Analog Devices AD9235 c Datasheet
12-Bit, 20/40/65 MSPS
FEATURES
Single 3 V supply operation (2.7 V to 3.6 V)
SNR = 70 dBc to Nyquist at 65 MSPS
SFDR = 85 dBc to Nyquist at 65 MSPS
Low power: 300 mW at 65 MSPS
Differential input with 500 MHz bandwidth
On-chip reference and SHA
DNL = ±0.4 LSB
Flexible analog input: 1 V p-p to 2 V p-p range
Offset binary or twos complement data format
Clock duty cycle stabilizer
APPLICATIONS
Ultrasound equipment
IF sampling in communications receivers
IS-95, CDMA-One, IMT-2000
Battery-powered instruments
Hand-held scopemeters
Low cost digital oscilloscopes
VIN+
VIN–
REFT
REFB
VREF
SENSE
3 V A/D Converter
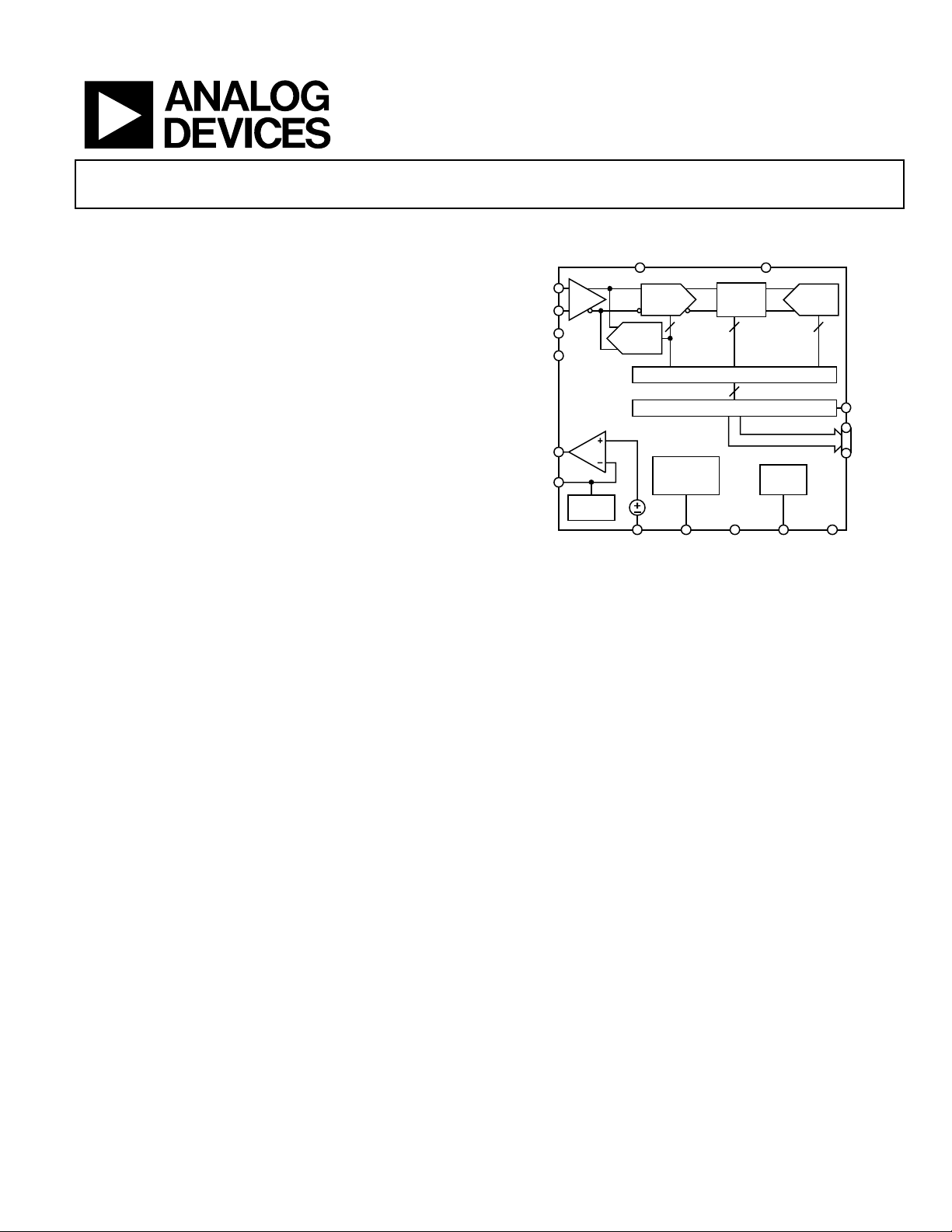
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
DRVDD
8-STAGE
1 1/2-BIT
PIPELINE
12
MODE
SELECT
SHA
REF
SELECT
AVDD
A/D
AGND
MDAC1
4 16
CORRECTION LOGIC
OUTPUT BUFFERS
AD9235
CLOCK
DUTY CYCLE
STABILIZER
0.5V
CLK PDWN MODE
Figure 1.
AD9235
A/D
3
OTR
D11
D0
DGND
02461-001
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9235 is a family of monolithic, single 3 V supply, 12-bit,
20/40/65 MSPS analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). This
family features a high performance sample-and-hold amplifier
(SHA) and voltage reference. The AD9235 uses a multistage
differential pipelined architecture with output error correction
logic to provide 12-bit accuracy at 20/40/65 MSPS data rates
and guarantee no missing codes over the full operating
temperature range.
The wide bandwidth, truly differential SHA allows a variety of
user-selectable input ranges and offsets including single-ended
applications. It is suitable for multiplexed systems that switch
full-scale voltage levels in successive channels and for sampling
single-channel inputs at frequencies well beyond the Nyquist
rate. Combined with power and cost savings over previously
available ADCs, the AD9235 is suitable for applications in
communications, imaging, and medical ultrasound.
A single-ended clock input is used to control all internal
conversion cycles. A duty cycle stabilizer (DCS) compensates
for wide variations in the clock duty cycle while maintaining
excellent overall ADC performance. The digital output data is
presented in straight binary or twos complement formats. An
out-of-range (OTR) signal indicates an overflow condition that
Rev. C
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable.
However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any
infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that may result from its use.
Specifications subject to change without notice. No license is granted by implication
or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
can be used with the most significant bit to determine low or
high overflow.
Fabricated on an advanced CMOS process, the AD9235 is available in a 28-lead TSSOP and a 32-lead LFCSP and is specified
over the industrial temperature range (–40°C to +85°C).
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. The AD9235 operates from a single 3 V power supply and
features a separate digital output driver supply to accommodate 2.5 V and 3.3 V logic families.
2. Operating at 65 MSPS, the AD9235 consumes a low 300 mW.
3. The patented SHA input maintains excellent performance for
input frequencies up to 100 MHz and can be configured for
single-ended or differential operation.
4. The AD9235 pinout is similar to the AD9214-65, a 10-bit,
65 MSPS ADC. This allows a simplified upgrade path from
10 bits to 12 bits for 65 MSPS systems.
5. The clock DCS maintains overall ADC performance over a
wide range of clock pulse widths.
6. The OTR output bit indicates when the signal is beyond the
selected input range.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700
Fax: 781.326.8703 © 2004 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.analog.com

AD9235
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Specifications..................................................................................... 3
Applying the AD9235 .................................................................... 15
DC Specifications ......................................................................... 3
Digital Specifications ................................................................... 4
Switching Specifications .............................................................. 4
AC Specifications.......................................................................... 5
Absolute Maximum Ratings............................................................ 7
Explanation of Test Levels........................................................... 7
ESD Caution.................................................................................. 7
Pin Configurations and Function Descriptions ........................... 8
Definitions of Specifications........................................................... 9
Equivalent Circuits......................................................................... 10
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 11
REVISION HISTORY
10/04—Data Sheet changed from Rev. B to Rev. C
Changes to Format ............................................................. Universal
Changes to Specifications.................................................................3
Changes to the Ordering Guide.................................................... 37
5/03—Data Sheet changed from Rev. A to Rev. B
Added CP-32 Package (LFCSP)........................................Universal
Changes to Several Pin Names .........................................Universal
Changes to Features...........................................................................1
Changes to Product Description .....................................................1
Changes to Product Highlights........................................................1
Changes to Specifications.................................................................2
Replaced Figure 1 ..............................................................................3
Changes to Absolute Maximum Ratings........................................5
Changes to Ordering Guide.............................................................5
Changes to Pin Function Descriptions...........................................6
New Definitions of Specifications Section .....................................7
Changes to TPCs 1 to 12...................................................................9
Changes to Theory of Operation Section.................................... 13
Theory of Operation.................................................................. 15
Analog Input............................................................................... 15
Clock Input Considerations...................................................... 16
Power Dissipation and Standby Mode .................................... 17
Digital Outputs ........................................................................... 18
Volt a ge R e fe r e nc e ....................................................................... 18
Operational Mode Selection ..................................................... 19
TSSOP Evaluation Board .......................................................... 19
LFCSP Evaluation Board........................................................... 20
Outline Dimensions....................................................................... 36
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 37
Changes to Analog Input Section..................................................13
Changes to Single-ended Input Configuration Section .............14
Replaced Figure 8 ............................................................................14
Changes to Clock Input Considerations Section ........................14
Changes to Table I ...........................................................................15
Changes to Power Dissipation and Standby Mode Section .......15
Changes to Digital Outputs Section..............................................15
Changes to Timing Section............................................................15
Changes to Figure 13.......................................................................16
Changes to Figures 16 to 26...........................................................17
Added LFCSP Evaluation Board Section .....................................17
Inserted Figures 27 to 35 ................................................................25
Added Table III................................................................................30
Updated Outline Dimensions........................................................31
8/02—Data Sheet changed from Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Updated RU-28 Package................................................................ 24
Rev. C | Page 2 of 40
AD9235
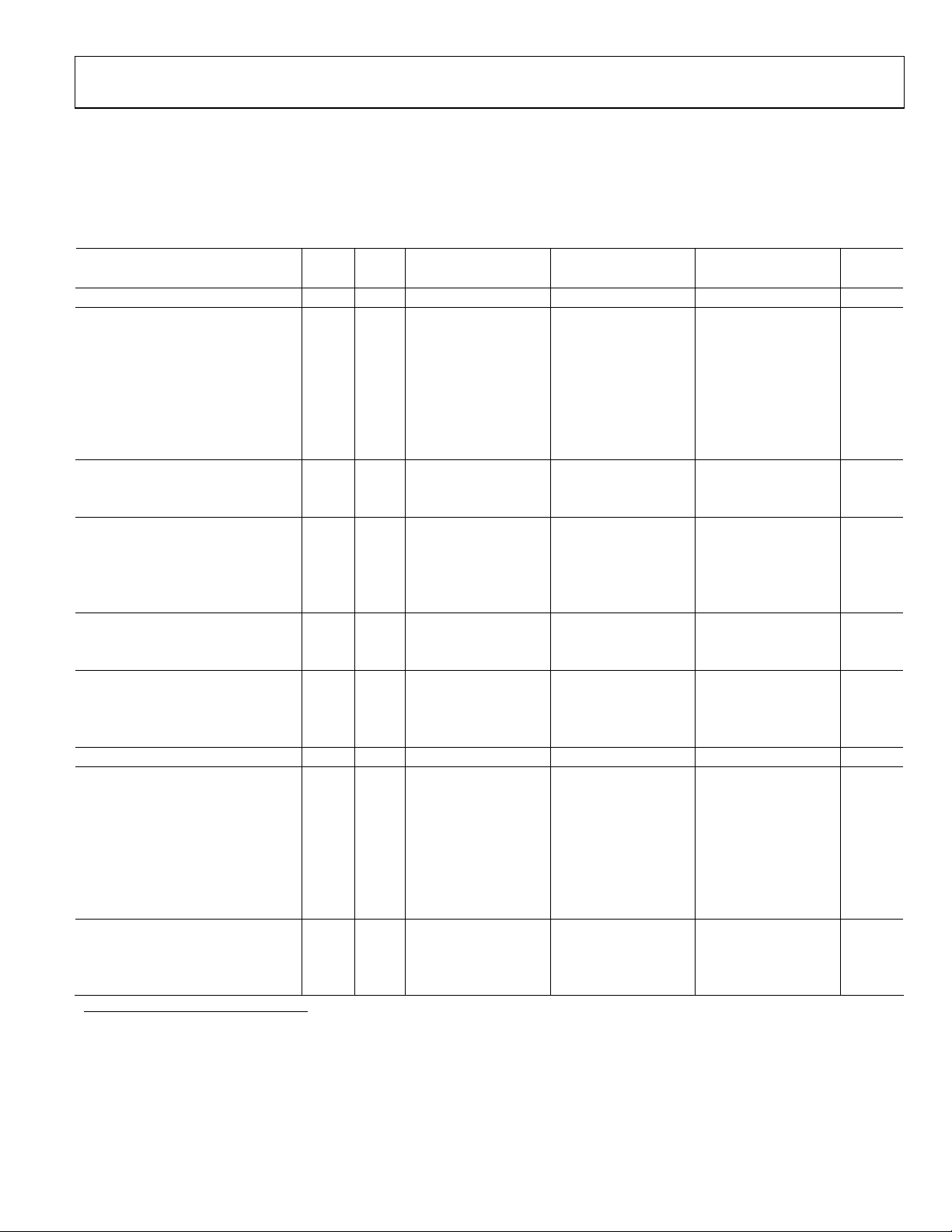
SPECIFICATIONS
DC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 3 V, DRVDD = 2.5 V, maximum sample rate, 2 V p-p differential input, 1.0 V internal reference, T
unless otherwise noted.
Table 1.
Test
Parameter Temp
Level
AD9235BRU/BCP-20 AD9235BRU/BCP-40 AD9235BRU/BCP-65
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
RESOLUTION Full VI 12 12 12 Bits
ACCURACY
No Missing Codes Guaranteed Full VI 12 12 12 Bits
Offset Error Full VI ±0.30 ±1.20 ±0.50 ±1.20 ±0.50 ±1.20 % FSR
Gain Error
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
1
Full VI ±0.30 ±2.40 ±0.50 ±2.50 ±0.50 ±2.60 % FSR
2
Full IV ±0.35 ±0.65 ±0.35 ±0.75 ±0.40 ±0.80 LSB
25°C I ±0.35 ±0.35 ±0.35 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)2 Full IV ±0.45 ±0.80 ±0.50 ±0.90 ±0.70 ±1.30 LSB
25°C I ±0.40 ±0.40 ±0.45 LSB
TEMPERATURE DRIFT
Offset Error Full V ±2 ±2 ±3 ppm/°C
Gain Error Full V ±12 ±12 ±12 ppm/°C
INTERNAL VOLTAGE REFERENCE
Output Voltage Error (1 V Mode) Full VI ±5 ±35 ±5 ±35 ±5 ±35 mV
Load Regulation @ 1.0 mA Full V 0.8 0.8 0.8 mV
Output Voltage Error (0.5 V Mode) Full V ±2.5 ±2.5 ±2.5 mV
Load Regulation @ 0.5 mA Full V 0.1 0.1 0.1 mV
INPUT REFERRED NOISE
VREF = 0.5 V 25°C V 0.54 0.54 0.54 LSB rms
VREF = 1.0 V 25°C V 0.27 0.27 0.27 LSB rms
ANALOG INPUT
Input Span, VREF = 0.5 V Full IV 1 1 1 V p-p
Input Span, VREF = 1.0 V Full IV 2 2 2 V p-p
Input Capacitance
3
Full V 7 7 7 pF
REFERENCE INPUT RESISTANCE Full V 7 7 7 kΩ
POWER SUPPLIES
Supply Voltages
AVDD Full IV 2.7 3.0 3.6 2.7 3.0 3.6 2.7 3.0 3.6 V
DRVDD Full IV 2.25 3.0 3.6 2.25 3.0 3.6 2.25 3.0 3.6 V
Supply Current
IAVDD2 Full V 30 55 100 mA
IDRVDD2 Full V 2 5 7 mA
PSRR Full V ±0.01 ±0.01 ±0.01 % FSR
POWER CONSUMPTION
DC Input
4
Full V 90 165 300 mW
Sine Wave Input2 Full VI 95 110 180 205 320 350 mW
Standby Power
5
Full V 1.0 1.0 1.0 mW
1
Gain error and gain temperature coefficient are based on the ADC only (with a fixed 1.0 V external reference).
2
Measured at maximum clock rate, fIN = 2.4 MHz, full-scale sine wave, with approximately 5 pF loading on each output bit.
3
Input capacitance refers to the effective capacitance between one differential input pin and AGND. Refer to for the equivalent analog input structure. Figure 5
4
Measured with dc input at maximum clock rate.
5
Standby power is measured with a dc input, the CLK pin inactive (i.e., set to AVDD or AGND).
MIN
to T
MAX
,
Unit
Rev. C | Page 3 of 40
AD9235
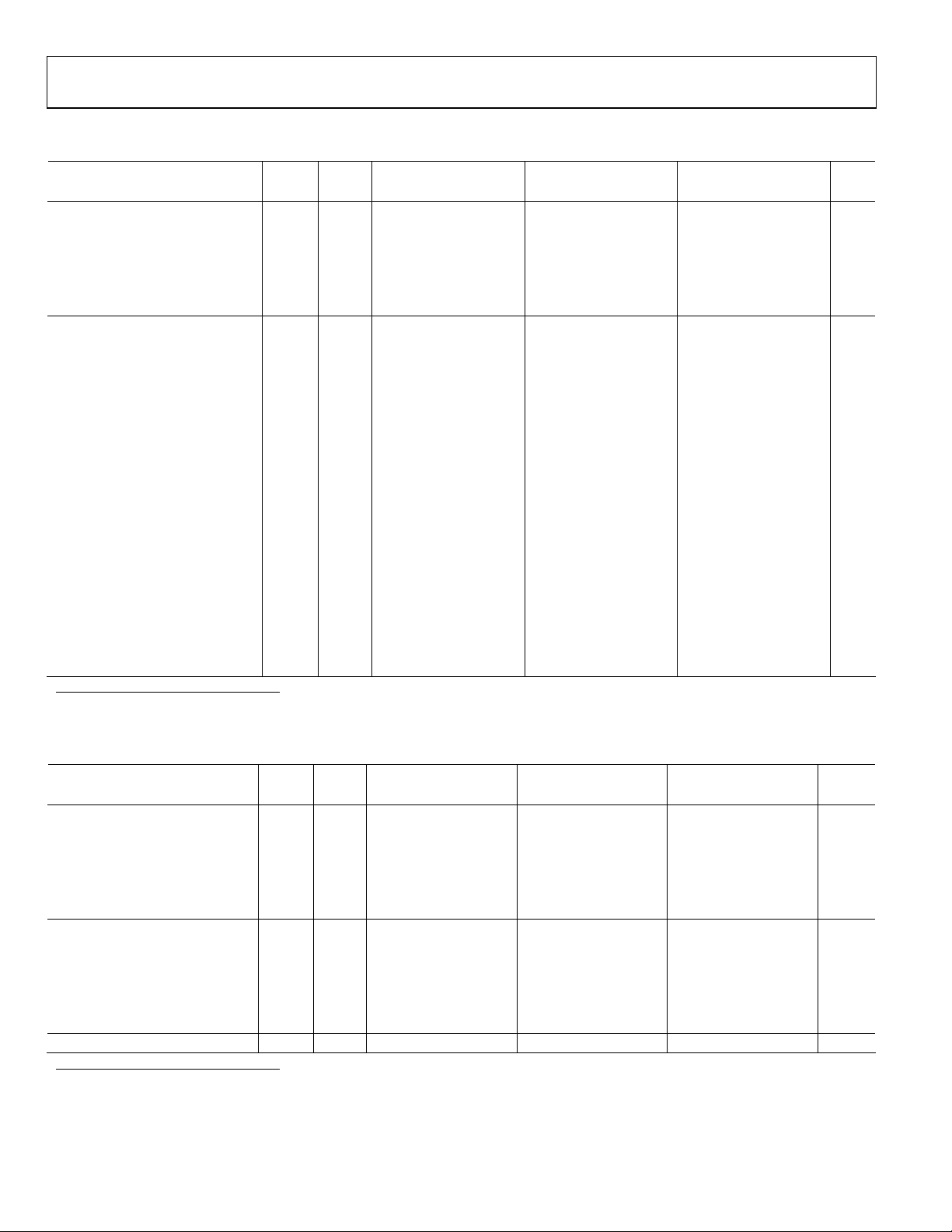
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
Table 2.
Test
Parameter Temp
Level
LOGIC INPUTS
High Level Input Voltage Full IV 2.0 2.0 2.0 V
Low Level Input Voltage Full IV 0.8 0.8 0.8 V
High Level Input Current Full IV –10 +10 –10 +10 –10 +10 µA
Low Level Input Current Full IV –10 +10 –10 +10 –10 +10 µA
Input Capacitance Full V 2 2 2 pF
LOGIC OUTPUTS
1
DRVDD = 3.3 V
High-Level Output Voltage Full IV 3.29 3.29 3.29 V
(IOH = 50 µA)
High-Level Output Voltage Full IV 3.25 3.25 3.25 V
(IOH = 0.5 mA)
Low-Level Output Voltage Full IV 0.2 0.2 0.2 V
(IOL = 1.6 mA)
Low-Level Output Voltage Full IV 0.05 0.05 0.05 V
(IOL = 50 µA)
DRVDD = 2.5 V
High-Level Output Voltage Full IV 2.49 2.49 2.49 V
(IOH = 50 µA)
High-Level Output Voltage Full IV 2.45 2.45 2.45 V
(IOH = 0.5 mA)
Low-Level Output Voltage Full IV 0.2 0.2 0.2 V
(IOL = 1.6 mA)
Low-Level Output Voltage Full IV 0.05 0.05 0.05 V
(IOL = 50 µA)
1
Output voltage levels measured with 5 pF load on each output.
SWITCHING SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.
Test
Parameter Temp
CLOCK INPUT PARAMETERS
Maximum Conversion Rate Full VI 20 40 65 MSPS
Minimum Conversion Rate Full V 1 1 1 MSPS
CLK Period Full V 50.0 25.0 15.4 ns
CLK Pulse-Width High
1
Full V 15.0 8.8 6.2 ns
CLK Pulse-Width Low1 Full V 15.0 8.8 6.2 ns
DATA OUTPUT PARAMETERS
Output Delay2 (tPD) Full V 3.5 3.5 3.5 ns
Pipeline Delay (Latency) Full V 7 7 7 Cycles
Aperture Delay (tA) Full V 1.0 1.0 1.0 ns
Aperture Uncertainty Jitter (tJ) Full V 0.5 0.5 0.5 ps rms
Wake-Up Time
3
Full V 3.0 3.0 3.0 ms
OUT-OF-RANGE RECOVERY TIME Full V 1 1 2 Cycles
1
For the AD9235-65 model only, with duty cycle stabilizer enabled. DCS function not applicable for -20 and -40 models.
2
Output delay is measured from CLK 50% transition to DATA 50% transition, with 5 pF load on each output.
3
Wake-up time is dependent on value of decoupling capacitors; typical values shown with 0.1 µF and 10 µF capacitors on REFT and REFB.
Level
AD9235BRU/BCP-20 AD9235BRU/BCP-40 AD9235BRU/BCP-65
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
AD9235BRU/BCP-20 AD9235BRU/BCP-40 AD9235BRU/BCP-65
Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max
Unit
Unit
Rev. C | Page 4 of 40
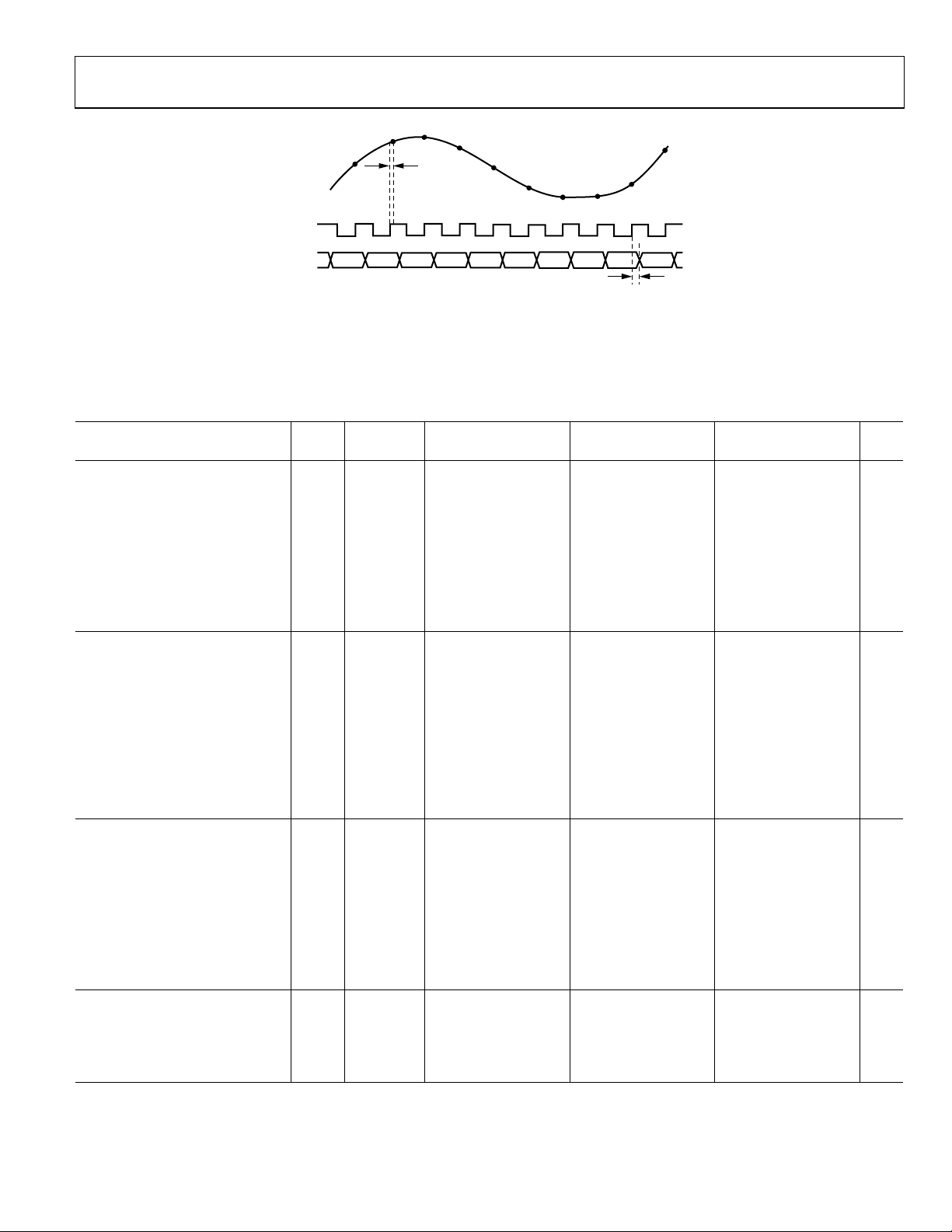
AD9235
A
G
NALO
INPUT
DATA
CLK
OUT
N–1
N–9 N–8 N–7 N–6 N–5 N–4 N–3 N–2 N–1 N
N+1
N
N+2
t
A
N+3
N+4
t
PD
N+6
N+5
= 6.0ns MAX
2.0ns MIN
N+7
N+8
02461-002
Figure 2. Timing Diagram
AC SPECIFICATIONS
AVDD = 3 V, DRVDD = 2.5 V, maximum sample rate, 2 V p-p differential input, AIN = –0.5 dBFS, 1.0 V internal reference, T
unless otherwise noted.
Table 4.
AD9235BRU/BCP-20 AD9235BRU/BCP-40 AD9235BRU/BCP-65
Parameter Temp Test Level Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO
f
= 2.4 MHz 25°C V 70.8 70.6 70.5 dBc
INPUT
f
= 9.7 MHz Full IV 70.0 70.4 dBc
INPUT
25°C I 70.6 dBc
f
= 19.6 MHz Full IV 69.9 70.3 dBc
INPUT
25°C I 70.4 dBc
f
= 32.5 MHz Full IV 68.7 69.7 dBc
INPUT
25°C I 70.1 dBc
f
= 100 MHz 25°C V 68.7 68.5 68.3 dBc
INPUT
SIGNAL-TO-NOISE RATIO
AND DISTORTION
f
= 2.4 MHz 25°C V 70.6 70.5 70.4 dBc
INPUT
f
= 9.7 MHz Full IV 69.9 70.3 dBc
INPUT
25°C I 70.5 dBc
f
= 19.6 MHz Full IV 69.7 70.2 dBc
INPUT
25°C I 70.3 dBc
f
= 32.5 MHz Full IV 68.3 69.5 dBc
INPUT
25°C I 69.9 dBc
f
= 100 MHz 25°C V 68.6 68.3 67.8 dBc
INPUT
TOTAL HARMONIC DISTORTION
f
= 2.4 MHz 25°C V –88.0 –89.0 –87.5 dBc
INPUT
f
= 9.7 MHz Full IV –86.0 –79.0 dBc
INPUT
25°C I –87.4 dBc
f
= 19.6 MHz Full IV –85.5 –79.0 dBc
INPUT
25°C I –86.0 dBc
f
= 32.5 MHz Full IV –81.8 –74.0 dBc
INPUT
25°C I –82.0 dBc
f
= 100 MHz 25°C V –84.0 –82.5 –78.0 dBc
INPUT
WORST HARMONIC
(SECOND OR THIRD)
f
= 9.7 MHz Full IV –90.0 –80.0 dBc
INPUT
f
= 19.6 MHz Full IV –90.0 –80.0 dBc
INPUT
f
= 32.5 MHz Full IV –83.5 –74.0 dBc
INPUT
MIN
to T
MAX
,
Rev. C | Page 5 of 40
AD9235
AD9235BRU/BCP-20 AD9235BRU/BCP-40 AD9235BRU/BCP-65
Parameter Temp Test Level Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Min Typ Max Unit
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE
f
= 2.4 MHz 25°C V 92.0 92.0 92.0 dBc
INPUT
f
= 9.7 MHz Full IV 80.0 88.5 dBc
INPUT
25°C I 91.0 dBc
f
= 19.6 MHz Full IV 80.0 89.0 dBc
INPUT
25°C I 90.0 dBc
f
= 32.5 MHz Full IV 74.0 83.0 dBc
INPUT
25°C I 85.0 dBc
f
= 100 MHz 25°C V 84.0 85.0 80.5 dBc
INPUT
Rev. C | Page 6 of 40
AD9235
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 5.
With
Pin Name
ELECTRICAL
AVDD AGND –0.3 +3.9 V
DRVDD DGND –0.3 +3.9 V
AGND DGND –0.3 +0.3 V
AVDD DRVDD –3.9 +3.9 V
Digital
Outputs
CLK, MODE AGND –0.3 AVDD + 0.3 V
VIN+, VIN– AGND –0.3 AVDD + 0.3 V
VREF AGND –0.3 AVDD + 0.3 V
SENSE AGND –0.3 AVDD + 0.3 V
REFB, REFT AGND –0.3 AVDD + 0.3 V
PDWN AGND –0.3 AVDD + 0.3 V
ENVIRONMENTAL
Operating Temperature –40 +85 °C
Junction Temperature 150 °C
Lead Temperature (10 sec) 300 °C
Storage Temperature –65 +150 °C
Respect to
DGND –0.3 DRVDD + 0.3 V
1
Min Max Unit
1
Typical thermal impedances (28-lead TSSOP), θJA = 67.7°C/W; (32-lead
LFCSP), θ
a 4-layer board in still air, in accordance with EIA/JESD51-1.
= 32.5°C/W, θJC = 32.71°C/W. These measurements were taken on
JA
Absolute maximum ratings are limiting values to be applied
individually and beyond which the serviceability of the circuit
may be impaired. Functional operability is not necessarily
implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating conditions for
an extended period of time may affect device reliability.
EXPLANATION OF TEST LEVELS
Test
Levels Description
I 100% production tested.
II
III Sample tested only.
IV
V Parameter is a typical value only.
VI
100% production tested at 25°C and sample tested at
specified temperatures.
Parameter is guaranteed by design and characterization testing.
100% production tested at 25°C; guaranteed by design and characterization testing for industrial temperature range; 100% production tested at temperature extremes for military devices.
ESD CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily accumulate
on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection. Although this product features
proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation
or loss of functionality.
Rev. C | Page 7 of 40
AD9235
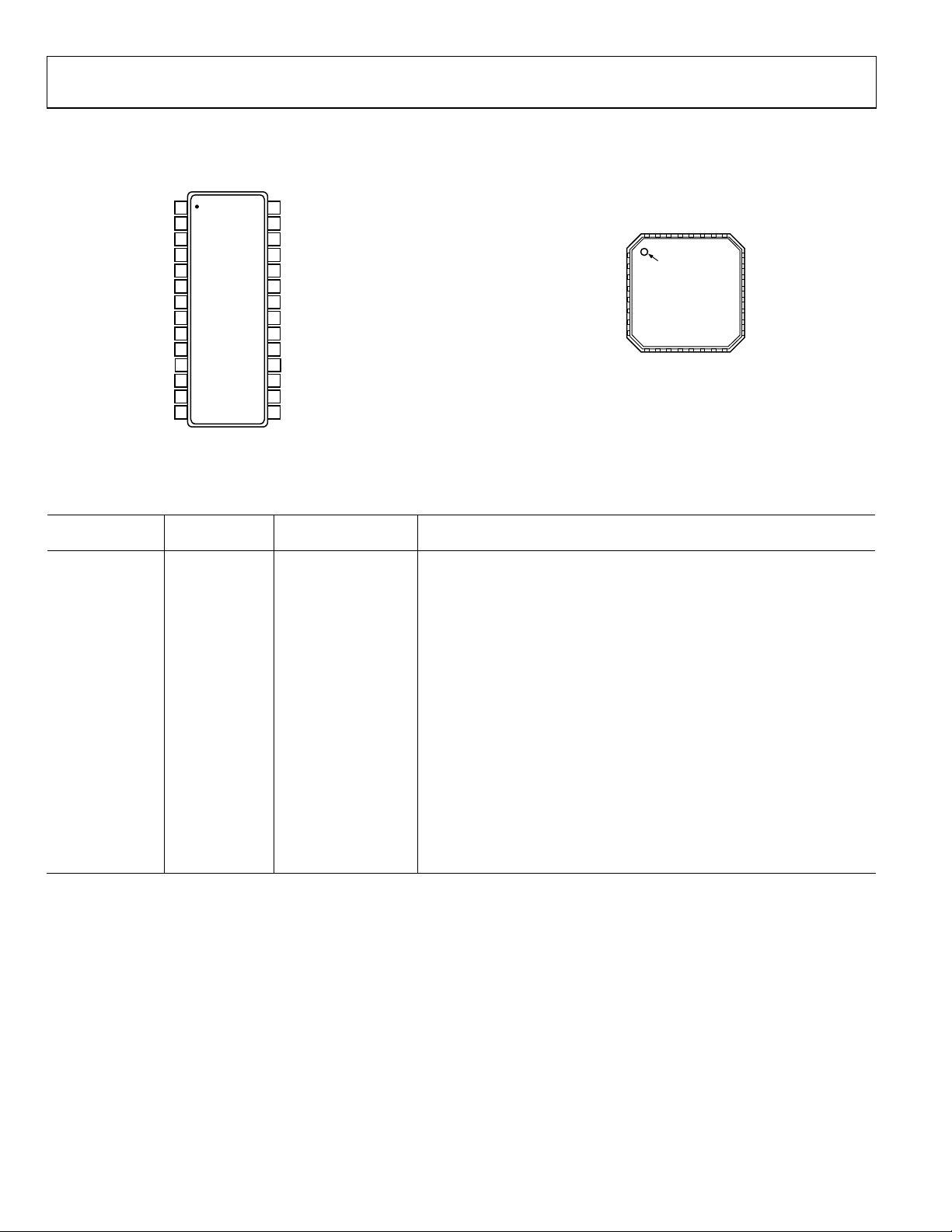
PIN CONFIGURATIONS AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
1
OTR
2
MODE
3
SENSE
4
VREF
5
REFB
REFT
AVDD
AGND
VIN+
VIN–
AGND
AVDD
CLK D1
PDWN
6
(Not to Scale)
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
AD9235
TOP VIEW
Figure 3. 28-Lead TSSOP Pin Configuration
28
D11 (MSB)
27
D10
26
D9
25
D8
24
DRVDD
23
DGND
22
D7
21
D6
20
D5
19
D4
18
D3
17
D2
16
15
D0 (LSB)
02461-003
AVDD
VIN+
VIN–
AGND
32
31302928272625
1
DNC
CLK
DNC
PDWN
DNC
DNC
(LSB)D0
D1
DNC = DO NOT CONNECT
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
PIN 1
INDICATOR
AD9235
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
9
101112
D5
D4
D3
D2
Figure 4. 32-Lead LFCSP Pin Configuration
AVDD
AGND
141516
13
D7
D6
REFB
REFT
DGND
DRVDD
VREF
24
23
SENSE
22
MODE
21
OTR
20
D11(MSB)
19
D10
18
D9
17
D8
02461-004
Table 6. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No.
28-Lead TSSOP
Pin No.
32-Lead LFCSP
Mnemonic Description
1 21 OTR Out-of-Range Indicator.
2 22 MODE Data Format and Clock Duty Cycle Stabilizer (DCS) Mode Selection.
3 23 SENSE Reference Mode Selection.
4 24 VREF Voltage Reference Input/Output.
5 25 REFB Differential Reference (−).
6 26 REFT Differential Reference (+).
7, 12 27, 32 AVDD Analog Power Supply.
8, 11 28, 31 AGND Analog Ground.
9 29 VIN+ Analog Input Pin (+).
10 30 VIN– Analog Input Pin (−).
13 2 CLK Clock Input Pin.
14 4 PDWN Power-Down Function Selection (Active High).
15 to 22, 25 to 28 7 to 14, 17 to 20 D0 (LSB) to D11 (MSB) Data Output Bits.
23 15 DGND Digital Output Ground.
24 16 DRVDD Digital Output Driver Supply. Must be decoupled to DGND with a minimum.
0.1 µF capacitor. Recommended decoupling is 0.1 µF in parallel with 10 µF.
1, 3, 5, 6 DNC Do Not Connect.
Rev. C | Page 8 of 40

AD9235
DEFINITIONS OF SPECIFICATIONS
Analog Bandwidth (Full Power Bandwidth)
The analog input frequency at which the spectral power of the
fundamental frequency (as determined by the FFT analysis) is
reduced by 3 dB.
Aperture Delay (t
)
A
The delay between the 50% point of the rising edge of the clock
and the instant at which the analog input is sampled.
Aperture Jitter (t
)
J
The sample-to-sample variation in aperture delay.
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
The deviation of each individual code from a line drawn from
negative full scale through positive full scale. The point used as
negative full scale occurs ½ LSB before the first code transition.
Positive full scale is defined as a level 1 ½ LSBs beyond the last
code transition. The deviation is measured from the middle of
each particular code to the true straight line.
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL, No Missing Codes)
An ideal ADC exhibits code transitions that are exactly 1 LSB
apart. DNL is the deviation from this ideal value. Guaranteed no
missing codes to 12-bit resolution indicates that all 4096 codes
must be present over all operating ranges.
Offset Error
The major carry transition should occur for an analog value
½ LSB below VIN+ = VIN–. Offset error is defined as the
deviation of the actual transition from that point.
Gain Error
The first code transition should occur at an analog value ½ LSB
above negative full scale. The last transition should occur at an
analog value 1 ½ LSB below the positive full scale. Gain error is
the deviation of the actual difference between first and last code
transitions and the ideal difference between first and last code
transitions.
Temperature Drift
The temperature drift for offset error and gain error specifies
the maximum change from the initial (25°C) value to the value
at T
MIN
or T
MAX
.
Power Supply Rejection Ratio
The change in full scale from the value with the supply
at the minimum limit to the value with the supply at its
maximum limit.
1
Total Harmonic Distortion (THD)
The ratio of the rms sum of the first six harmonic components
to the rms value of the measured input signal.
Signal-to-Noise and Distortion (SINAD)1
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set 0.5 dB below full
scale) to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist frequency, including harmonics but
excluding dc.
Effective Number of Bits (ENOB)
The ENOB for a device for sine wave inputs at a given input
frequency can be calculated directly from its measured SINAD
using the following formula
N = (SINAD − 1.76)/6.02
1
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
The ratio of the rms signal amplitude (set at 0.5 dB below full
scale) to the rms value of the sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist frequency, excluding the first six
harmonics and dc.
1
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
The difference in dB between the rms amplitude of the input
signal and the peak spurious signal.
1
Two -Ton e SFDR
The ratio of the rms value of either input tone to the rms value
of the peak spurious component. The peak spurious component
may or may not be an IMD product.
Clock Pulse Width and Duty Cycle
Pulse-width high is the minimum amount of time that the
clock pulse should be left in the Logic 1 state to achieve rated
performance. Pulse-width low is the minimum time the clock
pulse should be left in the low state. At a given clock rate, these
specifications define an acceptable clock duty cycle.
Minimum Conversion Rate
The clock rate at which the SNR of the lowest analog signal
frequency drops by no more than 3 dB below the
guaranteed limit.
Maximum Conversion Rate
The clock rate at which parametric testing is performed.
Output Propagation Delay (t
)
PD
The delay between the clock logic threshold and the time when
all bits are within valid logic levels.
Out-of-Range Recovery Time
The time it takes for the ADC to reacquire the analog input
after a transition from 10% above positive full scale to 10%
above negative full scale, or from 10% below negative full scale
to 10% below positive full scale.
1
AC specifications may be reported in dBc (degrades as signal levels are
lowered) or in dBFS (always related back to converter full scale).
Rev. C | Page 9 of 40
AD9235
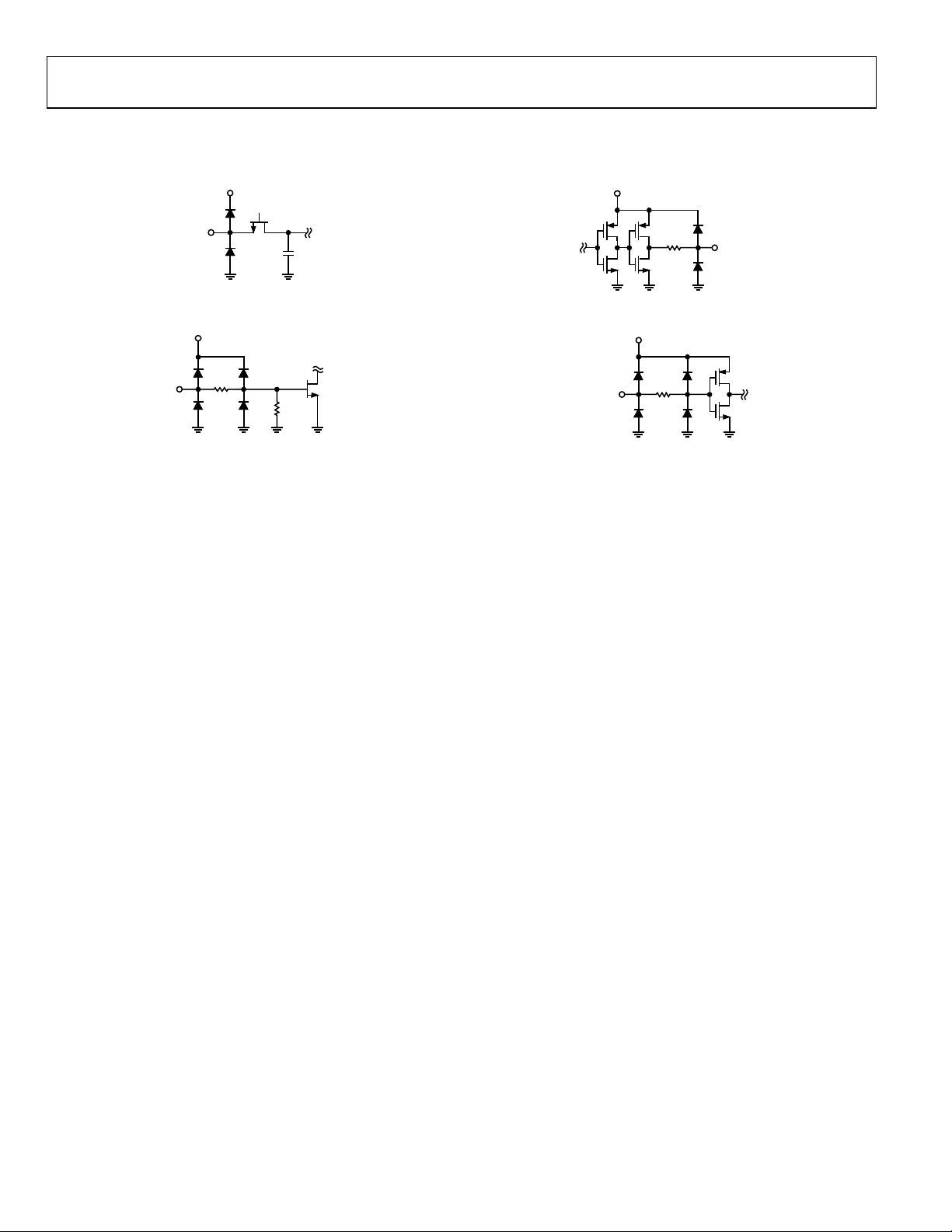
EQUIVALENT CIRCUITS
AVDD
DRVDD
VIN+, VIN–
02461-005
Figure 5. Equivalent Analog Input Circuit
AVDD
MODE
20kΩ
Figure 6. Equivalent MODE Input Circuit
02461-006
Figure 7. Equivalent Digital Output Circuit
AVDD
CLK,
PDWN
Figure 8. Equivalent Digital Input Circuit
D11–D0,
OTR
02461-007
02461-008
Rev. C | Page 10 of 40
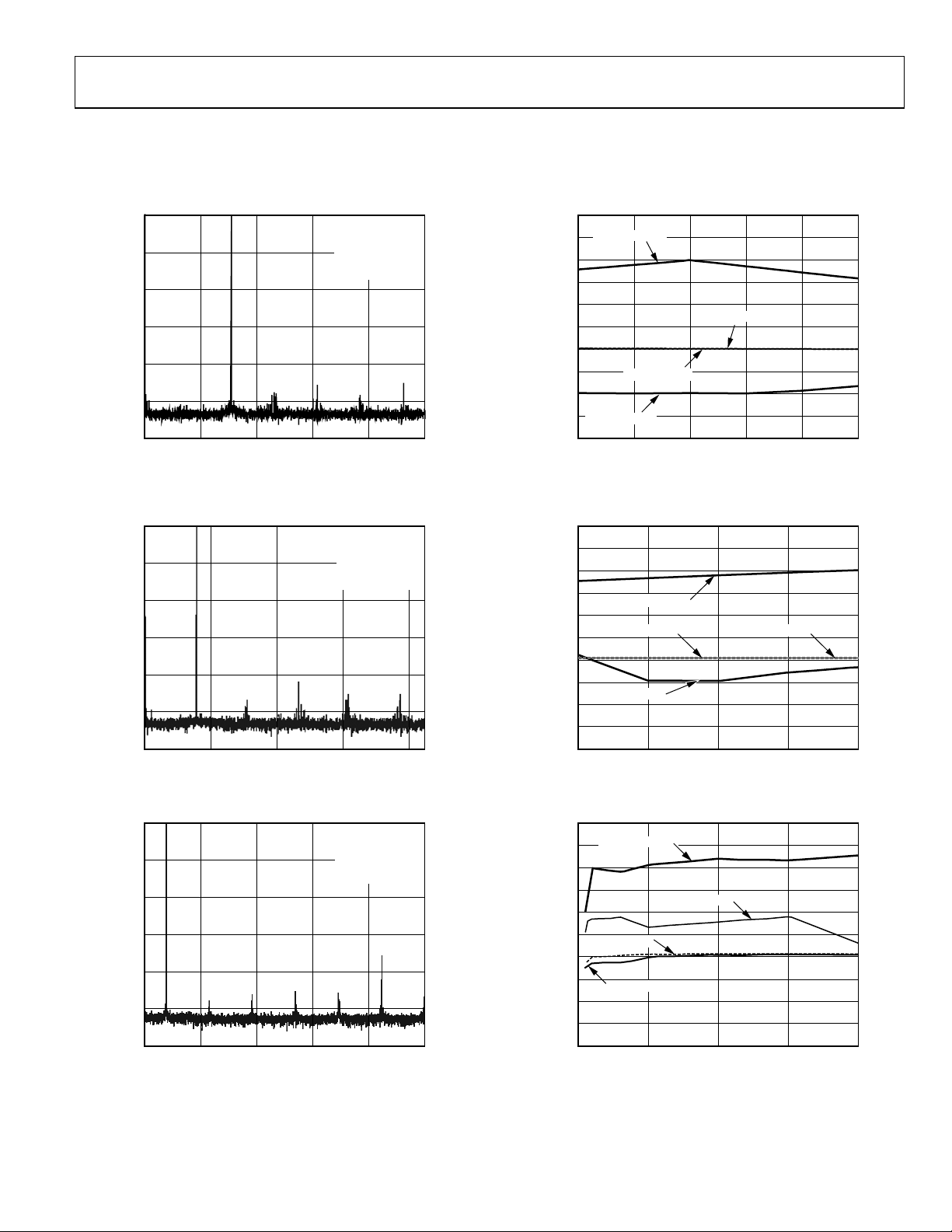
AD9235
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
AVDD = 3.0 V, DRVDD = 2.5 V, f
unless otherwise noted.
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
MAGNITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 9. Single Tone 8K FFT with f
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
MAGNITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 10. Single Tone 8K FFT with f
0
–20
–40
–60
–80
MAGNITUDE (dBFS)
–100
–120
FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 11. Single Tone 8K FFT with f
= 65 MSPS with DCS disabled, TA = 25°C, 2 V differential input, AIN = −0.5 dBFS, VREF = 1.0 V,
SAMPLE
SNR = 70.3dBc
SINAD = 70.2dBc
ENOB = 11.4 BITS
THD = –86.3dBc
SFDR = 89.9dBc
= 10 MHz
IN
SNR = 69.4dBc
SINAD = 69.1dBc
ENOB = 11.2 BITS
THD = –81.0dBc
SFDR = 83.8dBc
= 70 MHz
IN
SNR = 68.5dBc
SINAD = 66.5dBc
ENOB = 10.8 BITS
THD = –71.0dBc
SFDR = 71.2dBc
= 100 MHz
IN
32.50 6.5 13.0 19.5 26.0
02461-009
91.065.0 71.5 78.0 84.5
02461-010
130.097.5 104.0 110.5 117.0 123.5
02461-011
100
SFDR (2V DIFF)
95
90
85
SNR/SFDR (dBc)
80
75
70
65
60
55
50
SNR (2V DIFF)
SFDR (2V SE)
SAMPLE RATE (MSPS)
SNR (2V SE)
Figure 12. AD9235-65: Single Tone SNR/SFDR vs.
with fIN = Nyquist (32.5 MHz)
f
CLK
100
95
90
85
80
75
70
SNR/SFDR (dBc)
65
60
55
50
SFDR (2V DIFF)
SNR (2V SE)
SFDR (2V SE)
SNR (2V DIFF)
SAMPLE RATE (MSPS)
Figure 13. AD9235-40: Single Tone SNR/SFDR vs. f
100
SFDR (2V DIFF)
95
90
85
80
75
SNR (2V SE)
70
SNR/SFDR (dBc)
65
SNR (2V DIFF)
60
55
50
SFDR (2V SE)
SAMPLE RATE (MSPS)
Figure 14. AD9235-20: Single Tone SNR/SFDR vs. f
with fIN = Nyquist (20 MHz)
CLK
with fIN = Nyquist (10 MHz)
CLK
6540 45 50 55 60
02461-012
4020 25 30 35
02461-013
200 5 10 15
02461-014
Rev. C | Page 11 of 40
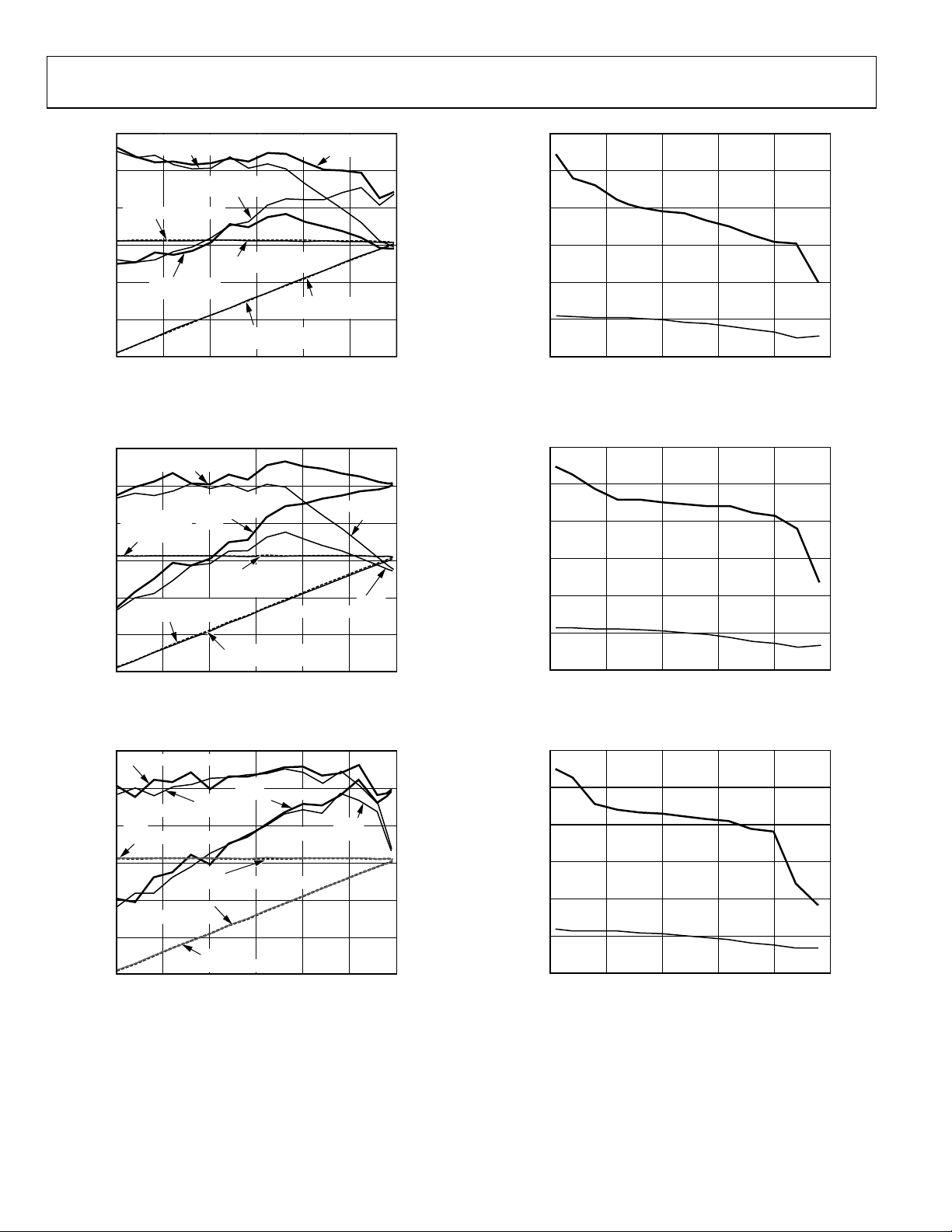
AD9235
100
90
80
SFDR
SINGLE-ENDED (dBFS)
SFDR
SNR
DIFFERENTIAL (dBFS)
DIFFERENTIAL (dBc)
SFDR
DIFFERENTIAL (dBFS)
95
90
SFDR
85
70
60
SNR/SFDR (dBFS and dBc)
50
40
SFDR
SINGLE-ENDED (dBc)
SNR
SINGLE-ENDED (dBFS)
SNR
DIFFERENTIAL (dBc)
AIN (dBFS)
Figure 15. AD9235-65: Single Tone SNR/SFDR vs.
with fIN = Nyquist (32.5 MHz)
A
IN
100
SFDR
DIFFERENTIAL (dBFS)
90
SFDR
DIFFERENTIAL
(dBc)
SNR
SINGLE-ENDED
(dBFS)
SNR
SINGLE-ENDED (dBc)
AIN (dBFS)
SINGLE-ENDED (dBc)
SNR/SFDR (dBFS and dBc)
SNR
80
DIFFERENTIAL
(dBFS)
70
60
SNR
DIFFERENTIAL (dBc)
50
40
Figure 16. AD9235-40: Single Tone SNR/SFDR vs. A
100
SFDR DIFFERENTIAL (dBFS)
90
SINGLE-ENDED (dBFS)
80
SNR
DIFFERENTIAL (dBFS)
70
60
DIFFERENTIAL(dBc)
SNR/SFDR (dBFS and dBc)
50
40
SFDR
DIFFERENTIAL (dBc)
SFDR
SINGLE-ENDED(dBc)
SNR
SINGLE-ENDED (dBFS)
SNR
SNR
SINGLE-ENDED (dBc)
AIN (dBFS)
Figure 17. AD9235-20: Single Tone SNR/SFDR vs. A
SNR
SINGLE-ENDED (dBc)
0–30 –25 –20 –15 –10 –5
SFDR
SINGLE-ENDED
(dBFS)
SFDR
0–30 –25 –20 –15 –10 –5
with fIN = Nyquist (20 MHz)
IN
SFDR
0–30 –25 –20 –15 –10 –5
with fIN = Nyquist (10 MHz)
IN
02461-015
02461-016
02461-017
80
75
SNR/SFDR (dBc)
70
65
95
90
85
80
75
SNR/SFDR (dBc)
70
65
95
90
85
80
75
SNR/SFDR (dBc)
70
65
SNR
INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 18. AD9235-65: SNR/SFDR vs. f
SFDR
SNR
INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 19. AD9235-40: SNR/SFDR vs. f
SFDR
SNR
INPUT FREQUENCY (MHz)
Figure 20. AD9235-20: SNR/SFDR vs. f
1250 25 50 75 100
02461-018
IN
1250 25 50 75 100
02461-019
IN
1250 25 50 75 100
02461-020
IN
Rev. C | Page 12 of 40
 Loading...
Loading...