
Dual Interface for
T
Flat Panel Displays
AD9887A
FEATURES
Analog Interface
170 MSPS Maximum Conversion Rate
Programmable Analog Bandwidth
0.5 V to 1.0 V Analog Input Range
500 ps p-p PLL Clock Jitter at 170 MSPS
3.3 V Power Supply
Full Sync Processing
Midscale Clamping
4:2:2 Output Format Mode
Digital Interface
DVI 1.0 Compatible Interface
170 MHz Operation (2 Pixel/Clock Mode)
High Skew Tolerance of 1 Full Input Clock
Sync Detect for “Hot Plugging”
Supports High Bandwidth Digital Content Protection
APPLICATIONS
RGB Graphics Processing
LCD Monitors and Projectors
Plasma Display Panels
Scan Converters
Micro Displays
Digital TVs
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9887A offers designers the flexibility of an analog interface
and digital visual interface (DVI) receiver integrated on a single
chip. Also included is support for High Bandwidth Digital Content
Protection (HDCP). The AD9887A is software and pin-to-pin
compatible with the AD9887.
Analog Interface
The AD9887A is a complete 8-bit 170 MSPS monolithic analog
interface optimized for capturing RGB graphics signals from
personal computers and workstations. Its 170 MSPS encode
rate capability and full-power analog bandwidth of 330 MHz
supports resolutions up to UXGA (1600 × 1200 at 60 Hz).
The analog interface includes a 170 MHz triple ADC with
internal 1.25 V reference, a phase-locked loop (PLL), and programmable gain, offset, and clamp control. The user provides
only a 3.3 V power supply, analog input, and HSYNC. Threestate CMOS outputs may be powered from 2.5 V to 3.3 V.
The AD9887A’s on-chip PLL generates a pixel clock from
HSYNC. Pixel clock output frequencies range from 12 MHz to
170 MHz. PLL clock jitter is typically 500 ps p-p at 170 MSPS.
The AD9887A also offers full sync processing for composite
sync and sync-on-green (SOG) applications.
REV. 0
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective companies.
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
REFIN
R
AIN
G
AIN
B
AIN
HSYNC
VSYNC
COAST
CLAMP
CKINV
CKEXT
FILT
SOGIN
SCL
SDA
Rx0+
Rx0–
Rx1+
Rx1–
Rx2+
Rx2–
RxC+
RxC–
R
TERM
DDCSCL
DDCSDA
MCL
MDA
ANALOG INTERFACE
A
1
A
0
CLAMP
CLAMP
CLAMP
SYNC
PROCESSING
AND CLOCK
GENERATION
SERIAL REGISTER
POWER MANAGEMENT
DIGITAL INTERFACE
DVI
RECEIVER
HDCP
A/D
A/D
A/D
AND
REF
R
OUTA
8
8
8
8
8
8
8
2
R
OUTB
8
G
OUTA
8
G
OUTB
8
B
8
OUTA
B
OUTB
8
DATACK
2
HSOUT
VSOUT
SOGOUT
S
CDT
R
OUTA
8
R
8
OUTB
G
OUTA
8
G
8
OUTB
B
8
OUTA
B
8
OUTB
DATACK
DE
HSOUT
VSOUT
REFOUT
8
R
OUTA
8
R
OUTB
8
G
OUTA
8
M
G
U
X
E
S
OUTB
8
B
OUTA
8
B
OUTB
2
DATACK
HSOUT
VSOUT
SOGOU
DE
AD9887A
Digital Interface
The AD9887A contains a DVI 1.0 compatible receiver and
supports display resolutions up to UXGA (1600 ⫻ 1200 at 60 Hz).
The receiver operates with true color (24-bit) panels in 1 or
2 pixel(s)/clock mode and features an intrapair skew tolerance
of up to one full clock cycle.
With the inclusion of HDCP, displays may now receive encrypted
video content. The AD9887A allows for authentication of a
video receiver, decryption of encoded data at the receiver, and
renewability of that authentication during transmission as specified
by the HDCP v1.0 protocol.
Fabricated in an advanced CMOS process, the AD9887A is
provided in a 160-lead MQFP surface-mount plastic package
and is specified over the 0°C to 70°C temperature range.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © 2003 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.

AD9887A
TABLE OF CONTENTS
FEATURES . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
APPLICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
GENERAL DESCRIPTION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Analog Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
Digital Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
ANALOG INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4
DIGITAL INTERFACE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
ORDERING GUIDE . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
PIN CONFIGURATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
DESCRIPTIONS OF PINS SHARED BETWEEN
ANALOG AND DIGITAL INTERFACES . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Serial Port (2-Wire) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Data Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Data Clock Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Various . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
SCAN Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
PIN FUNCTION DETAILS (ANALOG INTERFACE) . . 11
Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
THEORY OF OPERATION (INTERFACE DETECTION)13
Active Interface Detection and Selection . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Power Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
THEORY OF OPERATION AND DESIGN GUIDE
(ANALOG INTERFACE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
General Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Input Signal Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
HSYNC, VSYNC Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Serial Control Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Output Signal Handling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
Clamping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
RGB Clamping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
YUV Clamping . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Gain and Offset Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Sync-on-Green . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Clock Generation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Scan Function . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Alternate Pixel Sampling Mode . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Timing (Analog Interface) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Hsync Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Coast Timing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
DIGITAL INTERFACE PIN DESCRIPTIONS . . . . . . . . 25
Digital Video Data Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Digital Clock Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Termination Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Outputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Power Supply . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
THEORY OF OPERATION (DIGITAL INTERFACE) . . 25
Capturing of the Encoded Data . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Data Frames . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Special Characters . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Channel Resynchronization . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Data Decoder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
HDCP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
GENERAL TIMING DIAGRAMS
(DIGITAL INTERFACE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
TIMING MODE DIAGRAMS (DIGITAL INTERFACE) 27
2-Wire Serial Register Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
2-WIRE SERIAL CONTROL REGISTER DETAIL . . . . . 32
CHIP IDENTIFICATION . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
PLL DIVIDER CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
CLOCK GENERATOR CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
CLAMP TIMING . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
INPUT GAIN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
INPUT OFFSET . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
MODE CONTROL 1 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
MODE CONTROL 2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
SYNC DETECTION AND CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
DIGITAL CONTROL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
CONTROL BITS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
2-Wire Serial Control Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Data Transfer via Serial Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Serial Interface Read/Write Examples . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
THEORY OF OPERATION (SYNC PROCESSING) . . . . 40
Sync Stripper . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Sync Seperator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
PCB LAYOUT RECOMMENDATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Analog Interface Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Digital Interface Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Power Supply Bypassing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
PLL . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Outputs (Both Data and Clocks) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
Voltage Reference . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
TABLE INDEX
Table I. Complete Pinout List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Table II. Analog Interface Pin List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
Table III. Interface Selection Controls . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table IV. Power-Down Mode Descriptions . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Table V. VCO Frequency Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table VI. Charge Pump Current/Control Bits . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Table VII. Recommended VCO Range and Charge Pump
Current Settings for Standard Display Formats . . . . . . . . . . 18
Table VIII. Digital Interface Pin List . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Table IX. Control Register Map . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Table X. VCO Ranges . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table XI. Charge Pump Currents . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Table XII. Channel Mode Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table XIII. Output Mode Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table XIV. Output Port Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Table XV. HSYNC Output Polarity Settings . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table XVI. VSYNC Output Polarity Settings . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table XVII. HSNYC Input Polarity Settings . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table XVIII. COAST Input Polarity Settings . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table XIX. Clamp Input Signal Source Settings . . . . . . . . . 34
Table XX. CLAMP Input Signal Polarity Settings . . . . . . . 34
Table XXI. External Clock Select Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Table XXII. Red Clamp Select Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table XXIII. Green Clamp Select Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table XXIV. Blue Clamp Select Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table XXV. Clock Output Invert Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table XXVI. Pix Select Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table XXVII. Output Drive Strength Settings . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table XXVIII. Power-Down Output Settings . . . . . . . . . . . 35
REV. 0–2–

TABLE INDEX (continued)
Table XXIX. Sync Detect Polarity Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 35
Table XXX. HSYNC Detection Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table XXXI. Sync-on-Green Detection Results . . . . . . . . . 36
Table XXXII. VSYNC Detection Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table XXXIII. Digital Interface Clock Detection Results . . 36
Table XXXIV. Active Interface Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table XXXV. Active HSYNC Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
Table XXXVI. Active VSYNC Results . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table XXXVII. Active Interface Override Settings . . . . . . . 37
Table XXXVIII. Active Interface Select Settings . . . . . . . . . 37
Table XXXIX. Active Hsync Override Settings . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table XL. Active HSYNC Select Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table XLI. Active VSYNC Override Settings . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table XLII. Active VSYNC Select Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table XLIII. COAST Select Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table XLIV. Power-Down Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
Table XLV. Scan Enable Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table XLVI. Coast Input Polarity Override Settings . . . . . . 38
Table XLVII. HSYNC Input Polarity Override Settings . . . 38
Table XLVIII. Detected HSYNC Input Polarity Status . . . 38
Table XLIX. Detected VSYNC Input Polarity Status . . . . . 38
Table L. Detected Coast Input Polarity Status . . . . . . . . . . 38
Table LI. 4:2:2 Input/Output Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table LII. 4:2:2 Output Mode Select . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table LIII. Serial Port Addresses . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 39
Table LIV. Control of the Sync Block Muxes via the Serial
Register . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
AD9887A
REV. 0
–3–
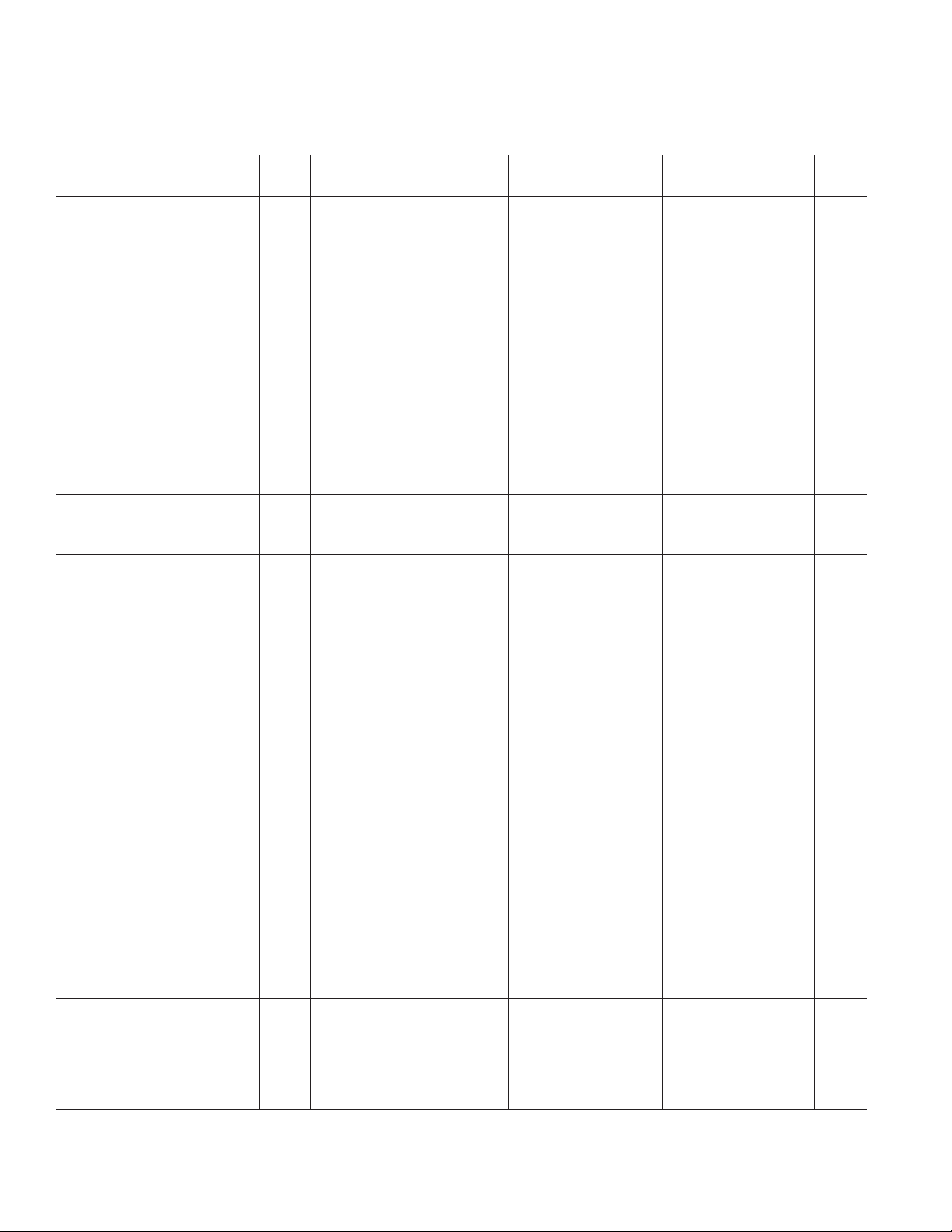
AD9887A–SPECIFICATIONS
ANALOG INTERFACE
(VD = 3.3 V, VDD = 3.3 V, ADC Clock = Maximum Conversion Rate, unless otherwise noted.)
Test AD9887AKS-100 AD9887AKS-140 AD9887AKS-170
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 8 8 8 Bits
DC ACCURACY
Differential Nonlinearity 25°CI ± 0.5 +1.15/–1.0 ±0.5 +1.25/–1.0 ±0.8 +1.25/–1.0 LSB
Full VI +1.15/–1.0 +1.25/–1.0 +1.50/–1.0 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity 25°CI ± 0.5 ±1.40 ± 0.5 ±1.4 ± 1.0 ±2.25 LSB
Full VI ± 1.75 ± 2.5 ± 2.75 LSB
No Missing Codes 25°CI Guaranteed Guaranteed Guaranteed
ANALOG INPUT
Input Voltage Range
Minimum Full VI 0.5 0.5 0.5 V p-p
Maximum Full VI 1.0 1.0 1.0 V p-p
Gain Tempco 25°CV 135 150 150 ppm/°C
Input Bias Current 25°CIV 111µA
Full IV 1 1 1 µA
Input Full-Scale Matching Full VI 8.0 8.0 8.0 % FS
Offset Adjustment Range Full VI 43 48 53 43 48 53 43 48 53 % FS
REFERENCE OUTPUT
Output Voltage Full V 1.3 1.3 1.3 V
Temperature Coefficient Full V 90 90 90 ppm/°C
SWITCHING PERFORMANCE
1
Maximum Conversion Rate Full VI 100 140 170 MSPS
Minimum Conversion Rate Full IV 10 10 10 MSPS
Clock to Data Skew, t
SKEW
Full IV –1.5 +2.5 –1.5 +2.5 –1.5 +2.5 ns
Serial Port Timing
t
BUFF
t
STAH
t
DHO
t
DAL
t
DAH
t
DSU
t
STASU
t
STOSU
Full VI 4.7 4.7 4.7 µs
Full VI 4.0 4.0 4.0 µs
Full VI 0 0 0 µs
Full VI 4.7 4.7 4.7 µs
Full VI 4.0 4.0 4.0 µs
Full VI 250 250 250 ns
Full VI 4.7 4.7 4.7 µs
Full VI 4.0 4.0 4.0 µs
HSYNC Input Frequency Full IV 15 110 15 110 15 110 kHz
Maximum PLL Clock Rate Full VI 100 140 170 MHz
Minimum PLL Clock Rate Full IV 12 12 12 MHz
PLL Jitter 25°CIV 500 700
Full IV 1000
Sampling Phase Tempco Full IV
10 10 10 ps/°C
2
2
440 650
700
3
3
370 500
700
4
4
ps p-p
ps p-p
DIGITAL INPUTS
Input Voltage, High (VIH) Full VI 2.6 2.6 2.6 V
Input Voltage, Low (VIL) Full VI 0.8 0.8 0.8 V
Input Current, High (V
) Full IV –1.0 –1.0 –1.0 µA
IH
Input Current, Low (VIL) Full IV +1.0 +1.0 +1.0 µA
Input Capacitance 25°CV 333pF
DIGITAL OUTPUTS
Output Voltage, High (VOH) Full VI 2.4 2.4 2.4 V
Output Voltage, Low (V
) Full VI 0.4 0.4 0.4 V
OL
Duty Cycle
DATACK, DATACK Full IV 45 55 60 45 55 60 45 55 65 %
Output Coding Binary Binary Binary
REV. 0–4–
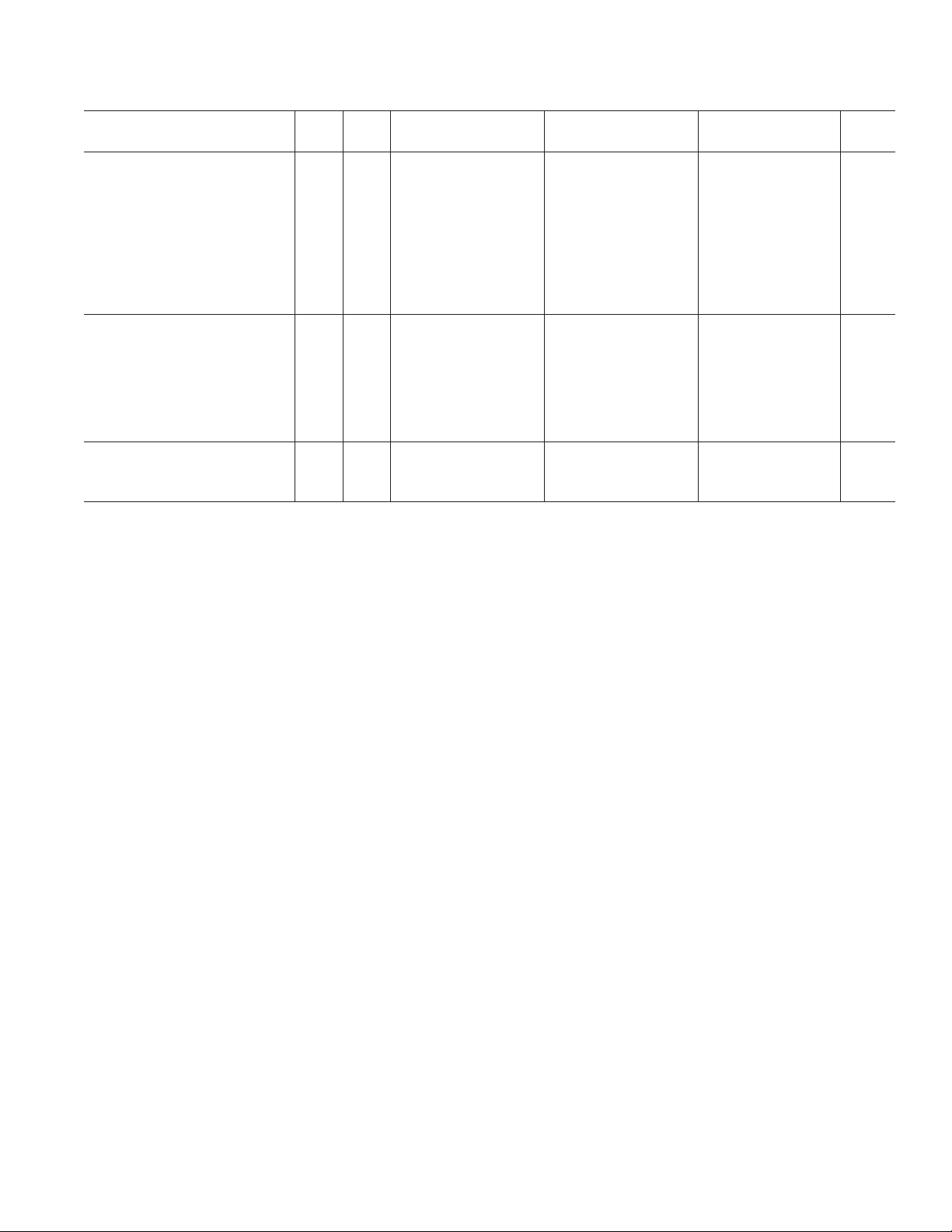
AD9887A
Test AD9887AKS-100 AD9887AKS-140 AD9887AKS-170
Parameter Temp Level Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
POWER SUPPLY
VD Supply Voltage Full IV 3.15 3.3 3.45 3.15 3.3 3.45 3.15 3.3 3.45 V
V
Supply Voltage Full IV 2.2 3.3 3.45 2.2 3.3 3.45 2.2 3.3 3.45 V
DD
Supply Voltage Full IV 3.15 3.3 3.45 3.15 3.3 3.45 3.15 3.3 3.45 V
P
VD
ID Supply Current (VD)25°CV 140 155 230 mA
I
Supply Current (VDD)
DD
Supply Current (PVD)25°CV 15 16 60 mA
IP
VD
Total Supply Current
Power-Down Supply Current Full VI 90 120 90 120 90 120 mA
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
Analog Bandwidth, Full Power 25°CV 330 330 330 MHz
Transient Response 25°CV 222ns
Overvoltage Recovery Time 25°CV 1.5 1.5 1.5 ns
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
= 40.7 MHz
f
IN
Crosstalk Full V 60 60 60 dBc
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
θJA Junction-to-Ambient
Thermal Resistance
NOTES
1
Drive Strength = 11.
2
VCO Range = 01, Charge Pump Current = 001, PLL Divider = 1693.
3
VCO Range = 10, Charge Pump Current = 110, PLL Divider = 1600.
4
VCO Range = 11, Charge Pump Current = 110, PLL Divider = 2159.
5
DEMUX = 1, DATACK and DATACK Load = 10 pF, Data Load = 5 pF.
6
Using external pixel clock.
7
Simulated typical performance with package mounted to a 4-layer board.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
5
5
7
25°CV 34 48 55 mA
Full VI 300 330 335 360 345 390 mA
6
25°CV 46 46 45 dB
V37 3737°C/W
REV. 0
–5–
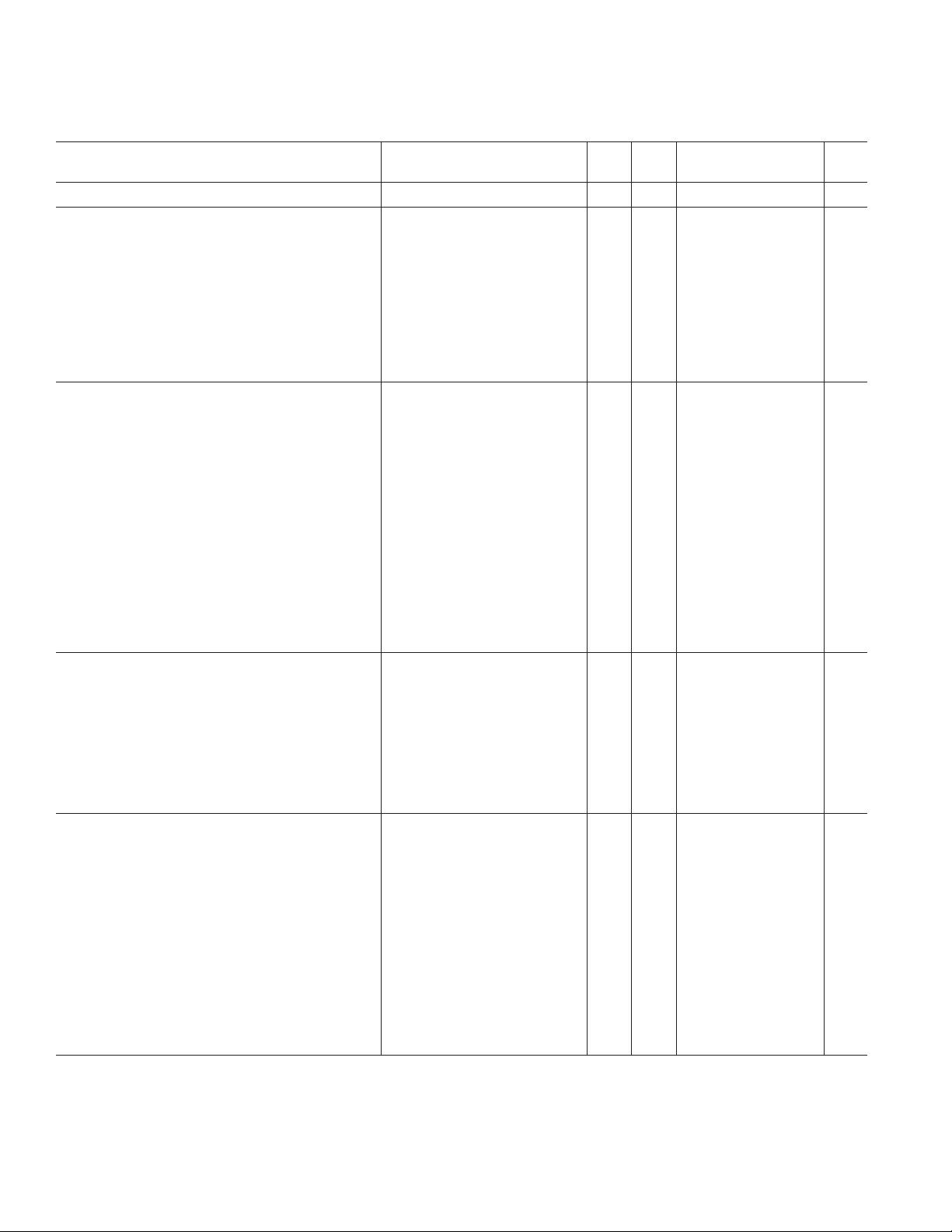
AD9887A–SPECIFICATIONS
DIGITAL INTERFACE
(VD = 3.3 V, VDD = 3.3 V, Clock = Maximum.)
Test AD9887AKS
Parameter Conditions Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 8Bits
DC DIGITAL I/O SPECIFICATIONS
High Level Input Voltage (V
Low Level Input Voltage (V
High Level Output Voltage (V
Low Level Output Voltage (V
Input Clamp Voltage (V
Input Clamp Voltage (V
Output Clamp Voltage (V
Output Clamp Voltage (V
)
IH
)
IL
)
OH
)
OL
)(I
CINL
)(I
CIPL
)(I
CONL
)(I
COPL
= –18 mA) IV GND – 0.8 V
CL
= +18 mA) IV VDD + 0.8 V
CL
= –18 mA) IV GND – 0.8 V
CL
= +18 mA) IV VDD + 0.8 V
CL
Output Leakage Current (IOL)(High Impedance)
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
VI 2.6 V
VI 0.8 V
VI 2.4 V
VI 0.4 V
IV –10 +10 µA
DC SPECIFICATIONS
Output High Drive Output Drive = High
) (V
(I
OHD
= VOH) Output Drive = Med
OUT
Output Drive = Low
Output Drive = High
(I
) (V
OLD
= VOL) Output Drive = Med
OUT
Output Drive = Low
Output Drive = High
) (V
(V
OHC
= VOH) Output Drive = Med
OUT
Output Drive = Low
DATACK Low Drive Output Drive = High
) (V
(V
OLC
= VOL) Output Drive = Med
OUT
Output Drive = Low
Differential Input Voltage Single-Ended Amplitude
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
IV 13 mA
IV 8 mA
IV 5 mA
IV –9mA
IV –7mA
IV –5mA
IV 25 mA
IV 12 mA
IV 8 mA
IV –25 mA
IV –19 mA
IV –8mA
IV 75 800 mV
POWER SUPPLY
V
Supply Voltage
D
Supply Voltage Minimum Value for 2 Pixels per
V
DD
Clock Mode
P
Supply Voltage
VD
Supply Current
I
D
Supply Current
I
DD
IP
Supply Current
VD
Total Supply Current with HDCP
1
1, 2
1
1, 2
AC SPECIFICATIONS
Intrapair (+ to –) Differential Input Skew (T
Channel-to-Channel Differential Input Skew (T
DPS
)
)
CCS
Low-to-High Transition Time for Data and Output Drive = High; C
Controls (D
) Output Drive = Med; CL = 7 pF
LHT
Output Drive = Low; C
Low-to-High Transition Time for DATACK (D
) Output Drive = High; CL = 10 pF
LHT
Output Drive = Med; C
Output Drive = Low; C
High-to-Low Transition Time for Data (D
) Output Drive = High; CL = 10 pF
HLT
Output Drive = Med; C
Output Drive = Low; CL = 5 pF
= 10 pF
L
= 5 pF
L
= 7 pF
L
= 5 pF
L
= 7 pF
L
Full
Full
Full
25°C
25°C
25°C
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
IV 3.15 3.3 3.45 V
IV 2.2 3.3 3.45 V
IV 3.15 3.3 3.45 V
V 350 mA
V40 mA
IV 130 mA
VI 520 560 mA
IV 360 ps
IV 1.0
Clock
Period
IV 2.5 ns
IV 3.1 ns
IV 5.4 ns
IV 1.2 ns
IV 1.6 ns
IV 2.3 ns
IV 2.6 ns
IV 3.0 ns
IV 3.7 ns
REV. 0–6–
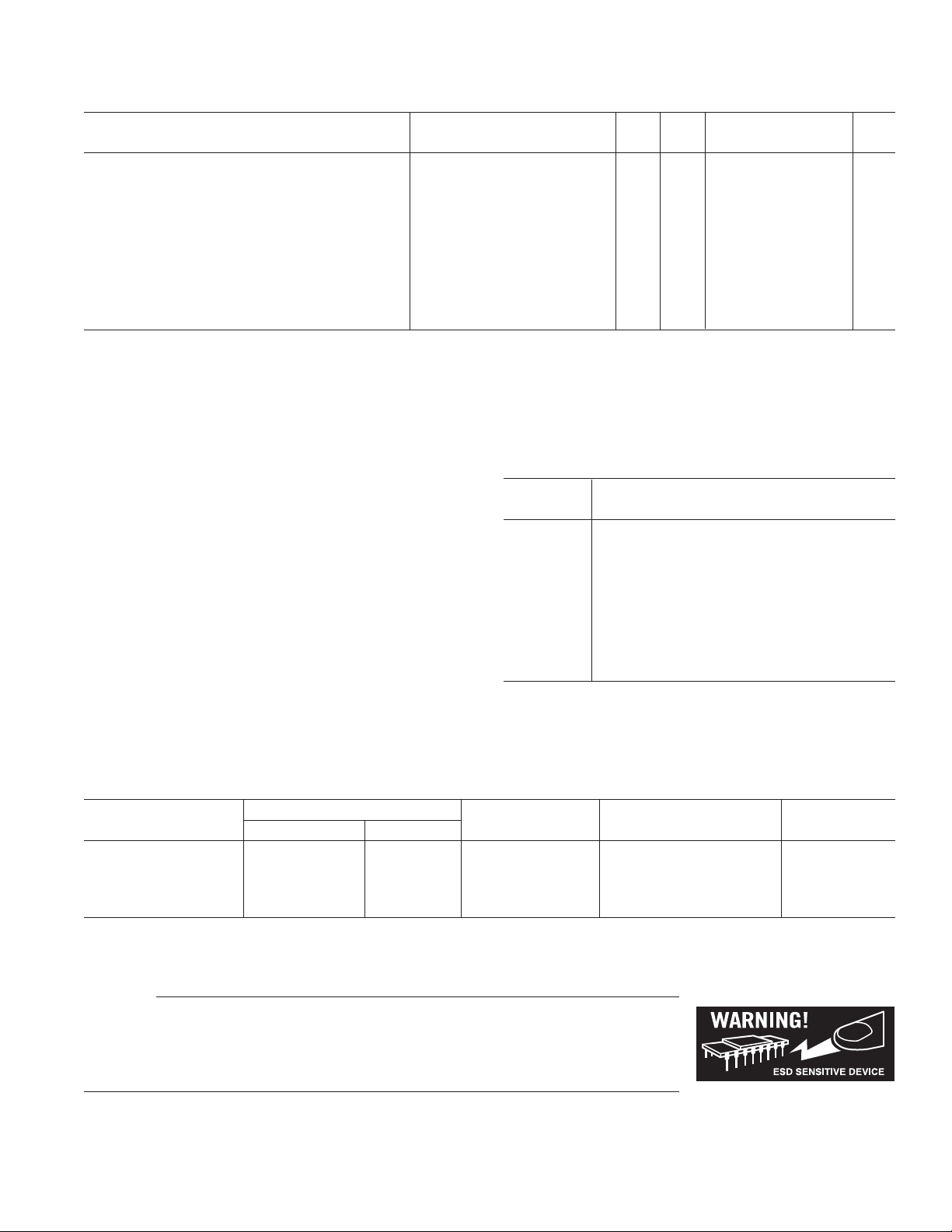
AD9887A
Test AD9887AKS
Parameter Conditions Temp Level Min Typ Max Unit
AC SPECIFICATIONS (continued)
High-to-Low Transition Time for DATACK (D
Clock to Data Skew, t
Duty Cycle, DATACK, DATACK
DATACK Frequency (f
DATACK Frequency (f
NOTES
1
The typical pattern contains a gray scale area, Output Drive = High.
2
DATACK and DATACK Load = 10 pF, Data Load = 5 pF, HDCP disabled.
3
Drive Strength = 11
Specifications subject to change without notice.
3
SKEW
) (1 Pixel/Clock)
CIP
) (2 Pixels/Clock)
CIP
3
) Output Drive = High; CL =10 pF
HLT
Output Drive = Med; C
Output Drive = Low; C
L
= 5 pF
L
= 7 pF
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
Full
IV 1.4 ns
IV 1.6 ns
IV 2.4 ns
IV 0 4.0 ns
IV 45 55 % of
Period
High
VI 20 140 MHz
IV 10 85 MHz
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
VD . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.6 V
V
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3.6 V
DD
Analog Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
VREF IN . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . V
to 0.0 V
D
to 0.0 V
D
Digital Inputs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5 V to 0.0 V
Digital Output Current . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20 mA
Operating Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –25°C to +85°C
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . – 65°C to +150°C
Maximum Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
Maximum Case Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150°C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions outside of those indicated in the operation
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum ratings
for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Test
Level Explanation
I 100% production tested.
II 100% production tested at 25°C and sample
III Sample tested only.
IV Parameter is guaranteed by design and charac-
V Parameter is a typical value only.
VI 100% production tested at 25°C; guaranteed
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
tested at specified temperatures.
terization testing.
by design and characterization testing.
ORDERING GUIDE
Max Speed (MHz) Temperature Package Package
Model Analog DVI Range Description Option
AD9887AKS-170 170 170 0°C to 70°CMetric Quad Flatpack S-160
AD9887AKS-140 140 140 0°C to 70°CMetric Quad Flatpack S-160
AD9887AKS-100 100 100 0°C to 70°CMetric Quad Flatpack S-160
AD9887A/PCB 25°CEvaluation Board
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although the
AD9887A features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices
subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended
to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
REV. 0
–7–
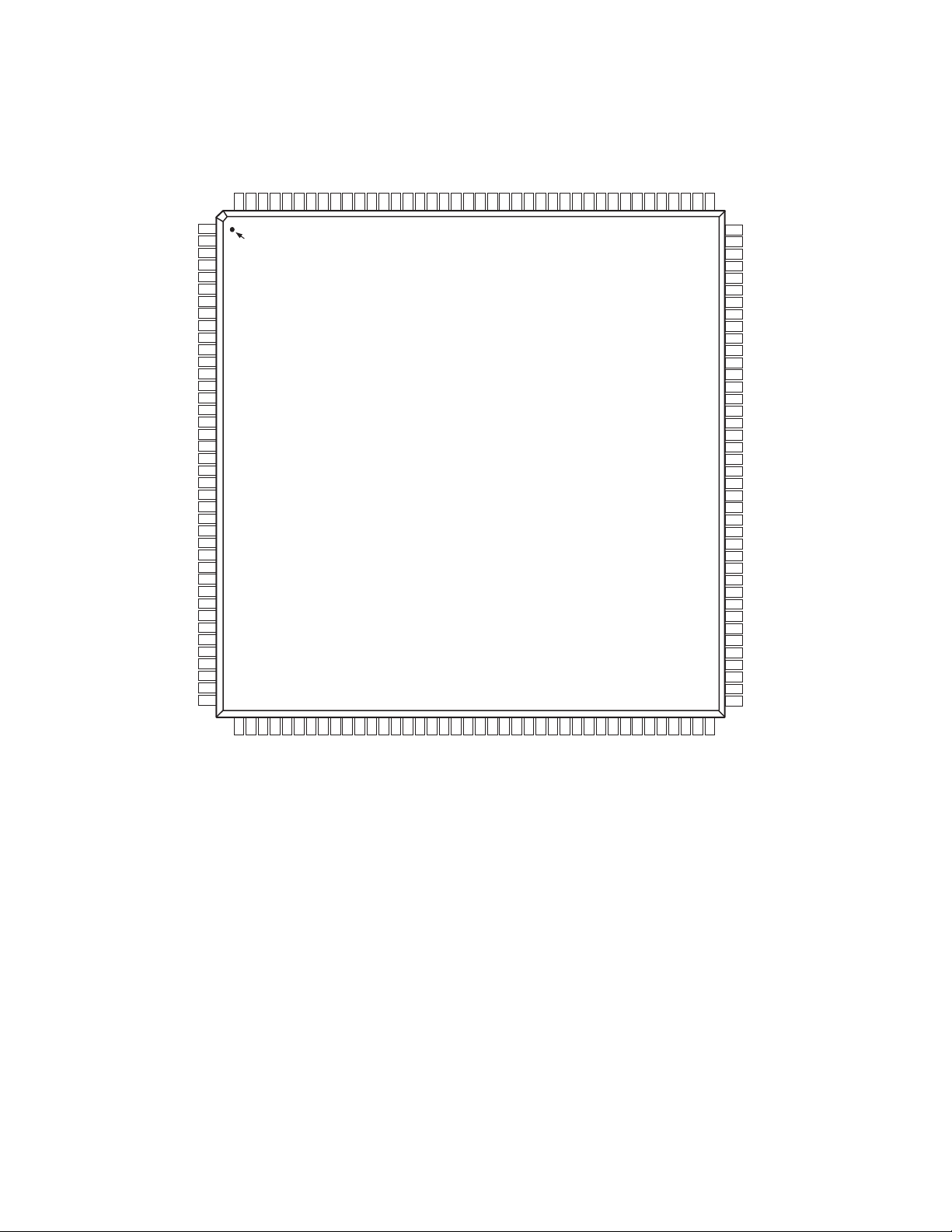
AD9887A
V
GND
GREEN A<7>
GREEN A<6>
GREEN A<5>
GREEN A<4>
GREEN A<3>
GREEN A<2>
GREEN A<1>
GREEN A<0>
V
GND
GREEN B<7>
GREEN B<6>
GREEN B<5>
GREEN B<4>
GREEN B<3>
GREEN B<2>
GREEN B<1>
GREEN B<0>
V
GND
BLUE A<7>
BLUE A<6>
BLUE A<5>
BLUE A<4>
BLUE A<3>
BLUE A<2>
BLUE A<1>
BLUE A<0>
V
GND
BLUE B<7>
BLUE B<6>
BLUE B<5>
BLUE B<4>
BLUE B<3>
BLUE B<2>
BLUE B<1>
BLUE B<0>
PIN CONFIGURATION
D
DD
RED B<0>
RED B<1>
RED B<2>
RED B<3>
RED B<4>
RED B<5>
160
159
158
157
156
155
1
DD
DD
DD
DD
PIN 1
2
IDENTIFIER
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
RED B<6>
RED B<7>
GND
154
153
152
V
RED A<0>
151
150
RED A<1>
RED A<2>
RED A<3>
149
147
148
RED A<4>
RED A<5>
146
145
DD
V
RED A<6>
RED A<7>
GND
144
143
142
141
AD9887A
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
SOGOUT
HSOUT
VSOUT
140
139
138
DE
137
136
CDT
S
DATACK
DATACK
GND
135
133
134
V
132
DD
GND
GND
SCANINGND
131
130
129
128
V
REFOUT
127
126
DVD
V
REFIN
125
124
123
GND
122
GND
121
120
119
118
117
116
115
114
113
112
111
110
109
108
107
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
R
MIDSC
R
AIN
R
CLAMP
V
D
GND
V
D
V
D
GND
GND
G
MIDSC
G
AIN
G
CLAMP
SOGIN
V
D
GND
V
D
V
D
GND
GND
B
MIDSC
B
AIN
B
CLAMP
V
D
GND
V
D
GND
CKINV
CLAMP
SDA
SCL
A0
A1
PV
D
PV
D
GND
GND
COAST
CKEXT
HSYNC
VSYNC
V
V
V
V
V
V
41
GND
42
GND
434445
DD
V
GND
OUT
SCAN
46
CTL0
47
CTL1
484950
MCL
CTL2
51
V
CLK
SCAN
61
Rx1+
Rx1–
GND
62
Rx0+
636465
GND
Rx0–
RxC+
66
67
V
RxC–
52
535455
56
585960
TERM
VDV
D
Rx2+
57
Rx2–
GND
D
GND
R
686970
DVD
GND
D
V
71
72
MDA
DDCSDA
737475
PV
GND
DDCSCL
76
787980
77
D
D
D
PV
PV
FILT
GND
GND
REV. 0–8–
AD9887A
Table I. Complete Pinout List
Pin Pin Pin
Type Mnemonic Function Value Number Interface
Analog Video R
Inputs G
AIN
AIN
B
AIN
External HSYNC Horizontal SYNC Input 3.3 V CMOS 82 Analog
Sync/Clock VSYNC Vertical SYNC Input 3.3 V CMOS 81 Analog
Inputs SOGIN Input for Sync-on-Green 0.0 V to 1.0 V 108 Analog
CLAMP Clamp Input (External CLAMP Signal) 3.3 V CMOS 93 Analog
COAST PLL COAST Signal Input 3.3 V CMOS 84 Analog
CKEXT External Pixel Clock Input (to Bypass the PLL) to V
CKINV ADC Sampling Clock Invert 3.3 V CMOS 94 Analog
Sync Outputs HSOUT HSYNC Output Clock (Phase-Aligned with DATACK) 3.3 V CMOS 139 Both
VSOUT VSYNC Output Clock 3.3 V CMOS 138 Both
SOGOUT Composite Sync 3.3 V CMOS 140 Analog
Voltage REFOUT Internal Reference Output (Bypass with 0.1 µF to Ground) 1.25 V 126 Analog
Reference REFIN Reference Input (1.25 V ± 10%) 1.25 V ± 10% 125 Analog
Clamp Voltages R
VRed Channel Midscale Clamp Voltage Output 120 Analog
MIDSC
R
VRed Channel Midscale Clamp Voltage Input 0.0 V to 0.75 V 118 Analog
CLAMP
G
VGreen Channel Midscale Clamp Voltage Output 111 Analog
MIDSC
VGreen Channel Midscale Clamp Voltage Input 0.0 V to 0.75 V 109 Analog
G
CLAMP
B
VBlue Channel Midscale Clamp Voltage Output 101 Analog
MIDSC
B
VBlue Channel Midscale Clamp Voltage Input 0.0 V to 0.75 V 99 Analog
CLAMP
PLL Filter FILT Connection for External Filter Components for Internal PLL 78 Analog
Power Supply V
V
PV
D
DD
D
GND Ground 0 V Both
Serial Port SDA Serial Port Data I/O 3.3 V CMOS 92 Both
(2-Wire SCL Serial Port Data Clock (100 kHz Max) 3.3 V CMOS 91 Both
Serial Interface) A0 Serial Port Address Input 1 3.3 V CMOS 90 Both
A1 Serial Port Address Input 2 3.3 V CMOS 89 Both
Data Outputs Red B[7:0] Port B/Odd Outputs of Converter “Red,” Bit 7 Is the MSB 3.3 V CMOS 153–160 Both
Green B[7:0] Port B/Odd Outputs of Converter “Green,” Bit 7 Is the MSB 3.3 V CMOS 13–20 Both
Blue B[7:0] Port B/Odd Outputs of Converter “Blue,” Bit 7 Is the MSB 3.3 V CMOS 33–40 Both
Red A[7:0] Port A/Even Outputs of Converter “Red,” Bit 7 Is the MSB 3.3 V CMOS 143–150 Both
Green A[7:0] Port A/Even Outputs of Converter “Green,” Bit 7 Is the MSB 3.3 V CMOS 3–10 Both
Blue A[7:0] Port A/Even Outputs of Converter “Blue,” Bit 7 Is the MSB 3.3 V CMOS 23–30 Both
Data Clock DATACK Data Output Clock for the Analog and Digital Interface 3.3 V CMOS 134 Both
Outputs DATACK Data Output Clock Complement for the Analog Interface Only 3.3 V CMOS 135 Both
Sync Detect S
Scan Function SCAN
CDT
SCAN
SCAN
IN
OUT
CLK
Digital Video Rx0+ Digital Input Channel 0 True 62 Digital
Data Inputs Rx0– Digital Input Channel 0 Complement 63 Digital
Rx1+ Digital Input Channel 1 True 59 Digital
Rx1– Digital Input Channel 1 Complement 60 Digital
Rx2+ Digital Input Channel 2 True 56 Digital
Rx2– Digital Input Channel 2 Complement 57 Digital
Analog Input for Converter R 0.0 V to 1.0 V 119 Analog
Analog Input for Converter G 0.0 V to 1.0 V 110 Analog
Analog Input for Converter B 0.0 V to 1.0 V 100 Analog
or Ground 3.3 V CMOS 83 Analog
DD
Analog Power Supply 3.3 V ± 10% Both
Output Power Supply 3.3 V ± 10% Both
PLL Power Supply 3.3 V ± 10% Both
Sync Detect Output 3.3 V CMOS 136 Both
Input for SCAN Function 3.3 V CMOS 129 Both
Output for SCAN Function 3.3 V CMOS 45 Both
Clock for SCAN Function 3.3 V CMOS 50 Both
REV. 0
–9–
AD9887A
P
in Pin Pin
Type Mnemonic Function Value Number Interface
Digital Video RxC+ Digital Data Clock True 65 Digital
Clock Inputs RxC– Digital Data Clock Complement 66 Digital
Data Enable DE Data Enable 3.3 V CMOS 137 Digital
Control Bits CTL[0:2] Decoded Control Bits 3.3 V CMOS 46–48 Digital
R
TERM
HDCP DDCSCL HDCP Slave Serial Port Data Clock 3.3 V CMOS 73 Digital
R
TERM
DDCSDA HDCP Slave Serial Port Data I/O 3.3 V CMOS 72 Digital
MCL HDCP Master Serial Port Data Clock 3.3 V CMOS 49 Digital
MDA HDCP Master Serial Port Data I/O 3.3 V CMOS 71 Digital
Sets Internal Termination Resistance 53 Digital
DESCRIPTIONS OF PINS SHARED BETWEEN ANALOG AND DIGITAL INTERFACES
HSOUT Horizontal Sync Output
A reconstructed and phase-aligned version of
the video HSYNC. The polarity of this output
can be controlled via a serial bus bit. In analog
interface mode, the placement and duration
are variable. In digital interface mode, the
placement and duration are set by the graphics
transmitter.
VSOUT Vertical Sync Output
The separated VSYNC from a composite
signal or a direct pass through of the VSYNC
input. The polarity of this output can be controlled via a serial bus bit. The placement and
duration in all modes is set by the graphics
transmitter.
Serial Port (2-Wire)
SDA Serial Port Data I/O
SCL Serial Port Data Clock
A0 Serial Port Address Input 1
A1 Serial Port Address Input 2
For a full description of the 2-wire serial register and how it works, refer to the Control
Register section.
Data Outputs
RED A Data Output, Red Channel, Port A/Even
RED B Data Output, Red Channel, Port B/Odd
GREEN A Data Output, Green Channel, Port A/Even
GREEN B Data Output, Green Channel, Port B/Odd
BLUE A Data Output, Blue Channel, Port A/Even
BLUE B Data Output, Blue Channel, Port B/Odd
The main data outputs. Bit 7 is the MSB.
These outputs are shared between the two
interfaces and behave according to which
interface is active. Refer to the sections on the
two interfaces for more information on how
these outputs behave.
Data Clock Outputs
DATACK Data Output Clock
DATACK Data Output Clock Complement
Just like the data outputs, the data clock outputs
are shared between the two interfaces. They
also behave differently depending on which
interface is active. Refer to the sections on the
two interfaces to determine how these pins
behave.
Various
S
CDT
Chip Active/Inactive Detect Output
The logic for the S
pin is [analog interface
CDT
HSYNC detection] OR [digital interface DE
detection]. So, the S
pin will switch to logic
CDT
LOW under two conditions, when neither
interface is active or when the chip is in full
chip power-down mode. The data outputs are
automatically three-stated when S
This pin can be read by a controller in order
to determine periods of inactivity.
SCAN Function
SCAN
IN
Data Input for SCAN Function
Data can be loaded serially into the 48-bit
SCAN register through this pin, clocking it in
with the SCAN
pin. It then comes out of
CLK
the 48 data outputs in parallel. This function is
useful for loading known data into a graphics
controller chip for testing purposes.
SCAN
OUT
Data Output for SCAN Function
The data in the 48-bit SCAN register can be
read through this pin. Data is read on a FIFO
basis and is clocked via the SCAN
SCAN
CLK
Data Clock for SCAN Function
This pin clocks the data through the SCAN
register. It controls both data input and data
output.
is LOW.
CDT
pin.
CLK
REV. 0–10–
AD9887A
Table II. Analog Interface Pin List
Pin Pin Pin
Type
Analog Video Inputs R
External HSYNC Horizontal SYNC Input 3.3 V CMOS 82
Sync/Clock SOGIN Sync-on-Green Input 0.0 V to 1.0 V 108
Inputs CLAMP Clamp Input (External CLAMP Signal) 3.3 V CMOS 93
Sync Outputs HSOUT HSYNC Output (Phase-Aligned with DATACK and DATACK) 3.3 V CMOS 139
Voltage Reference REFOUT Internal Reference Output (bypass with 0.1 µF to ground) 1.25 V 126
Clamp Voltages R
PLL Filter FILT Connection for External Filter Components for Internal PLL 78
Power Supply V
Mnemonic
AIN
G
AIN
B
AIN
Function Value Number
Analog Input for Converter R 0.0 V to 1.0 V 119
Analog Input for Converter G 0.0 V to 1.0 V 110
Analog Input for Converter B 0.0 V to 1.0 V 100
VSYNC Vertical SYNC Input 3.3 V CMOS 81
COAST PLL COAST Signal Input 3.3 V CMOS 84
CKEXT External Pixel Clock Input (to Bypass Internal PLL) 3.3 V CMOS 83
or 10 kΩ to V
DD
CKINV ADC Sampling Clock Invert 3.3 V CMOS 94
VSOUT VSYNC Output 3.3 V CMOS 138
SOGOUT Composite Sync 3.3 V CMOS 140
REFIN Reference Input (1.25 V ± 10%) 1.25 V ± 10% 125
V Voltage output equal to the RED converter midscale voltage. 0.5 V ± 50% 120
MIDSC
R
VDuring midscale clamping, the RED Input is clamped to this pin. 0.0 V to 0.75 V 118
CLAMP
V Voltage output equal to the GREEN converter midscale voltage. 0.5 V ± 50% 111
G
MIDSC
G
V During midscale clamping, the GREEN Input is clamped to this pin. 0.0 V to 0.75 V 109
CLAMP
B
V Voltage output equal to the BLUE converter midscale voltage. 0.5 V ± 50% 101
MIDSC
V During midscale clamping, the BLUE Input is clamped to this pin. 0.0 V to 0.75 V 99
B
CLAMP
Main Power Supply 3.3 V ± 5%
PLL Power Supply (Nominally 3.3 V) 3.3 V ± 5%
Output Power Supply 3.3 V or 2.5 V ± 5%
PV
V
D
D
DD
GND Ground 0 V
PIN FUNCTION DETAILS (ANALOG INTERFACE)
Inputs
R
AIN
G
AIN
B
AIN
Analog Input for RED Channel
Analog Input for GREEN Channel
Analog Input for BLUE Channel
High-impedance inputs that accept the RED,
GREEN, and BLUE channel graphics signals,
respectively. For RGB, the three channels
identical and can be used for any colors, but
colors are assigned for convenient reference.
For proper 4:2:2 formatting in a YUV
application, the Y channel must be connected
the G
B
R
input, U must be connected to the
AIN
input, and V must be connected to the
AIN
input.
AIN
They accommodate input signals ranging
from 0.5 V to 1.0 V full scale. Signals should
be ac-coupled to these pins to support clamp
operation.
HSYNC Horizontal Sync Input
This input receives a logic signal that establishes the horizontal timing reference and
provides the frequency reference for pixel
clock generation.
The logic sense of this pin is controlled by
serial register 0Fh Bit 7 (HSYNC Polarity).
Only the leading edge of HSYNC is active,
the trailing edge is ignored. When HSYNC
REV. 0
to
are
Polarity = 0, the falling edge of HSYNC is
used. When HSYNC Polarity = 1, the rising
edge is active.
The input includes a Schmitt trigger for noise
immunity, with a nominal input threshold
of 1.5 V.
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) protection
diodes will conduct heavily if this pin is driven
more than 0.5 V above the maximum tolerance voltage (3.3 V), or more than 0.5 V
below ground.
VSYNC Vertical Sync Input
This is the input for vertical sync.
SOGIN Sync-on-Green Input
This input is provided to assist with processing
signals with embedded sync, typically on the
GREEN channel. The pin is connected to a
high-speed comparator with an internally
generated threshold, which is set to 0.15 V
above the negative peak of the input signal.
When connected to an ac-coupled graphics
signal with embedded sync, it will produce a
noninverting digital output on SOGOUT.
When not used, this input should be left
unconnected. For more details on this function and how it should be configured, refer to
the Sync-on-Green section.
–11–

AD9887A
CLAMP External Clamp Input (Optional)
This logic input may be used to define the
time during which the input signal is clamped
to the reference dc level (ground for RGB or
midscale for YUV). It should be exercised
when the reference dc level is known to be
present on the analog input channels, typically
during the back porch of the graphics signal.
The CLAMP pin is enabled by setting con-
bit EXTCLMP to 1, (the default power-up
trol
is 0).
When disabled, this pin is ignored and
the clamp timing is determined internally by
counting a delay and duration from the trailing
edge of the HSYNC input. The logic sense of
this pin is controlled by CLAMPOL. When
not used, this pin must be grounded and
EXTCLMP programmed to 0.
COAST Clock Generator Coast Input (Optional)
This input may be used to cause the pixel clock
generator to stop synchronizing with HSYNC
and continue producing a clock at its current
frequency and phase. This is useful when
processing signals from sources that fail to
produce horizontal sync pulses when in the
vertical interval. The COAST signal is generally
not required for PC-generated signals. Applications requiring COAST can do so through
the internal COAST found in the SYNC
processing engine.
The logic sense of this pin is controlled by
COAST Polarity.
When not used, this pin may be grounded and
COAST Polarity programmed to 1, or tied
HIGH and COAST Polarity programmed to 0.
COAST Polarity defaults to 1 at power-up.
CKEXT External Clock Input (Optional)
This pin may be used to provide an external
clock to the AD9887A, in place of the clock
internally generated from HSYNC.
It is enabled by programming EXTCLK to 1.
When an external clock is used, all other internal
functions operate normally. When unused,
this pin should be tied to V
and EXTCLK programmed to 0. The clock
phase adjustment still operates when an external
clock source is used.
CKINV Sampling Clock Inversion (Optional)
This pin may be used to invert the pixel
sampling clock, which has the effect of
shifting the sampling phase 180°. This is in
support of Alternate Pixel Sampling mode,
wherein higher frequency input signals (up
to 340 Mpps) may be captured by first sampling the odd pixels, then capturing the even
pixels on the subsequent frame.
or to GROUND,
DD
This pin should be exercised only during blanking intervals (typically vertical blanking) as it
may produce several samples of corrupted data
during the phase shift.
CKINV should be grounded when not used.
Either or both signals may be used, depending
on the timing mode and interface design
employed.
HSOUT Horizontal Sync Output
A reconstructed and phase-aligned version of
the Hsync input. Both the polarity and duration
of this output can be programmed via serial
bus registers.
By maintaining alignment with DATACK,
DATACK, and Data, data timing with
respect to horizontal sync can always be
determined.
SOGOUT Sync-On-Green Slicer Output
This pin can be programmed to output
either the output from the Sync-On-Green
slicer comparator or an unprocessed but
delayed version of the HSYNC input. See
the Sync Block Diagram to view how this
pin is connected.
The output from this pin is the Composite
Sync without additional processing from the
AD9887A.
REFOUT Internal Reference Output
Output from the internal 1.25 V band gap reference. This output is intended to drive relatively
light loads. It can drive the AD9887A reference
input directly but should be externally buffered
if it is used to drive other loads as well.
The absolute accuracy of this output is ±4%,
and the temperature coefficient is ±50 ppm,
which is adequate for most AD9887A applications. If higher accuracy is required, an
external reference may be employed instead.
If an external reference is used, connect this
pin to ground through a 0.1 µF capacitor.
REFIN Reference Input
The reference input accepts the master reference voltage for all AD9887A internal circuitry
(1.25 V ±10%). It may be driven directly by the
REFOUT pin. Its high impedance presents a
very light load to the reference source.
This pin should always be bypassed to Ground
with a 0.1 µF capacitor.
FILT External Filter Connection
For proper operation, the pixel clock generator
PLL requires an external filter. Connect the
filter shown in Figure 7 to this pin. For optimal
performance, minimize noise and parasitics
on this node.
REV. 0–12–

AD9887A
Outputs
RED A Data Output, Red Channel, Port A/EVEN
RED B Data Output, Red Channel, Port B/ODD
GREEN A Data Output, Green Channel, Port A/EVEN
GREEN B Data Output, Green Channel, Port B/ODD
BLUE A Data Output, Blue Channel, Port A/EVEN
BLUE B Data Output, Blue Channel, Port B/ODD
These are the main data outputs. Bit 7 is the MSB.
Each channel has two ports. When the part is
operated in single-channel mode (DEMUX = 0),
all data are presented to Port A, and Port B is
placed in a high impedance state.
Programming DEMUX to 1 established dualchannel mode, wherein alternate pixels are
presented to Port A and Port B of each channel.
These will appear simultaneously, two pixels
presented at the time of every second input
pixel, when PAR is set to 1 (parallel mode).
When PAR = 0, pixel data appear alternately
on the two ports, one new sample with each
incoming pixel (interleaved mode).
In dual-channel mode, the first pixel after
HSYNC is routed to Port A. The second pixel
goes to Port B, the third to A, etc.
The delay from pixel sampling time to output is
fixed. When the sampling time is changed by
adjusting the PHASE register, the output timing is
shifted as well. The DATACK, DATACK, and
HSOUT outputs are also moved, so the timing
relationship among the signals is maintained.
DATACK Data Output Clock
DATACK Data Output Clock Complement
Differential data clock output signals to be
used to strobe the output data and HSOUT
into external logic.
They are produced by the internal clock generator and are synchronous with the internal
pixel sampling clock.
When the AD9887A is operated in singlechannel mode, the output frequency is equal
to the pixel sampling frequency. When operating
in dual-channel mode, the clock frequency is
one-half the pixel frequency.
When the sampling time is changed by adjusting
the PHASE register, the output timing is
as well. The Data, DATACK,
DATACK, and
shifted
HSOUT outputs are all moved, so the timing
relationship among the signals is maintained.
Power Supply
V
D
Main Power Supply
These pins supply power to the main elements
to be
of the circuit. It should be filtered
quiet
as possible.
V
DD
Digital Output Power Supply
as
These supply pins are identified separately
from the V
pins so special care can be taken
D
to minimize output noise transferred into the
sensitive analog circuitry.
If the AD9887A is interfacing with lowervoltage logic, V
may be connected to a lower
DD
supply voltage (as low as 2.2 V) for compatibility.
PV
D
Clock Generator Power Supply
The most sensitive portion of the AD9887A
is the clock generation circuitry. These pins
provide power to the clock PLL and help the
user design for optimal performance. The
designer should provide noise-free power to
these pins.
GND Ground
The ground return for all circuitry on-chip. It is
recommended that the application circuit
board have a single, solid ground plane.
THEORY OF OPERATION (INTERFACE DETECTION)
Active Interface Detection and Selection
The AD9887A includes circuitry to detect whether an interface
is active (see Table III).
For detecting the analog interface, the circuitry monitors the
presence of HSYNC, VSYNC, and Sync-on-Green. The result of
the detection circuitry can be read from the 2-wire serial interface
bus at Address 11H Bits 7, 6, and 5, respectively. If one of these
sync signals disappears, the maximum time it takes for the
circuitry to detect it is 100 ms.
There are two stages for detecting the digital interface. The first
stage searches for the presence of the digital interface clock. The
circuitry for detecting the digital interface clock is active even
when the digital interface is powered down. The result of this
detection stage can be read from the 2-wire serial interface bus at
Address 11H Bit 4. If the clock disappears, the maximum time it
takes for the circuitry to detect it is 100 ms. Once a digital interface clock is detected, the digital interface is powered up and the
second stage of detection begins. During the second stage, the
circuitry searches for 32 consecutive DEs. Once 32 DEs are
found, the detection process is complete.
There is an override for the automatic interface selection. It is
the AIO bit (active interface override). When the AIO bit is set
to Logic 0, the automatic circuitry will be used. When the AIO
bit is set to Logic 1, the AIS bit will be used to determine the
active interface rather than the automatic circuitry.
REV. 0
–13–
AD9887A
Power Management
The AD9887A is a dual interface device with shared outputs.
Only one interface can be used at a time. For this reason, the
chip automatically powers down the unused interface. When
the analog interface is being used, most of the digital interface
circuitry is powered down and vice versa. This helps to minimize the
AD9887A total power dissipation. In addition, if neither interface
has activity on it, the chip powers down both interfaces.
The AD9887A uses the activity detect circuits, the active interface
bits in the serial registers, the active interface override bits, and the
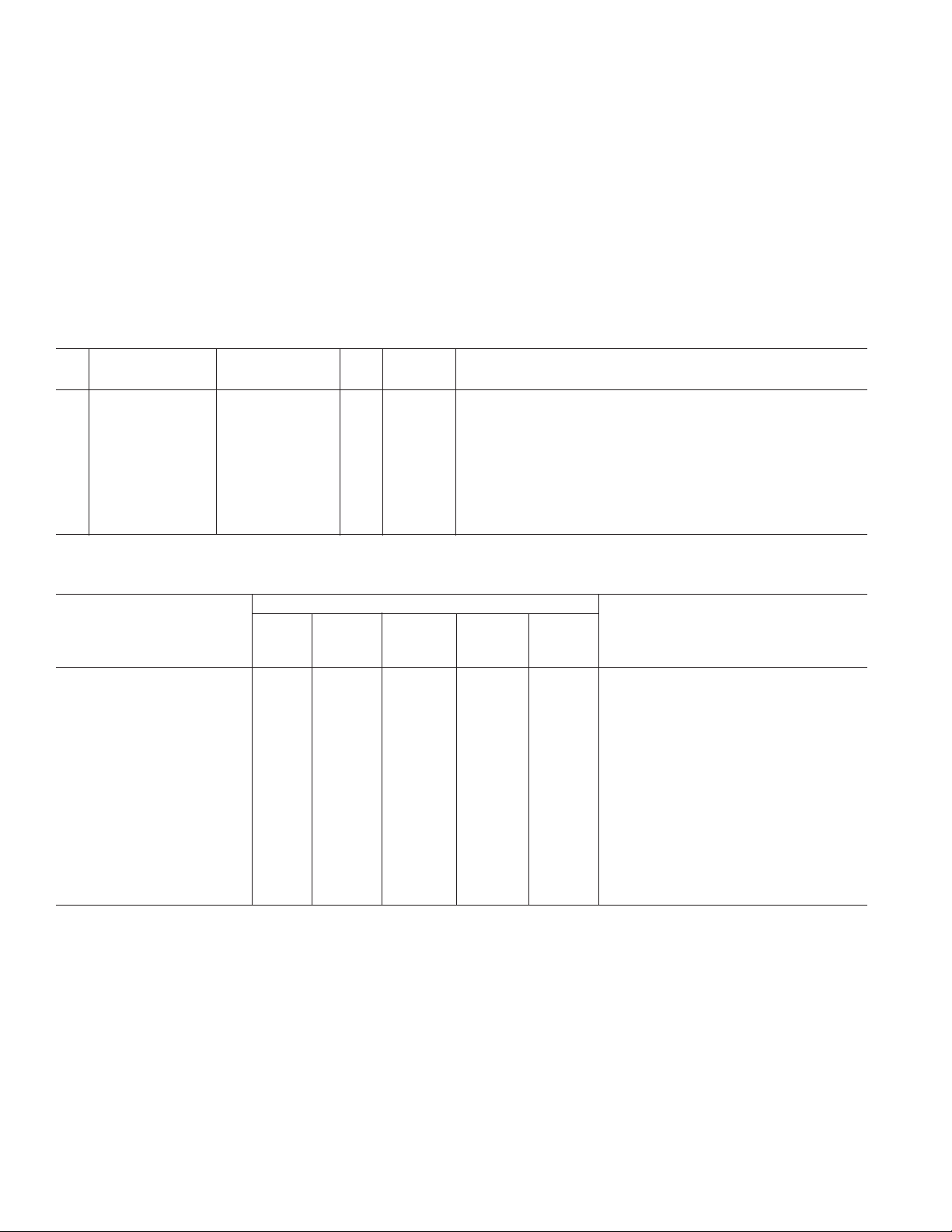
Table III. Interface Selection Controls
power-down bit to determine the correct power state. In a given
power mode not all circuitry in the inactive interface is powered
down completely. When the digital interface is active, the band
gap reference and HSYNC detect circuitry is not powered down.
When the analog interface is active, the digital interface clock
detect circuit is not powered down. Table IV summarizes how
the AD9887A determines which power mode to be in and what
circuitry is powered on/off in each of these modes. The powerdown command has priority, followed by the active interface
override, and then the automatic circuitry.
Analog Digital Active
AIO Interface Detect Interface Detect AIS Interface Description
1 XX0Analog Force the analog interface active.
1Digital Force the digital interface active.
0 00XNone Neither interface was detected. Both interfaces are
powered down and the SyncDT pin gets set to Logic 0.
01XDigital The digital interface was detected. Power down the analog interface.
10XAnalog The analog interface was detected. Power down the digital interface.
10XAnalog Both interfaces were detected. The analog interface has priority.
1Digital Both interfaces were detected. The digital interface has priority.
Table IV. Power-Down Mode Descriptions
Inputs
Analog Digital Active Active
Power- Interface Interface Interface Interface
Mode Down1Detect2Detect3Override Select Powered On or Comments
Soft Power-Down (Seek Mode) 1 0 0 0 X Serial Bus, Digital Interface Clock Detect,
Analog Interface Activity Detect, SOG,
Band Gap Reference
Digital Interface On 1 0 1 0 X Serial Bus, Digital Interface, Analog Interface
Activity Detect, SOG, Outputs, Band Gap
Reference
Analog Interface On 1 1 0 0 X Serial Bus, Analog Interface, Digital Interface
Clock Detect, SOG, Outputs, Band Gap
Reference
Serial Bus Arbitrated Interface 1 1 1 0 0 Same as Analog Interface On Mode
Serial Bus Arbitrated Interface 1 1 1 0 1 Same as Digital Interface On Mode
Override to Analog Interface 1 X X 1 0 Same as Analog Interface On Mode
Override to Digital Interface 1 X X 1 1 Same as Digital Interface On Mode
Absolute Power-Down 0 X X X X Serial Bus
NOTES
1
Power-down is controlled via bit 0 in serial bus Register 12h.
2
Analog Interface Detect is determined by OR-ing Bits 7, 6, and 5 in serial bus Register 11h.
3
Digital Interface Detect is determined by Bit 4 in serial bus Register 11h.
REV. 0–14–
 Loading...
Loading...