Page 1
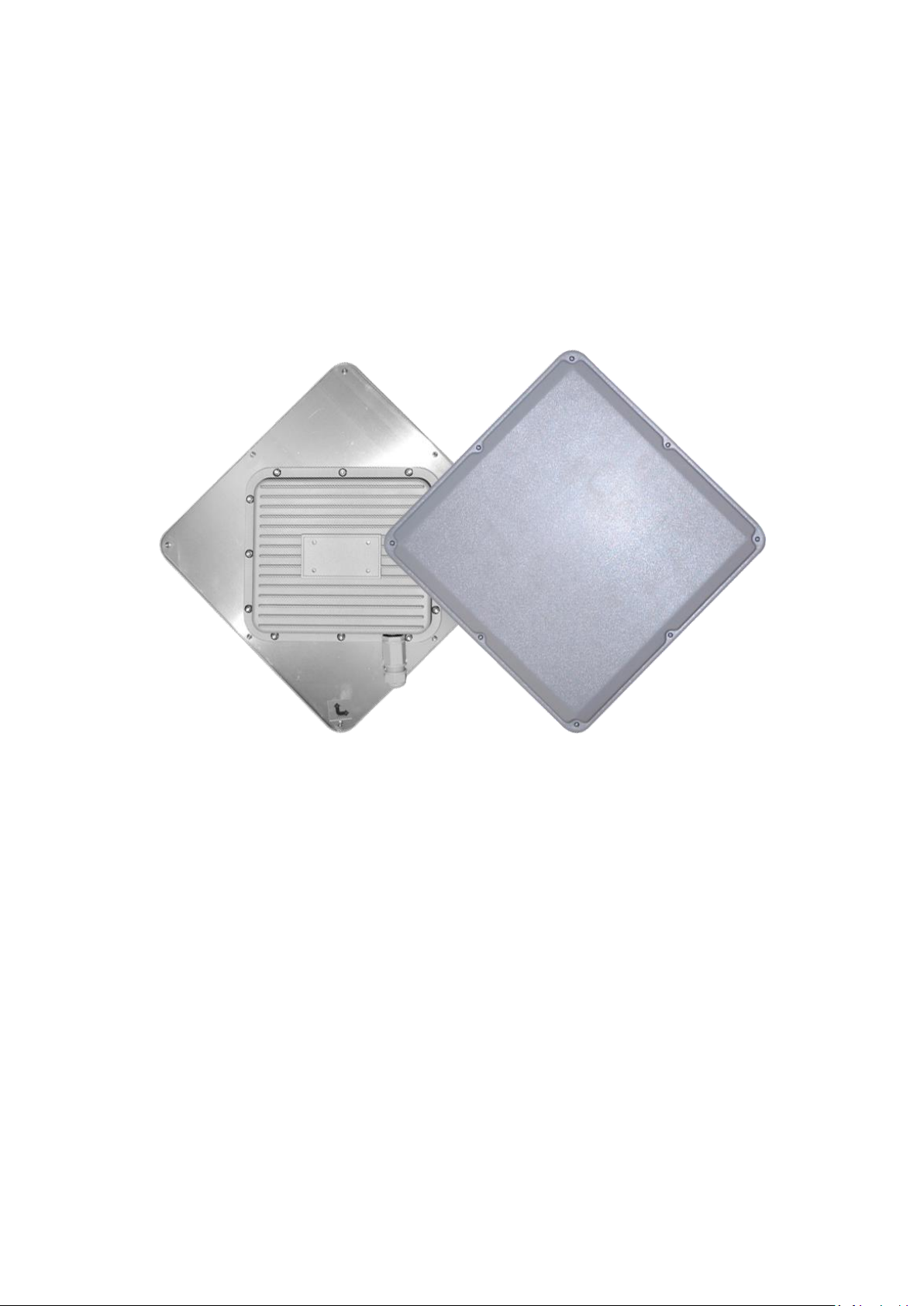
Bridge5-24
5GHz 802.11an Outdoor Bridge
User Guide
1
Page 2

INTRODUCTION ............................................................................................................... 3
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION ..................................................................................... 3
HARDWARE INSTALLATION ..................................................................................... 4
INITIAL CONFIGURATION ................................................................................................. 5
CONNECTING TO THE LOGIN PAGE ......................................................................... 5
STATUS PAGE ................................................................................................................ 5
EASY SETUP ................................................................................................................... 6
OPERATION MODE – AP ROUTER ......................................................................... 6
SETTINGS – PPPoE(ADSL) ......................................................................... 7
SETTINGS – STATIC (FIXED IP) ..................................................................... 8
SETTINGS – CABLE/DYNAMIC IP (DHCP) .................................................... 9
SETTINGS – PPTP / L2TP .......................................................................... 10
SETTINGS – IPSEC ...................................................................................... 12
OPERATION MODE – AP BRIDGE ........................................................................ 14
OPERATION MODE – CLIENT ROUTER ................................................................ 14
OPERATION MODE – CLIENT BRIDGE .................................................................. 16
ADVANCED SETUP ....................................................................................................... 19
MANAGEMENT .............................................................................................. 20
ADVANCED SETTINGS .................................................................................. 22
OPERATION MODE ....................................................................................... 24
FIREWALL CONFIGURATION ................................................................................. 24
MAC/IP/PORT FILTERING ........................................................................... 24
VIRTUAL SERVER SETTINGS ........................................................................ 26
DMZ ............................................................................................................. 27
FIREWALL ..................................................................................................... 27
QoS .............................................................................................................. 28
CONTENT FILTERING .................................................................................... 29
NETWORK SETTINGS............................................................................................ 30
WAN ............................................................................................................ 30
LAN .............................................................................................................. 34
VLAN ........................................................................................................... 35
DHCP STATIC LEASE LIST ........................................................................ 35
ADVANCED ROUTING ................................................................................... 36
WIRELESS SETTINGS ........................................................................................... 37
BASIC............................................................................................................ 37
SECURITY ..................................................................................................... 38
ADVANCED ................................................................................................... 43
ACCESS CONTROL ....................................................................................... 45
2
Page 3

①
②
① High-Gain 23dBi 5GHz Panel Antenna
② PoE LAN Port ( Passive 24V PoE )
INTRODUCTION
The Bridge5-24 is a IEEE 802.11an ISM band 5GHz wireless outdoor Bridge, which
support data rates up to 150Mbps. It is rain and splash proof when install in upright
position. Bridge5-24 also integrated 23dBi high-gain 5GHz patch antenna and
passive PoE for simplify use and installation.
HARDWARE DESCRIPTION
Below are Bridge5-24 hardware descriptions
3
Page 4

◆ Pole Mount Installation
HARDWARE INSTALLATION
4
Page 5

INITIAL CONFIGURATION
The outdoor 5GHz Bridge offers a user-friendly web-based management interface
for the configuration of all the unit’s features. Any PC directly attached to the unit
can access the management interface using a web browser, such as Internet
Explorer (version 6.0 or above).
CONNECTING TO THE LOGIN PAGE
It is recommended to make initial configuration changes by connecting a PC directly
to the OUTDOOR BRIDGE’s LAN port. The OUTDOOR BRIDGE has a default IP
address of 192.168.2.1 and a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. You must set your PC
IP address to be on the same subnet as the OUTDOOR BRIDGE (that is, the PC and
OUTDOOR BRIDGE addresses must both start 192.168.2.x). To access the
OUTDOOR BRIDGE’s management GUI interface, follow these steps:
1. Use your web browser to connect to the management interface using the default
IP address of 192.168.2.1.
2. Log into the interface by entering the default username ―admin‖ and password
―admin,‖ then click OK.
STATUS PAGE
After logging in to the web interface, the Status page displays. The Home page
top-menu-bar shows the Status, Easy Setup, Advanced and Language.
5
Page 6
EASY SETUP
The Easy Setup is designed to help you to configure the basic settings required to
get the OUTDOOR BRIDGE up and running. There are only a few basic steps you
need to set up the OUTDOOR BRIDGE to get the connection.
Click on Easy Setup to bring up the wizard
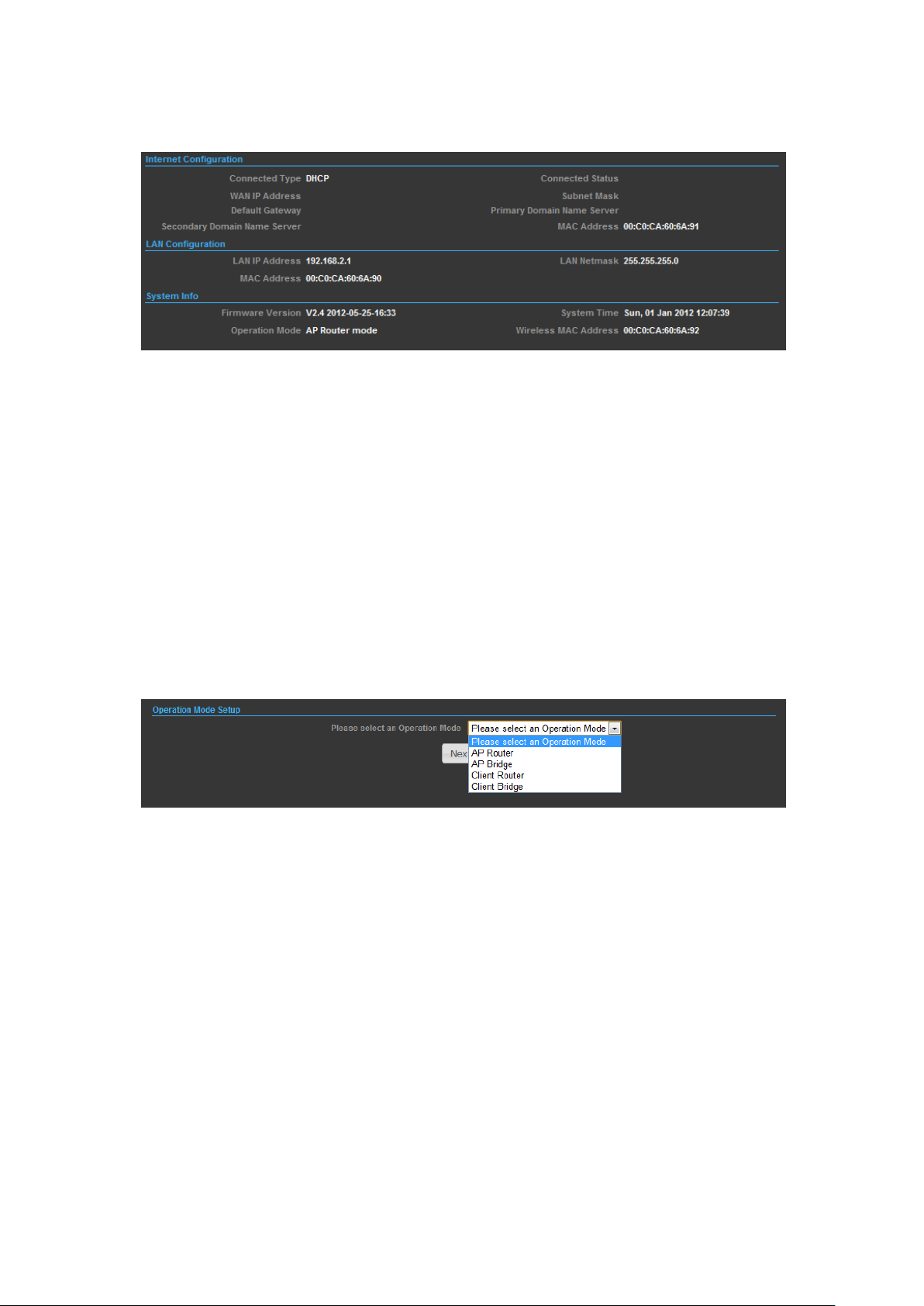
OPERATION MODE – AP ROUTER
In AP Router mode, your OUTDOOR BRIDGE unit is turned to a wireless router and
wireless interface will become the LAN side; if your PC is connected to the PoE port,
the management IP will change to the LAN IP (192.168.2.1). The remote
management will be automatically turned on to allow you managing the device from
the PoE LAN port.
6
Page 7

SETTINGS – PPPoE(ADSL)
1) Select PPPoE to be assigned automatically from an Internet service provider (ISP)
through a DSL modem using Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet (PPPoE).
2)
◆ User Name — Sets the PPPoE user name for the WAN port.
◆ Password — Sets a PPPoE password for the WAN port.
◆ Verify Password — Prompts you to re-enter your chosen password.
◆ Operation Mode — Enables and configures the keep alive time and configures the
on-demand idle time.
3)
Security Setup
7
Page 8
Network Name (SSID) — SSID (Service Set Identification) must be assigned to all
wireless devices in your network. Considering your wireless network security.
Security Mode — Select the security method and then configure the required
parameters. (Options: Disabled, WEP-AUTO, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-Auto-PSK,
WPA, WPA2, WPA-Auto, 802.1X; Default: Disabled)
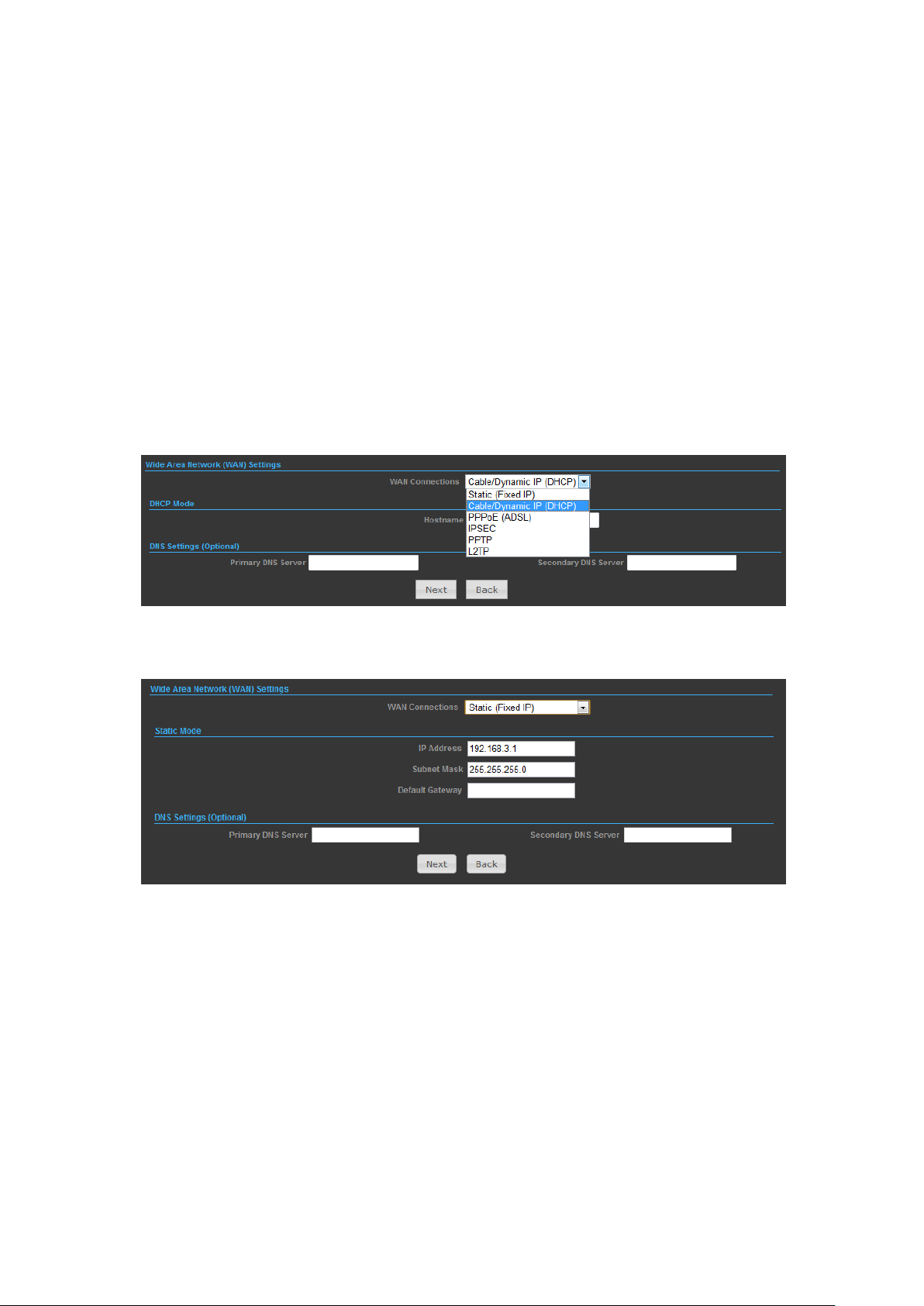
SETTINGS – STATIC (FIXED IP)
1) Select Static (Fixed IP), if your Internet service provider (ISP) to be permanent
address on the Internet. A Static IP address is a number (in the form of a dotted
quad)
2)
◆ IP Address — Sets the static IP address.
◆ Subnet Mask — Sets the static IP subnet mask. (Default: 255.255.255.0)
◆ Default Gateway — The IP address of a router that is used when the requested
destination IP address is not on the local subnet.
◆ Primary DNS Server — The IP address of the Primary Domain Name Server. A
DNS maps numerical IP addresses to domain names and can be used to identify
network hosts by familiar names instead of the IP addresses. To specify a DNS
server, type the IP addresses in the text field provided. Otherwise, leave the text
field blank.
◆ Secondary DNS Server — The IP address of the Secondary Domain Name Server.
8
Page 9

3)
Security Setup
Network Name (SSID) — SSID (Service Set Identification) must be assigned to all
wireless devices in your network. Considering your wireless network security.
Security Mode — Select the security method and then configure the required
parameters. (Options: Disabled, WEP-AUTO, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-Auto-PSK,
WPA, WPA2, WPA-Auto, 802.1X; Default: Disabled)
SETTINGS – CABLE/DYNAMIC IP (DHCP)
1) Select Cable/Dynamic IP (DHCP), if your Internet service provider (ISP) use a
DHCP service to assign your Router an IP address when connecting to the
Internet.
2)
The host name that you selected from the DHCP service provider.
3)
9
Page 10

Security Setup
Network Name (SSID) — SSID (Service Set Identification) must be assigned to all
wireless devices in your network. Considering your wireless network security.
Security Mode — Select the security method and then configure the required
parameters. (Options: Disabled, WEP-AUTO, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-Auto-PSK,
WPA, WPA2, WPA-Auto, 802.1X; Default: Disabled)
SETTINGS – PPTP / L2TP
1) Select PPTP, if you are using PPTP service to gain connection to the Internet.
2)
◆ Server IP — Sets the PPTP server IP Address. (Default: pptp_server)
◆ User Name — Sets the PPTP user name for the WAN port.
◆ Password — Sets a PPTP password for the WAN port.
◆ Address Mode — Sets a PPTP network mode. (Default: Dynamic IP)
◆ Operation Mode — Enables and configures the keep alive time.
◆ Primary DNS Server — The IP address of the Primary Domain Name Server. A
10
Page 11

DNS maps numerical IP addresses to domain names and can be used to identify
network hosts by familiar names instead of the IP addresses. To specify a DNS
server, type the IP addresses in the text field provided. Otherwise, leave the text
field blank.
◆ Secondary DNS Server — The IP address of the Secondary Domain
Name Server.
3)
Network Name (SSID) — SSID (Service Set Identification) must be assigned to all
wireless devices in your network. Considering your wireless network security.
Security Mode — Select the security method and then configure the required
parameters. (Options: Disabled, WEP-AUTO, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-Auto-PSK,
WPA, WPA2, WPA-Auto, 802.1X; Default: Disabled)
SETTINGS – L2TP
1) Select L2TP, if you are using PPTP service to gain connection to the Internet.
2)
11
Page 12

◆ Server IP — Sets the L2TP server IP Address. (Default: l2tp_server)
◆ User Name — Sets the L2TP user name for the WAN port.
◆ Password — Sets a L2TP password for the WAN port.
◆ Address Mode — Sets a L2TP network mode. (Default: Dynamic IP)
◆ Operation Mode — Enables and configures the keep alive time.
◆ Primary DNS Server — The IP address of the Primary Domain Name Server. A
DNS maps numerical IP addresses to domain names and can be used to identify
network hosts by familiar names instead of the IP addresses. To specify a DNS
server, type the IP addresses in the text field provided. Otherwise, leave the text
field blank.
◆ Secondary DNS Server — The IP address of the Secondary Domain Name Server.
3)
Network Name (SSID) — SSID (Service Set Identification) must be assigned to all
wireless devices in your network. Considering your wireless network security.
Security Mode — Select the security method and then configure the required
parameters. (Options: Disabled, WEP-AUTO, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-Auto-PSK,
WPA, WPA2, WPA-Auto, 802.1X; Default: Disabled)
SETTINGS – IPSEC
1) Select IPSec, if you are using IPSec service to gain connection to the Internet.
2)
12
Page 13

Verify the desire settings and use scroll down for more options.
◆ IPSec Connection Type – Use drop down menu to select from Road Warrior
Tunnel, Host to Host Tunnel, Subnet to Subnet Tunnel, Host to Host Transport,
Pass trough, Drop, or Reject. Default setting is Road Warrior Tunnel
◆ IPSec Authentication – Use drop down menu to select from SHA-1, or MD5.
◆ SA Connection Life Time – Specify how often each SA should be rekeyed,
measured in hour.
◆ Local IP address / Subnet / Gateway – Local end point IP address, Subnet, and
Gateway IP address.
◆ IPSec Operation Mode – Use drop down menu to select from Add, Route Start,
Manual, or Ignore.
◆ IKE Key Retry –Specify maximum retry limits for negotiate key to Internet Key
Exchange.
◆ Peer IP address / Subnet / Gateway – Remote end point IP address, Subnet, and
Gateway IP address.
3)
Network Name (SSID) — SSID (Service Set Identification) must be assigned to all
wireless devices in your network. Considering your wireless network security.
Security Mode — Select the security method and then configure the required
parameters. (Options: Disabled, WEP-AUTO, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-Auto-PSK,
13
Page 14
WPA, WPA2, WPA-Auto, 802.1X; Default: Disabled)
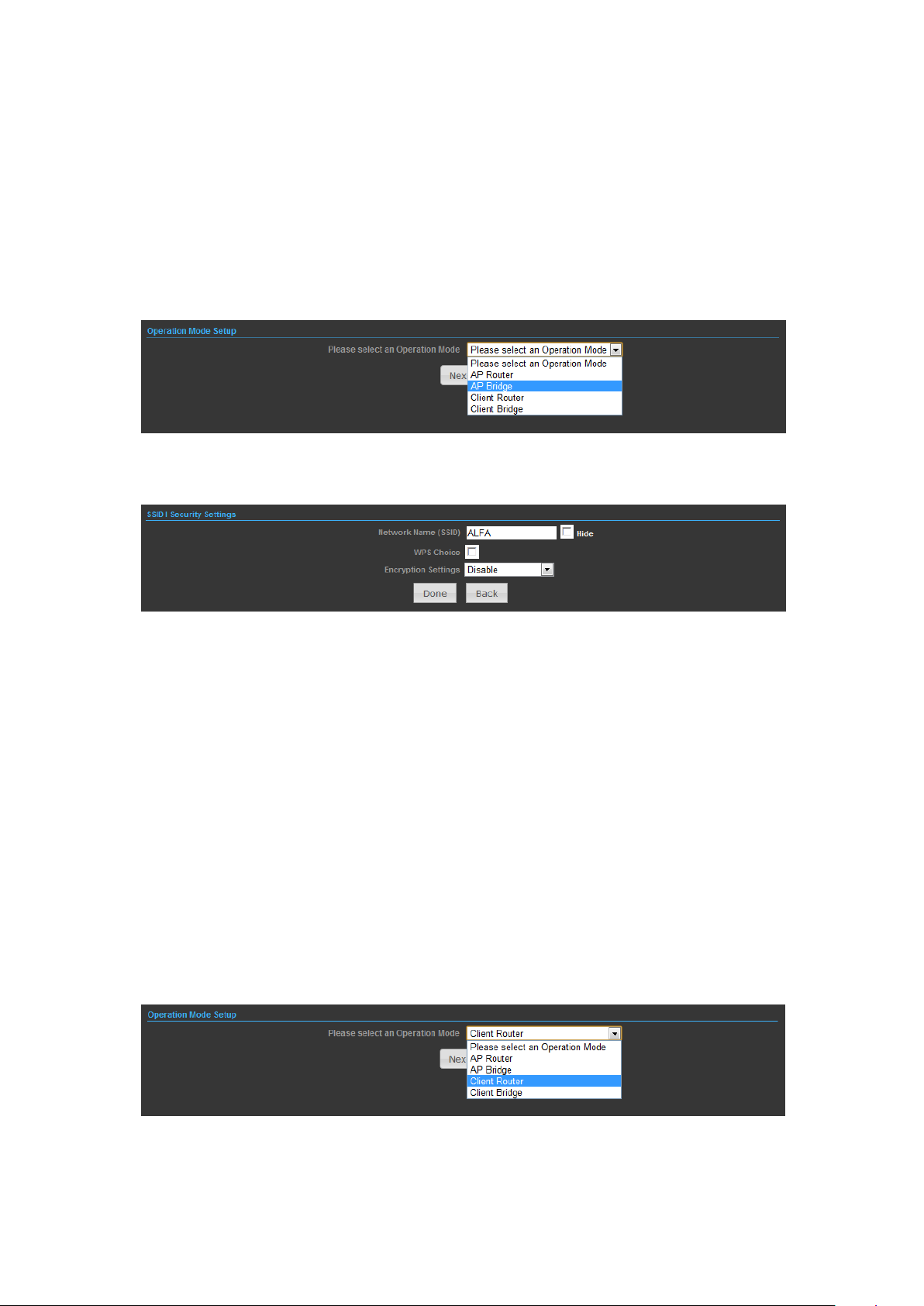
OPERATION MODE – AP BRIDGE
1) In this mode bridge your OUTDOOR BRIDGE to another Access Point.
2)
Network Name (SSID) — SSID (Service Set Identification) must be assigned to all
wireless devices in your network. Considering your wireless network security.
Security Mode — Select the security method and then configure the required
parameters. (Options: Disabled, Open, Shared, WEP-AUTO, WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK,
WPA-PSK_WPA2-PSK, WPA, WPA2, WPA1_WPA2, 802.1X; Default: Disabled
OPERATION MODE – CLIENT ROUTER
In the Client Router mode is also known as WISP. The OUTDOOR BRIDGE wireless
side is connected to the remote AP (Base-Station) as in Client Infrastructure mode.
Between the wireless and LAN is the IP sharing router function. This is used to
share Client Router connection. The WAN is on the wireless side.
2) Press Site Survey button and look for available wireless network then click on the
SSID that you attempt to connect to it; 5G is the SSID that we are going to
14
Page 15

connect in this example. Press Next button when finished.
3) Now, it shows the Profile Name, SSID, BSSID, and encryption type received from
your target network and press Next button to continue.
15
Page 16

4) Finally, you need to tell the system about IP address received from WAN, DHCP
Hostname, and DNS Server then press Next button to finish the wizard.
OPERATION MODE – CLIENT BRIDGE
In the Client Bridge mode your OUTDOOR BRIDGE will behave just the same as
Wireless adapter. With Client Bridges, the WLAN and the LAN are on the same
subnet. Consequently, NAT is no longer used and services that are running on the
original network.
16
Page 17

2) Press Site Survey button and look for available wireless network then click on the
SSID that you attempt to connect to it; 5G is the SSID that we are going to
connect in this example. Press Next button when finished.
17
Page 18

3) Now, it shows the Profile Name, SSID, BSSID, and encryption type received from
your target network and press Next button to finish the wizard.
18
Page 19

ADVANCED SETUP
In the Advanced Manual Bar, it includes all the settings such as firmware upgrade,
LAN, WAN and wireless settings that change the RF behaviors. It is important to
read through this section before attempting to make changes.
19
Page 20

MANAGEMENT
The Management section is provided for configuration of administrative needs such
as language type, user name / Password, firmware upgrade, export and import
settings, load factory defaults and reboots system.
◆ Password — The new password must not exceed 32 characters in length and
must not include any spaces. Enter the new password a second time to confirm it.
◆ Software Version - This displays the current firmware version.
To upgrade the Router's firmware, follow these instructions below:
1. Download a more recent firmware upgrade file from our website.
2. Type the path and file name of the update file into the File field. Or click the Browse
button to locate the update file.
3. Click the Upgrade button.
Note:
1. New firmware versions are posted at our website and can be downloaded for free.
There is no need to upgrade the firmware unless the new firmware has a new feature
you want to use. However, when experiencing problems caused by the Router rather
than the configuration, you can try to upgrade the firmware.
2. When you upgrade the Router's firmware, you may lose its current configurations, so
before upgrading the firmware please write down some of your customized settings to
avoid losing important settings.
3. Do not turn off the Router or press the Reset button while the firmware is being
upgraded, otherwise, the Router may be damaged.
20
Page 21

4. The Router will reboot after the upgrading has been finished.
◆ Export Settings — Click the Export Button to download current router
configuration to your PC.
◆ Import Settings — Click the Import Button to browse for the configuration file
that is currently saved on your PC. Click Import to overwrite all current
configurations with the one in the configuration file.
◆ Load Factory Defaults — If you have problems with OUTDOOR BRIDGE, which
might be a result from changing some settings, but you are unsure what settings
exactly, you can restore the factory defaults by click the Load Default Button.
◆ Reboot System — If you want to reboot the OUTDOOR BRIDGE, click the Reboot
Now Button.
21
Page 22

ADVANCED SETTINGS
The Advanced Settings section is provided for configuration of Time Zone, DDNS,
UPnP, SNMP, and Telnet/SSH.
◆ Time Zone Settings — The Time Zone Settings allows you to configure, update
and maintain the correct time on the OUTDOOR BRIDGE’s internal system clock.
◆ SNTP Server — Enter the address of an SNTP server to receive time updates.
◆ SNTP synchronization (minutes) — Specify the interval between SNTP server
updates.
DDNS Settings — DDNS lets you assign a fixed host and domain name to dynamic
Internet IP address. It is useful when you are hosting your own website, FTP server,
or other server behind the OUTDOOR BRIDGE. Before using this feature, you need
to sign up for DDNS service at www.dyndns.org , a DDNS service provider.
◆ User Name — Sets the DDNS user name for the connection.
◆ Password — Sets a DDNS password for the connection.
◆ HostName — The host name that you selected from the DDNS service provider.
22
Page 23

UPNP Settings – UPnP permits network devices to discover other network device(s)
preference and establish functional network services for data sharing,
communication, and entrainment.
SNMP Settings – Managing devices on IP networks.
◆ Telnet Settings – Enable your OUTDOOR BRIDGE unit to be accessed via
telnet utility.
◆ SSH Settings – Secure Shell. Enable your OUTDOOR BRIDGE unit to be
accessed via secure shell (SSH) based network device.
◆ Telnet/SSH Password Settings – Assign a password for telnet or secure shell
(SSH) access to your CPE unit.
23
Page 24

OPERATION MODE
The Operation Mode content four modes: AP Bridge, AP Router, Client Router and
Client Bridge.
◆ AP Bridge — The wired Ethernet and wireless are bridged together. Once the
mode is selected, all WAN related functions will be disabled.
◆ AP Router — The WAN port is used to connect with ADSL/Cable modem and the
wireless is used for your private WLAN. The NAT is existed between the 2 RJ45 ports
and all wireless clients share the same public IP address through the WAN port to
ISP. The default IP configuration for WAN port is DHCP client
◆ Client Router — The OUTDOOR BRIDGE will behave just the same as the client
mode for wireless function. However, router functions are added between the
wireless WAN side and the Ethernet LAN side. Therefore, the Client Router
subscriber can share the Client Router connection without the extra router.
◆ Client Bridge — The OUTDOOR BRIDGE will behave just the same as Wireless
adapter. With Client Bridges, the WLAN and the LAN are on the same subnet.
Consequently, NAT is no longer used and services that are running on the original
network.
FIREWALL CONFIGURATION
MAC/IP/PORT FILTERING
MAC/IP/Port filtering restricts connection parameters to limit the risk of intrusion
and defends against a wide array of common hacker attacks. MAC/IP/Port filtering
allows the unit to permit, deny or proxy traffic through its MAC addresses, IP
addresses and ports. The OUTDOOR BRIDGE allows you define a sequential list of
permit or deny filtering rules. This device tests ingress packets against the filter
rules one by one. A packet will be accepted as soon as it matches a permit rule, or
24
Page 25
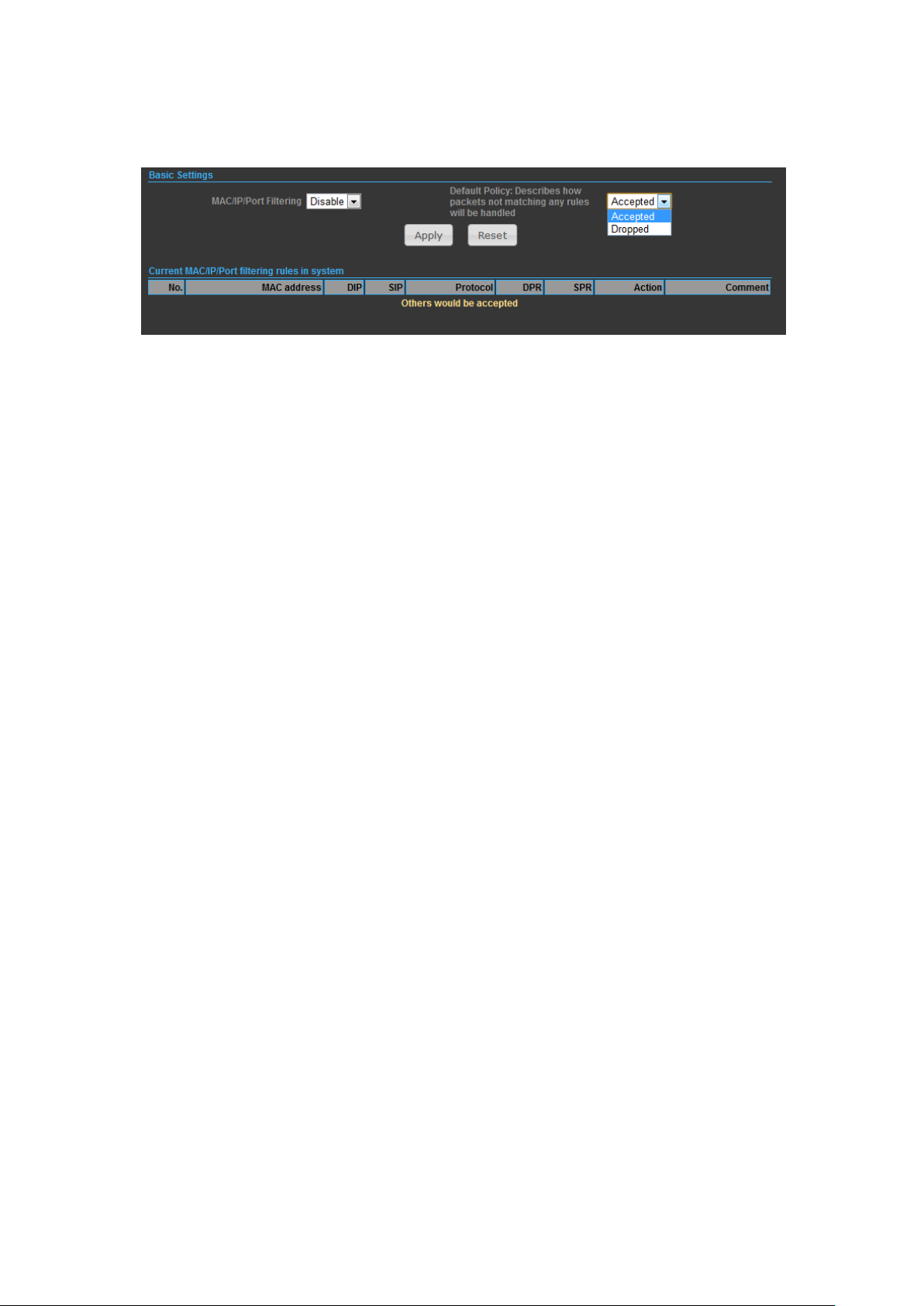
dropped as soon as it matches a deny rule. If no rules match, the packet is either
accepted or dropped depending on the default policy setting.
◆ MAC/IP/Port Filtering — Enables or disables MAC/IP/Port Filtering.
◆ Default Policy — When MAC/IP/Port Filtering is enabled, the default policy will be
enabled. If you set the default policy to ―Dropped‖, all incoming packets that don’t
match the rules will be dropped. If the policy is set to "Accepted," all incoming
packets that don't match the rules are accepted.
◆ MAC Address — Specifies the MAC address to block or allow traffic from.
◆ DIP — Specifies the destination IP address to block or allow traffic from.
◆ SIP — Specifies the source IP address to block or allow traffic from.
◆ Protocol — Specifies the destination port type, TCP, UDP or ICMP.
◆ Destination Port Range — Specifies the range of destination port to block traffic
from the specified LAN IP address from reaching.
◆ Source Port Range — Specifies the range of source port to block traffic from the
specified LAN IP address from reaching.
◆ Action — Specifies if traffic should be accepted or dropped. (Default: Accept)
◆ Comment — Enter a useful comment to help identify the filtering rules.
◆ Current Filtering rules — The Current Filter Table displays the configured IP
addresses and ports that are permitted or denied access to and from.
No. — The table entry number.
MAC Address — Displays a MAC address to filter.
Destination IP Address (DIP) — Displays the destination IP address.
Source IP Address (SIP) — Displays the source IP address.
Protocol — Displays the protocol type.
Destination Port Range (DPR) — Displays the destination port range.
Source Port Range (SPR) — Displays the source port range.
Action — Displays if the specified traffic is accepted or dropped.
Comment — Displays a useful comment to identify the filter rules.
25
Page 26

VIRTUAL SERVER SETTINGS
Virtual Server (sometimes referred to as Port Forwarding) is the act of forwarding
traffic from one network node to another based on received protocol port number.
This technique can allow an external user to reach a port on a private IP address
(inside a LAN) from the outside through a NAT enabled router.
◆ Virtual Server — Selects between enabling or disabling port forwarding the
virtual server. (Default: Disable)
◆ IP Address — Specifies the IP address of a server on the local network to allow
external access.
◆ Private Port — The protocol port number on the local server.
◆ Public Port — The protocol port number on the router’s WAN interface.
◆ Protocol — Specifies the protocol to forward, either TCP, UDP, or TCP&UDP.
◆ Comment — Enter a useful comment to help identify the port forwarding service
on the network.
◆ Current Virtual Servers in System — The Current Port Forwarding Table displays
the entries that are allowed to forward packets through the OUTDOOR BRIDGE’s
firewall.
IP Address — The IP address of a server on the local network to allow
external access.
Port Mapping — displays the port mapping for the server.
Protocol — Displays the protocol used for forwarding this port.
Comment — Displays a useful comment to identify the nature of the port to
26
Page 27

be forwarded.
DMZ
DMZ is to specified host PC on the local network to access the Internet without any
firewall protection. Some Internet applications, such as interactive games or video
conferencing, may not function properly behind the firewall. By specifying a
Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) host, the PC's TCP ports are completely exposed to the
Internet, allowing open two-way communication. The host PC should be assigned a
static IP address (which is mapped to its MAC address) and this must be configured
as the DMZ IP address.
◆ DMZ Settings — Sets the DMZ status. (Default: Disable)
◆ DMZ IP Address — Specifies an IP address on the local network allowed
unblocked access to the WAN.
FIREWALL
Firewall functions which will help to protect your network and computer. You can
utilized firmware functions to protect your network from hackers and malicious
intruders.
27
Page 28

◆ Remote Management (via WAN) — allow or deny to manage the router from
anywhere on the Internet.
◆ Remote Management Port — The port that you will use to address the
management from the Internet. For example, if you specify port 2020, then to
access the OUTDOOR BRIDGE from Internet, you would use a URL of the form:
http://xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx:2020/
◆ Ping from WAN Filter — When Allow, the OUTDOOR BRIDGE does not respond to
ping packets received on the WAN port.
◆ SPI Firewall — SIP firewall help to keep track of the state of network connections
(such as TCP streams, UDP communication) traveling across it. It is programmed to
distinguish legitimate packets for different types of connections. Only packets
matching a known active connection will be allowed by the firewall; others will be
rejected.
◆ Network Address Translation — NAT is the process of modifying IP address
information in IP packet headers while in transit across a traffic routing device.
QoS
Manage your network with independent bandwidth for every computer that
connects to this CPE.
28
Page 29

◆ QoS Setup — Enable or Disable the QoS service on your CPE.
◆ Upload Bandwidth / Download Bandwidth — Value you configure should be real
bandwidth your ISP provides to you.
◆ Target — Defined priority for the application in the QoS, and the application not
in the rule list would automatically have lower priority.
CONTENT FILTERING
The OUTDOOR BRIDGE provides a variety of options for blocking Internet access
based on content, URL and host name.
◆ Web URL Filter Settings — By filtering inbound Uniform Resource Locators (URLs)
the risk of compromising the network can be reduced. URLs are commonly used to
point to websites. By specifying a URL or a keyword contained in a URL traffic from
that site may be blocked.
29
Page 30

◆ Current URL Filters — Displays current URL filter.
◆ Add a URL Filter — Adds a URL filter to the settings.
◆ Delete a URL Filter — Deletes a URL filter entry from the list.
◆ Web Host Filter Settings — Allows Internet content access to be restricted based
on web address keywords and web domains. A domain name is the name of a
particular web site. For example, for the address www.HOST.com, the domain name
is HOST.com. Enter the Keyword then click ―Add.‖
◆ Current Host Filters — Displays current Host filter.
◆ Add a Host Filter — Enters the keyword for a host filtering.
◆ Delete a Host Filter — Deletes a Host filter entry from the list.
NETWORK SETTINGS
WAN
In this section, there are several connection types to choose from; Static IP, DHCP,
PPPoE, PPTP, L2TP and IPSec. If you are unsure of your connection method, please
contact your Internet Service Provider.
CABLE/DYNAMIC IP (DHCP)
◆ Hostname — Specifies the host name of the DHCP client.
30
Page 31

◆ Primary DNS Server — The IP address of the Primary Domain Name Server. A
DNS maps numerical IP addresses to domain names and can be used to identify
network hosts by familiar names instead of the IP addresses. To specify a DNS
server, type the IP addresses in the text field provided. Otherwise, leave the text
field blank.
◆ Secondary DNS Server — The IP address of the Secondary Domain
Name Server.
PPPoE (ADSL)
◆ User Name — Sets the PPPoE user name for the WAN port.
◆ Password — Sets a PPPoE password for the WAN port.
◆ Verify Password — Prompts you to re-enter your chosen password.
◆ Operation Mode — Enables and configures the keep alive time and configures the
on-demand idle time.
STATIC IP (FIXED IP)
◆ IP Address — Sets the static IP address.
◆ Subnet Mask — Sets the static IP subnet mask. (Default: 255.255.255.0)
◆ Default Gateway — The IP address of a router that is used when the requested
destination IP address is not on the local subnet.
◆ Primary DNS Server — The IP address of the Primary Domain Name Server. A
DNS maps numerical IP addresses to domain names and can be used to identify
network hosts by familiar names instead of the IP addresses. To specify a DNS
server, type the IP addresses in the text field provided. Otherwise, leave the text
field blank.
31
Page 32

◆ Secondary DNS Server — The IP address of the Secondary Domain Name Server.
PPTP
◆ Server IP — Sets the PPTP server IP Address. (Default: pptp_server)
◆ User Name — Sets the PPTP user name for the WAN port.
◆ Password — Sets a PPTP password for the WAN port.
◆ Address Mode — Sets a PPTP network mode. (Default: Dynamic IP)
◆ Operation Mode — Enables and configures the keep alive time.
◆ Primary DNS Server — The IP address of the Primary Domain Name Server. A
DNS maps numerical IP addresses to domain names and can be used to identify
network hosts by familiar names instead of the IP addresses. To specify a DNS
server, type the IP addresses in the text field provided. Otherwise, leave the text
field blank.
◆ Secondary DNS Server — The IP address of the Secondary Domain
Name Server.
IPSec
32
Page 33

Verify the desire settings and use scroll down for more options.
◆ IPSec Connection Type – Use drop down menu to select from Road Warrior
Tunnel, Host to Host Tunnel, Subnet to Subnet Tunnel, Host to Host Transport, Pass
trough, Drop, or Reject. Default setting is Road Warrior Tunnel
◆ IPSec Authentication – Use drop down menu to select from SHA-1, or MD5.
◆ SA Connection Life Time – Specify how often each SA should be rekeyed,
measured in hour.
◆ Local IP address / Subnet / Gateway – Local end point IP address, Subnet, and
Gateway IP address.
◆ IPSec Operation Mode – Use drop down menu to select from Add, Route Start,
Manual, or Ignore.
◆ IKE Key Retry –Specify maximum retry limits for negotiate key to Internet Key
Exchange.
◆ Peer IP address / Subnet / Gateway – Remote end point IP address, Subnet, and
Gateway IP address.
L2TP
33
Page 34

◆ Server IP — Sets the L2TP server IP Address. (Default: l2tp_server)
◆ User Name — Sets the L2TP user name for the WAN port.
◆ Password — Sets a L2TP password for the WAN port.
◆ Address Mode — Sets a L2TP network mode. (Default: Dynamic IP)
◆ Operation Mode — Enables and configures the keep alive time.
◆ Primary DNS Server — The IP address of the Primary Domain Name Server. A
DNS maps numerical IP addresses to domain names and can be used to identify
network hosts by familiar names instead of the IP addresses. To specify a DNS
server, type the IP addresses in the text field provided. Otherwise, leave the text
field blank.
◆ Secondary DNS Server — The IP address of the Secondary Domain Name Server.
LAN
In this section, the LAN settings are configured based on the IP Address and Subnet
Mask. The IP address is also used to access this Web-based management interface.
It is recommended to use the default settings if you do not have an existing
network.
◆ IP Address — The IP address of OUTDOOR BRIDGE on the local area network.
34
Page 35

( Default: 192.168.2.1 )
◆ Subnet Mask — The subnet mask of OUTDOOR BRIDGE on the local area
network
◆ DHCP Server — The DHCP Server is to assign private IP address to the
OUTDOOR BRIDGE in your local area network(LAN). The default LAN IP address is
192.168.2.1, changing IP address will also change the DHCP server’s IP subnet.
VLAN
If you want to configure the Guest and Internal networks on VLAN, the switch you
are using must support VLAN. As a prerequisite step, configure a port on the switch
for handling VLAN tagged packets as described in the IEEE802.1Q standard, and
enable this field.
VLAN ID — This will cause the device to send packets with VLAN tags. The switch
connecting with the device must support VLAN IEEE802.1Q frames. The wireless
stations connecting to the SSID of a specified VLANID can communicate with the PC
connecting to the port with the same VLANID on the Switch.
DHCP STATIC LEASE LIST
Choose menu “Advanced → DHCP Static Leases List”, you can view and add a
reserved address for clients via the next screen. When you specify a reserved IP
address for a PC on the LAN, that PC will always receive the same IP address each
time when it accesses the DHCP server. Reserved IP addresses should be assigned to
the servers that require permanent IP settings.
35
Page 36

ADVANCED ROUTING
In this section, allow to configure routing feature in the OUTDOOR BRIDGE.
◆ Destination — The IP address of packets that can be routed.
◆ Type — Defines the type of destination. ( Host: Signal IP address / Net: Portion
of Network )
◆ Netmask — Displays the subnetwork associated with the destination.
◆ Gateway — Defines the packets destination next hop
◆ Interface — Select interface to which a static routing subnet is to be applied
◆ Comment — Help identify the routing
◆ RIP — Enable or disable the RIP(Routing Information Protocol) for the WAN or
LAN interface.
36
Page 37

WIRELESS SETTINGS
BASIC
◆ Wireless On/Off — Enables or Disable the radio. (Default: Turn On)
◆ Wireless Mode — There are 4 wireless mode, those are Access Point, WDS
Access Point, WDS Repeater and WDS Client
Note.
If WEP authentication is selected for WDS communication, you will then only have
one set of encryption for the entire channel.
◆ Network Name (SSID) — The name of the wireless network service provided by
the OUTDOOR BRIDGE. Clients that want to connect to the network must set their
SSID to the same as that of OUTDOOR BRIDGE.
◆ Multiple SSID — One additional VAP interface supported on the device.
◆ Frequency (Channel) — The radio channel that the OUTDOOR BRIDGE uses to
communicate with wireless clients.
◆ Network Mode — Defines the radio operating mode.
37
Page 38

SECURITY
WIRED EQUIVALENT PRIVACY (WEP)
WEP provides a basic level of security, preventing unauthorized access to the
network, and encrypting data transmitted between wireless clients and an access
point. WEP uses static shared keys (fixed-length hexadecimal or alphanumeric
strings) that are manually distributed to all clients that want to use the network.
When you select to use WEP, be sure to define at least one static WEP key for user
authentication or data encryption. Also, be sure that the WEP shared keys are the
same for each client in the wireless network.
◆ WEP-AUTO — Allows wireless clients to connect to the network using
Open-WEP (uses WEP for encryption only) or Shared-WEP (uses WEP for
authentication and encryption).
◆ Encrypt Type — Selects WEP for data encryption (OPEN mode only).
◆ Security Key Index — Selects the WEP key number to use for authentication or
data encryption. If wireless clients have all four WEP keys configured to the same
values, you can change the encryption key to any of the settings without having to
38
Page 39

update the client keys.
◆ WEP Keys — Sets WEP key values. The user must first select ASCII or
hexadecimal keys. Each WEP key has an index number. Enter key values that match
the key type and length settings. Enter 5 alphanumeric characters or 10
hexadecimal digits for 64-bit keys, or enter 13 alphanumeric characters or 26
hexadecimal digits for 128-bit keys. (Default: Hex, no preset value)
Note.
If WEP authentication is selected for WDS communication, you will then only have
one set of encryption for the entire channel.
WPA & WPA2
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) was introduced as an interim solution for the
vulnerability of WEP pending the adoption of a more robust wireless security
standard. WPA2 includes the complete wireless security standard, but also offers
backward compatibility with WPA.
◆ WPA — Clients using WPA for authentication.
◆ WPA2 — Clients using WPA2 for authentication.
◆ WPA-Auto — Clients using WPA or WPA2 for authentication.
◆ WPA Algorithms — Selects the data encryption type to use. (Default is
determined by the Security Mode selected.)
■ TKIP — Uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) keys for encryption. WPA
specifies TKIP as the data encryption method to replace WEP. TKIP avoids the
problems of WEP static keys by dynamically changing data encryption keys.
■ AES — Uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) keys for encryption. WPA2 uses
AES Counter-Mode encryption with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication
Code (CBC-MAC) for message integrity. The AES Counter-Mode/CBCMAC Protocol
(AESCCMP) provides extremely robust data confidentiality using a 128- bit key. Use
of AES-CCMP encryption is specified as a standard requirement for WPA2. Before
implementing WPA2 in the network, be sure client devices are upgraded to
39
Page 40

WPA2-compliant hardware.
■ Auto — Uses either TKIP or AES keys for encryption. WPA and
WPA2 mixed modes allow both WPA and WPA2 clients to associate to a common
SSID. In mixed mode, the unicast encryption type (TKIP or AES) is negotiated for
each client.
◆ Key Renewal Interval — Sets the time period for automatically changing data
encryption keys and redistributing them to all connected clients.
RADIUS Server — Configures RADIUS server settings.
◆ IP Address — Specifies the IP address of the RADIUS server.
◆ Port — The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port number used by the
RADIUS server for authentication messages. (Range: 1024-65535;
Default: 1812)
◆ Shared Secret — A shared text string used to encrypt messages between the
access point and the RADIUS server. Be sure that the same text string is specified
on the RADIUS server. Do not use blank spaces in the string. (Maximum length: 20
characters)
WPA-PSK & WPA2-PSK
Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA) was introduced as an interim solution for the
vulnerability of WEP pending the adoption of a more robust wireless security
standard. WPA2 includes the complete wireless security standard, but also offers
backward compatibility with WPA. For small home or office networks, WPA and
WPA2 provide a simple ―personal‖ operating mode that uses just a pre-shared key
for network access. The WPA Pre-Shared Key (WPA-PSK) mode uses a common
password phrase for user authentication that is manually entered on the access
point and all wireless clients. Data encryption keys are automatically generated by
the access point and distributed to all clients connected to the network.
◆ WPA-PSK — Clients using WPA with a Pre-shared Key are accepted for
authentication.
◆ WPA2-PSK — Clients using WPA2 with a Pre-shared Key are accepted for
authentication.
◆ WPA- Auto-PSK — Clients using WPA or WPA2 with a Preshared
40
Page 41

Key are accepted for authentication. The default data encryption type is TKIP/AES.
◆ WPA Algorithms — Selects the data encryption type to use. (Default is
determined by the Security Mode selected.)
■ TKIP — Uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) keys for encryption. WPA
specifies TKIP as the data encryption method to replace WEP. TKIP avoids the
problems of WEP static keys by dynamically changing data encryption keys.
■ AES — Uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) keys for encryption. WPA2 uses
AES Counter-Mode encryption with Cipher Block Chaining Message Authentication
Code (CBC-MAC) for message integrity. The AES Counter-Mode/CBCMAC Protocol
(AESCCMP) provides extremely robust data confidentiality using a 128- bit key. Use
of AES-CCMP encryption is specified as a standard requirement for WPA2. Before
implementing WPA2 in the network, be sure client devices are upgraded to
WPA2-compliant hardware.
■ Auto — Uses either TKIP or AES keys for encryption. WPA and
WPA2 mixed modes allow both WPA and WPA2 clients to associate to a common
SSID. In mixed mode, the unicast encryption type (TKIP or AES) is negotiated for
each client.
◆ Pass Phrase — The WPA Preshared Key can be input as an ASCII string (an
easy-to-remember form of letters and numbers that can include spaces) or
Hexadecimal format. (Range: 8~63 ASCII characters, or exactly 64 Hexadecimal
digits)
◆ Key Renewal Interval — Sets the time period for automatically changing data
encryption keys and redistributing them to all connected clients.
IEEE 802.1X AND RADIUS
IEEE 802.1X is a standard framework for network access control that uses a central
RADIUS server for user authentication. This control feature prevents unauthorized
access to the network by requiring an 802.1X client application to submit user
credentials for authentication. The 802.1X standard uses the Extensible
Authentication Protocol (EAP) to pass user credentials (either digital certificates,
user names and passwords, or other) from the client to the RADIUS server. Client
authentication is then verified on the RADIUS server before the client can access the
network. Remote Authentication Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) is an authentication
protocol that uses software running on a central server to control access to
RADIUS-aware devices on the network. An authentication server contains a
database of user credentials for each user that requires network access.
The WPA and WPA2 enterprise security modes use 802.1X as the method of user
authentication. IEEE 802.1X can also be enabled on its own as a security mode for
41
Page 42

user authentication. When 802.1X is used, a RADIUS server must be configured and
be available on the connected wired network.
RADIUS Server — Configures RADIUS server settings.
◆ IP Address — Specifies the IP address of the RADIUS server.
◆ Port — The User Datagram Protocol (UDP) port number used by the
RADIUS server for authentication messages. (Range: 1024-65535; Default: 1812)
◆ Shared Secret — A shared text string used to encrypt messages between the
access point and the RADIUS server. Be sure that the same text string is specified
on the RADIUS server. Do not use blank spaces in the string. (Maximum length: 20
characters)
WI-FI PROTECTED SETUP (WPS)
Wi-Fi Protected Setup (WPS) is designed to ease installation and activation of
security features in wireless networks. WPS has two basic modes of operation,
Push-button Configuration (PBC) and Personal Identification Number (PIN). The
WPS PIN setup is optional to the PBC setup and provides more security. The WPS
button on the Wireless Router can be pressed at any time to allow a single device to
easily join the network. The WPS Settings page includes configuration options for
setting WPS device PIN codes and activating the virtual WPS button.
◆ WPS SSID — The service set identifier for the unit.
◆ AP PIN — Displays the PIN Code for the Wireless Router.
◆ WPS Name — WPS name for connecting to the device.
◆ Security Mode — Selects between methods of broadcasting the WPS beacon to
42
Page 43

network clients wanting to join the network:
WPA Algorithms — Selects the data encryption type to use. (Default is determined
by the Security Mode selected.)
◆ TKIP — Uses Temporal Key Integrity Protocol (TKIP) keys for encryption. WPA
specifies TKIP as the data encryption method to replace WEP. TKIP avoids the
problems of WEP static keys by dynamically changing data encryption keys.
◆ AES — Uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) keys for encryption. WPA2
uses AES Counter-Mode encryption with Cipher Block Chaining Message
Authentication Code (CBC-MAC) for message integrity. The AES
Counter-Mode/CBCMAC Protocol (AESCCMP) provides extremely robust data
confidentiality using a 128- bit key. Use of AES-CCMP encryption is specified as a
standard requirement for WPA2. Before implementing WPA2 in the network, be sure
client devices are upgraded to WPA2-compliant hardware.
◆ Auto — Uses either TKIP or AES keys for encryption. WPA and
WPA2 mixed modes allow both WPA and WPA2 clients to associate to a common
SSID. In mixed mode, the unicast encryption type (TKIP or AES) is negotiated for
each client.
◆ Key Renewal Interval — Sets the time period for automatically changing data
encryption keys and redistributing them to all connected clients.
◆ Pass Phrase — The WPA Preshared Key can be input as an ASCII string (an
easy-to-remember form of letters and numbers that can include spaces) or
Hexadecimal format. (Range: 8~63 ASCII characters, or exactly 64 Hexadecimal
digits)
ADVANCED
43
Page 44

◆ Packet Aggregate — A performance enhancement that combines data
packets together when the feature is supported by compatible clients. (Default:
Enabled)
◆ WMM — Sets the WMM operational mode on the access point. When enabled,
the QoS capabilities are advertised to WMM-enabled clients in the network. WMM
must be supported on any device trying to associated with the access point. Devices
that do not support this feature will not be allowed to associate with the access point.
(Default: Enabled)
◆ Beacon Interval — The rate at which beacon signals are transmitted from the
access point. The beacon signals allow wireless clients to maintain contact with the
access point. They may also carry powermanagement information.
◆ Data Beacon Rate (DTIM) — The rate at which stations in sleep mode must
wake up to receive broadcast/multicast transmissions. Known also as the Delivery
Traffic Indication Map (DTIM) interval, it indicates how often the MAC layer forwards
broadcast/multicast traffic, which is necessary to wake up stations that are using
Power Save mode. The default value of one beacon indicates that the access point
will save all broadcast/multicast frames for the Basic Service Set (BSS) and forward
them after every beacon. Using smaller DTIM intervals delivers broadcast/multicast
frames in a more timely manner, causing stations in Power Save mode to wake up
more often and drain power faster. Using higher DTIM values reduces the power
used by stations in Power Save mode, but delays the transmission of
broadcast/multicast frames.
◆ RTS Threshold — Sets the packet size threshold at which a Request to Send
(RTS) signal must be sent to a receiving station prior to the sending station starting
communications. The access point sends RTS frames to a receiving station to
44
Page 45

negotiate the sending of a data frame. After receiving an RTS frame, the station
sends a CTS (clear to send) frame to notify the sending station that it can start
sending data. If the RTS threshold is set to 0, the access point always sends RTS
signals. If set to 2347, the access point never sends RTS signals. If set to any other
value, and the packet size equals or exceeds the RTS threshold, the RTS/CTS
(Request to Send / Clear to Send) mechanism will be enabled. The access points
contending for the medium may not be aware of each other.
◆ Fragmentation Threshold – Configures the minimum packet size that can be
fragmented when passing through the access point. Fragmentation of the PDUs
(Package Data Unit) can increase the reliability of transmissions because it
increases the probability of a successful transmission due to smaller frame size. If
there is significant interference present, or collisions due to high network utilization,
try setting the fragment size to send smaller fragments. This will speed up the
retransmission of smaller frames. However, it is more efficient to set the fragment
size larger if very little or no interference is present because it requires overhead to
send multiple frames.
ACCESS CONTROL
Click on the drop down list to choose the access control mode. You may select Allow
Listed or Deny Listed. Allow Listed to allow those allowed MAC address or select
Deny Listed to ban those MAC address from accessing to this CPE.
45
 Loading...
Loading...