Page 1

HP 4286A RF LCR meter
User's Guide
SERIAL NUMBERS
This manual applies directly to instruments with serial number prex JP3KC and
above, or whose rmware is version 2.0. For additional important information
about serial numbers, read \Serial Number" in Appendix A of this manual.
HP Part No. 04286-90031
Printed in JAPAN April 1999
Forth Edition
Page 2

Notice
The information contained in this document is subject to change without notice.
This document contains proprietary information that is protected by copyright. All rights are
reserved. No part of this document may be photocopied, reproduced, or translated to another
language without the prior written consent of the Hewlett-Packard Company.
Hewlett-Packard Japan, LTD.
Kobe Instrument Division
1-3-2, Murotani, Nishi-ku, Kobe-shi,
Hyogo, 651-2241 Japan
R
MS-DOS
APC-7
is a U.S. registered trademark of Microsoft Corporation.
R
is a U.S. registered trademark of Bunker Ramo Corporation.
c
Copyright 1995, 1998, 1999 Hewlett-Packard Japan, LTD.
Page 3

Manual Printing History
The manual printing date and part number indicate its current edition. The printing date
changes when a new edition is printed. (Minor corrections and updates that are incorporated
at reprint do not cause the date to change.) The manual part number changes when extensive
technical changes are incorporated.
June 1995
July 1995
September 1998
April 1999
::::::: :::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::
::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: :
:::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: :
Second Edition
::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: ::::::: ::::::: :::::: :::
First Edition
Third Edition
Forth Edition
iii
Page 4

Safety Summary
The following general safety precautions must be observed during all phases of operation,
service, and repair of this instrument. Failure to comply with these precautions or with specic
WARNINGS
elsewhere in this manual may impair the protection provided by the equipment.
In addition it violates safety standards of design, manufacture, and intended use of the
instrument.
The Hewlett-Packard Company assumes no liability for the customer's failure to comply with
these requirements.
Note
HP 4286A is designed for use in INSTALLATION CATEGORY II according to IEC
61010-1 and POLLUTION DEGREE 1 according to IEC 61010-1 and IEC 60664-1.
HP 4286A is an INDOOR USE product.
Note
LEDs in HP 4286A are Class 1 in accordance with IEC60825-1.
CLASS 1 LED PRODUCT
Ground The Instrument
To avoid electric shock hazard, the instrument chassis and cabinet must be connected to a
safety earth ground by the supplied power cable with earth blade
.
DO NOT Operate In An Explosive Atmosphere
Do not operate the instrument in the presence of ammable gasses or fumes
. Operation of any
electrical instrument in such an environment constitutes a denite safety hazard.
Keep Away From Live Circuits
Operating personnel must not remove instrument covers. Component replacement and internal
adjustments must be made by qualied maintenance personnel. Do not replace components
with the power cable connected. Under certain conditions, dangerous voltages may exist even
with the power cable removed. To avoid injuries, always disconnect power and discharge
circuits before touching them.
DO NOT Service Or Adjust Alone
Do not attempt internal service or adjustment unless another person, capable of rendering rst
aid and resuscitation, is present.
DO NOT Substitute Parts Or Modify Instrument
Because of the danger of introducing additional hazards, do not install substitute parts
or perform unauthorized modications to the instrument. Return the instrument to a
Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Oce for service and repair to ensure that safety features
are maintained.
iv
Page 5

Dangerous Procedure Warnings
Warnings
, such as the example below, precede potentially dangerous procedures throughout
this manual. Instructions contained in the warnings must be followed.
Warning
Dangerous voltages, capable of causing death, are present in this
instrument. Use extreme caution when handling, testing, and adjusting
this instrument.
v
Page 6

Typeface Conventions
Bold
Boldface type is used when a term is dened. For example:
icons
are
symbols.
Italics
Italic type is used for emphasis and for titles of manuals and other
publications.
Italic type is also used for keyboard entries when a name or a variable
Computer
4
HARDKEYS
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SOFTKEYS
must be typed in place of the words in italics.For example:
lename
type the name of a le such as
means to type the word
file1
copy
, to type a space, and then to
.
Computer font is used for on-screen prompts and messages.
5
Labeled keys on the instrument front panel are enclosed in45.
Softkeys located to the right of the CRT are enclosed in
copy
NNNNN
.
Assistance
Product maintenance agreements and other customer assistance agreements are available for
Hewlett-Packard products.
For any assistance, contact your nearest Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Oce.Addresses
are provided at the back of this manual.
Safety Symbols
General denitions of safety symbols used on equipment or in manuals are listed below
Instruction manual symbol: the product is marked with this symbol when it is
necessary for the user to refer to the instruction manual.
Alternating current.
Direct current.
On (Supply).
O (Supply).
This
Warning
sign denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a procedure
condition or the like, which, if not correctly performed or adhered to, could
result in injury or death to personnel.
This
Caution
sign denotes a hazard. It calls attention to a procedure, practice,
condition or the like, which, if not correctly performed or adhered to, could
result in damage to or destruction of part or all of the product.
Note
denotes important information. It calls attention to a procedure,
practice, condition or the like, which is essential to highlight.
Axed to product containing static sensitive devices use anti-static handling
procedures to prevent electrostatic discharge damage to component.
.
, practice,
vi
Page 7

Contents
1. Brief Description of the HP 4286A
Front and Rear Panels ............................ 1-2
2. Installation and Set Up Guide
Incoming Inspection ............................. 2-1
Rack Mounting .............................. 2-3
Power Cable . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-5
Power Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Ventilation Requirements . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-7
Instruction for Cleaning ...... ...... ...... ...... ... 2-7
Connecting the Connector Box ........................
2-7
Connecting the Test Head . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting the Test Head with L-type Coaxial Adapter (Option 022 only) . . 2-9
Connecting the APC-3.5 to 7mm Adapter ...................
Connecting a Keyboard (Option 1C2 Only) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3. Basic Measurement Procedures
Measurement Outline ............................
Basic Measurement Flow . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Required Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
1. Power ON ................................
Line Input Receptacle ...........................
Fuse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Steps to turn on the power . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
2. Setting up the HP 4286A ......................... 3-5
2-1. Setting up for Ls-Q Frequency Characteristics Measurements . . . . . . . 3-5
2-2. Creating a sweep table ........................ 3-5
2-3. Setting the OSC level .... ...... ...... ...... ... 3-5
3. Calibration . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Calibration Procedure ...........................
4. Connecting the Test Fixture ........................
Selecting a Test Fixture ..........................
Connecting the Test Fixture to the Test Head ................ 3-12
5. Setting the Electrical Length of the Test Fixture ...... ...... .. 3-14
6. Fixture Compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Performing SHORT Compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SHORT Compensation Key Sequence ................... 3-17
Performing OPEN Compensation ...... ...... ..... ..... 3-18
OPEN Compensation Key Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
7. Connecting the DUT to the Test Fixture ...... ...... ......
8. Measuring the DUT ............................
2-9
2-10
2-11
3-2
3-2
3-3
3-4
3-4
3-4
3-7
3-7
3-12
3-12
3-15
3-15
3-18
3-19
3-20
Contents-1
Page 8

4. HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Dierentiation of DUTs through BIN Sorting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-2
Editing BIN Table ............................. 4-2
Setting up Handler Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-3
BIN Sorting ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... .. 4-3
GO/NO-GO Test with Limit Test Function ................... 4-4
Editing Limit Table . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-4
Setting up Handler Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-5
Limit Test................................. 4-6
Contact Check . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-7
Setting up Beeper .............................. 4-8
Display Updating ON/OFF .......................... 4-9
Setup Linking HP 4286A and Chip Handler .................. 4-10
Setting up Handler Interface Board . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-11
Checking Default Settings .. ...... ...... ...... ..... 4-11
Selecting Settings ............................. 4-12
Changing Settings ............................. 4-13
Removing the Top Cover . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
Setting up Control Output Signal and DC Isolated Input Signal ....... 4-13
Using External Power Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-14
Using Internal Power Source .. ...... ...... ...... ..
Setting up the Internal Power Source . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mounting the Top Cover .......... ...... ...... ...
Mounting a Pull-up Resistor ...... ...... ...... ......
Pull-up Resistor for Comparator Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pull-up Resistor for Control Output Signal . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Setting up Output Signal Pattern ......................
HP 4286A Measurement Time ...... ...... ...... ......
Electrical Specication of Handler Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Signal Output Mode ............................
Signal Lines . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Pin Assignment and Signal Denitions (Mode 1) ...............
Pin Assignment and Signal Denitions (Mode 2) ...............
Electrical Characteristics of Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DC Isolated Output Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DC Isolated Input Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-35
Handler Interface Board Switches ...... ...... ..... .... 4-37
Top Cover Removal ............................ 4-37
Tools Required . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-37
Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-37
Top Cover Attachment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Procedure . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Performing Calibration with Working Standard (only with option 004) . . . . . .
Measuring the Working Standard Value ...................
Calibration with Working Standard .....................
Restoring Settings After Power Interruption . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-14
4-14
4-14
4-15
4-15
4-15
4-16
4-19
4-21
4-22
4-22
4-23
4-27
4-33
4-33
4-37
4-37
4-39
4-39
4-39
4-41
Contents-2
Page 9

5. Typical Functions
Point Delay and Sweep Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Making a Point Delay Measurement . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-2
Making a Sweep Delay Measurement .. ...... ..... ...... . 5-2
Delay Description ............................. 5-2
Averaging . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
Further Discussion . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-3
OSC Level Monitor . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-4
Entering Titles on the Screen . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-5
Title Entry Procedure ...... ...... ...... ...... ... 5-5
Saving and Recalling . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-6
Saving HP 4286A Setting and Measurement Trace .............. 5-6
Recalling a Saved HP 4286A Setting and Measurement Trace . . . . . . . . . 5-6
Saving a Display Image to an HP-GL File .................. 5-7
Saving Measured Data for a Spreadsheet .................. 5-7
Purging a File . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-7
Initializing a Disk/RAM Disk for Use .................... 5-7
Printing or Plotting .. ...... ...... ...... ...... ... 5-9
Printing or Plotting a Display Image . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 5-9
Using a Dierent HP-IB Address for the Printer/Plotter .... ...... . 5-9
Logging the Key Sequence into a Program (Option 1C2 Only) . . . . . . . . . .
Resetting the HP 4286A ...........................
A. Manual Changes
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manual Changes . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Serial Number . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-10
5-11
A-1
A-1
A-2
B. Maintenance
Performance Verication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Repair .. ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...
Possible Problems and Their Solution ....................
Replacement of Center Conductor Collet ...................
Changing the Line Voltage Setting ...... ...... ...... ....
Replacing the Fuse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
C. Fixture Compensation Procedures for the HP 16191A and HP 16193A
HP 16191A ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ... C-1
SHORT Compensation ........................... C-1
SHORT Compensation Key Sequence ...................
OPEN Compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OPEN Compensation Key Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Connecting DUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
HP 16193A ...... ...... ...... ...... ...... ...
SHORT Compensation ...........................
SHORT Compensation Key Sequence ...................
OPEN Compensation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
OPEN Compensation Key Sequence . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-8
Connecting DUT . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . C-8
Index
B-1
B-1
B-1
B-2
B-4
B-6
C-3
C-3
C-4
C-4
C-6
C-6
C-7
C-7
Contents-3
Page 10

Figures
1-1. HP 4286A Front Panel . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 1-2
1-2. HP 4286A Rear Panel ........ ...... ...... ..... .. 1-2
2-1. Contents of Package . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-4
2-2. Power Cable Supplied ........................... 2-6
2-3. Connecting the Connector Box to the Mainframe .............. 2-8
2-4. Connecting a Keyboard .......................... 2-11
3-1. Basic Flow for Impedance Measurements .................. 3-2
3-2. Required Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-3
3-3. Line Input Receptacle and Fuse . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-4
3-4. Calibration ................................ 3-7
3-5. ...................................... 3-8
3-6. ......................................
3-7. ......................................
3-8. ......................................
3-9. ......................................
3-10. ......................................
3-11. ......................................
3-12. ......................................
3-13. ......................................
3-14. ......................................
3-15. Connecting the Test Fixtures (HP 16192A) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
3-16. Fixture Compensation ...........................
4-1. Example of BIN Table ...........................
4-2. Basic Flow of Handler Interface Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-3. BIN Sorting .... ...... ...... ...... ...... ....
4-4. Limit Test.................................
4-5. Timing Diagram (Mode 1) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-26
4-6. BIN Sorting .... ...... ...... ...... ...... .... 4-28
4-7. Limit Test................................. 4-28
4-8. Timing Diagram (mode 2: On Sweep Mode) .. ...... ...... ... 4-32
4-9. Timing Diagram (mode 2: On Point Mode) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-32
4-10. Circuit Conguration of Comparator Output Signals .............
4-11. Circuit Conguration of Control Output Signals ...............
4-12. Circuit Conguration of Handler Interface Input Signals ...........
4-13. Handler Interface Board Switches ...... ...... ..... ....
5-1. Point Delay and Sweep Delay . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
5-2. Point Averaging .......... ...... ...... ..... ...
5-3. Level Monitor Function ..........................
5-4. Label Function ..............................
A-1. Serial Number Plate .. ...... ...... ...... ..... ... A-2
3-8
3-8
3-9
3-9
3-9
3-10
3-10
3-13
3-13
3-13
3-15
4-2
4-17
4-23
4-23
4-34
4-35
4-36
4-37
5-2
5-3
5-4
5-5
Contents-4
Page 11

Tables
2-1. Contents .... ...... ...... ..... ...... ...... 2-2
2-2. Rack Mount Kits . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 2-3
3-1. Example of Measurement Conditions .................... 3-5
3-2. Test Fixture Specication . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 3-12
3-3. Dimension of Shorting Devices ...... ...... ...... ..... 3-15
3-4. Dimension of Shorting Devices ...... ...... ...... ..... 3-16
4-1. Example of limit setting .......................... 4-4
4-2. Handler Interface Board Setup Worksheet . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-12
4-3. SW1 Setting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 4-13
4-4. SW2 Setting (External power source:1) .. ...... ...... ..... 4-14
4-5. SW2 Setting (External Power Source:2) ................... 4-14
4-6. SW2 Setting(Internal Power Source) . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-7. Typical Pull-up Resistance for Comparator Signals . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-8. Typical Pull-up Resistance for DC Isolated Input Signal . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-9. Pin Assignment of Handler Interface Connector (Mode 1) . . . . . . . . . . .
4-10. Signal Denition (Mode 1) .........................
4-11. Handler Interface Connector Pin Assignment (Mode 2) . . . . . . . . . . . .
4-12. Signal Denition (Mode 2) .........................
4-13. Electrical Characteristics of DC Isolated Output Signals ...... .....
4-14. Electrical Characteristics of DC Isolated Input Signals .... ...... ..
4-15. Typical Values of Working Standard (with option 004) ...... ......
A-1. Manual Changes by Serial Number .....................
A-2. Manual Changes by Firmware Version . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
B-1. Line Voltage Ranges .......... ...... ...... ..... .
4-14
4-15
4-15
4-24
4-25
4-29
4-30
4-33
4-36
4-40
A-1
A-1
B-4
Contents-5
Page 12

Page 13

Brief Description of the HP 4286A
Key specication assuring high accuracy impedance measurement in the RF region
Measurement frequency: 1 MHz to 1 GHz
Basic measurement accuracy: 1%
Impedance measurement range: 200 m to 3 k
High accuracy Q factor measurement(6%, @Q=100, 100 Mhz)
Features simplifying integration to your system
HP-IB, Handler Interface
HP Instrument BASIC(Option 1C2)
1 m / 3 m selectable measurement cable
Test head with APC 3.5 connector
Capabilities allowing high throughput testing
High-speed measurement(15 ms)
Comparator function
Contact checking function
List sweep
1
Brief Description of the HP 4286A 1-1
Page 14
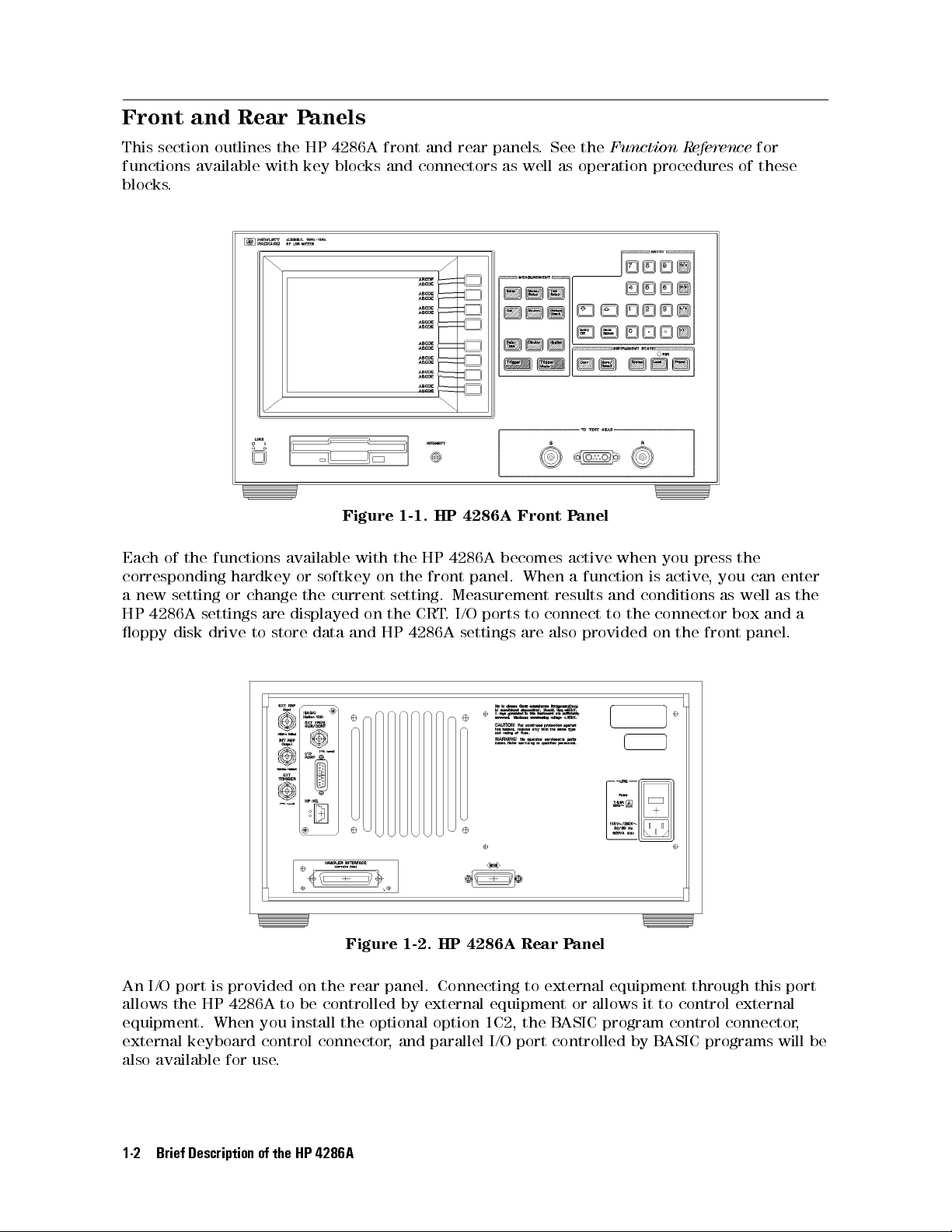
Front and Rear Panels
This section outlines the HP 4286A front and rear panels. See the
functions available with key blocks and connectors as well as operation procedures of these
blocks.
Figure 1-1. HP 4286A Front Panel
Each of the functions available with the HP 4286A becomes active when you press the
corresponding hardkey or softkey on the front panel. When a function is active
a new setting or change the current setting. Measurement results and conditions as well as the
HP 4286A settings are displayed on the CRT. I/O ports to connect to the connector box and a
oppy disk drive to store data and HP 4286A settings are also provided on the front panel.
Function Reference
, you can enter
for
Figure 1-2. HP 4286A Rear Panel
An I/O port is provided on the rear panel. Connecting to external equipment through this port
allows the HP 4286A to be controlled by external equipment or allows it to control external
equipment. When you install the optional option 1C2, the BASIC program control connector,
external keyboard control connector, and parallel I/O port controlled by B
also available for use.
1-2 Brief Description of the HP 4286A
ASIC programs will be
Page 15

Installation and Set Up Guide
This chapter provides the information necessary for performing an incoming inspection and
setting up your HP 4286A.
Incoming Inspection
2
Warning
Inspect the shipping container for damage. If the shipping container or cushioning material
is damaged, it should be kept until the contents of the shipment have been checked for
completeness and the HP 4286A has been checked mechanically and electrically
of the shipment should be as listed in T
mechanical damage or defect, or if the HP 4286A does not pass the power-on selftests
the nearest Hewlett Packard oce. If the shipping container is damaged, or the cushioning
material shows signs of unusual stress, notify the carrier as well as the Hewlett P
Keep the shipping materials for the carrier's inspection.
The line voltage selector is set at the factory to correspond to the most commonly used line
voltage of the country of destination. If you want to change the line voltage
the Line Voltage Setting" in Appendix B.
To avoid hazardous electrical shock, do not turn on the HP 4286A when
there are signs of shipping damage to any portion of the outer enclosure
(for example, covers, panel, or display)
. The contents
able 2-1 . If the contents are incomplete, if there is
, notify
ackard oce.
, see \Changing
Installation and Set Up Guide 2-1
Page 16

Table 2-1. Contents
Description HP Part Number
RF LCR meter HP 4286A
Mainframe
Fixture Stand
1
Right Angle Type Test Head with
1-m cable
Documents
User's Guide
Function Reference
Programming Manual
2
3
4
4
4
04286-90001
04286-90002
04291-90007
APC-3.5 to 7mm Adapter 1250-1746
Power Cable
Calibration Kit
4
8120-4753 (See Fig in Spec.)
5
0STermination 04186-85302
0Termination 04186-85300
50 Termination 04286-65006
LOW-LOSS Capacitor 04291-60042
Carrying Case
4
04291-60041
Option 021 only
Straight Angle Type Test Head
04286-60121
with 1-m cable
L-type Coaxial Adapter 1250-1249
Option 022 only
Straight Angle Type Test Head
with 3-m cable
L-type Coaxial Adapter 1250-1249
Option 032 only
Right Angle Type Test Head with
3-m cable
1
Not included when Option 002 is ordered.
2
Not included when Option 031 is ordered.
3
Not included when Option 0B0 is ordered.
4
Accessories are not shown in Figure 2-1 .
5
Not included when Option 001 is ordered.
2-2 Installation and Set Up Guide
04286-60122
04286-60132
Page 17

Description HP Part Number
Option 004 only
Shorting Device
1.020.5 mm 16191-29005
1.620.8 mm 16191-29006
2.021.25 mm 16191-29007
3.221.6 16191-29008
51 Chip Resistor
1.020.5 mm 5182-0433
1.620.8 mm 5182-0434
2.021.25 mm 5182-0435
3.221.6 mm 5182-0436
Device Case 1540-0692
Option 0BW only
Service Manual
Table 2-1. Contents (continued)
1
04291-90101
Option 1C2 only
Keyboard Template
HP-HIL Keyboard
Keyboard Cable
HP Instrument BASIC User's
Handbook
1
HP Instrument BASIC User's
1
1
1
08751-87111
HP 46021C Option ABA
46020-60001
E2083-90000
04286-90005
Handbook Supplement
1
This item is not shown in Figure 2-1.
Rack Mounting
Rack mounting information is provided with the rack mount kit. If the kit was not ordered
with the HP 4286A as an option, it may be ordered through the nearest Hewlett P
ackard oce.
The part numbers of the rack mount kit are shown in Table 2-2 .
Table 2-2. Rack Mount Kits
Option Description HP Part Number
1CN Handle Kit 5062-3991
1CM Rack Flange Kit 5062-3979
1CP Rack Mount & Handle Kit 5062-3985
Installation and Set Up Guide 2-3
Page 18

2-4 Installation and Set Up Guide
Figure 2-1. Contents of Package
Page 19

Power Cable
In accordance with international safety standards, this instrument is equipped with a
three-wire power cable. When connected to an appropriate ac power outlet, this cable grounds
the instrument frame. The type of power cable shipped with each instrument depends on the
country of destination. Refer to Figure 2-2 for the part numbers of the power cables available.
Warning
For protection from electrical shock, the power cable ground must not be
defeated.
The power plug must be plugged into an outlet that provides a protective
earth ground connection.
Installation and Set Up Guide 2-5
Page 20

2-6 Installation and Set Up Guide
Figure 2-2. Power Cable Supplied
Page 21

Power Requirements
HP 4286A requires a following power source:
Voltage : 90 to 132 Vac, 198 to 264 Vac
Frequency : 47 to 66 Hz
Power : 500 VA maximum
Ventilation Requirements
To ensure adequate ventilation, make sure that there is adequate clearance of at least 180 mm
behind, 60 mm sides and 15 mm above and below.
Instruction for Cleaning
For cleaning, wipe with soft cloth that is soaked with water and wrung tightly without undue
pressure.
Connecting the Connector Box
The HP 4286A consists of the mainframe, the test head, and the test xture stand. The
test head has a connector box that connects to the mainframe
Figure 2-3. While you connect the connector box to the mainframe
. This connection is shown in
, turn o the HP 4286A.
Installation and Set Up Guide 2-7
Page 22

Figure 2-3. Connecting the Connector Box to the Mainframe
1. Engage the two type-N connectors (labeledSandR, respectively) and the center connector.
2. Turn the two type-N connectors to tighten the connection.
2-8 Installation and Set Up Guide
Page 23

Connecting the Test Head
When you connect or replace the test head, turn o the HP 4286A.
1.
Place the test xture stand on a level surface. At this time, make sure that the
hexagonal hole on top of the stand is located in front of the two mounting posts as you look
at the stand. Then, lay the stand on its side.
2.
Allow the test head to pass under the xture stand from the side opposite to yours.
3.
Position the test head such that the connectors of the test head and holes on top of the
xture stand are aligned.
4.
Slightly tighten the two screws on the bottom surface of the xture stand to ensure
that the test head is suciently stable. Press screws to check for correct engagement of
their thread.
5.
Further tighten the screws while holding the test head with your hand to completely
secure the head in place.
6.
Place the xture stand with its bottom surface down.
Connecting the Test Head with L-type Coaxial Adapter
(Option 022 only)
When you connect or replace the test head, turn o the HP 4286A.
1.
Connect Connecting L-type Coaxial Adapter to the Test Head.
2.
Place the test xture stand on a level surface. At this time, make sure that the
hexagonal hole on top of the stand is located in front of the two mounting posts as you look
at the stand. Then, lay the stand on its side
.
3.
Allow the test head to pass under the xture stand from the side opposite to yours.
4.
Position the test head such that the connectors of the L-type Coaxial adapter and holes
on top of the xture stand are aligned.
5.
Slightly tighten the two screws on the bottom surface of the xture stand to ensure
that the test head is suciently stable. Press screws to check for correct engagement of
their thread.
Installation and Set Up Guide 2-9
Page 24

6.
Further tighten the screws while holding the test head with your hand to completely
secure the head in place.
7.
Place the xture stand with its bottom surface down.
Connecting the APC-3.5 to 7mm Adapter
1. Check that the connector sleeve is fully extended.
2. Connect APC-3.5 to 7mm adapter to the test head connector through the hole on top of the
xture stand.
3. Tighten the adapter nut to secure this adapter in place.
2-10 Installation and Set Up Guide
Page 25

Connecting a Keyboard (Option 1C2 Only)
When Option 1C2 is installed, an HP-HIL keyboard can be connected to the HP-HIL connector
on the rear panel of the HP 4286A. The HP-HIL keyboard provides an easier way to enter
characters for the le names, display titles, and Instrument BASIC programs. It can also access
the HP 4286A softkey functions by using keyboard function keys.For more information on the
HP-HIL keyboard, see the
HP Instrument BASIC User's Handbook Supplement
that is included
in Option 1C2.
Figure 2-4. Connecting a Keyboard
Installation and Set Up Guide 2-11
Page 26

Page 27

Basic Measurement Procedures
This chapter provides a quick start guide of the HP 4286A. New users can quickly become
familiar with the HP 4286A by following these procedures. In this chapter, to help you learn
how to use the HP 4286A, impedance of inductors are measured as examples.
At the end of the quick start procedures, you will have learned how to get the following
measurement results:
Calibration
Setting electrical length of test xture
Correction of test xture
List sweep
3
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-1
Page 28

Measurement Outline
This chapter describes how to measure the impedance of a 100 nH inductor as an example.
Measurement items and conditions are shown below.
Parameter Ls-Q
Frequency 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 500, 1000 MHz
OSC level 10 mA
Basic Measurement Flow
Figure 3-1 shows the basic ow for an impedance measurement.
Figure 3-1. Basic Flow for Impedance Measurements
3-2 Basic Measurement Procedures
Page 29

Required Equipment
To perform all the steps in this quick start, the following equipment is required:
HP 4286A RF LCR meter
Test Head
Fixture Stand
Calibration Kit
Test Fixture
HP 16191A Side Electrode SMD Test Fixture,or
HP 16192A Parallel Electrode SMD Test Fixture,or
HP 16193A Small Side Electrode SMD Test Fixture
Shorting Device Set (Included with HP 16191A, HP 16192A, HP 16193A, and Option 004
Working Standard Set)
Tweezers (Included with HP 16191A, HP 16192A, and HP 16193A)
Device Under Test (DUT) (A chip inductor is used in this guide.)
Figure 3-2. Required Equipment
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-3
Page 30

1. Power ON
Verify the connector box and the test head are correctly set up before turning ON the
HP 4286A. If they have not been set up, see Chapter 2.
Line Input Receptacle
ACPower cable is connected to this receptacle.
Figure 3-3. Line Input Receptacle and Fuse
Fuse
Use the following fuse:
HP Part Number : 2110-0917
(UL/CSA type, Semi Time Lag, 6.3 A 250 V)
If you need this fuse, contact your nearest Hewlett-Packard Sales and Service Oce.
Steps to turn on the power
1. Verify the power line setting is correct before you turning ON the meter. If necessary, see
\Changing the Line Voltage Setting" in Appendix B.
2. Connect AC power cable to the line input receptacle.
3. Press the LINE switch.
After the power-on self-test (approximately 10 seconds), the installed options and the
connected test head information are displayed.
Note
Only option numbers 1C2 and 001 are displayed at power-on (if they are
installed). Other installed option numbers are listed on the rear panel.
A 30 minute-warm-up period is required to stabilize the HP 4286A after it has been turned ON.
This ensures the HP 4286A its specied measurement accuracy
3-4 Basic Measurement Procedures
.
Page 31

2. Setting up the HP 4286A
Before you start the measurement, you must set up the HP 4286A to t your measurement
requirements. This section provides the set up procedures for Ls-Q frequency characteristics
measurements.
To set up the HP 4286A, press the front panel keys as shown below. All keys necessary for this
set up procedures are available on the MEASUREMENT Block.
2-1. Setting up for Ls-Q Frequency Characteristics Measurements
Table 3-1. Example of Measurement Conditions
Range
1MHz, 2MHz, 5MHz, 10MHz,
20MHz, 50MHz, 100MHz, 200MHz,
500MHz, 1GHz
OSC Level
10 mA
Select parameters to satisfy the conditions above.Follow the procedures below.
1. Press
2.
Press
4
Meas
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Ls-Q
5
.
. The
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Ls-Q
softkey label becomes underlined, showing that
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Ls-Q
has been
selected.
2-2. Creating a sweep table
Create a sweep table to set list sweep conditions
1. Press
2.
3. Press
4.
4
Sweep Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
EDIT LIST
4
5
2
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
SEGMENT DONE
, then
5
.
NNNNNNNNNNN
ADD
to create an additional segment.
4
5
to set the measurement frequency of the additional segment to 2 MHz.
M/
to complete the segment setting.
.Follow the procedures below.
5. Repeat steps 2 through 4 to create 8 additional segments. Set the frequency of each of these
segments to 5, 10, 20, 50, 100, 200, 500, and 1000 (=1G) MHz, respectively. (The frequency
of a segment available at power-on has automatically been set to 1 MHz.)
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
LIST DONE
to complete the table creation step.
6.
2-3. Setting the OSC level
Set the OSC signal level applied to the DUT.Follow the procedures below.
Press
4
5
.
Source
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
Press
Hints
AMPERE
415,405
to set the OSC level as current.
, and then
Use
4
5
k/m
4*5or4+5
to set the OSC level to 10 mA.
to quickly increase or decrease the value to be entered. The
value changes in steps of 1, 2, 5, and 10 with these keys
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-5
.
Page 32

To delete the value you have entered, simply press
pressed
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SEGMENT DONE
To start the segment condition setting all over again, rst press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SEGMENT QUIT
number using numeric keys and
4
5
, or enter a new value if you have already pressed
M/
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
and then
SEGMENT
4x15
. Next, specify the desired segment
. Finally, press
4
Back Space
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
EDIT
5
if you have not
4
M/
and then
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SEGMENT
You are now ready to specify the frequency for the selected segment.
5
but not
.
3-6 Basic Measurement Procedures
Page 33

3. Calibration
R
Calibration denes the measurement accuracy for the contact surface of the APC-7
on
the APC-3.5 to 7mm adapter which is connected to the test head. The calibration must be
performed when the HP 4286A is turned ON. After the calibration, the HP 4286A can measure
within its specied measurement accuracy.
The 0 S, 0 , and 50 terminations and low-loss capacitor in the calibration kit are required.
Figure 3-4. Calibration
Calibration Procedure
1. Press
2.
3.
4
5
Cal
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
Press
CALIBRATE MENU
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
CAL POINTS
.
.
to set the frequency for the Calibration
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
When you modify the measurement frequency, select
FIXED
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
When you do not modify the measurement frequency, select
USER
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
See
Function Reference
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
USER
(user-dened point calibration).
4. Turn the APC-7
R
for details on
FIXED
(xed point calibration) and
connector on the test head as shown in Figure 3-5.
5. Verify that the connector sleeve is extended fully as shown in Figure 3-6.
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-7
Page 34
Figure 3-5.
R
6. Connect the 0 S termination to the APC-7
Figure 3-7.
NNNNNNNNNNNNN
7. Press
N
OPEN
.
After an OPEN calibration sequence of about 20 seconds, the
underlined.
connector as shown in Figure 3-7.
Figure 3-6.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
OPEN
softkey label is
8. Disconnect the 0 S termination.
9. Connect the 0 termination on the APC-7
3-8 Basic Measurement Procedures
R
connector as shown in Figure 3-8.
Page 35

Figure 3-8.
10. Press
11. Disconnect the 0 termination.
12. Turn only the APC-7
13. Verify that the connector sleeve is retracted fully as shown in Figure 3-10.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SHORT
After a SHORT calibration sequence of about 20 seconds
underlined.
.
R
connector nut of the 50 termination as shown in Figure 3-9.
, the
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SHORT
softkey label is
Figure 3-9. Figure 3-10.
14. Connect the 50 termination on the APC-7
R
connector as shown in Figure 3-11 .
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-9
Page 36

Figure 3-11.
15. Press
LOAD
.
After a LOAD calibration sequence of about 20 seconds, the
underlined.
16. Disconnect the 50 termination.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
R
17. Connect the low-loss capacitor to the APC-7
connector as shown in Figure 3-12.
Figure 3-12.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
LOAD
softkey label is
18. Press
LOW-LOSS CAPACITOR
After a low-loss capacitor calibration sequence of about 20 seconds, the
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
LOW-LOSS CAPACITOR
.
softkey label is underlined.
19. Disconnect low-loss capacitor.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
20.
21.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
DONE:CAL
Verify that \
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
(
USER
) is displayed on the left of the screen.
.
CO+
" (when you have selected
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
FIXED
)or\
Co+
" (when you have selected
The calibration data is erased when the HP 4286A is turned o.
3-10 Basic Measurement Procedures
Page 37

Note
R
Handling and Storage of the APC-7
Connector:
Keep connectors clean.
Do not touch the mating plane surfaces.
Do not set connectors contact-end down.
Before storing, extend the sleeve or connector nut.
Use end caps over the mating plane surfaces.
Never store connectors loose in a box or a drawer.
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-11
Page 38

4. Connecting the Test Fixture
Selecting a Test Fixture
Hewlett-Packard provides the test xtures listed in Table 3-2 for dierent sizes of surface
mounted device (SMD) measurements. These xtures provide high stability and repeatability
measurements.
Table 3-2. Test Fixture Specication
HP 16191A HP 16192A HP 16193A
Mountable
DUT size
Length
(mm)
2.0 to 12.0 1.0 to 20.0
1
0.5 to 3.2
Width (mm) 0.5 to 5 0.5 to 5 3 or less
Height
0.5 to 5 0.5 to 5 3 or less
(mm)
Electrodes in contact
with DUT (shown with
8
)
1
See chapter 2 of the
Service Manual
HP 16192A Parallel Electrode SMD Test Fixture Operation and
for the electrodes' conguration when measuring a DUT of more
than 5 mm long.
This user's guide explains how to use these test xtures
.
Connecting the Test Fixture to the Test Head
To connect your xture to the Test Head, perform the steps listed below. (Figure 3-15 shows
the connection for HP 16192A as an example.)
R
1. Turn the APC-7
connector on the test head as shown in Figure 3-13.
2. Verify that the connector sleeve is retracted fully as shown in Figure 3-14.
3-12 Basic Measurement Procedures
Page 39
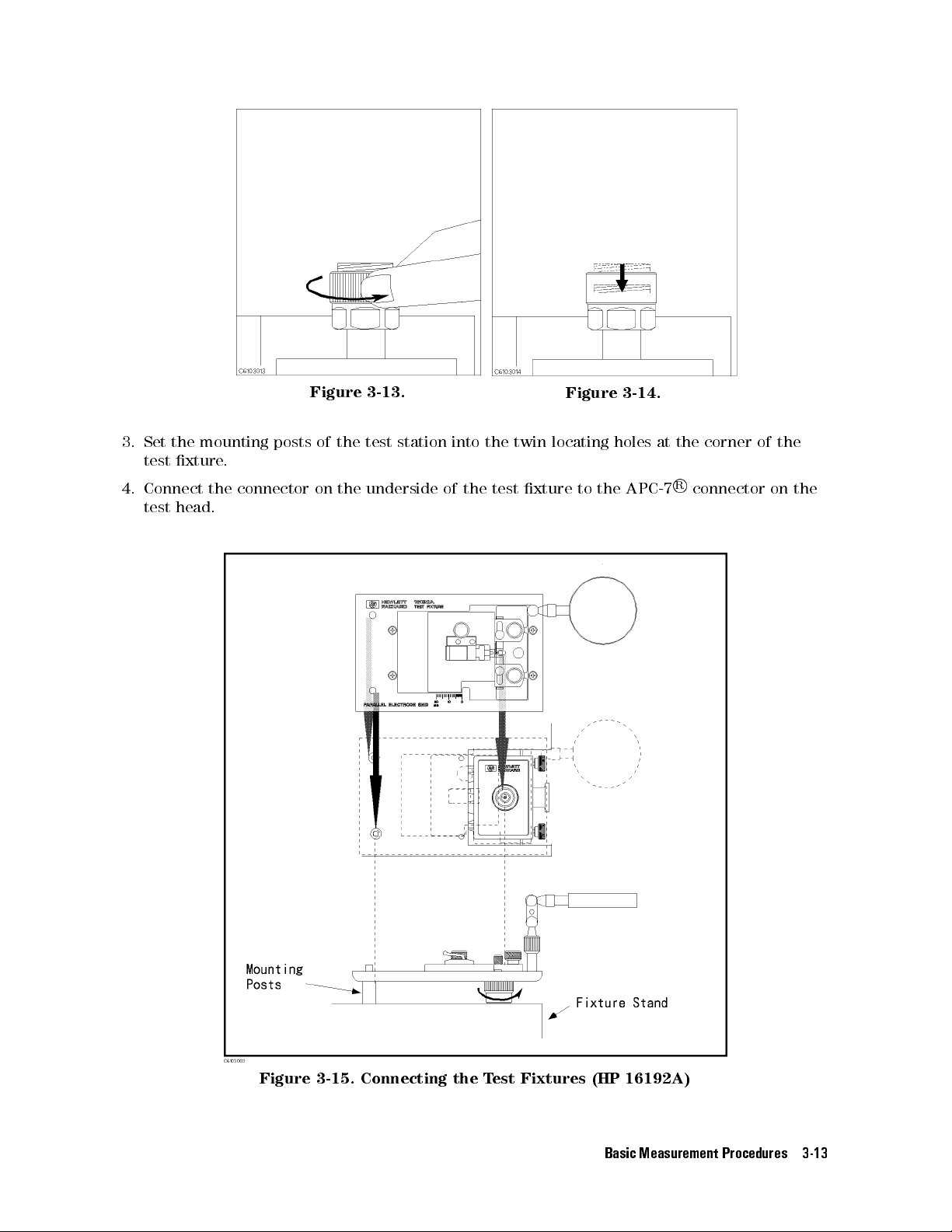
Figure 3-13.
Figure 3-14.
3. Set the mounting posts of the test station into the twin locating holes at the corner of the
test xture.
R
4. Connect the connector on the underside of the test xture to the APC-7
connector on the
test head.
Figure 3-15. Connecting the Test Fixtures (HP 16192A)
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-13
Page 40

5. Setting the Electrical Length of the Test Fixture
In the RF region, the wavelengths are short and are not negligible compared to the physical
transmission line length of the test xture. This causes a phase shift error. The phase shift
error is compensated by the electrical length parameter for the test xture. Because the
electrical length values for the Hewlett Packard test xtures are stored in the HP 4286A, you
can set the electrical length parameter by selecting the xture model number.
Setting Procedure
1. Press
2.
3. Select the xture model number that you are using.
4.
5. Verify that \
Press
Press
4
5
.
Cal
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
FIXTURE[]
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
RETURN
.
Del
and then
" appears on the left of the display.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SELECT FIXTURE
.
3-14 Basic Measurement Procedures
Page 41

6. Fixture Compensation
Fixture compensation reduces the parasitic error existing between the test xture electrode
and the test head APC-7
compensation consists of OPEN, SHORT and LOAD compensations.For basic measurements, the
OPEN and SHORT compensations are required.
R
connector (where the measurement accuracy is specied). Fixture
Figure 3-16. Fixture Compensation
Performing SHORT Compensation
SHORT Compensation compensates for the residual impedance due to the test xture
When you use a shorting device supplied with the HP 4286A (with option 004) or xture (with
option option 010), be sure to select the device of the same size as or at least closest to that of
the DUT. The dimensions for each shorting device are shown in Table 3-3.
Table 3-3. Dimension of Shorting Devices
Dimension (mm) HP Part Number
1.020.520.5 16191-29005
1.620.820.8 16191-29006
2.021.2520.8 16191-29007
3.221.620.8 16191-29008
Four shorting divices of dierent dimensions are supplied with each xture. The shorting
device that is closest to the size of the DUT should be used. The dimensions for each shorting
device are shown in Table 3-4.
.
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-15
Page 42
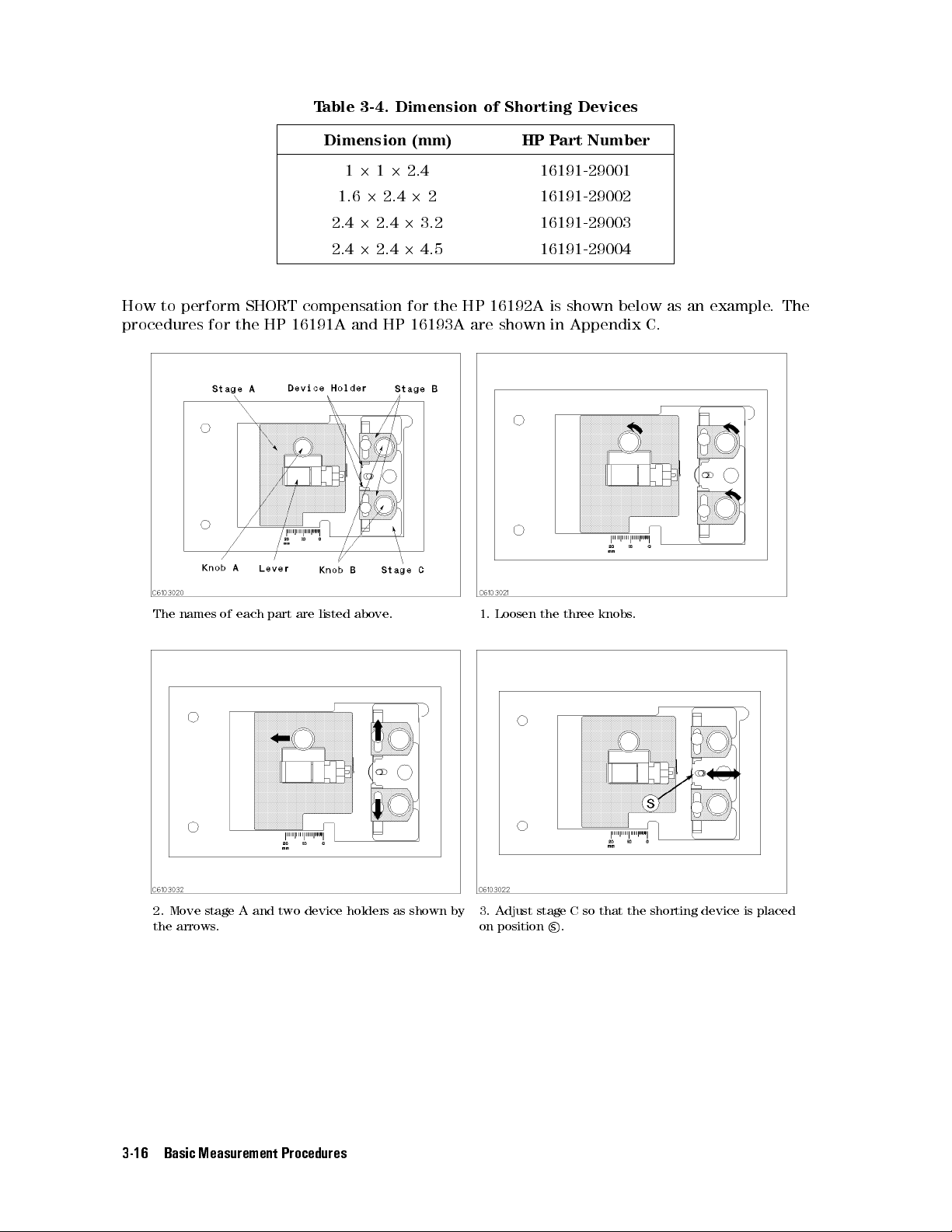
Table 3-4. Dimension of Shorting Devices
Dimension (mm) HP Part Number
12122.4 16191-29001
1.622.422 16191-29002
2.422.423.2 16191-29003
2.422.424.5 16191-29004
How to perform SHORT compensation for the HP 16192A is shown below as an example. The
procedures for the HP 16191A and HP 16193A are shown in Appendix C.
The names of each part are listed above. 1. Loosen the three knobs.
2. Move stage A and two device holders as shown by
the arrows.
3. Adjust stage C so that the shorting device is placed
on positions
.
3-16 Basic Measurement Procedures
Page 43

4. Place the shorting device so that it contacts the
electrode.
5. Adjust the two B stages and the two device holders
to hold the shorting device.
6. Tighten the two B knobs to x the B stages and the
device holders.
8. Tighten knob A while pushing the lever. 9. Release the lever to hold the shorting device.
SHORT Compensation Key Sequence
When the test xture is ready for the SHORT compensation sequence
panel keys:
7.1
Push the lever.2
the lever until the electrode on the stage A slightly
contacts the shorting device.
Slide stage A while pushing
, press the following front
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-17
Page 44

1.
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
4
5
FIXTURE COMPEN
Cal
After the SHORT compensation sequence is done, the
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
COMPEN MENU
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SHORT
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SHORT
softkey label is underlined.
Performing OPEN Compensation
OPEN Compensation corrects for stray admittance due to the test xture. How to perform an
OPEN compensation sequence for the HP 16192A is described as an example. The procedures
for the HP 16191A and HP 16193A are shown in Appendix C.
1. Set the DUT on the test xture just as you set the
2. Push the black lever and remove the DUT
shorting device in the SHORT compensation.
OPEN Compensation Key Sequence
When the test xture is ready for the OPEN compensation sequence
procedure:
1.
2.
3. Verify that \
Note
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
OPEN
.
After the OPEN compensation sequence is done, the
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
DONE: COMPEN
Cmp
" appears on the left of the display.
You can perform the desired xture compensation individually.To do this,
press
4
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
5
FIXTURE COMPEN
Cal
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
RESUME CAL SEQUENCE
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
OPEN
softkey label is underlined.
desired compensation.
.
, perform the following
and then the key for the
3-18 Basic Measurement Procedures
Page 45

7. Connecting the DUT to the Test Fixture
How to connect the DUT to the HP 16192A is shown in below as an example. The procedures
for the HP 16191A and HP 16193A are shown in Appendix C.
1. Push the lever and place the DUT on the electrode. 2. Release the lever to hold the DUT.
Caution
Protect the instrument from ESD damage by wearing a grounding strap
that provides a high resistance path to ground. Alternatively, ground yourself
to discharge any static charge built-up by touching the outer shell of any
grounded instrument chassis before touching the test port connectors
.
Basic Measurement Procedures 3-19
Page 46

8. Measuring the DUT
After you place the DUT on the test xture, the measured result is displayed.
3-20 Basic Measurement Procedures
Page 47

4
HP 4286A with Chip Handler
This chapter describes the functions available with the HP 4286A and operation procedures for
each of those functions when the HP 4286A is used with a chip handler.
Dierentiation of DUTs through BIN Sorting
GO/NO-GO Test with Limit Test Function
Contact Check
Enabling Beeper
Display Updating ON/OFF
Setup Linking HP 4286A and Chip Handler
Setting up Handler Interface Board
This chapter also includes the technical information for using HP 4286A with automatic
selection system in the production line.
HP 4286A Measurement Time
Electrical Specication of Handler Interface
Performing Calibration with Working Standard
Restoring Settings After Power Interruption
Note
When you use the HP 4286A together with a chip handler
interface board before performing limit test or BIN sorting. See \Setting up
Handler Interface Board" for details.
, be sure to set up the
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-1
Page 48

Dierentiation of DUTs through BIN Sorting
You can dierentiate DUTs by checking which BINs DUTs are classied into.To do this,
you need to set several combinations of upper and lower limits for a specic frequency as
measurement parameters.
Editing BIN Table
This section describes how to edit a BIN table as shown in Figure 4-1.
Figure 4-1. Example of BIN Table
1.
Press
4
Test Setup
5
, and then
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
BIN SORT MENU
.
2. Set desired frequency points for BIN sorting. Select frequency points for BIN sorting from
the segment of list table which is set by
4
Sweep Setup
5
. (The HP 4286A has been initially set to
segment 1 of the frequency point for BIN sorting.)
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
TEST SEG
Enter the desired segment number for BIN sorting, then press
.
4
5
.
x1
3. Primary Parameters
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
EDIT BIN SORT
.
NNNNNNNNNNN
Press
ADD
to create BIN1.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
UPPER LIMIT
Enter valueA
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
LOWER LIMIT
Press
Enter valueB
.
.
.
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
DONE
to complete the creation of BIN1.
4-2 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 49

Repeat the steps above to create BIN2 through BIN9.
4. Secondary Parameters
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
SEC REJECT MENU
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
UPPER LIMIT
.
Enter valuea
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
LOWER LIMIT
Enter valueb
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
SEC REJECT on OFF
.
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
to toggle it
ON off
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
5.
Press
RETURN
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
DONE
to complete the secondary parameter setting.
to complete the creation of BIN table.
Setting up Handler Interface
1. Set up the handler interface board. See \Setting up Handler Interface Board" for details
abount the mode.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
2. Press
3.
Select
4
Test Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
MODE 1
5
, and then
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
or
MODE 2
N
HANDLER IF
.
.
The pattern of output signals for BIN sorting can be selected from either Mode 1 or Mode 2.
Denitions in output signals for handler interface vary depending on the mode used. See
\Setting up Handler Interface Board" for details about the mode
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
RETURN
.
4.
.
BIN Sorting
1.
2.
Press
4
Test Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
BIN SORT on OFF
5
and then,
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
BIN SORT MENU
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
to toggle it
ON off
.
.
When the BIN sort key is ON, measured data outside the limits are output and displayed as
follows:
On-screen Message Showing Corresponding BIN or BIN OUT (if outside preset limits)
Beeper (ON/OFF selectable)
HP-IB Command
:DATA? BIN
Handler Interface Output
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-3
Page 50

GO/NO-GO Test with Limit Test Function
Use the limit test function to perform GO/NO-GO test. This function sets the upper and lower
limits to determine whether DUTs are acceptable. The limit dierentiation function compares
the measured data with preset limits and shows through its output and on-screen message
whether the DUT is within the limits.
Editing Limit Table
This section describes how to edit the limit table of primary parameters and secondary
parameters, as shown in Table 4-1.
Table 4-1. Example of limit setting
Segment Stimulus Value Primary Parameter Secondary Parameter
Lower limit Upper limit Lower limit Upper limit
1 1MHz 10nH 12nH 100.0 1G
2 10MHz 12nH 14nH 100.0 1G
3 100MHz 10nH 14nH 100.0 1G
1
Testing function is not actually performed.
1
1
1
Note
If you do not want to perform testing function for upper or lower limits
of secondary parameters, specify suciently large value for upper limit or
suciently small value for lower limit.
1. Press
2.
4
Test Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
EDIT PRI LIMIT
5
, and then
3. Segment 1
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
EDIT
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
and
STIMULUS VALUE
Enter Stimulus (1MHz).
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
LOWER LIMIT
Enter lower limit value (10nH).
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
UPPER LIMIT
Enter upper limit value (12nH).
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
DONE
to complete the editing of this segment.
4. Segment 2
NNNNNNNNNNN
Press
ADD
to edit the new segment.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
STIMULUS VALUE
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
LIMIT TEST MENU
.
.
.
.
.
.
Enter Stimulus (10MHz).
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
LOWER LIMIT
.
Enter lower limit value (12nH).
4-4 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 51

NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
UPPER LIMIT
.
Enter upper limit value (14nH).
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
DONE
to complete the editing of this segment.
5. Segment 3
NNNNNNNNNNN
Press
ADD
to edit the new segment.
Enter stimulus, lower limit, and upper limit values in the same manner above.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
DONE
to complete the editing of this segment.
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
DONE
to complete the editing of the primary parameter limit table.
6.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Then, press
EDIT SEC LIMIT
to edit the secondary parameter limit table.
1. Segment 1
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
LOWER LIMIT
.
Enter lower limit value (100.0).
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
UPPER LIMIT
.
Enter upper limit value (1G).
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
DONE
to complete the editing of this segment.
2. Segment 2,3
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Enter lower and upper limit values and press
DONE
to complete the editing of this
segment in the same manner as segment 1.
Setting up Handler Interface
1. Set up the handler interface board. See \Setting up Handler Interface Board" for the set up
procedure.
2.
3.
Press
Press
4
Test Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
MODE 1
5
, and then
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
or
MODE 2
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
HANDLER IF
.
.
When you perform limit test, select the signal pattern from either Mode 1 or Mode 2. The
output for the interface varies depending the mode used as follows.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
MODE 1
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
MODE 2
Outputs overall results of comparison for limit test.
Outputs results for each segment.
See \Setting up Handler Interface Board" for details abount the mode.
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
RETURN
.
4.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-5
Page 52

Limit Test
You can perform limit test for only primary or secondary parameters.
1.
Press
2.
4
Test Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
PRI LIMIT on OFF
5
, and then
parameters) to toggle it
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
LIMIT TEST MENU
(primary parameters) or
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
ON off
.
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SEC LIMIT on OFF
(secondary
When either of the limit test keys is ON, measured data outside the limits are output and
displayed as follows:
On-screen FAIL Message
Beeper (ON/OFF selectable)
HP-IB Command
Note
:DATA? LFA,:DATA? LLIS,:DATA? LMAR
The frequency (stimulus value) of limit table for setting limits can be set
independently of the frequency set in the list table.
If the frequency of the limit table does not equal to the measurement
frequency of list table, limit tests for all measurements can be performed using
interpolation of the limit values.
For example, if only one point is dened in limit table
with the constant upper limit and lower limit for all measurements
, limit test is performed
.
4-6 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 53

Contact Check
Contact check is used to check the electrical contact between the test head and DUT. This
check consists of measuring dc resistance between the two and determining whether the
resistance is within the preset limits.
Follow the procedure below.
1. Press
4
Contact Check
5
.
2. Set the upper and lower limits for dc resistance between the test head and DUT.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
RDC UPPER LIMIT
and enter the upper limit.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
3.
RDC LOWER LIMIT
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
RDC MEAS on OFF
and enter the lower limit.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
to toggle it
RDC MEAS ON off
.
Then, the measured dc resistance will be displayed on the screen.
4.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
RDC LIMIT on OFF
to toggle it
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
RDC LIMIT ON off
.
Whether the measured resistance is within the limits will be displayed on the screen.
Contact check results will be output and displayed as follows:
On-screen FAIL Message
Handler Interface
HP-IB Command
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-7
Page 54

Setting up Beeper
Beepers can be used to announce results of limit test and BIN sorting.
The beeper can be set to sound when both of BIN sorting and limit test passed or both of them
failed.
Follow the procedure below.
1.
Press
4
Test Setup
2.
If you wish to sound the beeper when both of BIN sorting and limit test passed, press
If you wish to sound it when both of BIN sorting and limit test failed, press
NNNNNNNNNNN
OFF
when you do not wish to sound the beeper regardless of test results. In other words,if
5
, and then
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
BEEP
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
FAIL
PASS
. Press
either of BIN sorting or limit test failed, the beeper does not sound for any settings.
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
RETURN
.
3.
.
4-8 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 55

Display Updating ON/OFF
You can select whether to display new measurement results on the screen by switching the
display updating function ON and OFF. Switch this function OFF to more quickly determine
whether the DUT is acceptable or not.
Switching display updating OFF gains 3ms + 6ms/point.
This updating function can be switched ON and OFF at any time.
Follow the procedure below.
1. Press
2.
Press
4
5
.
Display
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
MEAS DISP ON off
to switch the updating function ON and OFF.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-9
Page 56

Setup Linking HP 4286A and Chip Handler
The HP 4286A can be set up to read initial settings from exible disk during startup. This
setup allows the HP 4286A to run exclusively for your particular purpuse, the chip handler for
instance, from the moment of startup.
Follow the procedure below.
1. Set up the HP 4286A for use with the handler.
2. Insert a 3.5-inch LIF or DOS-formatted disk into the built-in disk drive.
3. Press
4.
Press
4
Save/Recall
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
STOR DEV
5
.
to switch it to
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
[DISK]
. This species the built-in disk drive as the storage
destination.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
5. Press
6.
Enter
Before turning on the HP 4286A, insert the disk containing the \
STATE
.
AUTOREC
as the lename and press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
DONE
.
AUTOREC
" le into the built-in
disk drive. Each time you turn on HP 4286A, it recalls settings in the le to operate exclusively
for the handler from the moment of startup
.
4-10 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 57

Setting up Handler Interface Board
This section describes the steps necessary to use the handler interface board.
There are 3 major steps as follows:
Mounting Pull-up Resistor
Mount a pull-up resistor to the handler. Where to mount a resistor and what resistance the
resistor needs to have depends on the signal I/O format.
Note
A pull-up resistor must be mounted to the handler for comparator signals.
Setting up Handler Interface
Set up the handler interface signal pattern that suits the HP 4286A operation mode. Set it up
on the HP 4286A.
The following step is required when the power supplies for I/O or COMMON setting should be
modied.
Changing Signal I/O Format
Change the switch setting on the handler interface board to change its signal I/O format.
This is necessary when you need the I/O format that requires the switch settings dierent
from the default settings.
Checking Default Settings
The handler interface board has been set as follows before shipment.
Signals Settings
Comparator Signal This signal is opto-isolated and is output through open-collector
COM1 is used as COMMON that is isolated from HP 4286A's
chassis ground. Pull-up resistors are mounted to the handler
.
Output voltage is supplied from an external power source (5 to
24V) on the handler.
Control Output Signal This signal is opto-isolated and is output through open-collector
COM2 is used as COMMON that is isolated from HP 4286A's
chassis ground. Pull-up resistors are mounted to the handler.
Output voltage is supplied from an external power source (5 to
15V) on the handler.
DC isolated Input Signal This signal is opto-isolated from the internal circuits of
HP 4286A. Driving voltage is supplied from an external power
source (5 to 7V) through EXT.DCV2. This signal turns \TRUE" if
input signal is connected to the COMMON of the external power
source.
Internal power source (5V) Not used.
.
.
See \Handler Interface Board Switches" for default switch settings.
Warning
Be sure to check the procedures in \Removing the Top Cover" before
removing the HP 4286A top cover.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-11
Page 58

Selecting Settings
Select the desired settings according to the table below.
Table 4-2. Handler Interface Board Setup Worksheet
Item Selection Default Power Source Pull-up
Comparator
Signal
Control
Output
Signal
A Default
External(COM1) Mount to the
Setting
B Internal(+5V)
C Default
External
2
Setting
D External
2
handler
1
Mount to the
handler
Use internal
pull-up
resistors(4.64k).
E Internal
3
Mount to the
handler
F Internal
3
Use internal
pull-up
resistors(4.64k).
DC Isolated
Input
Signal
G Default
Setting
External257V Use internal
pull-up resistors.
H External2715V Isolated Set SW2(6) and SW2(8) OFF.
I Internal
3
Resistor
Opt-
Modication to Default
isolation
Isolated
Not
isolated
Supply an internal power
source(+5V) to pull-up
resistors on the handler. Set
SW2(5) ON.
Isolated
Isolated Set SW2(1) through SW2(3)
ON.
Not
isolated
Not
isolated
Turn SW1
Internal(+5V)
side.
Set SW2(4) ON.
Set SW2(1)
through SW2(3)
and SW2(4) ON.
Isolated
Not
isolated
Turn SW1
Internal(+5V)
Set SW2(4) ON.
side.
1
Chassis grounding is used.
2
Supply through EXT.DCV2. COM2 is used as COMMON.
3
Set voltage +5V.
Follow the combination logic shown below according to power sources.
Comparator
Control Output Signal DC Isolated Input Signal
Signal
Select A or B. For external power source . . . Select C or D.
For internal power source . . . Select E or F.
Note
Review the check items below before selecting your settings.
For C or D . . . Select G or H.
For E or F . . . Select I.
You must use the same power source for control output signal and DC
isolated input signal.
If you select COM1 for COMMON and use internal power source output,
comparator signals will not be opto-isolated.
If you select COM2 for COMMON and choose to use internal power source
output, comparator signals will not be opto-isolated.
4-12 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 59

When you use the internal pull-up resistor and apply voltage to the control
output signal from an external power source, the permissible voltage range is
between 5 and 15V.
If your current settings are default settings or if you wish to change your settings, follow the
steps below.
Changing Settings
You need to change your settings depending on the signal output format (open-collector,
internal voltage output, or external voltage output) of your handler interface. Two switches
are provided for changing settings. The setting of both switches can be changed on the top
shield. (See \Handler Interface Board Switches".)
See \Electrical Specication of Handler Interface" rst to become familiar with electrical
characteristics of each signal and operations of the interface board and I/O circuits before
changing your settings.
Also, check the default settings in \Checking Default Settings". If you need to change the
default setting, follow the steps below.
Removing the Top Cover
1. Turn OFF the HP 4286A, disconnect the power cable
, and wait for a few minutes to allow
capacitors in the HP 4286A to discharge.
Warning
The HP 4286A internal circuits carry high voltage during operation and
immediately after it has been turned OFF.To prevent injuries due to
electrical shocks, be sure to wait for at least few minutes before removing
the cover to make sure that capacitors in the HP 4286A discharge
completely .
2. Remove 4 back legs that hold the top cover and rear panel together
3. Fully loosen the screw behind the top cover
.
.
4. Slide the top cover backward and lift it up to remove it. Find the top shield, which shows
the locations and default settings of SW1 and SW2.
Setting up Control Output Signal and DC Isolated Input Signal
Select either external or internal power source for supplying voltage to the control output and
DC isolated input signals.
Set SW1 as follows:
Table 4-3. SW1 Setting
Power Source SW1
External Source Switch it over toward the rear panel.
Internal Source Switch it over toward the front panel.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-13
Page 60
Using External Power Source.
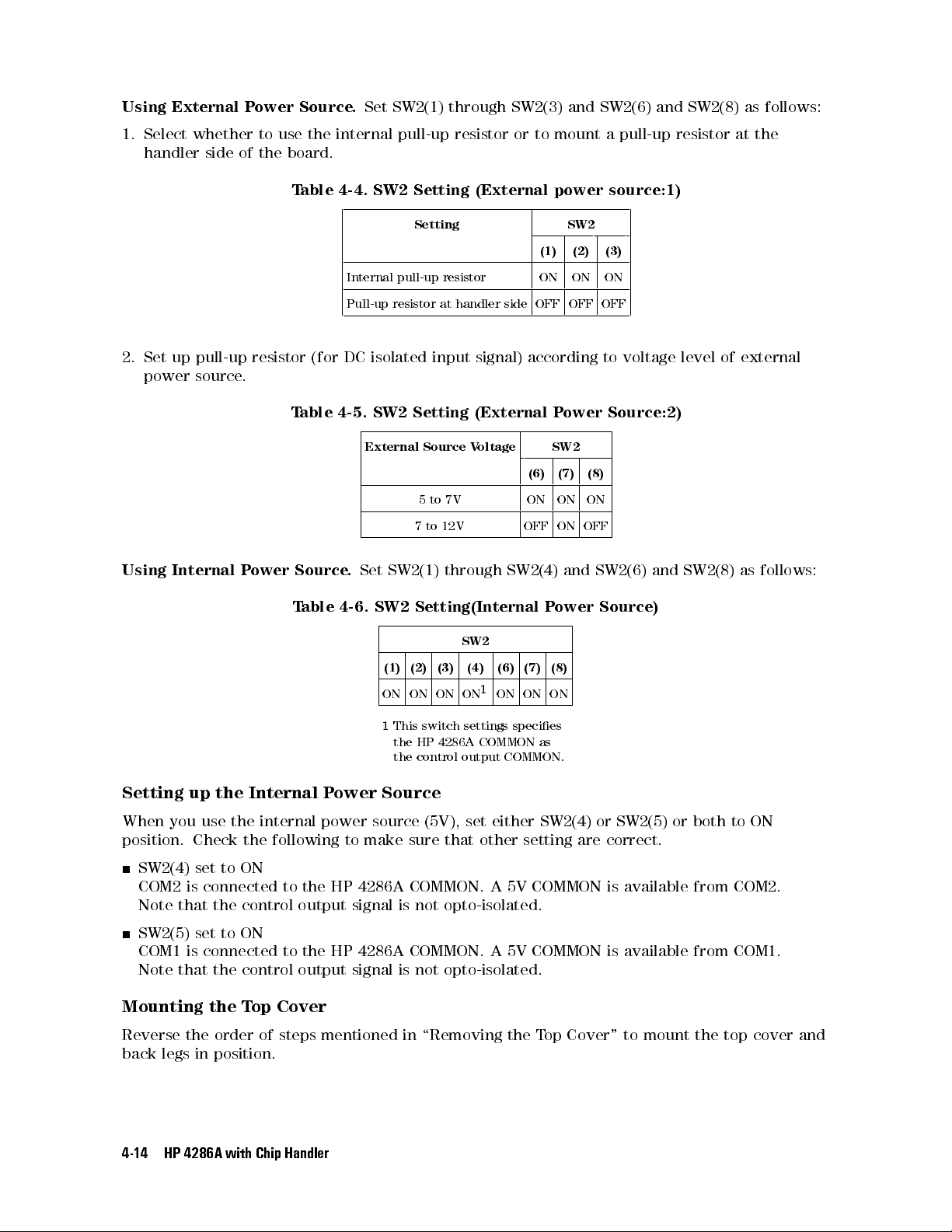
Set SW2(1) through SW2(3) and SW2(6) and SW2(8) as follows:
1. Select whether to use the internal pull-up resistor or to mount a pull-up resistor at the
handler side of the board.
Table 4-4. SW2 Setting (External power source:1)
Setting SW2
(1) (2) (3)
Internal pull-up resistor ON ON ON
Pull-up resistor at handler side OFF OFF OFF
2. Set up pull-up resistor (for DC isolated input signal) according to voltage level of external
power source.
Table 4-5. SW2 Setting (External Power Source:2)
External Source Voltage SW2
(6) (7) (8)
5to 7V ON ON ON
7 to 12V OFF ON OFF
Using Internal Power Source.
Set SW2(1) through SW2(4) and SW2(6) and SW2(8) as follows:
Table 4-6. SW2 Setting(Internal Power Source)
SW2
(1) (2) (3) (4) (6) (7) (8)
ON ON ON ON1ON ON ON
1
This switch settings species
the HP 4286A COMMON as
the control output COMMON.
Setting up the Internal Power Source
When you use the internal power source (5V), set either SW2(4) or SW2(5) or both to ON
position. Check the following to make sure that other setting are correct.
SW2(4) set to ON
COM2 is connected to the HP 4286A COMMON. A 5V COMMON is available from COM2.
Note that the control output signal is not opto-isolated.
SW2(5) set to ON
COM1 is connected to the HP 4286A COMMON. A 5V COMMON is available from COM1.
Note that the control output signal is not opto-isolated.
Mounting the Top Cover
Reverse the order of steps mentioned in \Removing the T
back legs in position.
4-14 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
op Cover" to mount the top cover and
Page 61

Mounting a Pull-up Resistor
Mount a pull-up resistor at the handler when you wish to use an external power source for I/O
signals.
Note
You must mount a pull-up resistor for comparator signals.
Pull-up Resistor for Comparator Signals
Be sure to use a pull-up resistor that meets the requirement of the equation below.
V
p
R
'
[k]
3
where
R
V
p
Typical pull-up resistance is given below
Pull-up Resistance [k]
Pull-up Voltage [V]
.
Table 4-7. Typical Pull-up Resistance for Comparator Signals
Pull-up Voltage [V] Pull-up Resistance [k]
5 1.78
12 3.16
24 8.25
Pull-up Resistor for Control Output Signal
Be sure to use a pull-up resistor that meets the requirement of the equation below when you
mount it at the handler side of the board.
V
p
R
'
[k]
2:5
where
R
V
p
Pull-up Resistance [k]
Pull-up Voltage [V]
Typical pull-up resistance is given below.
Table 4-8. Typical Pull-up Resistance for DC Isolated Input Signal
Pull-up Voltage [V] Pull-up Resistance [k]
5 1.78
9 3.16
12 4.22
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-15
Page 62

Setting up Output Signal Pattern
Set up the signal pattern for the handler interface. Settings vary depending on the HP 4286A
operation mode.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Mode 1(
MODE 1
)
BIN sorting is performed on one of the segments dened in the frequency list table. DUTs are
classied into 9 BINs maximum based on the results for the specied segment. For the other
segments, limit test is performed.
Output signal appears on the corresponding connector pin, indicating the BIN which DUT
falls into. The limit test result is output as overall results of comparison for all specied
segments.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Mode 2(
MODE 2
)
Outputs overall results of comparison for all specied segments. Also, outputs results of
comparison and BIN sorting for each segment. The BIN sorting results are output as 4 bit
code.
Mode 2 can be further divided into
On Sweep Mode
and
On Point Mode
, depending on the
type of triggering used. Denitions of some output signals are dierent between the two
modes. See \Electrical Specication of Handler Interface
Follow the steps shown in the owchart below to set your handler interface
" for details.
.
4-16 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 63

Figure 4-2. Basic Flow of Handler Interface Setting
Step 1: Setting up for BIN Sorting
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
1.
2.
Press
4
Test Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
BIN SORT on OFF
5
, and then
N
BIN SORT MENU
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
to toggle it
ON off
.
.
3. Dene a BIN table. See \Editing BIN Table" for details.
Step 2: Setting up for Limit Test
1.
2.
Press
4
Test Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
LIMIT TEST on OFF
5
, and then
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
LIMIT TEST MENU
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
to toggle it
ON off
.
.
3. Dene a limit table. See \Editing Limit Table" for details.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-17
Page 64

Step 3: Setting up for On Point Trigger
1. Press
2.
Press
4
Trigger Mo de
5
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
TRIG EVENT
.
to toggle it
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
ON POINT
.
Step 4: Setting up for On Sweep Trigger
1. Press
2.
Press
4
Trigger Mo de
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
TRIG EVENT
5
.
to toggle it
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
ON SWEEP
.
Step 5: Setting Mode 2
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
1.
2.
3.
Press
Press
Press
4
Test Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
MODE 2
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
RETURN
5
, and then
. Press
to conrm the entry of settings.
N
HANDLER IF
.
NNNNNNNNNNN
OFF
when you do not wish to send signals to the handler interface.
Step 6: Setting Mode 1
1.
2.
3.
Press
Press
Press
4
Test Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
MODE 1
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
RETURN
5
, and then
. Press
to conrm the entry of settings.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
HANDLER IF
.
NNNNNNNNNNN
OFF
when you do not wish to send signals to the handler interface
.
4-18 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 65

HP 4286A Measurement Time
Total measurement time of the LCR meter is calculated as follows:
Event Time
/EXT TRIG
A
#
Contact check 15ms
Analog measurement 15ms/point
1
/INDEX(until the end of list sweep)
Comparator
BIN sorting 2ms
B
#
Limit test 500s/point
Measured value display 3ms+6ms/point
Handler signal output 0.1ms
/EOM
Data transfer through HP-IB 20ms/
(contact check +2 measurement points)
1
By incrementing the averaging factor by 1, total measurement time becomes 5ms
longer.For example, analog measurement time is 30ms ( = 15ms + 5ms23 ) when you
select 4 for the averaging factor.
You can turn the measured value display ON/OFF on the front panel. When you set this
function to OFF, the duration of time between EOM(End of Measurement) and next trigger
becomes shorter.
The data transfer time through HP-IB shown above includes the time required to input a
contact check comparator signal and 2-point measurement results at the same time using the
HP 9000 Series 360.
Example
The following shows the approximate duration of time required to make a 2-point measurement
by list sweep.We assume that the measured value display, comparator, and handler signal
output are respectively OFF, ON, and ON.
Calculating the time for each operation from the above
Contact check 15ms
, we obtain the following:
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-19
Page 66

Analog
30ms ( = 15ms22)
measurement
Comparator 7ms ( = 6ms + 1ms )
Handler signal
1ms
output
Total time from assertion of external trigger to output of handler signal amounts to 53 ms.
4-20 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 67

Electrical Specication of Handler Interface
The handler interface sends results of comparison from the HP 4286A to the handler interface
and allows timing control signals for measurements and handler operation to be exchanged
between the HP 4286A and handler interface.
Using these signals you can congure a highly ecient chip handling system.
This section provides the pin assignment of the handler interface connector, description of each
signal, and timing diagram of these signals.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-21
Page 68

Signal Output Mode
The handler interface has 2 signal output modes. Signals in each mode carry dierent
information.
Mode 1
Mode 2
Outputs overall results of comparison for all specied segments. Also, outputs
BIN sorting results for segments specied using
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
TEST SEG[ ]
.
Outputs overall results of comparison for all specied segments. Also, outputs
results of comparison and BIN sorting for each segment. Results of BIN sorting
are represented in 4-bit code.
Mode 2 can be further divided into
On Sweep Mode
and
On Point Mode
depending on the type of triggering used. Denitions in output signals are
dierent in these mode. See Table 4-12 for details.
Signal Lines
Signals sent from and received by the handler interface can be classied into 3 groups as
follows:
Denitions of signals in each line vary depending on the mode (mode 1 or mode 2) used. See
Table 4-10 and Table 4-12 for details.
Comparator Output Signals
/BIN1 to /BIN9, /AUX BIN, /OUT OF BIN, /PHI, /PHO, /SREJ (comparator signal for mode
1)
/F1REJ to /F10REJ, DBIN0 to DBIN3(comparator signals for mode 2)
/FAIL(overall comparator signal)
/NO CONTACT(contact check fail signal)
Control Output Signals
/INDEX(analog measurement end signal)
/EOM(measurement cycle end or comparator data enable signal)
Control Input Signals
/EXT TRIG(external trigger)
/KEY LOCK(key lock signal)
Note
\/" before some signal names means those signals are negative logic
(low-asserted) signals.
4-22 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 69

Pin Assignment and Signal Denitions (Mode 1)
The relationship between the primary/secondary parameter values and signals /BIN1 to /BIN9,
/OUT OF BINS, /AUX BIN, /PHI, /PHO, /SREJ is as follows:
Figure 4-3. BIN Sorting
Figure 4-4. Limit Test
Signals are assigned to the connector pins as follows:
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-23
Page 70

Table 4-9. Pin Assignment of Handler Interface Connector (Mode 1)
Pin
Signal
No.
1 /BIN1
2 /BIN2
3 /BIN3
4 /BIN4
5 /BIN5
6 /BIN6
7 /BIN7
8 /BIN8
9 /BIN9
10 /OUT OF BIN
11 /AUX BIN
12 /EXT TRIG
13 /EXT TRIG
14 EXT.DCV2
15 EXT.DCV2
16 +5V
Pin
Signal
No.
19 /PHI
20 /PLO
21 /SREJ
22 /FAIL
23 N.C.
24 /NO CONTACT
25 /KEY LOCK
26 N.C.
27 N.C.
28 N.C.
29 /ALARM
30 /INDEX
31 /EOM
32 COM2
33 COM2
34 COM1
4-24 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
17 +5V
18 +5V
35 COM1
36 COM1
Page 71

Table 4-10. Signal Denition (Mode 1)
Pin
No.
Signal Input
/Output
Denition and Description
1 /BIN1 Output Comparator signal for DUT classication. Informs which BIN the DUT has
2 /BIN2
been classied into. All signals are output through open-collector.
3 /BIN3
4 /BIN4
5 /BIN5
6 /BIN6
7 /BIN7
8 /BIN8
9 /BIN9
10 /OUT OF BINS Output Is output if the primary parameter has no been classied into any BIN.
11 /AUX BIN Output Is output if the primary parameter has been classied into a BIN and the
secondary parameter has not been classied into any BIN.
12 /EXT TRIG Input External trigger. Used in the external trigger mode. Triggers the handler at
13 /EXT TRIG
the falling edge or rising edge of pulse, which can be selected through
HP 4286A's softkey setting.
14 EXT.DCV2 Input External DC voltage. This voltage is supplied to the DC isolated input signal
15 EXT.DCV2
(/EXT TRIG, /KEY LOCK) and DC isolated output signal (/ALARM, /INDEX,
/EOM). Change the switch settings on the top shield when using the internal
DC voltage.
16 +5V Output Internal DC voltage. Max. permissible current is 0.5A. If current above this
17 +5V
limit ows, the overcurrent detection circuit is activated to stop voltage
output.
18 +5V
19 /PHI Output Primary parameter upper limit OVER signal. Is output together with
/OUT OF BIN if the measured value exceeds the upper limit for BIN1 to 9.
(See Figure 4-3.)
20 /PHO Output Primary parameter lower limit UNDER signal. Is output together with
/OUT OF BIN if the measured value falls below the lower limit for BIN1 to
9. (See Figure 4-3.)
21 /SREJ Output Secondary parameter limit OUT signal. Is output when the measured value
is outside the preset limits. (See Figure 4-3 .)
22 /FAIL Output Overall comparator output signal. Is output at the end of measurement
cycle if one of the conditions below is met.
/NO CONTACT is output.
/OUT OF BINS or /AUX BIN is output for the segment currently under
BIN sorting.
Limit line test fails for segments other than the above.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-25
Page 72

Table 4-10. Signal Denition (Mode 1) (continued)
Pin
No.
Signal Input
/Output
Denition and Description
23 N.C. | Not used.
24 /NO CONTACT Output Contact check fail signal. Is output if the measured DC resistance is outside
the preset limits for contact check.
25 /KEY LOCK Input Key lock signal. All key operations on the HP 4286A front panel are
disabled if this signal is received.
26 N.C. | Not used.
27
28
29 /ALARM Output Failure signal. Is output if self-test results are faulty, if power is
instantaneously interrupted, or if a specic circuit malfunctions. During
power interruption, this signal remain ON only during loss of power.
30 /INDEX Output Analog measurement end signal. You can connect the handler to a new DUT
when this signal is received by the handler. Note that measured data will be
available only when /EOM is output.
31 /EOM Output Measurement cycle end signal. Measured data and comparator signals are
valid when this signal is output.
32 COM2 | External DC voltage COMMON for EXT.DCV2
33 COM2
34 COM1 | External DC voltage COMMON. This COMMON supplies DC voltage to DC
35 COM1
isolated output signals (/BIN1 to /BIN9, /OUT OF BIN, /AUX BIN, /PHI,
/PLO, /SREJ,/FAIL, /NO CONTACT).
36 COM1
Figure 4-5 shows timing diagram for mode 1.
Figure 4-5. Timing Diagram (Mode 1)
4-26 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 73

Time Min. Max.
Note
T1
T2
T3
1
T3 represents the
Trigger pulse width
Measurement start delay
Wait time from /EOM output to
triggering
1
minimum duration of time
1s |
| 600s
5ms 600ms
required for the
HP 4286A to function properly. Min. and Max. represents the time
required respectively when the most simple and most complex
measurement conditions are set. Note that when you specify
excessively short time, /EXT TRIG may be ignored, causing the
HP 4286A to malfunction.
The items which can aect on T3 are listed below. T3 gets
the items are ON and/or the number of frequency points increases.
a. Number of measurement points
b. Setting the beeper ON/OFF
c. Setting limit test ON/OFF, and number of frequency points
d. Setting BIN sorting ON/OFF, and number of frequency points
The beeper signicantly aects T3, adding 100ms when it is ON.
See
Function Reference
for detailed description of measurement time.
Comparison and output require about 0.5ms
The display time is about 3ms+6ms/points.
longer
if
Pin Assignment and Signal Denitions (Mode 2)
The relationship between the primary/secondary parameter values and signals /F1REJ to
/F10REJ and /DBIN0 to /DBIN3 is as follows:
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-27
Page 74

Figure 4-6. BIN Sorting
Figure 4-7. Limit Test
4-28 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 75

Table 4-11. Handler Interface Connector Pin Assignment (Mode 2)
Pin
No.
1 /F1REJ
2 /F2REJ
3 /F3REJ
4 /F4REJ
5 /F5REJ
6 /F6REJ
7 /F7REJ
8 /F8REJ
9 /F9REJ
10 /F10REJ
11 /FAIL
12 /EXT TRIG
13 /EXT TRIG
14 EXT.DCV2
15 EXT.DCV2
16 +5V
Signal
Pin
Signal
No.
19 DBIN0
20 DBIN1
21 DBIN2
22 DBIN3
23 N.C.
24 /NO CONTACT
25 /KEY LOCK
26 N.C.
27 N.C.
28 N.C.
29 /ALARM
30 /INDEX
31 /EOM
32 COM2
33 COM2
34 COM1
17 +5V
18 +5V
35 COM1
36 COM1
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-29
Page 76

Table 4-12. Signal Denition (Mode 2)
Pin
Signal Input/
No.
1 /F1REJ
2 /F2REJ
3 /F3REJ
4 /F4REJ
5 /F5REJ
6 /F6REJ
7 /F7REJ
8 /F8REJ
9 /F9REJ
10 /F10REJ
11 /FAIL
12
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
See Table 4-9. Same as
to
18
Output
Denition and Description
Output Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 1.
Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 2.
Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 3.
Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 4.
Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 5.
Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 6.
Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 7.
Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 8.
Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 9.
Output if the DUT is rejected at sweep point 10.
Output Test-failed or no-contact signal. This signal is output at the end of
measurement cycle if one of the conditions below is met.
/NO CONTACT is output.
/OUT OF BINS is output for the segment currently under BIN sorting.
Limit line test fails for segments other than the above
.
with mode
1. (See
Table 4-9.)
19 DBIN0 Output Comparator output for DUT classication. The range of acceptable
20 DBIN1
21 DBIN2
measurements for comparator output is the same as for mode1. A 4-bit
binary signal of DBIN0 to DBIN3 is output as comparator signal. See
Figure 4-6 for details.
22 DBIN3
23
See Table 4-9. | Same as with mode 1. (See Table 4-9.)
to
29
1
This signal is output at the end of sweep measurement.
4-30 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 77

Table 4-12. Signal Denition (Mode 2) (continued)
Pin
No.
Signal Input/
Output
Denition and Description
30 /INDEX Output Analog measurement end signal. Signal denition varies depending on the
sweep mode used, as shown below.
On Sweep Mode
Is output at the end of analog measurement of the last sweep point. You
can connect the handler to a new DUT when this signal is received by the
handler.
On Point Mode
Is output at the end of analog measurement of each sweep point. You can
start measurement of the next sweep point when this signal is received
by the handler.
Note that measured data will be available only when /EOM is output,
regardless of the sweep mode used.
31 /EOM Output Measurement cycle end signal. Signal denition varies depending on the
sweep mode used, as shown below.
On Sweep Mode
Is output at the end of sweep measurement. Measured data and
comparator signals are valid when this signal is output.
On Point Mode
Is output when valid data are obtained after measurement (including time
required for the comparator to make comparisons) of each sweep point.
Comparator signals are valid when /EOM is output at the end of
measurement of the last sweep point.
32
See Table 4-9. | Same as with mode 1. (See Table 4-9.)
to
36
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-31
Page 78

Figure 4-8 and Figure 4-9 shows timing diagram for mode 2.
Figure 4-8. Timing Diagram (mode 2: On Sweep Mode)
Figure 4-9. Timing Diagram (mode 2: On Point Mode)
Note
Settling time includes switching time of correction data.
See
Function Reference
Comparison and output require about 1ms+0.1ms/point, display about
3ms+6ms/point.
See Figure 4-5 for description of T1, T2, and T3.
4-32 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
for detailed description of measurement time.
Page 79

Electrical Characteristics of Signals
This section provides description of electrical characteristics of each signal and conguration of
I/O circuits.
Electrical characteristics of each signal do not change regardless of the function (comparator
function and list sweep comparator function) used.
DC Isolated Output Signals
Each of the DC isolated signals (pins 1 to 11, 19 to 24, 29 to 31) is output through an
open-collector and photocoupler.
You can use switches on the handler interface board to select the desired power source. The
internal source (5V) or an external power source (5 to 24V for comparator output signals or 5 to
15V for control output signals) can be selected. Note that you usually use an external power
source to supply voltage to control output signals.
You can connect the internal pull-up resistor of 4.7k to control signals by simply changing
switch settings. Note that you must mount a pull-up resistor to the handler side of the board
for comparator output signals.
Table 4-13. Electrical Characteristics of DC Isolated Output Signals
Output Rated Voltage Output Max. Current COMMON
LOW HIGH
Comparator Output Signal0.5V 5V to 24V 5mA COM1
Control Output Signal0.5V 5V to 15V 5mA COM2
Figure 4-10 and Figure 4-11 show the circuit conguration of comparator and control output
signals, respectively.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-33
Page 80

Figure 4-10. Circuit Conguration of Comparator Output Signals
4-34 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 81

Figure 4-11. Circuit Conguration of Control Output Signals
DC Isolated Input Signals
DC isolated input signals can be divided into /EXT TRIG and /KEY LOCK.
/EXT TRIG
/EXT TRIG (pins 12 and 13) is input to the cathode of photocoupler LED
is triggered at the falling edge or rising edge of pulse
HP 4286A's softkey setting. Drive voltage is applied to the anode of photocoupler LED
by the internal (5V) or external (EXT.DCV2) power source. (Use switches on the handler
interface board to select the desired source.)
, which can be selected through
. The HP 4286A
Note
/KEY LOCK
/KEY LOCK(pin 25) is input to the cathode of photocoupler LED. All keys on the HP 4286A
front panel are disabled when this signal is low. Drive voltage is applied to the anode of
photocoupler LED through pins 14 and 15 by the internal (5V) or external (EXT.DCV2) power
source. (Use switches on the handler interface board to select the desired source.)
Use SW2 to select the proper resistor according to the level of anode voltage
applied. This resistor is used to limit the trigger voltage to the specied level.
See Table 4-5 for details.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-35
Page 82

Table 4-14. Electrical Characteristics of DC Isolated Input Signals
Input Signal Input Voltage Input Current (at LOW) COMMON
LOW HIGH 5V 12V 15V
/EXT TRIG
/KEY LOCK
1V Voltage01V
HIGHVoltage
1V Voltage01V
HIGHVoltage
10.0mA 12.0mA 15.0mA Internal Power
12.5mA 12.0mA 15.0mA Internal Power
Figure 4-12 shows the circuit conguration of input signals.
Source
HP 4286A
COMMON
External Power
Source
COM2
Source
HP 4286A
COMMON
External Power
Source
COM2
Figure 4-12. Circuit Conguration of Handler Interface Input Signals
Note
When you use the internal power source, use COM2 as COMMON. To do this, set
SW2(4) to ON position to connect the HP 4286A COMMON to COM2.
4-36 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 83

Handler Interface Board Switches
You can select the desired signal I/O format for the handler interface by changing settings of
switches on the interface board. Two switches are provided for signal I/O interface and their
settings can be changed on the top shield.
Top Cover Removal
Tools Required
Torx screwdriver, T15
Pozidriv screwdriver, pt size #2 (medium)
Procedure
1. Disconnect the power cable from the analyzer.
2. Remove the two rear feet behind the top cover.
3. Loosen the top cover rear screw.
4. Slide the top cover toward the rear and lift it o.
Figure 4-13 illustrates the locations and default settings of the switches
Figure 4-13. Handler Interface Board Switches
Top Cover Attachment
.
Procedure
1. Put the top cover and slide it toward the front.
2. Tighten the top cover rear screw.
3. Attach the two rear feet behind the top cover
.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-37
Page 84

Warning
Do not connect the power cable to the meter during the top cover is
removed.
4-38 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 85

Performing Calibration with Working Standard (only with
option 004)
Note
This procedure is necessary when you use HP 4286A with option 004.
Measuring the Working Standard Value
Measure the working standard to obtain LSrequired for LOAD compensation. Specify 51 for
resistor.
1. Prepare the test head and perform OPEN/SHORT/LOAD calibrations for the contact surface
R
of APC-7
connector.
2. Connect xture to the test head and perform OPEN/SHORT compensations. Make sure that
you performed the xture compensation with shorting device for the working standard.
3. Connect the chip resistor for working standard to the xture.
4. Measure Lsof the connected chip resistor.We recommend the following conditions for
accurate and robust measurement.
Frequency 100 MHz
Measurement parameter L
s-Rs
Averaging factor 32
OSC level 0.5 V
5. Record the measurements.
Calibration with Working Standard
Follow the procedure below.
1. Make sure that you complete the procedure shown above
.
2. Set up calibration kit.
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
CAL KIT
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
,
USER KIT
to toggle it
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
USER
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
MODIFY
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
DEFINE STANDARD
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
LOAD RESIST. (R)
Press
4
5,4
5,4
5
1
5
consequently to set R to 51 .
x1
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
LOAD INDUCT. (L)
.
Set the value which is given by the procedure in \Measuring the Working Standard Value"
to LS.
3. Perform OPEN/LOAD/SHORT calibration procedures.
The table below lists typical values of the working standars with option 004. The values serves
as reference: use actually obtained results for calibration kit.
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-39
Page 86

Table 4-15. Typical Values of Working Standard (with option 004)
P/N Size R
5182-0433 1.020.5 mm
5182-0434 1.620.8 mm
5182-0435 2.021.25 mm
5182-0436 3.221.6 mm
'
200 pH
'
300 pH
'
500 pH
'
700 pH
L
s
s
'
51
'
51
'
51
'
51
4-40 HP 4286A with Chip Handler
Page 87

Restoring Settings After Power Interruption
Instantaneous power interruption resets the HP 4286A to default settings. The HP 4286A must,
therefore, be set to your own settings again after power interruption. To do this, you can use
the backup SRAM disk memory or built-in exible disk drive to automatically restore your
settings.
When you wish to use the exible disk drive, rst save your settings in the le named
on a exible disk. Then, insert this disk in the disk drive and keep it inserted while the
HP 4286A is running. When you wish to use the SRAM disk memory, save the
the disk memory. In either case, the HP 4286A will read the contents of this le to recall its
settings and calibration data if the power is interrupted. AutoRecall provides a fast way to
recover your HP 4286A settings after power interruption.
Note
When you have the
disk memory, the contents of the le in the exible disk will be read into the
HP 4286A.
All data in the disk memory will be lost in 3 days after power interruption.
Backup batteries can be automatically recharged when the HP 4286A is ON.
AUTOREC
le stored in both the exible disk and RAM
AUTOREC
AUTOREC
le on
HP 4286A with Chip Handler 4-41
Page 88

Page 89

5
Typical Functions
The HP 4286A has a number of functions other than those explained in the previous chapters.
This chapter describes the major features of and operation procedures associated with these
functions.
Functions available with the HP 4286A are listed below. If you nd a function that suits your
task, become familiar with the description of that function and its key operation sequence in
the associated section.
Key Features:
Measurement-related Functions:
Point Delay and Sweep Delay
Point Averaging
OSC Level Monitor
Display-related Function:
Entering Titles on the Screen
Other Functions
Saving and Recalling
Printing or Plotting
Logging Key Sequence into a Program (Option 1C2 Only)
Typical Functions 5-1
Page 90

Point Delay and Sweep Delay
Delay functions stabilize the measurements by delaying the measurement start for a specied
time after the stimulus is set.
Making a Point Delay Measurement
1. Press
2.
3. Enter the point delay time and press one of the unit keys such as
Press
4
Delay Time
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
5
.
POINT DELAY TIME
.
4x15
.
Making a Sweep Delay Measurement
1. Press
2.
3. Enter the sweep delay time and press one of the unit keys such as
4
Delay Time
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
SWEEP DELAY TIME
5
.
.
4x15
.
Delay Description
Point Delay
The measurement start for each point is delayed for a user-specied time after the
stimulus is set at each point.
Sweep Delay
The sweep start is delayed for a user-specied delay time after the trigger
.
5-2 Typical Functions
Figure 5-1. Point Delay and Sweep Delay
Page 91

Averaging
HP 4286A employs point averaging method, which allows data measured at the same frequency
to be averaged. This function reduces non-repeatable variations contained in measured values.
1. Press
2.
3.
4. Enter the averaging factor (number of measurements) and press
5.
4
Sweep Setup
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
Press
SEGMENT
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
EDIT
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
SEGMENT DONE
5
.
to select the desired segment for averaging.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
AVERAGING ON POINT
.
.
4x15
.
6. Repeat list item 2 through list item 5 for the segment selected.
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
LIST DONE
.
7.
Further Discussion
Point Averaging averages each data point by a user-specied averaging factor
. The HP 4286A
repeats measuring the same point until the averaging factor is reached. It then divides the
vector summation of measurement values by the averaging factor and starts measuring the
next point.
For some other impedance analyzers, 2 types of avaraging methods are available, which is
sweep averaging method and point avaraging method. When you compare results with those
obtained by other impedance meter or analyzer, be sure that the both measurement are
based on point averaging method.
Figure 5-2. Point Averaging
Typical Functions 5-3
Page 92

OSC Level Monitor
Level Monitor allows monitoring of voltage applied to or current owing through the DUT.
1. Press
2.
4
Select the desired parameter you wish to monitor. Press
monitor the OSC level.
Press
Press
Signal level is displayed on the screen.
Monitor
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
AC-V
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
AC-I
5
.
to monitor the voltage.
to monitor the current.
Figure 5-3. Level Monitor Function
NNNNNNNNNNN
OFF
when you do not wish to
5-4 Typical Functions
Page 93

Entering Titles on the Screen
The label function allows you to enter the desired characters on the screen as titles as long as
those characters can be used on the HP 4286A.
Figure 5-4. Label Function
Title Entry Procedure
N
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
TITLE
.
1.
2.
Press
4
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
LETTER MENU
Display
5
, and then
3. Enter the desired characters.
Use any of
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
<upper>
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
,
<lower>
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
,
<digit>
, and
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
<other>
lower characters, or numbers.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
MORE
repeatedly until the desired character appears on the screen
Press the key that corresponds to the character to be entered. Press
delete characters on the screen.
4. Continue to enter all characters as described above.
NNNNNNNNNNNNN
5. When you nish, press
Note
You can enter characters on your keyboard when your HP 4286A is equipped
N
DONE
.
with option 1C2.
as necessary to enter upper or
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
BACK SPACE
to
Typical Functions 5-5
Page 94

Saving and Recalling
The save/recall functions allow you to save and recall a HP 4286A setting, measurement data,
or display image.
The HP 4286A has two kinds of mass storage, a built-in exible drive and a RAM disk memory.
Each mass storage supports two kinds of format, LIF (Logical Interchange Format) and
MS-DOS
R
. The HP 4286A automatically detects the disk format as either LIF or MS-DOS
R
.
Caution
The les on the RAM disk are kept until the HP 4286A is turned o. When the
HP 4286A is turned o, the data on the RAM disk is lost.
Saving HP 4286A Setting and Measurement Trace
R
1. Insert a LIF or MS-DOS
formatted 3.5 inch disk into the built-in disk drive. When you are
saving an instrument state le to the RAM disk, skip this step. See \Initializing a Disk/RAM
Disk for Use" in the following section for how to initialize your disk.
2. Press
3.
4
Save/Recall
Select where to store the le by pressing either
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
STOR DEV [MEMORY]
5
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
(RAM disk). Press
STOR DEV [DISK]
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
STOR DEV [DISK]
to display the desired storage in
(built-in disk drive) or
[].
4.
5.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
STATE
.
Follow the procedure in \Title Entry Procedure" to enter a lename. Then press
N
NNNNNNNNNNNNN
DONE
.
Recalling a Saved HP 4286A Setting and Measurement Trace
1. Insert the appropriate disk (if you are recalling an instrument state le from the RAM disk,
skip this step).
2. Press
3.
4
Save/Recall
Select where to store the le pressing either
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
STOR DEV [MEMORY]
5
.
(RAM disk).
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
N
STOR DEV [DISK]
(built-in disk drive) or
4. Search for the lename you want to recall (the les are listed as softkey labels).
5.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
RECALL FILE
, and the name of each stored le is listed as a softkey label. Press the
softkey that corresponds to the target le.
6. If the target le is not found on any softkey label, scroll other labels by pressing
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
PREV FILES
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
or
NEXT FILES
.
7. Press the softkey corresponding to the target le.
Note
You can automatically recall the instrument state every time the HP 4286A is
turned ON. Use \
AUTOREC
" as a lename. The HP 4286A recalls this le from a
disk that is in the built-in disk drive when it is turned ON.
5-6 Typical Functions
Page 95

Saving a Display Image to an HP-GL File
1.
Press
4
Save/Recall
2.
3.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
Select where to store the le by pressing either
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
GRAPHICS
5
, then
STOR DEV [MEMORY]
4.
Enter lename. Then press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SAVE FILE
.
(RAM disk).
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
DONE
and
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
ASCII SAVE
.
N
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
STOR DEV [DISK]
(built-in disk drive) or
The HP 4286A saves an HP-GL le with an \
for a LIF format. If you want to change the extension for a DOS format, press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
SAVE FILE
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
,
ASCII SAVE
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
,
DEFINE EXTENSION
.HPG
" extension for a DOS format, or a \_G" sux
4
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
, and
GRAPHICS [.HPG]
Save/Recall
to call the extension
5
, then
dening menu. Then enter a new extension. This feature is only available for a DOS format
disk.
Saving Measured Data for a Spreadsheet
1. Insert a DOS format disk into the built-in disk drive
2. Press
3.
4.
5.
The HP 4286A saves an ASCII le with a \
extension, press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
ASCII DATA [.TXT]
4
Save/Recall
5
, then
SAVE FILE
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
DATA ONLY (ASCII)
.
Select the built-in disk drive as the storage device by toggling to
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Enter a lename. Then press
DONE
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
4
Save/Recall
5
, then
SAVE FILE
to call the extension dening menu.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
and
ASCII SAVE
.
.TXT
" extension. If you want to change the
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
,
ASCII SAVE
.
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
STOR DEV [DISK]
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
,
DEFINE EXTENSION
, and
Then enter a new extension. The measured data is saved as ASCII text. Each value is
separated by a tab. When you open this le from the spreadsheet software
, specify the le
format as the \TEXT with TAB delimiter".
Purging a File
If there is a le on the disk that has the same name you entered when saving a le, the error
message, \lename error" is displayed. To save the le, you must use another lename or purge
the old le.To purge a le, press
4
Save/Recall
5
, then
select the displayed lename by pressing the associated softkey
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
FILE UTILITIES
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
and
PURGE FILE
then
Initializing a Disk/RAM Disk for Use
1. Insert a disk that is not write protected (if you are initializing the RAM disk, skip this step).
2.
Press
4
Save/Recall
3.
Select the disk format (either DOS or LIF) by toggling
4.
Select the initialized storage device by toggling
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
INITIALIZE
5.
5
, and then
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
FILE UTILITIES
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
FORMAT [DOS]
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
STOR DEV [DISK]
or
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
or
[MEMORY]
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
[LIF]
.
.
Typical Functions 5-7
Page 96

6.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
INITIALIZE DISK: YES
to initialize the RAM disk or the disk.
5-8 Typical Functions
Page 97

Printing or Plotting
Printing or Plotting a Display Image
1. Connect a printer or a plotter to the HP 4286A with an HP-IB cable.
2. Set the HP-IB address as follows:
Printer : 1 (verify that the printer is NOT set to \Listen Always").
Plotter : 5
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
3. Press
4.
Press
4
5
. Then press
Local
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
4
5
PRINT [STANDARD]
Copy
SYSTEM CONTROLLER
to print or
4
.
Copy
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
5
PLOT
to plot.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
To stop printing or plotting in progress, press
4
Copy
5
COPY ABORT
.
Using a Dierent HP-IB Address for the Printer/Plotter
N
1.
2.
3.
Press
4
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
Press
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
5
SET ADDRESSES
Local
ADDRESS: PLOTTER
RETURN
to return to the top menu.
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
or
ADDRESS: PRINTER
. Then enter a new HP-IB address.
Typical Functions 5-9
Page 98

Logging the Key Sequence into a Program (Option 1C2 Only)
When Option 1C2 is installed, the logging function allows you to log your key sequence into an
instrument BASIC program. This function allows you to create a program without referring to
the
HP-IB Command Reference
1.
2.
Press
Toggle
4
System
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
5
IBASIC
LOGGING on OFF
.
.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
to
ON off
.
3. Press the front panel keys according to your required setting.
4.
5.
6.
Press
Toggle
Press
4
System
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
NNNNNNNNNNNNNN
EDIT
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
5
IBASIC
.
LOGGING ON off
to enter the edit mode.
NNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNNN
to
on OFF
.
7. Verify that the program was created according to your key sequence.
Note
When you log the calibration and the xture compensation procedure, you
must modify the program to wait for completion of the calibration or the
xture compensation.
5-10 Typical Functions
Page 99

Resetting the HP 4286A
Press
4
5
to reset all function parameters to the preset values.
Preset
See
Function Reference
for preset values.
Typical Functions 5-11
Page 100

 Loading...
Loading...