Page 1
24-bit USB Audio/MIDI Interface
Quick Start Owner’s Manual
BOX CONTENTS
• IO|2 USB AUDIO/MIDI INTERFACE
• USB CABLE
• QUICK START OWNER’S MANUAL
• IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
Manual de inicio rápido para el usuario
CONTENIDO DE LA CAJA
• INTERFAZ DE AUDIO/MIDI USB IO|2
• CABLE USB
• MANUAL DE INICIO RÁPIDO DEL USUARIO
• INSTRUCCIONES IMPORTANTES DE SEGURIDAD
Manuel d’utilisation du propriétaire
CONTENUE DE LA BOÎTE
• IO|2 AVEC INTERFACE USB AUDIO/MIDI
• CÂBLE USB
• GUIDE D’UTILISATION SIMPLIFIÉ
• CONSIGNES DE SÉCURITÉ
Kurzbedienungsanleitung
INHALT DER VERPACKUNG
• IO|2 USB AUDIO/MIDI INTERFACE
• USB KABEL
• KURZBEDIENUNGSANLEITUNG
• WICHTIGE SICHERHEITSHINWEISE
Manuale rapido di utilizzo
CONTENUTO DELLA CONFEZIONE
• INTERFACCIA AUDIO/MIDI IO|2 USB
• CAVO USB
• MANUALE RAPIDO DI UTILIZZO
• IMPORTANTI ISTRUZIONI DI SICUREZZA
Page 2

This page intentionally left blank.
Page 3

IO|2
Quick Start User’s Guide
(English)
1
Page 4

Introduction
Congratulations on your purchase of the Alesis IO|2 audio/MIDI interface!
We’re proud of this interface and we’ve taken a great deal of care in making the
IO|2 the best sounding, most rugged and easy to use audio interface on the
market.
We’ve made this quick start guide as short as possible, but please read it carefully.
It will guide you through the installation process as well as teach you how to get
the most out of your IO|2 interface.
We hope the IO|2 will serve you well for many years.
Sincerely,
The People of Alesis
2
Page 5

Key Features
Your IO|2 features the following:
• 24-bit recording and playback
• Balanced XLR and ¼” inputs with adjustable gain
• Switchable phantom power
• TRS inserts
• High quality mic preamps
• Comprehensive 4-segment input metering
• Low latency ASIO/WDM/Core Audio drivers
• Zero-Latency monitoring
• MIDI and S/PDIF inputs and outputs
• Headphone out with separate volume knob
• Bus powered for operation without power supply
• Ultra-rugged and lightweight case that’s built to last
Computer Requirements
Minimum PC Requirements:
• Pentium III 450 MHz Processor
• 128 MB RAM
• Available USB 1.1 Port
• Windows XP (with Service Pack 2 installed)
Recommended PC Requirements:
• Pentium 4 or Athlon Processor
• 512 MB RAM
• 7,200 RPM Hard Disk Drive
• Available USB 1.1 Port
• Windows XP (with Service Pack 2 installed)
Minimum Macintosh Requirements:
• Any Apple computer with native USB support
• Mac OS X “Jaguar” version 10.2 or later
• 128 MB RAM
Recommended Macintosh Requirements:
• G4 733-MHz Processor or faster
• 7,200 RPM Hard Disk Drive
• Mac OS X “Jaguar” version 10.2 or later
• 512 MB RAM
Memory Requirements
The IO|2 requires a minimum
of 128MB of RAM to operate,
but most audio applications
need more than 128MB of
RAM to run smoothly. If your
computer only has 128 MB of
memory and is sluggish while
running audio applications,
try adding memory to
improve performance.
3
Page 6

Product Registration
Please go to http://www.alesis.com and register your new IO|2.
Registering helps us to keep you up-to-date on any last minute product issues and
driver updates. If you would like, we can also send you information on other
products that might interest you.
By registering with us, you let us know what products you use (or dream about)
and this helps us bring you better products in the future.
4
Page 7
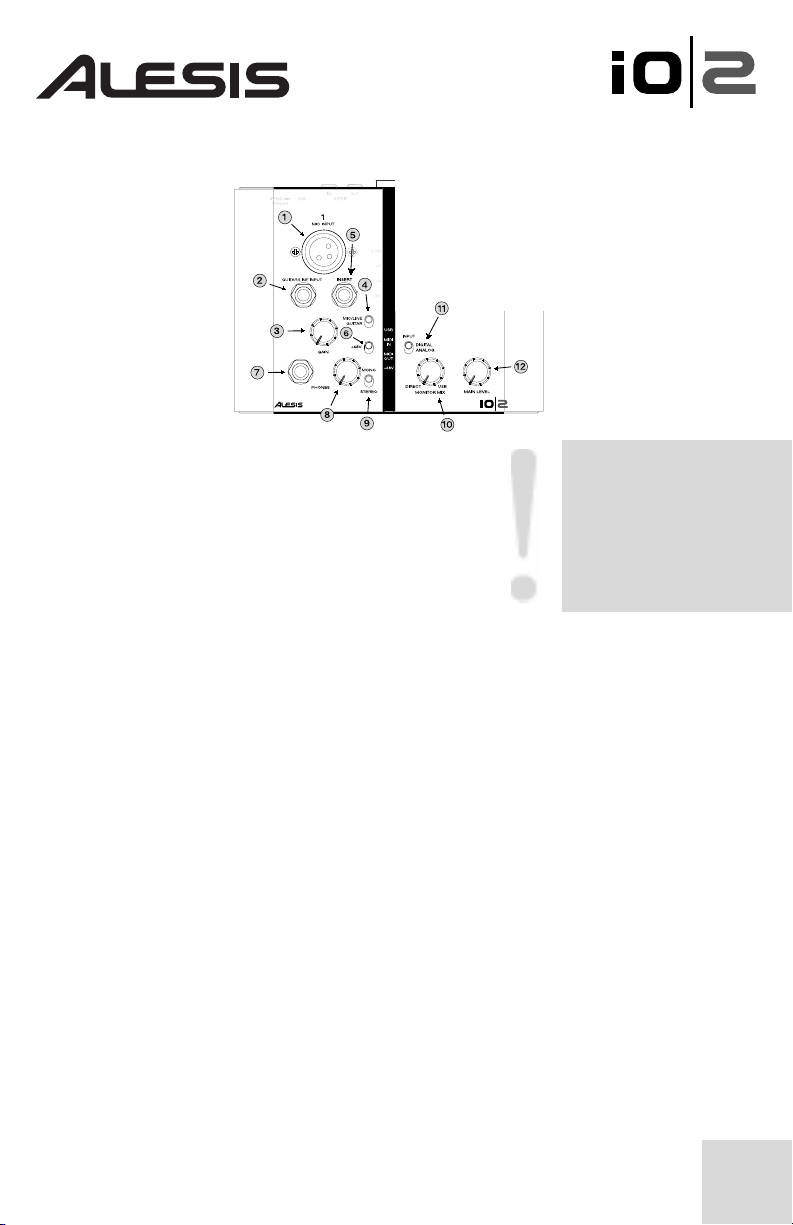
Top Panel Connections
1. Mic Input - Connect a microphone to this input.
2. Guitar/Line Input- Connect a guitar or line-level
instrument to the IO|2 using this connector. Make
sure the “Mic/Line Guitar” switch (see item #4
below) is set correctly.
3. Input Gain Knob - Set the gain level of each
channel with this knob.
4. Mic/Line or Guitar input select – Lets you select the type of instrument
you’ll be using with the Guitar/Line input (see #2 above). Select “Guitar” for
guitars and basses and “Line” for all line-level sources (synths, DATs, etc.)
5. Insert - The insert jack allows you to insert a compressor, EQ, or any other
signal processor in between IO|2’s preamplifier and the A/D converter.
6. +48v Phantom Power Switch - Phantom power switch allows you to power
condenser microphones requiring 48V phantom power. This switch activates
phantom power on both channels.
7. Headphone Output Jack - Plug your headphones into this jack.
8. Headphone Level Knob - Set your headphone level using this knob.
9. Mono/Stereo Monitoring Switch - Allows you to switch your headphones to
mono. This is useful for zero-latency monitoring situations where you may not
want your inputs panned hard left and hard right in your headphones.
10. Monitor Mix Knob - Blend in any amount of zero-latency signal from your
mic/line inputs with the output of your computer.
11. Digital/Analog Input Switch - Select the IO|2’s input source using this
switch. For normal operation, leave this switch set to “analog.” If this switch is
set to “digital,” the S/PDIF input will become active and the Lo-Z, Hi-Z, and
Insert inputs on the IO|2 will be ignored.
12. Main Level Knob - Set the level of the main outputs of the IO|2.
Audio Inputs
Do not use the Mic and
Guitar/Line inputs at the
same time on one channel.
This may overload the
channel and cause distortion.
5
Page 8
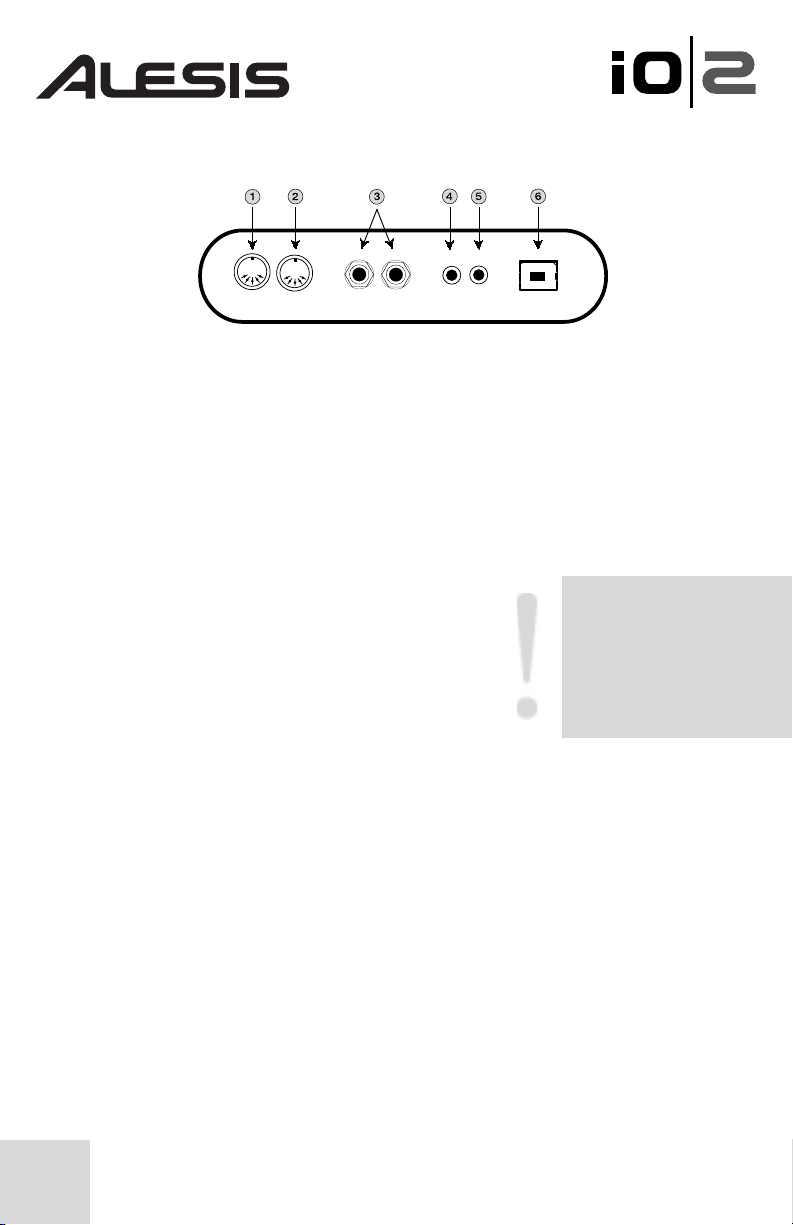
Back Panel Connections
1. MIDI Out Connector - Use a five-pin MIDI cable to connect the MIDI out of
the IO|2 to the MIDI input of an external MIDI device.
2. MIDI In Connector - Use a five-pin MIDI cable to connect the output of an
external MIDI device to the MIDI IN of the IO|2.
3. Stereo Main Output - Use balanced (TRS) or unbalanced (TS) ¼” cables to
connect the IO|2 to a mixer or powered studio monitors.
4. S/PDIF Out - Use a 110-ohm coaxial cable to connect the S/PDIF output of
your IO|2 to the digital input of another device.
5. S/PDIF In - Connect the digital output of another
device to your IO|2’s S/PDIF input using a 110-ohm
coaxial cable.
6. USB Connector - Use a standard USB cable to
hook up your IO|2 to the USB 1.1 (or higher)
connection on your computer.
Plug the IO|2 directly into
your computer, and avoid
using a USB hub. Hubs can
interfere with the IO|2’s
audio and MIDI timing
signals.
6
Page 9
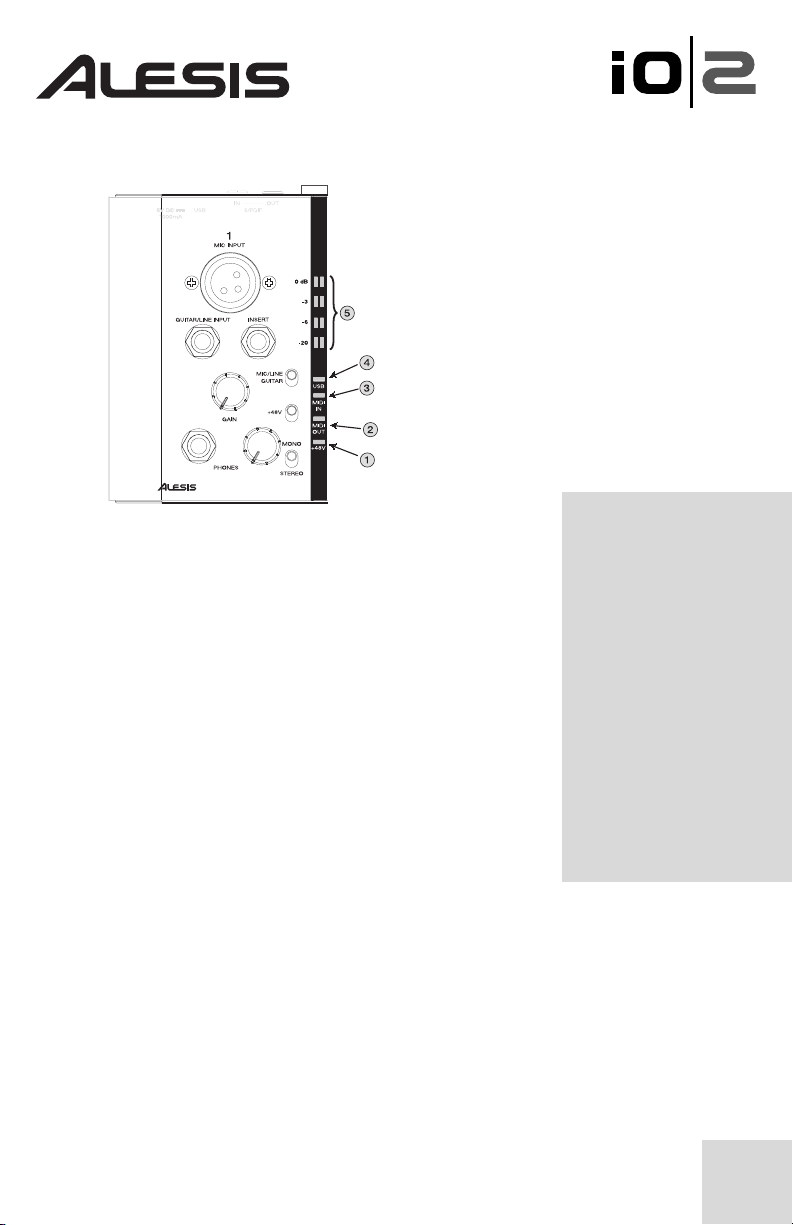
Status Lights
1. +48V – Lights up when phantom power is engaged.
2. MIDI Out – Flashes whenever MIDI data is sent out of
the IO|2.
3. MIDI In – Flashes whenever MIDI data is received from
an external MIDI controller.
4. USB – Lights up when a USB connection has been
established with your computer.
5. Stereo 4-segment input meters – Allow you to monitor
incoming levels. See the sidebar on the right for tips on how
to set levels.
Setting Gain Levels
The 4-segment input meters
are there to help you know
how loud your inputs are.
When you are adjusting the
gain knobs for each channel,
try to set your levels as loud
as possible without reaching
“0 dB.” If your input
reaches 0 dB, you are
overloading or “clipping”
the IO|2 and this results in
severe distortion.
Ideally, your levels should
peak between -6 and -3 dB on
the meters.
7
Page 10
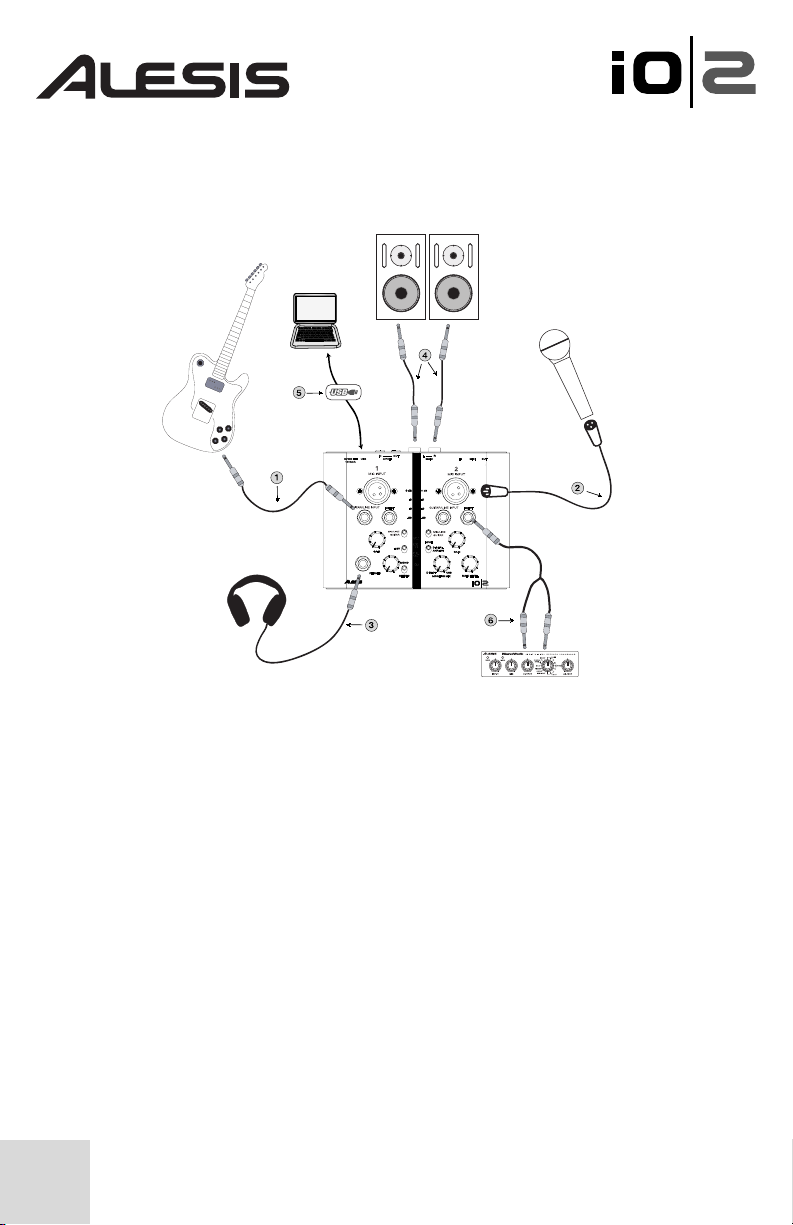
8
Hookup Diagrams
The following setup will work well for most guitarist/singers:
1. Guitars – Plug guitars into the Guitar/Line input and make sure the “Mic/Line
Guitar” switch is set to “Guitar” to ensure best recording quality.
2. Microphones – Plug microphones into the XLR input of the IO|2. Make sure
that the “Mic/Line Guitar” switch is set to “Mic/Line.” If you are using a
condenser microphone that requires phantom power (most condensers do), turn
on phantom power using the +48V switch.
3. Headphones – Plug your headphones into this jack. The IO|2’s headphone
output can be very loud, so turn the gain up slowly until you reach a level that is
comfortable for you. If you are experiencing distracting “latency delays” of your
guitar or voice, turn the Monitor Mix knob towards “direct” until you find a good
balance between the zero-latency mic inputs and the output of your computer.
4. Main Outputs – The IO|2 supports both balanced “TRS” and unbalanced
“TS” ¼” cables. If your speakers (or mixer) support balanced cables, use them as
they give you better performance and lower noise.
5. USB Cable – Plug in your USB cable directly into your computer and avoid
using a USB hub. Hubs can interfere with audio and MIDI timing signals and
cause problems for the IO|2.
6. Insert – The IO|2 allows you to easily insert an additional processor such as a
reverb or compressor in your recording path. Simply use a TRS to dual-TS “insert
cable” to connect the additional device to the IO|2’s insert jack.
Page 11
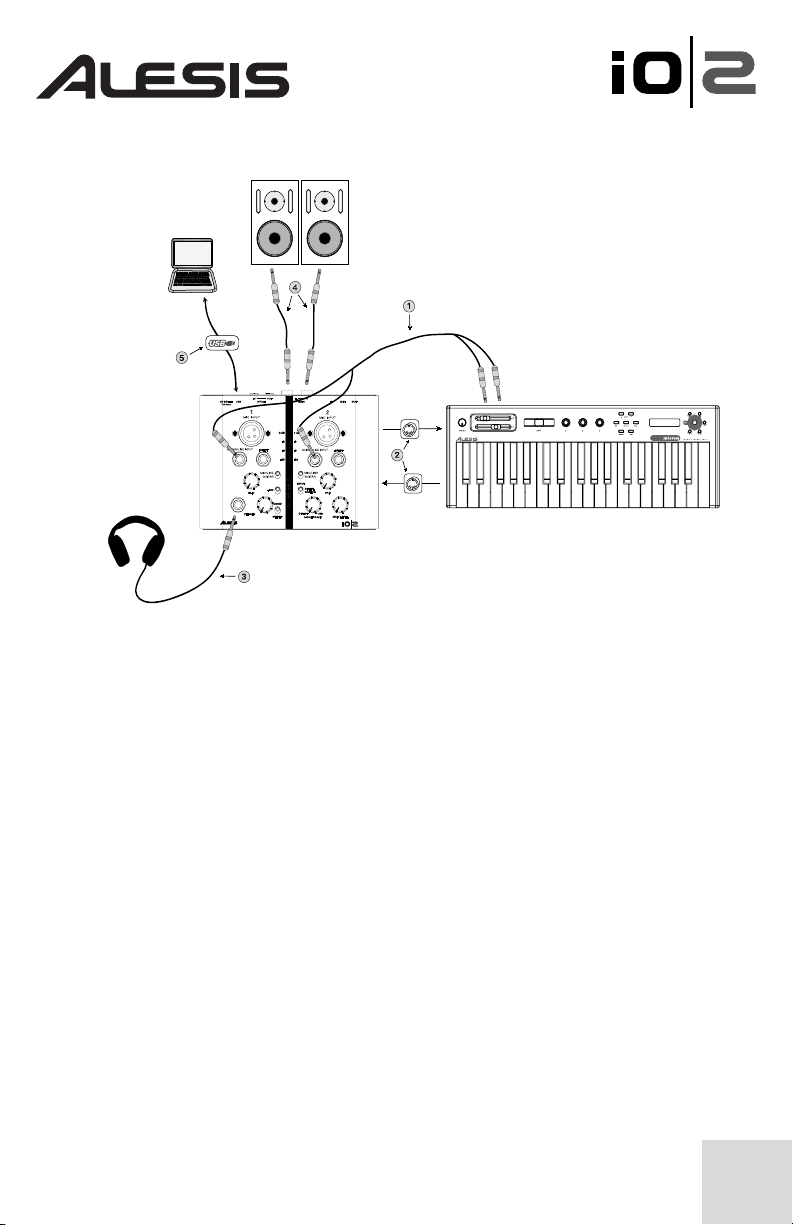
The following setup will work well for most keyboard players:
1. Keyboards – Connect the outputs of your keyboard into the “Guitar/Line”
inputs of the IO|2. If your keyboard only has one output, go ahead and connect
to whichever channel of the IO|2 you prefer. When connecting keyboards, be
sure to set the “Mic/Line Guitar” switch to “Mic/Line.”
2. MIDI – If you plan to use a MIDI sequencing program on your computer to
control your keyboard, go ahead and connect the MIDI OUT of your keyboard to
the MIDI IN of the IO|2 and the MIDI OUT of the IO|2 to the MIDI IN of
your keyboard.
3. Headphones – Plug your headphones into this jack. The IO|2’s headphone
output can be very loud, so turn the gain up slowly until you reach a level that is
comfortable for you. If you are experiencing distracting “latency delays” of your
guitar or voice, turn the Monitor Mix knob towards “direct” until you find a good
balance between the zero-latency mic inputs and the output of your computer.
4. Main Outputs – The IO|2 supports both balanced “TRS” and unbalanced
“TS” ¼” cables. If your speakers (or mixer) support balanced cables, use them as
they give you better performance and lower noise.
5. USB Cable – Plug in your USB cable directly into your computer and avoid
using a USB hub. Hubs can interfere with audio and MIDI timing signals and
cause problems for the IO|2.
9
Page 12

Plug-and-Play Connection to a Computer
Both Windows XP and Mac OS X see the IO|2 as a
plug-and play device. No installation is necessary on
Mac OS 10.2—Just connect the USB cable and you’re
ready to go. Driver installation is not required on
Windows XP since the IO|2 supports the default audio
drivers, but we highly recommend installing the Alesis
audio drivers. Our drivers will yield significantly lower
latency and better performance.
To install the IO|2 on Windows XP, simply insert the
supplied Alesis CD-ROM and wait for the following menu to pop up:
Click “Install Alesis Audio Driver,” to proceed with the driver
installation. During the installation process, Windows XP will
prompt you with the following warning:
Press “Continue Anyway,” to finish the installation. Restart the machine as the
software recommends. Once your computer is restarted, your IO|2 is ready to
record.
The IO|2 is not compatible
with earlier versions of
Windows or Mac OS.
Check http://www.Alesis.com
for driver updates and last
minute issues regarding the
IO|2
SysEx Transfers
When performing large
SysEx transfers over
Windows, you may need to
increase the buffer size on
your Windows software.
Otherwise, Windows may
process the transfer
incorrectly. Selecting a
buffer size equal to or larger
than the SysEx file virtually
assures that the transfer will
occur without errors.
10
Page 13

Troubleshooting:
Symptom Cause Solution
USB light does not
turn on.
The IO|2 is not
receiving power or
USB connection is
not being made to
your computer
Make sure you are connecting your IO|2
directly to your computer’s USB connector and
not into a USB hub. If this does not solve the
problem, double check your driver installation
and verify that the IO|2’s drivers have been
installed properly. If the problem persists, the
cable may be faulty. Try using another USB
cable.
Input meters are not
responding
S/PDIF I/O is not
working
The input switch is set
to “Analog” but my
incoming signal is still
not present (or it is
very soft).
My S/PDIF inputs
and outputs just put
out clicks, pops, or
white noise
The digital/analog
input switch may be
set incorrectly
The digital/analog
input switch may be
set incorrectly
Your phantom
power or mic/line
switches may not be
set correctly
Your coaxial cables
are not 110-ohm.
Make sure the input switch is set to “analog” if
you are recording using the XLR and 1/4”
inputs on the top of the IO|2. Only set this
switch to “digital” if you want to use the
S/PDIF connectors.
If you plan to use S/PDIF connections to
transfer audio digitally, make sure the input
switch is set to “digital.” Otherwise, leave this
switch set to “analog” for normal operation.
Double check that the mic/line switch is set
correctly for each channel. If you’re using
condenser microphones that require phantom
power, turn on the +48v phantom power
switch. Finally, make sure the gain knob is
turned up.
It is very important to use 110-ohm coaxial
cables for all S/PDIF connections. Most plain
RCA cables are NOT 110-ohm and cause
clocking problems between two digital devices.
This causes loud clicks, pops, and sustained
white noise.
11
Page 14

Specifications
Interface: IO|2 24-bit audio/MIDI interface
Features: Stereo, 24-bit inputs and outputs. Sample-rate
adjustable up to 48 kHz. Separate gain knob and
mic/line switch for each input. All balanced inputs
and outputs. Stereo ¼” headphone jack. S/PDIF
and MIDI I/O.
Audio I/O: Mic/line inputs
SNR 95dB (A-weighted) minimum -- 97dB typical
THD+N 0.007% maximum -- 0.005% typical
freq response +/-0.35dB typ
1/4" guitar inputs
SNR 94dB (A-weighted) minimum -- 96dB typical
THD+N 0.05% maximum -- 0.034% typical
freq response +/-1.2dB
Analog outputs
SNR 95dB (A-weighted) minimum -- 97dB typical
THD+N 0.007% maximum -- 0.005% typical
freq response +/-0.35dB typ
Software: Ultra-low latency ASIO/WDM drivers for
Windows XP. Full support for Core Audio on
Mac OS X.
Power options: USB bus power
Dimensions: 6.5” x 4.7” x 2.25” / 16.5 cm x 12.0 cm x 5.8 cm
Weight (net): 1.5 lbs / 0.68 kg
12
Page 15

IO|2
Guía de inicio rápido del usuario
(Español)
13
Page 16

Introducción
¡Felicitaciones por su compra de la interfaz de audio/MIDI Alesis IO|2! Estamos
orgullosos de esta interfaz y hemos tomado los mejores recaudos para hacer que la
IO|2 sea la interfaz de audio más sonora, robusta y fácil de usar del mercado.
Hemos hecho esta guía de inicio rápido lo más breve posible, pero léala
detenidamente. Lo guiará a través del proceso de instalación y le enseñará cómo
obtener los mejores resultados de su interfaz IO|2.
Esperamos que la IO|2 le brinde un buen servicio por muchos años.
Atentamente
La Gente de Alesis
14
Page 17

Características principales
Su interfaz IO|2 ofrece lo siguiente:
• Grabación y reproducción en 24 bits
• Entradas XLR y de ¼” balanceadas con ganancia ajustable
• Alimentación fantasma conmutable
• Inserciones TRS
• Preamplificadores de micrófono de alta calidad
• Medición completa de la entrada con 4 segmentos
• Drivers ASIO/WDM/Core Audio de baja latencia
• Monitoreo con cero latencia
• Entradas y salidas MIDI y S/PDIF
• Salida para auriculares con perilla de volumen independiente
• Alimentación por bus para operación sin fuente de alimentación
• Carcasa ultra robusta y liviana construida para durar
Requisitos de computadora
Requisitos mínimos de PC:
• Procesador Pentium III de 450 MHz
• 128 MB de RAM
• Puerto USB 1.1 disponible
• Windows XP (con Service Pack 2 instalado)
Requisitos de PC recomendados:
• Procesador Pentium 4 o Athlon
• 512 MB de RAM
• Disco duro de 7,200 RPM
• Puerto USB 1.1 disponible
• Windows XP (con Service Pack 2 instalado)
Requisitos mínimos de Macintosh:
• Cualquier computadora Apple con soporte de USB
nativo
• Mac OS X “Jaguar” versión 10.2 o posterior
• 128 MB de RAM
Requisitos de Macintosh recomendados:
• Procesador G4 de 733 MHz o más rápido
• Disco duro de 7,200 RPM
• Mac OS X “Jaguar” versión 10.2 o posterior
• 512 MB de RAM
Requisitos de memoria
La interfaz IO|2 requiere un
mínimo de 128 MB de RAM
para operar, pero la mayoría
de las aplicaciones de audio
requieren más de 128 MB de
RAM para funcionar
correctamente. Si su
computadora tiene sólo 128
MB de memoria y es lenta
para ejecutar aplicaciones de
audio, pruebe agregar
memoria para mejorar el
rendimiento.
15
Page 18

Registración del producto
Vaya a http://www.alesis.com y registre su nueva interfaz IO|2.
La registración nos ayuda a mantenerlo actualizado acerca de las novedades de
última hora sobre el producto y las actualizaciones de los drivers. Si desea,
también podemos enviarle información de otros productos que le puedan
interesar.
Al registrarse con nosotros, usted nos hace saber qué productos usa (o con qué
productos sueña) y eso nos ayuda a ofrecerle mejores productos en el futuro.
16
Page 19
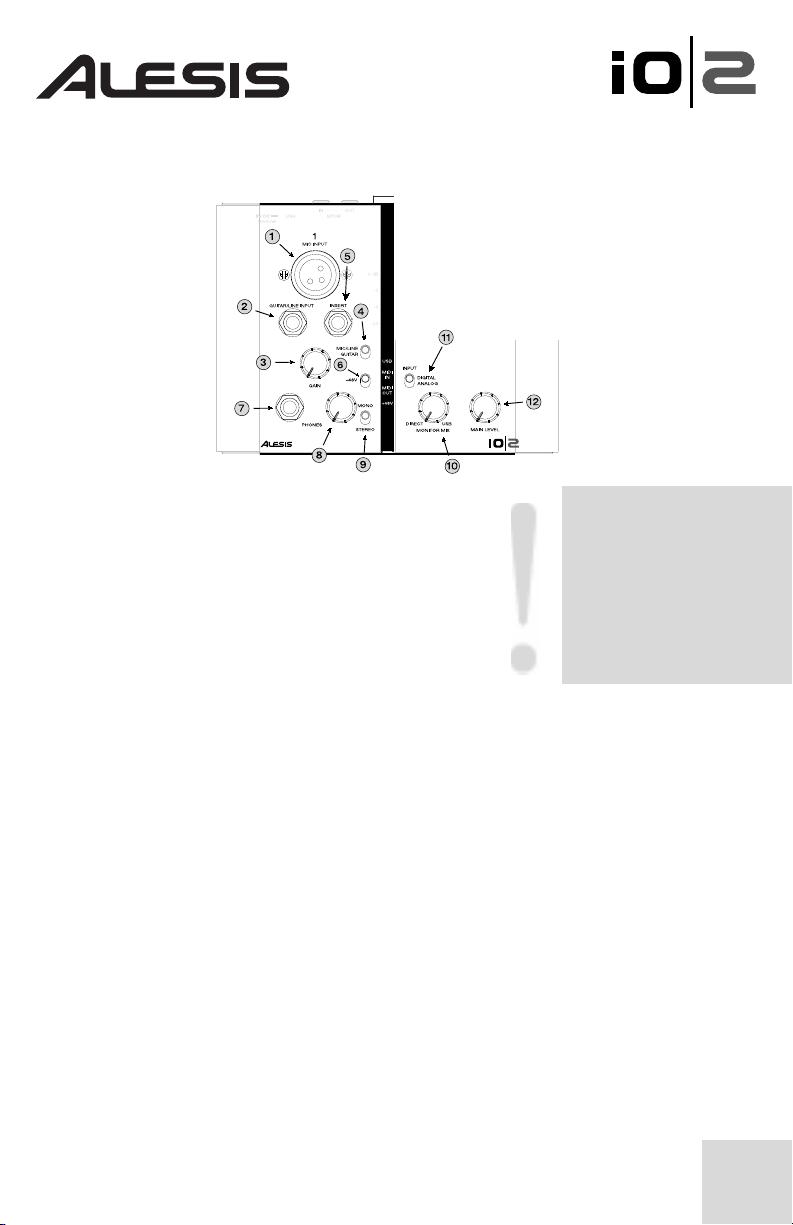
Conexiones del panel superior
1. Entrada XLR de micrófono – Conecte un
micrófono al IO/2 usando esta entrada.
2. Entrada de guitarra o instrumento – Conecte
una guitarra o instrumento al IO/2 usando este
conector. Asegúrese de que el switch de“Mic/Line
Guitar” (ver # 4) esté correctamente instalado.
3. Perilla de ganancia de entrada – Ajuste con esta
perilla el nivel de ganancia de cada canal.
4. Mic/Line o Guitar input select – Le permite elegir el tipo de instrumento a
utilizar con el “Guitar line input” (ver # 2 arriba). Seleccione “Guitar” para
guitarras y bajos, y “Line” para todas las otras fuentes niveladas como
(sintetizadores, DATs, etc).
5. Inserción – El conector de inserción permite insertar un compresor, un
ecualizador o cualquier otro procesador de señal entre el preamplificador y el
conversor A/D de la interfaz IO|2.
6. Interruptor de alimentación fantasma de +48 V – La alimentación fantasma
le permite alimentar los micrófonos de condensador que requieren esta
alimentación. Este interruptor activa la alimentación fantasma en ambos canales.
7. Conector de salida para auriculares – Enchufe sus auriculares en este
conector.
8. Perilla de nivel de auriculares – Ajuste el nivel de sus auriculares usando esta
perilla.
Entradas de audio
No utilice la entrada de
micrófono y guitarra ( Mic
and Guitar/line ) al mismo
tiempo en el mismo canal.
Esto puede saturar el canal y
causar distorsión.
17
Page 20

9. Conmutador de monitoreo mono/estéreo – Le permite conmutar sus
auriculares a mono. Este conmutador es útil para situaciones de monitoreo con
latencia cero en las que no es conveniente que sus entradas se desplacen
fuertemente a izquierda y derecha en sus auriculares.
10. Perilla de mezcla de monitor – Combine cualquier valor de señal de latencia
cero de sus entradas de micrófono/línea con la salida de su computadora.
11. Conmutador de entrada digital/analógica – Seleccione la fuente de entrada
de la interfaz IO|2 usando este conmutador. Para operación normal, deje este
conmutador en posición “analógica”. Si este conmutador se coloca en “digital,” se
activará la entrada S/PDIF y se ignorarán las entradas de baja impedancia, alta
impedancia e inserción de la interfaz IO|2.
12. Perilla de nivel principal – Ajuste el nivel de las entradas principales de la
interfaz IO|2.
18
Page 21
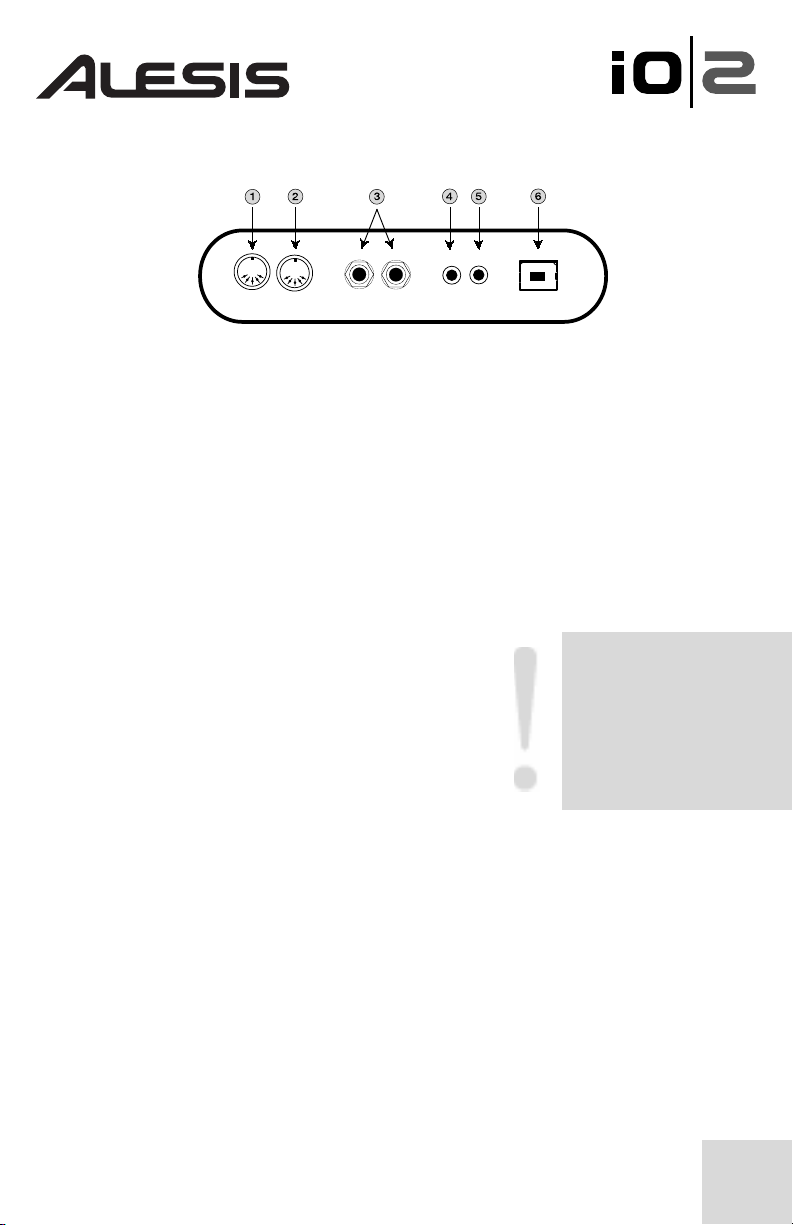
Conexiones del panel trasero
1. Conector de salida MIDI – Use un cable MIDI de cinco pines para conectar
la salida MIDI de la interfaz IO|2 a la entrada de un dispositivo MIDI externo.
2. Conector de entrada MIDI – Use un cable MIDI de cinco pines para
conectar la salida de un controlador MIDI externo a la entrada MIDI de la interfaz
IO|2.
3. Salida principal estéreo – Use cables de ¼” balanceados (TRS) o
desbalanceados (TS) para conectar la interfaz IO|2 a un mezclador o monitores
de estudio alimentados.
4. Salida S/PDIF – Use un cable coaxial de 110 ohmios para conectar la salida
S/PDIF de su interfaz IO|2 a la entrada digital de otro dispositivo.
5. Entrada S/PDIF – Conecte la salida digital de otro
dispositivo a la entrada S/PDIF de su interfaz IO|2
usando un cable coaxial de 110 ohmios.
6. Conector USB – Use un cable USB estándar para
conectar su interfaz IO|2 a la conexión USB 1.1 (o
superior) de su computadora.
Enchufe la IO|2 directamente
a su computador y evite usar
un hub USB. Los hubs
pueden interferir con las
señales de sincronización de
audio y MIDI de la interfaz
IO|2.
19
Page 22

Luces de estado
1. +48V – Se enciende cuando se acopla la alimentación
fantasma.
2. Salida MIDI – Destella toda vez que se envían datos hacia
afuera de la interfaz IO|2.
3. Entrada MIDI – Destella toda vez que se reciben datos
MIDI desde un controlador MIDI externo.
4. USB – Se enciende cuando se establece una conexión USB
con su computadora.
5. Medidores de entrada estéreo de 4 segmentos –
Permiten monitorear los niveles entrantes. Vea en la barra de
la izquierda las indicaciones para ajustar los niveles.
Cómo ajustar los niveles de
ganancia
Dispone de los medidores de
entrada de 4 segmentos para
ayudarle a conocer el nivel
de sonoridad de sus entradas.
Cuando ajuste las perillas de
ganancia de cada canal, trate
de configurar los niveles tan
altos como sea posible sin
llegar a “0 dB”. Si su
entrada llega a 0 dB, se
sobrecargará o “recortará”
(producirá “clipping”) la
interfaz IO|2 y esto
ocasionará una severa
distorsión.
Idealmente, sus niveles deben
alcanzar picos entre –6 y –3
dB en los medidores.
20
Page 23

Diagramas de conexión
La siguiente configuración funciona bien para la mayoría de los
guitarristas/cantantes:
1. Guitarras – Conecte las guitarras a la entrada de “Guitar/Line” y asegúrese de
que el switch esté colocado en “Guitar” para una mejor calidad de grabación.
2. Micrófonos – Conecte los micrófonos a la entrada de XLR del IO/2.
Asegúrese de que el switch “ Mic/Line Guitar’ esté en “Mic/Line.” Si está
utilizando un micrófono de condensador que requiera “phantom power” ( la
mayoría lo requiere), encienda el “phantom power” con el switch +48V.
3. Auriculares – Enchufe sus auriculares en este conector. La salida para
auriculares de la interfaz IO|2 puede tener una alta sonoridad, de modo que debe
aumentar la ganancia lentamente hasta alcanzar un nivel que le resulte cómodo. Si
experimenta “retardos de latencia” distractivos de su voz o guitarra, gire la perilla
de mezcla del monitor hacia “direct” hasta que encuentre un buen equilibrio entre
las entradas de micrófono de cero latencia y la salida de su computadora.
21
Page 24

4. Salidas principales – La interfaz IO|2 soporta cables de ¼” balanceados
“TRS” y desbalanceados “TS”. Si sus altavoces (o mezclador) soportan cables
balanceados, úselos puesto que le brindan una mejor performance y menor ruido.
5. Cable USB – Enchufe su cable USB directamente a su computadora y evite
usar un hub USB. Los hubs pueden interferir con las señales de sincronización de
audio y MIDI y causar problemas en la interfaz IO|2.
6. Inserción – La interfaz IO|2 le permite insertar fácilmente un procesador
adicional, tal como un reverberador o compresor en su circuito de grabación. Use
simplemente un “cable de inserción” TRS a TS doble para conectar el dispositivo
adicional al conector de inserción de la interfaz IO|2.
22
Page 25

La siguiente configuración funciona bien para la mayoría de los ejecutantes de
teclados:
1. Teclados – Conecte las salidas de su teclado a las entradas de “Guitar/Line”
del IO/2. Si su teclado tiene una sóla salida, conéctela a cualquier canal del IO/2
que ud. prefiera. Al conectar teclados, asegúrese de cambiar el switch de
“Mic/Line Guitar”a “Mic/line.”
2. MIDI – Si piensa usar un programa secuenciador MIDI en su computadora
para controlar su teclado, continúe y conecte la salida MIDI de su teclado a la
entrada MIDI de la interfaz IO|2 y la salida MIDI de esta última a la entrada
MIDI de su teclado.
3. Auriculares – Enchufe sus auriculares en este conector. La salida para
auriculares de la interfaz IO|2 puede tener una alta sonoridad, de modo que debe
aumentar la ganancia lentamente hasta alcanzar un nivel que le resulte cómodo. Si
experimenta “retardos de latencia” distractivos de su voz o guitarra, gire la perilla
de mezcla del monitor hacia “direct” hasta que encuentre un buen equilibrio entre
las entradas de micrófono de cero latencia y la salida de su computadora.
4. Salidas principales – La interfaz IO|2 soporta cables de ¼” balanceados
“TRS” y desbalanceados “TS”. Si sus altavoces (o mezclador) soportan cables
balanceados, úselos puesto que le brindan una mejor performance y menor ruido.
5. Cable USB – Enchufe su cable USB directamente a su computadora y evite
usar un hub USB. Los hubs pueden interferir con las señales de sincronización de
audio y MIDI y causar problemas en la interfaz IO|2.
23
Page 26

Conexión plug-and-play a una computadora
Tanto Windows XP como Mac OS X reconocen a la IO|2 como dispositivo tipo
plug-and-play. No es necesaria ninguna instalación en Mac OS 10.2 —
simplemente conecte el cable USB y ya está listo. No se requiere la instalación del
driver en Windows XP dado que la interfaz IO|2 soporta los drivers de audio por
defecto, pero recomendamos especialmente instalar los drivers de audio Alesis.
Nuestros drivers proporcionan una latencia significativamente inferior y una mejor
performance.
Para instalar la interfaz IO|2 en Windows XP, inserte simplemente el CD-ROM
de Alesis provisto y espere que aparezca el siguiente menú emergente:
Haga clic en “Install Alesis Audio Driver” (Instalar driver de
audio Alesis) para continuar con la instalación del driver.
Durante el proceso de instalación, Windows XP le presentará
la siguiente advertencia:
Pulse “Continue Anyway” (Continuar igualmente) para terminar la instalación.
Rearranque la máquina tal como lo recomienda el software. Una vez rearrancada
la computadora, la interfaz IO|2 está lista para grabar.
SysEx
Cuando realice
transferencias de SysEx
grandes en Windows, es
posible que necesite
aumentar el tamaño del
buffer en su software
Windows. De lo contrario,
puede suceder que Windows
procese incorrectamente la
transferencia. La selección
de un tamaño de buffer igual
o mayor que el archivo
SysEx asegura
prácticamente que la
transferencia se producirá
sin errores.
24
Page 27

Solución de problemas:
Síntoma Causa Solución
La luz USB no se
enciende.
La IO|2 no tiene
alimentación o no se
hizo la conexión
USB a su
computadora
Asegúrese de que está conectando su IO|2
directamente al conector USB de su
computadora y no a un hub USB. Si esto no
resuelve el problema, haga una doble
verificación de la instalación de su driver y
compruebe que los drivers de la IO|2 se hayan
instalado correctamente. Si el problema
persiste, puede ser una falla del cable. Pruebe
usando otro cable USB.
Los medidores de las
entradas no
responden
La entrada/salida
S/PDIF no funciona
El conmutador de
entrada está colocado
en “analógica” pero la
señal entrante no está
presente (o es muy
débil).
Las entradas S/PDIF
sólo producen clics,
chasquidos o ruido
blanco.
El conmutador de
entrada
digital/analógica
puede estar colocado
incorrectamente
El conmutador de
entrada
digital/analógica
puede estar colocado
incorrectamente
El interruptor de
alimentación
fantasma o el
conmutador de
micrófono/línea
pueden no estar
colocados en las
posiciones correctas.
Sus cables coaxiales
no son de 110
ohmios.
Asegúrese de que el conmutador de entrada
esté colocado en “analógica” sin está grabando
usando las entradas XLR y de 1/4” de la parte
superior de la IO|2. Coloque este conmutador
en “digital” sólo si desea usar los conectores
S/PDIF.
Si piensa usar las conexiones S/PDIF para
transferir audio digitalmente, asegúrese de que
el conmutador de entrada esté colocado en
“digital.” De lo contrario, deje este
conmutador en posición “analógica”.
Haga una doble verificación de que el
conmutador de micrófono/línea esté colocado
correctamente para cada canal. Si usa
micrófonos de condensador que requieren
alimentación fantasma, conecte el interruptor
de dicha alimentación de +48 V. Finalmente,
asegúrese de que la perilla de ganancia esté
girada a un valor que permita escuchar la señal.
Es muy importante usar cables coaxiales de 110
ohmios para todas las conexiones S/PDIF. La
mayoría de los cables RCA simples NO SON
de 110 ohmios y pueden causar problemas de
sincronización entre dos dispositivos digitales.
Esto causa fuertes clics, chasquidos y un ruido
blanco sostenido.
25
Page 28

Datos técnicos
Interfaz: Interfaz de audio/MIDI IO|2 de 24 bits / 48 K
Características: Entradas y salidas estéreo de 24 bits. Frecuencia de
muestreo ajustable hasta 48 kHz. Perilla de
ganancia y conmutador de micrófono/línea
independientes para cada entrada. Entradas y
salidas todas balanceadas. Conector de auriculares
estéreo de ¼”. Entradas y salidas S/PDIF y MIDI.
Entradas de micrófono/línea
Audio:
Relación S/R 95 dB (ponderación A) mínima – 97 dB típica
THD+N 0.007% máxima -- 0.005% típica
respuesta en frecuencia +/- 0.35 dB típ
Entradas de guitarra de 1/4"
Relación S/R 94 dB (ponderación A) mínima – 96 dB típica
THD+N 0.05% máxima – 0.034% típica
respuesta en frecuencia +/- 1.2 dB
Salidas analógicas
Relación S/R 95 dB (ponderación A) mínima – 97 dB típica
THD+N 0.007% máxima –0.005% típica
respuesta en frecuencia +/- 0.35 dB típ
Software: Drivers ASIO/WDM de latencia ultrabaja para
Windows XP. Soporte total de Core Audio en Mac
OS X.
Opciones de alimentación: Alimentado por bus USB
Dimensiones: 6.5” x 4.7” x 2.25” (16.5 x 12.0 x 5.8 cm)
Peso (neto): 1.5 lbs / 0.68 kg
26
Page 29

IO|2
Guide d’utilisation simplifié
(Français)
27
Page 30

Introduction
Félicitations pour l’achat de votre interface IO|2 USB audio/MIDI d’Alesis.
Nous sommes fier de cette interface et nous avons tout fait pour que l’IO|2 soit la
meilleure, la plus robuste et la plus facile l’interface à utiliser sur le marché.
Nous avons fait tout pour que ce guide soit le plus simple et le plus court possible,
alors s’il vous plaît, prenez le temps de le lire. Il vous guidera durant l’installation
et vous montera comment faire pour tirer le plus de votre interface IO|2.
Nous espérons que l’IO|2 vous servira bien pendant plusieurs années.
Cordialement,
Toute l’équipe d’Alesis
28
Page 31

Caractéristiques principales
Les caractéristiques principales de l’IO|2 sont:
• Enregistrement et lecture 24 bits/48 kHz
• Entrées XLR et de ¼ po symétriques à gain réglable
• Alimentation fantôme commutable
• Connecteurs TRS
• Préamplis micro de haute qualité
• Vumètres d’entrée stéréo à 4 segments
• Pilotes ASIO/WDM/Core Audio à faible latence
• Surveillance à temps d’attente zéro
• Entrées et sorties MIDI et S/PDIF
• Sortie casque d’écoute munie d’un régulateur de niveau séparé
• Alimenté par le bus USB pour un fonctionnement sans fil
• Boîtier ultra robuste, léger et durable
Configuration requise
Configuration minimale requise pour PC:
• Processeur Pentium III 450 MHz
• 128 Mo de mémoire vive
• Port USB 1.1
• Windows XP (Service Pack 2 installé)
Configuration recommandée pour PC:
• Processeur Pentium 4 ou Athlon
• 512 Mo de mémoire vive
• Disque dur 7,200 tr/min
• Port USB 1.1
• Windows XP (Service Pack 2 installé)
Configuration minimale requise pour Mac:
• Tout ordinateur Mac avec support USB
• Mac OS X Jaguar, version 10.2 ou supérieur
• 128 Mo de mémoire vive
Configuration recommandée pour Mac:
• Processeur G4 733 MHz ou plus rapide
• Disque dur 7,200 tr/min
• Mac OS X Jaguar, version 10.2 ou supérieur
• 512 Mo de mémoire vive
Mémoire requise
L’IO|2 requiert un minimum
de 128 Mo de mémoire vive,
mais la plupart des
applications audio requièrent
au-delà de 128 Mo de
mémoire vive de mémoire
pour fonctionner
correctement. Si votre
ordinateur ne possède que
128 Mo de mémoire vive et
qu’il répond moins
rapidement avec les
applications audio, l’ajout de
mémoire vive améliora sa
performance.
29
Page 32

Enregistrement du produit
Veuillez visiter le site internet http://www.alesis.com pour enregistrer votre IO|2.
L’enregistrement nous permet de vous informer sur les toutes dernières
nouveautés concernant les produits et la mise à jour des pilotes. Si vous le désirez,
nous pouvons également vous faire parvenir de l’information sur d’autres produits
qui pourraient vous intéresser.
En enregistrant vos produits, vous nous faites savoir quel type de produit vous
utilisez, ou rêvez d’utiliser, et cela nous permet d’améliorer nos produits.
30
Page 33

Connexions du panneau supérieur
1. Mic Input - Utilisez cette prise pour connecter un
micro au IO|2.
2. Guitar/Line Input - Connectez une guitare ou un
instrument line-level au IO|2 en utilisant cette prise.
Assurez-vous que le commutateur “Mic/Line Guitar”
(voir objet no 4 ci-dessous) soit ajusté correctement.
3. Contrôle du gain d’entrée - Bouton permettant le
réglage de chaque canal.
4. Sélection d’entrée Mic/Line ou Guitar - Vous permet de choisir quel type
d’instrument vous utiliserez avec l’entrée Guitar/Line (voir no 2 ci-dessus).
Sélectionnez “Guitar” pour guitares et basses et “Line” pour toutes les sources
line-level (synthétiseurs, DATs, etc.).
5. Connecteur - Le connecteur permet de brancher un compresseur, égaliseur ou
tout autre processeur de signaux entre le préamplificateur de l’IO|2 et le
convertisseur A/N.
6. Commutateur d’alimentation fantôme de +48 V - Le commutateur
d’alimentation fantôme permet d’alimenter des microphones à condensateur qui
requièrent une alimentation fantôme de 48 V. Ce commutateur permet d’activer
l’alimentation fantôme pour les deux canaux.
7. Sortie casque d’écoute - Branchez le casque d’écoute à cette prise.
8. Contrôle du niveau du casque d’écoute - Permet le réglage du niveau du
casque d’écoute.
Entrées audio
Ne pas utiliser les entrées
Mic et Guitar/Line en même
temps sur un canal. Ceci
pourrait surcharger le canal
et créer de la distorsion.
31
Page 34

9. Sélecteur mono/stéréo du casque d’écoute - Permet de sélectionner le
mode mono du casque d’écoute. Réglage très utile durant la pré écoute du signal
d’entrée sans latence et lorsque vous ne voulez pas que le panoramique du signal
du casque soit complètement à gauche ou complètement à droite.
10. Contrôle du mix de pré écoute - Permet d’ajouter un signal d’entrée sans
latence à partir des entrées micro/ligne et le signal provenant de votre ordinateur.
11. Commutateur d’entrée numérique/analogique - Ce réglage permet de
sélectionner la source d’entrée de l’IO|2. En mode de fonctionnement normal,
laissez le en mode analogique. Lorsque ce commutateur est réglé au mode
numérique, l’entrée S/PDIF devient active et les entrées Lo-Z, Hi-Z et le
connecteur de l’IO|2 deviennent inactives.
12. Contrôle principal des niveaux - Permet de régler le niveau des sorties
principales de l’IO|2.
32
Page 35

Connexions arrière
1. Connecteur de sortie MIDI - Branchez un câble MIDI doté de cinq broches
de raccordement à la sortie MIDI de l’IO|2 et l’extrémité du câble à l’entrée d’un
appareil MIDI externe.
2. Connecteur d’entrée MIDI - Branchez un câble MIDI doté de cinq broches
de raccordement à la sortie MIDI d’un appareil MIDI externe et l’extrémité du
câble à l’entrée de l’IO|2.
3. Sortie principale stéréo - Utilisez des câbles symétriques (TRS) ou
asymétriques (TS) de ¼ po pour brancher l’IO|2 à une console de mixage ou à un
système de pré écoute.
4. Sortie S/PDIF - Utilisez un câble coaxial 110
ohms pour brancher la sortie S/PDIF de l’IO|2 à
l’entrée numérique d’un autre appareil.
5. Entrée S/PDIF - Brancher la sortie numérique
d’un autre appareil à l’entrée S/PDIF de l’IO|2 à
l’aide d’un câble coaxial 110 ohms.
6. Connecteur USB - Utilisez un câble USB standard
pour brancher l’IO|2 dans le port USB 1.1 (ou
supérieur) d’un ordinateur.
Branchez l’IO|2 directement
à votre ordinateur, et éviter
l’utilisation d’un répéteur
USB. Les répéteurs peuvent
brouiller les signaux de
synchronisation audio et
MIDI de l’IO|2.
33
Page 36

Voyants de fonctionnement
1. Voyant +48 V - S’allume lorsque l’alimentation fantôme est
activée.
2. Voyant MIDI Out – Clignote lorsque des données MIDI
sont transmises à partir de l’IO|2.
3. Voyant MIDI In – Clignote lorsque des données MIDI
sont transmises à partir d’un contrôleur MIDI externe.
4. Voyant USB – S’allume lorsque qu’une connexion est
établit avec votre ordinateur.
5. Vumètres d’entrée stéréo à 4 segments – Permet de
surveiller le niveau des signaux entrant. Voir le menu latéral à
votre droite pour des conseils sur le réglage des niveaux.
Réglage du niveau de gain
Les vumètres d’entrée stéréo
à 4 segments indiquent le
niveau d’entrée. Lorsque
vous effectuez le réglage du
gain pour chaque canal,
essayez de régler les niveaux
au maximum sans toutefois
dépasser 0 dB. Si le niveau
du signal d’entrée atteint 0
dB, le signal provenant de
l’IO|2 devient alors saturé et
écrêté, provoquant une
distorsion du signal.
Idéalement, les niveaux
doivent se situer entre -6 dB
et -3 dB sur les vumètres.
34
Page 37

Schéma de raccordement
L’installation suivante convient à la plupart des guitaristes/chanteurs:
1. Guitares - Brancher les guitares dans l’entrée Guitar/Line et s’assurer que le
commutateur “Mic/Line Guitar” est ajusté sur “Guitar” afin de permettre la
meilleure qualité d’enregistrement.
2. Microphones - Brancher les micros dans l’entrée XLR du IO|2. S’assurer que
le commutateur “Mic/Line Guitar” est ajusté sur “Mic/Line.” Si vous utilisez un
micro à condensateur qui nécessite une alimentation fantôme (c’est le cas pour la
plupart des condensateurs), allumez l’alimentation fantôme en utilisant la prise
+48v.
3. Casque d’écoute - Branchez le casque d’écoute à cette prise. La sortie casque
d’écoute de l’IO|2 peut être très élevée, alors augmentez lentement le niveau du
gain jusqu’au niveau désiré. Si vous éprouvez des délais de latence, essayez de
régler le contrôle du mix de pré écoute vers « direct » jusqu’à ce que vous trouviez
l’équilibre entre les entrées micro sans latence et la sortie de votre ordinateur.
4. Sorties principales - L’IO|2 accepte les câbles TRS symétriques et les câbles
TS ¼ po asymétriques. Si vos haut parleurs (ou console) acceptent les câbles
symétriques, utilisez les, ils permettent une meilleure performance et diminuent le
bruit.
5. Câble USB - Branchez le câble USB directement à votre ordinateur, et évitez
d’utiliser un répéteur USB. Les répéteurs peuvent brouiller les signaux de
synchronisation audio et MIDI de l’IO|2.
6. Connecteur - L’IO|2 vous permet également la possibilité d’ajouter un
processeur tel qu’une réverbération ou un compresseur à l’étape d’enregistration.
Vous n’avez qu’a utiliser un câble TRS à TS double pour brancher l’appareil
additionnel à l’entrée connecteur de l’IO|2.
35
Page 38

L’installation suivante convient à la plupart des claviéristes:
1. Claviers - Branchez votre clavier sur la prise “Guitar/Line” du IO|2. Si votre
clavier n’a qu’une sortie, vous pouvez utiliser n’importe quel canal sur votre IO|2.
En branchant votre clavier, assurez-vous d’ajuster le commutateur “Mic/Line
Guitar” sur “Mic/Line.”
2. MIDI - Si vous désirez utiliser un séquencer MIDI sur votre ordinateur pour
commander votre clavier, branchez un câble à la sortie MIDI du clavier et à
l’entrée MIDI de l’IO|2 et ensuite un autre câble de la sortie MIDI de l’IO|2 à
l’entrée MIDI de clavier.
3. Casque d’écoute - Branchez le casque d’écoute à cette prise. La sortie casque
d’écoute de l’IO|2 peut être très élevée, alors augmentez lentement le niveau du
gain jusqu’au niveau désiré. Si vous éprouvez des délais de latence, essayez de
régler le contrôle du mix de pré-écoute vers « direct » jusqu’à ce que vous trouviez
l’équilibre entre les entrées micro sans latence et la sortie de votre ordinateur.
4. Sorties principales - L’IO|2 est compatible avec les câbles TRS symétriques et
les câbles TS ¼ po asymétriques. Si vos haut parleurs (ou console) acceptent les
câbles symétriques, utilisez les, ils permettent une meilleure performance et
diminuent le bruit.
5. Câble USB - Branchez le câble USB directement à votre ordinateur, et évitez
d’utiliser un répéteur USB. Les répéteurs peuvent brouiller les signaux de
synchronisation audio et MIDI de l’IO|2.
36
Page 39

Branchement à un ordinateur prêt à l’utilisation
Les systèmes d’exploitation Windows XP et Mac OS X perçoivent l’IO|2 comme
un appareil prêt à l’utilisation. Il n’y a aucune installation à faire sous Mac OS 10.2.
Il ne suffit que de brancher le câble USB et vous êtes prêt à jouer. Aucune
installation de pilote n’est nécessaire sous Windows XP puisse que l’IO|2
fonctionne avec les pilotes audio par défaut de votre ordinateur, cependant, nous
recommandons fortement l’installation des pilotes audio d’Alesis. Nos pilotes
permettront de diminuer de manière significative la latence et d’augmenter la
performance.
Pour installer l’IO|2 sous Windows XP, insérez tout simplement le CD ROM
d’Alesis fournit avec l’appareil et suivez les indications:
Cliquez sur « Install Alesis Audio Driver » pour commencer
l’installation du pilote. Durant l’installation Windows XP,
vous recevrez l’invite de commande suivante:
« Press Continue Anyway, to finish the installation .» Redémarrez votre ordinateur
tel qu’il est recommandé. Une fois le redémarrage terminé, l’IO|2 est prêt pour
l’enregistrement.
SysEx
Lors de gros transferts de
messages système (SysEx)
sous Windows, il se peut que
vous ayez à augmenter la
taille de la mémoire tampon
en conséquence.
Autrement, Windows peut ne
pas effectuer le transfert
correctement. Sélectionner
une taille de mémoire
tampon égale ou plus grande
que le fichier SysEx permet
de s’assurer que le transfert
s’effectuera correctement.
37
Page 40

Dépannage:
Symptôme Cause Solution
Le voyant USB est
éteint.
L’IO|2 n’est pas
alimenté ou la
connexion USB ne
se fait pas
Assurez vous que l’IO|2 est branché
directement au connecteur USB de votre
ordinateur et non à un répéteur USB. Si cela ne
fonctionne pas, vérifiez l’installation pilote de
l’ordinateur et assurez vous que les pilotes de
l’IO|2 ont été installé correctement. Si cela ne
fonctionne toujours pas, vérifiez le câble, il peut
être en cause. Essayez avec un autre câble USB.
Les vumètres ne
répondent pas.
Les connecteurs
S/PDIF (I/O) ne
fonctionnent pas
Le commutateur
d’entrée est en mode
analogique, mais le
signal entrant n’est pas
perceptible, ou il est à
peine.
Les connecteurs
S/PDIF n’émettent
que des clics,
claquement ou que du
bruit blanc
Le commutateur
d’entrée
numérique/analogiq
ue est peut être réglé
incorrectement
Le commutateur
d’entrée
numérique/analogiq
ue est peut être réglé
incorrectement
Les commutateurs
alimentation
fantôme et
micro/ligne sont
peut être réglés
incorrectement
Les câbles coaxiaux
que vous utilisez ne
sont pas 110 ohms.
Assurez vous que le commutateur d’entrée est
réglé au mode analogique si vous enregistrez à
l’aide des entrées XLR et de ¼ po situées sur le
dessus de l’IO|2. Ne réglez le commutateur
d’entrée au mode numérique que si vous
désirez utiliser les connecteurs S/PDIF.
Si vous désirez faire un transfert
audionumérique à l’aide des connecteurs
S/PDIF, assurez vous que le commutateur
d’entrée est réglé au mode numérique,
autrement, laissez le en mode analogique.
Assurez vous que le commutateur micro/ligne
soit réglé à la bonne position pour chaque
canal. Si vous utilisez des microphones à
condensateur qui requièrent une alimentation
fantôme, activez la à l’aide du commutateur
+48 V. Assurez-vous que le niveau du gain soit
assez élevé.
Il est très important d’utiliser des câbles
coaxiaux 110 ohms pour toutes les connexions
S/PDIF. La plupart des câbles RCA ne sont
pas 110 ohms et peuvent causer des problèmes
de synchronisation entre les deux appareils
numériques. Il pourrait en résulter des clics,
claquement ou que du bruit blanc soutenu.
38
Page 41

FICHE TECHNIQUE
Interface: Interface IO|2 audio/MIDI 24 bits/48 kHz
Caractéristiques: Stéréo, entrées et sorties 24 bits. Fréquence
d’échantillonnage réglable jusqu’à 48 kHz. Chaque
canal possède son propre réglage du gain et un
commutateur micro/ligne. Toutes les entrées et les
sorties sont symétriques. Prise stéréo ¼ po pour
casque d’écoute. S/PDIF et MIDI I/O.
Audio:
Logiciel: Pilotes ASIO/WDM/ à ultra faible latence pour
Alimentation: bus USB
Dimensions: 6,5 po x 4,7 po x 2,25 po
Poids (net): 1,5 lb/0,68 kg
Entrée Mic/ligne :
SNR 95 dB (niveau sonore pondéré A) minimum – 97 dB
typique
THD+N 0,007 % maximum – 0,005 % typique
Fréquence en réponse de +/-0,35 dB typique
Entrées guitare de ¼ po
SNR 94 dB (niveau sonore pondéré A) minimum – 96 dB
typique
THD+N 0,05 % maximum – 0,034 % typique
Fréquence en réponse de +/-1,2 dB
Sorties analogiques
SNR 95 dB (niveau sonore pondéré A) minimum – 97 dB
typique
THD+N 0,007 % maximum – 0,005 % typique
Fréquence en réponse de +/-0,35 dB typique
Windows XP. Plein soutien pour Core Audio sous
Mac OS X.
16,5 cm x 12,0 cm x 5,8 cm
39
Page 42

IO|2
Kurzbedienungsanleitung
(Deutsch)
40
Page 43

Einführung
Wir beglückwünschen Sie zu Ihrem Alesis IO|2 Audio/MIDI Interface! Wir
selbst sind sehr stolz auf das IO|2, haben wir doch mit großer Sorgfalt versucht,
ein professionell klingendes, extrem widerstandsfähiges und einfach zu
bedienendes Interface zu erschaffen.
In dem Bemühen, uns in dieser Anleitung wirklich kurz zu halten bitten wir Sie
jedoch, die Beschreibungen sorgfältig zu lesen. Sie werden durch den
Installationsvorgang geführt und Sie erfahren außerdem, wie Sie das IO|2
Interface am effektivsten einsetzen.
Wir hoffen, dass Sie mit dem IO|2 viele Jahre sorgenfrei arbeiten können.
Mit freundlichen Grüßen,
Die Mitarbeiter von Alesis
41
Page 44

Wichtige Eigenschaften
Ihr IO|2 besitzt die folgenden Features:
• 24-Bit Aufnahme und Wiedergabe
• Symmetrische XLR und 6,3mm Klinkeneingänge mit
einstellbarem Gain
• Einschaltbare Phantomspeisung
• 6,3mm Insertanschlüsse
• Professionelle Mikrofonvorverstärker
• Aussagekräftige 4-Segment Eingangspegel-Meter
• Verzögerungsarme ASIO/WDM/Core Audio Treiber
• Zero-Latency Monitoring
• MIDI und S/PDIF Ein- und Ausgänge
• Kopfhörerausgang mit eigenem Lautstärkeregler
• Stromversorgung über den USB-Bus
• Extrem robustes und leichtes Gehäuse
Systemanforderungen
Mindestanforderungen an einen PC:
• Pentium III 450 MHz Prozessor
• 128 MB RAM
• Freier USB 1.1
• Port Windows XP (mit installiertem Service Pack 2)
42
Empfohlene PC Ausstattung:
• Pentium 4 oder Athlon Prozessor
• 512 MB RAM
• 7.200 RPM Festplatte
• Freier USB 1.1 Port
• Windows XP (mit installiertem Service Pack 2)
Mindestanforderungen Macintosh:
• Jeder Apple Computer mit nativem USB Support
• Mac OS X Jaguar Version 10.2 oder neuer
• 128 MB RAM
Empfohlene Macintosh Ausstattung:
• G4 733-MHz Prozessor oder schneller
• 7.200 RPM Festplatte
• Mac OS X Jaguar Version 10.2 oder neuer
• 512 MB RAM
Anforderungen an den
Speicher
Das IO|2 benötigt zum
Betrieb mindestens 128MB
RAM. Die meisten
Audioprogramme benötigen
für ein vernünftiges Arbeiten
jedoch mehr. Sollte Ihr
Computer nur mit 128 MB
Speicher ausgestattet sein
und dadurch flüssiges
Arbeiten mit Ihrer
Audiosoftware unmöglich
sein, sollten Sie weiteren
RAM-Speicher einbauen
(lassen), um die Performance
des Rechners zu verbessern.
Page 45

Produktregistrierung
Registrieren Sie Ihr IO|2 auf http://www.alesis.de.
Ihre Registrierung hilft uns, Sie über die neuesten Produktthemen und
Treiberupdates auf dem Laufenden zu halten. Auf Ihren Wunsch hin können wir
Ihnen auch Informationen zu anderen interessanten Produkten zukommen lassen.
Mit Ihrer Registrierung lassen Sie uns wissen, welche anderen Geräte Sie
verwenden (oder von welchen Sie träumen). So helfen Sie mit, noch besseres
Equipment für die Zukunft zu entwickeln.
43
Page 46

Anschlüsse der Oberseite
1. Mic Eingang – Verbinden Sie diesen Eingang des
IO|2 mit Ihren Mikrofonen oder anderem XLR
Equipment.
2. Guitar/Line Eingang – Schließen Sie Ihre
Gitarren oder andere hochohmige
Instrumentenausgänge an.
3. Eingangs-Gain Regler – Bestimmen Sie den
Eingangspegel jedes Kanals mit diesem Regler.
4. Mic/Line oder Guitar Eingangsschalter – Dieser Schalter ermöglicht es, die
Empfindlichkeit des eingehenden Signals zu definieren. Verwenden Sie ihn mit
dem Gain Regler, um die Eingangssignale auszupegeln.
5. Insert – Über die Insertbuchsen können Sie einen Compressor, einen EQ oder
jeden anderen Signalprozessor zwischen die IO|2 Vorverstärker und die A/D
Wandler einschleifen.
6. +48v Phantom Power Schalter – Dieser Schalter aktiviert die 48V
Phantomspannung, mit deren Hilfe Sie Kondensatormikrofone an das IO/2
anschließen und mit Strom versorgen können, an beiden Kanälen.
Audioeingänge
Verwenden Sie die Mic und
Guitar/Line Eingänge eines
Kanals nicht gleichzeitig.
Dadurch könnten Sie den
Kanal übersteuern, wodurch
es zu Verzerrungen kommt.
44
Page 47

7. Kopfhörer Ausgangsbuchse -– Schließen Sie hier Ihren Kopfhörer an.
8. Kopfhörer Lautstärkeregler – Stellen Sie mit diesem Regler die
Kopfhörerlautstärke ein.
9. Mono/Stereo Monitoring Schalter – Hiermit aktivieren Sie den Monobetrieb
Ihrer Kopfhörer. Dieser nützt besonders in Zero-Latency Monitoring Situationen,
bei denen Sie die beiden Eingänge nicht nur links und rechts verteilt im
Kopfhörer hören möchten.
10. Monitor Mix Regler – Hiermit blenden Sie einen Anteil des Zero-Latency
Signals der Mic/Line Eingänge in das Ausgangssignal Ihres Computers ein.
11. Digital/Analog Eingangsschalter – Wählen Sie die Art der Eingangsquelle
mit diesem Schalter. Normalerweise befindet sich der Schalter auf “analog.” In der
Schalterstellung “digital”, wird der S/PDIF Eingang aktiviert. Gleichzeitig werden
die Lo-Z-, Hi-Z- und Inserteingänge des IO|2 ignoriert.
12. Gesamtlautstärkeregler – Regelt die Lautstärke der IO|2-Summenausgänge.
45
Page 48

Anschlüsse der Rückseite
1. MIDI Out Buchse – Mit Hilfe eines fünfpoligen MIDI-Kabels können Sie den
MIDI-Ausgang des IO|2 mit dem MIDI-Eingang eines externen MIDI-Gerätes
verbinden.
2. MIDI In Buchse – Verwenden Sie ein fünfpoliges MIDI-Kabel, um den
MIDI-Ausgang eines externen MIDI-Gerätes mit dem MIDI IN des IO|2 zu
verbinden.
3. Stereo Summenausgang – Das IO|2 können Sie entweder mit
symmetrischen oder unsymmetrischen 6,3mm Klinkenkabeln an einen Mixer oder
an aktive Studiomonitore anschließen.
4. S/PDIF Ausgang – Ein 110 Ohm Koaxialkabel ermöglicht den Anschluss des
S/PDIF-Ausgangs Ihres IO|2 an den Digitaleingang eines anderen Gerätes.
5. S/PDIF Eingang – Schließen die den
Digitalausgang eines anderen Gerätes an den S/PDIFEingang Ihres IO|2mit einem 110 Ohm Koaxialkabel
an.
6. USB Anschluss – Über ein normales USB Kabel
können Sie Ihr IO|2 an den USB 1.1 (oder besser)
Port Ihres Computers anschließen.
Stellen Sie eine direkte
Verbindung zwischen dem
IO|2 und Ihrem Computer
her und verwenden Sie zum
Anschluss keinen USB Hub.
Hubs können die Audio- und
MIDI-Clock des IO|2 stören.
46
Page 49

Leuchtanzeigen
1. +48V – Leuchtet bei aktivierter Phantomspeisung.
2. MIDI Out – Blinkt, wenn MIDI-Daten den IO|2
verlassen.
3. MIDI In – Blinkt, wenn MIDI-Daten von einem externen
MIDI-Gerät eintreffen.
4. USB – Leuchtet, wenn eine USB-Verbindung zwischen
IO|2 und Computer besteht.
5. Stereo 4-Segment Eingangsanzeigen – Visualisiert den
Pegel eingehender Signale. Beachten Sie die Hinweise zur
Signalaussteuerung in der rechten Textbox.
Signale richtig aussteuern
Die 4-Segment
Eingangsanzeigen helfen
Ihnen festzustellen, wie laut
Ihre Eingangssignale sind.
Beim Aussteuern mit den
Gain Reglern der Kanäle
sollten Sie versuchen, die
Pegel so hoch wie möglich
einzustellen, ohne dass
jedoch die ì0 dBî Marke
überschritten wird. Wenn die
Signale die 0 dB erreichen
übersteuert das IO|2,
wodurch unschöne
Verzerrungen verursacht
werden.
Im Idealfall sollten
Pegelspitzen zwischen -6 und
-3 dB in den
Aussteuerungsanzeigen
liegen.
47
Page 50

Anschlussübersichten
Der folgende Aufbau sollte sich für die meisten Gitarristen/Sänger eignen:
1. Gitarren – Verbinden Sie Gitarren mit dem Guitar/Line Eingang und setzen
Sie den “Mic/Line Guitar” Schalter auf “Guitar,“ um die bestmögliche
Signalqualität zu erhalten.
2. Mikrofone – Schließen Sie Mikrofone an den XLR Eingang des IO|2 an und
stellen Sie den “Mic/Line Guitar” Schalter auf “Mic/Line.” Wenn Sie ein
Kondensatormikrofon verwenden, das Phantomspeisung benötigt (wie die
meisten Kondensatormikrofone), schalten Sie den +48V Schalter ein.
3. Kopfhörer – Schließen Sie hier Ihre Kopfhörer an. Sie sollten die Lautstärke
des Ausgangs langsam und vorsichtig erhöhen, da der Kopfhörerausgang des
IO|2 sehr laut sein kann. Sollten störende “Latenzdelays” Ihrer Stimme oder
Ihrer Gitarre auftreten, drehen Sie den Monitor Mix Regler in Richtung “direct”,
bis Sie mit der Balance zwischen den verzögerungsarmen Mikrofoneingängen und
dem Ausgangssignal Ihre Computers zufrieden sind.
48
Page 51

4. Summenausgänge – Der IO|2 unterstützt sowohl symmetrische als auch
unsymmetrische Klinkenkabel. Wenn Ihre Lautsprecher (oder Ihr Mixer)
symmetrische Anschlüsse besitzen, sollten Sie diese auf Grund besserer
Audioqualität und geringerem Rauschpegels auch verwenden.
5. USB Kabel – Stellen Sie eine direkte Verbindung zwischen dem IO|2 und
Ihrem Computer her und verwenden Sie zum Anschluss keinen USB Hub. Hubs
können die Audio- und MIDI-Clock des IO|2 stören.
6. Insert – Mit Hilfe eines Insertkabels (Y-Kabel) können Sie beim IO|2 einen
zusätzlichen Signalprozessor, wie beispielsweise ein Hallgerät oder einen
Compressor in den Signalweg einschleifen. Schließen Sie die Stereoklinken an die
Insertbuchse des IO|2 und die beiden Monobuchsen an den Ein- bzw. Ausgang
des externen Gerätes an.
49
Page 52

Das folgende Setup sollte für die meisten Keyboarder das Passende sein:
1. Keyboards – Schließen Sie die Audioausgänge Ihres Keyboards an die
“Guitar/Line” Eingänge des IO|2 an. Sollte Ihr Keyboard nur einen Ausgang
besitzen, ist es egal, welchen Kanal Sie am IO|2 verwenden. Beachten Sie, dass
bei der Verwendung von Keyboards der “Mic/Line Guitar” Schalter auf
“Mic/Line” steht.
2. MIDI – Sollten Sie ein MIDI Sequencing Programm auf Ihrem Computer zur
Steuerung Ihres Keyboards einsetzen wollen, verbinden Sie den MIDI OUT des
Keyboards mit dem MIDI IN des IO|2 und schließen Sie den MIDI OUT des
IO|2 an den MIDI IN des Keyboards an.
3. Kopfhörer – Schließen Sie hier Ihre Kopfhörer an. Sie sollten die Lautstärke
des Ausgangs langsam und vorsichtig erhöhen, da der Kopfhörerausgang des
IO|2 sehr laut sein kann. Sollten störende “Latenzdelays” Ihrer Stimme oder
Ihrer Gitarre auftreten, drehen Sie den Monitor Mix Regler in Richtung “direct”,
bis Sie mit der Balance zwischen den verzögerungsarmen Mikrofoneingängen und
dem Ausgangssignal Ihre Computers zufrieden sind.
4. Summenausgänge – Der IO|2 unterstützt sowohl symmetrische als auch
unsymmetrische Klinkenkabel. Wenn Ihre Lautsprecher (oder Ihr Mixer)
symmetrische Anschlüsse besitzen, sollten Sie diese auf Grund besserer
Audioqualität und geringerem Rauschpegels auch verwenden.
5. USB Kabel – Stellen Sie eine direkte Verbindung zwischen dem IO|2 und
Ihrem Computer her und verwenden Sie zum Anschluss keinen USB Hub. Hubs
können die Audio- und MIDI-Clock des IO|2 stören.
50
Page 53

Plug-and-Play Anschluss an einen Computer
Sowohl Windows XP als auch Mac OS X erkennen das IO|2 als Plug-and-Play
Gerät. Unter Mac OS 10.2 ist keine Installation notwendigó Schließen Sie einfach
das USB-Kabel an - und schon kann es losgehen. Auch unter Windows XP muss
man keine Treiber installieren, da das IO|2 die systemeigenen Audiotreiber
unterstützt. Wir legen Ihnen aber nahe, die Alesis Audio Treiber zu installieren.
Unsere Treiber ermöglichen eine niedrigere Latenz und eine bessere Performance.
Zur Installation des IO|2 unter Windows XP legen Sie einfach die beiliegende
Alesis CD-ROM in das CD-Laufwerk Ihres Computers und warten, bis das
folgende Menü angezeigt wird:
Klicken Sie “Install Alesis Audio Driver,” um die
Treiberinstallation zu beginnen. Während der Installation
erscheint von Windows XP folgende Warnung:
Klicken Sie “Continue Anyway,” damit die Installation abgeschlossen wird.
Starten Sie dann den Computer neu. Jetzt ist Ihr IO|2 einsatzbereit.
SysEx
Bei großen SysExDatenübertragungen unter
Windows sollten Sie die
Puffergröße Ihrer WindowsSoftware erhöhen, da
Windows ansonsten die
Übertragung der Daten
nicht korrekt durchführen
kann. Eine
Puffergrößeneinstellung, die
der Größe der SysEx-Datei
oder höher entspricht,
gewährleistet hingegen eine
fehlerfreie Übertragung.
51
Page 54

Fehlerhilfe:
Symptom Ursache Lösung
USB Licht geht nicht
an.
Das IO|2 empfängt
keine Spannung oder
die USB Verbindung
zum Computer
wurde nicht
hergestellt
Vergewissern Sie sich, dass Sie das IO|2 direkt
mit einem USB-Ports des Computers
verbunden haben und kein USB Hub
dazwischen geschaltet wurde. Besteht das
Problem fort, überprüfen Sie nochmals Ihre
Treiberinstallation. Sehen Sie nach, ob die
Treiber des IO|2 korrekt installiert wurden. Ist
das Problem immer noch präsent, könnte das
USB Kabel defekt sein. Verwenden Sie ein
anderes USB Kabel.
Aussteuerungsanzeige
n gehen nicht an
S/PDIF I/O
funktioniert nicht
Obwohl der
Eingangswahlschalter
auf “Analog” steht,
höre ich kein Signal
oder es ist sehr leise.
Über die S/PDIF
Ein- und Ausgänge
bekomme ich nur
Clicks, Pops oder
weißes Rauschen
Möglicherweise steht
der Digital/Analog
Eingangswahlschalte
r auf der falschen
Position.
Der Digital/Analog
Eingangswahlschalte
r ist falsch eingestellt.
Falsche
Einstellungen der
Phantomspannungoder Mic/LineSchalter.
Sie verwenden keine
110 Ohm
Digitalkabel.
Wenn Sie über die XLR- und 6,3mm Klinken
Anschlüsse aufnehmen muss der Schalter auf
“analog” stehen. Stellen Sie ihn nur dann auf
“digital,” wenn Sie die S/PDIF Anschlüsse
verwenden wollen.
Wenn Sie die S/PDIF Anschlüsse zur digitalen
Audioübertragung verwenden wollen, muss der
Eingangswahlschalter auf “Digital” eingestellt
sein. Zum normalen Betrieb lassen Sie diesen
Schalter auf der “Analog” Stellung.
Überprüfen Sie noch einmal die Mic/Line
Schalter-Einstellungen für jeden Kanal. Wenn
Sie ein Kondensatormikrofon einsetzen,
benötigen Sie Phantomspannung, Sie mit dem
+48V Phantom Power Schalter zuschalten.
Schauen Sie außerdem nach, ob der Gain
Regler aufgedreht ist.
Es ist von bedeutender Wichtigkeit, dass Sie
110 Ohm Koaxialkabel für alle S/PDIF
Verbindungen verwenden. Die meisten
normalen RCA Kabel erfüllen die 110 OhmAnforderung NICHT und verursachen
Probleme der Audioclock zwischen zwei
Digitalgeräten. Dadurch kommt es zu lauten
Clicks, Pops und anhaltendem weißen
Rauschen.
52
Page 55

Specifications
Interface: IO|2 24-Bit Audio/MIDI Interface
Eigenschaften: Stereo, 24-Bit ein- und Ausgänge. Einstellbare
Sample Rate bis 48 kHz. Getrennte Gain Regler
und Mic/Line Schalter für jeden Kanal. Alle Einund Ausgänge sind symmetrisch ausgeführt. 6,3mm
Stereokopfhörerbuchse. S/PDIF und MIDI I/O.
Audio: Mic/Line Eingänge
Rauschabstand 95dB (A-bewertet) Minimum -- 97dB
durchschnittlich
Klirrfaktor 0.007% Maximum -- 0.005% durchschnittlich
Frequenzgang +/-0.35dB durchschnittlich
6,3mm Klinke Gitarreneingänge
Rauschabstand 94dB (A-bewertet) Minimum -- 96dB
durchschnittlich
Klirrfaktor 0.05% Maximum -- 0.034% durchschnittlich
Frequenzgang +/-1.2dB
Analoge Ausgänge
Rauschabstand 95dB (A-bewertet) Minimum -- 97dB
durchschnittlich
Klirrfaktor 0.007% Maximum -- 0.005% durchschnittlich
Frequenzgang +/-0.35dB durchschnittlich
Software: Verzögerungsarme ASIO/WDM Treiber für
Windows XP. Vollständige Core Audio
Unterstützung unter Mac OS X.
Stromversorgung: USB Bus Power
Abmessungen: 6.5” x 4.7” x 2.25” / 16.5 cm x 12.0 cm x 5.8 cm
Gewicht (net): 1.5 lbs / 0.68 kg
53
Page 56

IO|2
Guida rapida di utilizzo
(Italiano)
54
Page 57

Introduzione
Congratulazioni per aver acquistato la vostra nuova interfaccia Audio/MIDI
Alesis IO|2! Siamo orgogliosi di questa interfaccia e abbiamo prodigato
moltissime cure per rendere l’IO|2 l’interfaccia audio dal suono migliore, la più
robusta e la più facile da usare tra tutte quelle presenti sul mercato.
Abbiamo cercato di rendere questa guida più corta possibile, ma va letta con
attenzione. Vi guiderà nel processo di installazione e vi insegnerà come ottenere il
massimo dalla vostra interfaccia IO|2.
Ci auguriamo che l’IO|2 vi accompagni con soddisfazione per molti anni.
Cordialmente,
La squadra Alesis
55
Page 58

Caratteristiche principali
L’IO|2 presenta quanto segue:
• registrazione e riproduzione a 24-bit
• Ingressi bilanciati XLR e a ¼” con guadagno regolabile
• Alimentazione phantom commutabile
• Prese TRS
• Preamplificatori mic di alta qualità
• Misuratore d’ingressi globale a 4 segmenti
• Driver ASIO/WDM/Core Audio a bassa latenza
• Monitoraggio a latenza zero
• Ingressi e uscite MIDI e S/PDIF
• Uscita cuffie con manopola per il volume a parte
• Alimentata tramite la porta, per un funzionamento indipendente
dall’alimentazione elettrica
• Corpo ultraresistente e leggero, fatto per durare
Requisiti per computer
Requisiti minimi per PC:
• Processore Pentium III 450 MHz
• 128 MB RAM
• Porta USB 1.1 disponibile
• Windows XP (con Service Pack 2 instalato)
56
Requisiti per PC raccomandati:
• Processore Pentium 4 o Athlon
• 512 MB RAM
• Drive disco rigido 7,200 RPM
• Porta USB 1.1 disponibile
• Windows XP (con Service Pack 2 installato)
Requisiti minimi Macintosh:
• Qualsiasi computer Apple con supporto USB
originale
• Mac OS X “Jaguar” versione 10.2 o successiva
• 128 MB RAM
Requisiti per Macintosh raccomandati:
• Processore G4 733-MHz o superiore
• Drive disco rigido 7,200 RPM
• Mac OS X “Jaguar” versione 10.2 o successiva
• 512 MB RAM
Requisiti di memoria
Per funzionare, l’IO|2
richiede un minimo di 128MB
di RAM, ma la maggior parte
delle applicazioni audio
necessitano di più di 128MB
di RAM per girare al meglio.
Se il vostro computer è dotato
di soli 128 MB di memoria ed
è lento quando fa girare
applicazioni audio, provare
ad aggiungere memoria per
migliorarne le prestazioni.
Page 59

Registrazione del prodotto
Recarsi sul sito http://www.alesis.com per la registrazione del vostro nuovo IO|2.
La registrazione ci aiuta a mantenervi aggiornati su qualsiasi prodotto nuovo e
aggiornamenti dei driver. Se desiderato, possiamo inoltre inviarvi informazioni ad
altri prodotti che potrebbero essere di vostro interesse.
Effettuando la registrazione, ci fate sapere quali prodotti utilizzate (oppure
sognate) aiutandoci a portarvi prodotti migliori in futuro.
57
Page 60

Collegamenti pannello superiore
1. Mic Input - Collegare un microfono al IO|2 usando
quest’ingresso.
2. Guitar/Line Input - Collegare al IO|2 una
chitarra o uno strumento musicale con uscita a livello
di linea usando quest’ ingresso. Assicurarsi che il
elettore Mic/Line Guitar sia presettato orrettamente
(riferirsi al paragrafo 4 elencato sotto).
3. Manopola di guadagno ingresso - Impostare il
livello di guadagno di ciascun canale servendosi di
questa manopola.
4. Mic/Line or Guitar input select - Permette di selezionare il tipo di strumento
da connettere all’ingresso Guitar/Line input (riferirsi al paragrafo 2 elencato
sopra). Per chitarre e bassi, selezionate “Guitar”. Per Strumenti o apparecchi con
uscita a livello di linea (Sintetizzatori o DAT etc.) selezionate “Line”.
5. Inserto - questo jack permette l’inserimento di un compressore, di un EQ, o di
qualsiasi altro processore di segnali tra il preamplificatore dell’IO|2 e il
convertitore A/D.
6. Interruttore di alimentazione +48v Phantom - l’interruttore di alimentazione
phantom permette di alimentare microfoni condensatori che richiedano
un’alimentazione 48V phantom. Questo interruttore attiva l’alimentazione
phantom su entrambi i canali.
7. Jack di uscita cuffie - inserire le cuffie in questo jack.
8. Manopola di livello cuffie - impostare il livello delle cuffie servendosi di
questa manopola.
Ingressi Audio
Non usate gli ingressi Mic e
Guitar dello stesso canale
contemporaneamente.
Cio`potrebbe saturare il
canale in questione causando
distorsione.
58
Page 61

9. Interruttore di monitoraggio mono/stereo - permette di far passare le cuffie
in mono. Questo è utile in casi di monitoraggio a latenza zero in cui si potrebbe
non desiderare gli ingressi pannati a sinistra e adestra in cuffia.
10. Manopola monitor mix - mescola qualsiasi quantità di segnale a latenza zero
dagli ingressi mic/line con l’uscita del computer.
11. Interruttore d’ingresso digitale/analogico - servirsi di questo interruttore
per selezionare la sorgente d’ingresso dell’IO|2. Per un funzionamento normale,
lasciare questo interruttore impostato su “analog”. Se l’interruttore è su “digital”,
l’ingresso S/PDIF diventerà attivo e gli ingressi Lo-Z, Hi-Z, e Insert sull’IO|2
saranno ignorati.
12. Manopola di livello principale - impostare il livello delle uscite principali
dell’IO|2.
59
Page 62

Collegamenti pannello posteriore
1. Connettore MIDI Out - servirsi di un cavo MIDI a cinque poli per collegare
l’uscita MIDI out dell’IO|2 all’ingresso MIDI di un dispositivo MIDI esterno.
2. Connettore MIDI In - servirsi di un cavo MIDI a cinque poli per collegare
l’uscita di un dispositivo MIDI esterno al MIDI IN dell’IO|2.
3. Uscita stereo principale - servirsi di cavi bilanciati (TRS) o non bilanciati (TS)
da ¼” per collegare l’IO|2 ad un mixer o a monitor da studio alimentati.
4. S/PDIF Out - servirsi di un cavo coassiale da 110-ohm per collegare l’uscita
S/PDIF dell’IO|2 all’ingresso digitale di un altro dispositivo.
5. S/PDIF In - collegare l’uscita digitale di un altro
dispositivo all’ingresso S/PDIF dell’IO|2 servendosi di
un cavo coassiale da 110-ohm.
6. Connettore USB - Servirsi di un cavo USB standard
per collegare l’IO|2 alla porta USB 1.1 (o superiore) del
vostro computer.
Collegare l’IO|2 direttamente
al computer, ed evitare l’uso
di un hub USB. Gli hub
possono interferire con i
segnali di temporizzazione
dell’audio e MIDI dell’IO|2.
60
Page 63

Luci indicatrici di stato
1. +48V – si accende quando è attivata l’alimentazione
phantom.
2. MIDI Out – lampeggia ogniqualvolta vengono inviati dati
MIDI fuori dal IO|2.
3. MIDI In – lampeggia ogniqualvolta vengono ricevuti dati
MIDI da un controller MIDI esterno.
4. USB – si accende quando viene stabilito un collegamento
USB con il computer.
5. Misuratori stereo a 4 segmenti – permettono di
monitorare i livelli entranti. Vedi la barra laterale posta a
destra per consigli sull’impostazione dei livelli.
Impostazione dei livelli di
guadagno (gain)
I misuratori d’ingressi a 4
segmenti sono lì per
permettervi di sapere quanto
sono forti i vostri ingressi. Al
momento di regolare le
manopole di guadagno (gain)
per ciascun canale, provate a
impostare i livelli il più alto
possibile senza raggiungere
“0 dB”. Se l’ingresso
raggiunge 0 dB, state
sovraccaricando o mandando
in “clipping” l’IO|2 e ciò
darà origine a gravi
distorsioni.
Idealmente, i livelli
dovrebbero avere un picco
compreso tra -6 e -3 dB sui
misuratori.
61
Page 64

62
Schemi di collegamento
Le seguenti impostazioni sono ottime per la maggior parte dei chitarristi/cantanti:
1. Chitarre – Collegate la vostra chitarra all’ingresso Guitar/Line e controllate che
il selettore “Mic/Line Guitar” sia settato su Guitar in modo da assicurare una
qualita`di registrazione ottimale.
2. Microfoni – Collegate il vostro microfono al IO|2 usando l’ingresso XLR ed
assicuratevi che il selettore “Mic/Line Guitar”sia settato su “Mic/Line”. Nel caso
sia richiesto l’utilizzo di un microfono a condensatore che necessiti di
alimentazione “phantom power” (come la maggior parte dei microfoni di questo
tipo), procedete ad attivarla mediante l’uso dell’interruttore +48V.
3. Cuffie – inserire le cuffie in questo jack. L’uscita cuffie dell’IO|2 può essere
molto forte, quindi alzare il guadagno lentamente fino a raggiungere un livello
confortevole. In caso di “ritardi di latenza” della chitarra o della voce, girare la
manopola Monitor Mix su “direct” fino a trovare un buon equilibrio tra gli
ingressi mic a latenza zero e l’uscita del computer.
4. Uscite principali – l’IO|2 supporta sia cavi bilanciati “TRS” che non bilanciati
“TS” da ¼”. Se i vostri altparlanti (oppure il mixer) supportano cavi bilanciati,
servitevi di quelli, in quanto garantiscono migliori prestazioni e minor rumore.
5. Cavo USB – inserire il cavo USB direttamente nel computer ed evitare di
servirsi di un hub USB. Gli hub possono interferire con i segnali di
temporizzazione dell’audio e MIDI e causare problemi all’IO|2.
6. Inserto – l’IO|2 vi permette di inserire facilmente un ulteriore processore quale
un reverb oppure un compressore nella vostra via di registrazione. Servirsi
semplicemente di un cavo TRS a doppio TS per collegare il dispositivo addizionale
al jack dell’IO|2.
Page 65

L’impostazione seguente è ottima per la maggior parte dei tastieristi:
1. Tastiere – Collegate le uscite della vostra tastiera al IO|2 usando l’ingresso
“Guitar/Line”. Se la tastiera in questione dispone di una sola uscita, collegatela
pure all’ingresso che preferite. Quando collegate una tastiera, assicuratevi di settare
il selettore “Mic/line Guitar” su “Mic/line”.
2. MIDI – nel caso in cui desideriate servirvi di un programma sequenziatore
MIDI sul computer per controllare la tastiera, collegate pure l’uscita MIDI OUT
della tastiera al MIDI IN dell’IO|2 e la MIDI OUT dell’IO|2 al MIDI IN della
tastiera.
3. Cuffie – inserire le cuffie in questo jack. L’uscita cuffie dell’IO|2 può essere
molto forte, quindi alzare il guadagno lentamente fino a raggiungere un livello
confortevole. In caso di “ritardi di latenza” della chitarra o della voce, girare la
manopola Monitor Mix su “direct” fino a trovare un buon equilibrio tra gli
ingressi mic a latenza zero e l’uscita del computer.
4. Uscite principali – l’IO|2 supporta sia cavi bilanciati “TRS” che non bilanciati
“TS” da ¼”. Se i vostri altparlanti (oppure il mixer) supportano cavi bilanciati,
servitevi di quelli, in quanto garantiscono migliori prestazioni e minor rumore.
5. Cavo USB – inserire il cavo USB direttamente nel computer ed evitare di
servirsi di un hub USB. Gli hub possono interferire con i segnali di
temporizzazione dell’audio e MIDI e causare problemi all’IO|2.
63
Page 66

Collegamento Plug-and-Play al Computer
Sia Windows XP che Mac OS X riconoscono il IO|2 come un dispositivo plugand play. Non è necessaria alcuna installazione su Mac OS 10.2 — Collegare
semplicemente il cavo USB e si è pronti a partire. L’installazione del driver non è
richiesta su Windows XP in quanto l’IO|2 supporta i driver audio predefiniti, ma
raccomandiamo di installare ugualmente i driver audio Alesis. I nostri driver
comporteranno una latenza significativamente inferiore e garantiranno migliori
prestazioni.
Per installare l’IO|2 su Windows XP, inserire semplicemente il CD-ROM Alesis
in dotazione e attendere che appaia il seguente menu:
Cliccare su “Install Alesis Audio Driver” per procedere
all’installazione del driver. Durante il processo d’installazione,
Windows XP avvertirà come segue:
Premere “Continue Anyway” per terminare l’installazione. Riavviare come
raccomandato dal software. Una volta riavviato il computer, l’IO|2 è pronto a
registrare.
SysEx
Durante l’esecuzione di
voluminosi trasferimenti
SysEx su Windows, potrebbe
essere necessario aumentare
la dimensione del buffer del
software Windows. In caso
contrario, Windows
potrebbe processare il
trasferimento in maniera
scorretta. La scelta di una
dimensione di buffer pari o
superiore a quella del file
SysEx garantisce in teoria
che il trasferimento avvenga
senza errori.
64
Page 67

i
i
Risoluzione di problemi:
Sintomo Causa Soluzione
La luce USB non si
accende.
L’O|2 non riceve
l’alimentazione
oppure non è stato
effettuato il
collegamento USB al
computer.
Assicurarsi di collegare l’IO|2 direttamente alla
porta USB del vostro computer e non a livello
di un hub USB. Se questo non risolve il
problema, ricontrollare l’installazione del driver
e verificare che i driver del IO|2 siano stati
installati correttamente. Se il problema persiste,
il cavo potrebbe essere difettoso. Provare a
utilizzare un altro cavo USB.
I misuratori d’ingressi
non rispondono.
L’S/PDIF I/O non
funziona
L’interruttore
d’ingresso è impostato
su “Analog” ma il
segnale in ingresso è
tuttora assente (o è
molto debole).
Gli ingressi e le uscite
S/PDIF emettono
click, scoppiettii o
rumore bianco
L’interruttore
d’ingresso
digitale/analogico
potrebbe essere
mpostato in maniera
scorretta.
L’interruttore di
ingresso
digitale/analogico
potrebbe essere
mpostato in maniera
scorretta
Gli interruttori
phantom power o
mic/line potrebbero
non essere impostati
correttamente.
i cavi coassiali non
sono a 110-ohm.
Assicurarsi che l’interruttore d’ingressi sia
impostato su “analog” nel caso in cui stiate
registrando servendovi degli ingressi XLR e a
1/4” posti sulla parte superiore dell’IO|2.
Impostare l’interruttore su “digital” unicamente
se si desidera utilizzare i connettori S/PDIF.
Se desiderate servirvi di collegamenti S/PDIF
per trasferire audio digitalmente, assicuratevi
che l’interruttore di ingresso sia impostato su
“digital”. In caso contrario, lasciare
l’interruttore su “analog” per un uso normale.
Verificare che l’interruttore mic/line sia
impostato correttamente su ciascun canale. Nel
caso in cui vi serviate di un microfono
condensatore che richieda un’alimentazione
phantom, accendere l’interruttore di
alimentazione +48v phantom. Infine,
assicurarsi che la manopola di guadagno sia
girata.
L’uso di cavi coassiali a 110-ohm è molto
importante per tutti i collegamenti S/PDIF. La
maggior parte dei cavi RCA NON sono a 110ohm e provocano problemi di sincronizzazione
tra due dispositivi digitali. Questo causa click,
scoppiettii e rumore bianco sostenuto.
65
Page 68

Specifiche tecniche
Interfaccia: Interfaccia audio/MIDI IO|2 a 24-bit
Caratteristiche: Ingressi e uscite stereo a 24-bit. Frequenza di
campionamento regolabile fino a 48 kHz.
Manopola di guadagno e interruttore mic/linea
separati per ciascun ingresso. Tutti gli ingressi e le
uscite bilanciati. Jack cuffie stereo da ¼”. S/PDIF
e MIDI I/O.
Audio: Ingressi Mic/linea
SNR 95dB (pesato A) minimo -- 97dB tipico
THD+N 0.007% massimo -- 0.005% tipico
risposta di frequenza +/-0,35dB typ
Ingressi chitarra da 1/4"
SNR 94dB (pesato A) minimo -- 96dB tipico
THD+N 0.05% massimo -- 0.034% tipico
risposta di frequenza +/-1,2dB
Uscite analogiche
SNR 95dB (pesata A) minimo -- 97dB tipico
THD+N 0.007% massimo -- 0.005% tipico
risposta di frequenza +/-0,35dB typ
Software: Driver ASIO/WDM a latenza ultra-bassa per
Windows XP. Supporto pieno per Core Audio su
Mac OS X.
Opzioni di alimentazione: Alimentazione tramite porta USB
Dimensioni: 6.5” x 4.7” x 2.25” / 16.5 cm x 12.0 cm x 5.8 cm
Peso (netto): 1.5 lbs / 0.68 kg
66
Page 69

7-51-0173-E
67
 Loading...
Loading...