
Installation
and
Verification Manual
HP 8566B Spectrum
Analyzer
Includes Option 400, Option 462,
and Option 857
HP Part No. 08566-90169
Printed in USA September 1993

Notice.
The information contained in this document is subject to change
without notice.
Hewlett-Packard makes no warranty of any kind with regard to this
material, including but not limited to, the implied warranties of
merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Hewlett-Packard
shall not be liable for errors contained herein or for incidental
or consequential damages in connection with the furnishing,
performance, or use of this material.
@
Copyright Hewlett-Packard Company 1993
All Rights Reserved. Reproduction, adaptation, or translation without
prior written permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the
copyright laws.
1400 Fountaingrove Parkway, Santa Rosa CA, 95403-1799, USA

Certification
Hewlett-Packard Company certifies that this product met its
published specifications at the time of shipment from the factory.
Hewlett-Packard further certifies that its calibration measurements
are traceable to the United States National Institute of Standards and
Technology, to the extent allowed by the Institute’s calibration facility,
and to the calibration facilities of other International Standards
Organization members.
Information
Warranty
Regulatory
Chapter [cross reference to location of declaration of conformity
noise information] contains regulatory information.
This Hewlett-Packard instrument product is warranted against defects
in material and workmanship for a period of one year from date of
shipment. During the warranty period, Hewlett-Packard Company
will, at its option, either repair or replace products which prove to be
defective.
For warranty service or repair, this product must be returned to a
service facility designated by Hewlett-Packard. Buyer shall prepay
shipping charges to Hewlett-Packard and Hewlett-Packard
shipping charges to return the product to Buyer. However, Buyer shall
pay all shipping charges, duties, and taxes for products returned to
Hewlett-Packard from another country.
Hewlett-Packard warrants that its software and firmware designated
by Hewlett-Packard for use with an instrument will execute
its programming instructions when properly installed on that
instrument. Hewlett-Packard does not warrant that the operation
of the instrument, or software, or firmware will be uninterrupted or
error-free.
shall
&
pay
LIMITATION OF WARRANTY
The foregoing warranty shall not apply to defects resulting from
improper or inadequate maintenance by Buyer, Buyer-supplied
software or interfacing, unauthorized modification or misuse,
operation outside of the environmental specifications for the
product, or improper site preparation or maintenance.
NO OTHER WARRANTY IS EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED.
HEWLETT-PACKARD SPECIFICALLY DISCLAIMS THE IMPLIED
WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A
PARTICULAR PURPOSE.
EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES
THE REMEDIES PROVIDED HEREIN ARE BUYER’S SOLE AND
EXCLUSIVE REMEDIES. HEWLETT-PACKARD SHALL NOT BE
LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, OR
CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES, WHETHER BASED ON CONTRACT,
TORT, OR ANY OTHER LEGAL THEORY.
. . .
III

Assistance
Product
agreements are available
Rw
Service Ome.
maintenance agreewmats
for Hewlett-FWkard
any assistance, contact your nearest
and other customer assistance
products.
Him&&t-Rzckard Sales
and
Safety Notes
Caution
Warning
Instruction
ManuaI
The following safety notes are used throughout this manual.
Familiarize yourself with each of the notes and its meaning before
operating this instrument.
Caution denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a procedure that, if
not correctly performed or adhered to, could result in damage to or
destruction of the instrument. Do not proceed beyond a caution sign
until the indicated conditions are fully understood and met.
Warning denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a procedure
which, if not correctly performed or adhered to, could result in
injury or loss of life. Do not proceed beyond a warning note until
the indicated conditions are fully understood and met.
The instruction manual symbol. The product is marked with this
symbol when it is necessary for the user to refer to the instructions in
the manual.
iv

General Safety Considerations
Warning
Warning
Caution
Before this
properly grounded through the protective conductor of the ac
power cable to a socket outlet provided with protective earth
contact.
Any interruption of the protective (grounding) conductor, inside
or outside the instrument, or disconnection of the protective
earth terminal can result in personal injury.
There are many points in the instrument which can, if contacted,
cause personal injury. Be extremely careful.
Any adjustments or service procedures that require operation
of the instrument with protective covers removed should be
performed only by trained service personnel.
Before this
instruct
instruct
is switched
on, make sure it has been
is switched on,
make sure its primary power
circuitry has been adapted to the voltage of the ac power source.
Failure to set the ac power input to the correct voltage could cause
damage to the instrument when the ac power cable is plugged in.
V

How to Use This Manual
This manual uses the
following
conventions:
HP 8566B Documentation Description
HP 8566B Installation
and Verification
Manual
HP
8566B
and Programming
Operating
Manual
Front-Panel Ke
Screen Text This indicates text displayed on the instrument’s
Included with the HP Model 8566B spectrum analyzer are manuals:
The Installation and Verification, the Operating and Programming
Manual, and the Performance Tests and Adjustments Manual.
HP part number
Contents: General information, installation, specifications,
characteristics, and operation verification.
HP part number 08566-90040
Contents: Manual and remote operation, including complete syntax
and command description.
pocket-sized Quick Reference Guide, HP part number 59558970.
3
This represents a key physically located on the
instrument.
screen.
08566-90169
Accopanying
this manual is the seperate,
HP 8566B
Performance
Tests
and
Adjustments Manual
HP 8566B RF Section
Troubleshooting and
Repair Manual
HP 8566B IF-Display
Section
Troubleshooting and
Repair Manual
HP part number 08566-90168
Contents: Electrical performance tests and adjustment procedures.
HP part number 08566-90210 Contents: RF section service
information.
HP part number 08566-90085 Contents: IF-Display section service
information.
vi

Contents
1. General Information
What You’ll Find in This Chapter
Introducing
the
HP 8566B
...............
...........
Safety .......................
Accessories Supplied
Accessories Available
Options
......................
Instruments Covered by This Manual
Serial Numbers
...................
Calibration Cycle
HP-IB Address Selection
Bench Operation
Electrostatic Discharge Information
Static-Safe Accessories
Routine Maintenance
Cleaning the Display
Cleaning the RF Section’s Fan Filter
Replacing the RF Section’s Battery
Ordering Information
Direct Mail Order System
Direct Phone-Order System
Returning the Instrument for Service
................
................
........
..................
..............
..................
..........
...............
.................
................
.........
.........
.................
..............
.............
.........
Service lags ....................
Original Packaging
Other Packaging
Sales and Service Offices
.................
..................
...............
l-l
l-l
l-2
l-2
l-5
l-6
l-7
l-7
l-8
l-8
l-8
l-9
l-10
l-11
l-11
1-12
1-12
1-16
1-16
1-16
1-17
1-17
1-17
1-18
l-20
2. Instailation
What You’ll Find in This Chapter
...........
Safety .......................
Preparation for Use ..................
Initial Inspection
Operating Environment
Power Requirements
‘Ib
Install Standard Instruments
lb Install Option 908 and 913 Instruments
lb Install Option 010 Instruments
lb Set the HP-IB Address
From the Front Panel
From the HP-IB Bus
From the HP-IB Address
..................
...............
................
............
.......
...........
...............
................
................
Switch
...........
2-l
2-l
2-2
2-2
2-3
2-3
2-4
2-7
2-11
2-18
2-18
2-18
2-18
Contents-l

3. Specifications
Introduction .....................
Frequency ......................
Measurement Range
Displayed
Values
................
..................
Center Frequency ................
Frequency Span .................
Resolution
Resolution Bandwidth
Resolution Bandwidth (Option 462 6
.....................
......
dB*Bandwidthsj
Resolution Bandwidth (Option 462 Impulse
Bandwidth)
Bandwidth Shape
..................
.................
Spectral Purity ...................
Amplitude
Measurement Range
Displayed Values
Scale
Accuracy
Reference Lines Accuracy
Dynamic Range
Spurious Responses
Image, Multiple, and Out-of-Band Responses
Residual Responses
Gain Compression
Displayed Average Noise Level (Sensitivity)
......................
................
..................
......................
.....................
..............
...................
................
....
................
................
....
Amplitude Uncertainty ................
Table
Marker
Sweep
Footnotes
........................
........................
...................
Inputs ........................
RF INPUT
IF INPUT
.....................
.....................
outputs .......................
CAL OUTPUT
1STLOOUTPUT
SWEEP + TUNE OUTPUT
Options
.......................
: : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
.............
400 Hz Power Line Frequency Operation Option 400.3-16
General
HP-IB Interface Functions
Environmental
Power Requirements
Humidity
EM1
X-Rays
Warm-Up Time
.......................
..............
...................
Temperature
Altitude
...................
.....................
................
......................
Operation
Storage
....................
.....................
........................
.......................
Serial Prefix 3004A and Above
Serial Prefix 3001A and Below
..........
..........
...................
Operation
....................
Frequency Reference ...............
3-l
3-l
3-l
3-l
3-l
3-2
3-3
3-3
3-3
3-3
3-4
3-4
3-5
3-5
3-5
3-5
3-6
3-6
3-6
3-6
3-7
3-8
3-8
3-8
3-10
3-12
3-13
3-14
3-14
3-14
3-14
3-15
3-15
3-15
3-15
3-16
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-17
3-19
3-19
3-19
Contents-2

Weight
Dimensions
4. Performance Characteristics
Frequency
Resolution
Spectral Purity
Stability
Amplitude
.......................
.....................
......................
.....................
...................
Noise Sidebands
Power-Line Related Sidebands
.................
...........
......................
Residual FM
Drift
.......................
...................
......................
Third Order Intermodulation Distortion
Third Order Intercept
Synthesis-Related Spurious Sidebands
Input Attenuator Uncertainties
RF Gain Uncertainty
Inputs
........................
IF INPUT
RF INPUT
VIDEO INP
IF INP
.....................
.....................
.....................
.......................
EXT TRIGGER
FREQREFERENCEEXT
outputs
.......................
Display Outputs
Recorder Outputs
SWEEP
VIDEO
PENLIFT
......................
.......................
......................
21.4 MHz IF OUTPUT
FREQ REFERENCE INT
10MHzOUT
VIDEO OUT
....................
....................
(TOI)
.............
........
...........
................
...................
..............
..................
..................
................
...............
IF OUT
IF OUTPUT’ : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : : :
General
.......................
Acoustic Noise Emission/ Geraeuschemession
Function Descriptions
Sweep
.......................
Sweep Time
Zero Frequency Span
Marker
.....................
Video Bandwidth
Cathode Ray Tube
Instrument State Storage
Remote Operation
.................
...................
..............
.................
................
.............
................
.......
.....
3-19
3-20
4-l
4-l
4-l
4-l
4-l
4-3
4-3
4-3
4-4
4-4
4-4
4-5
4-5
4-5
4-6
4-6
4-6
4-7
4-7
4-7
4-8
4-8
4-8
4-8
4-8
4-9
4-9
4-9
4-9
4-9
4-10
4-10
4-10
4-10
4-10
4-11
4-11
4-11
4-11
4-11
4-11
4-12
4-12
4-12
Contents-3

5. Operation Verification
What You’ll Find in This Chapter
Test System Configuration
Equipment Connections
Program Loading
...................
Program Operation
HP-IB Addresses
Error Messages
Test Descriptions
...................
....................
...................
...............
................
..................
1. Input Attenuator Switching Check
...........
........
2. IF Gain Uncertainty ...............
3.
Scale
Fidelity (Log) ...............
4.
Scale
Fidelity (Linear)
5. Log
Scale
Switching Uncertainty
6. Resolution Bandwidths
..............
.........
..............
6. Impulse and Resolution Bandwidths (Option 462
Impulse Bandwidth)
7. Line Related Sidebands
8. Average Noise Level
9. Residual Responses
10. Sweep + Tune Out Accuracy
11. Second Harmonic Distortion
12. Frequency Span Accuracy
13. Gain Compression
14. Frequency Response
...............
.............
...............
...............
..........
...........
............
...............
..............
15. Third Order Intermodulation Distortion
16. Calibrator Output Amplitude Accuracy
17. First LO Output Power
.............
.....
......
5-1
5-4
5-5
5-6
5-7
5-8
5-9
5-9
5-10
5-11
5-12
5-13
5-14
5-15
5-16
5-17
5-18
5-19
5-20
5-21
5-22
5-23
5-24
5-25
5-26
5-27
Contents-4

Figures
l-l. HP 8566B with Accessories Supplied
l-2. AC Power Cables Available
l-3. Typical
Serial
Number Label
l-4. Static-Safe Workstation
l-5. Display Bezel Screws
................
l-6. Removing the Bottom Cover
.............
............
...............
............
l-7. Location of Al5 Controller Assembly
l-8. Location of Battery on Al5 Controller Assembly
l-9. Factory Packaging Materials for each Section
2-l. Rear-Panel Cable Connections
............
2-2. Voltage Selector Board and Fuse
2-3. Removing the Handles and Trim
2-4. Removing the Information-Card Tray
2-5. Attach the Rack Mount Flanges
2-6. Voltage Selector Board and Fuse
2-7. Rear-Panel Cable Connections
............
2-8. Removing the Handles and Trim
2-9. Removing the Information-Card Tray
2-10. Attaching the Rack Handles and Flanges
2-l 1. Rear-Panel Cable Connections
............
2-12. Voltage Selector Board and Fuse
2-13. Attaching
the
Inner-Member Brackets
2-14. Slide Adapter for Non-HP System Rack Cabinets
2-15. Removing the Bottom Cover
............
2-16. Location of Al5 Controller Assembly
.........
........
...
.....
...........
...........
........
...........
...........
...........
........
.......
...........
........
...
........
2-17. Address Switch (Shown In Factory Preset Position) . .
2-18. Address Switch Set to 4
...............
3-l. Specified Average Displayed Noise Level, 100 Hz to 2.5
GHz
Non-preselected Tuning Range
3-2. Specified Average Displayed Noise Level, 2.0
GHz
Preselected Tuning Range
3-3. Instrument Dimensions with Handles
3-4. Instrument Dimensions without Handles
4-l. Typical Spectrum Analyzer Resolution
........
GHz
to 22
..........
........
.......
........
4-2. Single Sideband Noise Normalized to 1 Hz BW versus
Offset from Carrier
4-3. Typical SSB Noise at 5.0
...............
GHz
Center Frequency
Normalized to 1 Hz BW versus Offset from Carrier
and Analyzer Resolution. May be Limited by
Average Noise Level.
4-4. Typical Optimum Dynamic Range
5-l.
Dual
Bus (MTS) System Connection
5-2. Single Bus System Connection
5-3. RF Input and Calibration Controls
..............
..........
.........
............
..........
l-3
l-4
l-8
l-9
l-11
1-13
1-13
1-14
1-18
2-4
2-5
2-7
2-8
2-8
2-9
2-10
2-11
2-12
2-12
2-13
2-14
2-15
2-16
2-19
2-19 .
2-20
2-21
3-9
3-9
3-20
3-20
4-l
4-2
4-3
4-4
5-5
5-6
5-8
Contents-5

lhbles
1 -
1. Static-Safe Accessories
...............
l-2. Factory Packaging Materials .............
l-3. Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Offices
......
2-l. Decimal and Binary Address Codes .........
5-l. Tests Performed
5-2.
Tests Not Performed
5-3.
5-4.
Equipment Summary
HP-IB Addresses
..................
................
................
..................
l-10
1-18
1-21
2-22
5-2
5-3
5-4
5-8
Contents-6

General Information
1
What You’ll Find in
This Chapter
This chapter introduces you to the HP 8566B spectrum analyzer
and its options and accessories. Refer to Chapter 2 for information
on inspecting and installing the HP 8566B. Refer to Chapter 3 and
Chapter 4 for a complete listing of instrument specifications and
characteristics. Refer to Chapter 5 for Operation Verification.
Introducing the HP 8566B
Safety ...........................................................
Accessories Supplied
Accessories Available
Options
Instruments Covered by This Manual
Serial
Calibration Cycle
HP-IB Address Selection
Bench Operation
Electrostatic Discharge Information
Static-Safe Accessories
Routine Maintenance
Cleaning the Display
Cleaning the RF Section’s Fan Filter
Replacing the RF Section’s Battery
Ordering Information
Returning the Instrument for Service
Service
Original Packaging
Other Packaging
Sales and Service Offices
..........................................................
Numbers
..............................................
..............................................
Tags
..................................................
...............................................
.........................................
............................................
..........................................
...........................
...............................................
........................................
..............................
........................................
............................................
...........................................
...........................
............................
............................................
...........................
.............................................
.........................................
..l- 5
..l-
..l-
l-10
. l-12
. l-13
1-13
l-14
1-14
. l-17
. l-18
..l-18
1
-
. l-19
l-21
l-2
l-2
l-2
l-6
l-7
l-8
8
l-9
9
18
Introducing the
HP 8566B
The HP 8566B spectrum analyzer is capable of measuring signals
from -135
22
GHz.
frequency range of the instrument can be extended, unpreselected,
to 110
commercially available mixers.
The HP 8566B is a complete, self-contained instrument that requires
only an external ac power source for operation. A set of two ac
power cables, suitable for use in the country to which the instrument
is originally shipped, are included with the instrument.
dBm
to
+30 dBm
The HP 8566B provides preselection from 2 to 22
GHz
using HP 11970 Series mixers, and to 325
over a frequency range of 100 Hz to
GHz
using other
General Information l-l
GHz.
The

Safety
Before installing or operating this instrument, you should familiarize
yourself with the safety marking on the instrument and the safety
instructions in the manuals. The instrument has been manufactured
and tested in accordance with international safety standards.
However, to ensure safe operation of the instrument and personal
safety of the user, the cautions and warnings in the manuals must be
followed. Refer to the summary of the safety information located
near the front of this manual.
Accessories Supplied
Figure l-l illustrates the instrument with the supplied accessories. In
accordance with international safety standards, both sections of this
instrument are equipped with three-wire ac power cables. Various
power cables are available to connect the HP 8566B to the types of ac
power outlets unique to specific geographic areas. See Figure l-2. The
cables appropriate for the area to which the instrument is originally
shipped are included with the instrument.
FRONT VIEW
I F-
Display
Sect ion
RF
Sect ion
REAR VIEW
h
1-2 General Information
IF- Display
Sect ion
RF Section
CABLES

Item
1
1ST
LO OUTPUT SMA termination
2
Front-panel IF semirigid jumper
3
BNC jumper cable (quantity 3)
4
Bus interconnect cable (W31)
5
Coax interconnect cable
6
Line power cables (2 each)
Figure l-l. HP 8566B with Accessories Supplied
Description HP Fart Number
1810-0118
85660-20101
85660-60117
85662-60220
(W30)
85662-60093
see Figure l-2
General Information
1.3

PLUG TYPE * *
CABLE
HP PART
NUMBER
I
PLUG
DESCRIPTION
I
CABLE
LENGTH
CM
(INCHES)
CABLE
COLOR
I
IN COUNTRY
FOR USE
250V
250V
II
FE%
0
-
250V
-
125V
0
ON Ed
0
-
250V
8120-1351
8120-1703
8120-1369 Straight*
8 120-0696 90°
8120-1689
8120-1692 go-
8120-1348
8120-1538
8120-1378
8 120-4753 Straight
8120-1521
8120-4754 9o”
8120-5182
8120-5181
Straight*
90”
Straight
Straight*
9on
Straight*
9o”
;traight*
JO0
BS1363A
NZSS198/ASCll
*
CEE7-Yl
NEMA5-15P
NEMA5-15P
NEMAS-15P
229 (90)
229 (90)
201 (79)
221 (87)
1
201 (79)
201 (79)
203 (80)
203 (80)
203 (80)
230 (90)
203 (80)
230 (90)
200 (78)
200 (78)
Mint Gray
Mint Gray
Gray
Gray
Mint Gray
Mint Gray
B I ock
Black
Jade Gray
Jade Gray
Jade Gray
Jade Gray
Jade Gray
Jade Gray
Great Britain,
Niger
Cyprus.
Singapore,
2 imbabwe
Argentina,
Australia,
New Zealand,
Mainland China
Iast
and West
!urope,
African
Jnited Arab
?epubl
(unpolarized in
nany nations)
United States
zanodo,
Japan (100 V or
200 V), Brazil,
Colombia, Mexico
Philippines,
Saudio
Taiwan
Israel
Central
Republic,
ic
Arabia,
ia,
-
*
Part number for plug is industry identifier for plug only. Number shown for cable is
HP Part Number for complete cable, including plug.
**
E = Earth Ground; L = Line; N = Neutral
FORMAT80
l-4
General Information
Figure l-2. AC Power Cables Available

Accessories Available
A number of accessories are available from Hewlett-Packard to help
configure the HP 8566B for your specific needs.
Preamplifiers
External Harmonic
Mixers
Microwave Power
Amplifier
Close-Field Probes
The HP 8447D preamplifier provides a
minimum of 26 dB gain from 100
1.3
GHz
to enhance measurements of very
kHz
to
low-level signals.
The HP 8449B preamplifier provides a
minimum of 28 dB gain from 1 to 26.5
GHz
to enhance measurements of very low-level
signals.
The HP 11970 Series harmonic mixers extend
the frequency range of the HP
110
GHz.
8566B
up to
The HP 11975A microwave power amplifier
boosts the LO power for external mixers. Its
frequency range is from 2 to 8
provides an output leveled to f 1
GHz,
dB.
and it
The HP 11940A and HP 11941A close-field
probes are small, hand-held,
electromagnetic-
field sensors. The probes can be used to
make repeatable, absolute, magnetic-field
measurements. When attached to a signal
source, the probes can be used to generate a
localized magnetic field for electromagnetic
interference
(EMI)
susceptibility testing. The
HP 11941A is specified over a frequency range
of 9
kHz
to 30 MHz. The HP 11940A operates
from 30 MHz to 1
GHz.
75
to 50 Ohm
Minimum-Loss Pad
Microwave Limiters
HP-IB Cable
Controllers
The minimum-loss pad (dc to 2.0
GHz),
HP part number 08568-60122, is a low-VSWR
resistive matching device for making
measurements in
The HP 11693A limiter protects
75-ohm
systems.
the
instrument input circuits from damage due
to high power levels. It operates over a
frequency range of 0.4 to 12.4
GHz
and is
rated 1 W continuous and 75 W peak power.
The HP 11867A limiter is similar to the
HP 11693A but has a frequency range of dc to
1.8
GHz
and is rated 10 W continuous and 100
W peak power.
Use HP
10833A/B/G/D
HP-IB cables.
The HP 8566B is fully HP-IB programmable.
The preferred controllers are HP 9000
Series 300 computers. Consult your local
Hewlett-Packard service representative for
other recommended controllers and available
software.
General Information
l-5

HP 85650A Quasi-Peak The HP 85650A adds to the spectrum
Adapter analyzer the resolution bandwidth filters and
quasi-peak detection capability specified by
CISPR. Together the quasi-peak adapter and
the spectrum analyzer provide many of the
elements needed for an EM1 receiver system.
HP
85685A
Preselector
RF
The HP
85685A
RF preselector can be used
with an HP 8566B to form a multi-purpose RF
test receiver. It improves spectrum analyzer
measurement sensitivity while providing
overload protection from out-of-band signals.
This enables low-level signals to be monitored
in the presence of high-level ambients. Its
frequency range is 20 Hz to 2
GHz.
Options
Troubleshooting and
Repair Manual
Service information for the HP 8566B is
available in the
and
Repair
HP 85660B Troubleshooting
Manual
and the
HP 85662A
Troubleshooting and I&pair Manual.
They include schematic diagrams, block
diagrams, component location illustrations,
circuit descriptions, repair procedures, and
troubleshooting information.
Service Kits
A service kit is available containing
troubleshooting and alignment accessories for
the HP 8566B. The kit includes a test cable
and extender boards. Order the kit as HP
part number 08566-60001. A combined kit,
HP part number 08566-60005, is available
containing accessories for both the HP 8566B
and HP
8568B
instruments.
Several options are available and can be ordered by option number
when you order the instrument. Some of the options are also
available as kits that can be ordered and installed after you have
received your HP 8566B.
Option 010
Rack Mount Slide Kit. This option supplies the
necessary hardware and installation instructions
for mounting an instrument on slides into a rack of
482.6 mm (19 inch) spacing. The heavy-duty slides
are designed specifically to support the weight of the
HP 8566B. Because of the weight of
the
HP
8566B,
approximately 50 kg (112 lb), the use of this option
is recommended. Option 010 is also available as a kit
(HP part number 5062-6407).
1-6 General Information
Option 080
Option 081
Option 400
Information Cards in Japanese
Information Cards in French
The standard HP 8566B requires that the power line
frequency be 50 or 60 Hz. Option 400 allows the
instrument to operate with a 400 Hz power line
frequency.

Option 462
This option provides 6 dB bandwidths for making
MIL-STD EM1 measurements. In addition to
enhancing instrument capability for MIL-STD
461D and 462D EM1 measurements, Option 462
spectrum analyzers can still make all commercial
EM1 and general-purpose measurements. Option
462 instruments with HP 85662A (top box) serial
prefixes below 3341A were compatible with MIL-STD
462A/B/C
(impulse bandwidths).
Option 857
Option 908
Option 910
Option 913
Option 915
The HP 8566B Option 857 is used in EMC receiver
applications. This option provides the cumulative
log fidelity and absolute amplitude performance
necessary for EMC receivers to meet their system
specs.
Rack Mount Flange Kit (to mount without handles).
This option supplies the necessary hardware and
installation instructions for mounting an instrument in
a rack of 482.6 mm (19 inch) spacing. Option 908 is
also available as a kit (HP part number 5062-3986).
Extra
HP 8566B Operating and Programming
Manual
and Adjustments Manual.
Rack Mount Flanges with Handles (handles provided).
This option supplies the
installation instructions for mounting an instrument
with handles in a rack of 482.6 mm (19 inch) spacing.
Option 913 is also available as a kit (HP part number
5062-3986).
This option supplies the HP 8566B troubleshooting
and repair manuals.
and an extra
HP
8566B Ryformance Ests
necessary
hardware and
Instruments Covered
by
This
Manual
Serial Numbers
This manual contains information for setting up and verifying
operation of HP
Option 400 (400 Hz operation), Option 857, or Option 462 (6
bandwidths or impulse bandwidths) installed. The procedures in this
manual can also be used to set up and verify the operation of HP
8566A spectrum analyzers that
spectrum analyzers through the installation of an HP 8566AB Retrofit
Kit (formerly the HP
Hewlett-Packard makes frequent improvements to its products to
enhance their performance, usability, or reliability. HP service
personnel have access to complete records of design changes to each
type of equipment, based
Whenever you contact Hewlett-Packard about your instrument, have
the complete serial number available to ensure obtaining the most
complete and accurate information possible.
A serial number label is attached to the rear of each instrument
section. The serial number has two parts: the prefix (the first four
8566B
spectrum analyzers, including those with
have
been converted into HP 8566B
8566A+OlK
on the
Retrofit Kit).
equipment’s serial number.
dB
General Information 1-7

numbers and a letter), and the suffix (the last five numbers). See
Figure l-3.
The first four numbers of the prefix are a code identifying the date of
the last major design change incorporated in your instrument.
The letter identifies the country in which the instrument was
manufactured. The five-digit suffix is a sequential number and is
different for each instrument. Whenever you list the serial number
or refer to it in obtaining information about your instrument section,
be sure to use the complete number, including the full prefix and the
suffix.
Calibration Cycle
HP-IB Address
Selection
fsER
To ensure that the HP 8566B meets the specifications listed in Chapter
3, the operation verification listed in Chapter 5 should be performed
every 6 months.
The instrument is shipped with the HP-IB address preset to 18 (ASCII
2R). The instrument stores this address in internal RAM memory
which is maintained by a lithium battery in STANDBY and when line
power is removed. This stored address can be changed from the
front panel or on switches located on the RF section’s Al5 controller
assembly. Refer to Chapter 2, Installation.
2730AOO427)
Figure 1-3. Typical Serial Number Label
Bench Operation
1-6 General Information
The instrument has plastic feet and foldaway tilt stands for
convenience in bench operation. The plastic feet are shaped to make
full-width modular instruments self-aligning when stacked. The
instrument is shipped with front handles attached for ease of moving.

Electrostatic Discharge Information
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage or destroy electronic
components. Therefore, observe the following precautions:
n
Be sure
that
all instruments are properly earth-grounded to prevent
buildup of static charge.
H
Before connecting any coaxial cable to an instrument connector for
the first time each day, momentarily short the center and outer
conductors of the cable together.
n Personnel should be grounded with a resistor-isolated wrist strap
before touching the center pin of any connector and before
removing any assembly from the instrument.
n When replacing the instrument’s battery (refer to “Replacing the RF
Section Battery” in this chapter), be sure to observe the following:
q Perform the work at a static-safe workstation. See Figure l-4.
q
Store or transport PC boards only in static-shielding containers.
q Always handle board assemblies by the edges. Do not touch the
edge-connector contacts or trace surfaces with bare hands.
Figure l-4 shows an example of a static-safe work station. Two types
of ESD protection are shown: a) conductive table mat and wrist strap
combination, and b) conductive floor mat and heel strap combination.
The two types must be used together to ensure adequate ESD
protection. Refer to
Table
l-l for a list of static-safe accessories and
their part numbers.
Building
1 MegOhm
Resistor
Ground
Figure 1-4. Static-Safe Workstation
General Information l-9

Static-Safe
Accessories
‘able
l-l. Static-Safe Accessories
HPFart
Number
Description
Order the following through any Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service
Office
9300-0797
Set includes: 3M static control mat 0.6 m x 1.2 m (2 ft
x 4 ft) and 4.6 cm (15 ft) ground wire. (The wrist-strap
and wrist-strap cord are not included. They must be
ordered
1
9300-0980 1 Wrist-strap cord 1.5 m (5 ft)
9300-1383
Wrist-strap, color black, stainless steel, without cord,
separatelv.)
has four adjustable links and a 7 mm post-type
connection.
9300-1169
ESD heel-strap (reusable 6 to 12 months).
I
l-10
General Information

Routine Maintenance
Cleaning the Display
Caution
The inside surface of the glass CRT shield is coated with a thin
metallic film that can be easily damaged. To clean the glass CRT
shield, use thin-film cleaner (HP part number 8500-2163) and a
lint-free cloth. lb clean the inside surface of the display glass, remove
the
glass CRT shield using the following procedure:
1. Disconnect the ac line power from the instrument sections.
2. Remove the two screws securing the display bezel and CRT glass
shield to the front panel. These screws are located on the bottom
edge of the bezel. See Figure l-5.
While removing the two bezel screws, use caution to prevent the glass
from falling.
3. Remove the bezel and CRT glass shield.
\
Bezel Screws
Figure 1-5. Display Bezel Screws
4. Clean the glass using the thin-film cleaner and a lint-free cloth.
5. Replace the glass shield. Place the side of the glass that has the
silver edge towards the CRT.
6. Replace the bezel and two screws.
General Information
l-11

Cleaning the RF
Section’s Fan Filter
The fan on the RF section has a air filter that should be regularly
inspected and cleaned. lb clean the air filter, perform the following:
1. Disconnect the ac line power from the RF section.
2. Remove the four screws securing the filter cover to the fan on the
RF Section. Remove the filter.
Replacing the RF
Section’s Battery
Warning
Warning
3. Clean
the
filter using mild soap and water. Dry the filter
thoroughly. If it is damaged, replace it with a new filter (HP part
number 85660-00049).
4. Replace the filter and its cover.
The RF section’s Al5 controller assembly has a battery for
maintaining internal RAM memory. This memory is primarily used
for storing instrument states, error correction data, and
DLPs
(downloadable programs). Under normal conditions, the battery
should typically last a minimum of 3 years. Refer to the HP
Troubleshooting and
Repair
Manual for the HP part number. Use the
8566023
following procedure to replace the battery.
Battery
or attempt to recharge this battery. Dispose of discharged
battery in a safe manner.
Changing the battery
requires the removal of the RF’ Section’s protective bottom cover.
This should be performed only by a qualified service person.
Refer all such servicing of the instrument to qualified service
persons.
BTl
contains lithium iodide. Do not incinerate, puncture,
BTl
on the Al5 controller assembly
Caution
ESD (electrostatic discharge) can damage or destroy electronic
components. Work at a static-safe workstation when replacing the
battery.
1. Place the HP
8566B
on a static-safe workstation. Refer to
“Electrostatic Discharge Information” in this chapter.
2. Disconnect the ac line power from the instrument sections. Place
the HP 8566B RF section upside down on the work surface so the
bottom of the RF section faces up.
3. Using a Pozidriv screw driver, remove the two bottom RF-Section
rear-panel bumpers. See Q) in Figure l-6.
1-12 General Information

TOP DOWN
Figure 1-6. Removing the Bottom Cover
4. Back out screw Q (Figure l-6) causing the cover to unseat from
the front frame. When the cover is clear of the front frame, lift
the cover up to remove it.
Al5 CONTROLLER
ASSEMBLY
Figure 1-7. Location of Al5 Controller Assembly
General Information l-13

5. Remove the cover from the Al5 controller assembly. See
Figure l-7.
6. Remove the Al5 controller assembly. Locate the battery on the
Al5 assembly. Figure 1-8 shows the location of the battery.
Battery
Figure 1-8. Location of Battery on Al5 Controller Assembly
(A15BTl)
7. Replace the battery with a new one (HP part number 1420-0331).
Be sure to install the battery with
the
polarity shown in
Figure l-8.
8. Replace the Al5 controller assembly.
9. Reconnect the power cables to the IF and RF sections.
l-14
General Information
10. Connect a jumper wire between the Al5 controller test points
A15TPl-8
T3 and
A15TPl-9
ST (to erase and initialize Al5
controller nonvolitile memory).
11. Set LINE switch to ON. The Al5 controller LED’s
A15DS14
the Al5 controller has
should all turn on, then turn off, sequentially, indicating
sucessfully
executed self-test. If they do
A15DSl
through
not the Al5 controller might be damaged or improperly installed.
In addition, all front panel LED’s should turn on momentarily,
indicating the HP 8566B has performed its’ power-on pretest.
In addition to normal HP 8566B power-up HP-IB address and
firmware revision information, a BATTERY flag should appear on
the CRT, indicating that information previously stored in
the Al5
controller nonvolitile memory has been lost or erased. Normally
the BATTERY flag appears after several years of use to indicate
that the lithium battery
12. Remove the jumper wire between
13. Set the LINE switch to STANDBY
A15BTl
needs to be replaced.
A15TPl-8
and
T3 and
A15TPl-9
then to ON. The HP 8566B
should power up normally, without any flags displayed on the
CRT.
ST.

14. Set the LINE switch to STANDBY and remove the power cable
from the rear of the RF section.
15. Install the controller cover.
16. Replace the RF section bottom cover and the two rear feet.
17. Place the HP 8566B top side up and reconnect the power cable to
the RF section.
18. Set the LINE switch to ON and allow a 2-hour warm-up.
19. Recalibrate the instrument with the following steps. (For a more
complete description of the calibration, refer to the HP
8566B
Operating and Programming Manual.)
Connect the front-panel CAL OUTPUT signal to the RF INPUT.
a.
Press
b.
cm]
adjust for a marker amplitude of -10.00
Press (RECALL) @, and then adjust the front-panel FREQ ZERO
C.
@, and then adjust the front-panel AMPTD CAL
dBm.
adjust for maximum signal amplitude.
Press (SHIFT_) [FREQUENCY SPAN) w
d.
data in the instrument’s memory.
to load the error correction
General Information
l-15

Ordering
Information
Parts can be ordered from any Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service
Office. Refer to
order a part or assembly, quote
‘fable
l-3 for a listing of sales and service offices. lb
the
Hewlett-Packard part number,
indicate the quantity required, and address the order to the nearest
Hewlett-Packard Office.
To
order a part that is not listed in the replaceable parts table, include
the instrument model number, the description and function of the
part, and the number of parts required. Address the order to the
nearest Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Office.
Direct Mail Order
System
Direct Phone-Order
System
Within the USA, Hewlett-Packard can supply parts through a direct
mail
order system. Advantages of using the system are as follows:
n Direct ordering and shipment from the HP Support Materials
Organization in Roseville, California.
n
No maximum or minimum on any mail order. (There is a minimum
order amount for parts ordered through a local Hewlett-Packard
Sales and Service Office when the orders require billing and
invoicing.)
n Prepaid transportation. (There is a small handling charge for each
order.)
n
No invoices.
‘lb provide these advantages, a check or money order must accompany
each order. Mail-order forms and specific ordering information is
available through your local Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Office.
Within the USA, a phone order system is available for regular and
hotline replacement parts service. A toll-free phone number is
available, and Mastercard and Visa are accepted.
Regular Orders: The toll-free phone number, (800) 227-8164, is
available 6 AM to 5 PM, Pacific time, Monday through Friday. Regular
orders have a 4 day delivery time.
l-16
General Information
Hotline Orders: Hotline service for ordering emergency parts is
available 24 hours a day, 365 days a year. There is an additional
hotline charge to cover
the
cost of freight and special handling.
The toll-free phone number, (800) 227-8164, is available 6 AM to 5 PM,
Pacific time, Monday through Friday and (916)
785-8HOT
is available
after-hours, weekends, and holidays. Hotline orders are normally
delivered the following business day.

Returning the
Instrument for
Service
The instrument may be shipped in environments within the following
limits:
Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .-40°C to
Humidity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5% to 90% at 0” to 40°C
Altitude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
The instrument should be protected from temperature extremes which
might cause condensation within the instrument.
Up to 15,240 meters (50,000 feet)
+75OC
Service
T&gs
Original Packaging
Note
If you are returning the instrument to Hewlett-Packard for servicing,
fill in and attach a blue service tag to each instrument section.
Service tags are supplied at the end of this chapter.
Please be as specific as possible about the nature of the problem. If
you have recorded any error messages that appeared on the screen or
have any other specific data on the performance of the instrument,
please send a copy of this information with the instrument.
lb protect the front panel, the front handles must be attached to each
instrument section before shipping.
It is recommended that the original factory packaging materials be
retained for use when shipping the instrument. Because the combined
weight of the two instrument sections is approximately 50 kg (112 lb),
do not package the instrument sections fastened together as one unit.
The instrument sections must be separated and packaged in separate
containers. Pack each section in the original factory packaging
materials if they are available (see Figure l-9). Refer to
the part numbers of items listed in the figure. Original materials are
available through any Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Office.
Table
l-2 for
General Information 1-17

ront handles must be
mounted for shipment.
Figure l-9. Factory Packaging Materials for each Section
‘Ihble
l-2. Factory Packaging Materials
Other Packaging
Caution
Note
Item
1
2
3
Description
Outer
Box
Inner
Box
Inner
Foam Pad
Qty
1
1
2
IIP
Fort Number
92 1 l-4487
5180-2320
5180-2319
Instrument damage can result from using packaging materials other
than those specified. Never use styrene pellets as packaging materials.
They do not adequately cushion the instrument nor prevent it from
shifting in the carton. They cause instrument damage by generating
static electricity.
To protect the front panel, the front handles should be attached to
each instrument section before shipping.
You can repackage the instrument with commercially available
materials, as follows:
1. Separate the two instrument sections.
2. Attach a completed service tag to each of the sections.
1-18 General Information
3. Wrap each section in antistatic plastic to reduce the possibility of
damage caused by electrostatic discharge.

4. Use a strong shipping container. A double-walled, corrugated
cardboard carton of 159-kg
(350-lb)
bursting strength is
adequate. The carton must be large enough and strong enough to
accommodate the instrument. Allow at least 3 to 4 inches on all
sides of the instrument for packing material.
5. Surround the instrument with 3 to 4 inches of packing material, to
protect the instrument and prevent it from moving in the carton.
If packing foam is not available, the best alternative is S.D.-240 Air
Cap from Sealed Air Corporation (Commerce, California 90001). Air
Cap looks like a plastic sheet filled with
l-1/4
inch air bubbles. Use
the pink (antistatic) Air Cap to reduce static electricity. Wrapping
the instrument section several times in this material should both
protect the instrument section and prevent it from moving in the
carton.
6. Seal the carton with strong nylon adhesive tape.
7. Mark the carton FRAGILE, HANDLE WITH CARE.
8. Retain copies of all shipping papers.
General Information 1-19

Sales and Service Offices
Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Offices provide worldwide support
for Hewlett-Packard products. lb obtain servicing information or to
order replacement parts, contact the nearest Hewlett-Packard Sales
and Service Office listed in
provide essential information, which includes model numbers, serial
numbers, and assembly part numbers.
Table
l-3. In any correspondence, always
l-20 General information

‘Ihble
1-3. Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Offices
US FIELD OPERATIONS
HEADQUARTERS
Hewlett-Packard Company
19320 Pruneridge Avenue
Cupertino, CA 95014, USA
(800) 752-0900
California
Hewlett-Packard Co.
1421 South Manhattan Ave.
Fullerton, CA 92631
(714) 999-6700
Hewlett-Packard Co.
301 E. Evelyn
Mountain View, CA 94041
(415) 694-2000
Colorado
Hewlett-Packard Co.
24 Inverness Place, East
Englewood, CO 80112
(303) 649-5000
Georgia
Hewlett-Packard Co.
2000 South Park Place
Atlanta, GA 30339
(404) 955-1500
Illinois
Hewlett-Packard Co.
5201
Tollview
Drive
Rolling Meadows, IL 60008
(708) 255-9800
New Jersey
Hewlett-Packard Co.
150 Green Pond Road
Rockaway, NJ 07866
(201) 627-6400
IkXaS
Hewlett-Packard Co.
930 E. Campbell Rd.
Richardson, TX 75081
:214) 231-6101
EUROPEAN OPERATIONS
HEADQUARTERS
Hewlett-Packard S.A.
150, Route du
Nant-d’Avri1
1217 Meyrin B/Geneva
Switzerland
(41 22) 780.8111
France
Hewlett-Packard France
1 Avenue Du Canada
Zone
D’Activite
De Courtaboeuf
F-91947 Les Ulis Cedex
France
(33 1) 69 82 60 60
Germany
Hewlett-Packard
GmbH
Hewlett-Packard Strasse
6380 Bad Homburg v.d.H
Germany
(49 6172) 16-O
Great Britain
Hewlett-Packard Ltd.
Eskdale Road, Winnersh Triangle
Wokingham, Berkshire
RGll
5DZ
England
(44 734) 696622
INTERCON
HEADQUARTERS
OPERATIONS
Hewlett-Packard Company
3495 Deer Creek Rd.
Palo
Alto, California 94304-1316
(415) 857-5027
Australia
Hewlett-Packard Australia Ltd.
31-41 Joseph Street
Blackburn, Victoria 3130
(61 3) 895-2895
Canada
Hewlett-Packard (Canada) Ltd.
17500 South Service Road
Trams-Canada Highway
Kirkland, Quebec
H9J 2X8
Canada
(514) 697-4232
Japan
Yokogawa-Hewlett-Packard Ltd.
1-27-15
Yabe,
Sagamihara
Kanagawa 229, Japan
(81 427) 59-1311
China
China Hewlett-Packard, Co.
38
Bei
San Huan Xl Road
Shuang Yu Shu
Hai
Dian District
Beijing, China
(86 1) 256-6888
Singapore
Hewlett-Packard Singapore
Pte. Ltd.
1150 Depot Road
Singapore 04 10
(65) 273 7388
Thiwan
Hewlett-Packard
‘Ihiwan
8th Floor, H-P Building
337 Fu Hsing North Road
l%ipei,
Taiwan
(886 2) 712-0404
General Information
l-21

Installation
2
What You’ll Find in
This Chapter
This chapter describes the process of getting the HP 8566B spectrum
analyzer ready to use. The process includes initial inspection and
installing the unit. Before installing the HP
the warnings, cautions, and notes listed in “Safety” below.
n If you’re
Standard Instruments” in this chapter.
w
To install Option 908 or 913 instruments, refer to “To Install Option
908 and 913 Instruments” in this chapter.
n
To install Option 010 instruments, refer to
Instruments” in this chapter.
Safety .............................................................
Preparation for Use ..............................................
Initial Inspection
Operating Environment
Power Requirements
To Install Standard Instruments
lb Install Option 908 and 913 Instruments .......................
To Install Option 010 Instruments
To Set the HP-IB Address
From the Front Panel .........................................
From the HP-IB Bus
From the HP-IB Address Switch
not
installing the instrument in a rack, refer to “To Install
...............................................
........................................
...........................................
..................................
...............................
........................................
...........................................
..............................
8566B,
be sure to read
“To
Install Option 010
all
.2-l
..2- 2
.2-3
.2-3
.2-3
.2-4
.2-7
.2-11
.2-18
.2-18
2-18
.2-18
Safety
Before installing or operating this instrument, you should familiarize
yourself with the safety marking on the instrument and the safety
instructions in the manuals. The instrument has been manufactured
and tested in accordance with international safety standards.
However, to ensure safe operation of the instrument and personal
safety of the user, the cautions and warnings in the manuals must be
followed. Refer to the summary of the safety information located
near the front of this manual.
Installation 2-1

Warning
Failure to ground the instrument properly can result in personal
injury. Before turning on the HP
protective earth terminals to the protective conductor of the
main power cable. Insert the main power cable plug only into a
socket outlet that has a protective earth contact. DO NOT defeat
the earth-grounding protection by using an extension cable,
power cable, or autotransformer without a protective ground
conductor. If you are using an autotransformer, make sure its
common terminal is connected to the protective earth contact of
the power source outlet socket.
8566B,
you must connect its
Warning
Warning
Caution
Preparation for Use
Initial Inspection
Power is still applied to this instrument with the
in STANDBY. There is no off position for the
remove power from the instrument, it is necessary to remove the
power cable from the rear of each of the instrument sections.
Because the combined weight of the instrument sections is
approximately 112 pounds, use appropriate caution when moving
or installing.
ILINE)
(LINE]
switch
switch.
‘Ib
Before switching on this instrument, make sure it is adapted to
the voltage of the ac power source as described in the following
procedures. Failure to set the ac power input to the correct voltage
could cause damage to the instrument when the ac power cable is
plugged in.
Inspect the shipping container for damage. If the shipping container
or cushioning material is damaged, keep it until you have verified
that the contents are complete and you have tested the instrument
mechanically and electrically.
2-2 Installation
Contents of the shipment are shown in Figure l-l. If the contents
are incomplete or if the instrument does not pass the operation
verification tests (procedures are provided in Chapter
5),
notify the
nearest Hewlett-Packard office. If the shipping container is damaged
or the cushioning material shows signs of stress, also notify the
carrier. Keep the shipping materials for the carrier’s inspection. The
HP office will arrange for repair or replacement without waiting for a
claim settlement.
If the shipping container and cushioning material are in good
condition, retain them for possible future use. You may wish to ship
the instrument to another location or to return it to Hewlett-Packard
for service. Chapter 1 provides instructions for repackaging and
shipping the instrument.

Operating
Environment
The instrument may be operated in environments within the following
limits:
Temperature . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Humidity . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5% to 90% at 0” to 40°C
Altitude . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
The instrument should be protected from temperature extremes which
might cause condensation within the instrument.
Up to 4,572 meters (15,000 feet)
0°C
to +
55OC
Power Requirements
The HP 8566B requires a power source of 100, 120, 220, or 240 V
ac
+5% -lo%,
sections combined is less than 650 volt-amperes.
50 to 60 Hz. Power consumption for the instrument
Installation 2-3

To Install Standard Instruments
1. Place the RF section right side up on a level work surface.
2. Place the IF-Display section on top of the RF section, offset far
enough forward to allow the RF section hooks to engage the
IF-Display Section frame when slid back. Slide the IF-Display
section back until the RF section hooks catch the bottom of the
IF-Display Section.
3. Line up the rear-panel lock feet, and tighten the thumb screws on
both lock feet.
4. Connect cable W31 between IF-Display section 32
J6. See Figure 2-l.
5. Connect cable
W30
between IF-Display section Jl and RF section
Jl.
J2
Jl
w31 w37 W38
and
RF section
2-4 Installation
Figure 2-l. Rear-Panel Cable Connections
6. Determine the ac line voltage to be used.
7. On each instrument section, slide open the power module’s fuse
cover (located on the rear panel). See Figure 2-2. Push the
fuse-pull lever to the left. Remove the fuse.

Line Voltage Setting
Figure 2-2. Voltage Selector Board and Fuse
Card Fuse
8. On each power-line module, check the voltage selector card for
the proper ac line voltage. The card’s voltage setting should
be visible on the card. See Figure 2-2. If you need to select a
different ac line voltage setting, perform the following:
a. Use needle-nose pliers to pull out the voltage-selector card.
Rotate the card so that the voltage label corresponding to the
actual line voltage will appear in the module window.
b. Push the card back into its slot.
9. Check the fuse to make sure it is of the correct rating and type
for the ac line voltage selected. Fuse ratings for different line
voltages are indicated in the following table.
ac Line Voltage IF-Display Section
100/120
2 amperes FAST BLO
RF section
4 amperes FAST BLO
HP part number 2110-0002 HP part number 21 lo-0055
220/240
1 ampere SLOW BLO
2 amperes SLOW BLO
HP part number 2110-0007 HP part number 2110-0006
10. Insert the correct fuse, and push the fuse-pull lever into its
normal right-hand position.
11. Connect the ac line power cords.
Installation 2-5

12. If the HP 8566B will be remotely controlled, refer to “To Set the
HP-IB Address” in this chapter.
13. When you turn your instrument on for the first time, you should
perform the verification tests in Chapter 5. Refer to the
Operating and Programming Manual
for instructions on using
HP8566B
the instrument.
Note
Cable W15 is normally connected between the FREQ REFERENCE
EXT and INT BNC ports, providing the HP 8566B with its own internal
10 MHz frequency reference. W15 is removed when an external
frequency reference is used. Cables W37 and
W38
are removed for
connection of the IF and VIDEO ports to the HP 85650A Quasi-Peak
Adapter. If the instrument is used without the HP 85650A Quasi-Peak
Adapter, W37 and W38 must be connected for the instrument to
operate.
Z-6
Installation

To Install Option 908 and 913 Instruments
Option 908 contains the necessary hardware to mount the HP 8566B
without handles in a rack of 482.6 mm (19 inch) spacing. Option 913
mounts the HP 8566B with handles.
1. Remove the front-handle trim from each side of the RF
and IF-Display sections. See Q of Figure 2-3.
Figure 2-3. Removing the Handles and Trim
2. Remove the three screws securing each handle, and remove the
handles. See Q and
3. The information-card tray located on the bottom of the RF section
requires a space of approximately 2 cm below the instrument
when rack mounting. See 6 of Figure 2-4. (No filler strip is
provided.) If you wish to remove the information-card tray,
remove the feet and tilt stands ( @ and @ in Figure 2-4).
(3J
Installation 2-7

Figure 2-4. Removing the Information-Card Tray
4. On each instrument section, attach the rack mount flange
(and front handles, for Option 913) using the three
M4x0.7~16
pan-head screws provided in the kit. See Figure 2-5.
2-8
Installation
Figure 2-5. Attach the Rack Mount Flanges
5. Determine the ac line voltage to be used.
6. On each instrument section, slide open the power module’s
fuse door (located on the rear panel). See Figure 2-6. Push the
fuse-pull lever to the left. Remove the fuse.

Note
Although Figure 2-6 shows the two instrument sections connected
together, they will be mounted separately in the rack.
Line Voltage Setting
Figure 2-6. Voltage Selector Board and Fuse
Card
7. On each power-line module, check the voltage selector card for
the proper ac line voltage. The card’s voltage setting should
be visible on the card. See Figure 2-6. If you need to select a
different ac line voltage setting, perform the following:
a. Use needle-nose pliers to pull out
Rotate
the
card so that the voltage label corresponding to the
the
voltage-selector card.
actual line voltage will appear in the module window.
b. Push the card back into its slot.
8. Check the fuse to make sure it is of the correct rating and type
for the ac line voltage selected. Fuse ratings for different line
voltages are indicated in the following table.
ac Line Voltage
100/120
IF-Display Section
2 amperes FAST BLO
RF Section
4 amperes FAST BLO
HP part number 2110-0002 HP part number 21 lo-0055
2 amperes SLOW BLO
i
220/240
1 ampere SLOW BLO
HP part number 2110-0007 HP part number 2110-0006
F;se
Installation
2-9

9. Insert the correct fuse, and push the fuse-pull lever into its
normal right-hand position.
10. Bolt each instrument section into the rack from its rack mount
flange. Place the IF-Display section just above the RF section.
11. Connect cable W31 between IF-Display section 52 and RF section
J6. See Figure 2-7.
12. Connect cable
Jl.
J2
w5u
Figure 2-7. Rear-Panel Cable Connections
W30
between IF-Display section Jl and RF section
Jl
WI5
w31
ji
w37 W38
J6
J7
Note
2-10 Installation
13. Connect the ac line power cords.
14. If the HP 8566B will be remotely controlled, refer to “To Set the
HP-IB Address” in this chapter.
15. When you turn your instrument on for the first time, you should
perform the verification tests in Chapter 5. Refer to the HP
Operating and Programming Manual
for instructions on using
8566B
the instrument.
Cable W15 is normally connected between the FREQ REFERENCE
EXT and INT BNC ports, providing the HP 8566B with its own internal
10 MHz frequency reference. W15 is removed when an external
frequency reference is used. Cables W37 and W38 are removed for
connection of the IF and VIDEO ports to
the
HP 85650A Quasi-Peak
Adapter. If the instrument is used without the HP 85650A Quasi-Peak
Adapter, W37 and W38 must be connected for
the
instrument to
operate.

To Install Option
010 Instruments
Option 010 mounts the HP 8566B on slides in a rack of 482.6 mm (19
inch) spacing. (Option 010 also contains adapters for mounting in
non-HP racks.)
1. Remove the strap handle on the IF-Display section’s left side
panel.
2. Remove the right-rear lock foot and the right-rear top foot from
the IF-Display section. Slide the right-side cover off to the rear.
Install the right-side cover included in the kit, and replace the
rear lock feet.
3. Remove the front-handle trim from each side of the RF and
Display sections. See @ of Figure 2-8.
Figure 2-8. Removing the Handles and Trim
IF-
4. Remove the three screws securing each handle, and remove the
handles. See @ and
5. The information-card tray located on the bottom of the RF section
requires a space of approximately 2 cm below the instrument
when rack mounting. See Q of Figure 2-9. (No filler strip is
provided.) If you wish to remove the information-card tray,
remove the feet and tilt stands ( @ and
0.
(3J
in Figure 2-9).
Installation
2-11

Figure 2-9. Removing the Information-Card Tray
6. Place the RF section right side up on a level work surface.
7. Place
the
IF-Display section on top of the RF section, offset far
enough forward to allow the RF section hooks to engage the
IF-Display section frame when slid back. Slide the IF-Display
section back until the RF section hooks catch
the
bottom of
the
IF-Display section.
8. Line up the rear-panel lock feet, and tighten the thumb screws on
both lock feet.
9. Attach the 10
l/2-inch
handles with flanges as shown in
Figure 2-10.
2-l
2 Installation
Figure 2-10. Attaching the Rack Handles and Flanges

10. Connect cable W31 between IF-Display section 52 and RF section
J6. See Figure 2-l 1.
11. Connect cable
Jl.
J2
Figure 2-11. Rear-Panel Cable Connections
W30
between IF-Display section Jl and RF section
Jl
w31
w37 W38
12. Determine the ac line voltage to be used.
13. On each instrument section, slide open the power module’s
door (located on the rear panel). See Figure 2-12. Push the
pull lever to the left. Remove the fuse.
fuse
fuse-
Installation 2-13

Line Voltage Setting Card Fuse
Figure 2-12. Voltage Selector Board and Fuse
14. On each power-line module, check the voltage selector card for
the proper ac line voltage. The card’s voltage setting should
be visible on the card. See Figure 2-l 1. If you need to select a
different ac line voltage setting, perform the following:
a. Use needle-nose pliers to pull out the voltage-selector card.
Rotate the card so that the voltage label corresponding to the
actual line voltage will appear in the module window.
b. Push the card back into its slot.
15. Check the fuse to make sure it is of the correct rating and type
for the ac line voltage selected. Fuse ratings for different line
voltages are indicated in the following table.
2-14 Installation
ac Line Voltage
IF-Display Section
100/120 2 amperes FAST BLO
RF Section
4 amperes FAST BLO
HP part number 2110-0002 HP part number 21 lo-0055
220/240
1 ampere SLOW BLO
2 amperes SLOW BLO
HP part number 2110-0007 HP part number 2110-0006
16. Insert the correct fuse, and push the fuse-pull lever into its
normal right-hand position.

17. Attach one slide inner-member bracket to each side of the
instrument using two
M5x0.8~10
pan-head screws per side. See
of Figure 2-13.
Figure 2-13. Attaching the Inner-Member Brackets
QJ
Note
18. Mounting in an HP System Rack Cabinet:
a. Insert two Unistrut nuts, item QJ of Figure 2-13, into each of
the two vertical columns on the left side of the system cabinet.
Insert two Unistrut nuts into each of the two vertical columns
on the right side of the system cabinet.
b. Bolt an outer slide mount to the Unistrut nuts in each side of
the systems cabinet, using four
M5x0.8xl2
pan-head screws per
side. See @ of Figure 2-13.
c. Expand the outer slide mounts to their full length. Mount the
instrument onto the system cabinet by bolting the outer slide
mount to the inner-member bracket on the instrument, using
three
M5x0.8xl2
flat-head screws per side.
If any binding is encountered in the slides after mounting, it will be
necessary to move the Unistrut nuts slightly. While supporting the
instrument, loosen one of the Unistrut nuts. Adjust the slides slightly
until they operate freely. Retighten the Unistrut nut.
19. Mounting in a non-HP System Rack Cabinet:
a. Using hole pattern B, see Figure 2-14, attach one adapter
bracket to the front of each outer slide mount, using two
M4x0.8~12
flat-head screws and nuts per bracket.
Installation 2-15

Figure 2-14. Slide Adapter for Non-HP System Rack Cabinets
b. Using hole pattern B, attach one adapter bracket to the rear of
each outer slide mount, using two
M5x0.8~12
pan-head screws
and nuts per bracket.
c. Bolt an outer slide mount to each side of the system rack
cabinet using
M5x0.8xl2
pan-head screws. Use the bar
nuts provided in the kit if the rack mounting strips have
through-holes.
Note
If any binding is encountered in the slides after mounting, it will be
necessary to slightly move the adapter brackets. While supporting
the instrument, loosen one of the adapter brackets. Adjust the slides
slightly until they operate freely. Retighten the adapter brackets.
20. Connect the ac line power cords.
21. If the HP 8566B will be remotely controlled, refer to “To Set the
HP-IB Address” in this chapter.
22. When you turn your instrument on for the first time, you should
perform the verification tests in Chapter 5. Refer to the HP
Operating and Programming Manual
for instructions on using
8566B
the instrument.
2-16 Installation

Note
Cable W15 is normally connected between the FREQ REFERENCE
EXT and INT BNC ports, providing the HP 8566B with its own internal
10 MHz frequency reference. W15 is removed when an external
frequency reference is used. Cables W37 and W38 are removed for
connection of the IF and VIDEO ports to the HP 85650A Quasi-Peak
Adapter. If the instrument is used without the HP 85650A Quasi-Peak
Adapter, W37 and W38 must be connected for the instrument to
operate.
Installation
2-l
7

To Set the HP-IB Address
The HP-IB address is used in remote programming to identify the
instrument. The decimal address is preset at the factory to 18 (ASCII
2R). Addresses may be decimal 0 through 30. The HP-IB address can
be changed manually from the instrument’s front panel, remotely via
the HP-IB bus, or by setting the instrument’s internal address switch.
The internal address switch is comprised of five switches located
on the Al5 controller assembly in the RF section. These switches
(A15SWl
at instrument power-up. These switches are preset at the factory
to binary 11111 (decimal
HP-IB address stored in RAM memory (or to the default value 18, if
the contents
or other cause). If the switches are set to a value other than 31,
the instrument will always reset the HP-IB address to this value at
power-up.
A2 through A6) determine the HP-IB address to be used
31),
which sets the instrument to the last
of RAM memory are ever lost due to a battery failure
From the Front Panel
From the HP-IB Bus
From the HP-IB
Address Switch
Warning
lb enter a new address from the front panel:
1.
Press
[SHIFT) [ZEXi) p.
2. Use the number keypad to enter the new decimal address.
3. Terminate the entry by pressing (Hz). This changes the current
HP-IB address and stores the new address value in RAM memory.
To enter a new address via the HP-IB bus, refer to the KSP command
in the
HP 8566B Operating and
Changing the HP-IB address by resetting the address switch on
the Al5 Controller Assembly requires the removal of the
section’s protective bottom cover. This should be performed
only by a qualified service person.
instrument to qualified service persons.
1. Disconnect the ac line cord from the RF section.
2. Using a Pozidriv screw driver, remove the two RF section
rear-panel bumpers. See Q in Figure 2-15.
Programming
Refer all such servicing of the
Manual.
RF
2-18 Installation

TOP DOWN
Figure 2-15. Removing the Bottom Cover
3. Back out screw Q (Figure 2-15) and the cover unseats from the
front frame. When the cover is clear of the rear frame, remove the
cover by lifting up.
4. Remove
the
cover from the Al5 controller assembly. See
Figure 2-16 to locate the assembly.
Al5 CONTROLLER
ASSEMBLY
I
I
/
(Locot
of HP-IB
/Switch)
ion
Figure 2-16. Location of Al5 Controller Assembly
Installation
2-19

5. Locate the address switch
A15SWl
as shown in Figure 2-16
and Figure 2-17. Change the switch’s setting according to the
information given below.
The switch comprises six segments, Al through A6. Al must
always be set to logic 1. Each of the remaining five segments, A2
through A6, corresponds to one of the digits of a 5-digit binary
equivalent of the address. See Figure 2-17. The switch is preset at
the factory to binary 11111 (decimal 31). This is a special code
which commands the instrument to use the last input address
(stored in memory) either from the front panel or from HP-IB.
You can reset the switch to correspond to the binary equivalent of
any desired decimal value indicated in Table 2-l. For example, if
the desired address is 4, the
A15SWl
would be set as shown in
Figure 2-18.
Note
Observe that 2’ is represented by the far-left segment of the address
switch.
20
21 22 23 24
I
,
-
= Logic 1
til
= Logic 0
4
\A6 A5 A4 A3
HP- I 8 YADDRESS
A21
Al
2-20 Installation
Figure 2-17. Address Switch (Shown In
Factory
Preset Position)

@6
A5 A4 A3
v
HP-IB ADDRESS
Figure 2-18. Address Switch Set to 4
A~J
Al (Always set at logic 1)
Installation 2-21

6. Replace the cover on the Al5 controller assembly.
7. Replace the RF section’s bottom cover.
able
2-1. Decimal and Binary Address Codes
Decimal Value B-Bit Binary Equivaleni
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
00000
0000 1
00010
00011
00100
00101
00110
00111
01000
01001
01010
01011
01100
01101
01110
01111
10000
10001
10010
10011
10100
10101
10110
10111
11000
11001
11010
11011
11100
11101
11110
2.22
Installation

Specifications
3
Introduction
Frequency
Measurement Range
Displayed Values
Note
Unless noted, all specifications are for AUTOCOUPLED FUNCTION
operation and are with the preselector tracking optimized using the
MARKER PRESELECTOR PEAK function. Where specifications are
subject to minimization
limits are given unless noted. Nominal values provide useful, but
nonwarranted, information about functional performance.
100 Hz to 22
Aging rate
Temperature stability ~7 x
The term frequency reference error, when used later in this manual,
is defined as: f [aging rate/day x number of days since calibration +
temperature stability].
GHz,
Frequency Reference Error and Accuracy
with
dc coupled input
<l
x
10wg/day
lo-’
the error-correction routine, corrected
and < 2.5 x
over
0°C
Accuracy
10B7/year
to 55°C range (25°C reference)
Note
Note
When the analyzer is in STANDBY, the frequency reference
temperature is maintained at a steady state. Frequency accuracy is
then subject to the standard instrument warm-up period indicated in
“General” in this chapter.
Changes in line voltage, gravitational field, and other environmental
conditions will affect
Center Frequency
0 Hz to 22
GHz
the
frequency reference accuracy.
Specifications
3-l

Center Frequency Readout Accuracy
I
1
Spans <n x 5 MHz
I
I&(2%
of frequency span + frequency reference error
Accuracv*
x center frequency + 10 Hz)
Spans >n x 5
MFIz &(2%
of frequency span + n x 100
kHz
+ frequency reference error x center frequency) where n is
the harmonic mixing number, depending on center frequency
Where:
n
= 1 for 100 Hz to 5.8
n
= 2 for 5.8
n
= 3 for 12.5
n
= 4 for > 18.6
Zero Suan
GHz
GHz
to 12.5
GHz
GHz
center frequency.
GHz
center frequency.
to 18.6
GHz
center frequency.
center frequency.
I f freauencv reference error x center freauencv
*After adjusting FREQ ZERO at stabilized temperature. Add 30% of the
resolution bandwidth setting if error correction is not used.
Frequency Span
0 Hz, 100 Hz to 22
GHz
over 10 division CRT horizontal axis; variable
in approximately 1% increments. Two FULL SPAN keys select spans
from 0 to 2.5
GHz
and 2 to 22
GHz.
Frequency Span Readout Accuracy
Range
Readout Accuracy
Spans 5 n x 5 MHz
Spans > n x 5 MHz
Start or Stop
Frequency
Accuracy
100 Hz to 20
f
1% of indicated frequency separation
f3%
of indicated frequency separation
GHz
Same as center frequency.
I
3-2 Specifications

Resolution
Resolution Bandwidth
3 dB bandwidths of 10 Hz to 3 MHz in a 1, 3, 10 sequence. Bandwidth
may be selected manually or coupled to frequency span (AUTO mode).
3 dB Bandwidth Accuracy*
3 MHz
3
kHz
to 1 MHz
10 Hz to 1
*30 kHz
590%
100
kHz
3
kHz
kHz
and 100
relative humidity,
60 dBf3 dB Bandwidth Selectivity Ratio*
to 3 MHz
to 30
kHz
30 Hz to 1 kHz
*60 dB
points on 10 Hz bandwidth are separated by
Bandwidths
kHz
bandwidth accuracy figures only applicable
<4O”C.
Bandwidths
Accuracy
Selectivity
~100
Hz.
f20%
flO%
f20%
<15:1
<13:1
<12:1
Resolution Bandwidth (Option 462 6 dB Bandwidths)
6 dB bandwidths of 10 Hz to 3 MHz in 1, 3, 10 sequence. Bandwidth
may
be selected manually or coupled to frequency span (AUTO mode).
6 dB Bandwidth Accuracy*
3 MHz
30 Hz to 1 MHz
10 Hz
*30 kHz
190%
100
30 Hz to 30
*60 dB
and 100
relative humidity
60 dB/6 dB Bandwidth Selectivity Ratio’
kHz
to 3 MHz
kHz
points on 10 Hz bandwidth are separated by
Bandwidths
kHz
bandwidth accuracy figures only applicable
140°C.
Bandwidths Selectivity
~100
Accuracy
f20%
flO%
+50,
-0%
<ll:l
<8:1
Hz.
Resolution Bandwidth (Option 462 Impulse Bandwidth)
Impulse bandwidth of 1
kHz
to 3 MHz and 6 dB bandwidth of 10 Hz to
300 Hz in 1, 3, 10 sequence. Bandwidth may be selected manually or
coupled to frequency span (AUTO mode).
Specifications 3-3

Impulse Bandwidth Accuracy*
Bandwidths
3 MHz (Impulse Bandwidth)t
1
kHz
to 1 MHz (Impulse Bandwidth)t
10 Hz to 300 Hz (6 dB Bandwidth)
*30 kHz
190%
t
Applicable in 10 dB/DIV
100
30 Hz to 30
*60 dB
Bandwidth Shape
and 100
relative humidity
kHz
to 3 MHz
kHz
bandwidth accuracy figures only applicable
540°C.
60 dB/6 dB Bandwidth Selectivity Ratio*
Bandwidths
kHz
points on 10 Hz bandwidth are separated by
Synchronously-tuned, five-pole filters for 10 Hz to 30
four-poles, 100
kHz
to 3 MHz bandwidth. Approximate Gaussian
Accuracy
+50,
Selectivity
~100
Hz.
kHz
bandwidths;
f20%
flO%
-0%
<ll:l
<8:1
shape optimized for minimum sweep time and smooth pulse response
with
calibrated display.
Spectral Purity
Noise Sidebands’
Offset from Carrier Sideband Level
320 Hz
1
kHz
10
kHz
100
kHz
*For frequency span 525
frequency
Offset from Carrier
from
100
Hz
Power-Line-Related Sidebands *
<360 Hz
360 Hz to
2
kHz
kHz
(except 100
to 5.8
GHz.
5100
-70
-75
Center Frequency
MHz
dBc
dBc
-80
dBc/Hz
-85
dBc/Hz
-90
dBc/Hz
-105
dBc/Hz
kHz
offset) and center
>lOO
MHz to 5.8
-60
-
dBc
*For line conditions specified in “Power Requirements” under
“General” at the end of this chapter.
GHz
3-4 Specifications

Amplitude
Measurement Range
Displayed Values
Measurement range is the total amplitude range over which
the analyzer can measure signal responses. The low value is
determined by sensitivity (10 Hz resolution bandwidth and 0 dB input
attenuation), and the high value by damage level.
Amplitude Measurement Range
Tuned Frequency
Non-Preselected
100 Hz
50
1
MHz to 2.5
Preselected
2.0
5.8
12.5
18.6
to 50
kHz to
GHz
to 5.8
GHz
to 12.5
GHz
GHz
1 MHz
to 18.6
to 22
kHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
-95
-112
-134
-
132
-
125
-119
-114
Range
dBmto+30
dBmto+30
dBm to
dBm to
dBm to
dBmto+30
dBm to
+30
+ 30
+ 30
+30
dBm
dBm
dBm
dBm
dBm
dBm
dBm
Scale
Over a lo-division CRT vertical axis with reference level (0
top graticule line.
dB)
at the
Calibration
Calibration
Lob
I
Log
Linear
L
*Maximum total input power not to exceed
+30.0
Readout expandable to
(-139.9
@iiF) [ATTEN]
7.07 V to 2.2 PV full scale. Readout expandable to 223.6 V*
to 2.2 PV (0.22
[SHIFT) (ATTEN-
10 dB/div for 90 dB display from reference level.
Expanded from reference level:
5 dB/div for 50 dB display
2 dB/div for 20 dB display
1 dB/div for 10 dB display
10% of reference
voltage.
Reference Level Range
to -99.9
dBm
dBm
for 51
(KSI).
,LJV
(KSI).
for <l
or equivalent in
kHz
level/div
+60.0* dBm
resolution bandwidth) using
kHz
resolution bandwidth) using
when calibrated in
dBmV, dBpV,
to -119.9
+30 dBm
volts.
dBm
damage level.
Specifications
3-5

Accuracy
The sum of several factors, listed in “Amplitude Uncertainty,”
determines the accuracy of the reference level readout. Refer to the
“Amplitude Uncertainty” section in this chapter.
Reference Lines
Accuracy
Dynamic Range
Note
Equals the sum of reference level accuracy plus the scale fidelity
between the reference level and the reference line level.
Spurious Responses
Spurious responses are signals generated by the analyzer due to input
signals. For total signal power
harmonic and intermodulation distortion
Input mixer level is defined as the input attenuation subtracted from
the total signal power at the input connector.
Second Harmonic Distortion
Frequency Range
100 Hz to 50 MHz (non-preselected)
50 MHz to 700 MHz (non-preselected)
700 MHz to 2.5
2
GHz
to 22
For mixer levels <- 10
GHz
(non-Dreselected)
GHz
(preselected)
dBm
Third Order Intermodulation
Distortion and Third Order Intercept
s-40 dBm
at the input mixer, all
>70 dB
below input signal.
Distortion
<-70
<-80
<-70
<-100
dBc
dBc
dBc
dBc
34
Specifications
Note
Note
Note
Frequency Range
100 Hz to 5 MHz
5
MHz to 5.8
5.8
GHz
GHz
to 18.6
GHz
>+5
>+7
>+5
TO1
dBm
dBm
dBm
For typical second and third order distortion characteristics, see
Figure 4-4 in Chapter 4, “Performance Characteristics.”
Dynamic range due to TO1 and noise level can be calculated from
[TOI -
displayed average noise level]. For example, at 18
GHz
2/3
the
analyzer’s specified dynamic range when using the 10 Hz resolution
BW is:
2/3
[+ 5
dBm -
(-120
dBm)]
=
2/3(125)
= 83
dB.
Two tone intermodulation distortion products can be calculated from
2 (TO1 - signal level). For example, for two tones at - 33
intermodulation products for a +5
2 [ +5
dBm -(-33)]
= 76 dB down.
dBm
TO1 will be:
dBm,
the

Image, Multiple, and Out-of-Band Responses
Image responses are due to input signals that are two times the IF
frequency above or below the tuned frequency. Multiple responses
are due to input signals mixing with more than one LO harmonic.
Out-of-band responses are due to input signals outside of the selected
frequency band.
Image, Multiple, and Out-of-Rand Responses
*Image Responses: -60
20.0-22
dBc,
18.6-20.0
GHz
GHz;
-50
dBc,
Specifications 3-7

Residual Responses
Residual responses are signals generated by the analyzer independent
of input signals.
Residual
Frequency Range
100 Hz to 5.8
5.8
GHz
12.5
GHz
18.6
GHz
tWith
0 dB input attenuation and no input signal.
$For
100 Hz to 5.8
GHz
to 12.5
to 18.6
to 22
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
range, residual responses are limited by the
appropriate displayed average noise level or -100
Responsest
Residual Responses
c-100 dBm $
c-95 dBm
c-85 dBm
c-80 dBm
dBm,
is
greater.
Gain Compression
cl.0 dB,
100 Hz to 22
GHz
with
s-5 dBm
at input mixer
Displayed Average Noise Level (Sensitivity)
Tuning Range Level
Non-preselected
100 Hz to 50
50
kHz to 1.0 MHz
1.0 MHz to 2.5
Preselected
2.0
GHz
to 5.8
5.8
GHz
to 12.5
12.5
GHz
to 18.6
18.6
GHz
to 22
Average Noise
kHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
*
c-95 dBm
c-112 dBm
c-134 dBm
c-132 dBm
c-125 dBm
c-119 dBm
c-114 dBm
*0 dB input attenuation and 10 Hz resolution bandwidth.
whichever
3-8 Specifications

-40
-50
3 MI
1
ML_
Inn kH,
I I
71 LILA7
I
I
I
I
Y
a
-100
E-110
a-
-140
-90
100
10 Hz
'
Hz
I
1
kHz
I
/
I
10
kHz
1
100
kH(7
kHz
1 MHz 10 MHz 100
1
100
I
I
l MHz
kHz 1
__,
FREQUENCY
Figure3- 1.
Specified Average Displayed Noise Level, 100 Hz to 2.5
Non-preselected Tuning Range
-60
-70
-
-80
E
m
Tl
v
-90
d
>-100
w
1
w
-110
v,
0
z-120
8
2
-130
Y
Q
-140
I
I
MHz
1
GHz
7
r
GHz
-150
2
GHz
3
GHz
5
GHz
10
FREQUENCY
Figure 3-2.
Specified Average Displayed Noise Level, 2.0
Preselected Tuning Range
GHz
GHz
to 22
20
^^ ^I,
LL bHZ
GHz
GHz
Specifications 3-9

Amplitude Uncertainty
The following table summarizes the amplitude measurement
uncertainties along with their respective dependent variables (such
as tuned frequency or reference level range) versus corrected and
uncorrected conditions and ambient temperature ranges.
3-10 Specifications

Amplitude Uncertainty
Source of
Uncertainty Variable
Calibrator
Frequency
Response
(flatness)2p6
Amplitudes
None
input
attenuation
10
dB)
kmulative
kmulative
Absolute
Amplitude
Z!alibration4v6
Dependent With Uncorrected
Tuned Frequency:
100 Hz to 2.5
2.0
GHz
to 12.5
12.5
GHz
to 18.6
18.6
GHz
to 20.0
20.0
GHz
to 22
100 Hz to 20
100 Hz to 22
Applicable when
making absolute
amplitude
measurements
Resolution
Bandwidth
Switching
leferenced
>o
1 MHz RES BW
Log Scale
Switching
Log
Fidelity6 Incremental error for
Resolution
BW:
10 Hz
30 Hz
100 Hz to 1 MHz
3
MHz
Changing Log
Scale
dB
differential
between calibration
and measured signal,
over 0 to 80 dB from
reference level
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
GHz
Readout
(SHIFT)
20°C
f0.3
f0.6
f1.7
f2.2
f2.2
f3.0
f2.2
f3.0
f0.6
f2.0
f0.8
f0.5
f1.0 dB
f0.5
[STOP)
to 30°C
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
(MY)
0°C to 55°C
ztO.3
dB
fl.O
dB
f1.7
dB
f2.2
dB
f3.3
dB
f4.1
dB
f3.3
dB
f4.1
dB
f0.6
dB
f4.0
dB
f2.3
dB
f2.0
dB
f2.0
dB
fl.O
dB
<*O.lO dB/dB 30.15 dB/dB
With Corrected Readoul
&m--
(FREQUENCY
CSTART
SPANS
ISHIFT)
FREQ)
20°C to 30°C
f0.3
f0.6
f1.7
i-2.2
f2.2
f
f
f3.0
f0.6
3.0
2.2
(KSX)’
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
(KSW)
fl.1 dB
f0.4
dB
f0.2
dB
f0.2
dB
fO.l
dB
s&O.
10
dB/dB
&ear
Option 857
Option 857
Fidelity6
Cumulative Error
10 Hz RES BW
Over 0 to 90
Over 0 to 70
130
Hz RES BW
Over 0 to 90
Over 0 to 80
Over 0 to 70
dB
dB
dB
dB
dB
Over top 9-l/2
divisions of displays
Lf2.1 dB
s&O.8
dB
31.5
dB
<ztl.O dB
skO.6
<f3%
dB
of
Reference
Level
sf2.8
dB
skl.5 dB
<iz3%
of
Reference
Level
32.1
skO.8
dB
dB
skl.5 dB
sf1.0 dB
<&to.6
dB
<f3%
of
Reference
Level
Specifications
3-l
1

Aplitude
Uncetainty
(continued)
Source of
Uncertainty Variable
IF
Gain’
RESBW>3kHz
Reference
to -10
dBm
Reference Level
Dependent
Reference Level
0 to -59.9
-60 to -100
with 10 dB input
attenuation
RJ3S
BW 100
Reference Level
0 to -79.9
-80 to -100
RRSBW3OHz
Reference Level
0 to -79.9
-80 to -100
dBm
dBm
Hz-1 kHz
dBm
dBm
dBm
dBm
With Uncorrected
Readout
(TiZ-j
CsTop](KSY)
20°C to 30°C 0°C to 55°C
sf0.6 dB
<&l.O dB
sf0.6 dB
<*l.O dB
sf0.6 dB
sf2.0 dB
<&LO dB
sf1.5 dB
sf1.0 dB
sf1.5 dB
sk1.0 dB
sf2.5 dB
With Corrected
Readout
m
(FREQUENCY
piiq
[START
FREQ](KSX)I
20°C to 30°C
sf0.3 dB
sf1.0 dB
sf0.3 dB
<*l.O dB
sf0.3 dB
sf2.0 dB
SPAN)(KSW)
Log
Digitizing
Linear
Xgitizing6
Zrror
2orrection”
6
Table
RRSBWlOHz
Reference Level
0 to -79.9
-80 to -100
Log Scale:
10
dB
5
dB
2
dB
1
dB
Corr’d function
off or on
Footnotes
dBm
dBm
1
Requires executing the error correction function
[FREQUENCY
SPAN_))
Otherwise a typical amplitude drift may be f0.05
-10
dBm
reference level, 10 dB input attenuation and 1 MHz
sf1.6 dB
sf2.0 dB
f0.2
dB
fO.l
dB
~4~0.04 dB
f0.02 dB
f0.2%
of
ref. level ref. level
N/A N/A
sf2.0 dB
crt2.5 dB
f0.2
dB
fO.l
dB
ho.04
fO.02
f0.2%
dB
dB
of f0.2% of ref.
<fl.O dB
c~t2.0 dB
f0.2
dB
fO.l
dB
f0.04
dB
f0.02 dB
level
f0.4
dB
(m
after stabilization at new ambient temperature.
dB/“C
(at
resolution SW.)
2
Includes input attenuator in 10 dB position, mixing mode, gain
variations, and assuming PRESELECTOR PEAK in current
instrument state. COUPLED FUNCTION not required as long as
MEAS
UNCAL message is not displayed.
3-12 Specifications
3
Supplemental characteristic (typical, nonwarranted performance
parameter).

Assuming internal calibration signal is used to calibrate the
reference level at -10
dBm
and the input attenuator is fixed at 10
dB.
When the error correction function is used, amplitude uncertainty
is introduced because additional IF gain is used to offset the
amplitude errors caused by resolution BW switching and display
scale switching errors.
Unaffected by error correction.
Usable reference level range is a function of resolution bandwidth.
Refer to Displayed Average Noise Level.
For IF-Display sections with serial prefixes 3014A and above,
specification applies over entire display.
Marker
The marker is a bright dot placed upon the display trace and is
positioned horizontally by the DATA controls. The marker amplitude
and frequency are read out continuously.
Frequency Accuracy
Marker
5w
Normal
A
Marker
5Pe
Normal
same as center frequency accuracy.
same as frequency span accuracy.
Amplitude Accuracy
same as reference level accuracy plus scale fidelity
Accuracy
Accuracy
between the reference level and marker position.
A
same as frequency response uncertainty and scale
fidelity between two markers.
Specifications 3-13

Sweep
Sweep Time Accuracy
Inputs
r
5200
seconds sweep times
>200
seconds
UPUT
RF1
Precision Type N female, front panel
100 Hz to 22
Continuous power: + 30
Mixer protected by diode limiter, 100 Hz to 2.5
Pulse power:
attenuation (10
~100 mA
0 to 70 dB in 10 dB steps
Note
GHz,
dc coupled
1100
W, 10
dBm
peak power to input mixer).
damage level
+30 dBm
(1 W) input damage level.
Sweep Time
sween
times
dBm
from
5062
~LS
pulse width and
source.
Accuracy
flO%
It3096
GHz.
11%
duty cycle with 150 dB input
IF INPUT
I Connector
Sensitivity
(
1
dc
SMA female, front panel
-30
dBm
at 321.4 MHz produces 0
Al.0 dB
level 0
bandwidth 1 MHz and a scale 1
+ 10
20 V with rise time of <l
display on CRT when (SHIFT) 0 (KSU) is executed, reference
dBm,
conversion loss set to 30
dBm
continuous power from
V/ps.
dB
dB/div.
5OQ
dB,
resolution
source.
3-14 Specifications

outputs
1ST
SWEEP + TUNE
CAL OUTPUT
LO OUTPUT
OUTPUT
Connector BNC female, front panel
Impedance 500 nominal
Frequency 100 MHz *(frequency reference error x 100 MHz)
AmDlitude
Connector SMA female, front panel
Impedance
Frequency
Amplitude
Maximum Safe Reverse Level +27 dBm
1
Connector 1 BNC female. rear
Impedance 10 kQ nominal
Amplitude
-10
-1
dBm
f0.3
V/GHz
dB
5OQ
nominal
2.3
to 6.1
GHz
>+5 dBm
(l/2 W) total power into
Dane1
of tuned frequency f(2% + 10
500
mV)
Specifications 3-l 5

Options
400 Hz Power Line
Frequency Operation
Option 400
Power Line Related Sidebands*
Offset from Carrier
<2 kHz
2
kHz
to 5.5
*For Center Frequency from 100 Hz to 5.8
Line
Frequency
Line Voltage
I
50 Hz to 60 Hz (service only, not for extended
periods)
400 Hz
kHz
Power Requirements
Specification
400 Hz
operation for servicing only)
I100
Operating Temperature Range
Power Line Frequency
flO%
line frequency (50 Hz to 60 Hz
or 120 V (+5%, -10%)
Sideband Level
GHz
-55
dBc
-65
dBc
Temperature
0°C to 40°C
0°C to 55°C
I
Range
3-16 Specifications

General
HP-IB Interface
Environmental
Functions
SHl,
AHl, T6, L4,
Temperature
SRl, RLl,
PPO,
DCl, DTl,
Cl, C2, C3, C28, E2
Power Requirements
Humidity
Operation:
Storage:
Increased internal temperatures may result if the rear-panel air filters
are not cleaned regularly.
Altitude
Operation:
Storage: 515,240 m (50,000 feet)
50 to
60 Hz; 100, 120, 220,
650 VA (40 VA in standby). 400 Hz operation is available as Option
400.
Operation
Except as noted in electrical specifications, type tested at
relative humidity, 25°C to 40°C for five days.
Storage
5% to 90% relative humidity, 0°C to
0°C to 55°C
-40°C to 75°C
~4,572 m (15,000 feet)
240
or
volts
(+5%, -10%);
40°C.
approximately
<95%
EMI
X-Rays
Conducted and radiated interference is within the requirements
of MIL-STD
within the requirements of CISPR Publication 11 and
Messempfaenger-Postverfuegung
F-Nummer/Funkschutzzeichen).
Serial Prefix 3004A and Above
X-rays generated by this instrument are sufficiently screened.
Die in
abgeschirmt .
accel. voltage / beschl. spg < 20
Serial Prefix 3001A and Below
When operating, this instrument emits x-rays; however, it is well
shielded and meets safety and health requirements of various
countries, such as the X-Ray Radiation Act of Germany. Radiation
emitted by this instrument is less than 0.5
(5) centimeters from the surface of the cathode-ray tube. The x-ray
diesem
461C,
Part 7 RE02 and CEO3 (Air Force), and
526/527/79
geraet entstehende roentgenstrahlung ist ausreichend
kV
(Kennzeichnung Mit
mR/hr
at a distance of five
Specifications 3-17

radiation primarily depends on the characteristics of the cathode-ray
tube and its associated low-voltage and high-voltage circuitry. To
ensure safe operation of the instrument, adjust both the low-voltage
and high-voltage power supplies as outlined in the Performance Tests
and Adjustments manual (if applicable).
Replace the cathode-ray tube with an identical CRT only.
Number of German License:
BW/50/79/ROE
Waehrend des Betriebs erzeugt dieses Geraet Roentgenstrahlung.
Das
Geraet ist so abgeschirmt, dass die Dosisleistung
weniger
als 36
PA/kg (0,5 mR/h)
in 5cm Abstand von der
Oberflaeche der Katodenstrahlroehre betraegt. Somit sind die
Sicherheitsbestimmungen verschiedener Laender,
u.A.
der deutschen
Roentgenverordnung eingehalten.
Die Staerke der Roentgenstrahlung haengt im Wesentlichen
von der Bauart der Katodenstrahlroehre ab, sowie von den
Spannungen,
welche
an dieser anliegen.
Urn
einen sicheren Betrieb zu
gewaehrleisten, duerfen die Einstellungen der Niederspannungsund
des Hochspannungsnetzteils nur
nach
der Anleitung des Handbuches
vorgenommen werden.
Die Katodenstrahlroehre darf nur
durch
die gleiche Type ersetzt
werden.
Das Geraet ist in Deutschland zugelassen unter der Nummer:
BW/50/79/ROE
3-18
Specifications

Warm-Up Time
Operation
Weight
Requires 30-minute warm-up from cold start,
0°C
to 55°C. Internal
temperature equilibrium is reached after 2-hour warm-up at stabilized
ambient temperature.
kequency Reference
From a cold start (no line power connected to HP
8566B),
the
following conditions apply:
~72
hours to meet aging rate specification after
<24-hour
off
period.
~30
days to meet aging rate specification after indefinite off period.
~30
minutes to be within 1 x
(at
25OC).
Total net
RF Section (net)
IF-Display Section (net)
RF Section (shipping)
IF-Display Section (shipping)
10ea
of 24-hour warm-up frequency
Weight
50
kg (112 lb)
29 kg (65 lb)
21 kg (47 lb)
35
kg (78 lb)
27
kg (60 lb)
Specifications
3-l
9

Dimensions
(Allow 100 rrm, 4 inch
clearance at rear
for interconnect cables.)
Dane1
II
-
TOP
457.2 m-r (18 in.)
7
d-626.4
rrm
Figure 3-3. Instrument Dimensions with Handles
(Allow 100
clearance at rear panel
for interconnect cables.)
rrm,
4 inch
(24.7 in)+
SIDE
TOP
3-20
Specifications
425.5 MM (16.75 IN)
Figure 3-4. Instrument Dimensions without Handles

Performance Characteristics
Frequency
Resolution
Note
Supplemental characteristics are intended to provide information
useful in applying the instrument by giving typical, nonwarranted,
performance parameters.
0
10
Spectral Purity
80
10
Hz
100 Hz
1
kHz
10
kHz
100
kHz
OFFSET FREQUENCY
1
MHz
10 MHz 100 MHz
Figure 4-l. Typical Spectrum Analyzer Resolution
Noise Sidebands
Refer to Figures 4-2 and 4-3 for typical noise sideband performance.
Power-Line Related Sidebands
For line conditions specified in “Power Requirements” under
“General” in Chapter 3.
Performance Characteristics
4-l

Power-Line Related Sidebands
Center Frequency
Offset from
Carrier
<360 Hz
360 Hz to 2
>2 kHz
-60
ci
ag
-70
;I”
-80
1,
kHz
5.8-12.6 GHz
-64
-69
-74
dBc
dBc
dBc
12.6-18.6
-60
-65
-70
dBc
dBc
dBc
GHz
18.6-22
-58
dBc
-63
dBc
-68
dBc
GHz
-130
100 Hz
1
kHz
Frequency Offset From Carrier
10
kHz
100
kHz
1 MHz
Figure 4-2.
Single Sideband Noise Normalized to 1 Hz BW versus Offset from
Carrier
4-2 Performance Characteristics

Stability
-
30
N
-
40
?
2- 50
72
-
-
60
0,
-z70
-J-80
73
:- 90
13
z
-100
.VI
-1 IO
a,
0)
-120
.Ii?
-Typical Resolution
-130
-Typical
-140
10
LSpecified
HZ 100 Hz
Noise SB at 5.0
Noise SB at 5.0
1
kHz
10
Frequency Offset From Carrier
GHz
kHz
GHz
100
kHz
1
MHz
IO
Figure 4-3.
Typical SSB Noise at 5.0
GHz
Center Frequency Normalized to 1
Hz BW versus Offset from Carrier and Analyzer Resolution. May
be Limited by Average Noise Level.
Residual FM
MHz
For fundamental mixing (n = 1)
~50 kHz
peak-to-peak, frequency
span >5 MHz
Drift
Because the analyzer is phase-locked at the beginning of each sweep,
drift occurs only during
Frequency Span
5100
kHz
100
kHz
to 5 MHz
25
MHz
the
time of one sweep.
Frequency Drift
Center Frequency Drift*
~10 Hz/minute of sweep time
~500
Hz/minute of sweep time
<5 kHz/minute
of sweep time
*Typical, after 1 hour warm-up at stabilized temperature. COUPLED
FUNCTION not required.
Performance Characteristics
4-3
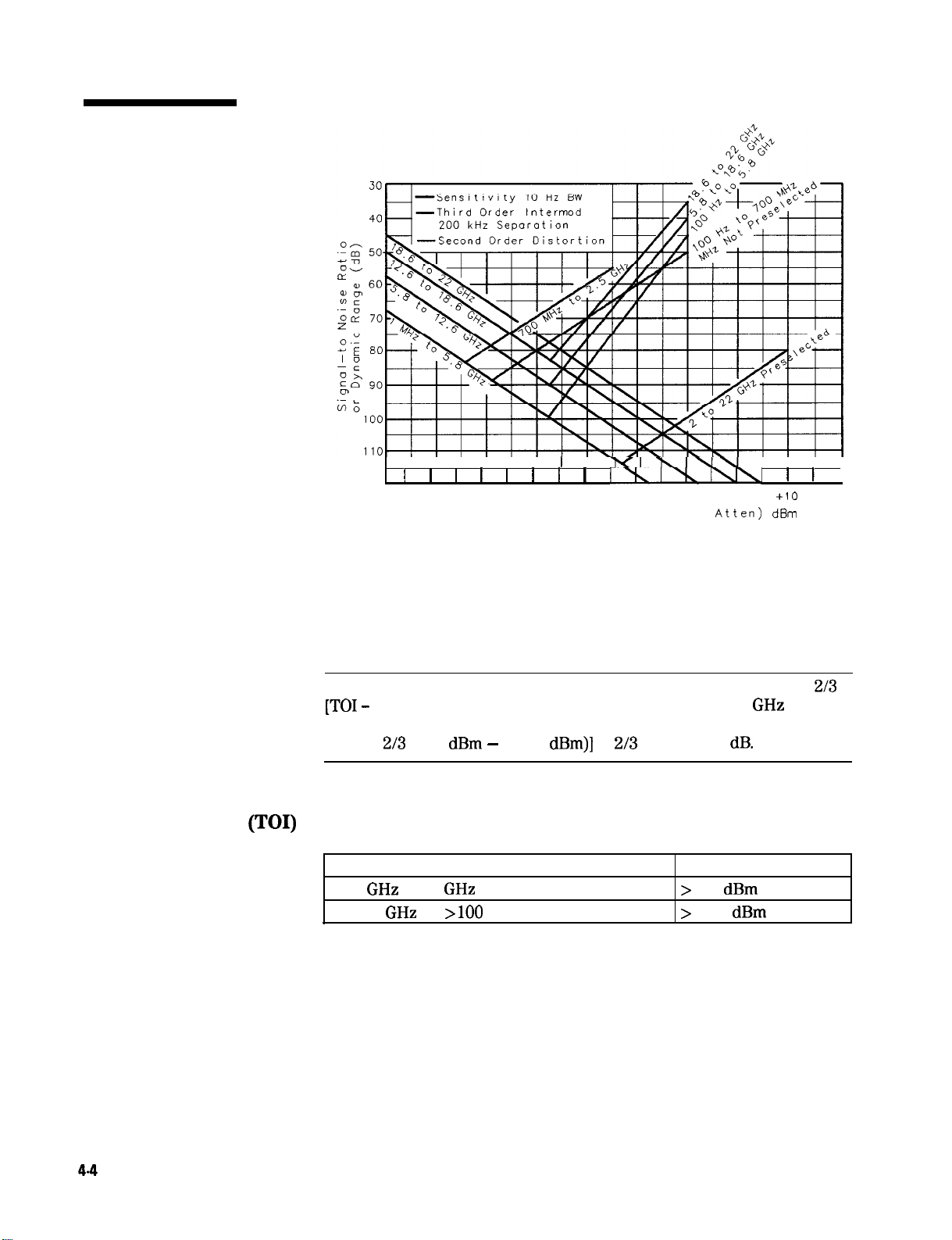
Amplitude
I
I
I
I
120 ’ ’ ’ ’ ’ ’ ’ ’
-70 -60
Effective Input (Signal Level-Input
-50 -40
I
I
I NI
-30 -20
hIUU
‘x’xn!
Figure 4-4. Typical Optimum Dynamic Range
-10
I
’
0
+10
Atten) dBm
I
I
’
Third Order
Intermodulation
Distortion
Note
Third Order Intercept
P-01)
See Figure 4-4 for typical second and third order distortion
characteristics.
Dynamic range due to TO1 and noise level can be calculated from
[TOI -
displayed average noise level]. For example, at 18
GHz
Z/3
the
analyzer’s specified dynamic range when using the 10 Hz resolution
BW is:
18.6
2 to 22
2/3
GHz
GHz
[+ 5
dBm -
Frequency Range
to 22
GHz >
for
>lOO
MHz signal separation
(-120
dBm)]
=
2/3
(125) = 83
Third Order Intercept
+ 5
>
+ 50
dB.
dBm
dBm
TO1
(typical)
(typical)
4-4
Performance Characteristics

Synthesis-Related
Spurious Sidebands
Input Attenuator
Uncertainties
<-90
dBc
Frequency Response Uncertainty (Flatness)
Center Frequency
Attenuator
Setting
0
dB
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
10to70 dB
attenuation
100 Hz to 2.0
2.5
GEtz 1
I
12.4
GHz
to 12.4
I
GHz 1I18
GHz
GHz
to
18
22
GHz
GHz
to
not specified
not specified, accounted for in Frequency Response Uncertainty
f0.4
dB
f0.5
dB 1
f0.7
dB
ho.8
dB
fl.O
dB
&l.O dB
f0.7
dB
dB
f0.9 dB 1 f1.2 dB
f1.6
f2.0
f2.4
f2.8
GHz
GHz
1.0
dB
dB
dB
dB
to 12.4
dB
f1.2
f1.5 dB
f1.8
f2.1
10
100 Hz to
2.5
GIIz
f
0.2
dB
dB
dB
dB
dl3
Step Uncertainty
Center Frequency
2.0
12.4
f
1
18
f
1.0
GEIz
GEz
dB
f1.2
dB
f2.0
dB
f2.5
dB
f3.0
dB
f3.5
dB
f4.0
dB
to 18
22
f
GFfz
GHz
1.5
f0.8
range
to
dB
RF Gain Uncertainty
Example: In changing the input attenuator from 40 to 60
uncertainty of the input attenuator from 2 to 18
the worst case flatness up to 18
GHz
for 60 dB attenuation, f2.4
GHz
is fl.O dB plus
total of f3.4 dB uncertainty.
RF Gain Uncertainty
Tuned Frequency
100 Hz to 2.5
20°C to 30°C
o”cto
55°C
2.0
GHz
to 22
2o"cto
o”cto
30°C
55OC
GHz
sf0.2
jtl.0 dB
GHz
<*0.7
s&1.0
Uncertaintv
dB
dB
dB
Performance Characteristics
dB
the
dB,
a
4-5

Inputs
IF INPUT
Reference Level
(external mixing bands)
Rand
6(K)
7(A)
8(Q)
WJ)
lo(V)
11(E)
WW)
13(P)
14(D)
15(G)
1W-)
17(J)
<2.0:1 at 321.4 MHz
The HP 8566B reference level defaults to a conversion
loss offset associated with
such that the conversion loss and reference level offset
sum to -30
following table.
Freq.
Raw9
18.0-26.5
25.5-40.0
33.0-50.0
40.0-60.0
50.0-75.0
60.0-90.0
75.0-110.0
90.0-140.0
110.0-170.0
140.0-220.0
170.0-260.0
420.0-325.0
dBm.
External Mixing Bands
f10
MHz
the
HP 11970 family of mixers
The default values are shown in the
Mixing
Harmonic
6+
8+
lO+
lO+
14+
16+
18+
24+
30+
36+
44+
54+
Conv.
Loss
18
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
36
38
40
Ref. Level
Offset
-12
-10
-8
-6
-4
-2
0
2
4
6
8
10
RF INPUT
Input
Attenuation
10
dB
0
dB*
*When tuned to within f3 MHz of
22.0
52.5
4-6 Performance Characteristics
Frequency Range
GHz
(preselected)
GHz
(not preselected)
Tune Frequency
100 Hz to 2GHzto
2.5
GElz
1.2
2.3
LO Emission
signal
5.8
GIIz
1.5
3.0
I
I
5.8
GHz
22
GHz
1.9
3.0
Emissions
c-80 dBm
c-90 dBm
to
1
I
I

VIDEO INP
IF INP
Connector BNC female, rear panel
Impedance 503
Frequency 21.4 MHz
-5
dBm
Amplitude
EXT TRIGGER
with 10 dB input attenuation and 0 dB reference level for full screen signal
Connector BNC female, rear panel
Cl
Connector BNC female, rear panel
1
kO,
>+2.4
nominal
V
Impedance
Trigger Level
Maximum Input 5 V
Performance Characteristics 4-7

FREQ REFERENCE
Connector
Impedence
Frequency
Amplitude
Phase Noise and Spurious Signals Analyzer performance will be degraded unless
outputs
EXT
1
BNC female, rear panel
500, nominal
5
MHz
f25
Hz or 10 MHz
f50
Hz
OdBmto +lOdBm
frequency reference phase-noise and spurious signals
are
1140 dBc/Hz,
1
to 10
kHz
offset.
referred to 10 MHz at a 100 Hz
Display Outputs
Recorder Outputs
X, Y, and Z outputs for auxiliary CRT displays. Compatible with
HP 1300 series displays.
3onnectors
BNC female, rear panel
4mplitude
X
Y
2
BLANK
1 V for full deflection
1 V for full deflection
0 to 1 V intensity modulation, -1 V blank
TTL level
>2.4
V for blanking.
Compatible with most oscilloscopes.
xise
Time
X
Y
Z
Outputs to drive all current HP X-Y recorders using positive
or TTL
CLOWER LEFT)
penlift
input.
and [UPPER RIGHT) keys calibrate the recorder SWEEP
and VIDEO outputs with
<75
<75
<30
ns
ns
ns
0,O
and
pencoils
10,l
V respectively, for adjusting X-Y
recorders.
SWEEP
4-8
Performance Characteristics
A voltage proportional to the horizontal sweep of the frequency
sweep generator.
Connector BNC female, rear panel
Amplitude
Impedance 1.7
0 V for left edge, + 10 V for right edge
kdl
nominal

VIDEO
PENLIFT
21.4 MHz IF OUTPUT
Connector BNC female, rear panel
Impedance
Frequency 2 1.4 MHz
Amplitude
Scaling
1
Bandwidth 1 Controlled by the analyzer’s resolution bandwidth setting.
Detected video output (before A-D conversion) proportional to
vertical deflection of the CRT trace.
Connector
Amplitude
During Sweep
(pen down)
During Retrace
(pen up)
5OQ
nominal
-20
dBm
for a signal at the reference level.
Controlled by the input attenuator and IF step gain positions.
Logarithmically related to the RF input signal when in log scales.
Linearlv related to RF
BNC female, rear panel
0 V from
+ 15 V from 10 kQ source
inout
signal when in linear scale.
1OQ
source
FREQ REFERENCE
INT
10 MHz OUT
1
Connector 1 BNC female. rear
Impedance 500 nominal
Freauencv 10.000 MHz
1
Amplitude IO
Connector BNC female, rear panel
dBm
Dane1 1
II::stdyIIIl
Performance Characteristics
4-9

VIDEO OUT
IF OUT
IF OUTPUT
Connector
Impedance 500 nominal
Frequency
Maximum Safe
Reverse Level
ac + 10
dc
SMA female, front panel
32 1.4 MHz nominal
dBm
continuous power from 503 source
20 V with rise time of <l
V/us
General
Acoustic Noise
Emission/
Geraeuschemession
This instrument is in conformance with the German Regulation
on Noise Declaration For Machines (Laermangabe nach der
Maschinenlaermrerordnung - 3. GSGV Deutschland).
LPWW
am
Arbeitsplatzl
(operator position)
1 Testing was conducted per IS0 7779
and DIN 45635 teil 1.
4-l 0 Performance Characteristics

Function Descriptions
Sweep
Trigger
Characteristics
Free Run
Line
Video
Sweep triggered by internal source.
Sweep triggered by power line frequency.
Sweep triggered by detected waveform of input signal at
an
adjustable level; signal must be 20.5 div peak-to-peak.
For sweeps of 10 ms and less (zero span) the signal must
have
>40 Hz rate. [SHIFT)
(VIDEO) (KSy)
allows any envelope
rate,
but display will blank between triggers when sweep is
<20
ms.
External
Sweep triggered by rising edge of signal input to
rear-panel
BNC connector; trigger source must be >2.4 V (10 V
maximum).
For sweep of 10
ms
and less (zero span), trigger source
must
have
>40
Hz rate.
[SHIFT_) IEXT_) (KSx)
allows any trigger
source rate, but display will blank between low
repetition rate
trigger when sweep is
2ontinuou sequential sweeps initiated by the trigger:
~20
ms.
20 ms full span to 1500 s full span in approximately 1%
increments.
Single
Single sweep armed on activation and initiated by trigger
(sweep
220
ms
only).
Sweep Time
Zero Frequency Span. 1
~LS
full sweep (10 divisions) to 10 ms full
sweep in 1, 2, 5 sequence (no digital storage); 20 ms full sweep to
1500 s full sweep in approximately 1% increments.
Marker. Sweeps 220 ms only. Normal: displays time from beginning
of sweep to marker position. A: Displays time difference between
stationary and tunable marker
Video Bandwidth
Post-detection low-pass filter used to average displayed noise;
bandwidth variable from 1 Hz to 3 MHz in a 1, 3, 10 sequence.
All bandwidths are nominal except 3 MHz, which is a minimum.
Video bandwidth may be selected manually or coupled to resolution
bandwidth.
Performance Characteristics
4-l
1

Cathode Ray Tube
Type: Post-deflection accelerator, aluminized P31 phosphor,
electrostatic focus and deflection.
Viewing Area: Approximately 9.6 cm vertically by 11.0 cm
horizontally (3.8 in x 4.7 in). The CRT is completely turned off with
(SHIFT)
(trace B,
CCLEAR
WRITE) (trace B,
KSh)
to avoid unnecessary aging of the CRT during long-term
KSg
and on with [SHIFT)
[MAXHOLD]
unattended operation of the analyzer.
Instrument State Storage
Up to six complete sets of user-defined control settings may be stored
and recalled by pressing SAVE or RECALL and the desired register
number (1 to 6) from the keyboard. Register 0 stores the current state
while register 7 stores the instrument state prior to the last function
change via the numeric/unit keyboard, step keys, or INSTR PRESET.
Registers 8 and 9 store the two instrument calibration states.
To lock the save registers press
save registers, press
[SHIFT)
(RECALL) (KS)
(SHIFT) (=I (KS( ).
).
To unlock the
Instrument state information stored in registers 0 through 7 is
retained in memory for approximately 1 year in STANDBY mode or
after line power is removed and analyzer is stored between 20°C and
30°C.
Remote Operation
The standard HP 8566B operates on the Hewlett-Packard Interface
Bus (HP-IB). All analyzer control settings (with the exception of
VIDEO TRIGGER LEVEL, FOCUS, ALIGN, INTENSITY, FREQ ZERO,
AMPTD CAL, and LINE power) are remotely programmable. Function
values, marker frequency/amplitude, and
A/B
traces may be output;
CRT labels and graphics may be input.
LCL: Returns analyzer to local control, if
Service Request: (SHIFT)
OLIN) (KSr)
not
locked out by controller.
calls an HP-IB request for service.
4-12 Performance Characteristics

Operation Verification
5
What You’ll Find in
This Chapter
This chapter describes the HP
Software and how to use it to verify spectrum analyzer operation.
Test System Configuration
Equipment Connections
Program Loading
Program Operation
HP-IBAddresses
Error Messages
Test Descriptions
1. Input Attenuator Switching Uncertainty
2. IF Gain Uncertainty
3. Scale Fidelity (Log)
4.
Scale
Fidelity (Linear)
5. Log
6. Resolution Bandwidths
6. Impulse and Resolution Bandwidths
7. Line Related Sidebands
8. Average Noise Level
9. Residual Responses
10. Sweep + Tune Out Accuracy
11. Second Harmonic Distortion
12. Frequency Span Accuracy
13. Gain Compression
14. Frequency Response
15. Third Order Intermodulation Distortion
16. Cal Output Amplitude Accuracy
17.
Scale
1st
LOOutput
..................................................
..............................................
.................................................
...................................................
.................................................
Switching
Power
8566A/B
........................................
..........................................
........................................
.........................................
.....................................
........................................
.....................................
....................................
.......................................
.........................................
.........................................
......................................
....................................
Operation Verification
..................
.......................
.............................
..............................
................................
..................
..........................
.5-4
.5-5
5-6
..5- 7
..5- 9
..5- 9
..5- 9
.5-10
.5-l
1
5-12
.5-13
.5-14
5-15
.5-16
.5-17
.5-18
5-19
.5-20
.5-2 1
.5-22
5-23
.5-24
.5-25
.5-26
..5-2 7
Operation Verification is automatic performance test software
designed to give a high confidence level in the operation of the
HP
8566A/B
to 85% of the manual performance tests in approximately 60 minutes
and is designed to test an instrument operating within a temperature
range of
If an HP 8566AB passes all Operation Verification Tests, be assured
that the spectrum analyzer is performing within the specifications
indicated in each test. These specifications are representative of the
specifications listed in Chapter 3. Refer to Chapter 3 for the actual
specifications. If a test does not pass, its related manual performance
test needs to be run. Related manual performance test are located in
the
HP
The HP 8566AB Operation Verification software automates
the majority of the manual performance tests for performance
verification.
included in the automated Operation Verification software.
Spectrum Analyzer in a reasonable time. It performs 80%
20”
to
30”
C. Refer to
8566A/B Rzrformance
‘lkble
5-2 lists the manual performance tests that are not
‘Ikble
5-1 for a list of tests performed.
Ests and Adjustments Manual.
Operation Verification
5-l

Note
The validity of the measurements in the Operation Verification
program is based in part on the accuracy of the test equipment
used to perform the test. Therefore, proper calibration of the test
equipment must be verified before instrument operation can be
checked using the Operation Verification program.
Note
Note
Measurement uncertainties may cause the Operation Verification
program to indicate that an instrument specification is out of
tolerance, even though the Performance Test in the Tests and
Adjustments Manual indicates it to be within tolerance. In this event,
the Performance Test Data is to be considered more valid.
The Option 462 6 dB Bandwidth instrument shares the same
Operation Verification software as the Option 462 Impluse Bandwidth
instrument. When testing the 6 dB version, Test 6 Impulse and
Resolution Bandwidths must not be performed and the following
manual tests must be performed:
n
6 dB Resolution Bandwidth Accuracy Test
n
6 dB Resolution Bandwidth Selectivity Test
The manual tests are located in the
HP 85668
Perforrnunce 2kt.s
Adjustments Manual.
lhble
5-l. Tests Performed
‘I&t
Number and Name
1. Input Attenuator Switching Check
2. IF Gain Uncertainty
3. Scale Fidelity (Log)
4. Scale Fidelity (Linear)
5. Log Scale Switching Uncertainty
6. Resolution Bandwidths
Equipment Required
HP 3335A
HP 3335A
HP 3335A
HP 3335A
HP 3335A
none
6. Impulse and Resolution Bandwidths HP 8112A or HP 8116A
(Option 462 Impulse Bandwidth)*
7. Line-Related Sidebands
8. Average Noise Level
9. Residual Responses
10. Sweep + Tune Out Accuracy
11. Second Harmonic Distortion
HP 3335A
none
HP
909A,
Option 012
HP
909A,
Option 012
HP 3456A or HP 3455A
HP 3335A
50 MHz Low Pass Filter
HP
12. Frequency Span Accuracy
83640At
APC 3.5 Low-Loss Microwave
Cable HP part number 8120-4921
and
5-2 Operation Verification

able
5-1. Tests Performed (continued)
Test Number and Name
13. Gain Compression
HP
83640At
Equipment Required
HP 8902A or HP 436A or HP 438A
HP 8485A or HP 8481A
HP 11667B or HP 11667A
APC 3.5 Low-Loss Microwave
Cable HP part number 8120-4921
14. Frequency Response
HP 3335A
HP
83640At
HP 8902A or HP 436A or HP 438A
HP 8485A or HP
HP
11667B
or HP
8481A$
11667At
APC 3.5 Low-Loss Microwave
Cable HP part number 8120-4921
15. Third Order Intermodulation
HP 3335A
HP
83640At
HP 8721A
APC 3.5 Low-Loss Microwave
Cable HP part number 8120-4921
50 MHz Low Pass Filters
16.
Cal
Output Amplitude Accuracy HP 8902A or HP 436A or HP 438A
HP 8485A or HP 8481A
17. First LO Output Power
HP 8902A or HP 436A or HP 438A
HP 8485A or HP 8481A
‘Option 462 6 dB Bandwidth instruments must be manually tested. See note.
IAlternate sources are :
HP
8341A/B.
(Frequency Response testing is limited by the frequency range of
83620A,
HP
83623A,
HP
83650A,
HP
8340A/B,
HP
the source)
ITesting
limited to 18.0
GHz
with HP 8481A and HP
11667A.
and
‘Ihble
5-2. Tests Not Performed
Center Frequency Readout Accuracy Test
Sweep Time Accuracy Test
Noise Sidebands Test
Harmonic and Intermodulation Distortion Test
Image, Multiple, and Out-of-Band Responses Test
Fast Sweep Time Accuracy Test (~20 ms)
Frequency Reference Error Test
Operation Verification
5-3

‘Ihble
5-3. Equipment Summary
HP Fart Number Equipment
HP 9000 Series 200 or HP 9000 Series 300 Computer*
HP 3335A
HP 3455A or HP 3456A
HP
83640At
HP 8902A
or HP 436A or HP 438A Power Meter
HP 8485A or HP
HP 8112A or HP
HP
909A
Option 012 50 Ohm Termination
HP 8721A
HP 11667B or HP
HP part number 0955-0306
HP part number 8120-4921
HP-IB Printer
Miscellaneous Cables and Adapters
‘HP 98624A HP-IB Interface is needed for dual-bus systems. 300K of free
memory is required for the test program.
8481Az
8116As
11667At
Frequency Synthesizer
System DVM
Synthesized Sweeper
Measuring Receiver
Power Sensor
Pulse Generator
Coaxial Directional Bridge
Power Splitter
50 MHz Low Pass Filter (2 needed)
APC 3.5 Low-Loss Microwave Test Cable
t
Alternate sources are HP
HP
tTesting
iRequired to test Option 462 Impulse Bandwidth.
Tkst
System
Configuration
8341A/B.
(Testing limited by the frequency range of the source.)
limited to 18.0
The HP
Series 200 or HP 9000 Series 300 Computer with HP BASIC 2.0 and
Extensions 2.1 or BASIC 3.0 or higher. An HP 362 or HP 382 can also
be used and requires BASIC 6.2 or higher. The program operates on
either a single or dual HP-IB computer system. For a dual bus system
it is also necessary to have an HP 98624A HP-IB Interface to connect
the HP
The Operation Verification software is designed for optimum operation
with a dual bus system. The dual bus system is used with the
Microwave Test Set (MTS). In this configuration, the bus for the test
equipment has a select code of 7, while the bus for the instrument
under test has a select code of 8. The software will adapt itself to a
single bus system if an HP 98624A HP-IB Interface at select code 8 is
not present.
83620A,
GHz
with HP 11667A and HP 8481A.
8566A/B
8566A/B
HP
83623A,
Operation Verification program requires an HP 9000
to the computer separately from the test equipment.
HP
83650A,
HP
8340AB,
and
5-4 Operation Verification

The equipment needed to perform the HP
Verification is listed in both
‘Ihble
5-l and
a test-by-test listing of the equipment needed, and
8566AD3
‘Ihble
5-3.
Operation
Table
5-l includes
‘Ihble
5-3 includes
a test equipment summary. To obtain a permanent record of the test
results an HP-IB printer is required. The HP
8566A/B
CRT display
may be selected to display the test results if a permanent test record
is not desired.
Note
Equipment Connections
Note
A change of the results for each test is expected over a period of
time; therefore, Hewlett-Packard warrants only the specification range
and not the repeatability of the data for any given specification.
For a dual bus system, connect the test equipment to the computer
as shown in Figure 5-l. The instrument under test is connected
separately to the HP 98624A Interface card. For a single bus system,
connect the test equipment and instrument under test to the
computer as shown in Figure 5-2.
Turn the HP
8566A/B
(LINE) switch on and allow a 2 hour warm-up.
Also, allow sufficient warm-up time for the other test equipment as
indicated in the individual operating and service manuals.
When connecting signals from the synthesized sweeper to the test
setup, it is necessary to use a microwave test cable with minimum
attenuation to 22
GHz.
BUS to Unit Under Test
Select Code of 8.
Figure 5-1. Dual Bus
(MTS)
System Connection
(HP8566B)
Operation Verification 5-5

BUS to Unit Under Test
(HP8566B)
Program Loading
L
Figure 5-2. Single Bus System Connection
To load and run the HP
8566A/B
Operation Verification program, one
BUS to MTS System
of the following HP BASIC Language Systems is required:
n
BASIC 2.0 with Extensions 2.1
w
BASIC 3.0 or higher including the following binaries:
•I MAT
0 IO
•I GRAPH
•I HPIB
•I ERR (not required but recommended)
w
BASIC 6.2 or higher must be installed in the HP
362/382
For additional computer configuration instructions, refer to the
Installation Reference Manual included with the HP BASIC Language
System.
5-6 Operation Verification
The HP 8566AB Operation Verification program stores configuration
and power sensor calibration data in files on the floppy disk. Inspect
the floppy disk to verify that it is not write-protected, and insert it
into
the
appropriate disk drive. Then type:
LOAD "VERIFY 66" 1
Press
(m)
-
,
on HP 9000 Series 200 computers, or
(W)
on
HP 9000 Series 300 computers, to load and run the program.

Program Operation
The Operation Verification program uses the HP
8566A/B
display to
display program options and status, and allows the user to select
options using the spectrum analyzer keyboard. The first few displays
provide the user with selection menus for configuring the software to
the available test equipment.
After the program name and revision is displayed for several seconds,
the LIST OF DEFAULTS display appears, providing the user with a
selection menu. At this point in the program, the user must enter
the HP model numbers and HP-IB addresses of
the
test equipment
that will be used, as well as the local ac power line frequency. lb
change one of the entries, position the pointer using the frontpanel
knob and press
IHz).
Then, enter the appropriate HP-IB address, serial
number, line frequency, or one of the valid model numbers listed in
Table 5-4. It is sometimes desirable to perform specific Operation
Verification tests without the full set of test equipment listed in
lhble 5-4. For example, several of the tests can be performed with no
test equipment by using the spectrum analyzer CAL OUTPUT signal
as an input signal. If an item of test equipment is not available, it
is not necessary to change the corresponding default entries in the
LIST OF DEFAULTS display. From the LIST OF DEFAULTS display,
the user may proceed with the program by pressing
1Hz).
However, a
valid power sensor calibration data file must exist on the software
disk before the program will proceed with testing. If such a file does
not exist, the program will prompt the user to enter calibration data
through the computer keyboard. The sensor calibration data is then
stored on the software disk. An existing power sensor calibration
data file may be reviewed or modified by reentering the power sensor
serial number in the LIST OF DEFAULTS display.
After the LIST OF DEFAULTS display, the next display allows the user
to select whether the test results will be printed out or displayed on
the spectrum analyzer CRT.
Next, the program checks to verify that each piece of test equipment
responds at its designated HP-IB address. The user is prompted with a
list of test equipment that does and does not respond, and is offered
the choice of continuing with the program, repeating the equipment
check, or returning to
the
LIST OF DEFAULTS display to change HP-IB
addresses. The program will automatically limit the number of tests
that can be performed, based on this list of available test equipment.
If the user chooses to proceed by pressing (Hz), the program attempts
to measure the spectrum analyzer CAL OUTPUT signal, and prompts
the user to connect the CAL OUTPUT to the RF INPUT and adjust the
front-panel AMPTD CAL and FREQ ZERO controls as appropriate.
Refer to Figure 5-3 for the location of the AMPTD CAL and FREQ
ZERO controls. Once these adjustments are within tolerance, the
program activates the spectrum analyzer error correction (KSW)
routine.
Once the error correction routine has completed, a test summary is
displayed on both the computer and the spectrum analyzer. Both test
summaries provide a status report on test progress. In addition, the
test summary displayed on the spectrum analyzer provides the user
with a selection menu of individual tests. The user enters the number
Operation Verification 5-7

of the desired test, followed by
(kHz)
to perform the test repetitively. If the user selects “All Tests”
IHz)
to perform the test one time, or
(selection 0), the program will run each of the tests in sequence,
skipping those tests that cannot be performed with the available test
equipment.
Test results are printed or displayed at the completion of each
individual test. Once a particular test is completed, the test summary
displays are updated to reflect whether the test passed.
FREQ. ZEROFREQ. ZERO
HP-IB Addresses
CdL
OUTPUT
Figure 5-3. RF Input and Calibration Controls
‘Ihble
5-4 lists the default assigned addresses and test equipment. For
AMbTD
CAL
dual bus systems, the select code for the test equipment is 7 and the
select code for the instrument under test is 8. (The address for the HP
8566A/B
under test is 818.) In single bus systems, the select code for
the test equipment is 7 and the select code for the instrument under
test is 7.
‘able
5-4. HP-IB Addresses
Equipment
Frequency Synthesizer
Pulse Generator’
System DVM
Synthesized Sweeper
Measuring Receiver
HP Model
HP 3335A
HP 8112A or HP 8116A
HP 3455 or HP 3456A
HP
8340A/B
HP 8902A
Address
04
16
22
19
14
5-8
Operation Verification
HP-IB Printer
1 Required to test Option 462 Impulse Bandwidth.
01

Error Messages
Self-explanatory error messages are incorporated into the Operation
Verification program to assist you in identifying errors.
‘I&t
Descriptions
The following test descriptions list the Specifications, Related
Performance Test, and Test Description for each test performed by the
Operation Verification program. The specifications listed below are
those of each Operation Verification test and are uncorrected (where
applicable). Operation Verification is designed to test an instrument
operating within a temperature range of
20°C
to
30°C.
Operation Verification 5-9

1. Input Attenuator Switching Check
Specification None
Related Performance
Test
Description
None
This is included as an aid to verify operation only and to assist in
troubleshooting.
A signal source of known amplitude is connected to the spectrum
analyzer and the analyzer is adjusted for a reference. The input
attenuator is stepped down from 10 dB to 70
level and the signal source are stepped up. This maintains the signal
peak at the same approximate location on the display. The amplitude
of the signal is measured at each step using the marker function on
the spectrum analyzer.
dB,
while the reference
5-l 0Operation Verification

2. IF Gain
Uncertainty
2. IF Gain Uncertainty
Specification
Related Performance
Test
Description
0.0
dBm
to -55.9
-56.0
dBm
to -129.9
IF Gain Uncertainty Test
A signal source of known amplitude is connected to the spectrum
analyzer and the analyzer is adjusted for a reference level. The
amplitude of the signal peak is measured in 0.1 dB steps from -0.1
to -1.9
from -10 dB to -120
dB,
in 2 dB steps from -1.9 dB to -9.9
dBm;
dB.
f0.6
dBm;
dB
fl.O
dB
dB,
and in 10 steps
dB
Operation Verification
5-11

3. Scale Fidelity
WV0
Specification
< f
1 .O dB max over 0 to 80 dB display
5 f1.5dBmax
over
0to90 dB
display
Related Performance
Test
Description
Scale Fidelity Test
The specification listed is for cumulative error. Only cumulative error
is measured in this procedure.
A signal source of known amplitude is connected to the spectrum
analyzer and the analyzer is adjusted for a reference. The signal
source is stepped down in 1 dB steps and the displayed signal
amplitude on the spectrum analyzer is measured at each step. This
measurement is performed in both the 3
kHz
and 300
kHz
bandwidths,
5-l 2Operation Verification

4. Scale Fidelity (Linear)
Specifkation
f
3% of Reference Level
4. Scale Fidelity (Linear)
Related Performance
Test
Description
Scale Fidelity Test
A signal source of known amplitude is connected to the spectrum
analyzer and the analyzer is adjusted for a reference. The signal
source is stepped down from -10 dB to -30 dB in 10 dB steps, and
the amplitude of the displayed signal is measured using the marker
function. This measured value is used to calculate the percent error
from the established reference level.
Operation Verification
5-13
 Loading...
Loading...