Analog Devices AD9888KS-205, AD9888KS-170, AD9888KS-140, AD9888KS-100, AD9888-PCB Datasheet
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
a
AD9888
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
100/140/170/205 MSPS Analog
Flat Panel Interface
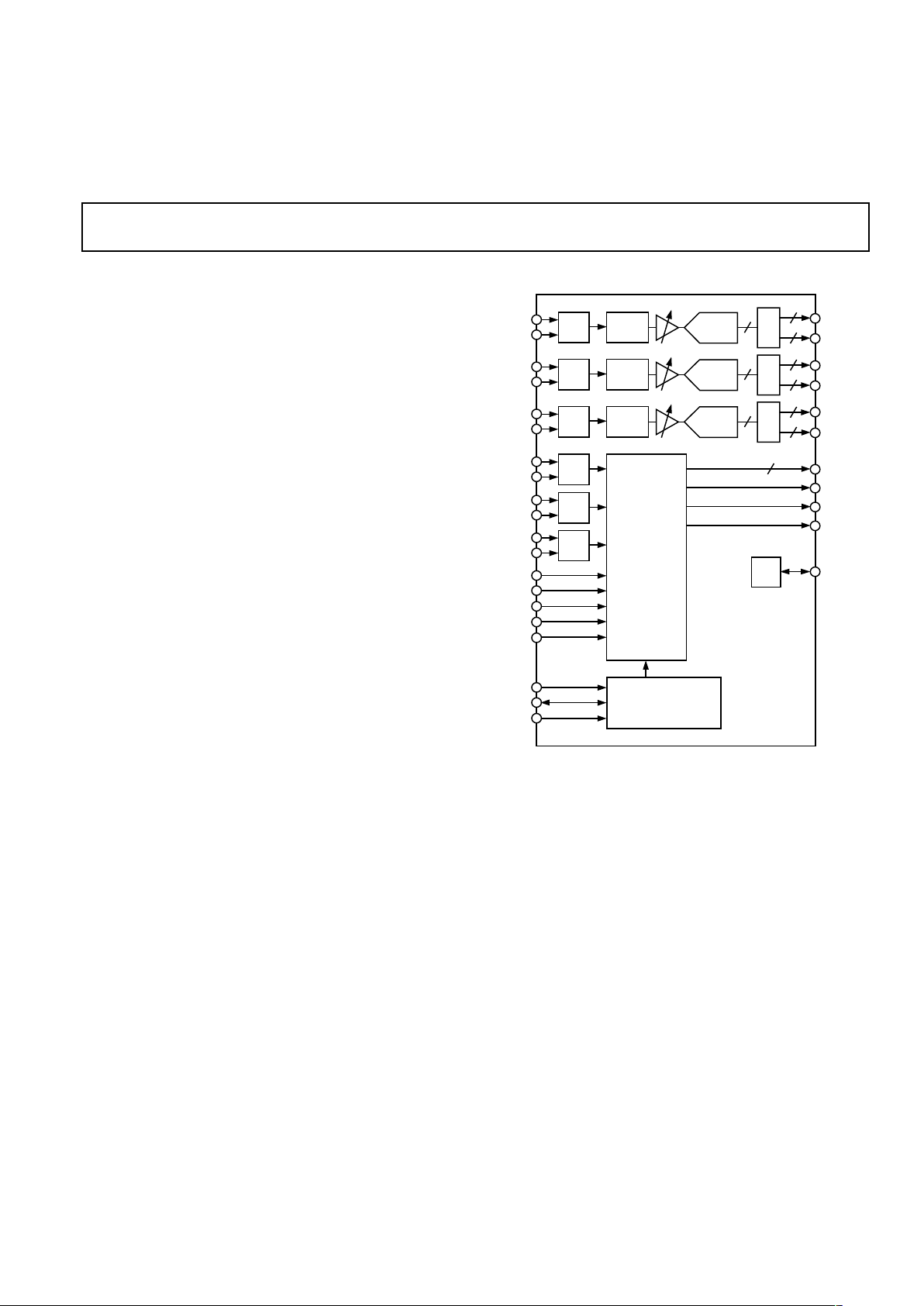
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
2:1
MUX
A/D
8
8
8
R
IN
R
OUTA
R
IN
R
OUTB
2:1
MUX
A/D
8
8
8
G
IN
G
OUTA
G
IN
G
OUTB
2:1
MUX
A/D
8
8
8
B
IN
B
OUTA
B
IN
B
OUTB
2:1
MUX
HSYNC
HSYNC
2:1
MUX
VSYNC
VSYNC
2:1
MUX
SOGIN
SOGIN
COAST
CLAMP
CKINV
CKEXT
FILT
SCL
SDA
A0
REF
BYPASS
DATACK
HSOUT
VSOUT
SOGOUT
SERIAL REGISTER
AND
POWER MANAGEMENT
REF
SYNC
PROCESSING
AND
CLOCK
GENERATION
CLAMP
CLAMP
CLAMP
AD9888
2
FEATURES
205 MSPS Maximum Conversion Rate
500 MHz Programmable Analog Bandwidth
0.5 V to 1.0 V Analog Input Range
Less than 450 ps p-p PLL Clock Jitter @ 205 MSPS
3.3 V Power Supply
Full Sync Processing
Sync Detect for “Hot Plugging”
2:1 Analog Input Mux
4:2:2 Output Format Mode
Midscale Clamping
Power-Down Mode
Low Power: <1 W Typical @ 205 MSPS
APPLICATIONS
RGB Graphics Processing
LCD Monitors and Projectors
Plasma Display Panels
Scan Converters
Microdisplays
Digital TV
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9888 is a complete 8-bit, 205 MSPS monolithic analog
interface optimized for capturing RGB graphics signals from
personal computers and workstations. Its 205 MSPS encode
rate capability and full-power analog bandwidth of 500 MHz
supports resolutions up to UXGA (1600 × 1200 at 75 Hz).
For ease of design and to minimize cost, the AD9888 is a fully
integrated interface solution for flat panel displays. The AD9888
includes an analog interface with a 205 MHz triple ADC with
internal 1.25 V reference, PLL to generate a pixel clock from
HSYNC and COAST, midscale clamping, and programmable
gain, offset, and clamp control. The user provides only a 3.3 V
power supply, analog input, and HSYNC and COAST signals.
Three-state CMOS outputs may be powered from 2.5 V to 3.3 V.
The AD9888’s on-chip PLL generates a pixel clock from HSYNC
and COAST inputs. Pixel clock output frequencies range from
10 MHz to 205 MHz. PLL clock jitter is less than 450 ps p-p
typical at 205 MSPS. When the COAST signal is presented, the
PLL maintains its output frequency in the absence of HSYNC.
A sampling phase adjustment is provided. Data, HSYNC, and
Clock output phase relationships are maintained. The PLL can
be disabled and an external clock input provided as the pixel
clock. The AD9888 also offers full sync processing for composite sync and Sync-on-Green applications.
A clamp signal is generated internally or may be provided by the
user through the CLAMP input pin. This interface is fully programmable via a 2-wire serial interface.
Fabricated in an advanced CMOS process, the AD9888 is provided in a space-saving 128-lead MQFP surface mount plastic
package and is specified over the 0°C to 70°C temperature range.
REV. A
–2–
AD9888–SPECIFICATIONS
(VD = 3.3 V, VDD = 3.3 V, ADC Clock = Maximum Conversion Rate)
Test AD9888KS-100/-140
1
AD9888KS-170 AD9888KS-205
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 8 8 8 Bits
DC ACCURACY
Differential Nonlinearity 25°CI ± 0.5 +1.25/–1.0 ± 0.6 +1.25/–1.0 ± 0.8 +1.50/–1.0 LSB
Full VI +1.35/–1.0 +1.50/–1.0 +1.80/–1.0 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity 25°CI ± 0.5 ± 2.0 ± 0.75 ±2.25 ± 1.0 ± 3.75 LSB
Full VI ± 2.5 ± 2.75 ± 4.25 LSB
No Missing Codes 25°C I Guaranteed Guaranteed Guaranteed
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Range
Minimum 25°C I 0.5 0.5 0.5 V p-p
Maximum 25°C I 1.0 1.0 1.0 V p-p
Gain Tempco 25°C V 100 100 100 ppm/°C
Input Bias Current 25°CIV 1 1 1 µA
Full IV 2 2 2 µA
Input Capacitance Full V 3 3 3 pF
Input Resistance Full IV 1 1 1 MΩ
Input Offset Voltage Full VI 7 90 7 90 7 90 mV
Input Full-Scale Matching Full VI 2.5 9.0 2.5 9.0 2.5 9.0 % FS
Offset Adjustment Range Full VI 44 49 53 44 49 53 44 49 53 % FS
REFERENCE OUTPUT
Output Voltage Full VI 1.20 1.25 1.30 1.20 1.25 1.30 1.20 1.25 1.30 V
Temperature Coefficient Full V ± 50 ±50 ± 50 ppm/°C
SWITCHING PERFORMANCE
Maximum Conversion Rate Full VI 100/140 170 205 MSPS
Minimum Conversion Rate Full IV 10 10 10 MSPS
Data to Clock Skew Full IV –1.25 +1.25 –1.25 +1.25 –1.25 +1.25 ns
t
BUFF
2
Full VI 4.7 4.7 4.7 µs
t
STAH
2
Full VI 4.0 4.0 4.0 µs
t
DHO
2
Full VI 0 0 0 µs
t
DAL
2
Full VI 4.7 4.7 4.7 µs
t
DAH
2
Full VI 4.0 4.0 4.0 µs
t
DSU
2
Full VI 250 250 250 ns
t
STASU
2
Full VI 4.7 4.7 4.7 µs
t
STOSU
2
Full VI 4.0 4.0 4.0 µs
HSYNC Input Frequency Full IV 15 110 15 110 15 110 kHz
Maximum PLL Clock Rate Full VI 100/140 170 205 MHz
Minimum PLL Clock Rate Full IV 10 10 10 MHz
PLL Jitter 25°C IV 470 700
3
450 700
4
440 700
4
ps p-p
Full IV 1000
3
1000
4
1000
4
ps p-p
Sampling Phase Tempco Full IV 15 15 15 ps/°C
DIGITAL INPUTS
Input Voltage, High (V
IH
) Full VI 2.5 2.5 2.5 V
Input Voltage, Low (V
IL
) Full VI 0.8 0.8 0.8 V
Input Current, High (I
IH
) Full IV –1.0 –1.0 –1.0 µA
Input Current, Low (I
IL
) Full IV +1.0 +1.0 +1.0 µA
Input Capacitance 25°CV 3 3 3 pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Output Voltage, High (V
OH
) Full VI VD – 0.1 VD – 0.1 VD – 0.1 V
Output Voltage, Low (V
OL
) Full VI 0.1 0 .1 0.1 V
Duty Cycle
DATACK, DATACK Full IV 44 49 55 44 49 55 44 49 55 %
Output Coding Binary Binary Binary
POWER SUPPLY
V
D
Supply Voltage Full IV 3.0 3.3 3.6 3.0 3.3 3.6 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
V
DD
Supply Voltage Full IV 2.2 3.3 3.6 2.2 3.3 3.6 2.2 3.3 3.6 V
P
VD
Supply Voltage Full IV 3.0 3.3 3.6 3.0 3.3 3.6 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
I
D
Supply Current (VD)25°C V 200 215 230 mA
I
DD
Supply Current (VDD)
5
25°C V 50 55 60 mA
IP
VD
Supply Current (PVD)25°CV 8 9 10 mA
Total Power Dissipation Full VI 850 1050 920 1150 990 1250 mW
Power-Down Supply Current Full VI 12 20 12 20 12 20 mA
Power-Down Dissipation Full VI 40 66 40 66 40 66 mW
REV. A
–3–
AD9888
Test AD9888KS-100/-140
1
AD9888KS-170 AD9888KS-205
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Analog Bandwidth, Full Power
6
25°C V 500 500 500 MHz
Transient Response 25°CV 2 2 2 ns
Overvoltage Recovery Time 25°C V 1.5 1.5 1.5 ns
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
7
25°CIV4245 4144 4042 dB
(Without Harmonics) Full V 44 43 41 dB
f
IN
= 40.7 MHz
Crosstalk Full V 50 50 50 dBc
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
θ
JC
–Junction-to-Case V 8.4 8.4 8.4 °C/W
Thermal Resistance
θ
JA
–Junction-to-Ambient V 35 35 35 °C/W
Thermal Resistance
NOTES
1
AD9888KS-100 specifications are tested at 100 MHz. AD9888KS-140 specifications are tested at 140 MHz.
2
See Figure 23.
3
VCO Range = 10, Charge Pump Current = 100, PLL Divider = 1693.
4
VCO Range = 11, Charge Pump Current = 100, PLL Divider = 2159.
5
DEMUX = 1, DATACK and DATACK Load = 15 pF, Data Load = 5 pF.
6
Maximum bandwidth setting. Bandwidth can also be programmed to 300 MHz, 150 MHz, and 75 MHz.
7
Using External Pixel Clock.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
Test Level
I. 100% production tested.
II. 100% production tested at 25°C and sample tested at
specified temperatures.
III. Sample tested only.
IV. Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization
testing.
V. Parameter is a typical value only.
VI. 100% production tested at 25°C; guaranteed by design and
characterization testing.
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
VD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.6 V
V
DD
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.6 V
Analog Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
D
to 0.0 V
VREF IN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
D
to 0.0 V
Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 V to 0.0 V
Digital Output Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 mA
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –25°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
Maximum Case Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause permanent
damage to the device. This is a stress rating only and functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions outside of those indicated in the operation
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings
for extended periods may affect device reliability.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although
the AD9888 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on
devices subjected to high-energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are
recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
ORDERING GUIDE
Temperature Package
Model Range Option
AD9888KS-100 0°C to 70°C S-128A
AD9888KS-140 0°C to 70°C S-128A
AD9888KS-170 0°C to 70°C S-128A
AD9888KS-205 0°C to 70°C S-128A
AD9888/PCB 25°C Evaluation Board
REV. A
AD9888
–4–
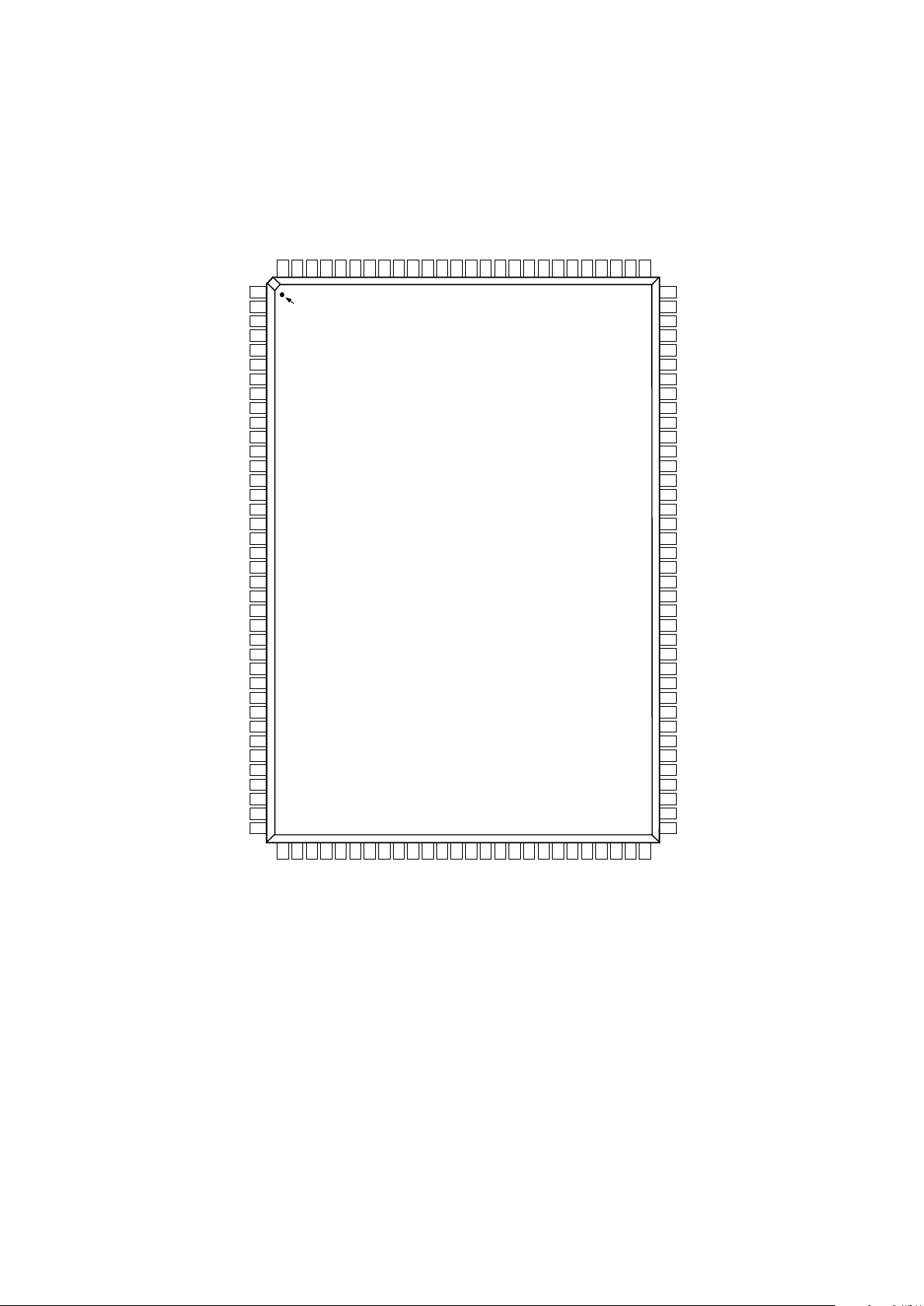
PIN CONFIGURATION
92
93
95
90
91
88
89
87
96
86
94
81
82
83
84
79
80
78
76
77
85
75
73
74
71
72
69
70
67
68
66
65
98
99
101
97
102
100
41
42
43
44
46
47
48
49
39
45
40
62
61
60
64
63
59
55
50
51
52
53
54
56
57
58
11
10
16
15
14
13
18
17
20
19
22
21
12
24
23
26
25
28
27
30
29
32
31
5
4
3
2
7
6
9
8
1
34
33
36
35
38
37
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
119
111
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
110
109
108
107
106
105
104
103
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
VSOUT
SOGOUT
HSOUT
DATAC KB
DATAC K
V
DD
GND
GND
GND
V
DD
GND
GND
GND
GND
V
DD
GND
DGA
0
FILT
DGA
1
DGA
2
DGA
3
COAST
DGA
4
CKEXT
DGA
5
GND
DGA
6
V
DD
DGA
7
DGB
7
V
DD
GND
D
BA0
DBA
1
DBA
2
DBA
3
DBA
4
V
D
REF BYPASS
GND
GND
R
AIN
0
V
D
V
D
R
AIN
1
RMIDSCV
V
D
GND
SOGIN0
G
AIN
0
V
D
GND
SOGIN1
G
AIN
1
V
D
GND
B
AIN
0
V
D
GND
B
AIN
1
BMIDSCV
V
D
V
D
GND
GND
CKINV
CLAMP
SDA
SCL
D
BA5
DBA
6
V
DD
GND
D
GB0
DGB
1
DGB
2
DGB
3
DGB
4
DGB
5
DGB
6
AD9888
A0
V
D
GND
GND
V
PV
D
D
D
DBA
7
V
DD
PV
DPVD
PV
D
PV
GND
GND
GND
GND
D
R
A
0
D
R
A
1
D
R
A
2
D
R
A
3
D
R
A
4
D
R
A
5
D
R
A
6
D
R
A
7
V
DD
D
R
B
0
D
R
B
1
GND
VSYNC1
HSYNC1
VSYNC0
HSYNC0
GND
D
B
B
7
D
B
B
6
D
B
B
5
D
B
B
4
D
B
B
3
D
B
B
2
D
B
B
1
D
B
B
0
D
R
B
2
D
R
B
3
D
R
B
4
D
R
B
5
D
R
B
6
D
R
B
7
GND
REV. A
AD9888
–5–
Table I. Complete Pinout List
Pin
Pin Type Mnemonic Function Value Number
Analog Video Inputs R
AIN
0 Channel 0 Analog Input for Converter R 0.0 V to 1.0 V 5
G
AIN
0 Channel 0 Analog Input for Converter G 0.0 V to 1.0 V 13
B
AIN
0 Channel 0 Analog Input for Converter B 0.0 V to 1.0 V 20
R
AIN
1 Channel 1 Analog Input for Converter R 0.0 V to 1.0 V 8
G
AIN
1 Channel 1 Analog Input for Converter G 0.0 V to 1.0 V 17
B
AIN
1 Channel 1 Analog Input for Converter B 0.0 V to 1.0 V 23
Sync/Clock Inputs HSYNC0 Channel 0 Horizontal SYNC Input 3.3 V CMOS 45
VSYNC0 Channel 0 Vertical SYNC Input 3.3 V CMOS 44
SOGIN0 Channel 0 Input for Sync-on-Green 0.0 V to 1.0 V 12
HSYNC1 Channel 1 Horizontal SYNC Input 3.3 V CMOS 43
VSYNC1 Channel 1 Vertical SYNC Input 3.3 V CMOS 42
SOGIN1 Channel 1 Input for Sync-on-Green 0.0 V to 1.0 V 16
CLAMP Clamp Input (External CLAMP signal) 3.3 V CMOS 30
COAST PLL Coast Signal Input 3.3 V CMOS 53
CKEXT External Pixel Clock Input (to Bypass the PLL) or 10 kΩ to Ground 3.3 V CMOS 54
CKINV ADC Sampling Clock Invert 3.3 V CMOS 29
Sync Outputs HSOUT HSYNC Output Clock (Phase-Aligned with DATACK) 3.3 V CMOS 125
VSOUT VSYNC Output Clock (Phase-Aligned with DATACK) 3.3 V CMOS 127
SOGOUT Sync-on-Green Slicer Output 3.3 V CMOS 126
Voltage REF BYPASS Internal Reference Bypass (Bypass with 0.1 µF to Ground) 1.25 V ± 10% 2
Clamp Voltages R
MIDSC
V Red Channel Midscale Clamp Voltage Bypass 9
B
MIDSC
V Blue Channel Midscale Clamp Voltage Bypass 24
PLL Filter FILT Connection for External Filter Components for Internal PLL 50
Power Supply V
D
Analog Power Supply 3.3 V ± 10%
V
DD
Output Power Supply 3.3 V ± 10%
PV
D
PLL Power Supply 3.3 V ± 10%
GND Ground 0 V
Serial Port SDA Serial Port Data I/O 3.3 V CMOS 31
(2-Wire SCL Serial Port Data Clock 3.3 V CMOS 32
Serial Interface) A0 Serial Port Address Input 1 3.3 V CMOS 33
Data Outputs Red A[7:0] Port A Outputs of Converter “Red,” Bit 7 is the MSB. 3.3 V CMOS 113–120
Red B[7:0] Port B Outputs of Converter “Red,” Bit 7 is the MSB. 3.3 V CMOS 103–110
Green A[7:0] Port A Outputs of Converter “Green,” Bit 7 is the MSB. 3.3 V CMOS 90–97
Green B[7:0] Port B Outputs of Converter “Green,” Bit 7 is the MSB. 3.3 V CMOS 80–87
Blue A[7:0] Port A Outputs of Converter “Blue,” Bit 7 is the MSB. 3.3 V CMOS 70–77
Blue B[7:0] Port B Outputs of Converter “Blue,” Bit 7 is the MSB. 3.3 V CMOS 57–64
Data Clock DATACK Data Output Clock 3.3 V CMOS 123
Output DATACK Data Output Clock Complement 3.3 V CMOS 124

REV. A
AD9888
–6–
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Description
Inputs
R
AIN
0 Channel 0 Analog Input for RED
G
AIN
0 Channel 0 Analog Input for GREEN
B
AIN
0 Channel 0 Analog Input for BLUE
R
AIN
1 Channel 1 Analog Input for RED
G
AIN
1 Channel 1 Analog Input for GREEN
B
AIN
1 Channel 1 Analog Input for BLUE
High-impedance inputs that accept the RED, GREEN, and BLUE channel graphics signals, respectively. (The six
channels are identical and can be used for any colors; colors are assigned for convenient reference.)
They accommodate input signals ranging from 0.5 V to 1.0 V full scale. Signals should be ac-coupled to these pins to
support clamp operation.
HSYNC0 Channel 0 Horizontal Sync Input
HSYNC1 Channel 1 Horizontal Sync Input
These inputs receive a logic signal that establishes the horizontal timing reference and provides the frequency reference
for pixel clock generation.
The logic sense of this pin is controlled by serial register 0Eh Bit 6 (Hsync Polarity). Only the leading edge of Hsync is
used by the PLL. The trailing edge is used for clamp timing only. When HSPOL = 0, the falling edge of Hsync is used.
When HSPOL = 1, the rising edge is active.
The input includes a Schmitt trigger for noise immunity, with a nominal input threshold of 1.5 V.
VSYNC0 Channel 0 Vertical Sync Input
VSYNC1 Channel 1 Vertical Sync Input
These are the inputs for vertical sync.
SOGIN0 Channel 0 Sync-on-Green Input
SOGIN1 Channel 1 Sync-on-Green Input
This input is provided to assist with processing signals with embedded sync, typically on the GREEN channel. The pin is
connected to a high-speed comparator with an internally generated, variable threshold level, which is nominally set to
0.15 V above the negative peak of the input signal.
When connected to an ac-coupled graphics signal with embedded sync, it will produce a noninverting digital output on
SOGOUT. (This is usually a composite sync signal, con taining both vertical and horizontal sync information.)
When not used, this input should be left unconnected. For more details on this function and how it should be configured, refer to the Sync-on-Green section.
CLAMP External Clamp Input
This logic input may be used to define the time during which the input signal is clamped to the reference dc level
(ground for RGB or midscale for YUV). It should be exercised when the reference dc level is known to be present
on
the analog input channels, typically during the back porch of the graphics signal. The CLAMP pin is enabled by setting
the external clamp control (register 0Fh, Bit 7) to 1 (default is 0). When disabled, this pin is ignored and the clamp
timing is determined internally by counting a delay and duration from the trailing edge of the HSYNC input. The logic
sense of this pin is controlled by the clamp polarity control (register 0Fh, Bit 6). When not used, this pin must be grounded
and external clamp programmed to 0.
COAST Clock Generator Coast Input (Optional)
This input may be used to cause the pixel clock generator to stop synchronizing with HSYNC and continue producing
a clock at its current frequency and phase. This is useful when processing signals from sources that fail to produce horizontal
sync pulses when in the vertical interval or that include equalization pulses. The Coast signal is usually not required for
PC-generated signals.
The logic sense of this pin is controlled by 0FH Bit 3 (Coast Polarity).
When not used, this pin may be grounded and Coast Polarity programmed to 1, or tied HIGH (to V
D
through a 10 kΩ resistor)
and Coast Polarity programmed to 0. The Coast Polarity register bit defaults to 1 at power-up.
CKEXT External Clock Input (Optional)
This pin may be used to provide an external clock to the AD9888, in place of the clock internally generated from
HSYNC. It is enabled by programming the External clock register to 1 (15H, Bit 0). When an external clock is used, all
other internal functions operate normally. When unused, this pin should be tied through a 10 kΩ resistor to GROUND,
and the External Clock register programmed to 0. The clock phase adjustment still operates when an external clock
source is used.
REV. A
AD9888
–7–
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS (continued)
Pin Description
CKINV Sampling Clock Inversion (Optional)
This pin may be used to invert the pixel sampling clock, which has the effect of shifting the sampling phase 180°. This is
in support of Alternate Pixel Sampling mode, wherein higher-frequency input signals (up to 410 Mpps) may be captured by
first sampling the odd pixels, then capturing the even pixels on the subsequent frame.
This pin should be exercised only during blanking intervals (typically vertical blanking) as it may produce several
samples of corrupted data during the phase shift.
CKINV should be grounded when not used.
Outputs
D
RA7-0
Data Output, Red Channel, Port A
D
RB7-0
Data Output, Red Channel, Port B
D
GA7-0
Data Output, Green Channel, Port A
D
GB7-0
Data Output, Green Channel, Port B
D
BA7-0
Data Output, Blue Channel, Port A
D
BB7-0
Data Output, Blue Channel, Port B
These are the main data outputs. Bit 7 is the MSB.
Each channel has two ports. When the part is operated in single-channel mode (Channel Mode bit (15H, Bit 7) = 0), all
data are presented to Port A, and Port B is placed in a high-impedance state.
Programming the Channel Mode bit to 1 establishes dual-channel mode, wherein alternate pixels are presented to Port A
and
Port B of each channel. These will appear simultaneously; two pixels are presented at the time of every second input
pixel, when the Output Mode bit (15H, Bit 6) is set to 1 (parallel mode). When the Output Mode bit is set
to 0, pixel
data appear alternately on the two ports, one new sample with each incoming pixel (interleaved mode).
In dual-channel mode, the first pixel after HSYNC is routed to Port A. The second pixel goes to Port B, the third to A,
etc. This can be reversed by setting the A/B Invert bit to 1 (15H, Bit 5).
The delay from pixel sampling time to output is fixed. When the sampling time is changed by adjusting the PHASE
regis-
ter, the output timing is shifted as well. The DATACK, DATACK and HSOUT outputs are also moved, so the
timing relationship among the signals is maintained.
DATACK Data Output Clock
DATACK Data Output Clock Complement
Differential data clock output signals to be used to strobe the output data and HSOUT into external logic.
They are produced by the internal clock generator and are synchronous with the internal pixel sampling clock.
When the AD9888 is operated in single-channel mode, the output frequency is equal to the pixel sampling frequency.
When operating in dual-channel mode, the clock frequency is one-half the pixel frequency, as is the output data frequency.
When the sampling time is changed by adjusting the PHASE register, the output timing is shifted as well. The Data,
DATACK, DATACK and HSOUT outputs are all moved, so the timing relationship among the signals is maintained.
Either or both signals may be used, depending on the timing mode and interface design employed.
HSOUT Horizontal Sync Output
A reconstructed and phase-aligned version of the Hsync input. Both the polarity and duration of this output can be
programmed via serial bus registers.
By maintaining alignment with DATACK, DATACK, and Data, data timing with respect to horizontal sync can always
be determined.
SOGOUT Sync-On-Green Slicer Output
This pin can be programmed to output either the output from the Sync-On-Green slicer comparator or an unprocessed but delayed version of the Hsync input. See the Sync Processing Block Diagram (Figure 25) to view how this pin is
connected. (Note: Besides slicing off SOG, the output from this pin gets no other additional processing on the AD9888.
Vsync separation is performed via the sync separator.)
REF BYPASS Internal Reference BYPASS
Bypass for the internal 1.25 V band gap reference. It should be connected to ground through a 0.1 µF capacitor. The absolute accuracy of this reference is ± 4%, and the temperature coefficient is ±50 ppm, which is adequate for most AD9888
applications. If higher accuracy is required, an external reference may be employed instead.
RMIDSCV RED Channel Midscale Voltage BYPASS
BMIDSCV BLUE Channel Midscale Voltage BYPASS
Bypasses for the internal midscale voltage references. They should each be connected to ground through 0.1 µF
capacitors. The exact voltage varies with the gain setting of the BLUE channel.
REV. A
AD9888
–8–
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS (continued)
Pin Description
FILT External Filter Connection
For proper operation, the pixel clock generator PLL requires an external filter. Connect the filter shown in Figure 6 to this
pin. For optimal performance, minimize noise and parasitics on this node.
Power Supply
V
D
Main Power Supply
These pins supply power to the main elements of the circuit. It should be as quiet and filtered as possible.
V
DD
Digital Output Power Supply
A large number of output pins (up to 52) switching at high speed (up to 110 MHz) generates a lot of power supply
transients (noise). These supply pins are identified separately from the V
D
pins, so special care can be taken to minimize output noise transferred into the sensitive analog circuitry. If the AD9888 is interfacing with lower voltage logic,
V
DD
may be connected to a lower supply voltage (as low as 2.5 V) for compatibility.
PV
D
Clock Generator Power Supply
The most sensitive portion of the AD9888 is the clock generation circuitry. These pins provide power to the clock PLL
and help the user design for optimal performance. The designer should provide “quiet,” noise-free power to these pins.
GND Ground
The ground return for all circuitry on chip. It is recommended that the AD9888 be assembled on a single solid ground plane,
with careful attention to ground current paths.
Serial Port (2-Wire)
SDA Serial Port Data I/O
SCL ISerial Port Data Clock
A0 Serial Port Address Input 1
For a full description of the 2-wire serial register and how it works, refer to the Control Register section.
DESIGN GUIDE
General Description
The AD9888 is a fully integrated solution for capturing analog
RGB signals and digitizing them for display on flat panel monitors
or projectors. The circuit is ideal for providing a computer interface for HDTV monitors or as the front-end to high-performance
video scan converters.
Implemented in a high-performance CMOS process, the interface can capture signals with pixel rates of up to 205 MHz, and
with an Alternate Pixel Sampling mode, up to 340 MHz.
The AD9888 includes all necessary input buffering, signal dc
restoration (clamping), offset and gain (brightness and contrast)
adjustment, pixel clock generation, sampling phase control, and
output data formatting. All controls are programmable via a
2-wire serial interface. Full integration of these sensitive analog
functions makes system design straightforward and less sensitive
to the physical and electrical environment.
With a typical power dissipation of only 650 mW and an operating temperature range of 0°C to 70°C, the device requires no
special environmental considerations.
Input Signal Handling
The AD9888 has six high-impedance analog input pins for the
red, green, and blue channels. They will accommodate signals
ranging from 0.5 V to 1.0 V p-p.
Signals are typically brought onto the interface board via a DVI-I
connector, a 15-pin D connector, or via BNC connectors. The
AD9888 should be located as close as practical to the input
connector. Signals should be routed via matched-impedance
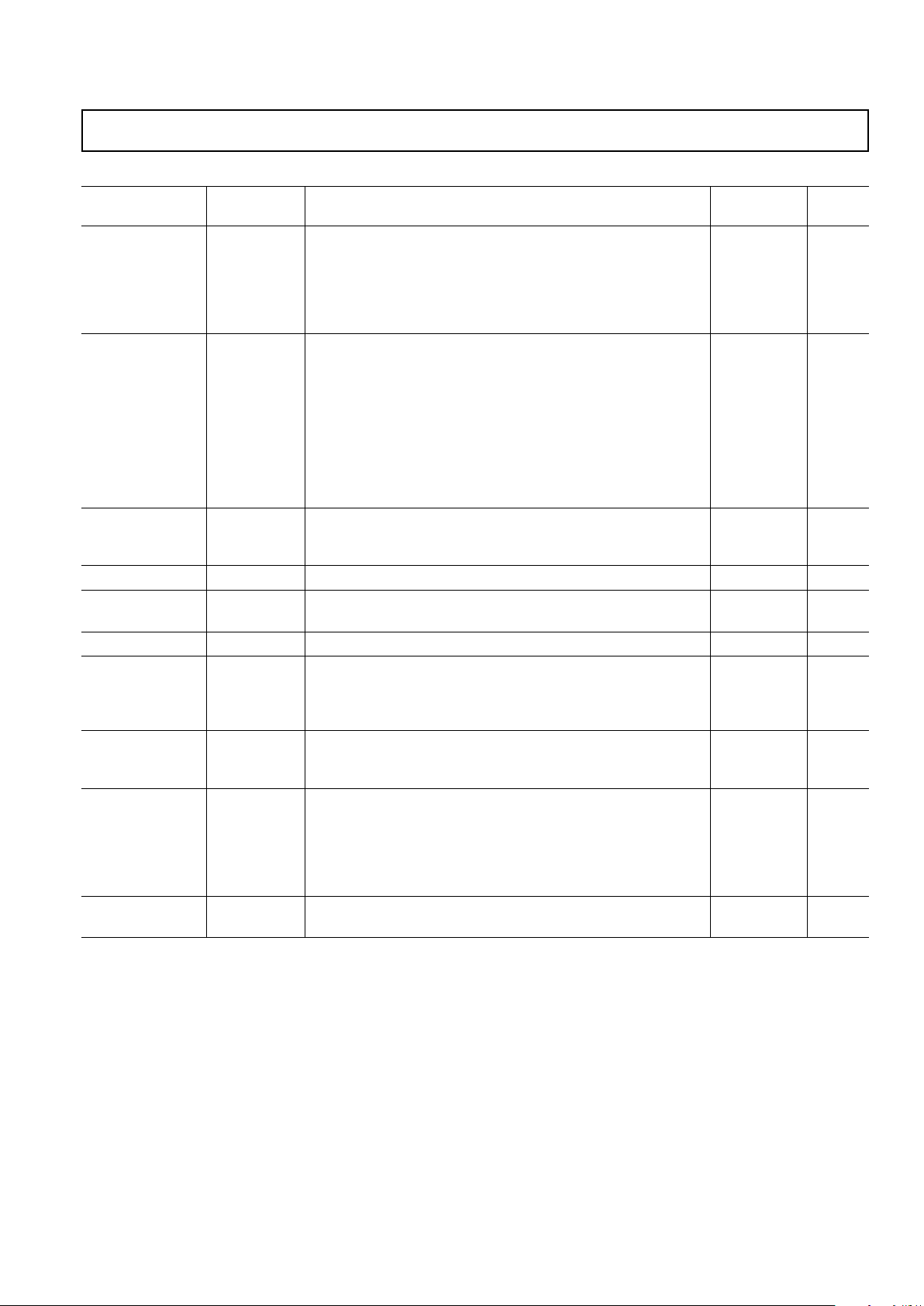
traces (normally 75 Ω) to the IC input pins.
At that point, the signal should be resistively terminated (to the
signal ground return) and capacitively coupled to the AD9888
inputs through 47 nF capacitors. These capacitors form part of
the dc restoration circuit.
In an ideal world of perfectly matched impedances, the best
performance can be obtained with the widest possible signal
bandwidth. The ultrawide bandwidth inputs of the AD9888
(500 MHz) can track the input signal continuously as it moves
from one pixel level to the next, and digitize the pixel during
a long, flat pixel time. In many systems, however, there are
mismatches, reflections, and noise, which can result in excessive
ringing and distortion of the input waveform. This makes it
more difficult to establish a sampling phase that provides good
image quality. The AD9888 can digitize graphics signals over a
very wide range of frequencies (10 MHz to 205 MHz). Often
characteristics that are beneficial at one frequency can be detrimental at another. Analog bandwidth is one such characteristic.
For UXGA resolutions (up to 205 MHz), a very high analog
bandwidth is desirable because of the fast input signal slew
rates. For VGA and lower resolutions (down to 12.5 MHz), a
very high bandwidth is not desirable, because it allows excess
noise to pass through. To accommodate these varying needs,
the AD9888 includes variable analog bandwidth control.
Four settings are available (75 MHz, 150 MHz, 300 MHz,
and 500 MHz), allowing the analog bandwidth to be matched
with the resolution of the incoming graphics signal.
R
AIN
G
AIN
B
AIN
75⍀
RGB
INPUT
47nF
Figure 1. Analog Input Interface Circuit

REV. A
AD9888
–9–
Sync Processing
The AD9888 contains circuitry that enables it to accept composite sync inputs, such as Sync-on-Green or the trilevel syncs
found in digital TV signals. A complete description of the sync
processing functionality is found in the Sync Slicer and Sync
Separator sections.
Hsync, Vsync Inputs
The interface also takes a horizontal sync signal, which is used
to generate the pixel clock and clamp timing. It is possible to
operate the AD9888 without applying Hsync (using an external
clock, external clamp, and single port output mode) but a number
of features of the chip will be unavailable, so it is recommended
that Hsync be provided. This can be either a sync signal directly
from the graphics source, or a preprocessed TTL or CMOS
level signal.
The Hsync input includes a Schmitt trigger buffer for immunity
to noise and signals with long rise times. In typical PC-based
graphic systems, the sync signals are simply TTL-level drivers
feeding unshielded wires in the monitor cable. As such, no termination is required or desired.
Serial Control Port
The serial control port is designed for 3.3 V logic. If there are
5 V drivers on the bus, these pins should be protected with
150 Ω series resistors placed between the pull-up resistors and
the input pins.
Output Signal Handling
The digital outputs are designed and specified to operate from a
3.3 V power supply (V
DD
). They can also work with a VDD as
low as 2.5 V for compatibility with other 2.5 V logic.
Clamping
RGB Clamping
To digitize the incoming signal properly, the dc offset of the input
must be adjusted to fit the range of the on-board A/D converters.
Most graphics systems produce RGB signals with black at ground
and white at approximately 0.75 V. However, if sync signals are
embedded in the graphics, the sync tip is often at ground and
black is at 300 mV. Then white is at approximately 1.0 V. Some
common RGB line amplifier boxes use emitter-follower buffers
to split signals and increase drive capability. This introduces a
700 mV dc offset to the signal, which must be removed for
proper capture by the AD9888.
The key to clamping is to identify a portion (time) of the signal
when the graphic system is known to be producing black. An
offset is then introduced which results in the A/D converters
producing a black output (code 00h) when the known black
input is present. The offset then remains in place when other
signal levels are processed, and the entire signal is shifted to
eliminate offset errors.
In most graphics systems, black is transmitted between active
video lines. Going back to CRT displays, when the electron
beam has completed writing a horizontal line on the screen
(at the right side), the beam is deflected quickly to the left side
of the screen (called horizontal retrace) and a black signal is
provided to prevent the beam from disturbing the image.
In systems with embedded sync, a blacker-than-black signal
(Hsync) is produced briefly to signal the CRT that it is time to
begin a retrace. For obvious reasons, it is important to avoid
clamping on the tip of Hsync. Fortunately, there is almost always
a period following Hsync called the back porch where a good
black reference is provided. This is the time when clamping
should be done.
The clamp timing can be established by simply exercising the
CLAMP pin at the appropriate time (with External Clamp = 1).
The polarity of this signal is set by the Clamp Polarity (Register
0Fh, Bit 6).
A simpler method of clamp timing employs the AD9888 internal clamp timing generator. The Clamp Placement register is
programmed with the number of pixel times that should pass
after the trailing edge of HSYNC before clamping starts. A
second register (Clamp Duration, Register 06h) sets the duration
of the clamp. These are both 8-bit values, providing considerable
flexibility in clamp generation. The clamp timing is referenced
to the trailing edge of Hsync because, though Hsync duration
can vary widely, the back porch (black reference) always follows
Hsync. A good starting point for establishing clamping is to set
the clamp placement to 08h (providing 8 pixel periods for the
graphics signal to stabilize after sync) and set the clamp duration to 14h (giving the clamp 20 pixel periods to reestablish the
black reference).
Clamping is accomplished by placing an appropriate charge on
the external input coupling capacitor. The value of this capacitor
affects the performance of the clamp. If it is too small, there will
be a significant amplitude change during a horizontal line time
(between clamping intervals). If the capacitor is too large, then
it will take excessively long for the clamp to recover from a large
change in incoming signal offset. The recommended value (47 nF)
results in recovering from a step error of 100 mV to within
1/2 LSB in 10 lines with a clamp duration of 20 pixel periods
on a 60 Hz SXGA signal.
YUV Clamping
YUV graphic signals are slightly different from RGB signals in
that the dc reference level (black level in RGB signals) can be at
the midpoint of the video signal rather than the bottom. For
these signals it can be necessary to clamp to the midscale range
of the A/D converter range (80h) rather than bottom of the
A/D converter range (00h).
Clamping to midscale rather than ground can be accomplished
by setting the clamp select bits in the series bus register. The red
and blue channels each have their own selection bit so that they
can be clamped to either midscale or ground independently. The
clamp controls are located in register 10h and are Bits 1 and 2.
The midscale reference voltage that each A/D converter clamps
to is provided independently on the RMIDSCV and BMIDSCV
pins. These two pins should be bypassed to ground with a
0.1 µF capacitor (even if midscale clamping is not required).
Gain and Offset Control
The AD9888 can accommodate input signals with inputs ranging
from 0.5 V to 1.0 V full scale. The full-scale range is set in three
8-bit registers (Red Gain, Green Gain, and Blue Gain; Registers
08h, 09h, and 10h respectively).
Note that increasing the gain setting results in an image with
less contrast.
The offset control shifts the entire input range, resulting in a
change in image brightness. Three 7-bit registers (Red Offset,
Green Offset, Blue Offset; Registers 0Bh, 0Ch, and 0Dh respectively) provide independent settings for each channel.
REV. A
AD9888
–10–
The offset controls provide a ±63 LSB adjustment range. This
range is connected with the full-scale range, so if the input range
is doubled (from 0.5 V to 1.0 V), the offset step size is also
doubled (from 2 mV per step to 4 mV per step).
Figure 2 illustrates the interaction of gain and offset controls.
The magnitude of an LSB in offset adjustment is proportional
to the full-scale range, so changing the full-scale range also
changes the offset. The change is minimal if the offset setting is
near midscale. When changing the offset, the full-scale range is
not affected, but the full-scale level is shifted by the same amount
as the zero-scale level.
GAIN
1.0
0.0
00h FFh
INPUT RANGE – V
0.5
OFFSET = 00h
OFFSET = 3Fh
OFFSET = 7Fh
OFFSET = 00h
OFFSET = 7Fh
OFFSET = 3Fh
Figure 2. Gain and Offset Control
Sync-on-Green
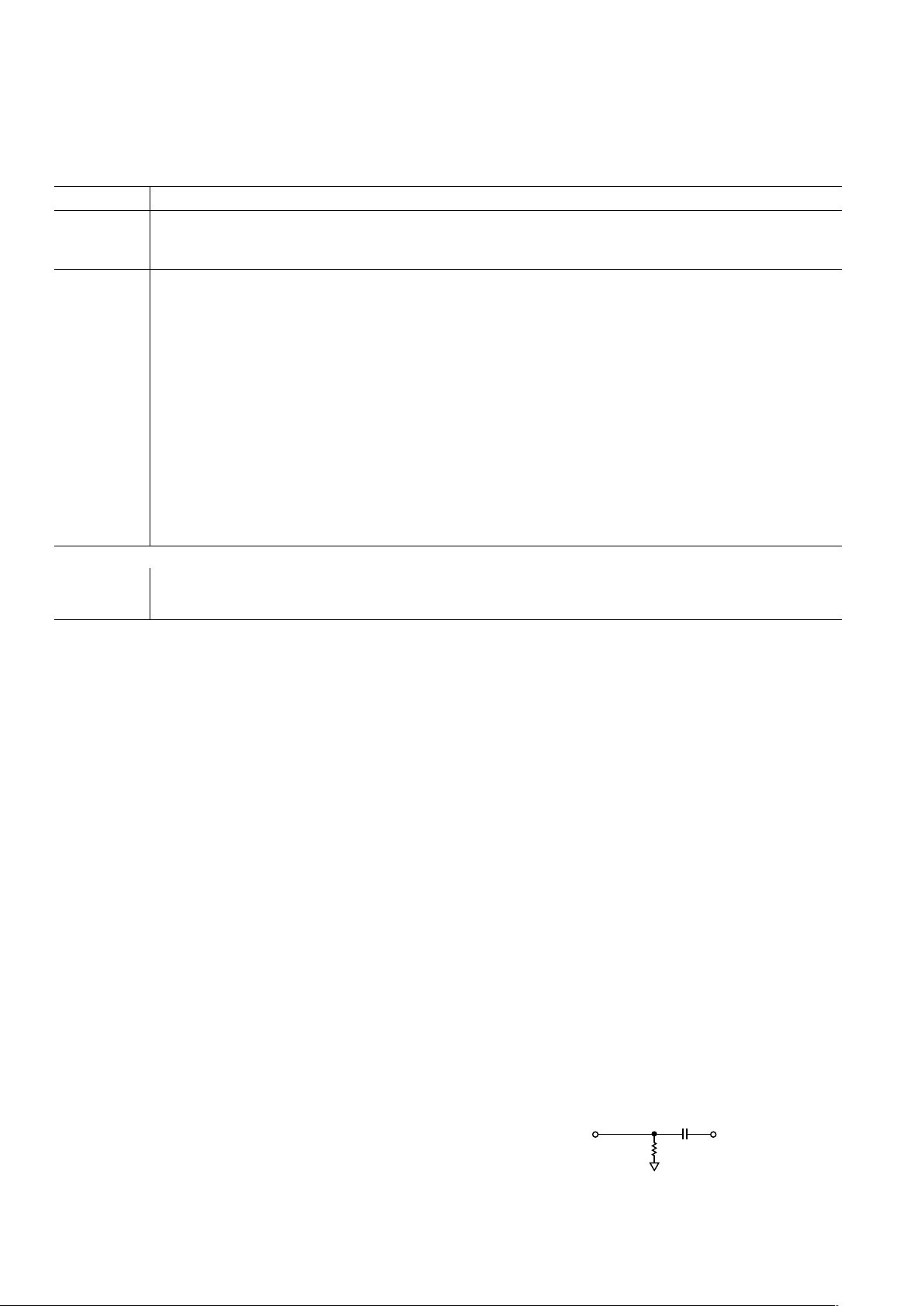
The Sync-on-Green input operates in two steps. First, it sets a
baseline clamp level off of the incoming video signal with a
negative peak detector. Second, it sets the sync trigger level
(nominally 150 mV above the negative peak). The exact trigger
level is variable and can be programmed via register 11H. The
Sync-on-Green input must be ac-coupled to the green analog
input through its own capacitor as shown in Figure 3. The value
of the capacitor must be 1 nF ± 20%. If Sync-on-Green is not
used, this connection is not required and the SOGIN pin should be
left unconnected. (Note: the Sync-on-Green signal is always
negative polarity.) For more details, see the Sync Processing section.
R
AIN
B
AIN
G
AIN
SOG
47nF
47nF
47nF
1nF
Figure 3. Typical Clamp Configuration for RGB/YUV
Applications
Clock Generation
A Phase Locked Loop (PLL) is employed to generate the pixel
clock. The Hsync input provides a reference frequency to the PLL.
A Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO) generates a much higher
pixel clock frequency. This pixel clock is divided by the PLL
divide value (registers 01H and 02H) and phase compared with
the Hsync input. Any error is used to shift the VCO frequency
and maintain lock between the two signals.
The stability of this clock is a very important element in providing the clearest and most stable image. During each pixel time,
there is a period during which the signal is slewing from the old
pixel amplitude and settling at its new value. Then there is a time
when the input voltage is stable, before the signal must slew to a
new value (Figure 4). The ratio of the slewing time to the stable
time is a function of the bandwidth of the graphics DAC and the
bandwidth of the transmission system (cable and termination). It
is also a function of the overall pixel rate. Clearly, if the dynamic
characteristics of the system remain fixed, then the slewing and
settling time is likewise fixed. This time must be subtracted from
the total pixel period, leaving the stable period. At higher pixel
frequencies, the total cycle time is shorter, and the stable pixel
time becomes shorter as well.
PIXEL CLOCK
INVALID SAMPLE
TIMES
Figure 4. Pixel Sampling Times
Any jitter in the clock reduces the precision with which the
sampling time can be determined, and must also be subtracted
from the stable pixel time.
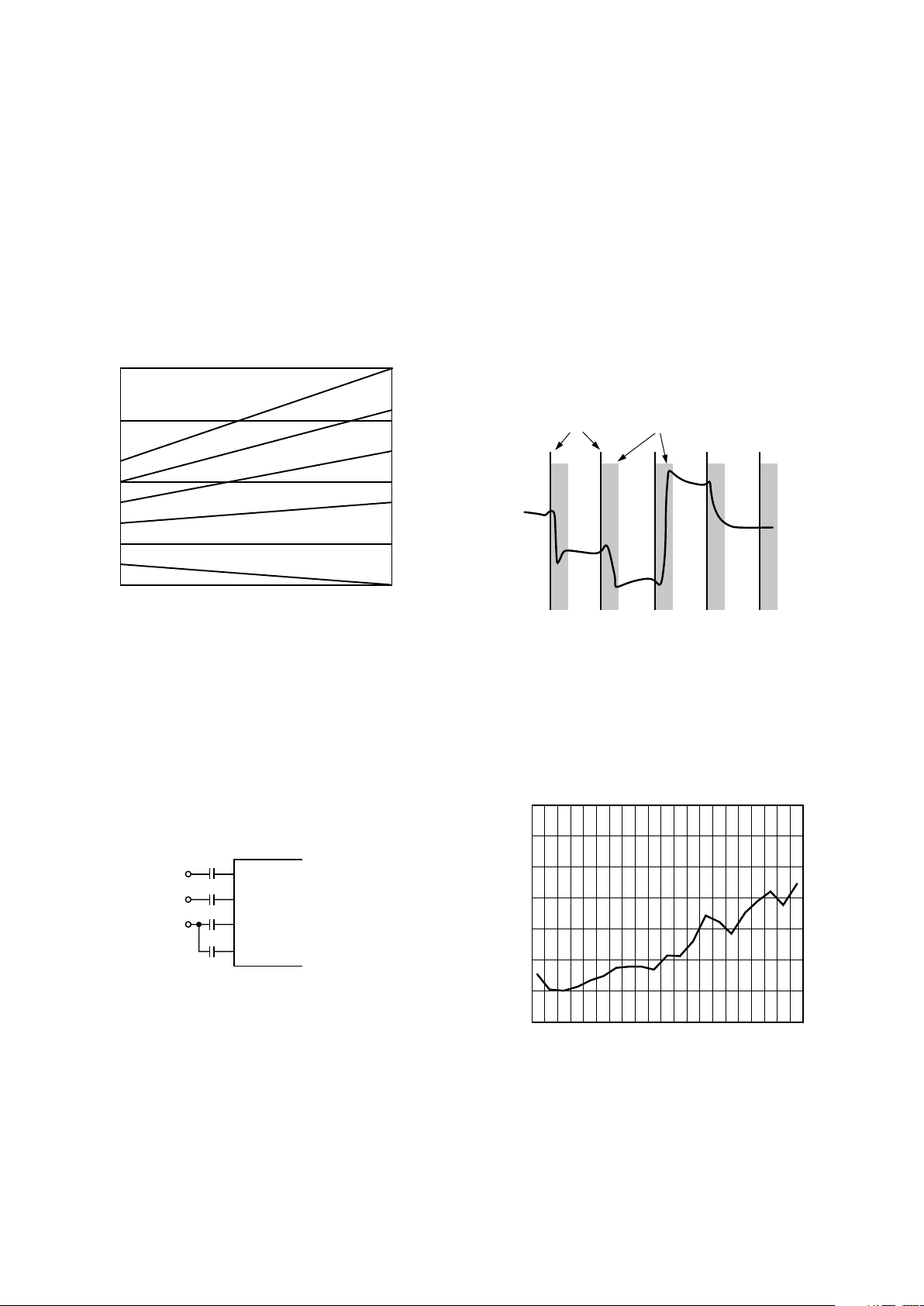
Considerable care has been taken in the design of the AD9888’s
clock generation circuit to minimize jitter. As indicated in Figure 5, the clock jitter of the AD9888 is less than 9% of the total
pixel time in all operating modes, making the reduction in the valid
sampling time due to jitter negligible.
PIXEL CLOCK – MHz
0
25.2
31.5
31.5
36.0
36.0
40.0
50.0
49.5
56.3
65.0
75.0
78.8
85.5
94.5
108.0
135.0
160.0
162.0
175.5
189.0
202.5
JITTER (p-p) – %
2
4
6
8
10
12
14
Figure 5. Pixel Clock Jitter vs. Frequency
The PLL characteristics are determined by the loop filter design,
by the PLL Charge Pump Current and by the VCO range setting.
The loop filter design is illustrated in Figure 6. Recommended
settings of VCO range and charge pump current for VESA standard
display modes are listed in Table IV.
 Loading...
Loading...