Page 1
5000V Megohmmeters
Models 5000N/5100/5110
USER MANUAL
1
0
0
0
1
5
0
0
1
k
0
1
0
5
3
k
0
2
0
k
3
0
3
0
1
0
0
5
0
0
2
k
2
k
5
0
0
2
0
5
0
2
0
2
0
0
5
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
5
0
0
3
0
5
0
2
k
0
4
0
0
1
0
0
0
5
k
2
0
0
1
0
0
5
0
0
2
k
1
0
k
5
0
2
6
V
0
0
5
3
0
0
V
k
1
G
2
0
Ω
k
M
3
Ω
0
k
k
Ω
2
M
Ω
5
G
0
0
V
Ω
M
Ω
Ω
1
M
V
0
0
0
Ω
G
Ω
G
Ω
Ω
M
k
Ω
3
3
µ
A
1
3
(
0
0
V
m
a
x
.
)
G
5
0
0
0
V
Page 2

Page 3
Limited Warranty
The Megohmmeters Model 5000N, 5100 and 5110 are warranted to the
owner for a period of 2 years from the date of original purchase
against defects in manufacture. This limited warranty is given by
AEMC® Instruments, not by the distributor from whom it was pur-
chased.
or if the defect is related to service not performed by AEMC
This warranty is void if the unit has been tampered with, abused
®
Instruments.
For full and detailed warranty coverage, please read the Warranty
Coverage Information, which is attached to the Warranty Registration
Card (if enclosed) or is available at www.aemc.com. Please keep the
Warranty Coverage Information with your records.
What AEMC
®
Instruments will do:
If a malfunction occurs within the warranty period, you may return the
instrument to us for repair, provided we have your warranty registration
information on file or a proof of purchase. AEMC® I
nstruments will, at its
option, repair or replace the faulty material.
REGISTER ONLINE AT:
www.aemc.com
Warranty Repairs
What you must do to return an Instrument for Warranty Repair:
First, request a Customer Service Authorization number (CSA#) by phone or
by fax from our Service Department (see address below), then return the
instrument along with the signed CSA Form. Please write the CSA number
on the outside of the shipping container. Return the instrument, postage or
shipment pre-paid to:
Chauvin Arnoux
®
, Inc. d.b.a. AEMC® Instruments
Service Department
15 Faraday Drive • Dover, NH 03820 USA
Tel: (800) 945-2362 (Ext. 360)
(603) 749-6434 (Ext. 360)
Fax: (603) 742-2346 or (603) 749-6309
Caution: To protect yourself against in-transit loss, we recommend you
insure your returned material.
Note: You must obtain a CSA# before returning any instrument.
Page 4

Table of Contents
Warning ......................................................................................4
International Electrical Symbols .................................................4
Megohmmeter Model 5000N....................................................5
Receiving Your Shipment.....................................................5
Ordering Information ............................................................5
Accessories And Replacement Parts...................................5
Description ...........................................................................6
Specifications ....................................................................... 7
Control & Connector Identification .......................................9
Battery Replacement..........................................................10
AC Supply Module .............................................................10
Megohmmeter Model 5100/5110............................................11
Receiving Your Shipment...................................................11
Ordering Information ..........................................................11
Accessories And Replacement Parts.................................11
Description .........................................................................12
Specifications - Model 5100 ...............................................13
Specifications - Model 5110 ...............................................15
Control & Connector Identification .....................................17
AC Supply Module .............................................................18
Disassembly.......................................................................19
Using the Clock/Timer........................................................20
Operation: Models 5000N, 5100 & 5110................................22
The Analog Scale...............................................................22
Preliminary Check ..............................................................23
How to use the Push-To-Test Button.................................23
Utilizing the Guard Terminal...............................................24
Voltage Measurements (Safety Check) ............................. 25
Audible Signal ....................................................................26
Precautions when making DC Insulation Tests .................27
Insulation Measurement - Connections .............................27
Insulation Resistance Measurements on Motors ...............30
- 2 -
Page 5

Understandi
Ratio Testing ......................................................................33
Types of Tests.................................................................... 34
Spot Reading Test .............................................................34
Polarization Index...............................................................35
Step Voltage Test...............................................................36
The Effects of Temperature ...............................................37
Interpreting the Results ......................................................38
Maintenance............................................................................39
Warning..............................................................................39
Cleaning ............................................................................. 39
Repair And Calibration...........................................................40
Technical And Sales Assistance...........................................40
ng Insulation Testing ........................................32
- 3 -
Page 6
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Warning
These safety warnings are provided to ensure the safety of
personnel and proper operation of the instrument.
WARNING: HIGH VOLTAGE PRESENT
• Do not attempt to perform any tests with these instruments
until you have read the instruction manual.
• Safety is the responsibility of the operator!
• Tests are to be carried out only on non-energized circuits!
Check for live circuits before making resistance measurements (safety chec
• These Megohmmeters are sources of high voltage, as is the
sample connected to them. All persons performing or
assisting in the tests must employ all safety precautions to
prevent electrical shock to themselves a
• AEMC
• When testing capacitance samples, make sure that they have
• Megoh
• Use the leads supplied with the megohmmeters. If they are
®
considers the use of rubber gloves to be an excellent
safety practice even if the equipment is properly operated and
correctly grou
been properly discharged and that they are safe to touch.
Dielectric insulation samples should be short-circuited for at
least five times the amount of time they were energiz
mmeters should never be used in an explosive
environment.
defective or worn, replace before testing.
k).
nd to others.
nded.
ed.
International Electrical Symbols
This symbol signifies that the instrument is protected by double
or reinforced insulation. Use only specified replacement parts
when servicing the instrument.
This symbol signifies CAUTION! and requests that the user refer
to the user manual before using the instrument.
Risk of electric shock. The voltage at the parts marked with this
symbol may be dangerous.
- 4 -
Page 7

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
MEGOHMMETER MODEL 5000N
Receiving Your Shipment
Upon receiving your shipment, make sure that the contents are
consistent with the packing list. Notify your distributor of any missing
items. If the equipment appears to be damaged, file a claim immediately
with the carrier and notify your distributor at once, giving a detailed
description of any damage.
Ordering Information
Megohmmeter Model 5000N................................................ Cat. #186.100
Includes megohmmeter, eight 1.5V “AA” batteries, one shielded lead,
two color-coded safety leads, insulated alligator clip, test probe
batteries,spare fuse, carrying case and user manual.
Accessories and Replacement Parts
AC power supply module with line cord and plug
for switch-selectable 110/220V
AC at 47 to 400Hz................ Cat. #100.142
Protective rubber case with handle, safety yellow ............... Cat. #2980.02
Fuse, set of five, 0.1A slow blow
for AC supply module...........................................................Cat. #100.438
Fuse, set of one, 0.3A .......................................................... Cat. #100.429
Replacement lead, (green and blue clips) ...........................Cat. #1017.23
7-pin shielded lead, 10 ft
for Models 1000N/5000N/5100 ............................................ Cat. #2950.10
Probe and clip for Model 1000N/5000N...............................Cat. #100.404
- 5 -
Page 8

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Description
AEMC® Instruments Model 5000N (Cat. #186.100) is a portable, multirange, high-sensitivity megohmmeter capable of measuring a wide range
of insulation resistances from 10 kilohms to 3000 gigohms (3,000,000
megohms). The Model 5000N has four test voltages of 500, 1000, 2500,
and 5000 volts. Each test voltage setting has two overlapping resistance
ranges of 30MΩ to 30,000MΩ and 3GΩ to 3000GΩ on a long (9.4") dial.
In addition, the Model 5000N has a unique low insulation test range of 10
to 30,000kΩ with a constant current of 33µA (maximum voltage of
DC), which is useful for testing old or flooded installations. A
1300V
voltmeter (safety check) with a range of 0 to 600 volts is standard.
The Model 5000N may be powered by either AC or DC. DC power is
supplied by eight 1.5V alkaline “AA” batteries. As an option, an AC line
supply module and cord for 110/220V
in the battery compartment.
An audible signal, consisting of approximately ten beeps per minute, is
present when the megohmmeter is ON, and serves as a time base for
tests of long duration. A green LED, when ON, indicates that the
batteries are good when the push-to-test button is depressed. It also
serves as a warning light when the instrument is in use, indicating that
the selected test voltage is present at the terminals.
AC at 47 to 400Hz can be inserted
- 6 -
Page 9

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Specifications
INSULATION TESTS
DC Test Voltages:
500, 1000, 2500, 5000V
Megohm Ranges:
For each test voltage two direct reading ranges:
30 to 30,000MΩ
3 to 3000GΩ
(3000 to 3,000,000MΩ)
Short Circuit Current: 3mA (max)
Accuracy: 5% of reading typical
Charging Time:
MΩ range: 0.3 seconds/µF
GΩ range: 3 seconds/µF
Discharging Time:
Automatic discharge when test button is released; 0.1 seconds/µF
Scale:
Two large overlapping scales: 4.7" (119 mm) for each range
Test Voltage Generation:
Solid state circuitry generating rated test voltage across the full range
RESISTANCE TESTS
Test Current: Constant 33 µA DC
Kilohm Range: 10 to 30,000kΩ (30MΩ)
Maximum Test Voltage: 1300V
Accuracy: 5% of reading typical
DC
VOLTAGE TESTS (SAFETY CHECK)
Voltage Range: 0 to 600VAC/DC
Accuracy: 3% of full scale
- 7 -
Page 10

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Audible Test Signal:
Ten beeps per minute
Power Supply:
Eight 1.5V “AA” alkaline batteries (NEDA 15A). Typical battery life: 350
one-minute tests; power consumed only when test button is depressed;
built-in battery check by green LED.
Option:
110/220V selectable
47 to 400Hz AC supply module
Dielectric Test: 4000V
AC, 60Hz, 1 minute
Fuse Protection:
0.3A high interrupting capacity fuse between line and guard terminals
Meter Movement: Rugged taut band suspension
Dimensions: 7.7 x 5.2 x 3.75" (196 x 132 x 95mm)
Weight: 2.2 lbs (1 kg)
Temperature Range: 23° to 122°F (-5° to +50°C)
Case: High impact gray polycarbonate
Terminals:
Color-coded safety terminals; guard terminal eliminates surface
leakage errors
Electromagnetic Compatibility:
CEI 801-2: Electrical Discharge
Class II
CEI 801-3: Magnetic Fields 3 V/m
CEI 801-4: Rapid Transients Class II
CEI 801-5: Electrical Shock (5KV 2 Joules)
- 8 -
Page 11
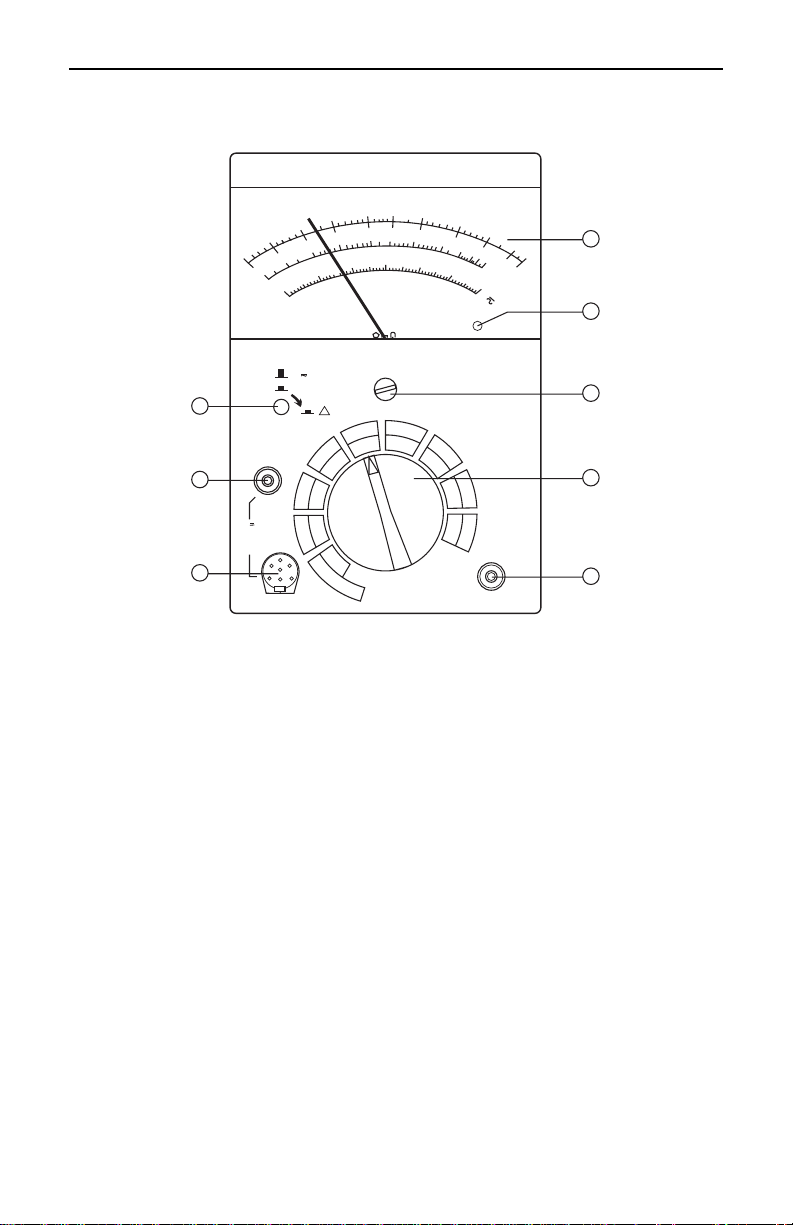
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Control & Connector Identification
1
0
0
0
5
2
0
0
2
0
1
0
0
5
3
0
k
3
0
3
OFF
ON
TURN TO
1
LOCK
2
+ EARTH
V
GΩ
MΩ
kΩ
3
2
k
0
5
0
1
k
0
1
0
5
k
0
2
0
0
0
2
0
0
1
V
!
0
0
0
1
V
G
0
0
0
Ω
1
M
V
0
Ω
0
5
G
V
Ω
0
M
0
5
k
3
Ω
3
µ
A
1
3
(
0
0
V
m
a
x
.
)
1. PUSH-TO-TEST button
Lock “ON” by turning button a quarter turn to the right.
OFF Position: Voltmeter position
ON Position: Test position with voltage present at outputs
2. EARTH terminal (green)
Connects to ground for insulation testing.
3. LINE terminal (black)
Connects to the equipment to be tested.
4. Analog Measurement Scale
5. Battery Power Indicator
Green light ON indicates that the batteries are good when the
PUSH-TO-TEST button is depressed. Audible “beep” is also
emitted approx every 6 seconds.
6. Mechanical Zero Adjust
7. Selection Switch
8. GUARD terminal (blue)
Used to minimize the effect of leakage current.
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
5
2
k
1
0
0
0
k
2
5
0
0
5
k
2
0
0
3
5
0
0
4
0
0
5
0
MEGOHMMETER
MODEL 5000N
2
5
0
V
0
V
2
M
5
Ω
Ω
0
0
G
V
Ω
M
Ω
G
Ω
5
0
0
1
0
0
0
2
1
0
k
1
0
0
k
5
0
2
0
1
G
2
0
k
M
3
Ω
0
k
0
k
Ω
6
0
V
Bat.
4
3
k
Ω
5
6
5
0
0
0
V
5
0
0
0
V
7
8
- GUARD- LINE
- 9 -
Page 12
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Battery Replacement
The Model 5000N is powered by eight 1.5V “AA” batteries. To replace
the batteries, disconnect the instrument from any circuits, verify the
PUSH-TO-TEST button is in the OFF position and proceed as follows:
• Unscrew the four standard
Access panel screws
Access panel
Figure 2
screws on the four corners of
the battery pack and remove
the battery pack.
• Replace the batteries,
observing the proper
polarities.
• Replace the battery case,
taking care not to pinch the
connecting wire, and tighten
the four screws.
AC Supply Module
The optional AC supply module (Cat. #100.142) provides power to the
Model 5000N at 110 or 220V
designed to plug into the back portion of the instrument, directly
replacing the batteries. The module is protected by a 0.1A slow-blow
fuse.
Note: Cat. #100.142 is supplied with 110V US plug.
• Unscrew the four screws on the corners of the back panel battery
pack.
• Disconnect and remove the battery pack.
• Connect the AC supply module to the power supply connector.
• Place the AC supply module into the back of the instrument and
tighten the four corner screws, making sure not to pinch the wires of
the power supply connector.
• With the tip of a screwdriver, select the proper voltage with the
110/220 supply switch on the back panel of the AC supply module
• Plug the AC supply cord into the appropriate voltage receptacle.
AC. The AC power supply module is
- 10 -
Page 13

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
MEGOHMMETER MODEL 5100/5110
Receiving Your Shipment
Upon receiving your shipment, make sure that the contents are
consistent with the packing list. Notify your distributor of any missing
items. If the equipment appears to be damaged, file a claim immediately
with the carrier and notify your distributor at once, giving a detailed
description of any damage.
Ordering Information
Megohmmeter Model 5100 .................................................. Cat. #1396.07
Megohmmeter Model 5110 .................................................. Cat. #1396.08
Both models include megohmmeter, set of three leads, hex key, 12V
NiCad battery, 110V
AC US line cord and instruction manual.
Accessories and Replacement Parts
7-pin shielded lead, 10 ft,
for Models 1000N/5000N/5100 ............................................ Cat. #2950.10
Color-coded safety leads, set of two, 10-ft........................... Cat. #2950.09
7-pin Shielded lead, 25 ft,
for Models 1100N/5000N/5100 ............................................ Cat. #2118.26
Safety leads, set of two 25 ft with alligator clips................... Cat. #2118.27
Fuse, set of five, 3.15 A .......................................................Cat. #1007.26
Rechargeable 12V NiCad battery ........................................Cat. #2960.10
Safety leads,
set of two 10 ft with heavy duty alligator clips ...................... Cat. #2950.23
-
- 11
Page 14

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Description
AEMC® Models 5100/5110 are portable, multi-range, high-sensitivity
megohmmeters capable of measuring a wide range of insulation
resistances from 10 kilohms to 3000 gigohms. The Model 5100 has four
test voltages of 500, 1000, 2500, and 5000 volts. Each test voltage
setting has two overlapping resistance ranges of 30MΩ to 30,000MΩ and
3GΩ to 3000GΩ (3,000,000MΩ). The Model 5110 features a color
display and also has test voltages of 500, 1000, 2500, and 5000 volts.
Each test voltage setting has two overlapping resistance ranges of 3MΩ
to 3000MΩ and 3GΩ to 3000GΩ (3,000,000MΩ).
The Models 5100 and 5110 have a unique low insulation test range of 10
to 30,000kΩ with a constant current of 33µA (maximum voltage of
DC), which is useful for testing old or flooded installations. A
1300V
voltmeter (safety check) with a range of 0 to 600 volts is standard.
Both models feature a digital clock timer that indicates time and date.
The timer allows accurate testing on time-based test applications. The
timer may be programmed in one of two modes: to indicate the elapsed
time of applied test voltage, or the time elapsed since the test voltage
has been stopped (discharge time).
An audible signal consisting of approximately ten beeps per minute is
present when the test voltage has been applied, and also serves as a
time base for tests of long duration.
The Models 5100/5110 may be powered by either AC or DC. DC power
is supplied by a 12V rechargeable nickel-cadmium battery. AC supply
voltage may be either 110V or 220V via the removable line cord, which
plugs directly into the front of the instrument. Neon lamps on the front
panel indicate battery status; a green light indicates battery charge/AC
supply, while a red light indicates the battery charge status.
The rugged field case in safety yellow is weatherproof and rainproof
when closed. The instrument cover is also removable. The Models
5100/5110 are specifically designed for field, utility, and industrial use.
- 12 -
Page 15

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Specifications - Model 5100
INSULATION TESTS
DC Test Voltages:
500, 1000, 2500, 5000V
Megohm Ranges:
For each test voltage two direct reading ranges:
30 to 30,000MΩ
3 to 3000GΩ
(3000 to 3,000,000MΩ)
Short Circuit Current: 6mA (max)
Accuracy: 5% of reading typical
Charging Time:
0.5 to 5 seconds/µF typical
Discharging Time:
Automatic discharge when test button is released; 0.1 seconds/µF.
Discharge voltage displayed on meter.
Test Voltage Generation:
Solid state circuitry generating rated test voltage across the full range
RESISTANCE TESTS
Test Current: Constant 33 µA DC
Kilohm Range: 10 to 30,000kΩ (30MΩ)
Maximum Test Voltage: 1300V
Accuracy: 5% of reading typical
DC
VOLTAGE TESTS (SAFETY CHECK)
Voltage Range: 0 to 600VAC/DC
Accuracy: 3% of full scale
- 13 -
Page 16

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Audible Test Signal:
Ten beeps per minute approx. (signal may be disabled)
Power Supply:
Rechargeable 12V NiCad battery
Typical life: 500 to 2500 1 min tests (depending on test voltage)
Recharging time: 14 hrs (max) for full charge
Fuse protection: 3.15A fast blow
Low battery indicators
AC Supply: 110/220V, 47 to 450Hz AC ± 20%
Dielectric Test: 4000V
AC, 60Hz, 1 minute
Overload: 600Vrms between one terminal and the other two
Meter Movement/Display:
Rugged taut band suspension;
4.4 x 2.2" (112 x 55mm) meter with 4 scales
Clock/Timer: Test voltage ON activates timer automatically
Dimensions: 9.8 x 10.2 x 15.4" (250 x 260 x 390mm)
Weight: 14.8 lbs (6.7kg)
Temperature Range: 14° to 131°F (-10 to 55°C)
Field Case:
High impact, fiberglass charged polycarbonate (fire resistant UL94);
sealed and weatherproofed; rainproof when closed
Terminals:
Color-coded safety terminals; guard terminal minimizes surface
leakage errors
Safety Standards:
4000V dielectric test
Double insulation
IEC 348
Electromagnetic Compatibility:
CEI 801-2: Electrical Discharge. Class II
CEI 801-3: Magnetic Fields 3V/m
CEI 801-4: Rapid Transients class II
CEI 801-5: Electrical shock (5KV 2 Joules)
- 14 -
Page 17

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Specifications - Model 5110
INSULATION TESTS
DC Test Voltages:
500, 1000, 2500, 5000V
Megohm Ranges:
For each test voltage two direct reading ranges:
3 to 3000MΩ
3 to 3000GΩ
Short Circuit Current: 6mA (max)
Accuracy: 5% of reading typical
Charging Time:
0.5 to 5 seconds/µF typical
Discharging Time:
Automatic discharge when test button is released; 0.1 seconds/µF.
Discharge voltage displayed on meter.
Test Voltage Generation:
Solid state circuitry generating rated test voltage across the full range
RESISTANCE TESTS
Test Current: Constant 33 µA DC
Kilohm Range: 10 to 30,000kΩ (30MΩ)
Maximum Test Voltage: 1300V
Accuracy: 5% of reading typical
DC
VOLTAGE TESTS (SAFETY CHECK)
Voltage Range: 0 to 600VAC/DC
Accuracy: 3% of full scale
- 15 -
Page 18

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
GENERAL SPECIFICATIONS
Audible Test Signal:
Ten beeps per minute approx. (signal may be disabled)
Power Supply:
Rechargeable 12V NiCad battery
Typical life: 500 to 2500 1 min tests (depending on test voltage)
Recharging time: 14 hrs (max) for full charge
Fuse protection: 3.15A fast blow
Low battery indicators
AC Supply: 110/220V, 47 to 450Hz AC ± 20%
Dielectric Test: 4000V
AC, 60Hz, 1 minute
Overload: 600Vrms between one terminal and the other two
Meter Movement/Display:
Rugged taut band suspension;
4.4 x 2.2" (112 x 55mm) meter with 4 scales
Clock/Timer: Test voltage ON activates timer automatically
Dimensions: 9.8 x 10.2 x 15.4" (250 x 260 x 390mm)
Weight: 14.8 lbs (6.7kg)
Temperature Range: 14° to 131°F (-10 to 55°C)
Field Case:
High impact, fiberglass charged polycarbonate (fire resistant UL94);
sealed and weatherproofed; rainproof when closed
Terminals:
Color-coded safety terminals; guard terminal minimizes surface
leakage errors
Safety Standards:
4000V dielectric test
Double insulation
IEC 348
Electromagnetic Compatibility:
CEI 801-2: Electrical Discharge. Class II
CEI 801-3: Magnetic Fields 3V/m
CEI 801-4: Rapid Transients class II
CEI 801-5: Electrical shock (5KV 2 Joules)
- 16 -
Page 19
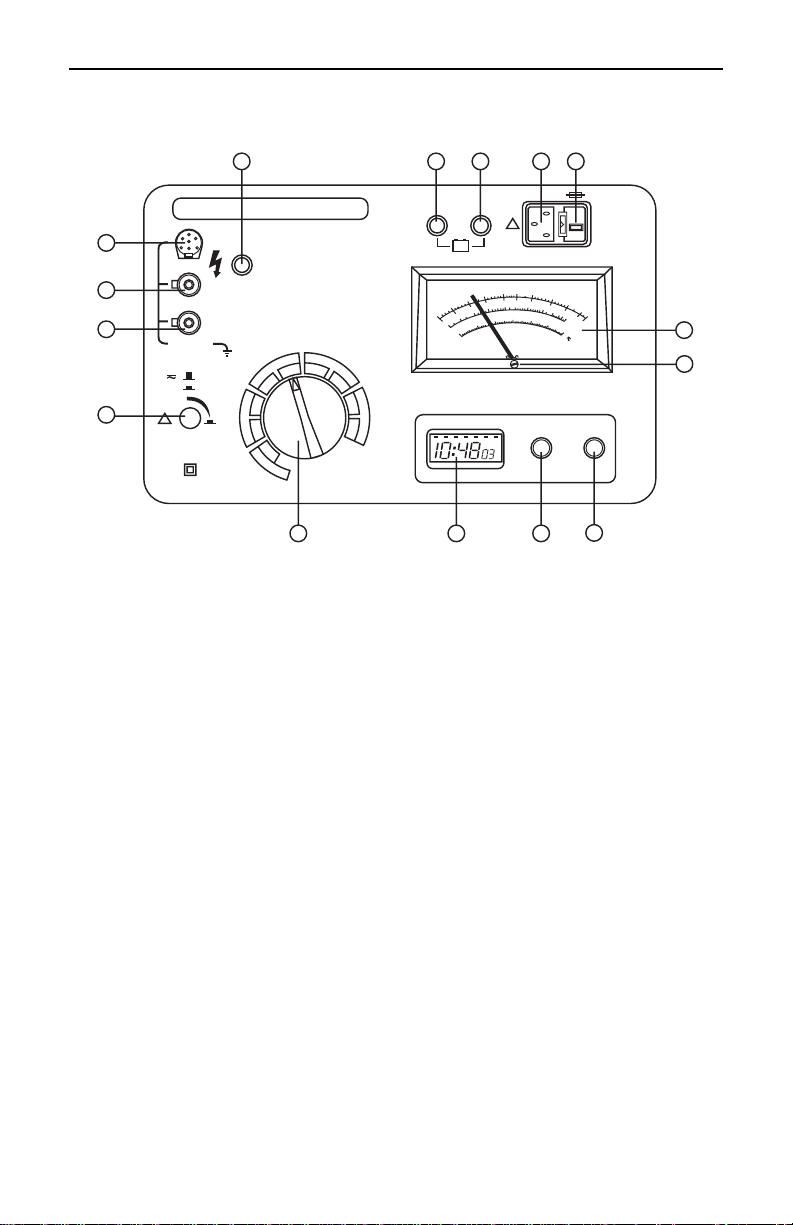
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Control & Connector Identification
5 6
AEMC
MEGOHMMETER MODEL 5100
INSTRUMENTS
4
Ñ LINE
7 8
LOW CHARGING
– +
!
9
50/60/400Hz
110V
660V max.
V
Ω
!
PUSH AND TURN
TO LOCK "ON"
+ EARTH
OFF
ON
GUARD
5
3
0
k
3
0
3
2
V
5
0
0
0
0
1
Ω
M
Ω
V
G
0
0
5
Ω
M
k
3
Ω
3
µ
A
1
(
m
0
V
M
Ω
Ω
G
G
Ω
M
Ω
5
0
0
0
G
V
Ω
3
0
0
V
a
x
.
)
15
14
3
2
1
0
1
0
0
1
k
0
1
0
5
k
0
2
1
0
1
0
0
0
5
0
2
1
0
0
0
0
0
5
0
0
2
1
0
0
k
2
k
5
0
3
0
0
0
2
0
0
5
CLOCK / TIMER RESET
2
0
0
5
0
0
1
0
0
2
k
0
0
5
0
0
5
k
2
0
2
0
k
1
1
0
0
0
k
3
5
0
k
2
0
1
2
G
0
4
Ω
k
0
0
M
3
0
Ω
5
k
0
0
k
Ω
6
0
V
12
13
1. PUSH-TO-TEST button:
Lock “ON” by turning button a quarter turn to the right.
OFF Position: Voltmeter position.
ON Position: Test position with voltage present at outputs.
2. EARTH terminal (green):
Connects to ground for insulation testing.
3. GUARD terminal (blue):
Used to minimize the effect of leakage current.
4. LINE terminal (black):
Connects to the equipment to be tested.
5. High Voltage Indicator:
Red light blinks when the measurement voltage is on the output
terminals. An audible “beep” is also emitted approx. every 6
seconds.
6. Battery Low Indicator:
Light OFF: battery good
Light ON: battery partially discharged. (Measurements possible for
20-60 minutes depending on voltage selection. Clock and voltmeter
still operational).
10
11
- 17 -
Page 20
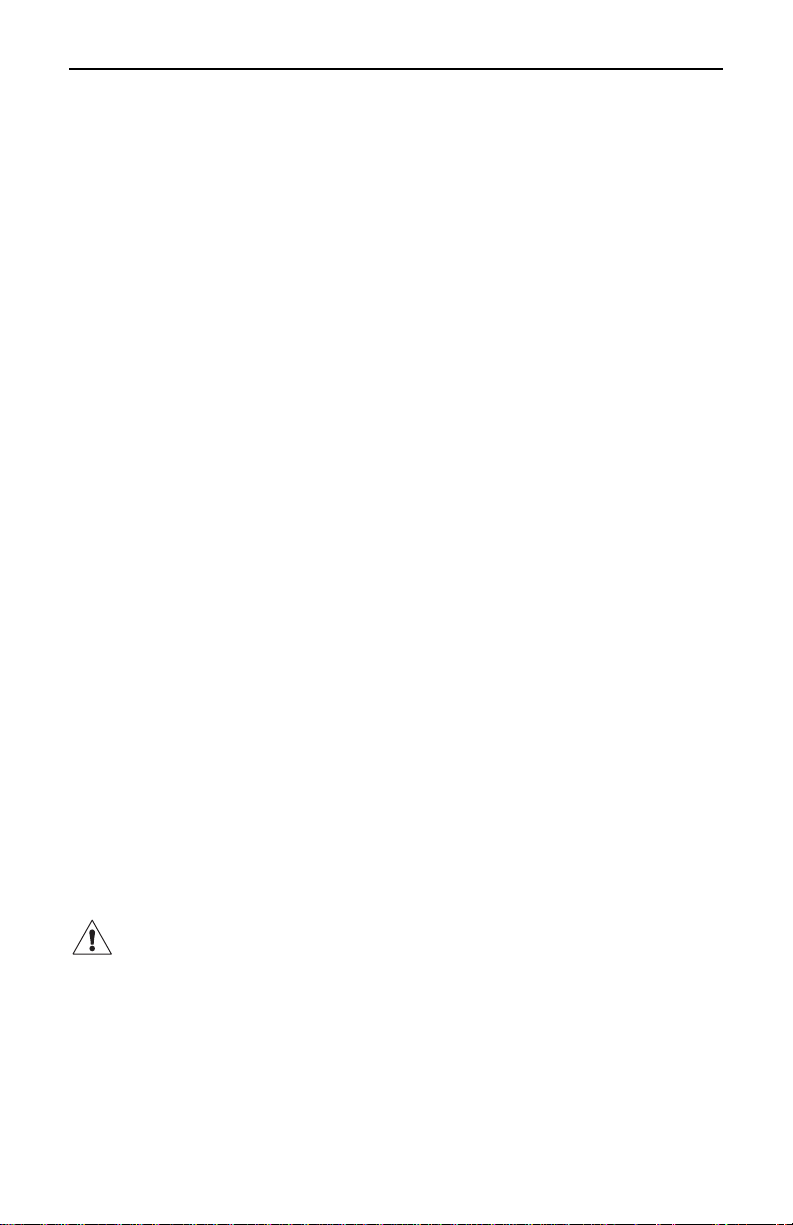
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
7. Charging Light:
Indicates the battery is charging or operation from AC supply
8. Power Line Socket
9. Fuse Socket:
Select 110/220V with small connector in this socket.
NOTE: When switching the power supply between 110V and 220V,
the selection module must be changed accordingly. Change fuse
before making any connections.
10. Analog Measurement Scale (Model 5110 has color scale)
11. Zero Adjust
12. Reset Button:
Resets chronometer and selects time values during programming.
13. Clock/Timer:
Toggles between the clock and timer on the display.
14. LCD Display: Clock or timer.
15. Selection Switch
AC Supply Module
Models 5100 and 5110 may be powered by 110V or 220VAC (47 to
450Hz). The instrument includes a 110V supply cord, which provides
power to the instrument as well as charging voltage for the rechargeable
battery. Verify that “110V” appears in the power supply module window
opening; this will permit operation with the 110V supply cord.
To change the power supply voltage selection, push the tab on the
selection module to the right and remove the module. Remove the
portion of the module that contains the fuse assembly and rotate 180° to
display “220V” in the module window. A 220V supply cord (not supplied)
is required for 220V operation.
CAUTION: Do not change the power supply voltage while operating
either Model 5100 or Model 5110 from the AC supply.
Both Models are protected by a 3.15A, 250V fuse (Cat. #1007.26).
- 18 -
Page 21
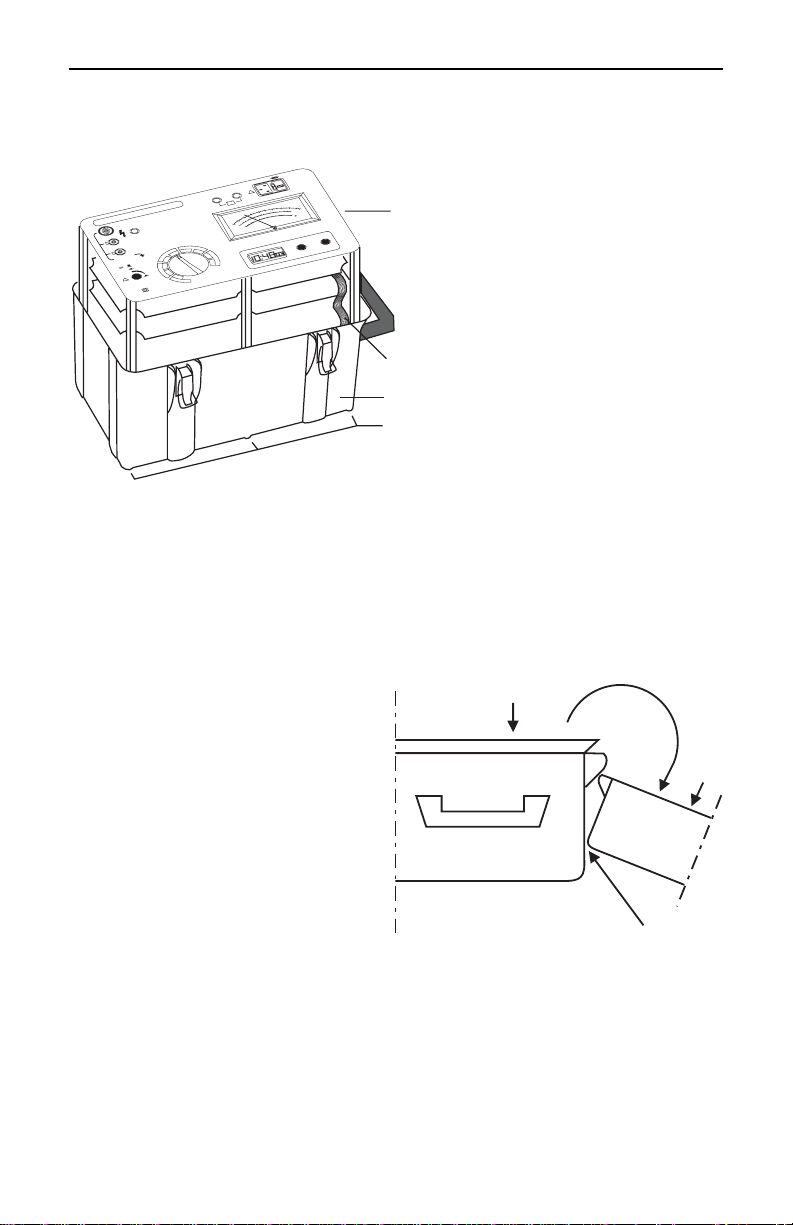
Disassembly
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
50/60/400Hz
110V
!
CHARGING
LOW
AEMC
INSTRUMENTS
MEGOHMMETER MODEL 5100
— LINE
GUARD
+ EARTH
660V max.
OFF
ON
V
Ω
!
PUSH AND TURN
TO LOCK "ON"
– +
2
5
0
0
V
Ω
G
M
Ω
Ω
5
V
M
0
0
G
0
0
Ω
0
0
1
V
Ω
G
M
Ω
Ω
G
V
0
0
Ω
5
M
k
Ω
3
3
µ
A
1
3
0
0
V
(
m
a
x
.
)
1
0
0
0
0
0
5
2
0
k
0
2
G
Ω
0
0
1
1
k
0
5
k
M
Ω
2
0
0
k
k
0
0
5
1
0
2
2
5
0
0
0
2
0
0
0
0
5
0
1
k
0
Ω
0
0
1
0
0
0
5
2
k
2
0
0
5
0
0
4
0
0
2
V
k
0
5
0
1
0
3
0
0
1
k
0
0
0
2
1
5
0
k
0
5
0
0
2
1
3
k
0
0
3
3
0
5
RESET
CLOCK / TIMER
SA
—
FR
—
E TH
— —
—
MO TU W
—
SU
—
Figure 4
Detachable Cover
The cover hinges are fitted with
spring loaded clips which allow
the cover to be removed. To
detach the cover from the
Models 5100 or 5110, open lid to
a horizontal position and apply
downward pressure to the hinge
side of the cover while gripping it
firmly.
To re-attach the cover, position
the cover in a horizontal position
and fit the hinges into the
respective housing. Apply strong
rear-to-front pressure to the
cover until it snaps into place.
Chassis
Ribbon Cable
Case
Fastening Screws
Use the hex key to
unscrew the six
fastening screws from
the chassis, which are
located on the bottom
of the case.
Pull out the chassis.
Do not forget to unplug
the ribbon cable which
connects the power
supply board in the
bottom of the case to
the boards which are
mounted in the
chassis.
Unhinging
Force
Force
Supporting Point
Figure 5
- 19 -
Page 22
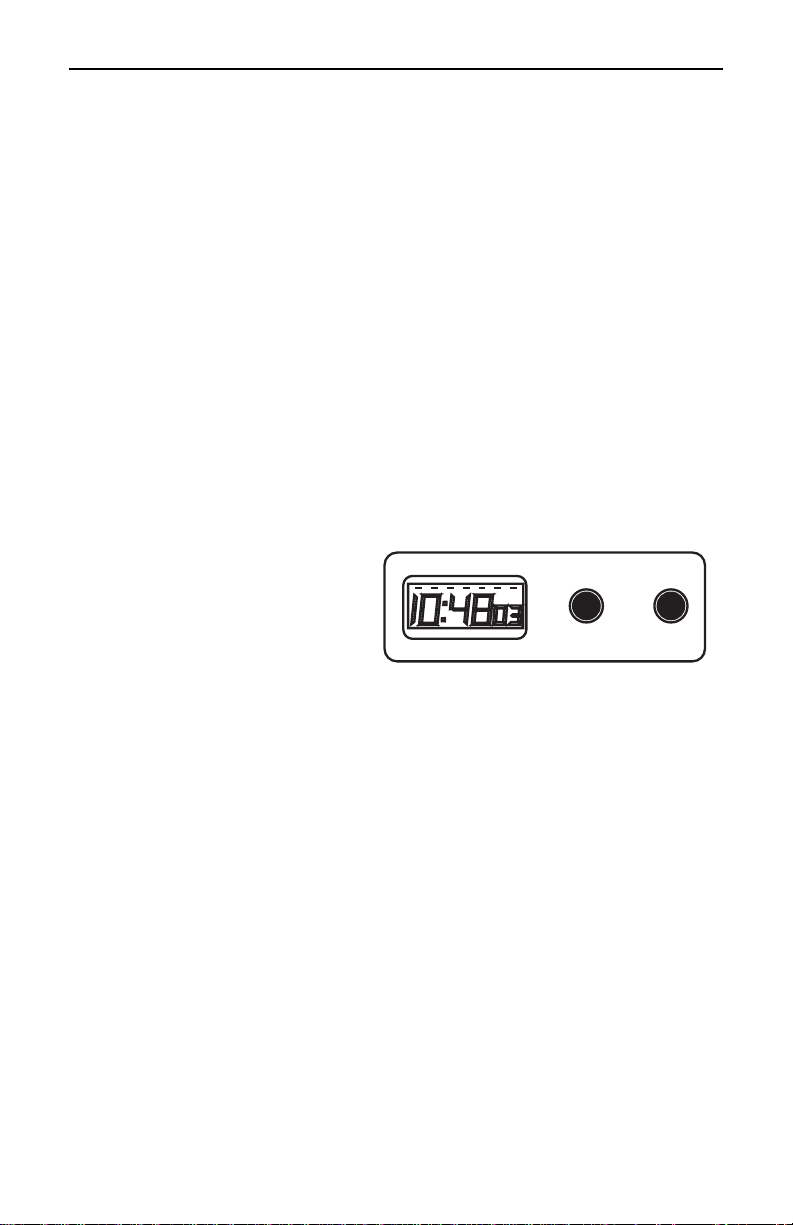
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Using the Clock/Timer
The clock/timer function may be used in three ways. First, a clock and
calendar indicate the current time (12-hour format). Second, a timer may
be used when performing insulation resistance tests that are dependent
upon an accurate time reading (e.g. dielectric absorption, polarization
index, step voltage). Third, the timer portion may be programmed as an
ascending timer in relation to applied test voltage or in relation to the
discharge time.
Note: Setting both the clock and timer requires the user to engage the
push-to-test button to access different modes. Potentially dangerous
voltage may be present. Select a position on the voltage selector switch
between voltage ranges (e.g. vertical position between 1000V and
2500V). This eliminates the possibility of voltage on the output while
programming the clock/timer.
Setting the Clock/Calendar
To program the clock, hold the
CLOCK/TIMER button down
continuously for approximately 4
sec. The “seconds” portion of the
display will begin to blink. Reset
to :00 with the RESET button.
Push and hold or lock (clockwise turn) the PUSH-TO-TEST button. The
“minutes” portion of the display will begin to blink 00:XX:00. Press the
RESET button to select minutes (00-59).
To access the hour portion of the display, release the PUSH-TO-TEST
button. Input the current hour using the RESET button. Hour inputs are
programmed using a 12-hour format.
Push and hold the PUSH-TO-TEST button for a second time. The
display switches from clock format to calendar (DD:MM). Input the
current day (1-31) with the RESET button. Release the PUSH-TO-TEST
to activate the “month” portion of the calendar (1-12). Input the current
month using the RESET key.
Pressing the PUSH-TO-TEST button a final time causes the day
segment indicator to blink (top of display). The format has seven
segments indicating days of the week. Select the proper day
representation with the RESET key.
Validate the choices by pressing the CLOCK/TIMER button once.
CLOCK / TIMER RESET
Figure 6
- 20 -
Page 23

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Using the Timer
The timer portion may be used in two different ways:
First, Voltage Timer indicates time elapsed since the application of the
selected test voltage. The timer begins the count (to a hundredth of
second) when the PUSH-TO-TEST button is pressed. Releasing the
PUSH-TO-TEST button suspends the timer operation. Reapply the test
voltage to start the clock again, beginning at the previously elapsed time.
Second, Discharge Timer indicates the time that elapses during the
portion of the test when the test voltage has been removed.
The timer may also be controlled (start and stop) using the RESET key.
Voltage Timer: This mode causes the timer to begin counting whenever
the test voltage is applied. Begin by toggling to the timer portion of the
display using the CLOCK/TIMER button (this mode is indicated by the
blinking segment(s) on the top portion of the display). Reset to 0 00 00
using the RESET key. The clock will activate each time the PUSH-TOTEST button is depressed.
Discharge Timer: This mode causes the timer to begin counting when
the applied test voltage has been removed (i.e., when the PUSH-TOTEST button is out). To activate this mode, put the display into the clock
mode (indicated by one stationary segment on top portion of display) and
push/lock the PUSH-TO-TEST button.
With the PUSH-TO-TEST button engaged, switch the display from clock
to timer and push the RESET key. The display will reset indicating 0 00
00.
Note: In the discharge mode (PUSH-TO-TEST button out), the meter
displays the voltage at the terminals. The voltage will drop indicating
discharging of the tested sample.
- 21 -
Page 24
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
OPERATION: MODELS 5000N, 5100 & 5110
The Analog Scale
Before taking any measurements, verify that the pointer is zeroed
correctly (red AC scale "0"). If it is not, adjust with the mechanical
zero adjust screw.
The analog scale serves two functions:
First, it indicates the actual resistance of the insulating material under
test (black scales). The TOP scale is used for measurement on the MΩ
and GΩ ranges. The bottom half (MΩ) covers the range of 30MΩ to
30,000MΩ (3MΩ to 30,000MΩ for Model 5110), reading from left to right.
The upper half of the scale (GΩ) covers the range of 3GΩ to 3000GΩ
and reads right to left.
The center portion of the scale is used for the low insulation test range of
10kΩ to 30,000kΩ, reading from right to left.
The bottom red arc is an AC/DC voltmeter that is divided into 10 volt
increments. The voltmeter function is operable any time the PUSH-TOTEST button is out. The voltmeter detects the presence of voltage on the
equipment to be tested. (If voltage is detected, do not proceed with
the insulation test).
The voltmeter function also indicates if, after completing insulation
testing, the sample under test has stored a dangerous capacitive charge.
The instrument discharges this capacitance internally and the needle will
drop accordingly. Disconnect the meter when the sample is discharged.
Warning:
Electrical equipment and cables may have sufficient capacitance to store
a dangerous charge from the instrument test current. For proper
discharge to occur the PUSH-TO-TEST button must be in the OFF
position with the sample connected between the EARTH and LINE
terminals.
On prolonged tests, the PUSH-TO-TEST button may be locked in the ON
position; care should be taken in this mode that no damage is done if the
instrument is left unattended.
-
- 22
Page 25

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Preliminary Check
When the push-to-test button is in the OFF position, the pointer should
be on zero of the voltmeter scale, and on three of the GΩ scale. If it is
not, use the mechanical zero adjust on the front of the instrument.
• Detach the leads from the instrument.
• Press the push-to-test button into the ON position. The pointer should
deflect completely to the far right of the scale. The green neon “Bat.”
lamp should light up (Model 5000N) or the red neon light will blink
(Models 5100 and 5110).
MODEL 5000N:
Note: Ensure that the “Bat.” light (green) does not go out at any point
during the testing. If the light does not illuminate, stop the test and
change the batteries before continuing.
MODELS 5100 and 5110:
Note: Ensure that the "battery low" light (red) is not illuminated at any
point during the testing. If the light illuminates, stop the test and charge
the battery using the AC supply cord.
Verify that NO VOLTAGE is present on the circuit to be tested.
How to Use the Push-to-Test Button
OFF: Push-to-test button is in the raised position. This is for
measurement of AC or DC voltages (safety check). NOTE: Do not
depress the push-to-test button if voltage is present.
ON: Push-to-test button is depressed and held down for the duration of
the test. This is for insulation resistance tests.
LOCK-ON: Push-to-test button is depressed and turned clockwise 90° to
lock into position. This is for insulation resistance tests of long duration
such as the Time Resistance or Absorption Test.
- 23 -
Page 26

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
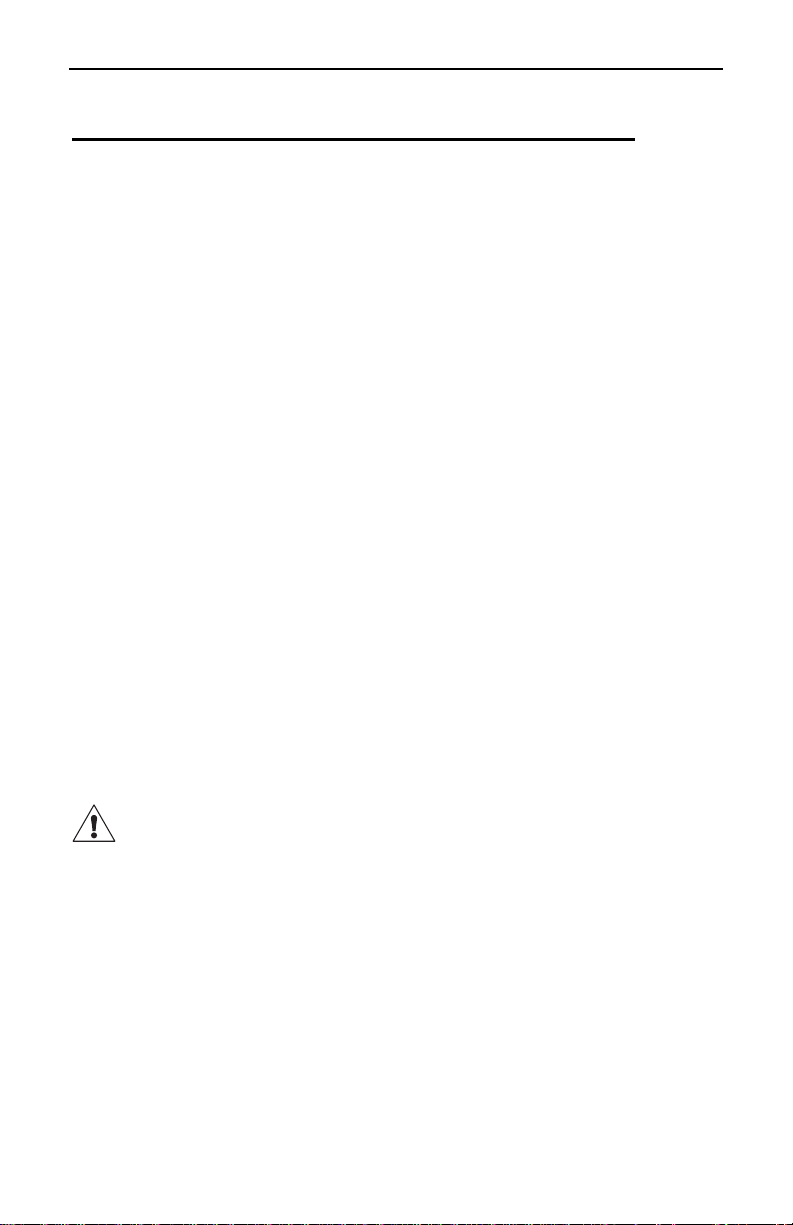
Utilizing the Guard Terminal
Guard terminals are useful when measuring high resistance values and
for stabilizing readings.
A BC
Exposed
Surface
Conductor
to
Line (-)
Terminal
Insulation
to
Guard
Terminal
Shield
to
Earth (+)
Terminal
Outer jacket
The guard terminal
is useful when
measuring very
high resistance
values.
Figure 7
When testing the insulation at the end of a cable, it is necessary to
eliminate the error from surface leakage that occurs, particularly at high
resistance values. The guard terminal provides a third terminal within the
path of the surface leakage. Connect the instrument as shown in Figure
7.
If there is no shield at “B”, use a copper wire wound several times around
the exposed surface “B”. (Note: If a shield is not available and you do
not make up a shield around “B” and connect to the guard terminal (-),
the measurement will be erroneous and lead to confusion as to the
cable’s state).
If the guard terminal is not
connected at “B”, the
instrument measures the
No Connection to
Guard Terminal
B
i
1
current “I” flowing through
the insulation and a
surface leakage current
”. See Figure 8.
“i
1
Ry
Rz
To EARTH
Terminal
AC
Figure 8
Rx
i
To LINE
Terminal
- 24 -
Page 27

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
To Guard
Terminal
i
1
B
When the guard terminal is
connected at “B”, the
instrument measures the
current “I” and not the
surface leakage current
”, which is not included in
“i
1
Ry
Rz
the measurement. See
Figure 9. This type of
measurement will give the
true value of the resistance
To EARTH
Terminal
Rx
AC
i
To LINE
Terminal
“Rx”, providing the “Ry”
and “Rz” are not too low.
Figure 9
Voltage Measurements (Safety Check)
These instruments can measure AC or DC voltages. For voltage
measurements, proceed as follows:
• The push-to-test button should be in the OFF position.
• Connect the instrument with the voltage leads connected between the
Line (–) and Earth (+) terminals on the unit.
• Read the voltage directly on the voltage scale.
Figure 10
- 25 -
— LINE
+ EARTH
MEGOHMMETER
Page 28

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Audible Signal
When the push-to-test button is in the ON or LOCK-IN position, an
audible signal will result. This signal consists of approximately one beep
every six seconds (ten beeps per minute). The signal can be used as a
time base for monitoring the duration of the test. On the MΩ and GΩ
ranges, the signal indicates that the instrument is in operation and that
the selected DC test voltage may be present on the terminals of the
instrument.
Note: On the Models 5100 and 5110, the audible signal may be
disconnected by means of a jumper located on the main circuit board.
Connector to
battery board
ON
OFF
Figure 11
- 26 -
Page 29

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Precautions When Making DC Insulation Tests
• The equipment should be taken off the line sufficiently in advance to
permit it to cool to ambient temperature.
• When you are testing windings, they should be clean and dry; let
solvents and cleaners evaporate. Should foreign matter or wet
surfaces be present, erroneous readings may result. (A clean, dry
sample’s resistance will rise for 10 to 15 minutes, whereas a wet,
dirty one will stabilize quickly.)
• Make
sure that the equipment tested is properly discharged and
grounded before testing.
• When testing individual windings, connect all other windings (not
under test) together and ground to motor frame.
• When testing phases, be sure they are open to test each individually.
• After applying a test voltage, allow sufficient discharge time. As a
rule, discharge twice as long as tested.
Note: The instrument voltmeter will indicate the discharge voltage at the
terminals.
Insulation Measurement - Connections
Figure 12 shows the connections to measure the insulation of one
conductor to the other conductors. The cable should be disconnected at
both ends to avoid leakage through switchboards and panels.
Conductor under test
GUARD
MEGOHMMETER
+ EARTH- LINE
Figure 12
- 27
-
Page 30

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Figures 13 and 14 show the connection for testing insulation from a
supply conductor to a ground (motor frame). The connection to the guard
terminal is used to eliminate the effects of surface leakage across
exposed insulation at one end of the cable. Refer to the section on
Utilizing the Guard Terminal (pg 24). The cable should be disconnected
at both ends to avoid leakage through switchboards and panels.
Conductor under test
GUARD
+ EARTH- LINE
MEGOHMMETER
Figure 13
Conductor under test
GUARD
+ EARTH- LINE
MEGOHMMETER
Figure 14
- 28 -
Page 31

Figure 15 shows the
connections to a transformer.
Make sure that the switches
and/or circuit breakers on
both sides are open. Check
the high voltage winding to
ground, low voltage to
ground, and the resistance
between them with no
winding grounded.
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Winding under test
Transformer
grounding lug
GUARD
+ EARTH- LINE
MEGOHMMETER
Figure 15
A
Jumper
B
Jumper
C
Figure 16 shows the connections for measuring the
insulation of a three-phase line
to ground by connecting the
jumpers between phases. This
gives a reading of all conductors at once. If a load such
as a motor, heater, etc., is
attached to the other end of
the line, it will read the load
resistance to ground at the
same time. By removing the
GUARD
+ EARTH- LINE
jumpers, readings can be
made between the individual
conductors and ground.
MEGOHMMETER
Figure 16
- 29 -
Page 32
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
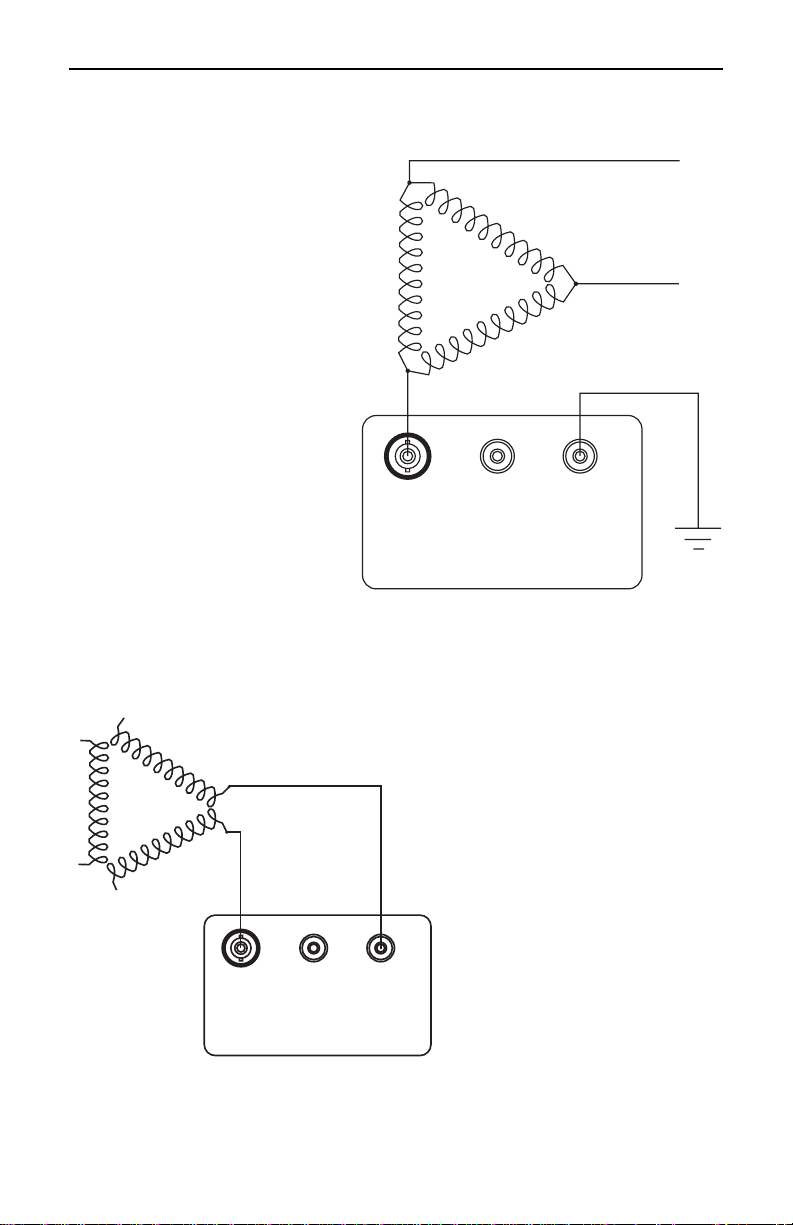
Insulation Resistance Measurements on Motors
Figure 17 shows reading the
resistance to ground of a
three-phase motor winding.
Since the three-phase motors
are internally connected, it is
only necessary to connect one
lead to the motor lead and the
other lead to the motor frame
as shown.
GUARD
+ EARTH- LINE
MEGOHMMETER
Figure 17
C
A
B
GUARD
MEGOHMMETER
Figure 18
+ EARTH— LINE
Figure 18 shows the
windings of a three-phase
motor separated. Sometimes
this can be done at the lead
terminals while other times
the end bells must be
removed to get at the lead
wires of the coils. By
connecting the megohmmeter as shown, the phase
insulation resistance value
can now be determined.
Read between phases “A”
and “B”, then “B” and “C”,
then “C” and “A”.
- 30 -
Page 33
Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
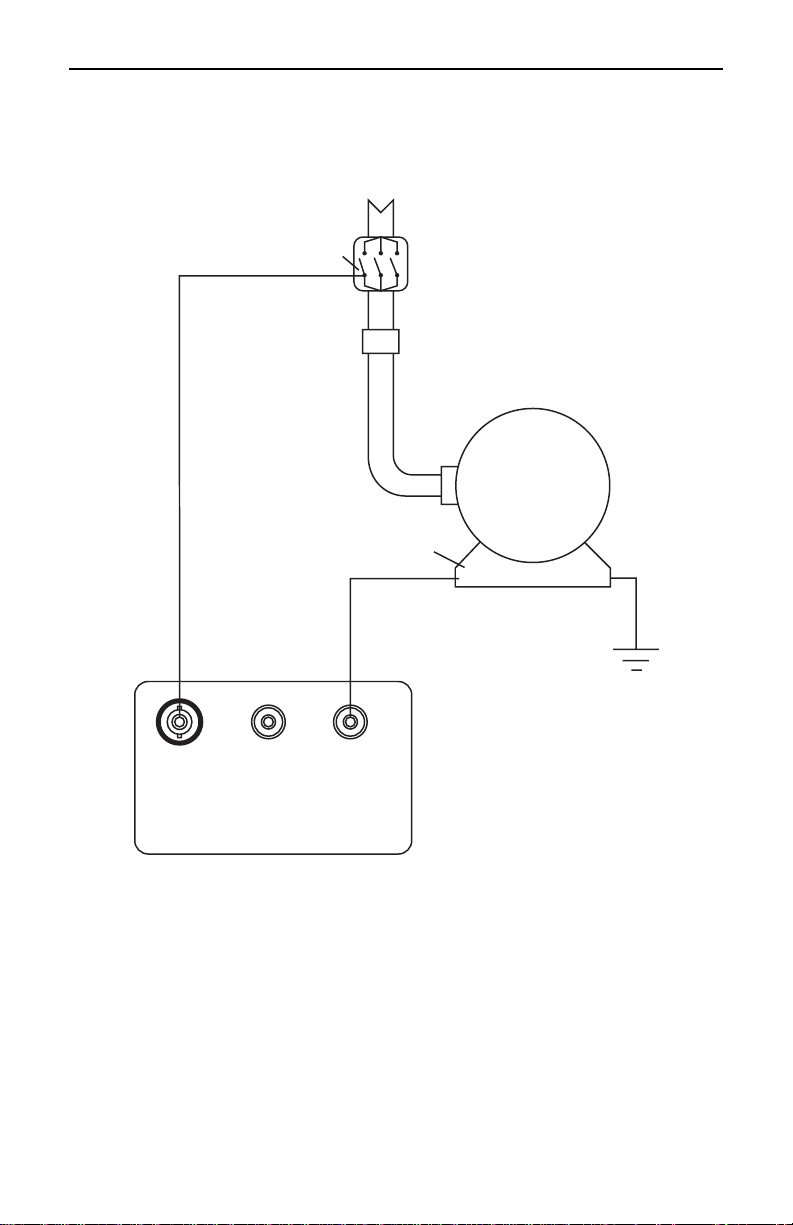
Figure 19 shows connections for testing insulation from a supply
conductor in a switchbox to ground (motor frame). An identical test may
be carried out from the motor starter.
Connect to one leg on
the motor side of the switch
Starter in
Grounded
motor frame
GUARD
+ EARTH- LINE
MEGOHMMETER
Figure 19
- 31 -
Page 34

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
UNDERSTANDING INSULATION TESTING
Insulation is the material between two points of different potential which,
through high resistivity, prevents the flow of current between those
points. Insulation failure is one of the most common problems associated
with electrical equipment breakdown.
A megohmmeter is an insulation resistance tester which is essentially a
high resistance ohmmeter (MΩ or greater) providing a high DC potential
(up to 5000V). This high potential causes low amounts of current to flow
through and over the insulation which is under test.
Many factors can cause insulation to fail: mechanical damage, moisture,
heat, foreign debris, corrosion, etc. As time passes, these factors
combine to permit excessive current to flow through insulation at points
where it would normally be blocked by the insulation resistance. Usually,
the resistance on degrading insulation will drop gradually, providing
plenty of warning. Other times it will drop suddenly, as when it is
immersed.
With periodic resistance tests and good record keeping, it is possible to
get an accurate picture of the insulation condition. Insulation resistance
testing is intended to indicate not only if equipment is bad, but also
whether it is becoming bad.
Resistance of many types of insulation can vary greatly with
temperature. The resistance data obtained should be corrected to the
standard temperature for the class of equipment under test.
Please note that although we present information on test procedures,
values and recommended frequency of testing, the manufacturer of your
particular piece of equipment is the definitive source for testing
parameters and procedures. While we refer to commonly applied rules
and practices, every test will not be practical to each piece of electrical
equipment in your facility.
- 32 -
Page 35

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
RATIO TESTING
In time resistance reading (dielectric absorption ratio), readings are taken
at 30 seconds and 60 seconds to obtain the dielectric absorption ratio.
Insulation resistance @ 60s
Insulation resistance @ 30s
This test is useful for increasing the accuracy of spot testing. In general,
a ratio of 1.25 to 2 or better should be required. (Below 1.1 is dangerous;
1.1 to 1.25 is questionable; 1.25 to 1.4 is fair; and 1.4 to 2 and above is
good.) A ratio below this indicates that repair is probably needed.
Remember that a DC insulation test may be used for acceptance testing,
but is more commonly used to check the gradual deterioration of
equipment over its lifetime. Consult your equipment manufacturer for
specific test or test voltage if not known.
Insulation resistance decreases with moisture, temperature and age, and
should be recorded over time at a given temperature and corrected.
= Dielectric Absorption Ratio (DAR)
- 33
-
Page 36

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
1
TYPES OF TESTS
Spot Reading Test
Method
For this test, the megohmmeter is connected across the insulation of the
windings of the machine being tested. A test voltage is applied for a fixed
period of time, usually 60 seconds, and a reading is taken. The spot
reading test should only be carried out when the winding temperature is
above the dewpoint
so that the reading may be corrected to a base temperature of 20°C
(68°F).
Test Duration
To obtain comparable results, tests must be of the same duration.
Usually the reading is taken after 60 seconds.
Interpreting the Results
Proper interpretation of spot reading tests requires access to records of
results from previous spot reading tests. For conclusive results, only use
results from tests performed at the same test voltage for the same
amount of time under similar temperature and humidity conditions. These
readings are used to plot a curve of the history of insulation resistance. A
curve showing a downward trend usually indicates a loss of insulation
resistance due to unfavorable conditions such as humidity, dust
accumulation, etc. A very sharp drop indicates an insulation failure.
1
. The operator should note the winding temperature
Dewpoint temperature is the temperature at which the moisture vapor in the air condenses as a liquid.
-
- 34
Page 37

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
2
Polarization Index
Method
This test is based on the comparison of absorption characteristics of
good insulation vs. the absorption characteristics of humid or otherwise
contaminated insulation. During the test, a test voltage is applied for an
extended period, usually 10 minutes. The operator takes a reading every
10 seconds for the first minute, and then every minute up to 10 minutes.
A curve is drawn showing the insulation resistance value versus time.
Test Duration
10 minutes
Interpreting the Results
If the results were plotted on a graph, the slope of the curve would
indicate the condition of the insulation under test. A good insulation will
show a continual increase in resistance for typically 10 to 15 minutes.
Contaminated, moist, or cracked insulation will produce a relatively flat
curve.
A ratio known as the polarization index can be obtained by dividing the
value from the 10-minute reading by the value from the one-minute
reading. This polarization index is indicative of the slope of the curve.
A low polarization index usually indicates excessive moisture and
contamination. On large motors or generators, values as high as 10 are
commonly expected.
Polarization index =
The IEEE Std 43-1974
2
polarization index for AC and DC rotating machines:
Class A: 1.5 Class B: 2.0 Class C: 2.0
10-minute reading
1-minute reading
lists the following minimum values for the
IEEE Std. 43-1974, - Recommended Practice for Testing Insulation Resistance of Rotating Machinery
-
- 35
Page 38

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Step Voltage Test
Method
In this test, the operator applies two or more test voltages in steps. The
recommended ratio for the test voltage steps is 1 to 5. At each step, test
voltage should be applied for the same length of time, usually 60
seconds. The application of increased voltage creates electrical stresses
on internal insulation cracks. This can reveal aging and physical
damage, even in relatively dry and clean insulation, which would not
have been apparent at lower voltages.
Test Duration
A series of “steps,” each step lasting 60 seconds.
Interpreting the Results
Compare the readings taken at different voltage levels, looking for any
excessive reduction in insulation resistance values at the higher voltage
levels. Insulation that is thoroughly dry, clean, and without physical
damage should provide roughly the same resistance values despite
changes in test voltage levels. If resistance values decrease substantially
when tested at higher voltage levels, this should serve as a warning that
insulation quality may be deteriorating due to dirt, moisture, cracking,
aging, etc.
- 36
-
Page 39

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
THE EFFECTS OF TEMPERATURE
Insulation resistance measurements are changed by variations in
temperature of the insulation material. Typically, when the temperature
goes up, the insulation resistance will go down. Inversely, when the
temperature drops the insulation resistance will increase in value.
The best way to obtain consistent measurement results is to test the
insulation at a standard temperature, typically 68°F (20°C). If the
temperature of the material you are testing is either higher or lower than
68°F (20°C), refer to the temperature correction chart (see table). As a
general rule the insulation resistance value may be corrected by:
• Halving the resistance measurement value for every 10°C above the
base temperature of 68°F (20°C), or
• Doubling the resistance value for every 10°C below 68°F (20°C)
°C °F
0 32 0.25
5 41 0.36
10 50 0.50
15 59 0.75
20 68 1.00
25 77 1.40
30 86 1.98
35 95 2.80
40 104 3.95
45 113 5.60
50 122 7.85
55 131 11.20
60 140 15.85
65 149 22.40
70 158 31.75
75 167 44.70
80 176 63.50
Multiplication
Facto
r
- 37
-
Page 40

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
INTERPRETING THE RESULTS
Insulation resistance values are a function of the type of insulating
material. The actual value you read may vary greatly and is not as
important as the trends of the values over time. This is why the
resistance measurement must be taken in a greater context. Some other
factors to consider are:
Previous Testing Results
These are very important, since they will indicate the decline in the
insulation resistance over time. All new equipment should be tested and
documented to serve as a benchmark for future testing.
Careful Visual Inspection
By taking a very close look at the equipment you are testing it may be
possible to see cracks, excessive moisture, burn marks, etc., which may,
over time, cause catastrophic equipment failure.
Manufacturers’ Recommendations for Specific Equipment
The definitive source for information on a specific piece of equipment is
its manufacturer. Most manufacturers will provide basic information
about the insulation resistance which may be encountered during testing.
Comparisons with Similar Equipment
Similar equipment should provide similar insulation resistance values.
This would also remain true when testing cables. For three-phase
systems, it would be very useful to compare resistive values between the
phases.
By performing insulation resistance tests regularly and recording the test
results, it may be possible to predict failure by detecting a downward
trend in the resistance. Careful notations should be made as to
time/date, temperature, applications, etc.
The information contained in this manual is intended only as a guide to
acceptable procedure; it is not intended to be used as a test specification
for specific electrical equipment.
-
- 38
Page 41

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
MAINTENANCE
Warning:
• For maintenance use only original factory replacement parts.
• To avoid electrical shock, do not attempt to perform any servicing
unless you are qualified to do so.
• Do not perform any service while the Megohmmeter is on any circuit.
• To avoid ele
water or other foreign agents into the electronic module.
ctrical shock and/or damage to the instrument, do not
get
Cleaning
The megohmmeter may be gently cleaned with a soft cloth, soap and
water. Dry immediately after cleaning. Avoid water penetration into the
electronic module.
Make sure the megohmmeter and all leads are dry before further use.
- 39
-
Page 42

Megohmmeter Models 5000N/5100/5110
Repair and Calibration
To ensure that your instrument meets factory specifications, we recommend
that it be submitted to our factory Service Center at one-year intervals for
recalibration, or as required by other standards or internal procedures.
For instrument repair and calibration:
You must contact our Service Center for a Customer Service Authorization
number (CSA#). This will ensure that when your instrument arrives, it will be
tracked and processed promptly. Please write the CSA number on the
outside of the shipping container. If the instrument is returned for calibration,
we need to know if you want a standard calibration, or a calibration traceable
to N.I.S.T. (Includes Calibration Certificate plus recorded calibration data).
Chauvin Arnoux
d.b.a. AEMC
15 Faraday Drive
Dover, NH 03820 USA
Tel: (800) 945-2362 (Ext. 360)
(603) 749-6434 (Ext. 360)
Fax: (603) 742-2346 or (603) 749-6309
(Or contact your authorized distributor)
Costs for repair, standard calibration, and calibration traceable to N.I.S.T. are
available.
Note: You must obtain a CSA# before returning any instrument.
®
, Inc.
®
Instruments
Technical and Sales Assistance
If you are experiencing any technical problems, or require any
assistance with the proper operation or application of your instrument,
please call, fax or e-mail our technical support hotline:
Chauvin Arnoux®, Inc.
d.b.a. AEMC® Instruments
Phone: (800) 945-2362 (Ext. 351)
(603) 749-6434 (Ext. 351)
Fax: (603) 742-2346
E-mail: techsupport@aemc.com
- 40 -
Page 43

Chauvin Arnoux®, Inc. d.b.a AEMC® Instruments
99-MAN 100016 v7 02/18
15 Faraday Drive • Dover, NH 03820, USA
www.aemc.com
 Loading...
Loading...