Page 1

MI-220
Mini-ITX Embedded Motherboard with Intel®
Core™ i7/i5/i3 CPU and QM67 PCH
User’s Manual
Manual Rev.: 2.02
Revision Date: August 29, 2013
Part No: 50-1Z086-1020
Advance Technologies; Automate the World.
Page 2
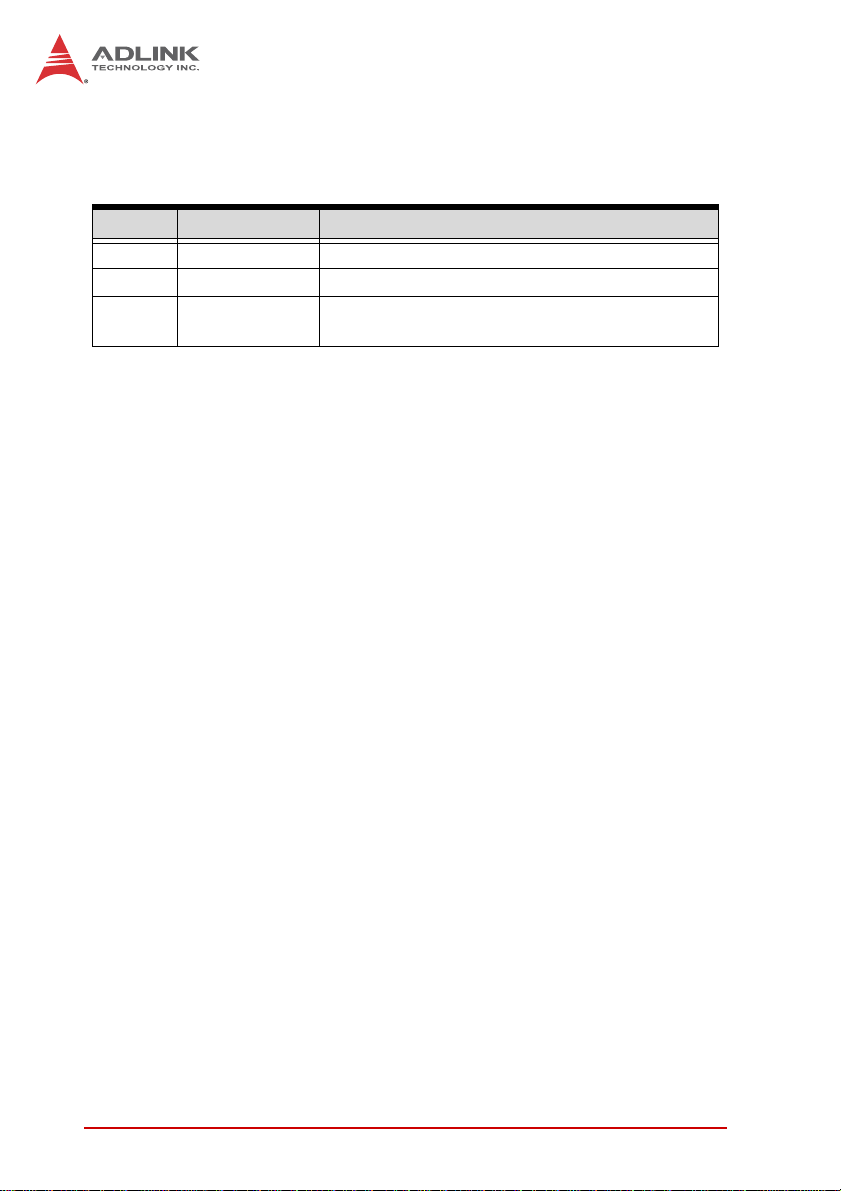
Revision History
Revision Release Date Description of Change(s)
2.00 2011/11/11 Initial release
2.01 2011/12/19 Correct F_PANEL1 pin definition
2.02 2013/08/29
Update memory capacity to 16 GB; correct
ATXPWR1 pinout; add HDMI connector note
ii Revision History
Page 3

MI-220
Preface
Copyright 2011-13 ADLINK Technology Inc.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by any mechanical, electronic, or other means in any form
without prior written permission of the manufacturer.
Disclaimer
The information in this document is subject to change without prior
notice in order to improve reliability, design, and function and does
not represent a commitment on the part of the manufacturer.
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages arising out of the use or
inability to use the product or documentation, even if advised of
the possibility of such damages.
Environmental Responsibility
ADLINK is committed to fulfill its social responsibility to global
environmental preservation through compliance with the European Union's Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive and Waste Electrical and Electronic Equipment (WEEE)
directive. Environmental protection is a top priority for ADLINK.
We have enforced measures to ensure that our products, manufacturing processes, components, and raw materials have as little
impact on the environment as possible. When products are at their
end of life, our customers are encouraged to dispose of them in
accordance with the product disposal and/or recovery programs
prescribed by their nation or company.
Trademarks
Product names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only and may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks
of their respective companies.
Preface iii
Page 4

Using this Manual
Audience and Scope
The MI-220 User’s Manual is intended for hardware technicians
and systems operators with knowledge of installing, configuring
and operating industrial grade computers.
Manual Organization
This manual is organized as follows:
Preface: Presents copyright notifications, disclaimers, trade-
marks, and associated information on the proper usage of this
document and its associated product(s).
Chapter 1, Introduction: Introduces the MI-220, its features,
applications, and specifications, including functional descriptions
and board layout.
Chapter 2, Connectors & Jumpers: Provides technical informa-
tion on connectors, jumpers and pin assignments for configuring
the MI-220.
Chapter 3, Getting Started: Describes how to install components
and drivers on the MI-220.
Chapter 4, BIOS Setup: Presents information and illustrations to
help understand and configure the system BIOS.
Appendix A, Watchdog Timer: Presents information on under-
standing and configuring the watchdog timer.
Appendix B, System Resources: Presents information on I/O
mapping, IRQ routing, and resource allocation.
Important Safety Instructions: Presents safety instructions all
users must follow for the proper setup, installation and usage of
equipment and/or software.
Getting Service: Contact information for ADLINK’s worldwide
offices.
iv Preface
Page 5

MI-220
Conventions
Take note of the following conventions used throughout this
manual to make sure that users perform certain tasks and
instructions properly.
Additional information, aids, and tips that help users perform
tasks.
NOTE:
NOTE:
Information to prevent minor physical injury, component dam-
age, data loss, and/or program corruption when trying to com-
CAUTION:
WARNING:
plete a task.
Information to prevent serious physical injury, component
damage, data loss, and/or program corruption when trying to
complete a specific task.
Preface v
Page 6

This page intentionally left blank.
vi Preface
Page 7

MI-220
Table of Contents
Revision History...................................................................... ii
Preface.................................................................................... iii
List of Figures........................................................................ ix
List of Tables.......................................................................... xi
1 Introduction ........................................................................ 1
1.1 Package Contents ............................................................... 1
1.2 Overview.............................................................................. 2
1.3 Features............................................................................... 2
1.4 Specifications....................................................................... 3
1.5 Block Diagram ..................................................................... 5
1.6 Functional Description ......................................................... 6
1.7 Power Consumption ............................................................ 8
1.8 Board Layout ....................................................................... 9
1.9 Mechanical Dimensions..................................................... 11
2 Connectors & Jumpers.................................................... 13
2.1 Rear I/O Connectors.......................................................... 13
2.2 Onboard Connectors and Jumpers.................................... 16
3 Getting Started ................................................................. 25
3.1 System Memory................................................................. 25
3.2 Driver Installation ............................................................... 26
4 BIOS Setup........................................................................ 29
4.1 Starting the BIOS............................................................... 29
4.2 Main Setup......................................................................... 33
4.3 Advanced BIOS Setup....................................................... 35
4.3.1 ACPI Settings ................................................................ 36
vii
Page 8

4.3.2 CPU Configuration......................................................... 37
4.3.3 SATA Configuration ....................................................... 39
4.3.4 PCH-FW Configuration .................................................. 40
4.3.5 AMT Configuration......................................................... 41
4.3.6 USB Configuration ......................................................... 44
4.3.7 Super IO Configuration .................................................. 46
4.3.8 H/W Monitor................................................................... 49
4.3.9 Serial Port Console Redirection..................................... 50
4.4 Chipset Setup .................................................................... 53
4.4.1 System Agent (SA) Configuration.................................. 54
4.4.2 PCI Express Configuration ............................................ 57
4.4.3 Memory Configuration ................................................... 58
4.4.4 PCH-IO Configuration.................................................... 59
4.5 Boot Configuration ............................................................. 61
4.6 Security Setup.................................................................... 63
4.7 Exit Menu ........................................................................... 64
A Appendix: Watchdog Timer..............................................67
B Appendix: System Resources..........................................69
B.1 System Memory Map ......................................................... 69
B.2 Direct Memory Access Channels....................................... 70
B.3 Fixed I/O Map .................................................................... 71
B.4 Variable I/O Map ................................................................ 73
B.5 Interrupt Request (IRQ) Lines............................................ 74
B.6 PCI Configuration Space Map ........................................... 75
B.7 PCI Interrupt Routing Map ................................................. 76
Important Safety Instructions............................................... 77
Getting Service...................................................................... 79
viii
Page 9

MI-220
List of Figures
Figure 1-1: MI-220 Block Diagram ..................................................... 5
Figure 1-2: MI-220 Board Layout ....................................................... 9
Figure 1-3: MI-220 Rear I/O Layout ................................................. 10
Figure 1-4: MI-220 Board Dimensions ............................................. 11
List of Figures ix
Page 10

This page intentionally left blank.
xList of Figures
Page 11

MI-220
List of Tables
Table 1-1: MI-220 General Specifications......................................... 4
Table 1-2: Intel® Core™ i7-2710QE Power Consumption ............... 8
Table 1-3: MI-220 Board Layout Legend ........................................ 10
Table B-1: System Memory Map..................................................... 69
Table B-2: Direct Memory Access Channels................................... 70
Table B-3: Fixed I/O Map ................................................................ 71
Table B-4: Variable I/O Map............................................................ 73
Table B-5: IRQ Lines APIC Mode ................................................... 74
Table B-6: PCI Configuration Space Map ....................................... 75
Table B-7: PCI Interrupt Routing Map............................................. 76
List of Tables xi
Page 12

This page intentionally left blank.
xii List of Tables
Page 13

1 Introduction
This chapter will introduce the MI-220, its features, specifications,
functional description, and mechanical layout.
1.1 Package Contents
Please check that your package contains the items below. If
you discover damaged or missing items, please contact your
vendor.
X MI-220 Mini-ITX Embedded Motherboard
X I/O shield
X 2x SATA cable
X Driver CD
X User’s Manual
DO NOT install or apply power to equipment that is damaged
or if there is missing/incomplete equipment. Retain the ship-
WARNING:
ping carton and packing materials for inspection. Please contact your ADLINK dealer/vendor immediately for assistance.
Obtain authorization from your dealer before returning any
product to ADLINK.
MI-220
Introduction 1
Page 14

1.2 Overview
The ADLINK MI-220 is a Mini-ITX embedded motherboard based
on the Intel® Core™ i7/i5/i3 Processor built on 32-nm process
technology in rPGA988B package and the Mobile Intel® QM67
Express Chipset. The MI-220 is ideal for embedded applications
requiring low power consumption in a standard small form factor
motherboard with a complete set of I/O functions and high-bandwidth network connectivity. These features, combined with two
SO-DIMM sockets supporting DDR3 1066/1333MHz SDRAM up
to 16 GB, SATA 6 Gb/s ports, PCIe x16, PCI, and Mini PCIe
expansion slots, HDMI, DVI-D, VGA, dual-channel 24-bit LVDS,
and audio interfaces make the MI-220 suitable for medical, transportation, industrial automation, and other applications requiring a
low noise/power, space-saving, multiple display platform.
1.3 Features
X Mini-ITX form factor (170 mm x 170 mm)
X Intel® Core™ i7/i5/i3 Processor:
Z Quad/dual cores with Hyper-Threading
Z DMI 5 GT/s
Z 6MB/3MB last level cache
Z rPGA988B package in Socket G2
X DDR3-1066/1333 up to 16 GB max. (2x SODIMM sockets)
X Intel® HD Graphics integrated in processor
Z VGA supporting 2048 x 1536 @ 60 Hz (QXGA)
Z DVI-D, HDMI Type A, Dual Channel 24-bit LVDS
X Mobile Intel® QM67 Express Chipset
X 1x PCIe x16 slot, 1x PCI slot, Mini PCIe expansion slot
X 2x SATA 6Gb/s ports, 1x SATA 3 Gb/s port
X 3x RS-232 + 1x RS-232/422/485 serial ports
X 2x GbE
X 6x USB 2.0 ports (4x faceplate, 2x onboard pin headers)
X PS/2 keyboard/mouse by internal pin header
X Line-in, Line-out, Mic-in
X RoHS compliant
2Introduction
Page 15

MI-220
1.4 Specifications
System
CPU Intel® Core™ Processor, rPGA988B package, Socket G2
• Core™ i7-2710QE, 2.1GHz, 6M LLC, 32nm, 45W TDP
• Core™ i5-2510E, 2.5GHz, 3M LLC, 32nm, 35W TDP
• Core™ i3-2330E, 2.2GHz, 3M LLC, 32nm, 35W TDP
Intel® Celeron® B810, 1.6GHz, 2M LLC, 32nm, 35W TDP
Chipset • Intel® QM67 Platform Controller Hub
Memory • Dual-Channel DDR3 1066/1333MHz, up to 16 GB
• 2x 204-pin SO-DIMM sockets, vertical type
BIOS • AMI 32 Mb SPI BIOS
Audio • Realtek ALC892 HD Audio
• Line-in, line-out and mic-in
Watchdog Timer • 1-255 second/minute programmable
Hardware Monitor • CPU/System temperature, fan speed and onboard DC
voltage
Operating System • Windows XP/7 32/64-bit, Fedora 14,
Redhat Enterprise Linux 5
I/O Interfaces
Serial ATA • 2x SATA 6Gb/s ports, 1x SATA 3 Gb/s port
Onboard I/O • 6x USB 2.0 (4x external, 2x by pin header)
• 3x RS-232 + 1x RS-232/422/485 serial ports
• PS/2 keyboard/mouse by internal pin header
Rear I/O • 2x RJ-45 LAN ports
• 4x USB 2.0 ports
• 1x D-Sub VGA connector
• 1x DVI-D connector
• 1x HDMI type A connector
• 3x audio jacks (line-in, line-out and mic-in)
Expansion Slot s • 1x PCIe x16 slot, 1x PCI slot, 1x Mini PCIe slot
Display
Processor • Intel® HD Graphics 3000
VGA • Dsub-15 connector up to 2048x1536 @ 60Hz (QXGA)
DVI • DVI-D connector, up to 1920x 1200 @ 60 Hz
(connector has DVI-I pinout; no VGA signals supported)
HDMI • HDMI type A connector, up to 1920x 1200 @ 60 Hz
LVDS • Dual-channel 24-bit LVDS up to 1600x1200 (UXGA)
Introduction 3
Page 16
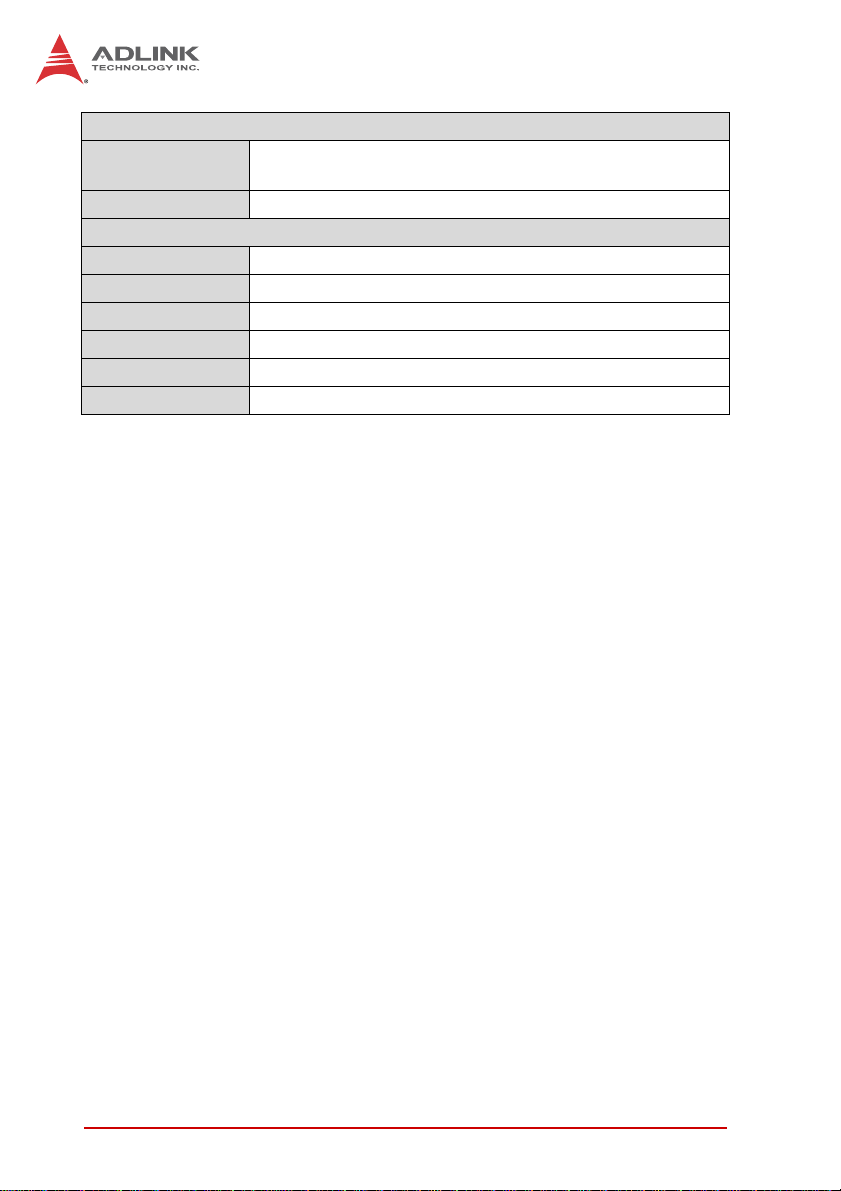
Ethernet
Controller • Intel® 82579LM + 82574L controllers
• Supports Wake-on-LAN
Ports • 2x RJ-45 Ethernet port
Mechanical and Environment
Form Factor • Mini-ITX Embedded Motherboard
Dimensions • 170 mm x 170 mm (L x W)
Operating Temp. • 0°C to 60°C
Storage Temp. • -20ºC to 80ºC
Rel. Humidity • 10 - 90% RH non-condensing
Safety • CE, FCC Class A
T able 1-1: MI-220 General Specifications
4Introduction
Page 17
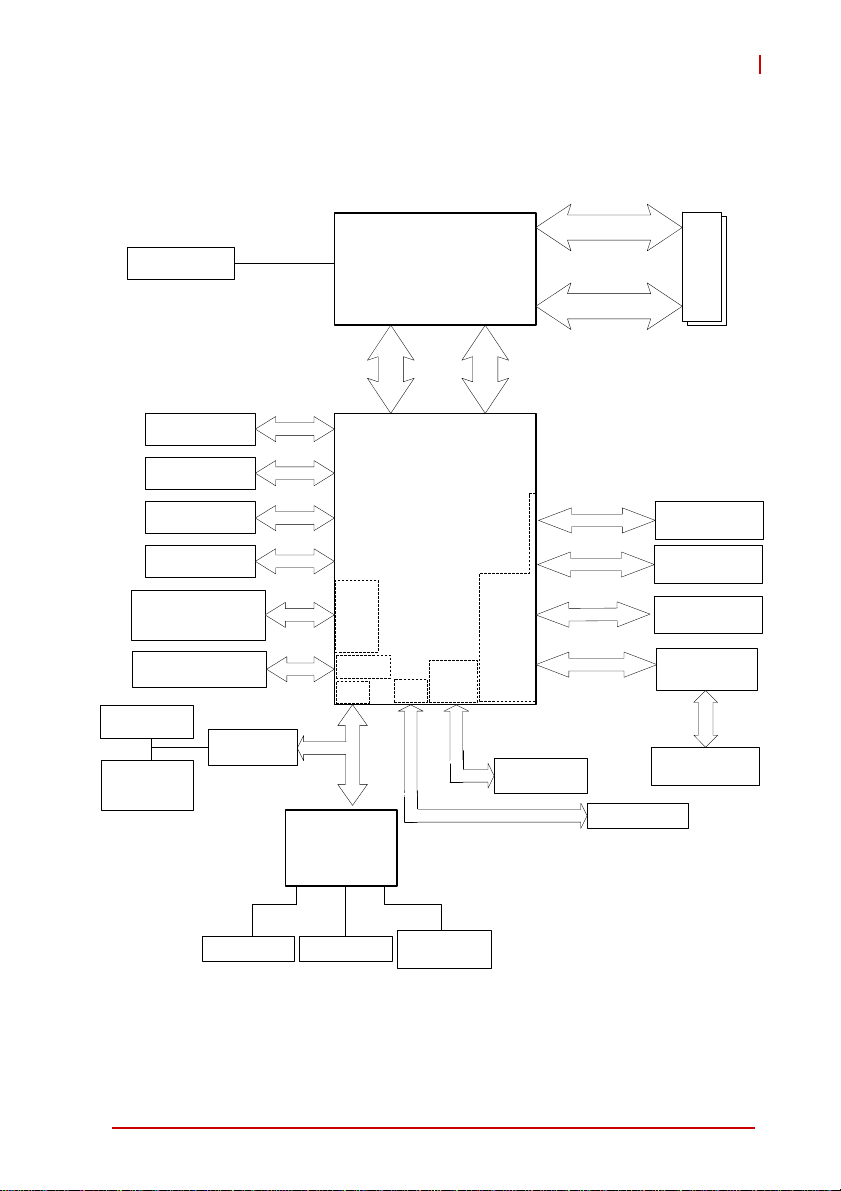
1.5 Block Diagram
MI-220
PCIe x16
Gen2, 5GT/s
Dual Channel 24-bit
(2x 6 Gb/s, 1x 3 Gb/s)
(4x rear, 2x internal)
RS-232
(COM2-4)
RS-232/422/
485/485+
(COM1)
VGA
LVDS
DVI-D
HDMI
SATA
USB 2.0
Fintek
81216AD
PCIe x16
NCT6776F
LPC Super I/O
CPU
Intel® Core™ i7/i5
quad/dual core
32nm process
rPGA988B package
FDI
Intel® QM67 PCH
SATA
USB 2.0
LPC
SPI
HD
Codec
DMI
PCIe
Controller
Audio
ALC892
SO-DIMM Channel A
DDR3 1066/1333 MHz
SO-DIMM Channel B
PCIe x1
PCIe x1
1
x
e
C
I
P
PCIe x1
SPI BIOS
DIMM x2
Intel 82579
RJ-45(LAN1)
Intel 82574L
RJ-45 (LAN2)
Mini-PCIe
PCIe-to-PCI
Bridge
XIO2001
PCI Slot
KB/Mouse 8-bit GPIO
Hardware
Monitor
Figure 1-1: MI-220 Block Diagram
Introduction 5
Page 18

1.6 Functional Description
Processor Support
The MI-220 is a Mini-ITX embedded board featuring the 2nd generation Intel® Core™ processor family (Intel® Core™i7/i5/i3) in
rPGA988B package. An integrated memory controller supports
dual channel 1066/1333 MHz DDR3 and Intel® HD Graphics is
integrated onboard the CPU. The CPU provides a PCI Express
x16 slot for external graphics or expansion. Direct Media Interface
(DMI) and Flexible Display Interface (FDI) provide connectivity to
the Mobile Intel® QM67 Express Chipset.
Mobile Intel® QM67 Express Chipset
The Intel® BD82QM67 Platform Controller Hub (PCH) combine
with the processor to provide a compact yet powerful 2-chip solution. Direct Media Interface (DMI) is the chip-to-chip connection
between the processor and PCH. Intel® Flexible Display Interface
carries display traffic from the integrated graphics on the processor to the legacy display interfaces on the PCH. The PCH supports all other required interfaces including PCI Express, SATA 6
Gb/s, USB 2.0, LPC, and SPI.
Dual-Channel DDR3 Memory
To meet the requirements of memory-intensive applications, the
MI-220 has a dual-channel memory architecture supporting DDR3
1066/1333 MHz SO-DIMMs. The key advantages of DDR3 are
higher bandwidth and increased performance at lower power than
DDR2. DDR3 memory technology meets the requirements of the
latest 3D graphics, multimedia and network applications, and
boosts system performance by eliminating bottlenecks.
Gigabit Ethernet
The MI-220 utilizes an Intel® 82579LM Gigabit Ethernet PHY and
Intel® 82574L Gigabit Ethernet Controller connected to the PCIe
bus of the QM67 PCH. Intel® AMT 7.0 (82579LM on LAN1),
Wake-on-LAN and PXE are supported.
6Introduction
Page 19

MI-220
Serial ATA
The MI-220 provides three SATA ports with data transfer rates of
up to 6.0 GB/s on 2 ports and up to 3.0 GB/s on 1 port. Intel®
Rapid Storage Technology supports AHCI and RAID 0/1/5/10
functionality.
USB 2.0
The MI-220 provides 6 USB 2.0 ports supporting transfer rates up
to 480 Mb/s. All ports are USB 1.1 compatible.
Hardware Monitoring
A built-in, proactive hardware monitoring system in the Super I/O
monitors the CPU temperature, system fan speed, and voltage
levels to prevent overheating and/or component damage, effect
timely failure detection, and ensure stable supply of current for
critical components.
Watchdog Timer
The watchdog timer (WDT) monitors system operations based on
user-defined settings. The WDT can be programmed for different
time-out periods, such as from 1 to 255 seconds or from 1 to 255
minutes. The WDT generates a reset signal, then a reset request,
after failure to strobe it within the programmed time period. A register bit may be enabled to indicate if the watchdog timer caused
the reset event. The WDT register is cleared during the power-on
sequence to enable the operating system to take appropriate
action when the watchdog generates a reboot.
Introduction 7
Page 20
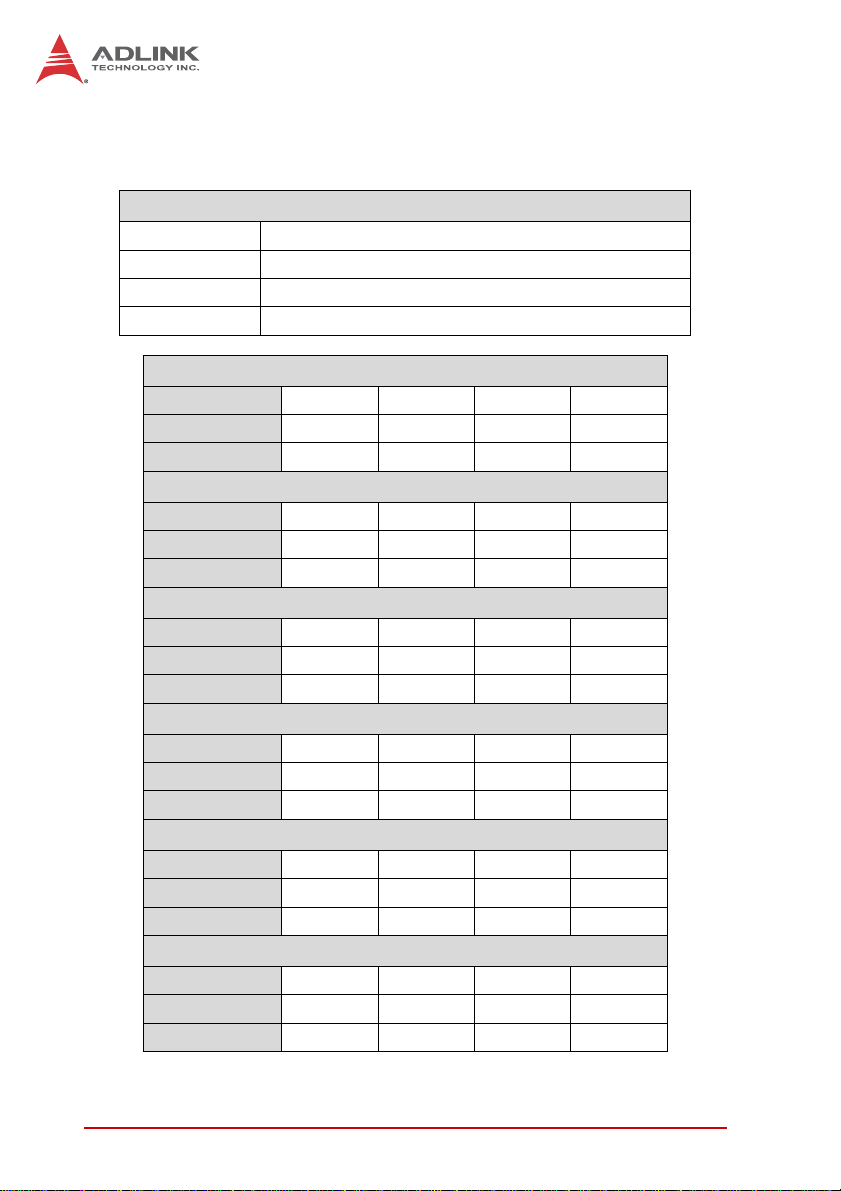
1.7 Power Consumption
Intel®
Core™ i7-2710QE, 2.1GHz, 6M LLC, 32nm, 45W TDP
T e st Con f ig uration
Memory Innodisk DDR3-1333 4GB M3SN-4GHJDC09-B (2x)
Graphics Intel® HD Graphics 3000
Storage Seagate ST9160412AS Momentus 7200.4 160G.
Power Supply SPI FSP350-60PLN 350W
DOS (idle)
Power Req. +12V +5VSB +3.3V Total
Current (A) 2.20 0.86 0.87 –
Watts (W) 26.4 4.30 2.34 33.0
Windows XP, Idle
Power Req. +12V +5V +3.3V Total
Current (A) 0.98 0.85 0.71 –
Watts (W) 11.8 4.25 2.34 18.4
Windows XP, CPU Stress (Kpower)
Power Req. +12V +5V +3.3V Total
Current (A) 4.00 0.93 0.76 –
Watts (W) 48.0 4.65 2.51 55.2
Windows XP, Total System Stress (Burnin)
Power Req. +12V +5V +3.3V Total
Current (A) 4.60 1.54 0.77 –
Watts (W) 55.2 7.70 2.54 65.4
S1 Mode
Power Req. +12V +5V +3.3V Total
Current (A) 0.57 0.59 0.73 –
Watts (W) 6.89 2.95 2.41 12.3
S5 Mode
Power Req. – +5VSB – Total
Current (A) –0.94– –
Watts (W) – 4.70 – 4.70
Table 1-2: Intel® Core™ i7-2710QE Power Consumption
8Introduction
Page 21
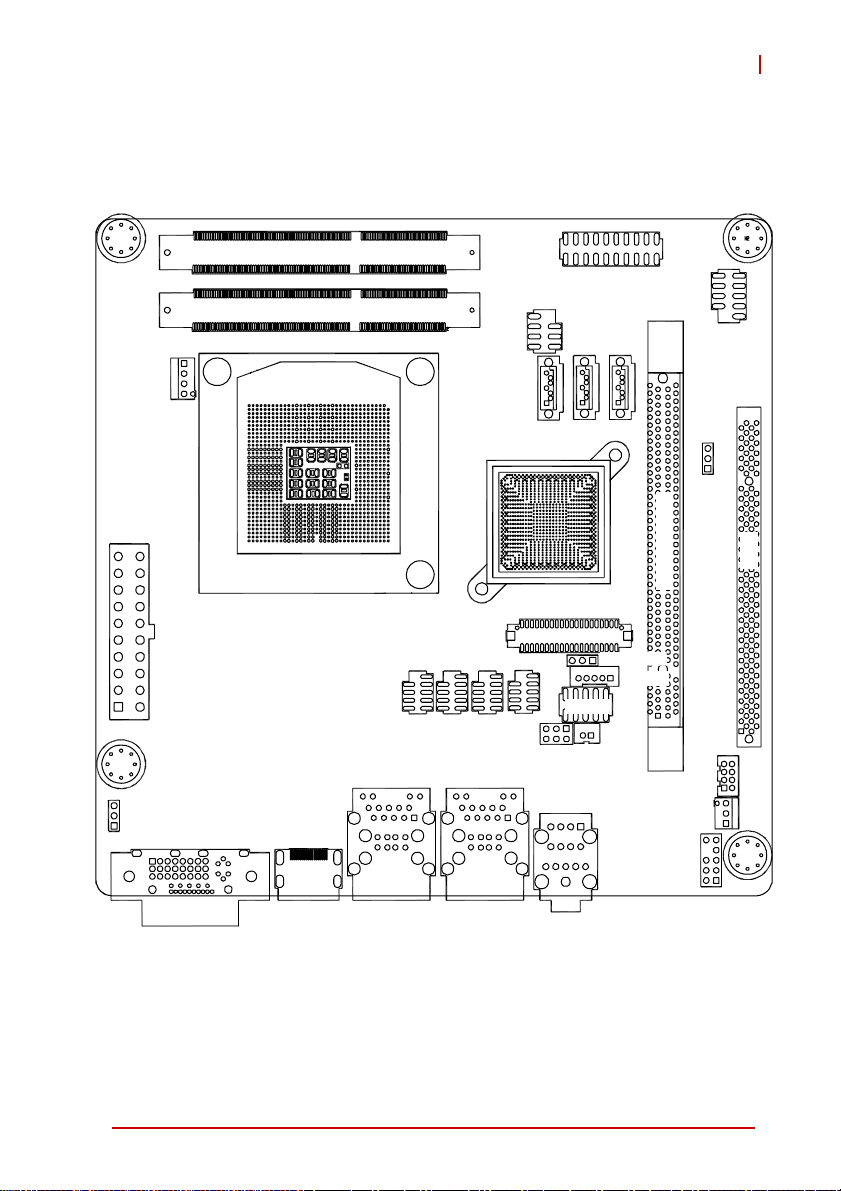
1.8 Board Layout
DIMMA1
DIMMB1
SPI_CN1
MI-220
F_PANEL1
USB56
CPU_FAN1
ATXPWR1
JPSON1
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4
SATA3
JCMOS1
SATA1/ 2
PCIEX16_1
PCI1
JLVDS1
JCLRTC2
JBKL1
JLPC1
JCASE1
DIO1
SYS_FAN1
AAFP1
Figure 1-2: MI-220 Board Layout
Introduction 9
Page 22
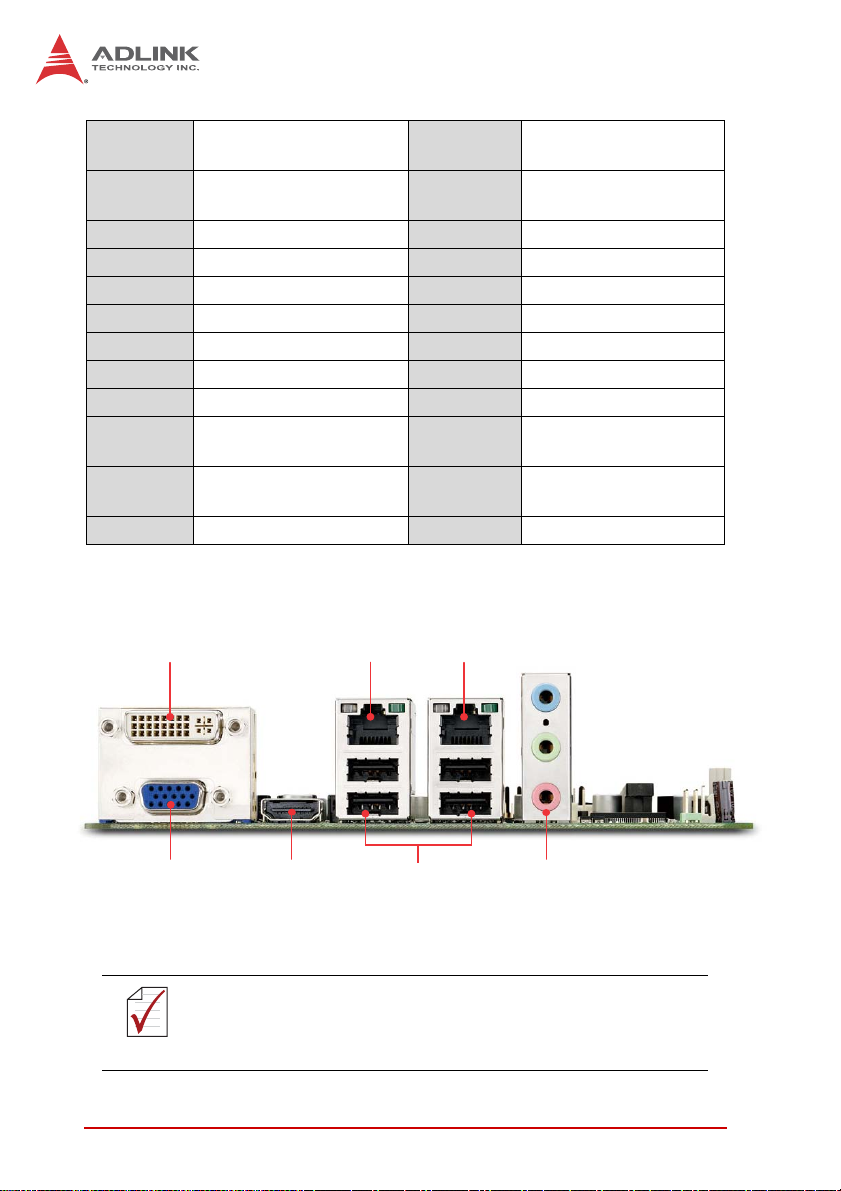
AAFP1
ATXPWR1 ATX Power connector JLVDS1
COM1~4 Serial Port connectors JPSON1 AT Mode jumper
CPU_FAN1 CPU Fan connector KBMS1 PS/2 KB/MS pin header
DIMMA1 SO-DIMM Channel A PCI1 PCI slot
DIMMB1 SO-DIMM Channel B PCIEX16_1 PCIe x16 slot
DIO1 Digital IO pin header SA TA1/2 SATA 6 Gb/s connectors
F_PANEL1 System Panel pin header SATA3 SATA 3 Gb/s connector
JBKL1 LCD Inverter connector SPDIF_OUT S/PDIF pin header
JCASE1
JCLRT_C2
JCMOS1 Clear CMOS jumper USB45 USB4/5 pin header
Front Panel Audio pin
header
Chassis Intrusion
connector
LCD Backlight Voltage
jumper
Table 1-3: MI-220 Board Layout Legend
JLPC1 LPC pin header
SPI_CN1 SPI pin header
SYS_FAN1 System Fan connector
LVDS Flat Panel
connector
DVI
Figure 1-3: MI-220 Rear I/O Layout
The HDMI port has limited clearance with the rear I/O shield.
Use an HDMI cable with a low-profile molding.
NOTE:
NOTE:
10 Introduction
LAN1 LAN2
USBHDMIVGA
Audio
Page 23
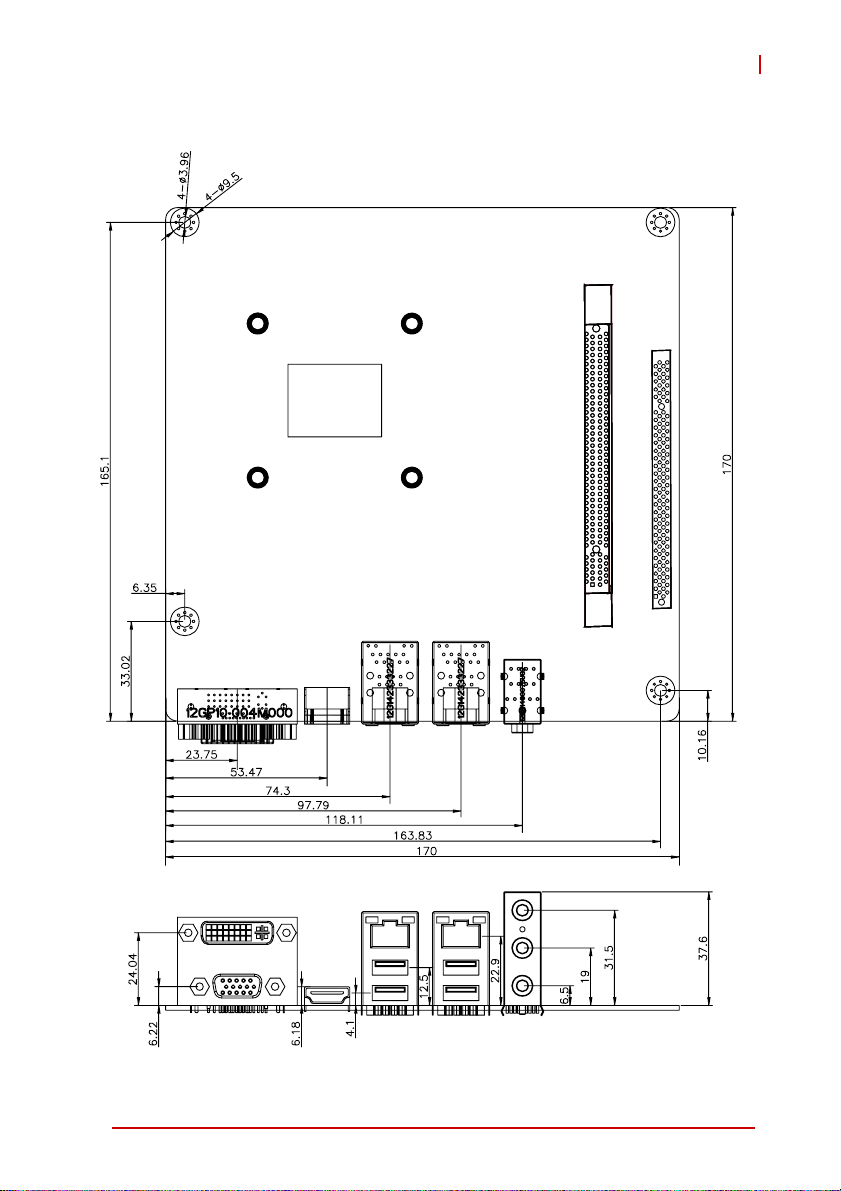
1.9 Mechanical Dimensions
MI-220
Dimensions in mm
Figure 1-4: MI-220 Board Dimensions
Introduction 11
Page 24

This page intentionally left blank.
12 Introduction
Page 25
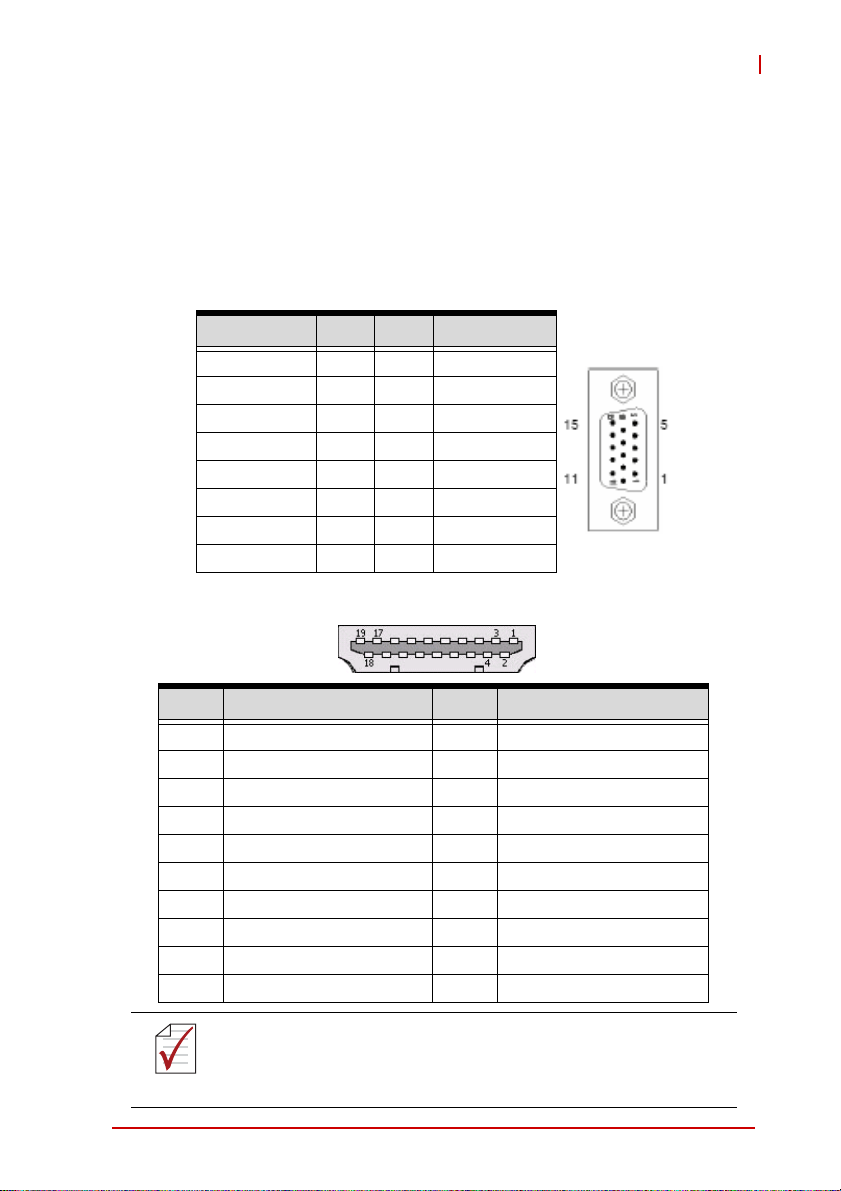
2 Connectors & Jumpers
Refer to Figure 1-2: MI-220 Board Layout and Figure 1-3: MI220 Rear I/O Layout for connector and jumper locations.
2.1 Rear I/O Connectors
VGA Connector.
Signal Name Pin # Pin # Signal Name
Red 1 2 Green
Blue 3 4 VCC pull-up
GND 5 6 GND
GND 7 8 GND
VCC 9 10 GND
VCC pull-up 11 12 DDC2B DATA
HSYNC 13 14 VSYNC
DDC2B CLK 15
HDMI Connector
MI-220
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 TMDS Data2+ 2 TMDS Data2 Shield
3 TMDS Data2– 4 TMDS Data1+
5 TMDS Data1 Shield 6 TMDS Data1–
7 TMDS Data0+ 8 TMDS Data0 Shield
9 TMDS Data0– 10 TMDS Clock+
11 TMDS Clock Shield 12 TMDS Clock–
13 CEC 14 Reserved
15 SCL 16 SDA
17 DDC/CEC Ground 18 +5 V Power
19 Hot Plug Detect
The HDMI port has limited clearance with the rear I/O shield.
Use an HDMI cable with a low-profile molding.
NOTE:
NOTE:
Connectors & Jumpers 13
Page 26
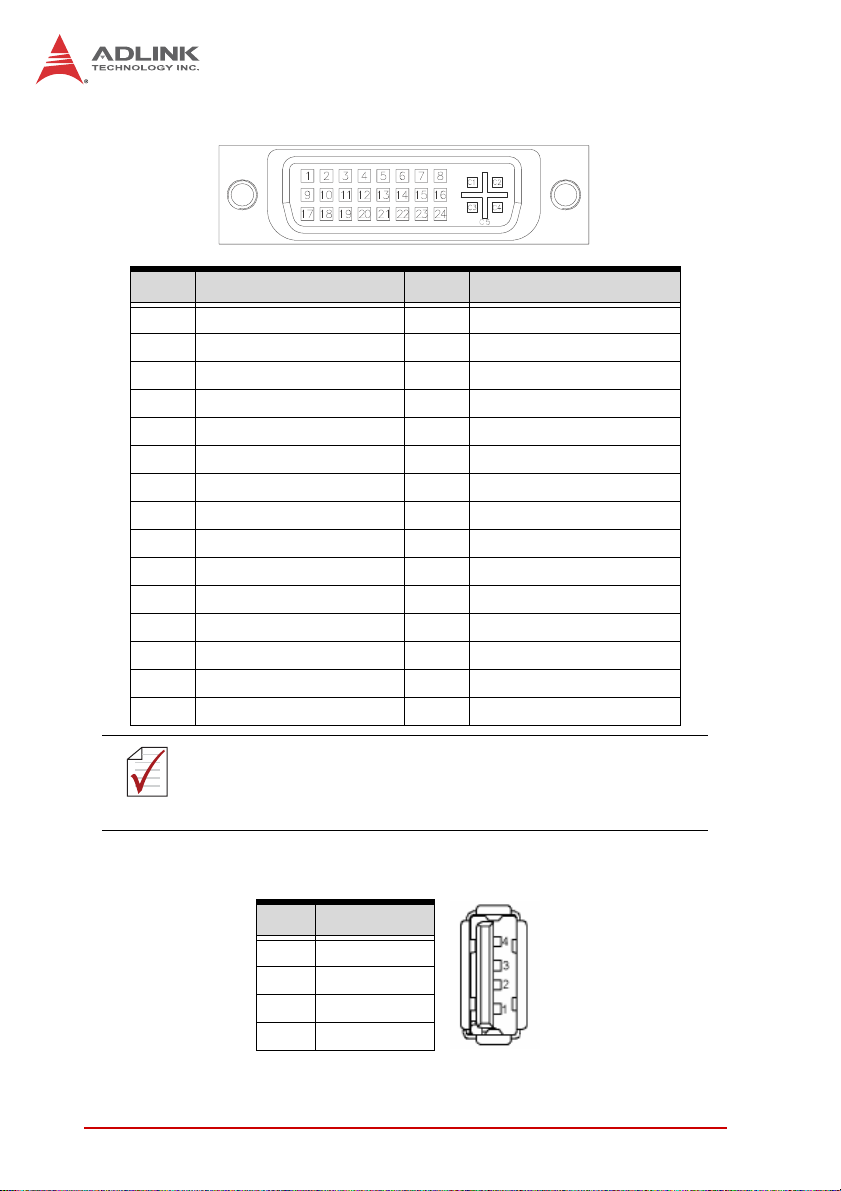
DVI-D Connector
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 TMDS Data2- 16 Hot Plug Detect
2 TMDS Data2+ 17 TMDS Data0-
3 TMDS Data2/4 Shield 18 TMDS Data0+
4 TMDS Data4- 19 TMDS Data0/5 Shield
5 TMDS Data4+ 20 TMDS Data5-
6 DDC Clock 21 TMDS Data5+
7 DDC Data 22 TMDS Clock Shield
8 Analog Vertical Sync 23 TMDS Clock +
9 TMDS Data1- 24 TMDS Clock -
10 TMDS Data1+ C1 NC
11 TMDS Data1/3 Shield C2 NC
12 TMDS Data3- C3 NC
13 TMDS Data3+ C4 NC
14 +5 V Power C5 NC
15 GND
Although the connector has a DVI-I type pinout, pins C1
through C5 are not connected and no VGA signals are sup-
NOTE:
NOTE:
ported.
USB Connectors
Pin # Signal Name
1Vcc
2 USB-
3 USB+
4GND
14 Connectors & Jumpers
Page 27
MI-220
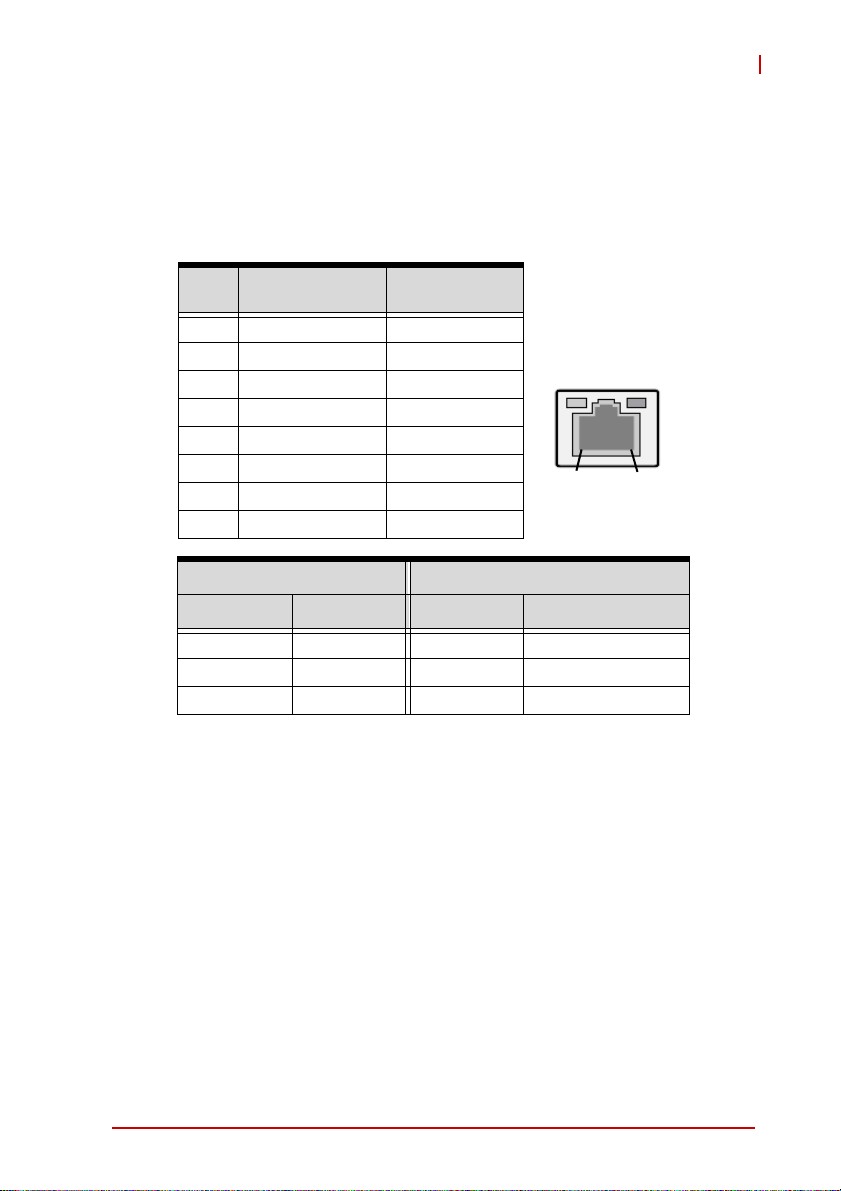
LAN Port (RJ-45)
This port allows gigabit connection to a Local Area Network (LAN)
using a network hub. The LAN port comes with two LEDs to indicate link, activity and speed. Refer to the tables below for the LAN
port pin and LED definitions.
Pin #
1 TX+ BI_DA+
2 TX- BI_DA-
3 RX+ BI_DB+
4 -- BI_DC+
5-- BI_DC-
6 RX- BI_DB-
7 -- BI_DD+
8-- BI_DD-
LED1 (Activity/Link) LED2 (Speed)
Status Description Status Description
Orange Linked Orange 100 Mb connection
Blinking Data Activity Green 1 Gb connection
10BASE-
T/100BASE-TX
Off No Link Off 10 Mb connection
1000BASE-T
LED1
LED2
18
Audio I/O port
The three-jack audio I/O supports Line-In, Line-Out, and Mic-In
functions. The blue Line-In jack onnects to an audio source such
as a CD player. The green Line-Out port connects to a speaker or
headphone, while the pink Mic-In jack connects to a microphone.
Connectors & Jumpers 15
Page 28
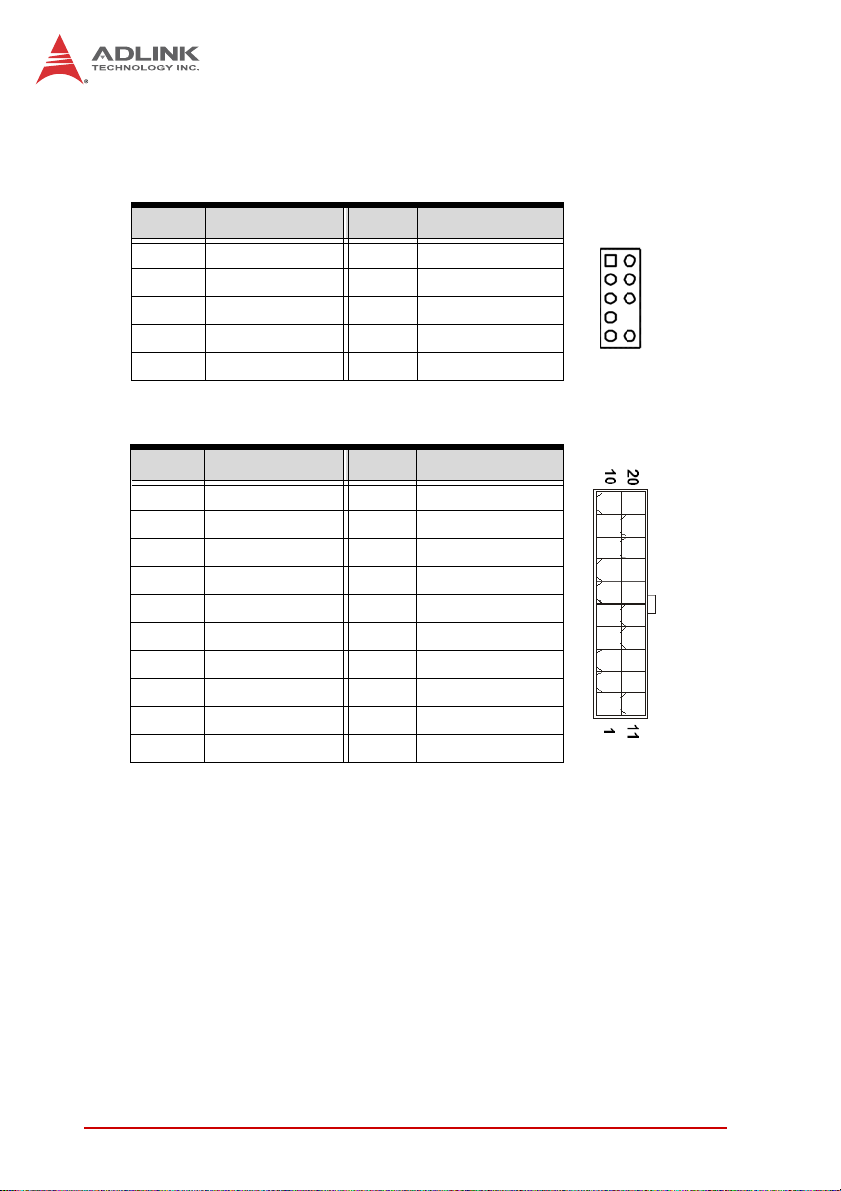
2.2 Onboard Connectors and Jumpers
Front Panel Audio Pin Header (AAFP1)
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 MIC2_L 2 GND
3 MIC2_R 4 3.3V
5 LIN2_R 6 SRTN1
7 SENSE A 8 NC
9 LIN2_L 10 SRTN2
ATX Power Connector (ATXPWR1)
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 +3.3V 11 +3.3V
2 +3.3V 12 -12V
3 GND 13 GND
4 +5V 14 PS-ON#
5 GND 15 GND
6 +5V 16 GND
7 GND 17 GND
8 PWRGD 18 NC
9 +5VSB 19 +5V
10 +12V 20 +5V
21
16 Connectors & Jumpers
Page 29

Serial Port Connectors - RS-232 (COM1~4)
Pin # Signal Function
1 DCD Data Carrier Detect
2 DSR Data Set Ready
3 RXD Receive Data
4 RTS Request to Send
12
5 TXD Transmit Data
6 CTS Clear to Send
910
7 DTR Data Terminal Ready
8 RI Ring Indicate
9 GND Ground
10 NC Key
Serial Port Connector - RS-422/485/485+ (COM1)
Pin # RS-422/485+ RS-485
1TX- DATA-
2N/A N/A
3TX+ DATA+
4N/A N/A
5RX+ N/A
6N/A N/A
7RX- N/A
8N/A N/A
9GND GND
10 Key Key
12
910
MI-220
To set COM1 to RS-422/485/485+, go the following BIOS setup
screen: Advanced > Super IO Configuration > Serial Port 1 Configuration > Device mode.
Connectors & Jumpers 17
Page 30

CPU Fan Connector (CPU__FAN1)
Pin # Signal
1GND
2 Fan power (+12V)
3 Fan Tachometer
4 Fan Speed Control
System Fan Connector (SYS_FAN1)
Pin # Signal
1 GND
2 Fan Power (+12V)
3 Fan Tachometer
Digital I/O Connector (DIO1)
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
2 DIO_4 1 DIO_0
4 DIO_5 3 DIO_1
6 DIO_6 5 DIO_2
8 DIO_7 7 DIO_3
14
13
12
18 Connectors & Jumpers
Page 31

System Panel Connector (F_PANEL1)
Pin # Signal Function Pin Group
1 WDSPK Speaker signal
3NC
5NC
7P5V Power
9NC
11 G N D Ground
13 KEYLOCK Keyboard lock
15 PLED Power LED signal
17 NC
19 P5V Power LED pull-up
2 GND Ground
4 RESETBT RESET signal
6NC
8 GND Ground
10 POWERBT Power-on signal
12 NC
14 NC
16 HDDLED Hard Disk LED signal
18 P3V3 Hard Disk LED pull-up
20 NC
Chassis Speaker
Key Lock
Power LED
RESET Button
Power On Button
Hard Disk LED
MI-220
1
19 20
2
Clear CMOS (JCMOS1)
The CMOS RAM data contains the date / time and BIOS setting
information. CMOS is powered by the onboard button cell battery.
To erase the CMOS RAM data: (1) Unplug the MI-220; (2) short
the JP1 pin 2-3; (3) turn the power on. After power on, remove the
jumper cap from pin 2-3 and reinstall it to pin 1-2.
RTC status Connection JP5
Normal 1 – 2
Clear CMOS 2 – 3
Connectors & Jumpers 19
Page 32

Chassis Intrusion Connector (JCASE1)
This header is connected to the chassis intrusion sensor to detect
if the case is opened.
Pin # Signal
1 SIO_CASEOP#
2GND
LVDS Flat Panel Connector (JLVDS1)
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
2 +5V 1 +3.3V
4 +5V 3 +3.3V
6 SD_DDC 5 SC_DDC
8 GND 7 GND
10 LVDS0_P0 9 LVDS0_P1
12 LVDS0_N0 11 LVDS0_N1
14 GND 13 GND
16 LVDS0_P2 15 LVDS0_P3
18 LVDS0_N2 17 LVDS0_N3
20 GND 19 GND
22 LVDS1_P0 21 LVDS1_P1
24 LVDS1_N0 23 LVDS1_N1
26 GND 25 GND
28 LVDS1_P2 27 LVDS1_P3
30 LVDS1_N2 29 LVDS1_N3
32 GND 31 GND
34 LVDS0_CLKP 33 LVDS1_CLKP
36 LVDS0_CLKN 35 LVDS1_CLKN
38 GND 37 GND
40 +12V 39 +12V
20 Connectors & Jumpers
Page 33

LCD Inverter Connector (JBLK1)
Pin # Signal
1 +12V
2 GND
3 LVDS_BKL
4 Bright
5 +5V
LCD Backlight Voltage Jumper (JCLRT_C2)
Status Connection JCLRT_C2
+5V (default) 1 – 2
MI-220
1
+3V
2 – 3
LPC Pin Header (JLPC1)
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 V3.3 2 GND
3 BIOS_DISABLE# 4 LPC_AD3
5 PRST_SIO 6 LPC_AD2
7 CLK33M_LPC 8 LPC_AD1
9 LPC_FRAME# 10 LPC_AD0
21
Connectors & Jumpers 21
Page 34

AT Mode Jumper (JPSON1)
Pin # Signal
1 PSON_AT
2 FRP_PANSWUN
3NC
Status Connection JCLRT_C2
AT Mode 1 – 2
ATX Mode 2 – 3 (default)
PS/2 Keyboard/Mouse Pin Header (KBMS1)
Pin # Signal Function
1 KDAT Keyboard data
2 KCLK Keyboard clock
3 MDAT Mouse data
4 MCLK Mouse data
5 P5V_KM +5 V
6 GND Ground
21
SATA Connectors (SATA1-3)
Pin # Signal
1 GND
2 TXP
3 TXN
4 GND
5 RXN
6 RXP
7 GND
SATA1/2 are 6 Gb/s ports, SATA3 is a 3 Gb/s port.
NOTE:
NOTE:
22 Connectors & Jumpers
1
7
Page 35

SPI Pin Header (SPI_CN1)
MI-220
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1 +3V ROM 2 GND
3 F_SPI_CS# 4 F_SPI_CLK
5 F_SPI_MISO 6 F_SPI_MOSI
7 SPI_HOLD# 8 NC
USB 2.0 Connector (USB45)
Pin # Signal Pin # Signal
1+5V2+5V
3 USB4- 4 USB5-
5 USB4+ 6 USB5+
7 GND 8 GND
9 Key 10 NC
1
Connectors & Jumpers 23
Page 36

This page intentionally left blank.
24 Connectors & Jumpers
Page 37

3 Getting Started
This chapter provides information on how to install components to
the MI-220 SBC.
3.1 System Memory
The MI-220 supports modules up to 8GB of DDR3 1066/1333MHz
in each of two 204-pin SO-DIMM sockets (total 16 GB). See
Figure 1-2 on page 9 for SO-DIMM socket locations.
Memory Module Installation
The DDR3 memory modules are notched to facilitate correct
installation in the DIMM sockets.
Disconnect all power supply to the board before installing a
memory module to prevent damaging the board and mem-
WARNING:
To install a memory module:
1. Locate the SO-DIMM slot on the motherboard.
ory module.
MI-220
2. Align the memory module on the socket, making sure
that the notch matches the break on the socket.
3. Insert the module firmly into the slot until the retaining clips
snap back inwards and the module is securely seated.
Getting Started 25
Page 38

3.2 Driver Installation
The MI-220 drivers for Windows XP 32-bit are located in the fol-
lowing directories on the Driver CD, or can be downloaded from
the ADLINK website (http://www.adlinktech.com):
Chipset X:\Driver\Step 1_CHIP\
Display X:\Driver\Step 2_VGA\winxp32
LAN X:\Driver\Step 3_LAN\XP_32
Audio X:\Driver\Step 4_AUDIO\XP 32_64
RAID X:\Driver\Step 5_RAID\
Mgmt. Engine X:\Driver\Step 6_ME\
Follow the instructions below to install the required MI-220 drivers:
1. Install the Windows operating system before installing any
driver. Most standard I/O device drivers are installed during
Windows installation.
In order to enable AHCI mode, you must pre-install the Intel®
Rapid Storage Technology driver using the F6 installation
NOTE:
NOTE:
method described in X:\Driver\Step 5_RAID\F6Readme.txt.
2. Install the Chipset driver by running the program
X:\Driver\Step 1_CHIP\\infinst_autol.exe. Follow the instruc-
tions given and reboot when instructed.
3. Install the Display driver and utilities by running the program
X:\Driver\Step 2_VGA\winxp32\winxp_14464.exe. Follow
the instructions given and reboot when instructed.
4. Install the LAN driver by running the program
X:\Driver\Step 3_LAN\XP_32\PROWin32.exe. Follow the
instructions given and reboot if required.
5. Install the Audio driver by running the program
X:\Driver\Step 4_AUDIO\XP 32_64\WDM_R261.exe. Follow
the instructions given and reboot if required.
26 Getting Started
Page 39

MI-220
6. Install the Intel Rapid Storage Technology Utility by extracting
and running the program iata_cd_10.6.0.1022.exe in
X:\Driver\Step 5_RAID\Intel_Rapid_Storage_Technology_
10.6.0.1022.zip.
The Intel Rapid Storage Technology Utility file may not be
included on the Driver CD. Please download it from the
NOTE:
NOTE:
ADLINK website if necessary.
7. Install the Management Engine driver by running the program
X:\Driver\Step 6_ME\setup.exe. Follow the instructions given
and reboot if required.
Getting Started 27
Page 40

This page intentionally left blank.
28 Getting Started
Page 41

4 BIOS Setup
The following chapter describes basic navigation for the
AMIBIOS® EFI BIOS setup utility.
4.1 Starting the BIOS
To enter the setup screen, follow these steps:
1. Power on the motherboard
2. Press the < Delete > key on your keyboard when you
see the following text prompt:
< Press DEL to run Setup >
3. After you press the < Delete > key, the main BIOS setup
menu displays. You can access the other setup screens
from the main BIOS setup menu, such as Chipset and
Power menus.
MI-220
Note: In most cases, the < Delete > key is used to invoke the setup
screen. There are several cases that use other keys, such as
< F1 >, < F2 >, and so on.
BIOS Setup 29
Page 42

Setup Menu
The main BIOS setup menu is the first screen that you can navigate. Each main BIOS setup menu option is described in this
user’s guide.
The Main BIOS setup menu screen has two main frames. The left
frame displays all the options that can be configured. “Grayed”
options cannot be configured, “Blue” options can be.
The right frame displays the key legend. Above the key legend is
an area reserved for a text message. When an option is selected
in the left frame, it is highlighted in white. Often a text message will
accompany it.
Navigation
The BIOS setup/utility uses a key-based navigation system called
hot keys. Most of the BIOS setup utility hot keys can be used at
any time during the setup navigation process.
These keys include < F1 >, < F10 >, < Enter >, < ESC >, < Arrow >
keys, and so on. .
30 BIOS Setup
Page 43

MI-220
Note: There is a hot key legend located in the right frame on most
setup screens.
The < F8 > key on your keyboard is the Fail-Safe key. It is not displayed on the key legend by default. To set the Fail-Safe settings
of the BIOS, press the < F8 > key on your keyboard. It is located
on the upper row of a standard 101 keyboard. The Fail-Safe settings allow the motherboard to boot up with the least amount of
options set. This can lessen the probability of conflicting settings.
Hotkey Descriptions
F1 The < F1 > key allows you to display the General Help
screen.
Press the < F1 > key to open the General Help screen.
BIOS Setup 31
Page 44

F10 The < F10 > key allows you to save any changes you have
made and exit Setup. Press the < F10 > key to save your
changes. The following screen will appear:
Press the < Enter > key to save the configuration and exit.
You can also use the < Arrow > key to select Cancel and
then press the < Enter > key to abort this function and return
to the previous screen.
ESC The < Esc > key allows you to discard any changes you have
made and exit the Setup. Press the < Esc > key to exit the
setup without saving your changes. The following screen will
appear:
Press the < Enter > key to discard changes and exit. You can
also use the < Arrow > key to select Cancel and then press
the < Enter > key to abort this function and return to the previous screen.
Enter The < Enter > key allows you to display or change the setup
option listed for a particular setup item. The < Enter > key
can also allow you to display the setup sub-screens.
32 BIOS Setup
Page 45

MI-220
4.2 Main Setup
When you first enter the Setup Utility, you will enter the Main setup
screen. You can always return to the Main setup screen by selecting the Main tab. There are two Main Setup options. They are
described in this section. The Main BIOS Setup screen is shown
below.
System & Board Info
BIOS Vendor
Displays the BIOS vendor.
Core Version
Displays the BIOS core version.
Compliancy
Displays the current BIOS compliancy.
Project Version
Displays the current BIOS revision.
Build Date and Time
Displays the BIOS build data.
BIOS Setup 33
Page 46

System Time/System Date
Use this option to change the system time and date. Highlight System Time or System Date using the < Arrow > keys. Enter new values using the keyboard. Press the < Tab > key or the < Arrow >
keys to move between fields. The date must be entered in MM/
DD/YY format. The time is entered in HH:MM:SS format.
Note: The time is in 24-hour format. For example, 5:30 A.M. ap-
pears as 05:30:00, and 5:30 P.M. as 17:30:00.
Access Level
Displays the current system access level.
34 BIOS Setup
Page 47

MI-220
4.3 Advanced BIOS Setup
Select the Advanced tab from the setup screen to enter the
Advanced BIOS Setup screen. You can select any of the items in
the left frame of the screen, such as SuperIO Configuration, to go
to the sub menu for that item. You can display an Advanced BIOS
Setup option by highlighting it using the < Arrow > keys. The
Advanced BIOS Setup screen is shown below.
The sub menus are described on the following pages.
BIOS Setup 35
Page 48

4.3.1 ACPI Settings
ACPI Sleep State
Select the highest ACPI sleep state the system will enter, when
the SUSPEND button is pressed. Options: S1, S3, Suspend
Disable.
Resume On RTC Alarm
Enable or disable system wake on alarm event. When enabled,
the system will wake at the hr/min/sec specified.
36 BIOS Setup
Page 49

4.3.2 CPU Configuration
MI-220
Hyper-Threading
Enables/disables Intel® Hyper-Threading Technology.
Active Processor Cores
Number of cores to enable in processor. Options: All, 1.
Limit CPUID Value Maximum
When Enabled, the processor will limit the maximum CPUID
input value to 03h when queried, even if the processor supports a higher CPUID input value. When Disabled, the processor will return the actual maximum CPUID input value of the
processor when queried. Enable this option to allow compatibility with older operating systems.
Execute Disable Bit
Allows you to enable or disable the No-Execution Page Protection Technology. Setting this item to [Disabled] forces the XD
BIOS Setup 37
Page 50

feature flag to always return a zero (0). Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Hardware Prefetcher
Enables/disables the Mid Level Cache (L2) streamer
prefetcher.
Adjacent Cache Line Prefetch
Enables/disables the prefetching of adjacent cache lines.
Intel® Virtualization Tech
When enabled, Intel® Virtualization Technology (Intel® VT)
makes a single system appear as multiple independent systems to software. This allows for multiple, independent operating systems to be running simultaneously on a single system.
Power Technology
Sets the power management features. Options: Disabled,
Energy Efficient, Custom.
Local x2APIC
Enables/disables Local x2APIC. Some OSes do not support
this.
Long Duration Power Limit
Sets the Long Duration Power Limit in watts.
Long Duration Maintained
Sets the time window for which the Long Duration Power Limit
is maintained in miliseconds.
Short Duration Power Limit
Sets the short duration power limit in watts.
38 BIOS Setup
Page 51

4.3.3 SATA Configuration
SATA Controlle r(s)
MI-220
Enable or disable the SATA controller(s).
SATA Mode
Options: IDE, RAID, AHCI.
BIOS Setup 39
Page 52

4.3.4 PCH-FW Configuration
You can use this screen to enter the options for the Firmware
Update Configuration Settings. The Firmware Update Configuration screen is shown below.
Firmware Update Configuration
ME FW Image Re-Flash
Enable or disable eanagement Engine Firmware Image ReFlash function.
40 BIOS Setup
Page 53

MI-220
4.3.5 AMT Configuration
You can use this screen to select options for the Intel Active Management Technology settings.
Intel AMT
This item allows the user to Enable/Disable the Intel AMT function.
Intel AMT Setup Prompt
Set the Intel AMT Setup Prompt to wait for hotkey to enter
setup. Options: Enabled, Disabled.
BIOS Hotkey Pressed
Enable or disable BIOS hotkey pressed.
MEBx Selection Screen
Enable or disable the MEBx selection screen.
Verbose MEBx Output
Enable or disable Verbose MEBx output.
BIOS Setup 41
Page 54

Hide Un-Configure ME Confirmation
Hide the Un-Configure ME prompt without password confirmation.
MEBx Debug Message Output
Enable or disable MEBx debug message output.
Un-Configure ME
This item allows the user to unprovision the ME function without a password. Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Intel AMT Password Write Enable
Enable or disable Intel AMT Password Write. Password is
writeable when set to Enabled.
AMT Wait Timer
Set the number of seconds to wait before sending
ASF_GET_BOOT_OPTIONS.
ASF
Enable or disable Alert Specification Format.
Activate Remote Assistance Process
Trigger CIRA boot. Options: Enabled, Disabled.
USB Configure
Enable or disable the USB Configure function.
PET Progress
User can set PET Events progress to enable or disable receipt
of PET events. Options: Enabled, Disabled.
Intel AMT SPI Protected
Enable or disable Intel AMT SPI write protect.
WatchDog
Enable or disable the WatchDog Timer.
42 BIOS Setup
Page 55

OS Timer
Sets the OS WatchDog Timer (seconds).
BIOS Timer
Sets the BIOS WatchDog Timer (seconds).
MI-220
BIOS Setup 43
Page 56

4.3.6 USB Configuration
Legacy USB Support
Legacy USB Support refers to USB mouse and keyboard support. Normally if this option is not enabled, any attached USB
mouse or USB keyboard will not become available until a USB
compatible operating system is fully booted with all USB drivers loaded. When this option is enabled, any attached USB
mouse or USB keyboard can control the system even when
there are no USB drivers loaded on the system. Set this value
to enable or disable the Legacy USB Support.
X Disabled: Set this value to prevent the use of any USB
device in DOS or during system boot.
X Enabled: Set this value to allow the use of USB devices
during boot and while using DOS.
X Auto: This option auto detects USB Keyboards or Mice and
if found, allows them to be utilized during boot and while
using DOS.
44 BIOS Setup
Page 57

MI-220
EHCI Hand-Off
This is a workaround for OSes without EHCI hand-off support.
The EHCI ownership change should be claimed by EHCI
driver. Options: Enable, Disable.
Mass Storage Devices:
Mass storage device emulation type. 'AUTO' enumerates
devices according to their media format. Optical drives are
emulated as 'CDROM', drives with no media will be emulated
according to a drive type. Options: Auto, Floppy, Forced FDD,
Hard Disk, CD-ROM.
BIOS Setup 45
Page 58

4.3.7 Super IO Configuration
Serial Port1-4 Configuration
Enter the submenu for each serial port to enable/disable and view
the I/O port and IRQ settings.
Serial Port
Enable or disable Serial Port 1~4.
46 BIOS Setup
Page 59

Device Settings
Set the serial port address and IRQ. Options: Auto, IO=3F8h;
IRQ=4, IO=3F8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9. 10, 11, 12, IO=2F8h;
IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9. 10, 11, 12, IO=3E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9.
10, 11, 12, IO=2E8h; IRQ=3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9. 10, 11, 12
Device Mode
Change the Serial Port mode of COM1. Options: RS232,
RS422, RS485 Half, RS485 Full
Smart Fan Function
Enable or disable the Smart Fan function.
Smart Fan Mode Configuration
MI-220
System Fan Mode
System Smart Fan mode select. Options: Manual Mode, Thermal Cruise Mode, SMART FAN IV Mode
SYSFAN PWM/DC Voltage Output Value
Range of setting: 0-255.
CPU Fan Mode
CPU Smart Fan mode select. Options: Manual Mode, Thermal
Cruise Mode, SMART FAN IV Mode
CPUFAN PWM/DC Voltage Output Value
Range of setting: 0-255.
BIOS Setup 47
Page 60

Power Loss
Determines what state the computer enters when AC power is
restored after a power loss. The options for this value are
Always Off, Always On and Auto.
X Always Off: Set this value to always power off the system
while AC power is restored.
X Always On: Set this value to always power on the system
while AC power is restored.
X Auto: Set this value to power off/on the system depending on
the last system power state while AC power is restored.
Resume on PS2 KB
Enable or disable Resume on PS/2 Keyboard function.
Resume on PS2 MS
Enable or disable Resume on PS2 Mouse function.
Watch Dog Timer
Enable or disable Watchdog Timer Function.
48 BIOS Setup
Page 61

MI-220
4.3.8 H/W Monitor
This screen displays the current status of all of the monitored
hardware devices/components such as voltages and temperatures.
CPU Warning Temperature
Enables or disables the CPU warning temperature function.
Options: Disable, 50 C/122 F, 55 C/131, 60 C/140 F, 65 C/149
F, 70 C/158 F, 75 C/167 F.
ACPI Shutdown Temperature
Enables or disables the ACPI shutdown temperature function.
Options: Disable, 70 C/158 F, 75 C/167 F, 80 C/176 F, 85 C/185
F, 90 C/194 F, 95 C/205 F.
BIOS Setup 49
Page 62

4.3.9 Serial Port Console Redirection
COM1/4 Console Redirection
Options: Enabled/Disabled.
Console Redirection Settings
The settings specify how the host computer and the remote computer exchange data. Both computers should have the same or
compatible settings.
Terminal Type
This option is used to select either VT100/VT-UTF8 or ANSI
terminal type. Options: VT100, VT100+, VT-UTF8, ASNI.
Bits per second
Select the bits per second you want the serial port to use for
console redirection. The options are 115200, 57600, 38400,
19200, 9600.
50 BIOS Setup
Page 63

MI-220
Data Bits
Select the data bits you want the serial port to use for console
redirection. Set this value to 7 and 8.
Parity
Set this option to select Parity for console redirection. The settings for this value are None, Even, Odd, Mark and Space.
Stop B its
Stop bits indicate the end of a serial data packet. (A start bit
indicates the beginning). The standard setting is 1 stop bit.
Communication with slow devices may require more than 1
stop bit. Set this value to 1 and 2.
Flow Control
Set this option to select Flow Control for console redirection.
The settings for this value are None, Hardware RTS/CTS.
Record Mode
With this mode enabled only text will be sent., allowing capture
of Terminal data. Set this value to Enabled or Disabled.
Resolution 100x31
Enable or disable extended terminal resolution. Set this value
to Enabled or Disabled.
Legacy OS Redirection Resolution
On a legacy OS, the number of Rows and Columns supported
by redirection. Set this value to 80x24 and 80x25.
Serial Port for Out-of-Band Management
These settings control the ACPI serial port redirection table
(SPCR) which is used by Windows servers to provide Windows
Emergency Management Services (EMS) and is independent from
console redirection output. OoB Management or EMS allows the
remote management of selected components of Windows servers,
even when a server is not connected to the network or the network
is not available
BIOS Setup 51
Page 64

Console Redirection
Options: Enabled/Disabled.
Out-of-Band Mgmt Port
Options: COM0, COM4 (PCI Dev22, Func3), Disabled.
Data Bits
Displays the frame width for Out-of-Band Management.
Parity
Displays the parity for Out-of-Band Management.
Stop B its
Displays the number of stop bits for Out-of-Band Management.
Terminal Type
VT-UTF8 is the preferred terminal type for out-of-band management. The next best choice is VT100+ and then VT100.
See above, in Console Redirection Settings page, for more
Help with Terminal Type/Emulation. Options: VT100, VT100+,
VT-UTF8, ANSI.
52 BIOS Setup
Page 65

MI-220
4.4 Chipset Setup
Select the Chipset tab from the setup screen to enter the Chipset
BIOS Setup screen. You can select any of the items in the left
frame of the screen to go to the sub menu for that item. The Chipset BIOS Setup screen is shown below.
BIOS Setup 53
Page 66

4.4.1 System Agent (SA) Configuration
VT-d
Intel Virtualization Technology for Directed I/O. Options: Enabled/
Disabled.
Graphics Configuration
Graphic Turbo IMON Current
Graphic Turbo IMON Current values supported: 14-31 μA.
Primary Display
Allows you to select which graphics controller to use as the primary boot device. Options: Auto, IGFX, PEG, PCI.
Internal Graphics
Keep IGD enabled based on the setup options. Options:Auto,
Disabled, Enabled
54 BIOS Setup
Page 67

MI-220
GTT Size
Set GTT (Graphics Memory Manager) size. Options:1MB, 2MB
Aperture Size
Options: 128MB, 256MB, 512MB
DVMT Total Gfx Mem
Select DVMT/Fixed memory size used by the Integrated
Graphics Device. Options: 128MB, 256MB, Maximum.
Gfx Low Power Mode
Options: Enabled, Disabled
LCD Control
Primary IGFX Boot Display
Select the display port active during POST. This has no effect
on any external graphics present. Options: VBIOS Default,
CRT (VGA), DVI, LFP (LVDS), HDMI. See table below for
VBIOS Default display output settings.
Connected Display(s) BIOS Mode DOS Mode
VGA VGA VGA
DVI DVI DVI
HDMI HDMI HDMI
LVDS N/A N/A
VGA + DVI VGA + DVI VGA
VGA + HDMI VGA + HDMI VGA
VGA + LVDS VGA VGA
BIOS Setup 55
Page 68

LCD Panel Type
Select the LCD panel used by the internal graphic device.
Options: VBIOS Default, 640x480 LVDS, 800x600 LVDS,
1024x768 LVDS, 1280x1024 LVDS, 1400x1050 LVDS1,
1400x1050 LVDS2, 1600x1200 LVDS, 1366x768 LVDS,
1680x1050 LVDS, 1920x1200 LVDS 1440x900 LVDS,
1600x900 LVDS, 1280x800 LVDS, 1920x1080 LVDS,
2048x1536 LVDS.
Panel Color Depth
Select the LFP panel color depth. Options:18 Bit, 24 Bit.
56 BIOS Setup
Page 69

4.4.2 PCI Express Configuration
PEG0 - Gen X
Configure PEG B0:D1:F0 Gen1-Gen2. Options: Auto, Gen1,
Gen2.
Always Enable PEG
Options: Enabled, Disabled
PEG ASPM
Control ASPM support for the PEG device. Options: Disabled,
Auto, ASPM L0s, ASPM L1, ASPM L0sL1
MI-220
BIOS Setup 57
Page 70

4.4.3 Memory Configuration
Memory Frequency
Maximum memory frequency in MHz. Options: Auto, 1067, 1333.
58 BIOS Setup
Page 71

4.4.4 PCH-IO Configuration
LAN1/2 Controller
MI-220
Controls the onboard LAN1/2 controller. Options: Enabled/Disabled.
LAN1/2 Option-ROM
Enable or disable LAN1/2 Boot Option for legacy network
devices.
Wake on LAN1/2 from S5
Enable or disable wake on LAN1/2 from S5.
Azalia Internal HDMI Codec
X Disabled: Azalia will be unconditionally Disabled.
X Enabled: Azalia will be unconditionally Enabled.
X Auto: Azalia will be enabled if present, disabled otherwise.
SMI Lock
Enable or disable SMI lockdown.
BIOS Setup 59
Page 72

BIOS Lock
Enable or disable BIOS interface lockdown.
GPIO Lock
Enable or disable GPIO lockdown.
USB Configuration
EHCI1/2
Enable or disable the USB EHCI1/2 (USB 2.0) functions.
60 BIOS Setup
Page 73

MI-220
4.5 Boot Configuration
Select the Boot tab from the setup screen to enter the Boot BIOS
Setup screen. You can select any of the items in the left frame of
the screen, such as Boot Device Priority, to go to the sub menu for
that item. You can display a Boot BIOS setup option by highlighting it using the < Arrow > keys. The Boot Configuration screen is
shown below:
Bootup NumLock State
This setting determines the state of the NumLock function on
bootup. Options: On, Off.
Quiet Boot
When this feature is enabled, the BIOS will display the fullscreen logo during the boot-up sequence, hiding normal POST
messages.
When it is disabled, the BIOS will display the normal POST
messages, instead of the full-screen logo.
BIOS Setup 61
Page 74

Option ROM Messages
Set the display mode for Option ROM messages. Options:
Force BIOS, Keep Current.
Interrupt 19 Capture
Allows Option ROMs to trap INT 19. Options: Disabled,
Enabled.
Set Boot Priorities
The Boot devices are listed in groups by device type. First
press <Enter> to enter the sub-menu. Then you may use the
arrow keys to select the desired device, then press <+>, <-> or
<PageUp>, <PageDown> key to move it up/down in the priority
list. For example, USB storage disks will be listed as "USB
Drives" in the sub-menu as below. Only the first device in each
device group will be available for selection in the Boot Device
Priority option.
UEFI Boot Drive BBS Priorities
Specifies the Boot Device priority sequence of UEFI Boot
drives.
62 BIOS Setup
Page 75

4.6 Security Setup
X
MI-220
Administrator Password
Select this option and press < Enter > to access the sub menu.
You can use the sub menu to change the Administrator password.
User Password
Select this option and press < Enter > to access the sub menu.
You can use the sub menu to change the User password.
BIOS Setup 63
Page 76

4.7 Exit Menu
Select the Exit tab from the setup screen to enter the Exit BIOS
Setup screen. You can display an Exit BIOS Setup option by highlighting it using the < Arrow > keys. The Exit BIOS Setup screen is
shown below.
Save Changes and Exit
When you have completed the system configuration changes,
select this option to leave Setup and reboot the computer so the
new system configuration parameters can take effect.
Save Configuration Changes and Exit Now?
[Yes] [No]
appears in the window. Select [Yes] to save changes and exit.
Discard Changes and Exit
Select this option to quit Setup without making any permanent
changes to the system configuration.
64 BIOS Setup
Page 77

MI-220
Discard Changes and Exit Setup Now?
[Yes] [No]
appears in the window. Select [Yes] to discard changes and exit.
Save Changes and Reset
Reset the system after saving the changes.
Discard Changes and Reset
Reset system setup without saving any changes.
Save Changes
Save changes made so far to any of the setup options.
Discard Changes
Select Discard Changes from the Exit menu and press < Enter >.
Select [Yes] to discard changes.
Restore Defaults
Restore/Load Default values for all the setup options.
Save as User Defaults
Save the changes made so far as User Defaults.
Restore User Defaults
Restore the User Defaults to all the setup options.
Boot Override
This group of functions includes a list of devices within the boot
order. Select a drive to immediately boot that device regardless of
the current boot order. If you are booting to the EFI Shell, an exit
from the shell returns to Setup.
BIOS Setup 65
Page 78

This page intentionally left blank.
66 BIOS Setup
Page 79

Appendix A - Watchdog Timer
Watchdog Timer sample code for the MI-220 is as follows.
WDT Sample Code
void SIOConfigEnter ()
{
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX ,
NCT6776F_CONFIG_MODE_ENTER_VALUE);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX ,
NCT6776F_CONFIG_MODE_ENTER_VALUE);
}
void SIOConfigExit ()
{
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX ,
NCT6776F_CONFIG_MODE_EXIT_VALUE);
}
void Oem_WDT_Init (
IN SETUP_DATA *SetupData
)
{
UINT8 Data8;
SIOConfigEnter();
MI-220
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX , 0x2C); //
Pin113 function selection to TSIC
Data8 = IoRead8(NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA) | 0x01;
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , Data8);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX ,
NCT6776F_LDN_SEL_REGISTER);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , NCT6776F_LDN_GPIO2);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX ,
NCT6776F_ACTIVATE_REGISTER);
Data8 = IoRead8(NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA) | 0x04;
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , Data8);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX ,
NCT6776F_LDN_SEL_REGISTER);
Watchdog Timer 67
Page 80

IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , NCT6776F_LDN_GPIOA);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX , 0xE0); //
selection Pin113 to GPO High
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , 0x00);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX , 0xE1);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , 0x01);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX , 0xE5); //
selection Pin113 to WDTO
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , 0x01);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX , 0x2C); //
Pin113 function selection to GPIOA0
Data8 = IoRead8(NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA) & 0xFE;
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , Data8);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX ,
NCT6776F_LDN_SEL_REGISTER);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , NCT6776F_LDN_GPIO2);
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX ,
NCT6776F_ACTIVATE_REGISTER);
Data8 = IoRead8(NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA) | SetupData-
>WDT_Control ;
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , Data8);
IoWrite8(NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX, 0xF5);
Data8 = IoRead8(NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA) | SetupData-
>WDT_CountMode;
IoWrite8 (NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA , Data8);
IoWrite8(NCT6776F_CONFIG_INDEX, 0xF6);
IoWrite8(NCT6776F_CONFIG_DATA, SetupData-
>WDT_TimeOut);
SIOConfigExit();
}
68 Watchdog Timer
Page 81

Appendix B - System Resources
B.1 System Memory Map
MI-220
Address Range
(decimal)
(4GB-8MB)
(4GB-18MB) –
(4GB-17MB-1)
(4GB-20MB) –
(4GB-19MB-1)
960 K – 1024 K F0000 – FFFFF 64 KB System BIOS Area
896 K – 960 K E0000 – EFFFF 64 KB Extended System BIOS Area
768 K – 896 K C0000 – DFFFF 128 KB
640 K – 768 K A0000 – BFFFF 128 KB Video Buffer & SMM space
0 K – 640 K 00000 – 9FFFF 640 KB DOS Area
Address Range
(hex)
FFE00000 –
FFFFFFFF
FEE00000 –
FEEFFFFF
FEC00000 –
FECFFFFF
Table B-1: System Memory Map
Size Description
8 MB High BIOS Area
1 MB FSB Interrupt Memory Space
1 MB APIC Configuration Space
PCI expansion ROM area
C0000 – C7FFF: Onboard VGA BIOS
CB800 – CC7FFF: Intel 82578DM
PXE option ROM when onboard LAN
boot ROM is enabled.
System Resources 69
Page 82

B.2 Direct Memory Access Channels
Channel Number Data Width System Resour ce
0Open
1Open
2Open
3Open
4 Direct Memory Access Controller
5Open
6Open
7Open
Table B-2: Direct Memory Access Channels
70 System Resources
Page 83

B.3 Fixed I/O Map
Hex Range Device
000-00F Direct memory access controller
010-01F Motherboard resources
020-021 Programmable interrupt controller
022-03F Motherboard resources
040-043 System timer
044-04F Motherboard resources
050-053 System timer
054-05F Motherboard resources
060-060 Standard 101/102-Key or Microsoft Natural PS/2
061-061 Motherboard resources
063-063 Motherboard resources
064-064 Standard 101/102-Key or Microsoft Natural PS/2
065-065 Motherboard resources
067-067 Motherboard resources
070-070 Motherboard resources
071-07F System CMOS/real time clock
072-07F Motherboard resources
080-080 Motherboard resources
081-083 Direct memory access controller
084-086 Motherboard resources
087-087 Direct memory access controller
088-088 Motherboard resources
089-08B Direct memory access controller
08C-08E Motherboard resources
08F-08F Direct memory access controller
090-092 Motherboard resources
093-09F Direct memory access controller
0A0-0A1 Programmable interrupt controller
0A2-0BF Motherboard resources
0C0-ODF Direct memory access controller
0E0-0EF Motherboard resources
Table B-3: Fixed I/O Map
MI-220
System Resources 71
Page 84

Hex Range Device
0F0-0FF Numeric data processor
274-277 ISAPNP Read Data Port
279-279 ISAPNP Read Data Port
290-29F Motherboard resources
3B0-3BB Intel HD Graphics Family
3C0-3DF Intel HD Graphics Family
400-453 Motherboard resources
454-457 Motherboard resources
458-47F Motherboard resources
4D0-4D1 Motherboard resources
500-57F Motherboard resources
680-69F Motherboard resources
A20-A2F Motherboard resources
A79-A79 ISAPNP Read Data Port
C80-C87 Communications Port (COM1)
C88-C8F Communications Port (COM2)
C90-C97 Communications Port (COM3)
C98-C9F Communications Port (COM4)
1000-100F Motherboard resources
164E-164F Motherboard resources
E000-E01F Intel 82574L Gigabit Network Connection
E020-EFFF Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family PCI Express
F000-F03F Intel HD Graphics Family
F040-F05F Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family SMBus
F060-F07F Intel 82579LM Gigabit Network Connection
F080-F08F Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 2 port Serial
F090-F09F Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 2 port Serial
F0A0-F0A3 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 2 port Serial
F080-F087 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 2 port Serial
F0C0-F0C3 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 2 port Serial
F0D0-F0D7 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 2 port Serial
F0E0-F0EF Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 4 port Serial
Table B-3: Fixed I/O Map
72 System Resources
Page 85

Hex Range Device
F0F0-F0FF Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 4 port Serial
F100-F103 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 4 port Serial
F110-F117 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 4 port Serial
F120-F123 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 4 port Serial
F130-F137 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 4 port Serial
FFFF-FFFF Motherboard resources
Table B-3: Fixed I/O Map
B.4 Variable I/O Map
Hex Range Device
400 ACPI
Anywhere in 64KB I/O Space
Anywhere in 64KB I/O Space USB UHCI Controller #2
580 SMBUS
460 TCO
500 GPIO
C80/C88/C90/C98 Serial Port 1, Serial Port 2, Serial Port 3,
290 Hardware Monitor
USB UHCI Controller #1
MI-220
Table B-4: Variable I/O Map
System Resources 73
Page 86

B.5 Interrupt Request (IRQ) Lines
IRQ Lines APIC Mode
IRQ# Typical Interrupt Resource
0 System timer
1 Standard 101/102-Key or Microsoft Natural PS/2 Keyboard
2N/A
3N/A
4N/A
5 Communications Port (COM1)
6N/A
7 Communications Port (COM2)
8 System CMOS/real time clock
9 Microsoft ACPI-Compliant System
10 Communications Port (COM3)
11 Communications Port (COM4)
12 Microsoft PS/2 Mouse
13 Numeric data Processor
3 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family SMBus Controller-
16 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family PCI Express Root
16 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family USB Enhanced
16 Intel HD Graphics Family
16 Intel Management Engine Interface
17
19
19
19 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family PCI Express Root
19 Intel 82574L Gigabit Network Connection
20 Intel 82579LM Gigabit Network Connection
22 Microsoft UAA Bus Driver for High definition Audio
23 Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family USB Enhanced
Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family PCI Express Root
Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 2 port Serial ATA
Intel 6 Series/C220 Series Chipset Family 4 port Serial ATA
T ab le B-5: IRQ Lines APIC Mode
74 System Resources
Page 87

MI-220
B.6 PCI Configuration Space Map
Bus # Device # Function # Routing Description
00h 00h 00h N/A Intel QM67 Host Processor Bridge
00h 02h 00h Internal Intel Integrated Graphics Device
00h 16h 00h Internal Intel Management Engine Interface
00h 16h 03h Internal KT Controller
00h 19h 00h Internal GbE Controller
00h 1Ah 00h Internal Intel USB EHCI Controller #2
00h 1Bh 00h Internal High Definition Audio controller
00h 1Ch 00h Internal Intel ICH Express Root port #1
00h 1Ch 01h Internal Intel ICH Express Root port #2
00h 1Ch 07h Internal Intel ICH Express Root port #8
00h 1Dh 00h Internal Intel USB EHCI Controller #1
00h 1Fh 00h Internal LPC Controller
00h 1Fh 02h Internal SATA Controller #1
00h 1Fh 03h Internal SMBus Controller
00h 1Fh 05h Internal SATA Controller #2
02h 00h 00h External Texas Instruments PCI Bridge
04h 00h 00h External Intel Ethernet
Table B-6: PCI Configuration Space Map
System Resources 75
Page 88

B.7 PCI Interrupt Routing Map
PIR A B C D E F G H
IGD X
Intel ME INTA INTD INTC INTB
GbE Controller X
EHCI Controller #1 X
EHCI Controller #0 X
HDA Controller X
PCIE port 0 INTA INTB INTC INTD
LPC Controller INTF NTD INTC INTA
SATA Controller0 X X
SATA Controller1 X
SMBus Controller X
Table B-7: PCI Interrupt Routing Map
76 System Resources
Page 89

MI-220
Important Safety Instructions
For user safety, please read and follow all instructions,
WARNINGS, CAUTIONS, and NOTES marked in this manual
and on the associated equipment before handling/operating the
equipment.
X Read these safety instructions carefully.
X Keep this user’s manual for future reference.
X Read the specifications section of this manual for detailed
information on the operating environment of this equipment.
X When installing/mounting or uninstalling/removing
equipment:
Z Turn off power and unplug any power cords/cables.
X To avoid electrical shock and/or damage to equipment:
Z Keep equipment away from water or liquid sources;
Z Keep equipment away from high heat or high humidity;
Z Keep equipment properly ventilated (do not block or
cover ventilation openings);
Z Make sure to use recommended voltage and power
source settings;
Z Always install and operate equipment near an easily
accessible electrical socket-outlet;
Z Secure the power cord (do not place any object on/over
the power cord);
Z Only install/attach and operate equipment on stable
surfaces and/or recommended mountings; and,
Z If the equipment will not be used for long periods of time,
turn off and unplug the equipment from its power source.
Important Safety Instructions 77
Page 90

X Never attempt to fix the equipment. Equipment should only
be serviced by qualified personnel.
A Lithium-type battery may be provided for uninterrupted, backup
or emergency power.
Risk of explosion if battery is replaced with one of an incorrect
WARNING:
type. Dispose of used batteries appropriately.
X Equipment must be serviced by authorized technicians
when:
Z The power cord or plug is damaged;
Z Liquid has penetrated the equipment;
Z It has been exposed to high humidity/moisture;
Z It is not functioning or does not function according to the
user’s manual;
Z It has been dropped and/or damaged; and/or,
Z It has an obvious sign of breakage.
78 Important Safety Instructions
Page 91

Getting Service
Contact us should you require any service or assistance.
ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 9F, No.166 Jian Yi Road, Zhonghe District
New Taipei City 235, Taiwan
ᄅקؑխࡉ৬ԫሁ 166 ᇆ 9 ᑔ
Tel: +886-2-8226-5877
Fax: +886-2-8226-5717
Email: service@adlinktech.com
Ampro ADLINK Technology, Inc.
Address: 5215 Hellyer Avenue, #110, San Jose, CA 95138, USA
Tel: +1-408-360-0200
Toll Free: +1-800-966-5200 (USA only)
Fax: +1-408-360-0222
Email: info@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (China) Co., Ltd.
Address: Ϟ⍋Ꮦ⌺ϰᮄᓴ∳催⾥ᡔು㢇䏃 300 ো(201203)
300 Fang Chun Rd., Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park,
Pudong New Area, Shanghai, 201203 China
Tel: +86-21-5132-8988
Fax: +86-21-5132-3588
Email: market@adlinktech.com
MI-220
ADLINK Technology Beijing
Address: ࣫ҀᏖ⍋⎔Ϟഄϰ䏃 1 োⲜ߯ࡼ E ᑻ 801 ᅸ(100085)
Tel: +86-10-5885-8666
Fax: +86-10-5885-8625
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Shenzhen
Address: ⏅ഇᏖቅ⾥ᡔು催ᮄϗ䘧᭄ᄫᡔᴃು
Tel: +86-755-2643-4858
Fax: +86-755-2664-6353
Email: market@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology (Europe) GmbH
Address: Nord Carree 3, 40477 Duesseldorf, Germany
Tel: +49-211-495-5552
Fax: +49-211-495-5557
Email: emea@adlinktech.com
Rm. 801, Power Creative E, No. 1, B/D
Shang Di East Rd., Beijing, 100085 China
A1 2 ὐ C (518057)
2F, C Block, Bldg. A1, Cyber-Tech Zone, Gao Xin Ave. Sec. 7,
High-Tech Industrial Park S., Shenzhen, 518054 China
Getting Service 79
Page 92

ADLINK Technology, Inc. (French Liaison Office)
Address: 15 rue Emile Baudot, 91300 Massy CEDEX, France
Tel: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Fax: +33 (0) 1 60 12 35 66
Email: france@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Japan Corporation
Address: ͱ101-0045 ᵅҀ䛑ҷ⬄⼲⬄䤯ފ⬎ 3-7-4
Tel: +81-3-4455-3722
Fax: +81-3-5209-6013
Email: japan@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Korean Liaison Office)
Address: 昢殾柢 昢爎割 昢爎壟 1675-12 微汾瘶捒娯 8猻
Tel: +82-2-2057-0565
Fax: +82-2-2057-0563
Email: korea@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd.
Address: 84 Genting Lane #07-02A, Cityneon Design Centre,
Tel: +65-6844-2261
Fax: +65-6844-2263
Email: singapore@adlinktech.com
ADLINK Technology Singapore Pte. Ltd. (Indian Liaison Office)
Address: 1st Floor, #50-56 (Between 16th/17th Cross) Margosa Plaza,
Tel: +91-80-65605817, +91-80-42246107
Fax: +91-80-23464606
Email: india@adlinktech.com
⼲⬄ 374 ɛɳ 4F
KANDA374 Bldg. 4F, 3-7-4 Kanda Kajicho,
Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 101-0045, Japan
8F Mointer B/D,1675-12, Seocho-Dong, Seocho-Gu,
Seoul 137-070, Korea
Singapore 349584
Margosa Main Road, Malleswaram, Bangalore-560055, India
ADLINK Technology, Inc. (Israeli Liaison Office)
Address: 6 Hasadna St., Kfar Saba 44424, Israel
Tel: +972-9-7446541
Fax: +972-9-7446542
Email: israel@adlinktech.com
80 Getting Service
 Loading...
Loading...