Page 1

AMD Geode™ LX Processor
DDR2 BIOS Porting Guide
1.0 Scope
The AMD Geode™ LX processor has an integrated DDR
memory controller. Due to the concerns over the availability
and increasing cost of DDR, AMD has developed a method
for operating DDR2 memory with the processor’s memory
controller. This application note details the software
changes necessary to enable this technology.
Note: The solution described in this document does not
conform to the JEDEC DDR2 Specification. This
solution may not work with all DDR2 memory.
Note: This is revision B of this document. The change
from revision A (also dated March 2009) is “AMD
Confidential” was removed.
2.0 Description
Initializing DDR2 SDRAM requires writing to additional
mode registers. In addition to the Mode Register (MR) and
Extended Mode Register (EMR), DDR2 defines two new
Extended Mode Registers, EMR(2) and EMR(3). The EMR
is renamed as EMR(1). Furthermore, the MR and EMR
definitions are not an exact match between DDR and
DDR2. Table 2-1 shows a comparison of the typical initialization steps for DDR vs. DDR2.
Addressing MR vs. EMR(1), EMR(2) or EMR(3) is determined by the states of BA[2:0] while the LOAD MODE command is presented on the control signals. The data written
to the registers is the pattern presented on A[15:0] when
the command is initiated. (Note, however, that A[15:13]=0,
and BA[2]=0 in all cases.)
Software on the LX processor issues LOAD MODE commands by writing the MC_CF07_DATA register. During the
operation, the memory controller (MC) uses various bits
and fields in the MC_CF07_DATA and MC_CF8F_DATA
registers. With the available settings, the LX processor is
not capable of generating the necessary signal patterns for
all the required LOAD MODE commands.
Table 2-1. Initialization Steps
DDR DDR2
Wait a minimum of 200µs
after clocks and power are
stable, then assert CKE.
Wait a minimum of 400ns,
then issue a PRECHARGE ALL command.
Issue a LOAD MODE
command to EMR to
enable the DLL.
Issue LOAD MODE command to MR with DLL
reset.
Wait at least 200 clock
cycles. Issue a PRECHARGE ALL command.
Issue two REFRESH
commands.
Issue LOAD MODE to MR
without DLL reset.
SDRAM initialization is
complete.
Wait a minimum of 200µs
after clocks and power are
stable, then assert CKE.
Wait a minimum of 400ns,
then issue a PRECHARGE ALL command.
Issue a LOAD MODE
command to EMR(2)
Issue a LOAD MODE
command to EMR(3).
Issue a LOAD MODE
command to EMR(1) to
enable the DLL.
Issue LOAD MODE command to MR with DLL
reset.
Wait at least 200 clock
cycles. Issue a PRECHARGE ALL command.
Issue two REFRESH
commands.
Issue LOAD MODE to MR
without DLL reset.
Issue LOAD MODE to
EMR(1) with OCD default.
Issue LOAD MODE to
EMR(1) with OCD exit.
SDRAM initialization is
complete.
46959A - March 2009 1
Page 2
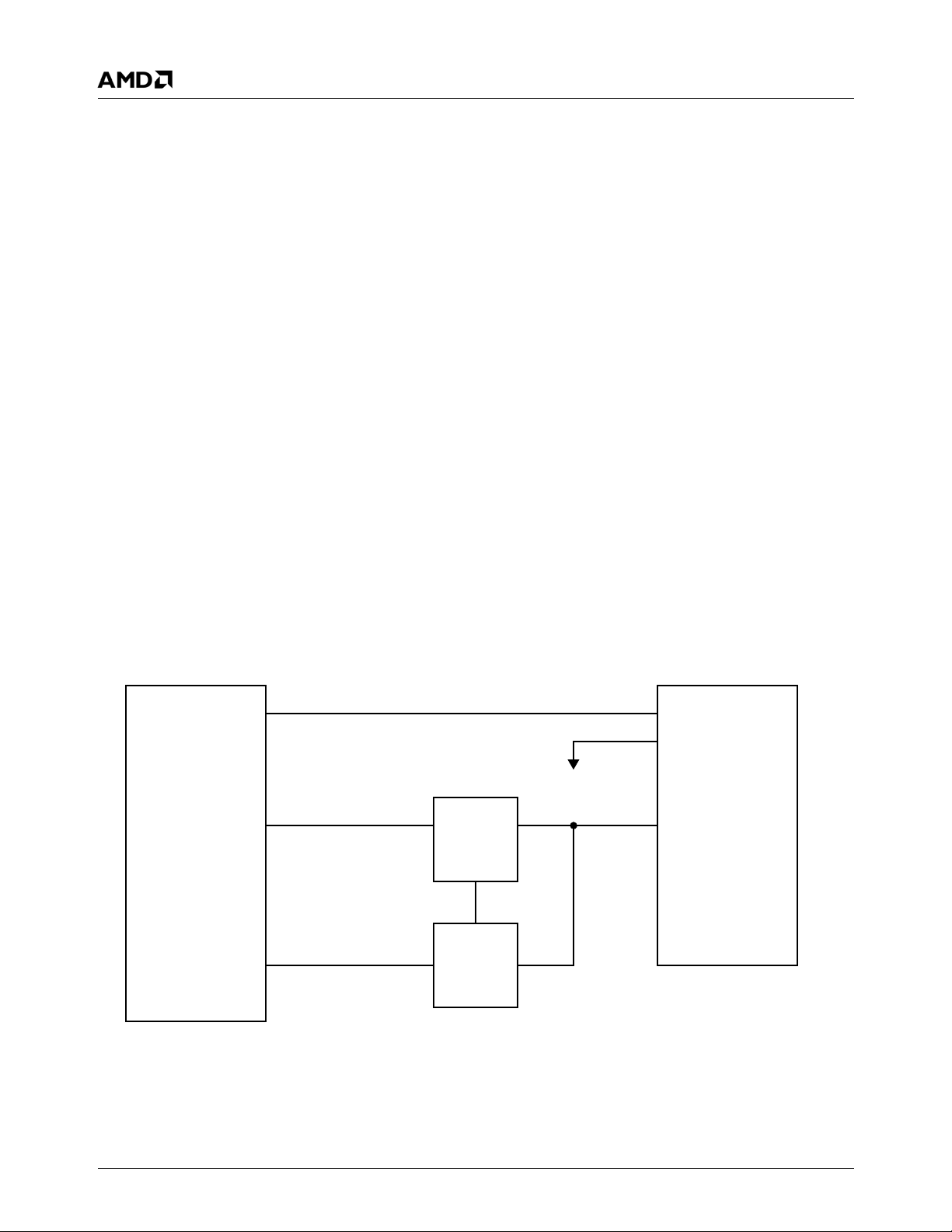
3.0 Solution
The method for initializing DDR2 memory on the processor
is to insert a CPLD and quick switches in the address and
BA signals. Figure 3-1 shows a block diagram of this
design. During initialization, the Enable signal opens
(default) the switches. BIOS tells the CPLD what pattern to
assert on the BA[n] and A[n] signals. Upon completion,
BIOS tells the CPLD to close the switches, giving control
over BA[n] and A[n] to the processor. Additional physical
and electrical details of the design are beyond the scope of
this document.
3.1 Hardware
This section explains the details of the initialization. First it’s
important to delineate two unique versions of this hardware
technology.
3.1.1 On-DIMM Design
This hardware form-factor has a DDR pin assignment (only
SO-DIMM as of this writing), but contains DDR2 SDRAM
modules, and the CPLD. This type of design will be attractive for customers wanting to upgrade existing systems.
The only board change required is a lower memory voltage.
Application Note
46959A - March 2009
Because the CPLD is contained on the DIMM assembly,
the only bus available for communication is I2C. The
CPLD’s I2C address is A0/A1 (i.e., the same as DIMM0).
The CPLD also contains the SPD information.
Also note that the CPLD uses CKE as its RESET# signal.
As a result, the list of BIOS changes may require moving
the assertion of CKE (e.g., if the SPD is accessed prior to
CKE).
3.1.2 On-board Design
This type of system will have the CPLD soldered onto the
motherboard, and will be able to use certain off-the-shelf
(OTS) DDR2 DIMMs. In this case, the CPLD does not contain SPD information.
Because the communication is not limited to I2C, using I/O
to send data to the CPLD simplifies the CPLD design and
speeds up initialization.
The I/O addresses selected for the AMD Geode™ LX Pro-
cessor Refresh Reference Design Kit (RDK) board are
AC10h and AC11h. This requires a modification to the Virtual PCI portion of the BIOS to identify the I/O range to an
operating system. As of this writing, the CPLD claims a
range of 8 bytes (i.e., AC10h-AC17h).
AMD Geode™
LX Processor
/
CS5536
A[13]
A[15:14],
BA[2]
A[12:0], BA[1:0]
Quick
Switches
A[12:0],
Enable
I2C
CPLD
BA[1:0]
Figure 3-1. AMD Geode™ LX Processor DDR2 Block Diagram
DDR2
SDRAM
2 AMD Geode™ LX Processor DDR2 BIOS Porting Guide
Page 3
Application Note
46959A - March 2009
3.2 CPLD Registers
The CPLD contains two registers that indicate how it
should assert the BA[1:0], A[12:0] signals and switch
enable signals.
• If accessing the registers via I2C, the register addresses
are 80h and 81h.
• If accessing with I/O, the addresses are AC10h and
AC11h.
The two registers are defined in Table 3-1 and 3-2. Instructing the CPLD to set or clear a signal causes the behavior to
occur immediately on its outputs.
Table 3-1. REG_A Definition
Bit Name Description
7 A[7] Address signal 7. If SW_EN# is high, setting this bit causes the CPLD to assert the A[7] signal.
This behavior is consistent for all the A[n] and BA[n] fields.
6 A[6] Address signal 6
5 A[5] Address signal 5
4 A[4] Address signal 4
3 A[3] Address signal 3
2 A[2] Address signal 2
1 A[1] Address signal 1
0 A[0] Address signal 0
Prior to executing a LOAD MODE command, the BIOS sets
the CPLD registers to the desired pattern. The DRAM registers are programmed with the A[n] signals. The register
being initialized is determined by the pattern on BA[1:0]
(MR=00b, EMR(1)=01b, EMR(2)=10b and EMR(3)=11b).
Then the BIOS generates the LOAD MODE command by
setting, and then clearing, the PROG_DRAM bit in the
MC_CF07_DATA register. AMD also recommends setting
the MSR_BA field (same register) to the desired BA[1:0]
levels (same procedure as initializing DDR).
Table 3-2. REG_B Definition
Bit Name Description
7 SW_EN# Switch enable. When high, the CPLD asserts all of its A[n] and BA[n] signals, according to the
current settings in the internal registers. When low, the CPLD closes the switches and tri-states
its A[n] and BA[n] signals.
6 BA[1] Bank Address 1
5 BA[0] Bank Address 0
4 A[12] Address signal 12
3 A[11] Address signal 11
2 A[10] Address signal 10
1 A[9] Address signal 9
0 A[8] Address signal 8
AMD Geode™ LX Processor DDR2 BIOS Porting Guide 3
Page 4

3.3 Initialization Steps
Some of the following steps may be optional, depending on
the specific implementation. The reader is encouraged to
have a copy of the JEDEC standard for DDR2 SDRAM,
including the SPD byte definitions. The AMD Geode™ LX
Processors Data Book, order# 33234, is also recommended. The chapters for the memory controller and
GeodeLink™ Control Processor (GLCP) register definitions
will be useful.
3.3.1 Memory Controller Initialization
1) Enable the CKE signal earlier, if necessary. With the
On-DIMM solution, this allows the CPLD to come out
of reset. The CPLD cannot respond to any SPD reads
while in the reset state.
2) Identify whether the installed DIMM(s) are DDR2. The
information in SPD[2] (i.e., SPD byte number 2) indicates the fundamental memory type. If this value
equals 8, then the memory type is DDR2. A mixture of
memory types is not supported and the BIOS should
not allow this configuration.
3) Program the memory speed by setting the appropriate
dividers in the GLCP_SYS_RSTPLL register. This
may be decided by retrieving data from NVRAM, from
jumpers, or by calculating the best speed dynamically.
If dynamic, the BIOS should set the memory speed
slow enough to support the installed memory. The
memory’s minimum cycle time is indicated in SPD[9],
which has additional bits defined beyond the DDR
specification. If more than one DIMM is installed, the
slower of the two memories should be used in calculating the memory frequency.
Note that if setting the speed dynamically, certain configurations should be avoided. These are unrelated to
the memory technology installed. As is the case with
DDR, the core frequency must never be lower than the
GLIU frequency. The BIOS should try to avoid setting
an unsupported GLIU frequency.
4) Determine the physical configuration of the installed
DIMM(s). This procedure populates the fields in
b[63:32] of the MSR_CF07_DATA register.
SPD[5] indicates the number of ranks on the DIMM
assembly. Note that DDR2 defines this SPD byte differently than the DDR spec. The LX processor’s memory controller only supports DIMMs with 1 or 2 ranks
(indicated by 0 or 1). This setting determines the value
in the Dn_MB fields (i.e., D0_MB and D1_MB fields).
SPD[17] indicates the number of component banks.
The LX processor’s memory controller only supports 2
or 4 banks, but DDR2 devices may support 4 or 8. The
Dn_CB fields should be programmed with a 1 to indicate 4 banks. The BIOS should not allow configurations indicating 8 banks.
Application Note
46959A - March 2009
Calculate the size of each DIMM. SPD[31] indicates
the density of each rank and it is defined differently
than in the DDR specification. Multiply this by the number of ranks from SPD[5] to find the DIMM size. This
value is used to program the Dn_SZ fields.
Calculate the page size (i.e. the size of each row) for
each DIMM. The page size is defined as:
DIMM width * 2
(# of columns)
SPD[4] indicates the number of column addresses.
The width should always be 8 bytes, but may also be
read from SPD[6]. The LX processor’s memory controller only supports memory configurations that are
64 bits wide. The size is used to program the Dn_PSZ
fields.
5) Calculate the CAS# Latency (CL) and Write Latency
(WL). The WL is set with the WR2DAT field of the
MC_CF1017_DATA register. This is a change from
DDR to DDR2. With DDR technology WL=1, but for
DDR2 the WL=CL-1.
As of this writing, the memory controller may only
operate at WL=1 (i.e., WR2DAT may only be programmed to equal 1). This condition forces all implementations to use a CAS# Latency of 2.
A typical CAS# Latency algorithm should use the data
in SPD[18], which is a bitmap of supported CL settings
(in units of memory clocks). The bitmap will have up to
3 bits set, representing (from most significant to least)
CL=X, CL=X-1 and CL=X-2, which is different than the
DDR definition. Additionally, SPD[9], SPD[23] and
SPD[25] will have the minimum cycle times at the
highest CAS# Latency setting, the next lower setting,
and second lower setting. Note that all cycle times
have additional bits defined in the DDR2 specification.
Normally, if two DIMMs are present, the algorithm
should set the lowest number that is supported by both
DIMMs at the current operating frequency. The process would be identical to DDR, however, it is simplified for DDR2 memory because of the requirement to
operate at CL=2.
In the event that SPD[18] does not indicate a supported CAS# Latency of 2, the BIOS may still take
some steps to determine if CL=2 is supportable. The
fundamental CAS# access time may be calculated
using the supported CAS# Latencies and their associated cycle times. Multiplying the number of clocks by
the cycle time equals the access time. Use the lowest
result from all the supported CL values. Then divide
this number by 2 to get the lowest cycle time supportable at CL=2. If the cycle time of the memory clock is
greater than or equal to this value, then CL=2 is typi-
4 AMD Geode™ LX Processor DDR2 BIOS Porting Guide
Page 5

Application Note
46959A - March 2009
cally supportable. As an example, consider the following DIMM characteristics:
CAS#
Latency
Min Cycle
Time (ns)
Max Cycle
Time (ns)
CL=5 3.0 8.0
CL=4 3.75 8.0
CL=3 5.0 8.0
This is has a fundamental access time of 15ns, and
therefore at CL=2, the minimum cycle time should be
7.5ns. This DIMM should be function normally at
133MHz, with a CL setting of 2.
6) Program the CAS_LAT field of the MC_CF8F_DATA
register with the CAS# Latency value (i.e., 2). Additional settings are programmed in the same register:
THZ_DLY: This adds 1 clock to the Read-Write turnaround time
TRUNC_DIS: This forces bursts of 4, preventing bursts
of 2 (unsupported in DDR2)
7) Program the memory controller with the appropriate
latencies for the memory. For DDR2, this step is nearly
identical to DDR technology. As a result, this document will not go into many details. The memory controller settings affected are fields in the
MC_CF8F_DATA register, and are determined by SPD
data:
Timing
Field
Parameter SPD Byte
ACT2PRE tRAS 30
PRE2ACT tRP 27
ACT2CMD tRCD 29
ACT2ACT tRRD 28
ACT2ACTREF tRC 41/40**
REF2ACT* tRFC 42/40**
* REF2ACT is in the MC_CF1017_DATA register.
**Contains an extension value, new for DDR2.
8) Program other timing control parameters. In the
MC_CF1017_DATA register:
WR_TO_RD (tWTR) should be set for 2 clocks.
RD_TMG_CTL should be set for 4 half-GLIU clocks
9) Set the drive strength control (EMR_DRV in
MC_CF07_DATA) to Reduced if the DIMM(s) support
it. This feature is indicated in SPD[22], bit 0.
The memory controller is now set up correctly, and is prepared for turning on the memory. Now follow the DDR2
memory initialization steps (as outlined Table 2-1 on page
1).
3.3.2 SDRAM Initialization
1) CKE may have already been asserted, due to the
requirement of the On-DIMM CPLD. If not, assert CKE
by clearing the MASK_CKEn bit(s) in the
MC_CFCLK_DBUG register. CKE needs to be
asserted for at least 400ns before executing step 2.
Also, set REF_STAG in MC_CF07_DATA to 4 clocks.
2) Issue a PRECHARGE ALL command. The memory
controller does not allow software to issue a single
PRECHARGE ALL command. Instead, the command
is inserted before a REFRESH or a LOAD MODE
command. Set the FORCE_PRE bit in the
MC_CFCLK_DBUG register to insert the PRECHARGE ALL.
Additionally, the PRECHARGE ALL command
requires that A[10] be set high. This presents a minor
architectural problem. The BIOS will not have the
opportunity to modify A[10] between the PRECHARGE ALL command and the subsequent LOAD
MODE command. So the CPLD must be prepared for
the LOAD MODE command to EMR(2) (i.e., the A[n]
and BA[n] bits set in its registers) and A[10] also set to
high.
3) Issue a LOAD MODE command to EMR(2). First set
the CPLD’s registers. Typical settings are REG_A=00h
and REG_B=C4h. The setting in REG_B is
SW_EN#=1, BA[1:0]=10b, and A[10]=1. Next, in
MC_CF07_DATA register, set MSR_BA to 10b and
PROG_DRAM to 1. Then clear PROG_DRAM and
FORCE_PRE.
Note that DDR2 defines A[10] of EMR(2) should be
programmed to 0. Setting A[10]=1 for the PRECHARGE ALL step causes a violation of the spec during the LOAD MODE command. However, AMD has
not observed any side effects of programming EMR(2)
with A[10]=1.
4) Issue a LOAD MODE command to EMR(3). Similar to
the previous step, set the CPLD’s registers. Typical
settings are REG_A=00h and REG_B=E0h. The setting in REG_B is SW_EN#=1, BA[1:0]=11b. Next, in
MC_CF07_DATA register, set MSR_BA=11b and
PROG_DRAM=1. Then clear PROG_DRAM.
5) Issue a LOAD MODE command to EMR(1) to enable
the DLL. Program the CPLD with the appropriate information for the EMR(1) definition. Note that in certain
cases, it might be appropriate to leave the DLL disabled to allow the DRAM to run at lower frequencies.
AMD does not recommend omitting this step, however.
DLL Enable is defined in b[0] of the EMR(1) register.
The desired setting goes into REG_A[0]. Also, the setting for the drive strength control goes into REG_A[1].
If previously set up, these two bits may be retrieved
from the MC_CF07_DATA register. All other A[n] bits in
AMD Geode™ LX Processor DDR2 BIOS Porting Guide 5
Page 6

Application Note
46959A - March 2009
the CPLD are typically 0. Set SW_EN# high and
BA[1:0] to 01b.
Next, in MC_CF07_DATA register, set MSR_BA=01b
and PROG_DRAM=1. Then clear PROG_DRAM.
6) Issue a LOAD MODE command to MR to reset the
DLL. Regardless of whether the DLL is running, AMD
does not recommend omitting this step.
Some memory devices require A[8]=1 and all other
A[n]=0 during this step. The JEDEC spec does not
indicate zeroing all other address pins. Therefore, it is
up to the BIOS to decide how to proceed during this
step. The other fields in the MR may be constructed
from existing settings in the MC.
Similar to the other LOAD MODE commands, set
SW_EN#=1 and BA[1:0]=00b. In the memory controller, set MSR_BA=00b and PROG_DRAM=1. Then
clear PROG_DRAM.
7) Wait 200 clock cycles, then issue a PRECHARGE ALL
command. As before, set the CPLD registers so that
A[10] will be high and all other A[n] signals are inconsequential. Keep SW_EN# high. Set the FORCE_PRE
bit in the MC_CFCLK_DBUG register to insert the
command before the subsequent step.
8) Generate two REFRESH commands by twice setting
then clearing the REF_TST bit in the CM_CF07_DATA
register. Clear the FORCE_PRE bit between the two
REFRESH commands to avoid an extra PRECHARGE
ALL command.
9) Issue a LOAD MODE command to MR to bring the
DLL out of reset. In the CPLD, set A[8]=0. Other A[n]
settings may need to be calculated.
– The burst length is in the MC_CF8F_DATA register
as TRUNC_DIS. Of course, 4 is the only common
setting, so this part may be abbreviated.
– The CAS# Latency may also be retrieved from the
MC_CF8F_DATA register. Due to the memory
controller restriction, this may be otherwise hardcoded to 2.
11) Issue a LOAD MODE command to EMR(1) to exit
OCD programming. A[1:0] (driver strength and DLL
enable) are retrieved from MC_CF07_DATA. Set
A[9:7]=000b for OCD default. Set SW_EN#=1 and
BA[1:0]=01b. In MC_CF07_DATA set MSR_BA=01b
and PROG_DRAM=1. Then clear PROG_DRAM.
12) Now the BIOS is finished with the CPLD and should
give control of the A[12:0] and BA[1:0] signals to the
memory controller. Write any value to REG_B with
SW_EN#=0.
13) Program the refresh rate in the REF_INT field of
MC_CF07_DATA. This process is identical to that used
with DDR technology. Each DIMM indicates its supported rate in SPD[12]. The BIOS determines an interval that is sufficiently short for both DIMMs.
Note, however, that the location for this step has
moved for DDR2. The reason is that I2C accesses to
an On-DIMM CPLD are very slow. If REF_INT is programmed earlier, the memory controller generates
REFRESH commands during the initialization
sequence. This disrupts initialization and prevents the
DRAM from operating properly.
There are some additional settings recommended by AMD.
• Typically the GLCP_DELAY_CONTROLS register is set
up very early in POST, and usually with hardcoded
values. AMD recommends an initial setting of
F2F100FF_56960304 in this register.
• If there is no DIMM1, the SDCLK[5,3,1] should be
disabled in the GLCP_DELAY_CONTROLS register. Set
b[55] to do this.
• Program the PMode Sensitivity Counter values in the
MC_CF_PMCTR register. Typical values are PMode0
counter set to 0 for most aggressive, and PMode1
counter set to 200h.
• Program the PMode1 Up Delay field of
MC_CF1017_DATA to 209 clocks.
– The Write Recovery for Autoprecharge field is
calculated using information in SPD[36], which is
new for DDR2.
Set SW_EN#=1 and BA[1:0]=00b. In the memory controller, set MSR_BA=00b and PROG_DRAM=1. Then
clear PROG_DRAM.
10) Issue a LOAD MODE command to EMR(1) with OCD
set to Default. A[1:0] (driver strength and DLL enable)
are retrieved from MC_CF07_DATA. Set A[9:7]=111b
for OCD default. Set SW_EN#=1 and BA[1:0]=01b. In
MC_CF07_DATA set MSR_BA=01b and PROG_DRAM
=1. Then clear PROG_DRAM.
6 AMD Geode™ LX Processor DDR2 BIOS Porting Guide
Page 7

Application Note
46959A - March 2009
3.4 Other Information and Restrictions
The LX processor/DDR2 solution does not do DQS training. The LX processor’s memory controller does not have
the adjustability to make this worthwhile, and the speeds
are slow enough that this is not a problem.
The memory must be organized with 4 component banks.
This means that only 512Mbits, and lower, devices are supported. In addition, the memory controller only supports 1
or 2 ranks. Any other configurations should be avoided.
The DRAM must support a CAS# Latency of 2 clocks. A
DIMM’s SPD may not indicate that this is supported, due to
the higher typical operating frequencies of the memory.
The BIOS may determine that CL=2 is possible by considering the fundamental access time of the memory (i.e.,
cycle time multiplied by the normal CAS# Latency). The
reason for this restriction is that the LX processor’s memory controller must operate with a Write Latency of 1 clock.
DDR2 defines CAS# Latency equal to Write Latency + 1.
Supporting CL=2 at higher frequencies implies that the
memory must be of higher performance. To run the memory at 166MHz, this means that the memory should have
an access time of 12ns. 133MHz requires 15ns.
The typical LX processor/DDR2 implementation will run the
memory at lower frequencies than average. While 166MHz
is within the DDR2 specification, some memory vendors
may recommend operating with the DLL disabled. The customer should investigate this with their memory supplier.
Some DRAM modules may operate at higher frequencies
by raising their supply voltage. The customer should consult the memory manufacturer before taking this approach.
The BIOS may implement an algorithm that accounts for
the higher frequency. AMD has seen only limited success
with this technique.
AMD Geode™ LX Processor DDR2 BIOS Porting Guide 7
Page 8

© 2009 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved.
The contents of this document are provided in connection with Advanced Micro
Devices, Inc. (“AMD”) products. AMD makes no representations or warranties with
respect to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this publication and
reserves the right to make changes to specifications and product descriptions at
any time without notice. No license, whether express, implied, arising by estoppel
or otherwise, to any intellectual property rights is granted by this publication.
Except as set forth in AMD’s Standard Terms and Conditions of Sale, AMD
assumes no liability whatsoever, and disclaims any express or implied warranty,
relating to its products including, but not limited to, the implied warranty of merchantability, fitness for a particular purpose, or infringement of any intellectual
property right.
AMD’s products are not designed, intended, authorized or warranted for use as
components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or in other
applications intended to support or sustain life, or in any other application in which
the failure of AMD’s product could create a situation where personal injury, death,
or severe property or environmental damage may occur. AMD reserves the right to
discontinue or make changes to its products at any time without notice.
www.amd.com
TRADEMARKS
AMD, the AMD Arrow logo, AMD Geode, GeodeLink, and combinations thereof, are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc.
Other product names used in this publication are for identification purposes only and may be trademarks of their respective companies.
One AMD Place • P.O. Box 3453 • Sunnyvale, CA 94088-3453 USA • Tel: 408-749-4000 or 800-538-8450 • TWX: 910-339-9280 • TELEX: 34-6306
 Loading...
Loading...