Dual, 16-Bit, 1230 MSPS,
TxDAC+ Digital-to-Analog Converter
FEATURES
Flexible LVDS interface allows word, byte, or nibble load
Single-carrier W-CDMA ACLR = 82 dBc at 122.88 MHz IF
Analog output: adjustable 8.7 mA to 31.7 mA,
R
= 25 Ω to 50 Ω
L
Integrated 2×/4×/8× interpolator/complex modulator allows
carrier placement anywhere in the DAC bandwidth
Gain, dc offset, and phase adjustment for sideband
suppression
Multiple chip synchronization interfaces
High performance, low noise PLL clock multiplier
Digital inverse sinc filter
Low power: 1.5 W at 1.2 GSPS, 800 mW at 500 MSPS,
full operating conditions
72-lead, exposed paddle LFCSP
APPLICATIONS
Wireless infrastructure
W-CDMA, CDMA2000, TD-SCDMA, WiMAX, GSM, LTE
Digital high or low IF synthesis
Transmit diversity
Wideband communications: LMDS/MMDS, point-to-point
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD9122 is a dual, 16-bit, high dynamic range digital-toanalog converter (DAC) that provides a sample rate of 1230 MSPS,
permitting multicarrier generation up to the Nyquist frequency.
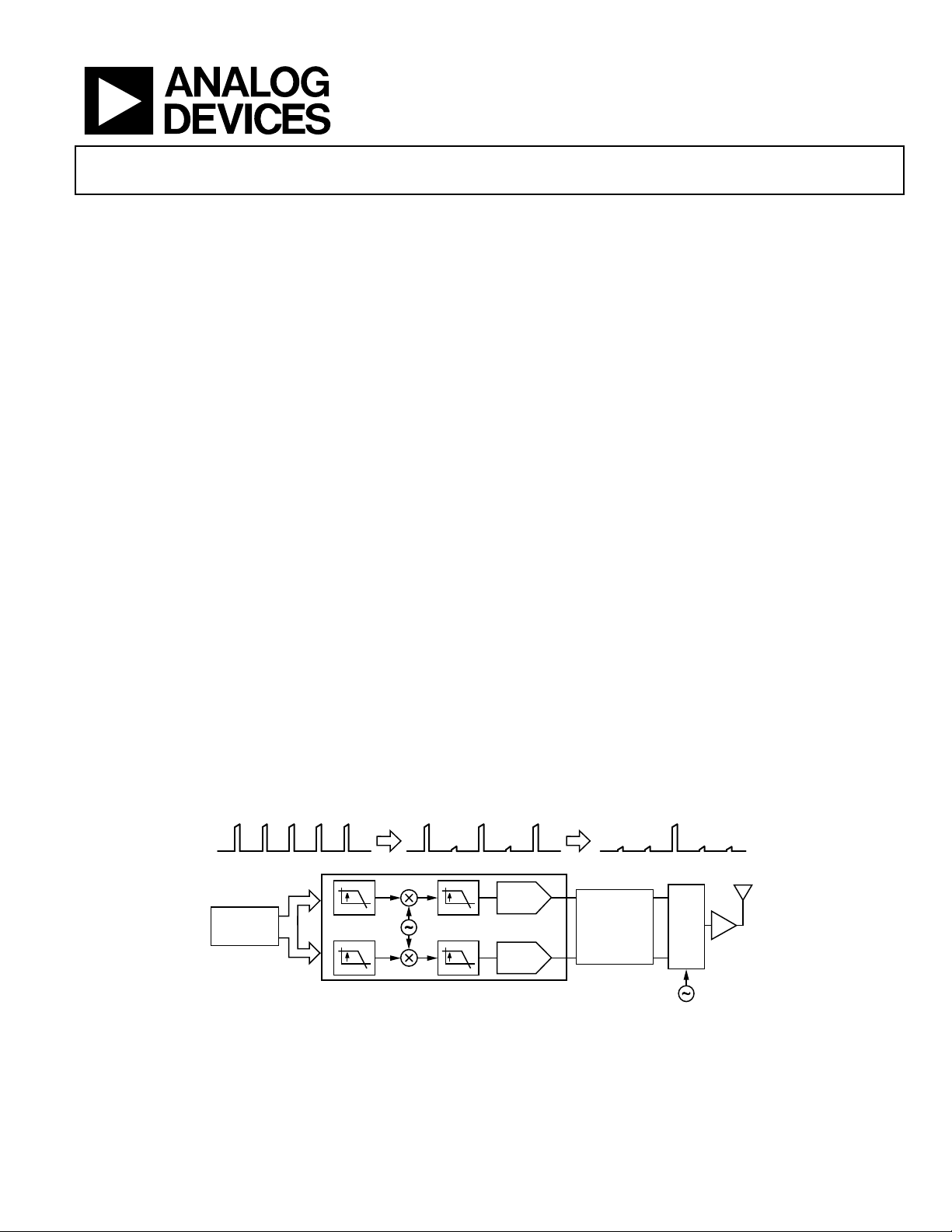
TYPICAL SIGNAL CHAIN
COMPLEX BAS EBAND
COMPL E X I F
AD9122
The AD9122 TxDAC+® includes features optimized for direct
conversion transmit applications, including complex digital modulation, and gain and offset compensation. The DAC outputs
are optimized to interface seamlessly with analog quadrature
modulators, such as the ADL537x F-MOD series from Analog
Devices, Inc. A 4-wire serial port interface provides for programming/readback of many internal parameters. Full-scale output
current can be programmed over a range of 8.7 mA to 31.7 mA.
The AD9122 comes in a 72-lead LFCSP.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. Ultralow noise and intermodulation distortion (IMD)
enable high quality synthesis of wideband signals from
baseband to high intermediate frequencies (IF).
2. Proprietary DAC output switching technique enhances
dynamic performance.
3. Current outputs are easily configured for various single-
ended or differential circuit topologies.
4. Flexible LVDS digital interface allows the standard 32-wire
bus to be reduced to one-half or one-quarter of the width.
COMPANION PRODUCTS
IQ Modulators: ADL5370, ADL537x family
IQ Modulators with PLL and VCO: ADRF6701, ADRF670x family
Clock Drivers: AD9516, AD951x family
Voltage Regulator Design Tool: ADIsimPower
Additional companion products on the AD9122 product page
RF
DC
2
DIGITAL
BASEBAND
PROCESSOR
NOTES
1. AQM = ANALOG QUADRATURE MODULATOR.
Rev. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, no
responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its use, nor for any infringements of patents or other
rights of third parties that may result from its use. Specifications subject to change without notice. No
license is granted by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
Trademarks and registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
SIN
COS
2
2/4
2/4
f
IF
I DAC
ANTIALIASING
FILTER
Q DAC
Figure 1.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781.329.4700 www.analog.com
Fax: 781.461.3113 ©2009–2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
LO – f
IF
AQM
LO
PA
08281-001

AD9122
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Features .............................................................................................. 1
Applications ....................................................................................... 1
General Description ......................................................................... 1
Product Highlights ........................................................................... 1
Companion Products ....................................................................... 1
Typical Signal Chain ......................................................................... 1
Revision History ............................................................................... 3
Functional Block Diagram .............................................................. 4
Specifications ..................................................................................... 5
DC Specifications ......................................................................... 5
Digital Specifications ................................................................... 6
Digital Input Data Timing Specifications ................................. 6
AC Specifications .......................................................................... 7
Absolute Maximum Ratings ............................................................ 8
Thermal Resistance ...................................................................... 8
ESD Caution .................................................................................. 8
Pin Configuration and Function Descriptions ............................. 9
Typical Performance Characteristics ........................................... 11
Terminolog y .................................................................................... 17
Differences Between AD9122R1 and AD9122R2 ...................... 18
Device Marking of AD9122R1 and AD9122R2 ..................... 18
Theory of Operation ...................................................................... 19
Serial Port Operation ................................................................. 19
Data Format ................................................................................ 19
Serial Port Pin Descriptions ...................................................... 19
Serial Port Options ..................................................................... 20
Device Configuration Register Map and Descriptions ......... 21
LVDS Input Data Ports .................................................................. 32
Word Interface Mode ................................................................. 32
Byte Interface Mode ................................................................... 32
Nibble Interface Mode ............................................................... 32
Interface Timing ......................................................................... 32
FIFO Operation .......................................................................... 33
Digital Datapath .............................................................................. 36
Premodulation ............................................................................ 36
Interpolation Filters ................................................................... 36
NCO Modulation ....................................................................... 39
Datapath Configuration ............................................................ 39
Determining Interpolation Filter Modes ................................ 40
Datapath Configuration Examples........................................... 41
Rev. B | Page 2 of 60
Data Rates vs. Interpolation Modes ......................................... 42
Coarse Modulation Mixing Sequences .................................... 42
Quadrature Phase Correction ................................................... 43
DC Offset Correction ................................................................ 43
Inverse Sinc Filter ....................................................................... 43
DAC Input Clock Configurations ................................................ 44
Driving the DACCLK and REFCLK Inputs ........................... 44
Direct Clocking .......................................................................... 44
Clock Multiplication .................................................................. 44
PLL Settings ................................................................................ 45
Configuring the VCO Tuning Band ........................................ 45
Analog Outputs............................................................................... 46
Transmit DAC Operation .......................................................... 46
Auxiliary DAC Operation ......................................................... 47
Interfacing to Modulators ......................................................... 48
Baseband Filter Implementation .............................................. 48
Driving the ADL5375-15 .......................................................... 48
Reducing LO Leakage and Unwanted Sidebands .................. 49
Device Power Management ........................................................... 50
Power Dissipation....................................................................... 50
Temperature Sensor ................................................................... 51
Multichip Synchronization ............................................................ 52
Synchronization with Clock Multiplication ............................... 52
Synchronization with Direct Clocking .................................... 53
Data Rate Mode Synchronization ............................................ 53
FIFO Rate Mode Synchronization ........................................... 54
Additional Synchronization Features ...................................... 55
Interrupt Request Operation ........................................................ 56
Interrupt Service Routine .......................................................... 56
Interface Timing Validation .......................................................... 57
SED Operation ............................................................................ 57
SED Example .............................................................................. 58
Example Start-Up Routine ............................................................ 59
Device Configuration ................................................................ 59
Derived PLL Settings ................................................................. 59
Derived NCO Settings ............................................................... 59
Start-Up Sequence ...................................................................... 59
Outline Dimensions ....................................................................... 60
Ordering Guide .......................................................................... 60

AD9122
REVISION HISTORY
5/11—Rev. A to Rev. B
Change to General Description Section ......................................... 1
Added Companion Products Section ............................................. 1
Moved Power Supply Rejection Ratio Parameter from Power
Consumption Section of Table 1 to Main DAC Outputs Section
of Table 1 ............................................................................................. 5
Moved Power-Up Time Parameter from Table 3 to Table 1 ........ 5
Changed Maximum Clock Rate Parameter in Table 2 ................. 6
Changes to Table 3 ............................................................................ 6
Changes to Table 5 ............................................................................ 7
Changes to Table 6 ............................................................................ 8
Changes to Figure 3 and Table 8 ..................................................... 9
Changes to Differences Between AD9122R1 and AD9122R2
Section and Device Marking of AD9122R1 and AD9122R2
Section .............................................................................................. 18
Changes to Figure 40 and Figure 41 ............................................. 20
Changes to Table 10 ........................................................................ 21
Changes to Table 11 ........................................................................ 23
Changes to LVDS Input Data Ports Section and Figure 45 ....... 32
Moved Interface Timing Section ................................................... 32
Moved Figure 46 and Table 13; Changes to Interface
Timing Section ................................................................................ 33
Changes to Resetting the FIFO Section, Serial Port Initiated
FIFO Reset Section, and Figure 48 ............................................... 34
Changes to FRAME Initiated Absolute FIFO Reset Section
and Monitoring the FIFO Status Section ..................................... 35
Changes to Table 22 ........................................................................ 42
Changes to Inverse Sinc Filter Section ......................................... 43
Change to Driving the DACCLK and REFCLK Inputs Section .... 44
Changes to Manual VCO Band Select Section ............................ 45
Changes to Transmit DAC Operation Section ............................ 46
Changes to Figure 69, Figure 70, Figure 71, and Figure 72 ....... 47
Changes to Power Dissipation Section ......................................... 50
Replaced Temperature Sensor Section ......................................... 51
Changes to Multichip Synchronization Section, Synchronization
with Clock Multiplication Section, and Procedure for
Synchronization When Using the PLL Section ........................... 52
Changes to Procedure for Data Rate Synchronization When
Directly Sourcing the DAC Sampling Clock Section ................. 53
Moved Table 25 and Figure 85 ...................................................... 54
Changes to Procedure for FIFO Rate Synchronization When
Directly Sourcing the DAC Sampling Clock Section ................. 54
Changes to Additional Synchronization Features Section and
Timing Optimization Section ........................................................ 55
Added One-Time Synchronization Section ................................ 55
Changes to Interrupt Request Operation Section ...................... 56
Changes to SED Operation Section .............................................. 57
Changes to SED Example Section ................................................. 58
Changes to Example Start-Up Routine Section .......................... 59
3/10—Rev. 0 to Rev. A
Changes to Reflect Differences Between R1 and R2
Silicon .................................................................................. Universal
Changes to Features Section ............................................................ 1
Changes to Table 1 ............................................................................ 5
Changes to Table 2 ............................................................................ 6
Changes to Table 5 ............................................................................ 7
Change to IOVDD Rating in Table 6 ............................................. 8
Changes to Table 8 ............................................................................ 9
Changes to Figure 10 through Figure 15 ...................................... 12
Added Differences Between AD9122R1 and AD9122R2
Section; Added Figure 36 and Figure 37; Renumbered Figures
Sequentially ...................................................................................... 18
Changes to Table 10 ........................................................................ 21
Changes to Table 11 ........................................................................ 23
Changes to FIFO Operation Section ............................................ 33
Changes to Resetting the FIFO Section; Replaced Table 13;
Added Serial Port Initiated FIFO Reset Section and FRAME
Initiated Relative FIFO Reset Section ........................................... 34
Added FRAME Initiated Absolute FIFO Reset Section;
Replaced Table 14 ............................................................................ 35
Changes to Figure 54 ...................................................................... 38
Changes to Table 18 ........................................................................ 39
Changes to SED Example Section ................................................. 58
Added Example Start-Up Routine Section .................................. 59
9/09—Revision 0: Initial Version
Rev. B | Page 3 of 60
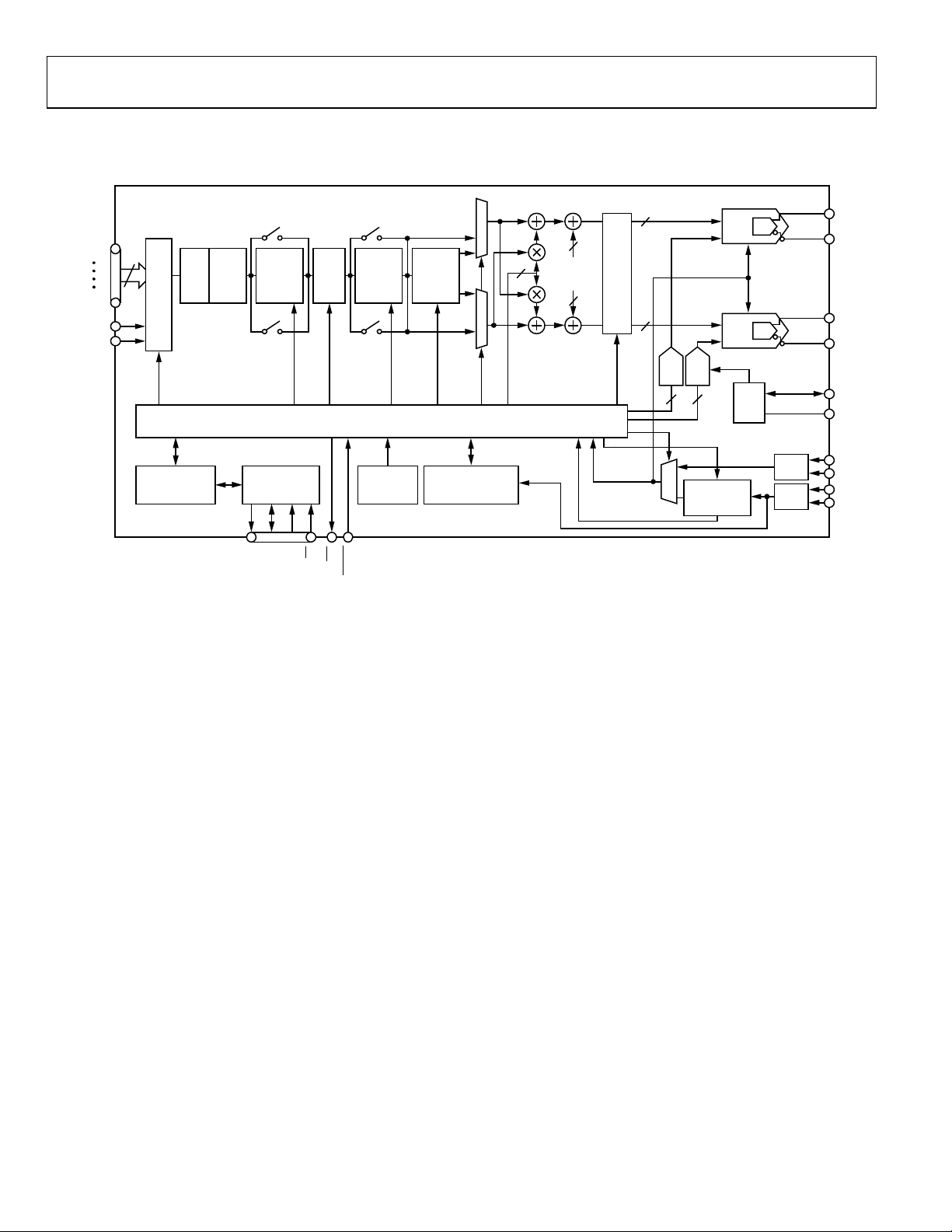
AD9122
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
D15P/D15N
D0P/D0N
DCI
FRAME
f
/2
DATA
PRE
FIFO HB1 HB2 HB3
MOD
DATA
RECEIVER
MODE
PROGRAMMING
REGISTERS
SERIAL
INPUT/OUTPUT
PORT
SDO
NCO
AND
MOD
HB1_CLK
INTERNAL CLO CK TIMING AND CONTROL L OGIC
CS
SDIO
IRQ
SCLK
POWER-ON
RESET
RESET
HB2_CLK
SYNCHRONIZATI ON
HB3_CLK
MULTICHIP
Figure 2.
16
16
I OFFSET
10
Q OFFSET
16
INTP
FACTOR
PHASE
CORRECTION
SYNC
INV
SINC
INVSINC_CLK
PLL
CONTRO L
DAC_CLK
PLL_LOCK
16
GAIN 110GAIN 2
10
DAC CLK_SEL
0
1
1.2G
DAC 1
16-BIT
DAC_CLK
1.2G
DAC 2
16-BIT
CLOCK
MULTIPLIER
(2× TO 16× )
REF
AND
BIAS
AUX
AUX
CLK
RCVR
CLK
RCVR
IOUT1P
IOUT1N
IOUT2P
IOUT2N
REFIO
FSADJ
DACCLKP
DACCLKN
REFCLKP
REFCLKN
08281-002
Rev. B | Page 4 of 60
AD9122
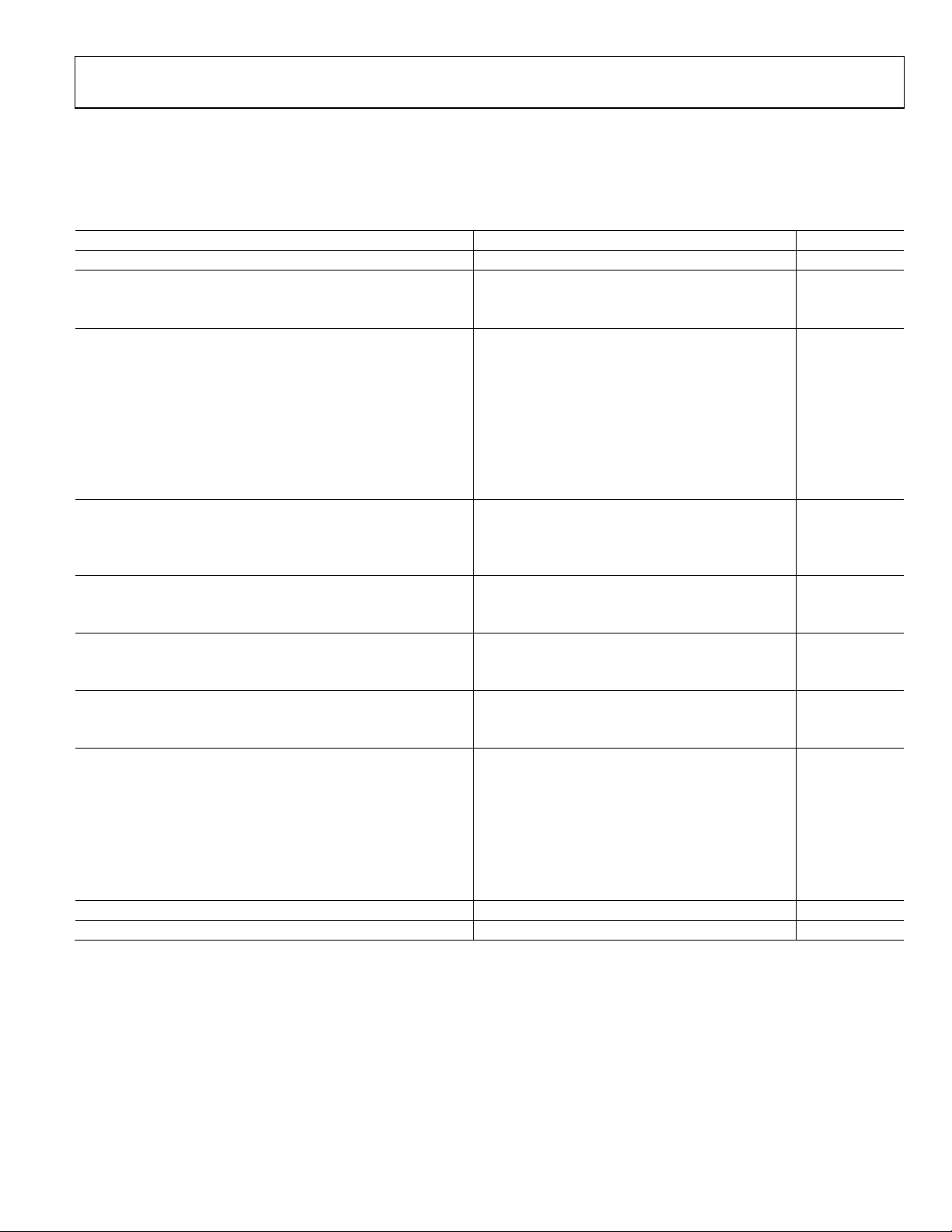
SPECIFICATIONS
DC SPECIFICATIONS
T
to T
MIN
Table 1.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
RESOLUTION 16 Bits
ACCURACY
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL) ±2.1 LSB
Integral Nonlinearity (INL) ±3.7 LSB
MAIN DAC OUTPUTS
Offset Error −0.001 0 +0.001 % FSR
Gain Error (with Internal Reference) −3.6 ±2 +3.6 % FSR
Full-Scale Output Current
Output Compliance Range −1.0 +1.0 V
Power Supply Rejection Ratio, AVDD33 −0.3 +0.3 % FSR/V
Output Resistance 10 MΩ
Gain DAC Monotonicity Guaranteed
Settling Time to Within ±0.5 LSB 20 ns
MAIN DAC TEMPERATURE DRIFT
Offset 0.04 ppm/°C
Gain 100 ppm/°C
Reference Voltage 30 ppm/°C
REFERENCE
Internal Reference Voltage 1.2 V
Output Resistance 5 kΩ
ANALOG SUPPLY VOLTAGES
AVDD33 3.13 3.3 3.47 V
CVDD18 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
DIGITAL SUPPLY VOLTAGES
DVDD18 1.71 1.8 1.89 V
IOVDD 1.71 1.8/3.3 3.47 V
POWER CONSUMPTION
2× Mode, f
2× Mode, f
8× Mode, f
AVDD33 55 57 mA
CVDD18 85 90 mA
DVDD18 444 495 mA
Power-Down Mode (Register 0x01 = 0xF0) 6.5 18.8 mW
POWER-UP TIME 260 ms
OPERATING RANGE −40 +25 +85 °C
1
Based on a 10 kΩ external resistor between FSADJ and AVSS.
, AVDD33 = 3.3 V, DVDD18 = 1.8 V, CVDD18 = 1.8 V, IFS = 20 mA, maximum sample rate, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
1
= 491.22 MSPS, IF = 10 MHz, PLL Off 834 mW
DAC
= 491.22 MSPS, IF = 10 MHz, PLL On 913 mW
DAC
= 800 MSPS, IF = 10 MHz, PLL Off 1135 1241 mW
DAC
8.66 19.6 31.66 mA
Rev. B | Page 5 of 60
AD9122
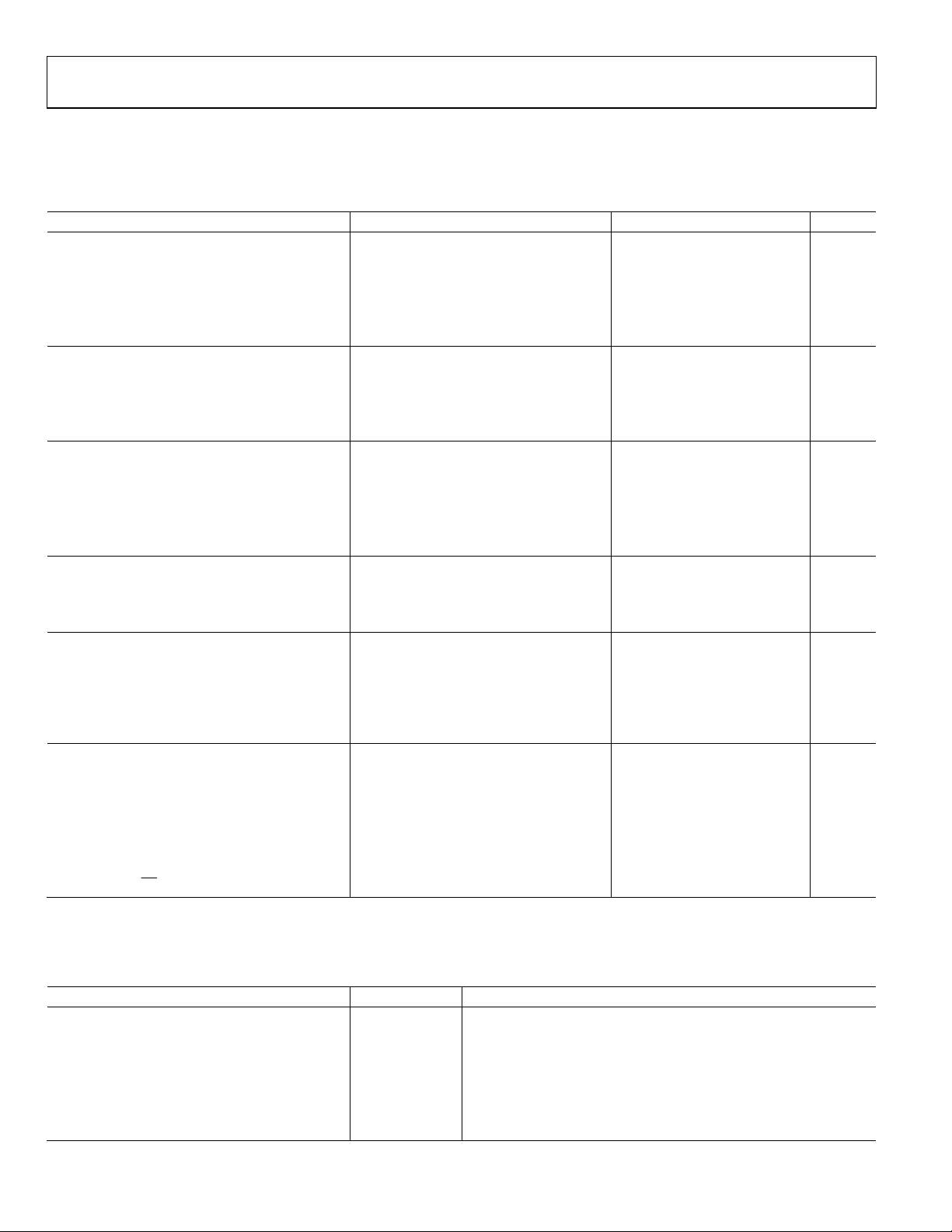
DIGITAL SPECIFICATIONS
T
to T
MIN
noted.
Table 2.
Parameter Test Conditions/Comments Min Typ Max Unit
CMOS INPUT LOGIC LEVEL
Input VIN Logic High IOVDD = 1.8 V 1.2 V
IOVDD = 2.5 V 1.6 V
IOVDD = 3.3 V 2.0 V
Input VIN Logic Low IOVDD = 1.8 V 0.6 V
IOVDD = 2.5 V, 3.3 V 0.8 V
CMOS OUTPUT LOGIC LEVEL
Output V
IOVDD = 2.5 V 1.8 V
IOVDD = 3.3 V 2.4 V
Output V
LVDS RECEIVER INPUTS
Input Voltage Range, VIA or VIB 825 1675 mV
Input Differential Threshold, V
Input Differential Hysteresis, V
Receiver Differential Input Impedance, RIN 80 120 Ω
LVDS Input Rate See Tab le 5
DAC CLOCK INPUT (DACCLKP, DACCLKN)
Differential Peak-to-Peak Voltage 100 500 2000 mV
Common-Mode Voltage Self-biased input, ac-coupled 1.25 V
Maximum Clock Rate 1230 MHz
REFCLK INPUT (REFCLKP, REFCLKN)
Differential Peak-to-Peak Voltage 100 500 2000 mV
Common-Mode Voltage 1.25 V
REFCLK Frequency (PLL Mode) 1 GHz ≤ f
REFCLK Frequency (SYNC Mode)
SERIAL PORT INTERFACE
Maximum Clock Rate (SCLK) 40 MHz
Minimum Pulse Width High (t
Minimum Pulse Width Low (t
Setup Time, SDIO to SCLK (tDS) 1.9 ns
Hold Time, SDIO to SCLK (tDH) 0.2 ns
Data Valid, SDO to SCLK (tDV) 2.3 ns
Setup Time, CS to SCLK (t
1
LVDS receiver is compliant with the IEEE 1596 reduced range link, unless otherwise noted.
DIGITAL INPUT DATA TIMING SPECIFICATIONS
Table 3.
Parameter Value Unit
LATENCY (DACCLK CYCLES)
1× Interpolation (With or Without Modulation) 64 Cycles
2× Interpolation (With or Without Modulation) 135 Cycles
4× Interpolation (With or Without Modulation) 292 Cycles
8× Interpolation (With or Without Modulation) 608 Cycles
Inverse Sinc 20 Cycles
Fine Modulation 8 Cycles
, AVDD33 = 3.3 V, IOVDD = 3.3 V, DVDD18 = 1.8 V, CVDD18 = 1.8 V, IFS = 20 mA, maximum sample rate, unless otherwise
MAX
Logic High IOVDD = 1.8 V 1.4 V
OUT
Logic Low IOVDD = 1.8 V, 2.5 V, 3.3 V 0.4 V
OUT
1
−100 +100 mV
IDTH
to V
IDTHH
IDTHL
Applies to data, DCI, and FRAME inputs
20 mV
≤ 2.1 GHz 15.625 600 MHz
VCO
See the Multichip Synchronization section
0 600 MHz
for conditions
) 12.5 ns
PWH
) 12.5 ns
PWL
DCSB
)
1.4 ns
Rev. B | Page 6 of 60
AD9122
AC SPECIFICATIONS
T
to T
MIN
Table 4.
Parameter Min Typ Max Unit
SPURIOUS-FREE DYNAMIC RANGE (SFDR)
f
DAC
f
DAC
f
DAC
f
DAC
TWO-TONE INTERMODULATION DISTORTION (IMD)
f
DAC
f
DAC
f
DAC
f
DAC
NOISE SPECTRAL DENSITY (NSD), EIGHT-TONE, 500 kHz TONE SPACING
f
DAC
f
DAC
f
DAC
W-CDMA ADJACENT CHANNEL LEAKAGE RATIO (ACLR), SINGLE-CARRIER
f
DAC
f
DAC
f
DAC
W-CDMA SECOND ACLR, SINGLE-CARRIER
f
DAC
f
DAC
f
DAC
, AVDD33 = 3.3 V, DVDD18 = 1.8 V, CVDD18 = 1.8 V, IFS = 20 mA, maximum sample rate, unless otherwise noted.
MAX
= 100 MSPS, f
= 200 MSPS, f
= 400 MSPS, f
= 800 MSPS, f
= 200 MSPS, f
= 400 MSPS, f
= 400 MSPS, f
= 800 MSPS, f
= 200 MSPS, f
= 400 MSPS, f
= 800 MSPS, f
= 491.52 MSPS, f
= 491.52 MSPS, f
= 983.04 MSPS, f
= 491.52 MSPS, f
= 491.52 MSPS, f
= 983.04 MSPS, f
= 20 MHz 78 dBc
OUT
= 50 MHz 80 dBc
OUT
= 70 MHz 69 dBc
OUT
= 70 MHz 72 dBc
OUT
= 50 MHz 84 dBc
OUT
= 60 MHz 86 dBc
OUT
= 80 MHz 84 dBc
OUT
= 100 MHz 81 dBc
OUT
= 80 MHz −162 dBm/Hz
OUT
= 80 MHz −163 dBm/Hz
OUT
= 80 MHz −164 dBm/Hz
OUT
= 10 MHz 84 dBc
OUT
= 122.88 MHz 82 dBc
OUT
= 122.88 MHz 83 dBc
OUT
= 10 MHz 88 dBc
OUT
= 122.88 MHz 86 dBc
OUT
= 122.88 MHz 88 dBc
OUT
Table 5. Maximum Rate (MSPS) with DVDD and CVDD Supply Regulation
f
Bus Width
Interpolation
Fac tor
(MSPS) f
INTERFACE
DVDD18, CVDD18 = DVDD18, CVDD18 =
1.8 V ± 5% 1.8 V ± 2% 1.9 V ± 2% 1.8 V ± 5% 1.8 V ± 2% 1.9 V ± 2%
(MSPS)
DAC
Nibble (4 Bits) 1× 1100 1200 1230 137.5 150 153.75
2× 1100 1200 1230 275 300 307.5
4× 1100 1200 1230 550 600 615
8× 1100 1200 1230 1100 1200 1230
Byte (8 Bits) 1× 1100 1200 1230 275 300 307.5
2× 1100 1200 1230 550 600 615
4× 1100 1200 1230 1100 1200 1230
8× 550 600 615 1100 1200 1230
Word (16 Bits) 1× 1100 1200 1230 550 600 615
2× (HB1) 900 1000 1000 900 1000 1000
2× (HB2) 1100 1200 1230 1100 1200 1230
4× 550 600 615 1100 1200 1230
8× 275 300 307.5 1100 1200 1230
Rev. B | Page 7 of 60

AD9122
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Table 6.
Parameter Rating
AVDD33 to AVSS, EPAD, CVSS, DVSS −0.3 V to +3.6 V
IOVDD to AVSS, EPAD, CVSS, DVSS −0.3 V to +3.6 V
DVDD18, CVDD18 to AVSS, EPAD,
CVSS, DVSS
AVSS to EPAD, CVSS, DVSS −0.3 V to +0.3 V
EPAD to AVSS, CVSS, DVSS −0.3 V to +0.3 V
CVSS to AVSS, EPAD, DVSS −0.3 V to +0.3 V
DVSS to AVSS, EPAD, CVSS −0.3 V to +0.3 V
FSADJ, REFIO, IOUT1P, IOUT1N,
IOUT2P, IOUT2N to AVSS
D[15:0]P, D[15:0]N, FRAMEP, FRAMEN,
DCIP, DCIN to EPAD, DVSS
DACCLKP, DACCLKN, REFCLKP,
REFCLKN to CVSS
RESET, IRQ, CS, SCLK, SDIO, SDO
to EPAD, DVSS
Junction Temperature 125°C
Storage Temperature Range −65°C to +150°C
Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings
may cause permanent damage to the device. This is a stress
rating only; functional operation of the device at these or any
other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute
maximum rating conditions for extended periods may affect
device reliability.
−0.3 V to +2.1 V
−0.3 V to AVDD33 + 0.3 V
−0.3 V to DVDD18 + 0.3 V
−0.3 V to CVDD18 + 0.3 V
−0.3 V to IOVDD + 0.3 V
THERMAL RESISTANCE
The exposed pad (EPAD) of the 72-lead LFCSP must be
soldered to the ground plane (AVSS). The EPAD provides an
electrical, thermal, and mechanical connection to the board.
Typical θ
, θJB, and θJC values are specified for a 4-layer board in
JA
still air. Airflow increases heat dissipation, effectively reducing
θ
and θJB.
JA
Table 7. Thermal Resistance
Package θJA θJB θJC Unit Conditions
72-Lead LFCSP 20.7 10.9 1.1 °C/W
EPAD soldered
to ground plane
ESD CAUTION
Rev. B | Page 8 of 60
AD9122
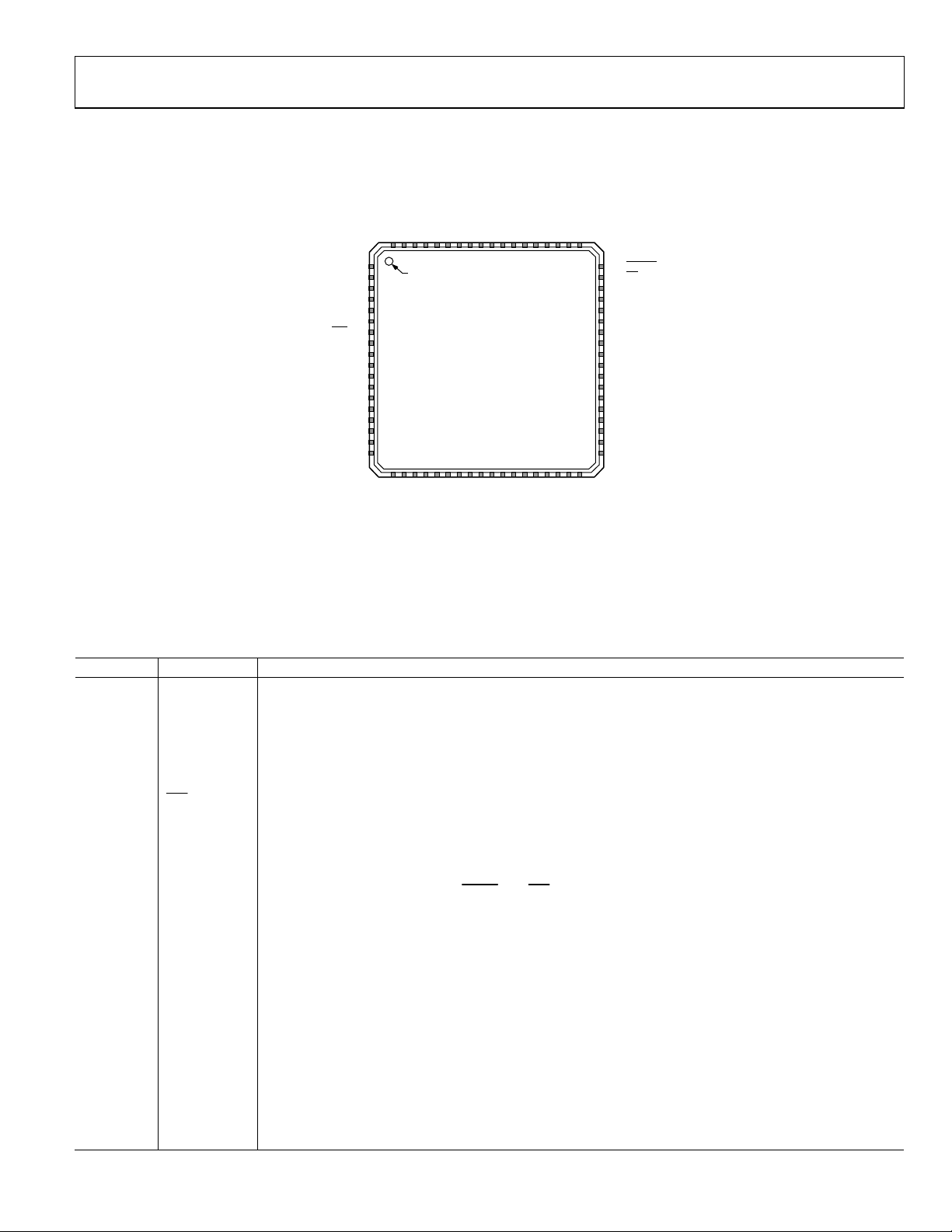
PIN CONFIGURATION AND FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
CVDD18
CVDD18
REFCLKP
REFCLKN
AVDD33
IOUT1P
IOUT1N
AVDD33
AVSS
FSADJ
REFIO
AVSS
AVDD33
IOUT2N
IOUT2P
AVDD33
AVSS
NC
CVDD18
DACCLKP
DACCLKN
CVSS
FRAMEP
FRAMEN
IRQ
D15P
D15N
NC
IOVDD
DVDD18
D14P
D14N
D13P
D13N
7271706968676665646362616059585756
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17D12P
18D12N
PIN 1
INDICATO R
AD9122
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
55
RESET
54
CS
53
SCLK
52
SDIO
51
SDO
50
DVDD18
49
D0N
48
D0P
47
D1N
46
D1P
45
DVSS
44
DVDD18
43
D2N
42
D2P
41
D3N
40
D3P
39
D4N
38
D4P
37
192021222324252627282930313233
D9P
D8P
D9N
D8N
DCIP
D11P
D10P
D11N
D10N
NOTES
1. EXPOSED PAD (EPAD) MUST BE SOLDERED TO THE GROUND PLANE (AVSS).
THE EPAD PROVI DES AN ELECTRICAL, THERMAL, AND MECHANICAL
CONNECTION T O THE BOARD.
2. NC = NO CONNECT . DO NOT CONNECT TO THIS PI N.
DCIN
DVDD18
34
35D5P
36D5N
D7P
D6P
D7N
D6N
DVSS
08281-003
Figure 3. Pin Configuration
Table 8. Pin Function Descriptions
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
1 CVDD18 1.8 V Clock Supply. Supplies clock receivers, clock distribution, and PLL circuitry.
2 DACCLKP DAC Clock Input, Positive.
3 DACCLKN DAC Clock Input, Negative.
4 CVSS Clock Supply Common.
5 FRAMEP Frame Input, Positive. This pin must be tied to DVSS if not used.
6 FRAMEN Frame Input, Negative. This pin must be tied to DVDD18 if not used.
7
IRQ
Interrupt Request. Open-drain, active low output. Connect an external pull-up to IOVDD through a 10 kΩ
resistor.
8 D15P Data Bit 15 (MSB), Positive.
9 D15N Data Bit 15 (MSB), Negative.
10 NC No Connect. Do not connect to this pin.
11 IOVDD
Supply Pin for Serial Port I/O Pins, RESET
, and IRQ. 1.8 V to 3.3 V can be supplied to this pin.
12 DVDD18 1.8 V Digital Supply. Supplies power to digital core and digital data ports.
13 D14P Data Bit 14, Positive.
14 D14N Data Bit 14, Negative.
15 D13P Data Bit 13, Positive.
16 D13N Data Bit 13, Negative.
17 D12P Data Bit 12, Positive.
18 D12N Data Bit 12, Negative.
19 D11P Data Bit 11, Positive.
20 D11N Data Bit 11, Negative.
21 D10P Data Bit 10, Positive.
22 D10N Data Bit 10, Negative.
23 D9P Data Bit 9, Positive.
24 D9N Data Bit 9, Negative.
Rev. B | Page 9 of 60
AD9122
Pin No. Mnemonic Description
25 D8P Data Bit 8, Positive.
26 D8N Data Bit 8, Negative.
27 DCIP Data Clock Input, Positive.
28 DCIN Data Clock Input, Negative.
29 DVDD18 1.8 V Digital Supply. Supplies power to digital core and digital data ports.
30 DVSS Digital Common.
31 D7P Data Bit 7, Positive.
32 D7N Data Bit 7, Negative.
33 D6P Data Bit 6, Positive.
34 D6N Data Bit 6, Negative.
35 D5P Data Bit 5, Positive.
36 D5N Data Bit 5, Negative.
37 D4P Data Bit 4, Positive.
38 D4N Data Bit 4, Negative.
39 D3P Data Bit 3, Positive.
40 D3N Data Bit 3, Negative.
41 D2P Data Bit 2, Positive.
42 D2N Data Bit 2, Negative.
43 DVDD18 1.8 V Digital Supply. Supplies power to digital core and digital data ports.
44 DVSS Digital Common.
45 D1P Data Bit 1, Positive.
46 D1N Data Bit 1, Negative.
47 D0P Data Bit 0 (LSB), Positive.
48 D0N Data Bit 0 (LSB), Negative.
49 DVDD18 1.8 V Digital Supply. Supplies power to digital core and digital data ports.
50 SDO Serial Port Data Output (CMOS Levels with Respect to IOVDD).
51 SDIO Serial Port Data Input/Output (CMOS Levels with Respect to IOVDD).
52 SCLK Serial Port Clock Input (CMOS Levels with Respect to IOVDD).
53
54
CS
RESET
55 NC No Connect. Do not connect to this pin.
56 AVSS Analog Supply Common.
57 AVDD33 3.3 V Analog Supply.
58 IOUT2P Q DAC Positive Current Output.
59 IOUT2N Q DAC Negative Current Output.
60 AVDD33 3.3 V Analog Supply.
61 AVSS Analog Supply Common.
62 REFIO Voltage Reference. Nominally 1.2 V output. Should be decoupled to AVSS.
63 FSADJ Full-Scale Current Output Adjust. Place a 10 kΩ resistor from this pin to AVSS.
64 AVSS Analog Supply Common.
65 AVDD33 3.3 V Analog Supply.
66 IOUT1N I DAC Negative Current Output.
67 IOUT1P I DAC Positive Current Output.
68 AVDD33 3.3 V Analog Supply.
69 REFCLKN PLL Reference Clock Input, Negative. This pin has a secondary function as a synchronization input.
70 REFCLKP PLL Reference Clock Input, Positive. This pin has a secondary function as a synchronization input.
71 CVDD18 1.8 V Clock Supply. Supplies clock receivers, clock distribution, and PLL circuitry.
72 CVDD18 1.8 V Clock Supply. Supplies clock receivers, clock distribution, and PLL circuitry.
EPAD
Serial Port Chip Select, Active Low (CMOS Levels with Respect to IOVDD).
Reset, Active Low (CMOS Levels with Respect to IOVDD).
The exposed pad (EPAD) must be soldered to the ground plane (AVSS). The EPAD provides an electrical,
thermal, and mechanical connection to the board.
Rev. B | Page 10 of 60
AD9122
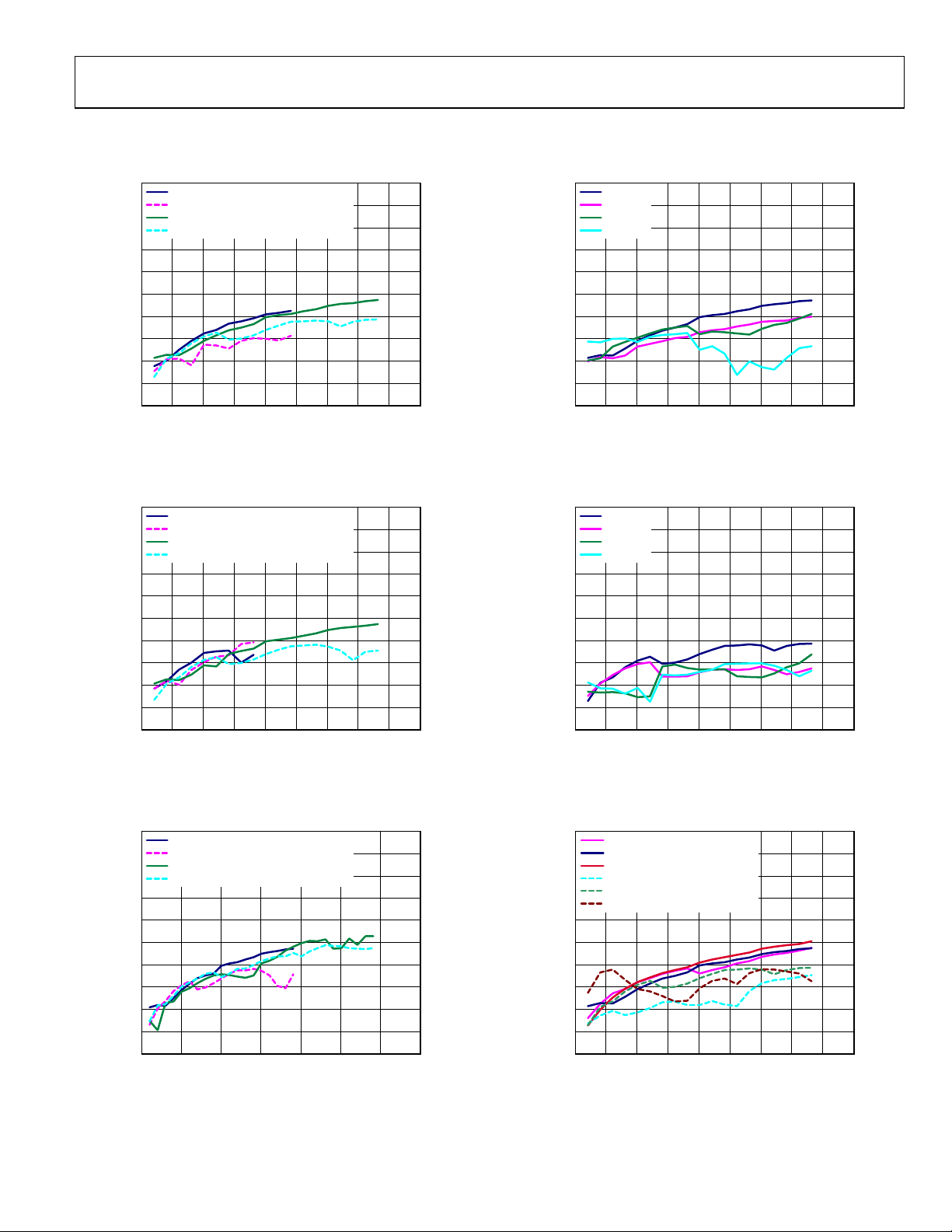
TYPICAL PERFORMANCE CHARACTERISTICS
0
f
= 250MSPS, SECO ND HARMONIC
DATA
f
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
HARMONICS (dBc)
–70
–80
–90
–100
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Figure 4. Harmonics vs. f
= 250MSPS, T HIRD HARMONIC
DATA
f
= 400MSPS, SECO ND HARMONIC
DATA
f
= 400MSPS, T HIRD HARMONIC
DATA
f
(MHz)
OUT
over f
OUT
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
, 2× Interpolation,
DATA
= 20 mA
FS
08281-101
0
0dBFS
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
SECOND HARMONIC (dBc)
–80
–90
–100
Figure 7. Second Harmonic vs. f
–6dBFS
–12dBFS
–18dBFS
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
over Digital Scale, 2× Interpolation,
OUT
= 400 MSPS, IFS = 20 mA
f
DATA
08281-104
0
f
= 100MSPS, SECO ND HARMONIC
DATA
f
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
HARMONICS (dBc)
–70
–80
–90
–100
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Figure 5. Harmonics vs. f
0
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
HARMONICS (dBc)
–70
–80
–90
–100
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700
Figure 6. Harmonics vs. f
= 100MSPS, T HIRD HARMONIC
DATA
f
= 200MSPS, SECO ND HARMONIC
DATA
f
= 200MSPS, T HIRD HARMONIC
DATA
f
(MHz)
OUT
over f
OUT
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
f
= 100MSPS, SECO ND HARMONIC
DATA
f
= 100MSPS, T HIRD HARMONIC
DATA
f
= 150MSPS, SECO ND HARMONIC
DATA
f
= 150MSPS, T HIRD HARMONIC
DATA
f
(MHz)
OUT
over f
OUT
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
, 4× Interpolation,
DATA
= 20 mA
FS
, 8× Interpolation,
DATA
= 20 mA
FS
0
0dBFS
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
–70
THIRD HARMONIC (dBc)
–80
–90
–100
08281-102
Figure 8. Third Harmonic vs. f
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
–60
HARMONICS (dBc)
–70
–80
–90
–100
08281-103
–6dBFS
–12dBFS
–18dBFS
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
over Digital Scale, 2× Interpolation,
OUT
= 400 MSPS, IFS = 20 mA
f
DATA
0
IFS = 10mA, SECOND HARMONIC
IFS = 20mA, SECOND HARMONIC
IFS = 30mA, SECOND HARMONIC
IFS = 10mA, THIRD HARMONI C
IFS = 20mA, THIRD HARMONI C
IFS = 30mA, THIRD HARMONI C
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 9. Harmonics vs. f
= 400 MSPS, Digital Scale = 0 dBFS
f
DATA
over IFS, 2× Interpolation,
OUT
08281-105
08281-106
Rev. B | Page 11 of 60
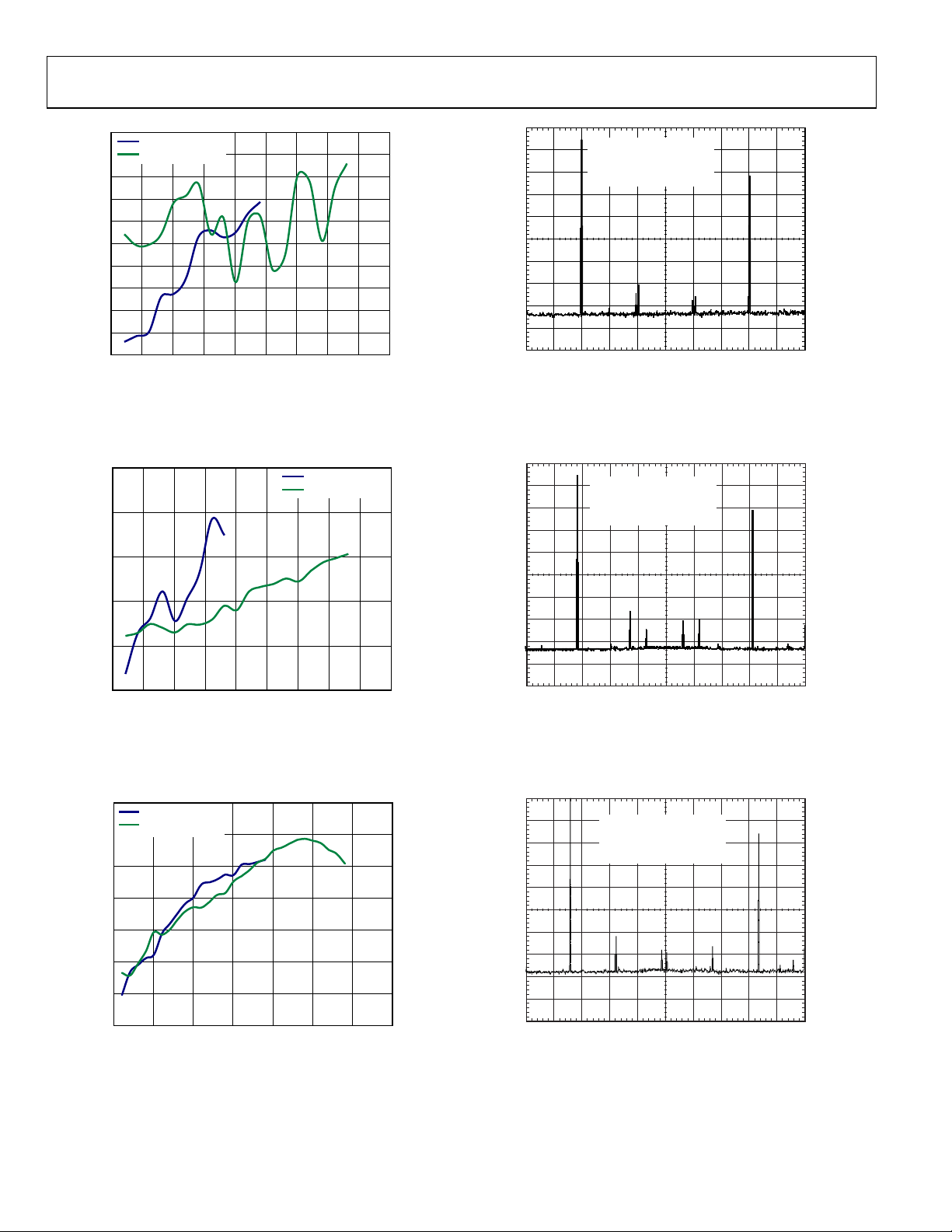
AD9122
–
–
–
69
–70
–71
–72
–73
–74
–75
–76
HIGHEST DI GITAL SPUR (dBc)
–77
–78
–79
Figure 10. Highest Digital Spur vs. f
f
= 250MSPS
DATA
f
= 400MSPS
DATA
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
f
OUT
(MHz)
OUT
over f
= 20 mA
FS
, 2× Interpolation,
DATA
2× INTERPOLATION,
SINGLE-TONE SPECTRUM,
f
= 250MSPS,
DATA
f
= 101MHz
OUT
START 1.0MHz
08281-107
#RES BW 10kHz
VBW 10kHz STOP 500.0MHz
SWEEP 6.017s (601 PTS)
08281-110
Figure 13. Single-Tone Spectrum, 2× Interpolation,
= 250 MSPS, f
f
DATA
= 101 MHz
OUT
60
–65
–70
–75
HIGHEST DI GITAL SPUR (dBc)
–80
–85
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Figure 11. Highest Digital Spur vs. f
f
OUT
(MHz)
OUT
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
60
f
= 100MSPS
DATA
f
= 150MSPS
–65
–70
–75
DATA
over f
= 20 mA
FS
f
DATA
f
DATA
, 4× Interpolation,
DATA
= 100MSPS
= 200MSPS
4× INTERPOLATION,
SINGLE-TONE SPECTRUM,
f
= 200MSPS,
DATA
f
= 151MHz
OUT
START 1.0MHz
08281-108
#RES BW 10kHz
VBW 10kHz STOP 800. 0MHz
SWEEP 9. 634s (601 PTS)
08281-111
Figure 14. Single-Tone Spectrum, 4× Interpolation,
= 200 MSPS, f
f
DATA
8× INTERPOLATION,
SINGLE-TONE SPECTRUM,
f
= 100MSPS,
DATA
f
= 131MHz
OUT
= 151 MHz
OUT
–80
–85
HIGHEST DI GITAL SPUR (dBc)
–90
–95
0 100 200 300 400 500 600 700
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 12. Highest Digital Spur vs. f
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
OUT
over f
= 20 mA
FS
, 8× Interpolation,
DATA
08281-109
START 1.0MHz
#RES BW 10kHz
VBW 10kHz STOP 800.0MHz
SWEEP 9.634s (601 PTS)
Figure 15. Single-Tone Spectrum, 8× Interpolation,
= 100 MSPS, f
f
DATA
= 131 MHz
OUT
08281-112
Rev. B | Page 12 of 60
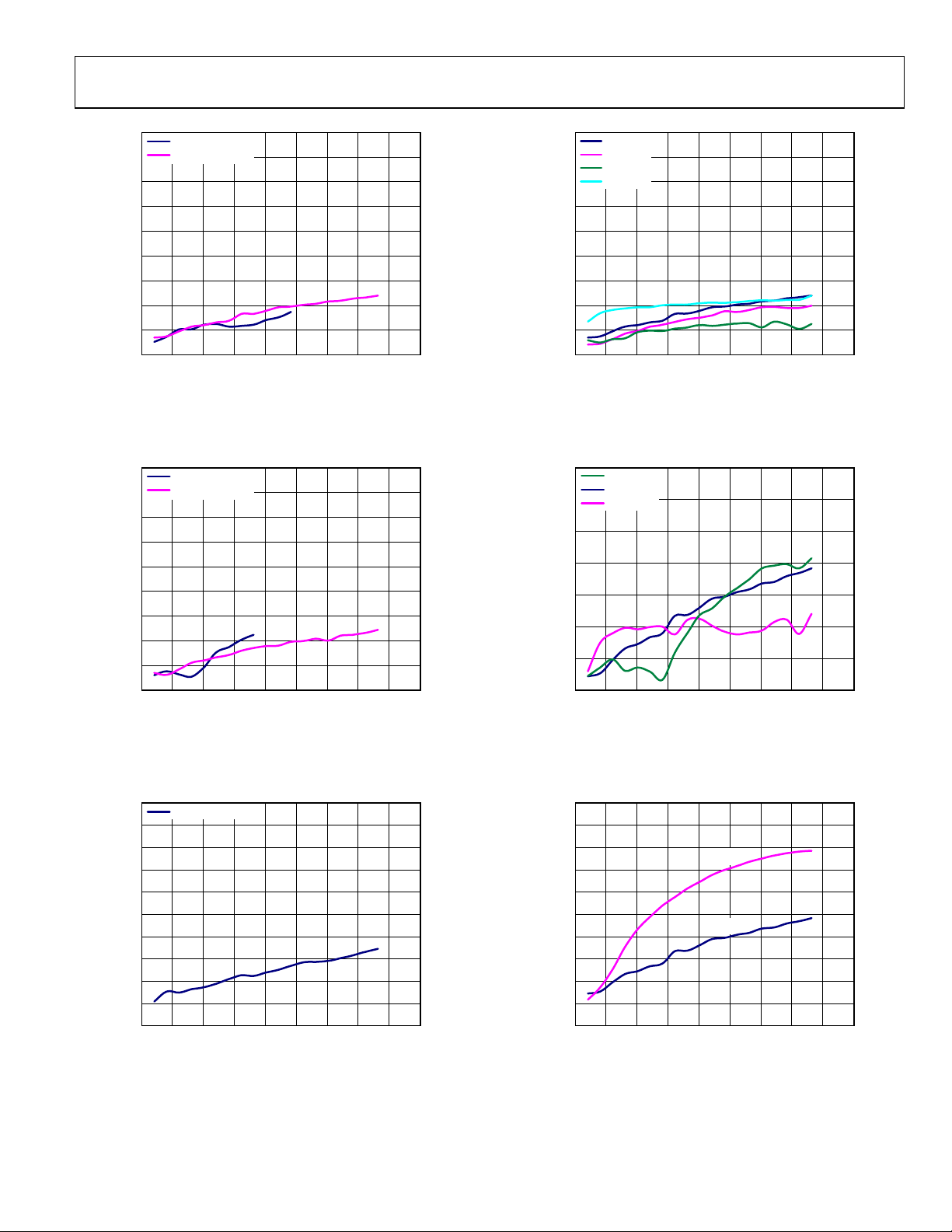
AD9122
–
–
0
f
= 250MSPS
DATA
f
= 400MSPS
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
IMD (dBc)
–60
–70
–80
–90
DATA
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 16. IMD vs. f
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
OUT
over f
DATA
, 2× Interpolation,
= 20 mA
FS
08281-113
0
0dBFS
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
IMD (dBc)
–60
–70
–80
–90
–6dBFS
–12dBFS
–18dBFS
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 19. IMD vs. f
over Digital Scale, 2× Interpolation,
OUT
= 400 MSPS, IFS = 20 mA
f
DATA
08281-116
0
f
= 100MSPS
DATA
f
= 200MSPS
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
IMD (dBc)
–60
–70
–80
–90
–10
–20
–30
–40
–50
IMD (dBc)
–60
–70
–80
–90
–100
DATA
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 17. IMD vs. f
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
0
f
= 100MSPS
DATA
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Figure 18. IMD vs. f
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
over f
OUT
DATA
f
(MHz)
OUT
, 8× Interpolation, f
OUT
, 4× Interpolation,
= 20 mA
FS
= 100 MSPS,
DATA
= 20 mA
FS
50
–55
–60
–65
–70
IMD (dBc)
–75
–80
–85
08281-114
40
–45
–50
–55
–60
–65
IMD (dBc)
–70
–75
–80
–85
–90
08281-115
IFS = 10mA
IFS = 20mA
IFS = 30mA
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 20. IMD vs. f
= 400 MSPS, Digital Scale = 0 dBFS
f
DATA
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Figure 21. IMD vs. f
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
over IFS, 2× Interpolation,
OUT
PLL ON
PLL OFF
f
(MHz)
OUT
, 4× Interpolation, f
OUT
= 20 mA, PLL On and PLL Off
FS
= 200 MSPS,
DATA
08281-117
08281-118
Rev. B | Page 13 of 60
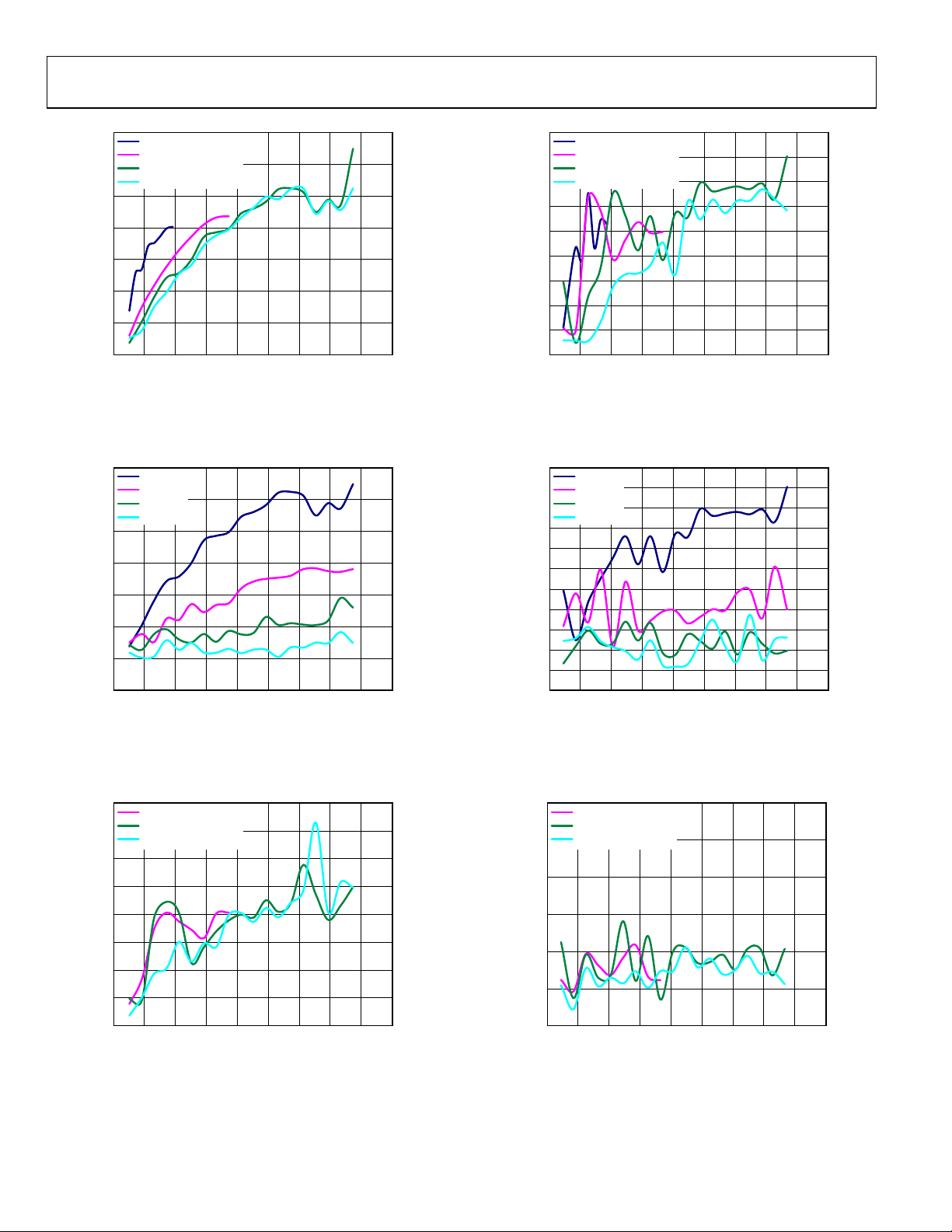
AD9122
–
–
–
–
–
–
152
–154
–156
–158
–160
NSD (dBm/Hz)
–162
–164
–166
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
Figure 22. One-Tone NSD vs. f
1×,
f
= 200MSPS
DATA
2×,
f
= 200MSPS
DATA
4×,
f
= 200MSPS
DATA
8×,
f
= 100MSPS
DATA
f
OUT
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
(MHz)
over Interpolation,
OUT
= 20 mA, PLL Off
FS
161.0
–161.5
–162.0
–162.5
–163.0
–163.5
NSD (dBm/Hz)
–164.0
–164.5
–165.0
–165.5
08281-119
1×,
f
= 200MSPS
DATA
2×,
f
= 200MSPS
DATA
4×,
f
= 200MSPS
DATA
8×,
f
= 100MSPS
DATA
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 25. Eight-Tone NSD vs. f
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
over Interpolation,
OUT
= 20 mA, PLL Off
FS
08281-122
154
–156
–158
–160
–162
NSD (dBm/Hz)
–164
–166
–168
Figure 23. One-Tone NSD vs. f
158
–159
–160
–161
–162
0dBFS
–6dBFS
–12dBFS
–18dBFS
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
over Digital Scale, 4× Interpolation,
OUT
= 200 MSPS, IFS = 20 mA, PLL Off
f
DATA
2×,
f
= 200MSPS
DATA
4×,
f
= 200MSPS
DATA
8×,
f
= 100MSPS
DATA
161.0
–161.5
–162.0
–162.5
–163.0
–163.5
–164.0
NSD (dBm/Hz)
–164.5
–165.0
–165.5
–166.0
–166.5
08281-120
Figure 26. Eight-Tone NSD vs. f
160
–161
–162
–163
0dBFS
–6dBFS
–12dBFS
–18dBFS
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
over Digital Scale, 4× Interpolation,
= 200 MSPS, IFS = 20 mA, PLL Off
f
DATA
2×,
f
DATA
4×,
f
DATA
8×,
f
DATA
OUT
= 200MSPS
= 200MSPS
= 100MSPS
08281-123
–163
NSD (dBm/ Hz)
–164
–165
–166
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 24. One-Tone NSD vs. f
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
over Interpolation,
OUT
= 20 mA, PLL On
FS
08281-121
NSD (dBm/ Hz)
–164
–165
–166
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 27. Eight-Tone NSD vs. f
Digital Scale = 0 dBFS, I
over Interpolation,
OUT
= 20 mA, PLL On
FS
08281-124
Rev. B | Page 14 of 60
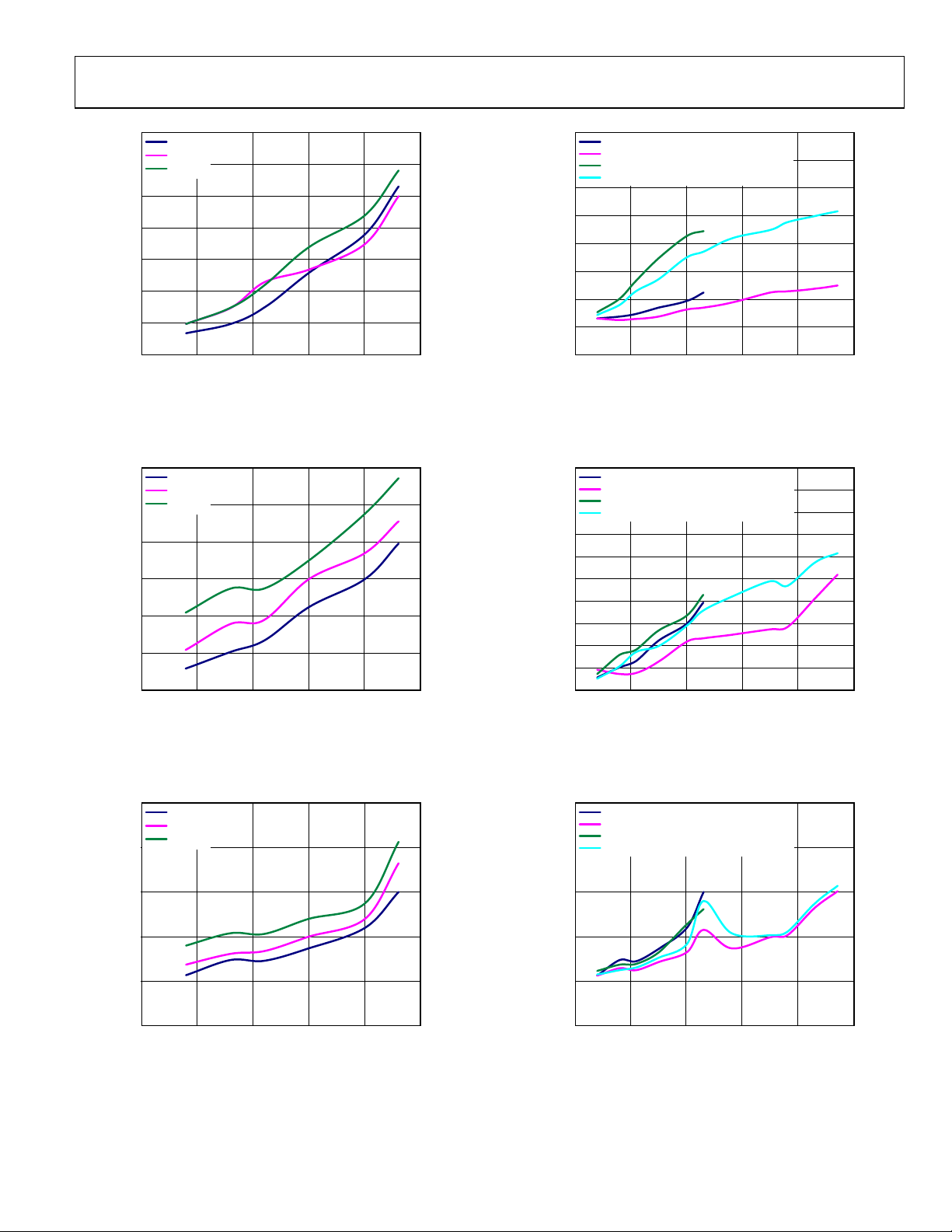
AD9122
–
–
–
–
–
–
ACLR (dBc)
–78
–79
–80
–81
–82
–83
77
0dBFS
–3dBFS
–6dBFS
ACLR (dBc)
–55
–60
–65
–70
–75
–80
–85
50
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 2×, PLL OFF
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 4×, PLL OFF
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 2×, PLL ON
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 4×, PLL ON
–84
0 50 100 150 200 250
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 28. One-Carrier W-CDMA ACLR vs. f
over Digital Scale,
OUT
Adjacent Channel, PLL Off
78
0dBFS
–3dBFS
–80
–82
–84
ACLR (dBc)
–86
–88
–90
Figure 29. One-Carrier W-CDMA ACLR vs. f
–6dBFS
0 50 100 150 200 250
f
(MHz)
OUT
over Digital Scale,
OUT
First Alternate Channel, PLL Off
70
0dBFS
–3dBFS
–75
–6dBFS
–90
0 100 200 300 400 500
f
(MHz)
08281-125
Figure 31. One-Carrier W-CDMA ACLR vs. f
OUT
over Interpolation,
OUT
08281-128
Adjacent Channel, PLL On and PLL Off
70
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 2×, PLL OFF
–72
–74
–76
–78
–80
–82
ACLR (dBc)
–84
–86
–88
–90
08281-126
Figure 32. One-Carrier W-CDMA ACLR vs. f
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 4×, PLL OFF
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 2×, PLL ON
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 4×, PLL ON
0 100 200 300 400 500
f
(MHz)
OUT
over Interpolation,
OUT
08281-129
First Alternate Channel, PLL On and PLL Off
70
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 2×, PLL OFF
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 4×, PLL OFF
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 2×, PLL ON
–75
INTERPOLATION FACTOR = 4×, PLL ON
–80
–85
ACLR (dBc)
–90
–95
0 50 100 150 200 250
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 30. One-Carrier W-CDMA ACLR vs. f
over Digital Scale,
OUT
Second Alternate Channel, PLL Off
08281-127
–80
ACLR (dBc)
–85
–90
–95
0 100 200 300 400 500
f
(MHz)
OUT
Figure 33. One-Carrier W-CDMA ACLR vs. f
over Interpolation,
OUT
Second Alternate Channel, PLL On and PLL Off
08281-130
Rev. B | Page 15 of 60
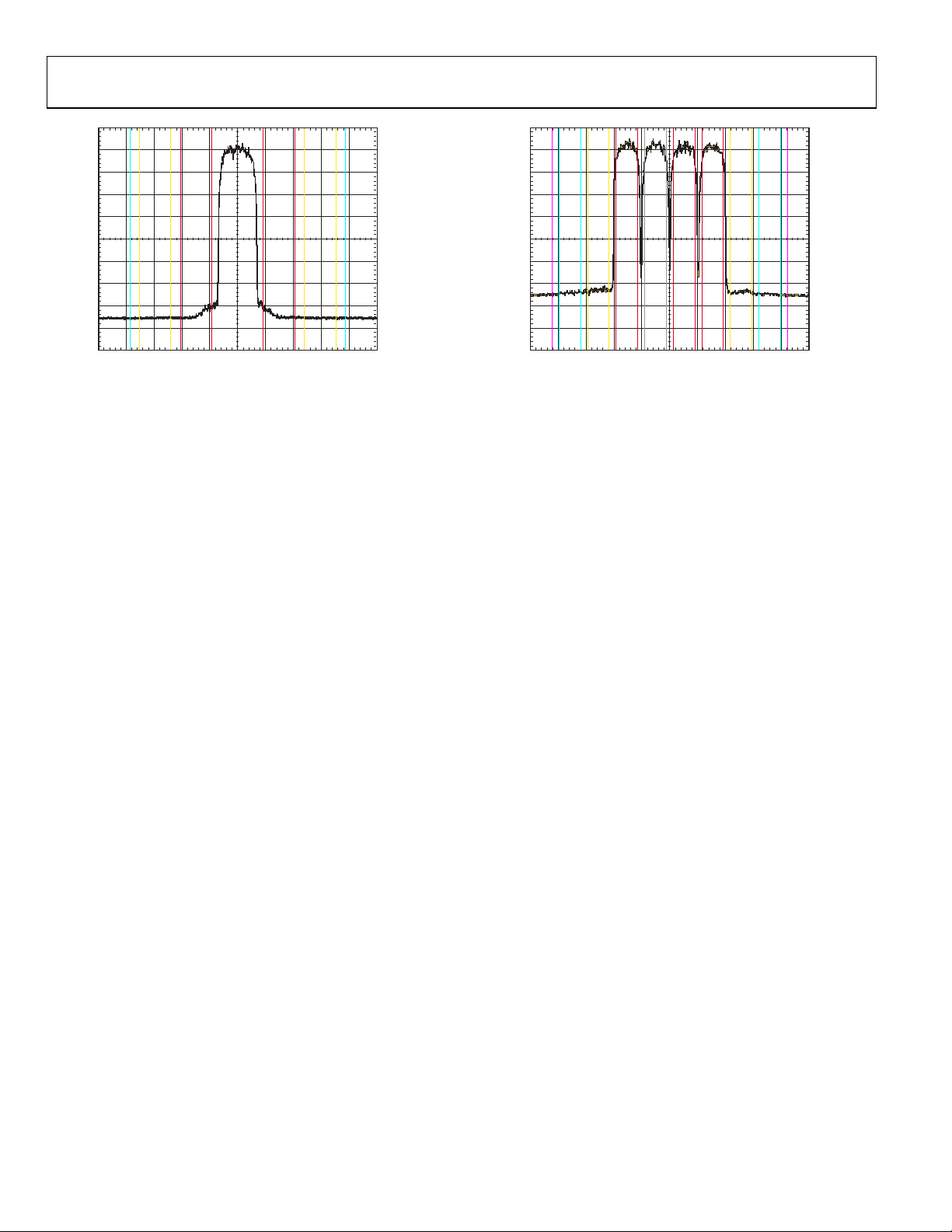
AD9122
START 133.06M Hz
#RES BW 30kHz
RMS RESULTS FREQ LO WER UPPER
CARRIER POWER 5.00MHz 3.840MHz –75.96 –85.96 –77.13 –87.13
–10.00dBm/ 10.00MHz 3.840MHz –85.33 –95.33 –85.24 –95.25
3.840MHz 15.00MHz 2.888MHz –95.81 –95.81 –85.43 –95.43
OFFSET REF BW dBc dBm dBc dBm
VBW 30kHz ST OP 166.94MHz
SWEEP 143. 6ms (601 PTS)
Figure 34. One-Carrier W-CDMA ACLR Performance, IF = ~150 MHz
START 125.88MHz
#RES BW 30kHz
TOTAL CARRIER POWER –11.19dBm/15.3600MHz
RRC FILTER: OFF FILTER ALPHA 0.22
REF CARRIER POWER –16.89dBm/3.84000MHz
08281-131
1 –16.92dBm 5.000MHz 3.840MHz –65.88 –82.76 –67.52 –84.40
2 –16.89dBm 10.00MHz 3.840MHz –68.17 –85.05 –69.91 –86.79
3 –17.43dBm 15.00MHz 3.840MHz –70.42 –87.31 –71.40 –88.28
4 –17.64dBm
OFFSET FREQ INTEG BW dBc dBm dBc dBm
VBW 30kHz ST OP 174.42MHz
SWEEP 206.9ms (601 PTS)
LOWER UPPER
08281-132
Figure 35. Four-Carrier W-CDMA ACLR Performance, IF = ~150 MHz
Rev. B | Page 16 of 60

AD9122
TERMINOLOGY
Integral Nonlinearity (INL)
INL is the maximum deviation of the actual analog output from
the ideal output, determined by a straight line drawn from zero
scale to full scale.
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
DNL is the measure of the variation in analog value, normalized
to full scale, associated with a 1 LSB change in digital input code.
Offset Error
Offset error is the deviation of the output current from the ideal
of 0 mA. For IOUT1P, 0 mA output is expected when all inputs
are set to 0. For IOUT1N, 0 mA output is expected when all
inputs are set to 1.
Gain Error
Gain error is the difference between the actual and ideal output
span. The actual span is determined by the difference between
the output when all inputs are set to 1 and the output when all
inputs are set to 0.
Output Compliance Range
The output compliance range is the range of allowable voltage
at the output of a current output DAC. Operation beyond the
maximum compliance limits can cause either output stage
saturation or breakdown, resulting in nonlinear performance.
Temp er at u re D ri ft
Temperature drift is specified as the maximum change from
the ambient (25°C) value to the value at either T
MIN
or T
MAX
.
For offset and gain drift, the drift is reported in ppm of full-scale
range (FSR) per degree Celsius. For reference voltage drift, the
drift is reported in ppm per degree Celsius.
Power Supply Rejection (PSR)
PSR is the maximum change in the full-scale output as the
supplies are varied from minimum to maximum specified
voltages.
Settling Time
Settling time is the time required for the output to reach and
remain within a specified error band around its final value,
measured from the start of the output transition.
Spurious-Free Dynamic Range (SFDR)
SFDR is the difference, in decibels, between the peak amplitude
of the output signal and the peak spurious signal within the dc
to Nyquist frequency of the DAC. Typically, energy in this band
is rejected by the interpolation filters. This specification, therefore, defines how well the interpolation filters work and the
effect of other parasitic coupling paths on the DAC output.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR)
SNR is the ratio of the rms value of the measured output signal
to the rms sum of all other spectral components below the Nyquist
frequency, excluding the first six harmonics and dc. The value
for SNR is expressed in decibels.
Interpolation Filter
If the digital inputs to the DAC are sampled at a multiple rate of
f
(interpolation rate), a digital filter can be constructed that
DATA
has a sharp transition band near f
appear around f
(output data rate) can be greatly suppressed.
DAC
/2. Images that typically
DATA
Adjacent Channel Leakage Ratio (ACLR)
ACLR is the ratio in decibels relative to the carrier (dBc) between
the measured power within a channel and that of its adjacent
channel.
Complex Image Rejection
In a traditional two-part upconversion, two images are created
around the second IF frequency. These images have the effect
of wasting transmitter power and system bandwidth. By placing
the real part of a second complex modulator in series with the
first complex modulator, either the upper or lower frequency
image near the second IF can be rejected.
Rev. B | Page 17 of 60
AD9122
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN AD9122R1 AND AD9122R2
The AD9122 underwent a die revision in early 2010, which
incremented the die revision from R1 to R2. The following list
explains the differences between the revisions.
• IOVDD supply voltage range.
For the AD9122R1, the valid operational voltage range
for IOVDD is 1.8 V to 2.5 V ± 10%. For the AD9122R2,
the valid operational voltage range for IOVDD is 1.8 V
to 3.3 V ± 10%.
• Reduction in spurs level variation.
The AD9122R1 has variation in the f
DATA
± f
spur level
OUT
between device startups. The AD9122R2 has a consistent
and lower f
DATA
± f
spur level. (The AD9122R2 still has
OUT
a spur level variation between power cycles of about 5 dB
if the PLL is enabled.)
• DCI delay feature added.
The AD9122R2 has a programmable delay associated with
the DCI signal. There are four programmable delay options.
The 00 setting gives the minimum delay and leaves the
timing unchanged from the AD9122R1. Additional delay
can be added to improve timing margins in some systems.
The resulting timing options are shown in Tab l e 13.
• Power-down mode power consumption increase.
The maximum power-down mode power consumption
of the R1 devices is 9.8 mW. This power consumption
increased to 18.8 mW in the R2 devices.
• Configuration register map changes.
Register 0x0B, Bit 5:
AD9122R1 Æ Enable VCO
AD9122R2 Æ Inactive bit. The VCO is now enabled
when the PLL is enabled.
Register 0x16, Bits[1:0]:
AD9122R1 Æ Unused
AD9122R2 Æ These bits control the delay of the DCI
signal (00 = minimum delay, 11 = maximum delay).
Register 0x7F:
AD9122R1 Æ Version ID = 0x04
AD9122R2 Æ Version ID = 0x0C
DEVICE MARKING OF AD9122R1 AND AD9122R2
Revision 1 devices are marked as shown in Figure 36. Revision 1
devices with TxDAC® as the top line have date codes earlier than
#1001. Revision 1 devices with AD80255 as the top line have date
codes of #1001 or later.
Revision 2 devices are marked as shown in Figure 37. Revision 2
devices have TxDAC® as the top line and date codes of #1001 or
later.
®
TxDAC
AD9122BCPZ
DATE CODE
Figure 36. Revision 1 Silicon, AD9122BCPZ Marking
Figure 37. Revision 2 Silicon, AD9122BCPZ Marking
#0935
1688587.1
KOREA
DATE CODE
TxDAC
AD9122BCPZ
#1021
1688782.1
KOREA
AD80255
AD9122BCPZ
#1001
1688586.1
KOREA
®
08281-136
08281-137
Rev. B | Page 18 of 60

AD9122
THEORY OF OPERATION
The AD9122 combines many features that make it a very attractive
DAC for wired and wireless communications systems. The dual
digital signal path and dual DAC structure allow an easy interface
to common quadrature modulators when designing single sideband (SSB) transmitters. The speed and performance of the
AD9122 allow wider bandwidths and more carriers to be synthesized than in previously available DACs. In addition, the
AD9122 includes an innovative low power, 32-bit, complex
NCO that greatly increases the ease of frequency placement.
The AD9122 offers features that allow simplified synchronization with incoming data and between multiple devices. Auxiliary
DACs are also provided on chip. The auxiliary DACs can be used
for output dc offset compensation (for LO compensation in SSB
transmitters) and for gain matching (for image rejection optimization in SSB transmitters).
SERIAL PORT OPERATION
The serial port is a flexible, synchronous serial communications
port that allows easy interfacing to many industry-standard microcontrollers and microprocessors. The serial I/O is compatible
with most synchronous transfer formats, including both the
Motorola SPI and Intel® SSR protocols. The interface allows
read/write access to all registers that configure the AD9122.
Single-byte or multiple-byte transfers are supported, as well as
MSB first or LSB first transfer formats. The serial port interface
can be configured as a single-pin I/O (SDIO) or as two unidirectional pins for input and output (SDIO and SDO).
50
SDO
51
SDIO
SCLK
Figure 38. Serial Port Interface Pins
A communication cycle with the AD9122 has two phases.
Phase 1 is the instruction cycle (the writing of an instruction
byte into the device), coincident with the first eight SCLK rising
edges. The instruction byte provides the serial port controller
with information regarding the data transfer cycle—Phase 2 of
the communication cycle. The Phase 1 instruction byte defines
whether the upcoming data transfer is a read or write, along with
the starting register address for the first byte of the data transfer.
The first eight SCLK rising edges of each communication cycle
are used to write the instruction byte into the device.
A logic high on the
CS
pin followed by a logic low resets the
serial port timing to the initial state of the instruction cycle.
From this state, the next eight rising SCLK edges represent the
instruction bits of the current I/O operation.
CS
SPI
PORT
52
53
08281-010
Rev. B | Page 19 of 60
The remaining SCLK edges are for Phase 2 of the communication
cycle. Phase 2 is the actual data transfer between the device and
the system controller. Phase 2 of the communication cycle is a
transfer of one or more data bytes. Registers change immediately
upon writing to the last bit of each transfer byte, except for the
frequency tuning word and NCO phase offsets, which change
only when the frequency tuning word (FTW) update bit
(Register 0x36, Bit 0) is set.
DATA FORMAT
The instruction byte contains the information shown in Tab l e 9.
Table 9. Serial Port Instruction Byte
I7 (MSB) I6 I5 I4 I3 I2 I1 I0 (LSB)
R/W
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
R/W, Bit 7 of the instruction byte, determines whether a read
or a write data transfer occurs after the instruction byte write.
Logic 1 indicates a read operation, and Logic 0 indicates a write
operation.
A6 to A0, Bit 6 to Bit 0 of the instruction byte, determine the
register that is accessed during the data transfer portion of the
communication cycle. For multibyte transfers, A6 is the starting
byte address. The remaining register addresses are generated by
the device based on the LSB_FIRST bit (Register 0x00, Bit 6).
SERIAL PORT PIN DESCRIPTIONS
Serial Clock (SCLK)
The serial clock pin synchronizes data to and from the device
and runs the internal state machines. The maximum frequency
of SCLK is 40 MHz. All data input is registered on the rising edge
of SCLK. All data is driven out on the falling edge of SCLK.
Chip Select (
An active low input starts and gates a communication cycle.
It allows more than one device to be used on the same serial
communications lines. When the
SDIO pins go to a high impedance state. During the communication cycle, the
Serial Data I/O (SDIO)
Data is always written into the device on this pin. However, this
pin can be used as a bidirectional data line. The configuration
of this pin is controlled by Register 0x00, Bit 7. The default is
Logic 0, configuring the SDIO pin as unidirectional.
Serial Data Output (SDO)
Data is read from this pin for protocols that use separate lines
for transmitting and receiving data. If the device operates in a
single bidirectional I/O mode, this pin does not output data and
is set to a high impedance state.
CS
)
CS
pin should stay low.
CS
pin is high, the SDO and

AD9122
K
K
SERIAL PORT OPTIONS
The serial port can support both MSB first and LSB first data
formats. This functionality is controlled by the LSB_FIRST bit
(Register 0x00, Bit 6). The default is MSB first (LSB_FIRST = 0).
When LSB_FIRST = 0 (MSB first), the instruction and data bits
must be written from MSB to LSB. Multibyte data transfers in
MSB first format start with an instruction byte that includes the
register address of the most significant data byte. Subsequent
data bytes should follow from high address to low address. In
MSB first mode, the serial port internal byte address generator
decrements for each data byte of the multibyte communication
cycle.
When LSB_FIRST = 1 (LSB first), the instruction and data bits
must be written from LSB to MSB. Multibyte data transfers in
LSB first format start with an instruction byte that includes the
register address of the least significant data byte. Subsequent
data bytes should follow from low address to high address. In
LSB first mode, the serial port internal byte address generator
increments for each data byte of the multibyte communication
cycle.
If the MSB first mode is active, the serial port controller data
address decrements from the data address written toward 0x00
for multibyte I/O operations. If the LSB first mode is active, the
serial port controller data address increments from the data
address written toward 0x7F for multibyte I/O operations.
INSTRUCTIO N CYCLE DATA TRANSFER CYCLE
CS
SCLK
SDIO
SCL
SDIO
SCL
SDIO,
INSTRUCTIO N CYCLE DATA TRANSFER CYCLE
CS
A0 A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 A6 D00D10D2
SDO
R/W
D00D10D2
Figure 40. Serial Port Interface Timing, LSB First
t
CS
DCSB
t
DS
t
PWH
t
t
SCLK
t
PWL
DH
INSTRUCTION BIT 6INSTRUCTION BIT 7
Figure 41. Timing Diagram for Serial Port Register Write
CS
t
DV
SDO
DATA BIT n – 1DATA BIT n
Figure 42. Timing Diagram for Serial Port Register Read
0
0
D7ND6ND5ND4
N
D7ND6ND5ND4
N
08281-012
08281-013
8281-014
SCLK
SDIO
SDO
R/W A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0 D7ND6ND5
D7ND6ND5
N
N
Figure 39. Serial Port Interface Timing, MSB First
D00D10D20D3
0
D00D10D20D3
0
08281-011
Rev. B | Page 20 of 60

AD9122
DEVICE CONFIGURATION REGISTER MAP AND DESCRIPTIONS
Table 10. Device Configuration Register Map
Addr
(Hex) Register Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Default
0x00 Comm SDIO LSB_FIRST Reset 0x00
0x01 Power control
0x03 Data format
0x04 Interrupt enable
0x05 Interrupt enable 0 0 0
0x06 Event flag
0x07 Event flag
0x08
0x0A PLL control
0x0C PLL control
0x0D PLL control N2[1:0]
0x0E PLL status PLL locked VCO Control Voltage[3:0] N/A
0x0F PLL status VCO Band Readback[5:0] N/A
0x10 Sync control
0x11 Sync control Sync Phase Request[5:0] 0x00
0x12 Sync status Sync lost
0x13 Sync status Sync Phase Readback[7:0] (6.2 format) N/A
0x15
0x16 DCI delay DCI Delay[1:0] 0x00
0x17 FIFO control FIFO Phase Offset[2:0] 0x04
0x18 FIFO status
0x19 FIFO status FIFO Level[7:0] N/A
0x1B
Clock receiver
control
Data receiver
status
Datapath
control
Power
down
I DAC
Binary
data
format
Enable
PLL lock
lost
PLL lock
lost
DACCLK
duty
correction
PLL
enable
Bandwidth[1:0]
Sync
enable
FIFO
Warning 1
Bypass
premod
Power
down
Q DAC
Q data
first
Enable
PLL
locked
PLL
locked
REFCLK
duty
correction
PLL
manual
enable
PLL Loop
Data/FIFO
rate toggle
Sync
locked
FIFO
Warning 2
Bypass
sinc−1
Power
down data
receiver
MSB swap Data Bus Width[1:0] 0x00
Enable
sync
signal lost
Sync
signal
lost
DACCLK
crosscorrection
PLL Charge Pump Current[4:0] 0xD1
N/A
LVD S
FRAME
level high
Bypass
NCO
Power
down
aux ADC
Enable
sync
signal
locked
Enable
AED
compare
pass
Sync
signal
locked
AED
compare
pass
REFCLK
crosscorrection
PLL crosscontrol
enable
LVD S
FRAME
level low
NCO gain
0x10
Enable
AED
compare
fail
AED
compare
fail
1 1 1 1 0x3F
Manual VCO Band[5:0] 0x40
Rising
edge sync
LVDS DCI
level high
Enable
SED
compare
fail
SED
compare
fail
N0[1:0] N1[1:0] 0xD9
LVDS DCI
level low
FIFO soft
align ack
Bypass
phase
comp and
dc offset
Enable
FIFO
Warning 1
0 0 0x00
FIFO
Warning 1
N/A
Sync Averaging[2:0] 0x48
LVDS data
level high
FIFO soft
align
request
Select
sideband
Enable
FIFO
Warning 2
FIFO
Warning 2
LVDS data
level low
N/A
Send
I data to
Q data
0x00
N/A
N/A
0xE4
Rev. B | Page 21 of 60

AD9122
Addr
(Hex) Register Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Default
0x1C HB1 control HB1[1:0] Bypass HB1 0x00
0x1D HB2 control HB2[5:0] Bypass HB2 0x00
0x1E HB3 control HB3[5:0] Bypass HB3 0x00
0x1F Chip ID Chip ID[7:0] 0x08
0x30 FTW LSB FTW[7:0] 0x00
0x31 FTW FTW[15:8] 0x00
0x32 FTW FTW[23:16] 0x00
0x33 FTW MSB FTW[31:24] 0x00
0x34
0x35
0x36
0x38 I phase adj LSB I Phase Adj[7:0] 0x00
0x39 I phase adj MSB I Phase Adj[9:8] 0x00
0x3A Q phase adj LSB Q Phase Adj[7:0] 0x00
0x3B Q phase adj MSB Q Phase Adj[9:8] 0x00
0x3C I DAC offset LSB I DAC Offset[7:0] 0x00
0x3D I DAC offset MSB I DAC Offset[15:8] 0x00
0x3E
0x3F
0x40 I DAC FS adjust I DAC FS Adj[7:0] 0xF9
0x41 I DAC control
0x42 I aux DAC data I Aux DAC[7:0] 0x00
0x43
0x44 Q DAC FS adjust Q DAC FS Adj[7:0] 0xF9
0x45 Q DAC control
0x46 Q aux DAC data Q Aux DAC[7:0] 0x00
0x47
0x48
0x49 Die temp LSB Die Temp[7:0] N/A
0x4A Die temp MSB Die Temp[15:8] N/A
0x67 SED control
0x68 Compare I0 LSBs Compare Value I0[7:0] 0xB6
0x69
0x6A
0x6B
NCO phase
offset LSB
NCO phase
offset MSB
NCO FTW
update
Q DAC offset
LSB
Q DAC offset
MSB
I aux DAC
control
Q aux DAC
control
Die temp range
control
Compare
I0 MSBs
Compare
Q0 LSBs
Compare
Q0 MSBs
I DAC
sleep
I aux
DAC sign
Q DAC
sleep
Q aux
DAC sign
SED
compare
enable
I DAC FS Adj[9:8] 0x01
I aux DAC
current
direction
Q DAC FS Adj[9:8] 0x01
Q aux DAC
current
direction
FS Current[2:0] Reference Current[2:0]
FRAME
FTW ack
I aux DAC
sleep
Q aux
DAC
sleep
Sample
error
detected
NCO Phase Offset[7:0] 0x00
NCO Phase Offset[15:8] 0x00
FRAME
FTW
request
Q DAC Offset[7:0] 0x00
Q DAC Offset[15:8] 0x00
I Aux DAC[9:8] 0x00
Q Aux DAC[9:8] 0x00
Compare Value I0[15:8] 0x7A
Compare Value Q0[7:0] 0x45
Compare Value Q0[15:8] 0xEA
Autoclear
enable
Update
FTW ack
Compare
fail
Update
FTW
request
Capacitor
value
Compare
pass
0x00
0x02
0x00
Rev. B | Page 22 of 60

AD9122
Addr
(Hex) Register Name Bit 7 Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 Bit 0 Default
0x6C Compare I1 LSBs Compare Value I1[7:0] 0x16
0x6D
0x6E
0x6F
0x70 SED I LSBs Errors Detected I_BITS[7:0] 0x00
0x71 SED I MSBs Errors Detected I_BITS[15:8] 0x00
0x72 SED Q LSBs Errors Detected Q_BITS[7:0] 0x00
0x73 SED Q MSBs Errors Detected Q_BITS[15:8] 0x00
0x7F Revision 0 0 Revision[3:0] 0 0 N/A
Compare
I1 MSBs
Compare
Q1 LSBs
Compare
Q1 MSBs
Table 11. Device Configuration Register Descriptions
Register
Name
Comm 0x00 7 SDIO SDIO pin operation. 0
0 = SDIO operates as an input only.
1 = SDIO operates as a bidirectional input/output.
6 LSB_FIRST Serial port communication, LSB or MSB first. 0
0 = MSB first.
1 = LSB first.
Power
Control
Data
Format
6 Q data first Indicates I/Q data pairing on data input. 0
0 = I data sent to data receiver first.
1 = Q data sent to data receiver first.
5 MSB swap Swaps the bit order of the data input port. 0
0 = order of the data bits corresponds to the pin descriptions.
00 = word mode; 16-bit interface bus width.
01 = byte mode; 8-bit interface bus width.
10 = nibble mode; 4-bit interface bus width.
11 = invalid.
Interrupt
Enable
Address
(Hex) Bits Name Description Default
5 Reset
0x01 7 Power down I DAC 1 = power down I DAC. 0
6 Power down Q DAC 1 = power down Q DAC. 0
5
Power down data
receiver
4
Power down auxiliary
ADC
0x03 7 Binary data format 0 = input data is in twos complement format. 0
1 = input data is in binary format.
[1:0] Data Bus Width[1:0]
0x04 7 Enable PLL lock lost 1 = enable interrupt for PLL lock lost. 0
6 Enable PLL locked 1 = enable interrupt for PLL locked. 0
5 Enable sync signal lost 1 = enable interrupt for sync signal lost. 0
4 Enable sync signal locked 1 = enable interrupt for sync signal locked. 0
1 Enable FIFO Warning 1 1 = enable interrupt for FIFO Warning 1. 0
0 Enable FIFO Warning 2 1 = enable interrupt for FIFO Warning 2. 0
Compare Value I1[15:8] 0x1A
Compare Value Q1[7:0] 0xC6
Compare Value Q1[15:8] 0xAA
The device is placed in reset when this bit is written high
and remains in reset until the bit is written low.
1 = power down the input data receiver. 0
1 = power down the auxiliary ADC for temperature sensor. 1
1 = bit designations are swapped; most significant bits
become the least significant bits.
Data receiver interface mode. See the LVDS Input Data Ports
section for information about the operation of the different
interface modes.
0
00
Rev. B | Page 23 of 60

AD9122
Register
Name
Interrupt
Enable
Event Flag 0x06 7 PLL lock lost
Note that all event flags are cleared by writing the respective bit high.
0x07 4 AED compare pass
Note that all event flags are cleared by writing the respective bit high.
Clock
Receiver
Control
4 REFCLK cross-correction
PLL Control 0x0A 7 PLL enable
0x0C [7:6] PLL Loop Bandwidth[1:0] Selects the PLL loop filter bandwidth. 11
Address
(Hex) Bits Name Description Default
0x05 [7:5] Set to 0 Set these bits to 0. 000
4 Enable AED compare pass 1 = enable interrupt for AED comparison pass. 0
3 Enable AED compare fail 1 = enable interrupt for AED comparison fail. 0
2 Enable SED compare fail 1 = enable interrupt for SED comparison fail. 0
[1:0] Set to 0 Set these bits to 0. 00
1 = indicates that the PLL, which had been previously
locked, has unlocked from the reference signal. This is a
latched signal.
6 PLL locked
5 Sync signal lost
4 Sync signal locked
1 FIFO Warning 1
0 FIFO Warning 2
3 AED compare fail
2 SED compare fail
0x08 7 DACCLK duty correction 1 = enable duty cycle correction on the DACCLK input. 0
6 REFCLK duty correction 1 = enable duty cycle correction on the REFCLK input. 0
5 DACCLK cross-correction
6 PLL manual enable
[5:0] Manual VCO Band[5:0] Selects the VCO band to be used. 000000
00 = widest bandwidth.
…
11 = narrowest bandwidth.
[4:0]
PLL Charge Pump
Current[4:0]
00000 = lowest current setting.
…
11111 = highest current setting.
1 = indicates that the PLL has locked to the reference
clock input.
1 = indicates that the sync logic, which had been previously
locked, has lost alignment. This is a latched signal.
1 = indicates that the sync logic has achieved sync
alignment. This is indicated when no phase changes
were requested for at least a few full averaging cycles.
1 = indicates that the difference between the FIFO read
and write pointers is 1.
1 = indicates that the difference between the FIFO read
and write pointers is 2.
1 = indicates that the SED logic detected a valid input data
pattern compared against the preprogrammed expected
values. This is a latched signal.
1 = indicates that the SED logic detected an invalid input
data pattern compared against the preprogrammed
expected values. This latched signal is automatically cleared
when eight valid I/Q data pairs are received.
1 = indicates that the SED logic detected an invalid input
data pattern compared against the preprogrammed
expected values. This is a latched signal.
1 = enable differential crossing correction on the DACCLK
input.
1 = enable differential crossing correction on the REFCLK
input.
1 = enable the PLL clock multiplier. The REFCLK input is used
as the PLL reference clock signal.
1 = enable manual selection of the VCO band. The correct
VCO band must be determined by the user and written to
Bits[5:0].
Sets the nominal PLL charge pump current. 10001
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
N/A
1
1
0
1
Rev. B | Page 24 of 60

AD9122
Register
Name
PLL Control 0x0D [7:6] N2[1:0]
00 = f
01 = f
10 = f
11 = f
PLL Status 0x0E 7 PLL locked
0x0F [5:0] VCO Band Readback[5:0] Indicates the VCO band currently selected. N/A
Sync
Control
000 = 1.
001 = 2.
010 = 4.
011 = 8.
100 = 16.
101 = 32.
110 = 64.
111 = 128.
0x11 [5:0] Sync Phase Request[5:0]
000000 = 0 DACCLK cycles.
000001 = 1 DACCLK cycle.
…
111111 = 63 DACCLK cycles.
Address
(Hex) Bits Name Description Default
PLL control clock divider. This divider determines the ratio of
11
the DACCLK frequency to the PLL controller clock frequency.
must always be less than 75 MHz.
f
PC_CLK
00 = f
01 = f
10 = f
11 = f
DACCLK/fPC_CLK
DACCLK/fPC_CLK
DACCLK/fPC_CLK
DACCLK/fPC_CLK
= 2.
= 4.
= 8.
= 16.
4 PLL cross-control enable 1 = enable PLL cross-point controller. 1
[3:2] N0[1:0]
PLL VCO divider. This divider determines the ratio of the VCO
10
frequency to the DACCLK frequency.
00 = f
01 = f
10 = f
11 = f
[1:0] N1[1:0]
PLL loop divider. This divider determines the ratio of the
VCO/fDACCLK
VCO/fDACCLK
VCO/fDACCLK
VCO/fDACCLK
= 1.
= 2.
= 4.
= 4.
01
DACCLK frequency to the REFCLK frequency.
DACCLK/fREFCLK
DACCLK/fREFCLK
DACCLK/fREFCLK
DACCLK/fREFCLK
1 = the PLL-generated clock is tracking the REFCLK input
= 2.
= 4.
= 8.
= 16.
N/A
signal.
[3:0] VCO Control Voltage[3:0] VCO control voltage readback. See Table 24 . N/A
0x10 7 Sync enable 1 = enable the synchronization logic. 0
6 Data/FIFO rate toggle 0 = operate the synchronization at the FIFO reset rate. 1
1 = operate the synchronization at the data rate.
3 Rising edge sync 0 = sync is initiated on the falling edge of the sync input. 1
1 = sync is initiated on the rising edge of the sync input.
[2:0] Sync Averaging[2:0]
Sets the number of input samples that are averaged in
000
determining the sync phase.
This register sets the requested clock phase offset after sync.
000000
The offset unit is in DACCLK cycles. This register enables
repositioning of the DAC output with respect to the sync
input. The offset can also be used to skew the DAC outputs
between the synchronized DACs.
Rev. B | Page 25 of 60

AD9122
Register
Name
Sync Status 0x12 7 Sync lost 1 = synchronization was attained but has been lost. N/A
0x13 [7:0] Sync Phase Readback[7:0]
00000000 = 0.0.
00000001 = 0.25.
…
11111110 = 63.50.
11111111 = 63.75.
Data
Receiver
Status
DCI Delay 0x16 [1:0] DCI Delay[1:0]
FIFO
Control
FIFO Status 0x18 7 FIFO Warning 1 1 = FIFO read and write pointers are within ±1. N/A
0x19 [7:0] FIFO Level[7:0] Thermometer encoded measure of the FIFO level. N/A
Address
(Hex) Bits Name Description Default
6 Sync locked 1 = synchronization has been attained. N/A
Indicates the averaged sync phase offset (6.2 format). If
this value differs from the Sync Phase Request[5:0] value
in Register 0x11, a sync timing error has occurred. For more
information, see the Sync Status Bits section.
0x15 5 LVDS FRAME level high One or both LVDS FRAME input signals have exceeded 1.7 V. N/A
4 LVDS FRAME level low
3 LVDS DCI level high One or both LVDS DCI input signals have exceeded 1.7 V. N/A
2 LVDS DCI level low
1 LVDS data level high One or more LVDS Dx input signals have exceeded 1.7 V. N/A
0 LVDS data level low One or more LVDS Dx input signals have crossed below 0.7 V. N/A
0x17 [2:0] FIFO Phase Offset[2:0]
000 = 0.
001 = 1.
…
111 = 7.
6 FIFO Warning 2 1 = FIFO read and write pointers are within ±2. N/A
2
FIFO soft align
acknowledge
1 FIFO soft align request
One or both LVDS FRAME input signals have crossed below
0.7 V.
One or both LVDS DCI input signals have crossed
below 0.7 V.
This option is available for the Revision 2 silicon only. The
DCI delay bits control the delay applied to the DCI signal.
The DCI delay affects the sampling interval of the DCI with
respect to the Dx inputs. See Table 1 3.
00 = 350 ps delay of DCI signal.
01 = 590 ps delay of DCI signal.
10 = 800 ps delay of DCI signal.
11 = 925 ps delay of DCI signal.
FIFO write pointer phase offset following FIFO reset. This
is the difference between the read pointer and the write
pointer values upon FIFO reset. The optimal value is
nominally 4 (100).
1 = FIFO read and write pointers are aligned after a serial
port initiated FIFO reset.
1 = request FIFO read and write pointer alignment via the
serial port.
N/A
N/A
N/A
00
100
N/A
0
Rev. B | Page 26 of 60

AD9122
Register
Name
Datapath
Control
HB1 Control 0x1C [2:1] HB1[1:0] Modulation mode for I Side Half-Band Filter 1. 00
HB2 Control 0x1D [6:1] HB2[5:0] Modulation mode for I Side Half-Band Filter 2. 000000
Address
(Hex) Bits Name Description Default
0x1B 7 Bypass premod 1 = bypass the f
/2 premodulator. 1
S
6 Bypass sinc−1 1 = bypass the inverse sinc filter. 1
5 Bypass NCO 1 = bypass the NCO. 1
3 NCO gain
0 = no gain scaling is applied to the NCO input to the
0
internal digital modulator (default).
1 = gain scaling of 0.5 is applied to the NCO input to the
internal digital modulator. Gain scaling can eliminate saturation of the modulator output for some combinations of
data inputs and NCO signals.
2
Bypass phase
1 = bypass phase compensation and dc offset. 1
compensation
and dc offset
1 Select sideband 0 = the modulator outputs the high-side image. 0
1 = the modulator outputs the low-side image. The image is
spectrally inverted compared to the input data.
0 Send I data to Q data
1 = ignore Q data from the interface and disable the clocks
0
to the Q datapath. Send I data to both the I and Q DACs.
00 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is from
−0.4 to +0.4 of f
.
IN1
01 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is from
0.1 to 0.9 of f
10 = input signal modulated by f
0.6 to 1.4 of f
11 = input signal modulated by f
1.1 to 1.9 of f
.
IN1
; filter pass band is from
.
IN1
.
IN1
IN1
; filter pass band is from
IN1
0 Bypass HB1 1 = bypass the first-stage interpolation filter. 0
000000 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is
from −0.25 to +0.25 of f
.
IN2
001001 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is
from 0.0 to 0.5 of f
.
IN2
010010 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is
from 0.25 to 0.75 of f
.
IN2
011011 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is
from 0.5 to 1.0 of f
100100 = input signal modulated by f
from 0.75 to 1.25 of f
101101 = input signal modulated by f
from 1.0 to 1.5 of f
110110 = input signal modulated by f
from 1.25 to 1.75 of f
111111 = input signal modulated by f
from 1.5 to 2.0 of f
.
IN2
; filter pass band is
.
IN2
.
IN2
.
IN2
.
IN2
IN2
; filter pass band is
IN2
; filter pass band is
IN2
; filter pass band is
IN2
0 Bypass HB2 1 = bypass the second-stage interpolation filter. 0
Rev. B | Page 27 of 60

AD9122
Register
Name
HB3 Control 0x1E [6:1] HB3[5:0] Modulation mode for I Side Half-Band Filter 3. 000000
0 Bypass HB3 1 = bypass the third-stage interpolation filter. 0
Chip ID 0x1F [7:0] Chip ID[7:0] This register identifies the device as an AD9122. 00001000
FTW LSB 0x30 [7:0] FTW[7:0] See Register 0x33. 00000000
FTW 0x31 [7:0] FTW[15:8] See Register 0x33. 00000000
FTW 0x32 [7:0] FTW[23:16] See Register 0x33. 00000000
FTW MSB 0x33 [7:0] FTW[31:24]
NCO Phase
Offset LSB
NCO Phase
Offset MSB
NCO FTW
Update
I Phase Adj
LSB
I Phase Adj
MSB
Q Phase Adj
LSB
Q Phase Adj
MSB
I DAC Offset
LSB
I DAC Offset
MSB
Address
(Hex) Bits Name Description Default
000000 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is
from −0.2 to +0.2 of f
.
IN3
001001 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is
from 0.05 to 0.45 of f
.
IN3
010010 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is
from 0.3 to 0.7 of f
.
IN3
011011 = input signal not modulated; filter pass band is
from 0.55 to 0.95 of f
100100 = input signal modulated by f
from 0.8 to 1.2 of f
101101 = input signal modulated by f
from 1.05 to 1.45 of f
110110 = input signal modulated by f
from 1.3 to 1.7 of f
111111 = input signal modulated by f
from 1.55 to 1.95 of f
.
IN3
; filter pass band is
.
IN3
.
IN3
.
IN3
.
IN3
IN3
; filter pass band is
IN3
; filter pass band is
IN3
; filter pass band is
IN3
FTW[31:0] is the 32-bit frequency tuning word that deter-
00000000
mines the frequency of the complex carrier generated by the
on-chip NCO. The frequency is not updated when the FTW
registers are written. The values are only updated when Bit 0
of Register 0x36 transitions from 0 to 1.
0x34 [7:0] NCO Phase Offset[7:0] See Register 0x35. 00000000
0x35 [7:0] NCO Phase Offset[15:8]
The NCO sets the phase of the complex carrier signal when
00000000
the NCO is reset. The phase offset spans from 0° to 360°.
Each bit represents an offset of 0.0055°. This value is in
twos complement format.
0x36 5 FRAME FTW acknowledge
1 = the NCO has been reset due to an extended FRAME
0
pulse signal.
4 FRAME FTW request
0 = the NCO is reset on the first extended FRAME pulse after
0
this bit is set to 1.
1 Update FTW acknowledge 1 = the FTW has been updated. 0
0 Update FTW request The FTW is updated on the 0-to-1 transition of this bit. 0
0x38 [7:0] I Phase Adj[7:0] See Register 0x39. 00000000
0x39 [1:0] I Phase Adj[9:8]
I Phase Adj[9:0] is used to insert a phase offset between
00
the I and Q datapaths. This offset can be used to correct
for phase imbalance in a quadrature modulator. See the
Quadrature Phase Correction section for more information.
0x3A [7:0] Q Phase Adj[7:0] See Register 0x3B. 00000000
0x3B [1:0] Q Phase Adj[9:8]
Q Phase Adj[9:0] is used to insert a phase offset between
00
the I and Q datapaths. This offset can be used to correct
for phase imbalance in a quadrature modulator. See the
Quadrature Phase Correction section for more information.
0x3C [7:0] I DAC Offset[7:0] See Register 0x3D. 00000000
0x3D [7:0] I DAC Offset[15:8]
I DAC Offset[15:0] is a value that is added directly to the
00000000
samples written to the I DAC.
Rev. B | Page 28 of 60

AD9122
Register
Name
Q DAC
Offset LSB
Q DAC
Offset MSB
I DAC
FS Adjust
I DAC
Control
0x000 = 8.64 mA.
…
0x200 = 20.16 mA.
…
0x3FF = 31.68 mA.
I Aux DAC
Data
I Aux DAC
Control
0x000 = 0.000 mA.
0x001 = 0.002 mA.
…
0x3FF = 2.046 mA.
Q DAC
FS Adjust
Q DAC
Control
0x000 = 8.64 mA.
…
0x200 = 20.16 mA.
…
0x3FF = 31.68 mA.
Q Aux DAC
Data
Address
(Hex) Bits Name Description Default
0x3E [7:0] Q DAC Offset[7:0] See Register 0x3F. 00000000
0x3F [7:0] Q DAC Offset[15:8]
0x40 [7:0] I DAC FS Adj[7:0] See Register 0x41, Bits[1:0]. 11111001
0x41 7 I DAC sleep 1 = puts the I DAC into sleep mode (fast wake-up mode). 0
[1:0] I DAC FS Adj[9:8]
0x42 [7:0] I Aux DAC[7:0] See Register 0x43, Bits[1:0]. 00000000
0x43 7 I aux DAC sign
6
I aux DAC current
direction
1 = the I auxiliary DAC sinks current.
5 I aux DAC sleep 1 = puts the I auxiliary DAC into sleep mode. 0
[1:0] I Aux DAC[9:8]
0x44 [7:0] Q DAC FS Adj[7:0] See Register 0x45, Bits[1:0]. 11111001
0x45 7 Q DAC sleep 1 = puts the Q DAC into sleep mode (fast wake-up mode). 0
[1:0] Q DAC FS Adj[9:8]
0x46 [7:0]
Q Aux DAC[7:0]
Q DAC Offset[15:0] is a value that is added directly to the
samples written to the Q DAC.
I DAC FS Adj[9:0] sets the full-scale current of the I DAC.
The full-scale current can be adjusted from 8.64 mA to
31.68 mA in step sizes of approximately 22.5 μA.
0 = the I auxiliary DAC sign is positive, and the current is
directed to the IOUT1P pin (Pin 67).
1 = the I auxiliary DAC sign is negative, and the current is
directed to the IOUT1N pin (Pin 66).
0 = the I auxiliary DAC sources current. 0
I Aux DAC[9:0] sets the magnitude of the auxiliary DAC
current. The range is 0 mA to 2 mA, and the step size is 2 μA.
Q DAC FS Adj[9:0] sets the full-scale current of the Q DAC.
The full-scale current can be adjusted from 8.64 mA to
31.68 mA in step sizes of approximately 22.5 μA.
See Register 0x47, Bits[1:0]. 00000000
00000000
01
0
00
01
Rev. B | Page 29 of 60

AD9122
Register
Name
Q Aux DAC
Control
0x000 = 0.000 mA.
0x001 = 0.002 mA.
…
0x3FF = 2.046 mA.
Die Temp
Range
Control
111 = highest current.
[3:1] Reference Current[2:0] Auxiliary ADC reference current. 001
000 = lowest current.
…
111 = highest current.
0 Capacitor value Auxiliary ADC internal capacitor value. 0
0 = 5 pF.
1 = 10 pF.
Die Temp
LSB
Die Temp
MSB
SED Control 0x67 7 SED compare enable
Compare
I0 LSBs
Compare
I0 MSBs
Compare
Q0 LSBs
Compare
Q0 MSBs
Compare
I1 LSBs
Compare
I1 MSBs
Address
(Hex) Bits Name Description Default
0x47 7 Q aux DAC sign
6
Q aux DAC current
direction
1 = the Q auxiliary DAC sinks current.
5 Q aux DAC sleep 1 = puts the Q auxiliary DAC into sleep mode. 0
[1:0] Q Aux DAC[9:8]
0x48 [6:4] FS Current[2:0] Auxiliary ADC full-scale current. 000
000 = lowest current.
…
0x49 [7:0] Die Temp[7:0] See Register 0x4A. N/A
0x4A [7:0] Die Temp[15:8]
5 Sample error detected
3 Autoclear enable
1 Compare fail
0 Compare pass 1 = indicates that the last sample comparison was error free. 0
0x68 [7:0] Compare Value I0[7:0] See Register 0x69. 10110110
0x69 [7:0] Compare Value I0[15:8]
0x6A [7:0] Compare Value Q0[7:0] See Register 0x6B. 01000101
0x6B [7:0] Compare Value Q0[15:8]
0x6C [7:0] Compare Value I1[7:0] See Register 0x6D. 00010110
0x6D [7:0] Compare Value I1[15:8]
0 = the Q auxiliary DAC sign is positive, and the current is
directed to the IOUT2P pin (Pin 58).
1 = the Q auxiliary DAC sign is negative, and the current is
directed to the IOUT2N pin (Pin 59).
0 = the Q auxiliary DAC sources current. 0
Q Aux DAC[9:0] sets the magnitude of the auxiliary DAC
current. The range is 0 mA to 2 mA, and the step size is 2 μA.
Die Temp[15:0] indicates the approximate die temperature.
For more information, see the Temperature Sensor section.
1 = enable the SED circuitry. None of the flags in this register
or the values in Register 0x70 through Register 0x73 are
significant if the SED is not enabled.
1 = indicates an error was detected. The bit remains set until
cleared. Any write to this register clears this bit to 0.
1 = enable autoclear mode. This activates Bit 1 and Bit 0 of
this register and causes Register 0x70 through Register 0x73
to be autocleared when eight consecutive sample data sets
are received error free.
1 = indicates an error was detected. This bit remains set until
it is autocleared by the reception of eight consecutive errorfree comparisons or is cleared by a write to this register.
Compare Value I0[15:0] is the word that is compared with
the I0 input sample captured at the input interface.
Compare Value Q0[15:0] is the word that is compared with
the Q0 input sample captured at the input interface.
Compare Value I1[15:0] is the word that is compared
with the I1 input sample captured at the input interface.
0
00
N/A
0
0
0
0
01111010
11101010
00011010
Rev. B | Page 30 of 60

AD9122
Register
Name
Compare
Q1 LSBs
Compare
Q1 MSBs
SED I
LSBs
SED I
MSBs
SED Q
LSBs
SED Q
MSBs
Revision 0x7F [5:2] Revision[3:0]
Address
(Hex) Bits Name Description Default
0x6E [7:0] Compare Value Q1[7:0] See Register 0x6F. 11000110
0x6F [7:0] Compare Value Q1[15:8]
0x70 [7:0]
0x71 [7:0]
0x72 [7:0]
0x73 [7:0]
Errors Detected
I_BITS[7:0]
Errors Detected
I_BITS[15:8]
Errors Detected
Q_BITS[7:0]
Errors Detected
Q_BITS[15:8]
Compare Value Q1[15:0] is the word that is compared
with the Q1 input sample captured at the input interface.
See Register 0x71. 00000000
Errors Detected I_BITS[15:0] indicates which bits were
received in error.
See Register 0x73. 00000000
Errors Detected Q_BITS[15:0] indicates which bits were
received in error.
This value corresponds to the die revision number.
0001 = Die Revision 1.
0011 = Die Revision 2.
10101010
00000000
00000000
N/A
Rev. B | Page 31 of 60

AD9122
LVDS INPUT DATA PORTS
The AD9122 has one LVDS data port that receives data for
both the I and Q transmit paths. The device can accept data in
word, byte, and nibble formats. In word, byte, and nibble modes,
the data is sent over 16-bit, 8-bit, and 4-bit LVDS data buses,
respectively. The pin assignments of the bus in each mode are
shown in Tab l e 12 .
Table 12. Data Bit Pair Assignments for Data Input Modes
Mode MSB to LSB
Word D15, D14, …, D0
Byte1 D14, D12, D10, D8, D7, D5, D3, D1
Nibble1 D10, D8, D7, D5
1
In byte and nibble modes, the unused pins can be left floating.
The data is accompanied by a reference bit (DCI) that is used
to generate a double data rate (DDR) clock. In byte and nibble
modes, a FRAME signal is required for controlling to which DAC
the data is sent. All of the interface signals are time aligned, so
there is a maximum skew requirement on the bus.
WORD INTERFACE MODE
In word mode, the DCI signal is a reference bit used to generate
the data sampling clock. The DCI signal should be time aligned
with the data. The I DAC data should correspond to DCI high,
and the Q DAC data should correspond to DCI low, as shown
in Figure 43.
DCI
DATA[15:0]
Q
0I1Q1I2Q2I3Q3
Figure 43. Timing Diagram for Word Mode
08281-015
BYTE INTERFACE MODE
In byte mode, the DCI signal is a reference bit used to generate
the data sampling clock. The DCI signal should be time aligned
with the data. The most significant byte of the data should correspond to DCI high, and the least significant byte of the data should
correspond to DCI low. The FRAME signal indicates to which
DAC the data is sent. When FRAME is high, data is sent to the
I DAC; when FRAME is low, data is sent to the Q DAC. The
complete timing diagram is shown in Figure 44.
NIBBLE INTERFACE MODE
In nibble mode, the DCI signal is a reference bit used to generate
the data sampling clock. The DCI signal should be time aligned
with the data. The FRAME signal indicates to which DAC the
data is sent. When FRAME is high, data is sent to the I DAC;
when FRAME is low, data is sent to the Q DAC. All four nibbles
must be written to the device for proper operation. For 12-bit
resolution devices, the data in the fourth nibble acts as a placeholder for the data framing structure. The complete timing
diagram is shown in Figure 45.
INTERFACE TIMING
The timing diagram for the digital interface port is shown in
Figure 46. The sampling point of the data bus nominally occurs
350 ps after each edge of the DCI signal and has an uncertainty
of ±300 ps, as illustrated by the sampling interval shown in
Figure 46. The data and FRAME signals must be valid throughout this sampling interval. The data and FRAME signals may
change at any time between sampling intervals.
DCI
DATA[15:0]
Q
0LSBI1MSBI1LSBQ1MSBQ1LSBI2MSBI2LSBQ2MSBQ2LSB
FRAME
Figure 44. Timing Diagram for Byte Mode
08281-016
DCI
DATA[15:0]
Q
0N0I1N3I1N2I1N1I1N0Q1N3Q1N2Q1N1Q1N0I2N3
FRAME
Figure 45. Timing Diagram for Nibble Mode
8281-017
Rev. B | Page 32 of 60

AD9122
A
The setup (tS) and hold (tH) times, with respect to the edges,
are shown in Figure 46. The minimum setup and hold times
are shown in Ta bl e 1 3 .
t
S
t
DATA
SAMPLING
INTERVAL
t
H
08281-146
DAT
DCI
t
DATA
SAMPLING
INTERVAL
t
S
t
H
Figure 46. Timing Diagram for Input Data Port
Table 13. Data to DCI Setup and Hold Times
DCI Delay
Register 0x16,
Bits[1:0]
Minimum Setup
(ns)
Time, t
S
00 −0.05 0.65 0.6
01 −0.23 0.95 0.72
10 −0.38 1.22 0.84
11 −0.47 1.38 0.91
Minimum Hold
Time, tH (ns)
Sampling
Interval (ns)
The data interface timing can be verified by using the sample
error detection (SED) circuitry. See the Interface Timing
Va l id a t i on section for more information.
WRITE
POINTER
DATA
INPUT
LATCH
DATA
FORMAT
FIFO OPERATION
The AD9122 contains a 2-channel, 16-bit wide, eight-word deep
FIFO designed to relax the timing relationship between the data
arriving at the DAC input ports and the internal DAC data rate
clock. The FIFO acts as a buffer that absorbs timing variations
between the data source and the DAC, such as the clock-to-data
variation of an FPGA or ASIC, which significantly increases the
timing budget of the interface.
Figure 47 shows the block diagram of the datapath through
the FIFO. The data is latched into the device, is formatted, and
is then written into the FIFO register determined by the FIFO
write pointer. The value of the write pointer is incremented
every time a new word is loaded into the FIFO. Meanwhile, data
is read from the FIFO register determined by the read pointer
and fed into the digital datapath. The value of the read pointer
is incremented every time data is read into the datapath from
the FIFO. The FIFO pointers are incremented at the data rate
(DACCLK rate divided by the interpolation ratio).
Valid data is transmitted through the FIFO as long as the FIFO
does not overflow or become empty. An overflow or empty
condition of the FIFO occurs when the write pointer and read
pointer point to the same FIFO location. This simultaneous
access of data leads to unreliable data transfer through the FIFO
and must be avoided.
Nominally, data is written to and read from the FIFO at the same
rate. This keeps the FIFO depth constant. If data is written to
the FIFO faster than data is read out, the FIFO depth increases.
If data is read out of the FIFO faster than data is written to it,
the FIFO depth decreases. For optimum timing margin, the
FIFO depth should be maintained near half full (a difference of
4 between the write pointer and read pointer values). The FIFO
depth represents the FIFO pipeline delay and is part of the overall latency of the AD9122.
32 BITS
REG 0
REG 1
REG 2
REG 3
REG 4
REG 5
REG 6
REG 7
READ
POINTER
I AND Q
DATA
PATHS
323232
I AND Q
DACS
DCI
READ POINTER
WRITE POINTER
FRAME
FIFO SOFT ALIGN REQUEST
REG 0x18[1]
DATA/FIFO RATE
REG 0x10[6]
Figure 47. Block Diagram of FIFO
Rev. B | Page 33 of 60
RESET
RESET
RESET
LOGIC
FIFO PHASE OFFSET
REG 0x17[2:0]
÷ INT
DACCLK
SYNC
08281-018

AD9122
Resetting the FIFO
When the AD9122 is powered on, the FIFO depth is unknown.
To avoid a concurrent read and write to the same FIFO address
and to ensure a fixed pipeline delay, it is important to reset the
FIFO pointers to known states. The FIFO pointers can be initialized in two ways: via a write sequence to the serial port or by
strobing the FRAME input. There are two types of FIFO resets:
a relative reset and an absolute reset. A relative reset enforces a
defined FIFO depth. An absolute reset enforces a particular write
pointer value when the reset is initiated. A serial port initiated
FIFO reset is always a relative reset. A FRAME strobe initiated
reset can be either a relative or an absolute reset.
If the FRAME differential inputs are not used for FIFO reset
or for framing the word width, they must be tied to logic low.
FRAMEP must be tied to DVSS, and FRAMEN must be tied
to DVDD18 to avoid accidental reset of the FIFO due to noise.
The operation of the FRAME initiated FIFO reset depends on
the synchronization mode chosen.
• When synchronization is disabled or when it is configured
for data rate mode synchronization, the FRAME strobe
initiates a relative FIFO reset. The reference point of the
relative reset is the position of the read pointer.
• When FIFO mode synchronization is chosen, the FRAME
strobe initiates an absolute FIFO reset.
For more information about the synchronization function, see
the Multichip Synchronization section.
A summary of the synchronization modes and the types of
FIFO reset used is provided in Tabl e 14.
Table 14. Summary of FIFO Resets
Synchronization Mode
FIFO Reset Signal
Serial Port Relative Relative Relative
FRAME Relative Relative Absolute
Disabled Data Rate FIFO Reset
Serial Port Initiated FIFO Reset
A serial port initiated FIFO reset can be issued in any synchronization mode and always results in a relative FIFO reset. To
initialize the FIFO data level through the serial port, Bit 1 of
Register 0x18 should be toggled from 0 to 1 and back. When the
write to this register is complete, the FIFO data level is initialized.
When the initialization is triggered, the next time that the read
pointer becomes 0, the write pointer is set to the value of the FIFO
start level variable (Register 0x17, Bits[2:0]) upon initialization.
By default, this value is 4, but it can be programmed to a value
from 0 to 7. It is recommended that a value of 5 (0x05) be programmed in Register 0x17.
The recommended procedure for a serial port FIFO data level
initialization is as follows:
1. Program Register 0x17 to 0x05.
2. Request FIFO level reset by setting Register 0x18, Bit 1, to 1.
3. Verify that the part acknowledges the request by ensuring
4. Remove the request by setting Register 0x18, Bit 1, to 0.
5. Verify that the part drops the acknowledge signal by
6. Read back Register 0x19 to verify that the pointer spacing
7. If the readback of Register 0x19 shows a pointer spacing of
8. If the readback of Register 0x19 shows a pointer spacing of
FRAME Initiated Relative FIFO Reset
The primary function of the FRAME input is to indicate to
which DAC the input data is written. Another function of the
FRAME input is to initialize the FIFO data level value. This is
done by asserting the FRAME signal high for at least the time
interval required to load complete data to the I and Q DACs.
This corresponds to one DCI period in word mode, two DCI
periods in byte mode, and four DCI periods in nibble mode.
To initiate a relative FIFO reset with the FRAME signal, the
device must be configured in data rate mode (Register 0x10,
Bit 6 = 1). When FRAME is asserted in data rate mode, the
write pointer is set to 4 by default (or to the FIFO start level)
the next time that the read pointer becomes 0 (see Figure 48).
POINTER
FRAME
POINTER
that Register 0x18, Bit 2, is set to 1.
ensuring that Register 0x18, Bit 2, is set to 0.
is set to 3 (0x07) or 4 (0x0F).
2 (0x03), increment Register 0x17 to a spacing of 0x06 and
repeat Step 2 through Step 5. Read back Register 0x19 again
to verify that the pointer spacing is now set to 3 (0x07).
5 (0x1F) after Step 6, decrement Register 0x17 to a spacing
of 0x04 and repeat Step 2 through Step 5. Read back
Register 0x19 again to verify that the pointer spacing is
now set to 4 (0x0F).
READ
WRITE
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3
FIFO WRITE RESETS
3 4 5 6 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Figure 48. FRAME Input vs. Write Pointer Value, Data Rate Mode
08281-019
Rev. B | Page 34 of 60

AD9122
FRAME Initiated Absolute FIFO Reset Monitoring the FIFO Status
In FIFO rate synchronization mode, the write pointer of the FIFO
is reset in an absolute manner. The synchronization signal aligns
the internal clocks on the part to a common reference clock so
that the pipeline delay in the digital circuit stays the same during
power cycles. The synchronization signal is sampled by the DAC
clock in the AD9122. The edge of the DAC clock used to sample
the synchronization signal is selected by Bit 3 of Register 0x10.
The FRAME signal is used to reset the FIFO write pointer. In
the FIFO rate synchronization mode, the FIFO write pointer is
reset immediately after the FRAME signal is asserted high for at
least the time interval required to load complete data to the I
and Q DACs. The FIFO write pointer is reset to the value of the
FIFO Phase Offset[2:0] bits in Register 0x17. FIFO rate synchronization is selected by setting Bit 6 of Register 0x10 to 0.
SYNC
FIFO READ RESET
READ
POINTER
FRAME
WRITE
POINTER
01 3210765432
FIFO WRITE
RESET
Figure 49. FRAME Input vs. Write Pointer Value, FIFO Rate Mode
FIFO PHASE OFF SET[2:0]
REG 0x17[2:0] = 101
321076566547
08281-148
The FIFO initialization and status can be read from Register 0x18.
This register provides information about the FIFO status and
whether the initialization was successful. The MSB of Register 0x18
is a FIFO warning flag that can optionally trigger a device
IRQ
This flag indicates that the FIFO is close to emptying (FIFO
level is 1) or overflowing (FIFO level is 7). In this case, data
may soon be corrupted, and action should be taken.
The FIFO data level can be read from Register 0x19 at any time.
The serial port reported FIFO data level is denoted as a 7-bit
thermometer code (Base 1 code) of the write counter state
relative to the absolute read counter being at 0. The optimum
FIFO data level of 4 is therefore reported as a value of 00001111
in the status register.
Note that, depending on the timing relationship between the
DCI and the main DACCLK, the FIFO level value can be off
by a ±1 count, that is, the readback of Register 0x19 can be
00011111 in the case of a +1 count and 00000111 in the case of
a −1 count. Therefore, it is important to keep the difference
between the read and write pointers to a value of at least 2.
.
Rev. B | Page 35 of 60

AD9122
DIGITAL DATAPATH
The block diagram in Figure 50 shows the functionality of the
digital datapath. The digital processing includes a premodulation
block, three half-band (HB) interpolation filters, a quadrature
modulator with a fine resolution NCO, phase and offset adjustment blocks, and an inverse sinc filter.
PHASE
PREMOD
HB1 HB2 HB3
Figure 50. Block Diagram of Digital Datapath
AND
OFFSET
ADJUST
The digital datapath accepts I and Q data streams and processes
them as a quadrature data stream. The signal processing blocks can
be used when the input data stream is represented as complex data.
The digital datapath can also be used to process an input data
stream representing two independent real data streams, but the
functionality is somewhat restricted. The premodulation block
and any of the nonshifted interpolation filter modes can be used
for an input data stream representing two independent real data
streams. See the Coarse Modulation Mixing Sequences section
for more information.
PREMODULATION
The half-band interpolation filters have selectable pass bands
that allow the center frequencies to be moved in increments of
one-half their input data rate. The premodulation block provides
a digital upconversion of the incoming waveform by one-half the
incoming data rate, f
. This can be used to frequency-shift base-
DATA
band input data to the center of the interpolation filter pass band.
INTERPOLATION FILTERS
The transmit path contains three interpolation filters. Each of the
three interpolation filters provides a 2× increase in output data
rate. The half-band (HB) filters can be individually bypassed or
cascaded to provide 1×, 2×, 4×, or 8× interpolation ratios. Each
half-band filter stage offers a different combination of bandwidths
and operating modes.
The bandwidth of the three half-band filters with respect to the
data rate at the filter input is as follows:
• Bandwidth of HB1 = 0.8 × f
• Bandwidth of HB2 = 0.5 × f
• Bandwidth of HB3 = 0.4 × f
The usable bandwidth is defined as the frequency over which
the filters have a pass-band ripple of less than ±0.001 dB and
an image rejection of greater than +85 dB. As described in the
Half-Band Filter 1 (HB1) section, the image rejection usually
sets the usable bandwidth of the filter, not the pass-band flatness.
IN1
IN2
IN3
SINC
–1
08281-020
The half-band filters operate in several modes, providing
programmable pass-band center frequencies as well as signal
modulation. The HB1 filter has four modes of operation, and
the HB2 and HB3 filters each have eight modes of operation.
Half-Band Filter 1 (HB1)
HB1 has four modes of operation, as shown in Figure 51. The
shape of the filter response is identical in each of the four modes.
The four modes are distinguished by two factors: the filter center
frequency and whether the input signal is modulated by the filter.
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–20
–40
–60
–80
–100
0
021.81.61.41.21.00.80.60.40.2
MODE 0
MODE 1 MODE 3
FREQUENCY (×
Figure 51. HB1 Filter Modes
MODE 2
f
) (Hz)
IN1
.0
08281-021
As shown in Figure 51, the center frequency in each mode is
offset by one-half the input data rate (f
) of the filter. Mode 0
IN1
and Mode 1 do not modulate the input signal. Mode 2 and
Mode 3 modulate the input signal by f
. When operating in
IN1
Mode 0 and Mode 2, the I and Q paths operate independently
and no mixing of the data between channels occurs. When operating in Mode 1 and Mode 3, mixing of the data between the
I and Q paths occurs; therefore, the data input into the filter is
assumed to be complex. Tabl e 15 summarizes the HB1 modes.
Table 15. HB1 Filter Modes
Mode f
f
CENTER
Input Data
MOD
0 DC None Real or complex
1 fIN/2 None Complex
2 f
3 3f
f
IN
/2 fIN Complex
IN
Real or complex
IN
Rev. B | Page 36 of 60

AD9122
Figure 52 shows the pass-band filter response for HB1. In most
applications, the usable bandwidth of the filter is limited by the
image suppression provided by the stop-band rejection and not
by the pass-band flatness. Tab l e 16 shows the pass-band flatness
and stop-band rejection supported by the HB1 filter at different
bandwidths.
0.02
0
–0.02
Half-Band Filter 2 (HB2)
HB2 has eight modes of operation, as shown in Figure 53 and
Figure 54. The shape of the filter response is identical in each of
the eight modes. The eight modes are distinguished by two factors:
the filter center frequency and whether the input signal is
modulated by the filter.
–20
MODE 0
0
MODE 2 MODE 6
MODE 4
–0.04
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–0.06
–0.08
–0.10
000.360.320.280.240.200.160.120.080.04
FREQUENCY (×
f
) (Hz)
IN1
40
.
08281-022
Figure 52. Pass-Band Detail of HB1
Table 16. HB1 Pass-Band and Stop-Band Performance by
Bandwidth
Bandwidth (% of f
IN1
)
Pass-Band
Flatness (dB)
Stop-Band
Rejection (dB)
80 0.001 85
80.4 0.0012 80
81.2 0.0033 70
82 0.0076 60
83.6 0.0271 50
85.6 0.1096 40
Rev. B | Page 37 of 60
–40
–60
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–80
–100
021.81.61.41.21.00.80.60.40.2
FREQUENCY (×
f
) (Hz)
IN2
.0
08281-023
Figure 53. HB2, Even Filter Modes
0
–20
–40
–60
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–80
–100
MODE 1
021.81.61.41.21.00.80.60.40.2
MODE 3
FREQUENCY (×
f
IN2
Figure 54. HB2, Odd Filter Modes
MODE 5
) (Hz)
MODE 7
.0
08281-024
As shown in Figure 53 and Figure 54, the center frequency in
each mode is offset by one-fourth the input data rate (f
IN2
) of
the filter. Mode 0 through Mode 3 do not modulate the input
signal. Mode 4 through Mode 7 modulate the input signal by
f
. When operating in Mode 0 and Mode 4, the I and Q paths
IN2
operate independently and no mixing of the data between channels occurs. When operating in the other six modes, mixing of
the data between the I and Q paths occurs; therefore, the data
input to the filter is assumed to be complex.

AD9122
Tabl e 17 summarizes the HB2 and HB3 modes.
Table 17. HB2 and HB3 Filter Modes
Mode f
0 DC None Real or complex
1 fIN/4 None Complex
2 f
3 3f
4 f
5 5f
6 3f
7 7f
Figure 55 shows the pass-band filter response for HB2. In most
applications, the usable bandwidth of the filter is limited by the
image suppression provided by the stop-band rejection and not
by the pass-band flatness. Tab l e 18 shows the pass-band flatness
and stop-band rejection supported by the HB2 filter at different
bandwidths.
0.02
0
–0.02
–0.04
f
CENTER
/2 None Complex
IN
/4 None Complex
IN
f
IN
/4 fIN Complex
IN
/2 fIN Complex
IN
/4 fIN Complex
IN
Input Data
MOD
Real or complex
IN
Half-Band Filter 3 (HB3)
HB3 has eight modes of operation that function the same as
HB2. The primary difference between HB2 and HB3 is the
filter bandwidths.
Figure 56 shows the pass-band filter response for HB3. In most
applications, the usable bandwidth of the filter is limited by the
image suppression provided by the stop-band rejection and not
by the pass-band flatness. Tab l e 19 shows the pass-band flatness
and stop-band rejection supported by the HB3 filter at different
bandwidths.
0.02
0
–0.02
–0.04
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–0.06
–0.08
–0.10
000.240.200.160.120.080.04
FREQUENCY (×
Figure 56. Pass-Band Detail of HB3
f
) (Hz)
IN3
.28
08281-026
MAGNITUDE (dB)
–0.06
–0.08
–0.10
000.280.240.200. 160.120.080.04
FREQUENCY (×
Figure 55. Pass-Band Detail of HB2
f
) (Hz)
IN2
.32
08281-025
Table 18. HB2 Pass-Band and Stop-Band Performance by
Bandwidth
Bandwidth (% of f
IN2
)
Pass-Band
Flatness (dB)
Stop-Band
Rejection (dB)
50 0.001 85
50.8 0.0012 80
52.8 0.0028 70
56 0.0089
60
60 0.0287 50
64.8 0.1877 40
Table 19. HB3 Pass-Band and Stop-Band Performance by
Bandwidth
Bandwidth (% of f
IN3
)
Pass-Band
Flatness (dB)
Stop-Band
Rejection (dB)
40 0.001 85
40.8 0.0014 80
42.4 0.002
45.6 0.0093
70
60
49.8 0.03 50
55.6 0.1 40
Rev. B | Page 38 of 60

AD9122
I DATA
Q DATA
INTERPOL ATION
FTW[31: 0]
NCO PHASE OFFSET
[15:0]
–1
SPECTRAL
INVERSION
INTERP OLAT ION
Figure 57. Digital Quadrature Modulator Block Diagram
NCO MODULATION
The digital quadrature modulator makes use of a numerically
controlled oscillator (NCO), a phase shifter, and a complex
modulator to provide a means for modulating the signal by a
programmable carrier signal. A block diagram of the digital
modulator is shown in Figure 57. The fine modulation provided
by the digital modulator, in conjunction with the coarse modulation of the interpolation filters and premodulation block,
allows the signal to be placed anywhere in the output spectrum
with very fine frequency resolution.
The quadrature modulator is used to mix the carrier signal
generated by the NCO with the I and Q signal. The NCO produces
a quadrature carrier signal to translate the input signal to a new
center frequency. A complex carrier signal is a pair of sinusoidal
waveforms of the same frequency, offset 90° from each other.
The frequency of the complex carrier signal is set via FTW[31:0]
in Register 0x30 through Register 0x33.
The NCO operating frequency, f
bypassed) or 2× f
(HB1 enabled). The frequency of the
DATA
complex carrier signal can be set from dc up to f
, is at either f
NCO
DATA
NCO
(HB1
. The
frequency tuning word (FTW) is calculated as
FTW
f
CARRIER
f
NCO
32
2×=
The generated quadrature carrier signal is mixed with the I and
Q data. The quadrature products are then summed into the I
and Q data paths, as shown in Figure 57.
Updating the Frequency Tuning Word
The frequency tuning word registers are not updated immediately
upon writing, as other configuration registers are. After loading
the FTW registers with the desired values, Bit 0 of Register 0x36
must transition from 0 to 1 for the new FTW to take effect.
DATAPATH CONFIGURATION
Configuring the AD9122 datapath starts with the application
requirements of the input data rate, the interpolation ratio, the
output signal bandwidth, and the output signal center frequency.
COSINE
NCO
SINE
–
1
0
OUT_I
OUT_Q
+
8281-027
Given these four parameters, the first step in configuring the
datapath is to verify that the device supports the bandwidth
requirements. The modes of the interpolation filters are then
chosen. Finally, any additional frequency offset requirements
are determined and applied with premodulation and NCO
modulation.
Determining the Datapath Signal Bandwidth
The available signal bandwidth of the datapath is dependent
on the center frequency of the output signal in relation to the
center frequency of the interpolation filters used. Signal center
frequencies offset from the center frequencies of the half-band
filters lower the available signal bandwidth.
When correctly configured, the available complex signal bandwidth for 2× interpolation is always 80% of the input data rate.
The available signal bandwidth for 4× interpolation vs. output
frequency varies between 50% and 80% of the input data rate,
as shown in Figure 58. Note that in 4× interpolation mode,
= 4 × f
f
DAC
four times from dc to f
0.8
DATA
0.5
0.3
BANDWIDTH/ f
Figure 58. Signal Bandwidth vs. Center Frequency of the Output Signal,
; therefore, the data shown in Figure 58 repeats
DATA
.
DAC
HB1 AND HB2
HB2 AND HB3
0.2
0.4 0. 6 0. 8 1.0
f
OUT/fDATA
4× Interpolation
Configuring 4× interpolation using the HB2 and HB3 filters can
lower the power consumption of the device at the expense of bandwidth. The lower curve in Figure 58 shows that the supported
bandwidth in this mode varies from 30% to 50% of f
DATA
08281-028
.
Rev. B | Page 39 of 60

AD9122
The available signal bandwidth for 8× interpolation vs. output
frequency varies between 50% and 80% of the input data rate,
as shown in Figure 59. Note that in 8× interpolation mode,
= 8 × f
f
DAC
eight times from dc to f
0.8
0.6
DATA
f
0.5
BANDWIDTH/
; therefore, the data shown in Figure 59 repeats
DATA
.
DAC
HB1, HB2, AND HB3
DETERMINING INTERPOLATION FILTER MODES
Tabl e 20 shows the recommended interpolation filter settings
for a variety of filter interpolation factors, filter center frequencies,
and signal modulation. The interpolation modes were chosen
based on the final center frequency of the signal and by determining the frequency shift of the signal required. When these
parameters are known and put in terms of the input data rate
), the filter configuration that comes closest to matching
(f
DATA
is selected from Tabl e 20 .
0.1 0.90.60.4
0.25
f
/
f
OUT
DATA
1.000.750.50
08281-029
Figure 59. Signal Bandwidth vs. Center Frequency of the Output Signal,
8× Interpolation
Table 20. Recommended Interpolation Filter Modes (Register 0x1C Through Register 0x1E)
Filter Modes
Interpolation Factor HB1[1:0] HB2[5:0] HB3[5:0] f
Modulation f
SIGNAL
CENTER
Shift
8 00 (Mode 0) 000000 000000 DC 0
8 01 (Mode 1) 001001 000000 DC1 f
2
10 (Mode 2) 010010 001001 f
8
8 11 (Mode 3) 011011 001001 f
8 00 (Mode 0) 100100 010010 2f
8 01 (Mode 1) 101101 010010 2f
8 10 (Mode 2) 110110 011011 3f
8 11 (Mode 3) 111111 011011 3f
8 00 (Mode 0) 000000 100100 4f
8 01 (Mode 1) 001001 100100 4f
8 10 (Mode 2) 010010 101101 5f
8 11 (Mode 3) 011011 101101 5f
8 00 (Mode 0) 100100 110110 6f
8 01 (Mode 1) 101101 110110 6f
8 10 (Mode 2) 110110 111111 7f
8 11 (Mode 3) 111111 111111 7f
f
DATA
1
3f
DATA
2f
DATA
1
5f
DATA
3f
DATA
1
7f
DATA
4f
DATA
1
9f
DATA
5f
DATA
1
11f
DATA
6f
DATA
1
13f
DATA
7f
DATA
1
15f
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
/2
DATA
DATA
DATA
/2
/2
/2
/2
/2
/2
/2
4 00 (Mode 0) 000000 Bypass DC 0
43 01 (Mode 1) 001001 Bypass DC1 f
4 10 (Mode 2) 010010 Bypass f
4 11 (Mode 3) 011011 Bypass f
4 00 (Mode 0) 100100 Bypass 2f
4 01 (Mode 1) 101101 Bypass 2f
4 10 (Mode 2) 110110 Bypass 3f
4 11 (Mode 3) 111111 Bypass 3f
f
DATA
1
3f
DATA
2f
DATA
1
5f
DATA
3f
DATA
1
7f
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
/2
/2
/2
/2
2 00 (Mode 0) Bypass Bypass DC 0
2 01 (Mode 1) Bypass Bypass DC1 f
2 10 (Mode 2) Bypass Bypass f
2 11 (Mode 3) Bypass Bypass f
1
When HB1 Mode 1 or Mode 3 is used, enabling premodulation provides an additional frequency translation of the input signal by f
input signal in the filter pass band.
2
This configuration was used in the 8× interpolation without NCO example (see the 8× Interpolation Without NCO section).
3
This configuration was used in the 4× interpolation with NCO example (see the 4× Interpolation with NCO section).
Rev. B | Page 40 of 60
f
DATA
1
3f
DATA
/2, which centers a baseband
DATA
DATA
DATA
DATA
/2
/2

AD9122
DATAPATH CONFIGURATION EXAMPLES
8× Interpolation Without NCO
For this example, the following parameters are given:
f
•
•
8× interpolation
•
f
•
f
The desired 75 MHz of bandwidth is 75% of f
the ratio of f
width supported at f
supports the bandwidth required in this configuration.
The signal center frequency is f
signal is at baseband, the frequency shift required is also f
Choosing the third row (highlighted by the superscripted
number 2) of the Interpolation Factor column from Tab le 2 0
selects filter modes that give a center frequency of f
frequency translation of f
half-band filters are HB1, Mode 2; HB2, Mode 2; and HB3,
Mode 1. Figure 60 shows how the signal propagates through the
interpolation filters.
Because 2 × f
frequency scaled by one-half into each consecutive stage. The
output signal band spans 0.15 to 0.35 of f
fore, the output frequency supported is 60 MHz to 140 MHz,
which covers the 75 MHz bandwidth centered at 100 MHz, as
desired.
= 100 MSPS
DATA
= 75 MHz
BW
= 100 MHz
CENTER
OUT/fDATA
DATA
= 100/100 = 1.0. From Figure 59, the band-
is 0.8, which verifies that the AD9122
DATA
and, assuming the input
DATA
. The selected modes for the three
DATA
= f
IN1
and 2 × f
IN2
= f
, the signal appears
IN2
IN3
(400 MHz). There-
IN3
HB1
. In this case,
DATA
and a
DATA
0
.
1
4× Interpolation with NCO
For this example, the following parameters are given:
f
•
•
4× interpolation
•
f
•
f
The desired 140 MHz of bandwidth is 56% of f
in Figure 58, the value at 0.7 × f
= 250 MSPS
DATA
= 140 MHz
BW
= 175 MHz
CENTER
. As shown
DATA
is 0.6. This is calculated as
DATA
0.8 − 2(0.7 − 0.6) = 0.6. This verifies that the AD9122 supports
a bandwidth of 60% of f
The signal center frequency is 0.7 × f
, which exceeds the required 56%.
DATA
and, assuming the
DATA
input signal is at baseband, the frequency shift required is also
0.7 × f
. Choosing the second row in the Interpolation Factor
DATA
column in the 4× interpolation section of Tabl e 2 0 selects the filter
modes that give a center frequency of f
/2 with no frequency
DATA
translation. The selected modes for the three half-band filters
are HB1, Mode 1; HB2, Mode 1; and HB3, bypassed.
Because Mode 1 of HB1 was selected, the premodulation block
should be enabled. This provides f
/2 modulation, which
DATA
centers the baseband input data at the center frequency of HB1.
The digital modulator can be used to provide the final frequency
translation of 0.2 × f
to place the output signal at 0.7 × f
DATA
as desired.
The formula for calculating the FTW of the NCO is as follows:
FTW
f
CARRIER
f
NCO
32
2×=
where:
f
= 0.2 × f
CARRIER
f
= 2 × f
NCO
Therefore, FTW = 2
2
3
DATA
.
DATA
.
32
/10.
0
DATA
,
–0.5 0. 5
HB2
–0.5 0. 5
HB3
–0.5 0. 5
0.1 0.4 0.6
1
2
0.25 0.75
0.3 0. 7
0
1
0.2–0. 2 0.3 0.7
0.15 0.35
1.00
40
1.00
4
1.00
1.5 2.0
6
1.25 1. 75
1.5 2.0
62
1.5 2.0
Figure 60. Signal Propagation for 8× Interpolation (f
753
753
DATA
f
×
IN1
f
×
IN2
f
×
IN3
Modulation)
08281-030
Rev. B | Page 41 of 60

AD9122
DATA RATES vs. INTERPOLATION MODES
Tabl e 22 summarizes the maximum bus speed (f
input data rates, and signal bandwidths with the various combinations of bus width modes and interpolation rates. The real
signal bandwidth supported is a fraction of the input data rate,
which depends on the interpolation filters (HB1, HB2, or HB3)
selected. The complex signal bandwidth supported is twice the
real signal bandwidth.
In general, 2× interpolation is best supported by enabling HB1,
and 4× interpolation is best supported by enabling HB1 and HB2.
However, in some cases, power dissipation can be lowered by not
using HB1. If the bandwidth required is low enough, 2× interpolation can be supported by using HB2, and 4× interpolation can
be supported by using HB2 and HB3.
COARSE MODULATION MIXING SEQUENCES
The coarse digital quadrature modulation occurs within the
interpolation filters. The modulation shifts the frequency
spectrum of the incoming data by the frequency offset selected.
The frequency offsets available are multiples of the input data
rate. The modulation is equivalent to multiplying the quadrature input signal by a complex carrier signal, C(t), of the form
C(t) = cos(ωct) + j sin(ωct)
), supported
BUS
In practice, this modulation results in the mixing functions
shown in Tab l e 21 .
Table 21. Modulation Mixing Sequences
Modulation Mixing Sequence
fS/2 I = I, −I, I, −I, …
Q = Q, −Q, Q, −Q, …
/4 I = I, Q, −I, −Q, …
f
S
Q = Q, −I, −Q, I, …
/4 I = I, −Q, −I, Q, …
3f
S
Q = Q, I, −Q, −I, …
f
/8 I = I, r(I + Q), Q, r(−I + Q), −I, −r(I + Q), −Q, r(I − Q), …
S
Q = Q, r(Q − I), −I, −r(Q + I), −Q, r(−Q + I), I, r(Q + I), …
Note that
2
=r
2
As shown in Tab l e 2 1, the mixing functions of most of the modes
cross-couple samples between the I and Q channels. The I and
Q channels operate independently only in f
/2 mode. This means
S
that real modulation using both the I and Q DAC outputs can
only be done in f
/2 mode. All other modulation modes require
S
complex input data and produce complex output signals.
Table 22. Summary of Data Rates and Bandwidths vs. Interpolation Modes (DVDD18, CVDD18 = 1.9 V ± 2%)
Filter Modes
Bus Width HB3 HB2 HB1 f
(Mbps) f
BUS
(Mbps) Real Signal Bandwidth (MHz) f
DATA
DAC
(MHz)
Nibble (4 Bits) 0 0 0 1230 153.75 75 153.75
0 0 1 1230 153.75 60 307.5
0 1 0 1230 153.75 37.5
0 1 1 1230 153.75 60
1 1 0 1230 153.75 37.5
1 1 1 1230 153.75 60
307.5
615
615
1230
Byte (8 Bits) 0 0 0 1230 307.5 150 307.5
0 0 1 1230 307.5 120 615
0 1 0 1230 307.5 75
0 1 1 1230 307.5 120
1 1 0 1230 307.5 75
1 1 1 615 153.75 60
615
1230
1230
1230
Word (16 Bits) 0 0 0 1230 615 300 615
0 0 1 1000 500 200 1000
0 1 0 1230 615 150
0 1 1 615 307.5 120
1 1 0 615 307.5 75
1230
1230
1230
1 1 1 307.5 153.75 60 1230
Rev. B | Page 42 of 60

AD9122
–
QUADRATURE PHASE CORRECTION
The purpose of the quadrature phase correction block is to
enable compensation of the phase imbalance of the analog
quadrature modulator following the DAC. If the quadrature
modulator has a phase imbalance, the unwanted sideband
appears with significant energy. Tuning the quadrature phase
adjust value can optimize image rejection in single sideband
radios.
Ordinarily, the I and Q channels have an angle of precisely 90°
between them. The quadrature phase adjustment is used to change
the angle between the I and Q channels. When I Phase Adj[9:0]
(Register 0x38 and Register 0x39) is set to 1000000000, the I DAC
output moves approximately 1.75° away from the Q DAC output,
creating an angle of 91.75° between the channels. When I Phase
Adj[9:0] is set to 0111111111, the I DAC output moves approximately 1.75° toward the Q DAC output, creating an angle of
88.25° between the channels.
Q Phase Adj[9:0] (Register 0x3A and Register 0x3B) works in
a similar fashion. When Q Phase Adj[9:0] is set to 1000000000,
the Q DAC output moves approximately 1.75° away from the
I DAC output, creating an angle of 91.75° between the channels.
When Q Phase Adj[9:0] is set to 0111111111, the Q DAC output
moves approximately 1.75° toward the I DAC output, creating
an angle of 88.25° between the channels.
Based on these two endpoints, the combined resolution of the
phase compensation register is approximately 3.5°/1024 or
0.00342° per code.
DC OFFSET CORRECTION
The dc value of the I datapath and the Q datapath can be
independently controlled by adjusting the I DAC Offset[15:0]
and Q DAC Offset[15:0] values in Register 0x3C through
Register 0x3F. These values are added directly to the datapath
values. Care should be taken not to overrange the transmitted
values.
Figure 61 shows how the DAC offset current varies as a function
of the I DAC Offset[15:0] and Q DAC Offset[15:0] values. With
the digital inputs fixed at midscale (0x0000, twos complement data
format), Figure 61 shows the nominal I
OUTxP
and I
as the DAC offset value is swept from 0 to 65,535. Because I
and I
and I
are complementary current outputs, the sum of I
OUTxN
is always 20 mA.
OUTxN
OUTxN
currents
OUTxP
OUTxP
20
15
(mA)
10
OUTxP
I
5
0
0x0000 0x4000 0x8000 0xC000 0xFFFF
Figure 61. DAC Output Currents vs. DAC Offset Value
DAC OFFSET VALUE
0
5
(mA)
10
OUTxN
I
15
20
INVERSE SINC FILTER
The inverse sinc (sinc−1) filter is a nine-tap FIR filter. The composite
response of the sinc
is shown in Figure 62. The composite response has a pass-band
ripple of less than ±0.05 dB up to a frequency of 0.4 × f
provide the necessary peaking at the upper end of the pass band,
the inverse sinc filters shown have an intrinsic insertion loss of
about 3.2 dB. Figure 62 shows the composite frequency response.
3.0
–3.2
–3.4
–3.6
MAGNITUDE (d B)
–3.8
–4.0
000.3 0.40.20.1
Figure 62. Sample Composite Responses of the Si nc
The sinc−1 filter is disabled by default. It can be enabled by
setting the bypass sinc
−1
filter and the sin(x)/x response of the DAC
DACCL K
.5
f
/
f
OUT
DAC
−1
Filter with sin(x)/x Roll-O ff
−1
bit to 0 (Register 0x1B, Bit 6).
. To
08281-032
08281-031
Rev. B | Page 43 of 60

AD9122
DAC INPUT CLOCK CONFIGURATIONS
The AD9122 DAC sampling clock (DACCLK) can be sourced
directly or by clock multiplying. Clock multiplying uses the
on-chip phase-locked loop (PLL), which accepts a reference clock
operating at a submultiple of the desired DACCLK rate, most
commonly the data input frequency. The PLL then multiplies
the reference clock up to the desired DACCLK frequency, which
can then be used to generate all the internal clocks required by
the DAC. The clock multiplier provides a high quality clock that
meets the performance requirements of most applications. Using
the on-chip clock multiplier eliminates the need to generate and
distribute the high speed DACCLK.
The second mode bypasses the clock multiplier circuitry and
allows the DACCLK to be sourced directly to the DAC core.
This mode enables the user to source a very high quality clock
directly to the DAC core. Sourcing the DACCLK directly through
the REFCLKP, REFCLKN, DACCLKP, and DACCLKN pins may
be necessary in demanding applications that require the lowest
possible DAC output noise, particularly when directly synthesizing
signals above 150 MHz.
DRIVING THE DACCLK AND REFCLK INPUTS
The differential DACCLK and REFCLK inputs share similar
clock receiver input circuitry. Figure 63 shows a simplified circuit
diagram of the inputs. The on-chip clock receiver has a differential
input impedance of about 10 kΩ. It is self-biased to a commonmode voltage of about 1.25 V. The inputs can be driven by
direct coupling differential PECL or LVDS drivers. The inputs
can also be ac-coupled if the driving source cannot meet the
input compliance voltage of the receiver.
DACCLKP,
REFCLKP
5kΩ
5kΩ
DACCLKN,
REFCLKN
Figure 63. Clock Receiver Input Simplified Equivalent Circuit
The minimum input drive level to either of the clock inputs is
100 mV p-p differential. The optimal performance is achieved
1.25V
08281-033
REG 0x06[7:6]
PLL LOCK LOST
PLL LOCKED
when the clock input signal is between 800 mV p-p differential
and 1.6 V p-p differential. Whether using the on-chip clock
multiplier or sourcing the DACCLK directly, it is necessary that
the input clock signal to the device have low jitter and fast edge
rates to optimize the DAC noise performance.
DIRECT CLOCKING
Direct clocking with a low noise clock produces the lowest noise
spectral density at the DAC outputs. To select the differential
CLK inputs as the source for the DAC sampling clock, set the
PLL enable bit (Register 0x0A, Bit 7) to 0. This powers down the
internal PLL clock multiplier and selects the input from the
DACCLKP and DACCLKN pins as the source for the internal
DAC sampling clock.
The device also has duty cycle correction circuitry and differential input level correction circuitry. Enabling these circuits can
provide improved performance in some cases. The control bits
for these functions are in Register 0x08 (see Tabl e 1 1).
CLOCK MULTIPLICATION
The on-chip PLL clock multiplication circuit can be used to generate the DAC sampling clock from a lower frequency reference
clock. When the PLL enable bit (Register 0x0A, Bit 7) is set to 1,
the clock multiplication circuit generates the DAC sampling clock
from the lower rate REFCLK input. The functional diagram of
the clock multiplier is shown in Figure 64.
The clock multiplication circuit operates such that the VCO
outputs a frequency, f
frequency multiplied by N1 × N0.
= f
f
VCO
REFCLK
The DAC sampling clock frequency, f
f
= f
DACCLK
REFCLK
The output frequency of the VCO must be chosen to keep f
in the optimal operating range of 1.0 GHz to 2.1 GHz. The
frequency of the reference clock and the values of N1 and N0
must be chosen so that the desired DACCLK frequency can be
synthesized and the VCO output frequency is in the correct range.
ADC
, equal to the REFCLK input signal
VCO
× (N1 × N0)
DACCLK
× N1
REG 0x0E[3:0]
VCO CONTROL
VOLTAGE
, is equal to
VCO
REFCLKP/REFCLKN
(PIN 69 AND PIN 70)
DACCLKP/DACCLKN
(PIN 2 AND PIN 3)
PHASE
DETECTIO N
REG 0x0D[1:0]
REG 0x0A[7]
PLL ENABLE
Figure 64. PLL Clock Multiplication Circuit
LOOP
FILTER
÷N1
N1
Rev. B | Page 44 of 60
REG 0x0D[3:2]
÷N0
N0
÷N2
PC_CLK
VCO
DACCLK
REG 0x0D[7:6]
N2
08281-034

AD9122
PLL SETTINGS
Three settings for the PLL circuitry should be programmed to
their nominal values. The PLL values shown in Tab le 2 3 are the
recommended settings for these parameters.
Table 23. PLL Settings
PLL Control Register
Register
Address Bits
Optimal
Setting
PLL Loop Bandwidth[1:0] 0x0C [7:6] 11
PLL Charge Pump Current[4:0] 0x0C [4:0] 10001
PLL Cross-Control Enable 0x0D 4 1
CONFIGURING THE VCO TUNING BAND
The PLL VCO has a valid operating range from approximately
1.0 GHz to 2.1 GHz covered in 63 overlapping frequency bands.
For any desired VCO output frequency, there may be several
valid PLL band select values. The frequency bands of a typical
device are shown in Figure 65. Device-to-device variations and
operating temperature affect the actual band frequency range.
Therefore, it is required that the optimal PLL band select value
be determined for each individual device.
0
4
8
12
16
20
24
28
32
36
PLL BAND
40
44
48
52
56
60
1000 220020001800160014001200
Figure 65. PLL Lock Range over Temperature for a Typical Device
Automatic VCO Band Select
The device has an automatic VCO band select feature on chip.
Using the automatic VCO band select feature is a simple and
reliable method of configuring the VCO frequency band. This
feature is enabled by starting the PLL in manual mode, then
placing the PLL in auto band select mode. This is done by
setting Register 0x0A to a value of 0xCF, then to a value of
0xA0. When these values are written, the device executes an
automated routine that determines the optimal VCO band
setting for the device. The setting selected by the device ensures
that the PLL remains locked over the full −40°C to +85°C
operating temperature range of the device without further
adjustment. (The PLL remains locked over the full temperature
range even if the temperature during initialization is at one of
the temperature extremes.)
VCO FREQUENCY (MHz)
08281-035
Manual VCO Band Select
The device also has a manual band select mode (PLL manual
enable, Register 0x0A, Bit 6 = 1) that allows the user to select
the VCO tuning band. In manual mode, the VCO band is set
directly with the value written to the manual VCO band bits
(Register 0x0A, Bits[5:0]). To properly select the VCO band,
follow these steps:
Put the device in manual band select mode by setting
1.
Register 0x0A, Bit 6 = 1.
Sweep the VCO band over a range of bands that results in
2.
the PLL being locked.
For each band, verify that the PLL is locked and read the PLL
3.
using the VCO control voltage bits (Register 0x0E, Bits[3:0]).
Select the band that results in the control voltage being
4.
closest to the center of the range, that is, 1001 or 1000 (see
Tabl e 24 ). The resulting VCO band should be the optimal
setting for the device. Write this value to the manual VCO
band bits (Register 0x0A, Bits[5:0]).
If desired, an indication of where the VCO is within the
5.
operating frequency band can be determined by querying the
VCO control voltage. Tabl e 24 shows how to interpret the
PLL VCO control voltage value (Register 0x0E, Bits[3:0]).
Table 24. VCO Control Voltage Range Indications
VCO Control Voltage
(Register 0x0E, Bits[3:0]) Indication
1111 Move to higher VCO band
1110
1101
1100
VCO is operating in the higher end
of the frequency band
1011
1010
1001
1000
VCO is operating within an optimal
region of the frequency band
0111
0110
0101
0100
VCO is operating in the lower end
of the frequency band
0011
0010
0001 Move to lower VCO band
0000
Rev. B | Page 45 of 60

AD9122
F
−
=
ANALOG OUTPUTS
TRANSMIT DAC OPERATION
Figure 66 shows a simplified block diagram of the transmit path
DACs. The DAC core consists of a current source array, a switch
core, digital control logic, and full-scale output current control.
The DAC full-scale output current (I
The output currents from the IOUT1P/IOUT2P and IOUT1N/
IOUT2N pins are complementary, meaning that the sum of the
two currents always equals the full-scale current of the DAC.
The digital input code to the DAC determines the effective
differential current delivered to the load.
I DAC FS ADJUST
REGISTER 0x40
Q DAC FS ADJUST
REGISTER 0x44
0.1µ
1.2V
REFIO
FSADJ
10kΩ
R
SET
Figure 66. Simplified Block Diagram of DAC Core
5kΩ
The DAC has a 1.2 V band gap reference with an output impedance of 5 kΩ. The reference output voltage appears on the REFIO
pin. When using the internal reference, decouple the REFIO pin
to AVSS with a 0.1 μF capacitor. Use the internal reference only for
external circuits that draw dc currents of 2 μA or less. For dynamic
loads or static loads greater than 2 μA, buffer the REFIO pin. If
desired, the internal reference can be overdriven by applying an
external reference (from 1.10 V to 1.30 V) to the REFIO pin.
A 10 kΩ external resistor, R
, must be connected from the
SET
FSADJ pin to AVSS. This resistor, along with the reference control
amplifier, sets up the correct internal bias currents for the DAC.
Because the full-scale current is inversely proportional to this
resistor, the tolerance of R
is reflected in the full-scale output
SET
amplitude.
The full-scale current equation, where the DAC gain is set individually for the I and Q DACs in Register 0x40 and Register 0x44,
respectively, is as follows:
V
REF
I
FS
R
SET
3
⎛
⎛
72
⎜
⎝
×+×= DAC gain
⎜
16
⎝
) is nominally 20 mA.
FS
I DAC
CURRENT
SCALING
Q DAC
⎞
⎞
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎠
IOUT1P
IOUT1N
IOUT2N
IOUT2P
For the nominal values of V
(1.2 V), R
REF
(10 kΩ), and
SET
DAC gain (512), the full-scale current of the DAC is typically
20.16 mA. The DAC full-scale current can be adjusted from
8.64 mA to 31.68 mA by setting the DAC gain parameter, as
shown in Figure 67.
35
30
25
20
(mA)
FS
I
15
10
5
0
08281-037
0 1000
Figure 67. DAC Full-Scale Current vs. DAC Gain Code
200 400 600 800
DAC GAIN CODE
08281-036
Transmit DAC Transfer Function
The output currents from the IOUT1P/IOUT2P and IOUT1N/
IOUT2N pins are complementary, meaning that the sum of the
two currents always equals the full-scale current of the DAC. The
digital input code to the DAC determines the effective differential
current delivered to the load. IOUT1P/IOUT2P provide maximum output current when all bits are high. The output currents
vs. DACCODE for the DAC outputs are expressed as
DACCODE
I ×
OUTxP
OUTxN
where
DACCODE = 0 to 2
⎡
=
⎢
⎣
FS
III
⎤
I
(1)
N
2
OUTxP
FS
⎥
⎦
(2)
N
− 1.
Transmit DAC Output Configurations
The optimum noise and distortion performance of the AD9122
is realized when it is configured for differential operation. The
common-mode error sources of the DAC outputs are significantly
reduced by the common-mode rejection of a transformer or
differential amplifier. These common-mode error sources include
even-order distortion products and noise. The enhancement in
distortion performance becomes more significant as the frequency
content of the reconstructed waveform increases and/or its
amplitude increases. This is due to the first-order cancellation
of various dynamic common-mode distortion mechanisms,
digital feedthrough, and noise.
Rev. B | Page 46 of 60

AD9122
V
V
I
–
–
V
Figure 68 shows the most basic transmit DAC output circuitry.
A pair of resistors, R
mentary output currents to a differential voltage output, V
, is used to convert each of the comple-
O
OUT
.
Because the current outputs of the DAC are high impedance,
the differential driving point impedance of the DAC outputs,
, is equal to 2 × RO. Figure 69 illustrates the output voltage
R
OUT
waveforms.
+
IOUT1P
R
R
IOUT1N
IOUT2P
R
R
IOUT2N
IP
O
O
O
O
V
OUTI
–
V
IN
+
V
QP
V
OUTQ
–
V
QN
08281-038
Figure 68. Basic Transmit DAC Output Circuit
+
PEAK
V
CM
V
N
0
–V
PEAK
V
P
V
OUT
08281-039
Figure 69. Output Voltage Waveforms
The common-mode signal voltage, VCM, is calculated as
FS
V ×=
CM
The peak output voltage, V
V
PEAK
R
2
= IFS × RO
O
, is calculated as
PEAK
With this circuit configuration, the single-ended peak voltage is
the same as the peak differential output voltage.
Transmit DAC Linear Output Signal Swing
To achieve optimum performance, the DAC outputs have a
linear output compliance voltage range that must be adhered
to. The linear output signal swing is dependent on the full-scale
output current, I
, and the common-mode level of the output.
FS
Figure 70 and Figure 71 show the IMD performance vs. the
output common-mode voltage at different full-scale currents
and output frequencies.
60
–65
–70
–75
IMD (dBc)
–80
–85
–90
Figure 70. IMD vs. Output Common-Mode Voltage (f
50
–55
–60
–65
–70
IMD (dBc)
–75
–80
–85
Figure 71. IMD vs. Output Common-Mode Voltage (f
IFS = 10mA
IFS = 20mA
IFS = 30mA
011.21.00. 80. 60.40. 2
= 50 Ω Differential, IFS = 10 mA, 20 mA, and 30 mA)
R
LOAD
IFS = 10mA
IFS = 20mA
IFS = 30mA
011.21.00. 80. 60.40. 2
= 50 Ω Differential, IFS = 10 mA, 20 mA, and 30 mA)
R
LOAD
VCM (V)
VCM (V)
= 61 MHz,
OUT
= 161 MHz,
OUT
.4
08281-168
.4
08281-169
AUXILIARY DAC OPERATION
The AD9122 has two auxiliary DACs: one associated with the
I path and one associated with the Q path. These auxiliary DACs
can be used to compensate for dc offsets in the transmitted signal.
Each auxiliary DAC has a single-ended current that can sink or
source current into either the positive (P) or negative (N) output
of the associated transmit DAC. The auxiliary DAC structure is
shown in Figure 72.
B
I AUX DAC[9:0]
I AUX DAC
CURRENT
DIRECTION
I AUX DAC
SIGN
I DAC
Figure 72. Auxiliary DAC Structure
IOUT1P
IOUT1N
08281-040
Rev. B | Page 47 of 60

AD9122
The control registers for the I and Q auxiliary DACs are
Register 0x42, Register 0x43, Register 0x46, and Register 0x47.
INTERFACING TO MODULATORS
The AD9122 interfaces to the ADL537x family of modulators
with a minimal number of components. An example of the
recommended interface circuitry is shown in Figure 73.
AD9122
67
IOUT1P
IOUT1N
IOUT2N
IOUT2P
RBIP
50Ω
RBIN
50Ω
66
59
RBQN
50Ω
RBQP
50Ω
58
100Ω
RLQ
100Ω
RLI
Figure 73. Typical Interface Circuitry Between the AD9122 and the ADL537x
Family of Modulators
The baseband inputs of the ADL537x family require a dc bias
of 500 mV. The nominal midscale output current on each output
of the DAC is 10 mA (one-half the full-scale current). Therefore,
a single 50 Ω resistor to ground from each of the DAC outputs
results in the desired 500 mV dc common-mode bias for the
inputs to the ADL537x. The signal level can be reduced through
the addition of the load resistor in parallel with the modulator
inputs. The peak-to-peak voltage swing of the transmitted signal is
)2(
RR
××
IV
×=
FSSIGNAL
LB
)2(
RR
+×
LB
BASEBAND FILTER IMPLEMENTATION
Most applications require a baseband anti-imaging filter between
the DAC and the modulator to filter out Nyquist images and
broadband DAC noise. The filter can be inserted between the
I-V resistors at the DAC output and the signal level setting
resistor across the modulator input. This establishes the input
and output impedances for the filter.
ADL537x
IBBP
IBBN
QBBN
QBBP
08281-041
50Ω
AD9122
50Ω
33nH
2pF
33nH
Figure 75. DAC Modulator Interface with Fifth-Order, Low-Pass Filter
Rev. B | Page 48 of 60
Figure 75 shows a fifth-order, low-pass filter. A common-mode
choke is used between the I-V resistors and the remainder of
the filter. This removes the common-mode signal produced by
the DAC and prevents the common-mode signal from being
converted to a differential signal, which can appear as unwanted
spurious signals in the output spectrum. Splitting the first filter
capacitor into two and grounding the center point creates a
common-mode low-pass filter, providing additional commonmode rejection of high frequency signals. A purely differential
filter can pass common-mode signals.
DRIVING THE ADL5375-15
The ADL5375-15 requires a 1500 mV dc bias and, therefore,
requires a slightly more complex interface than most other
Analog Devices modulators. It is necessary to level-shift the
DAC output from a 500 mV dc bias to the 1500 mV dc bias
required by the ADL5375-15. Level-shifting can be achieved
with a purely passive network, as shown in Figure 74. In this
network, the dc bias of the DAC remains at 500 mV, whereas
the input to the ADL5375-15 is 1500 mV. This passive, levelshifting network introduces approximately 2 dB of loss in the
ac signal.
22pF
AD9122
IOUT1P
IOUT1N
IOUT2N
IOUT2P
67
RBIP
45.3Ω
RBIN
45.3Ω
66
59
RBQN
45.3Ω
RBQP
45.3Ω
58
RSIP
1kΩ
RSIN
1kΩ
RSQN
1kΩ
RSQP
1kΩ
RLIP
3480Ω
RLIN
3480Ω
RLQN
3480Ω
RLQP
3480Ω
Figure 74. Passive, Level-Shifting Network for Biasing the ADL5375-15
22pF
56nH
56nH
3pF
3pF
140Ω6pF
ADL537x
08281-042
21
5V
22
9
5V
10
ADL5375-15
IBBP
IBBN
QBBN
QBBP
08281-043

AD9122
REDUCING LO LEAKAGE AND UNWANTED SIDEBANDS
Analog quadrature modulators can introduce unwanted signals at
the LO frequency due to dc offset voltages in the I and Q baseband
inputs, as well as feedthrough paths from the LO input to the output. The LO feedthrough can be nulled by applying the correct
dc offset voltages at the DAC output. This can be done using the
auxiliary DACs (Register 0x42, Register 0x43, Register 0x46, and
Register 0x47) or by using the digital dc offset adjustments
(Register 0x3C through Register 0x3F).
The advantage of using the auxiliary DACs is that none of
the main DAC dynamic range is used to perform the dc offset
adjustment. The disadvantage is that the common-mode level
of the output signal changes as a function of the auxiliary DAC
current. The opposite is true when the digital offset adjustment
is used.
Good sideband suppression requires both gain and phase
matching of the I and Q signals. The I/Q phase adjust registers
(Register 0x38 through Register 0x3B) and the DAC FS adjust
registers (Register 0x40 and Register 0x44) can be used to calibrate
the I and Q transmit paths to optimize sideband suppression.
Rev. B | Page 49 of 60

AD9122
DEVICE POWER MANAGEMENT
POWER DISSIPATION
The AD9122 has four supply rails: AVDD33, IOVDD, DVDD18,
and CVDD18.
The AVDD33 supply powers the DAC core circuitry. The power
dissipation of the AVDD33 supply rail is independent of the digital
operating mode and sample rate. The current drawn from the
AVDD33 supply rail is typically 55 mA (182 mW) when the fullscale current of the I and Q DACs is set to the nominal value of
20 mA. Changing the full-scale current directly affects the supply
current drawn from the AVDD33 rail. For example, if the full-scale
current of the I DAC and the Q DAC is changed to 10 mA, the
AVDD33 supply current drops by 20 mA to 35 mA.
The IOVDD voltage supplies the serial port I/O pins, the
pin, and the
IRQ
pin. The voltage applied to the IOVDD pin can
range from 1.8 V to 3.3 V. The current drawn by the IOVDD
supply pin is typically 3 mA.
The DVDD18 supply powers all of the digital signal processing
blocks of the device. The power consumption from this supply
is a function of which digital blocks are enabled and the frequency
at which the device is operating.
The CVDD18 supply powers the clock receiver and clock distribution circuitry. The power consumption from this supply varies
directly with the operating frequency of the device. CVDD18 also
powers the PLL. The power dissipation of the PLL is typically
80 mW when enabled.
Figure 76 through Figure 80 show the power dissipation of
the AD9122 under a variety of operating conditions. All of
the graphs were taken with data being supplied to both the I
and Q DACs. The power consumption of the device does not
vary significantly with changes in the coarse modulation mode
selected or the analog output frequency. Figure 76 through
Figure 80 show the total power dissipation, as well as the power
dissipation of the DVDD18 and CVDD18 supplies.
Maximum power dissipation can be estimated to be 20% higher
than the typical power dissipation.
RESET
1700
1500
1300
1100
POWER (mW)
Figure 76. Total Power Dissipation vs. f
900
700
500
300
100
0 30025020015010050
1× INTERPOLATION
2× INTERPOLATION
4× INTERPOLATION
8× INTERPOLATION
f
DATA
(MHz)
Without PLL, Fine NCO,
DATA
08281-044
or Inverse Sinc
1200
1000
POWER (mW)
Figure 77. DVDD18 Power Dissipation vs. f
800
600
400
200
0
0 30025020015010050
1× INTERPOLATION
2× INTERPOLATION
4× INTERPOLATION
8× INTERPOLATION
f
DATA
(MHz)
Without Fine NCO
DATA
08281-045
or Inverse Sinc
250
1× INTERPOLATION
2× INTERPOLATION
4× INTERPOLATION
8× INTERPOLATION
200
150
Rev. B | Page 50 of 60
100
POWER (mW)
50
0
0 30025020015010050
f
(MHz)
DATA
Figure 78. CVDD18 Power Dissipation vs. f
with PLL Disabled
DATA
08281-046

AD9122
300
250
200
150
POWER (mW)
100
50
0
0 12001000800600400200
f
DAC
Figure 79. DVDD18 Power Dissipation vs. f
300
250
200
1× INTERPOLATION
2×, 4×, 8× INTERPOLATION
(MHz)
Due to Inverse Sinc Filter
DAC
08281-047
TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The AD9122 has a band gap temperature sensor for monitoring
the temperature change of the AD9122. The temperature must
be calibrated against a known temperature to remove the partto-part variation on the band gap circuit used to sense the
temperature. The DACCLK must be running at a minimum
of 100 MHz to obtain a reliable temperature measurement.
To monitor temperature change, the user must take a reading
at a known ambient temperature for a single-point calibration
of each AD9122 device.
Tx = T
where:
Code_x is the readback code at the unknown temperature, Tx.
Code_ref is the readback code at the calibrated temperature, T
To use the temperature sensor, it must be enabled by setting
Register 0x01, Bit 4, to 0. In addition, to obtain accurate readings, the die temperature range control register (Register 0x48)
should be set to 0x02.
+ 7.7 × (Code_x − Code_ref)/1000 + 1
REF
REF
.
150
POWER (mW)
100
50
0
50 300250200150100
Figure 80. DVDD18 Power Dissipation vs. f
f
DATA
(MHz)
Due to Fine NCO
DATA
08281-048
Rev. B | Page 51 of 60

AD9122
MULTICHIP SYNCHRONIZATION
System demands may require that the outputs of multiple DACs
be synchronized with each other or with a system clock. Systems
that support transmit diversity or beamforming, where multiple
antennas are used to transmit a correlated signal, require multiple
DAC outputs to be phase aligned with each other. Systems with
a time division multiplexing transmit chain may require one or
more DACs to be synchronized with a system-level reference clock.
Multiple devices are considered synchronized to each other when
the state of the clock generation state machines is identical for all
parts and when time-aligned data is being read from the FIFOs
of all parts simultaneously. Devices are considered synchronized
to a system clock when there is a fixed and known relationship
between the clock generation state machine and the data being
read from the FIFO and a particular clock edge of the system
clock. The AD9122 has provisions for enabling multiple devices
to be synchronized to each other or to a system clock.
The AD9122 supports synchronization in two different modes:
data rate mode and FIFO rate mode. In data rate mode, the input
data rate represents the lowest synchronized clock rate. In FIFO
rate mode, the FIFO rate, which is the data rate divided by the
FIFO depth of 8, represents the lowest rate clock.
The advantage of FIFO rate synchronization is increased time
between the setup and hold time windows for DCI changes
relative to the DACCLK or REFCLK input. When the synchronization state machine is on in data rate mode, the elasticity of
the FIFO is not used to absorb timing variations between the data
source and the DAC, resulting in setup and hold time windows
repeating at the input data rate.
The method chosen for providing the DAC sampling clock
directly affects the synchronization methods available. When
the device clock multiplier is used, only data rate mode is
available. When the DAC sampling clock is sourced directly,
both data rate mode and FIFO rate mode synchronization are
available. The following sections describe the synchronization
methods for enabling both clocking modes and querying the
status of the synchronization logic.
The full synchronization methods described are used to align
multiple dual DACs within one DACCLK cycle. To achieve synchronization within one DACCLK cycle, both the REFCLK and
FRAME signals are required to perform back-end and front-end
alignment. If synchronization does not need to be this accurate,
other options can be used. In data rate mode or in FIFO rate mode,
using soft alignment of the FIFO for multiple DACs synchronizes
the DAC outputs within two data clock cycles (see the Serial Port
Initiated FIFO Reset section). For more information about
synchronization, see the AN-1093 Application Note, “Synchronization of Multiple AD9122 TxDAC+ Converters.”
SYNCHRONIZATION WITH CLOCK MULTIPLICATION
When using the clock multiplier to generate the DAC sample rate
clock, the REFCLK input signal acts as both the reference clock
for the PLL-based clock multiplier and the synchronization signal.
To synchronize devices, distribute the REFCLK signal with low
skew to all the devices that need to be synchronized. Skew between
the REFCLK signals of the different devices shows up directly as
a timing mismatch at the DAC outputs.
Because two clocks are shared on the same signal, an appropriate frequency must be chosen for the synchronization and
REFCLK signals. The FRAME and DCI signals can be created
in the FPGA along with the data. A circuit diagram of a typical
configuration is shown in Figure 81.
MATCHED
LENGTH TRACES
REFCLKP/
REFCLKN
FRAMEP/
FRAMEN
DCIP/
SYSTEM
CLOCK
FPGA
LOW SKEW
CLOCK DRIVER
Figure 81. Typical Circuit Diagram for Synchronizing Devices
DCIN
REFCLKP/
REFCLKN
FRAMEP/
FRAMEN
DCIP/
DCIN
The Procedure for Synchronization When Using the PLL section
outlines the steps required to synchronize multiple devices. The
procedure assumes that the REFCLK signal is applied to all the
devices and that the PLL of each device is phase locked to it. The
following procedure must be carried out on each individual device.
Procedure for Synchronization When Using the PLL
In the initialization of the AD9122, all the clock signals (DACCLK,
DCI, FRAME, synchronization, and REFCLK) must be present and
stable before the synchronization feature is turned on. Configure
the AD9122 for data rate, periodic synchronization by writing
0xC8 to the sync control register (Register 0x10). Additional
synchronization options are available (see the Additional
Synchronization Features section).
Read the sync status register (Register 0x12) to verify that
the sync locked bit (Bit 6) is set high, indicating that the device
achieved back-end synchronization, and that the sync lost bit
(Bit 7) is low. These levels indicate that the clocks are running
with a constant and known phase relative to the synchronization signal.
Reset the FIFO by strobing the FRAME signal high for the time
interval required to write two complete input data words. Resetting
the FIFO ensures that the correct data is being read from the FIFO.
This completes the synchronization procedure; all devices should
now be synchronized.
IOUT1P/
IOUT1N
IOUT2P/
IOUT2N
08281-049
Rev. B | Page 52 of 60

AD9122
t
SKEW
REFCLKP(1)/
REFCLKN(1)
REFCLKP(2)/
REFCLKN(2)
t
SDCItHDCI
DCIP(2)/
DCIN(2)
FRAMEP(2)/
FRAMEN(2)
08281-050
Figure 82. Timing Diagram Required for Synchronizing Devices
DACCLKP/
DACCLKN
SAMPLE
RATE CLOCK
SYNC
CLOCK
LOW SKEW
CLOCK DRI VER
LOW SKEW
CLOCK DRI VER
MATCHED
LENGTH TRACES
REFCLKP/
REFCLKN
FRAMEP/
FRAMEN
DCIP/
DCIN
DACCLKP/
DACCLKN
REFCLKP/
REFCLKN
FRAMEP/
FRAMEN
DCIP/
DCIN
IOUT1P/
IOUT1N
IOUT2P/
IOUT2N
FPGA
Figure 83. Typical Circuit Diagram for Synchronizing Devices to a System Clock
To maintain synchronization, the skew between the REFCLK
signals of the devices must be less than t
ns. When resetting
SKEW
the FIFO, the FRAME signal must be held high for the time
interval required to write two complete input data words. A
timing diagram of the input signals is shown in Figure 82.
Figure 82 shows a REFCLK frequency equal to the data rate.
Although this is the most common situation, it is not strictly
required for proper synchronization. Any REFCLK frequency
that satisfies the following equation is acceptable. (This
equation is valid only when the PLL is used because only data
rate mode is available with the PLL on.)
f
SYNC_I
= f
DACCLK
/2N and f
SYNC_I
≤ f
DATA
where N = 0, 1, 2, or 3.
As an example, a configuration with 4× interpolation and clock
frequencies of f
200 MHz, and f
= 1600 MHz, f
VCO
= 100 MHz is a viable solution.
SYNC_I
DACCLK
= 800 MHz, f
DATA
=
SYNCHRONIZATION WITH DIRECT CLOCKING
When directly sourcing the DAC sample rate clock, a separate
REFCLK input signal is required for synchronization. To synchronize devices, the DACCLK signal and the REFCLK signal
must be distributed with low skew to all the devices being
synchronized. If the devices need to be synchronized to a
Rev. B | Page 53 of 60
08281-051
master clock, use the master clock directly for generating the
REFCLK input (see Figure 83).
DATA RATE MODE SYNCHRONIZATION
The Procedure for Data Rate Synchronization When Directly
Sourcing the DAC Sampling Clock section outlines the steps
required to synchronize multiple devices in data rate mode. The
procedure assumes that the DACCLK and REFCLK signals are
applied to all the devices. The following procedure must be
carried out on each individual device.
Procedure for Data Rate Synchronization When Directly Sourcing the DAC Sampling Clock
Configure the AD9122 for data rate, periodic synchronization
by writing 0xC8 to the sync control register (Register 0x10).
Additional synchronization options are available (see the
Additional Synchronization Features section).
Read the sync locked bit (Register 0x12, Bit 6) to verify that the
device is back-end synchronized. A high level on this bit indicates
that the clocks are running with a constant and known phase
relative to the synchronization signal.
Reset the FIFO by strobing the FRAME signal high for one
complete DCI period. Resetting the FIFO ensures that the
correct data is being read from the FIFO of each of the devices
simultaneously.

AD9122
This completes the synchronization procedure; all devices
should now be synchronized.
To ensure that each DAC is updated with the correct data on
the same CLK edge, two timing relationships must be met on
each DAC.
•
DCIP/DCIN and D[15:0]P/D[15:0]N must meet the setup
and hold times with respect to the rising edge of DACCLK.
Synchronization (REFCLK) must also meet the setup and
•
hold times with respect to the rising edge of DACCLK.
When these conditions are met, the outputs of the DACs are
updated within one DAC clock cycle of each other. The timing
requirements of the input signals are shown in Figure 84.
t
SKEW
DACCLKP(1)/
DACCLKN(1)
DACCLKP(2)/
DACCLKN(2)
REFCLKP(2)/
REFCLKN(2)
DCIP(2)/
DCIN(2)
FRAMEP(2)/
FRAMEN(2)
t
SDCItHDCI
t
SUSYNC
t
HSYNC
Figure 84. Data Rate Synchronization Signal Timing Requirements,
2× Interpolation
Figure 84 shows the synchronization signal timing with 2×
interpolation; therefore, f
= ½ × f
DCI
. The REFCLK input is
CLK
shown to be equal to the data rate. The maximum frequency at
which the device can be resynchronized in data rate mode can
be expressed as
= f
f
SYNC_I
DATA
/2N
where N is any non-negative integer.
Generally, for values of N greater than or equal to 3, select the
FIFO rate synchronization mode.
When synchronization is used in data rate mode, the timing
constraint between the DCI and DACCLK must be met according
to Tab l e 2 5 . In data rate mode, the allowed phase drift between
the DCI and DACCLK is limited to one DCI cycle. The DCI to
DACCLK timing restriction is required to prevent corruption of
the data transfer when the FIFO is constantly reset. The required
timing between the DCI and DACCLK is shown in Figure 85.
t
DATA
DACCLK/
REFCLK
SAMPLING
INTERVAL
DCI
t
SDCI
t
HDCI
8281-147
Figure 85. Timing Diagram for Input Data Port (Data Rate Mode)
FIFO RATE MODE SYNCHRONIZATION
The Procedure for FIFO Rate Synchronization When Directly
Sourcing the DAC Sampling Clock section outlines the steps
required to synchronize multiple devices in FIFO rate mode.
The procedure assumes that the DACCLK and REFCLK signals
are applied to all the devices. The procedure must be carried out
on each individual device.
Procedure for FIFO Rate Synchronization When Directly Sourcing the DAC Sampling Clock
Configure the AD9122 for FIFO rate, periodic synchronization
08281-052
by writing 0x88 to the sync control register (Register 0x10). Additional synchronization options are available (see the Additional
Synchronization Features section).
Read the sync locked bit (Register 0x12, Bit 6) to verify that the
device is back-end synchronized. A high level on this bit indicates
that the clocks are running with a constant and known phase
relative to the synchronization signal.
Reset the FIFO by strobing the FRAME signal high for one complete DCI period. Resetting the FIFO ensures that the correct data
is being read from the FIFO of each of the devices simultaneously.
This completes the synchronization procedure; all devices should
now be synchronized.
When these conditions are met, the outputs of the DACs are
updated within one DAC clock cycle of each other. The timing
requirements of the input signals are shown in Figure 86.
t
SKEW
DACCLKP(1)/
DACCLKN(1)
Table 25. DCI to DACCLK Setup and Hold Times
DCI Delay
Register 0x16,
Bits[1:0]
Minimum Setup
SDCI
(ns)
Time, t
00 −0.07 0.82 0.75
01 −0.24 1.13 0.89
10 −0.39 1.40 1.01
11 −0.49 1.55 1.06
Minimum Hold
Time, t
HDCI
(ns)
Sampling
Interval (ns)
Rev. B | Page 54 of 60
DACCLKP(2)/
DACCLKN(2)
REFCLKP(2)/
REFCLKN(2)
DCIP(2)/
DCIN(2)
FRAMEP(2)/
FRAMEN(2)
t
SUSYNCtHSYNC
Figure 86. FIFO Rate Synchronization Signal Timing Requirements,
2× Interpolation
08281-053

AD9122
Figure 86 shows the synchronization signal timing with 2×
interpolation; therefore, f
= ½ × f
DCI
. The REFCLK input is
CLK
shown to be equal to the FIFO rate. The maximum frequency
at which the device can be resynchronized in FIFO rate mode
can be expressed as
= f
f
SYNC_I
DATA
/(8 × 2N)
where N is any non-negative integer.
ADDITIONAL SYNCHRONIZATION FEATURES
Tabl e 26 shows the required timing between the DACCLK and the
synchronization clock when synchronization is used. This timing
restriction applies to both data rate mode and FIFO rate mode.
Table 26. Synchronization Setup and Hold Times
Parameter Min Max Unit
t
−t
SKEW
t
100 ps
SUSYNC
t
330 ps
HSYNC
One-Time Synchronization
When implementing the full multichip synchronization feature
(with the REFCLK and FRAME signals aligned within one DACCLK
cycle), the user may experience difficulty meeting the DACCLK to
synchronization clock timing. In this case, a one-time synchronization method can be used. Before implementing the one-time
synchronization, make sure that the synchronization signal is
locked by checking both the sync signal locked and the sync signal
lost flags (Bit 4 and Bit 5 in Register 0x06). It is also important
that synchronization not be enabled before stable REFCLK signals
are present from the FPGA or ASIC. For more information and
a detailed flowchart of the one-time synchronization feature, see
the AN-1093 Application Note, “Synchronization of Multiple
AD9122 TxDAC+ Converters.”
Sync Status Bits
When the sync locked bit (Register 0x12, Bit 6) is set, it indicates
that the synchronization logic has reached alignment. This alignment is determined when the clock generation state machine
phase is constant.
Alignment takes from (11 + averaging) × 64 to (11 + averaging) ×
128 DACCLK cycles. The sync locked bit can also trigger an
as described in the section. Interrupt Request Operation
When the sync lost bit (Register 0x12, Bit 7) is set, it indicates
that a previously synchronized device has lost alignment. This
bit is latched and remains set until cleared by overwriting the
register. This bit can also trigger an
/2 +t
DACCLK
/2 ps
DACCLK
IRQ
,
IRQ
, as described in the
section. Interrupt Request Operation
The sync phase readback bits (Register 0x13, Bits[7:0]) report
the current clock phase in a 6.2 format. Bits[7:2] report which of
the 64 states (0 to 63) the clock is currently in. When averaging
is enabled, Bits[1:0] provide ¼ state accuracy (for 0, ¼, ½, ¾).
The lower two bits give an indication of the timing margin
issues that may exist. If the synchronization sampling is error
free, the fractional clock state should be 00.
Timing Optimization
The synchronization signal (REFCLK) is sampled by a version
of the DACCLK. If sampling errors are detected, the opposite
sampling edge can be selected to improve the sampling point.
The sampling edge can be selected by setting Register 0x10,
Bit 3 (1 = rising and 0 = falling).
The synchronization logic resynchronizes when a phase change
between the synchronization signal (REFCLK) and the state of the
clock generation state machine exceeds a threshold. To mitigate
the effects of jitter and prevent erroneous resynchronizations, the
relative phase can be averaged. The amount of averaging is set
by the sync averaging bits (Register 0x10, Bits[2:0]) and can be
set from 1 to 128. The higher the number of averages, the more
slowly the device recognizes and resynchronizes to a legitimate
phase correction. Generally, the averaging should be made as
large as possible while still meeting the allotted resynchronization time interval. Note that, if the average synchronization
sampling result is in approximately the middle of the probability
curve, the synchronization engine can be unstable, resulting in
corrupted output.
The value of the Sync Phase Request[5:0] bits (Register 0x11,
Bits[5:0]) is the state to which the clock generation state machine
resets upon initialization. By varying this value, the timing of
the internal clocks, with respect to the synchronization signal
(REFCLK), can be adjusted. Every increment of the Sync Phase
Request[5:0] value advances the internal clocks by one DACCLK
cycle. This offset can be used for two purposes: to skew the outputs of two synchronized DAC outputs in increments of the
DACCLK cycle, and to change the relative timing between the
DAC output and the SYNC input (REFCLK). This may allow
for a more optimal placement of the DCI sampling point in data
rate synchronization mode.
Rev. B | Page 55 of 60

AD9122
INTERRUPT REQUEST OPERATION
The AD9122 provides an interrupt request output signal on
IRQ
Pin 7 (
of significant device events. Upon assertion of the interrupt, the
device should be queried to determine the precise event that
occurred. The
the
the interrupt pins of other devices with open-drain outputs to
wire-OR these pins together.
The event flags provide visibility into the device. These flags
are located in the two event flag registers, Register 0x06 and
Register 0x07. The behavior of each event flag is independently
selected in the interrupt enable registers, Register 0x04 and
Register 0x05. When the flag interrupt enable is active, the event
flag latches and triggers an external interrupt. When the flag
interrupt is disabled, the event flag monitors the source signal,
but the
Figure 87 shows the
signals propagate to the
signal represents one bit from the interrupt enable register. The
EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE signal represents one bit from the event
flag register. The EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE signal represents
one of the device signals that can be monitored, such as the
PLL_LOCKED signal from the PLL phase detector or the
FIFO_WARNING_1 signal from the FIFO controller.
When an interrupt enable bit is set high, the corresponding
event flag bit reflects a positively tripped version of the
EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE signal; that is, the event flag bit is
latched on the rising edge of the EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE
signal. This signal also asserts the external
) that can be used to notify an external host processor
IRQ
pin is an open-drain, active low output. Pull
IRQ
pin high external to the device. This pin can be tied to
IRQ
pin remains inactive.
IRQ
-related circuitry and how the event flag
IRQ
output. The INTERRUPT_ENABLE
IRQ
pin.
When an interrupt enable bit is set low, the event flag bit reflects
the current status of the EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE signal, and
IRQ
the event flag has no effect on the external
pin.
The latched version of an event flag (the INTERRUPT_SOURCE
signal) can be cleared in two ways. The recommended way is by
writing 1 to the corresponding event flag bit. A hardware or software reset also clears the INTERRUPT_SOURCE signal.
INTERRUPT SERVICE ROUTINE
Interrupt request management starts by selecting the set of
event flags that require host intervention or monitoring. The
events that require host action should be enabled so that the
host is notified when they occur. For events requiring host
IRQ
intervention upon
to clear an interrupt request:
Read the status of the event flag bits that are being
1.
monitored.
Set the interrupt enable bit low so that the unlatched
2.
EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE signal can be monitored directly.
Perform any actions that may be required to clear the
3.
EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE. In many cases, no specific
actions may be required.
Read the event flag to verify that the actions taken have
4.
cleared the EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE.
Clear the interrupt by writing 1 to the event flag bit.
5.
Set the interrupt enable bits of the events to be monitored.
6.
Note that some EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE signals are latched
signals. These signals are cleared by writing to the corresponding event flag bit. For more information about each event flag,
see Register 0x06 and Register 0x07 in Tabl e 11 .
activation, run the following routine
INTERRUPT_ENABL E
EVENT_FLAG_SOURCE
WRITE_1_T O_EVENT _FLAG
DEVICE_RESET
0
1
INTERRUPT_
SOURCE
OTHER
INTERRUPT
SOURCES
Figure 87. Simplified Schematic of
IRQ
Circuitry
EVENT_FLAG
IRQ
08281-054
Rev. B | Page 56 of 60

AD9122
INTERFACE TIMING VALIDATION
The AD9122 provides on-chip sample error detection (SED)
circuitry that simplifies verification of the input data interface.
The SED circuitry compares the input data samples captured
at the digital input pins with a set of comparison values. The
comparison values are loaded into registers through the SPI
port. Differences between the captured values and the comparison values are detected and stored. Options are available for
customizing SED test sequencing and error handling.
SED OPERATION
The SED circuitry operates on a data set made up of four 16-bit
input words, denoted as I0, Q0, I1, and Q1. To properly align
the input samples, the first I data-word (that is, I0) is indicated
by asserting FRAME for at least one complete input sample.
Figure 88 shows the input timing of the interface in word mode.
The FRAME signal can be issued once at the start of the data
transmission, or it can be asserted repeatedly at intervals coinciding
with the I0 and Q0 data-words.
FRAME
DATA[15:0] Q1Q0I0 I1 I0 Q0
Figure 88. Timing Diagram of Extended FRAME Signal Required
to Align Input Data for SED
08281-056
The SED has three flag bits (Register 0x67, Bit 5, Bit 1, and Bit 0)
that indicate the results of the input sample comparisons. The
sample error detected bit (Register 0x67, Bit 5) is set when an
error is detected and remains set until cleared. The SED also
provides registers that indicate which input data bits experienced
errors (Register 0x70 through Register 0x73). These bits are
latched and indicate the accumulated errors detected until cleared.
Autosample error detection (AED) is an autoclear function in
the SED. The autoclear mode has two effects: it activates the
compare fail bit and the compare pass bit (Register 0x67, Bit 1
and Bit 0) and changes the behavior of Register 0x70 through
Register 0x73. The compare pass bit is set if the last comparison
indicated that the sample was error free. The compare fail bit is
set if an error is detected. The compare fail bit is automatically
cleared by the reception of eight consecutive error-free comparisons. When autoclear mode is enabled, Register 0x70 through
Register 0x73 accumulate errors as previously described but are
reset to all 0s after eight consecutive error-free sample comparisons
are made.
If desired, the sample error detected, compare pass, and com-
IRQ
pare fail flags can be configured to trigger the
pin when
active. This is done by enabling the appropriate bits in the event
flag register (Register 0x07).
Tabl e 27 shows a progression of the input sample comparison
results and the corresponding states of the error flags.
Table 27. Progression of Input Sample Comparison Results and the Resulting SED Register Values
Compare Results (Pass/Fail) P F F F P P P P P P P P P F P F
Register 0x67, Bit 5 (Sample Error Detected) 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Register 0x67, Bit 1 (Compare Fail) 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1
Register 0x67, Bit 0 (Compare Pass) 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
Register 0x70 to Register 0x73
(Errors Detected x_BITS[15:0])
1
Z = all 0s.
2
N = nonzero.
1
N2 N2 N2 N2 N2 N2 N2 N2 N2 N2 N2 Z1 N2 N2 N2
Z
0
Rev. B | Page 57 of 60

AD9122
SED EXAMPLE
Normal Operation
The following example illustrates the SED configuration for
continuously monitoring the input data and assertion of the
IRQ
pin when a single error is detected.
Load the following comparison values. (Comparison values
1.
can be chosen arbitrarily; however, choosing values that
require frequent bit toggling provides the most robust test.)
Register 0x68: I0[7:0]
Register 0x69: I0[15:8]
Register 0x6A: Q0[7:0]
Register 0x6B: Q0[15:8]
Register 0x6C: I1[7:0]
Register 0x6D: I1[15:8]
Register 0x6E: Q1[7:0]
Register 0x6F: Q1[15:8]
Enable the SED error detect flag to assert the
2.
(Set Register 0x05 to 0x04.)
3.
Begin transmitting the input data pattern.
IRQ
pin.
Write to Register 0x67 to enable the SED.
4.
(Set Register 0x67 to 0x80.)
Clear the SED errors in Register 0x67 and Register 0x07.
5.
When the SED is first turned on, the FRAME signal may
be detected immediately; therefore, the SED failure bit may
be asserted due to the unknown initial FRAME status. For
this reason, the SED compare fail status bit must be cleared
at least once immediately after enabling the SED.
IRQ
is asserted, read Register 0x67 and Register 0x70 through
If
Register 0x73 to verify that a SED error was detected and to determine which input bits were in error. The bits in Register 0x70
through Register 0x73 are latched; therefore, the bits indicate
any errors that occurred on those bits throughout the test (not
only the errors that caused the error detected flag to be set).
Note that the FRAME signal is not required during normal
operation when the device is configured for word mode.
Enabling the alignment of the I0 sample as described in the
SED Operation section requires the use of the FRAME signal.
The timing diagrams for byte and nibble modes are the same
as during normal operation and are shown in Figure 44 and
Figure 45, respectively.
Rev. B | Page 58 of 60

AD9122
EXAMPLE START-UP ROUTINE
To ensure reliable start-up of the AD9122, certain sequences
should be followed. This section shows an example start-up
routine. This example uses the configuration described in the
Device Configuration section.
DEVICE CONFIGURATION
The following device configuration is used for this example:
• f
= 122.88 MSPS
DATA
• Interpolation is 4×, using HB1 = 10 and HB2 = 010010
• Input data is baseband data
• f
• f
= 140 MHz
OUT
= 122.88 MHz
REFCLK
• PLL is enabled
• Fine NCO is enabled
• Inverse sinc filter is enabled
• Synchronization is enabled
• Silicon revision is R2
DERIVED PLL SETTINGS
The following PLL settings can be derived from the device
configuration:
= f
• f
DACCLK
• f
VCO
= 4 × f
• N1 = f
• N2 = f
× interpolation = 491.52 MHz
DATA
= 1966.08 MHz (1 GHz < f
DACCLK
DACCLK/fREFCLK
VCO/fDACCLK
= 4
= 4
< 2 GHz)
VCO
DERIVED NCO SETTINGS
The following NCO settings can be derived from the device
configuration:
• f
• f
= 2 × f
NCO
CARRIER
= f
• FTW = 17.12/(2 × 122.8) × 2
DATA
OUT
− f
= 140 − 122.88 = 17.12 MHz
MODHB1
32
= 0x11D55555
START-UP SEQUENCE
The following sequence configures the power clock and register
write sequencing for reliable device start-up in PLL ON mode:
Power up Device (no specific power supply
sequence is required)
Apply stable REFCLK input signal.
Apply stable DCI input signal.
Issue H/W RESET (Optional).
Device Configuration Register Write Sequence:
0x00 Æ 0x20 /* Issue Software Reset */
0x00 Æ 0x00
/* Start PLL */
0x0D Æ 0xD9
0x0A Æ 0xC0
0x0A Æ 0x80
/* Verify PLL is Locked */
Read 0x0E /* Expect bit 7 = 1 */
/* Configure Interpolation Filters */
0x1B Æ 0x84
0x1C Æ 0x04
0x1D Æ 0x24
/* Configure NCO */
0x1E Æ 0x01
0x30 Æ 0x55
0x31 Æ 0x55
0x32 Æ 0xD5
0x33 Æ 0x11
/* Update Frequency Tuning Word */
0x36 Æ 0x01
0x36 Æ 0x00
/* Choose Data Rate Mode */
0x10 Æ 0x48
/* Issue Software FIFO Reset */
0x17 Æ 0x04
0x18 Æ 0x02
/* Verify FIFO Reset */
Read 0x18 /* Expect 0x07 */
0x18 Æ 0x00
Read 0x19 /* Expect 0x1F or 0x0F or 0x07 */
Rev. B | Page 59 of 60

AD9122
OUTLINE DIMENSIONS
PIN 1
INDICATOR
10.00
BSC SQ
TOP VI EW
9.75
BSC SQ
0.60
0.42
0.24
0.50
BSC
0.60
0.42
0.24
55
54
EXPOSED PAD
(BOTTOM VIEW)
PIN 1
72
INDICATOR
1
6.15
6.00 SQ
5.85
1.00
0.85
0.80
SEATING
PLANE
12° MAX
0.50
0.40
0.30
0.80 MAX
0.65 TYP
0.30
0.23
0.18
COMPLIANT TO JEDEC STANDARDS MO-220-VNND-4
0.05 MAX
0.02 NOM
0.20 REF
COPLANARITY
0.08
37
36
8.50 REF
FOR PROPER CONNECTION OF
THE EXPOSED PAD, REFER TO
THE PIN CONFIGURATION AND
FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
SECTION OF THIS DATA SHEET.
18
19
052809-A
Figure 89. 72-Lead Lead Frame Chip Scale Package [LFCSP_VQ]
10 mm × 10 mm Body, Very Thin Quad
(CP-72-7)
Dimensions shown in millimeters
ORDERING GUIDE
Model1 Temperature Range Package Description Package Option
AD9122BCPZ −40°C to +85°C 72-lead LFCSP_VQ CP-72-7
AD9122BCPZRL −40°C to +85°C 72-lead LFCSP_VQ CP-72-7
AD9122-M5372-EBZ Evaluation Board Connected to ADL5372 Modulator
AD9122-M5375-EBZ Evaluation Board Connected to ADL5375 Modulator
1
Z = RoHS Compliant Part.
©2009–2011 Analog Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. Trademarks and
registered trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
D08281-0-5/11(B)
Rev. B | Page 60 of 60
 Loading...
Loading...