Page 1

NuDAM-6050 NuDAM-6052
NuDAM-6053 NuDAM-6054
NuDAM-6056 NuDAM-6058
NuDAM-6060 NuDAM-6063
Digital I/O Modules
Recycled Paper
Page 2

Page 3

© Copyright 1995~2001 ADLINK Technology Inc.
All Rights Reserved.
Manual Rev. 3.51: March 27, 2001
Part No : 50-12003-201
The information in this document is subject to change without prior notice in
order to improve reliability, design and function and does not represent a
commitment on the part of the manufacturer.
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special,
incidental, or consequential damages arising out of the use or inability to use
the product or documentation, even if advised of the possibility of such
damages.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All
rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by any
mechanical, electronic, or other means in any form without prior written
permission of the manufacturer.
Trademarks
ND-6050, ND-6052, ND-6053, ND-6054, ND-6056, ND6058, ND-6060 and
ND-6063 are registered trademarks of ADLink Technology Inc., IBM PC is a
registered trademark of International Business Machines Corporation. Intel
is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation. Other product names
mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only and may be
trademarks and/or registered trademarks of their respective companies.
Page 4
Getting service from ADLINK
♦Customer Satisfaction is always the most important thing for ADLINK Tech
Inc. If you need any help or service, please contact us and get it.
ADLINK Technology Inc.
Web Site
Sales & Service service@Adlink.com.tw
Technical
Support
TEL +886-2-82265877 FAX +886-2-82265717
Address 9F, No. 166, Jian Yi Road, Chungho City, Taipei, 235 Taiwan, R.O.C.
http://www.adlink.com.tw
http://www.adlinktechnology.com
NuDAQ nudaq@adlink.com.tw
NuDAM nudam@adlink.com.tw
NuIPC nuipc@adlink.com.tw
NuPRO nupro@adlink.com.tw
Software sw@adlink.com.tw
♦Please inform or FAX us of your detailed information for a prompt,
satisfactory and constant service.
Detailed Company Information
Company/Organization
Contact Person
E-mail Address
Address
Country
TEL FAX
Web Site
Questions
Product Model
Environment to Use
OS:
Computer Brand:
M/B: CPU:
Chipset: BIOS:
Video Card:
Network Interface Card:
Other:
Challenge Description
Suggestions for ADLINK
Page 5

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction ..................................................... 1
1.1 About the NuDAM DIO Modules .............................................1
1.2 Overview of NuDAM-6050 ...................................................... 2
1.2.1 What is NuDAM-6050? .......................................................2
1.2.2 Features of NuDAM-6050 ...................................................2
1.2.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6050 ...........................................2
1.2.4 A Look at ND-6050 & Pin Assignment ................................4
1.2.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6050 ..........................................5
1.2.6 ND-6050 Functional Block Diagram....................................6
1.3 Overview of NuDAM-6052 ...................................................... 7
1.3.1 What is NuDAM-6052 ? ......................................................7
1.3.2 Features of NuDAM-6052 ...................................................7
1.3.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6052 ...........................................7
1.3.4 A Look at ND-6052 & Pin Assignment ................................9
1.3.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6052 ..........................................10
1.3.6 ND-6052 Functional Block Diagram....................................11
1.4 Overview of NuDAM-6053 ...................................................... 12
1.4.1 What is NuDAM-6053 ? ......................................................12
1.4.2 Features of NuDAM-6053 ...................................................12
1.4.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6053 ...........................................12
1.4.4 A Look at ND-6053 & Pin Assignment ................................14
1.4.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6053 ..........................................15
1.4.6 ND-6053 Functional Block Diagram....................................16
1.5 Overview of NuDAM-6054 ...................................................... 17
1.5.1 What is NuDAM-6054 ? ......................................................17
1.5.2 Features of NuDAM-6054 ...................................................17
1.5.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6054 ...........................................17
1.5.4 A Look at ND-6054 & Pin Assignment ................................19
1.5.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6054 ..........................................20
1.5.6 ND-6054 Functional Block Diagram....................................21
1.6 Overview of NuDAM-6056 ...................................................... 22
1.6.1 What is NuDAM-6056 ? ......................................................22
1.6.2 Features of NuDAM-6056 ...................................................22
1.6.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6056 ...........................................22
1.6.4 A Look at ND-6056 & Pin Assignment ................................24
1.6.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6056 ..........................................24
1.6.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6056 ..........................................25
1.6.6 ND-6056 Functional Block Diagram....................................26
1.7 Overview of NuDAM-6058 ...................................................... 27
1.7.1 What is NuDAM-6058 ? ......................................................27
1.7.2 Features of NuDAM-6058 ...................................................27
Table of Contents • i
Page 6

1.7.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6058 ...........................................28
1.7.4 A Look at ND-6058 & Pin Assignment ................................30
1.7.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6058...........................................31
1.7.6 ND-6058 Functional Block Diagram ....................................32
1.8 Overview of NuDAM-6060 ...................................................... 33
1.8.1 What is NuDAM-6060 ? ......................................................33
1.8.2 Features of NuDAM-6060 ...................................................33
1.8.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6060 ...........................................33
1.8.4 Using Relay Output .............................................................35
1.8.5 A Look at ND-6060 & Pin Assignment ................................36
1.8.6 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6060...........................................37
1.8.7 ND-6060 Functional Block Diagram ....................................38
1.9 Overview of NuDAM-6063 ...................................................... 39
1.9.1 What is NuDAM-6063 ? ......................................................39
1.9.2 Features of NuDAM-6063 ...................................................39
1.9.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6063 ...........................................39
1.9.4 Using Relay Output .............................................................40
1.9.5 A Look at ND-6063 & Pin Assignment ................................41
1.9.6 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6063...........................................42
1.9.7 ND-6063 Functional Block Diagram ....................................43
Chapter 2 Initialization & Installation.............................. 44
2.1 Software Installation ................................................................44
2.2 Initializing a Brand-New Module.............................................. 45
2.2.1 Objective of Initializing a Brand-New NuDAM .....................45
2.2.2 Default State .......................................................................46
2.2.3 Initialization Equipments......................................................47
2.2.4 Initialization Procedure........................................................47
2.2.5 Initialization Wiring ..............................................................48
2.3 Install a New NuDAM to a Existing Network ........................... 49
2.3.1 Equipments for Install a New Module..................................49
2.3.2 Installing Procedures...........................................................49
2.4 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6050 .......................................50
2.5 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6052 .......................................51
2.6 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6053 .......................................52
2.7 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6054 .......................................53
2.8 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6056 .......................................53
2.9 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6058 .......................................54
2.10 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6060 ....................................... 55
2.11 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6063 ....................................... 56
Chapter 3 Command Set .................................................. 57
3.1 Command and Response ....................................................... 57
ii • Table of Contents
Page 7

3.1.1 Introduction .........................................................................57
3.1.2 Document Conventions....................................................... 58
3.1.3 Format of NuDAM Commands............................................ 58
3.1.4 Response of NuDAM Commands ....................................... 59
3.2 Summary of Command Set ..................................................... 60
3.3 Set Configuration..................................................................... 62
3.4 Read Configuration .................................................................64
3.5 Read Module Name ................................................................66
3.6 Read Firmware Version .......................................................... 67
3.7 Reset Status............................................................................ 68
3.8 Digital Output........................................................................... 69
3.9 Digital Output (Continued)....................................................... 71
3.10 Digital Output (Continued)....................................................... 73
3.11 Digital Output (Continued)....................................................... 75
3.12 Synchronized Sampling .......................................................... 77
3.13 Read Synchronized Data ........................................................ 78
3.14 Digital Input .............................................................................81
3.14 Programmable I/O Mode Setting............................................. 84
3.15 Read Leading Code Setting .................................................. 86
3.16 Change Leading Code Setting............................................... 88
3.17 Set Host Watchdog Timer & Safety Value ............................. 90
3.18 Read Host Watchdog Timer & Safety Value.......................... 93
3.19 Change Polarity....................................................................... 95
3.20 Read Polarity........................................................................... 96
3.21 Host is OK ............................................................................... 97
Product Warranty/Service ................................................ 98
Table of Contents • iii
Page 8

Page 9
1
Introduction
1.1 About the NuDAM DIO Modules
The NuDAM provides a series of digital input or output (DIO) modules to
sense the digital signal or to control the remote devices.
The specified features of each module are shown here.
NuDAM-6050 : Digital I/O module
•
NuDAM-6052 : Isolated digital input module
•
NuDAM-6053 : 16-channel digital input module
•
NuDAM-6054 : 15-channel isolated digital input module
•
NuDAM-6056 : 15-channel isolated digital output module
•
NuDAM-6058 : 28 programmable digital I/O module
•
NuDAM-6060 : relay output and isolated digital input module
•
NuDAM-6063 : 8-channel relay output module
•
Introduction • 1
Page 10

1.2 Overview of NuDAM-6050
1.2.1 What is NuDAM-6050?
NuDAM-6050 is a digital input and output module. The digital input channels
can monitor active TTL signals, and sense passive switch on/off signal
because of the internal pull high resistors. The convenient open collector
output channels can sink up to 50 mA current. Combining with the relay
devices, it is possible to control the high power devices by programming
output channel of the NuDAM-6050.
1.2.2 Features of NuDAM-6050
♦ 7 bits digital input
♦ 8 bits open collector digital output
♦ Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
♦ Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
♦ Easy programming by software
♦ Easy installation and wiring
1.2.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6050
Interface
♦
• Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
• Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 115.2K
(115.2K only for firmware reversion above A4.00)
Digital Input
♦
• Channel numbers : 7
• Logical level 0 : +1V maximum
• Logical level 1: +3.5V~30V
• Pull up resister : 10KΩ
• Maximum current : 0.5mA
2 • Introduction
Page 11

Digital Output
♦
• Channel numbers : 8
• Output characteristic : open collector transistor
• Maximum current sink : 50mA
• Max. power dissipation : 300mW
Watchdog Function
♦
• Module internal watchdog timer: 150 ms
• Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
• Safety value : 8 output channels
• Host programmable watchdog :
• 100 ms ~ 25.500 sec
Power
♦
• Power supply : +10V to +30V
• Current consumption : 0.5 W
Introduction • 3
Page 12
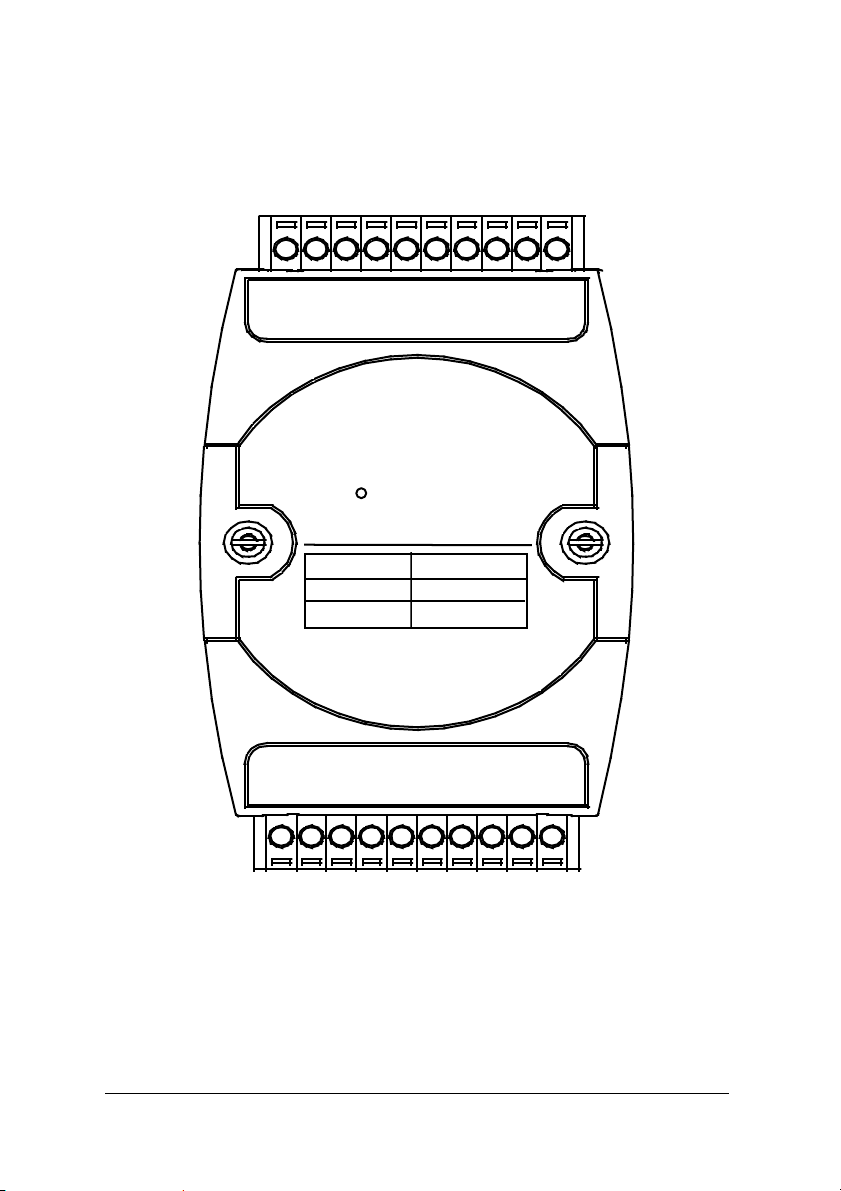
1.2.4 A Look at ND-6050 & Pin Assignment
DI 1
DI 0
DI 6
20
DI 3
DI 4
DI 5
ND-6050
I/O Type
Digital Output
Digital Input
DI 2
Digital
Input/Output
Signal
Bit 0-7
Bit 0-6
DO 0
DO 1
DO 2
11
4 • Introduction
1
DO 5
DO 7
DO 6
DO 4
DO 3
DEFAULT*
(Y)DATA+
(G)DATA-
(R)+Vs
10
(B)GND
Page 13

1.2.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6050
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DO 7 Digital output channel 7
2 DO 6 Digital output channel 6
3 DO 5 Digital output channel 5
4 DO 4 Digital output channel 4
5 DO 3 Digital output channel 3
6 Default* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +Vs Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 DO 2 Digital output channel 2
12 DO 1 Digital output channel 1
13 DO 0 Digital output channel 0
14 DI 0 Digital input channel 0
15 DI 1 Digital input channel 1
16 DI 2 Digital input channel 2
17 DI 3 Digital input channel 3
18 DI 4 Digital input channel 4
19 DI 5 Digital input channel 5
20 DI 6 Digital input channel 6
Introduction • 5
Page 14
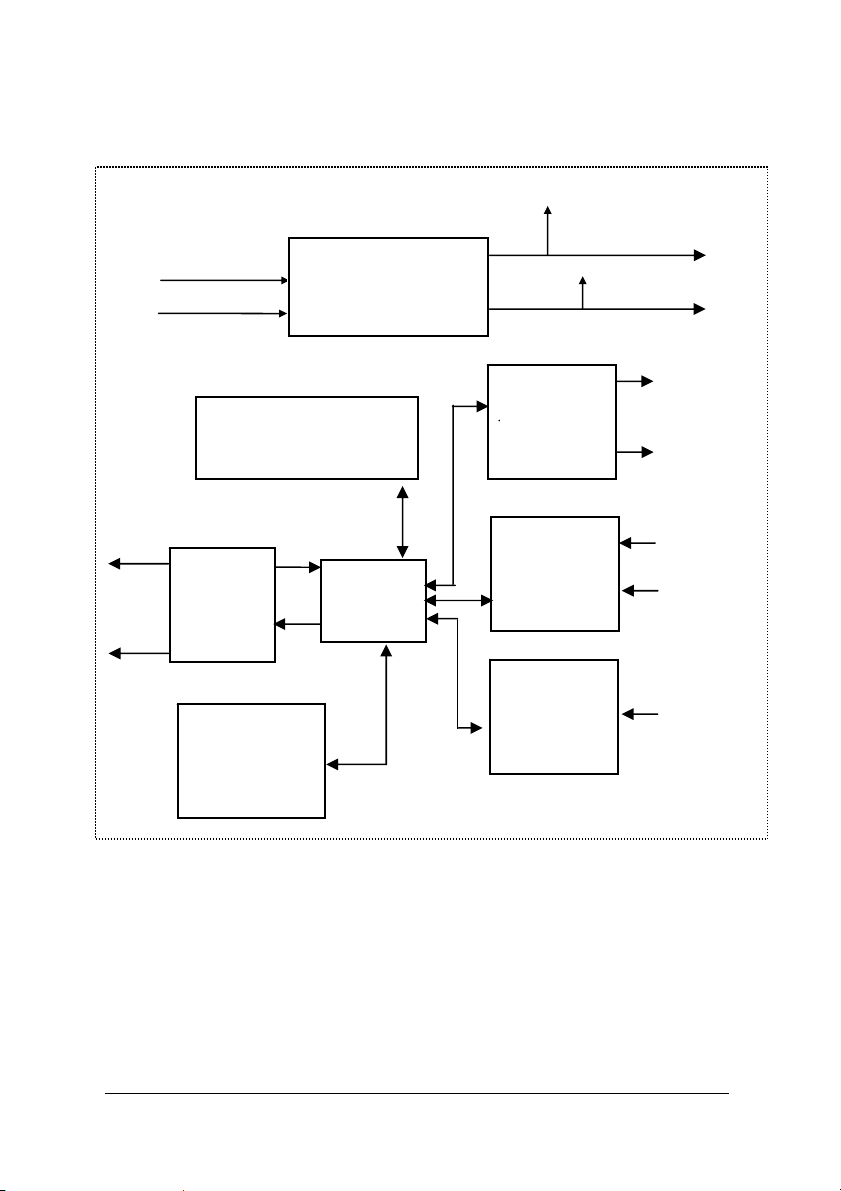
1.2.6 ND-6050 Functional Block Diagram
+ 5V
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Data +
Data -
Regulator & Filter
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
RS-485
Rec/Drv
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Micro
Processor
Power
8-bit
Digital/Output
7-bit
Digital/Input
1-bit
Digital/Input
GND
DO0
DO7
DI0
DI6
Default*
Pin
6 • Introduction
Page 15

1.3 Overview of NuDAM-6052
1.3.1 What is NuDAM-6052 ?
NuDAM-6052 provides 8 isolated digital input channels. Six of the input
channels are differential type and two of them are single-ended with common
ground. The isolation voltage is up to 5000 Vrms. It is suitable to use
NuDAM-6052 in industrial environment with the dangerous of high voltage
electric shock.
1.3.2 Features of NuDAM-6052
♦ 8 bits isolated input
♦ 5000 Vrms isolation voltage
♦ Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
♦ Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
♦ Easy programming by software
♦ Easy installation and wiring
1.3.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6052
Interface
♦
• Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
• Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 115.2K
(115.2K only for firmware reversion above A4.00)
Input
♦
• Channel numbers : 6 differential channels, 2 single ended
• Logical level 0 : +1V Max.
• Logical level 1: +3.5V ~ +24V
Watchdog Function
♦
• Module internal watchdog timer : 150ms
• Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
Introduction • 7
Page 16

• Safe value : 8 output channels
• Host programmable watchdog :100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Power
♦
• Power supply : +10V to +30V
• Current consumption : 0.4 W
8 • Introduction
Page 17
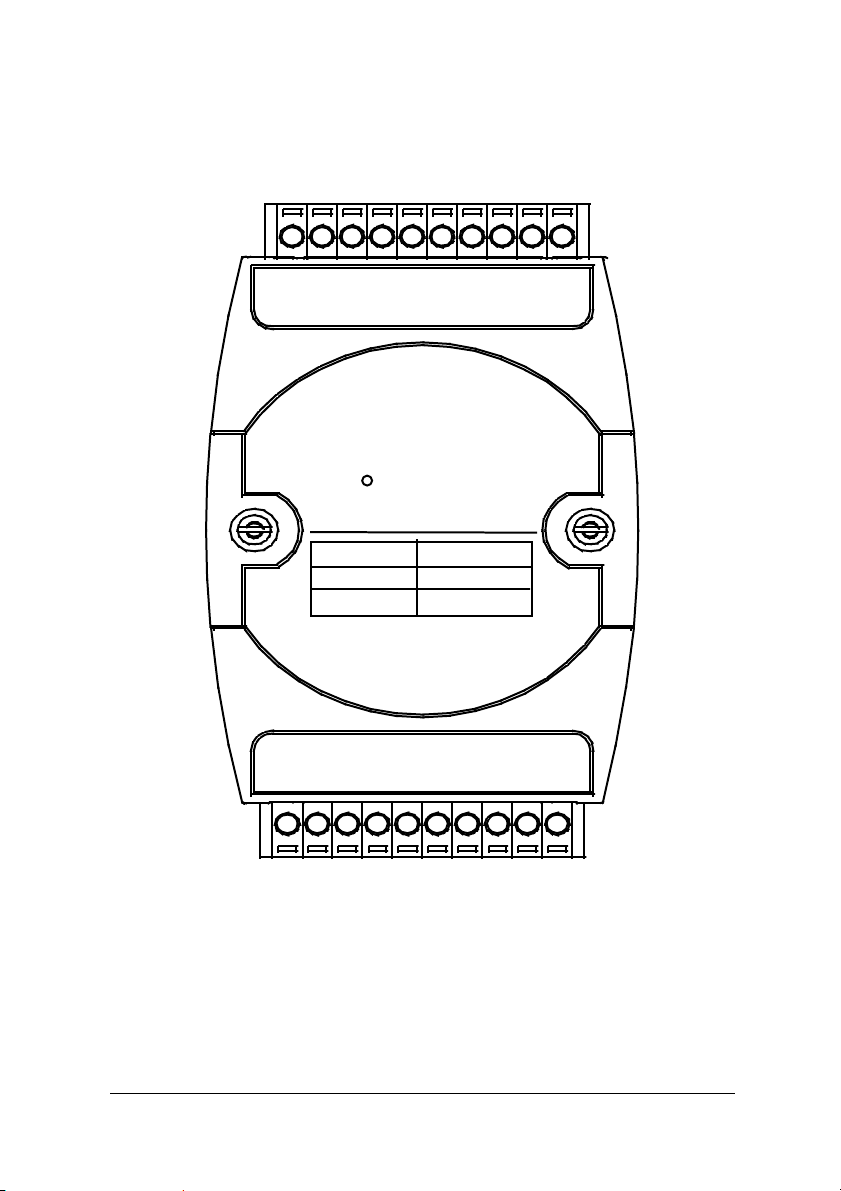
1.3.4 A Look at ND-6052 & Pin Assignment
DI 1+
DI 1-
DI 4-
20
DI 3-
DI 3+
DI 4+
ND-6052
Input Type
Diffential
Single Ended
DI 2+
DI 2-
Isolated
Digital Input
Channels
6
2
DI 0-
DI 0+
11
1
DI 5-
DI 5+
D.GND
DI 6+
DI 7+
DEFAULT*
(Y)DATA+
(G)DATA-
(R)+Vs
10
(B)GND
Introduction • 9
Page 18

1.3.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6052
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DI5+ Digital Input Channel 5+
2 DI5 - Digital Input Channel 5 -
3 DI6+ Digital Input Channel 6+
4 D.GND Digital Input Ground
5 DI7+ Digital Input Channel 7+
6 Default* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 DI0+ Digital Input Channel 0+
12 DI0 - Digital Input Channel 0 -
13 DI1+ Digital Input Channel 1+
14 DI1 - Digital Input Channel 1 -
15 DI2+ Digital Input Channel 2+
16 DI2 - Digital Input Channel 2 -
17 DI3+ Digital Input Channel 3+
18 DI3 - Digital Input Channel 3 -
19 DI4+ Digital Input Channel 4+
20 DI4 - Digital Input Channel 4 -
10 • Introduction
Page 19
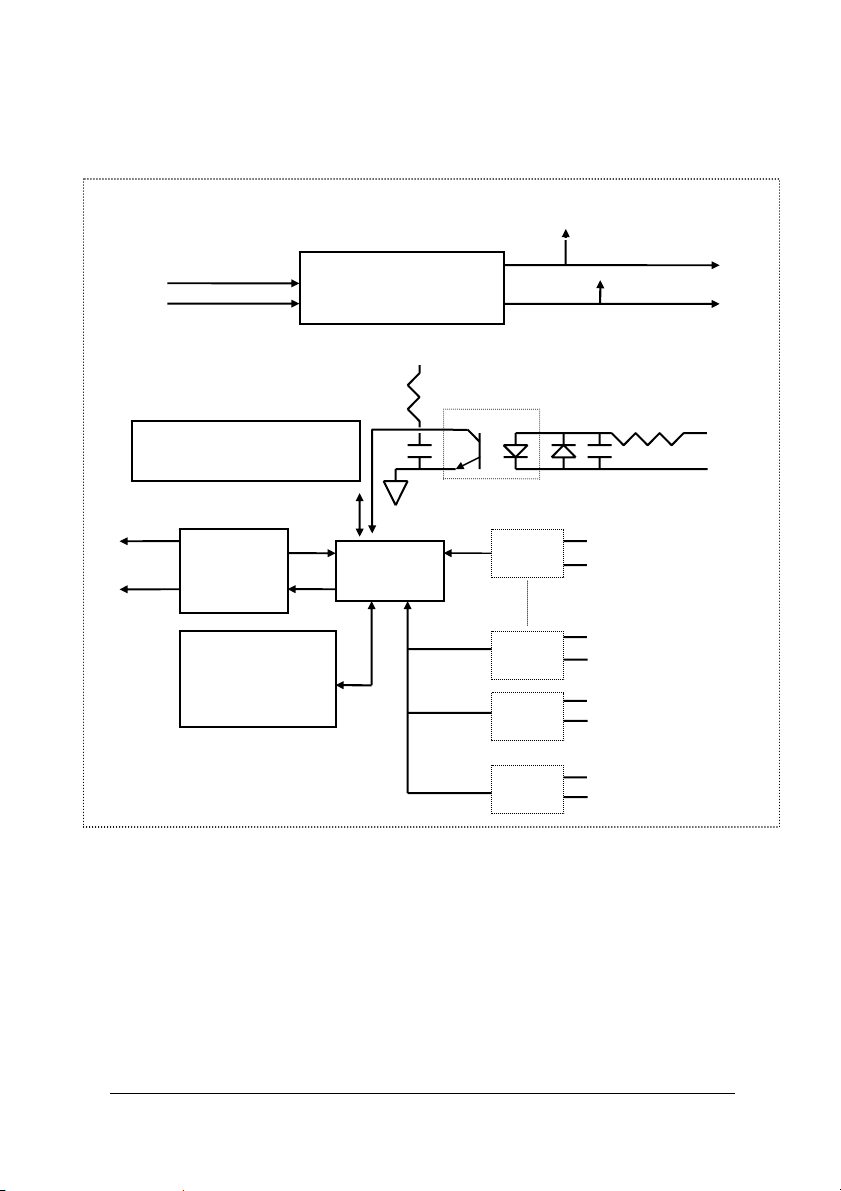
1.3.6 ND-6052 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Power
Regulator & Filter
+5V
+5V
GND
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Data -
RS-485
Rec/Drv
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Micro
Processor
DI0+
DI0-
DI0+
DI0-
DI5+
DI5-
DI6+
D.GND
DI7+
D.GND
Introduction • 11
Page 20

1.4 Overview of NuDAM-6053
1.4.1 What is NuDAM-6053 ?
NuDAM-6053 provides 16 digital input channels for dry contact or wet
contact signals. The effective distance from DI to contact point is up to 500m
for dry contact input.
1.4.2 Features of NuDAM-6053
• 16 bits digital input
• Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
• Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
• Easy programming by software
• Easy installation and wiring
1.4.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6053
Interface
♦
• Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
• Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 115.2K
(115.2K only for firmware reversion above A4.00)
Input
♦
• Channel numbers : 16
• Dry Contact:
• Logical level 0 : close to GND
• Logical level 1 : open
• Wet Contact :
• Logical level 0 : +2V max.
• Logical level 1 : +4V ~ + 30V
Watchdog Function
♦
• Module internal watchdog timer : 150ms
12 • Introduction
Page 21

• Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
• Host programmable watchdog : 100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Power
♦
• Power supply : +10V to +30V
• Current consumption : 0.4 W
Introduction • 13
Page 22
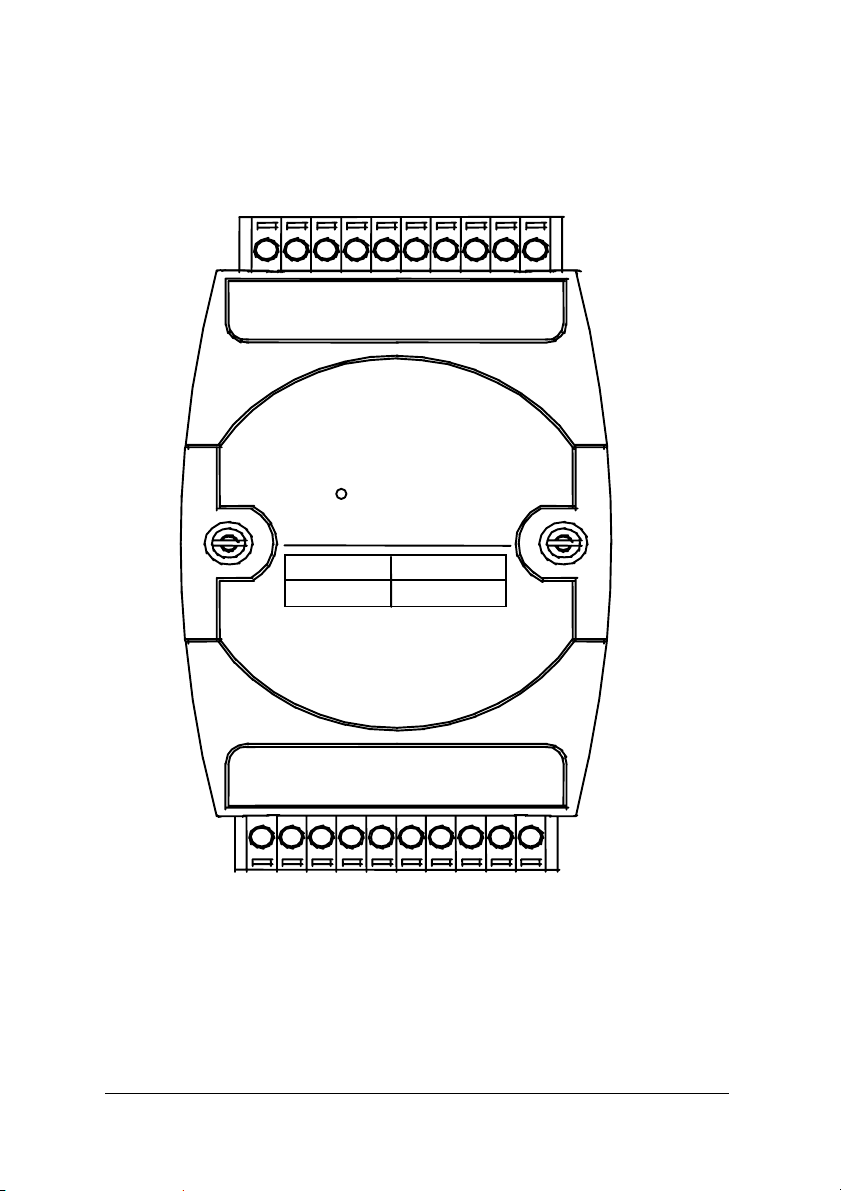
N
)
1.4.4 A Look at ND-6053 & Pin Assignment
DI 9
DI 7
20
DI 8
D-6053
DI 6
DI 5
16-CH
Digital
DI 4
DI 3 DI 2
DI 1
DI 0
11
14 • Introduction
1
DI 10
Input Type
Digital Input
DI 12 DI 13 DI 14
DI 11
Channels
16
DEFAULT
(R)+Vs
10
(B)GND
DATAG
(Y)DATA+
Page 23

1.4.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6053
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DI10 Digital Input Channel 10
2 DI11 Digital Input Channel 11
3 DI12 Digital Input Channel 12
4 DI13 Digital Input Channel 13
5 DI14 Digital Input Channel 14
6
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
Default*
/DI15
Initial state setting
/ Digital Input Channel 15
11 DI0 Digital Input Channel 0
12 DI1 Digital Input Channel 1
13 DI2 Digital Input Channel 2
14 DI3 Digital Input Channel 3
15 DI4 Digital Input Channel 4
16 DI5 Digital Input Channel 5
17 DI6 Digital Input Channel 6
18 DI7 Digital Input Channel 7
19 DI8 Digital Input Channel 8
20 DI9 Digital Input Channel 9
Introduction • 15
Page 24
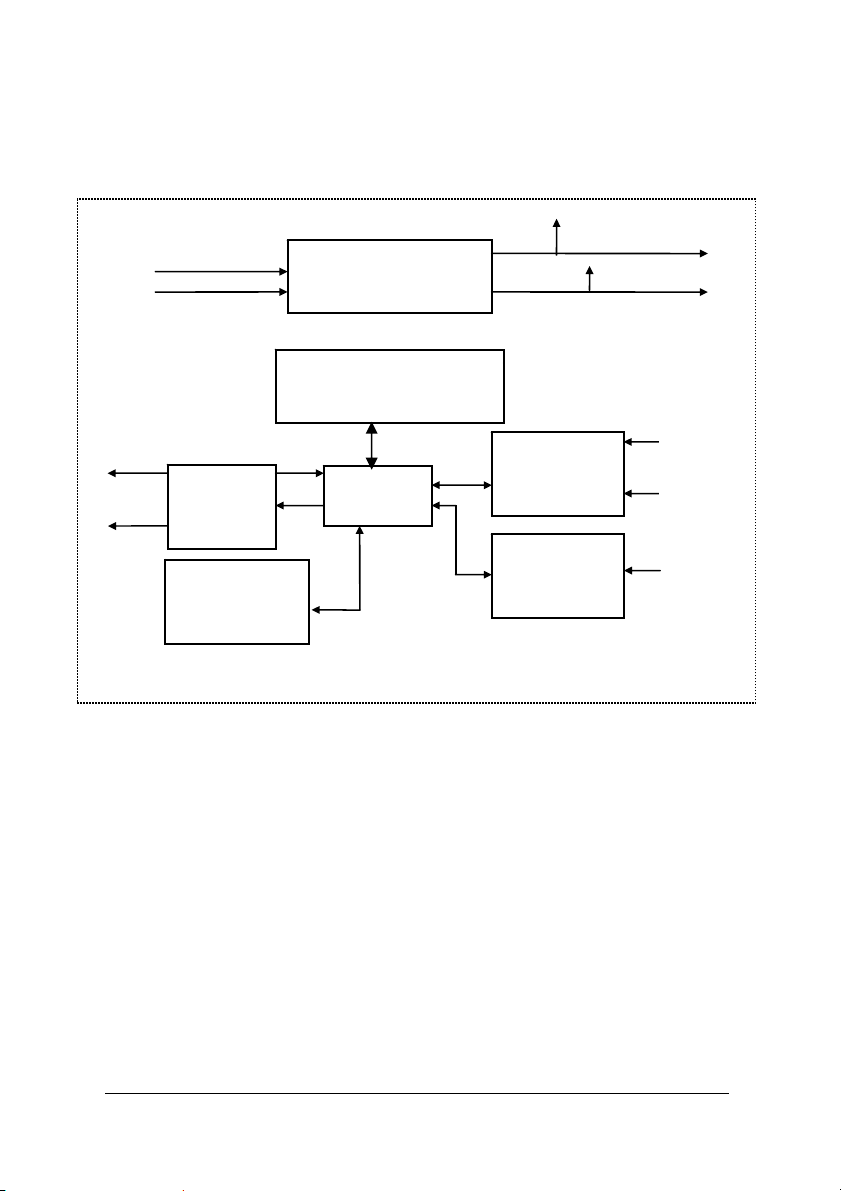
1.4.6 ND-6053 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Watchdog/Power Failure
Power
Regulator & Filter
Supervisor
+ 5V
GND
Data +
Data -
RS-485
Rec/Drv
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Micro
Processor
15-bit
Digital/Input
1-bit
Digital/Input
DI0
DI14
Default*
Pin/DI15
16 • Introduction
Page 25

1.5 Overview of NuDAM-6054
1.5.1 What is NuDAM-6054 ?
NuDAM-6054 provides 15 isolated digital input channels. All of the input
channels are common power type and one of them is using the same pin with
default (use jumper to choose). The isolation voltage is up to 5000 Vrms. It
is suitable to use NuDAM-6054 in industrial environment with the dangerous
of high voltage electric shock.
1.5.2 Features of NuDAM-6054
• 15 bits digital inputs with isolation protection and common power
• 5000 Vrms isolation voltage
• Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
• Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
• Easy programming by software
• Easy installation and wiring
1.5.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6054
Interface
♦
• Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
• Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 115.2K
(115.2K only for firmware reversion above A4.00)
Input
♦
• Channel numbers : 15 isolation common power input channels (the
fifteenth channel is the same with default pin, but can use jumper to
choose)
• Input type : source type
• Effective distance: 500 m
• Common external voltage: 24V
Watchdog Function
♦
Introduction • 17
Page 26

• Module internal watchdog timer : 150msec
• Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
• Host programmable watchdog :100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Power
♦
• Power supply : +10V to +30V
• Power consumption : 0.4 W
18 • Introduction
Page 27
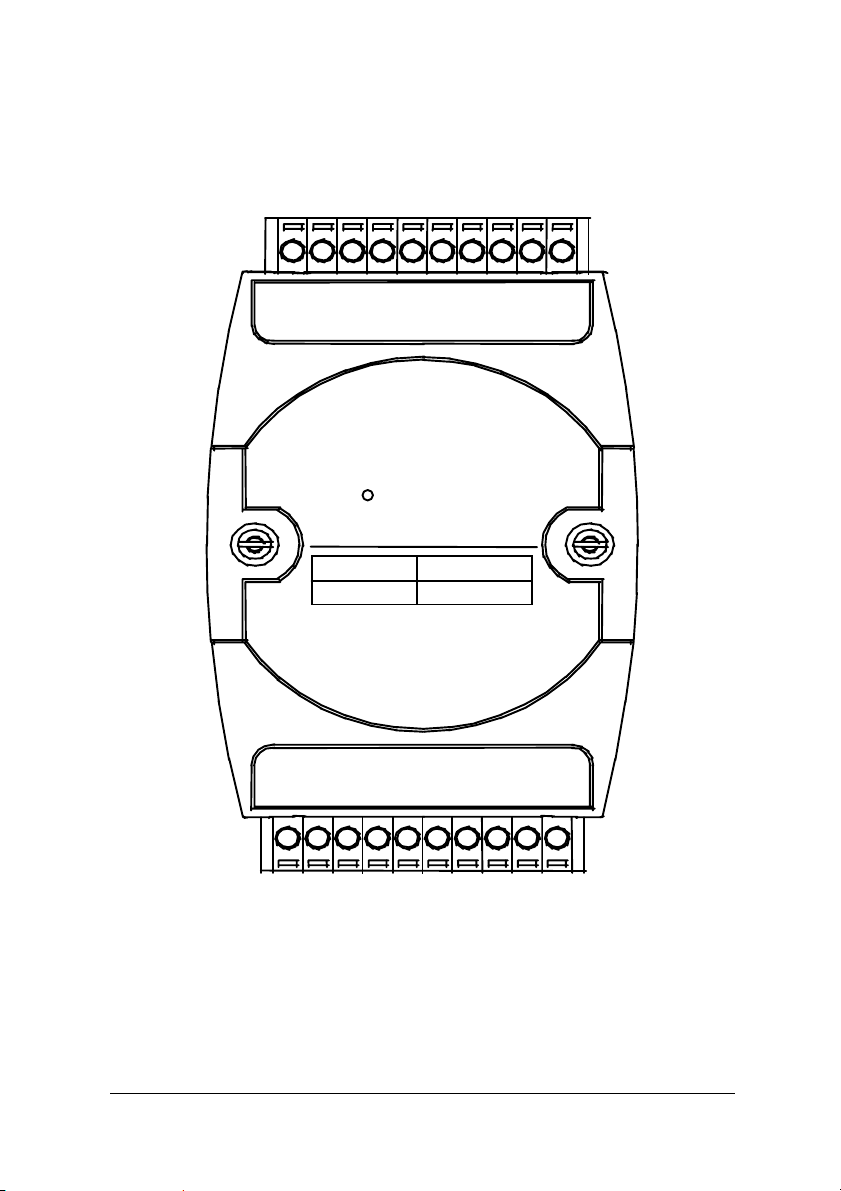
N
1.5.4 A Look at ND-6054 & Pin Assignment
DI7
DI5
DI1
DI2
DI0
20
D-6054
DI4
15-CH Isolated
Digital Input
DI3
Input Type
DI
DI6
Channels
15
DI8
DI9
11
*
DI11
DI10
DI13
DI12
Ext24V
DEFAULT/DI14
(G)DATA-
(Y)DATA+
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
Introduction • 19
Page 28

1.5.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6054
Pin #
10 (B) GND Ground
11 DI9 Digital input channel 9
12 DI8 Digital input channel 8
13 DI7 Digital input channel 7
Signal Name Description
1 DI10 Digital input channel 10
2 DI11 Digital input channel 11
3 DI12 Digital input channel 12
4 DI13 Digital input channel 13
5 Ext24V External common +24V
6 Default*/DI14
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
Initial state setting or digital
input channel 14
14 DI6 Digital input channel 6
15 DI5 Digital input channel 5
16 DI4 Digital input channel 4
17 DI3 Digital input channel 3
18 DI2 Digital input channel 2
19 DI1 Digital input channel 1
20 DI0 Digital input channel 0
20 • Introduction
Page 29
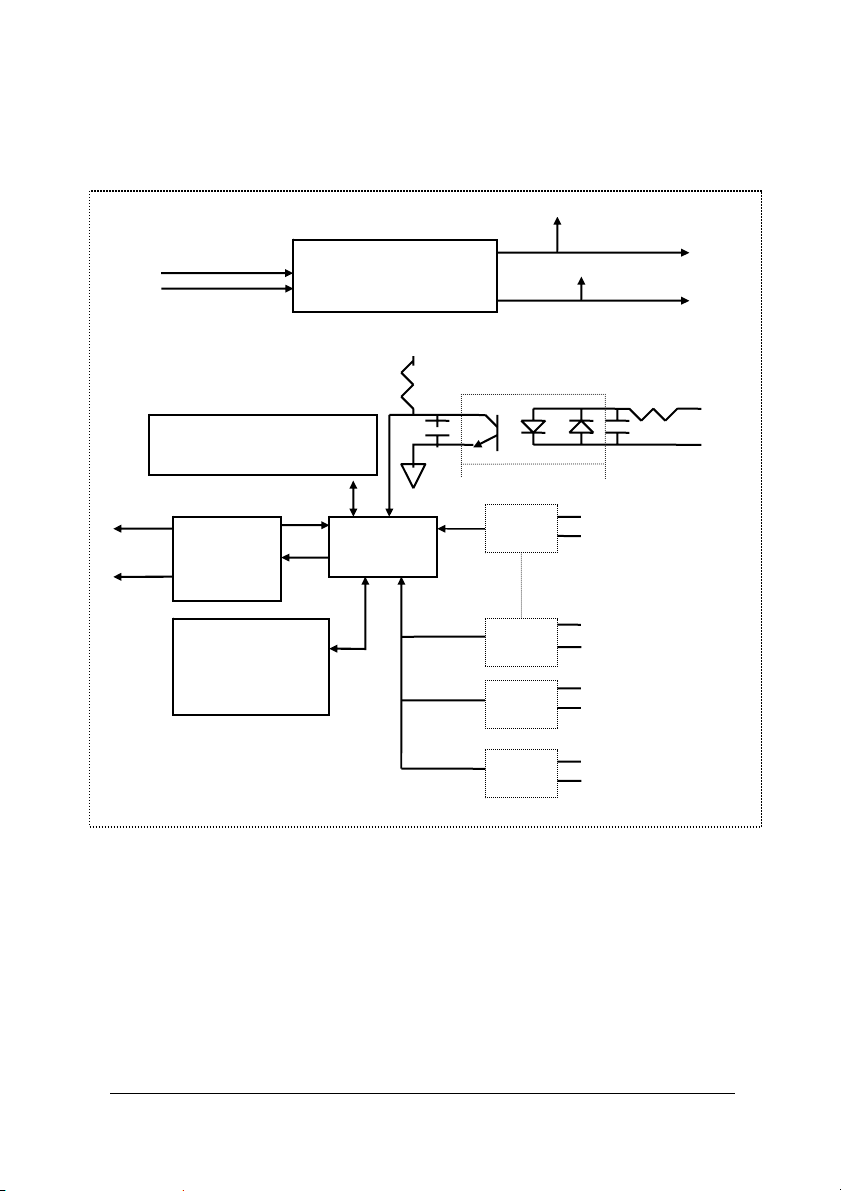
1.5.6 ND-6054 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Data +
RS-485
Rec/Drv
Data -
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Power
Regulator & Filter
+5V
Micro
Processor
+5V
GND
+24V
DI0
+24V
DI1
+24V
DI12
+24V
DI13
+24V
DI14
Introduction • 21
Page 30

1.6 Overview of NuDAM-6056
1.6.1 What is NuDAM-6056 ?
NuDAM-6056 provides 15 isolated digital output channels. All of the output
channels are common ground type and one of them is use the same pin with
default (use jumper to choose). The isolation voltage is up to 5000 Vrms. It
is suitable to use NuDAM-6056 in industrial environment with the dangerous
of high voltage electric shock.
1.6.2 Features of NuDAM-6056
♦ 15 bits digital open collector output with isolation protection and
common ground
♦ 5000 Vrms isolation voltage
♦ Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
♦ Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
♦ Easy programming by software
♦ Easy installation and wiring
1.6.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6056
Interface
♦
• Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
• Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 115.2K
(115.2K only for firmware reversion above A4.00)
Digital Output
♦
• Channel numbers : 15 isolation common ground output channels(the
fifteenth channel is the same with default pin,but could use jumper to
choose).
• Output characteristic:open collector transistor
• Maximum current sink:50mA(300mA for Hardware Reversion.A2)
• Max.power dissiation:200mW(3W for Hardware Reversion.A2)
• Isolation Voltage:5000Vrms
22 • Introduction
Page 31

Watchdog Function
♦
• Module internal watchdog timer : 150msec
• Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
• Safe value : 15 output channels
• Host programmable watchdog :100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Power
♦
• Power supply : +10V to +30V
• Current consumption : 0.3 W(Max 3.5W for Hardware Reversion.A2)
Introduction • 23
Page 32

N
e
1.6.4 A Look at ND-6056 & Pin Assignment
DO9
20
DO7
DO8
D-6056
Output Typ
DO
1
DO11 DO12 DO13
DO10
DO6
DO5
15-CH Isolated
Digita l Output
Ext .GND
DO4
DO3
Channels
15
DEFAULT
(Y)DATA+
DO2
DO1
DO0
11
(G)DATA-
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
24 • Introduction
Page 33

1.6.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6056
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DO10 Digital output channel 10
2 DO11 Digital output channel 11
3 DO12 Digital output channel 12
4 DO13 Digital output channel 13
5 ExtGND
6
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
Default*/
DO14
Initial state setting
Digital output channel 14
11 DO0 Digital output channel 0
12 DO1 Digital output channel 1
13 DO2 Digital output channel 2
14 DO3 Digital output channel 3
15 DO4 Digital output channel 4
16 DO5 Digital output channel 5
17 DO6 Digital output channel 6
18 DO7 Digital output channel 7
19 DO8 Digital output channel 8
20 DO9 Digital output channel 9
Introduction • 25
Page 34

1.6.6 ND-6056 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Data +
RS-485
Rec/Drv
Data -
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Power
Regulator & Filter
Micro
Processor
+5V
GND
+V
DO0
COM
DO1
COM
DO12
COM
DO13
COM
DO14
COM
26 • Introduction
Page 35

1.7 Overview of NuDAM-6058
1.7.1 What is NuDAM-6058 ?
NuDAM-6058 provides 28 digital I/O channels. It emulates industry
standard mode zero configuration of 8255 programmable peripheral
interface (PPI) chip. The PPI offers 3 ports A, B and C, the C port can also be
subdivided into 2 nibble-wide (4-bit) port – C upper and C lower. A 50 pin
SCSI connector equipped with ND-6058 which is corresponding to PPI chip
with 24 DIO points.
1.7.2 Features of NuDAM-6058
♦ Industry standard 8255 programmable peripheral interface mode 0
emulation
♦ 24 Programmable I/O channels
♦ 4 dedicated input channels
♦ Completely TTL compatible I/O lines
♦ Status read-back capability
♦ Direct bit set/reset capability
♦ Buffered circuits for higher driving capability
♦ Direct interface with OPTO-22 compatible I/O module
♦ Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
♦ Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
♦ On board resetable fuse to protect power supply form external
devices
♦ Easy programming by software
♦ Easy installation and wiring
Introduction • 27
Page 36

1.7.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6058
Interface
♦
• Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
• Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 115.2K
(115.2K only for firmware reversion above A4.00)
Programmable Digital Input/Output
♦
• Channel numbers : 24
• Input Signal:
• Logical level 0 : -0.5 ~ 0.8 V
• Logical level 1: 2.0 ~ 5.25 V
• Output Signal:
• Logical level 0: 0.5 V Maximum
• Logical level 1: 2.4 V Minimum Digital Output
Watchdog Function
♦
• Module internal watchdog timer : 150msec
• Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
• Safe value : 15 output channels
• Host programmable watchdog :100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Dedicated Digital Input
♦
• Channel numbers : 4
• Input Signal:
• Logical level 0: 2 V max.
• Logical level 1: 3 V ~ 5.25 V
Connector
♦
• 10-pin skew terminal block
28 • Introduction
Page 37

• 50-pin SCSI II connector
Power
♦
• Power supply : +10V to +30V
• Current consumption: 1.7 W
Introduction • 29
Page 38

N
1.7.4 A Look at ND-6058 & Pin Assignment
A7
~
B0
28-CH Pr ogram mable
Digita l I/O
Cha nnels
24
~
A0
1
D-6058
Typ e
PPI
B7
C0
~
C7
50
DI 4
1
DI1
DI0
DI2
*
DI3
DEFAULT
(G)DATA-
(Y)DATA+
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
30 • Introduction
Page 39

1.7.5 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6058
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DI0 Digital input channel 0
2 DI1 Digital input channel 1
3 DI2 Digital input channel 2
4 DI3 Digital input channel 3
5
6 Default* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
Introduction • 31
Page 40

1.7.6 ND-6058 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Power
Regulator & Filter
+5V
GND
Data +
Data -
RS-485
Rec/Drv
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Micro
Processor
PPI
DI0 … … DI3
A0~A7
B0~B7
C0~C7
32 • Introduction
Page 41

1.8 Overview of NuDAM-6060
1.8.1 What is NuDAM-6060 ?
NuDAM-6060 provides four relay output channels, two are form A and two
are form C. It can control high power devices without external circuits. The
isolation guarantees the industrial safety.
1.8.2 Features of NuDAM-6060
♦ 4 channels relay output
♦ 4 channels isolated digital input
♦ Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
♦ Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
♦ Easy programming by software
♦ Easy installation and wiring
1.8.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6060
Interface
♦
• Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
• Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 115.2K
(115.2K only for firmware reversion above A4.00)
Input
♦
• Channel numbers : 4
• Common External Voltage : +24 V
• Input Type : Source Type
Output
♦
• Channel numbers : 4 relay output
• Output type : 2 form C channels, 2 form A channels
• Contact rating : AC 0.6A /125 V, 0.3A / 250V
Introduction • 33
Page 42

• DC 2A / 30V, 0.6A / 110V
• Relay ON/OFF time interval : 3 ms / 1ms
• Breakdown voltage : 500 V
• Expected life : 108 times
• Insulation resistance : 1000 MΩ minimum
Watchdog Function
♦
• Module internal watchdog timer : 150ms
• Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
• Safety value : 4 output channels
• Host programmable watchdog : 100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Power
♦
• Power supply : +10V to +30V
• Current consumption : 0.8 W
34 • Introduction
Page 43

1.8.4 Using Relay Output
The ND-6060 contains two types of relay : Form C and Form A. The relay R3
and R4 are form C relays, and R1 and R2 are plain form A type. The
difference between these two types of relay are:
1. Form C Relay : ( R3, R4)
NO
COM
NC
Control Bit = High (1)
Form C relay has three contacts : NC ( Normal Close), NO ( Normal Open),
and COM( Common). The CM post, located at the middle, can make contact
either NO post or NC post. When the control bit is high (1), the COM post and
NO post are contacted. If the control bit is low (0), the COM post and NC post
make contact.
In normal power-up and reset, the relay is in low status.
2. Form A Relay : ( R1, R2)
NO
COM
Control Bit = High (1)
NO
COM
NC
Control Bit = Low (0)
NO
COM
Control Bit = Low (0)
Form A relay only has two contacts : NO (Normal Open) and
COM( Common). The COM post can make contact either NO post or not
contact NO post. When the control bit is high (1), the COM post and NO post
are contacted. If the control bit is low (0), the COM post and NO post does
not make contact. In normal power-up and reset, the relay is in low status.
Introduction • 35
Page 44

1.8.5 A Look at ND-6060 & Pin Assignment
20
1
DI 3
RL4 NC
RL4 COM
ND-6060
Type
Relay Output
Digital Input
DI 2
RL4 NO
RL3 COM
RL3 NC
RL3 NO
Relay Output
Digital Input
RL2 COM
RL2 NO
11
RL1 NO
RL1 COM
Channels
4
4
*
10
DI 1
DI 0
Ext24V
DEFAULT
(Y)DATA+
(R)+Vs
(G)DATA-
(B)GND
36 • Introduction
Page 45

1.8.6 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6060
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 DI3 Digital Input Channel 3
2 DI2 Digital Input Channel 2
3 DI1 Digital Input Channel 1
4 DI0 Digital Input Channel 0
5 Ext24 External Common +24V
6 Default* Initial state setting
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
11 RL1 NO Relay 1, normal open
12 RL1 COM Relay 1, common ground
13 RL2 NO Relay 2, normal open
14 RL2 COM Relay 2, common ground
15 RL3 NO Relay 3, normal open
16 RL3 NC Relay 3, normal close
17 RL3 COM Relay 3, common ground
18 RL4 NO Relay 4, normal open
19 RL4 NC Relay 4, normal close
20 RL4 COM Relay 4, common ground
Introduction • 37
Page 46

1.8.7 ND-6060 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Data+
RS-485
Rec/Drv
Data -
Power
Regulator & Filter
+5V
Micro
Processor
+5V
+
GND
Ext24V
DI0
Ext24V
DI3
RL1 NO
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
38 • Introduction
RL1 COM
+5V
RL4 NO
RL4
Page 47

1.9 Overview of NuDAM-6063
1.9.1 What is NuDAM-6063 ?
NuDAM-6063 provides eight from A relay output channels. It can control high
power devices without external circuits.
1.9.2 Features of NuDAM-6063
♦ 8 channel relay output
♦ Programmable host watchdog timer for host failure protection
♦ Internal watchdog timer for device failure protection
♦ Easy programming by software
♦ Easy installation and wiring
1.9.3 Specifications of NuDAM-6063
Interface
♦
• Interface : RS-485, 2 wires
• Speed (bps) : 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 19.2K, 38.4K, 115.2K
(115.2K only for firmware reversion above A4.00)
Digital Output
♦
• Channel numbers : 8
• Output Type : 8 form A channels
• Contact rating : AC 0.5A / 125V
• DC 1A / 30V
• Relay ON/OFF time interval : 3ms / 3ms
• Breakdown voltage : 1000Vrms
• Expected life : 107
Insulation Resistance: 1,000 MΩ
♦
Watchdog Function
♦
Introduction • 39
Page 48

• Module internal watchdog timer : 150ms
• Power failure threshold : 4.65 V
• Safety value : 8 output channels
• Host programmable watchdog : 100 ms ~ 25.5 sec
Power
♦
• Power supply : +10V to +30V
• Current consumption : 1.2 W
1.9.4 Using Relay Output
Form A Relay :
NO
COM
Control Bit = High (1)
Form A relay only has two contacts : NO (Normal Open) and
COM( Common). The COM post can make contact either NO post or not
contact NO post. When the control bit is high (1), the COM post and NO post
are contacted. If the control bit is low (0), the COM post and NO post does
not make contact.
In normal power-up and reset, the relay is in low status.
NO
COM
Control Bit = Low (0)
40 • Introduction
Page 49

N
1.9.5 A Look at ND-6063 & Pin Assignment
20
RL5 NO
RL5 COM
D-6063
Type
Relay Output
RL4 NO
RL4 COM
RL3 COM
8-CH Isolated
Relay Output
Channels
8
RL3 NO
RL2 NO
RL2 COM
11
RL1 NO
RL1 COM
1
RL6 NO
RL7 NO
RL6 COM
RL8 NO
DEFAULT* 1
RL7 COM
(G)DATA-
RL8 COM
(Y)DATA+
10
(R)+Vs
(B)GND
Introduction • 41
Page 50

1.9.6 Pin Definitions of NuDAM-6063
Pin # Signal Name Description
1 RL6 NO Relay 6, normal open
2 RL6 COM Relay 6, common ground
3 RL7 NO Relay 7, normal open
4 RL7 COM Relay 7, common ground
5 RL8 NO Relay 8, normal open
6 Default*/ RL8 NO
7 (Y) DATA+ RS-485 series signal, positive
8 (G) DATA- RS-485 series signal, negative
9 (R) +VS Power supply, +10V~+30V
10 (B) GND Ground
Initial state setting
Relay 8, normal open
11 RL1 NO Relay 1, normal open
12 RL1 COM Relay 1, common ground
13 RL2 NO Relay 2, normal open
14 RL2 COM Relay 2, common ground
15 RL3 NO Relay 3, normal open
16 RL3 COM Relay 3, common ground
17 RL4 NO Relay 4, normal open
18 RL4 COM Relay 4, common ground
19 RL5 NO Relay 5, normal open
20 RL5 COM Relay 5, common ground
42 • Introduction
Page 51

1.9.7 ND-6063 Functional Block Diagram
Power Input
+10V ~ +30V
Watchdog/Power Failure
Supervisor
Data+
Data -
RS-485
Rec/Drv
EEPROM
Config Data
Safe Value
Power
Regulator & Filter
Micro
Processor
+5V
GND
RL1 NO
RL1 COM
+5V
RL8 NO
RL8 COM
Introduction • 43
Page 52

2
Initialization & Installation
2.1 Software Installation
1. If you have already installed “NuDAM Administration” then skip other
steps.
2. Backup your software diskette.
3. Insert “NuDAM Administration” disc into CD-ROM.
4. Change drive to the path of CD-ROM. For example, your drive of
CD-ROM is F:, then change the drive to F:
5. Find the setup of NuDAM Administration and run it.
6. Please follow the steps of setup program then you can successful to
install the nudism Administration.
44 • Initializtion & Installation
Page 53

2.2 Initializing a Brand-New Module
2.2.1 Objective of Initializing a Brand-New NuDAM
All NuDAM modules. except NuDAM-6520 and NuDAM-6510, in a RS-485
network must have an unique address ID, however, every brand-new
NuDAM has a factory default setting as following :
♦ Address ID is 01.
♦ Baud rate is 9600 bps
♦ Check-sum disable
♦ Host Watchdog timer is disable
Therefore, to configure the brand-new NuDAM before using is necessary,
otherwise the address ID will be conflict with others modules because the ID
of new modules are identity . The baud rate may also be changed according
to user‘s requirements.
The following sections show how to initialize a brand-new module, which is
applicable for initializing NuDAM-6050, NuDAM-6052, NuDAM-6053,
NuDAM-6054, NuDAM-6056, NuDAM-6058, NuDAM-6060, and
NuDAM-6063.
Initializtion & Installation • 45
Page 54

2.2.2 Default State
The NuDAM I/O modules must be set at Default State when you want to
change the default settings, such as the ID address, baud rate, check-sum
status etc. All NuDAM I/O modules have an special pin labeled as
DEFAULT*
shorted to ground when power ON. Under this state, the default
configuration is set as following :
♦ Address ID is 00
♦ Baud rate is 9600 bps
♦ Check-sum disable
Therefore, the communication between host and the module will can be
easily set as the same configuration, the initialization of a module will be
possible no matter what configuration is set under operating state.
For ND-6053, ND-6054 and ND-6056, the pin 6 is used for both DI15(DO15)
and DEFAULT*, and also the ND-6063, the pin 6 is used for both RL8 COM
and DEFAULT*. The jumper setting is as below, and the default setting is
DI15(D015) or RL8 COM. When you want to use ND-6053, ND-6054,
ND-6056 or ND-6063 as Default*, you should open the module case to set
the JP2.
. The module will be in Default State if the
DEFAULT*
pin is
JP2
1 2 3
DI15
(DO15)
46 • Initializtion & Installation
INIT* DI15
JP2
1 2 3
INIT*
(DO15)
INIT* DI15, DO15, RL8 COM
Page 55

2.2.3 Initialization Equipments
♦ Host computer with an RS-232 port
♦ An installed RS-485 module (NuDAM-6520) with 9600 baud rate
♦ The brand new NuDAM module
♦ Power supply (+10 to +30 V
) for NuDAM modules
DC
♦ Administration utility software
Note1: Never Connect the DRFAULT* pin to Vs or power source just left it
open or wired to GND.
2.2.4 Initialization Procedure
1. Power off the host computer and the installed NuDAM-6520. Be
sure of the baud rate of the NuDAM-6520 is 9600 bps.
2. Connect a brand new NuDAM module with the RS-485. Set the
module in Default State by shorting the
Figure 2.1 for detailed wiring.
3. Power on the host computer.
4. Power on the power supply for NuDAM modules.
5. Use the NuDAM Administrating utility to configure the address ID,
Baud rate and check-sum status of the module.
DEFAULT*
pin. Refer to
Initializtion & Installation • 47
Page 56

2.2.5 Initialization Wiring
Computer
Local Power Supply
+10 V to +30 V
+Vs GND
Figure 2-1 Layout for Configuring the NuDAM module
Host
RS-232
NuDAM-6520
RS-232/RS-485
DATA +
DATA -
+Vs GND
New
NuDAM
module
DATA+
DATA Default*
+Vs GND
48 • Initializtion & Installation
Page 57

2.3 Install a New NuDAM to a Existing Network
2.3.1 Equipments for Install a New Module
♦ A existing NuDAM network
♦ New NuDAM modules.
♦ Power supply (+10 to +30 V
DC
)
2.3.2 Installing Procedures
1. Configure the new NuDAM module according to the initialization
procedure in section 2.2.
2. The baud rate and check-sum status of the new module must be
identity with the existing RS-485 network. The address ID must not
be conflict with other NuDAM modules on the network.
3. Power off the NuDAM power supply of the existing RS-485 network.
4. Power off the host computer.
5. Wire the power lines for the new NuDAM with the existing network.
Be careful about the signal polarity as wiring.
6. Wire the RS-485 data lines for the new NuDAM with the existing
network. Be careful about the signal polarity as wiring.
7. Wire to the input or output devices. Refer to section 2.4 for
illustrations.
8. Power on the host computer.
9. Power on the NuDAM local power supply.
10. Use the NuDAM administration utility to check entire network.
Initializtion & Installation • 49
Page 58

2.4 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6050
Digital Input Connect
with TTL Signal
TTL
Device
Digital Input Connect
with Switch or Push
Button
Switch
or
Push Button
Digital Output
Connect with Power Loading
NuDAM-6050 Digital Input Channel
+5V
TTL Buffer
DI n
GND
NuDAM-6050 Digital Input Channel
+5V
DI n
GND
TTL Buffer
To
Micro Processor
To
Micro Processor
NuDAM-6050 Digital Output Channel
From
Micro Processor
open
collector
50 • Initializtion & Installation
DO n
GND
R : current limit resistor
LED, SSR, Relay etc.
Power
Loading
R
+Vs
External
Power
Supply
Page 59

r
2.5 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6052
Isolated Differential Input
Floating
Digital
Signal
Source
Isolated Single Ended Input
Digital
Signal
Source
NuDAM-6052 Differential Input Channel
Photo
Coupler
DI n+
DI n-
GND
NuDAM-6052 Single-ended Input Channel
Photo
Coupler
DI n+
To
Micro Processor
To
Micro Processo
GND
Initializtion & Installation • 51
Page 60

2.6 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6053
Wet Contact Input
0~+30V
DC
Contact Closure Input
Contact
Closure
DI n
GND
DI n
GND
Vcc
Vcc
Digital
GND
Digital
GND
52 • Initializtion & Installation
Page 61

2.7 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6054
Isolated Common Power Input
NuDAM-6054 Common Power Channel
Photo
Common
Power
Digital
Signal
Source
Ext .24V
DI n
GND
Coupler
2.8 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6056
Isolated Common Ground Output
NuDAM-6056 Common Ground Channel
Photo
Digital
Output
Common
GND
DO n
COM
GND
Coupler
From
Micro Processor
To
Micro Processor
Initializtion & Installation • 53
Page 62

2.9 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6058
Digital Input Connect with TTL Signal
NuDAM-6058 Digital Input Channel
+5V
TTL Buffer
TTL
Device
DI n
GND
To
Micro Processor
6058
DIN-24P
DIN-24R
DIN-24G
DIN-50S
DIN-24P
24-CH Opt-Isolated Digital Input Termination Board with DIN Socket.
DIN-24R
24-CH Relay Output Termination Board with DIN Socket.
DIN-24G
24-CH Grayhill I/O Modules Termination Board with DIN Socket.
DIN-50S
50-Pin SCSI Connector Termination Board with DIN Socket.
54 • Initializtion & Installation
Page 63

2.10 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6060
Form C Relay Output
NuDAM-6060 Relay Output Channel
External Power Source
+Vs
From
Micro
Processor
Form A Relay Output
NuDAM-6060 Relay Output Channel
From
Micro
Processor
Digital Input : Contact Mode
NuDAM-6060 Digital Input Channel
Ext24V
DI n+
RL n
NO
COM
NC
RL n
NO
COM
External power ground
External Power Source
External power ground
Photo
Coupler
To
Micro Processor
Power
Loading
Power
Loading
Power
Loading
+Vs
External
Switch
DI n-
Initializtion & Installation • 55
Page 64

r
g
r
Digital Input : Transistor Mode
Ext24V
External
Signal
NuDAM-6060 Digital Input Channel
To
DI n+
DI n-
Photo
Coupler
Micro Processo
2.11 Application Wiring for NuDAM-6063
Form A Relay Output
NuDAM-6063 Relay Output Channel
RL n
NO
From
Micro
Processo
COM
External Power Source
Power
Loadin
External power ground
+Vs
56 • Initializtion & Installation
Page 65

3
Command Set
3.1 Command and Response
3.1.1 Introduction
The NuDAM command is composed by numbers of characteristics, including
the leading code, address ID, the variables, the optional check-sum byte,
and a carriage return to indicate the end of a command. The host computer
can only command only one NuDAM module except those syncronized
commands with wildcard address “**”. The NuDAM may or may not give
response to the command. The host should check the response to
handshake with the modules.
Command Set • 57
Page 66

3.1.2 Document Conventions
The following syntax conventions are used to describe the NuDAM
commands in this manual.
Leading Code is the first characteristic of the NuDAM
(Leading
Code)
(Addr)
(Comman
d
Variable)
[Data]
[Checksu
m]
< >
command. All NuDAM commands need a command
leading code, such as %,$,#,@,...etc.
1- character
Module’s address ID, the value is in the range of 00 - FF
(Hexadecimal) if no specified in the following
2- character
Items indicate command codes or value of variables
Variable length
Some output command need data
Variable length
Checksum in brackets indicate optional parameter,
only checksum is enable then this field is required
2- character
Identifies a control code character, such as <CR> for
carriage return, its value is 0x0D. 1- character
3.1.3 Format of NuDAM Commands
(Leading Code)(Addr)(Command)[Data]
When checksum is enable then
2-character.
How to calculate checksum value ?
[Checksum] = (
Example 1: checksum is
58 • Command Set
(LeadingCode)+(Addr)+(Command)+[Data]
User Command: $012<CR>
Response: !01400600<CR>
<CR> : Carriage return 0x0D
[Checksum]
disable
$ : LeadingCode
01 : Address
2 : Command (Read Configuration)
[Checksum]
is needed, it is
<CR>
) MOD 0x100
Page 67

Example 2: checksum is
User Command:
‘$’ = 0x24 ‘0’ = 0x30 ‘1’ = 0x31 ‘2’ = 0x30
B7 = (
0x24 + 0x30 + 0x31 + 0x32
‘!’ = 0x24 ‘0’ = 0x30 ‘1’ = 0x31 ‘4’ = 0x34
‘6’ = 0x36
AC
= ( 0x24 + 0x30 + 0x31 + 0x34 + 0x30 + 0x30 + 0x36 + 0x30
+ 0x30 )
Note : 1.There is no spacing between characters.
2. At end of command need a <CR> carriage return 0x0D.
3. Checksum is optional parameter.
enable
$012B7<CR>
Response:
<CR> : Carriage return 0x0D
!01400600AC<CR>
$ : LeadingCode
01 : Address
2 : Command (Read Configuration)
B7 : Checksum value
MOD 0x100
) MOD 0x100
3.1.4 Response of NuDAM Commands
The response message depends on NuDAM command. The response is
also composed with several characteristics, including leading code,
variables, and carriage return for ending. There are two kinds of leading
code for response message, ”!“ or ”>“ means valid command and ”?“ means
invalid. By checking the response message, user can monitor the command
is valid or invalid.
Note : Under the following conditions, there will have no response
message.
1. The specified address ID is not exist.
2. Syntax error.
3. Communication error
4. Some special commands does not have response.
Command Set • 59
Page 68

3.2 Summary of Command Set
There are three categories of NuDAM commands. One is the general
commands, including set configuration command, read configuration, reset,
read module‘s name or firmware version, etc. Every NuDAM can response
to the general commands.
The second category is the functional commands, which depends on
functions of each module, not every module can execute all functions.
The third category is the special commands, including functions about the
programmable watchdog timer, safe values, and the programmable leading
code.
60 • Command Set
Page 69

Command Set of Digital I/O Modules
Command Syntax Module
General Commands
Set Configuration
Read Configuration
Read Module Name
Read Firmware Version
Reset Status
Functional Commands
Synchronized Sampling
Read Synchronized Data
Digital Output
Digital Input
Set Programmable I/O Mode
Special Commands
Read Command Leading Code
Setting
Change Command Leading Code
Setting
Set Host Watchdog / Safety Value
Read Host WatchDog / Safe
Value
Change Polarity
Read Polarity
Host is OK
%(OldAddr)(NewAddr)
(TypeCode)(BaudRate)
(CheckSumFlag)
$(Addr)2
$(Addr)M
$(Addr)F
$(Addr)5
#**
$(Addr)4
#(Addr)(ChannelNo)
(OutData)
#(Addr)(Port)(Odata)
#(Addr)(Port)(ChannelNo)
(BitData)
#(Addr)T(OdataA)(OdataB
)(OdataC)
$(Addr)6
$(Addr)S(IOSts)
~(Addr)0
~(Addr)10(C1)(C2)(C3)
(C4)(C5)(C6)
~(Addr)2(Flag)(TimeOut)
(SafeValue)
~(Addr)3
~(Addr)CP(Status)
~(Addr)CR
~**
ALL
ALL
ALL
ALL
ALL
6050, 6052,
6053, 6054,
6058, 6060
6050, 6052,
6053, 6054,
6058, 6060
6050, 6060,
6063
6056, 6058
6056,6058
6058
ALL
6058
ALL
ALL
ALL
ALL
ALL
ALL
ALL
Command Set • 61
Page 70

3.3 Set Configuration
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054,
6056, 6058, 6060, 6063 )
@Description
Configure the basic setting about address ID, baud rate, and checksum.
@Syntax
%(OldAddr)(NewAddr)(TypeCode)(BaudRate)(CheckSumFlag)<CR>
%
(OldAddr)
(NewAddr)
(TypeCode)
(BaudRate)
(CheckSumFlag)
@Response
!(Addr)<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
(Addr) Address ID.
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid. Invalid parameter values,
Command leading code.
(1-character)
NuDAM module original address ID. The
default address ID of a brand new module is 01.
The value range of address ID is 00 to FF in
hexadecimal. (2-character)
New address ID, if you don’t want to change
address ID, let new address ID equals to the old
one. (2-character)
Type Code is fixed 40H for Digital I/O modules.
(2-character)
Communication baud rate, refer to Table 3-1 for
details. (2-character)
Define check-sum status, refer to Table 3-2 for
details. (2-character)
When you wanted to change the setting without
grounding the DEFAULT* pin.
62 • Command Set
Page 71

Note : When you want to change the checksum or baud rate then the
DEFAULT* pin should be grounded at first.
@Example
User command: %0130400600<CR>
Response: !30<CR>
Item Meaning Description
% (Leading Code) Command leading code.
01 (OldAddr) Original address ID is 01H.
30 (NewAddr)
40 (TypeCode) Digital I/O module.
06 (BaudRate) Baud rate is 9600.
00 (CheckSumFlag) 00 means checksum is disable.
<CR> Carriage return 0x0D.
Code Baudrate
03 1200 bps
04 2400 bps
05 4800 bps
06 9600 bps
07 19200 bps
08 38400 bps
09 115200 bps
New address ID is 30H
(Hexadecimal).
Table 0-1 Baud rate setting code
Checksum
0 : disable
1 : enable
6
7
Reserved
Must to be 0
Table 0-2 Check sum flag setting
4 3 2 1 0
5
Reserved
Must to be 000000
Command Set • 63
Page 72

3.4 Read Configuration
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054,
6056, 6058, 6060, 6063 )
@Description
Read the configuration of module on a specified address ID.
@Syntax
$(Addr)2<CR>
$ Command leading code
(Addr) Address ID.
2 Command code for reading configuration
@Response
!(Addr)(TypeCode)(BaudRate)(CheckSumFalg)<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID.
(TypeCode) It always be 40 (Hex) for digital I/O modules.
(BaudRate)
(CheckSumFlag)
Current setting of communication baud rate,
refer to Table 3-1 for details.
Current setting of check-sum flag, refer to Table
3-3. for details.
64 • Command Set
Page 73

Checksum
0 : disable
1 : enable
@Example
Reserved
Must to be 000
7 6 5 4 3
Reserved
Must to be 0
Table 0-3 Response of check sum flag
User command: $302<CR>
Response: !30400600<CR>
! Command is valid.
30 Address ID.
40 Digital I/O module.
06 Baud rate is 9600 bps.
00 checksum is disable.
1 2 0
Module Type
000: ND-6050
001: ND-6060
010: ND-6052
011: ND-6053
100: ND-6058
101: ND-6063
110: ND-6054
111: ND-6056
Command Set • 65
Page 74

3.5 Read Module Name
@Description
Read NuDAM module‘s name.
@Syntax
$(Addr)M<CR>
$ Command leading code.
(Addr) Address ID.
M Read module name.
@Response
!(Addr)(ModuleName) <CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID.
(ModuleName) NuDAM module‘s name.
@Example
User command: $30M<CR>
Response: !306050<CR>
! Command is valid
30 Address.
6050 ND-6050 (Digital I/O module).
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054,
6056, 6058, 6060, 6063 )
66 • Command Set
Page 75

3.6 Read Firmware Version
@Description
Read NuDAM module‘s firmware version.
@Syntax
$(Addr)F<CR>
$ Command leading code.
(Addr) Address ID
F Read module firmware version.
@Response
!(Addr)(FirmRev) <CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID.
(FirmRev) NuDAM module‘s firmware version.
@Example
User command: $30F<CR>
Response: !30A1.50<CR>
! Command is valid.
30 Address
A1.50 Firmware Version
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054,
6056, 6058, 6060, 6063 )
Command Set • 67
Page 76

3.7 Reset Status
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054,
6056, 6058, 6060, 6063 )
@Description
Checks the reset status of module at specified address to see whether it has
been reset since the last reset status command was issued to the module.
@Syntax
$(Addr)5<CR>
$ Command leading code.
(Addr) Address ID.
5 Reset Status Command.
@Response
!(Addr)(Status)<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID.
(Status) 0 : It has not been reset since the last reset status
command was issued.
1 : It has been reset since the last reset status
command was issued.
@Example
User command: $305<CR>
Response: !300<CR>
Status is 0 means this digital I/O module has not been reset,
since the last reset status command was issued.
68 • Command Set
Page 77

3.8 Digital Output
( 6050, 6060, 6063 )
@Description
Set digital output channel value at specified address. This command is only
available to modules involving the digital output function.
@Syntax
#(Addr)(ChannelNo)(OutData)<CR> (6050,6060,6063 Only)
#
(Addr) Address ID (2-character)
(ChannelNo)
(OutData)
@Response
<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
> Command is valid
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID.
Command leading code. (1-character)
00 : Set value to all channels
1X : Set value to single channel
First character is 1, Second character is
channel number. (2-character)
Set value to all channels :
Each bit is mapping to each channel number
Set value to single channel :
First character is 0, second character is set to value 0
or 1. (2-character)
@Example
User command: #300003<CR>
Response: ><CR>
30 Address ID
00 Set output to all channels
03
User command: #2F1201<CR>
Response: ><CR>
03 (00000011), Channel 0 and 1 are set ON other
channels are set to OFF
Command Set • 69
Page 78

2F Address ID
12
01 Set single channel to ON
1 : Set output to single channel
2 : Output single channel is channel 2
70 • Command Set
Page 79

3.9 Digital Output (Continued)
( 6056, 6058 )
@Description
Set digital output channel value at specified address. This command is only
available to modules involving the multiport digital output function.
@Syntax
#(Addr)T(OutDataH)(OutDataL)<CR> (6056 only)
#(Addr)T(OutDataA)(OutDataB)(OutDataC) (6058 only)
#
(Addr) Address ID (2-character)
T Set value to all channels
(OutDataH)
(OutDataL)
(OutDataA)
(OutDataB)
(OutDataC)
* if the port of ND-6058 is in input mode, output data to this port will be
ignore.
Command leading code. (1-character)
Each bit is mapping to each channel number from 14
to 8. (2-character)
Each bit is mapping to each channel number from 7 to
0. (2-character)
Output data for port A. Each bit is mapping to each
channel number from 7 to 0. (2-character)
Output data for port B. Each bit is mapping to each
channel number from 7 to 0. (2-character)
Output data for port C. Each bit is mapping to each
channel number from 7 to 0. (2-character)
@Response
<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
> Command is valid
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID.
Command Set • 71
Page 80

@Example
User command: #30T0303<CR> (for ND-6056)
Response: ><CR>
30 Address ID
T Set output to all port
0303 0303 (0000001100000011), Channel 0, 1, 8 and 9 are
set ON other channels are set to OFF
User command: #2FT010203<CR> (for ND-6058)
Response: ><CR>
2F Address ID
T Set output to all port
01 Set channel 0 of port A ON
02 Set channel 1 of port B ON
03 Set channel 0 and 1 of port C ON
72 • Command Set
Page 81

3.10 Digital Output (Continued)
( 6056, 6058 )
@Description
Set digital output port channel value at specified address. This command is
only available to modules involving the multiport digital output function.
@Syntax
#(Addr)(Port)(OutData)<CR> (6056, 6058 only)
#
(Addr) Address ID (2-character)
(Port)
(OutData)
* if the port of ND-6058 is in input mode, output data to this port will be
ignore.
Command leading code. (1-character)
Set value to indivisual port
0H: for 6056 channel 14 to 8
0L: for 6056 channel 7 to 0
0A: for 6058 port A
0B: for 6058 port B
0C: for 6058 port C (2-character)
Each bit is mapping to each channel number
(2-character)
@Response
<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
> Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID.
@Example
User command: #30H03<CR> (for ND-6056)
Response: <CR>
30 Address ID
0H Set output to high byte
03
03 (00000011), Channel 8 and 9 are set ON other
channels are set to OFF
Command Set • 73
Page 82

User command: #2F0A10<CR>
Response: <CR>
2F Address ID
0A Set output to port A
10 Set channel 4 of port A ON
74 • Command Set
Page 83

3.11 Digital Output (Continued)
( 6056, 6058 )
@Description
Set direct digital output channel value at specified address. This command
is only available to modules involving the multiport digital output function.
@Syntax
#(Addr)(Port)(ChNo)(OutData)<CR> (6056,6058 only)
#
(Addr) Address ID (2-character)
(Port)
(ChNo) Channel value 7 ~ 0
(OutData)
* if the port of ND-6058 is in input mode, output data to this port will be
ignore.
Command leading code. (1-character)
Set direct channel value to indivisual port
H: for 6056 channel 14 to 8
L: for 6056 channel 7 to 0
A: for 6058 port A
B: for 6058 port B
C: for 6058 port C (1-character)
1: ON
0: OFF
(1-character)
@Response
<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
> Command is valid
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID.
Command Set • 75
Page 84

@Example
User command: #30H31<CR> (for ND-6056)
Response: <CR>
30 Address ID
H Set output to high byte
3 Channel number is 3, that is channel 11
1 Set corresponding channel to ON
User command: #2FA20<CR>
Response: <CR>
2F Address ID
A Set output to port A
2 Channel number is 2
0 Set corresponding channel to OFF
76 • Command Set
Page 85

3.12 Synchronized Sampling
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054,6058, 6060, )
@Description
Synchronized all modules to sample input values and stored the values in
the module’s register at the same time and use “Read Synchronized Data”
command to read the data and process it one by one.
For digital I/O module, this command is only available to modules involving
the digital input function, such as NuDAM-6050, NuDAM-6052,
NuDAM-6053, NuDAM-6054, NuDAM-6058 and NuDAM-6060.
@Syntax
#**<CR>
# Command leading code.
** Synchronized sampling command
@Response
Note : Synchronized sampling command has NO response.
@Example
User command: #**<CR>
Synchronized sampling command
has no response
.
Command Set • 77
Page 86

3.13 Read Synchronized Data
( 6050, 6052, 6053,6054, 6058, 6060 )
@Description
After a synchronized sampling command
input value that was stored in the addressed module’s register and use same
method to process other module‘s data one by one.
@Syntax
$(Addr)4<CR>
$ Command leading code.
(Addr) Address ID.
4 Read synchronized data.
@Response
ND-6050 module response :
!(Status)(DataOut)(DataIn)00<CR>
ND-6052 module response :
!(Status)(DataIn)0000<CR>
ND-6053 module response :
!(Status)(DataInH)(DataInL)00<CR>
ND-6054 module response :
!(Status)(DataInH)(DataInL)00<CR>
ND-6058 module response :
!(Status)(IOFlag)(DIn)(DataInA)(DataInB)(DataInC)<CR>
ND-6060 module response :
!(Status)(DataOut)(DataIn)00<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
#**
was issued, you can read the
78 • Command Set
Page 87

0 : Data has been sent at least once before.
(Status)
(IOFlag)
(DataOut)
(DataIn)
(DIn)
(DataInH)
(DataInL)
(DataInA)
(DataInB)
(DataInC)
1 : Data has been sent for the first time since a
synchronized sampling command was
issued.(1-character)
Status of programmable I/O
0x00: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x01: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x02: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x03: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
0x04: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x05: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x06: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x07: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
0x08: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x09: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x0A: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x0B: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
0x0C: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x0D: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x0E: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x0F: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
*I/P input mode, O/P output mode.
Value of digital output channel. (2-character)
Value of digital input channel. (2-character)
Value of dedicated digital input channel 3-0 for
ND-6058. The first character is 0 (2-character)
Value of digital input channel 15-8 (2-character)
Value of digital input channel 7-0 (2-character)
Value of port A channel 7-0 (2-character)
Value of port B channel 7-0 (2-character)
Value of port C channel 7-0 (2-character)
Command Set • 79
Page 88

@Examples
Example for NuDAM-6050 :
User command: $304<CR>
Response: !1065200<CR>
! Command is valid.
1 Data has not been sent before.
06
52
Example for NuDAM-6058 :
User command: $304<CR>
Response: !10C0F010203<CR>
! Command is valid.
1 Data has not been sent before.
0C
0F Channel 0,1,2,3 of digital input is HIGH.
01
02
03
06 (00000110) means digital output channel 1,2
are ON, channel 0,3,4,5,6,7 are OFF.
52(01010010) means digital input channel 1,4, 6
are HIGH, channel 0,2,3,5,7 are LOW..
Port A and B are input mode, high and low half
byte of port C are output mode.
01 (00000001) means port A digital input channel
0 is HIGH, others are LOW.
02 (00000010) means port B digital input channel
1 is HIGH, others are LOW.
03 (00000011) mean port C digital output
channel 0,1 are ON, others are OFF.
80 • Command Set
Page 89

3.14 Digital Input
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054, 6058, 6060 )
@Description
Read the digital input channel value and readback the digital output channel
value.
@Syntax
$(Addr)6<CR>
$ Command leading code.
(Addr) Address ID
6 Digital data input command.
@Response
ND-6050 module response :
!(DataOut)(DataIn)00<CR>
ND-6052 module response :
!(DataIn)0000<CR>
ND-6053 module response :
!(DataInH)(DataInL)00<CR>
ND-6054 module response :
!(DataInH)(DataInL)00<CR>
ND-6056 module response :
!(DataOutH)(DataOutL)00<CR>
ND-6058 module response :
!(IoFlag)(DataIn)(DataA)(DataB)(DataC)<CR>
ND-6060 module response :
!(DataOut)(DataIn)00<CR>
ND-6063 module response :
!(DataOutH)0000<CR>
Command Set • 81
Page 90

or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(DataOut)
(DataIn)
(DataInH)
(DataInL)
(DataOutH)
(DataOutL)
(DataA)
(DataB)
(DataB)
(IOFlag)
Value of digital output channel. (2-character)
Value of digital input. (2-character)
Value of digital input channel 15-8.
(2-character)
Value of digital input channel 7-0.(2-character)
Value of digital output channel 15-8.
(2-character)
Value of digital output channel 7-0.(2-character)
Value of digital channel 7-0.(2-character)
Value of digital channel 7-0.(2-character)
Value of digital channel 7-0.(2-character)
Status of programmable I/O
0x00: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x01: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x02: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x03: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
0x04: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x05: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x06: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x07: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
0x08: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x09: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x0A: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x0B: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
0x0C: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x0D: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x0E: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x0F: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
*I/P input mode, O/P output mode.
82 • Command Set
Page 91

@Example
Example for NuDAM-6050 :
User command: $306<CR>
Response: !321100<CR>
! Command is valid.
32
11
00 No used
Example for NuDAM-6058 :
User command: $304<CR>
Response: !0C0F010203<CR>
! Command is valid.
0C
0F Channel 0,1,2,3 of digital input is HIGH.
01
02
03
32 (00110010) means digital output channel 1,
4, 5 are ON, channel 0, 2, 3, 6, 7 are OFF.
11 (00000011) means digital input channel 0, 1
are HIGH and channel 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 are LOW.
Port A and B are input mode, high and low half
byte of port C are output mode.
01 (00000001) means port A digital input
channel 0 is HIGH, others are LOW.
02 (00000010) means port B digital input
channel 1 is HIGH, others are LOW.
03 (00000011) mean port C digital output
channel 0,1 are ON, others are OFF.
Command Set • 83
Page 92

3.14 Programmable I/O Mode Setting
@Description
Set the programmable input or output mode for ND-6058.
@Syntax
$(Addr)S(IOFlag)<CR> (6058 only)
$ Command leading code.
(Addr) Address ID
S Set programmable I/O mode
Status of programmable I/O
0x00: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x01: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x02: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x03: A(O/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
0x04: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x05: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x06: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
(IOFlag)
0x07: A(O/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
0x08: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x09: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x0A: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x0B: A(I/P) B(O/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
0x0C: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(O/P)
0x0D: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(O/P) CL(I/P)
0x0E: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(O/P)
0x0F: A(I/P) B(I/P) CH(I/P) CL(I/P)
*I/P input mode, O/P output mode.
( 6058)
@Response
!(Addr)<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID
84 • Command Set
Page 93

@Example
User command: $060C<CR>
Response: !06<CR>
! Command is valid.
0C
Port A and B are input mode, high and low half
byte of port C are output mode.
Command Set • 85
Page 94

3.15 Read Leading Code Setting
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054,
6056, 6058, 6060, 6063 )
@Description
Read command leading code setting and host watchdog status.
@Syntax
~(Addr)0<CR>
~ Command leading code.
(Addr) Address ID
0 Read command leading code setting.
@Response
!(Addr)(Status)(C1)(C2)(C3)(C4)(C5)(C6)<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID
(2-character)
Bit 0 : Reserved
(Status)
(C1)
(C2)
(C3)
(C4)
(C5)
(C6)
Bit 1 : Power failure or watchdog failure
Bit 2 : Host watchdog is enable
Bit 3 : Host failure
Leading code 1, for read configuration status,
firmware version, etc. default is $.
(1-character)
Leading code 2, for read synchronize sampling,
digital output ,default is #. (1-character)
Leading code 3, for change configuration.
default is %. (1-character)
Leading code 4, for read alarm status, enable
alarm, etc. default is @. (1-character)
Leading code 5, for read command leading code,
change command leading code, etc. default is ~.
(1-character)
Leading code 6, this leading code is reserved.
Default is *. (1-character)
86 • Command Set
Page 95

@Example
User command: ~060<CR>
Response: !0600$#%@~*<CR>
Command leading code setting is $#%@~* for module address ID is 06,
current status is factory default setting.
Command Set • 87
Page 96

3.16 Change Leading Code Setting
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054,
6056, 6058, 6060, 6063 )
@Description
User can use this command to change command leading code setting as he
desired.
@Syntax
~(Addr)10(C1)(C2)(C3)(C4)(C5)(C6)<CR>
~ Command leading code.
(Addr) Address ID, range (00 - FF).
10 Change command leading code setting.
Leading code 1, for read configuration status,
(C1)
(C2)
(C3)
(C4)
(C5)
(C6)
@Response
!(Addr)< CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID.
firmware version, etc. default is $.
(1-character)
Leading code 2, for read synchronize sampling,
digital output ,default is #. (1-character)
Leading code 3, for change configuration.
default is %. (1-character)
Leading code 4, for read alarm status, enable
alarm, etc. default is @. (1-character)
Leading code 5, for read command leading
code, change leading code, etc. default is ~.
(1-character)
Leading code 6, this leading code is reserved.
default is *. (1-character)
88 • Command Set
Page 97

@Examples
User command: ~060<CR>
Response:
User command:
Response:
User command:
Response: !06A1.8<CR>
Read leading code setting is $#%@~* for module address 06 and change
leading code $ to A, then use A06F to read firmware version of module on
address 06.
*** WARNING ***
We do not recommend users to change the default setting of leading code,
because it will make you confuse
The leading code change only use the command conflicts other devices on
the network.
!0600$#%@~*<CR>
~0610A#%@~*<CR>
!06<CR>
A06F
Command Set • 89
Page 98

3.17 Set Host Watchdog Timer & Safety Value
( 6050, 6052, 6053, 6054,
6056, 6058, 6060, 6063 )
@Description
Set host watchdog timer, module will change to safety state when host is
failure. Define the output value in this command.
@Syntax
~(Addr)2(Flag)(TimeOut)(SafeValue)<CR>
~(Addr)2(Flag)(TimeOut)(SafeH)(SafeL)<CR> (6056 only)
~(Addr)2(Flag)(TimeOut)(SafeA)(SafeB)(SafeC)<CR> (6058only)
~ Command leading code.
(Addr) Address ID, range (00 - FF).
2 Set host watchdog timer and safe state value.
(Flag) 0 : Disable host watchdog timer
1 : Enable host watchdog timer (1-character)
Host timeout value, between this time period
host must send (Host is OK) command to
module, otherwise module will change to safety
(TimeOut)
(SafeValue) 8 channels safety value of digital output
(SafeH) Safety value of digital output channels 14 ~ 8
(SafeL) Safety value of digital output channels 7 ~ 0
(SafeA) Safety value of port A channels 7 ~ 0 when host
(SafeB) Safety value of port B channels 7 ~ 0 when host
(SafeC) Safety value of port C channels 7 ~ 0 when host
state.
Range 01 - FF. (2-character)
One unit is 100 ms
01 = 1 * 100 = 100 ms
FF = 255 * 100 = 25.5 sec
channels when host is failure. (2-character)
when host is failure. (2-character)
when host is failure. (2-character)
is failure while A in output mode. (2-character)
is failure while B in output mode. (2-character)
is failure while C in output mode. (2-character)
90 • Command Set
Page 99

@Response
!(Addr)<CR>
or
?(Addr)<CR>
! Command is valid.
? Command is invalid.
(Addr) Address ID
@Example
Example for NuDAM-6050 :
User command: ~0621121C<CR>
Response: !06<CR>
06 Address ID
2 Set host watchdog timer and safe state value.
1 Enable host watchdog timer.
12
1C
Example for NuDAM-6056 :
User command: ~0621121C1C<CR>
Response: !06<CR>
06 Address ID
2 Set host watchdog timer and safe state value.
1 Enable host watchdog timer.
12
1C1C
Timeout value. 0x12 = 18
18 * 100 = 1800 ms
1C (00011100) Digital output channel DO2, DO3
and DO4 are high, the others are low.
Timeout value. 0x12 = 18
18 * 53.3 = 959 ms
18 * 100 = 1800 ms
1C1C (0001110000011100) Digital output
channel DO2, DO3, DO4, DO10, DO11, DO12
are high, the others are low.
Command Set • 91
Page 100

Example for NuDAM-6058 :
User command: ~0621121C1C1C<CR>
Response: !06<CR>
06 Address ID
2 Set host watchdog timer and safe state value.
1 Enable host watchdog timer.
12 Timeout value. 0x12 = 18
1C1C1C 1C (00011100) port A, B and C channel 2, 3 and
18 * 100 = 1800 ms
4 are high, the other are low.
92 • Command Set
 Loading...
Loading...