx1− Differential Green Output Complement.
Tx0+ Differential Output of the Blue Data at 10× the Pixel Clock Rate; TMDS.
Tx0− Differential Blue Output Complement.
INT Monitor Sense.
SERIAL PORT (2-WIRE)
SDA Serial Port Data I/O.
SCL Serial Port Data Clock.
DDSDA Serial Port Data I/O Master to Receiver.
DDCSCL Serial Port Data Clock Master to Receiver.
MDA Serial Port Data I/O Master to HDCP Keys.
MCL Serial Port Data Clock Master to HDCP Keys.
For a full description of the 2-wire serial register and how it works, refer to the 2-Wire Serial Control Port section.
INPUTS
D[23:0] Digital Input in RGB or YCbCr Format.
CLK Video Clock Input.
DE Data Enable for Video Data.
HSYNC Horizontal Sync Input.
VSYNC Vertical Sync Input. This is the input for vertical sync.
EXT_SW
HPD Hot Plug Detect. This indicates to the interface whether the receiver is connected.
S/PDIF S/PDIF Audio Input. This is the audio input from a Sony/Philips Digital Interface.
MCLK Audio Reference Clock. Set either to 128 × fs or 256 × fs.
I2S[3:0] I2S Audio Inputs. These represent the eight channels of audio (two per input) available through I2S.
I2S CLK I2S Audio Clock.
LRCLK Left/Right Channel Selection.
PD/A0 Power Down.
15, 17, 18, 22,
26, 32, 39, 42,
43, 59, 60, 79,
80
Swing Adjust Sets the Differential Output Voltage or Swing. An 887 Ω resistor (1% tolerance) should be placed
between this pin and ground.
GND Ground 0 V
Rev. 0 | Page 7 of 48

AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Pin Mnemonic Description
POWER SUPPLY
DVDD
AVDD Output Power Supply
PVDD
GND
I2C ADDRESSES
The SDA/SCL programming address is 0x72 or 0x7A based on whether A0 is pulled high (10 kΩ resistor = 0x7A) or pulled low (10 kΩ
resistor = 0x72).
The MDA/MCL EEPROM address is 0xA0.
The EDID EEPROM on the receiver is expected to have an address of 0xA0.
LIST OF REFERENCE DOCUMENTS
Table 6.
Document Description
EIA/CEA-861B Describes audio and video infoframes as well as the E-EDID structure for HDMI.
HDMI V1.1 Defining document for HDMI Version 1.1. Can be located at www.hdmi.org.
HDCPv1.0 Defining document for HDCP Version 1.1. Can be located at www.digital-cp.com.
ITU-R BT.656-3 Defining document for BT656.
Main Power Supply. These pins supply power to the main elements of the circuit. They should be filtered and as
quiet as possible.
Clock Generator Power Supply. The most sensitive portion of the AD9889 is the clock generation circuitry. These
pins provide power to the clock PLL (phase-locked loop) and help the user design for optimal performance. The
designer should provide quiet, noise-free power to these pins.
Ground. The ground return for all circuitry on-chip. It is recommended that the AD9889 be assembled on a single
solid ground plane, with careful attention given to ground current paths.
FORMAT STANDARDS
In this document, data is represented in a variety of ways.
Table 7.
Data Type Format
0xNN Hexadecimal (base-16) numbers are represented using the C language notation, preceded by 0x.
0bNN Binary (base-2) numbers are represented using the C language notation, preceded by 0b.
NN Decimal (base-10) numbers are represented using no additional prefixes or suffixes.
Bit Bits are numbered in little-endian format, that is, the least significant bit (LSB) of a byte or word is referred to as Bit 0.
Rev. 0 | Page 8 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
DESIGN GUIDE
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9889 HDMI transmitter provides a high bandwidth digital
content protected (HDCP) digital link between a wide range of
digital input formats—both audio and video (see Tab le 8) a nd
output
formats (see Table 9). Video and audio data are captured
and
prepared for transmission while three separate I
2
C buses (two
of which are masters) are used to program and provide content
protection for the data to be transmitted.
VIDEO DATA CAPTURE
The AD9889 can accept video data from as few as eight pins
(YCbCr DDR) representing 8-bit data or as many as 24 pins
representing 12-bit data. The AD9889 is capable of detecting
all of the 34 video formats defined in the EIA/CEA-861B
specification. If video ID (VID) 32, 33, or 34 is present, the user
needs to set Register R0x15[0] to 0b1, as these modes have V
REF
frequencies of 30 Hz or less. The user can read the detected
video format at R0x3E[7:2]. Formats outside the EIA/CEA-861B
specification can be read in R0x3F[7:5]. Detailed line count
differences for 240p and 288p modes can be read from
R0x3F[4:3]. In order to distinguish between an aspect ratio of
4:3 and one of 16:9, R0x17[1] should be set accordingly.
INPUT FORMATS
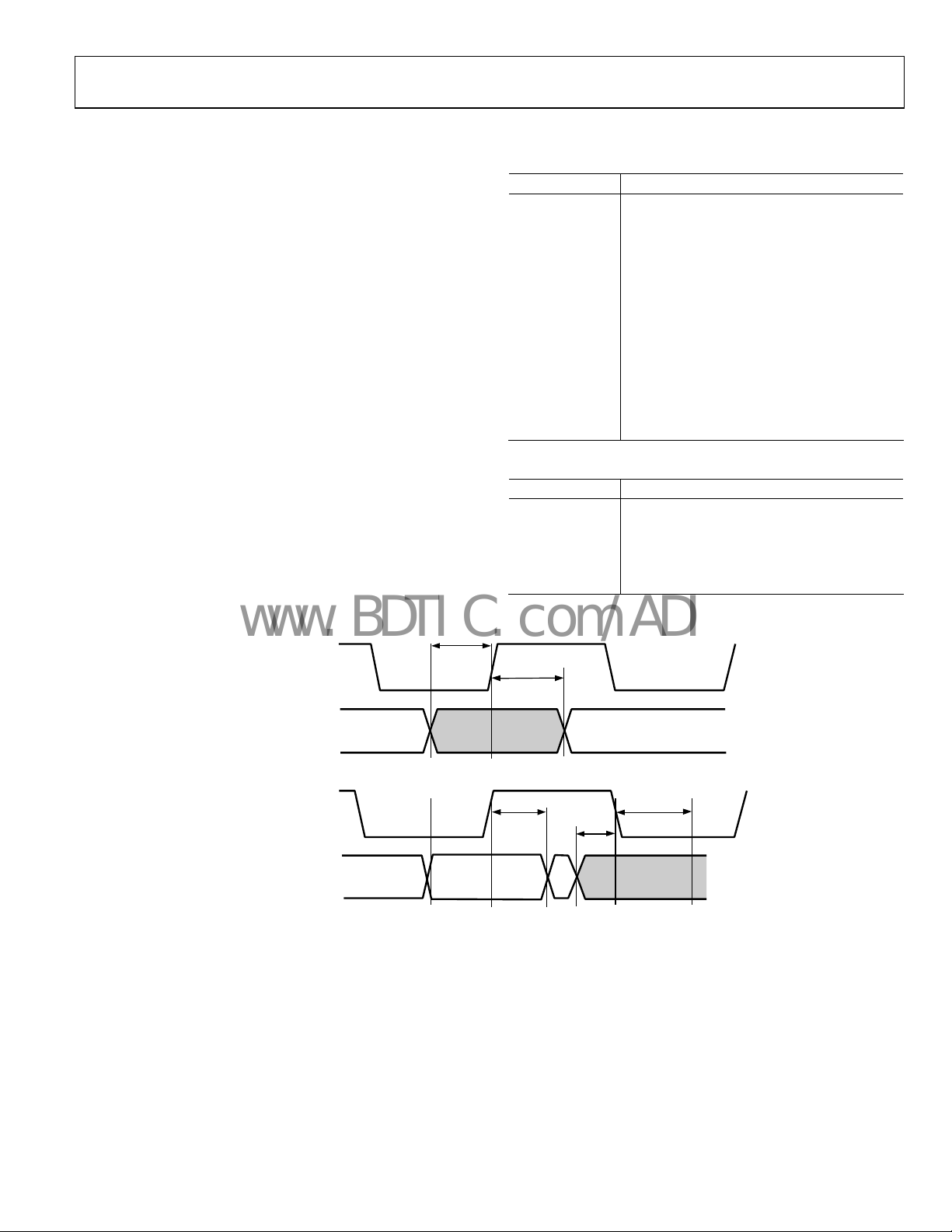
t
SETUP
Table 8. Input Formats Supported
No. of Bits Input Format
12 RGB (DDR)
12 YCbCr 4:4:4 (DDR)
24 RGB 4:4:4
24 YCbCr 4:4:4
16 YCbCr 4:2:2 (ITU.601)
20 YCbCr 4:2:2 (ITU.601)
24 YCbCr 4:2:2 (ITU.601)
8 YCbCr (DDR)
10 YCbCr (DDR)
12 YCbCr (DDR)
8 YCbCr 4:2:2 (ITU.656)
10 YCbCr 4:2:2 (ITU.656)
12 YCbCr 4:2:2 (ITU.656)
Table 9. Output Formats Supported
No. of Bits Output Format
24 RGB 4:4:4
24 YCbCr 4:4:4
16 YCbCr 4:2:2
20 YCbCr 4:2:2
24 YCbCr 4:2:2
INPUT CLOCK-
RISING EDGE
INPUT DATA:
D(23:0), DE, SYNCS
t
HOLD
t
HOLD
Figure 3. Timing for Data Input
t
SETUP
t
HOLD
05675-014
Rev. 0 | Page 9 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
Normal 4:4:4 Input Format (RGB or YCbCr) Input ID = 0
An input format of RGB 4:4:4 or YCbCr 4:4:4 can be selected by setting the input ID (R0x15[3:1]) to 0b000. The input color space (CS)
must be selected by setting R0x16[0] to 0b0 for RGB or 0b1 for YCbCr. There is no need to set the input style (R0x16[3:2]).
Table 10.
Data<23:0>
Input Format
RGB 4:4:4 R[7:0] G[7:0] B[7:0]
YCbCr 4:4:4 Cr[7:0] Y[7:0] Cb[7:0]
YCbCr 4:2:2 Formats (24 Bits, 20 Bits, or 16 Bits) with Separate Sync, Input ID = 1
An input with YCbCr 4:2:2 with separate syncs can be selected by setting the Input ID (R0x15[3:1]) to 0b001. The input CS (R0x16[0])
must be set to 0b1 for proper operation. The data bit width (24 bits, 20 bits, or 16 bits) must be set with R0x16[5:4]. The three input pin
assignment styles are shown in Table 11. The input style can be set in R0x16[3:2].
Table 11.
Data <23:0>
Input Format 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
YCbCr 4:2:2 Sep. Cb[11:4] Y[11:4] Cb[3:0] Y[3:0]
Sync (24 bit) Cr[11:4] Y[11:4] Cr[3:0] Y[3:0]
YCbCr 4:2:2 Sep. Cb[9:2] Y[9:2] Cb[1:0] Y[1:0]
Sync (20 bit) Cr[9:2] Y[9:2] Cr[1:0] Y[1:0]
YCbCr 4:2:2 Sep. Cb[7:0] Y[7:0]
Sync (20 bit) Cr[7:0] Y[7:0]
24-bit Cb[11:0] Y[11:0]
Cr[11:0] Y[11:0]
20-bit Cb[9:0] Y[9:0]
Cr[9:0] Y[9:0]
16-bit Cb[7:0] Y[7:0]
Cr[7:0] Y[7:0]
24-bit Y[11:0] Cb[11:0]
Y[11:0] Cr[11:0]
20-bit Y[9:0] Cb[9:0]
Y[9:0] Cr[9:0]
16-bit Y[7:0] Cb[7:0]
Y[7:0] Cr[7:0]
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Style 1
Style 2
Style 3
Rev. 0 | Page 10 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
YCbCr 4:2:2 Formats (24 Bits, 20 Bits, or 16 Bits) with Embedded Syncs, Input ID = 2
An input with YCbCr 4:2:2 with embedded syncs can be selected by setting the input ID (R0x15[3:1]) to 0b010. HS YNC and VSYNC are
embedded as Start of Active Video (SAV) and End of Active Video (EAV). The input CS (R0x16[0]) must be set to 0b1 for proper
operation. The data bit width (24 = 12 bits, 20 = 10 bits, or 16 = 8 bits) must be set with R0x16[5:4]. The three input pin assignment styles
are shown in Table 12. The input style can be set in R0x16[3:2]. The only difference between Input ID 1 and Input ID 2 is that the syncs
n ID 2 are embedded in the data much like ITU 656 running at 1× clock and double width.
o
Table 12.
Data <23:0>
Input Format 23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Style 1
YCbCr 4:2:2 Sep. Cb[11:4] Y[11:4] Cb[3:0] Y[3:0]
Sync (24 bit) Cr[11:4] Y[11:4] Cr[3:0] Y[3:0]
YCbCr 4:2:2 Sep. Cb[9:2] Y[9:2] Cb[1:0] Y[1:0]
Sync (20 bit) Cr[9:2] Y[9:2] Cr[1:0] Y[1:0]
YCbCr 4:2:2 Sep. Cb[7:0] Y[7:0]
Sync (16 bit) Cr[7:0] Y[7:0]
Style 2
24-bit Cb[11:0] Y[11:0]
Cr[11:0] Y[11:0]
20-bit Cb[9:0] Y[9:0]
Cr[9:0] Y[9:0]
16-bit Cb[7:0] Y[7:0]
Cr[7:0] Y[7:0]
Style 3
24-bit Y[11:0] Cb[11:0]
Y[11:0] Cr[11:0]
20-bit Y[9:0] Cb[9:0]
Y[9:0] Cr[9:0]
16-bit Y[7:0] Cb[7:0]
Y[7:0] Cr[7:0]
YCbCr 4:2:2 Formats (Double Data Rate) Formats (12, 10, or 8 bits) with Separate Syncs, Input ID = 3
An input with YCbCr 4:2:2 DDR data and separate syncs can be selected by setting the input ID (R0x15[3:1]) to 0b011. The input CS
(R0x16 [0]) must be set to 0b1. The data bit width (12 bits, 10 bits, or 8 bits) must be set with R0x16[5:4]. The two input pin assignment
styles are shown in
Table 13.
Input Format
12-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[11:4] [3:0]
10-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[9:2] [1:0]
8-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[7:0]
12-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[11:0]
10-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[9:0]
8-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[7:0]
Table 13. The input style can be set in R0x16[3:2].
Data <23:0>
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Style 1
Style 2
Rev. 0 | Page 11 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
YCbCr 4:2:2 DDR (Double Data Rate) Formats (12 Bits, 10 Bits, or 8 Bits) with Embedded Syncs. Input ID = 4
An input with YCbCr 4:2:2 DDR data and embedded syncs (ITU 656) can be selected by setting the input ID (R0x15[3:1]) to 0b100. The
input CS (R0x16[0]) must be set to 0b1. The data bit width (12 bits, 10 bits, or 8 bits) must be set with R0x16[5:4]. The two input pin
assignment styles are shown in Table 14. The input style can be set in R0x16[3:2]. The order of data input is the order in the table (for
exa
mple, 12-bit data is accepted as Cb0, Y0, Cr0, Y1, Cb2, Y2, Cr2, Y3).
Table 14.
Data <23:0>
Input Format
12-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[11:4] [3:0]
10-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[9:2] [1:0]
8-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[7:0]
12-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[11:0]
10-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[9:0]
8-bit Cb/Y/Cr/Y[7:0]
Normal 4:4:4 input format (RGB or YCbCr) Clocked at Double Data Rate (DDR), Input ID = 5
An input with YCbCr 4:2:2 DDR data and separate syncs can be selected by setting the input ID (R0x15[3:1]) to 0b011. The input CS
(R0x16[0]) must be set to 0b1. The data bit width (12 bits, 10 bits, or 8 bits) must be set with R0x16[5:4]. The three input pin assignment
styles are shown in Table 15. The input style can be set in R0x16[3:2].
Table 15.
Input Format
RGB 4:4:4 (DDR)
st
edge,
(1
nd
2
edge)
YCbCr 4:4:4 (DDR)
st
edge,
(1
nd
2
edge)
RGB 4:4:4 (DDR)
st
edge,
(1
nd
2
edge)
YCbCr 4:4:4 (DDR)
st
edge,
(1
nd
edge)
2
YCbCr 4:4:4 (DDR)
st
edge,
(1
nd
2
edge)
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Style 1
Style 2
Data <23:0>
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Style 1
G[3:0] B[7:0]
R[7:0] G[7:4]
Y[3:0] Cb[7:0]
Cr[7:0] Y[7:4]
Style 2
R[7:0] G[7:4]
G[3:0] B[7:0]
Cr[7:0] Y[7:4]
Y[3:0] Cb[7:0]
Style 3
Y[7:0] Cb[7:4]
Cb[3:0] Cr[7:0]
Rev. 0 | Page 12 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
YCbCr 4:2:2 Formats (24, 20, or 16 bits) DDR with Separate Sync, Input ID = 6
An input format of YCbCr 4:2:2 DDR can be selected by setting the input ID (R0x15[3:1]) to 0b110. The three different input pin
assignment styles are shown in Table 16. The input style can be set in R0x16[3:2]. The input CS (R0x16[0]) must be set to 0b1. The data
b
it width (12, 10, or 8 bits) must be set to with R0x16[5:4].
st
The 1
or the 2nd edge may be the rising or falling edge. The data input edge is defined in R0x16[1]. 0b0 = rising edge; 0b1 = falling edge.
Pixel 0 is the first pixel of the 4:2:2 word and should be where DE starts.
Table 16.
Data<23:0>
Input Format
YCbCr 4:2:2 Sep
Syncs (DDR)
12-bit
YCbCr 4:2:2 Sep
Syncs (DDR)
10-bit
YCbCr 4:2:2 Sep.
Syncs (DDR)
8-bit
12-bit
10-bit
8-bit
12-bit
10-bit
8-bit
23 22 21 20 19 18 17 16 15 14 13 12 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Style 1
1
Y[7:4] Cr[3:0] Y[3:0]
Y[5:4] Cb[3:0] Y[3:0]
Cb[9:4] Y[9:6]
Y[5:4] Cr[3:0] Y[3:0]
Cr[9:4] Y[9:6]
Cb[3:0] Y[3:0]
Cb[7:4] Y[7:4]
Cr[3:0] Y[3:0]
Cr[7:4] Y[7:4]
Y[11:0]
Cb[11:0]
Y[11:0]
Cr[11:0]
Y[9:0]
Cb[9:0]
Y[9:0]
Cr[9:0]
Y[7:0]
Cb[7:0]
Y[7:0]
Cr[7:0]
Cb[11:0]
Y[11:0]
Cr[11:0]
Y[11:0]
Cb[9:0]
Y[9:0]
Cr[9:0]
Y[9:0]
Cb[7:0]
Y[7:0]
Cr[7:0]
Y[7:0]
1
2
st
Pixel
nd
Pixel
Cr[11:4] Y[11:8]
nd
2
Edge
st
Edge Y[7:4] Cb[3:0] Y[3:0]
Cb[11:4] Y[11:8]
Style 2
Style 3
Rev. 0 | Page 13 of 48
AD9889
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
4:2:2 TO 4:4:4 DATA CONVERSION
The AD9889 has the ability to convert YCbCr video from 4:4:4
to 4:2:2 and 4:2:2 to 4:4:4. To convert from 4:4:4 to 4:2:2, the
video data goes through a filter first to remove any artificial
downsampling noise. To convert from 4:2:2 to 4:4:4, the
AD9889 utilizes either the zero-order upconversion (pixel
repetition) or first-order upconversion (linear interpolation).
The upconversion and downconversion are used when the
video output timing format does not match the video input
timing format. The video output format is set by Register
R0x16[7:6]. The video input format is set by the video ID
(R0x15[3:1]) and video color space (R0x16[0]). The default
mode for upconversion is pixel repetition. To use linear
interpolation, set Register R0x17[2] to 1.
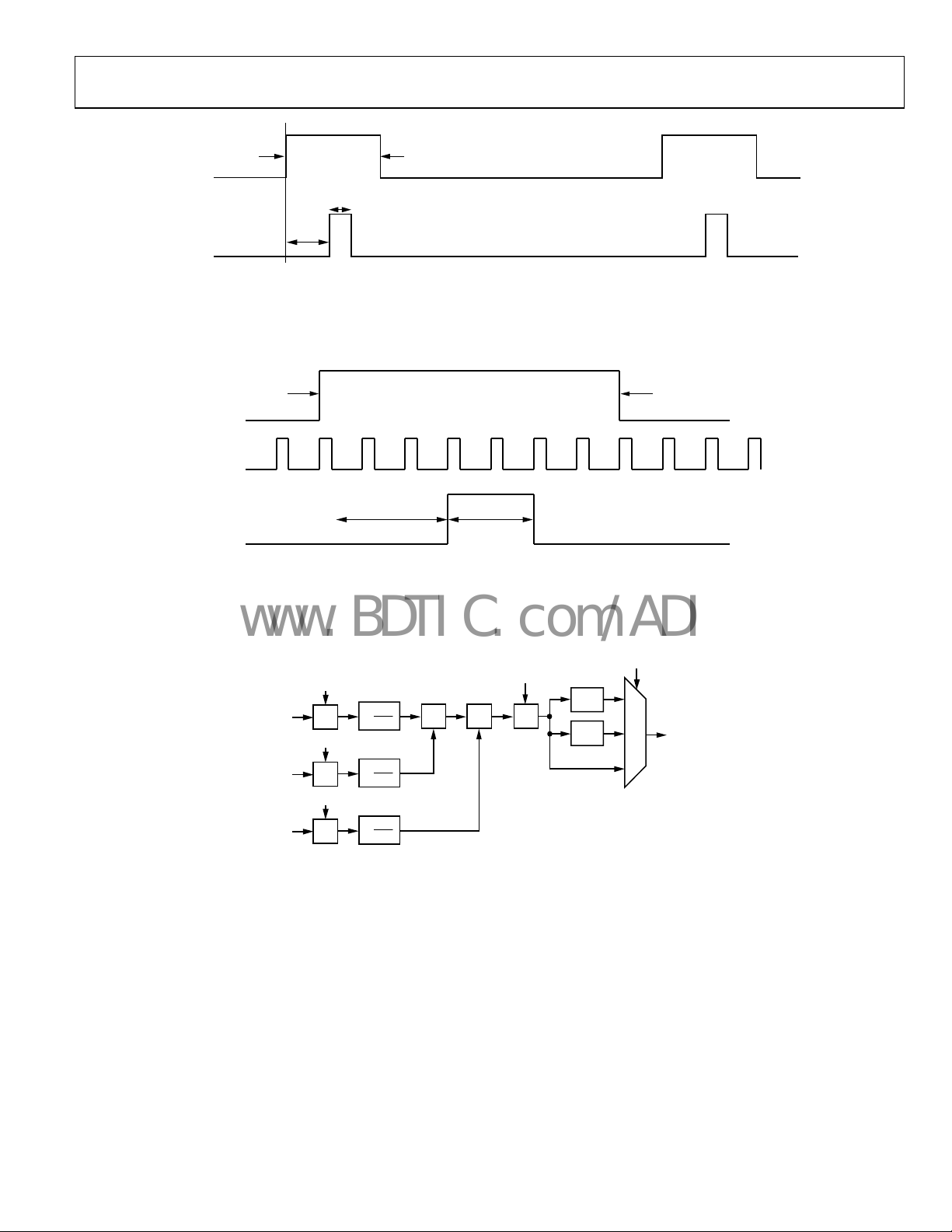
HORIZONTAL SYNC, VERTICAL SYNC, AND DEGENERATION
When transmitting video data across the TMDS interface, it
is necessary to have an HSYNC, VSYNC, and data enable (DE)
defined for the image. ITU-656 based sources have start of
active video (SAV) and end of active video (EAV) signals built
in, but the HSYNC and VSYNC must be generated (the DE is
implied by the SAV and EAV signals). Other sources (with
separate syncs) have HSYNC, VSYNC, and DE supplied at the
same time as the pixel data.
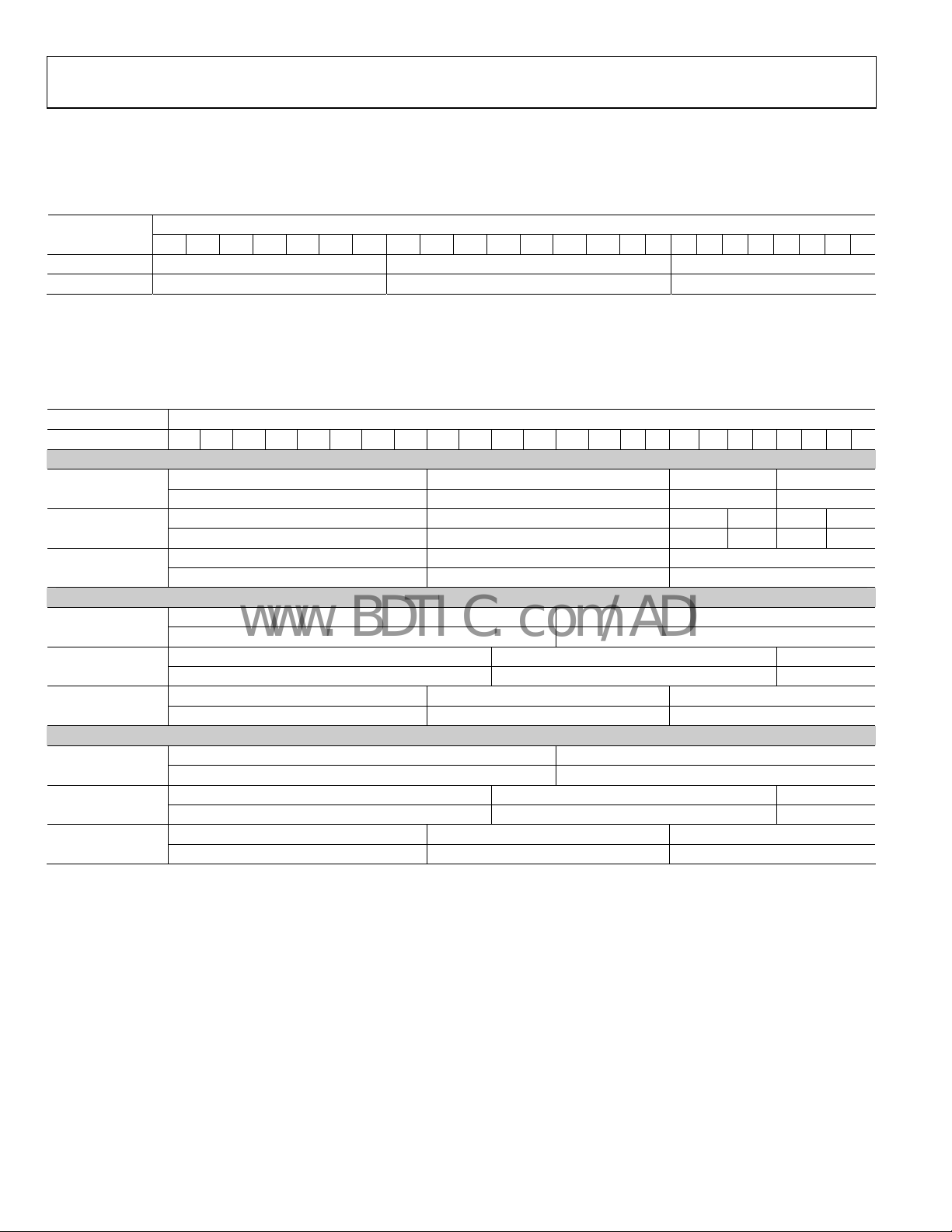
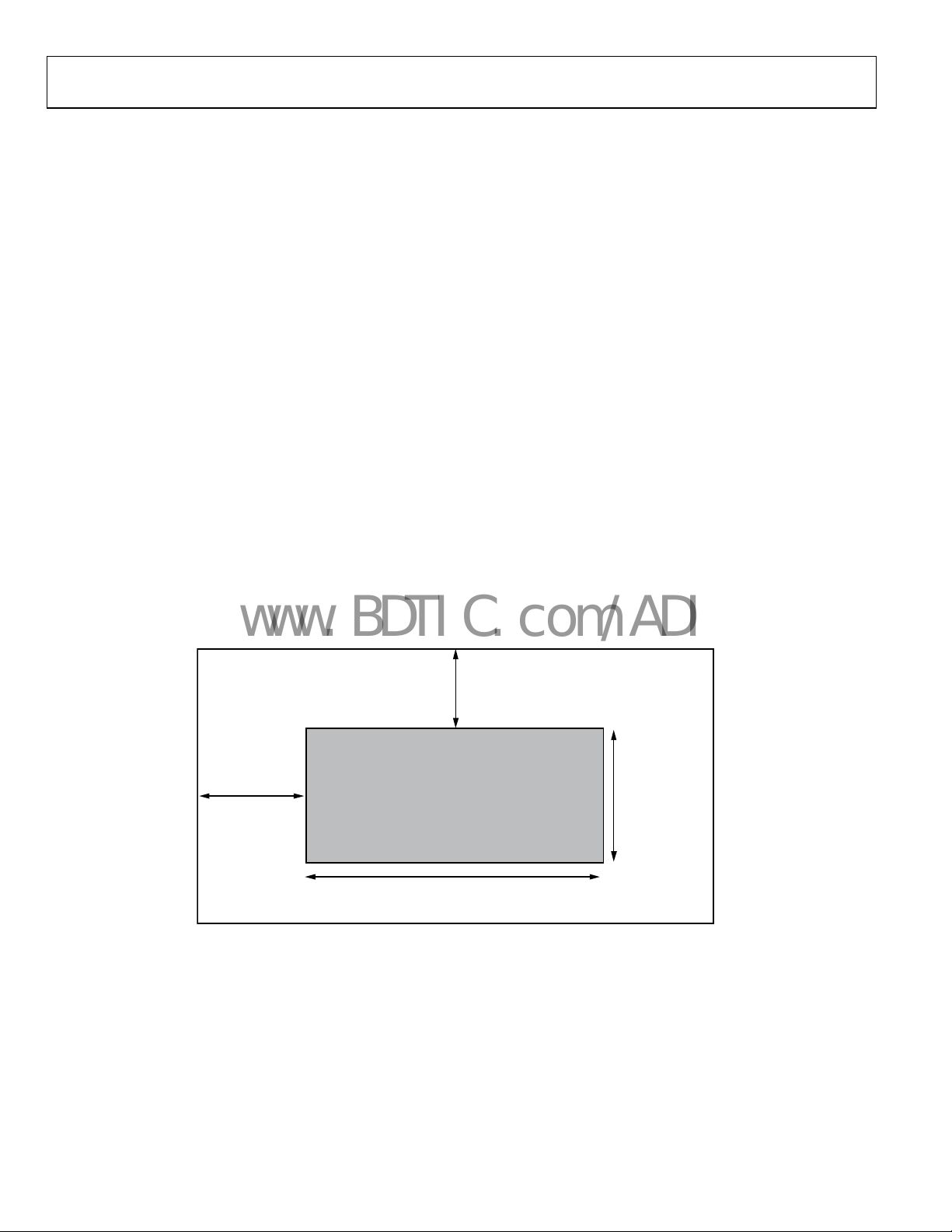
DEGENERATION
The AD9889 offers a choice of DE from an external pin, or an
internally generated DE. To activate the internal DE generation,
set Register R0x17[0] to 1. Register R0x35 to Register R0x3A
are used to define the DE. R0x35 and R0x36[7:6] define the
number of pixels from the HS leading edge to the DE leading
edge. R0x36[5:0] are the number of HSYNCs between the
leading edge of VS and DE. R0x37[7:5] defines the difference of
HS counts during VS blanking for interlace video. R0x37[4:0]
and R0x38[7:1] indicate the width of the DE. R0x39 and
R0x3A[7:4] are the number of lines of active video (see Figure
4).
HSYNC AND VSYNC GENERATION
For video with embedded HSYNC and VSYNC, such as EAV
and SAV, found in ITU 656 format, it is necessary to reconstruct
HSYNC and VSYNC. This is done with Register R0x30 to
Register R0x34. R0x30 and R0x31[7:6] specify the number of
pixels between the HSYNC leading edge and the trailing edge of
DE. Register R0x31[5:0] and Register R0x32[7:4] are the
duration of the HSYNC in pixel clocks. R0x32[3:0] and
R0x33[7:2] are the number of HS pulses between the trailing
edge of the last DE and the leading edge of the VSYNC pulse.
Register R0x33[1:0] and Register R0x34[7:0] are the duration of
VSYNC in units of HSYNCs. HSYNC and VSYNC polarity can
be specified by setting R0x17[6] (for VSYNC) and R0x17[5]
(for HSYNC).
VS DELAY
R0x36[5:0]
HS DELAY
R0x35, R0x36[7:6]
ACTIVE
VIDEO
WIDTH
R0x37[4:0], R0x38[7: 1]
Figure 4. Active Video
HEIGHT
R0x39, R0x3A[7:4]
05675-004
Rev. 0 | Page 14 of 48
AD9889
G
www.BDTIC.com/ADI
SAV
Figure 5. HSYNC Reconstruction
05675-005
HSYNC
a: HSYNC PLACEME NT
R0x30, R0x31[7:6]
b: HSYNC DURATION
R0x31[5:0], R0x32[ 7: 4]
EAV
b
a
EAV
VSYNC
a: VSYNC PLACEMENT
R0x32[3:0], R0x33[ 7: 2]
b: VSYNC DURATI ON
R0x33[1:0], R0x34
ab
Figure 6. VSYNC Reconstruction
SAV
05675-006
a1[12:0]
1
[11:0]
R
IN
a2[12:0]
[11:0]
B
IN
a3[12:0]
[11:0]
IN
×
×
×
×
4096
1
×
4096
1
×
4096
+ + +
a4[12:0]
Figure 7. Single CSC Channel
CSC_Mode[1:0]
×4
×2
2
1
0
[11:0]
R
OUT
05675-008
Rev. 0 | Page 15 of 48
 Loading...
Loading...