
Industrial Ni-Cd Batteries Standard Range
Technical Manual
Effective: October, 2009
Alpha Technologies
Alpha Technologies
Power
®

Alpha Ni-Cd Pocket Plate Battery
Technical Manual
EN-Alpha-TMSR-001
Effective Date: October, 2009
Copyright© 2009
Alpha Technologies, Inc.
member of The Group
NOTE:
Photographs contained in this manual are for illustrative purposes only. These photographs may not match
your installation.
NOTE:
Operator is cautioned to review the drawings and illustrations contained in this manual before proceeding. If
there are questions regarding the safe operation of this powering system, please contact Alpha Technologies
or your nearest Alpha representative.
NOTE:
Alpha shall not be held liable for any damage or injury involving its enclosures, power supplies, generators,
batteries, or other hardware if used or operated in any manner or subject to any condition not consistent with
its intended purpose, or is installed or operated in an unapproved manner, or improperly maintained.
TM
Contacting Alpha Technologies: www.alpha.com
For general product information and customer service (7 AM to 5 PM, Pacifi c Time), call
EN-ALPHA-TMSR-001 (10/09)
or
1-800-863-3930,
For complete technical support, call
1-800-863-3364
7 AM to 5 PM, Pacifi c Time or 24/7 emergency support
3

Table of Contents
1. 0 Alpha Ni-Cd Pocket Plate Cell ..................................................................................................................... 6
1.1 Features. ...................................................................................................................................................................................6
1.2 Venting System ..................................................................................................................................................................... 7
1.3 Electrode frame ....................................................................................................................................................................8
1.4 Separators .............................................................................................................................................................................. .8
1.5 Positive and negative electrode plate .........................................................................................................................8
1.6 Distance plate .......................................................................................................................................................................9
1.7 Cell cases .................................................................................................................................................................................9
1.8 Electrolyte ...............................................................................................................................................................................9
2. 0 Battery Range and Applications .......................................................................................................................................... 10
2.1 Battery ranges .................................................................................................................................................................... 10
2.2 Applications and choice of cell type ......................................................................................................................... 10
3.0 Electrochemistry of Ni-Cd Batteries .................................................................................................................................. 11
4. 0 Operating Features .................................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.1 Capacity .............................................................................................................................................................................. .12
4.2 Cell voltage .......................................................................................................................................................................... 12
4.3 Internal resistance ............................................................................................................................................................ 12
4.4 Impact of temperature on cell performance and available capacity .............................................................. 13
4.5 Impact of temperature on lifetime .............................................................................................................................. 14
4.6 Short-circuit values .......................................................................................................................................................... 14
4.7 Open circuit loss................................................................................................................................................................. 15
4.8 Cycling .................................................................................................................................................................................. 15
4.9 Water consumption and gas evolution ..................................................................................................................... 16
5.0 Battery Sizing. ............................................................................................................................................ 17
5.1 Voltage window ................................................................................................................................................................. 17
5.2 Load profi le ......................................................................................................................................................................... 17
5.3 Ambient temperature ...................................................................................................................................................... 17
5.4 Recharge time and state of charge ............................................................................................................................. 17
5.5 Aging ..................................................................................................................................................................................... 17
5.6 Floating effect - Voltage depression ........................................................................................................................... 18
6.0 Charging .................................................................................................................................................... 19
6.1 Constant voltage charge ................................................................................................................................................. 19
6.2 Charge acceptance .......................................................................................................................................................... 20
6.3 Charge effi ciency .............................................................................................................................................................. 21
6.4 Temperature infl uence ................................................................................................................................................... 22
6.5 Commissioning .................................................................................................................................................................. 22
4
EN-ALPHA-TMSR-001 (10/09)

Table of Contents
7.0 Installation and operating instructions .................................................................................................. 23
7.1 Receiving the battery ...................................................................................................................................................... 23
7.2 Storage ................................................................................................................................................................................. 23
7.2.1 Uncharged and unfi lled cells ...........................................................................................................................23
7.2.2 Charged and fi lled cells/discharged and fi lled cells ................................................................................ 23
7.3 Installation ............................................................................................................................................................................. 23
7.3.1 Location ................................................................................................................................................................... 23
7.3.2 Ventilation ............................................................................................................................................................... 23
7.3.3 Setting up ................................................................................................................................................................ 24
7.3.4 Electrolyte ............................................................................................................................................................... 24
7.3.5 Commissioning ..................................................................................................................................................... 25
7.3.5.1 Commissioning with constant current ............................................................................................ 25
7.3.5.2 Commissioning with constant voltage ............................................................................................ 26
7.4 Charging in operation ..................................................................................................................................................... 27
7.4.1 Continuous battery power supply (with occasional battery discharge) .......................................... 27
7.4.1.2 Two level charge ...................................................................................................................................... 27
7.4.1.3 Single level charge .................................................................................................................................. 27
7.4.2 Buffer operation ................................................................................................................................................... 27
7.5 Periodic Maintenance ...................................................................................................................................................... 27
7.5.1 Equalising charge ................................................................................................................................................. 27
7.5.2 Electrolyte check and topping up .................................................................................................................. 28
7.5.3 Replacing of electrolyte ..................................................................................................................................... 28
7.5.4 Electrolyte temperature ..................................................................................................................................... 28
7.6 Additional warning notes ............................................................................................................................................... 29
Figures, Graphs & Tables
Fig.1-1 Cutaway view of battery ................................................................................................................................... 6
Fig.1-2 Battery vents .........................................................................................................................................................7
Fig.1-3 Battery terminal cross-section ........................................................................................................................7
Fig.1-4 Components of the Electrode plates ...........................................................................................................8
Fig.1-5 Electrode plate linkage .....................................................................................................................................8
Fig.7-1 Terminal connection with Nuts ................................................................................................................... 24
Fig. 7-2 Terminal connection with Screws ..............................................................................................................24
Graph 4-1 NiCd-cell performance varation with temperature ............................................................................. 13
Graph 4-2 NiCd vs. Pb-acid battery lifetimes at 25°C .............................................................................................. 14
Graph 4-3 Self-discharge of NiCd-accumulators (fully charged) .........................................................................15
Graph 4-4 Cycle life vs. depth of discharge .................................................................................................................. 15
Graph 4-5 Relationship between water loss and charging voltages ................................................................. 16
Graph 5-1 Floating derating factor as a function of discharge time ..................................................................18
Graph 6-1 Time to reach state of charge (M-Range) ................................................................................................ 20
Graph 6-2 Time to reach state of charge (L-Range) .................................................................................................. 20
Graph 6-3 Time to reach state of charge (H-Range) ................................................................................................. 21
Graph 6-4 Temperature-corrected Float Voltage ....................................................................................................... 22
Table 2-1 Battery (cell type) selection matrix ............................................................................................................ 10
EN-ALPHA-TMSR-001 (10/09)
5
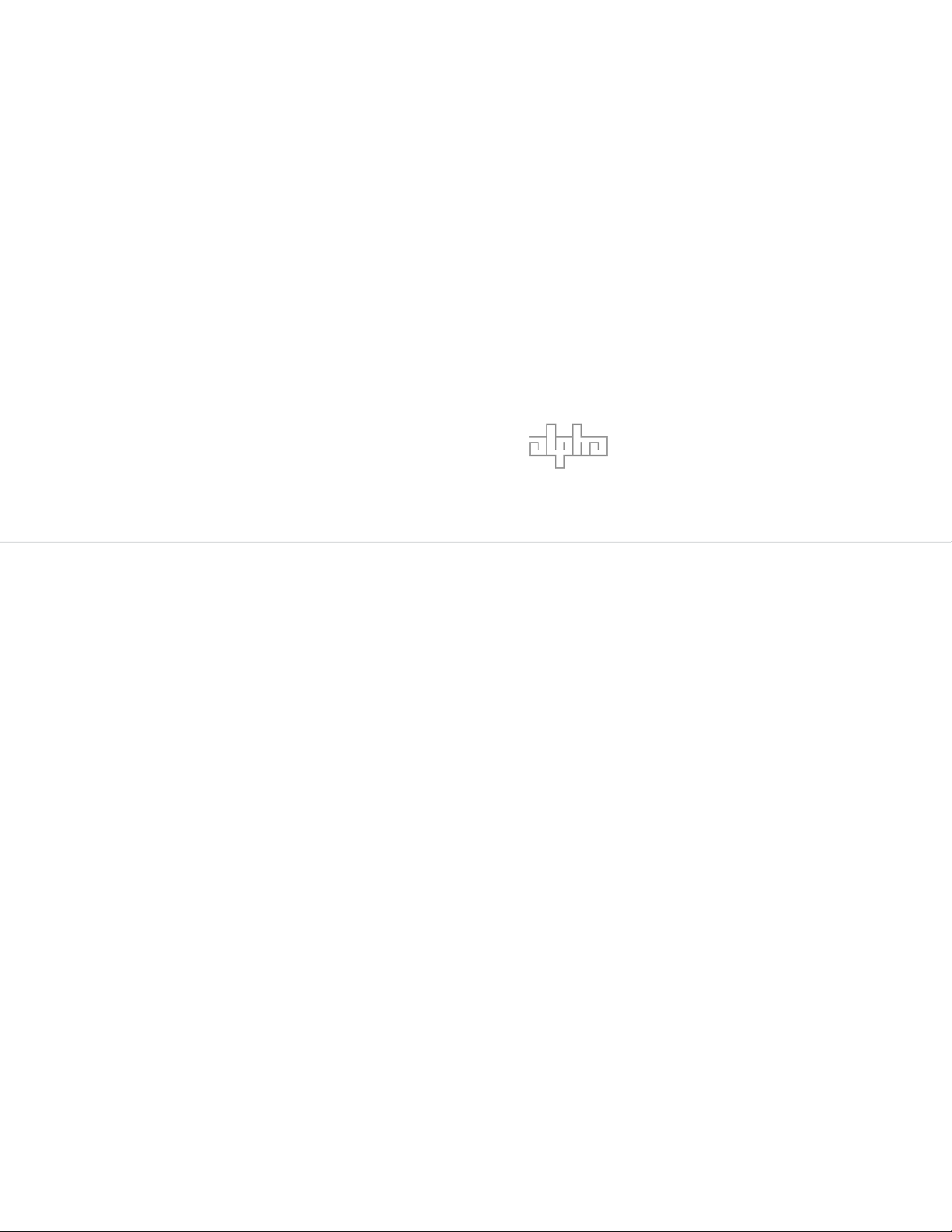
1.0 Alpha Ni-Cd pocket plate cell
1.1 Features
1
2
Low-pressure, fl ame-arresting vent; prevents
1
carbonate formation.
Safety terminal; Redundant leak protection
2
minimizes carbonate formation.
Electrode edge; connected to pole bolt via
3
hardware for high mechanical stability
Electrode frame; Comprised of electrode edge
and side bars. Seals the plates and serves as a
current collector Horizontal pockets; formed by
4
perforated steel strips containing the active material.
Corrugated, perforated plastic separator.
Insulates the plates and allows the free circulation
5
of electrolyte.
3
5
4
6
7
Fiber mat separator; special separator
insulates the plates and improves the internal
6
recombination.
Distance Plate; Prevents movement of the
7
electrode pack.
6
Fig.1-1 Cutaway view of battery
EN-ALPHA-TMSR-001 (10/09)
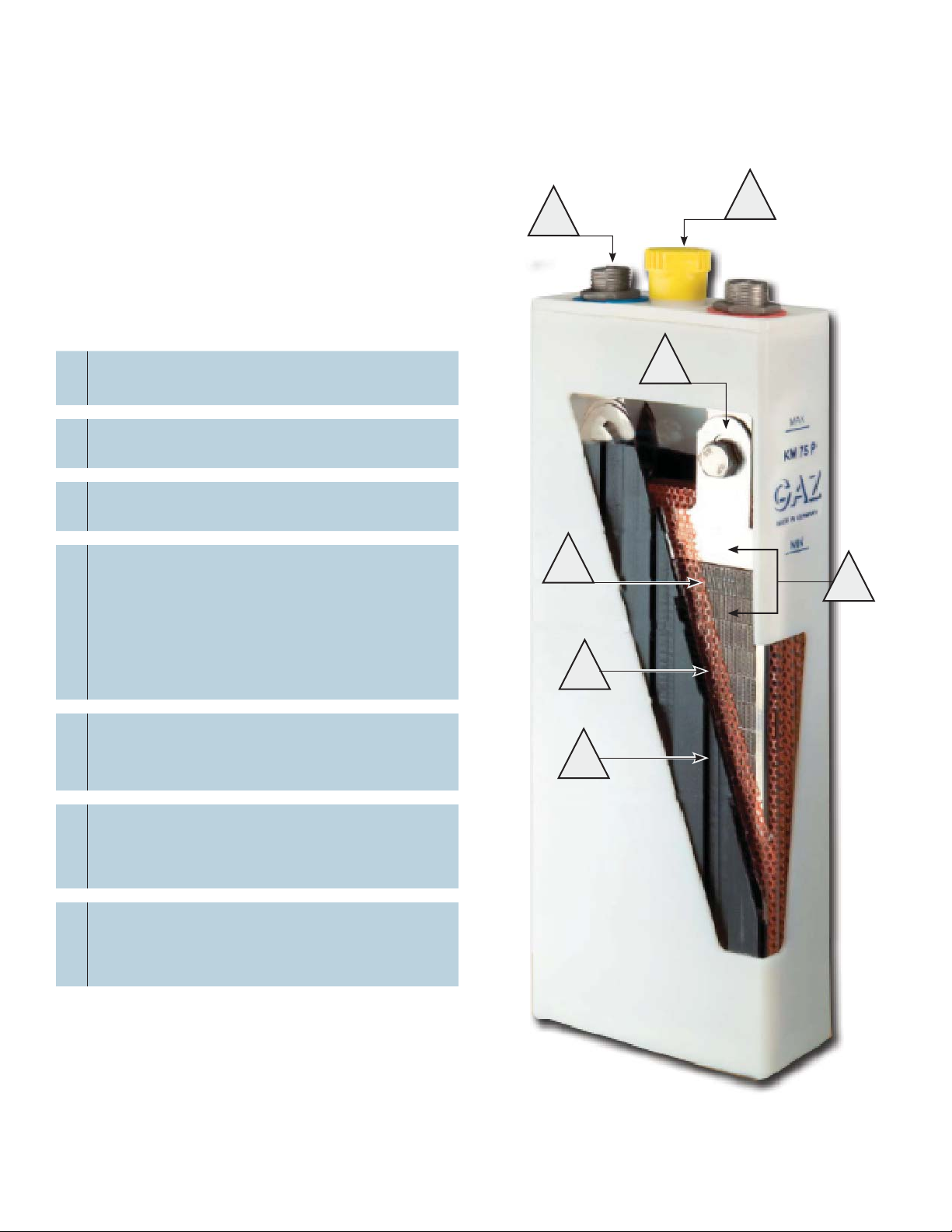
1.0 Alpha Ni-Cd pocket plate cell, continued
1.2 Venting System
Alpha batteries can be equipped with a normal fl ip-top vent or with a special gas drying as well as a fl ame
arresting vent.
The originated charging gases (hydrogen and oxygen), which occur during the charging process
of Ni-Cd batteries carry also small electrolyte drops of the electrolyte solution. This accellerates the decline of the
electrolyte level in comparison to the normal water decomposition during overcharging, resulting in more frequent
maintenance. Furthermore, a strong incrustation of the fi lling vents can be due to the creation of carbonate.
The use of the gas drying or fl ame arresting vents reduces the build-up of carbonate material. The vents
contain small plastic particles with a large surface area which capture the electrolyte drops. The capturing of the
electrolyte keeps it in the cell and prevents the build-up of carbonate.
The additional feature of the fl ame arresting vent is the microporous disc on the top. This feature results in a
diffused leakage of the charging gases. Moreover, high local concentrations can be prevented which fi nally leads
to a lower risk of fl ammability. According to IEC 60623 the total amount of entrained potassium hydroxide shall be
not more than 0.05 mg/ Ah during 2 hours overcharge. Alpha batteries with the special venting system improve
the required value many times over to 0.011 mg/ Ah during 2 hours overcharge.
A specially developed terminal design with redundant leak protection prevents any leakage of electrolyte. Depending on the cell range and type terminals are designed as female or male thread and polarity is colored marked.
Fig.1-2 Battery vents Fig.1-3 Battery terminal cross-section
EN-ALPHA-TMSR-001 (10/09)
7
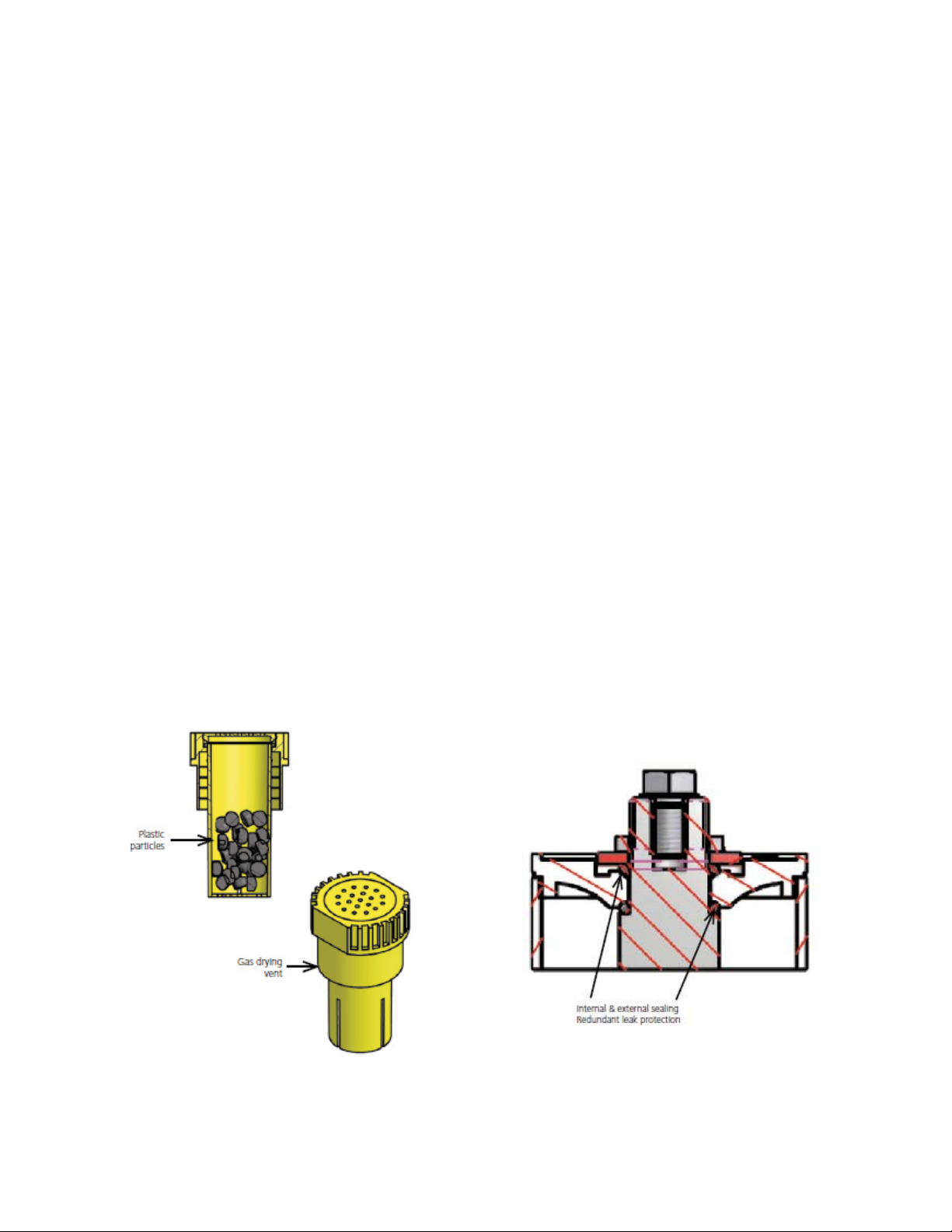
1.0 Alpha Ni-Cd pocket plate cell, continued
1.3 Electrode frame
The electrode frame of Alpha Ni-Cd-batteries consists of a right and a left side bar as well as the electrode edge
which are connected by welding shaping the electrode frame. The electrode frame operates as a current collector
and also seals the electrode plates. This procedure leads to an electrode design with high mechanical robustness
but also ensures a reliable service for the complete lifetime of the battery.
1.4 Separators
The separation of the electrodes is ensured by a corrugated perforated plastic (M- and L-types) or plastic grid
separator (H-types). The plastic grid separator is used for high discharge types (H-types) in order to achieve a
superior cell performance caused by a lower internal resistance, which is very typical and necessary for their
high discharge currents. The separator also ensures a large space between the electrodes, which allows free
circulation of the electrolyte and a good dissipation of the gases generated during end of charging.
1.5 Positive and negative electrode plate
The nickel-cadmium cell is composed of the positive plates containing nickel hydroxide and the negative plates
containing cadmium hydroxide. The pockets formed from a nickel plated and perforated steel tape, the so-called
pocket tape, infold strips of the active material.
The electrode strips are mechanically linked together forming the electrode plate and cut to size appropriate to the
width based on the cell type and range.
The plates then are welded or mechanically linked to the plate frame (see point 3) forming the electrodes - the
heart of the battery - and assembled to the plate block.
The basis for the extemely long useful lifetime and the very good cycle life features of the Ni-Cd pocket plate
batteries are the special plate designs whose structural components are made of steel. This prevents the
possibility of gradually deterioration by corrosion and since the alkaline electrolyte does not react with steel the
substructure of the battery remains intact for the total lifetime of the battery. Very important and unique is the
enfolding of the electrochemical active masses in the perforated nickel plated steel pockets, so that the risk of
shedding or penetration of material is very small and consequently also the risk of structural damages and of soft
short circuits is well under control.
Fig.1-4 Components of the Electrode plates Fig.1-5Electrode plate linkage
8
EN-ALPHA-TMSR-001 (10/09)

1.0 Alpha Ni-Cd pocket plate cell, continued
1.6 Distance plate
The distance plate operates as an additional stabilization to prevent any movement of the electrodes. It is an
additional feature for applications where vibrations are possible.
1.7 Cell cases
The cell cases are made from a translucent polypropylene or polystyrene, which ensures a visual control of
the electrolyte level. The exeptional sturdy Alpha cell cases provide a satisfactory service for the total lifetime
of the battery but also will have a superior fi nish at every stage. The lid and the container are welded or glued
together forming an integrative compound. All Alpha Ni-Cd cells have got a single cell design that prevents in the
greatest possible extend any leakage of the cell cases since they are made by injection molding out of one piece.
Therefore, the weld or glueseams of the cell cases and the lids lies over the electrolyte level. The Alpha single
cell design eliminates completely the risk of faulty welded seams on the sides and on the bottom of the cell cases.
Caused by the single cell design an economical replacement of faulty cells is possible, viz only the faulty cell can
be replaced. A special fl ame retardent material (acc. to standard UL 94 V0) is also available, which admittedly
brings along some impaired properties. By using this material a visual check of the electrolyte is no longer
possible.
1.8 Electrolyte
The electrolyte used in Alpha Ni-Cd batteries is a solution of potassium hydroxide and lithium hydroxide that
is optimized to give the best combination of performance, energy effi ciency and a wide temperature range of
use. The concentration of the standard electrolyte allows operations between - 30 °C and + 50 °C. For special
operations within very low temperatures a special high density electrolyte can be used. It is an important property
of the Alpha battery, and indeed all nickel-cadmium batteries, that the electrolyte does not change during charge
and discharge. It retains its ability to transfer ions between the cell plates, irrespective of the charge level. In most
applications the electrolyte will retain its effectiveness for the life of the battery and will never need replacing.
However, under certain conditions, such as extended use in high temperature situations, the electrolyte can
become carbonated. If this occurs the battery performance can be improved by replacing the electrolyte (see
“Maintenance and Handling Instructions”).
EN-ALPHA-TMSR-001 (10/09)
9
2.0 Battery Range and Applications
2.1 Battery ranges
In order to enable Alpha to offer an appropriate
solution in accordance with the customer's
requirements and to have a choice for any battery
application existing on the market, Alpha Ni-Cd
batteries are designed in four different performance
ranges.
KL ...P
This Alpha cell type has been especially designed
for low rates of discharge over long periods, viz the
current is relatively low in comparison with the total
stored energy. The discharges can generally be
infrequent and the recommended discharge time for
the KL ...P range is 1 hour to 100 hours.
KM ...P TP
The Alpha M type has been especially designed
for "mixed loads" that include a mixture of high
and low rates of discharge. It is used for frequent
and infrequent discharges and the recommended
discharge time is 30 min to 120min.
KM ...PN NON-STOP
This Alpha cell type is a further developed M type,
which provides caused by a special perforation
higher discharge currents for special application up
to 1 hour. It is especially used for UPS and similar
applications and the recommended discharge time is
10 min to 60 min.
KH ...P TSP
The Alpha H type was designed especially for high
current discharging over short discharge periods. The
recommended discharge time for this cell range is 1 s
to 30 min
2.2 Applications and choice of cell type
Alpha Ni-Cd batteries cover a wide range of
applications and are used in almost every sector,
no matter if it is a private, industrial, commercial,
governmental or military one. The table on page 8 on
which some examples can be found represents only
a small overview in te extended fi eld of applications.
Therefore, it is to be understood as a precept and
general information.
Rate of Discharge
Cell Type
Intercity and Urban Transport
Substations and signalling
UPS
Offshore and onshore oil and petrochemical refi neries
Emergency lighting
Telecommunication
Photovoltaic
Diesel start
Ship equipment
Electricity, gas & water production and distribution
Emergency supply
Alarm equipment
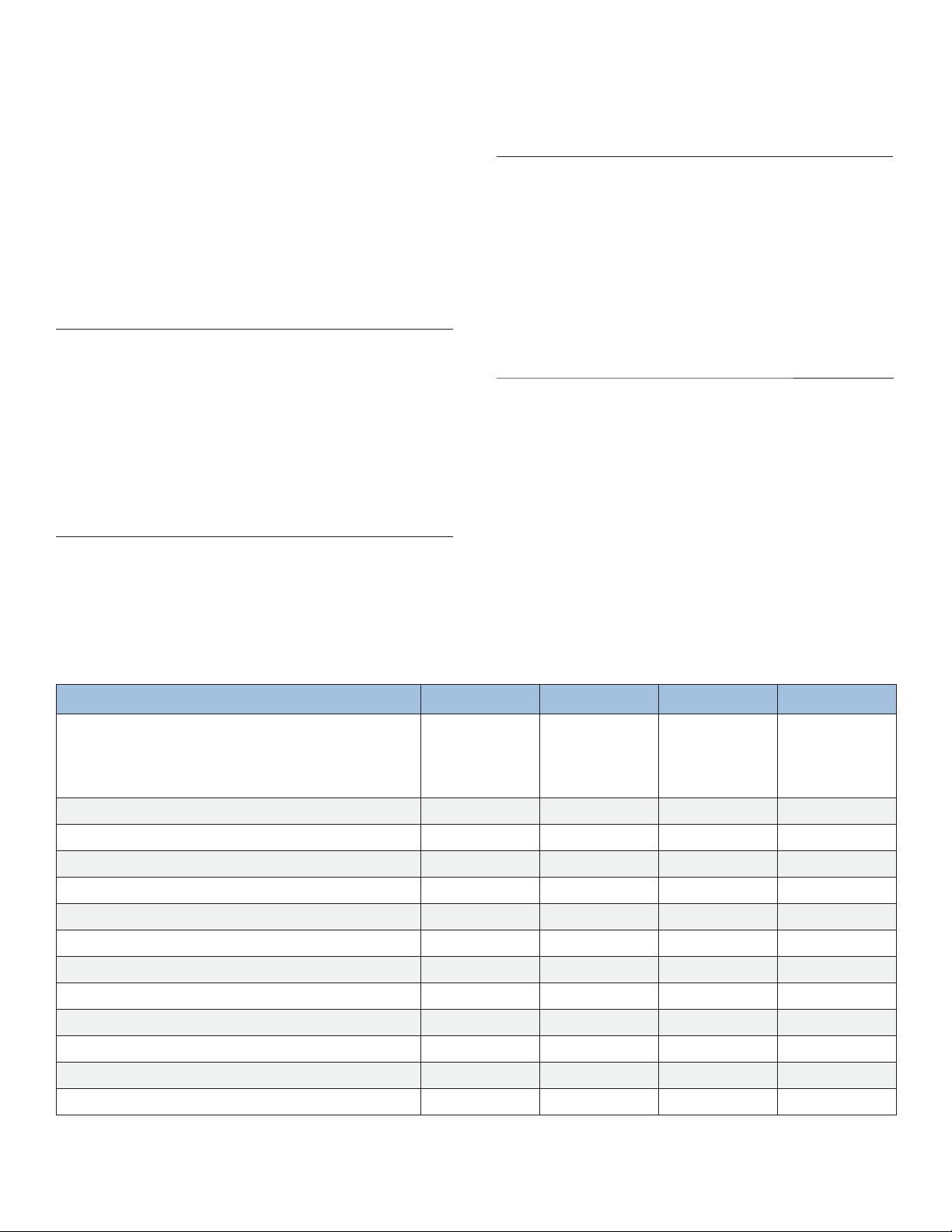
Table 2-1 Battery (cell type) selection matrix as a function of application and rate of discharge
L OW MEDIUM MEDIUM (M/N) HIGH
KL ...P
KL ...
KM ...P
KM ...
TP ...
T ...
KM ...P/N
KH ...P
KM ...
TSP ...
TS ...
XXXX
XXXX
XXXX
XXXX
X
XX
X
X
XXXX
XXXX
XX X
X
10
EN-ALPHA-TMSR-001 (10/09)
 Loading...
Loading...