Page 1

Solid State Graphics (SSG)
API User Manual
Page 2

2
Contents
1 Introduction .......................................................................................................................................... 3
2 Requirements ........................................................................................................................................ 3
3 OpenCL™ Extension Specification ......................................................................................................... 3
3.1 clCreateSsgFileObjectAMD ........................................................................................................... 3
3.2 clGetSsgFileObjectInfoAMD .......................................................................................................... 4
3.3 clRetainSsgFileObjectAMD ............................................................................................................ 4
3.4 clReleaseSsgFileObjectAMD .......................................................................................................... 5
3.5 clEnqueueReadSsgFileAMD .......................................................................................................... 5
3.6 clEnqueueWriteSsgFileAMD ......................................................................................................... 7
4 OpenCL Performance Guidelines and Caveats ..................................................................................... 8
5 AMD Code Sample for OpenCL ........................................................................................................... 10
6 OpenGL® Extension Specification ....................................................................................................... 11
6.1 glCreateFileAMD ......................................................................................................................... 11
6.2 glReleaseFileAMD ....................................................................................................................... 11
6.3 glGetFileParameteri64vAMD ...................................................................................................... 11
6.4 glReadFileAMD ............................................................................................................................ 12
6.5 glWriteFileAMD ........................................................................................................................... 13
7 OpenGL Performance Guidelines and Caveats ................................................................................... 14
8 AMD Code Sample for OpenGL ........................................................................................................... 16
9 DirectX® 11 Extension Specification ................................................................................................... 17
9.1 GetExtensionVersion ................................................................................................................... 18
9.2 CreateFile .................................................................................................................................... 18
9.3 ReleaseFile .................................................................................................................................. 18
9.4 GetFileInfo ................................................................................................................................... 19
9.5 CreateEvent ................................................................................................................................. 19
9.6 DeleteEvent ................................................................................................................................. 20
9.7 WaitEvent .................................................................................................................................... 20
9.8 ReadBufferFromFile .................................................................................................................... 21
9.9 WriteBufferToFile ........................................................................................................................ 22
10 AMD Code Sample for DirectX® ...................................................................................................... 23
Rev. 1.01
Page 3
3
C++
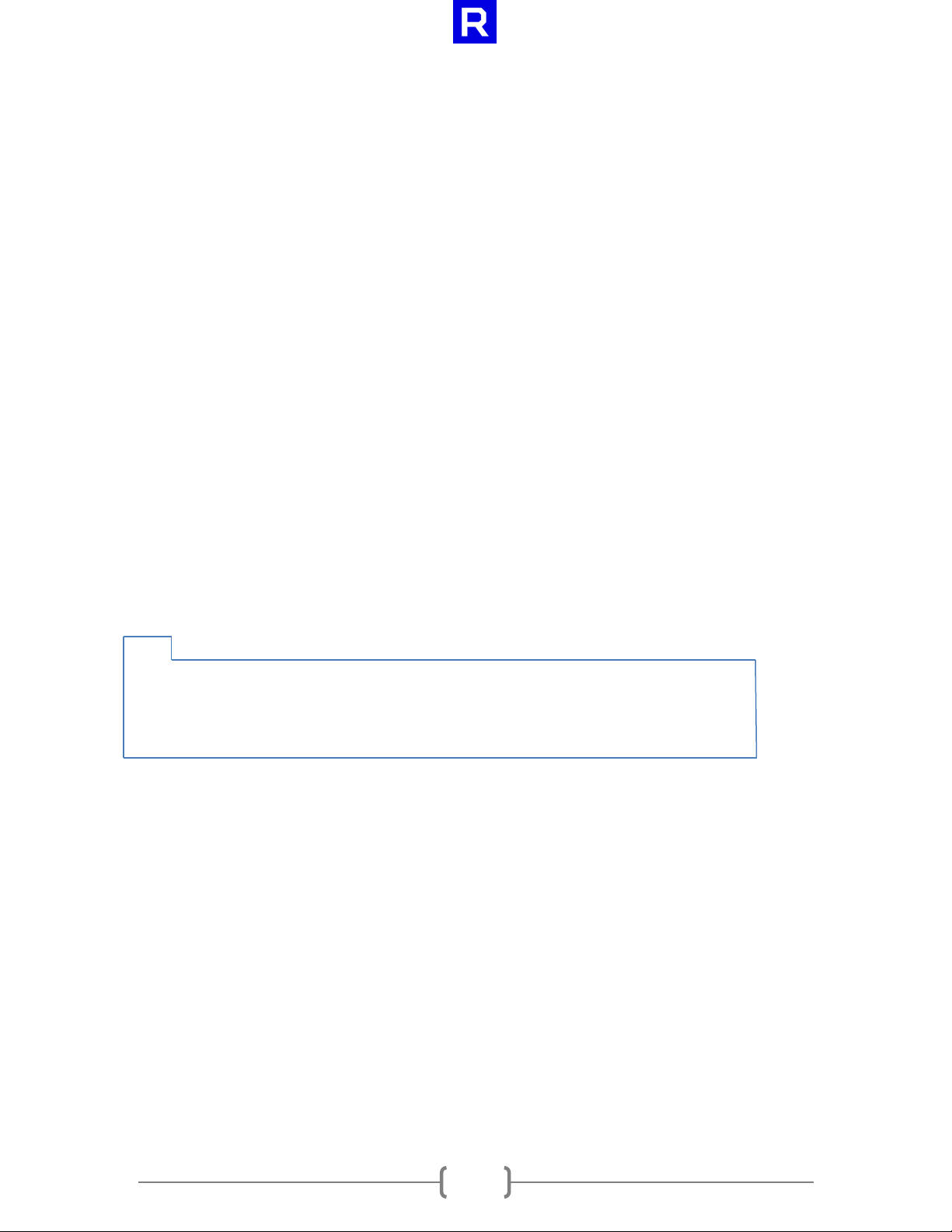
cl_file_amd clCreateSsgFileObjectAMD(cl_context context,
1 Introduction
The Radeon™ Pro SSG software library enables peer-to-peer (P2P) data transfers between GPU and
Radeon on board SSD devices. It allows a methodology to read OS file data from SSDs to OpenCL™,
OpenGL® and DirectX® buffers with very low-latency P2P communication. The development kit version
of this library supports only the Microsoft® Windows® 10 operating system.
2 Requirements
To use the development kit version of the SSG library, the following are required:
1.) A Radeon™ Pro SSG Professional Graphics Card
2.) Microsoft® Windows 10 (64 bit) or newer.
3 OpenCL™ Extension Specification
3.1 clCreateSsgFileObjectAMD
The clCreateSsgFileObjectAMD function creates a CL file object. Doing so over a file employs the same
semantics as when opening the file for reading/writing—that is, read/write privileges are required for
that file.
Context [in]
A CL context with which to associate the file.
Flags [in]
Access-privilege flag for the file. Currently, only CL_FILE_READ_ONLY_AMD and
CL_FILE_WRITE_ONLY_AMD are supported. Read (or write) privileges are required for the file, subject to
the same access rights as when opening any file.
file_name [in]
In Windows: the UTF-16-encoded name of the file to be opened.
In Linux: the UTF-8-encoded name of the file to be opened.
errcode_ret [out]
The return value.
Return Value Description
CL_SUCCESS The function executed successfully.
CL_INVALID_FILE_OBJECT_AMD The file is invalid for OpenCL.
cl_file_flags_amd flags,
const wchar_t* file_name,
cl_int* errcode_ret)
Rev. 1.01
Page 4
4
cl_file_info_amd
Return Type
Info Returned in
param_value
CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD
cl_uint
Alignment restriction for
the file object
CL_FILE_SIZE_AMD
cl_ulong
File size in bytes
C++
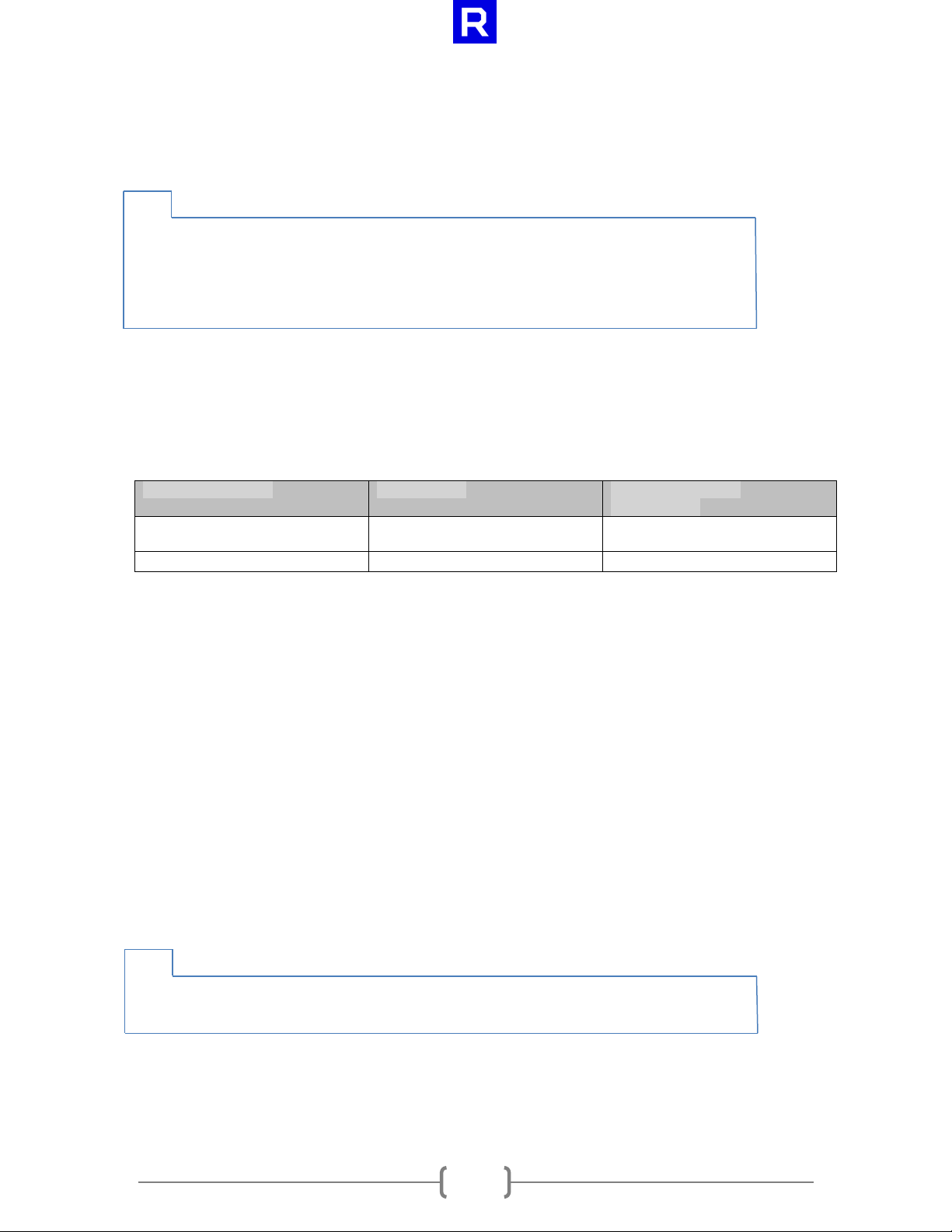
cl_int clGetSsgFileObjectInfoAMD(cl_file_amd file,
C++
cl_int clRetainSsgFileObjectAMD(cl_file_amd file)
3.2 clGetSsgFileObjectInfoAMD
The clGetSsgFileObjectInfoAMD function returns information about a file object.
file [in]
Specifies the file object of query.
param_name [in]
Specifies the information to query. The table below provides a list of supported param_name types and
the information that clGetSsgFileObjectInfoAMD will return in param_value.
cl_file_info_amd param_name,
size_t param_value_size,
void* param_value,
size_t* param_value_size_ret)
param_value_size [in]
Size of memory (in bytes) to which param_value points. It must be greater than or equal to the size of the
return type described in the table above.
param_value [out, optional]
Pointer to the memory region that stores the appropriate result being queried. If param_value is NULL,
the function ignores this pointer.
param_value_size_ret [out]
Returns the actual size in bytes.
Return Value Description
CL_SUCCESS The function executed successfully.
CL_INVALID_FILE_OBJECT_AMD The file is invalid for OpenCL.
3.3 clRetainSsgFileObjectAMD
The clRetainSsgFileObjectAMD function increments the file-object reference count.
file [in]
Specifies the file object to be retained.
Return Value Description
Rev. 1.01
Page 5
5
C++
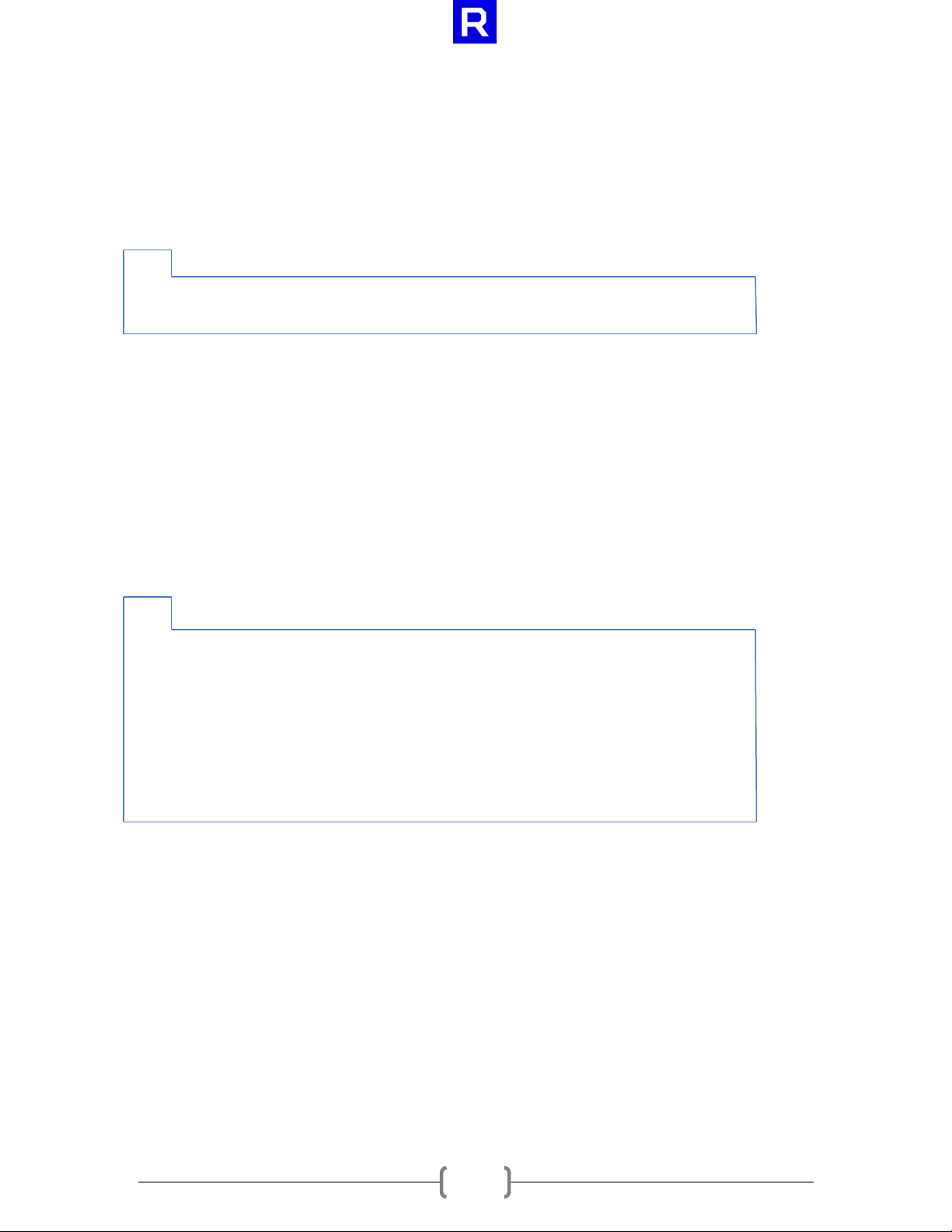
cl_int clReleaseSsgFileObjectAMD(cl_file_amd file)
C++
cl_int clEnqueueReadSsgFileAMD(cl_command_queue command_queue,
CL_SUCCESS The function executed successfully.
CL_INVALID_FILE_OBJECT_AMD The file is invalid for OpenCL.
3.4 clReleaseSsgFileObjectAMD
The clReleaseSsgFileObjectAMD function decrements the file-object reference count.
file [in]
Specifies the file object to be released.
Return Value Description
CL_SUCCESS The function executed successfully.
CL_INVALID_FILE_OBJECT_AMD The file is invalid for OpenCL.
3.5 clEnqueueReadSsgFileAMD
The clEnqueueReadSsgFileAMD function reads from a file object to a CL memory object.
command_queue [in]
Valid host command-queue in which the read command will be queued. Create the buffer and
command_queue using the same OpenCL context.
buffer [in]
A valid buffer object; buffer is the target memory object. Create the buffer using either
CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR, CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR or CL_MEM_USE_PERSISTENT_MEM_AMD.
blocking_read [in]
Indicates whether the read operation is blocking or non-blocking. If blocking_read is CL_TRUE, the
function call won’t return until the operation has completed. If blocking_read is CL_FALSE, the OpenCL
implementation will perform a non-blocking read. Because the read is non-blocking, the function can
return immediately. The event argument causes the function to return an event object, which can be used
to query the read command’s execution status.
cl_mem buffer,
cl_bool blocking_read,
size_t buffer_offset,
size_t size,
cl_file_amd file,
size_t file_offset,
cl_uint num_events_in_wait_list,
const cl_event* event_wait_list,
cl_event* event);
Rev. 1.01
Page 6

6
buffer_offset [in]
Offset (in bytes) in the buffer object to which the function is writing. It must be a multiple of
CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
size [in]
Size (in bytes) of data being read. It must be a multiple of CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD. If the file size isn’t
a multiple of the block size, read the end of the file by aligning the read size with the
next block multiple beyond the file size.
file [in]
File object from which to copy.
file_offset [in]
Offset (in bytes) for copying from the file; file_offset must be a multiple of CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
event_wait_list and num_events_in_wait_list [in, optional]
Specify events that must complete before the clEnqueueReadSsgFileAMD command can execute. If
event_wait_list is NULL, the command will proceed without waiting for events to finish. Also, if
event_wait_list is NULL, num_events_in_wait_list must be 0. Otherwise, the list of events to which
event_wait_list points must be valid and num_events_in_wait_list must be greater than 0. The events
specified in event_wait_list act as synchronization points, and the contexts associated with events in
event_wait_list and in command_queue must be the same. The memory associated with event_wait_list
can be reused or freed-up after the function returns.
event [out, optional]
Returns an event object that identifies the clEnqueueReadSsgFileAMD command and can query the
command status or queue a wait for the command to finish executing. The event argument can be NULL,
in which case the application will be unable to query the command status or queue a wait for the
command to finish. Unless event_wait_list and event are both NULL, event should avoid referring to an
element of the event_wait_list array.
Return Value Description
CL_SUCCESS The function executed successfully.
CL_INVALID_FILE_OBJECT_AMD The file is invalid for OpenCL.
CL_INVALID_COMMAND_QUEUE Command_queue is an invalid host command queue.
CL_INVALID_CONTEXT The contexts associated with command_queue and buffer are
different, or the context associated with command_queue and the
events in event_wait_list are different.
CL_INVALID_MEM_OBJECT The buffer object is invalid.
CL_INVALID_VALUE The region specified by buffer_offset, file_offset or size is out of
bounds or is misaligned with CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
CL_INVALID_EVENT_WAIT_LIST Event_wait_list is NULL and num_events_in_wait_list is greater than 0,
event_wait_list is not NULL and num_events_in_wait_list is 0, or the
event objects in event_wait_list are invalid.
CL_EXEC_STATUS_ERROR_FOR_EVENTS_IN_WAIT_LIST
Read operations are blocking, and the execution status of at least one
event in event_wait_list is a negative integer value.
Rev. 1.01
Page 7
7
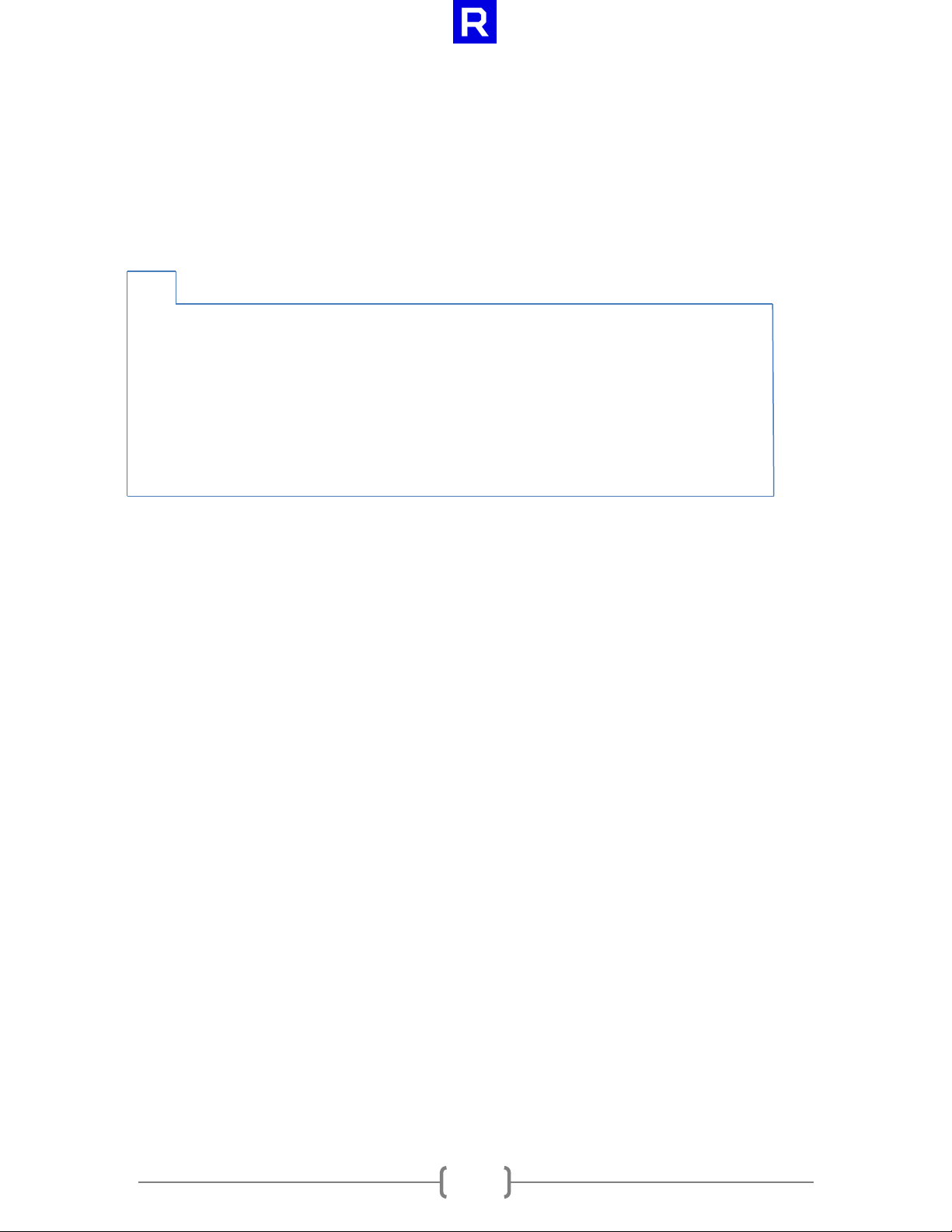
C++
cl_int clEnqueueWriteSsgFileAMD(cl_command_queue command_queue,
CL_MEM_OBJECT_ALLOCATION_FAILURE
Memory failed to allocate for data store associated with buffer.
3.6 clEnqueueWriteSsgFileAMD
The clEnqueueWriteSsgFileAMD function writes directly from a CL memory object to a file object.
command_queue [in]
Valid host command queue in which the write command will be queued. Create the
command_queue and buffer with the same OpenCL context.
buffer [in]
A valid buffer object. Buffer is the copy-source memory object. Create the buffer with either
CL_MEM_ALLOC_HOST_PTR, CL_MEM_USE_HOST_PTR or CL_MEM_USE_PERSISTENT_MEM_AMD.
blocking_write [in]
Indicates whether the write operation is blocking or non-blocking. If blocking_write is CL_TRUE, the
function call will not return until the operation is complete. If blocking_write is CL_FALSE, the OpenCL
implementation will perform a non-blocking write, and can return immediately. The event argument
returns an event object that can query the execution status of the write command.
buffer_offset [in]
Offset (in bytes) in the buffer object being read. It must be a multiple of CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
size [in]
Size (in bytes) of the data being written. It must be a multiple of CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD. If the file
size is not a multiple of the block size, write to the end of the file by aligning the write size with the next
block multiple beyond the file size.
file [in]
File object to which the copy is initiated.
file_offset [in]
Offset (in bytes) for copying to the file. It must be a multiple of CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
event_wait_list and num_events_in_wait_list [in, optional]
Specify events that must complete before clEnqueueWriteSsgFileAMD can execute. If event_wait_list is
NULL, the command will proceed without waiting for events to finish executing. If event_wait_list is NULL,
num_events_in_wait_list must be 0; otherwise, the list of events to which event_wait_list points must be
valid and num_events_in_wait_list must be greater than 0. The events specified in event_wait_list act as
cl_mem buffer,
cl_bool blocking_write,
size_t buffer_offset,
size_t size,
cl_file_amd file,
size_t file_offset,
cl_uint num_events_in_wait_list,
const cl_event* event_wait_list,
cl_event* event);
Rev. 1.01
Page 8

8
synchronization points, and the contexts associated with events in event_wait_list and command_queue
must be the same. Memory associated with event_wait_list can be reused or freed-up after the function
returns.
event [out, optional]
Returns an event object that identifies the clEnqueueWriteSsgFileAMD command and can query or queue
a wait for this command to finish executing. The event argument can be NULL, in which case the
application will be unable to query the command status or queue a wait for the command to finish. Unless
the event_wait_list and event arguments are NULL, the event argument should avoid referring to an
element of the event_wait_list array.
Return Value Description
CL_SUCCESS The function executed successfully.
CL_INVALID_FILE_OBJECT_AMD The file is invalid for OpenCL.
CL_INVALID_COMMAND_QUEUE Command_queue is an invalid host command queue.
CL_INVALID_CONTEXT The contexts associated with command_queue and buffer are
different, or the contexts associated with command_queue and the
events in event_wait_list are different.
CL_INVALID_MEM_OBJECT The buffer object is invalid.
CL_INVALID_VALUE The region specified by buffer_offset, file_offset or size is out of
bounds or misaligned with CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
CL_INVALID_EVENT_WAIT_LIST Either event_wait_list is NULL and num_events_in_wait_list is greater
than 0, event_wait_list is not NULL and num_events_in_wait_list is 0,
or event objects in event_wait_list are invalid.
CL_EXEC_STATUS_ERROR_FOR_EVENTS_IN_WAIT_LIST
Write operations are blocking and the execution status of at least one
event in event_wait_list is a negative integer value.
CL_MEM_OBJECT_ALLOCATION_FAILURE
Memory failed to allocate for data store associated with buffer.
4 OpenCL Performance Guidelines and Caveats
The following guidelines and caveats will optimize for the greatest performance from OpenCL.
• For best performance, create the target resources with the flag
CL_MEM_USE_PERSISTENT_MEM_AMD.
• Because of OS limitations, persistent memory must be referenced by the GPU once before it
truly becomes resident in GPU memory. A one-time performance drop may be experienced the
first time the buffer is used as a file-transfer target if the GPU has yet to access the resource.
Clear the buffer using clEnqueueFillBuffer to generate such a reference.
• The persistent-memory heap available to all applications is 128 MB. If the heap is entirely
consumed, the run time will silently fall back to standard allocations. If the data set is larger than
100 MB, the application should employ the persistent-memory allocation as a staging buffer and
Rev. 1.01
Page 9

9
copy the internal device memory to the destination buffer. Internal device copies will execute at
full memory-controller speed, which varies from 100 GB/s to 500 GB/s depending on the GPU
type.
• The copy size, buffer offset and file offset must adhere to the SSD’s alignment restrictions.
Discover these restrictions by calling clGetSsgFileObjectInfoAMD.
Rev. 1.01
Page 10

10
// Create file.
}
5 AMD Code Sample for OpenCL
std::cout << "Error: Unable to create file handle." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Error: Unable to retrieve file size." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Error: Invalid file size info returned." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Error: Unable to retrieve file size." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Error: Invalid sector size info returned." << std::endl;
DATA_SIZE_IN_BYTES, nullptr, &clStatus);
std::cout << "Error: Unable to create buffer." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Error: Data transfer failed." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Warning: Unable to release file." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Warning: Unable to release buffer." << std::endl;
cl_int clStatus = CL_SUCCESS;
cl_file_amd clSsgFile = clCreateSsgFileObjectAMD(m_clContext,
if (clStatus != CL_SUCCESS) {
return;
}
// Get the file-size information.
size_t retSize = 0;
LARGE_INTEGER SsgFileSize;
clStatus = clGetSsgFileObjectInfoAMD(clSsgFile, CL_FILE_SIZE_AMD,
if (clStatus != CL_SUCCESS) {
return;
}
if (retSize != sizeof(SsgFileSize)) {
return;
}
// Get the sector-size information.
// Allocated buffer must align with the sector size for best performance.
cl_uint sectorSize = 0;
clStatus = clGetSsgFileObjectInfoAMD(clSsgFile, CL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD,
if (clStatus != CL_SUCCESS) {
return;
}
if (retSize != sizeof(sectorSize)) {
return;
}
// Create buffer.
cl_mem clBuffer = clCreateBuffer(m_clContext, CL_MEM_ USE_PERSISTENT_MEM_AMD,
if (clStatus != CL_SUCCESS) {
return;
}
// Read information from the file; BUFF_OFFSET, SIZE_TO_READ and FILE_OFFSET must
// align with the sector size.
clStatus = clEnqueueReadSsgFileAMD(m_clCommandQueue, clBuffer, CL_TRUE, BUFF_OFFSET,
if (clStatus != CL_SUCCESS) {
}
// Release the file when you’re done with it.
clStatus = clReleaseSsgFileObjectAMD(clSsgFile);
if (clStatus != CL_SUCCESS) {
}
// Release the buffer when you’re done with it.
clStatus = clReleaseBuffer(clBuffer);
if (clStatus != CL_SUCCESS) {
CL_FILE_READ_ONLY_AMD, FILE_NAME, &clStatus);
sizeof(SsgFileSize), &SsgFileSize, &retSize);
sizeof(sectorSize), §orSize, &retSize);
SIZE_TO_READ, clSsgFile, FILE_OFFSET, 0, NULL, NULL);
Rev. 1.01
Page 11

11
C++
GLfilehandleAMD glCreateFileAMD(GLchar* name, GLenum mode);
C++
GLvoid glReleaseFileAMD(GLfilehandleAMD file);
6 OpenGL® Extension Specification
This OpenGL extension accelerates the data transfer between GPU and SSD devices. It introduces a new
file object that operates on the file in an SSD. The result of a file operation (read or write) can be any
named buffer object. GL file objects employ the same semantics as when the file is opened for
reading/writing—that is, the file must have read/write privileges.
6.1 glCreateFileAMD
The glCreateFileAMD function creates a GL file object. Doing so over a file employs the same semantics
as when the file is opened for reading/writing—that is, the file must have read/write privileges.
name [in]
Name of the file to open or create. The file name supports only UTF-8; wide-character Unicode strings are
currently unsupported.
mode [in]
Mode in which the file is to be created: GL_READ_ONLY, GL_WRITE_ONLY or GL_READ_WRITE.
Return Value Description
NULL The function is unable to create/open the file.
6.2 glReleaseFileAMD
The glReleaseFileAMD function detaches the native handle from a GL file and closes the GL file object.
file [in]
The GL file to be released and closed.
Error Description
INVALID_OPERATION The file object is invalid.
6.3 glGetFileParameteri64vAMD
The glGetFileParameteri64vAMD function returns the properties of the GL file.
Rev. 1.01
Page 12

12
C++
GLvoid glGetFileParameteri64vAMD(GLfilehandleAMD file,
C++
GLvoid glReadFileAMD(GLuint dstBuffer,
GLenum pname,
GLuint64* params);
file [in]
The GL file for which properties are required.
pname [in]
The property information being requested. It must be GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD or GL_FILE_SIZE_AMD.
params [out]
The value of the property requested.
Error Description
INVALID_VALUE The file object is invalid.
INVALID_ENUM The requested property is not GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
6.4 glReadFileAMD
The glReadFileAMD function reads from the specified file into the destination buffer. It can be
synchronous or asynchronous. Combining a number of read operations asynchronously yields better
performance.
GLfilehandleAMD file,
GLuint64 bufferOffset,
GLuint64 fileOffset,
GLuint64 size,
GLsync* sync);
dstBuffer [in]
A valid named buffer object that will hold the read result. The best performance is obtained by creating
the buffer with the MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT flag but without CLIENT_STORAGE_BIT.
file [in]
The GL file from which information is being read.
bufferOffset [in]
Location in the buffer from which data (of width size, in bytes) will be read. It must be a multiple of
GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
fileOffset [in]
Location in the file from which data (of width size, in bytes) will be read into the buffer. It must be a
multiple of GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
Rev. 1.01
Page 13

13
C++
GLvoid glWriteFileAMD(GLuint srcBuffer,
size [in]
The amount of information (in bytes) being read. It must be a multiple of GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD. If
the file size is not a multiple of the block size, read the end of the file by aligning the read size with the
next block multiple beyond the file size.
sync [in]
Sync the object for non-blocking operation. If sync is NULL, read operations will execute in blocking mode
and the function call will return only after the operation is complete. Otherwise, the function will use nonblocking mode and will return immediately; a valid GL sync object will also be returned in this case, to be
used in a WaitSync call to synchronize file operations. Non-blocking mode is only valid when the buffer is
created with the MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT flag but without CLIENT_STORAGE_BIT.
Error Description
INVALID_VALUE The file object is invalid.
INVALID_VALUE Invalid buffer-object name.
INVALID_VALUE The sum of bufferOffset and size exceeds the size of the target buffer.
INVALID_VALUE The fileOffset, size and bufferOffset values are not multiples of
GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
INVALID_OPERATION Failure to access the file with the specified fileOffset and size values.
INVALID_OPERATION The sync argument isn’t NULL and the buffer object wasn’t created
with the MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT flag but without
CLIENT_STORAGE_BIT.
6.5 glWriteFileAMD
The glWriteFileAMD function writes multiple target regions to the file. The write source is a named
buffer with specified offsets.
GLfilehandleAMD file,
GLuint64 bufferOffset,
GLuint64 fileOffset,
GLuint64 size,
GLsync* sync);
srcBuffer [in]
A valid named buffer object containing the information desired to be written to a file. The best
performance is obtained by creating the buffer with the MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT flag but without
CLIENT_STORAGE_BIT.
file [in]
The GL file to which the information is written.
bufferOffset [in]
Location in the buffer from which data (of width size, in bytes) will be read. It must be a multiple of
GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
Rev. 1.01
Page 14

14
fileOffset [in]
File location to which data (of width size, in bytes) will be written. It must be a multiple of
GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
size [in]
Amount of information (in bytes) being written. It must be a multiple of GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD. If
the file size is not a multiple of the block size, read the end of the file by aligning the read size with the
next block multiple beyond the file size.
sync [in]
Sync the object for non-blocking operation. If sync is NULL, the write operation will execute in blocking
mode and the function call will return only after the operation is complete. Otherwise, the function will use
non-blocking mode and will return immediately; a valid GL sync object will also be returned in this case, to
be used in a WaitSync call to synchronize file operations. Non-blocking mode is only valid when the buffer
is created with the MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT flag but without CLIENT_STORAGE_BIT.
Error Description
INVALID_VALUE The file object is invalid.
INVALID_VALUE Invalid buffer-object name.
INVALID_VALUE The sum of bufferOffset and size exceeds the size of the target buffer.
INVALID_VALUE The fileOffset, size and bufferOffset values are not multiples of
GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
INVALID_OPERATION Failure to access file with specified fileOffset and size.
INVALID_OPERATION The sync argument isn’t NULL and buffer object wasn’t created with
the MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT flag but without CLIENT_STORAGE_BIT.
7 OpenGL Performance Guidelines and Caveats
The following guidelines and caveats will help realize the greatest performance from OpenGL.
• The copy size, buffer offset and file offset must adhere to the SSD’s alignment restrictions.
Discover these restrictions by calling glGetFileParameteri64vAMD.
• Performing multiple asynchronous reads/writes will yield better performance than synchronous
operations. For asynchronous reads/writes, multiple read/writes share the same sync object,
and sync object must be initialized before passing it to glReadFileAMD/glWriteFileAMD.
Otherwise, asynchronous reads/writes will fail.
• OpenGL divides the video memory into two parts: local visible memory and local invisible
memory. Access to local visible memory enables the highest performance, but this memory is
only 256 MB and the system reserves most of it. The application can only allocate about 100
MB; attempts to allocate more than the unallocated local visible memory will fail. Access to local
invisible memory is slower than to local visible memory, but the application can allocate the
video memory in large amounts. The allocation of local invisible memory can be several
gigabytes, depending on the video-memory size.
• OpenGL provides a way to allocate the local visible memory: glNamedBufferStorage(bufferID,
bufferSize, dataPointer, GL_MAP_READ_BIT|GL_MAP_WRITE_BIT|GL_MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT).
Set the GL_MAP_READ_BIT|GL_MAP_WRITE_BIT|GL_MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT flag.
Rev. 1.01
Page 15

15
• The glNamedBufferStorage() API can also allocate local invisible memory; just set the
GL_MAP_READ_BIT or GL_MAP_WRITE_BIT flag without setting GL_MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT.
• OpenGL also provides other ways to allocate local invisible memory: glBufferData and
glBufferSubData.
• Only when the buffer is created in local visible video memory (using glNamedBufferStorage with
the GL_MAP_READ_BIT | GL_MAP_WRITE_BIT | GL_MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT flag set) will
read/write operations work in asynchronous mode. Otherwise, the driver will ignore the sync
object.
Rev. 1.01
Page 16

16
8 AMD Code Sample for OpenGL
// Create file: FILE_NAME is the file path.
GLfilehandleAMD hSsgFileFile = glCreateFileAMD(FILE_NAME, GL_READ_ONLY);
std::cout << "Error: Unable to open the file." << std::endl;
GLuint64 fileSize = 0;
glGetFileParameteri64vAMD(hSsgFileFile, GL_FILE_SIZE_AMD, &fileSize);
std::cout << "Error: Unable to retrieve file size." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Error: Unable to retrieve block size." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Error: Failed to allocate openGL buffer." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Error: Failed to read data from the file." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Warning: Unable to release file." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Warning: Unable to release buffer." << std::endl;
if (hSsgFileFile != NULL) {
return;
}
// Get the file-size information.
if (glGetError() != GL_NO_ERROR) {
return;
}
// Get the file-system information.
GLuint64 sectorSize = 0;
glGetFileParameteri64vAMD(hSsgFileFile, GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD, §orSize);
if (sectorSize == 0) {
return;
}
// Create buffer.
GLuint oglBuffer;
glCreateBuffers(1, &oglBuffer);
glNamedBufferStorage(oglBuffer, SIZE_TO_READ, nullptr,
GL_MAP_READ_BIT | GL_MAP_WRITE_BIT | GL_MAP_PERSISTENT_BIT);
if (glGetError() != GL_NO_ERROR) {
return;
}
// Read information from the file; BUFF_OFFSET, SIZE_TO_READ and FILE_OFFSET must
// align with the sector size.
glReadFileAMD(oglBuffer, hSsgFileFile, BUFF_OFFSET, FILE_OFFSET, SIZE_TO_READ, nullptr);
if (glGetError() != GL_NO_ERROR) {
return;
}
// Release the file when you’re done with it.
glReleaseFileAMD(hSsgFileFile);
if (glGetError() != GL_NO_ERROR) {
}
// Release the buffer when you’re done with it.
glDeleteBuffers(1, oglBuffer);
if (glGetError() != GL_NO_ERROR) {
}
Rev. 1.01
Page 17

17
C++
class IAmdDxExtSSG : public IAmdDxExtInterface
9 DirectX™ 11 Extension Specification
The DirectX 11 extension accelerates the data transfer between GPU and SSD devices. It introduces a
new interface that operates on the file in an SSD. The result of the operation (read or write) can be any
named buffer object. The DirectX file object employs the same semantics as when the file is opened for
reading/writing—that is, the file must have read/write privileges.
{
public:
// Version information.
virtual HRESULT GetExtensionVersion(AmdDxSsgVersion* pVersion) = 0;
// Open or create a file and get an SSG file handle for it.
// The handle will be used later in data-transfer calls.
virtual HRESULT CreateFile(const WCHAR* pFileName, AmdDxSsgFileAccess fileAccess,
AmdDxSsgFileHandle* phFile) = 0;
// Release a file when it’s no longer in use.
virtual HRESULT ReleaseFile(AmdDxSsgFileHandle hFile) = 0;
// Get the file-size information.
// The file transfer in the SSG extension requires that the transfer size and offset
// align with the block boundary.
virtual HRESULT GetFileInfo(AmdDxSsgFileHandle hFile, AmdDxSsgFileInfo* pInfo) = 0;
// Create an event to use in asynchronous file transfer.
virtual HRESULT CreateEvent(AmdDxSsgEventHandle* phEvent) = 0;
// Delete an event.
virtual HRESULT DestroyEvent(AmdDxSsgEventHandle hEvent) = 0;
// Wait for an asynchronous file transfer to complete.
// The event handle should have been submitted in a previous transfer call.
virtual HRESULT WaitEvent(AmdDxSsgEventHandle hEvent) = 0;
// P2P transfer of file data to a D3D11 buffer.
virtual HRESULT ReadBufferFromFile(ID3D11Buffer* pBuffer, AmdDxSsgFileHandle hFile,
// P2P transfer of D3D11 buffer data to a file.
virtual HRESULT WriteBufferToFile(ID3D11Buffer* pBuffer, AmdDxSsgFileHandle hFile,
UINT numRegions, AmdDxSsgRegionDesc* pRegions,
};
UINT numRegions, AmdDxSsgRegionDesc* pRegions,
AmdDxSsgEventHandle hEvent) = 0;
AmdDxSsgEventHandle hEvent) = 0;
Rev. 1.01
Page 18

18
C++
HRESULT GetExtensionVersion(AmdDxExtVersion* pExtVersion);
C++
HRESULT CreateFile(const WCHAR* pFileName,
9.1 GetExtensionVersion
The GetExtensionVersion function returns the SSG extension version information.
pExtVersion [in]
Address pointer to the returned version information.
Remarks
The extVersionMajor/Minor values will increase as the extension interface expands to add new functions.
The liquidFlashBuild number indicates the functional improvement in the Liquid Flash library. This value is
also necessary to determine the library version when a customer reports a problem.
Return Value Description
S_OK The function succeeded.
E_INVALIDARG The pExtVersion value is NULL.
9.2 CreateFile
The CreateFile function creates a DirectX file object. Using it over a file employs the same semantics as
when the file is opened for reading/writing— that is, the file must have read/write privileges.
pFileName [in]
Name of the file to be opened or created.
fileAccess [in]
Request read/write access for the file.
phFile [out]
SSG file handle for use in subsequent data-transfer calls.
Return Value Description
S_OK The function succeeded.
E_FAIL The handle is invalid or refers to an unsupported device.
AmdDxSsgFileAccess fileAccess, AmdDxSsgFileHandle* phFile)
9.3 ReleaseFile
The ReleaseFile function releases the SSG file handle and closes the file.
Rev. 1.01
Page 19

19
C++
HRESULT ReleaseFile(AmdDxLfFileHandle hFile);
C++
HRESULT CreateEvent(AmdDxLfEventHandle* phEvent);
C++
HRESULT GetFileInfo(AmdDxLfFileHandle hFile, AmdDxLfFileInfo* pInfo);
hFile [in]
Handle for the SSG file to close.
Remarks
This function will invalidate the hFile handle, which then becomes unusable. Avoid calling this function if
an asynchronous transfer is in progress.
Return Value Description
S_OK The function succeeded.
E_HANDLE The handle is invalid or the file failed to close.
E_INVALIDARG The handle is invalid or the file failed to close.
9.4 GetFileInfo
The GetFileInfo function retrieves information about the file on disk. Available information includes the
file size and sector size. Use the sector size when calculating the buffer-size alignment and the regions
desired to be read.
hFile [in]
Handle for SSG file from which information is to be retrieved.
pInfo [out]
Structure to be filled with the file- and sector-size information.
Return Value Description
S_OK The function succeeded.
9.5 CreateEvent
The CreateEvent function creates a synchronization event for use during asynchronous file transfers.
phEvent [out]
SSG event handle for use in subsequent asynchronous data-transfer calls.
Rev. 1.01
Page 20

20
C++
HRESULT DeleteEvent(AmdDxLfEventHandle hEvent);
C++
HRESULT WaitEvent(AmdDxLfEventHandle hEvent);
Return value
S_OK The function succeeded.
9.6 DeleteEvent
The DeleteEvent function deletes a synchronization event employed during asynchronous file transfers.
hEvent [in]
SSG event handle to be deleted.
Remarks
Avoid deleting an event handle if used in asynchronous file transfers but those transfers finished
executing before the event. Once the event handle is deleted, no longer wait on those transfers to finish.
Return Value Description
S_OK The function succeeded.
E_INVALIDARG Unable to delete event handle.
9.7 WaitEvent
The WaitEvent function waits for asynchronous file transfers to complete. The synchronization event
should have already been used in a previous transfer call.
hEvent [in]
Handle of SSG event to wait on.
Remarks
The wait time on an event yet to be used in an asynchronous call should be zero.
Return Value Description
S_OK The function succeeded.
E_INVALIDARG Unable to wait on the event.
Rev. 1.01
Page 21

21
C++
HRESULT ReadBufferFromFile(ID3D11Buffer* pBuffer,
9.8 ReadBufferFromFile
The ReadBufferFromFile function transfers file information to the D3D11 buffer. The call can be
synchronous or asynchronous, and it takes one or more regions to fill the destination buffer. Splitting
the request into multiple smaller regions can improve performance.
Note: During asynchronous transfers (between the transfer call and the WaitEvent call), avoid using the
D3D buffer in the D3D pipeline or lock/unlock. Also note that WaitEvent is required for every
asynchronous transfer. Do not assume that waiting for the last issued transfer means all asynchronous
transfers are complete.
AmdDxLfFileHandle hFile,
UINT numRegions,
AmdDxLfRegionDesc* pRegions,
AmdDxLfEventHandle hEvent);
pBuffer [in]
The D3D11 buffer that will be the transfer destination.
hFile [in]
SSG file handle that will be the data-transfer source.
numRegions [in]
Number of elements in pRegions array.
pRegions [in]
Array of regions for the data transfer. Each region contains the file offset to read from, the buffer offset to
write to and the size of the data to write, in bytes. They must be a multiple of sector-size.
hEvent [in]
SSG event handle to wait on. If the call omits an event, the function will be synchronous and will return
after the data transfer is complete. If the call includes an event, the function will return immediately, and
the caller is responsible for waiting on this event to ensure the data transfer is complete.
Return Value Description
S_OK The function succeeded.
E_HANDLE The file object is invalid.
E_INVALIDARG The file object is invalid.
E_FAIL The sum of dstOffset and length exceeds the size of the target buffer.
E_FAIL The value of srcOffset, length or dstOffset is not a multiple of
GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
E_FAIL The function failed to access the file with the specified srcOffset and
length values.
Rev. 1.01
Page 22

22
C++
HRESULT WriteBufferToFile(AmdDxLfFileHandle hFile,
9.9 WriteBufferToFile
The WriteBufferToFile function transfers information from the D3D11 buffer to a file. The call can be
synchronous or asynchronous. It takes one or more regions for writing to the file. Splitting the request
into multiple smaller regions can improve performance.
Note: During asynchronous transfers (between a transfer call and a WaitEvent call), avoid using the D3D
buffer in the D3D pipeline or lock/unlock. Also note that WaitEvent is required for every asynchronous
transfer. Do not assume that waiting for the last issued transfer means all asynchronous transfers are
complete.
hFile [in]
Handle for the SSG file that will be the data-transfer destination.
pBuffer [in]
D3D11 buffer that will be the transfer source.
numRegions [in]
Number of elements in pRegions array.
pRegions [in]
Array of regions for the data transfer. Each region contains the file offset to write to, the buffer offset to
read from and the size of the data to write, in bytes. They must be a multiple of sector-size.
hEvent [in]
SSG event handle to wait on. If the call omits an event, the function will be synchronous and will return
after the data transfer is complete. If the call includes an event, the function will return immediately and
the caller will be responsible for waiting on this event to ensure the data transfer is complete.
Return Value Description
S_OK The function succeeded.
E_HANDLE The file object is invalid.
E_INVALIDARG The file object is invalid.
E_FAIL The sum of dstOffset and length exceeds the size of target buffer.
E_FAIL The value of srcOffset, length or dstOffset is not a multiple of
E_FAIL The function failed to access the file with the specified srcOffset and
ID3D11Buffer* pBuffer,
UINT numRegions,
AmdDxLfRegionDesc* pRegions,
AmdDxLfEventHandle hEvent);
GL_FILE_BLOCK_SIZE_AMD.
length values.
Rev. 1.01
Page 23

23
// Create module handle.
}
10 AMD Code Sample for DirectX®
HMODULE hDxxDll = GetModuleHandle(DXX_DLL_NAME);
if (hDxxExt == NULL) {
}
// Initial function pointer from module.
PFNAmdDxExtCreate11 pAmdDxExtCreate =
reinterpret_cast<PFNAmdDxExtCreate11>(GetProcAddress(hDxxDll, "AmdDxExtCreate11"));
if (pAmdDxExtCreate == nullptr) {
std::cout << "Error: Unable to get DX information." << std::endl;
}
// Create general extension object.
IAmdDxExt* dxExt = nullptr;
pAmdDxExtCreate(D3D11DEVICE, &dxExt);
if (dxExt == nullptr) {
std::cout << "Error: Unable to get DX extension." << std::endl;
}
// Get SSG extension interface.
IAmdDxExtSsg* dxSsgExt = static_cast<IAmdDxExtSsg*>
if (dxSsgExt == nullptr) {
std::cout << "Error: Unable to get DX SSG extension." << std::endl;
}
// Create SSG file handle.
AmdDxSsgFileHandle hSsgFile;
HRESULT hr = dxSsgExt->CreateFile(FILE_NAME, AmdDxSsgFile_Read, &hSsgFile);
If (FAILED(hr)) {
}
// Get the file information: file size and block size.
AmdDxSsgFileInfo dxSsgFileInfo;
hr = dxSsgExt->GetFileInfo(hSsgFile, &dxSsgFileInfo);
if (FAILED(hr)) {
std::cout << "Error: Unable to retrieve file/block size." << std::endl;
}
// Create buffer: SIZE_TO_READ.
CComPtr<ID3D11Buffer> pDxBuffer;
D3D11_BUFFER_DESC bufferDesc;
ZeroMemory(&bufferDesc, sizeof(bufferDesc));
bufferDesc.ByteWidth = SIZE_TO_READ;
bufferDesc.Usage = D3D11_USAGE_DEFAULT;
bufferDesc.BindFlags = D3D11_BIND_SHADER_RESOURCE;
bufferDesc.MiscFlags = 0;
bufferDesc.StructureByteStride = 0;
bufferDesc.CPUAccessFlags = 0;
hr = D3D11DEVICE->CreateBuffer(&bufferDesc, NULL, &pDxBuffer);
if (FAILED(hr)) {
std::cout << "Error: Unable to create dx buffer." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Error: Unable to load DX library." << std::endl;
return;
return;
return;
return;
std::cout << "Error: Unable to create liquid flash file handle." << std::endl;
return;
return;
return;
(dxExt->GetExtInterface(AmdDxExtSsgID));
Rev. 1.01
Page 24

24
AmdDxLfRegionDesc regionDesc;
regionDesc.fileOffset = FILE_OFFSET;
regionDesc.bufferOffset = BUFF_OFFSET;
regionDesc.regionSize = dxLFFileInfo.blockSize;
// Read information from the file: BUFF_OFFSET, SIZE_TO_READ and FILE_OFFSET must
// align with the sector size.
hr = dxSsgExt->ReadBufferFromFile(pDxBuffer, hSsgFile, 1, ®ionDescs, nullptr);
std::cout << "Error: Unable to read data from file." << std::endl;
std::cout << "Warning: Unable to release file." << std::endl;
if (FAILED(hr)) {
}
// Release the file when you’re done with it.
hr = dxSsgExt->ReleaseFile(hSsgFile);
if (FAILED(hr)) {
}
Rev. 1.01
Page 25

25
DISCLAIMER
The information contained herein is for informational purposes only, and is subject to change without
notice. While every precaution has been taken in the preparation of this document, it may contain
technical inaccuracies, omissions and typographical errors, and AMD is under no obligation to update or
otherwise correct this information. Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. makes no representations or
warranties with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this document, and assumes
no liability of any kind, including the implied warranties of noninfringement, merchantability or fitness
for particular purposes, with respect to the operation or use of AMD hardware, software or other
products described herein. No license, including implied or arising by estoppel, to any intellectual
property rights is granted by this document. Terms and limitations applicable to the purchase or use of
AMD’s products are as set forth in a signed agreement between the parties or in AMD's Standard Terms
and Conditions of Sale.
Legal Attributions
© 2017 Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. All rights reserved. AMD, the AMD Arrow logo,
Radeon, and combinations thereof are trademarks of Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. in the United States
and/or other jurisdictions. PCIe and PCI Express are registered trademarks of PCI-SIG. OpenGL is a
registered trademark of Khronos Group. OpenCL is a trademark of Apple Inc. used by permission by
Khronos Group, Inc. DirectX, Windows are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. Other
names are for informational purposes only and may be trademarks of their respective owners.
Rev. 1.01
 Loading...
Loading...