Page 1

Alcatel 7670 RSP
Routing Switch Platform | Release 6.2
A multiservice IP routing and switching platform
supporting new and established services
The Alcatel 7670 Routing Switch Platform
(RSP) is a feature-rich, highly scalable,
multiservice platform optimized to deliver
IP/MPLS and ATM-based services reliably
and concurrently. The platform is ideal for
service providers seeking to preserve and
expand current services while transitioning towards an IP/MPLS infrastructure.
With separate control planes for
IP/MPLS and ATM, the Alcatel 7670 RSP
has been uniquely designed to support a
wide range of services including IP-VPNs,
Layer 2 VPNs, Ethernet, ATM, and frame
relay. The Alcatel 7670 RSP also offers
comprehensive network and service interworking capabilities leveraging standardsbased approaches over both MPLS and
ATM. Furthermore, the Alcatel 7670 RSP
supports high-density, channelized, multiservice cards that offer outstanding flexibility
with the ability to support multiple concurrent services at different speeds on a
single card.
Designed to accommodate traffic growth,
the Alcatel 7670 RSP scales rapidly and
without service interruption from 50 Gb/s
to 450 Gb/s (full duplex, redundant). The
breadth of supported configurations ensures
optimal node deployments at multiple
sites of varying size.
As a highly reliable, carrier-grade platform, the Alcatel 7670 RSP provides full
common equipment redundancy. Facility
protection capabilities include automatic
protection switching (APS) for SONET/
SDH interfaces and link aggregation group
(LAG) for Ethernet interfaces. With the
addition of MPLS fast reroute (FRR),
non-stop routing, non-stop signaling and
non-stop forwarding, the result is a highavailability architecture at all levels providing the foundation for true end-to-end,
non-stop Layer 2 and Layer 3 services.
The industry-leading Alcatel 5620
Network Manager (NM) provides a single
management platform to seamlessly manage
both legacy and IP/MPLS services. Only
Alcatel can provide a single tool for automated end-to-end provisioning of both label
switched paths (LSPs) and VCs across
multiple platforms, monitoring and enforcement of service level agreements (SLAs),
and open interfaces that enable simple
integration into any OSS environment.
The Alcatel 7670 RSP is deployed in
over 110 of the world’s largest fixed and
mobile service provider networks worldwide. Its unique platform enables the
deployment of flexible, scalable, highly
reliable and manageable networks capable
of supporting both today’s requirements
and tomorrow’s evolution.
This document, which refers to Alcatel, was issued prior to our merger.
It has not been modified to refer to Alcatel-Lucent since it is part of our archives.
Page 2
Alcatel 7670 RSP | Release 6.2
Product Summary
Services
Layer 3 VPNs
IP-VPN (RFC 4364)
>
Virtual routing and forwarding (VRF):
>
2,000 VRFs
> Inter-AS option-A and option-B
> Bandwidth guarantee per VRF
via MPLS-TE
Numbered and unnumbered VPN
>
interfaces with virtualized DHCP
relay agent
> Customer equipment (CE) –
provider edge (PE) routing:
static, BGP-4, OSPF, RIP v1/v2
> Integrated public Internet service
> Extranet
> Non-stop VRF routing/MPLS
Layer 2 VPNs
> Ethernet virtual LAN service
> Ethernet virtual leased line
> Circuit emulation (TDM) virtual
leased line
> Cell relay virtual leased line
> Cell relay and IMA v1.1 and
v1.0 switched services
> Frame relay and multilink frame relay
Network and service interworking
> Service interworking enables access
to Layer 2 VPN service via Ethernet,
cell relay and frame relay
> Network interworking enables IP/MPLS-
based services over ATM networks and
ATM-based services over IP/MPLS
networks
Ethernet, ATM and IP pseudowires
>
(a.k.a. draft Martini)
Residential broadband services
> IP aggregation: Ethernet, frame relay
> PPP, cell relay, POS, G.SHDSL
> Broadcast TV: IGMP v2/v3, PIM-SSM,
PIM-SM, static multicast
Video on demand (VoD)
>
Voice over IP (VoIP)
>
V
oice over packet service
> Reliable VoIP transport
(switching and routing) based
on quality of service (QoS)
> AAL2:
¬ G.711 encoding
¬ G.726 and G.729A/B compression,
silence suppression, comfort noise
generation, 128-ms echo cancellation
> Circuit emulation: AAL1, 128-ms echo
cancellation
Leased line service
> Leased line: AAL1 circuit emulation,
point-to-point and broadcast
> TDM over packet: AAL1 circuit emulation,
3/1/0 circuit grooming and packetbased digital cross-connect switching
IP-Enabled Multiservice
Networks
Self-paced migration to multiservice,
multiprotocol Layer 2 and 3 networks
> Configurable service and protocol
isolation and interworking
¬ ensures continuity of existing services
¬ enables controlled introduction
of new services and protocols
¬ leverages collective strengths of each
protocol to enable multiple SLA-based
services with statistical gain
Comprehensive tools enable hierar-
>
chical service definitions
¬ multiple service queues enable
differentiated Layer 2 and 3
vices with multiple QoS levels
ser
¬ hierarchical, multilayer service
definitions enable delivery of IP
traffic without loss by prioritizing
an IP flow according to Layer 3 CoS
and by shaping resulting stream to
its Layer 2 circuit’
s QoS parameters
> Service isolation and fairness enable
per-customer SLA enforcement
¬ shapes, polices and marks traffic
based on Layer 2 and 3 service
definitions
¬
hierarchical QoS
¬ bandwidth reservations per IP CoS,
LSP, VC (hierarchical connection
admission)
¬ per-IP flow, LSP and VC queuing
and shaping at ingress and egress
¬ per-IP flow, LSP and VC fairness
and flow control
¬ work-conserving hierarchical WFQ
coupled to admission policy
Technical Summary
IPv4 Features and Performance
> IPv4 interfaces: 100,000
> FIB size: 1 million unique routes
> RIB size: >2 million BGP routes (RIB-in)
> Wirespeed forwarding for 40-byte
packets at all ports
> Non-stop routing: BGP, OSPF, IS-IS and RIP
> Graceful restart helper for BGP and OSPF
> PE and provider router
Unicast IP routing protocols: BGP-4
>
(route reflector, confederation) IS-IS,
IS-IS-TE, OSPF, OSPF-TE
> Multicast IP routing protocols: IGMP
v2/v3, PIM-SSM, PIM-SM, static
multicast
> MD5 authentication between routing
peers
Layers 3 and 4 access control lists
>
> AS path lists, community lists
and route maps
> Flow-based rate limiting
> Reverse path filtering
> DiffServ and DSCP remarking
> Eight CoS classes (user-defined)
> Multiple field classification (MFC)
> ICMP
>
Flexible ECMP implementation:
applicable to routing protocols
and static routing
> DHCP relay agent
IPv6 Features and Performance
> IPv6 interfaces: 16,000
> FIB size: 100,000 unique routes
> RIB size: >500,000 BGP routes (RIB-in)
> Wirespeed forwarding for 60-byte
packets at all ports
> Non-stop routing
> MBGP with IPv6 AFI support
> 6PE tunneling
> ICMPv6
> Neighbor discovery
> EUI-64 support
> Stateless address autoconfiguration
> Eight CoS classes
> DiffServ and DSCP remarking
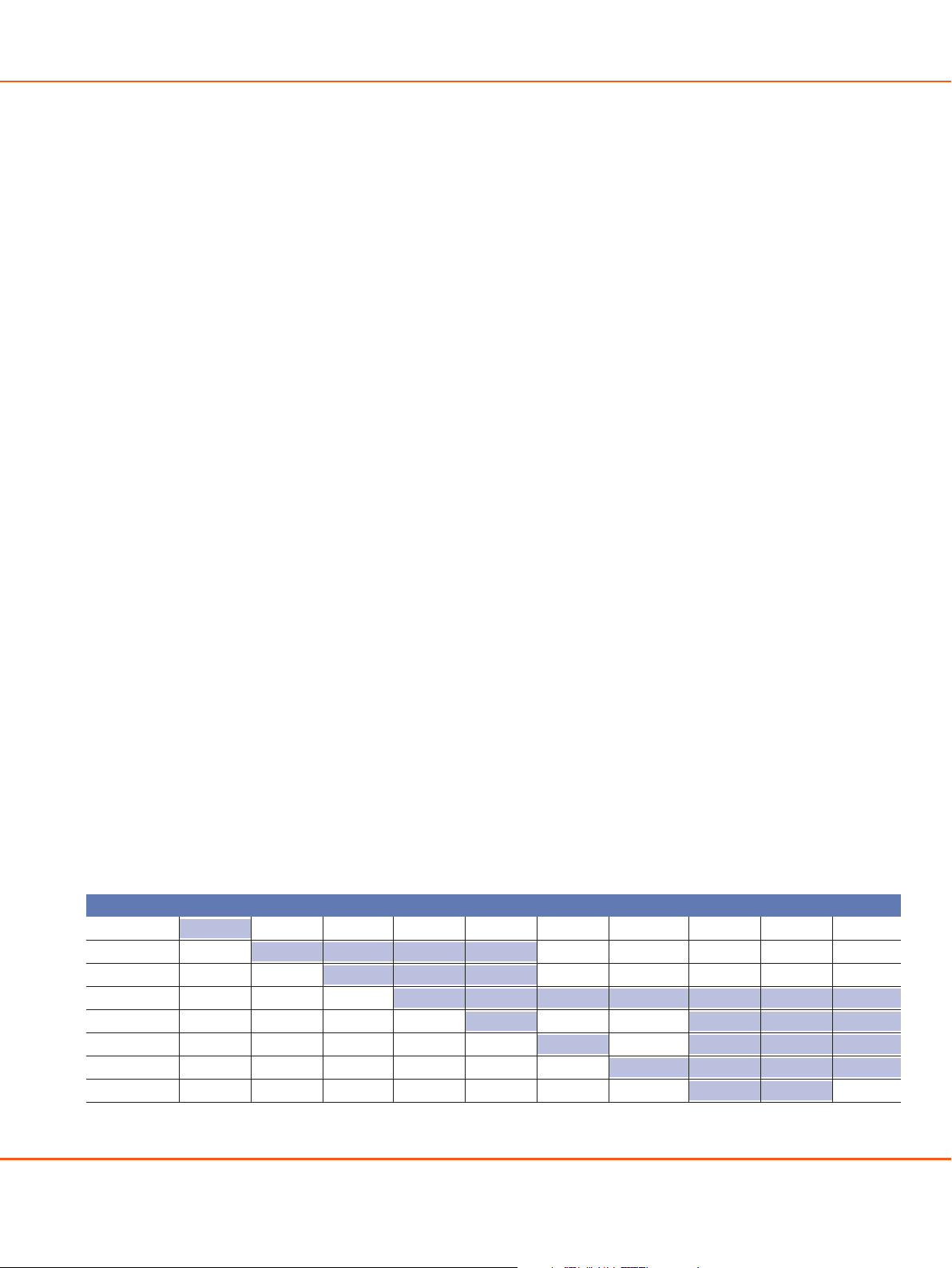
Physical Interfaces, Channels and Protocols
GigE, 10/100 OC-48/STM-16 OC-12/STM-4 OC-3/STM-1 DS-3* E3 n*DS-1/n*E1 DS-1/E1 n*DS-0 DS-0
net Eth
Ether
OC-48/STM-16 POS, ATM POS, ATM POS, ATM POS, ATM
OC-12/STM-4 POS, ATM POS, ATM POS, ATM
TM, CE ATM, CE ATM IMA ATM, CE ATM, CE CE, AAL2
TM
OC-3/STM-1
DS-3
E3
T1/E1 ATM IMA, MLFR ATM, FR, CE FR, CE CE, AAL2
g.SHDSL ATM ATM
* STS-1/DS-3 in channelized OC-48/STM-16 and OC-12/STM-4 inter
2 < ALCA
TEL
POS, A
faces
A
TM, FR, CE FR, CE FR, CE FR, CE
A
ATM, FR, CE CE CE CE
Page 3

Alcatel 7670 RSP | Release 6.2
MPLS Features
> LER and LSR
> Generic label (“shim header”) and
label control ATM (VPI/VCI)
> LSP signaling, RSVP-TE, LDP DoD,
LDP-DU and CR-LDP
¬ explicit route reservation
nate explicit route)
(and alter
¬ resource reservation
> Non-stop MPLS signaling, LDP graceful
restart
> Dynamic LSP and provisioned/static LSP
> CSPF for RSVP-TE
> LSP tunnels (BGP and IGP shortcuts)
> End-to-end LSP protection (FRR)
> Multiple parallel LSPs
Hitless “make before break”
>
LSP modification
> Directed ping and traceroute over MPLS
> LSP ping and traceroute
> ATM/MPLS mediation
> IPv6 tunneling over MPLS (6PE)
> Source-based forwarding to MPLS LSPs
> Network layer OA&M: MPLS ping
and traceroute
> Service layer OA&M: PW VCCV
ATM Features and Performance
> CBR, 2 x rt-VBR, 3 x nrt-VBR,
ABR and UBR with MDCR (UBR+)
> As per Telcordia GR-1110-CORE,
GR-1248-CORE, ATM Forum TM4.0
and ITU-T I.371; VS/VD and full ABR
as per ATM Forum TM4.0, including
ER marking
> PNNI, AINI, B-ICI v.2.0, ILMI 4.0,
UNI 3.1, UNI 4.0, Q.2931 and
Q.2961 signaling
vices from DS-1 through
UNI ser
>
OC-48/STM-16
> 3,000 SVC calls per second (sustained)
– equivalent to 10 million BHCAs
> 768,000 connections
Signaling congestion control
>
> ATM Forum policy-based routing
> PNNI QoS routing
> PNNI-H (hierarchy)
> NCCI
SVCs and SVPs
>
S-PVCs and S-PVPs
>
> S-PVC operator-directed routing
> Point-to-point and point-to-multipoint
PVCs, SVCs and S-PVCs
Logical multicast
>
S-PVC hitless connection moves
>
> Test access connections
> ILMI address registration
> ATM Forum PNNI path and
connection trace
Closed user groups
>
Address screening and address
>
translation
> Efficient support of real-time traffic
(CBR and rt-VBR)
> Explicit rate and virtual source/
virtual destination support for ABR
> Virtual path aggregation
> OA&M performance monitoring
> OA&M round trip delay
System Reliability
and Redundancy
> Hitless software upgrades
> Hardware redundancy: common control,
data plane fabric, control plane fabric
(separate from data), line and I/O
cards, power, cooling, synchronization
and management
> Control redundancy: 1+1 redundant
call processing, billing, routing, network
data collection and node control
> Non-stop routing for BGP, OSPF and IS-IS
> Non-stop RSVP-TE signaling
> Hot standby for PNNI routing and
signaling
> Non-stop IMA
> APS
> IEEE 802.3ad link aggregation
on GigE line card with LACP
F1- to F5-level OA&M functions
>
Circuit, equipment and line loopbacks
>
> Background and directed diagnostics
for fault isolation
> Performance monitoring with threshold
crossing alerts
EAC
>
> Alarm logs and remote alarm signaling
> Operational and diagnostic LED displays
> Network inventory support from
Alcatel 5620 NM
Network Management
> Management of VPs, VCs, LSPs and
IP service interfaces through Alcatel
5620 NM, or local management
interface (i.e., CLI)
Point-and-click provisioning
>
Centralized alarm management with
>
audible and visual alarm notification
> Centralized software management
administration
Router configuration templates
>
Dynamic routing protocol configuration
>
> IP diagnostics (ping and traceroute)
> Automatic discovery of equipment
additions, deletions and changes
> Sophisticated link and path management
> Extensive performance data for SLAs
and billing capabilities based on
AMA records
> Multiple graphical displays of
performance data
> Open interfaces at network and service
levels for maximum business automation
> SNMP support
¬ MIB II as per RFC 1213
¬ interface table MIB as per RFC 1573
¬ SONET MIB as per RFC 1595
¬ DS-3/E3 MIB as per RFC 1407
¬ ATM interface MIB as per RFC 1695
¬ ILMI MIB as per ATM Forum UNI v3.1
¬ enterprise MIB for PVC and S-PVC
setup
¬ frame relay services MIB
¬ call routing statistics MIB
¬ IPv6 MIB
Scalable Architecture
In-service system expansion
> Switching fabric scales from 50 Gb/s
to 450 Gb/s (full duplex, redundant,
APS enabled)
Single nodal entity (i.e., one logical
>
management interface)
> Parallel, redundant optics used to
interconnect shelves, integrated
on common control
Peripheral shelf (PS)
Single PS can be deployed as a stand
>
alone 50 Gb/s Alcatel 7670 RSP system
> 14 universal, multiprotocol IP/MPLS/
ATM slots, each supporting 2.4 Gb/s
user I/O, per PS
> Mid-plane design enables combinations
of different optical I/O per line card
> Optimized per-PS configuration enables
APS in all slots with zero fabric con
-
sumption for redundant cards
Switching shelf (SS)
> Fabric scales to 450 Gb/s
(full duplex) providing 320 Gb/s
user I/O (full duplex)
Enables 14 additional PSs to be
>
added (15 in total)
Edge services extender shelf (ESE)
Extends Alcatel 7670 RSP multiprotocol
>
capabilities to low-speed, multiservice
interfaces
> Subtended from PS via standard ATM
NNI STM-4/OC-12c or STM-1/OC-3c
interface
> Also deployable as a standalone
3.2 Gb/s multiservice switch
> 12 universal, multiservice slots,
each supporting channelized and
unchannelized interfaces up to
STM-1/OC-3
> two high-speed slots for STM-4/OC-12c
or multiport STM-1/OC-3c
Interfaces
Any service, any port
> Concurrent POS and ATM channels within
OC-48/STM-16 and OC-12/STM-4
interfaces (channelized to STS-1/DS-3)
> IP forwarding, MPLS and ATM switch-
ing supported in ATM channels
> IP forwarding, MPLS and ATM
mediation supported in POS
channels
> Bridged and Routed Encapsulation
(RFC 2684)
mediate- and long-reach
t-, inter
> Shor
optics
Gigabit Ethernet
> Per VLAN configuration for access
to Layer 3 service or as an endpoint
to Layer 2 service
Layer 2 network inter
>
working with
Ethernet over ATM, Ethernet over MPLS
> Layer 2 service interworking: Ethernet
VLAN to frame relay/A
> Short-, intermediate- and long-reach
TM VC
optics
Low speed, multiservice
TM IMA v1.1 and v1.0
A
>
> Frame relay and MLFR
Circuit emulation: private line,
>
TDM over packet
> Voice over packet (AAL2)
> 10/100 Ethernet
ALCA
TEL
> 3
Page 4

Alcatel 7670 RSP | Release 6.2
Physical Dimensions
Peripheral shelf
> Height: 93.3 cm (36.7 in.)
Width: 54.5 cm (21.4 in.)
>
> Depth: 54.5 cm (21.4 in.) without
cables; 60 cm (23.6 in.) with cables
Switching shelf
Height: 97.7 cm (38.4 in.)
>
> Width: 54.5 cm (21.4 in.)
> Depth: 54.5 cm (21.4 in.) without
cables; 60 cm (23.6 in.) with cables
Edge services extender shelf
> Height: 92.0 cm (36.7 in.)
> Width: 44.0 cm (17.3 in.)
> Depth: 31.0 cm (12.2 in.) without
cables; 39.0 cm (15.5 in.) with cables
Normal Operating Environment
> -5 C to +40 C (23 F to 104 F)
> 5% to 85% relative humidity,
non-condensing
Power
> DC power: -48 V to -60 V DC
> -60 m to 1,800 m (-197 ft. to
5,905 ft.) above sea level
Industry-Specific
Requirements
Telcordia (Bellcore)
> TR-NWT-000332
> GR-78-CORE
> GR-63-CORE
> GR-1089-CORE
ETSI
> ETS 300 019
> ETS 300 132-2
Telecom
> Telcordia (Bellcore) TR-NWT-1112
(Multimode)
> ITU G.957 (Optical STM-N)
Telcordia (Bellcore) TR-NWT-000499
>
(DS-N)
> AT&T Pub 62411 (DS-1)
> ITU G.703 (T1/E1/155 Mb/s)
> ITU G.707 (Synchronization Status)
Network Node Inter
face for Synchronous
Digital Hierarchy
> ITU G.825 Jitter/Wander, Digital Net-
works for Synchronous Digital Hierarchy
> Telcordia GR-253-CORE Issue 3
(Section 4: Physical Layer)
> Telcordia GR-253-CORE Issue 3
(Section 5.4 and 5.6: Network ITU-T
G.703 Physical Electrical Inter
faces
Requirements)
> ITU-T G.707 (SDH Mapping and
Overhead Requirements)
> ITU-T G.813 (Network Synchronization
Option 1(E rate))
> ITU-T G.823 (E-rate Jitter/Wander)
ITU-T G.824 (T-rate Jitter/Wander)
>
ITU-T G.825 (SDH Jitter/Wander)
>
> ITU-T G.957 (IR/LR/XLR)
> ANSI T1.403 (DS-1 Physical Layer)
> ANSI T1.404 (DS-3 Physical Layer)
> ANSI T1.102 (STM-1e)
> ANSI T1.105.06
The Alcatel 7670 RSP also supports
customer-specific qualification
requirements.
Qualification Summary
North and South America Europe, Middle East, Africa Asia, Pacific
Product Safety Approvals
CSA 60950-1 European Community IEC 60950-1
UL 60950-1 EN 60950-1 IEC 60825-1, -2
FDA/CDRH 21 CFR Part 1040 EN 60825-1, -2 AS/NZS 3260 and TS001
EMC Approvals
ICES-003 Class A European Community CISPR 22 Class A
EN 55022 Class A AS/NZS 3548 Class A
t 15 Class A
FCC Par
Network Attachment Approvals
IC CS-03 JATE Digital Services (Green Book)
ACTA TIA/EIA/IS-968 (formerly FCC Part 68) AS/ACIF S016
www
.alcatel-lucent.com
Alcatel, Lucent, Alcatel-Lucent, the Alcatel-Lucent logo, are trademarks of Alcatel-Lucent. All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners. Alcatel-Lucent assumes no responsibility
for the accuracy of the information presented, which is subject to change without notice. © 12 2006 Alcatel. All rights reserved. 3CL 00469 0020 TQZZA Ed.12 21350
ETS 300 386 Class B
MIC Notice no. 2001-115
MIC Notice no. 2001-116
MIC Proclamation No: 1998-62
MIC Proclamation No: 1998-18
MIC Notice no. 2001-03
 Loading...
Loading...