Analog Devices AD8039ART-REEL7, AD8039ART-REEL, AD8039AR-REEL7, AD8039AR-REEL, AD8039AR Datasheet
...
Low Power 350 MHz
8
7
6
5
1
2
3
4
NC
–IN
+IN
DISABLE
+V
S
V
OUT
NC–V
S
AD8038
NC = NO CONNECT
a
FEATURES
Low Power
1 mA Supply Current/Amp
High Speed
350 MHz, –3 dB Bandwidth (G = +1)
425 V/s Slew Rate
Low Cost
Low Noise
8 nV/√Hz @ 100 kHz
600 fA/√Hz @ 100 kHz
Low Input Bias Current: 750 nA Max
Low Distortion
–90 dB SFDR @ 1 MHz
–65 dB SFDR @ 5 MHz
Wide Supply Range: 3 V to 12 V
Small Packaging: SOT23-8, SC70-5, and SOIC-8
APPLICATIONS
Battery-Powered Instrumentation
Filters
A/D Driver
Level Shifting
Buffering
High Density PC Boards
Photo Multiplier
Voltage Feedback Amplifiers
AD8038/AD8039
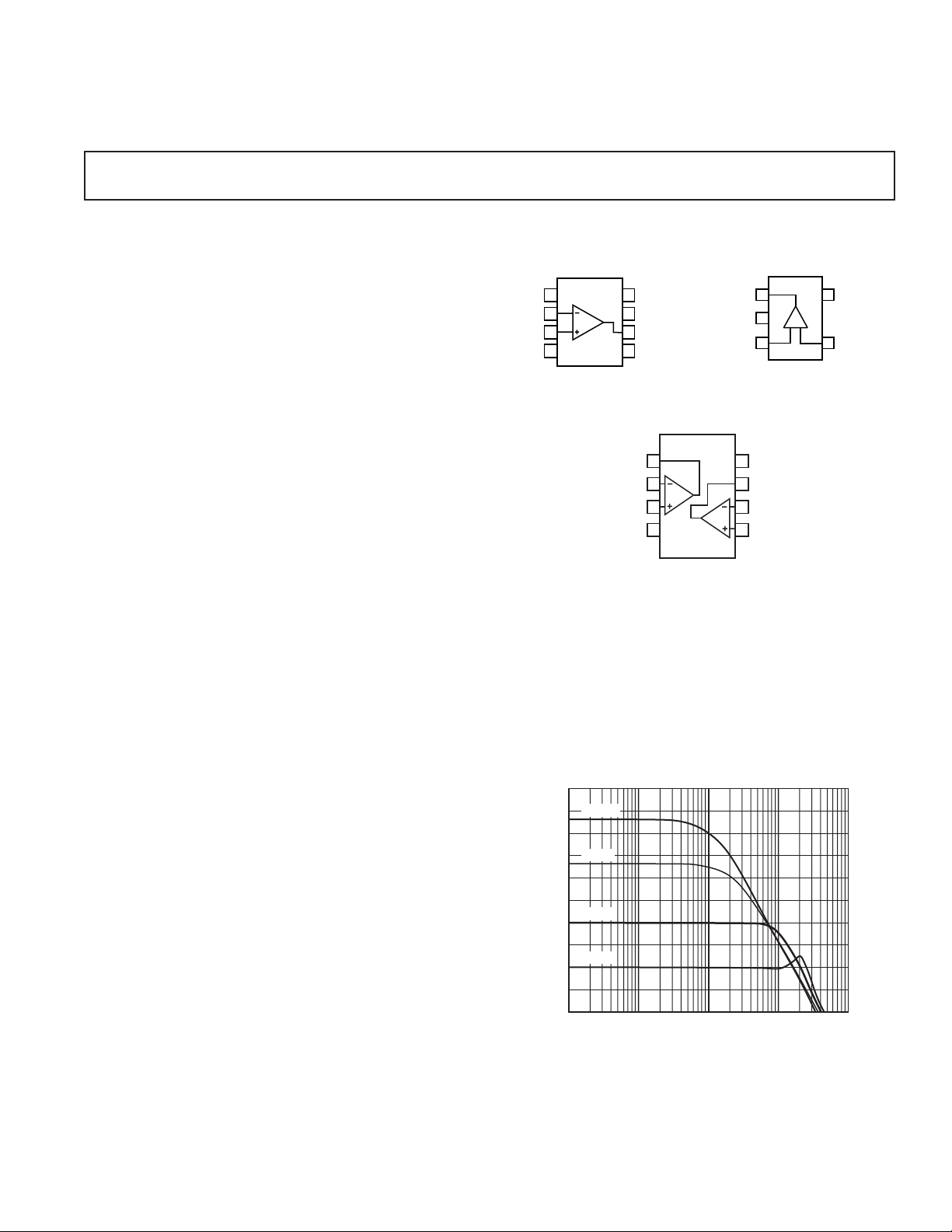
CONNECTION DIAGRAMS
SOIC-8 (R)
SOIC-8 (R) and SOT23-8 (RT)*
V
OUT1
–IN1
+IN1
–V
AD8039
1
2
3
4
S
SC70-5 (KS)
AD8038
V
1
OUT
–V
2
S
3
8
+V
S
7
V
OUT2
6
–IN2
5
+IN2
+–
5
+V
S
4
–IN+IN
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
The AD8038 (single) and AD8039 (dual) amplifiers are high
speed (350 MHz) voltage feedback amplifiers with an exceptionally
low quiescent current of 1.0 mA/amplifier typical (1.5 mA max).
The AD8038 single amplifier in the SOIC-8 package has a
The AD8039 amplifier is the only dual low power, high
amplifier available in a tiny SOT23-8 package, and the single
AD8038 is available in both a SOIC-8 and a SC70-5 package.
These amps are rated to work over the industrial temperature
range of –40°C to +85°C.
disable feature. Despite being low power and low cost, the
amplifier provides excellent overall performance. Additionally,
it offers a high slew rate of 425 V/µs and low input offset volt-
age of 3 mV max.
ADI’s proprietary XFCB process allows low noise operation
√
Hz and 600 fA/√Hz) at extremely low quiescent currents.
(8 nV/
Given a wide supply voltage range (3 V to 12 V), wide bandwidth,
and small packaging, the AD8038 and AD8039 amplifiers are
designed to work in a variety of applications where power and space
are at a premium.
The AD8038 and AD8039 amplifiers have a wide input commonmode range of 1 V from either rail and will swing within 1 V of
each rail on the output. These amplifiers are optimized for
driving capacitive loads up to 15 pF. If driving larger capacitive loads, a small series resistor is needed to avoid excessive
peaking or overshoot.
*Not yet released
REV. B
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties that
may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or otherwise
under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 2002
speed
24
G = +10
21
18
15
G = +5
12
9
G = +2
GAIN – dB
6
3
G = +1
0
–3
–6
0.1 1000110100
FREQUENCY – MHz
Figure 1. Small Signal Frequency Response for
Various Gains, V
= 500 mV p-p, VS = ±5 V
OUT
AD8038/AD8039–SPECIFICATIONS
(TA = 25ⴗC, VS = ⴞ5 V, RL = 2 k⍀, Gain = +1, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
–3 dB Bandwidth G = 1, VO = 0.5 V p-p 300 350 MHz
G = 2, V
G = 1, V
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness G = 2, V
Slew Rate G = 1, V
= 0.5 V p-p 175 MHz
O
= 2 V p-p 100 MHz
O
= 0.2 V p-p 45 MHz
O
= 2 V Step, RL = 2 kΩ 400 425 V/µs
O
Overdrive Recovery Time G = 2, 1 V Overdrive 50 ns
Settling Time to 0.1% G = 2, VO = 2 V Step 18 ns
NOISE/HARMONIC PERFORMANCE
SFDR
Second Harmonic f
Third Harmonic f
Second Harmonic f
Third Harmonic f
= 1 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, RL = 2 kΩ –90 dBc
C
= 1 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, RL = 2 kΩ –92 dBc
C
= 5 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, RL = 2 kΩ –65 dBc
C
= 5 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, RL = 2 kΩ –70 dBc
C
Crosstalk, Output-to-Output (AD8039) f = 5 MHz, G = 2 –70 dB
Input Voltage Noise f = 100 kHz 8 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz 600 fA/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Offset Voltage 0.5 3 mV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 4.5 µV/°C
Input Bias Current 400 750 nA
Input Bias Current Drift 3nA/°C
Input Offset Current 25 ±nA
Open-Loop Gain VO = ±2.5 V 70 dB
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Resistance 10 MΩ
Input Capacitance 2pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range R
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio V
= 1 kΩ±4V
L
= ±2.5 V 61 67 dB
CM
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
DC Output Voltage Swing R
= 2 kΩ, Saturated Output ±4V
L
Capacitive Load Drive 30% Overshoot, G = +2 20 pF
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range 3.0 12 V
Quiescent Current per Amplifier 1.0 1.5 mA
Power Supply Rejection Ratio – Supply –71 –77 dB
+ Supply –64 –70 dB
POWER-DOWN DISABLE*
Turn-On Time 180 ns
Turn-Off Time 700 ns
Disable Voltage – Part is OFF +V
Disable Voltage – Part is ON +V
– 4.5 V
S
– 2.5 V
S
Disabled Quiescent Current 0.2 mA
Disabled In/Out Isolation f = 1 MHz –60 dB
*Only available in AD8038 SOIC-8 package.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
REV. B–2–
AD8038/AD8039
SPECIFICATIONS
(TA = 25ⴗC, VS = 5 V, RL = 2 k⍀ to VS/2, Gain = +1, unless otherwise noted.)
Parameter Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
–3 dB Bandwidth G = 1, VO = 0.2 V p-p 275 300 MHz
G = 2, V
G = 1, V
= 0.2 V p-p 150 MHz
O
= 2 V p-p 30 MHz
O
Bandwidth for 0.1 dB Flatness G = 2, VO = 0.2 V p-p 45 MHz
Slew Rate G = 1, V
= 2 V Step, RL = 2 kΩ 340 365 V/µs
O
Overdrive Recovery Time G = 2, 1 V Overdrive 50 ns
Settling Time to 0.1% G = 2, VO = 2 V Step 18 ns
NOISE/HARMONIC PERFORMANCE
SFDR
Second Harmonic f
Third Harmonic f
Second Harmonic f
Third Harmonic f
= 1 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, RL = 2 kΩ –82 dBc
C
= 1 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, RL = 2 kΩ –79 dBc
C
= 5 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, RL = 2 kΩ –60 dBc
C
= 5 MHz, VO = 2 V p-p, RL = 2 kΩ –67 dBc
C
Crosstalk, Output-to-Output f = 5 MHz, G = 2 –70 dB
Input Voltage Noise f = 100 kHz 8 nV/√Hz
Input Current Noise f = 100 kHz 600 fA/√Hz
DC PERFORMANCE
Input Offset Voltage 0.8 3 mV
Input Offset Voltage Drift 3 µV/°C
Input Bias Current 400 750 nA
Input Bias Current Drift 3nA/°C
Input Offset Current 30 ±nA
Open-Loop Gain VO = ±2.5 V 70 dB
INPUT CHARACTERISTICS
Input Resistance 10 MΩ
Input Capacitance 2pF
Input Common-Mode Voltage Range R
= 1 kΩ 1.0–4.0 V
L
Common-Mode Rejection Ratio VCM = ±1 V 59 65 dB
OUTPUT CHARACTERISTICS
DC Output Voltage Swing RL = 2 kΩ, Saturated Output 0.9–4.1 V
Capacitive Load Drive 30% Overshoot 20 pF
POWER SUPPLY
Operating Range 3 12 V
Quiescent Current per Amplifier 0.9 1.5 mA
Power Supply Rejection Ratio –65 –71 dB
POWER-DOWN DISABLE*
Turn-On Time 210 ns
Turn-Off Time 700 ns
Disable Voltage – Part is OFF +V
Disable Voltage – Part is ON +V
– 4.5 V
S
– 2.5 V
S
Disabled Quiescent Current 0.2 mA
Disabled In/Out Isolation f = 1 MHz –60 dB
*Only available in AD8038 SOIC-8 package.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
REV. B
–3–
AD8038/AD8039
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
Supply Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12.6 V
Power Dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . See Figure 2
Common-Mode Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±V
S
Differential Input Voltage . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±4 V
Storage Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +125°C
Operating Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Lead Temperature Range (Soldering 10 sec) . . . . . . . . . 300°C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those indicated in the operational
section of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION
The maximum safe power dissipation in the AD8038/AD8039
package is limited by the associated rise in junction temperature (TJ)
on the die. The plastic encapsulating the die will locally reach the
junction temperature. At approximately 150°C, which is the glass
transition temperature, the plastic will change its properties. Even
temporarily exceeding this temperature limit may change the stresses
that the package exerts on the die, permanently shifting the parametric
performance of the AD8038/AD8039. Exceeding a junction tempera-
of 175°C for an extended period of time can result in changes
ture
in the silicon devices, potentially causing failure.
RMS output voltages should be considered. If RL is referenced to
V
V
If the RMS signal levels are indeterminate, then
worst case, when V
The still-air thermal properties of the package and PCB (JA), ambient
temperature (TA), and total power dissipated in the package (PD)
determine the junction temperature of the die. The junction
temperature can be calculated as follows:
TT P
=+ ×
ADAJ
θ
()
J
The power dissipated in the package (PD) is the sum of the quiescent
power dissipation and the power dissipated in the package due to the
load drive for all outputs. The quiescent power is the voltage between
the supply pins (VS) multiplied by the quiescent current (IS). Assuming
the load (RL) is referenced to midsupply, then the total drive power is
VS / 2 × I
in the load (V
some of which is dissipated in the package and some
OUT,
OUT
× I
). The difference between the total drive
OUT
In single-supply operation with RL referenced to VS–, worst case is
V
Airflow will increase heat dissipation effectively reducing
more metal directly in contact with the package leads from metal traces,
through holes, ground, and power planes, will reduce the JA. Care
must be taken to minimize parasitic capacitances at the input leads
of high speed op amps as discussed in the board layout section.
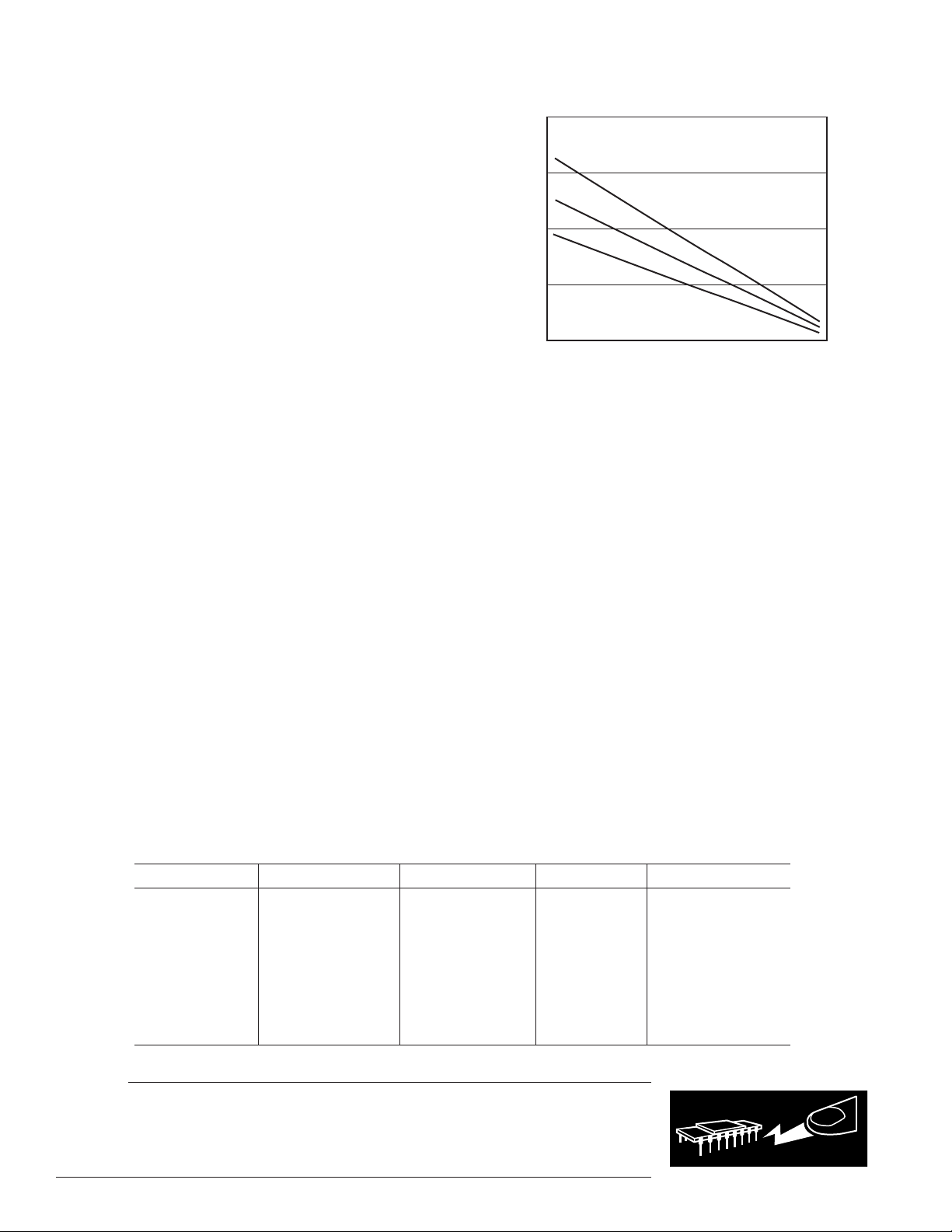
Figure 2 shows the maximum safe power dissipation in the package
versus the ambient temperature for the SOIC-8 (125°C/W), SC70-5
(210°C/W), and SOT23-8 (160°C/W) package on a JEDEC standard
four-layer board.
power and the load power is the drive power dissipated in the package.
PD = quiescent power + (total drive power – load power)
PVI V V R V R
=×
[]
DSS S OUT L OUT L
+
()
[]
×
//–/2
()
2
[]
ORDERING GUIDE
OUTPUT SHORT CIRCUIT
Shorting the output to ground or drawing excessive current from
the AD8038/AD8039 will likely cause a catastrophic failure.
2.0
1.5
SOIC-8
1.0
0.5
MAXIMUM POWER DISSIPATION – W
0
–55
SOT23-8
SC70-5
–25 5 35 65 95 125
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE – ⴗC
Figure 2. Maximum Power Dissipation vs.
Temperature for a Four-Layer Board
, as in single-supply operation, then the total drive power is
S–
I
OUT
.
S
consider the
= VS / 4 for RL to midsupply:
OUT
2
//4
()
. Also,
JA
OUT
= VS / 2.
PVI V R
=×
()
DSS S L
values are approximations.
JA
+
Model Temperature Range Package Description Package Outline Branding Information
AD8038AR –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead SOIC SO-8
AD8038AR-REEL –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead SOIC SO-8
AD8038AR-REEL7 –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead SOIC SO-8
AD8038AKS-REEL –40°C to +85°C 5-Lead SC70 KS-5 HUA
AD8038AKS-REEL7 –40°C to +85°C 5-Lead SC70 KS-5 HUA
AD8039AR –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead SOIC SO-8
AD8039AR-REEL –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead SOIC SO-8
AD8039AR-REEL7 –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead SOIC SO-8
AD8039ART-REEL* –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead SOT23 RT-8 HYA
AD8039ART-REEL7* –40°C to +85°C 8-Lead SOT23 RT-8 HYA
*Under development.
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD8038/AD8039 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage
may occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
REV. B–4–
 Loading...
Loading...