Page 1

High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
AT-9724TS
Installation and User’s Guide
PN D617/10032 Rev 1
Copyright.2004 Allied Telesyn, Inc.
19800 North Creek Parkway, Suite 200,Bothell WA 98011,USA
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesyn,
Inc.All product names,compan
of their respective owners.Allied Telesyn,Inc. reserves the right to make changes in specifications and other information
contained in this document without prior written notice.The information provided herein is subject to change
without notice. In no event shall
whatsoever, including but not limited to lost profits,arising out of or related to this manual or the information contained
herein, even if Allied Telesyn, Inc. has been advised of, known,or should have known, the possibility of such damages.
y names, logos or other designations mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks
Allied Telesyn Inc. be liable for any incidental,special, indirect, or consequential damages
Page 2

Electrical Safety and Emission Statement
Standards:This product meets the following standards.
CE Marking Warning: This is a Class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference in which case the user may be required to take adequate
measures.
Important: Appendix B contains translated safety statements for installing this equipment.When you see the go to Appendix A for the translated safety statement in your language.
ichtig:
W
Sprache nach.
Vigtigt: Tillæg B indeholder oversatte sikkerhedsadvarsler, der vedrører installation af dette udstyr. Når De ser symbolet,skal De slå op i tillæg A og finde de oversatte
sikkerhedsadvarsler i Deres eget sprog.
Belangrijk: Appendix B bevat vertaalde veiligheidsopmerkingen voor het installeren van deze apparatuur.Wanneer u de ziet, raadpleeg Appendix A voor vertaalde v
eiligheidsinstructies in uw taal.
Important: L'annexe B contient les instructions de sécurité relatives à l'installation de cet équipement.Lorsque vous voyez le symbole , reportez-vous à l'annexe A pour consulter la
traduction de ces instructions dans votre langue.
Tärkeää: Liite B sisältää tämän laitteen asentamiseen liittyvät käännetyt turvaohjeet. Kun näet -symbolin, katso käännettyä turvaohjetta liitteestä A.
Importante: l’Appendice B contiene avvisi di sicurezza tradotti per l’installazione di questa apparecchiatura. Il simbolo,indica di consultare l’Appendice A per l’avviso di sicurezza nella
propria lingua.
Viktig:Tillegg B inneholder oversatt sikkerhetsinformasjon for installering av dette utstyret. Når du ser ,åpner du til Tillegg A for å finne den oversatte sikkerhetsinformasjonen på
ønsket språk.
Importante: O Anexo B contém advertências de segurança traduzidas para instalar este equipamento. Quando vir o símbolo ,leia a advertência de segurança traduzida no seu idioma
no Anexo A.
Importante: El Apéndice B contiene mensajes de seguridad traducidos para la instalación de este equipo. Cuando vea el símbolo , vaya al Apéndice A para ver el mensaje de seguridad
traducido a su idioma.
Anhang B enthält übersetzte Sicherheitshinw
eise für die Installation dieses Geräts.Wenn Sie sehen,schlagen Sie in Anhang A den übersetzten Sicherheitshinweis in Ihrer
Obs! Bilaga B innehåller översatta säkerhetsmeddelanden avseende installationen av denna utrustning. När du ser, skall du gå till Bilaga A för att läsa det översatta säkerhetsmeddelandet
på ditt språk.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
1
Page 3

Table of Contents
Electrical Saf
Pr
Purpose of This Guide . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
Ho
Document Conventions. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 6
Wher
Contacting
Returning Products . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
FTP Ser
or Sales or Corporate Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
F
Tell Us What You Think . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9
Intr
Fast Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet Technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Switching
Switch Description
Ports. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
Installing the SFP por
Fr
LED Indicators . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
Rear Panel Components
Side Panel Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Installation
Package Contents. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Bef
Installing the Switch
Installing the Switch in a Rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Mounting the Switch in a Standar
Power On. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
ower Failure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
P
External Redundant Power System . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
Connecting The Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Switch To End Node. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Switch to Hub or Switch
Connecting To Network Backbone or Server. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Stacking and the AT-9724TS. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 18
Stacking Limitations utilizing a Ring Topology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 19
Introduction To Switch Management . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
AT-9724TS Gigabit Layer 3 Switch Management Options . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Web-based Management Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
SNMP-Based Management. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Command Line Console Interface Through The Serial Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
Connecting the Console Port (RS-232 DCE) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 20
First Time Connecting to The Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 21
Password Protection . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
SNMP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 22
Traps . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
MIBs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
IP
Connecting Devices to the Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 24
Intr
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
Login to Web Manager. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 25
W
Areas of the User Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 26
Web Pages . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 27
Configuring The Switch . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 28
Switch Inf
IP Address. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 29
Setting the Switch's IP Address using the Console Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Advanced Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 30
Box Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 31
Port Configurations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 32
Port Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 33
Port Mirroring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
Link
Understanding Port Trunk Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 34
LA
MAC Notification. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
MAC Notification Global Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 37
MAC Notification Port Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
IGMP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 38
IGMP Snooping. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 40
Static Router Ports . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 41
Spanning Tree . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
802.1s MSTP. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 42
802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
STP Bridge Global Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 43
MST Configuration Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
ety and Emission Statement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1
eface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
w This Guide is Organized . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5
e to Find Related Guides . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
Allied Telesyn Technical Support . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7
ver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 8
oduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
ont-Panel Components. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
ore You Connect to the Network. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Ad
oduction to
eb-based User Interface
CP P
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
Technology . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 10
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 11
ts. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 12
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 13
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 14
Without the Rack
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 17
Assignment
ess
dr
ormation
egation
Aggr
ort Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 36
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 23
eb-based Switch Configuration
W
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15
d 19" Rack . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 16
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. 28
. . .
25
26
34
45
2
Page 4

ort Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 48
MSTI P
STP Instance Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
ort Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 51
STP P
Forwarding & Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
orwarding . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Unicast F
Static Multicast F
VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Understanding IEEE 802.1p Priority
VLAN Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
Notes About VLANs on the AT-9724TS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
IEEE 802.1Q
802.1Q VLAN Tags. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
ort VLAN ID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
P
agging and Untagging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
T
Ingress Filtering . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Default
ort-based VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
P
VLAN Segmentation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
VLAN and
otocol VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Pr
Static VLAN Entry . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
GVRP Setting
Traffic Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 63
Port Security . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 64
ort Lock Entries . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 65
P
QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Advantages of QoS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
The
Understanding QoS
Bandwidth Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 67
QoS Scheduling Mechanism
Output Scheduling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
Configuring the Combination Queue
802.1p Default Priority
802.1p User Priority
raffic Segmentation. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 71
T
System Log Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 72
SNTP Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Current Time Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 74
Time Zone and DST . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
Access Profile Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Configuring the Access Profile Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 76
Port Access Entity (802.1X). . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Understanding 802.1x Port-based and MAC-based Network Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 84
Port-Based Network Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
MAC-Based Network Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 85
Configure Authenticator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 86
Local Users. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 87
PAE System Control. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Port Capability Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 88
Initializing Ports for Port Based 802.1x. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 89
Initializing Ports for MAC Based 802.1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Reauthenticate Port(s) for Port Based 802.1x . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 90
Reauthenticate Port(s) for MAC Based 802.1x. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 91
RADIUS Server . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 92
Layer 3 IP Networking. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Layer 3 Global Advanced Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
Setting Up IP Interfaces . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 93
MD5 K
Route Redistribution Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 96
Static/Default Route. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 97
Route Pr
Static ARP Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
RIP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 100
RIP 1 Route Interpretation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 101
RIP Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 102
Setting Up RIP
OSPF . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 103
General OSPF Settings
Ar
OSPF
OSPF Interface Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 118
Virtual Interface Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 120
OSPF
OSPF Area Aggregation Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
OSPF Host Route Settings. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 121
DHCP / BOO
DHCP / BOOTP Relay Information. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
DHCP/BootP Relay Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
DNS Relay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 123
Configuring DNS Rela
DNS Relay Static Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
VRRP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
VRRP Configuration
VRRP Interface Settings
IP Multicast Routing Protocol. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
IGMP Interface Configuration
DVMRP Interface Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
DVMRP Global Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 130
DVMRP Interface Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PIM-DM Interface Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 132
PIM-DM Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 131
orwarding.. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
VLANs. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 54
VLANs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Trunk Groups . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 62
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 68
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 70
ey Table Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 95
eference Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 98
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 117
ea ID Settings
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 122
y
TP Rela
y . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 124
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 125
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 69
102
. . .
117
126
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 129
130
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
3
Page 5

Security Management
Security IP . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
Accounts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
User
Admin and User Privileges. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 134
Authentication Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
Access
olicy & Parameters. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 135
P
Application's Authentication Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
Authentication Ser
Authentication Server Hosts . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 138
Login Method Lists. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 139
Enable Method Lists
Local Enable Password. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 141
Admin . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 142
Enable
e Socket Layer (SSL) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Secur
Download Certificate . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 143
Configuration
e Shell (SSH) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Secur
SSH Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
Algorithm . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 145
SSH
Authentication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 147
SSH User
SNMP Manager
SNMP Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
SNMP User Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 150
View Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 151
SNMP
SNMP Group Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 152
SNMP Comm
SNMP Host
SNMP Engine ID. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 155
Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
ort Utilization. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
P
CPU Utilization
ets . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Pack
ed (RX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 157
Receiv
UMB Cast (RX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 159
Transmitted (TX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 160
Errors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Received (RX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 162
Transmitted (TX) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 163
Size . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 165
Stacking Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 166
Device Status . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 167
MAC Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 168
Switch History Log . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 169
IGMP Snooping Group. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
IGMP Snooping Forwarding. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 170
Browse Router Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Port Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Authenticator State . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 171
Authenticator Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 172
Authenticator Session Statistics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 174
Authenticator Diagnostics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 175
RADIUS Authentication. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 176
RADIUS Accounting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 177
Layer 3 Feature. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
Browse IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 178
owse Routing Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Br
Browse ARP Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
Browse IP Multicast Forwarding Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 179
owse IGMP Group Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Br
OSPF Monitoring . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Browse OSPF LSDB Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 180
Browse OSPF Neighbor Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
OSPF Virtual Neighbor. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 181
VMRP Monitoring
D
Browse DVMRP Routing Table. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
owse DVMRP Neighbor Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 182
Br
VMRP Routing Next Hop
wse D
o
Br
PIM Monitoring. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
PIM Neighbor
Switch Maintenance . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
vices
TFTP Ser
Download Firmware . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Download Configuration File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 184
Upload Configuration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Upload Log
Multiple Image Services . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Firmware Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
Config Firmwar
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
est
T
Ping
Save Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Reset. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 188
Reboot Device . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Logout . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 189
Appendix A Technical Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 190
Appendix B Translated Electrical Safety and Emission Information . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 192
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 133
ver Group Settings . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 136
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 140
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 144
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 149
unity Table Configuration. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 153
Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 154
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 156
. . . 184
. . . . . . . .
182
183
187
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
able
T
Address Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 183
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 185
e Image . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 186
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
4
Page 6

Preface
Purpose of This Guide
This guide is intended f
or network administrators who are responsible for installing and maintaining the AT-9724TS Gigabit Switch.
How This Guide is Organized
This guide contains the following chapters and appendices:
Chapter 1, Introduction, describes the features, functions, LEDs,and ports on the Gigabit Switch.
Chapter 2 Installation, describes how to install the switch.
Chapter 3 Connecting the Switch.
Chapter 4. Introduction to Switch Management, basic management features, connecting devices to the switch.
Chapter 5. Introduction to Web-based Switch Management.
Chapter 6. Configuring the Switch, including accessing switch information, setting up network configurations.
Chapter 7. Management, security features, user accounts,access authentication control.
Chapter 8. SNMP Manager, description of features and brief introduction.
Chapter 9. Monitoring
Chapter 10. Maintenance, switch utility functions.
Appendix A, Specifications,provides Residential Gateway specifications.
Appendix B, Translated Electrical Safety and Emission Information, contains multi-language translations of the cautions and warnings in this manual.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
5
Page 7

Document Conventions
This guide uses several conventions that you should become familiar with before you begin to install the product:
Note
A note provides additional information.
c Warning
A warning indicates that performing or omitting a specific action may result in bodily injury.
m Ca
[ ] In a command line, square brackets indicate an optional entry. For example: [copy filename] means that optionally you can type copy
Bold font Indicates a button, a toolbar icon, menu,or menu item. For example: Open the File menu and choose Cancel. Used for emphasis.May
Typewriter Indicates commands and responses to prompts that must be typed exactly as printed in the manual.
Font
Italics Indicates a window name or a field.Also can indicate a variables or parameter that is replaced with an appropriate word or string.
Menu Name > Indicates the menu structure.
Menu Option Port menu option that is located under the Device menu.
ution
A caution indicates that performing or omitting a specific action may result in equipment damage or loss of data.
followed by the name of the file. Do not type the brackets.
also indicate system messages or prompts appearing on your screen.For example:You have mail.Bold font is also used to represent
filenames, program names and commands. For example: use the copy command.
For example: type
filename means that you should type the actual filename instead of the word shown in italic.
Device > Port > Port Properties means the Port Properties menu option under the
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
6
Page 8

Where to Find Related Guides
The Allied Telesyn web site at www.alliedtelesyn.com under the support section contains the most recent documentation for all of our products.All webbased documents relating to this product and other Allied Telesyn products can be downloaded from the web site.
Contacting Allied Telesyn Technical Support
You can contact Allied Telesyn technical support through the company’s web site www.alliedtelesyn.com under the support section or by telephone or fax.
EUROPEAN SUPPOR
T NUMBERS
Telephone support is available Monday through Friday between 0900 and 1730 local time (excluding national holidays).
Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, The Netherlands, Norway, Sweden, Switzerland
and the United Kingdom
Free phone 00 800 287 877 678 or +31 20 711 4333
europe_support@alliedtelesyn.com
in:
Spa
ee phone 00 800 287 877 67 or +31 20 711 4333
Fr
ope_support@alliedtelesyn.com
eur
Finland:
Free phone: 990 800 287 877 67 or +31 20 711 4333
ope_support@alliedtelesyn.com
eur
oatia and Slovenia:
Cr
t Telephone number:+385 1 382 1341
Suppor
Support Fax Number: + 385 1 382 1340
Support e-mail Address:ATIhelpdesk_Croatia@alliedtelesyn.com
Czech Republic:
Support Telephone number:+420 296 538 888
Support Fax Number: +420 296 538 889
Support e-mail Address: Czech_support@alliedtelesyn.com
Hungary:
Support Telephone number:+36 1 382 6385
Support Fax number: +36 1 382 6398
Support e-mail Address: Hungary_Helpdesk@alliedtelesyn.com
Poland:
Support Telephone number:+48 22 535 9670
Support Fax number: +48 22 535 9671
Support e-mail Address: Polska_pomoc@alliedtelesyn.com
Serbia, Montenegro, Macedonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina and Bulgaria:
Support Telephone number:+381 11 32 35 639
Support Fax Number: +381 11 3235 992
Support e-mail Address:Yug.Servis@alliedtelesyn.com
Russia and former Soviet Union Countries:
Support Telephone number:+7-095-935 8585
Support Fax Number: +7-095-935 8586
Support e-mail Address : support_CIS@alliedtelesyn.ru
Ukraine:
Telephone number: +7-095-935 8585
t
Suppor
Support Fax Number: +7-095-935 8586
Support e-mail Address : Ukraine support@alliedtelesyn.com
All other countries not listed above should refer their technical support request to:
+31 20 711 4333
:
elephone n
T
t
Suppor
Support e-mail Address: europe_support@alliedtelesyn.com
Americas:
T
echnical Support by Phone or Fax (8-5 PST M-F)
Toll-free: 1 800 428 4835
Fax: 1 425 481 3790
*Support for Puerto Rico and the US Virgin Islands is provided through our Technical Support Center in Latin America.
México
e-mail soporte_mexico@alliedtelesyn.com
Teléfono +52 55 5559 0611
umber
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
7
Page 9

Returning Products
Products for return or repair must first be assigned a Return Materials Authorization (RMA) number. RMA policy varies from country to country. Please check
the applicable RMA policy at www.alliedtelesyn.com. For Europe, you can also contact our European Customer Service centre by e-mail at
rma_europe@alliedtelesyn.com.
FTP Server
If you need management software for an Allied Telesyn managed device, you can download the software by connecting directly to our FTP server at
ftp.alliedtelesyn.com.At login, enter “anonymous” as the user name and your e-mail address as the password.
European & Latin America Headquarters
Allied Telesis International SA
Via Motta 24
6830 Chiasso
Switzerland
el: +41 91 6976900
T
+41 91 6976911
Fax:
Allied Telesis International Services
Tirana n.24/4 B
Piazza
20147 Milano
Italy
el: +39 02 4141121
T
+39 02 41411261
Fax:
NAL LOCATIONS
REGIO
ustria & Eastern Europe
A
Telesyn Vertriebsgesellschaft m.b.H.
Allied
Lainzer Strasse 16/5-6
1130,Vienna
Tel: +43-1-876 24 41
Fax: +43-1-876 25 72
oland
P
Allied Telesyn Vertriebsgesellschaft m.b.H.
Sp. z o.o.Oddzial w Polsce
ul. Elektoralna 13
00-137 Warszawa
Tel: +48 22 620 82 96
Fax: +48 22 654 48 56
Romania
Allied Telesyn Vertriebsgesellschaft m.b.H.
str.Thomas Masaryk 23
Sector 2, Bucharest 0209
Tel: +40-21-211-1817/8245
Fax: +40-21-210-5610
Russia
Allied Telesyn International
Ul. Korovij Vall
Dom 7 Str
119049 Moscow
Tel: +7095 9358585
Fax: +7095 9358586
Serbia & Montenegro
Allied Telesyn Vertriebsgesellschaft m.b.H.
Krunska 6
11000 Belgrade
T
+381 11 3033 209
+381 11 3235 639
France
Allied
12, avenue de Scandinavie
Parc Victoria, Immeuble “Le Toronto”
91953 Cour
Tel: +33 1 60 92 15 25
Fax: +33 1 69 28 37 49
Greece
Allied Telesyn International S.r.l
Kiriazi 14-16
145 62 Kifisia
Tel: +30 210 6234 200
Fax: +30 210 6234 209
1 Office 190
.
el & Fax: +381 11 3033 208
elesyn International SAS
T
taboeuf Cédex - Les Ulis
Italy – Nor
Allied
Via
20152 Milano
Tel: +39 02 41304.1
Fax:
Italy – East
el: +39 348 1522583
T
Tel & Fax: +39 049 8868175
Italy – South
Allied
Via Troilo il Grande 3
00131 Roma
el: +39 06 41294507
T
Fax: +39 06 41404801
urkey
T
Allied
6. Cadde 61/2 Öveçler
06460
Tel: +90 312 472 1054/55
Fax: +90 312 472 1056
Germa
Allied Telesyn International GmbH
Zeppelinstr
85399 Hallbergmoos
Tel: +49-811-999 37-0
Fax: +49-811-999 37-22
Germany - Koln
Allied Telesyn GmbH West
Edmund Rumpler-Str. 6b
51149 Koln
Deutschand
Tel.: +49 02203 1019685
Fax: +49 02203 1019678
Denmark
Allied Telesyn Internationa
Jyllinge ErhvervsCenter
Møllehaven 8
DK-4040 Jyllinge
Tel: +45 46734835
Fax:
Finland
Allied Telesyn International Ltd.
Metsänneidonkuja 10
02130 ESPOO
T
el: +358 9 7255 5290
Fax: +358 9 7255 5299
Iceland +47 22 70 04 70
Ireland (Freephone) 1 800 409 127
The Nether
Allied
Hoeksteen 26
2132 MS Hoofddorp
el:
T
Fax: +31 20 6540 249
Norw
Allied
Ole De
0666 Oslo
el: +47 22 70 04 70
T
Fax: +47 22 70 04 01
th
Telesyn International S.r.l.
Anna Kuliscioff,37
+39 02 41304.200
Telesyn International S.r.l.
Telesyn International
Ankara
ny – South
.1
+45 46734837
nds
la
elesyn International BV
T
+31 20 6540 246
ay
Telesyn International
ei 4
viksv
eden
Sw
Telesyn International
Allied
dsgatan 22, B5tr
Isafjor
164 40 Kista
Sweden
el.: +46 (0) 8131414
T
+46 (0) 87506004
Fax:
United Kingdom
Telesyn International Ltd.
Allied
100 Longwater
GreenPark
Reading,
el: +44 118 920 9800
T
Fax: +44 118 975 2456
Latin Amer
Allied
19800 North Creek Parkway, Suite 200
Bothell,W
+1 425 481 3852
el:
T
Fax: +1 425 489 9191
Toll Free (Mexico & Puerto Rico): (95-800) 424 5012 ext.
3852
Latin America – Mexico
Allied Telesyn International
AV. Insurgentes Sur # 800, Piso 8
Col. Del Valle
México, DF, 03100
Tel: +52 55 5448 4989
Fax: +52 55 5448 4910
Portugal
Allied Telesyn International
Centro de Escritórios das Laranjeiras
Praça Nuno Rodrigues dos Santos, Nº 7 Sala 211
1600-171 Lisbon
Tel: +351 21 721 74 00
Fax: +351 21 727 91 26
in
Spa
Allied Telesyn International S.L.U
Plaza de España
18-4ª Ofic. 3,28008 Madrid
Tel: +34 91 559 1055
+34 91 559 2644
Fax:
Allied Telesyn International, Corp.
19800 North Creek Parkway, Suite 200
Bothell,WA 98011
1 (425) 487-8880
el:
T
Fax: 1 (425) 489-9191
or cur
F
www
Avenue
RG2 6GP
ica – Support Office
elesyn International
T
A 98011 USA
ormation, please visit our web site
ent inf
r
.alliedtelesyn.com
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
8
Page 10

Tell Us What You Think
If you have any comments or suggestions on how we might improve this or other Allied Telesyn documents, please contact us at www.alliedtelesyn.com.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
9
Page 11

Chapter 1 - Introduction
1-1 Ethernet Technology
1-2 Switch Description
1-3 Features
1-4 Ports
1-5 Front Panel Components
1-6 Rear-Panel Description
1-7 Side-Panel Description
1-8 Gigabit Combo Ports
1-9 Ethernet Technology
1-10 Fast Ethernet Technology
1-1 Ethernet Technology
Fast Ethernet
The growing importance of LANs and the increasing complexity of desktop computing applications are fueling the need for high performance networks.
A number of high-speed LAN technologies are proposed to provide greater bandwidth and improve client/server response times. Among them, Fast Ethernet,or
100T, provides a non-disruptive, smooth evolution from 10T technology.
100Mbps Fast Ethernet is a standard specified by the IEEE 802.3 LAN committee. It is an extension of the 10Mbps Ethernet standard with the ability to transmit
and receive data at 100Mbps,while maintaining the Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) Ethernet protocol.
Gigabit Ethernet Technology
Gigabit Ethernet is an extension of IEEE 802.3 Ethernet utilizing the same packet structure, format, and support for CSMA/CD protocol, full duplex,flow control,
and management objects, but with a tenfold increase in theoretical throughput over 100Mbps Fast Ethernet and a one hundred-fold increase over 10Mbps
Ethernet. Since it is compatible with all 10Mbps and 100Mbps Ethernet environments, Gigabit Ethernet provides a straightforward upgrade without wasting a
company's existing investment in hardware, software, and trained personnel.
The increased speed and extra bandwidth offered by Gigabit Ethernet are essential to coping with the network bottlenecks that frequently develop as computers
and their busses get faster and more users use applications that generate more traffic.Upgrading key components, such as your backbone and servers to Gigabit
Ethernet can greatly improve network response times as well as significantly speed up the traffic between your subnetworks.
Gigabit Ethernet enables fast optical fibre connections to support video conferencing, complex imaging, and similar data-intensive applications. Likewise, since data
transfers occur 10 times faster than Fast Ethernet, servers outfitted with Gigabit Ethernet NIC's are able to perform 10 times the number of operations in the
same amount of time.
In addition, the phenomenal bandwidth delivered by Gigabit Ethernet is the most cost-effective method to take advantage of today and tomorrow's rapidly
improving switching and routing internetworking technologies.
Switching Technology
Another key development pushing the limits of Ethernet technology is in the field of switching technology. A switch bridges Ethernet packets at the MAC address
level of the Ethernet protocol transmitting among connected Ethernet or Fast Ethernet LAN segments.
Switching is a cost-eff
ork loading by making it possible for a local area network to be divided into different segments, which are not competing with each other for network
netw
transmission capacity, and therefore decreasing the load on each segment.
The Switch acts as a high-speed selectiv
another) is automatically forwarded by the Switch,without interfering with any other segments (ports).This allows the total network capacity to be multiplied,
while still maintaining the same network cabling and adapter cards.
or Fast Ethernet or Gigabit Ethernet netw
F
can be used to split parts of the network into different collision domains, for example, making it possible to expand your Fast Ethernet network beyond the 205meter network diameter limit for 100TX networks.Switches supporting both traditional 10Mbps Ethernet and 100Mbps Fast Ethernet are also ideal for bridging
een existing 10Mbps netw
betw
Switching LAN technolog
have also been used to segment local area networks, but the cost of a router and the setup and maintenance required make routers relatively impractical.Today's
switches are an ideal solution to most kinds of local area network congestion problems.
ectiv
e way of increasing the total network capacity available to users on a local area network. A switch increases capacity and decreases
Traffic that needs to go from one segment to another (from one port to
y of eliminating problems of chaining hubs beyond the "two-repeater limit." A switch
orks and ne
y is a mark
e bridge betw
orks,
w 100Mbps netw
ovement over the previous generation of network bridges, which were characterized by higher latencies. Routers
ed impr
een the individual segments.
e wa
witch is an eff
a s
ectiv
orks.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
10
Page 12

1-2 Switch Description
The AT-9724TS has 24 1000T Gigabit ports that may be used in uplinking various network devices to the Switch, including PCs, hubs and other switches to
provide a gigabit Ethernet uplink in full-duplex mode.
In addition, the AT-9724TS is equipped with 4 SFP (Small Form Factor Portable) combo ports, which are to be used with fibre-optical transceiver cabling in order
to uplink various other networking devices for a gigabit link that may span great distances.These 4 SFP ports support full-duplex transmissions, have autonegotiation and can be used with AT-MG8LX10 (1000LX),AT-MG8SX (1000SX) and AT-MG8ZX (1000ZX) transceivers.These four ports are referred to as
“combo” ports which means that both the SFP ports and the 1000T ports are numbered the same (21–24) and cannot be used simultaneously.Attempting to use
the ports simultaneously will cause a link down status for the 1000T ports. SFP ports will always have priority over these 1000T ports.
Also included at the rear of the Switch are two 10-gigabit stacking ports used to stack up to twelve switches in a ring topology.The AT-9724TS may be used as
the master unit of a switch stack when utilizing these ports and, in total, may provide a stacking solution of up to 288 gigabit ports.
Note: The four SFP combo ports on the Switch, numbered 21–24 cannot be used simultaneously with the corresponding 1000T ports, numbered
21–24. If both ports are in use at the same time (ex. port 21 of the SFP and port 21 of the 1000T), the SFP ports will take priority over the combo
ports and render the 1000T ports inoperable.
1-3 Features
• IEEE 802.3z compliant
• IEEE 802.3x Flow Control in full-duplex compliant
• IEEE 802.3u compliant
•
•
•
• IEEE 802.3ad Link Aggregation Control Protocol support.
• IEEE 802.1x Port-based and MAC-based Access Control
• IEEE 802.1Q VLAN
• IEEE 802.1D Spanning Tree, IEEE 802.1W Rapid Spanning Tree and IEEE 802.1s Multiple Spanning Tree support
• Stacking support in Ring topology
• Access Control List (ACL) support
• IP Multinetting support
• Protocol VLAN support
•
• Access Authentication Control utilizing TACACS,XTACACS,TACACS+ and RADIUS protocols
• Dual Image Firmware
• Simple Network Time Protocol support
•
•
•
•
• Full- and half-duplex for all gigabit ports. Full duplex allows the switch port to simultaneously transmit and receive data. It only works with
•
•
• Supports by-port Egress/Ingress rate control
• Efficient self-learning and address recognition mechanism enables forwarding rate at wire speed
•
•
• Supports a packet buffer of up to 3 Mbits
• Supports Port-based VLAN Groups
• Port Trunking with flexible load distribution and fail-over function
• IGMP Snooping support
• Layer 3 support including DVMRP, OSPF and RIP
IEEE 802.3ab compliant
IEEE 802.3ae compliant (for optional XFP module)
IEEE 802.1p Priority Queues
Single IP Management support
C Notification support
MA
System and P
System Log Support
High performance switching engine performs forwarding and filtering at full wire speed up to 128Gbps.
connections to full-duplex-ca
Suppor
Non-blocking stor
Support port-based enable and disable
Address table: Supports up to 8K MAC addresses per device
ort Utilization support
pable end stations and s
t broadcast storm filtering
orward switching scheme capability to support rate adaptation and protocol conversion
e and f
Connections to a hub m
witches.
ust take place at half-duplex.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
11
Page 13
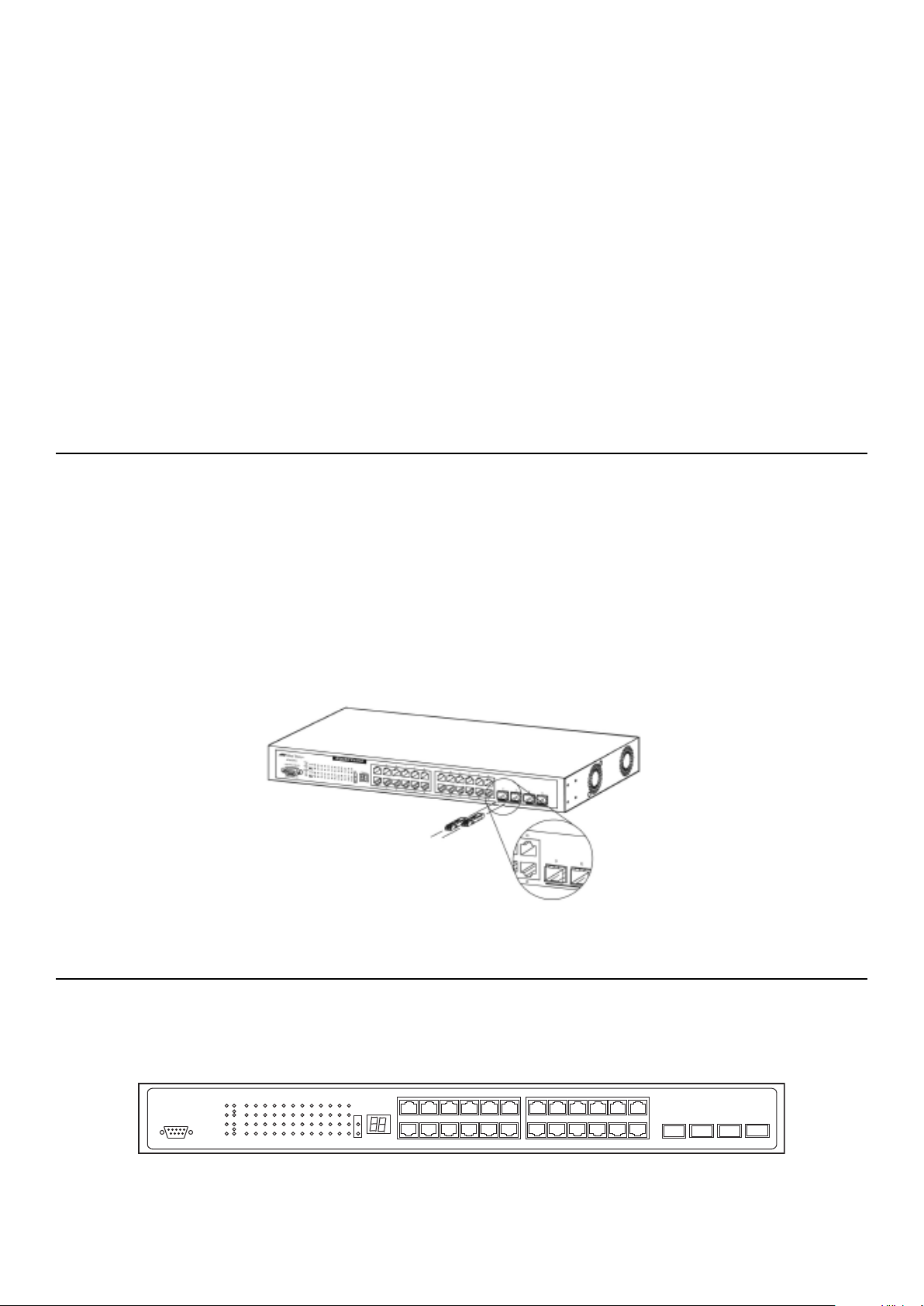
• SNMP support
13 5 7911
13 15
2
4 6 8 10 12 14
16
17
19 21
23
18
20
22
24
21 22
23
24
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
Power
Master
Console
RPS
1000
Link
Act
1000
Link
Act
1
2
SIO
Stack ID
AT- 9724TS
• Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Secure Shell (SSH) support
• Port Mirroring support
• MIB support for:
RFC1213 MIB II
RFC1493 Bridge
RFC1757 RMON
RFC1643 Ether-like MIB
RFC2233 Interface MIB
IF MIB
Private MIB
RFC2674 for 802.1p
IEEE 802.1x MIB
• RS-232 DCE console port for Switch management
• Provides parallel LED display for port status such as link/act,speed, etc.
1-4 Ports
Twenty-four (24) 1000T combo ports that may be used in uplinking various network devices to the Switch, including PCs, hubs and other switches to provide a
gigabit Ethernet uplink in full-duplex mode.
Four (4) high-performance SFP ports for a fibre-optic connection to various network connections,for use over great distances.
Two 10-gigabit stacking ports at the rear of the Switch for stacking switches utilizing ring topology.
RS-232 DCE Diagnostic port (console port) for setting up and managing the Switch via a connection to a console terminal or PC using a terminal emulation
program.
Installing the SFP ports
The Switch is equipped with four SFP (Small Form Factor Portable) ports, which are to be used with fibre-optical transceiver cabling in order to uplink various
other networking devices for a gigabit link that may span great distances.
Figure 1- 1. Inserting the fibre-optic transceivers into the AT-9724TS
1-5 Front Panel Components
, Console, RPS, SIO (stacking), a seven-segment Stack ID LED and for Link/Act for each
Master
,
er
w
o
ont panel of the Switch consists of LED indicators f
The fr
port on the Switch, as well as 24 1000T ports, 4 SFP gigabit Ethernet ports and a RS-232 DCE console port for Switch management.
or P
Figure 1- 2. Front Panel View of the AT-9724TS as shipped
Comprehensive LED indicators display the status of the Switch and the network.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
12
Page 14
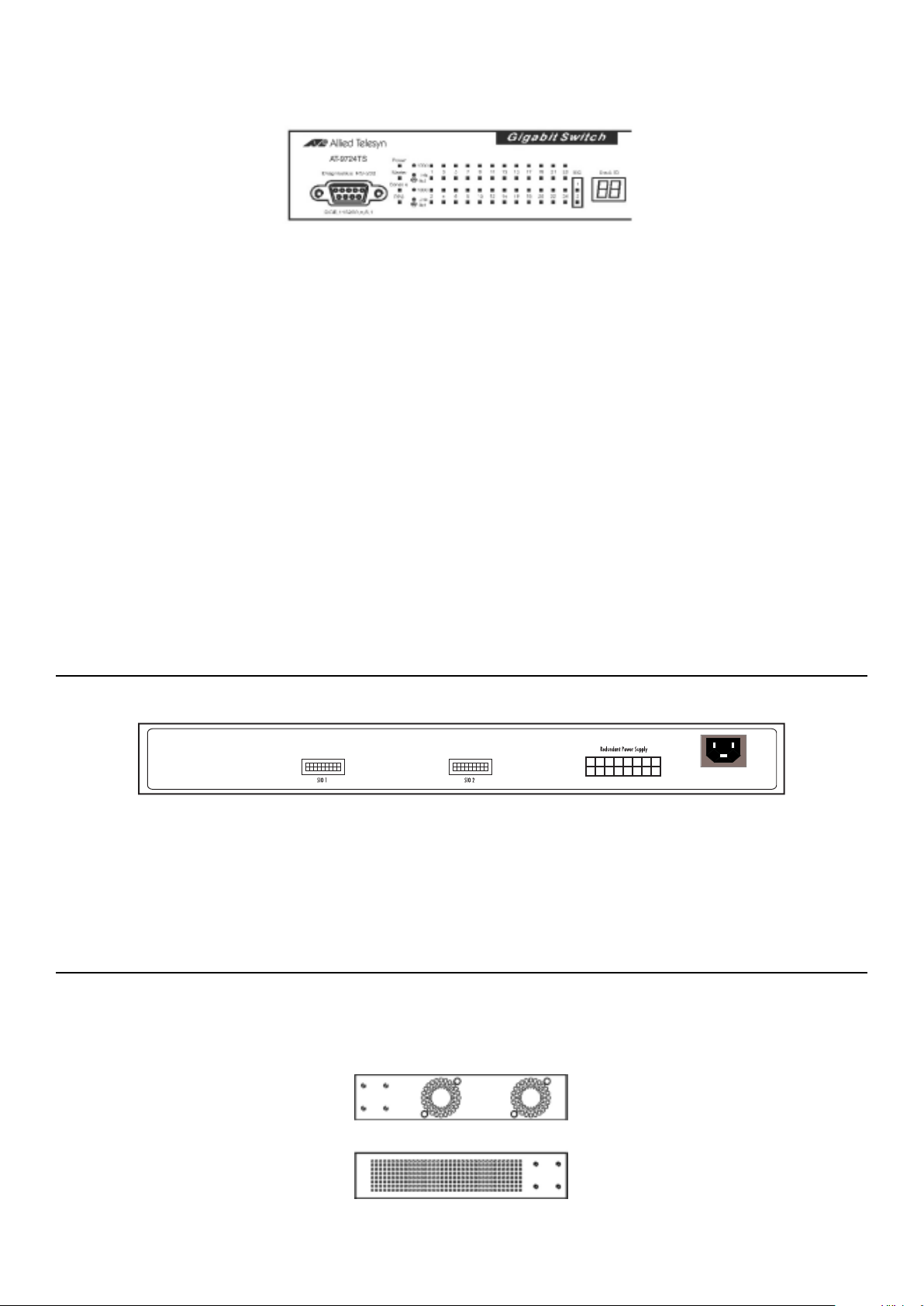
LED Indicators
The Switch supports LED indicators for Power, Master,Console, RPS,SIO (stacking indicators), a seven-segment Stack ID LED and Port LEDs.The following
ws the LED indicators for the Switch along with an explanation of each indicator.
sho
Figure 1- 3. LED Indicators
LED Description
Power This LED will light green after the Switch is powered on to indicate the ready state of the device.The indicator is dark when the Switch is
Master This LED will light solid green when the Switch is configured to be a master switch of a switch stack in a ring topology or when it is in use as a
Console This LED should blink during the Power-On Self Test (POST).When the POST is finished successfully, the LED goes dark.This indicator will light
RPS This LED will be lit when the internal power has failed and the RPS has taken over the power supply to the Switch. Otherwise,it will remain
Port LEDs One row of LEDs for each port is located above the ports on the front panel.The first LED is for the top port and the second one is for the
Stacking Ports
(SIO) There are two LEDs in the front of the Switch marked SIO, and they relate to the two 10-gigabit stacking ports at the rear of the Switch.These
Stack ID These two seven-segment LEDs display the current switch stack order of the Switch while in use. Possible numbers to be displayed range from
powered off.
stand-alone switch.This LED will remain dark if the Switch is not configured to be a master switch in a switch stack.
solid green when the Switch is being logged into via out-of-band/local console management through the RS-232 console port in the front of the
Switch using a straight-through serial cable.
This LED will light solid amber if the Power-On-Self-Test has failed.
dark.
bottom ports.A solid light denotes activity on the port while a blinking light indicates a valid link.These LEDs will remain dark if there is no
link/activity on the port.
LEDs are marked 1 and 2 and will light solid green to denote activity on the port,while a blinking light will indicate a valid link.
1-12 in use.
1-6 Rear Panel Components
The rear panel of the Switch contains an AC power connector, two 10-gigabit stacking ports and a redundant power supply connector.
Rear panel vie
e 1- 4.
Figur
AC power connector is a standard three-pronged connector that supports the power cord. Plug-in the female connector of the provided power cord into
The
this socket, and the male side of the cord into a power outlet.The Switch automatically adjusts its power setting to any supply voltage in the range from 100 ~
C at 50 ~ 60 Hz.
A
V
240
.When power fails, the optional external RPS will take over all the power
y
er suppl
or pr
w
entilation.
oper v
Figure 1- 5. Side Panels
ear panel also includes an outlet f
The r
immediately and automatically.
nel Components
1-7 Side-P
The right-hand side panel of the Switch contains 2 system fans, while the left hand panel includes a heat vent.
The system fans are used to dissipate heat.The sides of the system also provide heat vents to serve the same purpose. Do not block these openings, and leave at
least 6 inches of space at the r
components might overheat, which could lead to system failure.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
a
or an optional external po
ear and sides of the Switch f
w of the Switch
Be reminded that without proper heat dissipation and air circulation,system
13
Page 15

Chapter 2 - Installation
2-1 Package Contents
2-2 Before You Connect to the Network
2-3 Installing the Switch Without the Rack
2-4 Rack Installation
2-5 Power On
2-6 Power Failure
2-7 Redundant Power System
2-1 Package Contents
Open the shipping carton of the Switch and carefully unpack its contents.The carton should contain the following items:
• One AT-9724TS Switch
• One AC power cord
• One Stacking Cable
• One CD which includes the AT-9724TS Manual, and Net.Cover documents
• One Warranty Card
• Mounting kit (two brackets and screws)
•
• RS-232 console cable
• If any item is found missing or damaged, please contact your local Allied Telesyn Reseller for replacement.
Four rubber feet with adhesive backing
2-2 Before You Connect to the Network
The site where you install the Switch may greatly affect its performance. Please follow these guidelines for setting up the Switch.
• Install the Switch on a sturdy, level surface that can support at least 6.6lb.(3kg) of weight.Do not place heavy objects on the Switch.
• The power outlet should be within 1.82 metres (6 feet) of the Switch.
• Visually inspect the power cord and see that it is fully secured to the AC power port.
• Make sure that there is proper heat dissipation from and adequate ventilation around the Switch. Leave at least 10 cm (4 inches) of space at the front
• Install the Switch in a fairly cool and dry place for the acceptable temperature and humidity operating ranges.
• Install the Switch in a site free from strong electromagnetic field generators (such as motors), vibration,dust, and direct exposure to sunlight.
• When installing the Switch on a level surface, attach the rubber feet to the bottom of the device.The rubber feet cushion the Switch, protect the
• Ensure you program the Switch with a valid IP address – see section xxxx.
and rear of the Switch for ventilation.
casing from scratches and prevent it from scratching other surfaces.
2-3 Installing the Switch without a Rack
When installing the Switch on a desktop or shelf, the rubber feet included with the Switch should first be attached. Attach these cushioning feet on the bottom
at each corner of the device. Allow enough ventilation space between the Switch and any other objects in the vicinity.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
14
Page 16
Figure 2- 1. Prepare Switch for installation on a desktop or shelf
2-4 Installing the Switch in a Rack
The Switch can be mounted in a standard 19" rack. Use the following diagrams to guide you.
Fasten the mounting brackets to the Switch using the screws provided.With the brackets attached securely, you can mount the Switch in a standard rack as
shown in Figure 2-2.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
15
Page 17
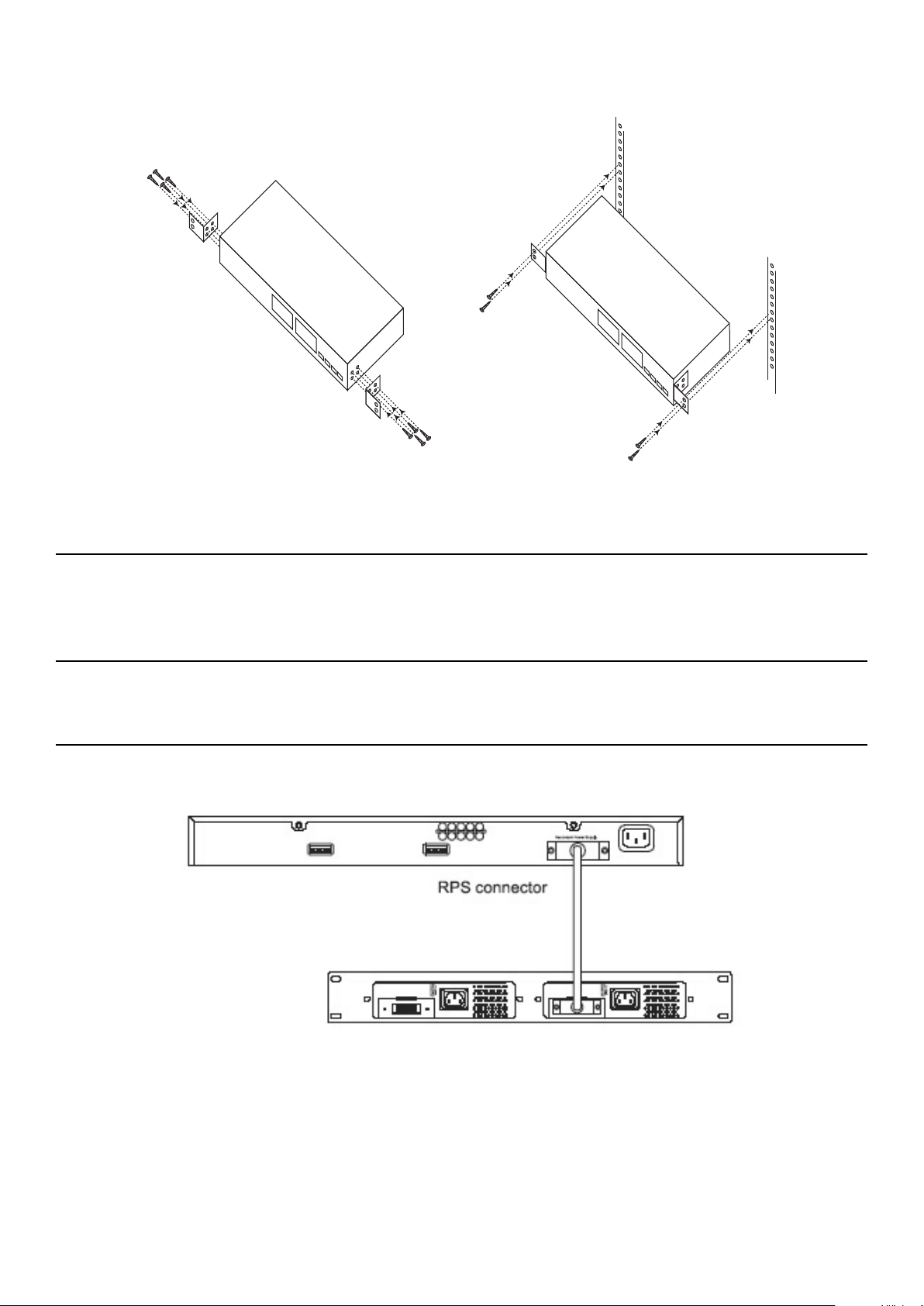
2-5 Mounting the Switch in a Standard 19" Rack
Figure 2- 2. Installing Switch in a rack
2-5 Power On
Plug one end of the AC power cord into the power connector of the Switch and the other end into the local power source outlet.
After the Switch is powered on,the LED indicators will momentarily blink.This blinking of the LED indicators represents a reset of the system.
2-6 Power Failure
As a precaution, in the event of a power failure, unplug the Switch.When power is resumed, plug the Switch back in.
2-7 External Redundant Power System
The Switch supports an external redundant power system.
Figure 2- 3.The AT-9724TS with the AT-RPS7000 Redundant External Power Supply
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
16
Page 18
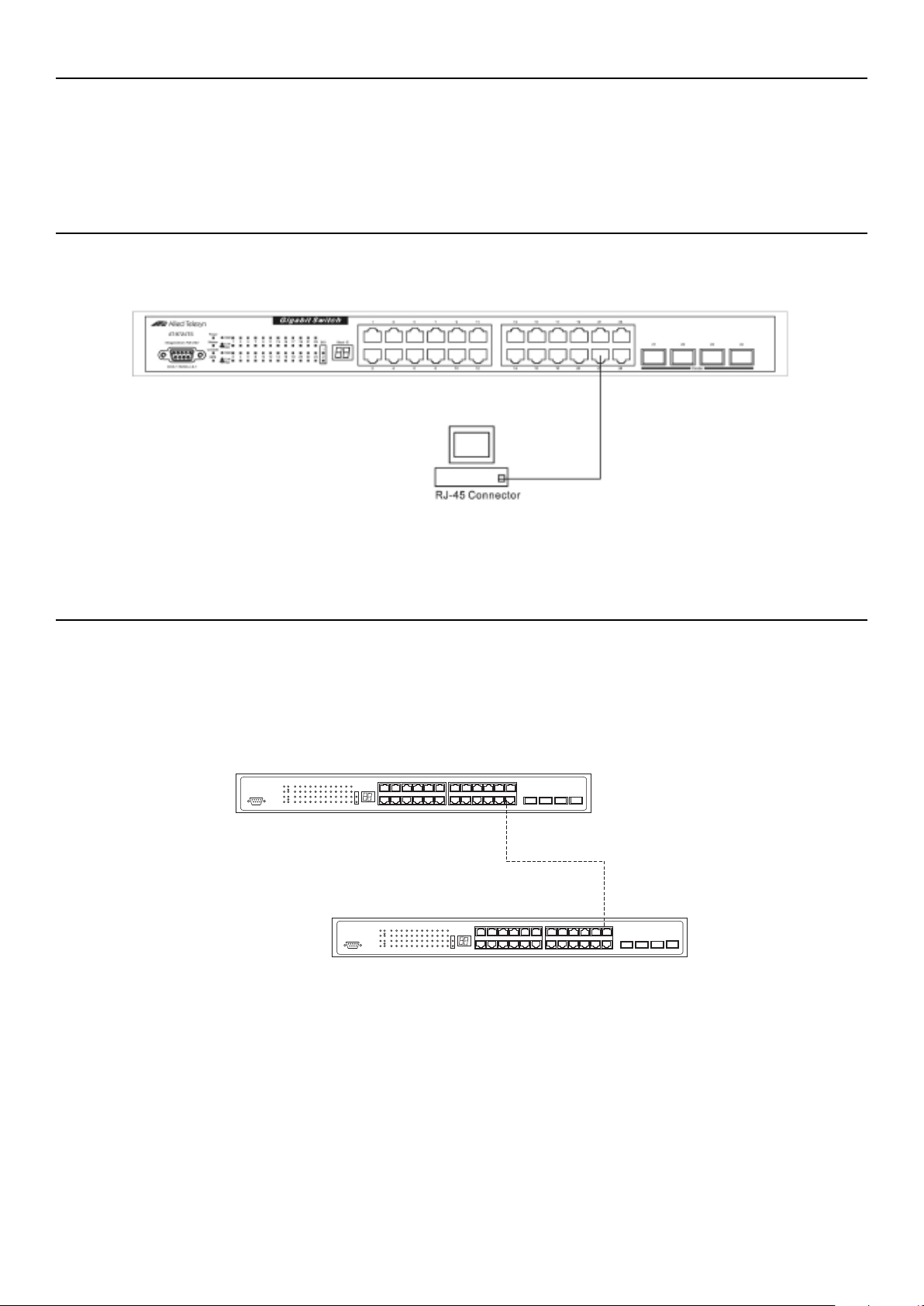
Chapter 3 - Connecting the Switch
135 7911
13 15
2
4 6 8 10 12 14
16
17
19 21
23
18
202224
21 22
23
24
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
Power
Mas
ter
Con
sole
RPS
1000
Link
Act
1000
Link
Act
1
2
SIO
Stack ID
AT-9724TS
1
357
9
11
13 15
2
4
6 8 10 12 14
16
17
19 21
23
18
202224
21 22
23
24
2
4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
1
3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
Pow
er
Mas
ter
Console
RPS
1000
Link
Act
1000
Link
Act
1
2
SIO
Stack ID
AT-
9724TS
UTP cable
• 3-1 Switch to End Node
• 3-2 Switch to Hub or Switch
• 3-3 Connecting to Network Backbone or Server
• 3-4 Stacking and the AT-9724TS
3-1 Switch To End Node
End nodes include PCs outfitted with a 10, 100 or 1000Mbps RJ45 Ethernet Network Interface Card (NIC) and most routers.
An end node can be connected to the Switch via a twisted-pair UTP/STP cable.The end node should be connected to any of the 24 1000T ports of the Switch.
Figure 3- 1. Switch connected to an end node
The Link/Act LEDs for each UTP port will light green or amber when the link is valid.A blinking LED indicates packet activity on that port.
3-2 Switch to Hub or Switch
These connections can be accomplished in a number of ways using a normal cable.
• A 10T hub or switch can be connected to the Switch via a twisted-pair Category 3, 4 or 5 UTP/STP cable.
• A 100TX hub or switch can be connected to the Switch via a twisted-pair Category 5 UTP/STP cable.
• A 1000T switch can be connected to the Switch via a twisted pair Category 5e UTP/STP cable.
• A switch supporting a fibre-optic uplink can be connected to the Switch’s SFP ports via fibre-optic cabling.
Figure 3- 2. Switch connected to a port on a hub or switch using either a straight or crossover cable – any normal cable is fine
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
17
Page 19
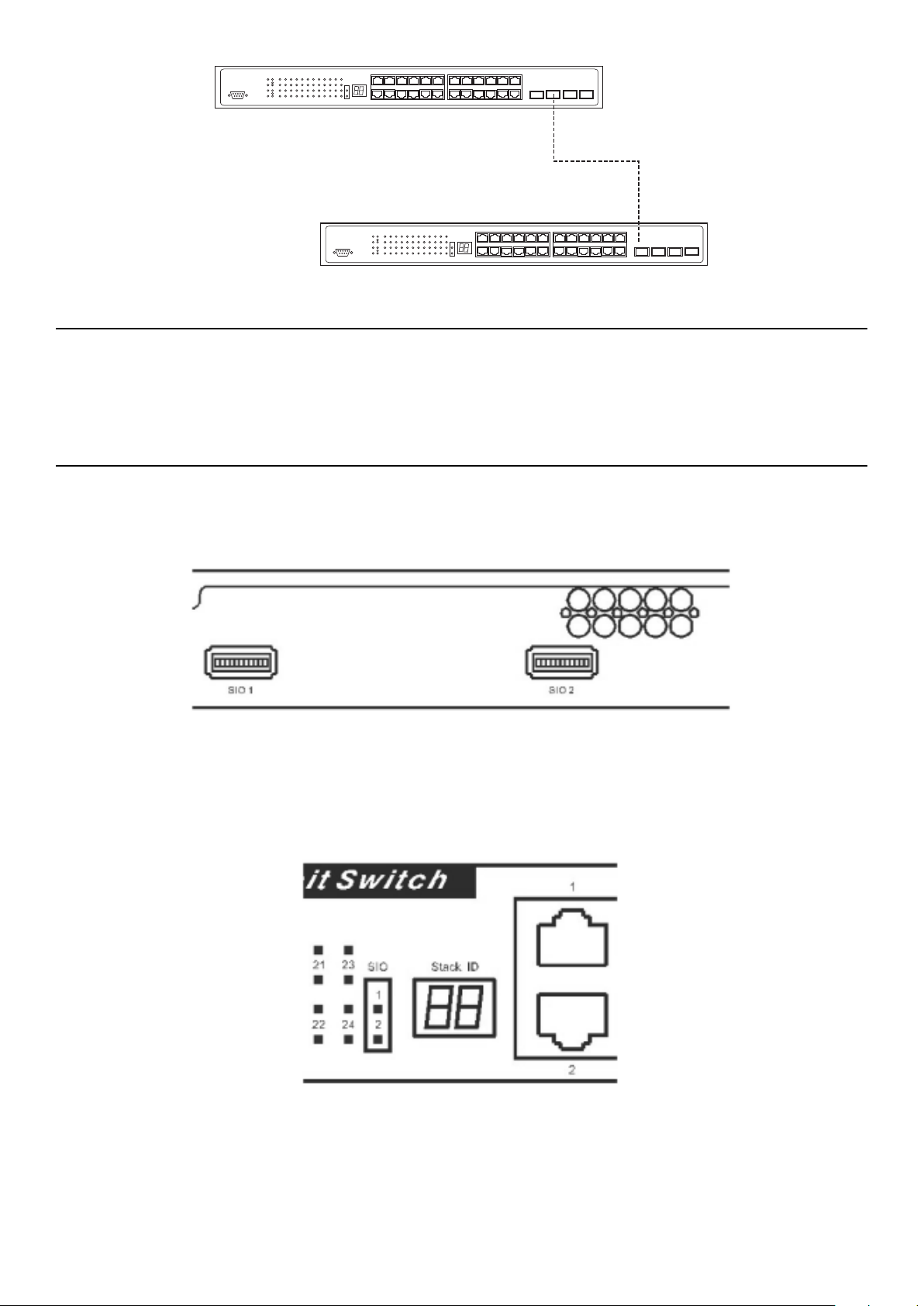
Figure 3- 3. Switch connected to switch using fibre-optic cabling
1
357
9
11
13
15
2
4
6 8 10 12 14
16
17
19
21
23
18
202224
21
22
23
24
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
1
3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
Power
Master
Console
RPS
1000
Link
Act
1000
Link
Act
1
2
SIO
Stack ID
AT-9724TS
135 7911
13 15
2
4 6 8 10 12 14
16
17
19 21
23
18
202224
21 22
23
24
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
Power
Master
Console
RPS
1000
Link
Act
1000
Link
Act
1
2
SIO
Stack ID
AT-
9724TS
Optical fibre cable
3-3 Connecting To Network Backbone or Server
The 4 combo SFP ports and the 24 1000T ports are ideal for uplinking to a network backbone, server or server farm.The copper ports operate at a speed of
1000, 100 or 10Mbps in full or half duplex mode.The fibre-optic ports can operate at 1000Mbps in full duplex mode only.
Connections to the Gigabit Ethernet ports are made using fibre-optic cable or Category 5e copper cable, depending on the type of port. A valid connection is
indicated when the Link LED is lit.
3-4 Stacking and the AT-9724TS
The AT-9724TS is equipped with two 10-gigabit stacking ports at the rear of the Switch, as seen in Figure 3-5.These stacking ports may be used to stack the AT9724TS to a master switch to be used in a switch stack.
Figure 3- 5. SIO 1 and SIO 2 Stacking ports at the rear of the AT-9724TS
These tw
These tw
o stacking por
o stacking por
ts, named SIO 1 and SIO 2 can be used with other stacking switches for a scalable stacking solution of up to 288 ports in a ring topology.
e corresponding LEDs at the front of the Switch,labelled SIO 1 and SIO 2 will light solid green whenever the corresponding port is
v
ts ha
in use.
Figur
Stacking LEDs (SIO) at the fr
e 3- 6.
ont of the
-9724TS
T
A
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
18
Page 20
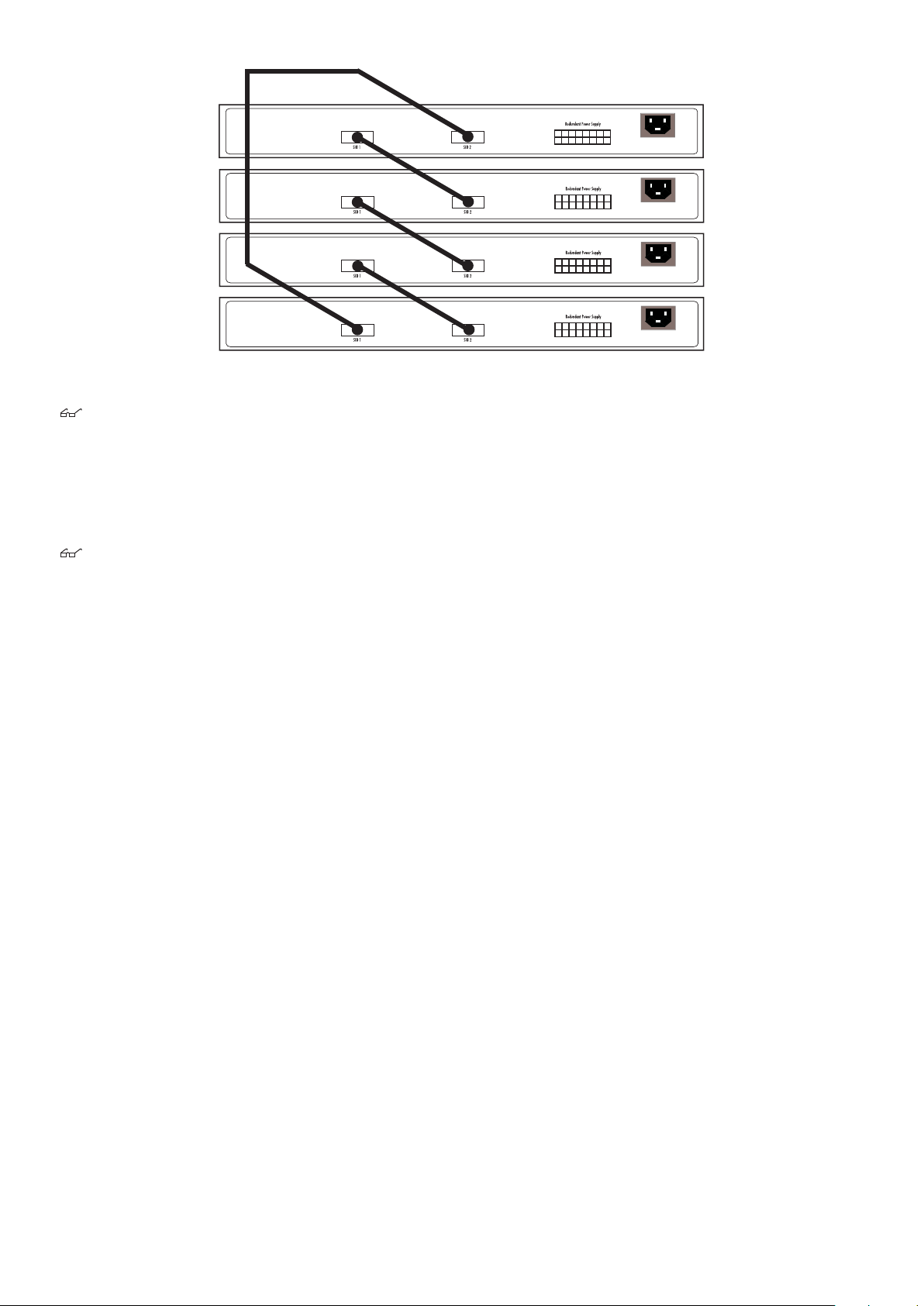
Figure 3- 8. Stacking in a Ring Architecture
Note: The Do not connect the stacked Switch group to the network until you have properly configured all Switches for stacking. An improperly
configured Switch stack can cause a broadcast storm.
Stacking Limitations Utilizing a Ring Topology
There is a limit to the number of AT-9724TS Switches that can be stacked in a ring topology. A maximum of 12 switches can be stacked.
Note: All Switches must have the same firmware rev.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
19
Page 21

Cha
pter 4 - Introduction to Switch Management
4-1 AT-9724TS Gigabit Layer 3 Switch Management Options
4-2 Web-based Management Interface
4-3 SNMP-Based Management
4-4 Command Line Console Interface Through The Serial Port
4-5 Connecting the Console Port (RS-232 DCE)
4-6 First Time Connecting to The Switch
4-7 Password Protection
4-8 SNMP Settings
4-9 IP Address Assignment
4-10 Connecting Devices to the Switch
4-1 AT-9724TS Gigabit Layer 3 Switch Management Options
This system may be managed out-of-band through the console port on the front panel or in-band using Telnet.The user may also choose the web-based
management, accessible through a web browser.
4-2 Web-based Management Interface
After you have successfully installed the Switch, you can configure the Switch,monitor the LED panel, and display statistics graphically using a web browser, such
as Netscape Navigator (version 6.2 and higher) or Microsoft® Internet Explorer (version 5.0).
4-3 SNMP-Based Management
You can manage the Switch with an SNMP-compatible console program.The Switch supports SNMP version 1.0, version 2.0 and version 3.0.The SNMP agent
decodes the incoming SNMP messages and responds to requests with MIB objects stored in the database.The SNMP agent updates the MIB objects to generate
statistics and counters.
4-4 Command Line Console Interface Through The Serial Port
You can also connect a computer or terminal to the serial console port to access the Switch.The command-line-driven interface provides complete access to all
Switch management features.
t (RS-232 DCE)
4-5 Connecting the Console P
The Switch provides an RS-232 serial port that enables a connection to a computer or terminal for monitoring and configuring the Switch.This port is a female
DB-9 connector
To use the console port, you need the following equipment:
• A terminal or a computer with both a serial port and the ability to emulate a terminal.
• A null modem or crossover RS-232 cable with a female DB-9 connector for the console port on the Switch (supplied with the switch).
, implemented as a data terminal equipment (DTE) connection.
or
To connect a terminal to the console port:
1. Connect the female connector of the RS-232 cable directly to the console port on the Switch, and tighten the captive retaining screws.
2. Connect the other end of the cable to a terminal or to the serial connector of a computer running terminal emulation software. Set the terminal
3. Select the appropriate serial port (COM port 1 or COM port 2).
4. Set the data rate to 115200 baud.
5. Set the data format to 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, and no parity.
6. Set flow control to none.
7. Under Properties, select VT100 for Emulation mode.
8. Select Terminal keys for Function,Arrow,and Ctrl keys.Ensure that you select Terminal keys (not Windows keys).
emulation software as follows:
Note: When y
or later installed.Windows 2000 Service Pack 2 allows you to use arrow keys in HyperTerminal's VT100 emulation. See www.microsoft.com for
information on Windows 2000 service packs.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
ou use HyperTerminal with the Microsoft® Windows® 2000 operating system, ensure that you have Windows 2000 Service Pack 2
20
Page 22

9. After you have correctly set up the terminal, plug the power cable into the power receptacle on the back of the Switch.The boot sequence appears in
10. After the boot sequence completes, the console login screen displays.
11. If you have not logged into the command line interface (CLI) program, press the Enter key at the User name and password prompts.There is one
12. Enter the commands to complete your desired tasks.Many commands require administrator-level access privileges. Read the next section for more
13. When you have completed your tasks, exit the session with the logout command or close the emulator program.
Make sure the terminal or PC you are using to make this connection is configured to match these settings.
If you are having problems making this connection on a PC, make sure the emulation is set to VT-100.You will be able to set the emulation by clicking on the
menu in you HyperTerminal window, clicking on Properties in the drop-down menu,and then clicking the Settings tab.This is where you will find the
Emulation options. If you still do not see anything, try rebooting the Switch by disconnecting its power supply.
Once connected to the console, the screen below will appear on your console screen.This is where the user will enter commands to perform all the available
management functions.The Switch will prompt the user to enter a user name and a password. Upon the initial connection, there is no user name or password
and therefore just press enter twice to access the command line interface.
the terminal.
default user name and password for the Switch.User names and passwords must first be created by the administrator.If you have previously set up
user accounts, log in and continue to configure the Switch.
information on setting up user accounts. See the AT-9724TS Command Line Interface Reference Manual on the documentation CD for a list of all
commands and additional information on using the CLI.
File
4-6 First Time Connecting to the Switch
The Switch supports user-based security that can allow you to prevent unauthorized users from accessing the Switch or changing its settings.This section tells
how to log onto the Switch.
Note: The passwords used to access the Switch are case-sensitive; therefore,"S" is not the same as "s."
ou first connect to the Switch, you will be presented with the first login screen (shown below).
When y
Note: Press Ctrl+R to refresh the screen.This command can be used at any time to force the console program in the Switch to refresh the
console screen.
The initial username and password are:
Figur
e 4- 1.
een, first time connecting to the Switch
Initial scr
Username: manager
Password: friend
You will be given access to the command prompt AT-9724TS:4# shown below.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
21
Page 23
Figure 4- 2. Command Prompt
Note: The first user automatically gets Administrator level privileges. It is recommended to create at least one Admin-level user account for the
Switch.
4-7 Password Protection
One of the first tasks when settings up the Switch is to create user accounts. If you log in using a predefined administrator-level user name, you have privileged
access to the Switch's management software.
After your initial login, define new passwords for both default user names to prevent unauthorized access to the Switch, and record the passwords for future
reference.
To create an administrator-level account for the Switch, do the following:
At the CLI login prompt, enter create account admin followed by the <
You will be asked to provide a password.Type the <
You will be prompted to enter the same password again to verify it.Type the same password and press the
Successful creation of the new administrator account will be verified by a Success message.
Note: Passwords are case sensitive.User names and passwords can be up to 15 characters in length.
The sample below illustrates a successful creation of a new administrator-level account with the user name "newmanager".
password> used for the administrator account being created and press the Enter key.
user name> and press the Enter key.
Enter key.
AT-9724TS:4#create account admin newmanager
Command: create account admin newmanager
Enter a case-sensitive new password:********
Enter the new password again for confirmation:********
Success.
AT-9724TS:4#
m Caution: CLI configuration commands only modify the running configuration file and are not saved when the Switch is rebooted.To save all your
you must use the save command to copy the running configuration file to the startup configuration.
olatile storage
configuration changes in non
v
4-8 SNMP Settings
Simple Netw
enables network management stations to r
features for proper operation,
Managed devices that suppor
maintained by the SNMP agent and used to manage the device.These objects are defined in a Management Information Base (MIB), which provides a standard
presentation of the information contr
access this information over the network.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
ork Management Protocol (SNMP) is an OSI Layer 7 (Application Layer) designed specifically for managing and monitoring network devices.SNMP
monitor performance and detect potential problems in the Switch,switch group or network.
t SNMP include softwar
ead and modify the settings of gateways,routers, switches, and other network devices. Use SNMP to configure system
y the on-boar
olled b
,
erred to as an agent), which runs locally on the device.A defined set of variables (managed objects) is
ef
e (r
d SNMP agent.
SNMP defines both the f
ormat of the MIB specifications and the pr
otocol used to
22
Page 24

The AT-9724TS supports SNMP versions 1, 2c,and 3.You can specify which version of SNMP you want to use to monitor and control the Switch.The three
versions of SNMP vary in the level of security provided between the management station and the network device.
In SNMP v.1 and v.2, user authentication is accomplished using 'community strings',which function like passwords.The remote user SNMP application and the
Switch SNMP must use the same community string. SNMP packets from any station that has not been authenticated are ignored (dropped).
The default community strings for the Switch used for SNMP v.1 and v.2 management access are:
public – Allows authorized management stations to retrieve MIB objects.
private – Allows authorized management stations to retrieve and modify MIB objects.
SNMP v.3 uses a more sophisticated authentication process that is separated into two parts.The first part is to maintain a list of users and their attributes that
are allowed to act as SNMP managers.The second part describes what each user on that list can do as an SNMP manager.
The Switch allows groups of users to be listed and configured with a shared set of privileges.The SNMP version may also be set for a listed group of SNMP
managers.Thus, you may create a group of SNMP managers that are allowed to view read-only information or receive traps using SNMP v.1 while assigning a
higher level of security to another group, granting read/write privileges using SNMP v.3.
Using SNMP v
functions.The functions allowed or restricted are defined using the Object Identifier (OID) associated with a specific MIB.An additional layer of security is
available for SNMP v.3 in that SNMP messages may be encrypted.To read more about how to configure SNMP v.3 settings for the Switch read the section
entitled Management.
.3 individual users or groups of SNMP managers can be allowed to perform or be restricted from performing specific SNMP management
Traps
Traps are messages that alert network personnel of events that occur on the Switch.The events can be as serious as a reboot (someone accidentally turned OFF
the Switch), or less serious like a port status change.The Switch generates traps and sends them to the trap recipient (or network manager).Typical traps include
trap messages for Authentication Failure,Topology Change and Broadcast/Multicast Storm.
MIBs
Management and counter inf
Information Base module. Consequently, values for MIB objects can be retrieved from any SNMP-based network management software. In addition to the
standard MIB-II, the Switch also supports its own proprietary enterprise MIB as an extended Management Information Base.The proprietary MIB may also be
retrieved by specifying the MIB Object Identifier. MIB values can be either read-only or read-write.
ormation are stored by the Switch in the Management Information Base (MIB).The Switch uses the standard MIB-II Management
4-9 IP Address Assignment
Each Switch must be assigned its own IP Address, which is used for communication with an SNMP network manager or other TCP/IP application (for example
BOOTP,TFTP).The Switch's default IP address is 10.0.0.1.You can change the default Switch IP address to meet the specification of your networking address
scheme.
The Switch is also assigned a unique MAC address by the factory.This MAC address cannot be changed, and can be found by entering the command "show
switch" into the command line interface, as shown below.
witch” command
w s
“sho
e 4- 3.
Figur
The Switch's MAC address can also be found from the Web management program on the
Configuration menu.
or the Switch must be set before it can be managed with the Web-based manager.The Switch IP address can be automatically set using BOOTP
ess f
The IP ad
or DHCP protocols, in which case the actual address assigned to the Switch must be known.
The IP address may be set using the Command Line Interface (CLI) over the console serial port as follows:
Starting at the command line pr
the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface named System and the y's represent the corresponding subnet mask.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
dr
enter the commands
ompt,
config ipif
System ipaddr
Switch Information (Basic Settings) window in the
ess xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/yyy
.yyy
.yyy.yyy
Wher
.
e the x's r
epr
esent
23
Page 25

Alternatively, you can enter config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z.Where the x's represent the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface
named System and the z represents the corresponding number of subnets in CIDR notation.
The IP interface named System on the Switch can be assigned an IP address and subnet mask which can then be used to connect a management station to the
Switch's Telnet or Web-based management agent.
Figure 4- 4.Assigning the Switch an IP Address
In the above example, the Switch was assigned an IP address of 10.53.13.144 with a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0.The system message Success indicates that the
command was executed successfully.The Switch can now be configured and managed via Telnet and the CLI or via the Web-based management.
4-10 Connecting Devices to the Switch
After you assign IP addresses to the Switch,you can connect devices to the Switch.
To connect a device to an SFP transceiver port:
• Use your cabling requirements to select an appropriate SFP transceiver type.
• Insert the SFP transceiver (sold separately) into the SFP transceiver slot.
• Use the appropriate network cabling to connect a device to the connectors on the SFP transceiver.
m Caution: When the SFP transceiver acquires a link, the associated integrated 10/100/1000T port is disabled.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
24
Page 26
Chapter 5 - Introduction to Web-based Switch Configuration
5-1 Introduction
5-2 Login to Web manager
5-3 Web-Based User Interface
5-4 Basic Setup
5-5 Reboot
5-6 Basic Switch Setup
5-7 Network Management
5-8 Switch Utilities
5-9 Network Monitoring
5-10 IGMP Snooping Status
5-1 Introduction
All software functions of the AT-9724TS can be managed, configured and monitored via the embedded web-based (HTML) interface.The Switch can be managed
from remote stations anywhere on the network through a standard browser such as Netscape Navigator/Communicator or Microsoft Internet Explorer.The
browser acts as a universal access tool and can communicate directly with the Switch using the HTTP protocol.
Web-based management module and the Console program (and Telnet) are different ways to access the same internal switching software and configure it.
The
Thus, all settings encountered in web-based management are the same as those found in the console program.
5-2 Login to Web Manager
To begin managing your Switch, simply run the browser you have installed on your computer and point it to the IP address you have defined for the device.The
URL in the address bar should read something like: http://123.123.123.123, where the numbers 123 represent the IP address of the Switch.
Note: The Factory default IP address for the Switch is 10.0.0.1.
e 5- 1. Login Button
Figur
This opens the management module's user authentication window,as seen below.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
25
Page 27
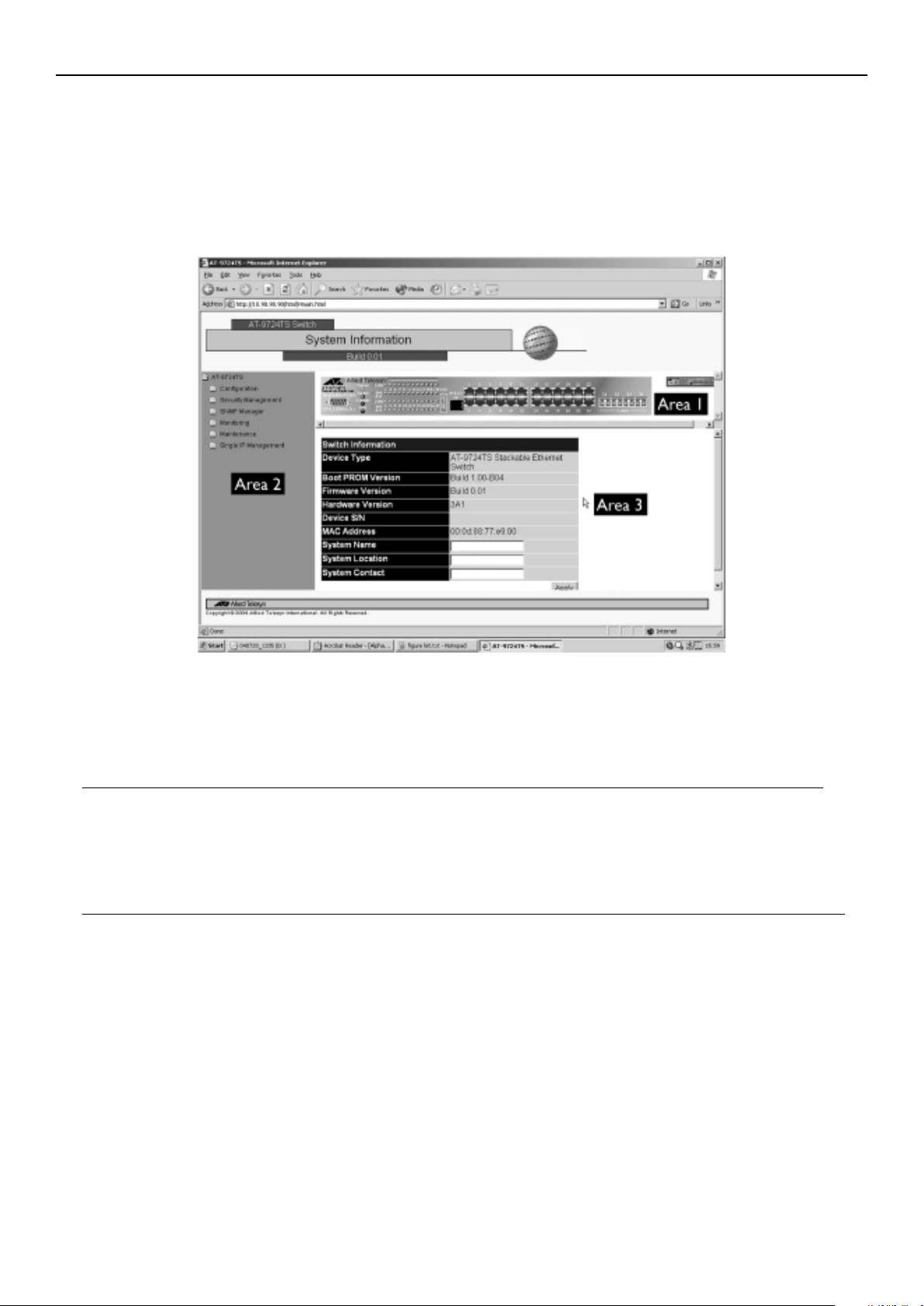
5-3 Web-based User Interface
The user interface provides access to various Switch configuration and management screens,allows you to view performance statistics,and permits you to
graphically monitor the system status.
Areas of the User Interface
The figure below shows the user interface.The user interface is divided into 3 distinct areas as described in the table.
Figure 5- 2. Main Web-Manager Screen
Area Function
The folder icons can be opened to display the hyperlinked menu buttons and
ed.
1
2 Pr
3 Presents switch information based on your selection and the entry of configuration data.
Select the men
olders contained within them. Click the Allied Telesyn logo to go to the Allied Telesyn website.
subf
esents a graphical near real-time image of the front panel of the Switch.This area displays the Switch's ports and expansion
modules, showing port activity, duplex mode, or flow control,depending on the specified mode.Various areas of the graphic can
be selected for performing management functions, including port configuration.
u or windo
w to be displa
y
m Caution: Any changes made to the Switch configuration during the current session must be saved in the Save Changes web menu (explained
below) or use the command line interface (CLI) command save.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
26
Page 28

Web Pages
Configurations – Contains screens concerning configurations for IP Address,Switch Information,Advanced Settings, Port Configuration, IGMP, Spanning Tree,
Forwarding Filtering,VLANs, Port Bandwidth, SNTP Settings,Port Security, QoS, MAC Notification, LACP,Access Profile Table, System Log Servers, PAE Access
Entity,and Layer 3 IP Networking.
Security Management – Contains screens concerning configurations for Security IP, User Accounts,Access Authentication Control (TACACS),Secure
Sockets Layer (SSL), and Secure Shell (SSH).
SNMP Manager – Contains screens and windows concerning the implementation and upkeep of the SNMP Manager of the Switch.
Monitoring – Contains screens concerning monitoring the Switch, pertaining to Port Utilization, CPU Utilization, Packets, Errors Size,MAC Address, IGMP
Snooping Group,IGMP Snooping Forwarding,VLAN Status, Router Port, Port Access Control and Layer 3 Feature.
Maintenance – Contains screens concerning configurations and information about Switch maintenance, including TFTP Services,CF Services, Dual Image
Information, Switch History, Ping Test, Save Changes, Reboot Services and Logout.
Single IP Management – Contains screens concerning information on Single IP Management, including SIM Settings,Topology and Firmware/Configuration
downloads.
Note: Be sur
e to configure the user name and password in the User Accounts menu before connecting the Switch to the greater network.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
27
Page 29

Chapter 6 - Configuring The Switch
6-1 Switch Information
6-2 IP Address
6-3 Box Information
6-4 Advanced Settings
6-5 Port Configuration
6-6 Port Description
6-7 Port Mirroring
6-8 Link Aggregation
6-9 LACP Port Setting
6-10MAC Notification
6-11GMP
6-12 Spanning Tree
6-13 Forward & Filtering
6-14 VLANs
6-15 Traffic Control
6-16 Port Security
6-17 Port Lock Entries
6-18 QoS
6-19 System Log Servers
6-20 SNTP Setting
6-21 Access Profile Table
6-22 Port Access Entity
6-23 Layer 3 IP Networking
6-1 Switch Information
The subsections below describe how to change some of the basic settings for the Switch such as changing IP settings and assigning user names and passwords for
management access privileges, as well as how to save the changes and restart the Switch.
Click the
Switch Information link in the Configuration menu.
Figure 6- 1. Switch Information – Basic Settings window
ws the
The
Switch Information windo
Version
into another network device's address table,if necessary.The user may also enter a
defining the Switch, to the user's pr
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
, and Hardware Version.This information is helpful to keep track of PROM and firmware updates and to obtain the Switch's MAC address for entry
w sho
erence.
ef
Switch's MA
C Addr
ess
(assigned b
y the factor
System Name, System Location and System Contact to aid in
y and unchangeable),
the
Boot PROM, Firmw
e
r
a
28
Page 30

6-2 IP Address
The IP Address may initially be set using the console interface prior to connecting to it through the Ethernet.If the Switch IP address has not yet been changed,
read the introduction of the AT-9724TS Command Line Interface Reference Manual or return to Chapter 4 of this manual for more information.
To change IP settings using the web manager you must access the IP Address menu located in the Configuration folder.
To configure the Switch's IP address:
Open the Configuration folder and click the IP Address menu link.The web manager will display the Switch's current IP settings in the IP configuration
menu, as seen below.
Figure 6- 2. IP Address Settings window
To manually assign the Switch's IP address,subnet mask, and default gateway address:
1. Select
2. Enter the appropriate
3. If you want to access the Switch from a different subnet from the one it is installed on, enter the IP address of the
4. If no VLANs have been previously configured on the Switch, you can use the default VLAN Name.The default VLAN contains all of the Switch ports
Manual from the Get IP From drop-down menu.
IP Address and Subnet Mask.
manage the Switch from the subnet on which it is installed, you can leave the default address (0.0.0.0) in this field.
as members. If VLANs have been previously configured on the Switch,you will need to enter the
connected to the management station that will access the Switch.The Switch will allow management access from stations with the same VID listed
here.
VLAN ID of the VLAN that contains the port
Default Gateway. If you will
Note: The Switch's factory default IP address is 10.0.0.1 with a subnet mask of 255.0.0.0 and a default gateway of 0.0.0.0.
To use the BOOTP or DHCP protocols to assign the Switch an IP address, subnet mask,and default gateway address:
Get IP From:<Manual> pull-down menu to choose from BOOTP or DHCP.This selects how the Switch will be assigned an IP address on the next
Use the
eboot.
r
The IP Address Settings options are:
Parameter Description
BOOTP
DHCP The Switch will send out a DHCP br
Manual Allows the entry of an IP address, Subnet Mask, and a Default Gateway for the Switch.These fields should be of
Subnet Mask A Bitmask that determines the extent of the subnet that the Switch is on.
Default Gateway IP ad
The Switch will send out a BOOTP broadcast request when it is powered up.The BOOTP protocol allows IP
esses, network masks, and default gateways to be assigned by a central BOOTP server. If this option is set,
dr
ad
the Switch will first look for a BOOTP server to provide it with this information before using the default or
previously entered settings.
addresses, network masks, and default gateways to be assigned by a DHCP server. If this option is set,the
Switch will first look f
previously entered settings.
the form xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx, where each xxx is a number (represented in decimal form) between 0 and 255.This
ess should be a unique ad
dr
ad
xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx,
should be 255.0.0.0 for a Class A network, 255.255.0.0 for a Class B network, and 255.255.255.0 for a Class C
netw
sent.
intranet, or you do not want the Switch to be accessible outside your local network, you can leave this field
unchanged.
but custom subnet masks are allowed.
ork,
dress that determines where packets with a destination address outside the current subnet should be
This is usuall
or a DHCP ser
wher
dr
y the ad
e each
oadcast r
ess on the netw
dr
xxx is a n
ess of a r
equest when it is po
vide it with this inf
o
er to pr
v
ork assigned f
epresented in decimal) between 0 and 255.The value
umber (r
outer or a host acting as an IP gate
w
ormation before using the default or
or use by the network administrator.
Should be of the f
our network is not part of an
If y
.
y
wa
The DHCP pr
.
ed up
er
otocol allows IP
orm
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
29
Page 31

VLAN Name This allows the entry of a VLAN Name from which a management station will be allowed to manage the Switch
Apply to let your changes take effect.
Click
using TCP/IP (in-band via web manager or Telnet). Management stations that are on VLANs other than the one
entered here will not be able to manage the Switch in-band unless their IP addresses are entered in the
Security IP Management menu. If VLANs have not yet been configured for the Switch,the default VLAN contains
all of the Switch's ports.There are no entries in the
management station that can connect to the Switch can access the Switch until a management VLAN is
specified or Management Station IP Addresses are assigned.
Security IP Management table, by default, so any
Setting the Switch's IP Address using the Console Interface
Each Switch must be assigned its own IP Address, which is used for communication with an SNMP network manager or other TCP/IP
application (for example BOOTP,TFTP).The Switch's default IP address is 10.0.0.1.You can change the default Switch IP address to meet the
specification of your networking address scheme.
The IP address for the Switch must be set before it can be managed with the Web-based manager.The Switch IP address can be automatically
set using BOOTP or DHCP protocols, in which case the actual address assigned to the Switch must be known.The IP address may be set using
the Command Line Interface (CLI) over the console serial port as follows:
Starting at the command line prompt, enter the commands config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/yyy.yyy.yyy.yyy.Where the x's
epresent the IP address to be assigned to the IP interface named System and the y's represent the corresponding subnet mask.
r
Alternatively, you can enter config ipif System ipaddress xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx/z.Where the x's represent the IP address to be assigned
to the IP interface named System and the z represents the corresponding number of subnets in CIDR notation.
The IP interface named System on the Switch can be assigned an IP address and subnet mask which can then be used to connect a management
station to the Switch's Telnet or Web-based management agent.
The system message
and the CLI or via the Web-based management agent using the above IP address to connect to the Switch.
Success indicates that the command was executed successfully.The Switch can now be configured and managed via Telnet
Advanced Settings
The Advanced Settings window contains the main settings for all major functions for the Switch.To view the Advanced Settings window,click its link in
Configuration folder.This will enable the following window to be viewed and configured.
the
Figure 6- 3. Switch Information (Advanced Settings)
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
30
Page 32

Parameter Description
Serial Port Auto Logout Time
Serial Port Baud Rate This field specifies the baud rate for the serial port on the Switch.This field’s menu is set at 115200 and cannot
MAC Address Aging Time This field specifies the length of time a learned MAC Address will remain in the forwarding table without being
(10-1000000) accessed (that is, how long a learned MAC Address is allowed to remain idle).The default age-out time for the
IGMP Snooping To enable system-wide IGMP Snooping capability select Enabled. IGMP snooping is Disabled by default. Enabling
Multicast router Only This field specifies that the Switch should only forward all multicast traffic to a multicast-enabled router, if
GVRP Status Use this pull-do
Telnet Status Telnet configuration is Enabled by default. If you do not want to allow configuration of the system through
Telnet TCP Port Number The TCP port number.TCP ports are numbered between 1 and 65535.The "well-known" TCP port for the
(1-65535) T
Web Status Web-based management is Enabled by default. If you choose to disable this by selecting Disabled,you will lose
RMON Status Remote monitoring (RMON) of the Switch is Enabled or Disabled here.
Link Aggregation Algorithm The algorithm that the Switch uses to balance the load across the ports that make up the port trunk group is
Switch 802.1x The Switch’s 802.1x function may be enabled by port or by MAC Address; the default is Disabled.This field must
Auth Protocol The user may use the pull down menu to choose between radius eap and radius pap for the 802.1x
ention
HOL Pr
J
Syslog State Enables or disables Syslog State; default is Disabled.
ev
umbo Frame
Select the logout time used for the console interface.This automatically logs the user out after an idle period of
time, as defined.Choose from the following options:
default setting is 10 minutes.
be changed.
Switch is 300 seconds.To change this, type in a different value representing the MAC address age-out time in
seconds.The
default setting is
IGMP snooping allows you to specify use of a multicast router only (see below).To configure IGMP Snooping
for individual VLANs, use the IGMP Snooping page under the
enabled. Otherwise, the Switch will forward all multicast traffic to any IP router.The default is
Telnet choose
elnet protocol is 23.
the ability to configure the system through the web interface as soon as these settings are applied.
defined b
& Dest
be enabled to view and configure certain windows for 802.1x.More information regarding 802.1x,its functions
and implementation can be found later in this section, under the
Port-Based 802.1x specifies that ports configured for 802.1x are initialized based on the port number only and
are subject to any authorization parameters configured.
MAC-based Authorization specifies that ports configured for 802.1x are initialized based on the port number
and the MAC address of the computer being authorized and are then subject to any authorization parameters
configured.
authentication protocol on the Switch.The default setting is
This field will enable or disable Head of Line Pr
This field will enable or disable the J
MAC Address Aging Time can be set to any value between 10 and 1,000,000 seconds.The
300 seconds.
wn menu to enable or disable GVRP on the Switch.
Disabled.
C Source
y this definition. Choose
(See the Link Aggregation section of this manual).
MA
umbo Frame function on the Switch.The default is
2 Minutes, 5 Minutes, 10 Minutes, 15 Minutes or Never.The
IGMP Snooping folder.
C Destination
, MA
ention on the Switch.The default is
v
e
C Src & Dest
, MA
Port Access Entity folder.
radius eap.
, IP Source, IP Destination or IP Src
Enabled.
Disabled.
Disabled.
Click A
pply
to implement changes made
.
6.3 Box Information
x Information Configur
The Bo
configure the Master switch of a switch stack.The Master switch is the switch that will be used to configure the software applications regarding the switch stack.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
ation
een can be f
scr
ound in the
Figure 6- 4. Box Information Configuration window
Configur
ationfolder under the heading Box Information.This windo
w is used to
31
Page 33

Parameter Description
Current Box ID The current Box ID of the Master switch in the stack.
New Box ID The new box ID of the Master switch in the stack.
Box Type The user may choose the model name of the Master switch in a stack to be the main configuring switch of that
Priority Displays the priority ID of the Switch.The lower the number, the higher the priority.The box (switch) with the
stack.
lowest priority number in the stack is the Master switch.
Information configured in this screen may be found in the
Monitoring folder under Stack Information.
6-4 Port Configuration
This section contains information for configuring various attributes and properties for individual physical ports,including port speed and address learning. Clicking
on Port Configurations in the Configuration menu will display the following window for the user:
Port Configuration and The Port Information Table window
e 6- 5.
Figur
o configur
T
1. Choose the port or sequential range of ports using the From…To… port pull-down menus, and the Unit ID of the Switch to be configured.
2. Use the remaining pull-down menus to configure the parameters described below:
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
e switch por
ts:
32
Page 34

Parameter Description
State Toggle the State <Enabled> field to either enable or disable a given port or group of ports.
Speed/Duplex Toggle the Speed/Duplex field to either select the speed and duplex/half-duplex state of the port. Auto
Flow Control Displays the flow control scheme used for the various port configurations. Ports configured for full-duplex use
Learning Enable or disable MAC address learning for the selected ports.When Enabled, destination and source MAC
denotes auto-negotiation between 10 and 100Mbps devices,in full- or half-duplex.The Auto setting allows the
port to automatically determine the fastest settings the device the port is connected to can handle, and then to
use those settings.
1000M/Full_S.There is no automatic adjustment of port settings with any option other than Auto.
The Switch allows the user to configure two types of gigabit connections;
Gigabit connections are only supported in full duplex connections and take on certain characteristics that are
different from the other choices listed.
1000M/Full_M (master) and 1000M/Full_S (slave) parameters refer to connections running a 1000T cable
The
for connection between the Switch port and other device capable of a gigabit connection.The master setting
1000M/Full_M) will allow the port to advertise capabilities related to duplex, speed and physical layer type.The
(
master setting will also determine the master and slave relationship between the two connected physical layers.
This relationship is necessary for establishing the timing control between the two physical layers.The timing
control is set on a master physical layer by a local source.The slave setting (1000M/Full_S) uses loop timing,
where the timing comes form a data stream received from the master.If one connection is set for
1000M/Full_M, the other side of the connection must be set for 1000M/Full_S.Any other configuration will
esult in a link down status for both ports.
r
802.3x flow control,half-duplex ports use backpressure flow control,and
of the two.The default is
addresses are automatically listed in the forwarding table.When learning is
manually entered into the forwarding table.This is sometimes done for reasons of security or efficiency. See the
section on
The default setting is Disabled.
The other options are
Disabled.
Forwarding/Filtering for information on entering MAC addresses into the forwarding table.
Auto, 10M/Half, 10M/Full,100M/Half and 100M/Full, 1000M/Full_M and
1000M/Full_M and 1000M/Full_S.
Auto ports use an automatic selection
Disabled, MAC addresses must be
Click
Apply to implement the new settings on the Switch.
6-5 Port Description
The AT-9724TS supports a port description feature where the user may name various ports on the Switch.To assign names to various ports, click the Port
Description
on the Configuration menu:
Port Description Setting and Port Description Table window
e 6- 6.
Figur
Use the
From and To pull down menu to choose a port or range of ports to describe and Unit to choose the Switch in the switch stack, and then enter a
description of the port(s).
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Click
pply
A
to set the descriptions in the P
or
t Descr
iption T
le
b
a
.
33
Page 35

6-6 Port Mirroring
PC PC PC PC PC PC PC PC PC
135 7911
13 15
2
4 6 8 10 12 14
16
17
19 21
23
18
202224
21 22
23
24
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23
Power
Master
Console
RPS
1000
Link
Act
1000
Link
Act
1
2
SIO
Stack ID
AT-9724TS
Port Trunk Group
135 7
2
468
10/100/1000Mbps Backbone Switch
100Mbps
100Mbps
100Mbps
10/100Mbps Hub 10/100Mbps Hub10/100Mbps Hub
100Mbps
100Mbps100Mbps
100Mbps10Mbps10Mbps
10Mbps10Mbps
The Switch allows you to copy frames transmitted and received on a port and redirect the copies to another port.You can attach a monitoring device to the
mirrored port,such as a sniffer or an RMON probe, to view details about the packets passing through the first port.This is useful for network monitoring and
troubleshooting purposes.To view the
Setup Port Mirroring window,click Port Mirroring in the Configuration folder.
Figure 6- 7. Setup Port Mirroring window
To configure a mirror port:
• Select the Source Port from where you want to copy frames and the Target Port, which receives the copies from the source port.
• Select the
• Click
Source Direction, Ingress, Egress, or Both and change the Status drop-down menu to Enabled.
Apply to let the changes take effect.
Note: You cannot mirror a fast port onto a slower port. For example, if you try to mirror the traffic from a 100Mbps port onto a 10Mbps port,
this can cause throughput problems.The port you are copying frames from should always support an equal or lower speed than the port to which
you are sending the copies.Also, the target port for the mirroring cannot be a member of a trunk group. Please note a target port and a source port
cannot be the same port.
6-7 Link Aggregation
Understanding Port Trunk Groups
Port trunk groups are used to combine a number of ports together to make a single high-bandwidth data pipeline.
-9724TS suppor
T
A
The
ts up to 32 por
t trunk gr
oups with 2 to 8 por
ts in each group.A potential bit rate of 8000Mbps can be achieved.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Example of Port Trunk Group
e 6- 8.
Figur
34
Page 36

The Switch treats all ports in a trunk group as a single port. Data transmitted to a specific host (destination address) will always be transmitted over the same
port in a trunk group.This allows packets in a data stream to arrive in the same order they were sent.
Note: If any ports within the trunk group become disconnected, packets intended for the disconnected port will be load shared among the other
uplinked ports of the link aggregation group.
Link aggregation allows several ports to be grouped together and to act as a single link.This gives a bandwidth that is a multiple of a single link's bandwidth.
Link aggregation is most commonly used to link a bandwidth intensive network device or devices, such as a server, to the backbone of a network.
The Switch allows the creation of up to 32 link aggregation groups,each group consisting of 2 to 8 links (ports). All of the ports in the group must be members
of the same VLAN, and their STP status, static multicast,traffic control, traffic segmentation and 802.1p default priority configurations must be identical. Port
locking, port mirroring and 802.1X must not be enabled on the trunk group. Further,the aggregated links must all be of the same speed and should be configured
as full-duplex.
The Master Port of the group is to be configured by the user, and all configuration options, including the VLAN configuration that can be applied to the Master
Port, are applied to the entire link aggregation group.
Load balancing is automatically applied to the ports in the aggregated group,and a link failure within the group causes the network traffic to be directed to the
remaining links in the group.
The Spanning Tree Protocol will treat a link aggregation group as a single link,on the switch level.On the port level, the STP will use the port parameters of the
Master Port in the calculation of port cost and in determining the state of the link aggregation group.If two redundant link aggregation groups are configured on
the Switch, STP will block one entire group, in the same way STP will block a single port that has a redundant link.
To configure port trunking, click on the
Link Aggregation hyperlink in the Configuration folder to bring up the Port Link Aggregation Group table:
Figure 6- 9. Current Link Aggregation Group Entries window
To configure port trunk groups, click the
up trunk groups.To modify a port trunk group, click the hyperlinked group number corresponding to the entry you wish to alter.To delete a port trunk group,
click the corresponding
8 under the Delete heading in the Current Link Aggregation Group Entries table.
Add button to add a new trunk group and use the Link Aggregation Settings menu (see example below) to set
egation Group Configuration window – Add
Aggr
Link
e 6- 10.
Figur
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
35
Page 37

Figure 6- 11. Link Aggregation Group Configuration window – Modify
The user-changeable parameters are as follows:
Parameter Description
Group ID Select an ID number for the group,between 1 and 32.
State Trunk groups can be toggled between Enabled and Disabled.This is used to turn a port trunking group on or off.
This is useful f
backup aggregation group that is not under automatic control.
Master Port Choose the Master Port for the trunk group using the pull down menu.
Member Ports Choose the members of a trunked group. 2 to 8 ports can be assigned to an individual group.
Flooding Port A trunking group must designate one port to allow transmission of broadcasts and unknown unicasts.
Active Port Shows the port that is currently forwarding packets.
Type This pull-down menu allows you to select between Static and LACP (Link Aggregation Control Protocol). LACP
allows for the automatic detection of links in a Port Trunking Group.
or diagnostics, to quickly isolate a bandwidth intensive network device or to have an absolute
After setting the previous parameters,click
Link Aggregation Group Entries
Apply to allow your changes to be implemented.Successfully created trunk groups will be show in the Current
.
6-8 LACP Port Setting
The LACP Port Setting window is used in conjunction with the Link Aggregation window to create port trunking groups on the Switch.Using the
following window, the user may set which ports will be active and passive in processing and sending LACP control frames.
Figure 6- 12. LACP Port Setting and LACP Port Information window
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
36
Page 38

The user may set the following parameters:
Parameter Description
Unit
From/To A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
Mode Active – Active LACP ports are capable of processing and sending LACP control frames.This allows LACP
After setting the previous parameters,click
passive.
6-9 MA
MAC Notification is used to monitor MAC addresses learned and entered into the forwarding database.
MA
To globally set MAC notification on the Switch,open the following screen by opening the MAC Notification folder and clicking the MAC Notification
Global Settings
C Notification
C Notification Global Settings
link:
Choose the switch in the switch stack to be configured by using the pull-down menu.
compliant devices to negotiate the aggregated link so the group may be changed dynamically as needs require.
In order to utilize the ability to change an aggregated port group,that is, to add or subtract ports from the
group,at least one of the participating devices must designate LACP ports as active. Both devices must support
LACP.
Passive – LACP ports that are designated as passive cannot initially send LACP control frames. In order to allow
the linked port group to negotiate adjustments and make changes dynamically, one end of the connection must
have "active" LACP ports (see above).
Apply to allow your changes to be implemented.The LACP Port Table shows which ports are active and/or
Figure 6- 13. Current and New MAC Notification Global Settings window
wing parameters may be modified:
ollo
The f
Parameter Description
State Enable or disable MAC notification globally on the Switch.The default setting is Disabled.
Interval (sec) The user ma
History size The maximum number of entries listed in the history log used for notification. Up to 500 entries can be
C notification configurations can be vie
ent MA
r
Cur
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
setting is 1 second.
specified.The default setting is 1.
y set the time, between 1 and 2,147,483,647 seconds, between MAC notifications.The default
wed in the
Curr
ent MA
Notification Gl
C
obal Settings
windo
as seen abo
,
w
ve.
37
Page 39

MAC Notification Port Settings
To change MAC notification settings for a port or group of ports on the Switch,click Port Settings in the MAC Notification folder, which will display the
following screen:
Figure 6- 14. MAC Notification Port Settings and Port State Table
wing parameters ma
ollo
The f
Parameter Description
Unit Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
o
om…T
Fr
State Enable MAC Notification for the ports selected using the pull down menu.
Apply to implement changes made.
Click
y be set:
Select a por
t or gr
oup of por
ts to enable f
or MAC notification using the pull down menus.
6-10 IGMP
Computers and network devices that want to receive multicast transmissions need to inform nearby routers that they will become members of a multicast
The
.
Internet Gr
oup
gr
multicast group for members that are no longer active.
In the case where there is more than one multicast router on a subnetwork, one router is elected as the ‘querier’.This router then keeps track of the
membership of the m
ded to a giv
orwar
f
there are no members on a subnetwork,packets will not be forwarded to that subnetwork.
oup Ma
ulticast groups that have active members.The information received from IGMP is then used to determine if multicast packets should be
en subnetw
gement Protocol (IGMP)
na
ork or not.
The router can check, using IGMP, to see if there is at least one member of a multicast group on a given subnetwork. If
is used to comm
unicate this inf
ormation.
IGMP is also used to periodically check the
IGMP Versions 1 and 2
e at any time. IGMP provides the method for members and multicast routers to communicate when joining or
Multicast groups allow members to join or lea
leaving a multicast group.
IGMP version 1 is defined in RFC 1112. It has a fixed packet size and no optional data.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
v
38
Page 40

The format of an IGMP packet is shown below:
NonMember
Delaying
Member
Member
IGMP State
Tr a nsitions
Join Group
Start Timer
Leave Group
Stop Timer
Timer Expires
Send Response
Query Received
Start Timer
Another Host
Responds
Stop Timer
Count
Becomes
Zero
Leave
Group
Octets
IGMP Message Format
Group Address (all zeros if this is a query)
08 16
31
Ty p eResponse Time Checksum
Figure 6- 15. IGMP Message Format
The IGMP Type codes are shown below:
Type Meaning
0x11 Membership Query (if Group Address is 0.0.0.0)
0x11 Specific Group Membership Query (if Group Address is Present)
0x16 Membership Report (version 2)
0x17 Leave a Group (version 2)
0x12 Membership Report (version 1)
Table 6- 1. IGMP Type Codes
IGMP packets enable multicast routers to keep track of the membership of multicast groups, on their respective subnetworks.The following outlines what is
communicated between a multicast router and a multicast group member using IGMP.
A host sends an IGMP “report” to join a group.
A host will never send a report when it wants to leave a group (for version 1).
A host will send a “leave” report when it wants to leave a group (for version 2).
Multicast routers send IGMP queries (to the all-hosts group address: 224.0.0.1) periodically to see whether any group members exist on their subnetworks. If
there is no response from a particular group, the router assumes that there are no group members on the network.
The Time-to-Live (TTL) field of query messages is set to 1 so that the queries will not be forwarded to other subnetworks.
IGMP version 2 introduces some enhancements such as a method to elect a multicast querier for each LAN,an explicit leave message,and query messages that
are specific to a given group.
The states a computer will go through to join or to leave a multicast group are shown below:
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figur
IGMP State Transitions
e 6- 16.
39
Page 41

IGMP Snooping
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) snooping allows the Switch to recognize IGMP queries and reports sent between network stations or
devices and an IGMP host.When enabled for IGMP snooping, the Switch can open or close a port to a specific device based on IGMP messages passing through
the Switch.
In order to use IGMP Snooping it must first be enabled for the entire Switch (see
using the
group member based on IGMP messages sent from the device to the IGMP host or vice versa.The Switch monitors IGMP messages and discontinues forwarding
multicast packets when there are no longer hosts requesting that they continue. Use the
status.To modify settings, click the
Use the Current IGMP Snooping Group Entries window to view IGMP Snooping settings.To modify settings, click the Modify button for the VLAN
ID you want to change.
IGMP Snooping link in the Configuration folder. When enabled for IGMP snooping, the Switch can open or close a port to a specific Multicast
Modify button for the VLAN Name entry you want to change.
Figure 6- 17. Current IGMP Snooping Group Entries
Advanced Settings).You may then fine-tune the settings for each VLAN
IGMP Snooping Group Entry Table to view IGMP Snooping
Clicking the
Modify button will open the IGMP Snooping Settings menu,shown below:
Figure 6- 18. IGMP Snooping Settings window
ollowing parameters may be viewed or modified:
The f
Parameter Description
VLAN ID This is the VLAN ID that, along with the VLAN Name,identifies the VLAN the user wishes to modify the
VLAN Name This is the VLAN Name that, along with the VLAN ID, identifies the VLAN the user wishes to modify the
Query Interval The Query Interval field is used to set the time (in seconds) between transmitting IGMP queries. Entries
Max Response Time This determines the maximum amount of time in seconds allowed before sending an IGMP response report.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
IGMP Snooping Settings for.
IGMP Snooping Settings for.
een 1 and 65535 seconds ar
betw
The
Max R
esponse T
ime
field allo
e allo
Default = 125.
ed.
w
ws an entr
y between 1 and 25 (seconds). Default = 10.
40
Page 42

Robustness Value Adjust this variable according to expected packet loss.If packet loss on the VLAN is expected to be high, the
Last Member Query Interval This field specifies the maximum amount of time between group-specific query messages, including those sent
Host Timeout This is the maximum amount of time in seconds allowed for a host to continue membership in a multicast
Router Timeout This is the maximum amount of time in seconds a route is kept in the forwarding table without receiving a
Leave Timer This specifies the maximum amount of time in seconds between the Switch receiving a leave group message
Querier State Choose Enabled to enable transmitting IGMP Query packets or Disabled to disable.The default is Disabled.
Querier Router Behavior This read-only field describes the behavior of the router for sending query packets. Querier will denote that the
State Select Enabled to implement IGMP Snooping.This field is Disabled by default.
Click
Apply to implement the new settings. Click the Show All IGMP Group Entries link to return to the Current IGMP Snooping Group Entries
w.
windo
Robustness Variable should be increased to accommodate increased packet loss.This entry field allows an
entry of 1 to 255. Default = 2.
in response to leave group messages. Default = 1.
group without the Switch receiving a host membership report.Default = 260.
membership report. Default = 260.
from a host, and the Switch issuing a group membership query.If no response to the membership query is
received before the
router is sending out IGMP query packets.
query packets.This field will only read Querier when the Querier State and the State fields have been
Enabled.
Leave Timer expires,the (multicast) forwarding entry for that host is deleted.
Non-Querier will denote that the router is not sending out IGMP
Static Router Ports
A static router port is a port that has a multicast router attached to it. Generally,this router would have a connection to a WAN or to the Internet. Establishing a
outer port will allow multicast packets coming from the router to be propagated through the network, as well as allowing multicast messages (IGMP) coming
r
from the network to be propagated to the router.
A router port has the following behavior:
• All IGMP Report packets will be forwarded to the router port.
• IGMP queries (from the router port) will be flooded to all ports.
• All UDP multicast packets will be forwarded to the router port. Because routers do not send IGMP reports or implement IGMP snooping,a multicast
A router port will be dynamically configured when IGMP query packets,RIPv2 multicast, DVMRP multicast or PIM-DM multicast packets are detected flowing
into a port.
Open the
below.
router connected to the router port of a Layer 3 switch would not be able to receive UDP data streams unless the UDP multicast packets were all
forwarded to the router port.
older and the click on the
IGMP f
Static Router P
Figure 6- 19. Current Static Router Ports Entries window
orts Entry
link to open the Curr
ent Static Router Ports Entries
page
, as shown
The
Current Static Router Ports Entries page (shown above) displays all of the current entries to the Switch's static router port table.To modify an
y,click the
entr
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Modify button.
This will open the
Static Router P
orts Settings
, as shown below.
page
41
Page 43

The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Figure 6- 20. Static Router Ports Settings window
VID (VLAN ID) This is the VLAN ID that, along with the VLAN Name, identifies the VLAN where the multicast router is
VLAN Name This is the name of the VLAN where the multicast router is attached.
Unit Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
Member Ports These are the ports on the Switch that will have a multicast router attached to them.
Apply to implement the new settings, click the Show All Static Router Port Entries link to return to the Current Static Router Port Entries
Click
window.
attached.
6.11 Spanning Tree
This Switch supports three versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol; 802.1d STP, 802.1w Rapid STP and 802.1s MSTP. 802.1d STP will be familiar to most
networking professionals.However, since 802.1w RSTP and 802.1s MSTP has been recently introduced to Allied Telesyn managed Ethernet switches, a brief
introduction to the technology is provided below followed by a description of how to set up 802.1d STP, 802.1w RSTP and 802.1s MSTP.
802.1s MSTP
Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol, or MSTP, is a standard defined by the IEEE community that allows multiple VLANs to be mapped to a single spanning tree
which will pr
,
instance
disruptions when a single spanning tree instance fails.This will allow for faster convergences of new topologies for the failed instance. Frames designated for these
VLANs will be processed quickly and completely throughout interconnected bridges utilizing either of the three spanning tree protocols (STP, RSTP or MSTP).
This protocol will also tag BDPU packets so receiving devices can distinguish spanning tree instances, spanning tree regions and the VLANs associated with them.
These instances will be classified b
automaticall
frames assigned to different VLANs will follow different data routes within administratively established regions on the network,continuing to allow simple and full
processing of frames, regardless of administrative errors in defining VLANs and their respective spanning trees.
Each switch utilizing the MSTP on a network will have a single MSTP configuration that will have the following three attributes:
1. A configuration name defined by an alphanumeric string of up to 32 characters (defined in the
2. A configuration revision number (named here as a
3.
o utilize the MSTP function on the Switch,
T
1. The Switch must be set to the MSTP setting (found in the
2. The correct spanning tree priority for the MSTP instance must be entered (defined here as a
3. VLANs that will be shar
y determine each MSTP r
Configur
A 4096 element table (defined her
VLANs supported by the Switch for a given instance.
when configuring an
when configuring an MSTI ID settings).
ultiple pathways across the network.Therefore,these MSTP configurations will balance the traffic load, preventing wide scale
vide m
o
ation Na
y an MSTI ID.MSTP will connect multiple spanning trees with a Common and Internal Spanning Tree (CIST).The CIST will
me
MSTI ID settings).
its maxim
egion,
field).
thr
ust be added to the
ed m
um possible extent and will appear as one virtual bridge that runs a single spanning tree. Consequentially,
MST Configuration Table window in the
Revision Level and found in the MST Configuration Table window) and;
e as a
VID List in the MST Configur
ee steps need to be tak
MSTP Insta
en:
STP Bridge Global Settings window in the STP Version field).
nce ID
(defined her
ation T
able
e as a
w) which will associate each of the possible 4096
windo
Priority in the STP Instance Settings window
VID List in the MST Configur
ation T
ble
a
windo
w
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
42
Page 44

802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree
The Switch implements three versions of the Spanning Tree Protocol, the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) as defined by the IEEE 802.1s, the Rapid
Tree Protocol (RSTP) as defined by the IEEE 802.1w specification and a version compatible with the IEEE 802.1d STP. RSTP can operate with legacy
Spanning
equipment implementing IEEE 802.1d, however the advantages of using RSTP will be lost.
The IEEE 802.1w Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) evolved from the 802.1d STP standard. RSTP was developed in order to overcome some limitations of
STP that impede the function of some recent switching innovations,in particular,certain Layer 3 functions that are increasingly handled by Ethernet switches.The
basic function and much of the terminology is the same as STP. Most of the settings configured for STP are also used for RSTP. This section introduces some new
Spanning Tree concepts and illustrates the main differences between the two protocols.
Port Transition States
An essential difference between the three protocols is in the way ports transition to a forwarding state and in the way this transition relates to the role of the
port (forwarding or not forwarding) in the topology. MSTP and RSTP combine the transition states disabled,blocking and listening used in 802.1d and creates a
single state Discarding. In either case, ports do not forward packets.In the STP port transition states disabled, blocking or listening or in the RSTP/MSTP port
state discarding, there is no functional difference, the port is not active in the network topology.Table 6-1 below compares how the three protocols differ
regarding the port state transition.
All three protocols calculate a stable topology in the same way. Every segment will have a single path to the root bridge.All bridges listen for BPDU packets.
However, BPDU packets are sent more frequently – with every Hello packet.BPDU packets are sent even if a BPDU packet was not received.Therefore, each link
between bridges is sensitive to the status of the link.Ultimately this difference results in faster detection of failed links,and thus faster topology adjustment.A
draw-back of 802.1d is this absence of immediate feedback from adjacent bridges.
802.1d MSTP 802.1w RSTP 802.1d STP Forwarding Learning
Discarding Discarding Disabled No No
Discarding Discarding Blocking No No
Discarding Discarding Listening No No
Learning Learning Learning No Yes
Forwarding Forwarding Forwarding Yes Yes
Table 6- 2. Comparing Port States
RSTP is capable of a more rapid transition to a forwarding state – it no longer relies on timer configurations – RSTP compliant bridges are sensitive to feedback
from other RSTP compliant bridge links. Ports do not need to wait for the topology to stabilize before transitioning to a forwarding state. In order to allow this
rapid transition, the protocol introduces two new variables:the edge port and the point-to-point (P2P) port.
Edge Port
The edge port is a configurable designation used for a port that is directly connected to a segment where a loop cannot be created. An example would be a port
connected directly to a single workstation.Ports that are designated as edge ports transition to a forwarding state immediately without going through the
listening and learning states.
An edge por
t loses its status if it receives a BPDU packet,immediately becoming a normal spanning tree port.
P2P Port
A P2P por
considered to be P2P ports, unless manually overridden through configuration.
t is also ca
pable of ra
pid transition. P2P ports may be used to connect to other bridges. Under RSTP/MSTP, all ports operating in full-duplex mode are
802.1d / 802.1w / 802.1s Compatibility
MSTP or RSTP can interoperate with legacy equipment and is capable of automatically adjusting BPDU packets to 802.1d format when necessary. However,any
segment using 802.1d STP will not benefit fr
variable used for migration in the event that legacy equipment on a segment is updated to use RSTP or MSTP.
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) operates on two levels:
the settings ar
el,
v
witch le
1.
2.
On the s
On the por
t le
el,
v
the settings ar
om the ra
e implemented on a per user
pid transition and ra
y implemented.
e globall
pid topolog
-defined gr
y change detection of MSTP or RSTP
oup of ports basis.
otocol also provides for a
The pr
.
STP Bridge Global Settings
, open the
To open the following windo
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
w
Spa
nning T
ee
r
older in the
f
Configur
ation
u and click the
men
STP Br
idge Gl
obal Settings
link.
43
Page 45

Figure 6- 21. STP Bridge Global Settings – STP compatible
Figure 6- 22. STP Bridge Global Settings – RSTP (default)
Figure 6- 23. STP Bridge Global Settings
The following parameters can be set:
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
44
Page 46

Parameter Description
STP Status Use the pull-down menu to enable or disable STP globally on the Switch.The default is Disabled.
STP Version Use the pull-down menu to choose the desired version of STP to be implemented on the Switch.There are
Hello Time: (1-10 sec) The Hello Time can be set from 1 to 10 seconds.This is the interval between two transmissions of BPDU
Max Age: (6 - 40 sec) The Max Age may be set to ensure that old information does not endlessly circulate through redundant
Forward Delay: (4 – 30 sec) The Forward Delay can be from 4 to 30 seconds.Any port on the Switch spends this time in the listening
Max Hops (1-20) Used to set the number of hops between devices in a spanning tree region before the BPDU (bridge protocol
TX Hold Count (1-10) Used to set the maximum number of Hello packets transmitted per interval.The count can be specified from 1
Forwarding BPDU This field can be Enabled or Disabled.When Enabled, it allows the forwarding of STP BPDU packets from other
three choices:
STP – Select this parameter to set the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) globally on the switch.
RSTP – Select this parameter to set the Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol (RSTP) globally on the Switch.
MSTP – Select this parameter to set the Multiple Spanning Tree Protocol (MSTP) globally on the Switch.
packets sent by the Root Bridge to tell all other switches that it is indeed the Root Bridge.This field will only
appear here when STP or RSTP is selected for the STP Version.For MSTP, the Hello Time must be set on a port
per port basis. See the MST Port Settings section for further details.
paths in the network, preventing the effective propagation of the new information. Set by the Root Bridge,this
value will aid in determining that the Switch has spanning tree configuration values consistent with other
devices on the bridged LAN. If the value ages out and a BPDU has still not been received from the Root Bridge,
the Switch will start sending its own BPDU to all other switches for permission to become the Root Bridge. If
it turns out that your switch has the lowest Bridge Identifier, it will become the Root Bridge.The user may
choose a time between 6 and 40 seconds.The default value is 20.
state while moving from the blocking state to the forwarding state.
data unit) pack
by one until the value reaches zero.The Switch will then discard the BDPU packet and the information held for
the port will age out.The user may set a hop count from 1 to 20.The default is 20.
to 10.The default is 3.
network devices.The default is Enabled.
et sent by the Switch will be discarded. Each switch on the hop count will reduce the hop count
Click
Apply to implement changes made.
Note: The Hello Time cannot be longer than the Max.Age. Otherwise, a configuration error will occur. Observe the following formulas when
setting the above parameters:
Max.Age ≤ 2 x (Forward Delay - 1 second)
Max.Age ≤ 2 x (Hello Time + 1 second)
MST Configuration Table
The following screens in the MST Configuration Table window allow the user to configure a MSTI instance on the Switch.These settings will uniquely
identify a m
modify the parameters for but cannot change the MSTI ID for, and cannot be deleted.To view the
click
ultiple spanning tr
Configur
ation > Spa
ee instance set on the Switch.
ee > MST Configur
nning T
r
The Switch initiall
ation Table
y possesses one
:
ee of which the user ma
r
CIST or Common Internal Spanning
Current MST Configuration Identification window,
T
y
Figure 6- 24. Current MST Configuration Identification window
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
45
Page 47

The window above contains the following information:
Parameter Description
Configuration Name
Revision Level This value, along with the Configuration Name will identify the MSTP region configured on the Switch.
MSTI ID This field shows the MSTI IDs currently set on the Switch.This field will always have the CIST MSTI, which
VID List This field displays the VLAN IDs associated with the specific MSTI.
To delete a previously set MSTI Instance ID, click the corresponding
window.Clicking the Add button will reveal the following window to configure:
A previously configured name set on the Switch to uniquely identify the MSTI (Multiple Spanning Tree Instance).
If a configuration name is not set, this field will show the MAC address to the device running MSTP.
may be configured but not deleted.Clicking the hyperlinked name will open a new window for configuring
parameters associated with that particular MSTI.
8 under the Delete heading in the Current MST Configuration Identification
Figure 6- 25. Instance ID Settings window – Add
The user may configure the following parameters to create a MSTI in the Switch.
Parameter Description
MSTI ID
Type Create is selected to create a new MSTI.No other choices are available for this field when creating a new
VID List (1-4094) This field is used to specify the
Click
Apply to implement changes made.
To configure the settings for the CIST, click on its hyperlinked
reveal the following window to configure:
Enter a number between 1 and 15 to set a new MSTI on the Switch.
MSTI.
Switch range from ID number 1 to 4094.
VID range fr
MSTI ID number in the Current MST Configuration Identification window, which will
om configured VLANs set on the Switch. Supported VIDs on the
Figure 6- 26. Instance ID Settings window – CIST modify
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
46
Page 48

The user may configure the following parameters to configure the CIST on the Switch.
Parameter Description
MSTI ID
The MSTI ID of the CIST is 0 and cannot be altered.
Type The type of configuration about to be processed.This window is used to add or delete VIDs to the configured
MSTI or internal CIST. All other parameters are permanently set and therefore unchangeable.
VID List (1-4094) This field is used to specify the VID range from configured VLANs set on the Switch. Supported VIDs on the
Switch range from ID number 1 to 4094.
Click
Apply to implement changes made.
To configure the parameters for a previously set MSTI,click on its hyperlinked
MSTI ID number, which will reveal the following screen for configuration.
Figure 6- 27. Instance ID Settings window – modify
The user may configure the following parameters for a MSTI on the Switch.
meter
a
r
a
P
MSTI ID
Description
Displays the MSTI ID previously set by the user.
Type This field allows the user to choose a desired method for altering the MSTI settings.The user has 4 choices.
Add VID – Select this parameter to add VIDs to the MSTI ID, in conjunction with the VID List parameter.
Remo
parameter
VID List (1-4094) This field is used to specify the
– Select this parameter to r
ve VID
.
emove VIDs from the MSTI ID, in conjunction with the VID List
VID range from configured VLANs set on the Switch that the user wishes to add
to this MSTI ID.Supported VIDs on the Switch range from ID number 1 to 4094.This parameter can only be
utilized if the Type chosen is Add or Remove.
Click Apply to implement changes made.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
47
Page 49

MSTI Port Information
This window displays the current MSTI configuration settings and can be used to update the port configuration for an MSTI ID. If a loop occurs, the MSTP
function will use the por
first. In instances where the priority value is identical, the MSTP function will implement the lowest port number into the forwarding state and other interfaces
will be blocked. Remember that lower priority values mean higher priorities for forwarding packets.
To view the following window, click Configuration > Spanning Tree > MST Port Information:
To view the MSTI settings for a particular port, select the
corner of the screen and click
window.
t priority to select an interface to put into the forwarding state. Set a higher priority value for interfaces to be selected for forwarding
Figure 6- 28. MSTP Port Information window
Port number and the Unit ID number of the switch in the switch stack, located in the top left hand
Apply. To modify the settings for a particular MSTI Instance, click on its hyperlinked MSTI ID, which will reveal the following
Figure 6- 29. MSTI Settings window
Parameter Description
Instance ID Displays the MSTI ID of the instance being configured.An entry of 0 in this field denotes the CIST (default
Internal cost (0=Auto) This parameter is set to represent the relative cost of forwarding packets to specified ports when an interface
iority
Pr
Click
Apply to implement changes made.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
MSTI).
is selected within a STP instance.The default setting is 0 (auto).There are two options:
0 (auto) – Selecting this parameter for the internal Cost will set quickest route automatically and optimally for
an interface.The default value is derived from the media speed of the interface.
value 1-2000000 – Selecting this parameter with a value in the range of 1-2000000 will set the quickest route
when a loop occurs.
Enter a value betw
interface to forward packets first.A lower number denotes a higher priority.This entry must be divisible by 16.
The default priority setting is 128.
A lower Internal cost represents a quicker transmission.
een 0 and 240 to set the priority for the port interface. A higher priority will designate the
48
Page 50

STP Instance Settings
The following window displays MSTIs currently set on the Switch.To view the following table, click Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Instance
Settings
The following information is displayed:
:
Figure 6- 30. STP Instance Settings
Parameter Description
Instance Type Displays the instance type(s) currently configured on the Switch.Each instance type is classified by a MSTI ID.
CIST refers to the default MSTI configuration set on the Switch.
Instance Status Displays the current status of the corresponding MSTI ID.
Instance Priority Displays the priority of the corresponding MSTI ID.The lowest priority will be the root bridge.
Priority Click the Modify button to change the priority of the MSTI.This will open the Instance ID Settings window to
configure.The Type field in this window will be permanently set to Set Priority Only.Enter the new priority in
the Priority field and click Apply to implement the new priority setting.
Apply to implement changes made.
Click
Clicking the hyperlinked name will allow the user to view the current parameters set for the MSTI Instance.
Figure 6- 31. STP Instance Operational Status – CIST
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
49
Page 51

Figure 6- 32. STP Instance Operational Status – Previously Configured MSTI
The following parameters may be viewed in the
STP Instance Operational Status windows:
Parameter Description
Designated Root Bridge This field will show the priority and MAC address of the Root Bridge.
External Root Cost This defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding packets to the specified port list. Port cost
can be set automatically or as a metric value.The default value is 0 (auto).
0 (auto) – Setting 0 for the external cost will automatically set the speed for forwarding packets to the specified
port(s) in the list for optimal efficiency.Default port cost: 100Mbps port = 200000. Gigabit port = 20000.
value 1-200000000 – Define a value between 1 and 200000000 to determine the external cost.The lower the
number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen to forward packets.
Regional Root Bridge This field will show the priority and MAC address of the Regional (Internal) Root Bridge.This MAC address
should be the MAC address of the Switch.
Internal Root Cost This parameter is set to represent the relative cost of forwarding packets to specified ports when an interface
is selected within a STP instance.The default setting is 0 (auto).There are two options:
0 (auto) – Selecting this parameter for the internalCost will set quickest route automatically and optimally for an
.The default value is derived from the media speed of the interface.
interface
value 1-2000000 – Selecting this parameter with a value in the range of 1-2000000 will set the quickest route
when a loop occurs.A lower Internal cost represents a quicker transmission.
Designated Bridge This field will show the priority and MAC address of the Designated Bridge.The information shown in this table
comes from a BPDU packet originating from this bridge.
ort
Root P
This is the por
Max Age The Max Age ma
t on the Switch that is physically connected to the Root Bridge.
y be set to ensur
e that old inf
ormation does not endlessl
culate through redundant
y cir
paths in the network, preventing the effective propagation of the new information. Set by the Root Bridge,this
value will aid in determining that the Switch has spanning tr
ee configuration values consistent with other
devices on the bridged LAN. If the value ages out and a BPDU has still not been received from the Root Bridge,
the Switch will start sending its own BPDU to all other switches for permission to become the Root Bridge. If
it turns out that your switch has the lowest Bridge Identifier, it will become the Root Bridge.The user may
The default value is 20.
Any port on the Switch spends this time in the listening
ding state
orwar
.
F
orw
ard Delay
choose a time betw
ard Delay
orw
The F
state while mo
ving fr
een 6 and 40 seconds.
om 4 to 30 seconds.
can be fr
om the blocking state to the f
Last Topology Change This field shows the time, in seconds,since the last spanning tree topology change.
Topology Changes Count This field displays the number of times that the spanning tree topology has changed since the original initial
boot up of the Switch.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
50
Page 52

STP Port Settings
STP can be set up on a port per port basis.To view the following window click Configuration > Spanning Tree > STP Port Settings:
Figure 6- 33. STP Port Settings and MSTP Port Information Table
In addition to setting Spanning Tree parameters for use on the switch level, the Switch allows for the configuration of groups of ports, each port-group of which
will have its own spanning tree,and will require some of its own configuration settings. An STP Group will use the switch-level parameters entered above, with
the addition of
An STP Group spanning tree works in the same way as the switch-level spanning tree, but the root bridge concept is replaced with a root port concept. A root
port is a port of the group that is elected based on port priority and port cost, to be the connection to the network for the group. Redundant links will be
blocked, just as redundant links are blocked on the switch level.
The STP on the switch level blocks redundant links between switches (and similar network devices).The port level STP will block redundant links within an STP
Group.
It is advisable to define an STP Group to correspond to a VLAN group of ports.
The following fields can be set:
P
Unit
From/To A consecutive group of ports may be configured starting with the selected port.
External Cost This defines a metric that indicates the relative cost of forwarding packets to the specified port list.Port cost
Port Priority and Port Cost.
meter
a
r
a
Description
Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
can be set automaticall
y or as a metric value.The default value is 0 (auto).
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
51
Page 53

0 (auto) – Setting 0 for the external cost will automatically set the speed for forwarding packets to the specified
port(s) in the list for optimal efficiency.Default port cost: 100Mbps port = 200000. Gigabit port = 20000.
value 1-200000000 – Define a value between 1 and 200000000 to determine the external cost.The lower the
number, the greater the probability the port will be chosen to forward packets.
Hello Time The time interval between the transmission of configuration messages by the designated port,to other devices
Migration Setting this parameter as "yes" will set the ports to send out BDPU packets to other bridges,requesting
Edge Choosing the true parameter designates the port as an edge port. Edge ports cannot create loops,however an
P2P Choosing the T
State This dr
on the bridged LAN, thus stating that the Switch is still functioning.The user may choose a time between 1 and
10 seconds.The default is 2 seconds.This field is only operable when the Switch is enabled for MSTP.
information on their STP setting If the Switch is configured for RSTP, the port will be capable to migrate from
802.1d STP to 802.1w RSTP. If the Switch is configured for MSTP, the port is capable of migrating from 802.1d
STP to 802.1s MSTP. RSTP and MSTP can coexist with standard STP, however the benefits of RSTP and MSTP
are not realized on a port where an 802.1d network connects to an 802.1w or 802.1s enabled network.
Migration should be set as yes on ports connected to network stations or segments that are capable of being
upgraded to 802.1w RSTP or 802.1s MSTP on all or some por
edge port can lose edge port status if a topology change creates a potential for a loop. An edge port normally
should not receive BPDU packets.If a BPDU packet is received, it automatically loses edge port status.
Choosing the false parameter indicates that the port does not have edge port status.
rue
however they are restricted in that a P2P port must operate in full-duplex. Like edge ports, P2P ports transition
to a forwarding state rapidly thus benefiting from RSTP. A p2p value of
p2p status
true. If the port cannot maintain this status,(for example if the port is forced to half-duplex operation) the p2p
status changes to operate as if the p2p value were
op-down menu allows you to enable or disable STP for the selected group of ports.The default is
Enabled.
parameter indicates a point-to-point (P2P) shar
.Auto allows the port to have p2p status whenever possible and operate as if the p2p status were
False.The default setting for this parameter is True.
tion of the segment.
ed link. P2P ports are similar to edge ports,
false indicates that the port cannot have
Click
Apply to implement changes made.
6-13 Forwarding & Filtering
Unicast Forwarding
Open the Forwarding & Filtering folder in the Configuration menu and click on the Unicast Forwarding link.This will open the Setup Static
Unicast Forwarding Table
, as shown below:
Setup Static Unicast F
e 6- 34.
Figur
orwarding Table and Static Unicast Forwarding Table window
To add or edit an entry,define the following parameters and then click
P
a
rameter Description
VLAN ID (VID) The VLAN ID number of the VLAN on which the above Unicast MAC address resides.
MAC Address The MAC address to which packets will be statically forwarded.This must be a unicast MAC address.
Unit Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
Port Allows the selection of the port number on which the MAC address entered above resides.
Apply to implement the changes made.To delete an entry in the Static Unicast Forwarding Table, click the corresponding 8 under the Delete
Click
heading.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Add/Modify:
52
Page 54

Static Multicast Forwarding
The following figure and table describe how to set up Multicast Forwarding on the Switch. Open the Forwarding Filtering folder and click on the
Multicast Forwarding link to see the entry screen below:
Figure 6- 35. Static Multicast Forwarding Settings and Current Multicast Forwarding Entries
The Static Multicast F
to open the
The f
Setup Static Multicast Forwarding Table, as shown below:
wing parameters can be set:
ollo
orwarding Settings
page displa
ys all of the entries made into the Switch's static multicast forwarding table. Click the
Figure 6- 36. Setup Static Multicast Forwarding Table
Add button
Parameter Description
Unit Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
VID The VLAN ID of the VLAN the corresponding MAC address belongs to.
Multicast MAC Address The MAC address of the static source of multicast packets.This must be a multicast MAC address.
Port Allows the selection of ports that will be members of the static multicast group.The options are:
None – No restrictions on the port dynamically joining the multicast group.When None is chosen, the port will
not be a member of the Static Multicast Gr
ess– The port is a static member of the multicast group.
Egr
Click
Apply to implement the changes made.To delete an entry in the Static Multicast Forwarding Table, click the corresponding 8 under the Delete
heading. Click the Show All Multicast Forwarding Entries link to return to the Static Multicast Forwarding Settings window.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
oup.
53
Page 55

6-14 VLANs
Under
Priority tagging is a function defined by the IEEE 802.1p standard designed to provide a means of managing traffic on a network where many different types of
data may be transmitted simultaneously. It is intended to alleviate problems associated with the delivery of time critical data over congested networks.The quality
of applications that are dependent on such time critical data, such as video conferencing, can be severely and adversely affected by even very small delays in
transmission.
Network devices that are in compliance with the IEEE 802.1p standard have the ability to recognize the priority level of data packets.These devices can also
assign a priority label or tag to packets. Compliant devices can also strip priority tags from packets.This priority tag determines the packet's degree of
expeditiousness and determines the queue to which it will be assigned.
Priority tags are given values from 0 to 7 with 0 being assigned to the lowest priority data and 7 assigned to the highest.The highest priority tag 7 is generally
only used for data associated with video or audio applications,which are sensitive to even slight delays, or for data from specified end users whose data
transmissions warrant special consideration.
The Switch allows you to further tailor how priority tagged data packets are handled on your network. Using queues to manage priority tagged data allows you
to specify its relative priority to suit the needs of your network.There may be circumstances where it would be advantageous to group two or more differently
tagged packets into the same queue.
Generally, however,it is recommended that the highest priority queue, Queue 1, be reserved for data packets with a priority value of 7. Packets that have not
been given any priority value are placed in Queue 0 and thus given the lowest priority for delivery.
A weighted round robin system is employed on the Switch to determine the rate at which the queues are emptied of packets.The ratio used for clearing the
queues is 4:1.This means that the highest priority queue, Queue 1, will clear 4 packets for every 1 packet cleared from Queue 0.
Remember, the priority queue settings on the Switch are for all ports,and all devices connected to the Switch will be affected.This priority queuing system will
be especially beneficial if your network employs switches with the capability of assigning priority tags.
standing IEEE 802.1p Priority
VLAN Description
A Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) is a network topology configured according to a logical scheme rather than the physical layout.VLANs can be used to
combine any collection of LAN segments into an autonomous user group that appears as a single LAN.VLANs also logically segment the network into different
broadcast domains so that packets are forwarded only between ports within the VLAN. Typically, a VLAN corresponds to a particular subnet, although not
necessarily.
VLANs can enhance performance by conserving bandwidth, and improve security by limiting traffic to specific domains.
A VLAN is a collection of end nodes grouped by logic instead of physical location.End nodes that frequently communicate with each other are assigned to the
same VLAN, regardless of where they are physically on the network. Logically, a VLAN can be equated to a broadcast domain, because broadcast packets are
forwarded to only members of the VLAN on which the broadcast was initiated.
Notes About VLANs on the AT-9724TS
No matter what basis is used to uniquely identify end nodes and assign these nodes VLAN membership,packets cannot cross VLANs without a network device
performing a routing function between the VLANs.
The AT-9724TS supports IEEE 802.1Q VLANs and Port-Based VLANs. The port untagging function can be used to remove the 802.1Q tag from packet headers to
maintain compatibility with de
The "default" VLAN has a VID = 1.
The member ports of Port-based VLANs may overlap, if desired.
vices that ar
e tag-unaware.The Switch's default is to assign all ports to a single 802.1Q VLAN named "default."
IEEE 802.1Q VLANs
Some relevant terms:
Tagging – The act of putting 802.1Q VLAN information into the header of a packet.
Untagging – The act of stripping 802.1Q VLAN information out of the packet header.
Ing
ress port– A port on a switch where packets are flowing into the Switch and VLAN decisions must be made.
r
Eg
made.
IEEE 802.1Q (tagged) VLANs are implemented on the Switch. 802.1Q VLANs require tagging, which enables them to span the entire network (assuming all
switches on the network are IEEE 802.1Q-compliant).
VLANs allow a network to be segmented in order to reduce the size of broadcast domains. All packets entering a VLAN will only be forwarded to the stations
er IEEE 802.1Q enabled s
v
(o
VLANs can also provide a level of security to your network. IEEE 802.1Q VLANs will only deliver packets between stations that are members of the VLAN.
Any port can be configured as either tagging or untagging.The untagging feature of IEEE 802.1Q VLANs allows VLANs to work with legacy switches that don't
recognize VLAN tags in pack
allows Spanning Tree to be enabled on all ports and work normally.
The IEEE 802.1Q standard restricts the forwarding of untagged packets to the VLAN the receiving port is a member of.
A por
–
t
ess por
witch where packets are flowing out of the Switch,either to another switch or to an end station,and tagging decisions must be
t on a s
witches) that ar
et headers.
e members of that VLAN, and this includes broadcast, multicast and unicast packets from unknown sources.
The tagging f
eature allows VLANs to span multiple 802.1Q-compliant switches through a single physical connection and
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
54
Page 56

The main characteristics of IEEE 802.1Q are as follows:
Packet
Receive
Ingress
Rules
Ingress
Filtering
Packet
Tr a nsmit
Egress
Rules
Forwarding
Process
Filtering
Database
Port
State
Ta g ged or Untagged
PVID to VID
VLAN Table
• Assigns packets to VLANs by filtering.
• Assumes the presence of a single global spanning tree.
• Uses an explicit tagging scheme with one-level tagging.
• 802.1Q VLAN Packet Forwarding
•
Packet forwarding decisions are made based upon the following three types of rules:
• Ingress rules – rules relevant to the classification of received frames belonging to a VLAN.
• Forwarding rules between ports – decides whether to filter or forward the packet.
• Egress rules – determines if the packet must be sent tagged or untagged.
Figure 6- 37. IEEE 802.1Q Packet Forwarding
802.1Q VLAN Tags
The figure below shows the 802.1Q VLAN tag.There are four additional octets inserted after the source MAC address.Their presence is indicated by a value of
0x8100 in the EtherType field.When a packet's EtherType field is equal to 0x8100,the packet carries the IEEE 802.1Q/802.1p tag.The tag is contained in the
ollo
f
carried across Ethernet backbones),and 12 bits of VLAN ID (VID).The 3 bits of user priority are used by 802.1p.The VID is the VLAN identifier and is used by
the 802.1Q standard. Because the VID is 12 bits long, 4094 unique VLANs can be identified.
The tag is inserted into the packet header making the entire packet longer by 4 octets.All of the information originally contained in the packet is retained.
o octets and consists of 3 bits of user priority, 1 bit of Canonical Format Identifier (CFI - used for encapsulating Token Ring packets so they can be
wing tw
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
55
Page 57

Figure 6- 38. IEEE 802.1Q Tag
Octets
0 123
IEEE 802.1Q Tag
Destination Address (6 Octets)
Cyclic Redundancy Check (4 Octets)
VLAN ID (VID)
Source Address (6 Octets)
Ether Type = 0x8100 Tag Control Information
MAC Length/Type Beginning of Data
CFIUser Priority
3 bits 1 bit 12 bits
4
Adding an IEEE 802.1 Tag
Length/EType
Dest. Src. Data Old CRC
ETypeDest. Src. Data New CRCTa g
Priority VLAN ID
Original Ethernet Packet
New Tagged Packet
The EtherType and VLAN ID are inserted after the MAC source address,but before the original EtherType/Length or Logical Link Control.Because the packet is
now a bit longer than it was originally, the Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) must be recalculated.
Figure 6- 39.Adding an IEEE 802.1Q Tag
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
56
Page 58

Port VLAN ID
Packets that are tagged (are carrying the 802.1Q VID information) can be transmitted from one 802.1Q compliant network device to another with the VLAN
ormation intact.This allows 802.1Q VLANs to span network devices (and indeed, the entire network, if all network devices are 802.1Q compliant).
inf
Unfortunately,not all network devices are 802.1Q compliant.These devices are referred to as tag-unaware. 802.1Q devices are referred to as tag-aware.
Prior to the adoption of 802.1Q VLANs, port-based and MAC-based VLANs were in common use.These VLANs relied upon a Port VLAN ID (PVID) to forward
packets.A packet received on a given port would be assigned that port's PVID and then be forwarded to the port that corresponded to the packet's destination
address (found in the Switch's forwarding table).If the PVID of the port that received the packet is different from the PVID of the port that is to transmit the
packet, the Switch will drop the packet.
Within the Switch, different PVIDs mean different VLANs (remember that two VLANs cannot communicate without an external router). So,VLAN identification
based upon the PVIDs cannot create VLANs that extend outside a given switch (or switch stack).
Every physical port on a switch has a PVID. 802.1Q ports are also assigned a PVID, for use within the Switch.If no VLANs are defined on the Switch,all ports are
then assigned to a default VLAN with a PVID equal to 1. Untagged packets are assigned the PVID of the port on which they were received.Forwarding decisions
are based upon this PVID, in so far as VLANs are concerned.Tagged packets are forwarded according to the VID contained within the tag.Tagged packets are also
assigned a PVID,but the PVID is not used to make packet forwarding decisions, the VID is.
Tag-aware switches must keep a table to relate PVIDs within the Switch to VIDs on the network.The Switch will compare the VID of a packet to be transmitted
to the VID of the port that is to transmit the packet. If the two VIDs are different, the Switch will drop the packet. Because of the existence of the PVID for
untagged packets and the VID for tagged packets, tag-aware and tag-unaware network devices can coexist on the same network.
A switch port can have only one PVID, but can have as many VIDs as the Switch has memory in its VLAN table to store them.
Because some devices on a network may be tag-unaware, a decision must be made at each port on a tag-aware device before packets are transmitted – should
et to be transmitted have a tag or not? If the transmitting port is connected to a tag-unaware device, the packet should be untagged.If the transmitting
the pack
port is connected to a tag-aware device, the packet should be tagged.
Tagging and Untagging
Every port on an 802.1Q compliant switch can be configured as tagging or untagging.
ts with tagging enabled will put the VID number, priority and other VLAN information into the header of all packets that flow into and out of it. If a packet has
Por
previously been tagged,the port will not alter the packet, thus keeping the VLAN information intact.The VLAN information in the tag can then be used by other
802.1Q compliant devices on the network to make packet-forwarding decisions.
Ports with untagging enabled will strip the 802.1Q tag from all packets that flow into and out of those ports.If the packet doesn't have an 802.1Q VLAN tag, the
port will not alter the packet.Thus, all packets received by and forwarded by an untagging port will have no 802.1Q VLAN information. (Remember that the PVID
is only used internally within the Switch). Untagging is used to send packets from an 802.1Q-compliant network device to a non-compliant network device.
Ingress Filtering
A port on a switch where packets are flowing into the Switch and VLAN decisions must be made is referred to as an ingress port.If ingress filtering is enabled for
a port, the Switch will examine the VLAN information in the packet header (if present) and decide whether or not to forward the packet.
If the packet is tagged with VLAN information, the ingress port will first determine if the ingress port itself is a member of the tagged VLAN. If it is not, the packet
will be dropped. If the ingress port is a member of the 802.1Q VLAN, the Switch then determines if the destination port is a member of the 802.1Q VLAN. If it is
not, the packet is dropped. If the destination port is a member of the 802.1Q VLAN,the packet is forwarded and the destination port transmits it to its attached
network segment.
If the packet is not tagged with VLAN information, the ingress port will tag the packet with its own PVID as a VID (if the port is a tagging port).The switch then
determines if the destination port is a member of the same VLAN (has the same VID) as the ingress port. If it does not,the packet is dropped. If it has the same
,
VID
This pr
ingress port at the point of reception.This eliminates the subsequent processing of packets that will just be dropped by the destination port.
Def
The Switch initiall
configured in Port-based mode, their respective member ports are removed from the "default."
Packets cannot cross VLANs. If a member of one VLAN wants to connect to another VLAN, the link must be through an external router.
et is forwarded and the destination port transmits it on its attached network segment.
the pack
erred to as ingress filtering and is used to conserve bandwidth within the Switch by dropping packets that are not on the same VLAN as the
ult VL
ef
ANs
y configur
VLAN,VID = 1, called "default." The factory default setting assigns all ports on the Switch to the "default." As new VLANs are
es one
ocess is r
a
Note: If no VLANs are configured on the Switch,then all packets will be forwarded to any destination port.Packets with unknown source
esses will be flooded to all por
dr
ad
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
oadcast and m
Br
ts.
ulticast packets will also be flooded to all ports.
57
Page 59

An example is presented below:
VLAN Name VID Switch Ports
System (default) 1 5, 6, 7, 8,21, 22, 23,24
Engineering 2 9, 10, 11,12
Marketing 3 13, 14,15, 16
Finance 4 17,18, 19, 20
Sales 5 1,2, 3, 4
Table 6- 3.VLAN Example – Assigned Ports
Port-based VLANs
Port-based VLANs limit traffic that flows into and out of switch ports.Thus, all devices connected to a port are members of the VLAN(s) the port belongs to,
whether ther
On port-based VLANs, NICs do not need to be able to identify 802.1Q tags in packet headers. NICs send and receive normal Ethernet packets. If the packet's
destination lies on the same segment, communications take place using normal Ethernet protocols. Even though this is always the case, when the destination for a
packet lies on another switch port,VLAN considerations come into play to decide if the packet gets dropped by the Switch or delivered.
e is a single computer directly connected to a switch,or an entire department.
VLAN Segmentation
Take for example a packet that is transmitted by a machine on Port 1 that is a member of VLAN 2. If the destination lies on another port (found through a
orwarding table lookup), the Switch then looks to see if the other port (Port 10) is a member of VLAN 2 (and can therefore receive VLAN 2 packets). If
normal f
Port 10 is not a member of VLAN 2, then the packet will be dropped by the Switch and will not reach its destination.If Port 10 is a member of VLAN 2, the
packet will go through.This selective forwarding feature based on VLAN criteria is how VLANs segment networks.The key point being that Port 1 will only
transmit on VLAN 2.
Network resources such as printers and servers however,can be shared across VLANs.This is achieved by setting up overlapping VLANs.That is ports can belong
to more than one VLAN group.For example, setting VLAN 1 members to ports 1, 2,3, and 4 and VLAN 2 members to ports 1,5, 6, and 7. Port 1 belongs to two
VLAN groups. Ports 8, 9,and 10 are not configured to any VLAN group.This means ports 8,9, and 10 are in the same VLAN group.
VLAN and Trunk Groups
The members of a trunk group have the same VLAN setting.Any VLAN setting on the members of a trunk group will apply to the other member ports.
Note: In or
configure VLAN settings. If you wish to change the port trunk grouping with VLANs already in place, you will not need to reconfigure the VLAN
settings after changing the por
settings.
der to use
VLAN segmentation in conjunction with por
t trunk group settings.VLAN settings will automatically change in conjunction with the change of the port trunk group
t trunk gr
oups, you can first set the port trunk group(s), and then you may
Protocol VLANs
The AT-9724TS incorporates the idea of protocol-based VLANs.This standard, defined by the IEEE 802.1v standard maps packets to protocol-defined VLANs by
examining the type octet within the packet header to discover the type of protocol associated with it.After assessing the protocol, the Switch will forward the
ets to all ports within the protocol-assigned VLAN.This feature will benefit the administrator by better balancing load sharing and enhancing traffic
pack
classification.The Switch supports fifteen (15) pre-defined protocols for configuration.The user may also choose a protocol that is not one of the fifteen defined
protocols by properly configuring the userDefined protocol VLAN.The supported protocols for the protocol VLAN function on this switch include IP, IPX,DEC,
DEC LAT,SNAP, NetBIOS,AppleTalk, XNS,SNA, IPv6, RARP and VINES.
The following is a list of type headers for each protocol listed for VLAN configuration.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
58
Page 60

Protocol Type Header in Hexadecimal Form
IP over Ethernet 0x0800
IPX 802.3 0xFFFF
IPX 802.2 0xE0E0
IPX SNAP 0x8137
IPX over Ethernet2 0x8137
DecLAT 0x6000
DecOther 0x6009
SNA 802.2 0x0404
NetBios 0xF0F0
XNS 0x0600
VINES 0x0BAD
IPv6 0x86DD
AppleTalk 0x809B
RARP 0x8035
Table 6- 4. Protocol VLAN and the corresponding type header
In configuring the user-defined protocol, the administrator must make sure that the pre-defined user type header does not match any other type header.A match
may cause discrepancies within the local network and failure to define the VLAN to forward packets to.
Static VLAN Entry
In the Configuration folder, open the VLAN folder and click the Static VLAN Entry link to open the following window:
Figure 6- 40. Current 802.1Q Static VLANs Entries window
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
59
Page 61

The 802.1Q Static VLANs menu lists all previously configured VLANs by VLAN ID and VLAN Name.To delete an existing 802.1Q VLAN, click the
corresponding button under the
To create a new 802.1Q VLAN, click the Add button in the
Delete heading.
802.1Q Static VLANs menu. A new menu will appear,as shown below, to configure the port
settings and to assign a unique name and number to the new VLAN. See the table below for a description of the parameters in the new menu.
Figure 6- 41. 802.1Q Static VLANs – Add
To return to the
click the
Current 802.1Q Static VLANs Entries window,click the Show All Static VLAN Entries link.To change an existing 802.1Q VLAN entry,
Modify button of the corresponding entry you wish to modify.A new menu will appear to configure the port settings and to assign a unique name and
number to the new VLAN. See the table below for a description of the parameters in the new menu.
Figure 6- 42. 802.1Q Static VLANs – Modify
The following fields can then be set in either the Add or Modify 802.1Q Static VLANs menus:
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
60
Page 62

Parameter Description
Unit Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
VID (VLAN ID) Allows the entry of a VLAN ID in the Add dialog box, or displays the VLAN ID of an existing VLAN in the
Modify dialog box.VLANs can be identified by either the VID or the VLAN name.
VLAN Name Allows the entry of a name for the new VLAN in the Add dialog box, or for editing the VLAN name in the
Modify dialog box.
Advertisement Enabling this function will allow the Switch to send out GVRP packets to outside sources, notifying that they
may join the existing VLAN.
Type Displays the type of protocol associated with this VLAN.
Protocol ID The following parameters allow for the creation of protocol-based VLANs.The Switch supports 15 pre-
configured protocol-based VLANs plus one user-defined protocol based VLAN where the administrator may
configure the settings for the appropriate protocol and forwarding of packets (16 total). Selecting a specific
protocol will indicate which protocol will be utilized in determining the VLAN ownership of a tagged packet.
Pre-set protocol-based VLANs on the switch include:
port – Using this parameter will allow the creation of a normal 802.1Q VLAN on the Switch.
ip – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the packet
header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is based on the Ethernet protocol.
rarp – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the packet
header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the Reverse Address
Resolution (RARP) Pr
otocol.
ipx802dot3 – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the
packet header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by Novell NetWare
802.3 (IPX - Internet Packet Exchange).
ipx802dot2 – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the
packet header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by Novell NetWare
802.2 (IPX - Internet Packet Exchange).
ipxSnap – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the packet
header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by Novell and the Sub
Network Access Protocol (SNAP).
ipxEthernet2 – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the
packet header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the Ethernet
Protocol.
AppleTalk – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the
packet header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the AppleTalk
protocol.
decLAT – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the packet
header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the Digital Equipment
Corporation (DEC) Local Area Transport (LAT) protocol.
decOther – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to f
orward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the
packet header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the Digital
Equipment Corporation (DEC) Protocol.
sna802dot2 – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the
packet header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the Systems
chitecture(SNA) 802.2 Protocol.
Ar
ork
Netw
netBios – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to f
orward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the packet
header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the NetBIOS Protocol.
xns – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the packet
header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the Xerox Network
Systems (XNS) Protocol.
vines – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the packet
header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the Banyan Virtual
Integrated Network Service (VINES) Protocol.
d packets to this VLAN if the tag in the packet
ipV6 – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to f
orwar
header is concurrent with this protocol.This packet header information is defined by the Internet Protocol
Version 6 (IPv6) Protocol.
userDefined – Using this parameter will instruct the Switch to forward packets to this VLAN if the tag in the
packet header is concurrent with this protocol defined by the user.This packet header information is defined by
ormation:
wing inf
entering the f
ollo
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
61
Page 63

User Defined Pid – Specifies that the VLAN will only accept packets with this hexadecimal 802.1Q Ethernet type
value in the packet header.The user may define an entry, in the hexadecimal form (ffff) to define the packet
identification. (
0x0 0xffff}
encap [ethernet | llc | snap | all] – Specifies that the Switch will examine the octet of the packet header referring
to one of the protocols listed (Ethernet, LLC or SNAP), looking for a match of the hexadecimal value
previously entered . all will instruct the Switch to examine the total packet header.After a match is found, the
Switch will forward the packet to this VLAN.This field is only operable if userDefined is selected in the Protocol
ID field.
Port Settings Allows an individual port to be specified as member of a VLAN.
Tag Specifies the port as either 802.1Q tagging or 802.1Q untagged. Checking the box will designate the port as
None Allows an individual port to be specified as a non-VLAN member.
Egress Select this to specify the port as a static member of the VLAN. Egress member ports are ports that will be
Forbidden Select this to specify the port as not being a member of the VLAN and that the port is forbidden from
Click
Apply to implement changes made. Click the Show All Static VLAN Entries link to return to the Current 802.1Q Static VLAN Entries window.
Tagged.
transmitting traffic for the VLAN.These ports can be either tagged or untagged.
becoming a member of the VLAN dynamically.
The user only need enter the final four integers of the hexadecimal format to define the packet ID –{hex
) This field is only operable if userDefined is selected in the Protocol ID field.
GVRP Setting
In the Configuration menu,open the VLANs folder and click GVRP Setting.
802.1Q Port Settings dialog box,shown below, allows you to determine whether the Switch will share its VLAN configuration information with other
The
GARP VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) enabled switches. In addition,
PVID does not match the PVID of the port. Results can be seen in the table under the configuration settings,as seen below.
Ingress Checking can be used to limit traffic by filtering incoming packets whose
Figure 6- 43. GVRP Settings and Table window
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
62
Page 64

The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Unit
From/To These two fields allow you to specify the range of ports that will be included in the Port-based VLAN that you
GVRP The Group VLAN Registration Protocol (GVRP) enables the port to dynamically become a member of a VLAN.
Ingress Check This field can be toggled using the space bar between Enabled and Disabled. Enabled enables the port to
Acceptable Frame Type This field denotes the type of frame that will be accepted by the port.The user may choose between Tagged
PVID The read only field in the GVRP Table shows the current PVID assignment for each port, which may be
Click
Apply to implement changes made.
Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
are creating using the
Disabled by default.
GVRP is
compare the VID tag of an incoming packet with the PVID number assigned to the port.If the two are different,
the port filters (drops) the packet.
Only
, which means only VLAN tagged frames will be accepted, and Admit_All,which means both tagged and
untagged frames will be accepted. Admit_All is enabled by default.
manually assigned to a VLAN when created in the 802.1Q Static VLANs table.The Switch's default is to assign
all ports to the default VLAN with a VID of 1.The PVID is used by the port to tag outgoing, untagged packets,
and to make filtering decisions about incoming packets.If the port is specified to accept only tagged frames – as
tagging, and an untagged packet is forwarded to the port for transmission, the port will add an 802.1Q tag using
the PVID to write the VID in the tag.When the packet arrives at its destination, the receiving device will use the
PVID to make VLAN forwarding decisions. If a packet is received by the port, and Ingress filtering is enabled,the
port will compare the VID of the incoming packet to its PVID. If the two are unequal, the port will drop the
packet. If the two are equal, the port will receive the packet.
802.1Q Static VLANs page.
Disabled disables ingress filtering. Ingress Checking is Disabled by default.
6-15 Traffic Control
Use the Traffic Control menu to enable or disable storm control and adjust the threshold for multicast and broadcast storms, as well as DLF (Destination
Look Up Failure).Traffic control settings are applied to individual Switch modules.
To view the following window, click
Configuration > Traffic Control:
Figure 6- 44.Traffic Control Settings and Traffic Control Table window
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
63
Page 65

To configure Traffic Control,first select the Switch’s Unit ID number from the pull down menu and then a group of ports by using the Group pull down
menu. Finally,enable or disable the
The purpose of this window is to limit too many broadcast,multicast or unknown unicast packets folding the network. Each port has a counter that tracks the
number of broadcast packets received per second, and this counter is cleared once every second. If the broadcast,multicast or unknown unicast storm control is
enabled, the port will discard all broadcast, multicast or unknown unicast packets received when the counter exceeds or equals the Threshold specified.
Threshold value is the upper threshold at which the specified traffic control is switched on.This is the number of Broadcast,Multicast or DLF packets,in
The
Kpps (kilopackets per second), received by the Switch that will trigger the storm traffic control measures.The
kilopackets per second.The default setting is 128.The settings of each port may be viewed in the
implement changes made.
Broadcast Storm,Multicast Storm and Destination Unknown using their corresponding pull-down menus.
Threshold value can be set from 0 to 255
Traffic Control Table in the same window.Click Apply to
6-16 Port Security
A given port's (or a range of ports') dynamic MAC address learning can be locked such that the current source MAC addresses entered into the MAC address
forwarding table can not be changed once the port lock is enabled.The port can be locked by using the Admin State pull-down menu to Enabled, and clicking
Apply.
Port Security is a security feature that prevents unauthorized computers (with source MAC addresses) unknown to the Switch prior to locking the port (or
ports) from connecting to the Switch's locked ports and gaining access to the network.
Figure 6- 45. Port Security Settings and Port Security Table window
wing parameters can be set:
ollo
The f
Parameter Description
Unit Choose the Switch ID n
o
om/T
Fr
Admin State This pull-down menu allows you to enable or disable Port Security (locked MAC address table for the selected
Max. Learning Addr. (0-64) The number of MAC addresses that will be in the MAC address forwarding table for the selected switch and
Mode This pull-do
Click
Apply to implement changes made.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
A consecutiv
ports).
oup of por
gr
Switch, for the selected group of ports.The options are:
Permanent – The locked addresses will not age out after the aging timer expires.
DeleteOnTimeout – The locked addresses will age out after the aging timer expires.
DeleteOnReset – The locked addresses will not age out until the Switch has been reset.
e gr
ts.
wn menu allows you to select how the MAC address table locking will be implemented on the
umber of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
ting with the selected port.
oup of por
ts ma
y be configur
ed star
64
Page 66

6-17 Port Lock Entries
The Port Lock Entry Delete window is used to remove an entry from the port security entries learned by the Switch and entered into the forwarding
database.To view the following window, click
Configuration > Port Lock Entries:
Figure 6- 46. Port Lock Entries Table
This function is only operable if the
that are permanently learned by the Switch can be deleted.Once the entry has been defined by entering the correct information into the window above, click
8 under the Delete heading of the corresponding MAC address to be deleted. Click the Next button to view the next page of entries listed in this table.
the
This window displays the following information:
ameter Description
r
a
P
VID
VLAN NAME The VLAN Name of the entry in the forwarding database table that has been permanently learned by the
ess
C Addr
MA
Unit The ID n
Port The ID number of the port that has permanently learned the MAC address.
Type The type of MAC address in the forwarding database table. Only entries marked Secured_Permanent can
Delete Click the 8 in this field to delete the corresponding MAC address that was permanently learned by the
Mode in the Port Security window is selected as Permanent or DeleteOnReset, or in other words, only addresses
The VLAN ID of the entry in the forwarding database table that has been permanently learned by the Switch.
Switch.
ess of the entr
dr
C ad
The MA
Switch.
umber of the Switch in the switch stack that has permanently learned the MAC address.
be deleted.
Switch.
y in the forwarding database table that has been permanently learned by the
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
65
Page 67

6-18 QoS
7 priority queues
How 802.1p works (Switch default settings)
Class 0 Class 1
Class 2 Class 3
Class 4
Class 5 Class 6
Queues
0 1
2 3
4
5 6 7
Priority
Por
t
1 2 3
Port default
priority
0 0 0 1 4 2 6 .........................................
4 5 6 7 ............................
The AT-9724TS supports 802.1p priority queuing Quality of Service.The following section discusses the implementation of QoS (Quality of Service) and benefits
of using 802.1p priority queuing.
The Advantages of QoS
QoS is an implementation of the IEEE 802.1p standard that allows network administrators a method of reserving bandwidth for important functions that require
a large bandwidth or have a high priority, such as VoIP (voice-over Internet Protocol), web browsing applications, file server applications or video conferencing.
Not only can a larger bandwidth be created, but other less critical traffic can be limited, so excessive bandwidth can be saved.The Switch has separate hardware
queues on every physical port to which packets from various applications can be mapped to, and,in turn prioritized.View the following map to see how the AT9724TS implements 802.1P priority queuing.
The picture above shows the default priority setting for the Switch.Class-6 has the highest priority of the seven priority classes of service on the Switch. In order
to implement QoS, the user is required to instruct the Switch to examine the header of a packet to see if it has the proper identifying tag tagged.Then the user
d these tagged pack
orwar
y f
ma
For example, lets say a user wishes to have a video conference between two remotely set computers.The administrator can add priority tags to the video
ets being sent out,
pack
utilizing the
acquires the tagged packets and maps them to a class queue on the Switch.Then in turn, the administrator will set a priority for this queue so that will be
emptied before any other packet is forwarded.This results in the end user receiving all packets sent as quickly as possible, thus prioritizing the queue and allowing
for an uninterrupted stream of packets,which optimizes the use of bandwidth available for the video conference.
Understanding QoS
The Switch has eight priority classes of service, one of which is internal and unconfigurable.These priority classes of service are labelled as 6, the high class to 0,
the lo
west class.The eight priority tags, specified in IEEE 802.1p are mapped to the Switch's priority classes of service as follows:
Priority 0 is assigned to the Switch's Q2 class.
Priority 1 is assigned to the Switch's Q0 class.
Priority 2 is assigned to the Switch's Q1 class.
Priority 3 is assigned to the Switch's Q3 class.
Priority 4 is assigned to the Switch's Q4 class.
Priority 5 is assigned to the Switch's Q5 class.
Priority 6 is assigned to the Switch's Q6 class.
Priority 7 is assigned to the Switch's Q6 class.
For strict priority-based scheduling, any packets residing in the higher priority classes of service are transmitted first. Multiple strict priority classes of service are
emptied based on their priority tags. Only when these classes are empty,are packets of lower priority transmitted.
For weighted round-robin queuing, the number of packets sent from each priority queue depends upon the assigned weight. For a configuration of 8 CoS queues,
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 6- 47. Mapping QoS on the Switch
ets to designated classes of service on the Switch where they will be emptied, based on priority.
Access Pr
ofile commands.Then, on the receiving end,the administrator instructs the Switch to examine packets for this tag,
66
Page 68

A~H with their respective weight value:8~1, the packets are sent in the following sequence:A1, B1,C1, D1, E1,F1, G1, H1,A2, B2,C2, D2, E2,F2, G2,A3, B3, C3,
D3, E3, F3,A4, B4,C4, D4, E4,A5, B5,C5, D5,A6, B6, C6,A7, B7,A8,A1, B1, C1,D1, E1, F1,G1, H1.
For weighted round-robin queuing, if each CoS queue has the same weight value,then each CoS queue has an equal opportunity to send packets just like roundrobin queuing.
For weighted round-robin queuing, if the weight for a CoS is set to 0,then it will continue processing the packets from this CoS until there are no more packets
for this CoS.The other CoS queues that have been given a nonzero value,and depending upon the weight, will follow a common weighted round-robin scheme.
Remember that the AT-9724TS has 7 configurable priority queues (and seven Classes of Service) for each port on the Switch.
m Caution: The Switch contains eight classes of service for each port on the Switch. One of these classes is reserved for internal use on the
Switch and is therefore unconfigurable.All references in the following section regarding classes of service will refer to only the seven classes of
service that may be used and configured by the Switch’s Administrator.
Bandwidth Control
The bandwidth control settings are used to place a ceiling on the transmitting and receiving data rates for any selected port. In the Configuration folder, click
Bandwidth Control, to view the screen shown below.
Figure 6- 48. Bandwidth Settings and Port Bandwidth Table
yed:
wing parameters can be set or ar
ollo
The f
Parameter Description
Unit
o
om/T
Fr
Type This drop-down menu allows you to select between RX (receive,) TX (transmit,) and Both.This setting will
no_limit This drop-down menu allows you to specify that the selected port will have no bandwidth limit.Enabled
Rate This field allows you to enter the data rate, in Mbit/s,that will be the limit for the selected port.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
e displa
Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
oup of por
A consecutiv
determine whether the bandwidth ceiling is a
packets.
disables the limit.
e gr
ts may be configured starting with the selected port.
transmitting,
pplied to r
eceiving,
or both r
eceiving and transmitting
67
Page 69

Click Apply to set the bandwidth control for the selected ports. Results of configured Bandwidth Settings will be displayed in the Port Bandwidth
.
Table
QoS Scheduling Mechanism
This drop-down menu allows you to select between a Weight Fair and a Strict mechanism for emptying the classes of service. In the Configuration folder
open the
QoS folder and click QoS Scheduling Mechanism, to view the screen shown below.
Figure 6- 49. Scheduling Mechanism Configuration and QoS Scheduling Mechanism Table
Scheduling Mechanism has the following parameters.
The
Parameter Description
Strict
Weight fair Use the weighted round-robin (WRR) algorithm to handle packets in an even distribution in priority queues.
Apply to let your changes take effect.
Click
The highest queue is the first to process traffic.That is, the highest queue will finish before other queues empty.
Output Scheduling
QoS can be customized b
consideration should be given to how network traffic in lower classes of service is affected.Changes in scheduling may result in unacceptable levels of packet loss
or significant transmission delay. If you choose to customize this setting, it is important to monitor network performance, especially during peak demand, as
bottlenecks can quickly develop if the QoS settings are not suitable.In the
to view the screen shown below.
y changing the output scheduling used f
or the classes of ser
Configuration folder open the QoS folder and click QoS Output Scheduling,
vice in the Switch.
As with any changes to QoS implementation, careful
QoS Output Scheduling Configuration windo
e 6- 50.
Figur
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
w
68
Page 70

You may assign the following values to the QoS classes to set the scheduling.
Parameter Description
Max. Packets Specifies the maximum number of packets the above specified hardware priority queue will be allowed to
Click
Apply to implement changes made.
Note: Entering a 0 f
Queue. For more information on implementation of this feature, see the next section,
or the
transmit before allowing the next lowest priority queue to transmit its packets.A value between 0 and 15 can
be specified.
Max P
ackets
field in the QoS Output Scheduling Configur
Configuring the Combination Queue.
ation
w above will create a Combination
windo
Configuring the Combination Queue
Utilizing the QoS Output Scheduling Configuration window shown above,the AT-9724TS can implement a combination queue for forwarding packets.
This combination queue allows for a combination of strict and weight-fair (weighted round-robin “
the combination queue, enter a 0 for the Max Packets entry of the corresponding priority classes of service listed in the window above. Priority classes of service
that have a 0 in the Max Packet field will forward packets with strict priority scheduling.The remaining classes of service, that do not have a
Packet
field, will follow a weighted round-robin (WRR) method of forwarding packets – as long as the priority classes of service with a 0 in their Max Packet
field are empty.When a packet arrives in a priority class with a 0 in its Max Packet field, this class of service will automatically begin forwarding packets until it
is empty.Once a priority class of service with a 0 in its
WRR) cycle of forwarding packets,starting with the highest available priority class of service. Priority classes of service with an equal level of priority and equal
(
entries in their Max Packet field will empty their fields based on hardware priority scheduling.The
number of packets a given priority class of service can transmit per weighted round-robin (
while allowing other classes to empty as well.A value between 0 and 15 packets can be specified per priority class of service to create the combination queue.
The example window below displays an example of the combination queue where Class-1 will have a strict priority for emptying its class, while the other classes
will follow a weight fair scheduling.
Max Packet field is empty, the remaining priority classes of service will reset the weighted round-robin
WRR”) scheduling for emptying given classes of service.To set
0 in their Max
Max Packet parameter allows you to specify the maximum
WRR) scheduling cycle.This provides for a controllable CoS behavior
Figure 6- 51. QoS Output Scheduling Configuration window – Combination queue example
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
69
Page 71

802.1p Default Priority
The Switch allows the assignment of a default 802.1p priority to each port on the Switch. In the Configuration folder open the QoS folder and click 802.1p
Default Priority
, to view the screen shown below.
Figure 6- 52. Port Default Priority Assignment and The Port Priority Table window
This page allows you to assign a default 802.1p priority to any given port on the Switch.The priority queues are numbered from 0,the lowest priority, to 7, the
highest priority.To implement a new default priority, choose the Switch of the Switch stack to be configured by using the
range by using the
From and To pull-down menus and then insert a priority value, from 0-7 in the Priority field.Click Apply to implement your settings.
Unit pull-down menu,choose a port
802.1p User Priority
The AT-9724TS allows the assignment of classes of service to each of the 802.1p priorities. In the Configuration folder open the QoS folder and click
802.1p User Priority, to view the screen shown below.
Figure 6- 53. User Priority Configuration window
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
70
Page 72

Once you have assigned a priority to the port groups on the Switch, you can then assign this Class to each of the7 levels of 802.1p priorities. Click Apply to set
your changes.
Traffic Segmentation
Traffic segmentation is used to limit traffic flow from a single port to a group of ports on either a single Switch (in standalone mode) or a group of ports on
another switch in a switch stack.This method of segmenting the flow of traffic is similar to using VLANs to limit traffic, but is more restrictive. It provides a
method of directing traffic that does not increase the overhead of the Master switch CPU.
In the Configuration folder open the
QoS folder and click Traffic Segmentation, to view the screen shown below.
Figure 6- 54. Current Traffic Segmentation Table
Click on the
This page allo
Configuring traffic segmentation on the AT-9724TS is accomplished in two parts. First,you specify a switch from a switch stack by using the
men
er
diff
Clicking the
The
allows you to select a port from that switch.This is the port that will be transmitting packets.
The
Forward Port click box
allowed to receive packets from the port specified above.
Click
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Setup button to open the Setup Forwarding Ports page, as shown below.
Figure 6- 55. Setup Forwarding Ports window
witch in a switch stack will be allowed to forward packets to other ports on that switch.
en s
ou to determine which por
ws y
u, and then a port from that switch, using the
ts on the same s
ent por
Apply button will enter the combination of transmitting port and allowed receiving ports into the Switch’s Traffic Segmentation table.
Unit drop-down menu at the top of the page allows you to select a switch from a switch stack using that switch’s Unit ID.The Port drop-down menu
Unit drop-down menu under the Setup Forwarding ports heading allows you to select a switch from a switch stack using that switch’s Unit ID.The
Apply to enter the settings into the Switch’s Traffic Segmentation table.
witch,) on that s
ou to select which of the ports on the selected switch will be able to forward packets.These are the ports that will be
w y
es allo
t on a giv
ort
P
witch that y
wn menu.Then specify a second switch from the switch stack, and then you select which ports (or
pull-do
ou want to be able to r
e packets from the switch and port you specified in the first part.
eceiv
Unit pull-down
71
Page 73

Clicking the Apply button will enter the combination of transmitting port and allowed receiving ports into the Switch's Traffic Segmentation Table.
6-19 System Log Server
The Switch can send Syslog messages to up to four designated servers using the System Log Server. In the Configuration folder, click System Log
, to view the screen shown below.
Server
e 6- 56. System Log Servers window
Figur
The parameters configured for adding and editing
current entry,click the hyperlinked number of the server in the
description of the parameters in the following window.
wing parameters can be set:
ollo
The f
System Log Server settings are the same.To add a new Syslog Server, click the Add button.To modify a
Figure 6- 57. System Log Servers – Add
Index field. Both actions will result in the same screen to configure. See the table below for a
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
72
Page 74

Parameter Description
Index
Server IP The IP address of the Syslog server.
Severity This drop-down menu allows you to select the level of messages that will be sent.The options are Warning,
Facility Some of the operating system daemons and processes have been assigned Facility values.Processes and
UDP Port (514 or 6000-65535)
Status Choose Enabled or Disabled to activate or deactivate
Syslog server settings index (1-4).
Informational
daemons that have not been explicitly assigned a Facility may use any of the "local use" facilities or they may use
the "user-level" Facility.Those Facilities that have been designated are shown in the following:
denotes the facility values that the Switch currently implements.
Numerical Code Facility
0 kernel messages
1 user-level messages
2 mail system
3 system daemons
4 security/authorization messages
5 messages generated internally by syslog line printer subsystem
7 network news subsystem
8 UUCP subsystem
9 clock daemon
10 security/authorization messages
11 FTP daemon
12 NTP subsystem
13 log audit
14 log alert
15 clock daemon
16 local use 0 (local0)
17 local use 1 (local1)
18 local use 2 (local2)
19 local use 3 (local3)
20 local use 4 (local4)
21 local use 5 (local5)
22 local use 6 (local6)
23
Type the UDP port number used for sending Syslog messages.The default is 514.
, and All.
ocal use 7 (l
l
Bold font
ocal7)
.
er configuration, click
o set the System Log Ser
T
under the Delete heading of the entry to delete.To return to the Current System Log Servers window, click the Show All System Log Servers link.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
v
pply.T
A
o delete an entr
y from the
ent System Log Serv
Curr
er
click the corresponding
,
w
windo
8
73
Page 75

6-20 SNTP Settings
Current Time Settings
To configure the time settings for the Switch, open the Configuration folder, then the SNTP folder and click on the Current Time Setting link, revealing
the following screen for the user to configure.
Figure 6- 58.Time Settings Page
The following parameters can be set or are displayed:
Parameter Description
Current Time: Status
System Boot Time Displays the time when the Switch was initially started for this session.
.
ime
ent T
Curr
ime Source
T
Current Time: SNTP Settings
SNTP State Use this pull-down menu to Enable or Disable SNTP.
SNTP Primary Server This is the IP address of the primary server the SNTP information will be taken from.
SNTP Secondary Server This is the IP address of the secondary server the SNTP information will be taken from.
SNTP Poll Interval in Seconds This is the interval, in seconds,between requests for updated SNTP information.
(30-99999)
ime
Curr
ime: Set Curr
ent T
ent T
ys the cur
Displa
ys the source of the time settings viewed here.
Displa
ent time
r
Year
Month Enter the current month, if you would like to update the system clock.
Day Enter the current day, if you would like to update the system clock.
Time in HH MM SS Enter the current time in hours and minutes,if you would like to update the system clock.
Click Apply to implement your changes.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Enter the current year, if you want to update the system clock.
74
Page 76

Time Zone and DST
The following are screens used to configure time zones and Daylight Savings time settings for SNTP. Open the Configuration folder, then the SNTP folder
and click on the
Time Zone and DST link, revealing the following screen.
Figure 6- 59.Time Zone and DST Settings Page
The following parameters can be set:
Parameter Description
Daylight Saving Time State Use this pull-down menu to Enable or Disable the DST Settings.
Daylight Saving Time Offset Use this pull-down menu to specify the amount of time that will constitute your local DST offset - 30, 60,90, or
in Minutes 120 minutes.
Time Zone Offset from GMT in Use these pull-down menus to specify your local time zone's offset from Greenwich Mean Time (GMT.)
+/- HH:MM
DST Repeating Settings
om: Which Day
Fr
From: Day of Week Enter the day of the week that DST will start on.
From: Month Enter the month DST will start on.
From: Time in HH:MM Enter the time of day that DST will start on.
To: Which Day Enter the week of the month the DST will end.
To: Day of Week Enter the day of the week that DST will end.
To: Month Enter the month that DST will end.
To: time in HH:MM Enter the time DST will end.
DST Annual Settings Using annual mode will enable DST seasonal time adjustment.Annual mode requires that the DST beginning and
om: Month
Fr
From: Day Enter the day of the month DST will start on, each year.
From: Time in HH:MM Enter the time of day DST will start on, each year.
To: Month Enter the month DST will end on, each year.
To: Day Enter the day of the month DST will end on, each year.
To: Time in HH:MM Enter the time of day that DST will end on, each year.
Using repeating mode will enable DST seasonal time adjustment. Repeating mode requires that the DST
beginning and ending date be specified using a formula. For example, specify to begin DST on Saturday during
the second w
Enter the w
ending date be specified concisel
Enter the month DST will star
April and end DST on Sunday during the last week of October.
eek of
eek of the month that DST will star
y.For example, specify to begin DST on April 3 and end DST on October 14.
t on, each year.
t.
Click Apply to implement changes made to the T
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
ime Zone a
nd DST
windo
.
w
75
Page 77

6-21 Access Profile Table
Configur
Access profiles allow you to establish criteria to determine whether or not the Switch will forward packets based on the information contained in each packet's
header.These criteria can be specified on a basis of VLAN, MAC address or IP address.
Creating an access profile is divided into two basic parts.The first is to specify which part or parts of a frame the Switch will examine, such as the MAC source
address or the IP destination address.The second part is entering the criteria the Switch will use to determine what to do with the frame.The entire process is
described below in two parts.
To display the currently configured Access Profiles on the Switch,open the
the
Access Profile Table page, as shown below.
ing the Access Profile Table
Configuration folder and click on the Access Profile Table link.This will open
Figure 6- 60.Access Profile Table
To add an entry to the
Access Profile Configuration pages;one for Ethernet (or MAC address-based) profile configuration, one for IP address-based profile configuration
three
and one for the
The page shown below is the
Access Profile Table, click the Add button.This will open the Access Profile Configuration page, as shown below.There are
Packet Content Mask.You can switch between the three Access Profile Configuration pages by using the Type drop-down menu.
Ethernet Access Profile Configuration page.
Figure 6- 61.Access Profile Table (Ethernet)
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
76
Page 78

The following parameters can be set, for the Ethernet type:
Parameter Description
Profile ID (1-8)
Type in a unique identifier number for this profile set.This value can be set from 1 - 8.
Type Select profile based on Ethernet (MAC Address),IP address or packet content mask.This will change the menu
according to the requirements for the type of profile.
Ethernet to instruct the Switch to examine the layer 2 part of each packet header.
Select
Select IP to instruct the Switch to examine the IP address in each frame's header.
Select
Packet Content Mask to specify a mask to hide the content of the packet header.
VLAN Selecting this option instructs the Switch to examine the VLAN identifier of each packet header and use this as
the full or partial criterion for forwarding.
Source MAC Source MAC Mask – Enter a MAC address mask for the source MAC address.
Destination MAC Destination MAC Mask – Enter a MAC address mask for the destination MAC address.
802.1p Selecting this option instructs the Switch to examine the 802.1p priority value of each packet header and use
this as the, or part of the criterion for forwarding.
Ethernet type Selecting this option instructs the Switch to examine the Ethernet type value in each frame's header.
Port The user may set the Access Profile Table on a per-port basis by entering a port number in this field.The port
list is specified by listing the lowest switch number and the beginning port number on that switch,separated by
a colon.Then the highest switch number,and the highest port number of the range (also separated by a colon)
are specified.The beginning and end of the port list range are separated by a dash. For example, 1:3 specifies
switch number 1, port 3. 2:4 specifies switch number 2,port 4. 1:3 -2:4 specifies all of the ports between switch
1, port 3 and switch 2, port 4 • in numerical order. Entering all will denote all ports on the Switch.
The page shown below is the
IP Access Profile Configuration page.
Figure 6- 62.Access Profile Configuration (IP)
or
wing parameters can be set,
ollo
The f
f
IP:
Parameter Description
Profile ID (1-8) Type in a unique identifier number for this profile set.This value can be set from 1 - 8.
Address), IP address or packet content mask.This will change the menu
T
ype
ofile based on Ethernet (MA
Select pr
ding to the r
accor
Select
Ethernet to instruct the Switch to examine the layer 2 part of each packet header.
Select
IP to instruct the Switch to examine the IP address in each frame's header.
equir
ements f
C
or the type of pr
ofile
.
Select Packet Content Mask to specify a mask to hide the content of the packet header.
VLAN Selecting this option instructs the Switch to examine the VLAN part of each packet header and use this as the,
orwarding.
t of the criterion f
or par
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
or f
77
Page 79

Source IP Mask Enter an IP address mask for the source IP address.
Destination IP Mask Enter an IP address mask for the destination IP address.
DSCP Selecting this option instructs the Switch to examine the DiffServ Code part of each packet header and use this
as the, or part of the criterion for forwarding.
Protocol Selecting this option instructs the Switch to examine the protocol type value in each frame's header.You must
then specify what protocol(s) to include according to the following guidelines:
Select
ICMP to instruct the Switch to examine the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) field in each
frame's header.
Type to further specify that the access profile will apply an ICMP type value,or specify Code
Select
to further specify that the access profile will apply an ICMP code value.
IGMP to instruct the Switch to examine the Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) field in each
Select
frame's header.
Select
Type to further specify that the access profile will apply an IGMP type value.
Select
TCP to use the TCP port number contained in an incoming packet as the forwarding criterion. Selecting
TCP requires that you specify a source port mask and/or a destination port mask.The user may also identify
which flag bits to filter. Flag bits are parts of a packet that determine what to do with the packet.The user may
filter packets by filtering certain flag bits within the packets,by checking the boxes corresponding to the flag
bits of the TCP field.The user may choose between
urg (urgent),ack (acknowledgement), psh (push), rst
(reset), syn (synchronize), fin (finish).
src port mask – Specify a TCP port mask for the source port in hex form (hex 0x0-0xffff),which
ou wish to deny.
y
dest port mask – Specify a TCP port mask for the destination port in hex form (hex 0x0-0xffff)
ou wish to deny.
which y
UDP to use the UDP port number contained in an incoming packet as the forwarding criterion.
Select
Selecting UDP requires that you specify a source port mask and/or a destination port mask.
src port mask – Specify a TCP port mask for the source port in hex form (hex 0x0-0xffff).
dest port mask – Specify a TCP port mask for the destination port in hex form (hex 0x0-0xffff).
protocol id – Enter a value defining the protocol ID in the packet header to mask. Specify the protocol ID
mask in hex form (hex 0x0-0xffffffff).
Port The user may set the Access Profile Table on a per-port basis by entering an entry in this field. Entering all will
denote all ports on the Switch.The port list is specified by listing the lowest switch number and the beginning
port number on that switch, separated by a colon.Then the highest switch number, and the highest port
number of the range (also separated by a colon) are specified.The beginning and end of the port list range are
separated by a dash. For example, 1:3 specifies switch number 1,port 3. 2:4 specifies switch number 2, port 4.
1:3 - 2:4 specifies all of the ports between switch 1, port 3 and switch 2, port 4 •in numerical order. Entering all
will denote all ports on the Switch.
The page shown below is the Packet Content Mask configuration window.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Figure 6- 63.Access Profile Configuration window (Packet Content Mask)
78
Page 80

This screen will aid the user in configuring the Switch to mask packet headers beginning with the offset value specified.The following fields are used to configure
the Packet Content Mask:
Parameter Description
Profile ID (1-8)
Type Select profile based on Ethernet (MAC Address),IP address or packet content mask.This will change the menu
Offset This field will instruct the Switch to mask the packet header beginning with the offset value specified:
Port The user may set the Access Profile Table on a per-port basis by entering an entry in this field. Entering all will
Click
Apply to implement changes made.
Type in a unique identifier number for this profile set.This value can be set from 1 - 8.
according to the requirements for the type of profile.
Ethernet to instruct the Switch to examine the layer 2 part of each packet header.
Select
Select
IP to instruct the Switch to examine the IP address in each frame's header.
Select
Packet Content Mask to specify a mask to hide the content of the packet header.
value (0-15) - Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from the beginning of the packet to the 15th byte.
value (16-31) – Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from byte 16 to byte 31.
value (32-47) – Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from byte 32 to byte 47.
value (48-63) – Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from byte 48 to byte 63.
value (64-79) – Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from byte 64 to byte 79.
denote all ports on the Switch.The port list is specified by listing the lowest switch number and the beginning
port number on that switch, separated by a colon.Then the highest switch number, and the highest port
number of the range (also separated by a colon) are specified.The beginning and end of the port list range are
separated by a dash. For example, 1:3 specifies switch number 1,port 3. 2:4 specifies switch number 2, port 4.
1:3 - 2:4 specifies all of the ports between switch 1, port 3 and switch 2, port 4 •in numerical order. Entering all
will denote all ports on the Switch.
To establish the rule for a previously created Access Profile:
In the Configuration folder, click the Access Profile Table link opening the Access Profile Table. Under the heading Access Rule, clicking Modify,
will open the following window.
Figure 6- 64.Access Rule Table window – IP
o cr
T
button.
eate a ne
w rule set f
or an access profile click the
Add button.
A ne
w windo
w is displa
yed.To remove a previously created rule,click the corresponding
8
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
79
Page 81

Figure 6- 65.Access Rule Configuration window (IP)
Configure the following
Access Rule Configuration settings for IP:
Parameter Description
Profile ID
This is the identifier number for this profile set.
Mode Select Permit to specify that the packets that match the access profile are forwarded by the Switch, according
to any additional rule added (see below).
Deny to specify that packets that do not match the access profile are not forwarded by the Switch and
Select
will be filtered.
Access ID Type in a unique identifier number for this access.This value can be set from 1-50.
Type Selected profile based on Ethernet (MAC Address),IP address or Packet Content Mask.
Ethernet instructs the Switch to examine the layer 2 part of each packet header.
IP instructs the Switch to examine the IP address in each frame's header.
Packet Content Mask instructs the Switch to examine the packet header.
Priority (0-7) This parameter is specified if you want to re-write the 802.1p default priority previously set in the Switch,
which is used to determine the CoS queue to which packets are forwarded to. Once this field is specified,
ets accepted by the Switch that match this priority are forwarded to the CoS queue specified previously by
pack
.
the user
Replace priority with – Click the corresponding box if you want to re-write the 802.1p default priority of a
y in this
et to the value enter
pack
ed in the
Pr
ior
ity
which meets the criteria specified pr
field,
viousl
e
command, before forwarding it on to the specified CoS queue. Otherwise,a packet will have its incoming
802.1p user priority r
e-written to its original value bef
information on priority queues, CoS queues and mapping for 802.1p, see the
or
QoS section of this manual.
orwarded by the Switch. For more
e being f
Replace Dscp (0-63) Select this option to instruct the Switch to replace the DSCP value (in a packet that meets the selected
criteria) with the value entered in the adjacent field.
VLAN.
me
AN Na
VL
Sour
ce IP
ws the entr
Allo
Enter an IP
Destination IP Enter an IP
y of a name f
or a pr
y configur
viousl
e
Address mask for the source IP address.
Ad
ess mask f
dr
or the destination IP ad
ed
ess.
dr
Dscp (0-63) This field allows the user to enter a DSCP value in the space provided, which will instruct the Switch to
examine the DiffServ Code part of each packet header and use this as the, or part of the criterion for
forwarding.The user may choose a value between 0 and 63.
depending on which
able;
Protocol This field allo
ws the user to modify the pr
otocol used to configur
e the
Access Rule
T
protocol the user has chosen in the Access Profile Table.
viously correctly configured rule,click
To view the settings of a pr
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
e
w
ie
V
in the Access R
ule T
le
b
a
to vie
w the f
ollo
wing scr
een:
80
Page 82

Figure 6- 66.Access Rule Display window (IP)
To configure the
To remove a previously created rule, select it and click the
Access Rule for Ethernet, open the Access Profile Table and click Modify for an Ethernet entry.This will open the following screen:
Figure 6- 67.Access Rule Table
8 button.To add a new Access Rule,click the Add button:
Figure 6- 68.Access Rule Configuration window – Ethernet
To set the Access Rule for Ethernet, adjust the following parameters and click
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Apply.
81
Page 83

Parameter Description
Profile ID
This is the identifier number for this profile set.
Mode Select Permit to specify that the packets that match the access profile are forwarded by the Switch, according
to any additional rule added (see below).
Select
Deny to specify that packets that do not match the access profile are not forwarded by the Switch and
will be filtered.
Access ID Type in a unique identifier number for this access.This value can be set from 1 - 50.
Type Selected profile based on Ethernet (MAC Address), IP address or Packet Content Mask.
Ethernet instructs the Switch to examine the layer 2 part of each packet header.
IP instructs the Switch to examine the IP address in each frame's header.
Packet Content Mask instructs the Switch to examine the packet header
Priority (0-7) This parameter is specified if you want to re-write the 802.1p default priority previously set in the Switch,
which is used to determine the CoS queue to which packets are forwarded to. Once this field is specified,
packets accepted by the Switch that match this priority are forwarded to the CoS queue specified previously by
the user.
Replace priority with – Click the corresponding box if you want to re-write the 802.1p default priority of a
packet to the value entered in the
Priority field, which meets the criteria specified previously in this
command, before forwarding it on to the specified CoS queue. Otherwise,a packet will have its incoming
802.1p user priority re-written to its original value before being forwarded by the Switch.
For more information on priority queues,CoS queues and mapping for 802.1p,see the
QoS section of this
manual.
VLAN Name Allows the entry of a name for a previously configured VLAN.
Source MAC Source Enter a MAC Address for the source MAC address.
Destination MAC Destination Enter a MAC Address mask for the destination MAC address.
802.1p (0-7) Enter a value from 0-7 to specify that the access profile will apply only to packets with this 802.1p priority
value.
Ethernet Type Specifies that the access profile will apply only to packets with this hexadecimal 802.1Q Ethernet type value
(hex 0x0-0xffff) in the packet header.The Ethernet type value may be set in the form: hex 0x0-0xffff,which
means the user may choose any combination of letters and numbers ranging from a-f and from 0-9999.
To view the settings of a previously correctly configured rule, click
Figure 6- 69.Access Rule Display window (Ethernet)
To configure the Access Rule for
Packet Content Mask,open the Access Profile Table and click Modify for a Packet Content Mask entry.This
will open the following screen:
View in the Access Rule Table to view the following screen:
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
82
Page 84

Figure 6- 70.Access Rule Table (Packet Content Mask)
To remove a previously created rule, select it and click the 8 button.To add a new Access Rule, click the Add button:
Figure 6- 71.Access Rule Configuration – Packet Content Mask
To set the Access Rule for the
Packet Content Mask,adjust the following parameters and click Apply.
Parameter Description
ofile ID
Pr
This is the identifier n
umber f
or this pr
ofile set.
Mode Select Permit to specify that the packets that match the access profile are forwarded by the Switch, according
to any additional rule added (see below).
Deny to specify that packets that do not match the access profile are not forwarded by the Switch and
Select
will be filter
Access ID T
ype in a unique identifier number for this access.This value can be set from 1 - 50.
Type Selected pr
ed.
ofile based on Ethernet (MA
ess), IP address or Packet Content Mask.
dr
Ad
C
Ethernet instructs the Switch to examine the layer 2 part of each packet header.
IP instructs the Switch to examine the IP address in each frame's header.
et Content Mask
k
ac
P
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
instructs the Switch to examine the pack
et header
.
83
Page 85

Priority This parameter is specified if you want to re-write the 802.1p default priority previously set in the Switch,
Offset This field will instruct the Switch to mask the packet header beginning with the offset value specified:
which is used to determine the CoS queue to which packets are forwarded to. Once this field is specified,
packets accepted by the Switch that match this priority are forwarded to the CoS queue specified previously by
the user.
Replace priority with – Click the corresponding box if you want to re-write the 802.1p default priority of a
packet to the value entered in the
command, before forwarding it on to the specified CoS queue. Otherwise,a packet will have its incoming
802.1p user priority re-written to its original value before being forwarded by the Switch.
For more information on priority queues,CoS queues and mapping for 802.1p,see the
manual.
value (0-15) – Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from the beginning of the packet to the 15th byte.
value (16-31) – Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from byte 16 to byte 31.
value (32-47) – Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from byte 32 to byte 47.
value (48-63) – Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from byte 48 to byte 63.
value (64-79) – Enter a value in hex form to mask the packet from byte 64 to byte 79.
Priority field, which meets the criteria specified previously in this
QoS section of this
To view the settings of a previously correctly configured rule, click
View in the Access Rule Table to view the following screen:
Figur
Access Rule Displa
e 6- 72.
y window (Packet Content Mask)
6-22 Port Access Entity (802.1x)
t-based a
nding 802.1x P
Under
The original intent behind the development of 802.1X was to leverage the characteristics of point-to-point connections associated with UTP based LANs.All
single LAN segment in such infrastructures has no more than two devices attached to it,one of which is a Bridge Port.The Bridge Port detects events that
indicate the attachment of an active device at the remote end of the link,or an active device becoming inactive.These events can be used to control the
authorization state of the P
Control.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
sta
or
or
t and initiate the process of authenticating the attached device if the Port is unauthorized.This is the Port-Based Network Access
nd MAC-based Network Access Control
84
Page 86

Port-Based Network Access Control
AT -9724TS Switch
Uncontrolled Port
Controlled Port - port blocked
RADIUS
Server
802.1X
Client
802.1X
Client
802.1X
Client
802.1X
Client
802.1X
Client
802.1X
Client
802.1X
Client
802.1X
Client
802.1X
Client
AT -9724TS Switch
802.1X Client802.1X Client802.1X Client
802.1X Client
RADIUS
Server
Uncontrolled Port
Con
trolled Port - port blocked
Figur
e 6- 73. Example of Typical Port-Based Configuration
Once the connected device has successfully been authenticated, the Port then becomes Authorized,and all subsequent traffic on the Port is not subject to access
control restriction until an event occurs that causes the Port to become Unauthorized. Hence, if the Port is actually connected to a shared media LAN segment
with more than one attached device, successfully authenticating one of the attached devices effectively provides access to the LAN for all devices on the shared
segment. Clearly,the security offered in this situation is open to attack.
MAC-Based Network Access Control
Figure 6- 74. Example of Typical MAC-Based Configuration
In order to successfully make use of 802.1X in a shared media LAN segment,it would be necessary to create “logical” Ports, one for each attached device that
required access to the LAN.The Switch would regard the single physical Port connecting it to the shared media segment as consisting of a number of distinct
logical Ports, each logical Port being independently controlled from the point of view of EAPOL exchanges and authorization state.The Switch learns each
attached devices’ individual MAC addresses, and effectively creates a logical Port that the attached device can then use to communicate with the LAN via the
Switch.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
85
Page 87

Configure Authenticator
To configure the 802.1X Authenticator Settings, click PAE Access Entity > Configure Authenticator:
Figure 6- 75. 802.1X Authenticator Settings window
To view the 802.1X Authenticator settings on a different switch in the switch stack, use the
switch stack.To configure the settings by port, click on the hyperlinked port number under the
Unit pull-down menu to select that switch by its ID number in the
Port heading, which will display the following table to configure:
Figure 6- 76. 802.1X Authenticator Settings – Modify
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
86
Page 88

This screen allows you to set the following features:
Parameter Description
Unit
From [ ] To [ ] Enter the port or ports to be set.
AdmCtrlDir Sets the administrative-controlled direction to either in or both.
PortControl This allows you to control the port authorization state.
TxPeriod This sets the TxPeriod of time for the authenticator PAE state machine.This value determines the period of
QuietPeriod This allows you to set the number of seconds that the Switch remains in the quiet state following a failed
SuppTimeout This value determines timeout conditions in the exchanges between the Authenticator and the client.The
ServerTimeout This value determines timeout conditions in the exchanges between the Authenticator and the authentication
MaxReq The maximum number of times that the Switch will retransmit an EAP Request to the client before it times out
ReAuthPeriod A constant that defines a nonzero number of seconds between periodic reauthentication of the client.The
ReAuth Determines whether regular reauthentication will take place on this port.The default setting is Disabled.
Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
in is selected, control is only exerted over incoming traffic through the port you selected in the first field.
If
If
both is selected, control is exerted over both incoming and outgoing traffic through the controlled port
selected in the first field.
Select
forceAuthorized to disable 802.1X and cause the port to transition to the authorized state without any
authentication exchange required.This means the port transmits and receives normal traffic without 802.1Xbased authentication of the client.
forceUnauthorized is selected, the port will remain in the unauthorized state, ignoring all attempts by the client
If
to authenticate.The Switch cannot provide authentication services to the client through the interface.
If
Auto is selected, it will enable 802.1X and cause the port to begin in the unauthorized state, allowing only
EAPOL frames to be sent and received through the port.The authentication process begins when the link state
of the port transitions from down to up,or when an EAPOL-start frame is received.The Switch then requests
the identity of the client and begins relaying authentication messages between the client and the authentication
server.
The default setting is
an EAP Request/Identity packet transmitted to the client.The default setting is 30 seconds.
authentication exchange with the client.The default setting is 60 seconds.
default setting is 30 seconds.
server.The default setting is 30 seconds.
of the authentication sessions.The default setting is 2.
default setting is 3600 seconds.
Auto.
pply
A
Click
802.1X Authenticator Settings table.
to implement y
our configuration changes.
T
802.1X A
uthenticator Settings
on a por
t-b
y-por
o view configurations for the
Local Users
open the
,
In the configuration f
This windo
Enter a
the same window.
w will allow the user to set different local users on the Switch.
User Name, Password and confirmation of that password. Properly configured local users will be displayed in the 802.1x Local User Table in
older
t Access Entity
or
P
Figure 6- 77. 802.1x Local User Table Configuration and 802.1x Local User Table window
older and click
f
Local usersto open the 802.1x Local User T
le Configuration
b
a
t basis, see the
windo
.
w
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
87
Page 89

PAE System Control
Existing 802.1x port settings are displayed and can be configured using the windows below.
Port Capability Settings
Click Port Access Entity > PAE System Control > 802.1X Capability Settings to view the following window:
Figure 6- 78. 802.1x Capability Settings and Table window
To set up the Switch's 802.1x port-based authentication, select the switch in the switch stack by using the
to be configured in the
your change take effect.
Configure the following 802.1x capability settings:
Parameter Description
Unit
From and To Ports being configured for 802.1x settings.
bility
pa
Ca
From and To fields. Next, enable the ports by selecting Authenticator from the drop-down menu under Capability. Click Apply to let
Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
ole choices can be selected:
o r
w
T
Authenticator –
None –
A user must pass the authentication process to gain access to the network.
y the 802.1x functions.
The por
t is not contr
olled b
Unit pull-down menu and then select which ports are
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
88
Page 90

Initializing Ports for Port Based 802.1x
Existing 802.1x port settings are displayed and can be configured using the window below.
Note: Ensure Port Based 802.1x is enabled under Configuration > Advanced Settings.
Port Access Entity > PAE System Control > Initialize Port(s) to open the following window:
Click
Figur
e 6- 79. Initialize Port window (Port-based)
This window allows you to initialize a port or group of ports.The
port(s).
This window displays the following information:
Parameter Description
Unit Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
From and To Select ports to be initialized.
t
or
P
Auth PAE State The Authenticator PAE State will display one of the following:Initialize, Disconnected, Connecting,,Authenticating,,
Backend State The Backend Authentication State will display one of the following:Request, Response, Success,Fail, Timeout, Idle,
Port Status The status of the controlled port can be Authorized, Unauthorized, or N/A.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
A r
Authenticated
Initialize,
y field indicating a por
ead onl
and
Initialize Port Table in the bottom half of the window displays the current status of the
t on the Switch.
, Aborting, Held, ForceAuth, ForceUnauth,and N/A.
N/A.
89
Page 91

Initializing Ports for MAC Based 802.1x
To initialize ports for the MAC side of 802.1x, the user must first enable 802.1x by MAC address in the Advanced Settings window. Click Port Access
Entity > PAE System Control > Initialize Port(s)
To initialize ports, first choose the switch in the switch stack by using the
user must specify the MAC address to be initialized by entering it into the
initialization, click
Apply.
Note: The user must first globally enable 802.1X in the Advanced Settings window in the Configuration folder before initializing ports.
Information in the
Initialize Ports Table cannot be viewed before enabling 802.1X.
to open the following window:
Figure 6- 80. Initialize Ports window (MAC based 802.1x)
Unit pull-down menu,then the range of ports in the From and To field.Then the
MAC Address field and checking the corresponding check box.To begin the
Reauthenticate Port(s) for Port Based 802.1x
This window allows you to reauthenticate a port or group of ports by choosing a port or group of ports by using the pull down menus From and To and
Apply.The Reauthenticate Port Table displays the current status of the reauthenticated port(s) once you have clicked Apply.
clicking
Click
Port Access Entity > PAE System Control > Reauthenticate Port(s) to open the Reauthenticate Port(s) window:
Reauthenticate Port and Reauthenticate Port Table window
e 6- 81.
Figur
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
90
Page 92

This window displays the following information:
Parameter Description
Unit
Port The port number of the reauthenticated port.
Auth State The Authenticator State will display one of the following: Initialize, Disconnected,Connecting, Authenticating,
BackendState The Backend State will display one of the following: Request, Response,Success, Fail, Timeout, Idle,Initialize, and N/A.
OpenDir Operational Controlled Directions are both and in.
PortStatus The status of the controlled port can be Authorized, Unauthorized, or N/A.
Note: The user must first globally enable 802.1X in the Advanced Settings window in the Configuration folder before reauthenticating
ports. Information in the
Choose the Switch ID number of the Switch in the switch stack to be modified.
Authenticated, Aborting, Held, ForceAuth, ForceUnauth,and N/A.
Reauthenticate Ports Table cannot be viewed before enabling 802.1X.
Reauthenticate Port(s) for MAC Based 802.1x
To reauthenticate ports for the MAC side of 802.1x,the user must first enable 802.1x by MAC address in the Advanced Settings window. Click Port
Access Entity > PAE System Control > Reauthenticate Port(s)
to open the following window:
Figure 6- 82. Reauthenticate Ports – MAC based 802.1x
To reauthenticate ports, first choose the switch in the switch stack by using the
the user must specify the MAC address to be reauthenticated by entering it into the
the reauthentication, click
Apply.
Unit pull-down menu,then the range of ports in the From and To field.Then
MAC Address field and checking the corresponding check box.To begin
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
91
Page 93

RADIUS Server
The RADIUS feature of the Switch allows you to facilitate centralized user administration as well as providing protection against a sniffing, active hacker.The Web
Manager off
Click
shown below:
ers three windows.
Port Access Entity > RADIUS Server > Authentic Radius Server to open the RADIUS Server Authentication Setting window
Figure 6- 83.Authentic RADIUS Server Setting and Current RADIUS Server Settings Table window
This window displays the following information:
Parameter Description
Succession Choose the desired RADIUS server to configure: First,Second or Third.
RADIUS Server Set the RADIUS server IP.
Authentic Port Set the RADIUS authentic server(s) UDP port.The default port is 1812.
Accounting Port Set the RADIUS account server(s) UDP port.The default port is 1813.
.
er
ey
K
Confirm Key Confirm the shared key is the same as that of the RADIUS server.
Status This allo
Click
pply
A
to implement changes made
Set the k
.
y the same as that of the RADIUS ser
e
ws you to set the RADIUS Server as Valid (Enabled) or Invalid (Disabled).
v
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
92
Page 94

6-23 Layer 3 IP Networking
er 3 Global Advanced Settings
Lay
The L3 Global Advanced Settings window allows the user to enable and disable Layer 3 settings and functions from a single window.The full settings and
descriptions for these functions will appear later in this section.To view this window,open the
folder and click on the L3 Global Advanced Settings link to access the following window.
Figure 6- 84. L3 Global Advanced Settings window
The user may set the following:
Parameter Description
DVMRP State
PIM-DM State The user may globally enable or disable the Protocol Independent Multicast – Dense Mode (PIM-DM) function
RIP State The user may globally enable or disable the Routing Information Protocol (RIP) function by using the pull down
OSPF State The user may globally enable or disable the Open Shortest Path first (OSPF) function by using the pull down
ARP Aging Time (0-65535) The user may globally set the maximum amount of time,in minutes, that an Address Resolution Protocol (ARP)
The user may globally enable or disable the Distance Vector Multicast Routing Protocol (DVMRP) function by
using the pull down menu.
by using the pull down menu.
menu.
menu.
entry can remain in the Switch’s ARP table, without being accessed, before it is dropped from the table.The
value may be set in the range of 0-65535 minutes with a default setting of 20 minutes.
Configuration folder and then the Layer 3 IP Networking
Setting Up IP Interfaces
Each VLAN must be configured prior to setting up the VLAN’s corresponding IP interface.
An example is presented below:
VLAN Name VID Switch Ports
System (default) 1 5, 6,7, 8, 21,22, 23, 24
Engineer 2 9, 10, 11,12
Marketing 3 13, 14,15, 16
Finance 4 17,18, 19, 20
Sales 5 1,2, 3, 4
Backbone 6 25, 26
ts
able 6- 5.
T
ed, so a CIDR notation of 10.32.0.0/11 (or a 11-bit) addressing scheme will work.This addressing scheme will give a subnet
equir
six IP interfaces ar
In this case
mask of 11111111.11100000.00000000.00000000 (binary) or 255.224.0.0 (decimal).
Using a 10.xxx.xxx.xxx IP address notation, the above example would give 6 network addresses and 6 subnets.
Any IP address from the allowed range of IP addresses for each subnet can be chosen as an IP address for an IP interface on the switch.
For this example, we have chosen the next IP address above the network address for the IP interface’s IP Address:
,
e r
VLAN Example –
Assigned P
or
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
93
Page 95

VLAN Name VID Network Number IP Address
System (default) 1 10.32.0.0 10.32.0.1
Engineer 2 10.64.0.0 10.64.0.1
Marketing 3 10.96.0.0 10.96.0.1
Finance 4 10.128.0.0 10.128.0.1
Sales 5 10.160.0.0 10.160.0.1
Backbone 6 10.192.0.0 10.192.0.1
Table 6- 6.VLAN Example – Assigned IP Interfaces
The 6 IP interfaces, each with an IP address (listed in the table above), and a subnet mask of 255.224.0.0 can be entered into the
To setup IP Interfaces on the Switch:
Go to the Configur
ationfolder, and click on the
er 3 IP Networkingfolder, and then click on the
Lay
IP Interf
aces Table
dialog box:
Figure 6- 85. IP Interface Table window
To setup a new IP interface, click the
Add button.To edit an existing IP Interface entry, click on an entry under the Interface Name heading. Both actions will
result in the same screen to configure,as shown below.
Setup IP Interface window.
link to open the f
ollowing
e 6- 86.
Figur
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
IP Interface Configuration – Add window
94
Page 96

Figure 6- 87. IP Interface Configuration – Edit window
Choose a name for the interface to be added and enter it in the
be in the top field as seen in the window above).Enter the interface’s IP address and subnet mask in the corresponding fields. Pull the
Enabled and click Apply to enter to make the IP interface effective.To view entries in the IP Interface Table, click the Show All IP Interface Entries
hyperlink. Use the Save Changes dialog box from the Maintenance folder to enter the changes into NV-RAM.
The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Interface Name
IP Address This field allows the entry of an IP address to be assigned to this IP interface.
Subnet Mask This field allows the entry of a subnet mask to be applied to this IP interface.
VLAN Name This field allows the entry of the VLAN Name for the VLAN the IP interface belongs to.
Secondary Use the pull-down menu to set the IP interface as True or False. True will set the interface as secondary and
State This field may be altered between Enabled and Disabled using the pull down menu.This entry determines
Link Status This read only field states the current status of the IP Interface on the Switch. Link Up denotes that the IP
Apply to implement changes made.
Click
This field displays the name for the IP interface.The default IP interface is named “System”.
False will denote the interface as the primary interface of the VLAN entered above.Secondary interfaces can
only be configured if a
whether the interface will be active or not.
interface is up and running on the Switch. Link Down will denote that the IP interface is not currently set
and/or enabled on the Switch.
Interface Name field (if you are editing an IP Interface, the Interface Name will already
State pull-down menu to
primary interface is first configured.
MD5 Key Table Configuration
The MD5 K
er
v
e
domain.
MD5 Keys created here can be used in the
o configur
T
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
ey Table Configuration
et exchanged betw
y pack
e an
MD5 Key,
een OSPF r
click the
u allows the entry of a sixteen-character Message Digest – version 5 (MD5) key which can be used to authenticate
men
It is used as a security mechanism to limit the exchange of network topology information to the OSPF routing
outers.
OSPF Interface Configuration menu below.
MD5 Keylink to open the f
e 6- 88. MD5 Key Setting and Table window
Figur
wing dialog bo
ollo
x:
95
Page 97

The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Key ID
Key A alphanumeric string of between 1 and 16 case-sensitive characters used to generate the Message Digest
Click
Apply to enter the new Key ID settings.To delete a Key ID entry, click the corresponding 8 under the Delete heading.
A number from 1 to 255 used to identify the MD5 Key.
which is in turn, used to authenticate OSPF packets within the OSPF routing domain.
Route Redistribution Settings
Route redistribution allows routers on the network,which are running different routing protocols to exchange routing information.This is accomplished by
comparing the routes stored in the various routers routing tables and assigning appropriate metrics.This information is then exchanged among the various
routers according to the individual routers current routing protocol.The Switch can redistribute routing information between the OSPF and RIP routing
protocols to all routers on the network that are running OSPF or RIP. Routing information entered into the
switch is also redistributed.
Routing information source – OSPF and the Static Route table. Routing information will be redistributed to RIP.The following table lists the allowed values for
the routing metrics and the types (or forms) of the routing information that will be redistributed.
Route Source Metric Type
OSPF 0 to 16 All
Internal
External
ExtType1
ExtType2
Inter-E1
Inter-E2
RIP 0 to 16777214 Type 1
Type 2
Static 0 to 16777214 Type 1
Type 2
Local 0 to 16777214 Type 1
Type 2
Static Routing Table on the local AT-9724TS
Table 6- 7. Route Redistribution Source table
Entering the Type combination – internal type_1 type_2 is functionally equivalent to all. Entering the combination type_1 type_2 is functionally equivalent to
Entering the combination internal external is functionall
external.
Entering the metric 0 specifies transparency.
This window will redistribute routing information between the OSPF and RIP routing protocols to all routers on the network that are running OSPF or RIP.To
access the
Settings
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
Route R
:
edistr
ibution T
le Configur
b
a
Figur
y equivalent to all.
ation
windo
e 6- 89. Route Redistribution Settings and Table window
o to
g
,
w
Configur
ation > Lay
er 3 IP Netw
king > Route R
or
edistr
ibution
96
Page 98

The following parameters may be set or viewed:
Parameter Description
Dest Protocol
Src Protocol Allows for the selection of the protocol for the source device. Choose between RIP, OSPF, Static and Local.
Type Allows for the selection of one of six methods of calculating the metric value.The user may choose between
Metric Allows the entry of an OSPF interface cost.This is analogous to a Hop Count in the RIP routing protocol.
Click Add/Modify to implement changes made.
Note: The source protocol (Src Protocol) entry and the destination protocol (Dest Protocol) entry cannot be the same.
Allows for the selection of the protocol for the destination device.Choose between RIP and OSPF.
All, Internal, External,ExtType1,ExtType2, Inter-E1,Inter-E2. See the table above for available metric value types for
each source protocol.
Static/Default Route
Entries into the Switch’s forwarding table can be made using both MAC addresses and IP addresses.Static IP forwarding is accomplished by the entry of an IP
address into the
Switch’s Static IP Routing Table.
Figure 6- 90. Static/Default Route Settings window
This window shows the following values:
meter Description
a
r
a
P
IP Address
Subnet Mask The cor
Gateway The corresponding Gateway of the IP address entered into the table.
Hops Repr
Protocol Represents the protocol used for the Routing Table entry of the IP interface.This field may read OSPF, RIP,
up State
Back
Delete Click the 8 if you would like to delete this entry from the Static/Default Route Settings table.
To enter an IP Interface into the Switch’s
The IP address of the Static/Default Route.
ess entered into the table.
esponding Subnet Mask of the IP ad
r
esents the metric value of the IP interface enter
65535 for an OSPF setting, and 1-16 for a RIP setting.
Static or Local.
esents the Backup state that this IP interface is configur
Repr
Static/Default Routes window,click the Add button, revealing the following window to configure.
dr
ed into the table.This field may read a number between 1-
This field may read Primary or Backup.
.
or
ed f
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
97
Page 99

The following fields can be set:
Parameter Description
Figure 6- 91. Static/Default Route Settings – Add window
IP Address
Subnet Mask Allows the entry of a subnet mask corresponding to the IP address above.
Gateway IP Allows the entry of an IP address of a gateway for the IP address above.
Metric (1-65535) Allows the entry of a routing protocol metric representing the number of routers between the Switch and the
Backup State The user may choose between Primary and Backup.If the Primary Static/Default Route fails, the Backup Route
Apply to implement changes made.
Click
Allows the entry of an IP address that will be a static entry into the Switch’s Routing Table.
IP address above.
will support the entry. Please take note that the Primary and Backup entries cannot have the same Gateway.
Route Preference Settings
Route Preference is a way for routers to select the best path when there are two or more different routes to the same destination from two different routing
protocols.The majority of routing protocols are not compatible when used in conjunction with each other.This Switch supports and may be configured for many
routing protocols,as a stand-alone switch or more importantly, in utilizing the stacking function and Single IP Management of the Switch.Therefore, the ability to
exchange route information and select the best path is essential to optimal use of the Switch and its capabilities.
The first decision the Switch will make in selecting the best path is to consult the Route Preference Settings table of the switch.This table can be viewed by
Configuration > Layer 3 IP Networking > Route Preference Settings, and it holds the list of possible routing protocols currently
clicking
implemented on the Switch, along with a
list of the default r
Route T
Local 0 – P
Static 1 – 999 60
OSPF Intra
OSPF Inter 1 – 999 90
RIP 1 – 999 100
OSPF ExtT1 1 – 999 110
OSPF ExtT2 1 – 999 115
oute pr
ype Validity Range Default Value
ences set on the Switch.
er
ef
Preference value which determines which routing protocol will be the most dependable to route packets.Below is a
nently set on the switch and unconfigurable.
erma
1 – 999
0
80
able 6- 8.
T
wn above, Local will always be the first choice for routing purposes and the next most reliable path is Static due to the fact that its has the next lowest
As sho
o set a higher reliability for a route,change its value to a number less than the value of a route preference that has a greater reliability value using the
T
.
value
New Route Preference Settings windo
one that is less than the lowest value (Static - 60) or the user could change the other route values to more than 100.
The user should be aware of three points before configuring the route preference:
1. No two route preference values can be the same. Entering the same route preference may cause the switch to crash due to indecision by the switch.
2. If the user is not fully aware of all the features and functions of the routing protocols on the switch, a change in the default route preference value
may cause routing loops or black holes.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
w command.
or example
F
Route Pr
if the user wishes to make RIP the most reliable route,the user can change its value to
,
erence Table
ef
98
Page 100

3. After changing the route preference value for a specific routing protocol, that protocol needs to be restarted because the previously learned routes
have been dropped from the Switch.The Switch must learn the routes again before the new settings can take effect.
To view the
Route Preference Settings window, click Configuration > Layer 3 IP Networking > Route Preference Settings:
Figure 6- 92. Current and New Route Preference Settings window
The following fields can be viewed or set:
Parameter Description
RIP (1-999)
Enter a value between 1 and 999 to set the route preference for RIP.The lower the value, the higher the chance
the specified protocol will be chosen as the best path for routing packets.The default value is 100.
OSPF Intr
a (1-999)
Enter a value betw
een 1 and 999 to set the r
oute pr
er
ef
ence for
OSPF Intra.
The lo
er the value
w
the higher the
,
chance the specified protocol will be chosen as the best path for routing packets.The default value is 80.
STATIC (1-999) Enter a value between 1 and 999 to set the route preference for Static.The lower the value,the higher the
chance the specified protocol will be chosen as the best path for routing packets.The default value is 60.
OSPF Inter (1-999) Enter a value between 1 and 999 to set the route preference for OSPF Inter.The lower the value, the higher the
chance the specified protocol will be chosen as the best path for routing packets.The default value is 90.
OSPF ExtT1 (1-999) Enter a value between 1 and 999 to set the route preference for OSPF ExtT1.The lower the value, the higher
the chance the specified protocol will be chosen as the best path for routing packets.The default value is 110.
OSPF ExtT2 (1-999) Enter a value between 1 and 999 to set the route preference for OSPF ExtT2.The lower the value, the higher
the chance the specified protocol will be chosen as the best path for routing packets.The default value is 115.
Click
pply
A
to implement changes made
.
Allied Telesyn AT-9724TS High-Density Layer 3 Stackable Gigabit Ethernet Switch
99
 Loading...
Loading...