Page 1
USER’S GUIDE
VERSION 1.4.3
Ethernet
Fast
Ethernet
FORMULA
Fiber
8200
ATM
™
Fast Ethernet Workgroup Switch
PN 613-10611-00 Rev. A
Page 2

Copyright © 1998 Allied Telesyn International, Corp.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesyn
International, Corp.
FORMULA 8200 is a trademark of Allied Telesyn International, Corp.
Ethernet is a registered trademark of Xerox Corporation. SNMPc is a registered trademark of Castle Rock. UNIX is a registered
trademark of X/Open Company, LTD. Windows 95 and Windows NT are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation. All
other product names, company names, logos or other designations mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of
their respective owners.
Allied Telesyn International, Corp. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this
document without prior written notice. The information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall
Allied Telesyn International, Corp. be liable for any incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including
but not limited to lost profits, arising out of or related to this manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesyn
International, Corp. has been advised of, known, or should have known, the possibility of such damages.
Page 3

Table of Contents
Preface ...................................................................................................................................................................vii
Who Should Use This Guide ............................................................................................................................................................................viii
How This Guide Is Organized ............................................................................................................................................................................ix
Document Conventions Used in This Guide ................................................................................................................................................x
Related Documents ..............................................................................................................................................................................................xi
Recommended Reading ....................................................................................................................................................................................xii
Allied Telesyn’s Software Library ...................................................................................................................................................................xiii
Chapter 1
Overview ..............................................................................................................................................................1-1
Product Features ................................................................................................................................................................................................1-1
Chapter 2
Accessing the Command Line Interface (CLI) ...............................................................................................2-1
Connecting the Console ..................................................................................................................................................................................2-2
Terminal Configuration ...........................................................................................................................................................................2-2
Viewing Terminal Configuration Using the CLI ..............................................................................................................................2-2
Observing the Power-On Self Test ...............................................................................................................................................................2-3
Observing the LEDs ..................................................................................................................................................................................2-4
Logging In .............................................................................................................................................................................................................2-6
Logging In Without a Password ...........................................................................................................................................................2-7
Entering Commands .........................................................................................................................................................................................2-8
Use of Square Brackets [ ] .......................................................................................................................................................................2-8
Use of Angle Brackets <> .......................................................................................................................................................................2-8
The LOOKUP Command ..........................................................................................................................................................................2-9
Command Formats ...................................................................................................................................................................................2-9
Moving Through the Menus ................................................................................................................................................................2-10
Configuring IP Information ...........................................................................................................................................................................2-11
Verifying Firmware Information .................................................................................................................................................................2-13
Updating Your Ethernet Ports ............................................................................................................................................................2-13
Updating System Information ............................................................................................................................................................2-13
Using Telnet to Access the Switch .............................................................................................................................................................2-14
Resetting and Rebooting the Switch ........................................................................................................................................................2-15
Where to Go Next .............................................................................................................................................................................................2-15
iii
Page 4

Table of Contents
Chapter 3
Configuring the FORMULA 8200 Switch .........................................................................................................3-1
Default Configurations .....................................................................................................................................................................................3-1
Optimizing Functionality for Your Application .......................................................................................................................................3-2
Virtual LANs ..........................................................................................................................................................................................................3-2
FORMULA 8200 Implementation of VLANs ......................................................................................................................................3-3
Virtual Bridges, Virtual Interfaces, Virtual Routers .........................................................................................................................3-5
Spanning Tree .............................................................................................................................................................................................3-6
Configuring a Virtual LAN (VLAN) .................................................................................................................................................................3-8
Configuring a Virtual Bridge ........................................................................................................................................................................3-11
Chapter 4
Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch .................................................................................. 4-1
Using Online Help ..............................................................................................................................................................................................4-2
Displaying the System Configuration .........................................................................................................................................................4-2
Displaying Console Port Parameters ...........................................................................................................................................................4-4
Displaying Ethernet Port Settings Information .......................................................................................................................................4-5
Configuring Ethernet Port Settings .............................................................................................................................................................4-6
Configuring Ethernet Port Statistics ............................................................................................................................................................4-7
Displaying Ethernet Port Statistics Information ......................................................................................................................................4-8
Clearing a Port’s Statistics Counters ............................................................................................................................................................4-9
Using Ethernet Port Mirroring .......................................................................................................................................................................4-9
Displaying Virtual LAN (VLAN) Information ...........................................................................................................................................4-12
Displaying Virtual Router Information ..................................................................................................................................................... 4-13
Displaying Virtual Port Information ..........................................................................................................................................................4-14
Displaying Virtual Port Statistics ................................................................................................................................................................4-15
Displaying Virtual Bridge Information .....................................................................................................................................................4-16
Displaying Spanning Tree Port Parameters ...........................................................................................................................................4-17
Displaying the Bridge Forwarding Table ................................................................................................................................................4-18
Upgrading Firmware ......................................................................................................................................................................................4-19
Backing Up Your Current Configurations ...................................................................................................................................... 4-20
Configuring for the Download Process .......................................................................................................................................... 4-21
Downloading the Firmware ................................................................................................................................................................ 4-22
Restoring Your Configurations .......................................................................................................................................................... 4-24
In Case of Problems With the Software Upgrade ........................................................................................................................4-25
Displaying RIP Support Information ......................................................................................................................................................... 4-26
Modifying the IP RIP Mode ...........................................................................................................................................................................4-27
Configuring Static Routes ............................................................................................................................................................................4-28
Deleting Static Routes ...........................................................................................................................................................................4-28
Removing an IP Default Gateway ..............................................................................................................................................................4-29
Configuring SNMP Parameters ................................................................................................................................................................... 4-30
Displaying SNMP Parameters ......................................................................................................................................................................4-31
iv
Page 5

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Chapter 5
Command Reference ..........................................................................................................................................5-1
ATM and FDDI Support ....................................................................................................................................................................................5-5
Command Edit Mode ........................................................................................................................................................................................5-6
Edit Mode Commands .............................................................................................................................................................................5-6
Command Descriptions ..........................................................................................................................................................................5-6
ALIAS Command ................................................................................................................................................................................................5-7
ALLCMD Command ...........................................................................................................................................................................................5-8
ATM Command ...................................................................................................................................................................................................5-9
BOOT Command ..............................................................................................................................................................................................5-10
CONSOLE Command ......................................................................................................................................................................................5-12
ELOG Command ...............................................................................................................................................................................................5-14
ETHERNET Command .....................................................................................................................................................................................5-17
EXIT Command .................................................................................................................................................................................................5-24
FILE Command ..................................................................................................................................................................................................5-25
INET Command .................................................................................................................................................................................................5-27
LOOKUP Command .........................................................................................................................................................................................5-30
MODE Command .............................................................................................................................................................................................5-31
PORTSERV Command .....................................................................................................................................................................................5-33
REBOOT Command .........................................................................................................................................................................................5-34
SNMP Command ..............................................................................................................................................................................................5-35
SYSTEM Command ..........................................................................................................................................................................................5-38
TFTP Command ................................................................................................................................................................................................5-39
TOP Command ..................................................................................................................................................................................................5-40
UP Command ....................................................................................................................................................................................................5-41
VBRIDGE Command ........................................................................................................................................................................................5-42
VLAN Command ...............................................................................................................................................................................................5-51
Appendix A
Command Summary ......................................................................................................................................... A-1
Appendix B
RMON Configuration ......................................................................................................................................... B-1
MIB Support .........................................................................................................................................................................................................B-2
SNMP Management Using Castle Rock’s SNMPc“ ..................................................................................................................................B-3
RMON Support ....................................................................................................................................................................................................B-5
Enabling RMON Objects .........................................................................................................................................................................B-5
Disabling RMON Objects ........................................................................................................................................................................B-6
Appendix C
Downloading Software at the [VxWorks] Prompt ........................................................................................ C-1
Firmware Upgrade Using FTP/TFTP ............................................................................................................................................................C-2
Backing Up Your Current Configurations .........................................................................................................................................C-3
Configuring for the TFTP Download Process ..................................................................................................................................C-4
Downloading the Firmware Using FTP/TFTP ..................................................................................................................................C-5
Restoring Your Configurations .............................................................................................................................................................C-9
Firmware Upgrade Using Zmodem ..........................................................................................................................................................C-10
In Case of Problems With the Software Upgrade ................................................................................................................................C-13
Index ............................................................................................................................................................INDEX-1
v
Page 6

Page 7

Preface
This guide includes information about configuring and operating
Allied Telesyn International Corp.’s FORMULA 8200™ 10/100 Mbps
Fast Ethernet Workgroup Switch with any of the following
configurations:
❑
AT-8208 or AT-8216, the FORMULA 8200 switch with either 8
or 16 10/100 Mbps TX ports with firmware version 1.4.3 or later
❑
AT-8208F/SC or AT-8216F/SC, the FORMULA 8200 switch with
either 8 or 16 100 Mbps FX ports with firmware version 1.4.3 or
later
❑
Any of the above switch models with one of the following
uplink cards:
— AT-8202 ATM uplink card
— AT-8203 FDDI uplink card
This guide assumes that a FORMULA 8200 switch has been installed
and is operational. For more information on installing the switch,
refer to the
FORMULA 8200 Installation Guide .
vii
Page 8

Preface
Who Should Use This Guide
This guide is designed for you, the network administrator, to help
you configure, operate, and manage the FORMULA 8200 switch as a
device on your local area network. It assumes that you understand
some of the basic concepts of local area networks, including:
❑
Ethernet MAC addresses
❑
Collision domains
❑
Broadcast domains
❑
CSMA/CD
❑
Differences between repeaters, bridges, and routers
❑
Spanning Tree Protocol
❑
Virtual LANs (VLANs)
❑
TCP/IP and associated protocols and applications
For detailed information about any of the above topics, see
Recommended Reading at the end of this Preface.
If you have any uplink card installed, you must be familiar with
the ATM or FDDI technology.
viii
Page 9

How This Guide Is Organized
This guide consists of the following sections:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Chapter 1,
common features that apply to all switch models.
Chapter 2,
information on attaching a console port and accessing the command
line interface (CLI) to enter basic configuration parameters.
Chapter 3,
procedures to configure the FORMULA 8200.
Chapter 4,
provides procedures to monitor the FORMULA 8200 and perform
routine management tasks using the CLI.
Chapter 5,
commands and provides examples on where to use these
commands.
Appendix A,
FORMULA 8200 commands in alphabetical order, their
corresponding aliases, and the purpose of each command.
Overview , provides a product overview and a list of
Accessing the Command Line Interface (CLI) , provides
Configuring the FORMULA 8200 Switch , provides
Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch ,
Command Reference , includes a description of all the
Command Summary , is a table that lists all
Appendix B,
configure your SNMP management station to manage and monitor
the FORMULA 8200 switch.
Appendix C,
provides the alternative procedures to upgrade switch software if
the switch CLI is not accessible.
The Index at the back of this guide is according to subject matter.
For a definition of terms commonly used in Allied Telesyn technical
publications, refer to the website glossary at
www.alliedtelesyn.com
RMON Configuration , provides a sample procedure to
Downloading Software at the [VxWorks] Prompt ,
.
ix
Page 10

Preface
Document Conventions Used in This Guide
This section describes the typographic conventions used in this
guide.
Note
The command line interface (CLI) portion of the FORMULA 8200 is not
case sensitive; however, this manual shows commands in uppercase
letters. You may type your commands in either uppercase or
lowercase, as shown in some of the examples.
Example Meaning
Local IP configuration
The
VLAN/CONFIG/CREATE
to configure a VLAN.
Enter
BRIDGE <VLAN#>
Press the [Enter] key to execute a command.
Read Chapter 6 in the User Guide . Book titles are shown in italic type.
.
:
command is used
To install the switch on a flat surface:
System prompts and messages are shown in
COURIER
Commands or other input the user must supply are
shown in
Text in angle brackets after a command indicates userdefined input must follow the command. (Example:
BRIDGE 2
Keys named in text are shown enclosed in square
brackets. (
key and the Return key.)
The Procedure icon denotes a series of numbered
steps the user must perform. Each step may be
followed by text that explains the result of the user
action.
font..
BOLDFACE
)
[Enter]
is used to denote both the
capital letters.
1. User action
2. User action
Enter
This guide uses the following symbols to highlight special messages:
Note
A note includes information of importance or special interest.
Caution
A caution includes information that will help you prevent equipment
failure or loss of data .
x
Page 11

Related Documents
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Warning
A warning includes information that will help you prevent injury or
equipment damage .
Refer to the following related publications from Allied Telesyn for
additional information on the FORMULA 8200 switch:
FORMULA 8200 Installation Guide for information on how
❑
to install and set up the switch
Note
There are two versions of the FORMULA 8200 Installation Guide :
one for 10Bse-T/100Base-TX ports and one for 100Base-FX ports.
AT-8201 Installation Guide for information on how to install
❑
the eight-port 10/100Base-TX expansion module
AT-8201 F/SC Installation Guide for information on how to
❑
install the eight-port 100Base-FX fiber expansion module
AT-8202 and AT-8203 ATM and FDDI Uplink Installation
❑
Guide
for information on how to install the ATM or FDDI
uplink card and the accelerator card
AT-8202 ATM Uplink User’s Guide for information about
❑
configuring and using the ATM uplink card
AT-8203 FDDI Uplink User’s Guide for information about
❑
configuring and using the FDDI uplink card
Release Notes that may be included in the package or
❑
distributed from Allied Telesyn’s website for the latest
information about the product
These guides are available in PDF format from Allied Telesyn’s
website at
www.alliedtelesyn.com/manuals.htm .
xi
Page 12

Preface
Recommended Reading
The following documents provide additional information on the
topics described in this manual:
Interconnections: Bridges and Routers , Radia Perlman (1992).
Troubleshooting T CP/IP , Mark Miller (1992).
Internetworking with TCP/IP , Douglas Comer (1991).
IEEE 802.1D (Spanning Tree Protocol) (1990).
IEEE 802.3 (CSMA/CD) (1996).
IEEE 802.3u (Supplement to 802.3 100BT Operation) (1995).
RFC 791, Internet Protocol , J. Postel (1981).
RFC 951, Bootstrap Protocol , W. Croft, J Gilmore (1985).
RFC 1023, HEMS monitoring and control language , C. Partridge, G.
Trewitt (1987).
RFC 1024, HEMS variable definitions , C. Partridge, G. Trewitt (1987).
RFC 1058, Routing Information Protocol, C. Hedrick (1988).
RFC 1122, Requirements for Internet hosts — application and
support, R. Braden (1989).
RFC 1123, Requirements for Internet hosts — communication layers,
R. Braden (1989).
RFC 1157, A Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP), J. Case,
M. Fedor, K. Schoffstall, and J. Davin (1990).
RFC 1350, The TFTP Protocol (Revision 2), K.R. Sollins (1992).
xii
Page 13

Allied Telesyn’s Software Library
Allied T elesyn’ s website, www.alliedtelesyn.com, maintains a
Software Library that contains Allied Telesyn’s adapter drivers,
system and management utilities, software updates, and ASCII
documents.
You may also access the Software Library from Allied Telesyn’s FTP
server. Enter the following information to access the FTP server:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Address:
Login: anonymous [lowercase letters]
Password: your e-mail address [requested by the server at
login]
ftp.alliedtelesyn.com [lowercase letters]
xiii
Page 14

Page 15
Chapter 1
Overview
The FORMULA 8200™ switch provides a cost effective solution for
improving Ethernet network performance by reducing
communications traffic congestion. It is a high-speed, multi-protocol
workgroup F ast Ethernet switch that can be configured with up t o 16
Fast Ethernet (10/100 Mbps) LAN switch ports.
The FORMULA 8200 offers virtual LAN (VLAN) support, including
virtual routing and Spanning Tree Protocol, as well as network
management using Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
Product Features
The FORMULA 8200 includes the following hardware and software
product features:
❑ Eight 10/100 Mbps Fast Ethernet ports (IEEE 802.3u)
❑ Optional 8-port 10/100 Mbps expansion module
❑ Virtual LAN (VLAN) support for up to 16 port-based VLANs
❑ IP Routing to provide communication between VLANs
❑ Loop detection using Spanning Tree Protocol (IEEE 802.1d)
❑ Front panel LEDs that provide operating status and a Reset
button for front panel control of switch
❑ RS232C console port interface for local switch management
and Telnet support for remote switch management
❑ Rack mount or table mount capabilities (hardware for either
option included)
1-1
Page 16

Overview
❑
Support for multiple hardware configurations and provides
support for the following port configurations:
— 10Base-T/100Base-TX expansion ports
— 100Base-FX expansion ports
— OC3 ATM uplink card (optional)
— FDDI uplink card (optional)
❑ Field-upgradeable expansion modules for maximum
customization
❑ Autonegotiation on all 10/100 Mbps TX ports
❑ Full or half duplex on all 10/100 Mbps TX ports and 100 Mbps
full duplex on FX ports
❑ Port mirroring to allow monitoring of one’s port activities from
any port
❑ Flow control to autosense buffer limits on the transmit port
❑ Support for RMON Groups 1, 2, 3, and 9
❑ Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) agent for
Management Information Bases (MIB) II and private enterprise
MIBs
❑ TFTP, FTP, and ZModem support for software upgrades and
backup
For information about available configurations, see the
FORMULA 8200 Installation Guide.
1-2
Page 17

Chapter 2
Accessing the Command Line Interface (CLI)
This chapter describes how to access the CLI once you have
completed the installation, as described in the FORMULA 8200
Installation Guide. The information provided here includes the
following:
❑ Connecting the console
❑ Logging in (via preinstalled software)
❑ Entering commands
❑ Entering basic configuration parameters
❑ Accessing via Telnet
2-1
Page 18

Connecting the Console
Connecting the Console
The RS232C console port permits you to connect a terminal or local
workstation for system management. The console terminal interface
is a DB9 (DCE) male connection.
The console is required to confirm that the switch is configured and
operating correctly after installation.
Connect a VT-100 terminal or equivalent to the FORMULA 8200 using
a 9-pin null-modem RS232 serial cable. You can also use a DOS®,
Windows®, or UNIX® workstation running in terminal emulation
mode. The cable connection to the switch must have a female DB9
connector.
Note
Terminal
Configuration
Viewing
Terminal
Configuration
Using the CLI
To configure the terminal:
Use the following parameters:
❑ Baud rate: 9600
❑ Data bits: 8
❑ Stop bits: 1
❑ Parity: none
❑ Number of lines per page: 25
Once you have completed the installation, you can then use the
following command to show the console parameters:
CONSOLE/SHOW - show console parameters
For a complete description and additional information about this
and other commands, see Chapter 5, Command Reference
.
2-2
Page 19
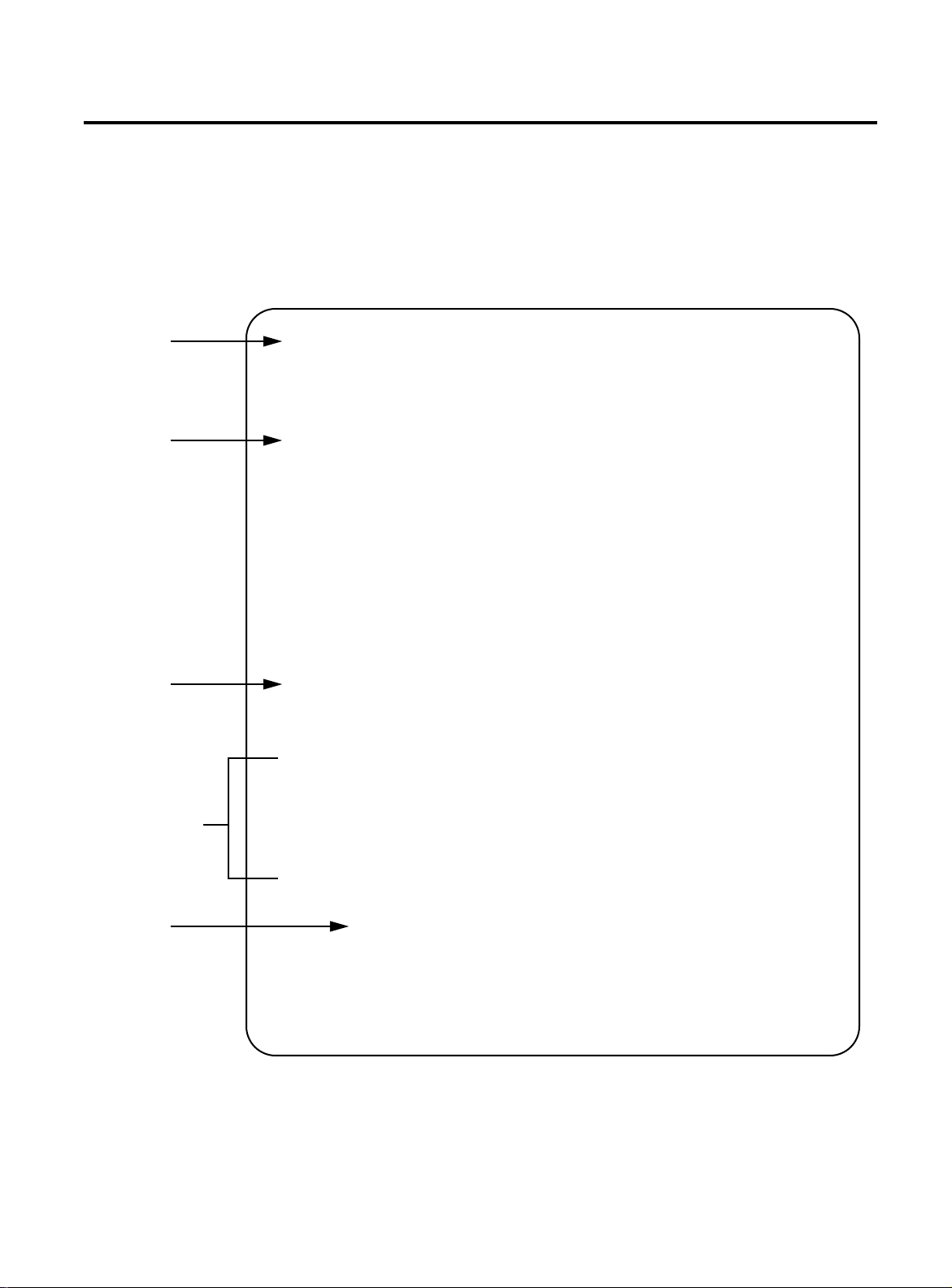
Observing the Power-On Self Test
When the FORMULA 8200 is powered on, it automatically runs a
power-on self-test (POST) to verify that all components are
functioning normally.
As POST verifies the basic operation of the switch, it displays a series
of messages on the console. A similar screen display appears:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Post
begins
Component
tests
Firmware
loads
System
information
Boot POST in progress...
PROM version: 1.0.7
Sizing DRAM (value displayed is bank size or error code)...
DRAM now configured into a contiguous block:
Address: ............. 0xa0000000 - 0xa07ffffc
Running DRAM test...
Initializing 4650 icache and dcache...
Initializing PIG chip...
Initializing PMIU chips...
.
.
Boot POST complete, passing control to firmware...
Loading /flash/firmware...Starting at 0x80010000...
Firmware version 1.4.3
Date= 1/26/98 time= 11:34:27
Restore configuration for system
IP address = 0.0.0.0
Number of ports = 16
Configuration changed
srm_init success
Vendor
information
Allied Telesyn International
Copyright@ 1997 Allied Telesyn All rights reserved.
Switch Init Success
Login:
2-3
Page 20
Observing the Power-On Self Test
If any error messages are displayed, report them to the
Allied Telesyn’s Technical Support (see Allied Telesyn’s website at
www.alliedtelesyn.com) or your reseller. The rest of the messages
are for your information only; no action is required.
Observing the
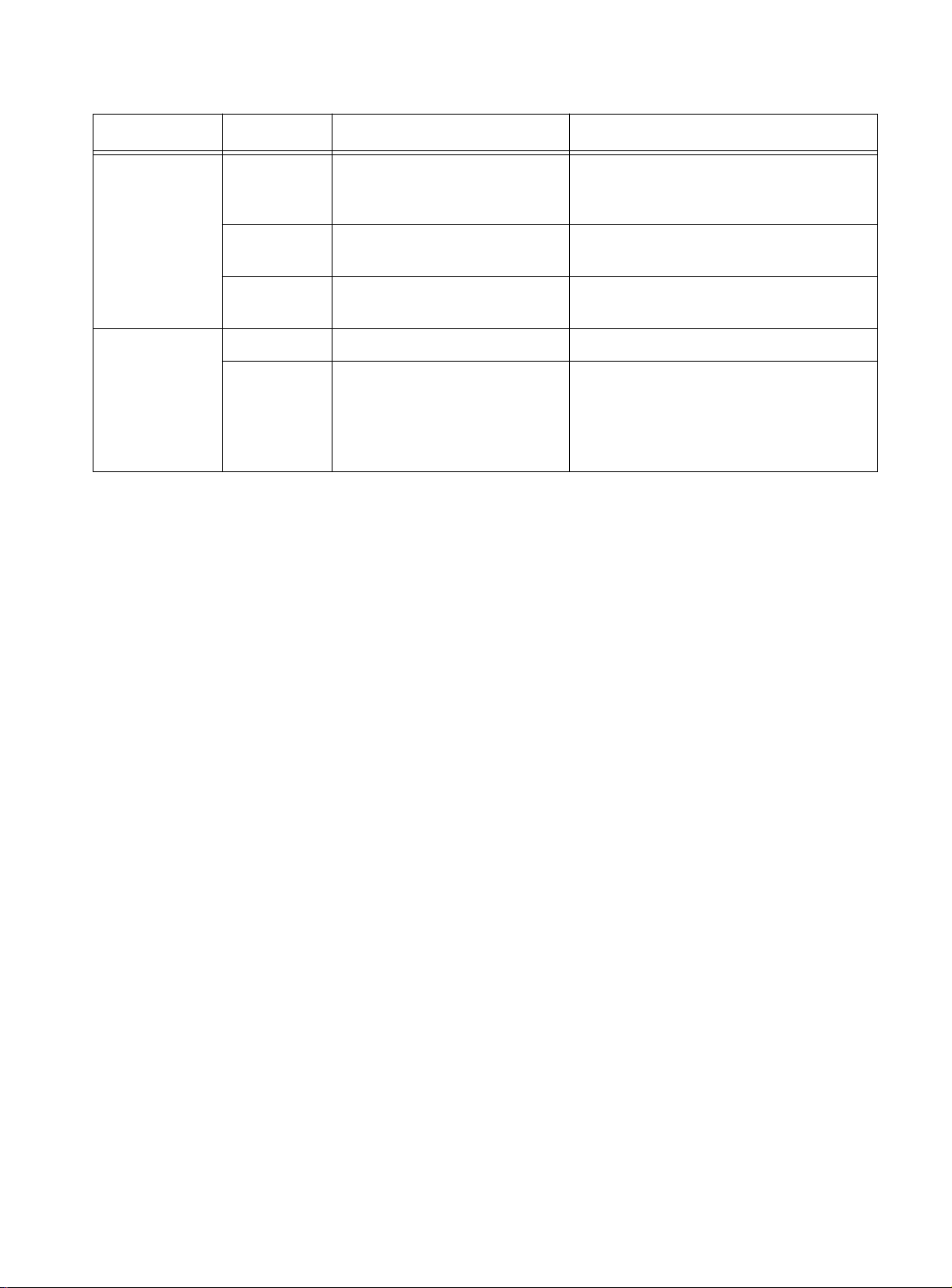
LEDs
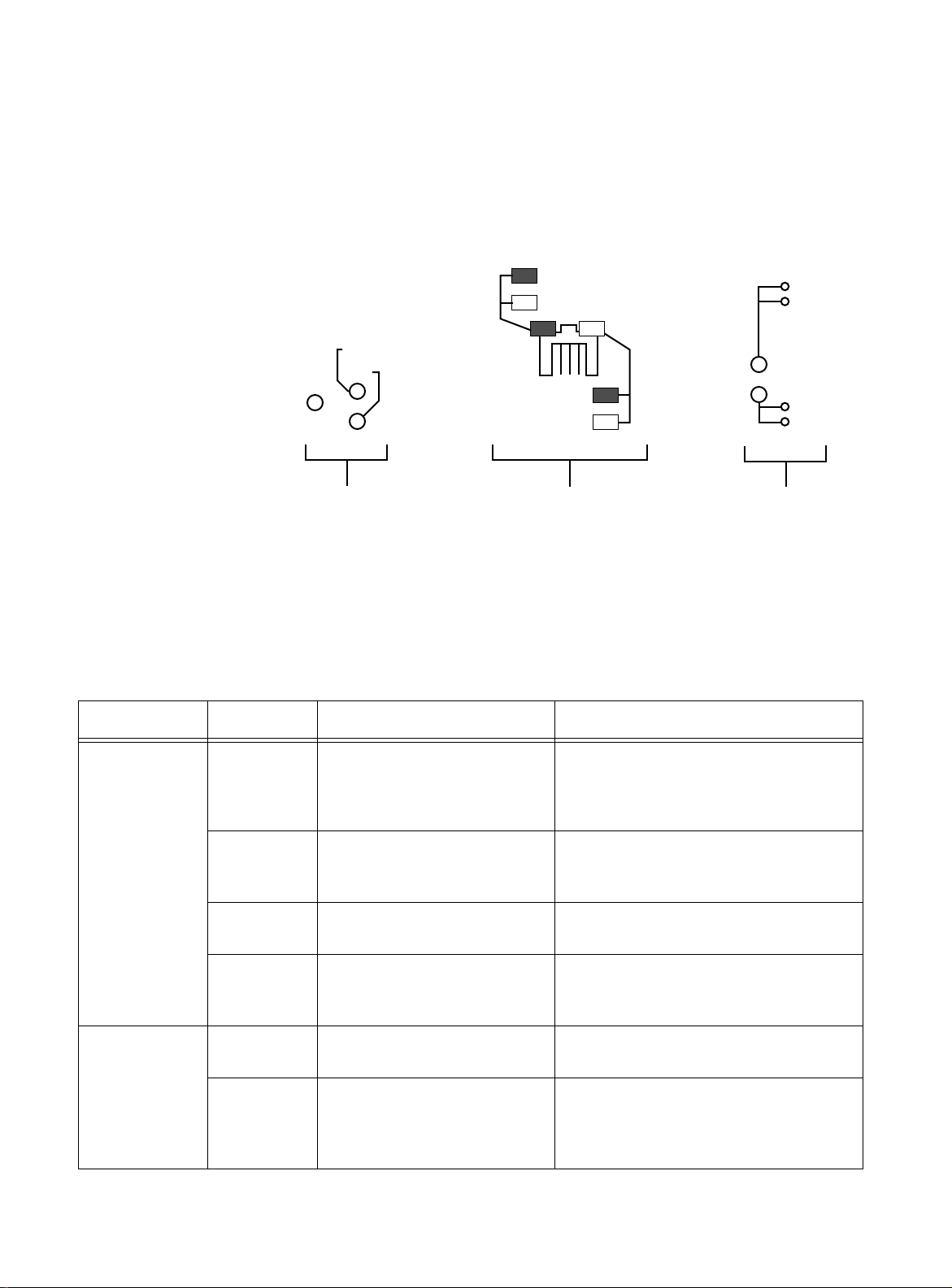
You can verify proper operation by observing the LEDs. In Figure 2-1,
three LEDs are shown as examples.
Link
DIAG
Status
Power
Reset
Activity
Collision
Status and Power LEDs TX LEDs FX LEDs
Figure 2-1
FORMULA 8200 LEDs
Activity
Collision
Link
DIAG
T able 2-1 pro vides information about what the LEDs mean in various
states.
Table 2-1 FORMULA 8200 LED States
LED LED Color Status Action Required
System
Status
Indicator
Flashing
green
Normal operation None. LED should flash every second.
This
indicates that the switch is functioning
normally.
Solid green You probably cannot log in to
Reboot the switch.
the switch. This indicates the
switch is locked up.
Flashing
amber
Solid amber Switch is still functioning, but
Switch encountered
abnormal condition
with problems; or boot is in
Reboot the switch.
Determine if the switch is in the boot
process; otherwise, reboot.
process.
Power
Indicator
Solid green Normal operation when
power is applied.
None
Unlit There is no power to switch. Check the power plug and the state of
the on/off switch in the back of the unit.
If On, turn it off and reboot. If LED
remains unlit, replace the switch.
2-4
Page 21
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Table 2-1 FORMULA 8200 LED States (Continued)
LED LED Color Status Action Required
Port LED —
Activity/
Collision
(green/amber)
Port LED —
Link/Diag
(green)
Flashing or
solid green
Unlit No traffic None. This state does not indicate any
Flashing
amber
Solid green Good cable link status None
Off or
flashing
Normal operation when
port receives or transmits
traffic.
Collisions in half-duplex mode
Note: applies to TX ports only.
No link if off; a link problem if
flashing
None
problems on the port.
None. Intermittent collisions are normal.
Try the following: Verify cable, verify
port speed, verify the state of the
autonegotiation to ensure the port
speeds match (ETHERNET/SHOW/
PORT).
2-5
Page 22

Logging In
Logging In
The FORMULA 8200 switch ships from the factory with pre-installed
software. Once the hardware has been installed, the switch displays
the login prompt.
To begin using the CLI:
1. Log in by entering admin in lowercase letters, as follows:
Login: admin
The FORMULA 8200 displays the password prompt.
2. Enter
switch, all in lowercase, as follows:
Password: switch
Note
When you type your password, the text does not appear on the
screen.
After you have entered the password, the FORMULA 8200 command
line interface (CLI) prompt is displayed:
Login: admin
Password: ******
/>
For security reasons, change the admin password as soon as
possible. To do so, use the
SYSTEM/CONFIG/ADMINPW command
(explained in detail in Chapter 5).
2-6
Note
If you forget your administrator password, contact Allied Telesyn’s
Technical Support. Visit Allied Telesyn’s website at
www.alliedtelesyn.com for contact information.
Use the
EXIT command to log out from the CLI session.
Page 23

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Logging In
Without a
Password
The FORMULA 8200 also provides you a “user login” feature. No
password is required. It permits you to use commands to view the
operating status and configuration, but you cannot configure the
switch.
To log in without a password:
Enter the following at the login prompt in lowercase letters
and press [Enter] at the password prompt:
Login: user
Password: [ENTER]
Logged in as USER (not ADMIN)
/>
2-7
Page 24
Entering Commands
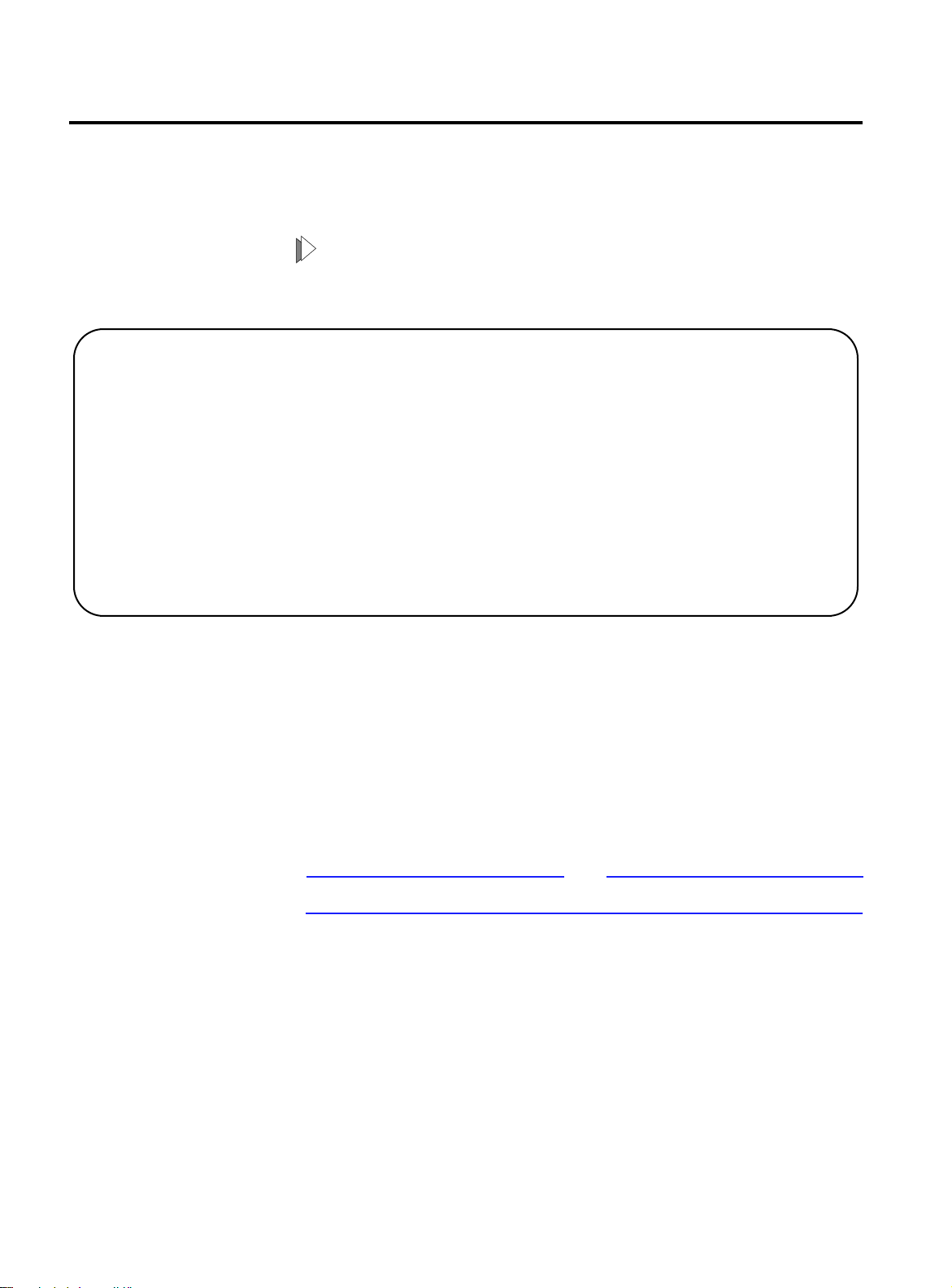
Entering Commands
The FORMULA 8200 command line interface (CLI) is a hierarchical
menu-driven interface with menus, submenus, and commands
arranged in a tree structure.
? ALIAS ALLCMD
[ATM] [BOOT] [CONSOLE]
[ELOG] [ETHERNET] EXIT
[FDDI] [FILE] [INET]
LOOKUP [MODE] [PORTSERV]
REBOOT [SNMP] [SYSTEM]
[TFTP] TOP UP
[VBRIDGE] [VLAN] [TRACE]
To access the main command menu:
Enter ? at the FORMULA 8200 prompt, as shown below.
== MAIN MENU ==
Use of Square
Brackets [ ]
Use of Angle
Brackets <>
/ >
Enter commands by typing selections from each successive menu;
then press [Enter]. You can also enter the entire command at the
prompt or you can use an alias; both methods are described in this
chapter in Command Formats.
Some commands in the main menu have square brackets around
them to indicate that the command requires additional parameters.
When you enter one of these commands, a submenu appears that
lists the available parameters.
Note
Do not enter the brackets when you enter the command.
This manual sometimes directs you to enter a command with a
variable that is specific to your environment, such as IP addresses.
The variables you must supply are enclosed in angle brackets.
For example, to configure a gateway address, enter:
2-8
/INET/CONFIG/ROUTE/DEFAULT <default route or
gateway IP address>
where <default route or gateway address> can be in the format,
123.123.123.123.
Page 25

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Note
Do not enter the brackets when you enter the command.
The LOOKUP
Command
Command
Formats
Entering LOOKUP is a way to get a list of commands, their
corresponding aliases, and descriptions.
The software allows you to enter commands in three ways:
❑ By entering the complete command
❑ By using a shortcut
❑ By using an alias
Separating Command Words
When you enter any command, you may separate the command
words with a slash (/). For example:
/FDDI/SHOW/SMT
You may also use a space to separate the command words.
Shortcuts
Use a shortcut by typing the first few characters needed to
distinguish the command from others that start with the same
letters, such as:
/FD/SH/SMT
This works unless your shortened version is ambiguous, which
causes an error message to appear.
Aliases
An alias is an abbreviated command that can be accessed from
anywhere in the command line interface. For example, the following
alias is equivalent to the
fsmt
FDDI/SHOW/SMT command:
Aliases are listed in Appendix A, and are also listed in Chapter 5 with
each command description.
2-9
Page 26
Entering Commands
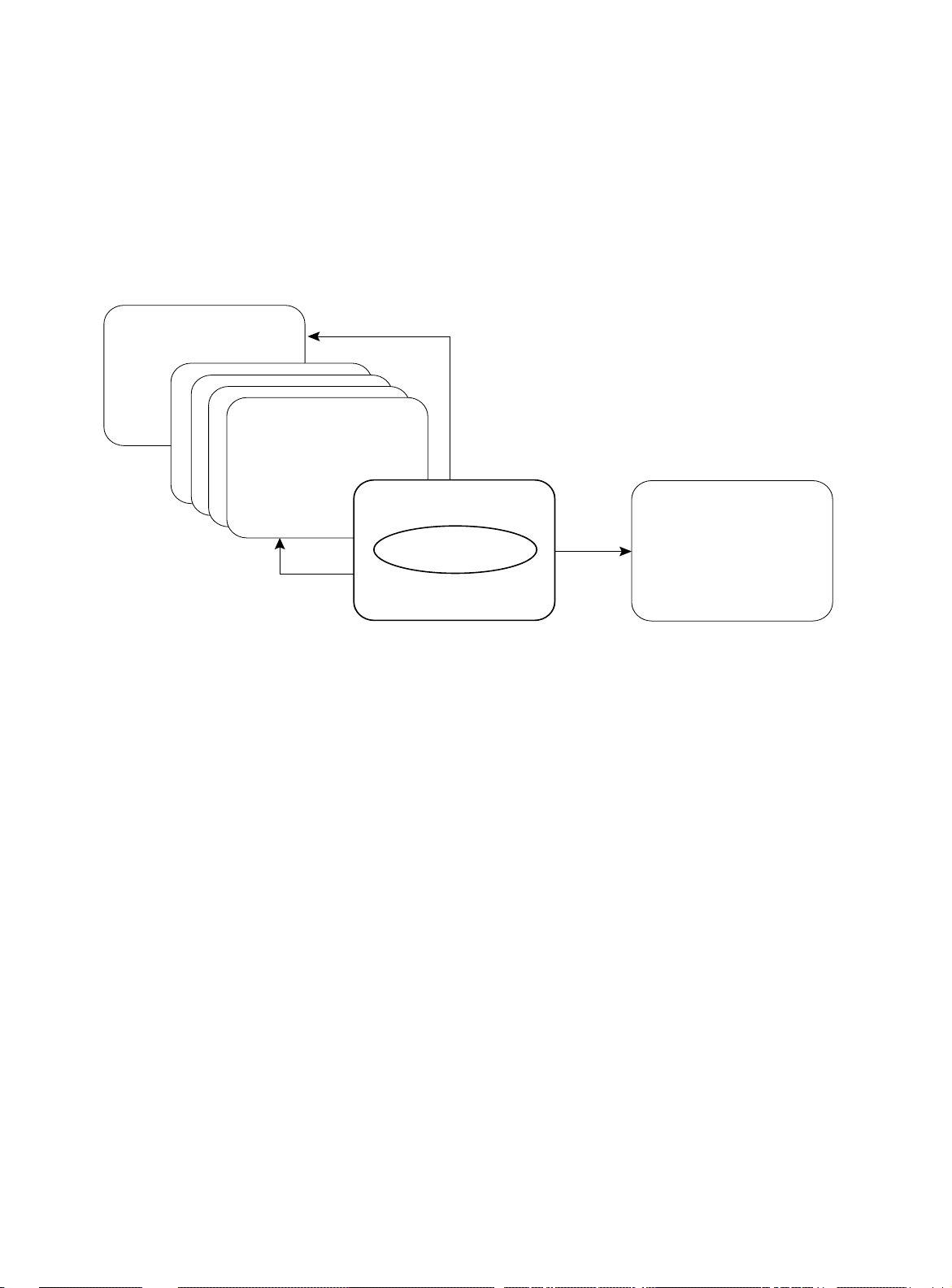
Moving
Through the
Menus
== Main Menu ==
The following commands allow you to navigate the menu structure
(Figure 2-2):
❑ UP returns to the previous menu.
❑ TOP returns to the main menu.
❑ ? displays the commands that are available at your current
level
TOP
Previous
Menu
/ >
UP
You Are Here
?
Available
Commands
Figure 2-2
Navigating the Menus
For a complete list of commands, see Chapter 5.
2-10
Page 27
Configuring IP Information
1. Use the BOOT/IP/CONFIG and BOOT/IP/EEPROM commands
to configure Internet protocol information for the switch,
including:
❑ IP address
❑ Local host name
❑ Default gateway
❑ Subnet mask
The IP command displays the local IP configuration
parameters. After each parameter is displayed, the system
prompts you for any changes. If you don’t want to change any
parameter, press [Enter] at each prompt.
/BOOT/IP/CONFIG
Local IP configuration:
IP address (149.35.101.31) :
Local Host name (SWITCH#1) :
Default gateway (149.35.27.1) :
Net mask (255.255.255.0) :
OK to write config to flash (y/n) ? Y
Writing new configuration to flash ...
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
/BOOT/IP/EEPROM
EEPROM IP:
IP address (149.35.27.1) :
OK to write config to EEPROM (y/n) ? Y
2. Enter the default gateway address again using the
CONFIG/ROUTE/DEFAULT command:
INET/CONFIG/ROUTE/DEFAULT
gateway address ( ) : 149.35.27.1
3. Confirm your entry with the following command:
INET/SHOW/ROUTE
A similar table displays on the screen:
INET/
2-11
Page 28

Configuring IP Information
/INET/SHOW >route
ROUTE NET TABLE:
Address
===============
0.0.0.0 149.35.27.1 1 1 DEFAULT
149.35.27.0 149.35.27.30 1 1 VLAN INTERFACE
ROUTE HOST TABLE:
Address
===============
127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 1 LOOPBACK
Gateway
===============
Gateway
===============
Metric
=======
Metric
=======
VLAN
=======
VLAN
=======
Type
=======
Type
=======
2-12
Page 29

Verifying Firmware Information
To ensure that you have the latest information about product
features and fixes, verify that the version of any release notes you
have received match the version of the firmware installed on the
unit.
You also need to verify that the Internet protocol information you
entered is correct.
To display firmware information:
Use the SYSTEM/SHOW command.
This displays your overall system configuration. For more
information about using this command, see Displaying the
System Configuration in Chapter 4; also see the SYSTEM
command in Chapter 5.
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Updating Your Ethernet Ports
Updating
System
Information
Before you connect the FORMULA 8200 to your network, use the
ETHERNET/SHOW/PORT command to display, and if necessary, the
ETHERNET/CONFIG/PORT command to modify your port
configuration. For more details, see the
Chapter 5.
Use the SYSTEM/CONFIG command to update your system
information, including date, time, and admin password. It is
especially important to ensure the security of your configuration by
updating the admin password as soon as possible.
ETHERNET command in
2-13
Page 30

Using Telnet to Access the Switch
Using Telnet to Access the Switch
In addition to local console access, you can access the switch from a
remote location by using Telnet to make a TCP/IP connection.
The Telnet command syntax depends on the type of terminal or TCP/
IP software you are using. Check the appropriate manual for
information about connecting to a host using Telnet. Telnet requires
the FORMULA 8200’s IP address information has been configured.
To use Telnet to access a remote switch
(example):
The following steps initiate a Telnet session to the switch at IP
address 123.126.22.77.
1. Enter the Telnet command and the IP address at the system
prompt:
telnet 123.126.22.77
2. Enter admin at the login prompt.
Login:
admin
3. Enter the password at the password prompt. (If you have not yet
changed the default password, enter
switch.)
The system prompt now appears, giving you full access to the
command line interface.
/ >
4. Use the
EXIT command to log out from the CLI session.
Note
The EXIT command does not end the Telnet session. On certain
systems, pressing the CTRL-6, CTRL-], and [Enter] keys in sequence
disconnects the Telnet session. Refer to your current Telnet manual
for the correct command to disconnect the Telnet session.
2-14
Page 31

Resetting and Rebooting the Switch
You may occasionally need to reset the FORMULA 8200. You can do
this in one of three ways:
❑ The Reset button on the front panel permits you to perform a
“hardware reset,” and does not require you to use the
command line interface.
❑ The REBOOT command permits you to reset the switch via
the command line interface, either from the local console, or
from a remote location via Telnet. The current Telnet session is
disconnected by this command.
❑ The On/Off switch in the rear panel recycles the power to the
switch.
Either method initializes the hardware, loads the system software
from the flash, restores the switch to the current (saved)
configuration settings, and restarts the switch. Upon restart, the
POST and other diagnostic information appear on the local console,
followed by the login and password prompts.
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Where to Go Next
Go to Chapter 3, Configuring the FORMULA 8200 Switch, for
information about the default switch configurations, to reconfigure
the switch for your particular application, or to create VLANs.
2-15
Page 32

Page 33

Chapter 3
Configuring the FORMULA 8200
Switch
This chapter describes:
❑ System default configurations
❑ An overview of virtual LANs (VLANs) and related parameters,
including Spanning Tree (virtual bridges) and virtual routers,
and how to configure them
Default Configurations
The FORMULA 8200 is shipped from the factory with the following
default configurations:
❑ Console speed is 9600
❑ Login is admin and password is switch
❑ Autonegotiation is ON (enabled) for 10/100 Mbps TX ports
❑ Ethernet statistics are disabled
❑ All ports belong to the default VLAN 1
❑ Spanning Tree is enabled
❑ RIP (virtual routing) is silent
These settings provide for switching a single broadcast domain. To
display and configure port settings, refer to Chapter 4 beginning on
page 4-5.
3-1
Page 34

Optimizing Functionality for Your Application
Optimizing Functionality for Your Application
The FORMULA 8200, unlike shared media switching hubs, allows you
to divide your LAN into smaller segments. This incr eases and uses full
LAN bandwidth for each segment. By providing high end devices
such as workstations, servers, and routers their own dedicated
connections to the switch, you can significantly increase throughput
and decrease latency.
In addition to creating one or more VLANs to reduce broadcast
traffic, you can also customize the configuration to meet your
specific needs. Use the information in the remainder of this chapter;
you can also review the command set in Chapter 5 for more specific
information.
Virtual LANs
A Virtual LAN (VLAN) is a logical group of LANs or individual devices,
established without regard to their physical location on the network.
You can group any collection of ports on one or more
FORMULA 8200 switches into a VLAN.
Since you can connect either a LAN or a device to a port in the
FORMULA 8200, any group of LANs or individual devices connected
to the switch can be connected together in a VLAN.
The LAN segments that comprise a VLAN can be distributed among
multiple switches that are interconnected by a backbone network.
This grouping of LAN segments into VLANs reduces the amount of
work required when moving an end station from one LAN segment
to another.
VLANs also maximize the efficient use of the bandwidth on any given
LAN segment, since packets are forwarded only between segments
as required. The separation of segments into VLANs also provides
security, since data from a workgroup on one VLAN will not be seen
on the VLANs for other workgroups. VLANs also create smaller
broadcast domains, which reduce broadcast traffic across the
network.
3-2
Note
To communicate between VLANs, the FORMULA 8200 must be
configured to enable RIP for IP routing. If additional protocols are
required, a connection on each VLAN must go to an external router.
Page 35

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
FORMULA 8200
Implementation
of VLANs
The FORMULA 8200 consists of up to 16 physical network interfaces.
In its simplest configuration, all of these network interfaces are
grouped together into a single bridged virtual LAN (VLAN). Traffic
flowing between end stations on separate LAN segments is switched
by a virtual bridge.
You may configure up to 16 VLANs.
Each FORMULA 8200 has a default VLAN, called VLAN 1 (Figure 3-1).
The default VLAN cannot be remo ved . It contains all virtual interfaces
not assigned to other VLANs. Initially, all interfaces are members of
the default VLAN.
VLAN1 (Default VLAN)
Switch 1
Switch 2
Switch 3
Figure 3-1: Default VLAN 1
You can, however, create up to 16 VLANs on each switch on a perport basis. This feature allows you to move network interfaces from
the default VLAN to other VLANs (see Figure 3-2). Traffic can then
flow between VLANs by using either an external router or by using
the virtual router service provided internally by the FORMULA 8200.
3-3
Page 36

Virtual LANs
VLAN1
Switch 1
VLAN4
Switch 2
VLAN5
Switch 3
Figure 3-2: Multiple VLANs
VLAN2
VLAN3
VLAN6
FORMULA 8200 VLANs are port-based. A port cannot be part of more
than one VLAN. That is, if your FORMULA 8200 is configured for 8
ports, the switch can support up to 8 VLANs; if your switch includes
an 8-port expansion module, it supports up to 16 VLANs.
Use the
VLAN/SHOW/VPORT command to see the virtual port
information. Refer to Chapter 5 for details on the command.
Each VLAN represents one IP subnet. Unlike a traditional router,
where each interface represents a different subnet, FORMULA 8200
VLAN switching allows multiple interfaces to share an IP subnet. If
you move an end station from one LAN segment to another within
the same VLAN, whether it is a local segment or a remote one, there
is no need to reconfigure its IP address.
3-4
Page 37

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Virtual Bridges,
Virtual
Interfaces,
Virtual Routers
Each VLAN has a virtual bridge that maintains the locations of the
end stations on each segment and controls the switching hardware.
Each of the interfaces on a virtual bridge is called a
virtual interface.
Each VLAN is identified by a number. These numbers are global to all
FORMULA 8200 switches that are connected by a backbone network.
Traffic can be exchanged over a backbone network in order to allow
a VLAN to have segments that are distributed among multiple
FORMULA 8200 switches. Traffic can be exchanged between VLANs
by either internal or external routing.
Use the
VLAN/SHOW/VLAN command to see the virtual VLAN
information. Refer to Chapter 5 for details on the command.
An optional virtual router interface can be configured to forward
traffic between VLANs by using the
VLAN/CONFIG command; see
Configuring a Virtual LAN (VLAN) later in this chapter.
Use the
VLAN/SHOW/VROUTER command to see the virtual router
information. Refer to Chapter 5 for details on the command.
To access the FORMULA 8200 management applications remotely
via TCP/IP, the IP interface must be enabled on at least one VLAN
(usually VLAN 1). The management applications may then be
accessed from a station that has access to one of the LAN segments
comprising that VLAN. If the interface over which management
functions are taking place is disabled, it is possible to lose contact
with the FORMULA 8200. In this case, you must use the console port
to reestablish remote TCP/IP management capabilities.
Each VLAN has an associated virtual bridge. A distributed VLAN has
one virtual bridge on each FORMULA 8200 that has interfaces
participating in the VLAN. The virtual bridge implements the IEEE
802.1-D Spanning Tree Algorithm and Protocol, described in the next
section.
Use the
information, and
VLAN/SHOW/VPORT command to view the virtual port
VLAN/SHOW/VSTATS command to view the
virtual port statistics.
3-5
Page 38

Virtual LANs
Spanning Tree Spanning Tree is a configuration algorithm and protocol that ensures
that no data loops exist within a single broadcast domain. For
example, Figure 3-3 shows bridges 1 and 2 in a loop; in this
configuration without Spanning Tree, the network is unusable.
VLAN 1
forwarding
forwarding
Bridge 1
forwarding
data looping
forwarding
Bridge 3
forwarding
Bridge 2
forwarding
VLAN 2
VLAN 3
3011
Figure 3-3: Data Looping
When Spanning Tree is implemented, redundant bridge ports are
blocked and looping is eliminated, as shown in Figure 3-4.
VLAN 1
Bridge 1
Bridge 2
blocking
not forwarding
VLAN 2
3-6
Bridge 3
VLAN 3
3012
Figure 3-4: Spanning Tree Eliminating Data Looping
By blocking the port at Bridge 2, data can pass to all three segments.
In this example, either Bridge 1 or Bridge 3 becomes the “root”
bridge, depending on priority or MAC address, and the remaining
bridge then becomes a “standb y” bridge , ready to function if a failure
should occur in the Bridge 1.
Page 39

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
In addition to preventing looping, Spanning Tree provides the
following functions:
❑ Automatic reconfiguring of the topology in the event of a
failure or the addition of a bridge or a bridged port
❑ Topology stability, regardless of the size of the bridged VLAN
❑ Configuration management, by displaying statistics and user-
specified bridge and port priorities, parameters, and timers
Spanning Tree performs the above functions by exchanging BPDUs
(Bridge Protocol Data Units) packets between bridges. When the
topology changes, the time it takes for Spanning Tree to stabilize
depends on the size of the bridged network and several userconfigurable parameters.
Spanning T r ee Protoc ol functions by putting its ports in the following
modes or states:
Blocking State - In this state, ports do not forward packets
and do not learn addresses. The ports are in standby mode
until a topology change occurs.
Listening State - In this state, ports do not forward packets
and do not learn addresses.
Learning State - In this state, ports do not forward packets in
either direction, but they learn station addresses.
Forwarding State - In this state, ports forward and learn all
packets in either direction.
The listening state and learning state are both temporary states as
the port moves into forwarding state.
Use the
VBRIDGE/SHOW/BRIDGE<VLAN#> command to view the
current configuration settings.
To enable and configure Spanning Tree, use the
BRIDGE<VLAN#> command, or refer to Configuring a Virtual
VBRIDGE/CONFIG/
Bridge later in this chapter.
3-7
Page 40

Configuring a Virtual LAN (VLAN)
Configuring a Virtual LAN (VLAN)
Use this procedure to assign ports to create a VLAN, including a
virtual router, if desired. By default, all the ports on your
FORMULA 8200 are assigned to VLAN 1. If this configuration suits
your needs, use VLAN 1 to define port assignments. Otherwise,
create more VLANs to establish user groups and manage network
traffic.
As you create additional VLANs, the ports you assign to them are
removed from VLAN 1 (that is, a port cannot be in two VLANs at the
same time).
To configure a VLAN:
The following steps are for cr eating VLAN 2 and for assigning ports 4
and 5 to VLAN 2. If you use these steps to create a VLAN, be sure to
assign your own VLAN name, port numbers, IP address, and so on.
1. From the switch on which the ports reside, enter:
/VLAN/CONFIG
2. Create VLAN 2 by entering:
CREATE 2
3. Answer each prompt as it appears, and then confirm with a y at
the end. Refer to the following example (bolded text represents
user entries):
/VLAN/CONFIG/CREATE 2
VLAN ID : 2
VLAN Description (VLAN 2) : TEST
Initial Ports : 4 5
VLAN enabled (yes) : y
VLAN 2 is successfully created
In the example:
❑ The VLAN Description shown here is TEST, but you can enter
any text up to 32 characters.
3-8
❑ The Initial Ports parameter allows you to specify which ports
are included in the VLAN. This can be modified later by using
one of the following commands:
VLAN/CONFIG/ADDPORT<PORT#> <VLAN#> to add one or
more ports.
Page 41

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
VLAN/CONFIG/MOVPORT
VLAN/CONFIG/DELPORT<PORT#> <VLAN#> to delete one
to move one or more ports.
or more ports.
You can also use the following commands to change VLAN
configuration:
VLAN/CONFIG/MODIFY <VLAN#> to modify a VLAN.
VLAN/CONFIG/REMOVE <VLAN#> to remove a VLAN.
VLAN/CONFIG/ENABLE <VLAN#> to enable the entire
VLAN.
VLAN/CONFIG/DISABLE <VLAN#> to disable the entire
VLAN.
4. Proceed to the next series of prompts to enable the IP interface
and a virtual router. Refer to the following example (bolded text
represents user entries) and to Table 1-1 for an explanation of
each prompt:
VLAN 2 is successfully created
Enable IP interface (yes):
Virtual router of VLAN 2
IP address: 149.35.101.31
IP Subnet Mask (255.255.255.0): [Enter]
IP Broadcast Address: 149.35.101.255
Router Desription (Router for VLAN2): TESTROUTER
IP RIP mode (Active (a), Silent (s), Deaf (d), Inactive (i)) (s): a
A router is sucessfully configured for VLAN 2
....... Updating system/VLAN configuration ............
y
If you enter n at the first prompt, no virtual router is configured
for the VLAN.
Table 1-1: IP Interface and Virtual Router Configuration
Prompt Description
Enable IP
interface
IP address This address must be on a separate subnet from other VLAN IP addresses.
Subnet mask All subnet masks for the VLANs must be the same. The FORMULA 8200 does not
RIP mode Active provides IP routing between VLANs with RIP, sends RIP messages every 30
Enter y to enable virtual routing. Enter n if you have an external router.
support variable length subnet masks.
seconds, and updates routing tables.
Silent does not provide IP routing between VLANs or send IP messages, but updates
routing tables.
Deaf or inactive does not provide routing between VLANs, does not send RIP
messages, and does not update routing tables.
Repeat the steps to create additional VLANs.
3-9
Page 42

Configuring a Virtual LAN (VLAN)
VLAN/SHOW/VLAN 2
VLAN ID:2
VLAN Description:TEST
Router Description:TESTROUTER
Network Address:149.35.101.31
Subnetwork Mask:255.255.255.0
Broadcast Address:149.35.101.255
Admin Status:EMABLE
Operation Status:ACTIVE
Port Members:
To display the configuration of a virtual LAN:
Use the VLAN/SHOW/VLAN <VLAN#> command.
The following is an example configuration display of the
previously-created VLAN 2:
Virtual
Port ID
=======
4 4 2 Bridge 0:60:e8:ff:ff:23 Disable Enable Inactive
5 5 2 Bridge 0:60:e8:ff:ff:24 Forward Enable Active
18 33 2 Router 0:60:e8:ff:ff:50 Enable Active
Physical
Port ID
=======
VLAN
ID
====
Port
Type
====
Port
MAC Address
===========
Bridge
State
======
Admin
Status
======
Operation
Status
==========
3-10
Page 43

Configuring a Virtual Bridge
A virtual bridge is created when you create a VLAN.
To configure bridge parameters for an existing
bridge:
1. Enter the VBRIDGE/CONFIG/BRIDGE <VLAN#> command.
For example, enter:
BRIDGE 1
When you enter this command, a full menu of configurable
choices appears, as shown below:
/VBRIDGE/CONFIG/BRIDGE 1
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Spanning Tree Parameters Modification for VLAN 1:
1) Spanning tree Status is ON for this VLAN, set to OFF? (y/n)
2) New Priority (0..65535) (current value is 32768):
3) New Bridge Hello Time (1..10 secs) (current value is 2):
4) New Bridge Max Age (6..40 secs) (current value is 20):
5) New Bridge Forward Delay (4..30 secs)(current value is 15):
6) New Aging Time (10..1000000 secs) (current value is 300):
Enter selection (modification or 0 to commit, c to cancel) >
2. Enter the desired information by entering the item number with
an equal sign (=) and the value.
3. Enter
0 at the prompt to save changes and exit the menu.
Caution
Do not change any of the values unless you are very familiar with
spanning tree parameters and how they affect the status of your
network. Incorrect settings can lead to serious network problems.
For more detailed information about this command and its
parameters, refer to the
VBRIDGE command in Chapter 5.
3-11
Page 44

Configuring a Virtual Bridge
VBRIDGE/CONFIG/FILTER >add
Adding Static Filter Entry:
VLAN
vlan | port | dom | mac_address | entryId | flags | age
0 7 0 00:00:00:00:00:00 0
1 33 0 00:60:e8:00:34:31 1
To optimize Spanning Tree functionality:
1. Use the VBRIDGE/CONFIG/FILTER command. This command permits you to modify the Static Entry Table by
adding or deleting entries. Creating a static entry ensures that
the MAC address does not age out. This is recommended for
devices that require a permanent connection.
For example, the following menu appears when you enter the
VBRIDGE/CONFIG/FILTER/ADD command:
STATIC ENTRY TABLE
—
— 0
1
Enter port number (1..16) or Q=Quit:
The table includes VLAN and ARL fields. (ARL, or Address
Resolution Logic, performs the bridge learning functions.)
Most of the information in this table is provided and used
internally by the system.
2. Enter the port number, then provide the required information by
following the prompts.
The
VBRIDGE/CONFIG/PARAPORT <VLAN#> command permits
you to set virtual bridge port parameters. This allo ws you to manually
set, on a per port basis, the priority, path costs, and port status (block
or forward) with or without Spanning Tree enabled. For example, a
similar following screen appears when you enter the
CONFIG/PARAPORT <VLAN#> command:
/VBRIDGE/CONFIG/PARAPORT
Port
Number
Port
Priority (a)
1 128 10 Y f
Path
Cost (b)
Enable
Spanning Tree(c)
VBRIDGE/
Manual
Mode (d)
3-12
Page 45

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
To display virtual bridge parameters:
Use the VBRIDGE/SHOW/BRIDGE <VLAN#> command.
See Chapter 5, Command Reference, for more information.
3-13
Page 46

Page 47

Chapter 4
Operating and Managing the
FORMULA 8200 Switch
This chapter provides an overview of tasks that you may want to
perform in the course of normal operation, including displaying or
configuring parameters related to the following:
❑ System configuration
❑ Internet Protocol (IP)
❑ Ethernet configuration
❑ Port mirroring
❑ Virtual LANs
❑ Virtual bridges
❑ Spanning Tree
❑ RIP
❑ Firmware upgrades
4-1
Page 48

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Using Online Help
Use the following command to obtain online information about the
CLI:
ALIAS Lists command shortcuts and briefly describes each.
ALLCMD List available commands and briefly describes each.
LOOKUP Displays information about a specific command.
HELP <COMMAND> Provides brief descriptions of command usage.
For additional information about using these commands (and all
FORMULA 8200 commands), see Chapter 5.
Displaying the System Configuration
The FORMULA 8200 SYSTEM/SHOW command displays system
information, including the version numbers of your:
❑ Boot PROM
❑ Firmware
❑ Operating system
❑ Chassis type
❑ Board serial number
❑ Chassis serial number
❑ MAC address
SYSTEM command also displays your Internet configuration
The
data:
❑ Local IP address
❑ Host name
❑ Default gateway
❑ Subnet mask
4-2
To display system information:
Enter the
SYSTEM/SHOW command. A similar screen appears:
Page 49

Boot PROM version
Console configuration
Operating system version
Firmware version
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
/SYSTEM/SHOW
Configuration used = cfg
System boot sector:
Startup boot flag0
DRAM size in bytes8388608
Flash in bytes4194304
Board versionb.0
CPU version10.0
ISC version1.0
PIG version15.0
POST diag version1.2.0
ISD diag version0.0.0
Boot PROM version1.0.7
QME memory size4195316
CRC checksum0
Console Baud Rate9600
Data Bits8
Paritynone
Stop Bitsone
Chassis configuration:
Number of qmus4
Number of ports16
Chassis Type10002
OS version5.2
FW version1.4.3
Local IP address149.35.101.1
Host nameSWITCH#1
Default gateway149.35.101.1
Net mask255.255.255.0
TFTP server
TFTP firmware file
TFTP config file
Board Serial number = H6970318 Chassis Serial Number= JS000434
Mac Address = 0 ff ff ff ff 0
Boot flag = ff ff ff ff
Boot IP = 149.35.101.31
Machine Type = BT
Motherboard physical type = TExpand board physical type = T
In the last line, T indicates the switch has TX ports on the
onboard and expansion modules. FX ports will be shown as F.
Note
Your firmware version number might be different from the example.
4-3
Page 50

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Displaying Console Port Parameters
To display the console parameters:
Use the
CONSOLE command. You can perform the following
functions:
CONSOLE/LOCK 1 Locks the console from remote sessions.
CONSOLE/LOCK 0 Unlocks the console from remote sessions.
CONSOLE/SHOW Displays the console parameters.
For additional information about using these commands, refer to
CONSOLE Command in Chapter 5.
4-4
Page 51

Displaying Ethernet Port Settings Information
To display Ethernet port information:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
FX ports
Use the
ETHERNET/SHOW/PORT command. The following
screen shows the port configuration for a FORMULA 8200
switch with 8 TX ports and 8 FX expansion ports.
/ETHERNET/SHOW> port
Physical Port#
==============
1 on 100MBPS HALF
2 on 100MBPS HALF
3 on 100MBPS HALF
4 on 100MBPS HALF
5 on 100MBPS HALF
6 on 100MBPS HALF
7 on 100MBPS HALF
8 on 100MBPS HALF
9 off 100MBPS FULL
10 off 100MBPS FULL
11 off 100MBPS FULL
12 off 100MBPS FULL
13 off 100MBPS FULL
14 off 100MBPS FULL
15 off 100MBPS FULL
16 off 100MBPS FULL
Autoneg
=======
Speed
=======
Duplex
=======
4-5
Page 52

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Configuring Ethernet Port Settings
You cannot configure FX ports. They are fixed at 100 Mbps, full
duplex.
You can configure the following parameters for TX ports:
❑ Autonegotiation
❑ Port speed
❑ Port duplex
To configure Ethernet port parameters:
Note
1. Use the
/ETHERNET/CONFIG/PORT
Ethernet Port Configuration
(Press <Return> to take default value, Q to Quit)
Enter port(s) number to configure (1..16) (<port#-port#>):1 2 3
Autonegotiation enable? (y/n) (default=y):N
Port speed (1=10MBPS, 2=100MBPS) (default=100MBPS):1
Half duplex/Full duplex (1=Half, 2=Full) (default=Half):1
Transmission enable? (y/n) (default=y):Y
Receiving enable? (y/n) (default=y): Y
Enter (S=save, Q=quit): S
ETHERNET/CONFIG/PORT command.
2. Enter new configurations, or accept the defaults.
For example, if the screen shows autonegotiation as being
disabled (
N), and you want to keep it disabled, enter N again.
Otherwise, if you just press Enter, the autonegotiation reverts
to the default setting as enabled (
Y).
4-6
Page 53

Configuring Ethernet Port Statistics
Ethernet statistics disabled by default.
To enable or disable port statistics
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
1. Use the
ETHERNET/CONFIG/STAT commands to enter the port
number(s) for which statistics are enabled.
2. Enter y to confirm statistics gathering.
Note
Pressing Enter without entering a value does not change current
settings.
See the following screen as an example:
/ETHERNET/CONFIG/STAT/PORT
Ethernet Port Statistics Configuration (Press <Return> to take default
value,
Q to Quit)
Enter port(s) number to configure (1..16) (<port#>, <port#-port#>):1
Enable port statistics? (y/n) (default=n): y
3. Enter s to save the configuration, as in the following screen:
Port(s) number to configure: 1
Collect Port Statistics: Enabled
Enter (S=save, Q=quit):
.... Updating system/VLAN configuration ....
s
4-7
Page 54

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Displaying Ethernet Port Statistics Information
When enabled, you can display port statistics, such as transmit and
receive frames and errors.
Note
Before using this command, ensure that statistics are enabled via the
ETHERNET/CONFIG/STAT command (previous section).
To display Ethernet port statistics (when enabled):
Transmit (TX)
port statistics
Receive (RX)
port statistics
CPU/memory
statistics
Use the
ETHERNET/SHOW/STAT command to determine if a port has
its statistics gathering function on. Then use
COUNT <PORT#>
/ETHERNET/SHOW/COUNT 1
PORT#1 RX/TX Statistics
**************************************************
TX bytes: 103488
TX frames:
UniCast: 0 MultiCast: 1617 BroadCast: 0
TX errors:
Fcs: 0 txUndrErrs: 0
ExcessColl: 0 OneColl: 0 multiColl: 0
RX bytes: 0
RX frames:
UniCast: 0 MultiCast: 0 BroadCast: 0
rx64: 0 rx65to127: 0 rx128to255: 0
rx256to511: 0 rx512to1023: 0 rx1024to1518: 0
RX errors:
Fcs: 0 AlignOrErr: 0 rxGoodOverSz: 0
rxErrOverSz: 0 rxGoodUndSz: 0 rxErrUndSz: 0
discBuffFull: 0 discMemFull: 0
to display statistical information about a port.
ETHERNET/SHOW/
4-8
Page 55

Clearing a Port’s Statistics Counters
To clear a port’s statistics counters:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Use the
ETHERNET/CONFIG/CLEAR <PORT#> command.
This command resets the port’s statistics to 0. If polling is
enabled, the counters begin to increment at the next polling
interval.
Using Ethernet Port Mirroring
You need to provide a network analyzer to monitor traffic on the
FORMULA 8200.
Port mirroring lets you nonintrusively monitor the network traffic on
one port from another port. You can set up port mirroring for any
pair of Ethernet ports within the same switch. When you enable port
mirroring, the active or mirrored port transmits and receives
normally, and the mirroring or snoop port receives a copy of the
receive traffic of that active port.
Before using the port mirroring feature, you must enable port
statistics hardware and statistics polling by using the
CONFIG/STAT command.
Note
ETHERNET/
The following procedure shows you how to configure port mirroring
using four basic steps:
❑ Configure the snoop port to mirror receive (rx) traffic
❑ Configure the port to be monitored
❑ Verify the configuration
❑ View the mirrored information
At the end of this section, a procedure also shows you how to clear
the snoop port.
4-9
Page 56

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
To configure port mirroring:
1. Enter
ETHERNET/CONFIG/SETSNOOP <PORT# rxFLAG > to
configure the snoop port.
The snoop can monitor receive (rx) traffic. After entering the
port number (port#), enter one of the following two rxFLAG/
txFLAG combinations:
rxFLAG txFLAG Function
1 0 Receive
0 0 Reset (clear snoop port)
For example, enter the following command to configure port
1 as the snoop port in receive-only (rx) mode:
/ETHERNET/CONFIG > SETSNOOP 1 1 0
2. Configure Ethernet ports to be monitored by entering one of the
following commands:
If you specified the receive flag (1 0) in Step 1, enter:
ETHERNET/CONFIG/RXMIRROR
to see the following display:
Enter the mirror types, any combination of
u=unicast, b=broadcast, d=discarded, a= ARL,D=Disable:
3. Specify the type of traffic to be viewed on the monitored port
(unicast, broadcast, and so on).
For example, enter
u.
4. Enter the number of the port to be the monitored.
For example, enter 6 as in the following display. You may also
enter a series of ports by separating the numbers with a space.
Enter the mirror types, any combination of
u=unicast,b=broadcast,d=discarded,a=marked by ARL,D=Disable: U
Enter physical port number(s): 6
5. Display the port mirroring configuration to confirm the correct
settings by entering the following command:
ETHERNET/CONFIG/SNOOPMIRROR
4-10
Page 57

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
This displays both the monitor port as well as the port to be
monitored. In the following example, port 1 is set to monitor
port 6’s receive (rx) traffic of the unicast type:
Monitor or “snoop” port = 1
Port to monitor = 6
Communication = receive
Traffic type = unicast
/ETHERNET/CONFIG/SNOOPMIRROR
Snoop port: 1 RX
RX unicast: 6
RX broadcast
RX discarded:
RX ARL:
TX unicast &
broadcast:
TX ARL:
6. View the mirrored information by entering:
ETHERNET/SHOW/STAT <PORT#>
where <PORT#> is the number of the snoop port.
To clear a snoop port:
1. Enter ETHERNET/CONFIG/SETSNOOP <SNOOP PORT# 0 0> to
remove the flag from the snoop port.
2. Enter the following command:
ETHERNET/CONFIG/RXMIRROR
The following prompt is displayed:
>/ethernet/config/rxmirror
Enter the mirror types, any combination of
u=unicast, b=broadcast, d=discarded, a= ARL,D=Disable:
3. Enter
4. Enter
D (uppercase) for Disable.
ETHERNET/CONFIG/SNOOPMIRROR to make sure the
display does not show any ports in the snoop mirror
configuration.
4-11
Page 58

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Displaying Virtual LAN (VLAN) Information
To display the VLAN information:
Use the
/VLAN/SHOW/VLAN
Virtual LAN Information :
VLAN
ID
====
1 Default VLAN (#1) 137.168.24.190 ENABLE ACTIVE 1-16
VLAN
Description
===============
VLAN/SHOW/VLAN command.
IP Network
Address
==============
Admin
Status
======
Operation
Status
=========
Port
Membership
===========
If this is the first time you are displaying VLAN information
prior to configuring any VLANs, the screen shows all ports
belonging to the default, VLAN 1.
4-12
Page 59

Displaying Virtual Router Information
To display virtual router information:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Use the
/VLAN/SHOW/VROUTER
Virtual Router Information :
VLAN
ID
====
1 Default VLAN 137.168.28.0 255.255.255.0 17 ENABLE ACTIVE
Router
Description
===========
IP Network
Address
============
VLAN/SHOW/VROUTER command.
Subnet
Mask
============
Virtual
Port ID
=======
Admin
Status
=======
Operation
Status
=======
In addition, the following commands display or modify information
about routing:
❑ INET/SHOW/ROUTE displays the routing table.
❑ VLAN/CONFIG/MODIFY <VLAN#> modifies VLAN parameters.
❑ INET/CONFIG/ROUTE adds or deletes routes.
For more information about these commands, see Chapter 5.
4-13
Page 60

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Displaying Virtual Port Information
To display virtual port information about a transparent
bridge port:
Use the
/VLAN/SHOW/VPORT
Virtual Port Information :
Virtual
Port ID
=======
1 1 10 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:20 FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
2 2 10 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:21 FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
3 3 2 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:22 FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
4 4 2 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:23 DISABLE ENABLE INACTIVE
5 5 10 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:24 FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
6 6 10 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:25 FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
7 7 10 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:26 FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
8 8 10 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:27 FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
9 9 9 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:28 DISABLE ENABLE INACTIVE
10 10 1 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:29 FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
11 11 1 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:2a FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
12 12 9 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:2b FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
13 13 9 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:2c FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
14 14 15 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:2d FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
15 15 15 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:2e FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
16 16 15 BRIDGE 0:60:e8:ff:ff:2f FORWARD ENABLE ACTIVE
17 33 1 ROUTER 0:60:e8:ff:ff:50 ENABLE ACTIVE
Physical
Port ID
========
VLAN
ID
====
Port
Type
======
VLAN/SHOW/VPORT command.
Port
MAC Address
================
Bridge
State
=======
Admin
Status
=======
Operation
Status
=======
4-14
The screen shows a 16-port FORMULA 8200 (Physical
Port ID) and their VLAN assignments (VLAN ID) with
spanning tree status (Bridge State). Ports that are linked
and operational as shown as active (Operation Status),
and VLAN is enabled on all ports (Admin Status).
The system automatically creates Virtual Port ID 17 and its
corresponding Virtual Physical Port ID 33 for VLAN 1 routing
functions. As you create additional VLANs and enable routing
for them (Chapter 3, Configuring a Virtual LAN (VLAN) on
page 3-8), the system creates additional Virtual Port IDs but
assigns the same Physical Port ID number, 33, for the routing
function.
Page 61

Displaying Virtual Port Statistics
To display virtual port statistics:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Use the
/VLAN/SHOW/VSTATS
Virtual Port Statistics:
VLAN/SHOW/VSTATS command.
INBOUND
Virtual
Port ID
=======
10 0 0000
20 0 0000
30 0 0000
.
.
.
17 4 256 0 4 0 0
Virtual
Port ID
=======
10 0 0000
20 0 0000
30 0 0000
.
.
.
17 2 84 0 2 0 0
Frames
=======
Frames
=======
Octets
=======
Octets
=======
Ucast
=======
Ucast
=======
BCast
=======
BCast
=======
Mcast
=======
OUTBOUND
Mcast
=======
BufDisc
=======
BufDisc
=======
You can enable or disable compiling of the virtual port statistics by
using the
ETHERNET/CONFIG/STAT command.
4-15
Page 62

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Displaying Virtual Bridge Information
You can display three types of virtual bridge parameters:
❑ Spanning tree bridge parameters
❑ Spanning tree port parameters
❑ The bridge forwarding table
To display spanning tree bridge parameters:
Local parameters
Use the
VBRIDGE/SHOW/BRIDGE <VLAN#> command.
The following display is an example of what you might see
when you enter the command for VLAN 1:
/VBRIDGE/SHOW/BRIDGE 1
Spanning Tree Parameters for VLAN 1
Spanning Tree Status : ON
Priority : 32768 (0x8000)
Bridge ID : 8000-0060e8ffff00
Designated Root : 8000-0060e8ffff00
Cost to Root Bridge : 0
Root Port : None
Hold Time : 1
Topology Changes : 0
Last Topology Change : No Topology Change So Far
Bridge Aging Timer : 300
Parameters System Uses When
Current Parameters Attempting to Become Root:
-------------------------------------------------------Max Age 20 secs System Max Age 20 secs
Forward Delay 15 secs System Forward Delay15 secs
Hello Time 2 secs System Hello Time 2 secs
Global parameters
4-16
For more detailed information about this command, refer to the
VBRIDGE command in Chapter 5.
Page 63

Displaying Spanning Tree Port Parameters
To display spanning tree port parameters:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Use the
VBRIDGE/SHOW/PORT <VLAN#> command.
The following display is an example of what you might see
when you enter the command for VLAN 1:
/VBRIDGE/SHOW/PORT 1
Spanning Tree Port Parameters for VLAN 1
Port
Number
------16 128 FORWDING 10 0 8000-16 None 8000-0060e8ffff00
15 128 FORWDING 10 0 8000-15 None 8000-0060e8ffff00
14 128 FORWDING 10 0 8000-14 None 8000-0060e8ffff00
.
.
.
3 128 FORWDING 10 0 8000-03 None 8000-0060e8ffff00
2 128 FORWDING 10 0 8000-02 None 8000-0060e8ffff00
1 128 FORWDING 10 0 8000-01 None 8000-0060e8ffff00
Pri
---
State
--------
Path
Cost
-----
Desig
Cost
-----
Desig
Port
-------
Root
Port
----
Root Bridge ID
Desig Bridge ID
--------------
8000-0060e8ffff00
8000-0060e8ffff00
8000-0060e8ffff00
8000-0060e8ffff00
8000-0060e8ffff00
8000-0060e8ffff00
For more detailed information about this command, refer to the
VBRIDGE command in Chapter 5.
4-17
Page 64

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Displaying the Bridge Forwarding Table
The Bridge Forwarding Table displays the MAC addresses and their
forwarding and filtering information for a given group. The
transparent bridging function uses the information in the table to
determine how to forward frames.
To display the bridge forwarding table:
Use the
VBRIDGE/SHOW/FWT command.
A table similar to the following appears:
/VBRIDGE/SHOW/FWT
VLAN ARL
vlan port dom mac_address flags age
1 7 0 00:a0:d2:c1:55:01 — 5
1 33 0 00:60:e8:ff:ff:50 — 0
For more detailed information about this command, refer to
VBRIDGE in Chapter 5.
To display the total number of addresses in the table:
Use the command
srccnt) to display a screen similar to the following:
ETHERNET/SHOW/MACADDRCOUNT (alias
4-18
/ETHERNET/SHOW/SRCCNT
MAC address Count in Source Table = 22
Other related commands:
Refer to the
ETHERNET command in Chapter 5 for details.
ETHERNET/CONFIG/FLUSH example under the
Page 65

Upgrading Firmware
This section describes the procedures for using TFTP to download
the FORMULA 8200 system software (image file, binary) from your
TFTP server to the FORMULA 8200 switch.
Prior to the TFTP download process:
1. Your TFTP server must be running the TFTP daemon (UNIX) or a
2. If you have Solaris
3. If you have DOS or Windows, you have several options:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
TFTP process (DOS/Windows). Without the daemon or the
process, your download from your server will fail.
, refer to Appendix B for the procedures to
configure a TFTP server on that platform.
❑ Castle Rock’s SNMPc
includes a TFTP server. Refer to the
documentation for server setup.
❑ Shareware TFTP servers are available for Windows
WindowsNT
❑ For other TCP/IP stacks, check your software applications for
.
95 or
details.
4. The IP address of the switch and the TFTP server must be on the
same subnet.
5. You need the latest FORMULA 8200’s system software file from
Allied Telesyn. The software is available from the World Wide Web
or from Allied Telesyn’s anonymous FTP server. For questions,
please phone the Allied Telesyn’s Technical Support. For
information on how to contact the nearest Allied Telesyn location,
refer to Appendix A.
6. Note the name of the FORMULA 8200 system software file that
resides on your TFTP server. This is the software file you will
download.
7. Make sure the software file on your server has read and write
access. In UNIX, enter
chmod 777 <filename>
to give read and write access to the files. Then copy the
software file to the appropriate directory on your TFTP server.
8. Verify the physical connection from your TFTP server to the
FORMULA 8200.
4-19
Page 66

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Backing Up
Your Current
Configurations
/ >tftp/server
IP address of the tftp server ( ) :192.48.127.124
Save TFTP configuration to flash? (y/n) y
Writing new TFTP configuration to flash...
Updating system/VLAN configuration..
The upgrade may change some settings to new defaults, and this
may or may not cause a problem.
To ensure your ability to restore your current switch configurations
after the software upgrade, you need to back up the following
configuration files to your TFTP server:
❑ SYSTEM.CUR contains the majority of the configuration files
❑ AGENT.CNF contains location, contact, and SNMP
management information (backup optional)
1. Log in to the switch and
PING the TFTP server to verify
communications:
ping 192.48.127.124
/ >
192.48.127.124 is alive
2. Assign an IP address to the TFTP server:
.
3. If you are using a UNIX TFTP server, the file must exist (for
example, system.001) in the directory path indicated in the
/etc/inetd.conf file. It must also have read, write, and
execute permissions for everyone:
cd /tftpboot
touch system.001
chmod 777 system.001
4. In your switch, backup the configuration files by using the
UPLOAD/CFG
command. In this command, you need to specify
the name of the file(s) you want to backup:
TFTP/
4-20
Page 67

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
/>tftp/upload/cfg
Name of file on switch ( ) : system.cur
Name of file on tftp server ( ) : system.001
File “/flash/system.cur” on switch to be copied to server “192.48.127.124” as
“system.001”
Are they correct? (y/n) y
Save TFTP configuration to flash? (y/n) n
LF = /flash/system.cur, RF = system.001, SRV = 192.48.127.124, op = put
/TFTP/UPLOAD>
Repeat the procedure to upload AGENT.CNF to a
corresponding pre-existing file (for example, agent.001) in
the server.
You are done backing up your files. You may proceed with the
software upgrade.
Configuring for
the Download
Process
To configure the FORMULA 8200 for the TFTP download
process:
The following steps provide the FORMULA 8200 with the IP
address of your TFTP server:
1. Log in to the switch and enter:
/TFTP/SERVER
2. Enter the IP address of your TFTP server. Enter
Y in the Save the configuration to flash?
(y/n) prompt to save the TFTP server configuration for later
use.
/TFTP/SERVER
IP address of the tftp server () : 192.5.5.18
Save the configuration to flash? (y/n) Y
Writing new configuration to flash ...
Updating system/VLAN configuration....
3. Verify that you can
PING the TFTP server from the
FORMULA 8200.
You are now ready to download software to your
FORMULA 8200 switch.
Caution
There is only enough space on the switch to store one version of
software. Do not attempt to download multiple versions on the
switch.
4-21
Page 68

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Downloading
the Firmware
/TFTP/DOWNLOAD/Firmware
Name of file on tftp server (v13r28.z) : <filename>
File <filename> on server (192.5.5.18) is to be copied to switch as "/flash/
firmware"
Are they correct? (y/n) Y
Save the configuration to flash? (y/n) Y
To download:
The following steps provide the FORMULA 8200 with the
name of the switch system file that resides on your TFTP
server:
1. Enter:
TFTP/DOWNLOAD/FIRMWARE
2. Verify that the information displayed on the screen is correct and
enter
Y. Then enter Y again to save the configuration to flash.
A similar screen appears:
3. Verify that the information on the screen is correct. Confirmation
of the above information invokes the TFTP download process.
This process takes approximately 5 minutes.
After the TFTP download process completes, the switch
system software is saved to flash memory and you see the
following prompt:
/TFTP/DOWNLOAD >
4. Reboot the switch either by using the
pressing the
Reset button on the front of the switch.
REBOOT command or by
Rebooting enables the FORMULA 8200 to load the new
system software from flash to running memory (DRAM). The
system then runs and displays POST (power on self test) and
other diagnostic information, as shown in the following
example:
4-22
Page 69

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Boot POST in progress...
PROM version: 1.0.7
Sizing DRAM (value displayed is bank size or error code)...
DRAM now configured into a contiguous block:
Address: ............. 0xa0000000 - 0xa07ffffc
Running DRAM test...
Initializing 4650 icache and dcache...
Initializing PIG chip...
Initializing PMIU chips...
PMIU_0 revision: ..... 0x0000000f
PMIU_1 revision: ..... 0x0000000f
PMIU_2 revision: ..... 0x0000000f
PMIU_3 revision: ..... 0x0000000f
Initializing PHY chips...
Initializing interrupt vectors in DRAM...
Running Extended DRAM test...
Boot POST complete, passing control to firmware...
Press the spacebar to stop auto-boot...
This completes the software upgrade on the switch. You must now
restore the configuration files you backed up.
4-23
Page 70

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
n
Restoring Your
Configurations
/ >tftp/server
IP address of the tftp server ( ) :192.48.127.124
Save TFTP configuration to flash? (y/n) y
Writing new TFTP configuration to flash...
Updating system/VLAN configuration..
After making sure the software upgrade is stable, you may restore
your old configurations using the following procedure.
To restore your configurations;
1. Log in to the switch and
PING the TFTP server to verify
communications:
/ >ping 192.48.127.124
192.48.127.124 is alive
2. Assign an IP address to the TFTP server:
.
3. Restore the configuration files by using the
CFG
command. In this command, you need to specify the name
TFTP/DOWNLOAD//
of the file(s) you want to restore:
/ >tftp/download/cfg
Name of file on switch (system.cur) :
Name of file on tftp server (system.001) :
File “system.001” on server (192.48.12.124) is to be copied to switch as
flash/system.cur”
Are they correct? (y/n) y
Save TFTP configuration to flash? (y/n) y
Writing new TFTP configuration to flash ...Updating system/VLAN configuratio
LF = /flash/system.cur, RF = system.001, SRV = 192.48.127.124, op = get
/TFTP/DOWNLOAD>
4. Reboot the switch using the
REBOOT command on the console
prompt.
/ TFTP/DOWNLOAD>top
/ >reboot
Are you sure, you want to reboot ? [y/n]: y
4-24
Page 71

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
In Case of
Problems With
the Software
Upgrade
This section tells you what to do if the software upgrade fails due to
interruptions or if you see error messages while rebooting the switch
as part of the upgrade process.
Interruptions during the download process
Interrupting a software download (for example, rebooting the switch
or disconnecting the power cord) creates files of 0 bytes. Attempts to
download again will not succeed because the download process
cannot write over these files.
If you encounter these problems:
1. Log in to the switch.
2. Manually delete the firmware file by entering:
/FILE/DELETE firmware
3. Download the firmware again.
Error message during the boot process
If you see the following error message:
error uncompressing file
status=0X3D00Q can’t load boot file.
this means you can not use the CLI to download. Refer to
Appendix C, Downloading Software at the [VxWorks] Prompt, for
alternate procedures on how to download software to the
FORMULA 8200.
4-25
Page 72

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Displaying RIP Support Information
The FORMULA 8200 IP routing function is implemented on an
individual-VLAN basis. When a VLAN is created, the FORMULA 8200
provides an option to configure its interface as an IP router and
allows the network manager to choose from four RIP modes: active
(send and receive RIP packets), deaf (send only), inactive (RIP
disabled) or silent (receive only).
To display routes:
Use the
/INET/SHOW/ROUTE
ROUTE NET TABLE:
Address
============
192.18.29.0 192.18.29.200 1 1 VLAN INTERFACE
192.18.30.0 192.18.30.200 1 2 VLAN INTERFACE
ROUTE HOST TABLE:
Address
============
132.10.10.1 192.18.29.200 2 1 STATIC
131.20.20.1 192.18.29.200 1 1 STATIC
193.10.10.1 192.18.29.200 1 1 STATIC
127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 1 1 LOOPBACK
Gateway
=============
Gateway
=============
INET/SHOW/ROUTE command.
Metric
======
Metric
======
VLAN
=====
VLAN
=====
Type
==============
Type
==============
4-26
Page 73

Modifying the IP RIP Mode
This section shows you how to modify the IP RIP mode once a VLAN
has been created. You can set the RIP mode to one of four available
states:
❑ Active (a) - to send and receive RIP packets
❑ Deaf (d) - to send only
❑ Inactive (i) - to disable RIP
❑ Silent (s) - to receive only
In the example below, the initial mode is silent and is modified to
active. Use the same procedure to change the mode to any other
state.
To modify the IP RIP mode:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
1. Enter the
VLAN/CONFIG/MODIFY <VLAN#> command.
The following display appears:
VLAN Modification :
VLAN 3 Configuration Parameters Current Value
------------------------------------------------------
1) VLAN ID :- 3
2) Description :- VLAN 3
3) VLAN enabled :- Y
4) IP enabled :- Y
5) Network Address : - 192.18.31.200
6) Subnetwork Mask :- 255.255.255.0
7) Broadcast Address : - 192.18.31.255
8) Router Description :- Router for VLAN 3
9) IP RIP Mode (Active(a), Silent(s), Deaf(d), Inactive(i)) : Silent
-----------------------------------------------------Modification instruction :
usage: <number of parameter> = <new vlaue>
command example: 2 = Engineering VLAN(#1)
--------------------------------------------Enter selection (0 to commit, c to cancel) >
2. Set RIP mode to Active by entering the following at the prompt:
9=A
3. Confirm the change by entering 0 at the prompt:
Enter selection (0 to commit, c to cancel) >
0
4-27
Page 74

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Configuring Static Routes
To add static routes:
/INET/CONFIG/ROUTE/ADD
Add static route Host/network IP address: 132.10.10.1
Gateway IP address: 192.18.29.200
Metric:
Add route? (yes) y
Updating system/VLAN configuration....
Route has been added.
Deleting Static
Routes
/INET/CONFIG/ROUTE/DELETE
Delete static route Host/network IP address: 130.10.10.1
Gateway IP address: 192.18.29.200
Delete route? (yes) y
Updating system/VLAN configuration....
Static route has been deleted.
Use the
2
INET/CONFIG/ROUTE/ADD command.
All static routes are saved into the FORMULA 8200 flash memory and
downloaded at startup or system reset.
To delete a static route:
Use the
INET/CONFIG/ROUTE/DELETE command:
4-28
Page 75

Removing an IP Default Gateway
To remove an IP default gateway:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Use the
Remove default route Gateway IP address: 192.18.29.200
Delete route? (yes) y
Route has been deleted.
Updating system/VLAN configuration....
Static route has been deleted from the flash.
Default route has been deleted.
/INET/CONFIG/ROUTE >
ROUTE NET TABLE:
Address
============
192.18.29.0 192.18.29.200 1 1 VLAN INTERFACE
192.18.30.0 192.18.30.200 1 2 VLAN INTERFACE
VIR
Gateway
=============
INET/CONFIG/ROUTE/RMDEFAULT command.
Metric
======
VLAN
=====
Type
==============
ROUTE HOST TABLE:
Address
============
132.10.10.1 192.18.29.200 2 1 STATIC
131.20.20.1 192.18.29.200 1 1 STATIC
193.10.10.1 192.18.29.200 1 1 STATIC
127.0.0.1 127.0.0.1 1 1 LOOPBACK
Gateway
=============
Metric
======
VLAN
=====
Type
==============
4-29
Page 76

Operating and Managing the FORMULA 8200 Switch
Configuring SNMP Parameters
You can configure the FORMULA 8200 to communicate with a
network management station via SNMP (SNMP v.1 only). To
configure the FORMULA 8200 as an SNMP managed networking
device, you can provide system description, system contact, system
location, and both read and write community strings.
To configure the FORMULA 8200 as an SNMP managed
device:
1. Use the
SNMP/CONFIG command to configure SNMP parameters
as in the following screen:
/SNMP/CONFIG
SNMP Agent configuration:
system contact () : JOE ADMIN
system location () : ENGINEERING LAB
Read community string (public) :
Write community string (private) :
SNMP trap destination table is empty.
Enter A=add, C=change, D=delete, Q=quit
2. Enter
A to create a trap destination table and then respond to the
prompts. For example:
— Enter
192.2.150.49 as the destination IP address.
— Press Enter to accept 162 as the default UDP port number.
— Enter
public as the community string.
The screen displays the following similar information:
4-30
SNMP Trap Destination Table
Index
=====
1. 192.2.150.49 162 public
Enter A=add, C=change, D=delete, Q=Quit:
IP Address
==========
UDP Port
==========
Community
==========
3. Enter q to quit and then y to save the information to flash as in the
following example:
Enter A=add, C=change, D=delete, Q=Quit: q
OK to write SNMP config file (y/n)? y
Page 77

Displaying SNMP Parameters
To display system description, location and contact:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
1. Use the
/SNMP/SHOW/PARAM
System Description:
System location :
System contact :
SNMP/SHOW/PARAM command:
2. Enter the information at the prompts.
To display the read community string:
Use the
SNMP/SHOW/READCOMM command.
To display the write community string:
Use the SNMP/SHOW/WRITECOMM command.
4-31
Page 78

Page 79

Chapter 5
Command Reference
The FORMULA 8200 command line interface (CLI) is a hierarchical
menu-driven interface with menus, submenus, and commands
arranged in a tree structure. This chapter includes:
❑ Information about how to enter commands
❑ A list of commands, subcommands, and aliases
❑ A description of each command, including syntax, default
settings, and examples
To access the main command menu:
? at the FORMULA 8200 prompt, as shown below:
Enter
== MAIN MENU ==
? ALIAS ALLCMD
[ATM] [BOOT] [CONSOLE]
[ELOG] [ETHERNET] EXIT
[FDDI] [FILE] [INET]
LOOKUP [MODE] [PORTSERV]
REBOOT [SNMP] [SYSTEM]
[TFTP] TOP UP
[VBRIDGE] [VLAN] [TRACE]
/ >
Figure 5-1 illustrates the FORMULA 8200 CLI command tree.
5-1
Page 80

Command Reference
ALIAS
ALLCMD
ATM
CONFIG
CREATE
DELETE
DISABLE
ENABLE
MODIFY
CIP (ccip)
LEC (clec)
PTOP (cptop)
TRUNK (ctrunk)
CIP (dcip)
LEC (dlec)
PTOP (dptop)
TRUNK (dtrunk)
CIP (cipdis)
PTOP (ptopdis)
TRUNK (trunkdis)
CIP (cipen)
PTOP (ptopen)
TRUNK (trunken)
CIP (mcip)
LEC (mlec)
PORT (map)
PTOP (mptop)
TRUNK (mtrunk)
BOOT
CONSOLE
ELOG
SHOW
STATS
IP (ipb)
SHOW (vboot)
UPDATE
LOCK (lcn)
SHOW (vcon)
CLEAR (clrelog)
CURRENT (current)
DETAIL (detail)
RANGE (range)
SEVERITY (severe)
SHORT (srtelog)
SHOW (velog)
AUTOREBOOT (elogboot)
ARP
ARP CIP (vciparp)
ARP LEC (vlecarp)
CIP (vcip)
CONNECTION (vac)
LEC (vlec)
PORT (vap)
PTOP (vptop)
TRUNK (vtrunk)
IP CONFIG (ipcfg)
IP EEPROM (ipprom)
ALL (updcfg)
ATM (udatm)
SYSTEM (udsys)
5-2
Figure 5-1: CLI Command Tree With Aliases, 1 of 3
Page 81

CONFIG
FLUSH
CLEAR (epclr)
PORT (epcfg)
RXMIRROR (rxm)
SETSNOOP (snp)
SNOOPMIRROR (snpm)
STAT
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
PORTFLUSH (pf)
ALLPORTFLUSH (allpf)
UPLINKFLUSH (uplnkpf)
PORT (estcfg)
ETHERNET
EXIT
FDDI
FILE
SHOW
CONFIG
SHOW
COPY (cp)
DELETE (rm)
LIST (ls)
RENAME (mv)
RMCFG (rmall)
RZ (load)
SZ
TYPE (cat)
TXMIRROR (txm)
PORT (vep)
STAT (ves)
COUNT (est)
MACADDRCOUNT (srccnt)
BRIDGE
BRIDGE
MAC
PORT
STAT
ADD (fbradd)
AGE (fage)
DELETE (fbrdel)
MODE (fbrcfg
TABLE (fbr)
COUNTERS (fmacc)
NBRADDR (fmacnbr)
STATS (fmacs+)
STATUS (fmacs)
COUNTERS (fportc)
STATUS (fports)
SUMMARY (fport)
ID (fsmtid)
STATUS (fsmts)
SUMMARY (fsmt)
INET
LOOKUP (lookup)
CONFIG
PING (ping)
RLOGIN (rlogin)
SHOW
STATS
ADD (circa)
ROUTE (cir)
IPR (cipr)
ARP (varp)
ROUTE (vir)
STATIC (vis)
ICONNECT (vicon)
RTCACHE (virc)
FORWARD (fwdst)
ICMP (icmpst)
IP (ipst)
SNMP (snmpst)
TCP (tcpst)
UDP (udpst)
DEFAULT (cirsdr)
DELETE (cird)
RMDEFAULT (cirdir)
Figure 5-1. CLI Command Tree With Aliases, 2 of 3
5-3
Page 82

Command Reference
MODE
CONFIG
SHOW (vmode)
BATCHIN (batchin)
CLOSE (close)
OUTPUT (output)
SAVECMD (savecmd)
PORTSERV
REBOOT (reset)
SNMP
SYSTEM
TFTP
TOP (top)
CONFIG
SHOW
CONFIG (snmpcfg)
SHOW
CONFIG
SHOW (vsys)
DOWNLOAD
SERVER (tftpcfg)
UPLOAD
CREATE (cps)
MOVE (mvps)
REMOVE (rmps)
PARAM (vsnmpp)
READCOMM (vread)
WRITECOMM (vwrite)
ADMINPW (admpw)
DATE (date)
TIME (time)
UPTIME (uptime)
CFG (dldcfg)
FIRMWARE (dldfrm)
CFG (uldcfg)
FIRMWARE (uldfrm)
UP (up)
VBRIDGE
VLAN
CONFIG
SHOW
CONFIG
SHOW
THROTTLE (ctb)
BRIDGE (cvb)
FILTER
PARAPORT (vbpa)
BRIDGE (vvb)
FILTER
FWT (vfwt)
PORT (vvbp)
ADDPORT (addvp)
CREATE (cvl)
DELPORT (delvp)
DISABLE (vldisb)
ENABLE (vlenb)
MODIFY (mdvl)
MOVPORT (mvvp)
REMOVE (rmvl)
VLAN (vvl)
VPORT (vvp)
VROUTER (vvr)
VSTATS (vpst)
ADD (addfl)
DELETE (delfl)
ALL (fl)
Figure 5-1. CLI Command Tree With Aliases, 3 of 3
5-4
Page 83

ATM and FDDI Support
The ATM and FDDI commands in this chapter are enabled if you hav e
the appropriate card installed in the uplink slot: the AT-8202 for ATM
or the AT-8203 for FDDI connectivity.
For details about ATM commands, refer to the AT-8202 ATM Uplink
User’s Guide. For details about FDDI commands, refer to the
AT-8203 FDDI Uplink User’s Guide. These guides are available in
PDF format from Allied Telesyn website at www.alliedtelesyn.com/
manuals.htm.
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
5-5
Page 84

Command Reference
Command Edit Mode
The command interface provides a history mechanism similar to the
UNIX K-shell history facility, which allows you to automatically
display and edit previously typed commands. This feature may help
save time when entering frequently used commands.
Edit Mode
Commands
Table 5-1 lists commonly used edit commands. There are other
advanced commands available; however, only the most common are
listed here. If you are familiar with the UNIX K-shell history facility,
most of the same commands may be used in the FORMULA 8200
command line interface.
Table 5-1 FORMULA 8200 Edit Commands
Command Action
Esc k
Esc j
Esc l or [Spacebar]
Esc h
Esc dd
Esc i
Display the previous command backward in history.
Continue pressing k to scroll through the last 20
commands.
Display the next command forward in history.
Continue pressing j to scroll forward.
Go right one character.
Go left one character.
Delete entire line.
Insert (characters typed after you press i
are inserted from the cursor forward.)
Press [Escape] to return to edit mode.
Command
Descriptions
5-6
Esc x
Esc /<sample>
Esc ?<sample>
Esc 0 (zero)
Esc cw
Delete a character from cursor forward.
Search for string sample backward in history.
Search for string sample forward in history.
Go to beginning of line.
Change word (deletes the word your
cursor is on and lets you type a new one).
The remainder of this chapter provides a description of each
command, including its syntax, a description of the command and
any subcommands, any default settings, and examples showing
command usage.
Page 85

ALIAS Command
/ >alias
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Syntax
ALIAS
Menu
Alias
=====
AAL5ST Show AAL5 Layer Statistics
ADDFL Add a static filter table entry
ADDVP Add port(s) to a VLAN
ADMPW Change password for admin
ALIAS Look up aliases that match a pattern
ATMST Show ATM Layer Statistics
BATCHIN Read the command sequence from a file and execute one by one
BYE Close host connection
CAT Type a file to console
.
Description
===========
Description
The
ALIAS command lists all available command aliases and
provides a brief description for each.
Aliases are abbreviated versions of commands or command strings.
For example, instead of entering the command
ADDPORT
, you can enter the following alias:
VLAN/CONFIG/
addvp
The command aliases are shown in Figure 5-1 earlier in this chapter,
and are also included in the description for each command.
Note
You cannot create an alias.
5-7
Page 86

Command Reference
ALLCMD Command
Syntax
ALLCMD
Menu
/ >allcmd
Command/Path AlliasDescription
============ ===================
? Display the current menu commands
ALIAS (ALIAS )Look up aliases that match a pattern
ALLCMD List all commands available in CLI
ATM Menu to configure/show ATM parameters/statistics
CONFIG Menu to configure ATM parameters
CREATE Menu to create ATM specific services
CIP(CCIP)Create CIP logical subnet
LEC(CLEC)Create an ELAN
.
.
.
Description
ALLCMD command provides a list of available commands and a
The
brief description for each.
5-8
Page 87

ATM Command
/ > atm
[CONFIG] [SHOW] [STATS]
[TEST]
/ATM >
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Syntax
ATM
ATM/CONFIG
ATM/SHOW
ATM/STATS
ATM/TEST
Menu
== ATM MENU ==
Description
A T M commands are listed in the AT-8202 ATM Uplink User’s Guide .
Download the document in PDF format from Allied Telesyn’s website
at www.alliedtelesyn.com/manuals.htm.
5-9
Page 88

Command Reference
BOOT Command
/ >boot
[IP] SHOW [UPDATE]
Syntax
BOOT
BOOT/IP
BOOT/SHOW
BOOT/UPDATE/<subcommand>
Menu
== BOOT MENU ==
Description
The BOOT command displays and defines boot sector information.
Table 5-2 describes the parameters.
Table 5-2 BOOT Command Parameters
Subcommands Alias Description
IP CONFIG
EEPROM
SHOW
UPDATE
ALL updcfg
ATM udatm
SYSTEM updsys
ipcfg
ipprom
vboot
Configure IP, gateway, etc. for
system boot.
Configure EEPROM IP
Show boot post-test results.
Update all configuration from
RAM to flash.
Update ATM configuration to
flash.
Update system or VLAN
configuration to flash
5-10
Page 89

BOOT/IP/CONFIG Example
To assign a new IP address:
1. Enter the following command:
BOOT/IP/CONFIG
2. Enter the information after each prompt, or press [Enter] to keep
the default.
The following screen is an example of the prompts:
/BOOT >ip/config
Local IP configuration:
IP address (137.168.24.190) :149.35.101.31
Local host name () :
Default gateway (0.0.0.0) :
Net mask (255.255.255.0) :
OK to write config to flash (y/n) ?
/BOOT/IP >
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
BOOT/UPDATE/SYSTEM Example
To update the system and VLAN configuration to flash:
Enter the following command:
BOOT/UPDATE/SYSTEM
The following display appears:
/BOOT/UPDATE >system
Updating system/VLAN configuration....
/BOOT/UPDATE >
5-11
Page 90

Command Reference
CONSOLE Command
Syntax
Menu
/ >console
== CONSOLE MENU ==
LOCK SHOW
Description
CONSOLE/LOCK
CONSOLE/SHOW
The CONSOLE command displays, restricts, or configures the
console parameters. Table 5-3 describes the parameters in
that display.
Table 5-3 CONSOLE Command Parameters
Subcommand Alias Description
LOCK 1 lcn 1
LOCK O lcn 0
SHOW vcon
Locks the console from remote sessions. This
command can be entered from the local console
only, and is not available via remote access.
Unlocks a console to enable remote sessions. This
command can be entered from the local console
only, and is not available via remote access.
Shows console parameters.
5-12
Page 91

CONSOLE/LOCK Example
To disallow remote access to the console:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Use the
/CONSOLE >lock 1
Console Locked
/CONSOLE
To unlock the console:
Use the
/CONSOLE >lock 0
Console Unlocked
CONSOLE/SHOW Example
To display the console parameters:
CONSOLE/LOCK command:
CONSOLE/LOCK 0 command:
Use the
CONSOLE/SHOW command.
A similar display appears:
/CONSOLE >show
Speed = 9600
Stopbit = 1
Databits = 8
Parity = no
No. of lines per page = 25
/CONSOLE >
5-13
Page 92

Command Reference
ELOG Command
Syntax
ELOG
ELOG/CLEAR
ELOG/CURRENT
ELOG/DETAIL
ELOG/RANGE
ELOG/SEVERITY
ELOG/SHORT
ELOG/SHOW
ELOG/AUTOREBOOT
Menu
/elog
== ELOG MENU ==
CLEAR CURRENT DETAIL
RANGE SEVERITY SHORT
SHOW AUTOREBOOT
Description
ELOG command allows you to display or clear the error log.
The
Table 5-4 describes the parameters in that display.
Table 5-4 ELOG Command Parameters
Subcommand Alias Description
CLEAR clrelog
CURRENT current
DETAIL detail
RANGE range
SEVERITY range
SHORT srtelog
SHOW velog
Clear the error log.
Display the current ten (default) errors.
Display the detailed error log.
Display the errors within the error code
range.
Display the errors of a specific severity.
Display the essential information from
the error log.
Display total log message number and
size.
5-14
AUTOREBOOT elogboot
Enable or disable automatic reboot
during fatal errors.
Page 93

ELOG/CLEAR Example
To clear the error log:
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
Use the
ELOG/CLEAR command.
A similar display appears:
ELOG/clear
System trace log is reset to record 0
/ELOG >
ELOG/CURRENT Example
To show the error log’s current ten default errors:
Use the
ELOG/CURRENT command.
A similar display appears:
/ELOG >current
(4/21/97 14:8:22) Code: 3 Level: 0 - Warning : Not tested
(4/21/97 14:8:22) Code: 3 Level: 0 - Warning : Not tested
(4/21/97 14:8:22) Code: 3 Level: 0 - Warning : Not tested
(4/21/97 14:8:22) Code: 3 Level: 0 - Warning : Not tested
(4/21/97 14:8:22) Code: 3 Level: 0 - Warning : Not tested
(4/21/97 14:8:22) Code: 3 Level: 0 - Warning : Not tested
(4/21/97 14:8:22) Code: 3 Level: 0 - Warning : Not tested
(4/21/97 14:8:22) Code: 3 Level: 0 - Warning : Not tested
(4/21/97 14:8:22) Code: 3 Level: 0 - Warning : Not tested
(4/21/97 14:8:32) Code: 1702 Level: 2 - GSR Error = 0x0xff000000
/ELOG >
Note
The error log is for Allied Telesyn’s Technical Support use.
5-15
Page 94

Command Reference
ELOG/SHOW Example
To display the number and size of the error log:
Use the
ELOG/SHOW command.
A similar display appears:
/ELOG >show
Event log is enabled
Log size per message=100
Current message index=16
Total number of messages since reboot=16
/ELOG >
In the above display, the following default settings are shown:
❑ Event log is enabled
❑ Log size per message=100
5-16
Page 95

ETHERNET Command
Syntax
Menu
/ethernet
== ETHERNET MENU ==
[SHOW] [CONFIG]
Description
FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
ETHERNET
ETHERNET/CONFIG/<subcommand>
ETHERNET/SHOW/<subcommand>
SHOW
CONFIG
ETHERNET command allows you to configure and display
The
Ethernet port information, and allows you to configure port
mirroring. Table 5-5 describes the parameters in that display.
Table 5-5 ETHERNET Command Parameters
Subcommand Alias Description
PORT
STAT
COUNT
MACADDRCOUNT
CLEAR
PORT
RXMIRROR
SETSNOOP
SNOOPMIRROR
vep
ves
est
srccnt
epclr
epcfg
rsm
snp
snpm
Show Ethernet interface unit (EIU) port configuration.
Show EIU statistics configuration.
Show EIU statistics and counters.
Show total number of MAC addresses in the source table.
Clear Ethernet statistics counters for a specific port.
Configure Ethernet port parameters.
Set the receive (RX) mirror port.
Set the snoop port.
Show snoop and mirror ports.
STAT PORT
TXMIRROR
FLUSH Display the flush menu.
FLUSH PORTFLU
estcfg
txm
pf
Display the Ethernet statistics configuration menu.
Set the transmit (TX) mirror port.
Flush all Ethernet entries per port
5-17
Page 96

Command Reference
Subcommand Alias Description
Table 5-5 ETHERNET Command Parameters (Continued)
CONFIG
(continued)
FLUSH ALLPORT
FLUSH UPLINKF
ETHERNET/CONFIG/PORT Example
100Base-FX fiber ports are fixed at 100 Mbps and full duplex and
cannot be configured.
1. Use the
2. Enter the desired information at the prompts, which are shown in
allpf
uplinkf
Flush all Ethernet port entries
Flush all uplink entries
To enable autonegotiation for Ethernet TX ports 1,2, and
3:
Note
ETHERNET/CONFIG/PORT command.
the display below.
If a port is set to other than the default, pressing the Enter key
resets it back to the default setting. It does not retain the
previously configured port setting.
Autonegotiation prompt
/ETHERNET/CONFIG> port
Ethernet Port Configuration
(Press <Return> to take default value, Q to Quit)
Enter port(s) number to configure (1...16) (<port#-port#>):1 2 3
Autonegotiation enable? (y/n) (default=y): Y
Transmission enable? (y/n) (default=y):Y
Receiving enable? (y/n) (default=y): Y
Port(s) number to configure: 1 2 3
Autonegotiation enable? (y/n) (default=y): Y
Transmission enable? (y/n) (default=y): Y
Receiving enable? (y/n) (default=y): Y
Enter (S=save, Q=quit): S
Once you have responded to each of the prompts, the settings
are displayed, and you are prompted to save your responses
or to quit.
5-18
Page 97

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
ETHERNET/CONFIG/RXMIRROR Example
To set the receive mirror port for port mirroring:
Enter the following command:
ETHERNET/CONFIG>
rxmirror
Refer to Using Ethernet Port Mirroring in Chapter 4 for more
information.
ETHERNET/CONFIG/SETSNOOP Example
To set the snoop (monitoring) port for port mirroring:
Enter the following command:
ETHERNET/CONFIG>
setsnoop
Refer to Using Ethernet Port Mirroring in Chapter 4 for more
detailed information.
ETHERNET/CONFIG/STAT Example
To configure Ethernet statistics parameters:
1. Enter
ETHERNET/CONFIG/STAT/PORT to enable statistics.
/ETHERNET/CONFIG/STAT/PORT
default value,
Q to Quit)
Enter port(s) number to configure (1..16)(<port#>,<port#-port#>): 1-8
Enable port statistics? (y/n) (default=n): y
Port(s) to configure: 1-8
Collect poll statistics:Enabled
Enter (S=save, Q-quit):
............ Updating system/VLAN configuration ..........
Ethernet Port Statistics Configuration (Press <Return> to take
s
2. Use the ETHERNET/SHOW/STAT command to verify that
statistics is turned on, that is, port(s) are shown as Enabled.
5-19
Page 98

Command Reference
ETHERNET/CONFIG/FLUSH Example
To clear dynamically learned MAC addresses from the
bridge table:
1. Enter
/ETHERNET/CONFIG/FLUSH
=== FLUSH (ETHERNET CONFIG) MENU ==
PORTFLUSH ALLPORTFLUSH UPLINKFLUSH
ETHERNET/CONFIG/FLUSH to display the following menu:
2. Enter one of the following commands:
PORTFLUSH <port #> to clear the bridge table of dynamically
learned MAC addresses on a designated port
ALLPORTFLUSH to clear the bridge table of dynamically
learned MAC addresses on all ports
UPLINKFLUSH to clear the bridge table of dynamically
learned MAC addresses on an uplink port only
To view the table, use the VBRIDGE/SHOW/FWT command
(page 5-50).
Note
The FLUSH command does not work on static addresses. Static
addresses are manually entered and must therefore be manually
deleted. See also Configuring a Virtual Bridge in Chapter 3,
beginning on page 3-11, for the procedure to add static addresses to
the table using the VBRIDGE/CONFIG/FILTER/ADD command.
5-20
Page 99

FORMULA 8200 User’s Guide
ETHERNET/SHOW/PORT Example
To display information about the Ethernet interface port
configuration:
Use the
ETHERNET/SHOW/PORT command.
A similar display appears:
/ETHERNET/SHOW> port
Physical Port#
================
1 off 100MBPS HALF
2 on 100MBPS HALF
3 off 100MBPS HALF
4 off 100MBPS HALF
5 on 100MBPS HALF
Autoneg
=========
Speed
=======
Duplex
=======
ETHERNET/SHOW/COUNT Example
To display Ethernet statistics:
Use the
ETHERNET/SHOW/COUNT command.
A similar display appears:
/ETHERNET/SHOW/COUNT 1
PORT#1 RX/TX Statistics
**************************************************
TX bytes: 103488
TX frames:
UniCast: 0 MultiCast: 1617 BroadCast: 0
TX errors:
Fcs: 0 txUndrErrs: 0
ExcessColl: 0 OneColl: 0 multiColl: 0
RX bytes: 0
RX frames:
UniCast: 0 MultiCast: 0 BroadCast: 0
rx64: 0 rx65to127: 0 rx128to255: 0
rx256to511: 0 rx512to1023: 0 rx1024to1518: 0
RX errors:
Fcs: 0 AlignOrErr: 0 rxGoodOverSz: 0
rxErrOverSz: 0 rxGoodUndSz: 0 rxErrUndSz: 0
discBuffFull: 0 discMemFull: 0
5-21
Page 100

Command Reference
Parameter Description
Table 5-6 describes the parameters shown in the ETHERNET/
SHOW/COUNT
Table 5-6 ETHERNET/SHOW/COUNT Parameters
display.
TX bytes
Tx frames
TX errors
Rx bytes The number of received bytes since the last time Ethernet statistics were
RX
frames
UniCast The number of unicast frames transmitted from one network device to
MultiCast The number of multicast frames transmitted from one network device to
BroadCast The number of broadcast frames transmitted to all network devices
Fcs The number of frames that were discarded on the transmit side because of
txUndrErrs The number of frames that were discarded on the transmit side because of
ExcessColl The number of frames that were dropped because of excessive collisions
OneColl The number of frames that were transmitted after exactly one collision
multiColl The number of frames that were transmitted after more than one collision
UniCast The number of received unicast frames
MultiCast The number of received multicast frames
The number of transmitted bytes since the last time Ethernet statistics were
enabled or cleared
another single network device
multiple network devices
FCS (Frame Check Sequence) error
underrun
enabled or cleared
BroadCast The number of received broadcast frames
rx64 The number of frames (including frames with errors) that were 64 bytes in
length
rx65to127 The number of frames (including frames with errors) that were between 65
and 127 bytes long
rx128to255 The number of frames (including frames with errors) that were between
127 and 255 bytes long
rx256to511 The number of frames (including frames with errors) that were between
256 and 511 bytes long
rx512to1023 The number of frames (including frames with errors) that were between
512 and 1023 bytes long
rx1024to1518 The number of frames (including frames with errors) that were between
1024 and 1518 bytes long
5-22
 Loading...
Loading...