Page 1

Agilent 8860 Gas Chromatograph
Site Preparation Guide
Page 2
Notices
CAUTION
WARNING
© Agilent Technologies, Inc. 2019
No part of this manual may be reproduced in
any form or by any means (including
electronic storage and retrieval or translation
into a foreign language) without prior
agreement and written consent from Agilent
Technologies, Inc. as governed by United
States and international copyright laws.
Manual Part Number
G2790-90012
Edition
First edition, January 2019
Printed in USA
Agilent Technologies, Inc.
2850 Centerville Road
Wilmington, DE 19808-1610 USA
安捷伦科技 (上海)有限公司
上海市浦东新区外高桥保税区
英伦路 412 号
联系电话:(800)820 3278
Warranty
The material contained in this document is
provided “as is,” and is subject to being
changed, without notice, in future editions.
Further, to the maximum extent permitted
by applicable law, Agilent disclaims all
warranties, either express or implied, with
regard to this manual and any information
contained herein, including but not limited
to the implied warranties of merchantability
and fitness for a particular purpose. Agilent
shall not be liable for errors or for incidental
or consequential damages in connection
with the furnishing, use, or performance of
this document or of any information
contained herein. Should Agilent and the
user have a separate written agreement
with warranty terms covering the material in
this document that conflict with these
terms, the warranty terms in the separate
agreement shall control.
Technology Licenses
The hardware and/or software described in
this document are furnished under a license
and may be used or copied only in accordance
with the terms of such license.
Restricted Rights Legend
U.S. Government Restricted Rights. Software
and technical data rights granted to the
federal government include only those rights
customarily provided to end user customers.
Agilent provides this customary commercial
license in Software and technical data
pursuant to FAR 12.211 (Technical Data) and
12.212 (Computer Software) and, for the
Department of Defense, DFARS 252.227-7015
(Technical Data -Commercial Items) and
DFARS 227.7202-3 (Rights in Commercial
Computer Software or Computer Software
Documentation).
Safety Notices
A CAUTION notice denotes a
hazard. It calls attention to an
operating procedure, practice, or
the like that, if not correctly
performed or adhered to, could
result in damage to the product or
loss of important data. Do not
proceed beyond a CAUTION notice
until the indicated conditions are
fully understood and met.
A WARNING notice denotes a
hazard. It calls attention to an
operating procedure, practice, or
the like that, if not correctly
performed or adhered to, could
result in personal injury or death.
Do not proceed beyond a WARNING
notice until the indicated conditions
are fully understood and met.
Site Preparation Guide
Page 3

Contents
1 Agilent 8860 GC Site Preparation
Site Preparation Checklist 6
Bench Preparation 7
Maximum Length of Cables and Hoses 10
2 GC Installation Kits
Installation Kits 14
3 Dimensions and Weights
Dimensions and Weight 18
Foreline Pump Requirements for Systems Including an MSD 20
ALS Dimensions and Weight 21
4 Environmental Conditions
Environmental Conditions 24
Heat Dissipation 25
ALS Environmental Conditions 26
5 Exhaust Venting
Exhaust Venting 28
Venting hot air 28
Venting other gases 29
Exhaust vent fittings 30
6 GC System Power Requirements
Power Requirements 32
USA fast heating oven, 240 V 34
Canadian installation 34
Common instrument power cord plugs 34
ALS Power Requirements 38
7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
Gas and Reagent Selection 40
Hydrogen Carrier Gas 42
Gas and Reagent Purity 42
Site Preparation Guide 3
Page 4

Gas Supplies 43
GC/MS Gas Requirements 45
Performance verification 48
Gas Plumbing 49
Supply tubing for most carrier and detector gases 50
Supply tubing for hydrogen gas 50
Two-stage pressure regulators 51
Pressure regulator-gas supply tubing connections 51
Filters and traps 52
A LAN Requirements
Site LAN Network 56
4 Site Preparation Guide
Page 5

1 Agilent 8860 GC Site Preparation
Site Preparation Checklist 6
Bench Preparation 7
Maximum Length of Cables and Hoses 10
This guide outlines the site requirements for GC, GC/MS, and automatic liquid sampler (ALS)
installation. Site requirements include the necessary space, electrical supplies, gas supplies,
operating supplies and consumables required to successfully install the GC and related
instruments and systems.
The site must meet the requirements specified in this guide before beginning installation.
Refer to the Agilent Web site at www.agilent.com for the most up-to-date listing of GC, GC/MS,
and ALS supplies and consumables.
Site Preparation Guide 5
Page 6

1 Agilent 8860 GC Site Preparation
Site Preparation Checklist
Site Preparation Checklist
For typical system requirements for system installation, see the diagrams on page 8 through
page 9.
Use the following checklist to ensure that the site is properly prepared for GC system
installation.
1 Ensure that the appropriate installation hardware has been acquired.
See “Installation Kits” on page 14.
2 Ensure that the location in which the GC system is being installed meets the
requirements for environmental conditions. See “Environmental Conditions” on
page 24. Also see “Heat Dissipation” on page 25.
3 Prepare bench space for the GC system. Ensure that the bench has the size and
weight capacity to accommodate the GC and associated components. See “Bench
Preparation” on page 7. Also see “Dimensions and Weight” on page 18.
4 Ensure that system components are oriented so that they can be connected
properly. See “Maximum Length of Cables and Hoses” on page 10.
5 If the system being installed includes an MSD, ensure that the bench allows for
proper installation and connection of the foreline pump. See “Foreline Pump
Requirements for Systems Including an MSD” on page 20.
6 Ensure that appropriate venting is provided for the GC system. See “Exhaust
Venting” on page 28.
7 Ensure that a dedicated power circuit is available for each device in the system.
See “Power Requirements” on page 32.
8 Ensure that appropriate gas and reagent supplies are provided for the GC system.
See “Gas and Reagent Selection” on page 40.
9 Ensure that appropriate gas plumbing is provided for the GC system. See “Gas
Plumbing” on page 49.
10 If the GC system being installed includes a data system, ensure that the PC meets
the requirements necessary to properly support the GC system. For more
information, see the site prep guide for your data system.
11 If the GC being installed is to be connected to a site LAN, ensure that the appropriate
cabling is available. See “Site LAN Network” on page 56.
6 Site Preparation Guide
Page 7

1 Agilent 8860 GC Site Preparation
Bench Preparation
Bench Preparation
When planning a bench layout:
• Consider component dimensions, weights, and space requirements. See “Dimensions and
Weight” on page 18.
• Consider the lengths of cables and hoses for connection of components. See “Maximum
Length of Cables and Hoses” on page 10.
• For systems that include an MS, consider foreline pump requirements. See “Foreline
Pump Requirements for Systems Including an MSD” on page 20.
• Allow space for operational access.
• Note that the 7200 Q-TOF requires 48 cm (1.6 ft) of space in front to allow for the RIS
probe extraction tool handle when installed.
• Note that some repairs to the GC/MS, or to the GC itself, will require access to the back of
the instrument(s).
Examples are provided here for systems including a GC with an ALS, computer and printer.
Most examples also include an MS.
See several example layouts below.
Site Preparation Guide 7
Page 8
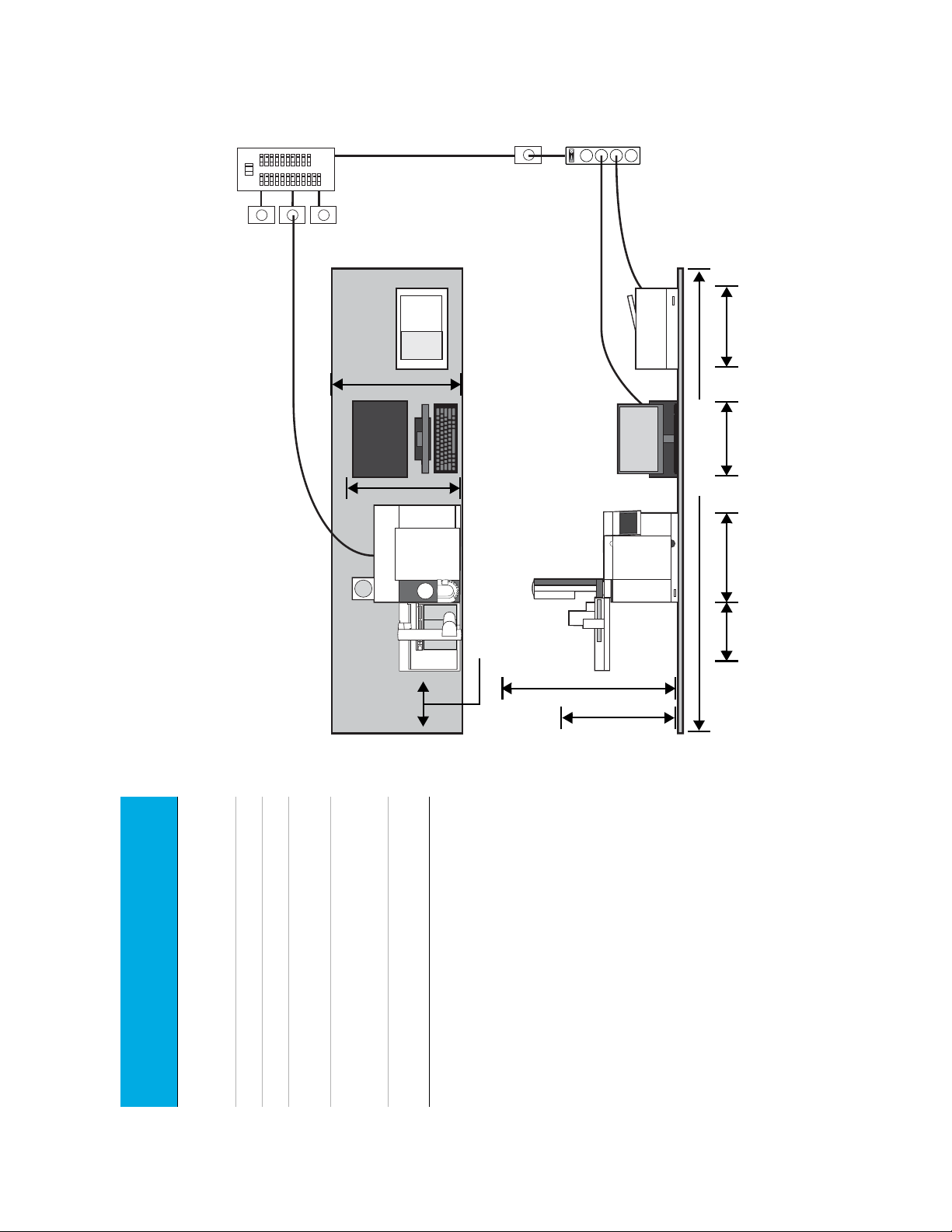
1 Agilent 8860 GC Site Preparation
Typical GC System - 8860 GC with computer and printer.
Total weight: ~84 kg (186 lb)
Maximum power consumption: ~3,250 VA (11,090 btu/hr)
78 cm (31-in.)
without heat
deflector
65 cm (26-in.)
with heat
deflector
Leave 30 cm (12-in.)
open space for
operational access
Use isolated circuits with
dedicated grounds for GC
and MSD.
Application
Gas
*
* Use 1/8-in. Swagelok gas connections
Purity
Supply
Pressure
(psi)
†
† 1 psi = 6.89 kPa
Carrier Helium
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
99.9995
99.9995
99.9995
50 - 80
50 - 80
50 - 80
Detectors
TCD Helium 99.9995 50 - 80
FID, NPD,
FPD, TCD
Hydrogen 99.9995 50 - 80
ECD, FID,
FPD, NPD,
TCD
Nitrogen 99.9995 50 - 80
FID, NPD,
FPD
Air Zero
grade
50 - 80
80 cm
(32-in.)
(without
ALS)
100 cm (40-in.)
(with ALS)
~2.35 m (7.7 ft.)
~86 cm (34-in.) ~56 cm (22-in.) ~56 cm (22-in.)~44 cm (17.3-in.)
Bench Preparation
8 Site Preparation Guide
Page 9
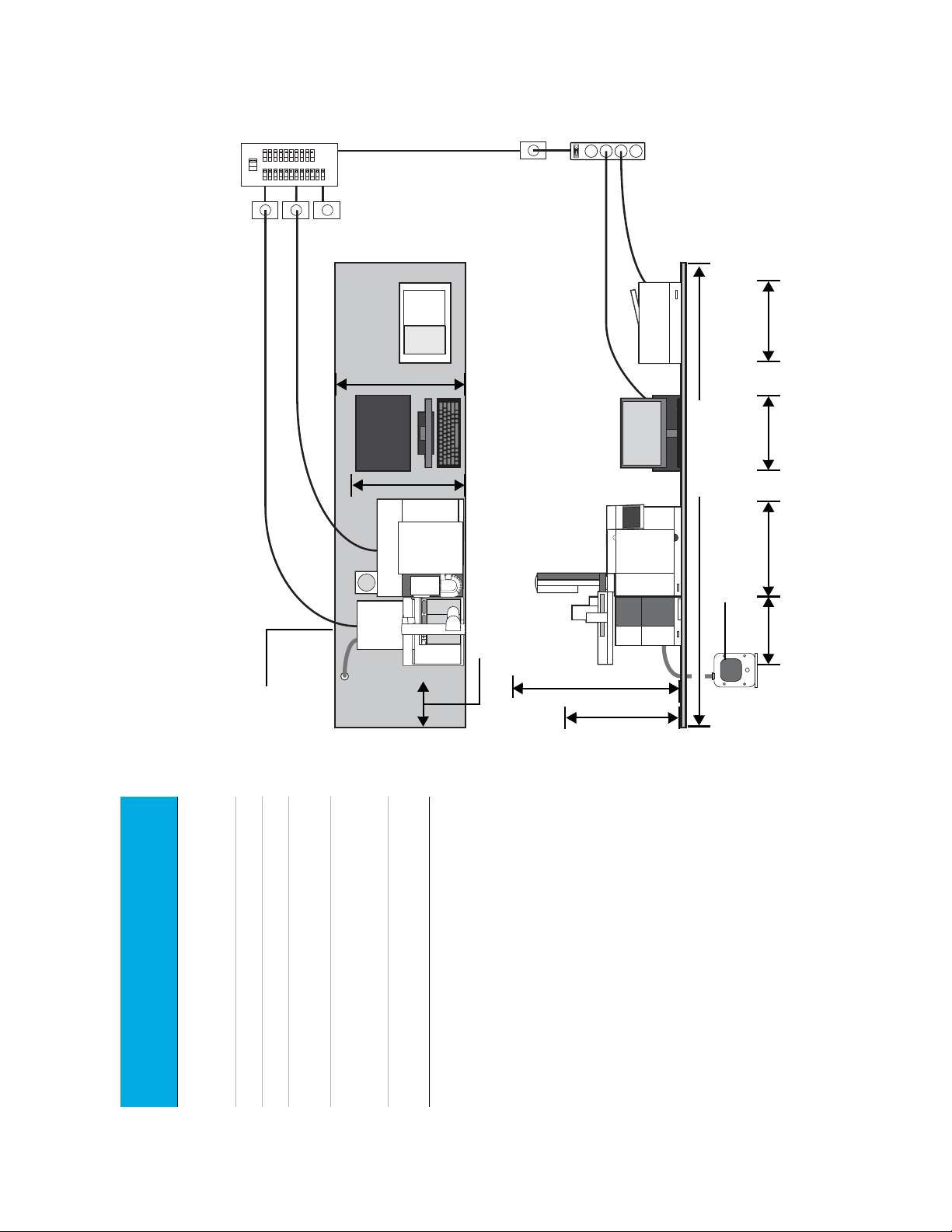
1 Agilent 8860 GC Site Preparation
Typical GC/MS System - 8860 GC, 5977 MSD, with computer and
printer.
Total weight: ~123 kg (271 lb)
Maximum power consumption: ~4,350 VA (14,843 btu/hr)
78 cm (31-in.)
without heat
deflector
65 cm (26-in.)
with heat
deflector
If bench backs up to
wall, drill 1.5-in. hole
for foreline pump
hose.
Leave 30 cm (12-in.) open
space for operational
access
Use isolated circuits with
dedicated grounds for GC
and MSD.
Place foreline pump on floor or
on vibration reducing bench.
Application
Gas
*
* Use 1/8-in. Swagelok gas connections
Purity
Supply
Pressure
(psi)
†
† 1 psi = 6.89 kPa
Carrier Helium
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
99.9995
99.9995
99.9995
50 - 80
50 - 80
50 - 80
Detectors
TCD Helium 99.9995 50 - 80
FID, NPD,
FPD, TCD
Hydrogen 99.9995 50 - 80
ECD, FID,
FPD, NPD,
TCD
Nitrogen 99.9995 50 - 80
FID, NPD,
FPD
Air Zero
grade
50 - 80
80 cm
(32-in.)
(without
ALS)
100 cm (40-in.)
(with ALS)
~2.35 m (7.7 ft.)
~86 cm (34-in.) ~56 cm (22-in.) ~56 cm (22-in.)~44 cm (17.3-in.)
Bench Preparation
Site Preparation Guide 9
Page 10

1 Agilent 8860 GC Site Preparation
CAUTION
Maximum Length of Cables and Hoses
Maximum Length of Cables and Hoses
The distance between system modules may be limited by some of the cabling and the vent or
vacuum hoses.
Table 1 Cable and hose lengths
Item Length
Remote cable 2 m (6.6 ft)
LAN cable 10 m (32.8 ft)
Power cords 2 m (6.6 ft)
Vacuum hose 1.3 m (4.24 ft)
Foreline pump power cord 2 m (6.6 ft)
7697A Headspace Sampler transfer line 99 cm (39-in.)
G1888 Headspace Sampler transfer line 80 cm (31.5-in.)
The supporting surface for the 7200/7250 Q-TOF GC/MS system should be kept relatively
vibration free. Do not put the rough pump on your laboratory bench with the 7200/7250
Q-TOF GC/MS due to the vibration that the pump creates. Vibration can lead to a loss of
mass accuracy and resolution.
10 Site Preparation Guide
Page 11

2 GC Installation Kits
Installation Kits 14
This section provides details for available installation hardware.
Refer to the Agilent Web site at www.agilent.com for the most up-to-date listing of GC, GC/MS,
and ALS supplies and consumables.
Site Preparation Guide 13
Page 12
2 GC Installation Kits
NOTE
Installation Kits
Installation Kits
Installation kits are not supplied with the GC. If you did not order the GC with the factory
plumbing option (305), Agilent highly recommends the following kits in Table 2.
• Agilent recommends purchasing the installation kit(s) that provides parts useful for GC
installation. (Tab le 2 lists the appropriate installation kits.)
In addition to these installation kits, fittings and reducers are required to convert gas cylinder
regulator fittings (for example, 1/4-inch male NPT) to the 1/8-inch female Swagelok fittings
needed to connect gases to the instrument. These fittings are not included with the GC or with
the installation kits. See “Gas Plumbing” on page 49 for details.
Table 2 Installation kits
Kit Part number Contents
Recom mended for GCs wit h FID, NPD, F PD:
GC Supply Gas Installation
Kit with Gas Purifiers
See Figure 1.
Recommended for GCs with TCD/ECD, MS, and MSD:
19199N Includes Gas Clean Filter system kit
CP736530 (with 1 oxygen, 1 moisture,
and 2 charcoal filters), 1/8-inch brass
nuts and ferrules, copper tubing,
1/8-inch brass tees, tubing cutter,
1/8-inch brass caps, universal external
split vent trap with replacement
cartridges, and 1/8-inch ball valve.
GC Supply Gas Installation
Kit
See Figure 2.
Gas Clean carrier gas filter
kit, 1/8-inch
See Figure 3.
19199M Includes 1/8-inch brass nuts and
ferrules (20), copper tubing, 1/8-inch
brass tees, tubing cutter, 1/8-inch brass
caps, 7-mm nut driver, T-10 Torx driver,
T-20 Torx driver, 4 open-end wrenches,
and 1/8-inch ball valve
CP17974
14 Site Preparation Guide
Page 13

2 GC Installation Kits
Installation Kits
Figure 1. GC Supply Gas Installation Kit with Gas Purifiers 19199N
Figure 2. GC Supply Gas Installation Kit 19199M
Figure 3. Gas Clean carrier gas filter kit, 1/8-inch CP17974
Site Preparation Guide 15
Page 14

2 GC Installation Kits
Installation Kits
16 Site Preparation Guide
Page 15

3 Dimensions and Weights
Dimensions and Weight 18
Foreline Pump Requirements for Systems Including an MSD 20
ALS Dimensions and Weight 21
This section lists the dimensions of the GC, GC/MS, and automatic liquid samplers (ALS).
Site Preparation Guide 17
Page 16

3 Dimensions and Weights
Dimensions and Weight
Dimensions and Weight
1 Ensure that you can accommodate the shipping pallets when you take delivery.
See Table 3.
2 Prepare laboratory bench space before the system arrives. Make sure the prepared area is
clean, clear, and level. Pay special attention to the total height requirements. Avoid bench
space with overhanging shelves. See Table 4 .
Table 3 Pal let d i mens ions and weights
Product Height Width Depth Weight
GC
8860 Series GC shipping pallet
With third side detector (side mount)
MS
7200/7250 Q-TOF MS 96 cm (38-inch) 130 cm (51-inch) 91 cm (36-inch) 175 kg (385 lb)
7200 Flight Tube 66 cm (26-inch) 66 cm (26-inch) 147 cm (58-inch) 36.4 kg (80 lb)
7250 Flight Tube 66 cm (26-inch) 206 cm (81-inch) 81 cm (32-inch) 87 kg (191 lb)
76 cm (30-inch)
76 cm (30-inch)
86 cm (34-inch)
87 cm (34-inch)
103 cm (40.5-inch)
108 cm (42.5-inch)
N/A
Table 4 Instrument dimensions, weights, and required clearances
Product Height Width Depth Weight
GC
8860 Series GC
With third side detector (side mount)
• GC operational /oven access Requires
• GC rear ventilation / maintenance
clearance
MSD
5975 Series MSD
• Diffusion pump 41 cm (16-inch) 30 cm (12-inch) 54 cm (22-inch) 39 kg (85 lb)
• Standard turbo pump 41 cm (16-inch) 30 cm (12-inch) 54 cm (22-inch) 39 kg (85 lb)
• Foreline pump
Standard
Oil-free
• GC/MS operational and maintenance
access
5977 Series MSD
• Diffusion pump 41 cm (16-inch) 30 cm (12-inch) 54 cm (22-inch) 39 kg (85 lb)
50 cm (19.2-inch)
50 cm (19.2-inch)
21 cm (8-inch)
19 cm (7.5-inch)
59 cm (23-inch)
68 cm (27-inch)
54 cm (21-inch)
54 cm (21-inch)
50 kg (112 lb)
57 kg (125.4 lb)
≥ 30 cm (12-inch) open space above GC.
Requires
Requires
wall to dissipate hot air and allow for routine maintenance.
13 cm (5-inch)
32 cm (13-inch)
Requires 30 cm (1 ft) to the left of the unit.
≥ 27 cm (10.7-inch) open space in front of GC.
≥ 25 cm (10-inch) clearance between back of instrument and
31 cm (12-inch)
28 cm (11-inch)
11 kg (23.1 lb)
16 kg (35.2 lb)
• Performance turbo pump 41 cm (16-inch) 30 cm (12-inch) 54 cm (22-inch) 41 kg (90 lb)
18 Site Preparation Guide
Page 17

3 Dimensions and Weights
Dimensions and Weight
Table 4 Instrument dimensions, weights, and required clearances (continued)
Product Height Width Depth Weight
• Foreline pump
Standard
Oil-free (MVP-070)
Oil-free (IDP3)
21 cm (8-inch)
19 cm (7.5-inch)
18 cm (7-inch)
13 cm (5-inch)
32 cm (13-inch)
35 cm (14-incn)
31 cm (12-inch)
28 cm (11-inch)
14 cm (6-inch)
11 kg (23.1 lb)
16 kg (35.2 lb)
10 kg (21 lb)
• GC/MS operational and maintenance
access
MS
7000 and 7010 Triple Quad MS
• EI Mainframe 47 cm (18.5-inch) 35 cm (14-inch) 86 cm (34-inch) 59 kg (130 lb)
• EI/CI Mainframe 47 cm (18.5-inch) 35 cm (14-inch) 86 cm (34-inch) 63.5 kg (140 lb)
• Foreline pump 28 cm (11-inch) 18 cm (7-inch) 35 cm (14-inch) 21.5 kg (47.3 lb)
• GC/MS operational and maintenance
access
7200 Q-TOF MS
• Mainframe 133 cm (52.5-inch) 90 cm (34.5-inch) 100 cm (39.5-inch) 138 kg (305 lb)
• Foreline pump 28 cm (11-inch) 18 cm (7-inch) 35 cm (14-inch) 21.5 kg (47.3 lb)
7250 Q-TOF MS
• Mainframe 190 cm (74.8-inch) 90 cm (34.5-inch) 100 cm (39.5-inch) 138 kg (350 lb)
• Foreline pump DS202 28 cm (11-inch) 18 cm (7-inch) 35 cm (14-inch) 21.5 kg (47.3 lb)
• Foreline pump IDP-15 36.4 cm (14.3-inch) 33.3 cm (13.1-inch) 48.5 cm (19.1-inch) 45.5 kg (100 lb)
• GC/Q-TOF operational and maintenance
access
Headspace sampler (HS)
7697A Headspace sampler
111 vial model
12 vial model
• GC with 7697A Headspace sampler Requires 69 cm (27-inch) to the right of the GC (G4557A), or 64 cm
G1888 Headspace sampler 56 cm (22-inch) 46 cm (18.1-inch) 64 cm (25-inch) 46.3 kg (102 lb)
ALS
80 cm (32-inch)
61 cm (24-inch)
Requires 30 cm (1 ft) to the left of the unit.
Requires 30 cm (1 ft) to the left of the unit.
Requires 40 cm (16-inch) clearance on both sides of the unit.
Requires 30 cm (12-inch) clearance behind the unit.
69 cm (27-inch)
64 cm (25-inch)
(25-inch) to the right of the GC (G4556A).
70 cm (27.5-inch)
69 cm (27-inch)
46 kg (101 lb)
38.2 kg (84 lb)
• GC with 7693A ALS injector Requires 50 cm (19.5-inch) above the GC 3.9 kg (8.6 lb) each
• GC with 7693A ALS tray Requires 43 cm (16.8-inch) left of the GC
Requires 4.2 cm (1.7-inch) in front of GC
• GC with 7650A ALS injector Requires 50 cm (19.5-inch) above the GC 3.9 kg (8.6 lb) each
• GC with CTC PAL Autosampler Requires 76.6 cm (30.2-inch) above the GC and
65 to 98 cm (25.6 to 38.6-inch) to the right of the
GC, depending on configuration
6.8 kg (15 lb) each
Site Preparation Guide 19
Page 18

3 Dimensions and Weights
CAUTION
Foreline Pump Requirements for Systems Including an MSD
Foreline Pump Requirements for Systems
Including an MSD
1 If using a 7200 or 7250 Q-TOF MS, the length of the quadrupole vacuum hose is 130 cm
(4 ft 3-inch) from the high vacuum pump to the foreline pump, and the length of the foreline
pump power cord is 2 m (6 ft 6-inch).
2 If your bench abuts a wall, drill 4 cm (1.5-inch) diameter holes through the rear of the bench
for the vacuum hose and power cord.
Make sure the 7200/7250 Q-TOF GC/MS foreline pump is located where it is not likely to be
touched by operators.
20 Site Preparation Guide
Page 19

3 Dimensions and Weights
ALS Dimensions and Weight
ALS Dimensions and Weight
Select the laboratory bench space before the system arrives. Pay special attention to the total
height requirements. Avoid bench space with overhanging shelves. See Table 5.
The instrument needs space for proper convection of heat and ventilation. Allow at least
20 cm clearance between the back of the instrument and wall to dissipate hot air.
Table 5 Required height, width, depth, and weight
Product Height (cm) Width (cm) Depth (cm) Weight (kg)
G4513A Injector 51 16.5 16.5 3.9
G4514A Tray
7650A Injector 51 22 24 4.5
Additional space requirements
• GC with 7693A ALS injector 50 cm (19.5-inch) above the GC
• GC with 7693A ALS tray 45 cm (17.5-inch) left of the GC
• GC with 7650 ALS injector 50 cm (19.5-inch) above the GC
*
29 44 43 6.8
9 cm (3.6-inch) in front of the GC
3 cm (1.2-inch) to the left of the GC
* The G4520A Tray with a bar code reader is available with a G4514A Tray and G4515A bar code reader.
Site Preparation Guide 21
Page 20

3 Dimensions and Weights
ALS Dimensions and Weight
22 Site Preparation Guide
Page 21

4 Environmental Conditions
Environmental Conditions 24
Heat Dissipation 25
ALS Environmental Conditions 26
This section outlines the environmental requirements for use or storage of the GC, GC/MS, and
automatic liquid sampler (ALS). Heat dissipation information is also provided.
Site Preparation Guide 23
Page 22

4 Environmental Conditions
NOTE
NOTE
Environmental Conditions
Environmental Conditions
Ensure that the instrument will be operated or stored within the recommended environmental
ranges. This optimizes instrument performance and lifetime. The specified conditions assume
a non-condensing, non-corrosive atmosphere. See Tab le 6 .
Also, see “Heat Dissipation” on page 25.
Performance can be affected by sources of heat and cold from heating, air conditioning
systems, or drafts.
Table 6 Environmental conditions for operation and storage
Product Condition Temperature range Humidity range Maximum altitude
8860 GC Standard oven ramp 5 to 45 °C 5 to 90% 3,100 m
Storage –20 to 65 °C 0 to 90%
MSD
5975 Series MSD Operation 15 to 35 °C
(59 to 95 °F)
Storage –20 to 70 °C
(–4 to 158 °F)
5977 Series MSD Operation 15 to 35 °C
(59 to 95 °F)
Storage –20 to 70 °C
(–4 to 158 °F)
MS
7010 or 7000 Triple Quad MSOperation 15 to 35 °C
(59 to 95 °F)
Storage –20 to 70 °C
(–4 to 158 °F)
7200 or 7250 Q-TOF MS Operation 15 to 35 °C
(59 to 95 °F)
Storage –20 to 70 °C
(–4 to 158 °F)
*
*
†
†
20 to 80% 4,615 m
0 to 95%
20 to 80% 4,615 m
0 to 95%
40 to 80% 5,000 m
0 to 95%
20 to 80% 2,500 m
0 to 95%
‡
* Operation requires constant temperature (variations < 2 oC/hour)
† Operation requires constant temperature (variations < 2 oC/hour)
‡ An altitude of 3,700 meters (12,000 feet) is supported if the ambient temperature is less than 30 °C
Air pressure 75 kPa to 106 kPa. No hoar-frost, dew, water, rain, or percolating
24 Site Preparation Guide
Page 23

4 Environmental Conditions
Heat Dissipation
Heat Dissipation
• Use Table 7 to estimate the additional heat dissipated from the equipment. Maximums
represent the heat given off when heated zones are set for maximum temperatures.
Table 7 Heat dissipation
Instrument
8860 GC 7681 BTU/hour maximum
5975 Series MSD 3000 BTU/hour (3165 kJ/h)
5977 Series MSD 3000 BTU/hour (3165 kJ/h)
7010 or 7000 Triple Quad MS3700 BTU/hour (3904 kJ/h)
7200 or 7250 Q-TOF MS 6200 BTU/hour (6541 kJ/h)
If using the optional G4522A Cooling Accessory, you will need to supply:
(8103 kJ/h)
5120 BTU/hour maximum (100 V
power option) (5402 kJ/h)
• A water chiller.
• Tubing and 1/8-inch Swagelok fittings to connect the chilled water and return water to the
chiller.
A container or drain to dispose of condensate from the tray.
Site Preparation Guide 25
Page 24

4 Environmental Conditions
ALS Environmental Conditions
ALS Environmental Conditions
Operating the instrument within the recommended ranges optimizes instrument performance
and lifetime. The sampler system operates in the same environment as its parent GC.
See “Environmental Conditions” on page 24.
The conditions assume a non-condensing, noncorrosive atmosphere.
Table 8 Environmental conditions for operation and storage
Product
G4513A Injector
G4514A Tray
G4515A Bar Code Reader*
7650 Injector Operation 0 to 40 °C 5–95% 4,300 m
G4517A Controller Operation –5 to 45 °C Maximum relative humidity of 80% for
* The G4520A Tray with a bar code reader is available with a G4514A Tray and G4515A bar code reader.
*
Conditions
Operation 0 to 40 °C 5–95% 4,300 m
Storage
Operating temp
range
Operating humidity range
temperatures up to 31 °C decreasing
linearly to 50% relative humidity at 40 °C
Maximum altitude
2,000 m
26 Site Preparation Guide
Page 25

5 Exhaust Venting
Exhaust Venting 28
Venting hot air 28
Venting other gases 29
Exhaust vent fittings 30
This section outlines the exhaust venting requirements for GC, GC/MS, and automatic liquid
sampler (ALS) installation.
Site Preparation Guide 27
Page 26

5 Exhaust Venting
WARNING
Exhaust Venting
Exhaust Venting
During normal operation, the GC exhausts hot oven air. Depending on the installed inlet and
detector types, the GC can also exhaust (or vent) uncombusted carrier gas and sample. Proper
venting of these exhausts is required for operation and safety.
Venting hot air
Do not place temperature-sensitive items (for example, gas cylinders, chemicals, regulators,
and plastic tubing) in the path of the heated exhaust. These items will be damaged and
plastic tubing will melt. Be careful when working behind the instrument during cool-down
cycles to avoid burns from the hot exhaust.
1 Hot air (up to 450 °C) from the oven exits through a vent in the rear of the instrument. Allow
at least 25 cm (10-inch) clearance behind the instrument, or 30 cm (12-inch) behind a
Q-TOF GC/MS to dissipate this hot air. See Figure 4.
Figure 4. Exhaust outlet.
2 For most applications, an optional oven exhaust deflector is available. The exhaust
deflector allows for less bench depth than a GC without the exhaust deflector installed.
• The GC exhaust deflector is included if GC option 306 is ordered. The exhaust deflector
requires 14 cm (5.5 inches) behind the instrument. For GCs with the exhaust deflector
option installed, the exhaust rate is about 65 ft
deflector, the exhaust rate is about 99 ft
diameter is 10 cm (4 in). See Figure 5.
• For part numbers for the exhaust deflectors, see Tab l e 9.
28 Site Preparation Guide
3
3
/min (1.84 m3/min). Without the
/min (2.8 m3/min). The deflector outlet
Page 27

5 Exhaust Venting
NOTE
Venting other gases
Table 9 Exhaust deflector part numbers
Instrument Part number
GC G1530-80650
7200/7250 Q-TOF GC/MS, GC Q-TOF G3850-80650
Figure 5. Exhaust deflector G1530-80650
Venting other gases
During normal operation of the GC with many detector and inlet types, some of the carrier gas
and sample vents outside the instrument through the split vent, septum purge vent, and
detector exhaust. If any sample components are toxic or noxious, or if hydrogen is used as the
carrier gas or detector fuel gas, these exhausts must be vented to a fume hood.
Exhaust venting must comply with all local environmental and safety codes. Contact your
Environmental Health & Safety (EHS) specialist.
1 Place the GC in the hood or attach a large diameter venting tube to the relevant outlet for
proper ventilation. See “Exhaust vent fittings” on page 30.
2 To further prevent contamination from noxious gases, attach a chemical trap to the
vent(s).
3 If using an ECD, always connect the ECD exhaust vent to a fume hood or vent it to the
outside. See the latest revision of 10 CFR Part 20 (including Appendix B), or the applicable
state regulation. For countries other than the United States, consult with the appropriate
agency for equivalent requirements. Agilent recommends a vent line internal diameter of
6 mm (1/4-inch) or greater. With a line of this diameter, the length is not critical.
Site Preparation Guide 29
Page 28

5 Exhaust Venting
Exhaust vent fittings
4 Vent the GC/MS system externally to the building via an ambient-pressure vent system,
within 460 cm (15 ft) of both the GC split vent and GC/MS foreline pump, or vent to a fume
hood.
Exhaust vent fittings
The various inlet and detector vents terminate in the following fittings:
• TCD, ECD: The detector exhaust terminates in a 1/8-inch od tube.
• SSL: The split vent terminates in a 1/8-inch Swagelok female fitting.
• All inlets: The septum purge vent terminates in 1/8-inch od tubing.
30 Site Preparation Guide
Page 29

6 GC System Power Requirements
Power Requirements 32
USA fast heating oven, 240 V 34
Canadian installation 34
Common instrument power cord plugs 34
ALS Power Requirements 38
This section details the power requirements for GC, GC/MS, and automatic liquid sampler
(ALS) installation.
Site Preparation Guide 31
Page 30

6 GC System Power Requirements
WARNING
WARNING
CAUTION
Power Requirements
Power Requirements
Power consumption and requirements depend on the country to which the unit ships.
The number and type of electrical outlets depend on the size and complexity of the system.
To protect users, the metal instrument panels and cabinet are grounded through the
three-conductor power line cord in accordance with International Electrotechnical
Commission (IEC) requirements.
A proper earth ground is required for GC operations. Any interruption of the grounding
conductor or disconnection of the power cord could cause a shock that could result in
personal injury.
Be sure to verify proper receptacle grounding.
Do not use extension cords with Agilent instruments. Extension cords normally are not rated
to carry enough power and can be a safety hazard.
The length of the power cord is 2 meters (6.6 feet).
Do not use power line conditioners with Agilent instruments. Doing so may cause damage to
the equipment.
1 Ensure that each instrument in your GC system can be connected to a dedicated circuit
with an isolated ground. (Note that ALS instruments receive their power from the GC.)
2 Power requirements are printed near the power cord attachment on the rear panel of each
instrument. Although your GC should arrive ready for operation in your country, compare
its power requirements with those listed in Ta ble 10. If the voltage option you ordered is
not suitable for your installation, contact Agilent Technologies.
Table 10 Power requirements
Product
8860 GC Standard 100
8860 GC Standard 120
8860 GC Standard 200/220/230/240
Oven type
Line voltage (VAC)
single phase
(–10% / +10%)
single phase
(–10% / +10%)
single phase
(–10% / +10%)
Frequency
(Hz)
48–63 1500 12.5 15 Amp
48–63 2250 18.8 20 Amp
48–63 2250 9.6/9.3/
Maximum
continuous power
consumption (VA)
Current
rating
(amps)
9.3/9.2
Power outlet
current rating
Dedicated
Dedicated
10 Amp
Dedicated
32 Site Preparation Guide
Page 31

6 GC System Power Requirements
NOTE
Power Requirements
Table 10 Power requirements (continued)
Product
MSD
5975 Series MSD 120
5975 Series MSD 220–240
5975 Series MSD 200
5977 Series MSD 120
5977 Series MSD 220–240
5977 Series MSD 200
MS
7010 or 7000 Triple Quad MS 120
7010 or 7000 Triple Quad MS 220–240
7010 or 7000 Triple Quad MS 200
Oven type
Line voltage (VAC)
(–10% / +5%)
(–10% / +5%)
(–10% / +5%)
(–10% / +5%)
(–10% / +5%)
(–10% / +5%)
(–10% / +5%)
(–10% / +5%)
(–10% / +5%)
Frequency
(Hz)
50/60 ± 5% 1100 (400 for foreline
50/60 ± 5% 1100 (400 for foreline
50/60 ± 5% 1100 (400 for foreline
50/60 ± 5% 1100 (400 for foreline
50/60 ± 5% 1100 (400 for foreline
50/60 ± 5% 1100 (400 for foreline
50/60 ± 5% 1600 15 15 Amp
50/60 ± 5% 1600 15 15 Amp
50/60 ± 5% 1600 15 15 Amp
Maximum
continuous power
consumption (VA)
pump only)
pump only)
pump only)
pump only)
pump only)
pump only)
Current
rating
(amps)
8 10 Amp
8 10 Amp
8 10 Amp
8 10 Amp
8 10 Amp
8 10 Amp
Power outlet
current rating
Dedicated
Dedicated
Dedicated
Dedicated
Dedicated
Dedicated
Dedicated
Dedicated
Dedicated
7200 or 7250 Q-TOF MS 200–240
HS
7697A Headspace Americas: 120
7697A Headspace 200/220/230/240
All
Data system PC
(monitor, CPU, printer)
Data system PC
(monitor, CPU, printer)
(–10% / +5%)
single phase
(–10% / +10%)
single/split phase
(–10% / +10%)
100/120
(–10% / +5%)
200-240
(–10% / +5%)
The GC and related equipment meet the following International Electrotechnical Commission
(IEC) classifications: Equipment Class I, Laboratory Equipment, Installation Category II, and
Pollution Degree 2.
50/60 ± 5% 1800 (1200 for
foreline pump)
50/60 ± 5% 850 6.2 15 Amp
50/60 ± 5% 850 3.8/3.4/
50/60 ± 5% 1000 10/8.3 15 Amp
50/60 ± 5% 1000 4.1-5 10 Amp
15 15 Amp
3.3/3.1
Dedicated
Dedicated
10 Amp
Dedicated
Dedicated
Dedicated
Site Preparation Guide 33
Page 32

6 GC System Power Requirements
USA fast heating oven, 240 V
USA fast heating oven, 240 V
The 240 V fast heating oven requires 240 V/15 A power. Do not use 208 V power. Lower
voltage causes slow oven ramps and prevents proper temperature control. The power cord
supplied with your GC is rated for 250 V/15 A, and is a two-pole, three-wire cord with grounding
(type L6-15R/L6-15P).
Canadian installation
When installing a GC in Canada, make sure your GC power supply circuit meets the following
additional requirements:
• The circuit breaker for the branch circuit, which is dedicated to the instrument, is rated for
continuous operation.
• The service box branch circuit is marked as a “Dedicated Circuit.”
Common instrument power cord plugs
Table 11 shows common Agilent power cord plugs.
Table 11 Power cord terminations
Part number
8121-0675 Argentina 240 16 4.5 C19 AS 3112
8120-1369 Australia,
8120-8619 Australia 240 16 2.5 C19 AS 3112
8121-1787 Brazil 240 16 2.5 C19 IEC 60906-1
Country
New Zealand
Voltage Amps
240 10 2.5 C13 AS 3112
Cable
length (m)
GC connector
type
Termination type Plug
8121-1809 Brazil 240 10 2.5 C13 IEC 60906-1
34 Site Preparation Guide
Page 33

6 GC System Power Requirements
Common instrument power cord plugs
Table 11 Power cord terminations
Part number
8120-6978 Chile 240 10 2.5 C13 CEI 23-16
8121-0070 China 220 16 2.5 C19 GB 1002
8121-0723 China 220 10 2.5 C13 GB 1002
8120-3997 Denmark,
Country
Greenland
Voltage Amps
230 10 2.5 C13 AFSNIT 107-2-01
Cable
length (m)
GC connector
type
Termination type Plug
8120-8622 Denmark,
Switzerland
8120-8621 Europe 220 / 230
8121-1222 Korea 220 / 230
8121-1226 Korea 220 / 230
230 16 2.5 C19 Swiss/Denmark
/ 240
/ 240
/ 240
1302
16 2.5 C19 CEE/7/V11
16 2.5 C19 CEE/7/V11
10 2.5 C13 CEE/7/V11
Site Preparation Guide 35
Page 34

6 GC System Power Requirements
Common instrument power cord plugs
Table 11 Power cord terminations
Part number
8121-0710 India, South
8120-5182 Israel 230 10 2.5 C13 Israeli SI32
8120-0161 Israel 230 16, 16
8120-6903 Japan 200 20 4.5 C19 NEMA L6-20P
Country
Africa
Voltage Amps
240 15 2.5 C19 AS 3112
AWG
Cable
length (m)
2.5 C19 Israeli SI32
GC connector
type
Termination type Plug
8120-8620 United Kingdom,
Hong Kong,
Singapore,
Malaysia
8120-8705 United Kingdom,
Hong Kong,
Singapore,
Malaysia
8120-6894 United States 120 20 2.5 C19 NEMA 5-20P
8120-1992 United States 120 13 2.5 C13 NEMA 5-20P
240 13 2.5 C19 BS1363/A
240 10 2.3 C13 BS1363/A
36 Site Preparation Guide
Page 35

6 GC System Power Requirements
Common instrument power cord plugs
Table 11 Power cord terminations
Part number
8121-0075 United States 240 15 2.5 C19 NEMA L6-15P
8120-6360 Taiwan, South
8121-1301 Thailand 220 15 1.8 C19
Country
America
Voltage Amps
120 20 2.5 C19 NEMA 5-20P
Cable
length (m)
GC connector
type
Termination type Plug
G
Site Preparation Guide 37
Page 36

6 GC System Power Requirements
WARNING
ALS Power Requirements
ALS Power Requirements
The ALS components draw power from the GC. No other power source is required.
The G4517A controller, used with the 8860 Series GC, requires one electrical outlet with a
dedicated ground. The controller can be set for either 100-120 V or 200-240 V.
Do not use extension cords with Agilent instruments. Extension cords normally are not rated
to carry enough power and can be a safety hazard.
The length of the power cord is 2 meters (6.6 feet).
38 Site Preparation Guide
Page 37

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
Gas and Reagent Selection 40
Hydrogen Carrier Gas 42
Gas and Reagent Purity 42
Gas Supplies 43
GC/MS Gas Requirements 45
Gas Plumbing 49
Supply tubing for most carrier and detector gases 50
Supply tubing for hydrogen gas 50
Two-stage pressure regulators 51
Pressure regulator-gas supply tubing connections 51
Filters and traps 52
This section outlines the requirements for gas selection and plumbing.
Refer to the Agilent Web site at www.agilent.com for the most up-to-date listing of GC, GC/MS,
and ALS supplies and consumables.
Site Preparation Guide 39
Page 38

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
WARNING
NOTE
Gas and Reagent Selection
Gas and Reagent Selection
Table 12 lists gases usable with Agilent GCs and capillary columns. When used with capillary
columns, GC detectors require a separate makeup gas for optimum sensitivity. The MS and
MSD use GC carrier gas.
If you are using any MS system, use of hydrogen as the carrier gas may require hardware
modifications for the best performance. Contact your Agilent service representative. Hydrogen
is not supported as a carrier gas with the 7200/7250 GC/Q-TOF system.
When using hydrogen (H2) as the carrier gas or fuel gas, be aware that hydrogen gas can flow
into the GC and create an explosion hazard. Therefore, be sure that the supply is turned off
until all connections are made and ensure the inlet and detector column fittings are either
connected to a column or capped at all times when hydrogen gas is supplied to the
instrument.
Hydrogen is flammable. Leaks, when confined in an enclosed space, may create a fire or
explosion hazard. In any application using hydrogen, periodically leak test all connections,
lines, and valves before operating the instrument or after maintenance. Always turn off the
hydrogen supply at its source before working on the instrument.
Please refer to the Hydrogen Safety Guide shipped with your instrument.
Hydrogen use is specifically prohibited with the 7200 or 7250 GC/Q-TOF system.
Nitrogen and Argon/Methane are generally not suitable for GC/MS carrier gas.
Table 12 Gases usable with Agilent GCs and capillary columns
Detector type
Electron capture (ECD) Hydrogen
Flame ionization (FID) Hydrogen
Flame photometric (FPD) Hydrogen
Nitrogen-Phosphorus (NPD) Helium
Carrier
Helium
Nitrogen
Argon/Methane (5%)
Helium
Nitrogen
Helium
Nitrogen
Argon
Nitrogen
Preferred makeup
Nitrogen Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen
Alternate choice
Nitrogen
Argon/Methane (5%)
Nitrogen
Helium
Helium
Helium
*
Helium
Helium
Detector, anode
purge, or reference
Anode purge must be
same as makeup
Hydrogen and air for
detector
Hydrogen and air for
detector
Hydrogen and air for
detector
40 Site Preparation Guide
Page 39

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
Gas and Reagent Selection
Table 12 Gases usable with Agilent GCs and capillary columns (continued)
Detector type
Thermal conductivity (TCD) Hydrogen
* Depending on bead type, higher makeup gas flow rates (> 5 mL/min) may introduce cooling effects or shorten bead life.
Carrier
Helium
Nitrogen
Preferred makeup
Must be same as carrier
and reference
Alternate choice
Must be same as carrier
and reference
Table 13 lists gas recommendations for packed column use. In general, makeup gases are not
required with packed columns.
Table 13 Gases usable with Agilent GCs and packed columns
Detector type
Electron capture (ECD) Nitrogen
Flame ionization (FID) Nitrogen
Flame photometric (FPD) Hydrogen
Nitrogen-Phosphorus (NPD) Helium
Carrier gas
Argon/methane
Helium
Helium
Nitrogen
Argon
Comments
Maximum sensitivity
Maximum dynamic range
Maximum sensitivity
Acceptable alternative
Optimum performance
Detector, anode purge, or
reference
Nitrogen
Argon/Methane
Hydrogen and air for detector.
Hydrogen and air for detector.
Hydrogen and air for detector.
Detector, anode
purge, or reference
Reference must be
same as carrier and
makeup
Nitrogen
Thermal conductivity (TCD) Helium
Hydrogen
Nitrogen
Argon
* Slightly greater sensitivity than helium. Incompatible with some compounds.
† For analysis of hydrogen or helium. Greatly reduces sensitivity for other compounds.
Acceptable alternative
General use
Maximum sensitivity
Hydrogen detection
Maximum hydrogen sensitivity
For installation checkout, Agilent requires the gas types shown in Tab le 14.
Table 14 Gases and reagents required for checkout
Detector Gases required
FID Carrier: helium
Makeup: nitrogen
Fuel: hydrogen
Aux gas: Air
TCD Carrier and reference: helium
Reference must be same as
*
†
carrier and makeup.
*
Site Preparation Guide 41
Page 40

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
Hydrogen Carrier Gas
Table 14 Gases and reagents required for checkout (continued)
Detector Gases required
NPD Carrier: helium
Makeup: nitrogen
Fuel: hydrogen
Aux gas: Air
ECD Carrier: helium
FPD Carrier: helium
CI MS (external) Reagent gas: methane
CI MS (internal) Reagent: methanol
Anode purge and makeup: nitrogen
Makeup: nitrogen
Fuel: hydrogen
Aux gas: Air
MS and MSD systems purchased with a Self-Cleaning Ion Source also require a source of
hydrogen gas in addition to helium carrier gas. This source can be shared but must meet
carrier gas purity requirements.
Hydrogen Carrier Gas
Refer to the Agilent 8860 GC Safety Manual for important safety information about hydrogen
gas.
If hydrogen is being used as a carrier gas, or for the JetClean ion source system, special
considerations apply due to hydrogen’s flammability and chromatographic properties.
• Agilent highly recommends the G3388B Leak Detector to safely check for leaks.
• Hydrogen carrier gas requires special considerations for supply tubing. See “Gas
Plumbing” on page 49.
• In addition to the supply pressure requirements listed in “Gas Supplies” on page 43, Agilent
also recommends users of hydrogen gas consider gas source and purification needs. See
the additional recommendations in “Requirements for hydrogen as a carrier gas or for
use in JetClean systems” on page 45.
• When using hydrogen carrier gas with a ECD, TCD, or any other detector that vents
uncombusted gases, plan to vent the detector output to a fume hood or similar location.
Uncombusted hydrogen can present a safety hazard. See “Exhaust Venting” on page 28.
• When using hydrogen carrier gas, also plan to safely vent inlet split vent flows and purge
vent flows. See “Exhaust Venting” on page 28.
Gas and Reagent Purity
Agilent recommends that carrier and detector gases be 99.9995% pure. See Table 1 5 . Air
needs to be zero grade or better. Agilent also recommends using high quality traps to remove
hydrocarbons, water, and oxygen.
42 Site Preparation Guide
Page 41

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
NOTE
Swagelok nut and ferrules
Female Swagelok fittings on GC
Gas Supplies
Table 15 Carrier, collision and reagent gas purity
Carrier, collision and reagent gas
requirements
Helium (carrier) 99.9995% Hydrocarbon free
Hydrogen (carrier) (carrier and
self-cleaning ion source)
Nitrogen (carrier) 99.9995%
Nitrogen (drying gas, nebulizer
pressure)
Methanol
* Purity specification is the minimum acceptable purity. Major contaminants can be water,
† Required reagent for performance verification in internal CI mode only. Evaporation residue
*
†
oxygen, or air. Drying gas and nebulizer pressure gas can be supplied by a nitrogen gas
generator, house nitrogen system, or liquid nitrogen dewar.
<.0001%.
Purity
99.9995% SFC grade
99.999% Research grade
99.9% Reagent grade. Purge and
Notes
trap grade
recommended.
Gas Supplies
General requirements
Supply instrument gases using tanks, an internal distribution system, or gas generators. If
used, tanks require two-stage pressure regulators with packless, stainless steel diaphragms.
The instrument requires 1/8-inch Swagelok connections to its gas supply fittings.
See Figure 6.
Site Preparation Guide 43
Plumb the gas supply tubing/regulators so that one 1/8-inch Swagelok female connector is
available for each gas needed at the instrument.
Figure 6. Example Swagelok connector and hardware
Page 42

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
Gas Supplies
Table 16 lists available Agilent two-stage tank regulators. All Agilent regulators are supplied
with the 1/8-inch Swagelok female connector.
Table 1 6 Tank r egul a tors
Gas type CGA number Max pressure Part number
Air 346 125 psig (8.6 Bar) 5183-4641
Industrial Air 590 125 psig (8.6 Bar) 5183-4645
Hydrogen, Argon/Methane 350 125 psig (8.6 Bar) 5183-4642
Oxygen 540 125 psig (8.6 Bar) 5183-4643
Helium, Argon, Nitrogen 580 125 psig (8.6 Bar) 5183-4644
Table 17 and Ta b le 1 8 list minimum and maximum delivery pressures for inlets and detectors,
measured at the bulkhead fittings on the back of the instrument.
Table 17 Delivery pressures for inlets required at the GC, in kPa (psig)
Carrier (max) 827 (120) 827 (120)
Inlet type
Split/Splitless (SSL)
Purged packed
(PPI)
Packed
column(PCI)
Carrier (min) (20 psi) above pressure used in method
Table 18 Delivery pressures for detectors required at the GC/MS
Detector type
FID NPD TCD ECD FPD
Hydrogen 240–690 kPa
(35–100 psig)
Air 380–690 kPa
(55–100 psig)
Makeup 380–690 kPa
(55–100 psig)
Reference 380–690 kPa
* Conversions: 1 psi = 6.8947 kPa = 0.068947 Bar = 0.068 ATM
240–690 kPa
(35–100 psig)
380–690 kPa
(55–100 psig)
380–690 kPa
(55–100 psig)
380–690 kPa
(55–100 psig)
(55–100 psig)
The minimum supply pressure for Auxiliary EPC and PCM modules is 138 kPa (20 psi) greater
than the pressure used in your method. For example, if you need a pressure of 138 kPa (20 psi)
for the method, the supply pressure must be at least 276 kPa (40 psi). Table 1 9 lists the
maximum carrier pressure for Auxiliary EPC and PCM modules.
*
310–690 kPa
(45–100 psig)
690–827 kPa
(100–120 sig)
380–690 kPa
(55–100 psig)
380–690 kPa
(55–100 psig)
44 Site Preparation Guide
Page 43

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
GC/MS Gas Requirements
Table 19 Delivery pressures for Auxiliary EPC and PCM modules, in kPa (psig)
Aux EPC PCM 1 PCM 2 or PCM Aux
Carrier (max) 827 (120) 827 (120) 827 (120) with Forward pressure control
345 (50) with Backpressure control
Requirements for hydrogen as a carrier gas or for use in JetClean systems
Not all systems can use hydrogen as a carrier gas. See Gas Selection.
Hydrogen can be supplied from a generator or from a cylinder.
Agilent recommends use of a high-quality hydrogen gas generator. A high-quality generator
can consistently produce purity > 99.9999%, and the generator can include built-in safety
features such as limited storage, limited flow rates, and auto-shutdown. Select a hydrogen
generator that provides low (good) specifications for water and oxygen content.
If using a hydrogen gas cylinder, Agilent recommends use of Gas Clean Filters to purify the
gas. Consider additional safety equipment as recommended by your company safety
personnel.
GC/MS Gas Requirements
Table 20 lists typical flows resulting from selected carrier gas source pressures.
Table 20 5977 and 5975 Series MSD carrier gases
Carrier gas requirements Typical pressure range Typical flow (mL/min)
Helium (required)
(column and split flow)
*
Hydrogen (optional)
(column and split flow)
Methane reagent gas
(required for CI operation)
Isobutane reagent gas (optional) 103 to 172 kPa
Ammonia reagent gas (optional) 34 to 55 kPa
Carbon dioxide reagent gas
(optional)
* Hydrogen gas can be used for the carrier gas but specifications are based on helium as the
carrier gas. Please observe all hydrogen gas safety cautions.
345 to 552 kPa
(50 to 80 psi)
345 to 552 kPa
(50 to 80 psi)
103 to 172 kPa
(15 to 25 psi)
(15 to 25 psi)
(5 to 8 psi)
103 to 138 kPa
(15 to 0 psi)
20 to 50
20 to 50
1 to 2
1 to 2
1 to 2
1 to 2
7010 and 7000 Series MS
Table 21 lists typical flows resulting from selected carrier gas source pressures.
Site Preparation Guide 45
Page 44

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
GC/MS Gas Requirements
Table 21 7010 and 7000 Triple Quad MS carrier gases
Carrier gas requirements Typical pressure range Typical flow (mL/min)
Helium (required)
(column and split flow)
*
Hydrogen (optional)
(column and split flow)
Methane reagent gas
(required for CI operation)
Ammonia reagent gas (optional) 34 to 55 kPa
Isobutane reagent gas (optional)
Carbon dioxide reagent gas (optional)
Nitrogen for collision cell (nitrogen source is supplied to EPC
module in GC.)
* Hydrogen gas can be used for the carrier gas but specifications are based on helium as the carrier gas. Please observe all hydrogen gas safety
cautions.
† Reagent available with manual tune only.
†
†
345 to 552 kPa
(50 to 80 psi)
345 to 552 kPa
(50 to 80 psi)
103 to 172 kPa
(15 to 25 psi)
(5 to 8 psi)
103 to 172 kPa
(15 to 25 psi)
103 to 138 kPa
(15 to 20 psi)
1.03 to 1.72 bar
(104 to 172 kPa, or 15 to 25 psi)
20 to 50
20 to 50
1 to 2
1 to 2
1 to 2
1 to 2
1 to 2 (mL/min)
7200 and 7250 Series Q-TOF MS
Table 22 lists the limits on total gas flow into the 7200/7250 Q-TOF GC/MS.
Table 22 7200/7250 Q-TOF GC/MS total gas flow limitations
Feature 7200 7250
High vacuum pump 1 Split-flow turbo Split-flow turbo
High vacuum pump 2 Split-flow turbo Turbo
High vacuum pump 3 Turbo Turbo
Carrier gas optimal gas flow, mL/min
Carrier gas maximum recommended gas flow, mL/min 2.0 2.0
Carrier gas maximum gas flow, mL/min
Reagent gas flow (EI/CI – CI application) 1.0 to 2.0 NA
Collision cell gas flow rate, mL/min (Nitrogen) 1.5 1.0
Collision cell gas flow rate, mL/min (Helium) 4.0
Maximum column id 0.32 mm (30 m long) 0.32 mm (30 m long)
* Total gas flow into the MS = column flow + reagent gas flow (if applicable) + collision cell gas flow.
† Expect degradation of spectral performance and sensitivity.
*
†
1.0 to 1.5 1.0 to 1.5
2.4 2.4
Table 23 lists typical flows resulting from selected carrier and reagent gas source pressures.
46 Site Preparation Guide
Page 45

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
WARNING
GC/MS Gas Requirements
Table 23 7200/7250 Q-TOF GC/MS carrier and reagent gas flows
Carrier and reagent gas requirements Q-TOF Typical pressure range Typical flow
Helium (required for carrier and IRM) 7200 173 to 207 kPa
Nitrogen for RIS transfer line actuator 7200 6.1 to 6.8 bar
Nitrogen for collision cell (nitrogen source is supplied to
EPC module in GC.)
Helium for collision cell (helium source is supplied to
EPC module in GC.)
7200/7250 0.7 to 2.0 ar
7250 0.7 to 2.0 bar
(25 to 30 psi)
(612 to 690 kPa, or
(90 to 100 psi)
(70 to 207 kPa, or
10 to 30 psi)
(70 to 207 kPa, or
10 to 30 psi)
The use of hydrogen is specifically prohibited with the 7200/7250 GC/Q-TOF.
1.0 to 2.0 (mL/min)
Up to 30 L/min
1 to 2 (mL/min)
4 (mL/min)
Site Preparation Guide 47
Page 46

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
Performance verification
GC/MS systems with a JetClean ion source system installed use helium as the GC carrier gas
and an additional supply of hydrogen gas to the MS analyzer. Table 2 4 shows typical supply
pressures needed for operation. These values reflect the pressures supplied to the
instruments, not setpoints.
Table 24 JetClean ion source system gas supply pressures
Gas supply Pressure delivered at the GC
Helium 690 kPa (100 psi)
Hydrogen
* Any delivery pressure ≤ 621 kPa (90 psi) is acceptable as long as it is 69 kPa (10 psi) higher
than the maximum hydrogen pressure needed during operation.
Performance verification
Performance verification requires the following:
• Helium carrier gas.
• For MS systems using chemical ionization or methane reagent gas.
≤ 621 kPa (90 psi)
*
48 Site Preparation Guide
Page 47

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
WARNING
Two-stage regulator
Main supply
on/off valve
Main gas
supply
On/off valve
Gas Clean filter
system. See “Filters
and traps”
on page 52
for more information.
Shutoff valve
Gas Clean filter configuration will vary depending on the
application.
Gas Plumbing
Gas Plumbing
All compressed gas cylinders should be securely fastened to an immovable structure or
permanent wall. Compressed gases should be stored and handled in accordance with the
relevant safety codes.
Gas cylinders should not be located in the path of heated oven exhaust.
To avoid possible eye injury, wear eye protection when using compressed gas.
Site Preparation Guide 49
Figure 7. Recommended filters and plumbing configuration from a carrier gas cylinder
• If you have not requested option 305 (pre-plumbed tubing), you must supply pre-cleaned,
1/8-inch copper tubing and a variety of 1/8-inch Swagelok fittings to connect the GC to
inlet and detector gas supplies. See the Installation Kits for recommended parts.
• Agilent strongly recommends two-stage regulators to eliminate pressure surges.
High-quality, stainless-steel diaphragm-type regulators are especially recommended.
• On/off valves mounted on the outlet fitting of the two-stage regulator are not essential but
are very useful. Be sure the valves have stainless-steel, packless diaphragms.
• Agilent strongly recommends installation of shut-off valves at each GC inlet supply fitting
to allow the GC to be isolated for maintenance and troubleshooting. Order part number
0100-2144. (Note that some optional installation kits include one shut-off valve. See
“Installation Kits” on page 14 for more information.)
• If you purchased automated valving, the valve actuation requires a separate pressurized,
dry air supply at 380 kPa (55 psig). This air supply must end in a male fitting compatible
with a 1/4-inch id plastic tube at the GC.
Page 48

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
CAUTION
CAUTION
Supply tubing for most carrier and detector gases
• FID, FPD, and NPD detectors require a dedicated air supply. Operation may be affected by
pressure pulses in air lines shared with other devices.
• Flow- and pressure-controlling devices require at least
10 psi (138 kPa) pressure differential across them to operate properly. Set source
pressures and capacities high enough to ensure this.
• Situate auxiliary pressure regulators close to the GC inlet fittings. This ensures that the
supply pressure is measured at the instrument (rather than at the source); pressure at the
source may be different if the gas supply lines are long or narrow.
• Never use liquid thread sealer to connect fittings.
• Never use chlorinated solvents to clean tubing or fittings.
See “Installation Kits” on page 14 for more information.
Supply tubing for most carrier and detector gases
Use only preconditioned copper tubing (part number 5180-4196) to supply gases to the
instrument. Do not use ordinary copper tubing—it contains oils and contaminants.
Do not use methylene chloride or other halogenated solvent to clean tubing that will be used
with an electron capture detector. They will cause elevated baselines and detector noise until
they are completely flushed out of the system.
Do not use plastic tubing for suppling detector and inlet gases to the GC. It is permeable to
oxygen and other contaminants that can damage columns and detectors.
Plastic tubing can melt if near hot exhaust or components.
The tubing diameter depends on the distance between the supply gas and the GC and the total
flow rate for the particular gas. Tubing of 1/8-in diameter is adequate when the supply line is
less than 15 feet (4.6 m) long.
Use larger diameter tubing (1/4-inch) for distances greater then 15 feet (4.6 m) or when
multiple instruments are connected to the same source. Use larger diameter tubing if high
demand is anticipated (for example, air for an FID).
Be generous when cutting tubing for local supply lines—a coil of flexible tubing between the
supply and the instrument lets you move the GC without moving the gas supply. Take this
extra length into account when choosing the tubing diameter.
Supply tubing for hydrogen gas
Agilent recommends using new chromatographic quality stainless steel tubing and fittings
when using hydrogen.
• Do not re-use old tubing when installing or switching to hydrogen supply lines for carrier
gas or the JetClean ion source system. Hydrogen gas tends to remove contaminants left
on old tubing by previous gases (by helium, for example). These contaminants can appear
in output as high background noise or hydrocarbon contamination for several weeks.
• Especially do not use old copper tubing, which can become brittle.
50 Site Preparation Guide
Page 49

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
WARNING
Two-stage regulator
Adapter to 1/8-inch female
Swagelok fitting
Two-stage pressure regulators
Do not use old copper tubing with hydrogen gas. Old copper tubing can become brittle and
create a safety hazard.
Two-stage pressure regulators
To eliminate pressure surges, use a two-stage regulator with each gas tank. Stainless steel,
diaphragm-type regulators are recommended.
The type of regulator you use depends on the gas type and supplier. The Agilent catalog for
consumables and supplies contains information to help you identify the correct regulator, as
determined by the Compressed Gas Association (CGA). Agilent Technologies offers
pressure-regulator kits that contain all the materials needed to install regulators properly.
Pressure regulator-gas supply tubing connections
Use PTFE tape to seal the pipe-thread connection between the pressure regulator outlet and
Site Preparation Guide 51
the fitting to which you connect the gas tubing. Instrument grade PTFE tape (part number
0460-1266), from which volatiles have been removed, is recommended for all fittings. Do not
use pipe dope to seal the threads; it contains volatile materials that will contaminate the
tubing.
Pressure regulators typically end in fittings that must be adapted to the correct style or size.
Table 25 lists parts needed to adapt a standard 1/4-inch male NPT fitting to a 1/8-inch or
1/4-inch Swagelok fitting.
Page 50

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
Filters and traps
Table 25 Parts for adapting NPT fittings
Description Part number
Swagelok 1/8-inch to female 1/4-inch NPT, brass 0100-0118
Swagelok 1/4-inch to female 1/4-inch NPT, brass 0100-0119
Reducing union, 1/4-inch to 1/8-inch, brass, 2/pk 5180-4131
Filters and traps
Using chromatographic-grade gases ensures that the gas in your system is pure. However, for
optimum sensitivity, install high-quality filters or traps to remove traces of water or other
contaminants. After installing a filter, check the gas supply lines for leaks.
Agilent recommends the Gas Clean Filter system. The Gas Clean Filter system delivers high
purity gases to your analytical instruments, reducing the risk of column damage, sensitivity
loss, and instrument downtime. The filters are designed for use with the GC, GC/MS, ICP-OES,
ICP-MS, LC/MS, and any other analysis instrument using carrier gas. Six filters are available,
including CO2, oxygen, moisture, and organics trap (charcoal).
Filter types
Each Gas Clean Filter type is designed to filter out a specific impurity that may exist in the gas
supply. The following filter types are available:
•Oxygen - Prevents oxidation of the GC column, septum, liner, and glass wool.
•Moisture - Delivers fast stabilization times for increased GC productivity, and prevents
hydrolization damage to the stationary phase, column, liner, glass wool, or septum in the
GC.
• Process Moisture - Prevents oxidation of GC components and is safe to use with acetylene
in process GC applications.
•Charcoal - Removes organic compounds and ensures correct performance of FID
detectors in the GC.
•GC/MS - Delivers fast stabilization times for increased GC productivity, removes oxygen,
moisture, and hydrocarbons from the carrier gas for MS applications, and provides
ultimate GC column protection.
Table 26 lists the most common Gas Clean Filter system kits. See the Agilent online store or
contact your local Agilent sales representative for additional filters, parts, and accessories
applicable to your instrument configuration.
52 Site Preparation Guide
Page 51

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
Filters and traps
Table 26 Recommended Gas Clean Filter kits
Description Part number Use
Gas Clean Filter kit (connecting unit for one filter, including one carrier gas filter, 1/8-inch
connections, a smart sensor, and mounting bracket for the GC)
Gas Clean Filter kit (connecting unit for four filters, including four filters, 1/4-inch
connections)
Gas Clean Filter kit (connecting unit for four filters, including four filters, 1/8-inch
connections)
GC/MS Gas Clean Filter kit (includes one connecting unit and two GC/MS filters, 1/8-inch
connections)
GC/MS Gas Clean Filter kit (includes one connecting unit and two GC/MS filters, 1/4-inch
connections)
GC/MS Gas Clean Filter installation kit (includes CP17976, 1 m copper tubing, and two
1/8-inch nuts and ferrules)
TCD filter kit (with oxygen and moisture filters) CP738408 TCD
CP179880 Carrier gas only
CP7995 FID, FPD, NPD
CP736530 FID, FPD, NPD
CP17976 ECD, GC/MS
CP17977 ECD, GC/MS
CP17978 ECD, GC/MS
Each separate gas supply requires its own filters.
See also “Installation Kits” on page 14.
Site Preparation Guide 53
Page 52

7 Gas Selection and Plumbing
Filters and traps
54 Site Preparation Guide
Page 53

A LAN Requirements
Site LAN Network 56
This section outlines the site LAN requirements for GC, GC/MS, and automatic liquid sampler
(ALS) installation.
Site Preparation Guide 55
Page 54

ALAN Requirements
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
NOTE
Site LAN Network
Site LAN Network
Agilent Technologies is not responsible for connecting to or establishing communication
with your site LAN network. The Agilent representative will test the system’s ability to
communicate on a mini-hub or LAN switch only.
If you intend to connect your system to your site’s LAN network, you must have an additional
shielded twisted pair network cable (8121-0940).
The IP addresses assigned to the instrument(s) must be fixed (permanently assigned)
addresses. If you intend to connect your system to your site’s network, each piece of
equipment must have a unique, fixed (static) IP address assigned to it.
For a Single Quad GC/MS system, Agilent recommends, sells, and supports the use of a PC
with one (1) network interface card (NIC) and a network switch to isolate the GC/MS system
from the site LAN. The network switch supplied with Agilent systems prevents
instrument-to-PC network traffic from entering the site LAN and keeps site LAN network
traffic from interfering with instrument-to-PC communications. Agilent develops and tests all
Single Quad GC/MS hardware and software using the single NIC configuration and has no
known network configuration issues. Alternate network configurations can be configured
and managed by the end user at their own risk and expense.
For Triple Quad and 7200 Q-TOF GC/MS systems, Agilent recommends, sells, and supports
the use of a PC with two network interface cards (NIC) to provide both a site LAN connection
and an isolated GC/MS system connection. Agilent develops and tests all Triple Quad and
Q-TOF GC/MS hardware and software using the dual NIC configuration, and has no known
network configuration issues. Alternate network configurations can be configured and
managed by the end user at their own risk and expense.
For the 7250 Q-TOF GC/MS systems, Agilent recommends, sells, and supports the use of a
PC with three network interface cards (NIC) to provide a site LAN connection, MS only
connection, and an isolated GC/MS system connection. Agilent develops and tests Q-TOF
GC/MS hardware and software using the triple NIC configuration, and has no known network
configuration issues. Alternate network configurations can be configured and managed by
the end user at their own risk and expense.
56 Site Preparation Guide
Page 55

This page intentionally left blank.
57 Site Preparation Guide
Page 56

 Loading...
Loading...