Analog Devices AD7865 Datasheet
Four-Channel, Simultaneous
SIGNAL
SCALING
SIGNAL
SCALING
SIGNAL
SCALING
SIGNAL
SCALING
FRSTDATA
AGND
CHANNEL
SELECT
REGISTER
MUX
DB0–DB3
+2.5V
REFERENCE
TRACK/HOLD
3 4
6kV
AD7865
EOC
V
DRIVE
RD
CLK IN
/SL1
INT/EXT
CLK/SL2
SL3 SL4
H/S
SEL
DGND
AV
DD
V
REF
AGND
CONVST
BUSY
DB13
DV
DD
V
IN4A
V
IN3B
V
IN3A
V
IN2B
V
IN1B
STBY
V
REFAGND
AGND
V
IN1A
V
IN2A
14-BIT
ADC
CONVERSION
CONTROL LOGIC
INT
CLOCK
INT/EXT
CLOCK
SELECT
OUTPUT
LATCH
WR
CS
DB0
V
IN4B
a
FEATURES
Fast (2.4␣ s) 14-Bit ADC
Four Simultaneously Sampled Inputs
Four Track/Hold Amplifiers
0.35␣ s Track/Hold Acquisition Time
2.4 s Conversion Time per Channel
HW/SW Select of Channel Sequence for Conversion
Single Supply Operation
Selection of Input Ranges: ⴞ10 V, ⴞ5 V and ⴞ2.5 V,
0 V to +5 V and 0 V to +2.5 V
High Speed Parallel Interface Which Also Allows
Interfacing to 3 V Processors
Low Power, 115 mW Typ
Power Saving Mode, 15␣ W Typ
Overvoltage Protection on Analog Inputs
APPLICATIONS
AC Motor Control
Uninterruptible Power Supplies
Industrial Power Meters/Monitors
Data Acquisition Systems
Communications
Sampling, Fast, 14-Bit ADC
AD7865
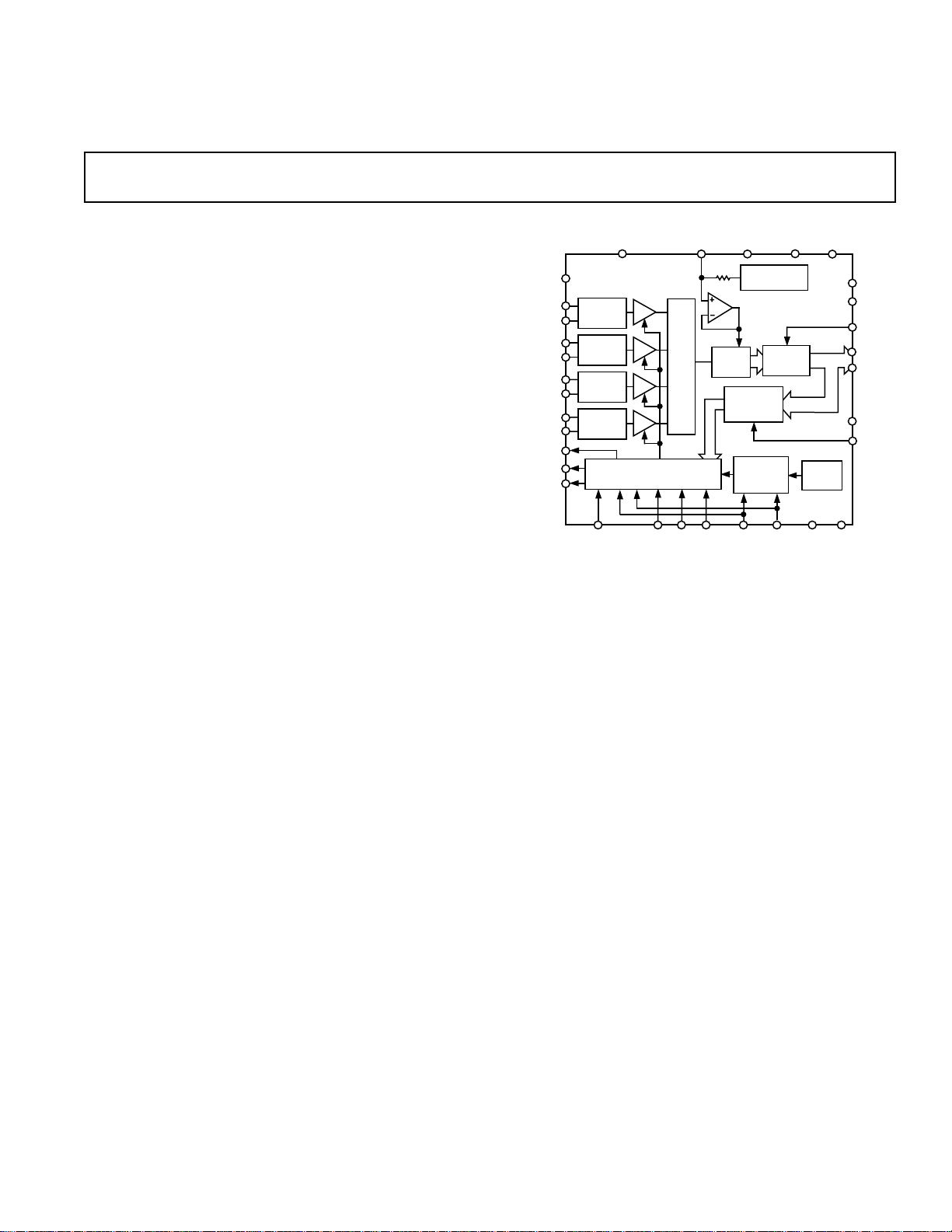
FUNCTIONAL BLOCK DIAGRAM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The AD7865 is a fast, low power, four-channel simultaneous
sampling 14-bit A/D converter that operates from a single +5␣ V
supply. The part contains a 2.4 µs successive approximation
ADC, four track/hold amplifiers, 2.5 V reference, on-chip clock
oscillator, signal conditioning circuitry and a high speed parallel
interface. The input signals on four channels are sampled simultaneously thus preserving the relative phase information of the
signals on the four analog inputs. The part accepts analog input
ranges of ±10␣ V, ±5 V, ±2.5 V, 0 V to +2.5 V and 0 V to +5 V.
The part allows any subset of the four channels to be converted
in order to maximize the throughput rate on the selected sequence. The channels to be converted can be selected either via
hardware (channel select input pins) or via software (programming the channel select register).
A single conversion start signal (CONVST) simultaneously places
all the track/holds into hold and initiates conversion sequence
for the selected channels. The EOC signal indicates the end of
each individual conversion in the selected conversion sequence.
The BUSY signal indicates the end of the conversion sequence.
Data is read from the part via a 14-bit parallel data bus using the
standard CS and RD signals. Maximum throughput for a single
channel is 350 kSPS. For all four channels the maximum throughput is 100 kSPS.
REV. A
Information furnished by Analog Devices is believed to be accurate and
reliable. However, no responsibility is assumed by Analog Devices for its
use, nor for any infringements of patents or other rights of third parties
which may result from its use. No license is granted by implication or
otherwise under any patent or patent rights of Analog Devices.
The AD7865 is available in a small (0.3 sq. inch area) 44-lead
PQFP.
PRODUCT HIGHLIGHTS
1. The AD7865 features four Track/Hold amplifiers and a fast
(2.4 µs) ADC allowing simultaneous sampling and then
conversion of any subset of the four channels.
2. The AD7865 operates from a single +5␣ V supply and consumes only 115 mW typ, making it ideal for low power and
portable applications.
3. The part offers a high speed parallel interface for easy connection to microprocessors, microcontrollers and digital
signal processors.
4. The part is offered in three versions with different analog
input ranges. The AD7865-1 offers the standard industrial
ranges of ±10 V and ±5 V; the AD7865-2 offers a unipolar
range of 0 V to +2.5 V or 0 V to +5 V and the AD7865-3
offers the common signal processing input range of ±2.5 V.
5. The part features very tight aperture delay matching between
the four input sample and hold amplifiers.
One Technology Way, P.O. Box 9106, Norwood, MA 02062-9106, U.S.A.
Tel: 781/329-4700 World Wide Web Site: http://www.analog.com
Fax: 781/326-8703 © Analog Devices, Inc., 1999
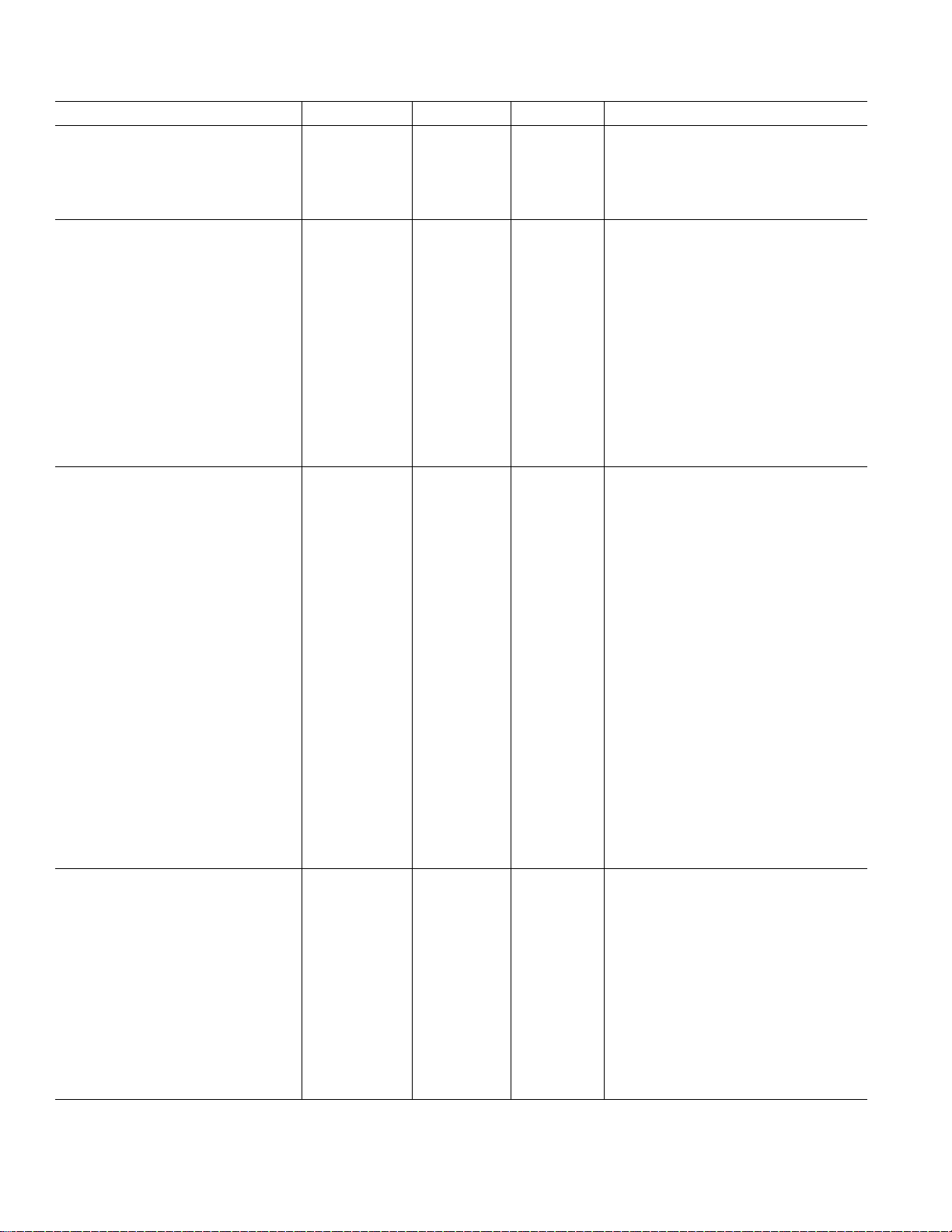
AD7865–SPECIFICATIONS
(VDD = +5 V ⴞ 5%, AGND = DGND = 0 V, V
cations T
MIN
to T
unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
= Internal. Clock = Internal; all specifi-
REF
Parameter A, Y Versions1B Version Units Test Conditions/Comments
SAMPLE AND HOLD
–3 dB Full Power Bandwidth 3 3 MHz typ
Aperture Delay 20 20 ns max
Aperture Jitter 50 50 ps typ
Aperture Delay Matching 4 4 ns max
DYNAMIC PERFORMANCE
2
Signal to (Noise + Distortion) Ratio
3
fIN = 100 kHz, fS = 350 kSPS
@ +25°C
AD7865-1, AD7865-3 78 78 dB min Typically 80 dB
AD7865-2 77 77 dB min Typically 78 dB
T
to T
MIN
MAX
AD7865-1, AD7865-3 77 77 dB min
AD7865-2 76 76 dB min
Total Harmonic Distortion
Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise
Intermodulation Distortion
3, 4
3
–86 –86 dB max
3, 4
–86 –86 dB max
fa = 49 kHz, fb = 50 kHz
2nd Order Terms –95 –95 dB typ
3rd Order Terms –95 –95 dB typ
Channel-to-Channel Isolation
3, 5
–88 –88 dB max fIN = 50 kHz Sine Wave
DC ACCURACY Any Channel
Resolution 14 14 Bits
Relative Accuracy (INL)
Differential Nonlinearity (DNL)
AD7865-1
Positive Gain Error
Positive Gain Error Match
Negative Gain Error
Negative Gain Error Match
3
3
3
3
3
3
±2 ±1.5 LSB max Typically 0.6 LSBs
±1 ±1 LSB max No Missing Codes Guaranteed
±10 ±8 LSB max Typically ±2 LSBs
8 8 LSB max Typically 2 LSBs
±10 ±8 LSB max Typically ±2 LSBs
8 8 LSB max Typically 2 LSBs
Bipolar Zero Error ±12 ±10 LSB max Typically ±2 LSBs
Bipolar Zero Error Match 6 6 LSB max Typically 1.5 LSBs
AD7865-2
Positive Gain Error
Positive Gain Error Match
Unipolar Offset Error
Unipolar Offset Error Match
AD7865-3
Positive Gain Error
Positive Gain Error Match
Negative Gain Error
Negative Gain Error Match
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
3
±16 ±16 LSB max Typically ±2 LSBs
8 8 LSB max Typically 2 LSBs
±10 ±10 LSB max Typically ±2 LSBs
10 10 LSB max Typically 2 LSBs
±16 ±14 LSB max Typically ±6 LSBs
8 8 LSB max Typically 2 LSBs
±16 ±14 LSB max Typically ±6 LSBs
8 8 LSB max Typically 2 LSBs
Bipolar Zero Error ±14 ±12 LSB max Typically ±5 LSBs
Bipolar Zero Error Match 8 6 LSB max Typically 2 LSBs
ANALOG INPUTS
AD7865-1
Input Voltage Range ±5,␣ ±10␣ ±5,␣ ±10␣ Volts
Input Current 1, 1 1, 1 mA max V
= –5 V and –10 V Respectively,
IN
Typically 0.7 mA
AD7865-2
Input Voltage Range 0 V to +2.5 V, 0 V to +2.5 V,
0 V to +5 V 0 V to +5 V Volts
Input Current 10 10 µA max V
1 1 mA max V
= 2.5 V, 0 V to 2.5 V Range, Typ 1 µA
IN
= 5 V, 0 V to 5 V Range, Typ 0.7 mA
IN
AD7865-3
Input Voltage Range ±2.5 ±2.5␣ Volts
Input Current 1 1 mA max VIN = –2.5 V, Typically 0.7 mA
–2–
REV. A
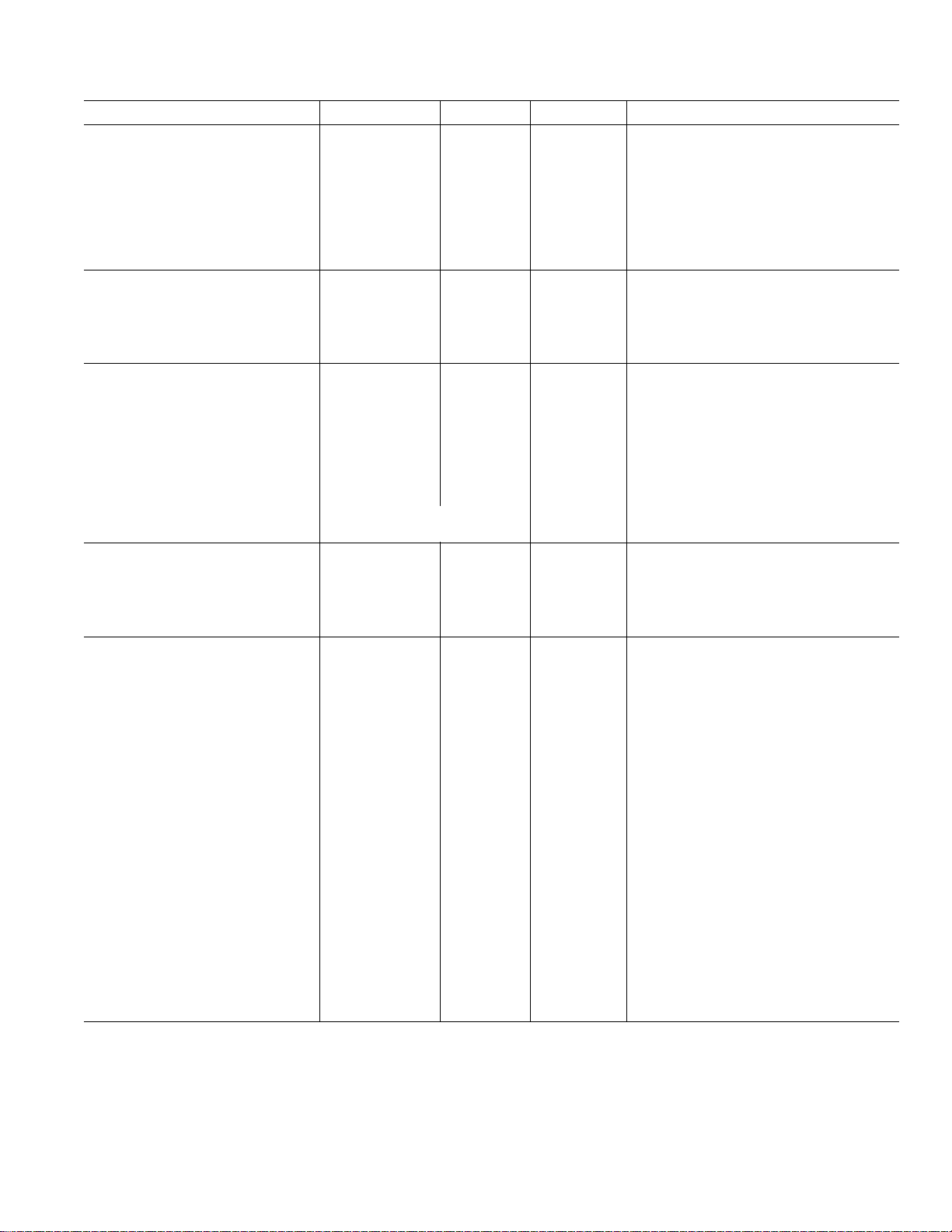
Parameter A, Y Versions1B Version Units Test Conditions/Comments
REFERENCE INPUT/OUTPUT
V
IN Input Voltage Range 2.375/2.625 2.375/2.625 V
REF
V
IN Input Capacitance
REF
V
OUT Output Voltage 2.5 2.5 V␣ nom
REF
V
OUT Error @ +25°C ±10 ±10 mV max
REF
V
OUT Error T
REF
V
OUT Temperature Coefficient 25 25 ppm/°C typ
REF
V
OUT Output Impedance 6 6 kΩ typ See Reference Section
REF
MIN
to T
6
MAX
10 10 pF max
±20 ±20 mV max
MIN/VMAX
2.5 V ± 5%
LOGIC INPUTS
Input High Voltage, V
Input Low Voltage, V
Input Current, I
Input Capacitance, C
INL
IN
IN
INH
6
2.4 2.4 V min V
0.8 0.8 V max V
±10 ±10 µA max
10 10 pF max
= 5 V ± 5%
DD
= 5 V ± 5%
DD
LOGIC OUTPUTS
Output High Voltage, V
Output Low Voltage, V
OL
OH
4.0 4.0 V min I
0.4 0.4 V max I
SOURCE
= 1.6 mA
SINK
= 400 µA
DB13–DB0
High Impedance
Leakage Current ±10 ±10 µA max
Capacitance
6
10 10 pF max
Output Coding
AD7865-1, AD7865-3 Twos Complement
AD7865-2 Straight (Natural) Binary
CONVERSION RATE
Conversion Time 2.4 2.4 µs max For Single Channel
Track/Hold Acquisition Time
2, 3
0.35 0.35 µs max
Throughput Time 350 350 kSPS max For Single Channel
100 100 kSPS max For All Four Channels
POWER REQUIREMENTS
V
DD
I
DD
+5 +5 V nom ±5% for Specified Performance
AD7865-1 Typically 23 mA, Logic Inputs = 0 V or V
Normal Mode 32 32 mA max
Standby Mode 20 20 µA max
AD7865-2 Typically 20 mA, Logic Inputs = 0 V or V
Normal Mode 30 30 mA max
Standby Mode 20 20 µA max
AD7865-3 Typically 23 mA, Logic Inputs = 0 V or V
Normal Mode 32 32 mA max
Standby Mode 20 20 µA max
Power Dissipation
AD7865-1
Normal Mode 160 160 mW max Typically 115␣ mW. V
= +5 V
DD
Standby Mode 100 100 µW max Typically 15␣ µW
AD7865-2
Normal Mode 150 150 mW max Typically 100␣ mW. V
= +5 V
DD
Standby Mode 100 100 µW max Typically 15␣ µW
AD7865-3
Normal Mode 160 160 mW max Typically 115␣ mW. V
= +5 V
DD
Standby Mode 100 100 µW max Typically 15␣ µW
NOTES
1
Temperature ranges are as follows : A, B Versions: –40°C to +85°C, Y Version: –40°C to +105°C.
2
Performance measured through full channel (SHA and ADC).
3
See Terminology.
4
Total Harmonic Distortion and Peak Harmonic or Spurious Noise are specified at –83 dBs for the AD7865-2.
5
Measured between any two channels with the other two channels grounded.
6
Sample tested @ +25°C to ensure compliance.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
AD7865
DD
DD
DD
REV. A
–3–
AD7865
(VDD = +5 V ⴞ 5%, AGND = DGND = 0 V, V
1, 2
T
to T
TIMING CHARACTERISTICS
MIN
unless otherwise noted.)
MAX
Parameter A, B, Y Versions Units Test Conditions/Comments
t
CONV
2.4 µs max Conversion Time, Internal Clock
3.2 µs max Conversion Time, External Clock (5 MHz)
t
ACQ
t
BUSY
t
WAKE-UP
t
1
t
2
—External V
REF
3
0.35 µs max Acquisition Time
No. of Channels Selected Number of Channels Multiplied by t
× (t
) µs max
CONV
1 µs max STBY Rising Edge to CONVST Rising Edge
35 ns min CONVST Pulsewidth
70 ns min CONVST Rising Edge to BUSY Rising Edge
Read Operation
t
3
t
4
t
5
4
t
6
5
t
7
0 ns min CS to RD Setup Time
0 ns min CS to RD Hold Time
35 ns min Read Pulsewidth
35 ns max Data Access Time After Falling Edge of RD, V
40 ns max Data Access Time After Falling Edge of RD, V
5 ns min Bus Relinquish Time After Rising Edge of RD
30 ns max
t
8
t
9
15 ns min Time Between Consecutive Reads
120 ns min EOC Pulsewidth
180 ns max
t
10
t
11
t
12
70 ns max RD Rising Edge to FRSTDATA Edge (Rising or Falling)
15 ns max EOC Falling Edge to FRSTDATA Falling Delay
0 ns min EOC to RD Delay
Write Operation
t
13
t
14
t
15
t
16
t
17
20 ns min WR Pulsewidth
0 ns min CS to WR Setup Time
0 ns min WR to CS Hold Time
5 ns min Input Data Setup Time of Rising Edge of WR
5 ns min Input Data Hold Time
External Clock
t
18
NOTES
1
Sample tested at +25°C to ensure compliance. All input signals are measured with tr = tf = 1 ns (10% to 90% of +5 V) and timed from a voltage level of +1.6␣ V.
2
See Figures 6, 7 and 8.
3
Refer to the Standby Mode Operation section. The MAX specification of 1 µs is valid when using a 0.1 µF decoupling capacitor on the V
4
Measured with the load circuit of Figure 1 and defined as the time required for an output to cross 0.8␣ V or 2.4 V.
5
These times are derived from the measured time taken by the data outputs to change 0.5␣ V when loaded with the circuit of Figure 1. The measured number is then
extrapolated back to remove the effects of charging or discharging the 50 pF capacitor. This means that the times quoted in the timing characteristics are the true bus
relinquish times of the part and as such are independent of external bus loading capacitances.
Specifications subject to change without notice.
200 ns min CONVST Falling Edge to CLK Rising Edge
= Internal, Clock = Internal; all specifications
REF
CONV
DRIVE
DRIVE
pin.
REF
= 5 V
= 3 V
1.6mA
TO OUTPUT
PIN
50pF
400mA
+1.6V
Figure 1. Load Circuit for Access Time and Bus Relinquish Time
–4– REV. A
AD7865
WARNING!
ESD SENSITIVE DEVICE
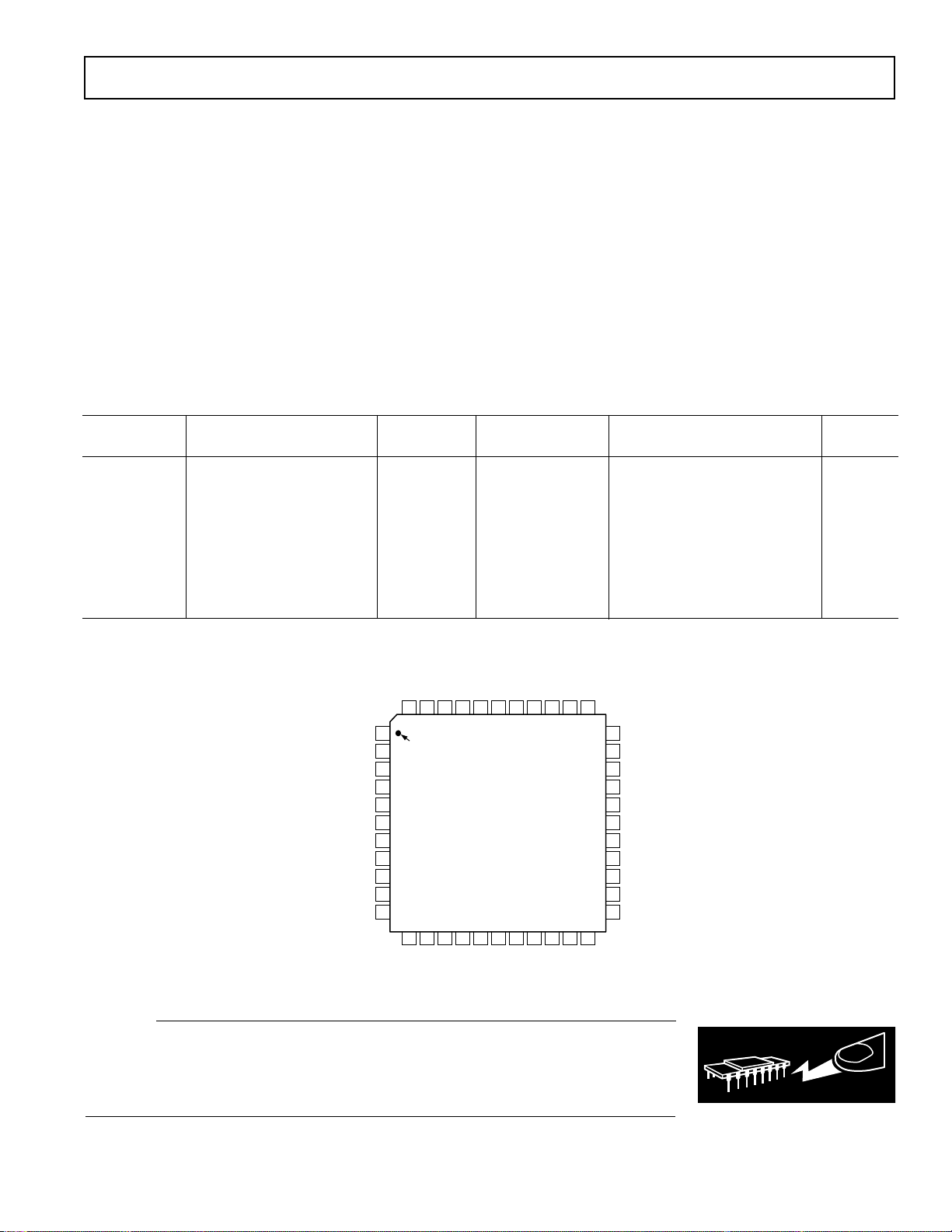
12 13 14 15 16 17 18 192021 22
3
4
5
6
7
1
2
10
11
8
9
40 39 3841
42
4344 36 35 3437
PIN 1
IDENTIFIER
TOP VIEW
(Not to Scale)
29
30
31
32
27
28
25
26
23
24
33
DB7
DB8
DB0
DB1
DB2
DB3
DB4
DB5
DGND
V
DRIVE
DV
DD
DB6
EOC
DB9
DB10
DB12
DB13
AGND
AGND
AGND
V
IN4B
V
IN4A
V
IN3B
V
IN3A
V
IN2B
BUSY
FRSTDATA
CONVST
CS
RD
WR
CLK IN/SL1
INT/EXT CLK/SL2
SL3
SL4
H/S SEL
AV
DD
V
REF
AGND
V
I
N2A
V
IN1B
V
I
N1A
STBY
AD7865
DB11
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS*
(T
= +25°C unless otherwise noted)
A
VDD to AGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–0.3␣ V to +7␣ V
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .–0.3␣ V to +7␣ V
V
DD
to DGND . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . VDD + 0.3 V
V
DRIVE
Analog Input Voltage to AGND
AD7865-1 (±10 V Input Range) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±18 V
AD7865-1 (±5 V Input Range) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . ±9 V
AD7865-2 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –1 V to +18 V
AD7865-3 . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –4 V to +18 V
Reference Input Voltage to AGND . . . . –0.3 V to V
Digital Input Voltage to DGND . . . . . . –0.3 V to V
Digital Output Voltage to DGND . . . . . –0.3 V to V
+ 0.3␣ V
DD
+ 0.3 V
DD
+ 0.3 V
DD
Operating Temperature Range
Commercial (A, B Versions) . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +85°C
Automotive (Y Version) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . –40°C to +105°C
Storage Temperature Range . . . . . . . . . . . . –65°C to +150°C
Junction Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .+150°C
PQFP Package, Power Dissipation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 450 mW
Thermal Impedance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95°C/W
θ
JA
Lead Temperature, Soldering
Vapor Phase (60 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +215°C
Infrared (15 sec) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . +220°C
*Stresses above those listed under Absolute Maximum Ratings may cause perma-
nent damage to the device. This is a stress rating only; functional operation of the
device at these or any other conditions above those listed in the operational
sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to absolute maximum rating
conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability.
ORDERING GUIDE
Input Relative Temperature Package Package
Model Ranges Accuracy Ranges Description Option
AD7865AS-1 ±5 V, ±10 V ±2 LSB –40°C to +85°C Plastic Lead Quad Flatpack S-44
AD7865BS-1 ±5 V, ±10 V ±1.5 LSB –40°C to +85°C Plastic Lead Quad Flatpack S-44
AD7865YS-1 ±5 V, ±10 V ±2 LSB –40°C to +105°C Plastic Lead Quad Flatpack S-44
AD7865AS-2 0 V to +2.5 V, 0 V to +5 V ±2 LSB –40°C to +85°C Plastic Lead Quad Flatpack S-44
AD7865BS-2 0 V to +2.5 V, 0 V to +5 V ±1.5 LSB –40°C to +85°C Plastic Lead Quad Flatpack S-44
AD7865YS-2 0 V to +2.5 V, 0 V to +5 V ±2 LSB –40°C to +105°C Plastic Lead Quad Flatpack S-44
AD7865AS-3 ±2.5 V ±2 LSB –40°C to +85°C Plastic Lead Quad Flatpack S-44
AD7865BS-3 ±2.5 V ±1.5 LSB –40°C to +85°C Plastic Lead Quad Flatpack S-44
AD7865YS-3 ±2.5 V ±2 LSB –40°C to +105°C Plastic Lead Quad Flatpack S-44
PIN CONFIGURATION
CAUTION
ESD (electrostatic discharge) sensitive device. Electrostatic charges as high as 4000 V readily
accumulate on the human body and test equipment and can discharge without detection.
Although the AD7865 features proprietary ESD protection circuitry, permanent damage may
occur on devices subjected to high energy electrostatic discharges. Therefore, proper ESD
precautions are recommended to avoid performance degradation or loss of functionality.
–5–REV. A

AD7865
PIN FUNCTION DESCRIPTIONS
Pin Mnemonic Description
1 BUSY Busy Output. The busy output is triggered high by the rising edge of CONVST and remains
high until conversion is completed on all selected channels.
2 FRSTDATA First Data Output. FRSTDATA is a logic output which, when high, indicates that the Output
Data Register Pointer is addressing Register 1—See Accessing the Output Data Registers.
3 CONVST Convert Start Input. Logic Input. A low-to-high transition on this input puts all track/holds
into their hold mode and starts conversion on the selected channels. In addition, the state of
the Channel Sequence Selection is also latched on the rising edge of CONVST.
4 CS Chip Select Input. Active low logic input. The device is selected when this input is active.
5 RD Read Input. Active low logic input which is used in conjunction with CS low to enable the
data outputs. Ensure the WR pin is at logic high while performing a read operation.
6 WR Write Input. A rising edge on the WR input, with CS low and RD high, latches the logic state
on DB0 to DB3 into the channel select register.
7 CLK IN/SL1 Conversion Clock Input/Hardware Channel Select. The function of this pin depends upon the
H/S SEL input. When the H/S SEL input is high (choosing software control of the channel
selection sequence), this pin assumes its CLK IN function. CLK IN is an externally applied
clock (that is only necessary when INT/EXT CLK is high) this allows the user to control the
conversion rate of the AD7865. Each conversion needs 16 clock cycles in order for the conver-
sion to be completed. The clock should have a duty cycle that is no greater than 60/40. See
Using an External Clock.
When the H/S SEL input is low (choosing hardware control of the channel conversion se-
quence), this pin assumes its Hardware Channel Select function. The SL1 input determines
whether Channel 1 is included in the channel conversion sequence. The selection is latched
on the rising edge of CONVST. See Selecting a Conversion Sequence.
8 INT/EXT CLK/SL2 Internal/External Clock/Hardware Channel Select. The function of this pin depends upon the
H/S SEL input. When the H/S SEL input is high (choosing software control of the channel
selection sequence), this pin assumes its INT/EXT CLK function. When INT/EXT CLK is at
a Logic 0, the AD7865 uses its internally generated master clock. When INT/EXT CLK is at
Logic 1, the master clock is generated externally to the device and applied to CLK IN.
When the H/S SEL input is low (choosing hardware control of the channel conversion se-
quence), this pin assumes its Hardware Channel Select function. The SL2 input determines
whether Channel 2 is included in the channel conversion sequence. The selection is latched
on the rising edge of CONVST. When H/S is at Logic 1 these pins have no function and can
be tied to Logic 1 or Logic 0. See Selecting a Conversion Sequence.
9–10 SL3–SL4 Hardware Channel Select. When the H/S SEL input is at Logic 1, the SL3 input determines
whether Channel 3 is included in the channel conversion sequence while SL4 determines
whether Channel 4 is included in the channel conversion sequence. When the pin is at Logic
1, the channel is included in the conversion sequence. When the pin is at Logic 0, the channel
is excluded from the conversion sequence. The selection is latched on the rising edge of
CONVST. See Selecting a Conversion Sequence.
11 H/S SEL Hardware/Software Select Input. When this pin is at a Logic 0, the AD7865 conversion se-
quence selection is controlled via the SL1–SL4 input pins and runs off an internal clock.
When this pin is at Logic 1, the conversion sequence is controlled via the channel select regis-
ter and allows the ADC to run with an internal or external clock. See Selecting a Conversion
Sequence.
12 AGND Analog Ground. General Analog Ground. This AGND␣ pin should be connected to the system’s
AGND
13–16 V
IN4x
, V
IN3x
Analog Inputs. See Analog Input section.
17 AGND Analog Ground. Analog Ground reference for the attenuator circuitry. This AGND␣ pin
should be connected to the system’s AGND
18–21 V
IN2x
, V
IN1x
Analog Inputs. See Analog Input section.
22 STBY Standby Mode Input. This pin is used to put the device into the power save or standby mode.
The STBY input is high for normal operation and low for standby operation.
23 AGND Analog Ground. General Analog Ground. This AGND pin should be connected to the
system’s AGND plane.
plane.
plane.
–6– REV. A
 Loading...
Loading...