Page 1

NetExtreme II
Family Adapters
AT-2973SX
AT-2973T
AT-2973T/4
Installation and User’s Guide
613-001252 Rev. A
Page 2

Copyright 2010 Allied Telesis, Inc.
All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced without prior written permission from Allied Telesis, Inc.
®
Broadcom
and the pulse logo are among the trademarks of Broadcom Corporation. All other product names, company names,
logos or other designations mentioned herein are trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Page 3
Electrical Safety and Emissions Standards
This product meets the following standards.
Federal Communications Commission Interference Statement
Declaration of Conformity
Manufacturer Name: Allied Telesis, Inc.
Declares that the product: NetExtreme II Family Adapters
Model Numbers: AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, AT-2973T/4
This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to Part 15 of
FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential
installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in
accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio or television reception. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this equipment does cause harmful interference to
radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, the user is encouraged to try
to correct the interference by one of the following measures:
- Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
- Increase the separation between the equipment and the receiver.
- Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
- Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
This device complies with part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation is subject to the following two conditions:
(1) This device must not cause harmful interference, and
(2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause undesired operation.
FCC Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance could void
the user’s authority to operate this equipment.
IMPORTANT NOTE:
FCC Radiation Exposure Statement:
This equipment complies with FCC radiation exposure limits set forth for an uncontrolled environment. End users must
follow the specific operating instructions for satisfying RF exposure compliance.
This transmitter must not be co-located or operating in conjunction with any other antenna or transmitter.
IEEE802.11b or 802.11g operation of this product in the U.S.A. is firmware-limited to channels 1 through 11.
Industry Canada
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
European Union Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous Substances
(RoHS) in Electrical and Electronic Equipment
This Allied Telesis RoHS-compliant product conforms to the European Union Restriction of the Use of Certain Hazardous
Substances (RoHS) in Electrical and Electronic Equipment. Allied Telesis ensures RoHS conformance by requiring
supplier Declarations of Conformity, monitoring incoming materials, and maintaining manufacturing process controls.
3
Page 4

RFI Emissions FCC Class B, EN55022 Class B, VCCI Class B, C-TICK, CE
Immunity EN55024
Electrical Safety EN60950-1 (TUV), UL 60950-1 (
Laser Safety EN60825
CULUS
)
Translated Safety Statements
Important: The indicates that a translation of the safety statement is available in a PDF
document titled “Translated Safety Statements” on the Allied Telesis website at
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software. After you have accessed this website, enter the model
number in the Search by Product Name box and then click Find to view the current list of
documents.
4
Page 5

Contents
Preface ................................................................................................................................................................................11
Safety Symbols Used in this Document................................................................................................................................12
Where to Find Web-based Guides .......................................................................................................................................13
Contacting Allied Telesis ......................................................................................................................................................14
Online Support ..............................................................................................................................................................14
Email and Telephone Support .......................................................................................................................................14
Returning Products........................................................................................................................................................14
For Sales or Corporate Information...............................................................................................................................14
Warranty........................................................................................................................................................................14
Management Software Updates ....................................................................................................................................14
Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 Adapters .............................................................15
Functional Descriptions ........................................................................................................................................................16
AT-2973SX Adapter ......................................................................................................................................................17
AT-2973T Adapter.........................................................................................................................................................18
AT-2973T/4 Adapter......................................................................................................................................................20
Features ...............................................................................................................................................................................22
TCP Offload Engine (TOE)............................................................................................................................................23
Internet Small Computer Systems Interface (iSCSI) .....................................................................................................24
Power Management ......................................................................................................................................................24
Wake on LAN (WOL) Feature .......................................................................................................................................24
Adaptive Interrupt Frequency ........................................................................................................................................25
ASIC with Embedded RISC Processor..........................................................................................................................25
Supported Operating Environments ..............................................................................................................................25
Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware ..................................................................................................................................27
Reviewing the Contents of Your Shipment...........................................................................................................................28
Reviewing Safety Precautions..............................................................................................................................................29
Pre-Installation Checklist ......................................................................................................................................................31
Replacing the Bracket ..........................................................................................................................................................32
Installing a Network Adapter Card ........................................................................................................................................34
Connecting the Network Cables ...........................................................................................................................................38
Chapter 3: Installing Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software .......................................................................................41
Overview...............................................................................................................................................................................42
Setting Up MBA in a Client Environment..............................................................................................................................43
Enabling the MBA Driver ...............................................................................................................................................43
Configuring the MBA Driver...........................................................................................................................................43
Setting Up the BIOS ......................................................................................................................................................44
Setting Up MBA in a Server Environment: Red Hat Linux PXE Server................................................................................45
Chapter 4: Installing the Monolithic Software Driver .....................................................................................................47
Using the NetXtreme II Monolithic Driver..............................................................................................................................48
Inserting the NetXtreme II Monolithic Driver in a WinPE 2.0 Image .....................................................................................50
Configuring the Speed and Duplex Settings.........................................................................................................................52
Chapter 5: Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software .............................................................................................................55
Overview...............................................................................................................................................................................56
Checking Pre-installation Requirements...............................................................................................................................57
Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software on MS-DOS Platforms................................................................................................58
Creating a Startup Disk .................................................................................................................................................58
Modifying the Startup Disk ............................................................................................................................................59
5
Page 6

Contents
Installing the DOS NDIS2 Driver Software ....................................................................................................................61
Using Keywords for the Drivers ............................................................................................................................................63
Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers ............................................................................................................................65
Overview...............................................................................................................................................................................66
Limitations .....................................................................................................................................................................66
Packaging......................................................................................................................................................................67
Installing Linux Driver Software ............................................................................................................................................68
Installing the Source RPM Package ..............................................................................................................................68
Building the Driver from the Source TAR File................................................................................................................70
Load and Run Necessary iSCSI Software Components ...............................................................................................72
Unloading the Linux Driver ............................................................................................................................................72
Patching PCI Files (Optional) ........................................................................................................................................73
Network Installations .....................................................................................................................................................74
Setting Values for Optional Properties...........................................................................................................................74
Checking the bnx2 Driver Defaults ................................................................................................................................77
Checking Driver Messages............................................................................................................................................78
Teaming with Channel Bonding.....................................................................................................................................82
Statistics ........................................................................................................................................................................82
Linux iSCSI Offload .......................................................................................................................................................82
Chapter 7: Installing the Windows Drivers ......................................................................................................................87
Installing the Windows Driver Software ................................................................................................................................88
Using the Installer..........................................................................................................................................................89
Using Silent Installation .................................................................................................................................................94
Removing the Device Drivers ....................................................................................................
...........................................97
Chapter 8: Setting Advanced Properties .........................................................................................................................99
Accessing the Advanced Tab .............................................................................................................................................100
Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Server 2003................................................................................................100
Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows 7 ..........................103
Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Vista ...........................................................................................................104
Modifying Advanced Properties ..........................................................................................................................................107
Updating the Ethernet@
WireSpeed Property............................................................................................................................................................108
Updating the Flow Control Property.............................................................................................................................108
Updating the Interrupt Moderation Property ................................................................................................................110
Updating the Checksum Offload Property ...................................................................................................................111
Updating the Large Send Offload Property .................................................................................................................112
Updating the Jumbo MTU Property .............................................................................................................................113
Updating the Network Address Property .....................................................................................................................114
Updating the RSS Queues Property............................................................................................................................115
Updating the Priority & VLAN Property........................................................................................................................116
Updating the Receive Buffers Property .......................................................................................................................117
Updating the Receive Side Scaling Property...............................................................................................................117
Updating the Speed & Duplex Mode Property.............................................................................................................118
Updating the TCP Connection Offload Properties.......................................................................................................120
Updating the Transmit Buffers Property ......................................................................................................................121
Updating the VLAN ID Property...................................................................................................................................121
Chapter 9: Installing CIM and SNMP for Manageability ...............................................................................................123
Installing CIM ......................................................................................................................................................................124
Loading the CIM Libraries ...........................................................................................................................................125
Installing SNMP ..................................................................................................................................................................127
BASP Subagent..................................................................................................................
BASP Extensible-Agent...............................................................................................................................................127
Loading the SNMP Libraries........................................................................................................................................128
.........................................127
Chapter 10: Installing Management Applications .........................................................................................................131
Installing Broadcom Advanced Control Suite 3 and Related Management Applications....................................................132
Checking .NET Framework Requirements ..................................................................................................................133
Using the Installer........................................................................................................................................................134
6
Page 7

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Using the Silent Install Option .....................................................................................................................................134
Modifying Management Applications..................................................................................................................................137
Repairing Management Applications..................................................................................................................................138
Removing Management Applications .................................................................................................................................139
Chapter 11: Troubleshooting ..........................................................................................................................................141
Checking Hardware Diagnostics.........................................................................................................................................142
Checking Port LEDs ...........................................................................................................................................................143
Consulting the Troubleshooting Checklist ..........................................................................................................................144
Checking Current Drivers ............................................................................................................................................144
Running a Cable Length Test......................................................................................................................................145
Testing Network Connectivity......................................................................................................................................145
Solving Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V Issues .............................................................................................147
Single Network Adapter...............................................................................................................................................147
Teamed Network Adapters..........................................................................................................................................147
Removing the Device Drivers......................................................................................................................................148
Upgrading from Windows Server 2000 to Windows Server 2003 ...............................................................................148
Preparing an Answer File ............................................................................................................................................148
Solving Broadcom Boot Agent and Broadcom Advanced Server Program (BASP) Issues................................................150
Solving Miscellaneous Issues.............................................................................................................................................152
Chapter 12: User Diagnostics .........................................................................................................................................155
Overview.............................................................................................................................................................................156
System Requirements ........................................................................................................................................................157
Performing Diagnostics.......................................................................................................................................................158
Diagnostic Test Descriptions ..............................................................................................................................................161
Appendix A: Specifications ............................................................................................................................................167
Physical Specifications .......................................................................................................................................................167
Environmental Specifications...................................................................................................
Power Specifications ..........................................................................................................................................................168
Performance Specifications................................................................................................................................................168
Operating Specifications.....................................................................................................................................................168
10/100/1000Base-T Twisted-Pair Port Connectors ............................................................................................................168
Appendix B: Cleaning Fiber Optic Connectors ............................................................................................................171
Using a Cartridge-Type Cleaner.........................................................................................................................................172
Using a Swab .....................................................................................................................................................................174
...........................................167
7
Page 8

Contents
8
Page 9

Figures
Figure 1. AT-2973SX Adapter .............................................................................................................................................17
Figure 2. AT-2973SX Faceplate ..........................................................................................................................................17
Figure 3. AT-2973T Adapter ................................................................................................................................................18
Figure 4. AT-2973T Faceplate.............................................................................................................................................19
Figure 5. AT-2973T/4 Adapter .............................................................................................................................................20
Figure 6. AT-2973T/4 Faceplate..........................................................................................................................................21
Figure 7. Removing the Low-Profile Bracket .......................................................................................................................32
Figure 8. Fastening Screws onto Standard Bracket ............................................................................................................33
Figure 9. Removing the PC Cover.......................................................................................................................................35
Figure 10. Removing the Faceplate From PCI Slot .............................................................................................................35
Figure 11. Inserting the Adapter with a High-profile Bracket ...............................................................................................36
Figure 12. Securing the Adapter with a High-profile Bracket...............................................................................................37
Figure 13. Found New Hardware Wizard Page...................................................................................................................90
Figure 14. Broadcom NetXtreme II Driver Installer - InstallShield Wizard Page..................................................................91
Figure 15. License Agreement Page ...................................................................................................................................92
Figure 16. Ready to Install the Program Page.....................................................................................................................93
Figure 17. InstallShield Wizard Completed Page ................................................................................................................94
Figure 18. System Properties Dialog Box..........................................................................................................................101
Figure 19. Advanced Tab ..................................................................................................................................................102
Figure 20. Windows Server 2008, Windows Server 2008 R2, and Windows 7 Search Box .............................................103
Figure 21. Device Manager Window..................................................................................................................................104
Figure 22. Windows Vista Start Menu ...............................................................................................................................105
Figure 23. Windows Vista Run Window.............................................................................................................................105
Figure 24. BACS CIM Option Window...............................................................................................................................126
Figure 25. BACS SNMP Option Window...........................................................................................................................129
Figure 26. RJ-45 Connector and Port Pin Layout..............................................................................................................168
Figure 27. Ferrule in an SC Connector Plug......................................................................................................................171
Figure 28. Unclean and Clean Ferrule...............................................................................................................................171
Figure 29. Cartridge Cleaner .............................................................................................................................................172
Figure 30. Rubbing the Ferrule Tip on the Cleaning Surface ............................................................................................172
Figure 31. Lint-Free and Alcohol-Free Swabs ...................................................................................................................174
Figure 32. Cleaning a Recessed Ferrule...........................................................................................................................174
9
Page 10

Figures
10
Page 11

Preface
This guide contains instructions on how to install the AT-2973SX,
AT-2973T, AT-2973T/4 adapters and configure the adapters using the
driver software.
The Preface discusses the following topics:
“Safety Symbols Used in this Document” on page 12
“Where to Find Web-based Guides” on page 13
“Contacting Allied Telesis” on page 14
“Management Software Updates” on page 14
11
Page 12

Preface
Safety Symbols Used in this Document
This document uses the safety symbols defined in Table 1.
Table 1. Safety Symbols
Symbol Meaning Description
Caution Performing or omitting a specific action may
result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warning Performing or omitting a specific action may
result in electrical shock.
12
Page 13

AT-2973SX,, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Where to Find Web-based Guides
The installation and user guides for all Allied Telesis products are available
in portable document format (PDF) on our web site at
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software. After you have accessed this
website, enter the model number in the Search by Product Name box
and then click Find to view the current list of documents.
13
Page 14

Preface
Contacting Allied Telesis
This section provides Allied Telesis contact information for technical
support as well as sales or corporate information.
Online Support You can request technical support online by accessing the Allied Telesis
Knowledge Base: www.alliedtelesis.com/support/kb.aspx. You can use
the Knowledge Base to submit questions to our technical support staff and
review answers to previously asked questions.
Email and
Telephone
Support
Returning
Products
For Sales or
Corporate
Information
Warranty Go to www.alliedtelesis.com/warranty for the specific terms and
Management
Software Updates
For Technical Support via email or telephone, refer to the Support section
of the Allied Telesis web site: www.alliedtelesis.com/support.
Products for return or repair must first be assigned a return materials
authorization (RMA) number. A product sent to Allied Telesis without an
RMA number will be returned to the sender at the sender’s expense. For
instructions on how to obtain an RMA number, go to the Support section
on our web site at www.alliedtelesis.com/support/rma.aspx.
You can contact Allied Telesis for sales or corporate information through
our web site at http://www.alliedtelesis.com/purchase.
conditions of the warranty and for warranty registration for the AT-2973SX,
AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 adapters.
New releases of management software for our managed products are
available from both of the following web sites:
14
Allied Telesis web site: www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software/
Allied Telesis FTP server:ftp://ftp.alliedtelesis.com
If you prefer to download new software from the Allied Telesis FTP server
from your workstation’s command prompt, you will need FTP client
software and you must log in to the server. Enter “anonymous” for the user
name and your email address for the password.
Page 15

Chapter 1
Introducing the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 Adapters
This chapter provides an introduction to the Allied Telesis AT-2973SX,
AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters and discusses
the following topics:
“Functional Descriptions” on page 16
“Features” on page 22
15
Page 16

Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 Adapters
Functional Descriptions
The AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 Broadcom NetXtreme II
adapters are a new class of Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) converged network
interface controller (C-NIC) that can simultaneously perform accelerated
data networking and storage networking on a standard Ethernet network.
The C-NIC offers acceleration for all popular protocols used in the data
center, such as:
TCP Offload Engine (TOE) for accelerating TCP
Internet Small Computer Systems Interface (iSCSI) offload for
accelerating network storage access featuring centralized boot
functionality (iSCSI boot)
Enterprise networks that use multiple protocols and multiple network
fabrics benefit from the C-NICs ability to combine data communications,
storage, and clustering over a single Ethernet fabric by boosting server
CPU processing performance and memory utilization while alleviating I/O
bottlenecks.
The AT-2973SX adapter is set to a speed of 1000 Mbps in full duplex
mode automatically. You cannot change the speed or duplex mode of this
adapter.
The AT-2973T and AT-2973T/4 adapters include a 10/100/1000-Mbps
Ethernet MAC with both half-duplex and full-duplex capability and a 10/
100/1000-Mbps PHY. The transceiver is fully compatible with the IEEE
802.3 standard for auto-negotiation of speed.
As part of the company’s green range, all of three adapters are
engineered to reduce power consumption. They incorporate centralized
power management features that automatically place idle circuitry into a
lower power mode to save energy.
The following sections provide functional descriptions of the AT-2973SX,
AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 adapters:
“AT-2973SX Adapter” on page 17
“AT-2973T Adapter” on page 18
“AT-2973T/4 Adapter” on page 20
16
Page 17
AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
1696
100
ACT LNK
ATI
100
ACT LNK
AT-2973SX
Adapter
The AT-2973SX adapter connects a PCI-E compliant server or workstation
to a Gigabit Ethernet network using fiber optic cabling and a connector that
meets 62.5/125 µm or 50/125 µm multimode specifications. This adapter
operates at speeds of 1000 Mbps in full-duplex mode.
The AT-2973SX adapter is show in Figure 1.
Figure 1. AT-2973SX Adapter
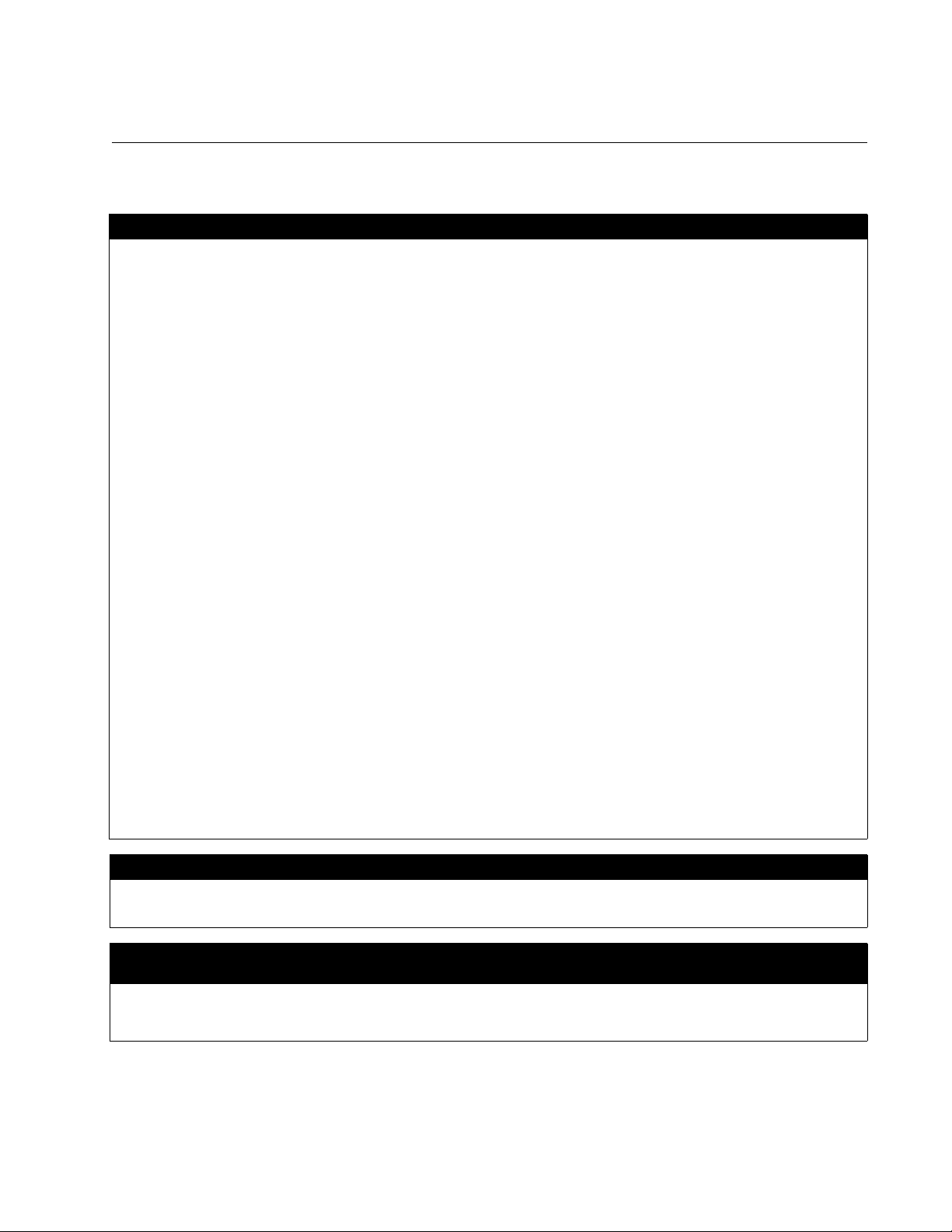
AT-2973SX Adapter Physical Description
The faceplate on the AT-2973SX adapter provides two fiber optic
connectors for attaching the adapter to a compatible link partner. See
Figure 2 for an illustration of the adapter’s faceplate.
The AT-2973SX adapter has two fiber ports and two LEDs per port, as
shown in Figure 2 and described in Table 1 on page 18. The state of the
network link and activity is indicated by a single LED located adjacent to
the port connector.
1699
Figure 2. AT-2973SX Faceplate
17
Page 18
Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 Adapters
For AT-2973SX LED information, see Table 1.
Table 1. Network Link and Activity Indicated by the RJ-45 Port LEDs
Port LED LED Appearance Network State
Link LED Off No link (cable disconnected)
AT-2973T
Adapter
Continuously
Link
illuminated
Activity LED Off No network activity
Blinking No network activity
The AT-2973T adapter operates at speeds of 10/100/1000T Mbps in both
full-duplex and half-duplex modes. This adapter has two twisted-pair
connectors and two LEDs, as shown in Figure 3.
L/A 1
100
L/A 2
18
ATI
1700
Figure 3. AT-2973T Adapter
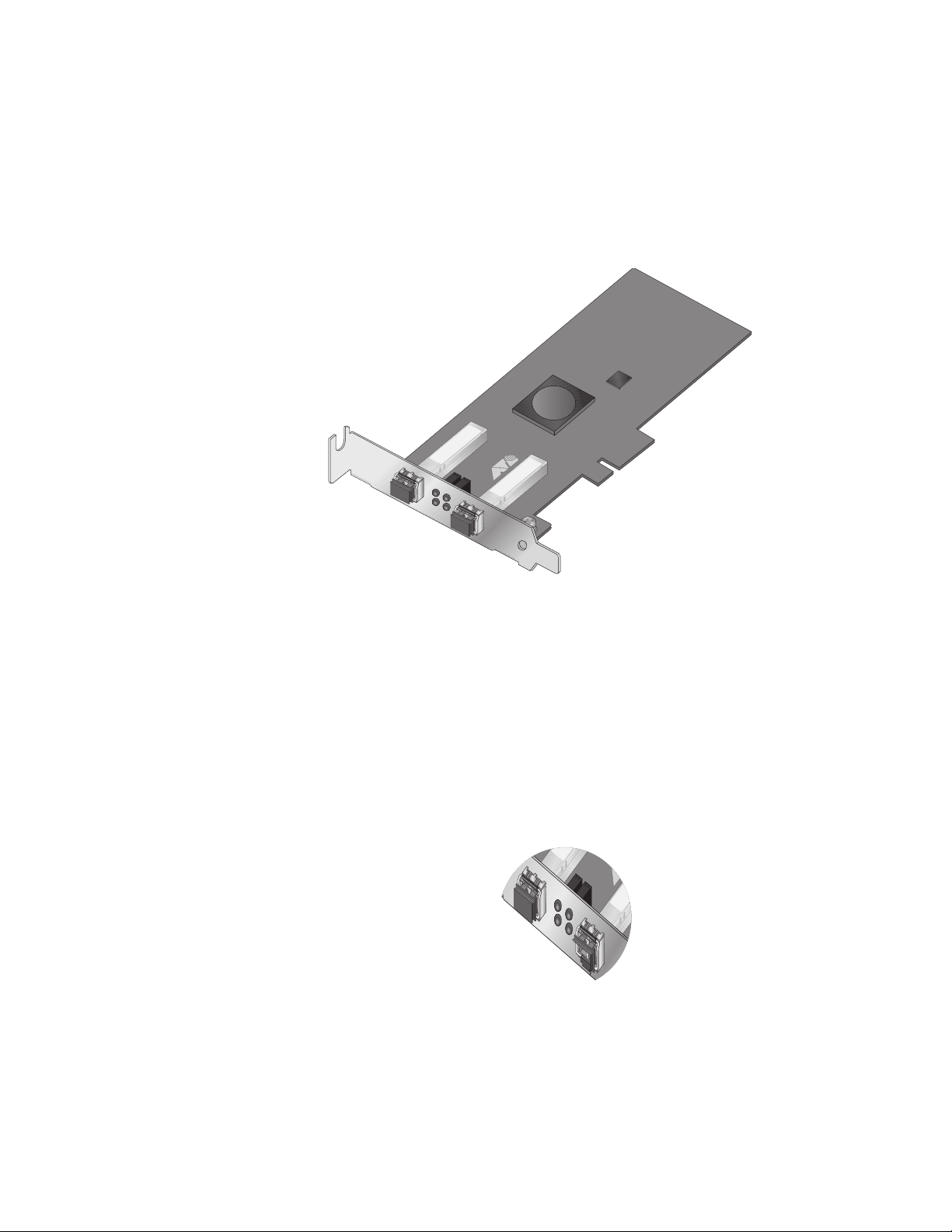
AT-2973T Adapter Physical Description
The faceplate on the AT-2973T adapter provides two twisted-pair
connectors for attaching the adapter to a compatible link partner. See
Figure 4 on page 19 for an illustration of the adapter’s faceplate and LEDs.
Page 19
AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
100
L/A 1
L/A 2
1701
Figure 4. AT-2973T Faceplate
For copper-wire Ethernet connections, the state of the network link and
activity is indicated by the LEDs on the RJ-45 connector. The LED labeled
L/A1 indicates port 1 and the LED labeled L/A2 indicates port 2. See
Table 2.
Table 2. Network Link and Activity Indicated by the RJ-45 Port LEDs
Port LED LED Appearance Network State
Link LED Off No link (cable disconnected)
Continuously
illuminated
Activity LED Off No network activity
Blinking No network activity
Link
19
Page 20
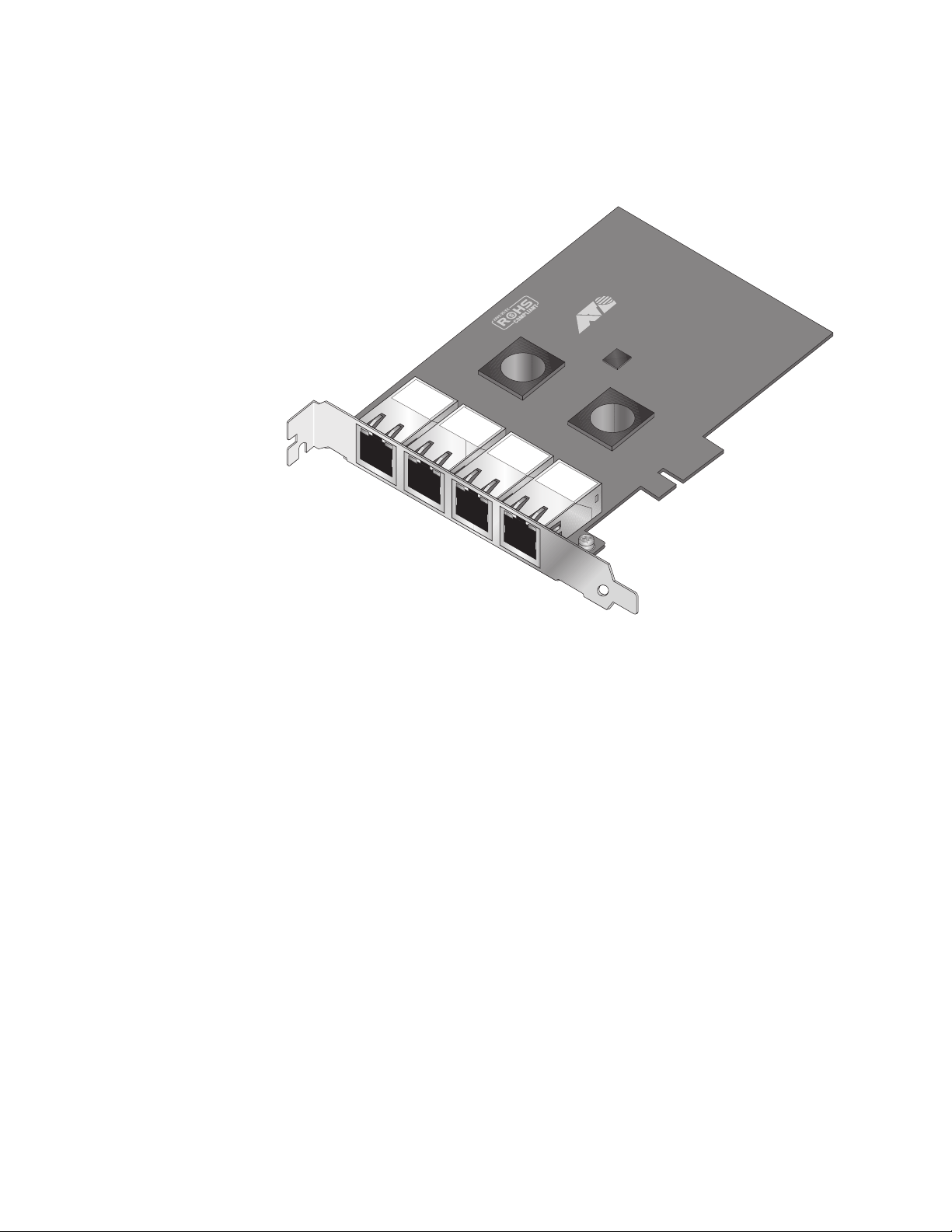
Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 Adapters
AT-2973T/4
Adapter
The AT-2973T/4 adapter is a PCI-Express adapter that operates at
speeds of 10/100/1000T Mbps in both full-duplex and half-duplex modes.
This adapter has four twisted-pair connectors and eight LEDs, as shown in
Figure 5.
LNK
T
ACT
AT I
1861
Figure 5. AT-2973T/4 Adapter
20
Page 21
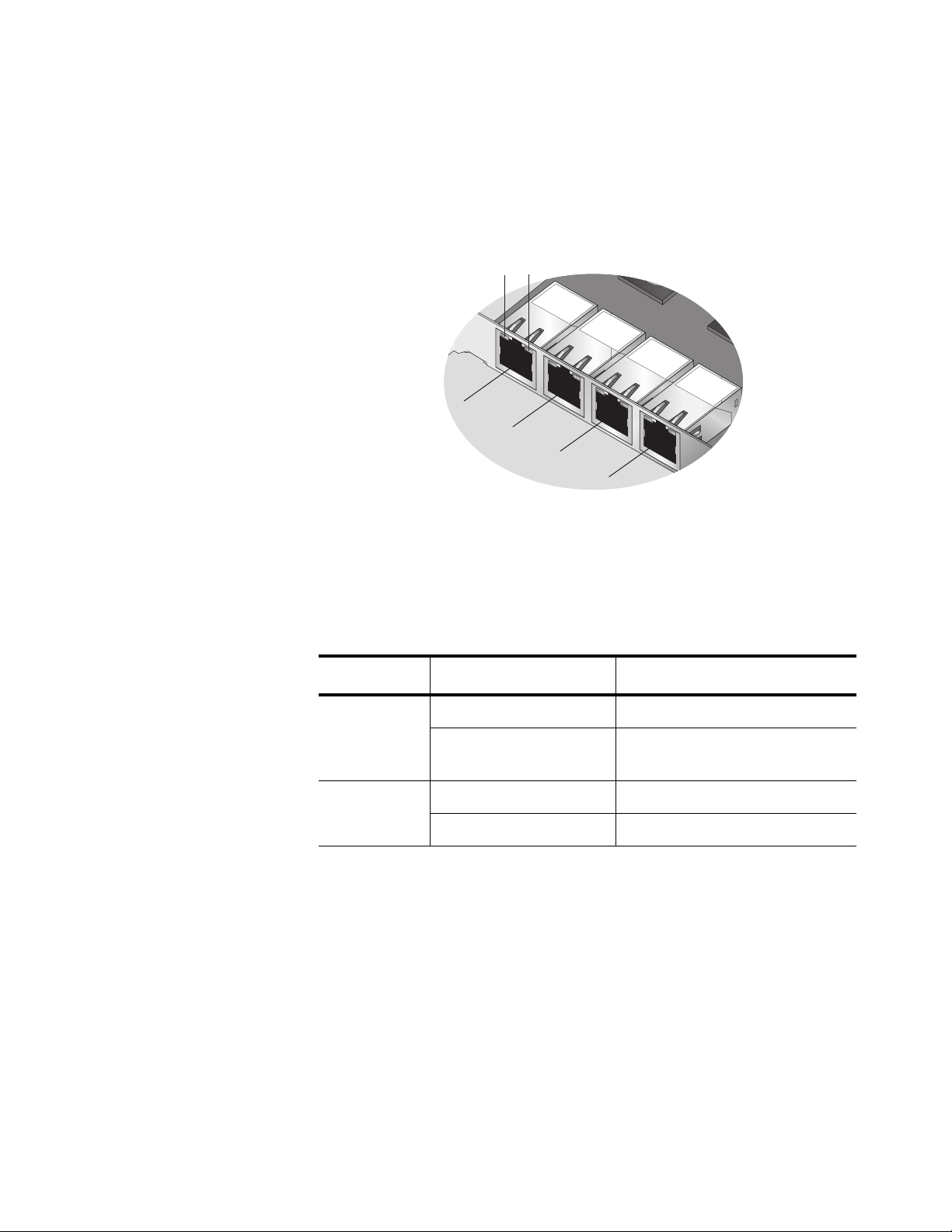
AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
T
LNK
ACT
AT-2973T/4 Adapter Physical Description
The faceplate on the AT-2973T/4 adapter provides four twisted-pair
connectors for attaching the adapter to a compatible link partner. The ports
numbers are not shown on the card. See Figure 6 for the port numbers
and the LED assignments. When the adapter is mounted vertically, the top
LED is the Link LED and the bottom LED is the activity (ACT) LED.
LINK ACT
PORT 1
PORT 2
PORT 3
PORT 4
1862
Figure 6. AT-2973T/4 Faceplate
For copper-wire Ethernet connections, the state of the network link and
activity is indicated by the LEDs on the RJ-45 connector, as described in
Table 3.
Table 3. Network Link and Activity Indicated by the RJ-45 Port LEDs
Port LED LED Appearance Network State
Link LED Off No link (cable disconnected)
Continuously
Link
illuminated
Activity LED Off No network activity
Blinking Network activity
21
Page 22

Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 Adapters
Features
The following list of features for the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, AT-2973T/4
adapters applies to all of the supported operating systems:
TCP Offload Engine (TOE)
Internet Small Computer Systems Interface (iSCSI) offload
Single-chip solution
– Integrated 10/100/1000BASE-T transceivers
– 10/100/1000 triple-speed MAC
– Host interfaces
– SerDes interface for optical transceiver
connection
– PCI Express v1.1 x4 and v2.0 compliant (Gigabit
Ethernet)
– Full fast-path TCP offload
Other performance features
– TCP, IP, UDP checksum
– TCP segmentation
– Adaptive interrupts
– Receive Side Scaling (RSS)
Manageability
– Broadcom Advanced Control Suite (BACS) 3
diagnostic and configuration software suite
– Supports PXE 2.0 specification (Linux Red
Hat PXE Server, SUSE Linux Enterprise
Server, Windows Server 2000, Windows Server
2003, Windows Server 2008, Windows Server
2008 R2, Intel APITEST, DOS UNDI)
22
– Wake on LAN support
– Statistics for Simple Network Management
Protocol (SNMP) MIB II, Ethernet-like MIB, and
Ethernet MIB (IEEE Std 802.3z, Clause 30)
Page 23

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
– SMBus controller
– ACPI 1.1a compliant (multiple power modes)
– IPMI support
Advanced network features
– Jumbo frames (up to 9 KB). The OS and the link
partner must support jumbo frames.
– Virtual LANs
– IEEE Std 802.3ad Teaming
– Smart Load Balancing Teaming
– Smart Load Balancing TOE Teaming (with the
correct configuration)
– Flow Control (IEEE Std 802.3x)
TCP Offload
Engine (TOE)
– LiveLink™ (supported in both the 32-bit and 64-bit
Windows operating systems)
– Logical Link Control (IEEE Std 802.2)
Layer-2 Priority Encoding (IEEE Std 802.1p)
High-speed on-chip RISC processor
Up to 4 classes of service (CoS)
Integrated 96 KB frame buffer memory
iSCSI Boot support
The TCP/IP protocol suite is used to provide transport services for a wide
range of applications for the Internet, LAN, and for file transfer. The TCP
protocol is specifically designed to insure that data packets are delivered
error free and in the correct sequence from an application running a one
computer to the receiving application. The TCP protocol suite historically
has run on the host CPU, but with higher data rates, this consumes a very
high percentage of its resources while leaving little resources for the
applications. With the use of the Broadcom NetXtreme II adapter and the
TCP Offload Engine feature, the TCP/IP processing can be moved to
hardware, freeing the CPU for application processing and other higher
priority tasks
.
The TCP/IP protocol suite is used to provide transport services for a wide
range of applications for the Internet, LAN, and for file transfer. Without the
TCP Offload Engine, the TCP/IP protocol suite runs on the host CPU,
consuming a very high percentage of its resources and leaving little
resources for the applications. With the use of the Broadcom NetXtreme II
23
Page 24

Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 Adapters
Note
adapter, the TCP/IP processing can be moved to hardware, freeing the
CPU for more important tasks such as application processing.
The Broadcom NetXtreme II adapter's TOE functionality allows
simultaneous operation of up to 1024 fully offloaded TCP connections for
1-Gbps network adapters. The TOE support on the adapter significantly
reduces the host CPU utilization while preserving the implementation of
the operating system stack.
Internet Small
Computer
Systems Interface
(iSCSI)
Power
Management
The IETF has standardized the Internet Small Computer Systems
Interface (iSCSI). SCSI is a popular protocol that enables systems to
communicate with storage devices, using block-level transfer (that is,
address data stored on a storage device that is not a whole file). In
addition, iSCSI maps the SCSI request and response application
protocols and its standardized command set over TCP/IP networks.
As iSCSI utilizes TCP as its sole transport protocol, it greatly benefits from
hardware acceleration of the TCP processing (that is, use of a TOE).
However, iSCSI as a Layer 5 protocol has additional mechanisms beyond
the TCP layer. iSCSI processing can also be offloaded, thereby reducing
CPU utilization even further.
The Broadcom NetXtreme II adapter targets best-system performance,
maintains system flexibility to changes, and supports current and future
OS convergence and integration. Therefore, the adapter's iSCSI offload
architecture is unique as evident by the split between hardware and host
processing.
When the system is down and waiting for a wake-up signal, the adapter
speed connection may be at 10 Mbps or 100 Mbps. However, it can return
to 1000 Mbps when the system is up and running if it is connected to a
1000 Mbps capable switch. For this reason, connect systems that use the
Wake on LAN (WOL) feature to a switch capable of both 1000 and 10/100
Mbps speeds.
Wake on LAN
(WOL) Feature
24
The WOL feature sets the speed at which the network adapter connects to
the network while the adapter is in Wake on LAN (WOL) mode which is
enabled automatically. The default speed for WOL mode is 100 Mb. An
adapter can negotiate speeds between 10 Mb and 100 Mb. You cannot
configure this feature because it is enabled automatically.
The WOL feature is supported on the AT-2973T and AT-2973T/4
adapters. It is not supported on the AT-2973SX adapter. For more
information, see “Limitations” on page 66.
Page 25

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
For specific systems, see your system documentation for
information about support of the WOL feature.
Adaptive
Interrupt
Frequency
ASIC with
Embedded RISC
Processor
Supported
Operating
Environments
The adapter driver intelligently adjusts host interrupt frequency based on
traffic conditions to increase overall application throughput. When traffic is
light, the adapter driver interrupts the host for each received packet,
minimizing latency. When traffic is heavy, the adapter issues one host
interrupt for multiple, back-to-back incoming packets, preserving host CPU
cycles.
The core control for Broadcom NetXtreme II adapters resides in a tightly
integrated, high-performance ASIC. The ASIC includes a RISC processor.
This functionality provides the flexibility to add new features to the card
and adapts it to future network requirements through software downloads.
This functionality also enables the adapter drivers to exploit the built-in
host offload functions on the adapter as host operating systems are
enhanced to take advantage of these functions.
The Broadcom NetXtreme II adapter has software support for the following
operating systems:
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows Vista (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows 7 (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 Hyper-V
Linux
MS-DOS
ESX Server (VMware)
Citrix XenServer
(32-bit and 64-bit extended)
25
Page 26

Chapter 1: Introducing the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 Adapters
26
Page 27

Chapter 2
Installing the Hardware
This chapter describes how to install the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and
AT-2973T/4 adapters in a PC and discusses the following topics:
“Reviewing the Contents of Your Shipment” on page 28
“Reviewing Safety Precautions” on page 29
“Pre-Installation Checklist” on page 31
“Replacing the Bracket” on page 32
“Installing a Network Adapter Card” on page 34
“Connecting the Network Cables” on page 38
27
Page 28

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Reviewing the Contents of Your Shipment
The following items are included with your adapter:
Antistatic bag (used for protecting the adapter when stored or
shipped). Keep the adapter in its packaging until ready for installation.
Low-profile bracket (The low-profile bracket is not included with the
AT-2973T/4 adapter.)
Standard bracket
Inform your network supplier of any missing or damaged items. If you
need to return the adapter, you must pack it in the original (or equivalent)
packing material or the warranty will be voided. See “Returning Products”
on page 14.
The documentation for these adapters is available in portable document
format (PDF) on our web site at www.alliedtelesis.com/support/
software. After you have accessed this website, enter the model number
in the Search by Product Name box and then click Find to view the
current list of documents.
28
Page 29

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Warning
Note
Warning
Reviewing Safety Precautions
Please review the following safety precautions before you begin to install a
network adapter card.
The indicates that a translation of the safety statement is
available in a PDF document titled “Translated Safety Statements”
on the Allied Telesis website at www.alliedtelesis.com/support/
software. After you have accessed this website, enter the model
number in the Search by Product Name box and then click Find to
view the current list of documents.
This is a “Class 1 Laser product”. L1
Do not stare into the laser beam. L2
Do not look directly at the fiber optic cable ends or inspect the cable
ends with an optical lens. E29
Do not work on this equipment or cables during periods of lightning
activity. E2
Operating Temperature: This product is designed for a maximum
ambient temperature of 40 degrees C. E7
All Countries: Install this product in accordance with local and
National Electric Codes. E8
The adapter is being installed in a system that operates with
voltages that can be lethal. Before you remove the cover of your
system, you must observe the following precautions to protect
yourself and to prevent damage to the system components.
29
Page 30

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
- Remove any metallic objects or jewelry from your hands and
wrists.
- Make sure to use only insulated or nonconducting tools.
- Verify that the system is powered OFF and unplugged before
accessing internal components.
- Installation or removal of adapters must be performed in a staticfree environment. The use of a properly grounded wrist strap or
other personal antistatic devices and an antistatic mat is strongly
recommended.
30
Page 31

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Caution
Pre-Installation Checklist
Before you install an adapter card, do the following:
1. Verify that your system is using the latest BIOS.
If you acquired the adapter software from the Allied Telesis support
website, enter the path to where the adapter driver files reside on
your system.
2. If your system is active, shut it down.
3. When the system shut down is complete, power OFF and unplug your
system.
4. Holding the adapter card by the edges, remove it from its shipping
package and place it on an antistatic surface.
5. Check the adapter for visible signs of damage, particularly on the
card’s edge connector.
Do not attempt to install a damaged adapter. If the adapter is
damaged, report it to Allied Telesis. See “Contacting Allied Telesis”
on page 14.
31
Page 32

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Note
Replacing the Bracket
Both the AT-2973SX and AT-2973T adapters are shipped with the lowprofile bracket attached to the adapter. In addition, the standard bracket is
included in the shipment. Depending on your PC, you may need to replace
the bracket attached to your adapter.
The following procedure describes how to remove the low-profile bracket
from the adapter and replace it with the standard bracket. You can also
use this procedure to remove the standard bracket and replace it with the
low-profile bracket.
To replace the low-profile bracket with the standard bracket, do the
following:
The AT-2973T/4 adapter is shipped with a standard bracket
attached to the card. A low-profile bracket is not included with this
adapter.
1. Remove the screws that attach the bracket to the adapter. See
Figure 7.
ACT LNK
ATI
1697
Figure 7. Removing the Low-Profile Bracket
32
Page 33

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
1698
ACT LNK
ATI
2. Align the tabs of the standard bracket with the holes on the adapter
and fasten the screws onto the adapter. See Figure 8.
Figure 8. Fastening Screws onto Standard Bracket
33
Page 34

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Note
Note
Warning
Installing a Network Adapter Card
The following instructions apply to installing the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T,
and AT-2973T/4 adapters in most systems. For details about performing
these tasks on your particular system, refer to the manuals that were
supplied with your system.
To perform this procedure, you need to supply a Phillips-head
screw.
The AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 adapters require a
PCIe x4 PC.
To install an AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, or AT-2973T/4 adapter, do the
following:
1. Review the “Pre-Installation Checklist” on page 31 and “Reviewing
Safety Precautions” on page 29.
Before installing the adapter, ensure the system power is OFF and
unplugged from the power outlet, and that proper electrical grounding
procedures have been followed.
High voltage inside the system presents a safety hazard. Make sure
the power is off before removing the cover.
2. Remove the system cover and select any appropriate empty PCI slot.
See Figure 9 on page 35.
If you do not know how to identify an appropriate PCI slot, refer to the
system documentation that was included with your PC.
34
Page 35

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Figure 9. Removing the PC Cover
3. Select an empty, non-shared PCI slot and remove the faceplate.
Keep the faceplate in a safe place. You may need it for future use. See
Figure 10.
Figure 10. Removing the Faceplate From PCI Slot
If you cannot locate or do not know how to find an appropriate PCI
slot, refer to the documentation that came with your system.
35
Page 36

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Caution
Caution
4. Remove the network adapter card from the shipping package and
store the packaging material in a safe location.
Wear a grounding device and observe electrostatic discharge
precautions when installing the network adapter card in a system.
Failure to observe this caution could result in damage to the card.
5. Applying even pressure at both corners of the card, push the adapter
card until it is firmly seated in the appropriate PCI slot.
Make sure the card is securely seated. To insert the network adapter
card, see Figure 11.
36
Figure 11. Inserting the Adapter with a High-profile Bracket
Do not use excessive force when seating the card, because this
may damage the system or the adapter. If the card resists seating,
remove it from the system, realign it, and try again.
6. Secure the network adapter card to the chassis with a Phillips-head
screw (not provided). See Figure 12 on page 37.
Page 37

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Figure 12. Securing the Adapter with a High-profile Bracket
7. Replace the system’s cover and secure it with the screws removed in
Step 2.
8. Disconnect any personal antistatic devices.
9. Power the system on.
Once the system returns to proper operation, the adapter hardware is
fully installed. Next, connect the network cables. See “Connecting the
Network Cables” on page 38.
37
Page 38

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
Note
Warning
Note
Connecting the Network Cables
After you install the adapter in your PC, attach the system to a compatible
link partner or an IEEE 802.3z compliant Gigabit Ethernet switch.
The AT-2973SX adapter has two fiber optic connectors, each with a
transmit and receive connector. This adapter requires a fiber optic cable.
For cable specifications, see the AT-2973SX adapter data sheet.
For information about cleaning a fiber optic connector, see Appendix
B “Cleaning Fiber Optic Connectors” on page 171.
The AT-2973T adapter has two twisted-pair connectors and the
AT-2973T/4 adapter has four twisted-pair connectors. Both adapters
require twisted-pair cables. For pin signals and pinout information, see
“10/100/1000Base-T Twisted-Pair Port Connectors” on page 168.
To connect the network cables to an AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, or
AT-2973T/4 adapter, do the following:
The fiber optic ports contain a Class 1 laser device. When the ports
are disconnected, always cover them with the provided plug.
Exposed ports may cause skin or eye damage. L4
1. Connect one end of the cable to the adapter.
– For the AT-2973SX adapter, use a fiber optic
cable.
– For the AT-2973T and AT-2973T/4 adapters, use
a twisted-pair cable.
2. For the AT-2973SX adapter, connect the other end of the cable to the
appropriate Ethernet fiber optic port. For the AT-2973T and
AT-2973T/4 adapters, connect the other end of the cable to another
twisted pair port.
38
After the cable is properly connected at both ends, the adapter port
LEDs should be functional. See “AT-2973SX Adapter Physical
Description” on page 17, “AT-2973T Adapter Physical Description”
on page 18, or “AT-2973T/4 Adapter Physical Description” on
page 21 for a description of LED operation for each adapter model.
Page 39

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
After you connect the system to the network and power is supplied, the
AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 adapters attempt to establish
the connection at 1000 Mbps in full-duplex mode.
39
Page 40

Chapter 2: Installing the Hardware
40
Page 41

Chapter 3
Installing Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software
This chapter provides information about how to install the Broadcom Boot
Agent Driver Software and discusses the following topics:
“Overview” on page 42
“Setting Up MBA in a Client Environment” on page 43
“Setting Up MBA in a Server Environment: Red Hat Linux PXE Server”
on page 45
41
Page 42

Chapter 3: Installing Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software
Overview
The AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetXtreme II Family
adapters support Preboot Execution Environment (PXE). Multi-Boot Agent
(MBA) is a software module that allows your network computer to boot
with the images provided by remote servers across the network. The
Broadcom MBA driver complies with PXE 2.1 code.
The MBA module operates in a client/server environment. A network
consists of one or more boot servers that provide boot images to multiple
computers through the network. The Broadcom implementation of the
MBA module has been tested successfully in the following environments:
Linux Red Hat PXE Server. Broadcom PXE clients are able to
remotely boot and use network resources (NFS mount, and so forth)
as well as perform Linux installations. In the case of a remote boot, the
Linux universal driver binds seamlessly with the Broadcom Universal
Network Driver Interface (UNDI) and provides a network interface in
the Linux remotely-booted client environment.
Intel APITEST. The Broadcom PXE driver passes all API compliance
test suites.
MS-DOS UNDI. The MS-DOS Universal Network Driver Interface
(UNDI) seamlessly binds with the Broadcom UNDI to provide a
network adapter driver interface specification (NDIS2) interface to the
upper layer protocol stack. This allows computers to connect to
network resources in an MS-DOS environment.
Remote Installation Service (RIS). The Broadcom PXE clients are
able to remotely boot to a Windows Server 2003 (SP1 and older)
system running RIS to initialize and install Windows Server 2003 and
prior operating systems. To extend functionalities beyond basic
network connectivity when loading an operating system through RIS,
see “Using the NetXtreme II Monolithic Driver” on page 48.
Windows Deployment Service (WDS). For Windows Server 2003
SP2, RIS was replaced by WDS, which offers a Broadcom PXE client
to install Windows operating systems, including Windows Vista,
Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2. To extend
functionalities beyond basic network connectivity when loading an
operating system through WDS, see “Using the NetXtreme II
Monolithic Driver” on page 48.
Automated Deployment Service (ADS). The Broadcom PXE client
can connect to a Windows Server 2003 system and run a deployment
agent that allows one to perform some administrative functions,
including, but not limited to, deploying a Windows Server 2003 image.
To extend functionalities beyond basic network connectivity when
loading an operating system through ADS, see “Using the NetXtreme
II Monolithic Driver” on page 48.
42
Page 43

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Note
Setting Up MBA in a Client Environment
Setting up a Multiple Book Agent (MBA) in a client environment involves
the following:
“Enabling the MBA Driver” on page 43
“Configuring the MBA Driver” on page 43
“Setting Up the BIOS” on page 44
Enabling the
MBA Driver
Configuring the
MBA Driver
To enable or disable the MBA driver, do the following:
1. Boot up your system in DOS mode.
The uxdiag.exe file is included in when you download the driver
software files from the Allied Telesis web site.
2. Enter the following:
uxdiag -mba [ 0-disable | 1-enable ] -c
where
devnum is the specific device(s) number (0,1,2, ...) to be programmed.
This procedure describes how to configure the MBA driver on the
AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 adapters.
To configure the MBA driver, do the following:
devnum
You can use the MBA Configuration Menu to configure the MBA
driver one adapter at a time as described below, or you can use the
MS-DOS based application to simultaneously configure the MBA
driver for multiple adapters. See Chapter 12, “User Diagnostics” on
page 155.
1. Restart your system.
You are prompted to press CTRL +S.
2. Press CTRL+S within 4 seconds after the prompt is displayed.
43
Page 44

Chapter 3: Installing Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software
Note
Note
The message prompting you to press CTRL+S is displayed once for
each Broadcom NetXtreme II adapter you have in your system that
has MBA enabled. The messages are displayed in the same order
as the assigned adapter device number.
3. Use the UP ARROW and DOWN ARROW keys to move to the Boot
Protocol menu item.
If you have multiple adapters in your system and you are unsure
which adapter you are configuring, press CTRL+F6, which causes
the port LEDs on the adapter to start blinking.
4. Use the UP ARROW, DOWN ARROW, LEFT ARROW, and RIGHT
ARROW keys to move to and change the values for other menu items,
as desired.
Setting Up the
BIOS
5. Press F4 to save your settings.
6. Press ESC when you are finished.
To boot from the network with the MBA, make the MBA enabled adapter
the first bootable device under the BIOS. This procedure depends on the
system BIOS implementation. Refer to the user manual for the system
BIOS implementation for instructions.
44
Page 45

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Setting Up MBA in a Server Environment: Red Hat Linux PXE Server
The Red Hat Enterprise Linux distribution has PXE Server support. It
allows users to remotely perform a complete Linux installation over the
network. The distribution comes with the boot images boot kernel
(vmlinuz) and initial ram disk (initrd), which are located on the Red Hat
disk#1:
/images/pxeboot/vmlinuz
/images/pxeboot/initrd.img
Refer to the Red Hat documentation for instructions on how to install PXE
Server on Linux.
However, the Initrd.img file distributed with Red Hat Enterprise Linux, does
not have a Linux network driver for the Broadcom NetXtreme II adapters.
This version requires a driver disk for drivers that are not part of the
standard distribution. You download the driver software files from the
Allied Telesis web site.
45
Page 46

Chapter 3: Installing Broadcom Boot Agent Driver Software
46
Page 47

Chapter 4
Installing the Monolithic Software Driver
A monolithic driver allows you to download an image of a PC onto an
image server and then to another PC with an adapter installed. Often,
multiple images are downloaded. The NetXtreme II Monolithic software
driver allows remote installation of an image of a PC with an AT-2973SX,
AT-2973T, or AT-2973T/4 adapter installed. This chapter describes how to
install the monolithic driver software for remote installation and discusses
the following topics:
“Using the NetXtreme II Monolithic Driver” on page 48
“Inserting the NetXtreme II Monolithic Driver in a WinPE 2.0 Image” on
page 50
“Configuring the Speed and Duplex Settings” on page 52
47
Page 48

Chapter 4: Installing the Monolithic Software Driver
Using the NetXtreme II Monolithic Driver
The NetXtreme II Monolithic driver is used with a remote imaging software
such as WinPE, although it is not associated with any operating system.
Before you install a monolithic driver, you must install an AT-2973SX, AT2973T, or AT-2973T/4 adapter in a PC (or multiple PCs) that you want to
act as a remote node. Once you install the adapter and the monolithic
driver software, your can download the image from an image server to the
PCs with an installed adapter.
The NetXtreme II Family Adapters, based on its advanced functionalities,
uses a software architecture that includes a Virtual Bus Device (VBD) to
extend functionalities beyond basic network connectivity. However,
Microsoft, does not currently support this architecture when loading an
operating system through its Windows Deployment Services (WDS),
which was previously known as Remote Installation Services (RIS), or for
the deployment agent used in the Automated Deployment Services (ADS).
Therefore, a separate driver was created to accommodate these Microsoft
deficiencies. This driver is known as the NetXtreme II monolithic driver,
but it is sometimes referred to as the RIS driver.
The NetXtreme II monolithic driver was developed to work only for the text
mode portion of a WDS legacy installation and to establish connectivity
with a deployment agent for ADS. It is not intended to be used as a driver
loaded in the running state of an operating system. The exception to this is
the Windows Preinstallation Environment (WinPE).
For WDS, this driver is used similarly to any other network adapter driver
for supporting network connectivity after the PXE boot to the WDS server.
When placed in the I386 or AMD64 directory (depending on the version of
the operating system being deployed), the monolithic driver is called to
establish that there is driver support for the NetXtreme II Family Adapter
included in the WDS legacy image.
For ADS, the driver is placed in the PreSystem directory on the server
running ADS to establish connectivity with the deployment agent on
remote systems with NetXtreme II adapters when booting from PXE.
While Windows PE 2005 natively supports the VBD architecture, it was
found that using the minint switch in the startnet.cmd file does not. The
minint switch performs a limited scan of the system bus to identify network
devices only and, therefore, does not support the VBD architecture. Since
only network connectivity is required in Windows PE, the only supported
driver is the monolithic driver for the NetXtreme II Family adapter in this
environment as well. Place the b06nd.inf file in the INF directory within the
Windows PE image, and place the appropriate driver file (b06nd51a.sys
for x64-based builds or b06nd51.sys for x86-based builds) in the driver's
48
Page 49

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
directory. If Windows PE is deployed as a flat image from a RIS or WDS
server, you must also place both the b06nd.inf and the appropriate driver
file in the I386 or AMD64 directory containing the image.
49
Page 50

Chapter 4: Installing the Monolithic Software Driver
Note
Inserting the NetXtreme II Monolithic Driver in a WinPE 2.0 Image
By default, the monolithic driver is not included in the boot.wim and
install.wim files that come with the Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008,
and Windows Server 2008 R2 Operating Systems. Microsoft's Windows
Automated Installation Kit (AIK) allows you to modify the default boot.wim
and install.wim files and create WinPE 2.0 images to include the
NetXtreme II monolithic driver in the Windows Vista, Windows Server
2008, and Windows Server 2008 R2 installation.
To insert Broadcom's NetXtreme II monolithic driver in a WinPE 2.0 image
(for Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and Windows Server 2008
R2), download AIK from www.microsoft.com/downloads/
Search.aspx?displaylang=en, type in “automated install kit” in the Search
field. Then install AIK.
After installing AIK, copy the latest monolithic driver to a directory on the
local hard drive of the system you installed the AIK. Follow the procedure
below to insert the monolithic driver into a WinPE 2.0 boot image.
The directory structure c:\VistaPEx86 is used throughout this
procedure.
To insert the monolithic driver into a WinPE 2.0 boot image, do the
following:
1. Download the monolithic driver files, b06nd.inf and b06nd.sys.
Go to the Allied Telesis website at www.alliedtelesis.com/support/
software. After you have accessed this website, enter the model
number in the Search by Product Name box and then click Find to
view the current list of files.
2. From All Programs, open Windows AIK and select Windows PE
Tools Command prompt.
3. At the command prompt, run the copype.cmd script. The script
requires two arguments: hardware architecture and destination
location. The command syntax is:
copype.cmd <arch> <destination>
For example: copype x86 c:\VistaPEx86
50
Page 51

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
4. Mount the base image to a local directory so that you can add or
remove packages by entering:
imagex /mountrw c:\VistaPEx86\winpe.wim 1
c:\VistaPEx86\mount
5. Place the monolithic driver and inf file in c:\drivers\x32\ by entering:
peimg /inf=c:\Drivers\x32\b06nd.inf
c:\VistaPEx86\mount\windows
AIK inserts the driver into the WinPE 2.0 image.
6. To complete the customization of the image, prepare the image for
deployment, enter:
peimg /prep c:\VistaPEx86\mount\windows
7. When asked to continue and have the program prepare the image for
deployment, enter:
yes
8. To commit the changes to the original image file (Winpe.wim), enter:
imagex /unmount c:\VistaPEx86\mount /commit
9. To replace the default Boot.wim file in the \ISO directory with your new
custom image, enter:
copy c:\VistaPex86\winpe.wim
c:\VistaPEx86\ISO\sources\boot.wim
51
Page 52

Chapter 4: Installing the Monolithic Software Driver
Configuring the Speed and Duplex Settings
Since the typical environment where the NetXtreme II monolithic driver is
used does not provide the means to configure advanced network adapter
properties, the driver file (b06nd.inf) was modified to include a section that
allows it to be configured for a specific speed and duplex mode. This
provides a more robust connection to the network as it allows the adapter
to match the settings of its link partner (for example, a switch or a router).
To manually configure the speed and duplex, do the following:
1. Open the b06nd.inf file with a text editor like Microsoft Notepad or
WordPad.
2. Search the file for Registry parameters to locate the section that allows
you to configure the adapter speed and duplex mode.
Once located, notice the following information:
[params_utp]
hkr, , req_medium, 2, "0"
[params_fiber]
hkr, , req_medium, 2, "65283"
These are two separate sections that can be configured: one for
standard RJ-45 copper interfaces (params_utp) and one for fiber
devices (params_fiber).
3. As described in the file, replace the value above in quotation marks
under the correct section, depending upon the network adapter in your
system. The available values are shown below.
Options for copper interfaces:
– Auto (1 Gbps is enabled when that speed is
supported) = "0"
– 10 Mbps Half Duplex = "65794"
– 10 Mbps Full Duplex = "258"
52
– 100 Mbps Half Duplex = "66050"
– 100 Mbps Full Duplex = "514"
Page 53

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Options for fiber interfaces:
– Auto (1 Gbps is enabled when that speed is
supported) = "0"
– 1 Gbps Full Duplex = "771"
– Auto with 1 Gbps Fallback = "33539"
– Hardware default = "65283"
The following example shows how to configure a copper interface for a
10 Mbps Full Duplex connection:
hkr, , req_medium, 2, "258"
53
Page 54

Chapter 4: Installing the Monolithic Software Driver
54
Page 55

Chapter 5
Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software
This chapter provides procedures to install the NDIS2 driver on the
Microsoft Network Client and DOS NDIS platforms.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
“Overview” on page 56
“Checking Pre-installation Requirements” on page 57
“Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software on MS-DOS Platforms” on
page 58
“Using Keywords for the Drivers” on page 63
55
Page 56

Chapter 5: Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software
Overview
The BXND20X Broadcom NetXtreme II Gigabit Ethernet driver is
described in this chapter. This driver can be installed on AT-2973SX,
AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 adapters that are installed in systems running
an MS-DOS platform. See the following sections:
“Checking Pre-installation Requirements” on page 57
“Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software on MS-DOS Platforms” on
page 58
“Using Keywords for the Drivers” on page 63
56
Page 57

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Checking Pre-installation Requirements
Before you can successfully install the NDIS2 driver software, you must do
the following:
Physically install the network adapter in the server.
Install the networking software that is appropriate to the operating
system (such as Microsoft LAN Manager 2.2 for MS-DOS). The
networking software must be running on your server.
57
Page 58

Chapter 5: Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software
Note
Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software on MS-DOS Platforms
The NDIS2 driver software can be run from an MS-DOS startup disk using
Microsoft Network Client 3.0 or from the hard disk using Microsoft LAN
Manager 2.2.
This section describes how to create a startup disk and modify it. See the
following:
“Creating a Startup Disk” on page 58
“Modifying the Startup Disk” on page 59
Creating a
Startup Disk
To create a startup disk to run a Microsoft Network client, you must have
the following:
Windows NT Server 4.0 CD-ROM
A blank MS-DOS system disk (3.5" high-density floppy disk)
Access to the Broadcom NDIS2 driver file (BXND20X.dos). This file is
located on the driver source media.
After creating the startup disk, follow the instructions in “Modifying the
Startup Disk” on page 59.
Windows NT Server 4.0 users: When running Setup for Microsoft
Network Client v3.0 for MS-DOS, click any network card from the list
(NE2000 Compatible, for example) to create the startup disk.
To create a startup disk, do the following:
1. Create a folder called NCADMIN in the root of the C drive.
2. Copy the NCADMIN.CN_, NCADMIN.EX_, and NCADMIN.HL_ files
from the I386 folder on the Windows NT Server 4.0 CD-ROM.
3. Open a command prompt window and change the directory to
C:\NCADMIN.
4. Enter the following:
expand -r ncadmin.*
5. Close the command prompt window by typing exit and then pressing
Enter.
6. Start Windows Explorer.
58
Page 59

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
7. Open the NCADMIN folder and double-click ncadmin.exe.
8. Follow the on-screen instructions to make the network startup disk
(choose NE2000 Compatible from the list of adapters).
Modifying the
Startup Disk
To modify the startup disk, do the following:
1. Edit A:\Net\Protocol.ini with Notepad or a similar text editor.
a. Change DriverName=$ to DriverName=BXND20X$.
b. Remove all other parameter entries under the [MS$NE2CLONE] or
equivalent section such as IOBASE=0x300 or INTERRUPT=3, and
so on.
Example Protocol.ini file for IP
The following is an example of an protocol.ini file for IP:
[network.setup]
version=0x3110
netcard=ms$ne2clone,1,MS$NE2CLONE,1
transport=tcpip,TCPIP
lana0=ms$ne2clone,1,tcpip
[MS$NE2CLONE]
DriverName=BXND20X$
[protman]
DriverName=PROTMAN$
PRIORITY=MS$NDISHLP
[tcpip]
NBSessions=6
DefaultGateway=0
SubNetMask=255 0 0 0
IPAddress=192 168 0 1
DisableDHCP=0
DriverName=TCPIP$
BINDINGS=MS$NE2CLONE
LANABASE=0
Example Protocol.ini file for NetBEUI
The following is an example of an protocol.ini file for NetBEUI:
[network.setup]
version=0x3110
netcard=ms$ne2clone,1,MS$NE2CLONE,1
transport=ms$ndishlp,MS$NDISHLP
transport=ms$netbeui,MS$NETBEUI
lana0=ms$ne2clone,1,ms$ndishlp
lana1=ms$ne2clone,1,ms$netbeui
[MS$NE2CLONE]
59
Page 60

Chapter 5: Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software
DriverName=BXND20X$
[protman]
DriverName=PROTMAN$
PRIORITY=MS$NDISHLP
[MS$NDISHLP]
DriverName=ndishlp$
BINDINGS=MS$NE2CLONE
[MS$NETBEUI]
DriverName=netbeui$
SESSIONS=10
NCBS=12
BINDINGS=MS$NE2CLONE
LANABASE=0
2. Edit A:\Net\System.ini.
3. Change netcard= to netcard=BXND20X.dos.
4. Check for references to C:\NET and change C:\NET to A:\NET if
necessary.
Example system.ini file
The following is an example of a system.ini file:
[network]
sizworkbuf=1498
filesharing=no
printsharing=no
autologon=yes
computername=MYPC
lanroot=A:\NET
username=USER1
workgroup=WORKGROUP
reconnect=yes
dospophotkey=N
lmlogon=0
logondomain=
preferredredir=basic
autostart=basic
maxconnections=8
[network drivers]
netcard=BXND20X.dos
transport=ndishlp.sys,*netbeui
devdir=A:\NET
LoadRMDrivers=yes
60
5. Copy BXND20X.dos to A:\Net.
Page 61

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
6. Create the appropriate Autoexec.bat file in drive A for the chosen
protocol as shown:
TCP/IP
Here is an example of the TCP/IP autoexec.bat file:
path=a:\net
a:\net\net initialize
a:\net\netbind.com
a:\net\umb.com
a:\net\tcptsr.exe
a:\net\tinyrfc.exe
a:\net\nmtsr.exe
a:\net\emsbfr.exe
a:\net\net start basic
net use z: \\SERVERNAME\SHARENAME
NetBEUI
Here is an example of the NetBEUI autoexec.bat file:
Installing the
DOS NDIS2
Driver Software
SET PATH=A:\NET
A:\NET\NET START BASIC
net use z: \\SERVERNAME\SHARENAME
7. Create a Config.sys file on the startup disk in drive A as shown:
files=30
device=a:\net\ifshlp.sys
lastdrive=z
To install the DOS NDIS2 Driver Software on the hard disk, do the
following:
1. Verify that the system has Microsoft LAN Manager 2.2 installed, with a
protocol such as NetBEUI configured.
2. Create a folder on your hard disk to store the NDIS 2.01 driver.
Example: C:\LANMAN
3. Copy the BXND20X.dos file to this folder.
4. Edit the Config.sys file by adding the following lines:
DEVICE = C:\LANMAN\PROTMAN.DOS
DEVICE = C:\LANMAN\BXND20X.DOS
DEVICE = C:\LANMAN\NETBEUI.DOS
61
Page 62

Chapter 5: Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software
Note
5. Edit the Autoexec.bat file by adding the following lines:
C:\ LANMAN\NETBIND.EXE
C:\LANMAN\NET START WORKSTATION
C:\LANMAN\NET USE
name\resource name
6. Edit the Protocol.ini file (located in C:\LANMAN) to configure the
driver to bind with NetBEUI or any other protocols.
Here is an example:
[PROTOCOL MANAGER]
DriverName = PROTMAN$
[NETBEUI_XIF]
DriverName = netbeui$
BINDINGS = BXND20X
[BXND20X]
DriverName = "BXND20X$"
7. Restart the computer to complete the installation.
drive letter
: \\
server
The driver loads during system configuration and displays the
Broadcom banner, controller name, MAC address, IRQ number,
detected line speed, and the controller BusNum and DevNum. If the
driver fails to load, an initialization fail message is displayed. For
more information about the BusNum and DevNum keywords, see
“Using Keywords for the Drivers” on page 63.
62
Page 63

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Using Keywords for the Drivers
The Protocol.ini file contains certain keywords that are used by the
BXND20X.dos driver. These keywords are listed below:
BusNum. Specifies the number of the PCI bus on which the network
adapter is located. This keyword requires a value ranging from 0 to
255.
DevNum. Specifies the device number assigned to the network
adapter when it is configured by the PCI BIOS. This keyword requires
a value ranging from 0 to 255.
FuncNum or PortNum. Specifies the PCI function or port number
assigned to the network controller. This keyword requires a value
ranging from 0 to 7.
The BusNum, DevNum, and FuncNum (or PortNum) keywords are
needed when multiple adapters are installed in the server and when
a specific controller must be loaded in a certain order. These
keywords are used concurrently and are included for manufacturing
purposes. Do not use them unless you are familiar with how to
configure PCI devices. A PCI device scan utility is needed to find this
information.
LineSpeed. Specifies the speed of the network connection in Mbit/s.
The values are 10, 100, or 1000 Mbit/s. Technically, a line speed of
1000 Mbit/s cannot be forced and is achievable only through
auto-negotiation. For the sake of simplicity, the driver performs autonegotiation when the line speed is set to a value of 1000.
Duplex. Specifies the duplex mode of the network adapter. Requires a
setting of either Half or Full. When this keyword is used, the
LineSpeed keyword must also be used. If neither keyword is used, the
network adapter defaults to auto-negotiation mode.
NodeAddress. Specifies the network address used by the network
adapter. If a multicast address or a broadcast address is specified, the
adapter uses the default MAC address.
FixCheckSumOff. Turns off the driver's workaround for the TCP/IP
stack to recognize the 1s complemented version of the checksum.
AcceptAllMC. Informs the driver to deliver all multicast packets to the
upper protocol.
63
Page 64

Chapter 5: Installing the NDIS2 Driver Software
See below for an example of the keywords:
[BXND20X]
DriverName = "BXND20X$"
BusNum = 3
DevNum = 14
PortNum = 2
LineSpeed = 1000
Duplex = Full
NodeAddress = 001020304050
64
Page 65

Chapter 6
Installing the Linux Drivers
This chapter provides procedures to install the Linux drivers for the
AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 adapters.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
“Overview” on page 66
“Installing Linux Driver Software” on page 68
65
Page 66

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
Overview
This chapter discusses the Linux drivers for the Broadcom NetXtreme II
network adapters and describes how to install them. For a description of
the drivers, see Table 4.
Table 4. Broadcom NetXtreme II Linux Drivers
Linux Driver Description
bnx2
cnic
bnx2i Indicates the Linux driver that enables iSCSI
Indicates the Linux drivers for the AT-2973SX
AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 network adapters.
The bnx2 driver is the networking driver and
the cnic driver supports additional features
required by the bnx2i iSCSI offload driver. The
bnx2i iSCSI driver is packaged separately.
offload on the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT2973T/4 network adapters.
Limitations This section describes the testing limitations of the following Linux drivers:
“bnx2 Driver” on page 66
“bnx2i Driver” on page 67
bnx2 Driver
The current version of the driver has been tested on 2.4.x kernels (starting
from 2.4.24) and all 2.6.x kernels. The driver may not compile on kernels
older than 2.4.24.
66
Testing is concentrated on i386 and x86_64 architectures. Only limited
testing has been done on other architectures. You may need to make
minor changes to some source files and the Makefile on some kernels. In
addition, the Makefile does not compile the cnic driver on kernels older
than 2.6.16. iSCSI offload is only supported on 2.6.16 and newer kernels.
Support for the 2.4.21 kernels is provided in Red Hat Enterprise Linux 3.
Page 67

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
bnx2i Driver
The current version of the driver has been tested on 2.6.x kernels, starting
from 2.6.18 kernel. The driver may not compile on older kernels with the
exception of SLES 10 SP1, which runs the 2.6.16.46 kernel. SUSE
upgraded the iscsi_transport kernel module in SLES 10 SP1. In addition,
Broadcom iSCSI offload initiators is supported on SLES 10 SP1. Testing is
concentrated on i386 and x86_64 architectures, Red Hat EL5, and SUSE
10 SP1 distributions.
Packaging The Linux driver is released in the packaging formats shown in Table 5.
The NetXtreme2 package contains the bnx2 (1 Gb network adapter) and
drivers for source RPM and compressed tar.
Table 5. Linux Driver Packaging
Format
Source RPM netxtreme2-
bnx2 Driver bnx2i (iSCSI) Driver
bnx2i-version.src.rpm
version.src.rpm
Compressed tar netxtreme2-
bnx2i-version.tar.gz
version.tar.gz
Supplemental tar netxtreme2_sup-
bnx2i_sup-version.tar.gz
version.tar.gz
Identical source files to build the driver are included in both RPM and TAR
source packages. The supplemental tar file contains additional utilities
such as patches and driver diskette images for network installation.
The following updated open-iSCSI components are released in source
RPM format:
iscsi-initiator-utils-6.2.0.868-0.7c.src.rpm: updated open-iscsi for Red
Hat 5 distributions
open-iscsi-2.0.707-0.25b.src.rpm: updated open-iscsi components for
SLES 10 SP1 distribution
open-iscsi-2.0.707-0.44b.src.rpm: updated open-iscsi components for
SLES 10 SP2 distribution
67
Page 68

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
Note
Note
Installing Linux Driver Software
There are two ways to install the Linux driver software— from the Source
RPM Package or build the driver from the source TAR file. See the
following sections:
“Installing the Source RPM Package” on page 68
“Building the Driver from the Source TAR File” on page 70
If a bnx2 or bnx2i driver is loaded and you update the Linux kernel,
you must recompile the driver module if it was installed using the
source RPM or the TAR package.
Installing the
Source RPM
Package
The procedure in this section describes how to install the Source RPM
Package. The examples in the following procedure refer to the bnx2
driver, but also apply to the bnx2i driver.
To install the Source RPM Package, do the following:
1. Enter the following command:
rpm -ivh netxtreme2-version.src.rpm
2. Change the directory to the RPM path and build the binary driver for
your kernel (the RPM path is different for each Linux distribution):
cd /usr/src/
rpm -bb SPECS/bnx2.spec
or
rpmbuild -bb SPECS/bnx2.spec (for RPM version 4.x.x)
During your attempt to install a source RPM package, the following
message may be displayed: error: cannot create
%sourcedir /usr/src/redhat/SOURCES
The most likely cause of the error is that the rpm-build package has
not been installed. Locate the rpm-build package on the Linux
installation media and install it using the following command: rpm -
ivh rpm-build-version.arch.rpm
Then complete the installation of the source RPM.
redhat,OpenLinux,turbo,packages,rpm
...
68
Page 69

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
3. Install the newly built package which includes the driver and man
page:
rpm -ivh RPMS/i386/bnx2-
version
.arch.rpm
If you are installing over an existing distribution that may already
contain an older version of the driver, the —force option is needed.
Depending on the kernel, the driver is installed to one of the following
paths:
2.4.x kernels
/lib/modules/kernel_version/kernel/drivers/net/
bnx2.o
2.6.x kernels
/lib/modules/kernel_version/kernel/drivers/net/
bnx2.ko
For the bnx2i driver, the driver is installed on one of the following
paths:
– 2.6.16 kernels and newer (bnx2 driver)
/lib/modules/kernel_version/kernel/drivers/
net/bnx2.ko
/lib/modules/kernel_version/kernel/drivers/
net/cnic.ko
– 2.6.16 kernels and newer (bnx2i driver)
/lib/modules/kernel_version/kernel/drivers/
iscsi/bnx2i.ko
4. To load the driver, enter one of the following commands:
insmod bnx2
or
modprobe bnx2
5. To load the cnic driver (if applicable), enter one of the following
commands:
insmod cnic.ko
or
modprobe cnic
69
Page 70

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
Note
To configure the network protocol and address, refer to the documentation
provided with your operating system.
Building the
Driver from the
Source TAR File
This procedure describes how to build the bnx2 and bnx2i Linux drivers
from the Source TAR file. See the following sections:
“Building the bnx2 Driver” on page 70
“Building the bnx2i Driver” on page 71
Building the bnx2 Driver
To build the bnx2 Linux driver from the Source TAR file, do the following:
1. Create a directory and extract the TAR files to the following directory:
tar xvzf netxtreme2-
2. Build the driver bnx2.ko (or bnx2.o) as a loadable module for the
running kernel. Enter the following commands:
cd bnx2make
3. Test the driver by loading it (if necessary, first unload the existing
driver). Enter the following commands:
rmmod bnx2
insmod bnx2.o
modprobe crc32 && insmod bnx2.o
version
/src
version
.tar.gz
70
or, for Linux 2.6 kernels:
rmmod bnx2
insmod bnx2.ko
4. Load the cnic driver, if applicable. Enter the following command:
insmod cnic.ko
5. Install the driver and man page by entering the following command:
make install
See the “Installing the Source RPM Package” on page 68 for the
location of the installed driver.
To configure the network protocol and address after building the driver,
refer to the manuals supplied with your operating system.
Page 71

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Building the bnx2i Driver
To build the bnx2i Linux driver from the Source TAR file, do the following:
1. Create a directory and extract the TAR files to the directory by entering
the following command:
tar xvzf bnx2-version.tar.gz
2. Build the driver bnx2.ko as a loadable module for the running kernel by
entering the following command:
cd bnx2i-version/drivermake
3. Test the driver by loading it (if necessary, first unload the existing
driver). Enter the following commands:
rmmod bnx2i
insmod bnx2i.ko
4. Install the driver and man page, by entering:
make install
See the “Installing the Source RPM Package” on page 68 for the
location of the installed driver.
5. Install the user daemon (bnx2id), by entering:
cd ${DRV_BASE}/driver
make install_usr
The make install_usr command installs the bnx2id binary under
/sbin.
To use Broadcom iSCSI, see “Load and Run Necessary iSCSI
Software Components” on page 72 to load the necessary software
components.
71
Page 72

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
Note
Load and Run
Necessary iSCSI
Software
Components
The Broadcom iSCSI Offload software suite consists of three kernel
modules and a user daemon. To load the required software components
either manually or through system services, do the following:
1. Unload existing driver and kill the user daemon, if necessary. Do the
following:
Manual:
rmmod bnx2i
pkill -9 bnx2id
Using system service:
service bnx2id stop
2. Load the iSCSI driver and the user daemon. Do the following:
Manual:
bnx2id
insmod bnx2i.ko
Unloading the
Linux Driver
or
modprobe bnx2i
Using system service:
service bnx2id start
You can unload, or remove, the Linux Driver from an RPM or TAR
installation. See the following:
“Unloading the Driver from an RPM Installation” on page 72
“Unloading the Driver from a TAR Installation” on page 73
Unloading the Driver from an RPM Installation
This section describes how to unload, or remove, a Linux driver from an
RPM installation.
The examples used in this procedure refer to the bnx2 driver, but
also apply to the bnx2i driver.
72
Page 73

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Note
Note
Note
On 2.6 kernels, it is not necessary to bring down the eth# interfaces
before unloading the driver module.
If the cnic driver is loaded, unload the cnic driver before unloading
the bnx2 driver.
Before unloading the bnx2i driver, disconnect all active iSCSI
sessions to targets.
To unload the driver, use ifconfig to bring down all eth# interfaces
opened by the driver, and then enter:
rmmod bnx2
Patching PCI
Files (Optional)
If the driver was installed using the rpm command, enter the following
command to remove it:
rpm -e netxtreme2
Unloading the Driver from a TAR Installation
If the driver was installed using make install from the tar file, manually
delete the bnx2.o or bnx2.ko driver file from the operating system. See
“Installing the Source RPM Package” on page 68 for the location of the
installed driver.
This is an optional procedure that describes how to patch PCI files for
identification by other vendors.
For hardware detection utilities, such as Red Hat kudzu, to properly
identify bnx2 supported devices, you may need to update a number of files
containing PCI vendor and device information.
The examples used in this procedure refer to the bnx2 driver, but
also apply to the bnx2i driver.
73
Page 74

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
Apply the updates by running the scripts provided in the supplemental tar
file. For example, on Red Hat Enterprise Linux, apply the updates by
entering the following commands:
./patch_pcitbl.sh /usr/share/hwdata/pcitable
pci.updates
/usr/share/hwdata/pcitable.new bnx2
./patch_pciids.sh /usr/share/hwdata/pci.ids
pci.updates
/usr/share/hwdata/pci.ids.new
Next, back up the old files and the rename the new files by entering the
following copy commands:
cp /usr/share/hwdata/pci.ids /usr/share/hwdata/
old.pci.ids
cp /usr/share/hwdata/pci.ids.new /usr/share/hwdata/
pci.ids
Network
Installations
Setting Values for
Optional
Properties
cp /usr/share/hwdata/pcitable /usr/share/hwdata/
old.pcitable
cp /usr/share/hwdata/pcitable.new /usr/share/hwdata/
pcitable
For network installations through NFS, FTP, or HTTP (using a network
boot disk or PXE), a driver disk that contains the bnx2 driver may be
needed. The driver disk images for the most recent Red Hat and SuSE
versions are included. Boot drivers for other Linux versions can be
compiled by modifying the Makefile and the make environment. Further
information is available from the Red Hat website at http://
www.redhat.com.
You can set values for optional properties for the bnx2 and bnx2i Linux
drivers. See the following sections:
“Setting Optional Properties for the bnx2 Driver” on page 75
“Setting Optional Properties for the bnx2i Driver” on page 75
74
Page 75

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Caution
Setting Optional Properties for the bnx2 Driver
The disable_msi optional property can be supplied as a command line
argument to the insmod or modprobe command. The property can also be
set in the modprobe.conf command. See the man page for more
information.
All other driver settings can be queried and changed using the ethtool
utility. See the ethtool man page for more information. The ethtool
settings do not persist across a reboot or module reload. In addition, you
can put the ethtool commands in a startup script, such as
/etc/rc.local, to preserve the settings across a reboot.
Some combinations of property values may conflict and result in
failures. The driver cannot detect all conflicting combinations.
This property is used to disable Message Signal Interrupts (MSI). The
property is valid only on 2.6 kernels that support MSI. This property cannot
be used on 2.4 kernels. By default, the driver enables MSI if it is supported
by the kernel. It runs an interrupt test during initialization to determine if
MSI is working. If the test passes, the driver enables MSI. Otherwise, it
uses legacy INTx mode. To set the bnx2 driver, enter one of the following:
insmod bnx2.ko disable_msi=1
or
modprobe bnx2 disable_msi=1
Setting Optional Properties for the bnx2i Driver
You can supply the optional parameters en_tcp_dack, error_mask1 and
error_mask2 as command line arguments to the insmod or modprobe
command for the bnx2i driver.
error_mask1 and error_mask2
Use “Config FW iSCSI Error Mask #" to configure certain iSCSI protocol
violations to be treated either as a warning or a fatal error. All fatal iSCSI
protocol violations result in session recovery (ERL 0). These are bit
masks. By default, all violations are treated as errors.
Do not use the error_mask parameter if you are not sure about the
consequences. Discuss these values with the Broadcom
development team on a case-by-case basis. This is a mechanism to
work around iSCSI implementation issues on the target side and
75
Page 76

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
Note
without proper knowledge of iSCSI protocol details, users are
advised not to experiment with these parameters.
en_tcp_dack
The "Enable TCP Delayed ACK" parameter enables or disables the TCP
delayed ACK feature on offloaded iSCSI connections. The TCP delayed
ACK feature is ENABLED by default. To set the en_tcp_dack parameter in
the bnx2i driver, enter one of the following commands:
insmod bnx2i.ko en_tcp_dack=0
or
modprobe bnx2i en_tcp_dack=0
Default: ENABLED
sq_size
Use the "Configure SQ size" parameter to select the send-queue size for
offloaded connections. The SQ size determines the maximum SCSI
commands that can be queued. Also, SQ size has a bearing on the
number of connections that can be offloaded; as QP size increases, the
number of connections supported decreases. With the default values, the
AT-2973SX and AT-2973T, and AT—2973T/4 adapters can offload 28
connections.
Defaults: 128
Range: 32 to 128
Broadcom validation is limited to a power of 2; for example, 32, 64,
or 128.
rq_size
Use the "Configure RQ size" parameter to choose the size of
asynchronous buffer queue size per offloaded connections. The RQ size
is not required to be greater than 16 because it is used to place iSCSI
ASYNC/NOP/REJECT messages and SCSI sense data.
Defaults: 16
Range: 16 to 32
76
Page 77

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Broadcom validation is limited to a power of 2; for example, 16, 32,
or 128.
event_coal_div
The Event Coalescing Divide Factor parameter is a performance tuning
parameter used to moderate the rate of interrupt generation by the iscsi
firmware.
Defaults: 1
Valid values: 1, 2, 4, 8
bnx2i_nopout_when_commands_active
The "iSCSI NOOP even when connection is not idle" parameter enables
the offload initiator to send iSCSI NOP-OUT on wire even when the link is
not truly idle. This parameter was introduced to avoid unnecessary
session recoveries induced by some older targets when iSCSI NOP-OUT
and iSCSI CMD pdus are intermixed. Newer iSCSI target systems are
immune to this condition and this parameter is turned ON for quite some
time.
Checking the
bnx2 Driver
Defaults
Defaults: 1
Values: Binary parameter, 0/1
The parameters can also be set in the modprobe.conf command. See
the man page for more information.
The bnx2 driver defaults to the following settings:
Speed: Autonegotiation with all speeds advertised
Flow Control: Autonegotiation with RX and TX advertised
MTU: 1500 (range is 46–9000)
RX Ring Size: 255 (range is 0–4080)
RX Jumbo Ring Size: 0 (range 0–16320) adjusted by the driver based on
MTU and RX Ring Size
TX Ring Size: 255 (range is (MAX_SKB_FRAGS+1)–255).
MAX_SKB_FRAGS varies on different kernels and different architectures.
On a 2.6 kernel for x86, MAX_SKB_FRAGS is 18.
Coalesce RX Microseconds: 18 (range is 0–1023)
Coalesce RX Microseconds IRQ: 18 (range is 0–1023)
77
Page 78

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
Coalesce RX Frames: 6 (range is 0–255)
Coalesce RX Frames IRQ: 6 (range is 0–255)
Coalesce TX Microseconds: 80 (range is 0–1023)
Coalesce TX Microseconds IRQ: 80 (range is 0–1023)
Coalesce TX Frames: 20 (range is 0–255)
Coalesce TX Frames IRQ: 20 (range is 0–255)
Coalesce Statistics Microseconds: 999936 (approximately 1 second)
(range is 0–16776960 in increments of 256)
MSI: Enabled (if supported by the 2.6 kernel and the interrupt test passes)
TSO: Enabled (on 2.6 kernels)
WoL: Initial setting based on NVRAM's setting
Checking Driver
Messages
The following are the most common sample messages that may be logged
in the /var/log/messages file for the bnx2 and bnx2i drivers. Use dmesg -
n <level> command to control the level at which messages appear on
the console. Most systems are set to level 6 by default. To see all
messages, set the level higher. See the following sections:
“Checking the bnx2 Driver Messages” on page 78
“Checking bnx2i Driver Messages” on page 79
Checking the bnx2 Driver Messages
The following are the most common bnx2 driver messages:
Driver Sign on
Broadcom NetXtreme II Gigabit Ethernet Driver
bnx2 v1.6.3c (July 23, 2007)
CNIC Driver Sign on
Broadcom NetXtreme II cnic v1.1.19 (Sep 25, 2007)
78
NIC Detected
eth#: Broadcom NetXtreme II BCM5708 1000Base-T (B0)
PCI-X 64-bit 133MHz found at mem f6000000, IRQ 16, node
addr 0010180476ae
cnic: Added CNIC device: eth0
Page 79

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Link Up and Speed Indication
bnx2: eth# NIC Link is Up, 1000 Mbps full duplex
Link Down Indication
bnx2: eth# NIC Link is Down
MSI enabled successfully (bnx2 only)
bnx2: eth0: using MSI
Checking bnx2i Driver Messages
The following are the most common bnx2i driver messages:
BNX2I Driver signon
Broadcom NetXtreme II iSCSI Driver bnx2i v1.0.30 (Sep
29, 2007)
Network port to iSCSI transport name binding
bnx2i: netif=eth2, iscsi=bcm570x-050000
bnx2i: netif=eth1, iscsi=bcm570x-030c00
Driver completes handshake with iSCSI offload-enabled CNIC device
bnx2i [05:00.00]: ISCSI_INIT passed
This message is displayed only when the user attempts to make an
iSCSI connection.
Driver detects iSCSI offload is not enabled on the CNIC device
bnx2i: iSCSI not supported, dev=eth3
bnx2i: bnx2i: LOM is not enabled to offload iSCSI
connections, dev=eth0
Driver unable to allocate TCP port for iSCSI connection
bnx2i: run 'bnx2id' daemon to alloc TCP ports
Exceeds maximum allowed iSCSI connection offload limit
bnx2i: unable to allocate iSCSI context resources
79
Page 80

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
Note
Network route to target node and transport name binding are two
different devices
bnx2i: conn bind, ep=0x... ($ROUTE_HBA) does not
belong to hba $USER_CHOSEN_HBA
where
ROUTE_HBA is the net device on which connection was offloaded based
on route information
USER_CHOSEN_HBA is the HBA to which target node is bound (using
iscsi transport name)
Target cannot be reached on any of the CNIC devices
bnx2i: check route, cannot connect using cnic
Network route is assigned to network interface, which is down
bnx2i: check route, hba not found
Attempting to offload iSCSI connection onto a Jumbo Frame-enabled
device
bnx2i: eth# network i/f mtu is set to #mtu
bnx2i: iSCSI HBA can support mtu of 1500
Change mtu to 1500 using ifconfig and restart the interface in
order to offload iSCSI connections.
SCSI-ML initiated host reset (session recovery)
bnx2i: attempting to reset host, #3
CNIC detects iSCSI protocol violation - Fatal errors
bnx2i: iscsi_error - wrong StatSN rcvd
bnx2i: iscsi_error - hdr digest err
bnx2i: iscsi_error - data digest err
bnx2i: iscsi_error - wrong opcode rcvd
bnx2i: iscsi_error - AHS len > 0 rcvd
bnx2i: iscsi_error - invalid ITT rcvd
bnx2i: iscsi_error - wrong StatSN rcvd
bnx2i: iscsi_error - wrong DataSN rcvd
bnx2i: iscsi_error - pend R2T violation
bnx2i: iscsi_error - ERL0, UO
bnx2i: iscsi_error - ERL0, U1
80
Page 81

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
bnx2i: iscsi_error - ERL0, U2
bnx2i: iscsi_error - ERL0, U3
bnx2i: iscsi_error - ERL0, U4
bnx2i: iscsi_error - ERL0, U5
bnx2i: iscsi_error - ERL0, U
bnx2i: iscsi_error - invalid resi len
bnx2i: iscsi_error - MRDSL violation
bnx2i: iscsi_error - F-bit not set
bnx2i: iscsi_error - invalid TTT
bnx2i: iscsi_error - invalid DataSN
bnx2i: iscsi_error - burst len violation
bnx2i: iscsi_error - buf offset violation
bnx2i: iscsi_error - invalid LUN field
bnx2i: iscsi_error - invalid R2TSN field
bnx2i: iscsi_error - invalid cmd len1
bnx2i: iscsi_error - invalid cmd len2
bnx2i: iscsi_error - pend r2t exceeds
MaxOutstandingR2T value
bnx2i: iscsi_error - TTT is rsvd
bnx2i: iscsi_error - MBL violation
bnx2i: iscsi_error - data seg len != 0
bnx2i: iscsi_error - reject pdu len error
bnx2i: iscsi_error - async pdu len error
bnx2i: iscsi_error - nopin pdu len error
bnx2i: iscsi_error - pend r2t in cleanup
bnx2i: iscsi_error - IP fragments rcvd
bnx2i: iscsi_error - IP options error
bnx2i: iscsi_error - urgent flag error
CNIC detects iSCSI protocol violation - non-FATAL, warning
bnx2i: iscsi_warning - invalid TTT
bnx2i: iscsi_warning - invalid DataSN
bnx2i: iscsi_warning - invalid LUN field
The driver needs to be configured to consider certain violations as a
warning and not as a critical error.
Driver puts a session through recovery
conn_err - hostno 3 conn 03fbcd00, iscsi_cid 2 cid
a1800
81
Page 82

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
Reject iSCSI PDU received from the target
bnx2i - printing rejected PDU contents
[0]: 1 ffffffa1 0 0 0 0 20 0
[8]: 0 7 0 0 0 0 0 0
[10]: 0 0 40 24 0 0 ffffff80 0
[18]: 0 0 3 ffffff88 0 0 3 4b
[20]: 2a 0 0 2 ffffffc8 14 0 0
[28]: 40 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Open-iSCSI daemon handing over session to driver
bnx2i: conn update - MBL 0x800 FBL 0x800MRDSL_I 0x800
MRDSL_T 0x2000
Teaming with
Channel Bonding
Statistics You can view detailed statistics and configuration information using the
Linux iSCSI
Offload
With the Linux drivers, you can team adapters together using the bonding
kernel module and a channel bonding interface. For more information, see
the Channel Bonding information in your operating system documentation.
ethtool utility. See the ethtool man page for more information.
This section describes how to install and run Linux iSCSI applications. The
following recommendations apply to offloading Linux iSCSI programs:
Not all Broadcom NetXtreme II adapters support iSCSI offload.
The iSCSI session will not recover after a hot remove and hot plug.
The iSCSI driver/firmware will not offload iSCSI connections onto a
jumbo frame-enabled CNIC device.
For MPIO to work properly, iSCSI nopout should be enabled on each
iSCSI session. Refer to open-iscsi documentation for procedures on
setting up noop_out_interval and noop_out_timeout values.
In the scenario where multiple CNIC devices are in the system and the
system is booted via Broadcom's iSCSI boot solution, ensure that the
iscsi node under /etc/iscsi/nodes for the boot target is bound to the
NIC that is used for booting.
82
See the following sections:
“Installing User Application - bnx2id” on page 83
“Installing Open iSCSI User Applications” on page 83
“Binding iSCSI Target to Broadcom NX2 iSCSI Transport Name” on
page 84
“Making Connections to iSCSI Targets” on page 85
“Maximizing Offload iSCSI Connections” on page 85
Page 83

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Installing User Application - bnx2id
When the bnx2i RPM package is installed, install the bnx2id application
under /sbin. See “Installing the Source RPM Package” on page 68 for
information. Run the bnx2id daemon before attempting to create iSCSI
connections. The driver does not establish connections to the iSCSI target
without the daemon's assistance.
bnx2id
The bnx2id daemon requires mknod and sh shell, which are standard on
any regular server. For iSCSI boot using NetXtreme II offload support,
binaries for mknod and sh need to be bundled into an initrd image.
Installing Open iSCSI User Applications
Install and run the open-iscsi programs, iscsid and iscsiadm, from the
Broadcom distributed open-iscsi packages. See “Packaging” on page 67
for details. Before you can install the Broadcom iSCSI-supported
packages, remove all pre-installed open-iscsi packages.
To install and run the iscsid and iscsiadm programs, do the following:
1. Remove all existing open-iscsi packages.
RHEL5
rpm -e iscsi-initiator-utils
SLES10 SP1
rpm -e open-iscsi
2. Install the source RPM package by entering:
rpm -ivh <open-iscsi-package-name>.src.rpm
3. CD to the RPM path and build the binary driver for your kernel. Enter:
cd /usr/src/{redhat,OpenLinux,turbo,packages,rpm
..}
rpm -bb SPECS/<open-iscsi-package-name>.spec
or
rpmbuild -bb SPECS/<open-iscsi-package-name>.spec
(for RPM version 4.x.x)
The RPM path is different for each Linux distribution.
83
Page 84

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
4. Install the newly built package by entering:
rpm -ivh RPMS/<arch>/<open-iscsi-package-
name>.<arch>.rpm
where <arch> is the machine architecture such as i386.
rpm -ivh RPMS/i386/<open-iscsi-package-
name>.i386.rpm
5. Start the daemon by entering:
iscsid
Binding iSCSI Target to Broadcom NX2 iSCSI Transport Name
By default, the open-iscsi daemon connects to discovered targets using
software initiator (transport name = 'tcp'). If you want to offload an iSCSI
connection onto CNIC device should explicitly change the transport
binding of the iSCSI node. This can be done using iscsiadm cli utility as
follows:
iscsiadm --mode node --targetname iqn.2004-
06.com.broadcom:tg1 \
--portal 192.168.1.100 --op=update \
--name=node.transport_name -value=${XPORT_NAME}
where XPORT_NAME=bcm570x-xxyyzz
xx - pci bus number of the NX2 device
yy - pci device number of the NX2 device
zz - pci function number of the NX2 device
Network interface to iscsi transport name binding can be obtained by
executing:
dmesg | grep "bnx2i: netif"
Sample output in a system with two NetXtreme II devices:
bnx2i: netif=eth1, iscsi=bcm570x-050000
bnx2i: netif=eth0, iscsi=bcm570x-030000
84
Page 85

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
If you want to switch back to using the software initiator, enter the
following:
iscsiadm --mode node --targetname iqn.2004-
06.com.broadcom:tg1 \
--portal 192.168.1.100 --op=update \
--name=node.transport_name --value=tcp
Making Connections to iSCSI Targets
Refer to open-iscsi documentation for a comprehensive list of iscsiadm
commands. The following is a sample list of commands to discovery
targets and to create iscsi connections to a target:
Adding static entry
iscsiadm -m node -p <ipaddr[:port]> -T iqn.2007-
05.com.broadcom:target1 -o new
iSCSI target discovery using 'SendTargets'
iscsiadm -m discovery --type sendtargets -p
<ipaddr[:port]>
Login to target using 'iscsiadm' command
iscsiadm --mode node --targetname <iqn.targetname> -portal <ipaddr[:port]> --login
List all drives active in the system
'fdisk -l'
Maximizing Offload iSCSI Connections
With default driver parameters set, which includes 128 outstanding
commands, bnx2i can offload a maximum of 28 iSCSI connections. This is
not a hard limit, but simple on-chip resource allocation math. The bnx2i
driver can offload > 28 connections by reducing the shared queue size
which, in turn, limits the maximum outstanding tasks on a connection. See
“Setting Values for Optional Properties” on page 74 for information on
sq_size and rq_size. The driver logs the following message to syslog when
the maximum allowed connection offload limit is reached - "bnx2i: unable
to allocate iSCSI context resources."
85
Page 86

Chapter 6: Installing the Linux Drivers
86
Page 87

Chapter 7
Installing the Windows Drivers
This chapter provides procedures to install and remove the driver software
for all of the Windows Operating Systems supported by the AT-2973SX,
AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 adapters. In addition, it describes how to
display and change adapter properties including power management
options. This chapter discusses the following topics:
“Installing the Windows Driver Software” on page 88
“Removing the Device Drivers” on page 97
87
Page 88

Chapter 7: Installing the Windows Drivers
Note
Note
Installing the Windows Driver Software
This chapter describes how to install all of the following Windows
Operating Systems:
Microsoft Windows Server 2003 (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows Server 2008 R2 (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows Vista™ (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
Microsoft Windows 7™ (32-bit and 64-bit extended)
The Windows driver software for all of the Windows Operating Systems is
available on the Allied Telesis website at www.alliedtelesis.com/
support/software. After you have accessed this website, enter the model
number in the Search by Product Name box and then click Find to
display the current list of software drivers.
When Windows starts after the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, or AT-2973T/4
adapter has been installed, the operating system automatically detects the
hardware and prompts you to install the driver software for that device.
You also receive this same prompt when you remove an existing device
driver.
There are two methods used to install the software drivers on all of the
Windows Operating Systems supported by the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T,
and AT-2973T/4 adapters: the Installer and Silent installation. The Installer
uses a graphical interactive mode. The Silent Installation is a commandline interface for unattended installation. See the following sections:
“Using the Installer” on page 89
“Using Silent Installation” on page 94
These instructions are based on the assumption that your adapter
was not factory installed. If your controller was installed at the
factory, the driver software has been installed for you.
Before installing the driver software, verify that the Windows
operating system has been upgraded to the latest version with the
latest service pack applied.
88
Page 89

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Note
You must physically install a network device driver before the
Broadcom NetXtreme II Controller can be used with your Windows
Operating System. There is no installation CD. You must download
the drivers from the Allied Telesis website at
www.alliedtelesis.com/support/software. After you have
accessed this website, enter the model number in the Search by
Product Name box and then click Find to view the current list of
documents and drivers.
To use the TCP/IP Offload Engine (TOE), you must have Windows
Server 2003 with Service Pack 2 (SP2) and a license key
preprogrammed in the hardware. If supported, for iSCSI you only
need a license key.
Using the
Installer
The Installer has a graphical interactive installation mode. To install the
AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 drivers on a Windows Operating
System, do the following:
1. When the Found New Hardware Wizard appears, click No, not this
time.
See Figure 13 on page 90 for the Found New Hardware Wizard Page.
89
Page 90

Chapter 7: Installing the Windows Drivers
90
Figure 13. Found New Hardware Wizard Page
2. From the driver directory, select the setup.exe file and Run.
Page 91

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
The Broadcom NetXtreme II Driver Installer - InstallShield Wizard
Page is displayed. See Figure 14.
Figure 14. Broadcom NetXtreme II Driver Installer - InstallShield Wizard
Page
3. Click Next to continue.
The License Agreement Page is displayed. See Figure 15 on page 92.
91
Page 92

Chapter 7: Installing the Windows Drivers
92
Figure 15. License Agreement Page
4. After you review the license agreement, click I accept the terms in
the license agreement and then click Next to continue.
The Ready to Install the Program Page is displayed. See Figure 16 on
page 93.
Page 93

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Figure 16. Ready to Install the Program Page
5. Click Install.
The InstallShield Wizard Completed Page is displayed. See Figure 17
on page 94.
93
Page 94

Chapter 7: Installing the Windows Drivers
Using Silent
Installation
Figure 17. InstallShield Wizard Completed Page
6. Click Finish to close the wizard.
7. The installer determines if a system restart is necessary. Follow the
on-screen instructions.
Silent installation provides a command-line silent mode which allows for
unattended installation. This section discusses the various ways to
perform a silent installation on all of the Windows Operating Systems
supported by the AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 adapters. See
the following:
“Performing a Silent Install” on page 95
“Performing a Silent Install and Creating a Log File” on page 95
“Performing a Silent Upgrade” on page 95
“Performing a Silent Uninstall” on page 95
“Performing a Silent Reinstall” on page 96
94
Page 95

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Note
Note
All commands are case sensitive.
User must "Run as Administrator" for Vista when using "msiexec" for
"silent" install or uninstall procedures.
For detailed instructions and information about unattended installs,
refer to the Silent.txt file in the DrvInst folder.
Performing a Silent Install
To perform a silent install from within the installer source folder, enter one
of the following:
setup /s /v/qn
or
msiexec /i "BDrv5706.msi" /qn
Performing a Silent Install and Creating a Log File
To perform a silent install and create a log file at (f:\1testlog.txt), enter:
setup /s /v"/qn /L f:\1testlog.txt"
Performing a Silent Upgrade
To perform a silent upgrade from within the installer source folder, enter:
setup /s /v/qn
Performing a Silent Uninstall
There are two ways to perform a silent uninstall— from the installer source
folder and from the any folder.
In some circumstances, you must reboot your system before uninstallation
can continue. If you used REBOOT=ReallySuppress to suppress the
reboot, the uninstallation may be suspended. In this case, you need
to reboot manually for the uninstallation to continue.
95
Page 96

Chapter 7: Installing the Windows Drivers
Note
Note
To perform a silent uninstall from within the installer source folder, enter:
msiexec /x "BDrv5706.msi" /qn
To perform a silent uninstall from any folder, enter:
msiexec /x "{F0DA8A3F-1457-419E-96F4-235DD3EF41E1}" /
qn
Performing a Silent Reinstall
To perform a silent reinstall of the same installer, enter:
The hexidecimal number above may differ from your current
installer. Check the Key name corresponding with the Broadcom
Advanced Control Suite 3 (BACS) application in
HKLM\Software\Mictrosoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall for
the correct hexidecimal number.
setup /s /v"/qn REINSTALL=ALL"
Use REINSTALL switch only if the same installer is already installed
on the system. If you are upgrading an earlier version of the installer,
use setup /s /v/qn as described above.
96
Page 97

AT-2973SX, AT-2973T, and AT-2973T/4 NetExtreme II Family Adapters Installation and User’s Guide
Note
Removing the Device Drivers
This section discusses how to remove the device drivers.
Windows Server 2003, Windows Server 2008, and Windows Server
2008 R2 provide the Device Driver Rollback feature to replace a
device driver with one that was previously installed. However, the
complex software architecture of the NetXtreme II device may
present problems if the rollback feature is used on one of the
individual components. Therefore, Allied Telesis recommends that
changes to driver versions be made only through the use of a driver
installer.
To remove the device drivers, do the following:
1. In Control Panel, double-click Add or Remove Programs.
2. Click Broadcom NetXtreme II GigE Driver Installer, and then click
Remove. Follow the on screen prompts.
3. Click Yes to restart your system.
- or -
4. Click No to restart your system at a later time.
5. Click OK to acknowledge that the installation has been suspended.
The uninstallation of the driver is postponed until the next restart of
your system.
97
Page 98

Chapter 7: Installing the Windows Drivers
98
Page 99

Chapter 8
Setting Advanced Properties
For all of the Windows operating systems, you access the Windows
Advanced Properties from the Advanced Tab. Although the default values
of the Advanced Properties are appropriate in most cases, you can change
any of the available options to meet the requirements of your system.
This chapter discusses the following topics:
“Accessing the Advanced Tab” on page 100
“Modifying Advanced Properties” on page 107
99
Page 100

Chapter 8: Setting Advanced Properties
Accessing the Advanced Tab
To modify the configuration properties of the Windows Operating systems,
you must access the Advanced Tab. Depending on your operating
system, there are several ways to do this. See the following procedures:
“Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Server 2003” on page 100
“Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Server 2008, Windows
Server 2008 R2, and Windows 7” on page 103
“Selecting the Advanced Tab in Windows Vista” on page 104
Selecting the
Advanced Tab in
Windows Server
2003
After you have installed the adapter driver software, you can use this
procedure to access the System Property Dialog box which provides
access to the Advanced Properties on the Advanced Tab.
To access the System Properties Dialog box, do the following:
1. Start a Windows Server 2003 system and log in.
You must have Administrator privileges to update the driver software.
2. On the desktop, right click My Computer.
The My Computer window opens.
3. Select Properties from the menu.
The System Properties Dialog box opens, as shown in Figure 18 on
page 101.
100
 Loading...
Loading...