Page 1

TQ5403 Series
Enterprise-class 802.11ac Wave 2 Wireless Access Points
with 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
AT-TQ5403
AT-TQm5403
AT-TQ5403e
Management Software User’s Guide
613-002651 Rev.C
Page 2

Copyright 2019 Allied Telesis, Inc.
All rights reserved.
This product includes software licensed under the BSD License. As such, the following language applies for those
portions of the software licensed under the BSD License:
Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without modification, are permitted provided that the following
conditions are met:
* Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
disclaimer.
* Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice, this list of conditions and the following
disclaimer in the documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* Neither the name of Allied Telesis, Inc. nor the names of the respective companies above may be used to endorse or
promote products derived from this software without specific prior written permission.
THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS" AND ANY
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF
MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT
SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED
TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR
BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN
CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY
WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
Copyright (c) [dates as appropriate to package] by The Regents of the University of California - All rights reserved.
Copyright (c) 2000-2003 by Intel Corporation - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 1997-2003, 2004 by Thomas E. Dickey
<dickey@invisible-island.net> - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 2001-2009 by Brandon Long (ClearSilver is now
licensed under the New BSD License.) Copyright (c) 1984-2000 by Carnegie Mellon University - All rights reserved.
Copyright (c) 2002,2003 by Matt Johnston - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 1995 by Tatu Ylonen <ylo@cs.hut.fi> - All
rights reserved. Copyright 1997-2003 by Simon Tatham. Portions copyright by Robert de Bath, Joris van Rantwijk,
Delian Delchev, Andreas Schultz, Jeroen Massar, Wez Furlong, Nicolas Barry, Justin Bradford, and CORE SDI S.A.
Copyright (c) 1989, 1991 by Free Software Foundation, Inc. (GNU General Public License, Version 2, June 1991).
Copyright (c) 2002-2005 by Jouni Malinen <jkmaline@cc.hut.fi> and contributors. Copyright (c) 1991, 1999 by Free
Software Foundation, Inc. (GNU Lesser General Public License, Version 2.1, February 1999). Copyright (c) 1998-2002
by Daniel Veillard - All rights reserved. Copyright (c) 1998-2004 by The OpenSSL Project - All rights reserved.
Copyright (c) 1995-1998 by Eric Young (eay@cryptsoft.com) - All rights reserved.
This product also includes software licensed under the GNU General Public License available from:
http://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl2.html
Allied Telesis is committed to meeting the requirements of the open source licenses including the GNU General Public
License (GPL) and will make all required source code available.
If you would like a copy of the GPL source code contained in this product, please send us a request by registered mail
including a check for US$15 to cover production and shipping costs, and a CD with the GPL code will be mailed to you.
GPL Code Request
Allied Telesis Labs (Ltd)
PO Box 8011
Christchurch, New Zealand
No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesis, Inc.
Allied Telesis™ and the Allied Telesis logo are trademarks of Allied Telesis, Incorporated.
Ethernet™ is a trademark of the Xerox Corporation.
Wi-Fi®, Wi-Fi Alliance®, WMM®, Wi-Fi Protected Access® (WPA), the Wi-Fi CERTIFIED logo, the Wi-Fi logo, the
Wi-Fi ZONE logo, and the Wi-Fi Protected Setup logo are registered trademarks of the Wi-Fi Alliance. Wi-Fi
CERTIFIED™, Wi-Fi Multimedia™, WPA2™ and the Wi-Fi Alliance logo are trademarks of the Wi-Fi Alliance.
Microsoft is a registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
Page 3

All other product names, company names, logos or other designations mentioned herein are trademarks or registered
trademarks of their respective owners.
Allied Telesis, Inc. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information contained in this document
without prior written notice. The information provided herein is subject to change without notice. In no event shall Allied
Telesis, Inc. be liable for any incidental, special, indirect, or consequential damages whatsoever, including but not limited
to lost profits, arising out of or related to this manual or the information contained herein, even if Allied Telesis, Inc. has
been advised of, known, or should have known, the possibility of such damages.
Page 4

Page 5

Contents
Preface ............................................................................................................................................................ 13
Safety Symbols Used in this Document ........................................................................................................... 14
Contacting Allied Telesis .................................................................................................................................. 15
Chapter 1: Getting Started ............................................................................................................................ 17
Features ........................................................................................................................................................... 18
Management Tools........................................................................................................................................... 20
Web Browser.............................................................................................................................................. 20
Vista Manager EX and AWC Plug-in.......................................................................................................... 20
SNMPv1 and v2c........................................................................................................................................ 21
Starting the First Management Session ........................................................................................................... 22
Starting the First Management Session with a Direct Connection ............................................................. 23
Starting the First Management Session without a DHCP Server ............................................................... 23
Starting a Management Session ...................................................................................................................... 25
Management Windows ..................................................................................................................................... 27
Main Menu.................................................................................................................................................. 27
Navigation .................................................................................................................................................. 28
Sub-menu................................................................................................................................................... 28
Content....................................................................................................................................................... 28
Saving and Applying Your Changes................................................................................................................. 29
Ending Management Sessions......................................................................................................................... 30
What to Configure First..................................................................................................................................... 31
Chapter 2: Basic Settings ............................................................................................................................. 33
Assigning a Dynamic IP Address from a DHCP Server ................................................................................... 34
Assigning a Static IP Address to the Access Point........................................................................................... 37
Setting the Date and Time with the Network Time Protocol (NTP) .................................................................. 40
Manually Setting the Date and Time ................................................................................................................ 43
Configuring SNMPv1 and v2c .......................................................................................................................... 45
Configuring SNMP Traps.................................................................................................................................. 49
Enabling or Disabling the LEDs........................................................................................................................ 51
Enabling or Disabling the Reset Button............................................................................................................ 52
Chapter 3: Web Browser Interface ............................................................................................................... 55
Configuring the Web Browser Interface............................................................................................................ 56
Changing the Manager’s Login Name and Password ...................................................................................... 58
Setting the Language of the Web Browser Interface........................................................................................ 60
Chapter 4: 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios ........................................................................................................... 61
Configuring the Radios ..................................................................................................................................... 62
Configuring Basic Radio Settings............................................................................................................... 62
Configuring Advanced Radio Settings........................................................................................................ 66
Displaying Radio Status ................................................................................................................................... 71
Dynamic Frequency Selection.......................................................................................................................... 73
Setting the Country Code Setting ..................................................................................................................... 74
Selecting the Location ...................................................................................................................................... 75
5
Page 6

Contents
Guidelines to Changing the Location..........................................................................................................75
Changing the Location to Outdoor..............................................................................................................76
Changing the Location to Indoor.................................................................................................................76
Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points .................................................................................................................77
VAP Introduction ...............................................................................................................................................78
Configuring Basic VAP Parameters ..................................................................................................................79
Configuring Captive Portal ................................................................................................................................84
Captive Portal Configurations .....................................................................................................................84
Port Numbers..............................................................................................................................................85
Requiring Wireless Clients to Click the Agree Button to Access to the Network ........................................85
Delegating a Proxy Server to Interact with Wireless Clients....................................................................... 87
Delegating RADIUS Servers and a Proxy Server.......................................................................................88
Delegating RADIUS Servers to Authenticate Wireless Clients...................................................................90
Creating Pages in HTML for a Proxy Server ..............................................................................................91
Requirements for the click_through_login.html and click_through_login_fail.html ........................92
HTML Code and Display Examples of Login Page .......................................................................92
Creating Login Pages in HTML When External RADIUS is Selected.........................................................92
Requirements for the radius_login.html and radius_login_fail.html ...............................................93
HTML Code and Display Examples of Login Page .......................................................................93
Configuring VAP Security .................................................................................................................................94
No Security .................................................................................................................................................94
Static WEP..................................................................................................................................................95
WPA Personal (Pre-Shared Key) ...............................................................................................................97
WPA Enterprise ........................................................................................................................................100
Configuring VAP Fast Roaming ......................................................................................................................104
Configuring the MAC Address List..................................................................................................................106
Displaying VAP and LAN Ports Statistics .......................................................................................................108
Advanced Settings ..........................................................................................................................................110
Chapter 6: Quality of Service ......................................................................................................................113
Introduction to Quality of Service ....................................................................................................................114
Configuring QoS Basic Settings......................................................................................................................116
Configuring AP EDCA Parameters .................................................................................................................117
Configuring Station EDCA Parameters...........................................................................................................120
Chapter 7: LAN1 and LAN2 Ports ...............................................................................................................123
Configuring the Management VLAN ...............................................................................................................124
Enabling or Disabling the LAN2 Port ..............................................................................................................126
Configuring PoE Negotiation with Link Layer Discovery Protocol................................................................... 128
Displaying the Status of LAN1 and LAN2 Ports..............................................................................................130
Chapter 8: Wireless Distribution System Bridges ....................................................................................133
Introduction to Wireless Distribution Bridges ..................................................................................................134
WDS Bridge Elements ....................................................................................................................................137
Radio ........................................................................................................................................................137
VAP0.........................................................................................................................................................137
Radio Channel ..........................................................................................................................................137
Parents and Children ................................................................................................................................137
Security.....................................................................................................................................................137
Dynamic Frequency Selection ..................................................................................................................138
Guidelines .......................................................................................................................................................139
Preparing Access Points for a WDS Bridge....................................................................................................140
Chapter 9: Monitoring .................................................................................................................................. 143
Displaying Basic System Information.............................................................................................................. 144
Displaying Neighboring Access Points ...........................................................................................................147
6
Page 7

Displaying Associated Clients148
Chapter 10: System Log 149
Displaying the System Log150
Sending Log Messages to a Syslog Server152
Chapter 11: Maintenance 155
Downloading the Configuration of the Access Point to Your Computer156
Restoring a Configuration to the Access Point158
Restoring the Default Settings to the Access Point159
Uploading New Management Software to the Access Point160
Rebooting the Access Point162
Sending Technical Support Information to Allied Telesis163
AT-TQ5403 Access Point User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Contents
8
Page 9

List of Figures
Figure 1: Log On Window................................................................................................................................ 25
Figure 2: Sample Management Window ......................................................................................................... 27
Figure 3: Main Menu Button ............................................................................................................................ 28
Figure 4: Network DHCP Window ................................................................................................................... 35
Figure 5: Network Static IP Address Window.................................................................................................. 37
Figure 6: Time Window - NTP Option.............................................................................................................. 40
Figure 7: Daylight Savings Time Settings........................................................................................................ 42
Figure 8: Time Window - Manually Option ...................................................................................................... 43
Figure 9: SNMP Agent Settings Window......................................................................................................... 45
Figure 10: Trap Settings Window .................................................................................................................... 49
Figure 11: LED Window................................................................................................................................... 51
Figure 12: Hardware Window .......................................................................................................................... 52
Figure 13: Web Window .................................................................................................................................. 56
Figure 14: User Window .................................................................................................................................. 58
Figure 15: Language Window.......................................................................................................................... 60
Figure 16: Basic Radio Settings Window on AT-TQ5403and AT-TQm5403................................................... 62
Figure 17: Basic Radio Settings Window on AT-TQ5403e.............................................................................. 63
Figure 18: Advanced Radio Settings Window ................................................................................................. 67
Figure 19: Radio Status Window ..................................................................................................................... 71
Figure 20: Virtual Access Point Tab ................................................................................................................ 79
Figure 21: Captive Portal - Click-Through ....................................................................................................... 86
Figure 22: Captive Portal - Using a Proxy Server............................................................................................ 88
Figure 23: Captive Portal - External RADIUS.................................................................................................. 89
Figure 24: Captive Portal - External RADIUS.................................................................................................. 91
Figure 25: Captive Portal - Terms of Service Page Sample............................................................................ 92
Figure 26: Captive Portal - Login Page Sample .............................................................................................. 93
Figure 27: None Selection in the VAP Security Tab........................................................................................ 94
Figure 28: Static WEP Security Tab ................................................................................................................ 95
Figure 29: WPA Personal Security Tab........................................................................................................... 98
Figure 30: WPA Enterprise Tab..................................................................................................................... 100
Figure 31: Fast Roaming Window ................................................................................................................. 104
Figure 32: MAC Address List Window........................................................................................................... 106
Figure 33: Statistics Window ......................................................................................................................... 108
Figure 34: Advanced Settings Tab ................................................................................................................ 110
Figure 35: QoS Window ................................................................................................................................ 115
Figure 36: LAN Settings Window................................................................................................................... 124
Figure 37: LLDP Window............................................................................................................................... 129
Figure 38: LAN1 Window............................................................................................................................... 130
Figure 39: LAN2 Window............................................................................................................................... 130
Figure 40: WDS Bridge.................................................................................................................................. 134
Figure 41: Example of Radio and Channel Assignments in a WDS Bridge .................................................. 135
Figure 42: Example of an Access Point as Both Parent and Child................................................................ 136
Figure 43: System Window............................................................................................................................ 144
Figure 44: Neighbor AP Window ................................................................................................................... 147
Figure 45: Associated Client Window............................................................................................................ 148
9
Page 10

List of Figures
Figure 46: Log Window for Event Messages ................................................................................................. 151
Figure 47: Log Window for Syslog Client....................................................................................................... 152
Figure 48: Configuration Window................................................................................................................... 156
Figure 49: Upgrade Window .......................................................................................................................... 161
Figure 50: Reboot Window ............................................................................................................................ 162
Figure 51: Support Window ........................................................................................................................... 163
10
Page 11

List of Tables
Table 1. TQ5403 Series Access Points Differences ...................................................................................... 19
Table 2. Network DHCP Window ................................................................................................................... 35
Table 3. Network Static IP Selection Window ................................................................................................ 38
Table 4. Time Window - NTP Option .............................................................................................................. 41
Table 5. Time Window - Manually Option ....................................................................................................... 44
Table 6. SNMP Agent Settings Window ......................................................................................................... 46
Table 7. SNMP Trap Settings Window ........................................................................................................... 50
Table 8. Default Settings for Reset Button ..................................................................................................... 52
Table 9. Web Window .................................................................................................................................... 57
Table 10. Basic Radio Settings Window ......................................................................................................... 63
Table 11. Advanced Radio Settings Window ................................................................................................. 67
Table 12. Radio Status Window ..................................................................................................................... 71
Table 13. Virtual Access Point Tab ................................................................................................................ 80
Table 14. Captive Portal ................................................................................................................................. 86
Table 15. Captive Portal - External RADIUS .................................................................................................. 89
Table 16. Static WEP Security Tab ................................................................................................................ 96
Table 17. WPA Personal Security Tab ........................................................................................................... 98
Table 18. WPA Enterprise Tab ..................................................................................................................... 101
Table 19. Fast Roaming Window ................................................................................................................. 105
Table 20. Statistics Window ......................................................................................................................... 109
Table 21. Advanced Settings Tab ................................................................................................................ 110
Table 22. QoS Window - Basic Settings ....................................................................................................... 116
Table 23. QoS Window - AP EDCA Parameters .......................................................................................... 117
Table 24. QoS Window - Station EDCA Parameters .................................................................................... 120
Table 25. LAN Settings Window - VLAN Configuration Section ................................................................... 125
Table 26. LAN1 or LAN2 Window ................................................................................................................. 131
Table 27. System Window ............................................................................................................................ 144
Table 28. Neighbor AP Window ................................................................................................................... 147
Table 29. Associated Client Window ............................................................................................................ 148
Table 30. Message Severity Levels .............................................................................................................. 150
Table 31. Log Window for Syslog Client ....................................................................................................... 152
11
Page 12

List of Tables
12
Page 13

Preface
This guide contains instructions on how to manage the features of the
TQ5403 series access points with the web browser management interface.
The access point models included in this guide are:
AT-TQ5403
AT-TQm5403
AT-TQ5403e
This preface contains the following sections:
“Safety Symbols Used in this Document” on page 14
“Contacting Allied Telesis” on page 15
13
Page 14

Preface
Safety Symbols Used in this Document
This document uses the following conventions.
Note
Notes provide additional information.
Caution
Cautions inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warning
Warnings inform you that performing or omitting a specific action
may result in bodily injury.
Warning
Laser warnings inform you that an eye or skin hazard exists due to
the presence of a Class 1 laser device.
14
Page 15

Contacting Allied Telesis
If you need assistance with this product, you can contact Allied Telesis
technical support by going to the Support & Services section of the Allied
Telesis web site at www.alliedtelesis.com/support. You can find links for
the following services on the page:
24/7 Online Support - Enter our interactive support center to
search for answers to your questions in our knowledge database,
check support tickets, learn about Return Merchandise
Authorizations (RMAs), and contact Allied Telesis technical
experts.
USA and EMEA phone support - Select the phone number that
best fits your location and customer type.
Hardware warranty information - Learn about Allied Telesis
warranties and register your product online.
Replacement Services - Submit an RMA request via our interactive
support center.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Documentation - View the most recent installation guides, user
guides, software release notes, white papers and data sheets for
your product.
Software Updates - Download the latest software releases for your
product.
For sales or corporate contact information, select your region and country
and then go to www.alliedtelesis.com/contact.
15
Page 16

Preface
16
Page 17

Chapter 1
Getting Started
Here are the sections in this chapter:
“Features” on page 18
“Management Tools” on page 20
“Starting the First Management Session” on page 22
“Starting a Management Session” on page 25
“Management Windows” on page 27
“Saving and Applying Your Changes” on page 29
“Ending Management Sessions” on page 30
“What to Configure First” on page 31
17
Page 18

Chapter 1: Getting Started
Features
The TQ5403 series wireless access points have the following features:
One 2.4GHz radio
Two 5GHz radios
Eight virtual access points per radio
WPA Personal and WPA Enterprise with WPA, WPA2, TKIP, and
CCMP authentication and encryption
Static WEP encryption
MAC address filter for wireless clients
Multicast rate limiting
Band steering
Automatic channel selection
Adjustable transmission power
Fast roaming
Airtime fairness
Quality of Service
Wireless Distribution System (WDS) bridges
Channel blankets (AT-TQ5403 and AT-TQ5403e only)
DHCP client
RADIUS accounting with external RADIUS server
Network Time Protocol client
HTTP and HTTPS web browser management
SNMPv1 and v2c management
Event log
Syslog client
LAN1 port: 10/100/1000Base-T Ethernet port with Power over
Ethernet (PoE), Auto-Negotiation, and auto MDI/MDIX (ATTQ5403 and AT-TQm5403 only)
LAN2 port: 10/100/1000Base-T Ethernet port with Auto-
Negotiation and auto MDI/MDIX (AT-TQ5403 and AT-TQm5403
only)
18
LAN(PoE) port: 10/100/1000Base-T Ethernet port with IEEE
802.3at PoE+, Auto-Negotiation, and auto MDI/MDIX
(AT-TQ5403e only)
Static link aggregation for LAN1 and LAN2 ports (AT-TQ5403 and
AT-TQm5403 only)
Page 19
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
IEEE 802.3 (10Base-T), IEEE 802.3u (100Base-TX), and IEEE
802.3ab (1000Base-T) compliance on LAN1, LAN2, LAN(PoE)
ports.
Outdoor installation on a wall or pole (AT-TQ5403e only)
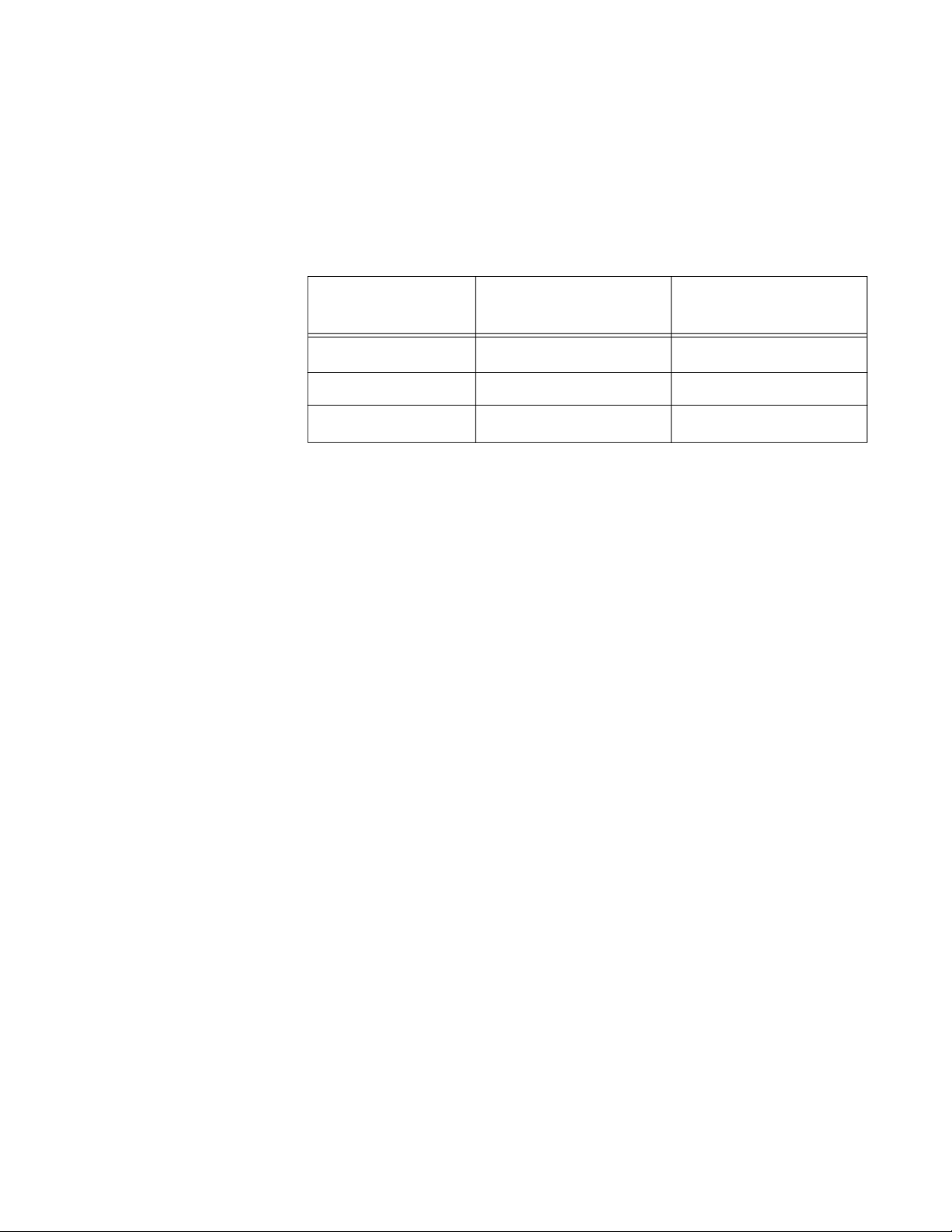
Table 1 lists the differences among the TQ5403 series access points.
Table 1. TQ5403 Series Access Points Differences
Access Point Channel Blankets
AT-TQ5403
Supported
1
Maximum Number of
Wireless Clients
200
AT-TQm5403 Not supported 127
AT-TQ5403e
1. Requires Vista Manager EX and Autonomous Wireless Controller (AWC) plugin.
Supported
1
200
19
Page 20

Chapter 1: Getting Started
Management Tools
The access points support the following management tools.
Web Browser The access point has a web browser management interface for
configuring the device from your management workstations. The web
browser interface allows you to manage one unit at a time and supports
both non-secure HTTP and secure HTTPS management sessions. The
default is HTTP.
Note
The product has been tested with Microsoft Windows Internet
Explorer Version 9 or later and Microsoft Edge.
Vista Manager
EX and AWC
Plug-in
The access point is supported with Vista Manager and the Autonomous
Wave Control (AWC) plug-in. Configuring and monitoring large numbers
of devices is simplified with AWC because you can add multiple devices to
management groups and manage them as one unit. The application can
also monitor the operations of the access points and automatically adjust
operating properties to optimize the performance of your wireless network.
Note
The AT-TQ5403 access point requires Vista Manager 2.4 or later.
The AT-TQm5403 and AT-TQ5403e access points require Vista
Manager 2.5 or later.
Note
The channel blanket feature of the AT-TQ5403 and AT-TQ5403e
access points requires Vista Manager EX and the AWC plug-in.
You cannot configure the following access point settings with Vista
Manager EX and the AWC plug-in. These settings require the web
browser interface:
Hostname
20
DHCP client or static IP address
Domain Name Server name
Timezone
Daylight savings time
System date or time
HTTP and HTTPS modes
System name, location, and contact
Page 21

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
LLDP PoE negotiation
Enable or disable the Reset button
SNMPv1 and v2c You can use SNMPv1 or SNMPv2 to view the parameter settings of the
devices. The MIB is available from the Allied Telesis web site. For
instructions on how to configure the unit for SNMP, refer to “Configuring
SNMPv1 and v2c” on page 45 and “Configuring SNMP Traps” on page 49.
Note
You cannot use SNMP to change the parameter settings on the
access points.
Note
The access points do not support SNMPv3 or the AT-UWC Wireless
LAN Controller.
21
Page 22

Chapter 1: Getting Started
Starting the First Management Session
Note
If you are using the AT-TQ5403 or AT-TQm5403 access point, use
the LAN1 port. If you are using the AT-TQ5403e access point, use
the LAN(PoE) port.
After you install and power on the access point, it queries the subnet on
the LAN1 or LAN(PoE) port for a DHCP server. If a DHCP server
responds to its query, the unit uses the IP address the server assigns to it.
If there is no DHCP server, the access point uses the default IP address
192.168.1.230.
If your network has a DHCP server, use the IP address the server assigns
it to it to start the management session. For directions, refer to “Starting a
Management Session” on page 25
If your network does not have a DHCP server, you can start the first
management session by establishing a direct connection between your
computer and the unit by connecting an Ethernet cable to the Ethernet
port on the computer and the LAN1 or LAN(PoE) port on the access point.
This procedure requires changing the IP address on your computer to
make it a member of the same subnet as the default IP address on the
access point.
The first management session can also be performed while the device is
connected to your network. However, If your network does not have a
DHCP server, you still have to change the IP address of your computer to
match the subnet of the default address of the access point. Furthermore,
if your network is divided into virtual LANs (VLANs), you have to be sure to
connect the access point and your computer to ports on an Ethernet
switch that are members of the same VLAN.
The instructions for starting the first management session are found in the
following sections:
“Starting the First Management Session with a Direct Connection” on
page 23. This section is for the AT-TQ5403 and AT-TQm5403 models
only.
“Starting the First Management Session without a DHCP Server” on
page 23
22
Note
The first management session of the access point has to be
conducted through the LAN1 or LAN(PoE) port because the default
setting for the radios is off.
Page 23

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Starting the First
Management
Session with a
Direct
Connection
To start the management session with a direct Ethernet connection
between your computer and the LAN1 port on the access point, perform
the following procedure:
Note
This section is for the AT-TQ5403 and AT-TQm5403 models only.
Note
If the access point is using PoE, you cannot perform this procedure
because it requires a direct connection between your computer and
the LAN1 port on the access point. If you have the optional power
supply, you can connect it to the unit until after you have completed
the first management session, or you can perform “Starting the First
Management Session without a DHCP Server” on page 23.
1. Connect one end of a network cable to the LAN1 port on the access
point and the other end to the Ethernet network port on your computer.
2. Change the IP address on your computer to 192.168.1.n, where n is a
number from 1 to 254, but not 230. Refer to the documentation that
accompanies your computer for instructions on how to set the IP
address.
Starting the First
Management
Session without a
DHCP Server
3. Set the subnet mask on your computer to 255.255.255.0.
4. Power on the access point.
5. Start the web browser on your computer.
6. Enter the IP address 192.168.1.230 in the URL field of the browser and
press the Enter key.
You should now see the login window, shown in Figure 1 on page 25.
7. Enter “manager” for the user name and “friend” for the password. The
user name and password are case-sensitive.
8. Click the Login button.
This procedure explains how to start the first management session on the
access point when the LAN port is connected to an Ethernet switch on a
network that does not have a DHCP server. To start the management
session, perform the following procedure:
1. To use the PoE feature on the access point, be sure to connect the
LAN1 or LAN(PoE) port to a PoE source device.
23
Page 24

Chapter 1: Getting Started
2. If your network has VLANs, check to be sure that your computer and
the access point are connected to ports on the Ethernet switch that are
members of the same VLAN. This might require accessing the
management software on the switch and listing the VLANS and their
port assignments. For example, if the access point is connected to a
port that is a member of the Sales VLAN, your computer must be
connected to a port that is also a member of that VLAN. If your
network is small and does not have VLANs or routers, you can
connect your computer to any port on the Ethernet switch.
3. Change the IP address on your computer to 192.168.1.n, where n is a
number from 1 to 254, but not 230. Refer to the documentation that
accompanies your computer for instructions on how to set the IP
address.
4. Set the subnet mask on your computer to 255.255.255.0.
5. Power on the access point.
6. Start the web browser on your computer.
7. Enter the IP address 192.168.1.230 in the URL field of the browser
and press the Return key.
You should now see the logon window, shown in Figure 1 on page 25.
8. Enter “manager” for the user name and “friend” for the password. The
user name and password are case-sensitive.
9. Click the Login button.
24
Page 25
Starting a Management Session
This section explains how to start a management session on the access
point from your management workstation, using a web browser. The
procedure assumes that the access point has already been assigned an IP
address, either manually or from a DHCP server.
Note
If the access point is using its default address 192.168.1.230, refer
to “Starting the First Management Session” on page 22 for
instructions.
To start a management session on the access point, perform the following
procedure:
1. Open the web browser on your management workstation.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
2. Enter the IP address of the access point in the URL field of the web
browser.
Note
Precede the IP address with HTTPS:// if the access point is already
configured for HTTPS management. The default is HTTP
management.
See the log on window shown in Figure 1 as an example.
Figure 1. Log On Window
25
Page 26

Chapter 1: Getting Started
Note
If you use HTTPS management, your web browser might display a
warning message stating that the site certificate is invalid. If this
occurs, select an appropriate option to continue to the web site. To
avoid the message in future management sessions, make the web
site a trusted site in your web browser.
3. Enter the user name and password for the unit. The default values are
“manager” for the user name and “friend” for the password. The user
name and password are case-sensitive.
4. Click the Login button.
26
Page 27
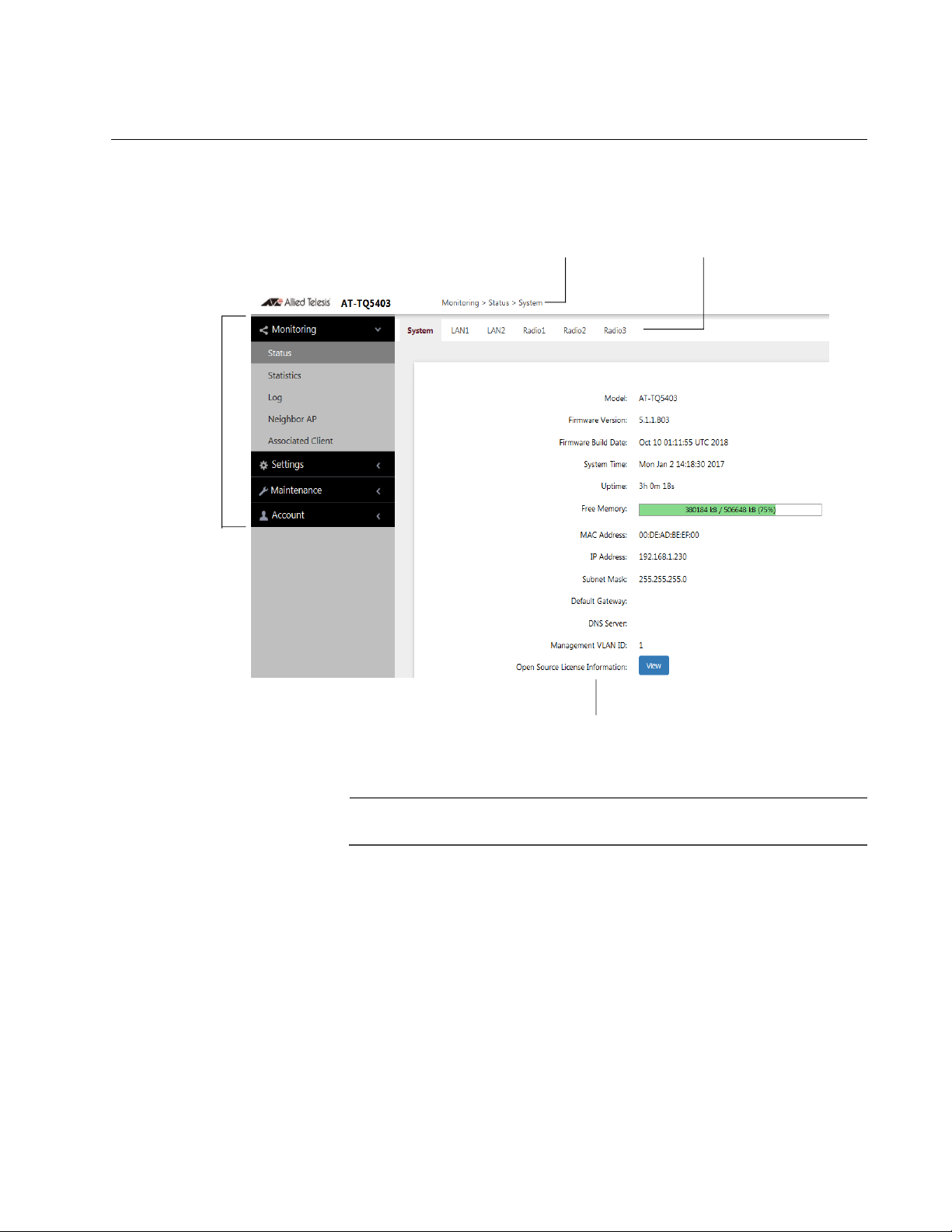
Management Windows
This section has a brief overview of the management windows and menus.
The main parts of the management windows are identified in Figure 2.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Main
Menu
Navigator
Sub-menu
Content
Figure 2. Sample Management Window
Note
The AT-TQ5403e does not have LAN2 on the sub-menu.
Main Menu The main menu is displayed on the left side of the windows and consists of
the following selections:
Monitoring
Settings
Maintenance
Account
Clicking a main menu option expands it to display the sub-items. The
Monitoring option is expanded by default at the start of management
sessions.
27
Page 28

Chapter 1: Getting Started
Navigation The Navigator shows the menu path of the current window.
If the main menu is not displayed, the window might be too small to display
the menu and content together. To display the main menu, you can either
enlarge the window or click the main menu button, shown in Figure 3.
Clicking the main menu button displays the menu over the content
window. The menu is hidden again after you make a menu selection.
Main Menu Button
Figure 3. Main Menu Button
Sub-menu Sub-menus are located across the tops of many management windows.
Content This is the main body of the windows. It displays parameters for you to
configure or status or statistics information.
28
Page 29

Saving and Applying Your Changes
You need to click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and activate your
changes when you are finished configuring the parameters in a
management window. The button is located in the bottom of the windows.
When you click the button, the access point immediately activates your
changes and saves them in its configuration file. If you change the
parameter settings in a window and navigate to a different window without
clicking the button, the access point discards your changes.
The access point displays the following messages when you click the
SAVE & APPLY button:
Please wait...
Waiting for changes to be applied...
Changes applied.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
29
Page 30

Chapter 1: Getting Started
Ending Management Sessions
You should always log off when you are finished managing the unit. To log
off, select Account > Logout. Click OK at the confirmation prompt. For
added security, close your web browser.
30
Page 31

What to Configure First
Here are suggestions on what to configure during the first management
session:
1. Set the country code. Refer to “Setting the Country Code Setting” on
page 74.
Note
The country code for units sold in North America, Japan, Canada,
Taiwan is preset and cannot be changed.
Note
Changing the country setting disables the radios. The procedure is
disruptive to network operations if the unit is actively forwarding
client traffic.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
2. Change the manager’s login name and password. Refer to “Changing
the Manager’s Login Name and Password” on page 58.
3. If you prefer to use HTTPS management sessions, perform
“Configuring the Web Browser Interface” on page 56.
4. Set the language of the management interface to English or Japanese.
The default is English. Refer to “Setting the Language of the Web
Browser Interface” on page 60.
5. Activate the LAN2 port to double the bandwidth to your wired network.
Refer to “Enabling or Disabling the LAN2 Port” on page 126.
Note
Skip Step 5 if you are using the AT-TQ5403e model because it does
not have the LAN2 port.
31
Page 32

Chapter 1: Getting Started
32
Page 33

Chapter 2
Basic Settings
This chapter contains the following procedures:
“Assigning a Dynamic IP Address from a DHCP Server” on page 34
“Assigning a Static IP Address to the Access Point” on page 37
“Setting the Date and Time with the Network Time Protocol (NTP)” on
page 40
“Manually Setting the Date and Time” on page 43
“Configuring SNMPv1 and v2c” on page 45
“Configuring SNMP Traps” on page 49
“Enabling or Disabling the LEDs” on page 51
“Enabling or Disabling the Reset Button” on page 52
33
Page 34

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Assigning a Dynamic IP Address from a DHCP Server
This section explains how to activate the DHCP client so that the access
point receives its IP address from a DHCP server on your network. The
unit uses the address to communicate with devices on your network, such
as management workstations, syslog servers, and RADIUS servers. The
access point can have only one IP address.
If your network does not have a DHCP server or you prefer to manually
assign it an IP address, refer to “Assigning a Static IP Address to the
Access Point” on page 37.
Note
Changing the IP address of the access point might interrupt your
management session. To resume managing the device, start
another session using the access point’s new IP address.
Note
The default setting for the DHCP client is enabled. You only need to
perform this procedure if you disabled the client and assigned the
device a static IP address, but now want to reactivate the client.
To configure the access point to receive its IP address from a DHCP
server, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > System from the main menu.
2. Select Network from the sub-menu.
3. Select DHCP from the Connection Type pull-down menu. The options
in the window change. Refer to Figure 4 on page 35.
34
Page 35

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Figure 4. Network DHCP Window
4. Configure the fields by referring to Table 2.
Table 2. Network DHCP Window
Parameter Description
Hostname Enter a hostname for the access point. Here
are the guidelines:
- The hostname can be from 1 to 63
alphanumeric characters.
- The hostname cannot contain spaces or
any special characters, except hyphens.
- The first or last character cannot be a
hyphen.
- The access point can have only one
hostname.
- The default is AT-TQ5403, AT-TQm5403,
or AT-TQ5403e.
- If you want the DHCP server to supply the
hostname, enable the Get Hostname from
DHCP Server option in this window.
Connection Type Select DHCP. This is the default. The Static
IP selection is explained in “Assigning a
Static IP Address to the Access Point” on
page 37.
35
Page 36

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Table 2. Network DHCP Window (Continued)
Parameter Description
Get Hostname from
DHCP Server
Control how the access point obtains its
hostname. The options are listed here:
- Enabled: The access point queries the
DHCP server for its hostname.
- Disabled: The access point does not query
the DHCP server for a hostname. Instead,
it uses the entry in the Hostname field in
this window.
DNS Name Server Enter the IP address of the DNS name
server. If this field is left blank, the access
point tries to obtain the address from the
DHCP server. The default is no name.
5. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
Note
If the access point stops responding to the web browser
management windows, start a new management session using the
new IP address that the access point received from the DHCP
server.
36
Page 37

Assigning a Static IP Address to the Access Point
This section explains how to manually assign an IP address to the access
point. The unit uses the address to communicate with devices on your
network, such as management workstations, syslog servers, and RADIUS
servers. The access point can have only one IP address.
If you prefer the access point obtain its IP configuration from a DHCP
server on your network, refer to “Assigning a Dynamic IP Address from a
DHCP Server” on page 34.
Note
Changing the IP address of the access point might interrupt your
management session. To resume managing the device, start a new
session using the access point’s new IP address.
To assign a static IP address to the device, perform the following
procedure:
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
1. Select Settings > System from the main menu.
2. Select Network from the sub-menu.
3. Select Static IP from the Connection Type pull-down menu. The
options in the window change. Refer to Figure 5.
Figure 5. Network Static IP Address Window
4. Configure the field values by referring to Table 3 on page 38.
37
Page 38

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Table 3. Network Static IP Selection Window
Item Name Description
Host Name Enter a host name for the access point. Here
are the guidelines:
- The host name can be from 1 to 63
alphanumeric characters.
- The hostname cannot contain spaces or
any special characters, except hyphens.
- The first or last character cannot be a
hyphen.
- The access point can have only one
hostname.
- The default is AT-TQ5403, AT-TQm5403,
or AT-TQ5403e.
Connection Type Select Static IP.
Static IP Address Enter the new IP address for the access
point. The device can have only one IP
address. The default is 192.168.1.230.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask for the IP address.
The default is 255.255.255.0.
Default Gateway Enter the default gateway address for the
unit. The default is 192.168.1.254.
The default gateway is an IP address of an
interface on a router or other Layer 3 routing
device. It specifies the first hop to reaching
the subnets or networks where your
management devices, such as management
workstations and syslog servers, reside. The
access point can have only one default
gateway and the network portion of the
address must be the same as the IP address
entered in step 3.
You have to assign a default gateway to the
access point. If your network does not have
a default gateway or you do not want to
assign one to the access point at this time,
enter an unused IP address of the same
network as the IP address.
38
Page 39

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Table 3. Network Static IP Selection Window (Continued)
Item Name Description
DNS Name Server Specify the Domain Name Service name
server address. This field is optional The
default is no name.
5. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
39
Page 40

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Setting the Date and Time with the Network Time Protocol (NTP)
The access point has a Network Time Protocol (NTP) client for setting its
date and time from an SNTP server on your network or the Internet. The
access point adds the date and time to log messages and SNMP traps.
Here are the guidelines to using the client:
You need to know the host name or IP address of an SNTP server
on your network or the Internet. You can specify only one server.
The access point must have an IP address and subnet mask.
The access point must also have a default gateway address if the
NTP server is on a different subnet or network. The default
gateway must specify the first router hop to the subnet or network
of the SNTP server.
The client is compatible with SNTP servers. It is not compatible
with NTP servers.
To configure the NTP client, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > System from the main menu.
2. Select Time from the sub-menu. Refer to Figure 8 on page 43.
3. From the Set System Time pull-down menu, select Using Network
Time Protocol (NTP). The window is updated with new options. Refer
to Figure 6.
40
Figure 6. Time Window - NTP Option
Page 41

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
4. Configure the fields by referring to Table 4.
Table 4. Time Window - NTP Option
Item Name Description
Set System Time Select Network time protocol (NTP) to
synchronize the date and time of the product with
the NTP server. The factory default is Manually.
Timezone Use this pull-down menu to set the time zone of
the location of the access point.
If the SNTP server is providing Coordinated
Universal Time (UTC), the access point uses the
time zone parameter to determine its UTC offset,
which is the number of hours its location is ahead
or behind UTC. It adjusts the time accordingly.
Enable Daylight
Saving
If the location of the access point observes
daylight savings time, click the check box for this
option. The window displays the fields in Figure 7
on page 42.
If the area does not observe Daylight Savings
time, leave the check box empty.
Start Use the pull-down menus to set the date and time
for the start of Daylight Savings Time.
End Use the pull-down menus to set the date and time
for the end of Daylight Savings Time.
Offset Use the pull-down menu to select the number of
minutes to adjust the time at the start and end
Daylight Saving Time. The default is 60 minutes.
Current System
Displays the date and time of the access point.
Time (24 HR)
Interval to
Synchronize
Enter the interval in minutes at which the access
point synchronizes its time with the SNTP server.
The range is 1 to 9999 minutes. The default is 10
minutes.
41
Page 42

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Table 4. Time Window - NTP Option (Continued)
Item Name Description
NTP Server Specify the SNTP server using one of the
following methods:
- IP address (example, 12.34.56.78)
- Fully qualified domain name (FQDN) (example,
ntp.mydomain.com)
Here are the guidelines:
- You can specify only one server.
- The first character must be a letter or number.
It cannot be a special character.
- The last character cannot be a hyphen or
period.
- The factory default is no server.
Observe these guidelines when using an FQDN
to identify the server:
- It cannot start or end with a hyphen.
- Domain labels can have a maximum of 63
characters.
- An FQDN can have up to 253 characters.
Figure 7 contains the settings for Daylight Savings Time.
Figure 7. Daylight Savings Time Settings
42
5. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
Page 43

Manually Setting the Date and Time
This section explains how to manually set the date and time on the access
point.
Note
The access point does not have a real-time clock with backed up
batteries. Consequently, the date and time, when set manually, are
returned to their default values (Jan 1 00: 00: 00 2018) when the
device is reset or powered off.
Note
Allied Telesis recommends using a SNTP server to set the date and
time. For instructions, refer to “Setting the Date and Time with the
Network Time Protocol (NTP)” on page 40.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
To manually set the date and time, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > System from the main menu.
2. Select Time from the sub-menu. Refer to Figure 8.
Figure 8. Time Window - Manually Option
3. Configure the parameters by referring to Table 5 on page 44.
43
Page 44

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Table 5. Time Window - Manually Option
Field Description
Set System Time Select Manually. This is the default.
Current System
Displays the current date and time settings.
Time (24 HR)
Click the AUTO button to set the date and
time on the access point according to your
management workstation.
Timezone Select the Time Zone of the access point
from the pull-down menu.
Enable Daylight
Savings
If the location of the access point observes
daylight savings time, click the dialog box for
the Adjust Time for Daylight Savings
parameter. The window displays the fields in
Figure 7 on page 42
If the area does not observe Daylight
Savings time, leave the check box empty.
Start Use the pull-down menus to set the date and
time for the start of Daylight Savings Time.
End Use the pull-down menus to set the date and
time for the end of Daylight Savings Time.
Offset Use the pull-down menu to select the
number of minutes to adjust the time at the
start and end Daylight Saving Time. The
default is 60 minutes.
44
System Date Use the pull-down menus to set the current
month, day, and year.
System Time Use the pull-down menus to set the current
hours and minutes. The hours are in 24
hours. For example, 14 represent 2:00 p.m.
4. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
Page 45

Configuring SNMPv1 and v2c
You can use SNMPv1 and v2c to view the settings and client statistics on
the access point, and receive traps. Here are the guidelines:
You cannot use SNMP to change the settings on the access point.
The access point does not support SNMPv3.
The access point has one read-only community string.
The unit must have an IP address for SNMP management. For
instructions, refer to “Assigning a Static IP Address to the Access
Point” on page 37 or “Assigning a Dynamic IP Address from a
DHCP Server” on page 34.
To enable or disable SNMP, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > System from the main menu.
2. Select SNMP from the sub-menu.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
3. Click the Agent Settings tab. This is the default tab. Refer to Figure 9.
Figure 9. SNMP Agent Settings Window
4. Configure the fields by referring to Table 6 on page 46.
45
Page 46

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Note
To configure the parameters in the window, you must first set the
Status parameter to Enabled. You cannot adjust the settings when
Status is Disabled.
Table 6. SNMP Agent Settings Window
Field Description
Status Use this option to activate or deactivate the
SNMP agent on the access point. The options are
explained here:
- Enabled: Select this option to activate the
SNMP agent and trap settings. This allows you
to use SNMP to view the parameter settings on
the access point. It also allows the access point
to send traps. You have to enable SNMP to
configure the settings in this window and the
Trap Settings window.
Read-only
Community
Name
- Disabled: Select this option to disable SNMP
and the trap settings. This is the default setting.
Use this option to specify the read-only
community string for the access point. The
community string is used to view the MIB settings
of the device. Here are the guidelines:
- The community string can be from 1 to 256
alphanumeric characters.
- The community string cannot contain any
spaces.
- The community string is case sensitive.
- You can specify only one read-only community
string.
- You can not leave the field empty.
- The default read-only community string is
“public”.
- The community string cannot contain any of the
following symbols: "" (Double quote), '' (single
quote), '¥' or '/' (Yen sign or backslash), '&', '<',
'>'.
46
Page 47

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Table 6. SNMP Agent Settings Window (Continued)
Field Description
Port Use this parameter to specify the port number for
SNMP. The range is 1 to 65535. The default is
161.
Restrict the
Source of
SNMP
Requests
Only allow
from the
designated
hosts or
subnets
Use this option to increase the security of the
access point by restricting the use of SNMP to
specific subnets or individual workstations. The
options are described here:
- Enabled: Check this option to restrict the use of
SNMP on the access point to only those
management stations specified in the next field
in the window.
- Disabled: Check this option to disable this
feature and permit any workstation to use the
community string to view the unit. This is the
default setting.
Use this field to identify the management
workstations permitted to use SNMP to view the
device. This field only applies if you select the
Enabled option in the previous field. Here are the
guidelines:
- You can specify only one value in the field.
- You can specify a specific workstation by its IP
address (for example,149.23.45.102).
System
Name
- You can specify a subnet by including the
subnet mask (for example, 67.101.4.0/24).
- You can specify a workstation by its FQDN.
- The default is blank.
Observe these guidelines when using an FQDN
to identify the workstation:
- It cannot start or end with a hyphen.
- Domain labels can have a maximum of 63
characters.
- An FQDN can have up to 253 characters.
Specify the SNMP system name of the access
point. The default is AT-TQ5403, AT-TQm5403,
or AT-TQ5403e.
47
Page 48

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Table 6. SNMP Agent Settings Window (Continued)
Field Description
System
Contact
Specify the system administrator name. The
system contact can be up to 64 alphanumeric
characters. The default is Unknown.
System
Location
Enter the location of the device. It can be up to 64
alphanumeric characters. The default is
Unknown.
5. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
48
Page 49

Configuring SNMP Traps
To configure the access point to transmit SNMP traps, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select Settings > System from the main menu.
2. Select SNMP from the sub-menu.
3. Click the Trap Settings tab. Refer to Figure 10.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Figure 10. Trap Settings Window
Note
The Status parameter has to be set to Enabled in the Agent Settings
tab before you can configure the parameters in this window. Refer to
“Configuring SNMPv1 and v2c” on page 45.
4. Configure the fields by referring to Table 7 on page 50.
49
Page 50

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Table 7. SNMP Trap Settings Window
Parameter Description
Community
Name for
Traps
Use this field to specify the community name the
access point is to use to transmit traps. Here are
the guidelines:
- The community name can be from 1 to 256
alphanumeric characters.
- The default is blank.
- The name cannot contain any of the following
characters: "" (Double quote), '' (single quote),
'¥' or '/' (Yen sign or backslash), '&', '<', '>.'
Trap Types Select radio button for the trap type you want to
generate:
- Cold Start - This trap is sent when the SNMP
agent started.
- Link - This trap is sent when a radio enabled or
disabled.
- Authentication - This trap is sent when an
SNMP authentication fails
Trap Host IP
Address /
Hostname
Specify the SNMP hosts to receive the traps.
Here are the guidelines:
- You can specify up to three hosts.
50
- The hosts can be identified by IP addresses or
hostnames.
- The default is blank.
Observe these guidelines when using an FQDN
to identify a host:
- It cannot start or end with a hyphen.
- Domain labels can have a maximum of 63
characters.
- An FQDN can have up to 253 characters.
5. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
Page 51

Enabling or Disabling the LEDs
The access point has an Eco Mode. When activated, it turns off the LEDs
on the top panel. You might activate the mode when you are not using the
LEDS to monitor or troubleshoot the device. The default setting for the
LEDs is on.
To turn the LEDs on or off, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > System in the main menu.
2. Select LED in the sub-menu. Refer to Figure 11.
F
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Figure 11. LED Window
3. From the Eco Mode pull-down menu, select one of the following:
Enabled: The Eco Mode is enabled. The LEDs are off.
Disabled: The Eco Mode is disabled. The LEDs are on. This is the
default setting.
4. Click the Save & Apply button to save and update the configuration.
51
Page 52

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
Enabling or Disabling the Reset Button
This section explains how to enable or disable the Reset button on the
rear panel of the access point. You use the Reset button to restore the
default settings to the device.
The default setting for each model is shown in Table 8.
Table 8. Default Settings for Reset Button
Model Default Setting for Reset Button
AT-TQ5403 Enabled
AT-TQm5403 Enabled
AT-TQ5403e Disabled
If the unit is installed in a non-secure area, you might disable the button to
prevent unauthorized individuals from pressing it and disrupting the
operations of your wireless network.
Note
If you disable the Reset button, be sure not to forget the manager
account password. Otherwise, you will not be able to manage the
unit with the web browser interface.
To enable or disable the Reset button, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > System from the main menu.
2. Select Hardware from the sub-menu. Refer to Figure 12.
52
Figure 12. Hardware Window
Page 53

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
3. Configure the fields by referring to Table 7 on page 50:
Enabled: The Reset button is enabled.
Disabled: The Reset button is disabled.
4. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
53
Page 54

Chapter 2: Basic Settings
54
Page 55

Chapter 3
Web Browser Interface
This chapter contains the following procedures:
“Configuring the Web Browser Interface” on page 56
“Changing the Manager’s Login Name and Password” on page 58
“Setting the Language of the Web Browser Interface” on page 60
55
Page 56

Chapter 3: Web Browser Interface
Configuring the Web Browser Interface
This section has the following management functions:
Specify the maximum number of administrators that can manage
the access point at one time with the web browser interface.
Specify the time interval after which the access point automatically
ends inactive management sessions.
Enable or disable HTTP or HTTPS web management.
Generate a self-signed HTTPS certificate.
Note
Do not disable both HTTP and HTTPS. Otherwise, you will not be
able to manage the access point with a web browser.
Note
HTTP management is non-secure, meaning the packets exchanged
between the access point and your workstation are sent in clear text,
leaving them vulnerable to snooping. For this reason, Allied Telesis
recommends using HTTPS to manage the access point.
To configure the above functions, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > System from the main menu.
2. Select Web from the sub-menu. Refer to Figure 13.
56
Figure 13. Web Window
Page 57

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
3. Configure the fields by referring to Table 9.
Table 9. Web Window
Field Description
Maximum Sessions Specify the maximum number of active
management sessions the access point will
support at one time. Here are the guidelines:
- The range is 1 to 10 sessions.
- The number of sessions is the sum of
HTTP and HTTPS connections.
- The default is five sessions.
- The access point blocks new management
session after reaching the maximum
number of sessions.
Session Timeout Specify the time interval in minutes after
which the access point automatically ends
inactive sessions. The range is 1 to 1440
minutes (1440 minutes = 1 day). The default
is five minutes.
HTTP Status Enable or disable HTTP management. The
default is enabled.
HTTP Port Specify the port number of the HTTP server.
The range is 0 to 65535. The default is 80.
HTTPS Status Enable or disable HTTPS management. The
default is disabled. The HTTPS server uses
port 443. It cannot be changed.
Self Signed
Certificate
Generate a self-signed certificate for HTTPS
management. The access point comes with
a certificate, but you can generate a new one
with this option. The new certificate
automatically replaces the old certificate.
4. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
Note
If you disabled the HTTP or HTTPS mode you are currently using to
manage the device, the access point ends your management
session. To resume managing the device, start a new session using
the other mode.
57
Page 58

Chapter 3: Web Browser Interface
Changing the Manager’s Login Name and Password
This procedure explains how to change the login name and password of
the manager account on the access point. The default values are
“manager” and “friend”, respectively. The access point has only one
manager account.
Changing the name and password does not affect your current
management session.
Note
Allied Telesis strongly recommends changing the factory default
password during the first management session to protect the device
from unauthorized access.
To change the login name and password of the manager account, perform
the following procedure:
1. Select Account > User from the main menu, Refer to Figure 14.
Figure 14. User Window
2. To change the manager name, select the Administrator Name field
and enter a new name. Here are the guidelines:
The name can be up to 12 alphanumeric characters.
58
The first character must be a letter. It cannot be a number or
special character.
The name is case-sensitive.
The default name is “manager”.
Page 59

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
3. To change the password, select the Current Password field and enter
the account’s current password. The default is “friend”.
To display the password as alphanumeric characters or asterisks, click
the green, double arrow symbol.
4. Select the New Password field and enter a new password. The new
password. Here are the guidelines:
The password can be up to 32 alphanumeric characters.
It can not contain spaces or any of these special characters: “, $, :,
<, >, ’, &, *.
It is case-sensitive.
5. Select the Confirm New Password field and enter the new password
again.
6. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
You must use the new manager name and password in all future
management sessions.
59
Page 60

Chapter 3: Web Browser Interface
Setting the Language of the Web Browser Interface
The access point can display the web browser interface in either English
or Japanese. The default is English. To set the language, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select Account > Language from the main menu. Refer to Figure 15.
Figure 15. Language Window
2. From the Language pull-down menu, select one of the following:
English
Japanese
3. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
The management interface changes to the designated language.
60
Page 61

Chapter 4
2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
This chapter has the following procedures:
“Configuring the Radios” on page 62
“Displaying Radio Status” on page 71
“Dynamic Frequency Selection” on page 73
“Setting the Country Code Setting” on page 74
“Selecting the Location” on page 75
61
Page 62

Chapter 4: 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
Configuring the Radios
The radio settings are divided into two groups:
“Configuring Basic Radio Settings” next
“Configuring Advanced Radio Settings” on page 66
Configuring
Basic Radio
Settings
To configure the basic settings for Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select Settings > Radio.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. You can
configure only one radio at a time.
3. Click the Basic Settings tab. This is the default tab.
The AT-TQ5403 and AT-TQm5403 access points display a window
shown in Figure 16. The AT-TQ5403e access point displays a window
shown in Figure 17 on page 63.
62
Figure 16. Basic Radio Settings Window on AT-TQ5403and AT-TQm5403
Page 63

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Figure 17. Basic Radio Settings Window on AT-TQ5403e
4. Configure the settings by referring to Table 10.
Table 10. Basic Radio Settings Window
Field Description
Country Code Select the country code that applies to your
country or region. The country code ensures that
the device operates in compliance with the codes
and regulations of your region or country.
Here are the guidelines:
- You can select only one country.
- The Country Code parameter is shown in the
Basic Settings windows of all three radios but it
can only be set from Radio1.
- The same country code applies to all three
radios.
- Changing the country code disables the radios.
- You have to reconfigure the radio settings if
you change the country code.
- You cannot change the country code on units
sold in North America, Japan, Canada, or
Taiwan.
63
Page 64

Chapter 4: 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
Table 10. Basic Radio Settings Window (Continued)
Field Description
Location
(AT-TQ5403e
Select a location where the AT-TQ5403e access
point is installed.
Only)
The selections are:
- Indoor: This is the default setting.
- Outdoor
For more information, see “Selecting the
Location” on page 75.
Status Activate or deactivate the radio. The selections in
the pull-down menu are described here:
- Enabled: Activates the radio.
- Disabled: Deactivates the radio. This is the
default setting.
Mode
(Radio1)
Select the communications protocol for Radio1
from the pull-down menu. The selections are
listed here:
- IEEE 802.11b/g: The access point accepts only
802.11b or 802.11g clients.
Mode
(Radio2 or
Radio3)
- IEEE 802.11b/g/n: The access point accepts
802.11b, 802.11g, or 802.11n clients operating
at 2.4GHz. This is the default for Radio1.
Select the communications protocol for Radio2 or
Radio3 from the pull-down menu. The selections
are listed here:
- IEEE 802.11a: The access point accepts
802.11a clients.
- IEEE 802.11a/n/ac: The access point accepts
802.11a, 802.11n, and 802.11ac clients
operating. This is the default setting for Radio2
and Radio3.
Wi-Fi multimedia (WMM) has to be enabled
(default) to use IEEE 802.11n or IEEE 802.11ac.
Refer to “Configuring QoS Basic Settings” on
page 116.
64
Page 65

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Table 10. Basic Radio Settings Window (Continued)
Field Description
Channel Select the channel for the radio from the
pull-down menu. Here are the guidelines:
- You can select only one channel.
- The channels vary by radio, bandwidth, and
country.
- Select "auto", the default setting, to have the
radio select the channel automatically. The
access point scans the available channels on
the radio and selects the one with the least
interference.
- If you select Auto, you can use the Auto
Channel Selection parameter in this window to
restrict the channels from which the access
point can choose.
Bandwidth
(Radio1)
- You must set the channel manually when using
the Wireless Distribution System (WDS) bridge
feature. For information, refer to “WDS Bridge
Elements” on page 137.
- To view the current active channel, refer to
“Displaying Radio Status” on page 71.
Select the bandwidth for Radio1 from the
pull-down menu. The selections for IEEE 802.11n
are listed here:
- 20 MHz. This is the default setting.
- 40 MHz
For IEEE 802.11n modes, channel width can be
40 MHz-wide or the legacy 20 MHz-wide. The 40
MHz-wide channel allows for higher data rates,
but reduces the number of available channels for
other wireless devices.
The only bandwidth for IEEE 802.11b/g is 20
MHz.
65
Page 66

Chapter 4: 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
Table 10. Basic Radio Settings Window (Continued)
Field Description
Bandwidth
(Radio2 or
Radio3)
Auto Channel
Selection
Select the bandwidth for Radio2 or Radio3 from
the pull-down menu. The available bandwidths for
IEEE 802.11n/ac are listed here:
- 20 MHz. This is the default setting.
- 40 MHz
- 80 MHz
The only bandwidth for IEEE 802.11a is 20 MHz.
Select the channels that the radio can chose from
when the Channel parameter is set to Auto. Here
are the guidelines.
- A channel is enabled when its check box has a
check and disabled when the check box is
empty.
- The available channels vary by radio, mode,
bandwidth, and country.
- The default is all available channels are
enabled.
Configuring
Advanced Radio
Settings
- This parameter is disabled when the channel is
selected manually.
Tx Power Select the strength of the radio transmitter. The
selections are Max (maximum), High, Middle,
Low, Min (minimum). The default is Max.
5. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
To configure the advanced parameters for Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3,
perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > Radio from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. You can
configure only one radio at a time.
3. Click the Advanced Settings tab. Refer to Figure 18.
66
Page 67

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Figure 18. Advanced Radio Settings Window
4. Configure the parameters by referring to Table 11.
Table 11. Advanced Radio Settings Window
Field Description
Maximum
Clients
Use this option to specify the maximum number
of wireless clients that a radio will support at one
time. You might use the option to control the
distribution of clients over the radios. The
guidelines are given here:
- The range is 0 to 200 clients. The default is 200
clients.
- The AT-TQ5403 access point can support a
maximum of 200 clients on all radios at one
time.
- The AT-TQm5403 access point can support a
maximum of 127 clients on all radios at one
time.
- The AT-TQ5403e access point can support a
maximum of 200 clients on all radios at one
time.
67
Page 68

Chapter 4: 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
Table 11. Advanced Radio Settings Window (Continued)
Field Description
Maximum
Clients
- A radio rejects all clients when the parameter is
set to 0.
(continued)
In the following example for the AT-TQ5403
access point, Radio1 is limited to a maximum of
50 clients while Radio2 and Radio3 are permitted
up to 75 clients each:
- 2.4GHz Radio1 - 50 clients
- 5GHz Radio2 - 75 clients
- 5GHz Radio3 - 75 clients
Client Isolation Use this option to enable or disable client
isolation. When the feature is enabled, the
access point does not allow clients in the same
VAP to communicate with each other. However,
they can communicate with the wired LAN port
and with clients in other VAPs.
The feature is typically used to enhance wireless
security. For instance, by activating this feature
on a publicly accessible access point, you enable
clients to communicate with the wired LAN port,
but not with each other.
The options are listed here:
- Enabled: Activates station isolation. The
access point does not allow wireless clients of
the same VAP to communicate with each other.
- Disabled: Deactivates client isolation. The
access point allows wireless clients to
communicate with other clients in the same
VAP or different VAPs, and with the wired LAN.
This is the default setting.
This feature does not apply to WDS. Refer to
“Introduction to Wireless Distribution Bridges” on
page 134.
68
Page 69

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Table 11. Advanced Radio Settings Window (Continued)
Field Description
Neighbor AP
Detection
Use this option to control whether the access
point listens for neighboring access points. Here
are the options:
- Enabled: The access point listens for
neighboring access points and displays them in
the Neighbor AP window. Refer to “Displaying
Neighboring Access Points” on page 147.
- Disabled: The access point does not listen for
neighboring access points. This is the default
setting.
RTS Threshold Specifies the size in octets of MPDUs that initiate
a Request to Send (RTS) and Clear to Send
(CTS) handshake, in IEEE 802.11b/g. The range
is 0 to 2347 octets. The default is 2347 octets.
You can use this parameter to control the use of
RTS/CTS handshakes when the access point
transmits MPDUs. The access point uses the
handshake before transmitting MPDUs that
exceed the defined threshold. If you specify a low
value, RTS packets are sent more frequently,
which may consume more bandwidth and reduce
the throughput. But more RTS packets may help
a network recover from interference or collisions,
which might occur on a busy network.
Legacy Rates Select the supported and advertised data
transmission rates for IEEE 802.11b/g of the
radio. Here are the guidelines:
- The data rates vary by country.
- The default is all data rates are enabled.
- Radios are generally more efficient when they
advertise subsets of their supported data rates.
Multicast Tx
Rate
Select the maximum amount of multicast packets
the radio can transmit per second. The default
values are listed here:
- 2.4GHz Radio1: 11Mbps
- 5GHz Radio2: 6Mbps
- 5GHz Radio3: 6Mbps
69
Page 70

Chapter 4: 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
Table 11. Advanced Radio Settings Window (Continued)
Field Description
Airtime Fairness Select Enabled to activate airtime fairness to
provide the same communication time (air time)
to all connected clients regardless of
communication speed. Select Disabled, the
default, to turn Airtime Fairness off.
Band Steering Use this option to enable or disable band steering
on the radios. Band steering reduces radio
congestion by forcing wireless clients that support
both 2.4GHz and 5GHz radios to associate with
VAPs on a different radio during periods of traffic
congestion. Band steering forces clients to
associate with VAPs on a 5GHz radio when there
is traffic congestion on the 2.4GHz radio.
Conversely, clients are forced to associate with
VAPs on the 2.4GHz radio when the 5GHz radios
are congested. Here are the guidelines:
- Enabling band steering on one radio activates
it on all three radios. Conversely, disabling the
feature on one radio disables it on all radios.
- Ideally, the VAP settings on all radios should be
identical. This includes SSID names, VLAN
IDs, and security settings.
- The default setting is disabled.
5. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
70
Page 71

Displaying Radio Status
To display operational information about a radio, perform the following
procedure:
1. Select Monitoring > Status from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. You can view
only one radio at a time. The example in Figure 19 is for Radio1.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Figure 19. Radio Status Window
Note
The radio status windows for Radio2 and Radio3 include a DFS
(Dynamic Frequency Selection) field. For information, refer to
“Dynamic Frequency Selection” on page 73.
The fields are defined in Table 12.
Table 12. Radio Status Window
Field Description
MAC Address Displays the MAC address of the wireless
interface.
71
Page 72

Chapter 4: 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
Table 12. Radio Status Window (Continued)
Field Description
Status Displays the status (up, down) of the wireless
interface.
Mode Displays the current wireless communication
mode. Radio1 has these modes:
- IEEE 802.11b/g
- IEEE 802.11b/g/n
Radio2 and Radio3 have these modes
- IEEE 802.11a
- IEEE 802.11a/n/ac
Operational
Channel
Displays the active channel. The channel may
have been selected manually or automatically.
Bandwidth Displays the current bandwidth.
Transmission
Displays the transmission power, in dBm.
Power
DFS
(Radio2 and
Radio3 only)
Displays the status of DFS (Dynamic Frequency
Selection). For background information, refer to
“Dynamic Frequency Selection” on page 73. The
possible states are listed here:
- IDLE: DFS is inactive because the radio is
using a W52 or W58 channel. Those channels
are not used by DFS.
- CAC: Channel Availability Check: The radio
has selected a W53 or W56 channel and is
performing the DFS radar detection period for
one minute before beginning to transmit or
receive wireless traffic. If no radar is detected,
the radio moves to the ISM status.
- ISM: In-Service Monitoring: The radio is using
a DFS target channel. If radar is detected, it
changes the channel. The DFS status changes
to IDLE if the new channel is W52 or W58, or to
CAC if the new channel is W53 or W56.
72
- OOC: Out Of Channels: The radio has stopped
transmitting and receiving client packets
because radar signals are detected on all
channel candidates. After 30 minutes, it
transitions to CAC.
Page 73

Dynamic Frequency Selection
Dynamic frequency selection (DFS) is an industry standard that defines
how wireless access points are to respond to the presence of radar signals
on 5GHz channels. The standard states that a wireless access point that
detects radar signals on its current 5GHz channel has to stop transmitting
and select another channel to avoid interfering with the signals.
The wireless access points support DFS on 5GHz channels that countries
or regions have designated as DFS channels. If an access point detects a
radar signal on its current 5GHz channel and if the channel is designated
as a DFS channel, it immediately marks the channel as unusable for a
minimum of thirty minutes and randomly selects another channel with
which to communicate with its clients.
If a wireless access point is using a DFS 5GHz channel for a WDS bridge
and it detects radar signals, it randomly selects another channel so as not
to interfere with the signals. This action, however, renders the bridge
non-functional. For background information, refer to “Introduction to
Wireless Distribution Bridges” on page 134.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
You can prevent this from occurring by selecting a non-DFS 5GHz channel
as the communication link between the wireless access points of a WDS
bridge. Here are three examples of non-DFS channels:
36 - 5180 MHz
40 - 5200 MHz
44 - 5220 MHz
Here are the guidelines for DFS on the wireless access points:
DFS channels vary by country or region.
DFS cannot be disabled on the wireless access points.
DFS does not apply to channels on the 2.4GHz radio.
Note
To determine whether Radio2 and Radio3 are using DFS channels,
refer to “Displaying Radio Status” on page 71.
73
Page 74

Chapter 4: 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
Setting the Country Code Setting
You should set the country code setting of the access point as soon as
you install the unit so that it operates in compliance with the codes and
regulations of your region or country.
Note
Changing the country setting disables the radios. The procedure is
disruptive to the operations of your network if the unit is actively
forwarding network traffic.
To set the country code setting, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > Radio.
2. Select Radio1 from the sub-menu. The country code must be set from
Radio1.
3. Click the Basic Settings tab. This is the default tab. Refer to Figure 16
on page 62.
4. Select the Country Code pull-down menu and choose your country or
region. Here are the guidelines:
You can select only one country.
The Country Code parameter is shown in the Basic Settings
windows of all three radios, but can only be set from Radio1.
The same country code applies to all three radios.
Changing the country code disables the radios.
You have to reconfigure the radio settings after changing this
parameter.
5. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
74
Page 75

Selecting the Location
When your AT-TQ5403e access point is used outdoors, select the
Outdoor option in the Location parameter.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Note
The location parameter is available only for the AT-TQ5403e access
point.
Guidelines to
Changing the
Location
Here are the guidelines to changing the location:
The location parameter is shown in the Basic Settings windows of
all three radios but it can only be set from Radio1.
The same location applies to all three radios.
The default setting is “Indoor.”
When you use AT-TQ5403e access point in a country that has
outdoor channel restrictions and select the Outdoor option in the
location parameter, the radio will be disabled.
Warning
Regulatory restrictions prohibit the use of the following frequencies
on the 5GHz radio on the AT-TQ5403e access point when the unit is
deployed outdoors. The restrictions do not apply when the unit is
installed indoors:
European Community (CE mark): 5180 to 5240MHz (channels 36 to
48) and 5260 to 5320MHz (channels 52 to 64)
Japan (TELEC mark): 5180 to 5240MHz (channels 36 to 48) and
5260 to 5320MHz (channels 52 to 64)
Australia and New Zealand (RCM): 5180 to 5240MHz (channels 36
to 48) and 5250 to 5350MHz (channels 52 to 64)
Russia (EAC mark): 5150 to 5250MHz (channels 36 to 48) and 5250
to 5350MHz (channels 52 to 64)
Canada (IC mark): 5180 to 5240MHz (channels 36 to 48)
Brazil (ANATEL mark):5150 to 5250MHz (channels 36 to 48)
Mexico (NOM mark): 2412 to 2447MHz (channels 1 to 8)
75
Page 76

Chapter 4: 2.4GHz and 5GHz Radios
Changing the
Location to
Outdoor
Changing the
Location to
Indoor
To change the location to the Outdoor option, perform the following
procedure:
1. Select Settings > Radio.
2. Select Radio1 from the sub-menu. The location must be set from
Radio1.
3. Click the Basic Settings tab. This is the default tab. See Figure 17 on
page 63.
4. Select the Location pull-down menu and choose the Outdoor option.
The access point displays the prompt “Do you want to use this AP
outdoors? If yes, in case no legal outdoor channel for a radio, this
radio will be disabled. Are you sure?”
5. Click OK or Cancel.
6. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
To change the location to the Outdoor option, perform the following
procedure:
1. Select Settings > Radio.
2. Select Radio1 from the sub-menu. The location must be set from
Radio1.
3. Click the Basic Settings tab. This is the default tab. See Figure 17 on
page 63.
4. Select the Location pull-down menu and choose the Indoor option.
5. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
76
Page 77

Chapter 5
Virtual Access Points
This chapter contains the procedures for managing virtual access points
(VAPs). The chapter contains the following sections:
“VAP Introduction” on page 78
“Configuring Basic VAP Parameters” on page 79
“Configuring Captive Portal” on page 84
“Configuring VAP Security” on page 94
“Configuring VAP Fast Roaming” on page 104
“Configuring the MAC Address List” on page 106
“Displaying VAP and LAN Ports Statistics” on page 108
“Advanced Settings” on page 110
77
Page 78

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
VAP Introduction
Virtual access points (VAPs) are independent broadcast domains that
function as the wireless equivalent of Ethernet VLANs. They are seen by
clients as independent access points, with their own VIDs, SSIDs, and
security methods. Here are VAP guidelines:
Each radio can have up to eight VAPs. Allied Telesis recommends
no more than five VAPs per radio for best performance.
The VAPs are numbered from 0 to 7.
You can enable or disable the VAPs individually, except for VAP0,
which can only be disabled by disabling its radio.
The VAP securities are static WEP, Enterprise WPA, and Personal
WPA.
The VAPs of a radio can have different security methods.
VAPs can have the same or different VLAN IDs.
VAP parameters are divided into these three groups:
“Configuring Basic VAP Parameters” on page 79
“Configuring VAP Security” on page 94
“Configuring VAP Fast Roaming” on page 104
78
Page 79

Configuring Basic VAP Parameters
To configure basic VAP settings, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > VAP / Security from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. The default is
Radio1. You can configure only one radio at a time.
3. Select a VAP to configure from the next sub-menu. The default is
VAP0. You can configure only one VAP at a time.
4. Select the Virtual Access Point tab. This is the default tab. The
example in Figure 20 shows the settings for VAP0 on Radio1.
TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Figure 20. Virtual Access Point Tab
5. Configure the parameters by referring to Table 13 on page 80.
79
Page 80

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
Table 13. Virtual Access Point Tab
Field Description
Status Enable or disable the VAP. Here are the guidelines.
- A disabled VAP does not forward any ingress or
egress traffic.
- The default setting for VAP0 is enabled.
- The default setting for VAP1 to VAP7 is disabled.
- You cannot disable VAP0. To stop VAP0 from
forwarding traffic from wireless clients, you have
to disable its radio.
Mode Select a mode setting from the pull-down menu. This
parameter applies only to VAP0. The menu choices
are listed here:
- Access Point: Select this mode to have a VAP
function as a normal VAP, without WDS bridging.
This is the default setting.
- WDS Parent: Select this mode to have VAP0
function as the parent in a WDS bridge. A WDS
parent access point has its LAN port connected to
the wired network. For background information,
refer to “Introduction to Wireless Distribution
Bridges” on page 134.
- WDS Child: Select this mode to have VAP0
function as a child in a WDS bridge. A child
access point communicates with the wired
network through the parent unit.
The only mode for VAP1 to VAP7 is Access Point.
80
Page 81

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Table 13. Virtual Access Point Tab (Continued)
Field Description
SSID Enter a name for the VAP. Here are the guidelines:
A VAP must have a name.
A name can be from 1 to 32 alphanumeric
characters.
Spaces are allowed.
You can assign the same name to more than
one VAP.
The default names for VAP0 on Radio1,
Radio2, and Radio3 are allied24, allied5-1,
and allied5-2, respectively.
The default names for VAP1 to VAP7 are
Virtual Access Points 1 to 7.
VLAN ID Enter a VID for the VAP. Here are the guidelines:
The range is 1 to 4094.
The default is VID 1.
A VAP can have only one VID.
You can assign the same VID to more than
one VAP.
This VID is ignored for wireless clients
receive their VIDs from a RADIUS server for
WPA Enterprise security. VIDs from a
RADIUS server override the number in this
field.
Hidden SSID Select whether the access point should advertise
the VAP SSID to clients. Here are the options:
Disabled: The access point transmits the
SSID to advertise the VAP to clients. This is
the default setting.
Enabled: The access point does not
advertise the VAP. Clients who want to
connect to an unauthorized VAP have to
know its name.
81
Page 82

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
Table 13. Virtual Access Point Tab (Continued)
Field Description
MAC Filtering Select whether the VAP is to use the MAC filter to
control access by wireless clients. For instructions,
refer to “Configuring the MAC Address List” on
page 106. The options are listed here:
Enabled: The VAP uses the MAC filter to
control which wireless clients can connect to
it. When wireless clients connect to the VAP,
the access point compares their MAC
addresses to the addresses in the MAC filter
and either accepts or rejects the client traffic
depending on the filter settings.
Disabled: The VAP does not use the MAC
filter.
The MAC address filter requires that the Mode
setting be Access Point. You cannot use the MAC
filter on VAP0 in the WDS Parent or WDS Child
mode.
Captive Portal Configure Captive Portal. The options are:
Click-Through: See “Requiring Wireless
Clients to Click the Agree Button to Access
to the Network” on page 85 and “Delegating
a Proxy Server to Interact with Wireless
Clients” on page 87.
External RADIUS: See “Delegating RADIUS
Servers and a Proxy Server” on page 88 and
“Delegating RADIUS Servers to Authenticate
Wireless Clients” on page 90.
Disabled: See “Allowing any wireless clients
to access to your networks” on page 84. This
is the default setting.
Inactivity Timer Specify the inactivity timer in seconds. When a
wireless client is inactive exceeding the value of the
inactivity timer, the client is aged out and needs to
associate the wireless network again. The default
value is 300 seconds.
82
Page 83

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Table 13. Virtual Access Point Tab (Continued)
Field Description
Association
Advertisement
Enable or disable Association Advertisement. With
Association Advertisement enabled, the access
point notifies wireless clients when they are newly
associated. With the association confirmation,
wireless clients remove the information from
previously associated access points. The default
setting is disabled.
6. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
83
Page 84

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
Configuring Captive Portal
A Captive Portal is a web page that wireless clients view before their
access is granted. Captive Portal pages usually identify the owners of the
wireless networks, or require them to agree to the terms of use. Captive
Portal pages can require wireless clients to login, or require information
such as their email addresses, prior to allowing access to the networks.
Captive Portal
Configurations
You can use Captive Portal to interact with wireless clients before allowing
them to access your network resources: You can configure Captive Portal
in the following ways:
Allowing any wireless clients to access to your networks
When Captive Portal is disabled, any wireless clients can access
to your network without authentication or interaction. This is the
default setting.
“Requiring Wireless Clients to Click the Agree Button to Access to
the Network” on page 85
A web page including your message and the Agree button is
displayed. Your message is stored on the access point. Wireless
clients do not go through an authentication process.
“Delegating a Proxy Server to Interact with Wireless Clients” on
page 87
Interacting with wireless clients is conducted by the proxy server
that you specify. The proxy server hosts web pages so that you
can create your own web pages and applications if necessary. See
“Creating Pages in HTML for a Proxy Server” on page 91.
84
“Delegating RADIUS Servers and a Proxy Server” on page 88
An authentication process is conducted by a RADIUS server that
you specify. You also specify a proxy server to host web pages to
interact with wireless clients. You can create your own HTML files
on the proxy server. See “Creating Login Pages in HTML When
External RADIUS is Selected” on page 92.
“Delegating RADIUS Servers to Authenticate Wireless Clients” on
page 90
An authentication process is conducted by a RADIUS server that
you specify. The pre-fixed HTML files stored in the access point
are used to interact with wireless clients. You cannot change these
HTML files.
Page 85

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Port Numbers The following port numbers are used with the IP address of the access
point:
8080 for HTTP
http://[access point’s IP address]:8080/auth?redirect=[wireless client’s
originally requested URL]
8443 for HTTPS
https://[access point’s IPv4 address]:8443/auth?redirect=[wireless
client’s originally requested URL]
Requiring
Wireless Clients
to Click the Agree
Button to Access
to the Network
To require wireless clients to click the Agree button to access to the
networks, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > VAP / Security from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu.
The default is Radio1. You can configure only one radio at a time.
3. Select a VAP to configure from the next sub-menu.
The default is VAP0. You can configure only one VAP at a time.
4. Select the Virtual Access Point tab. See the example in Figure 20 on
page 79.
5. Select Click-Through from the Captive Portal pull-down menu. See
Figure 21 on page 86.
85
Page 86

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
c
Figure 21. Captive Portal - Click-Through
6. Select Disabled from the Authentication Page Proxy pull-down menu.
By default, the Authentication Page Proxy is disabled.
7. Configure the parameters by referring to Table 14.
Table 14. Captive Portal
Field Description
Agreement
Message
Enter Conditions of Use or other information in the
HTML code format to be displayed in the
introductory web page.
86
Page 87

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Table 14. Captive Portal (Continued)
Field Description
Redirect Type
(after user is
authenticated)
Fixed URL Specify the URL of a web page. Wireless clients are
8. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
Select the following options to control a Web page
to be displayed to wireless clients after they are
allowed to access to the network.
The options are:
- Fixed URL: Allows you to specify a URL to
redirect to wireless clients. When this option is
selected, the Fixed URL field becomes available.
- Session Keep: Displays a web page that wireless
clients originally requested.
- Disabled: Redirect is disabled. The welcome.html
that you prepared is displayed. When the Capital
Portal field is Click-Through and the
Authentication Proxy Page is Disabled, the
welcome page on the access point is displayed.
This is the default setting.
redirected to the specified web page. To use this
field, the Redirect Type must be Fixed URL.
Delegating a
Proxy Server to
Interact with
Wireless Clients
You can delegate a proxy server to conduct authentication or interaction
without authentication. The proxy server that you specify hosts web pages
so that you must create web pages and applications on the proxy server.
To delegate a proxy server to interact with wireless clients, perform the
following procedure:
1. Select Settings > VAP / Security from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. The default is
Radio1. You can configure only one radio at a time.
3. Select a VAP to configure from the next sub-menu. The default is
VAP0. You can configure only one VAP at a time.
4. Select the Virtual Access Point tab. See the example in Figure 20 on
page 79.
5. Select Click-Through from the Captive Portal pull-down menu. See
Figure 22 on page 88.
6. Select Enabled from the Authentication Page Proxy pull-down menu.
See Figure 22 on page 88.
87
Page 88

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
c
Figure 22. Captive Portal - Using a Proxy Server
Delegating
RADIUS Servers
and a Proxy
Server
7. Specify a URL of your web server in the Base URL field.
8. Specify the Redirect Type field by referring to Table 14 on page 86.
9. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
10. Go to “Creating Pages in HTML for a Proxy Server” on page 91 to
create the HTML files.
You can delegate RADIUS servers to authentication wireless clients and
delegate a proxy server to interaction with these wireless clients. The
RADIUS servers authenticate wireless clients. The proxy server hosts web
pages so that you can create your own web pages and applications on the
proxy server.
To delegate RADIUS servers and a proxy server, perform the following
procedure:
To display an authentication page hosted by a RADIUS server when
wireless clients access to network resources, perform the following
procedure:
1. Select Settings > VAP / Security from the main menu.
88
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. The default is
Radio1. You can configure only one radio at a time.
3. Select a VAP to configure from the next sub-menu. The default is
VAP0. You can configure only one VAP at a time.
Page 89

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
4. Select the Virtual Access Point tab. See the example in Figure 20 on
page 79.
5. Select External RADIUS from the Captive Portal pull-down menu. See
Figure 23.
6. Select Enabled from the Authentication Page Proxy pull-down menu.
See Figure 23.
Figure 23. Captive Portal - External RADIUS
7. Configure the parameters by referring to Table 15.
Table 15. Captive Portal - External RADIUS
Field Description
Authentication
See Table 14 on page 86.
Page Proxy
Redirect Type See Table 14 on page 86.
Primary RADIUS
Server IP
Enter the IPv4 address of the primary FADIUS
server. The default is 192.168.1.1
89
Page 90

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
Table 15. Captive Portal - External RADIUS (Continued)
Field Description
Primary RADIUS
Server Key
Secondary
RADIUS Server
IP
Secondary
RADIUS Server
Key
RADIUS Port Enter the RADIUS port number of the RADIUS
Enter the shared secret key for the primary
RADIUS server.
Here are the guidelines:
The key can be up to 128 alphanumeric
characters.
It is case-sensitive.
It must be same on the access point and
server.
The default is no key.
Enter the IPv4 address of a secondary RADIUS
server. This field is optional. The access point
sends authentication requests to this address if
the primary RADIUS server does not respond to
requests.
Enter the shared secret key for the secondary
RADIUS server.
server. If you entered IP addresses for both
primary and secondary servers, the units must be
using the same port number. The range is 0 to
65535. The default is 1812.
Delegating
RADIUS Servers
to Authenticate
Wireless Clients
90
8. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
9. Go to “Creating Login Pages in HTML When External RADIUS is
Selected” on page 92 to create the HTML files.
You can delegate RADIUS servers to authenticate wireless clients. The
pre-fixed HTML files stored in the access point are used to interact with
wireless clients.
To delegate RADIUS servers, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > VAP / Security from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. The default is
Radio1. You can configure only one radio at a time.
3. Select a VAP to configure from the next sub-menu. The default is
VAP0. You can configure only one VAP at a time.
Page 91

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
4. Select the Virtual Access Point tab. See the example in Figure 20 on
page 79.
5. Select External RADIUS from the Captive Portal pull-down menu. See
Figure 24.
6. Select Disabled from the Authentication Page Proxy pull-down menu.
See Figure 24.
Creating Pages in
HTML for a
Proxy Server
Figure 24. Captive Portal - External RADIUS
7. Configure the parameters by referring to Table 15 on page 89.
8. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
When you are configuring Captive Portal to be hosted by a proxy server,
create the following HTML files on the proxy server:
[Base URL]/click_through_login.html
[Base URL]/click_through_login_fail.html
[Base URL]/welcome.html (Optional)
91
Page 92

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
Requirements for the click_through_login.html and
click_through_login_fail.html
Here is a list of requirements:
You must include a <form> element with the method attribute
specified to “post” and no action attribute.
In the <form> element, you must include a <button> tag or an
<input> tag with the type attribute specified to “submit” for a
wireless client to submit the data to the proxy server.
No requirement for a welcome.html
HTML Code and Display Examples of Login Page
The following is an example of HTML code:
<html>
<head>
<title>Terms of Service</title>
</head>
<form method=”post”>
By using our service, you acknowledge that there
are risks <br>inherent in accessing information
through the internet.<br><br>
<input type=”submit” value=Agree></input>
</form>
</html>
Creating Login
Pages in HTML
When External
RADIUS is
Selected
Figure 25 shows its web page displayed in a web browser.
Figure 25. Captive Portal - Terms of Service Page Sample
When you are configuring Captive Portal to be authenticated by a RADIUS
server and hosted by a proxy server, create the following HTML files on
the proxy server:
[Base URL]/radius_login.html
[Base URL]/radius_login_fail.html
[Base URL]/welcome.html (Optional)
92
Page 93

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Requirements for the radius_login.html and radius_login_fail.html
Here is a list of requirements:
You must include a <form> element with the method attribute
specified to “post” and no action attribute.
In the <form> element, you must include an <input> tag with the
name attribute specified to “userid” for a wireless client to enter a
user ID. The <form> element ends at the </form> end tag.
In the <form> element, you must include anther <input> tag with
the name attribute specified to “password” for a wireless client to
enter a password.
In the <form> element, you must include a <button> tag or an
<input> tag with the type attribute specified to “submit” for a
wireless client to submit the data to the RADIUS server.
There is no requirements for a welcome.html
HTML Code and Display Examples of Login Page
The following is an example of HTML code:
<html>
<head>
<title>Web Authentication Page</title>
</head>
<form method=”post”>
Username: <input type=”text” name=”userid”><br>
Password: <input type=”password”
name=”password”><br>
<input type=”submit” value=”Connect”></input>
</form>
</html>
Figure 26 shows its web page displayed in a web browser.
Figure 26. Captive Portal - Login Page Sample
93
Page 94

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
Configuring VAP Security
The procedures for configuring VAP security is provided in the following
sections:
“No Security” on page 94
“Static WEP” on page 95
“WPA Personal (Pre-Shared Key)” on page 97
“WPA Enterprise” on page 100
No Security VAPs not requiring any security can be set to the None security level.
Wireless clients do not use encryption or authentication to access VAPs
with no security. This is the default setting.
To configure a VAP for no security, perform the following procedure:
1. Select Settings > VAP / Security from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. The default is
Radio1. You can configure only one radio at a time.
3. Select a VAP to configure from the next sub-menu. The default is
VAP0. You can configure only one VAP at a time.
4. Select the Security tab.
5. Select None from the Mode pull-down menu. This is the default
setting. Refer to Figure 27.
94
Figure 27. None Selection in the VAP Security Tab
6. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
Page 95

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Static WEP To configure a VAP for Static WEP security, perform the following
procedure:
Note
Static WEP is only supported in VAP0 when the mode is
IEEE802.11b/g/a. It is not supported in VAP1 to VAP7 nor the VAP0
with IEEE802.11n or ac. See “Configuring Basic Radio Settings” on
page 62.
1. Select Settings > VAP / Security from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. The default is
Radio1. You can configure only one radio at a time.
3. Select a VAP to configure from the next sub-menu. The default is
VAP0. You can configure only one VAP at a time.
4. Select the Security tab.
5. Select Static WEP from the Mode pull-down menu. Refer to Figure 29.
Figure 28. Static WEP Security Tab
6. Configure the parameters by referring to Table 16 on page 96.
95
Page 96

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
Table 16. Static WEP Security Tab
Field Description
Mode Select Static WEP.
Authentication Specify whether the access point
authenticates VAP clients. Here are the
options.
- Open System: The access point does
not authenticate VAP clients. All clients,
even those without correct WEP keys,
can connect to the VAP. This is the
default setting. (Clients in an open
system VAP still must have the correct
WEP key to encrypt and decrypt the
traffic they exchange with the access
point.)
- Shared Key: Clients must have the
correct WEP key to connect with the
VAP. Clients without the correct WEP
key cannot associate with it.
Key Length Select a key length. The options are:
- 128 bits. This is the default setting.
- 64 bits
Key Type Select a key type: The options are:
- Hex: Enter keys in hexadecimal
numbers. This is the default setting.
- ASCII: Enter keys in ASCII.
Transfer Key Index Select the key the access point should
use to encrypt network traffic. You can
select only one key.
96
Page 97

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Table 16. Static WEP Security Tab (Continued)
Field Description
WEP Keys Enter up to four WEP keys in the fields
numbered 1 to 4. Here are the guidelines:
- When the key length is set to 128 bits:
26 hexadecimal numbers in Hex
13 alphanumeric characters in ASCII
- When the key length is set to 64 bits:
10 hexadecimal numbers in Hex
5 alphanumeric characters in ASCII
- Keys are case-sensitive.
- The order of the keys has be the same
on the access point and clients.
The small double-arrow symbols by the
fields toggle the keys between
alphanumeric characters and asterisks.
WPA Personal
(Pre-Shared Key)
7. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
To configure a VAP for WPA Personal security, perform the following
procedure:
1. Select Settings > VAP / Security from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. The default is
Radio1. You can configure only one radio at a time.
3. Select a VAP to configure from the next sub-menu. The default is
VAP0. You can configure only one VAP at a time.
4. Select the Security tab.
5. Select WPA Personal from the Mode pull-down menu. Refer to
Figure 29.
97
Page 98

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
Figure 29. WPA Personal Security Tab
6. Configure the parameters by referring to Table 17.
Table 17. WPA Personal Security Tab
Field Description
Mode Select WPA Personal.
WPA Version Select the WPA version. The options are listed
here:
- WPA and WPA2: Select this option if the VAP
has both WPA and WPA2 clients.
- WPA2: Select this option if clients support
WPA2, but not WPA. This is the default setting.
Cipher Suites Select the cipher suite for the VAP. The options
are listed here:
- CCMP. This is the default.
- TKIP and CCMP
When both TKIP and CCMP are selected, clients
who are using WPA must have one of the
following:
98
- A valid TKIP key.
- A valid CCMP (AES) key.
Page 99

TQ5403 Series Access Points User’s Guide
Table 17. WPA Personal Security Tab (Continued)
Field Description
Key Enter a shared secret key Here are the
guidelines:
- The key can be from 8 to 63 alphanumeric
characters.
- It can include special characters.
- It is case sensitive.
- The default is no key.
The small double-arrow symbol next to the field
toggles the key between alphanumeric
characters and asterisks.
IEEE802.11w (MFP) Control IEEE 802.11w management frame
protection. This feature is only supported with
WPA2 as the WPA Version. It is not supported
with WPA and WPA2.The options are listed here:
- Enabled: Activates management frame
protection. This is the default.
- Disabled: Deactivates management frame
protection.
Broadcast Key
Refresh Rate
Specify the refresh interval rate for the broadcast
(group) key. The range is 0 to 86400 seconds.
The key is not refreshed when this parameter is
set to 0 seconds, which is the default.
7. Click the SAVE & APPLY button to save and update the configuration.
99
Page 100

Chapter 5: Virtual Access Points
WPA Enterprise To configure a VAP for WPA Enterprise security, perform the following
procedure:
Note
WPA Enterprise is not available on VAP0 when it is the parent or
child of a WDS bridge.
1. Select Settings > VAP / Security from the main menu.
2. Select Radio1, Radio2, or Radio3 from the sub-menu. The default is
Radio1. You can configure only one radio at a time.
3. Select a VAP to configure from the next sub-menu. The default is
VAP0. You can configure only one VAP at a time.
4. Select the Security tab.
5. Select WPA Enterprise from the Mode pull-down menu. Refer to
Figure 30.
100
Figure 30. WPA Enterprise Tab
 Loading...
Loading...