Page 1

HSL-4XMO
High Speed Link
4-Axis Motion Control Module
User’s Manual
Manual Rev. 2.02
Revision Date: December 21, 2006
Part No: 50-1I001-200
Advance Technologies; Automate the World.
Page 2

Copyright 2005 ADLINK TECHNOLOGY INC.
All Rights Reserved.
The information in this document is subject to change without prior
notice in order to improve reliability, design, and function and does
not represent a commitment on the part of the manufacturer.
In no event will the manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental, or consequential damages arising out of the use or
inability to use the product or documentation, even if advised of
the possibility of such damages.
This document contains proprietary information protected by copyright. All rights are reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced by any mechanical, electronic, or other means in any form
without prior written permission of the manufacturer.
Trademarks
Product names mentioned herein are used for identification purposes only and may be trademarks and/or registered trademarks
of their respective companies.
Page 3
Getting Service from ADLINK
Customer Satisfaction is top priority for ADLINK Technology Inc.
Please contact us should you require any service or assistance.
ADLINK TECHNOLOGY INC.
Web Site: http://www.adlinktech.com
Sales & Service: Service@adlinktech.com
TEL: +886-2-82265877
FAX: +886-2-82265717
Address: 9F, No. 166, Jian Yi Road, Chungho City,
Taipei, 235 Taiwan
Please email or FAX this completed service form for prompt and
satisfactory service.
Company Information
Company/Organization
Contact Person
E-mail Address
Address
Country
TEL FAX:
Web Site
Product Information
Product Model
OS:
Environment
M/B: CPU:
Chipset: Bios:
Please give a detailed description of the problem(s):
Page 4

Page 5

Table of Contents
Table of Contents..................................................................... i
List of Tables.......................................................................... iv
List of Figures ......................................................................... v
1 Introduction ........................................................................ 1
1.1 Features............................................................................... 2
1.2 Specifications....................................................................... 3
1.3 Supported Software ............................................................. 5
Programming Library ...................................................... 5
Motion Creator on LinkMaster Utility ............................... 5
2 Installation .......................................................................... 7
2.1 Package Contents ............................................................... 7
2.2 HSL-4XMO-CG-N/P Mechanical Drawing ........................... 8
2.3 HSL-4XMO-CD-N/P Mechanical Drawing ........................... 9
2.4 CN1 Pin Assignments: External Power Input .................... 10
2.5 CN2 Pin Assignment: Emergency Input and General Input Com-
mon.......................................................................... 10
2.6 HS1,2 Pin Assignments: HSL Communication Signal (RJ-45).
11
2.7 HS3 Pin Assignments: HSL Communication Signal (WAGO
Type) ....................................................................... 11
2.8 CM1-CM4 Pin Assignments: For HSL-4XMO-CG-N/P ...... 11
2.9 CM1-CM4 Pin Assignments: For HSL-4XMO-CD-N/P ...... 13
2.10 IOIF1-4 Pin Assignments: Mechanical I/O and GPIO Signal
Connector ................................................................ 13
2.11 S1: Switch Setting for HSL Slave ID .................................. 14
2.12 JP1: Jumper Setting for HSL Communication Speed Selection
14
2.13 JP2 - 3: Jumper Setting for HSL Transmission Mode........ 15
2.14 JP4: Jumper Setting for HSL Termination Resistor ........... 15
2.15 JP5-8, JP10-13: Enable/Disable DO to reset servo driver. 16
2.16 JP9: NPN/PNP setting of EMG signal ............................... 16
3 Signal Connections.......................................................... 17
3.1 Pulse Output Signals OUT and DIR .................................. 18
Table of Contents i
Page 6

3.2 Encoder Feedback Signals EA, EB and EZ....................... 20
3.3 Origin Signal ORG ............................................................. 22
3.4 End-Limit Signals PEL and MEL........................................ 23
3.5 Ramping-down & Position Latch........................................ 23
3.6 In-position Signal INP ........................................................ 24
3.7 Alarm Signal ALM .............................................................. 25
3.8 Deviation Counter Clear Signal (ERC)............................... 25
3.9 General-purpose Signal SVON.......................................... 26
3.10 General-purpose Signal RDY ............................................ 26
3.11 Position Compare Output CMP.......................................... 27
3.12 Emergency Stop Input EMG .............................................. 27
3.13 General-purpose Input ....................................................... 28
3.14 General-purpose Output .................................................... 28
4 Operation Theory .............................................................. 31
4.1 Communication Block Diagram.......................................... 31
4.2 Host Command .................................................................. 31
4.3 Command Delivering Time ................................................ 32
4.4 Command Dispatching in DSP .......................................... 34
4.5 The role of DSP and motion ASIC ..................................... 35
4.6 Motion Control Modes........................................................ 35
Pulse Command Output ............................................... 35
Velocity Mode Motion ................................................... 37
Trapezoidal Motion ....................................................... 38
S-curve Profile Motion .................................................. 41
Linear interpolation for 2-4 axes ................................... 44
Circular interpolation for 2 axes .................................... 48
Circular Interpolation with Acc/dec Time ...................... 49
Relationship between Velocity and Acceleration Time . 50
Home Return Mode ...................................................... 53
4.7 The Motor Driver Interface ................................................. 63
INP ................................................................................ 63
ALM .............................................................................. 64
ERC .............................................................................. 64
SVON and RDY ............................................................ 65
4.8 The Limit Switch Interface and I/O Status......................... 66
SD/LTC ......................................................................... 66
EL ................................................................................. 67
ORG .............................................................................. 67
4.9 The Counters ..................................................................... 68
ii Table of Contents
Page 7

Command Position Counter .......................................... 68
Feedback Position Counter .......................................... 69
Position Error Counter .................................................. 71
General Purpose Counter ............................................. 71
Target Position Recorder .............................................. 72
4.10 Multiple HSL-4XMO Operations ........................................ 73
4.11 Change Position Or Speed On The Fly ............................. 74
Change Speed on the Fly ............................................. 74
Change Position on the Fly ........................................... 80
4.12 Position Compare .............................................................. 82
Comparators of the HSL-4XMO .................................... 82
Position Compare ......................................................... 83
4.13 Backlash Compensator and Vibration Suppression .......... 86
4.14 Software Limit Function ..................................................... 87
4.15 Point Table Management................................................... 87
4.16 Motion Script Download.................................................... 88
5 Motion Creator in LinkMaster.......................................... 89
5.1 Execute Motion Creator in LinkMaster............................... 89
5.2 About Motion Creator in LinkMaster .................................. 89
5.3 Motion Creator Form Introducing....................................... 91
Main Menu .................................................................... 91
Interface I/O Configuration Menu .................................. 92
Pulse IO Configuration Menu ........................................ 93
Operation Menu ............................................................ 95
6 Appendix......................................................................... 103
6.1 HSL-4XMO Commmand Executuion Time ...................... 103
Warranty Policy................................................................... 105
Table of Contents iii
Page 8

List of Tables
Table 2-1: CN1 Pin Assignments: External Power Input ......... 10
Table 2-2: CN2 Pin Assignments: Emergency Input and General In-
put Common ........................................................... 10
Table 2-3: HS1-HS2 Pin Assignments: HSL Communication Signal
(RJ-45) .................................................................... 11
Table 2-4: HS3 Pin Assignments: HSL Communication Signal (WA-
GO type) ................................................................. 11
Table 2-5: CM1-CM4 Pin Assignments: Servo Interface ......... 11
Table 2-6: CM1-CM4 Pin Assignments: For HSL-4XMO-CD-N/P
13
Table 2-7: IOIF1-4 Pin Assignments: Mechanical I/O and GPIO Sig-
nal Connector ......................................................... 13
Table 3-1: Encoder Power / External Resistor ......................... 21
Table 4-1: Base Scan Times .................................................... 33
Table 4-2: Pulse Command Output ......................................... 35
Table 4-3: Single Axis Motion Functions .................................. 44
Table 4-4: Counter Summary ................................................... 72
Table 4-5: Multiple HSL-4XMO Operations ............................. 73
Table 4-6: HSL_M_v_change() Example ................................. 77
Table 4-7: HSL_M_p_change() Constraints ............................ 82
Table 4-8: HSL-4XMO Comparators ........................................ 82
Table 6-1: Commmand Executuion Classifications ............... 103
Table 6-2: HSL-4XMO Commmand Executuion Times ......... 103
iv List of Tables
Page 9

List of Figures
Figure 2-1: HSL-4XMO-CG-N/P Mechanical Drawing ................. 8
Figure 2-2: HSL-4XMO-CD-N/P Mechanical Drawing ................. 9
Figure 2-3: S1: Switch Setting for HSL Slave ID........................ 14
Figure 2-4: JP1: HSL Communication Speed Selection Jumper Set-
ting........................................................................... 14
Figure 2-5: JP2 - 3: Jumper Setting for HSL Transmission Mode 15
Figure 2-6: JP4: HSL Termination Resistor Jumper Setting ...... 15
Figure 2-7: JP5-8, JP10-13: Enable/Disable DO to reset servo driver
16
Figure 2-8: JP9: NPN/PNP setting of EMG signal ..................... 16
Figure 3-1: OUT and DIR Signals on the 4 Axes ....................... 18
Figure 3-2: Non-differential Type Wiring Example ..................... 19
Figure 3-3: EA, EB, and EZ signals ........................................... 20
Figure 3-4: Connection to Line Driver Output ............................ 21
Figure 3-5: Connection to Open Collector Output...................... 22
Figure 3-6: Origin Signal ORG ................................................... 22
Figure 3-7: End-Limit Signals PEL and MEL ............................. 23
Figure 3-8: Ramping-down & Position Latch ............................. 24
Figure 3-9: In-position Signal INP .............................................. 24
Figure 3-10: Alarm Signal ALM.................................................... 25
Figure 3-11: Deviation Counter Clear Signal (ERC) .................... 26
Figure 3-12: General-purpose Signal SVON ............................... 26
Figure 3-13: General-purpose Signal RDY .................................. 27
Figure 3-14: Position Compare Output CMP ............................... 27
Figure 3-15: Emergency Stop Input EMG.................................... 28
Figure 3-16: General-purpose Input............................................. 28
Figure 3-17: NPN Type General Purpose Output ........................ 29
Figure 3-18: PNP Type General Purpose Output ........................ 29
Figure 4-1: Communication Block Diagram ............................... 31
Figure 4-2: Single Command Timing ......................................... 33
Figure 4-3: DSP Multi-Tasks ...................................................... 34
Figure 4-4: Single Pulse Output Mode (OUT/DIR Mode)........... 36
Figure 4-5: Dual Pulse Output Mode (CW/CCW Mode) ............ 37
Figure 4-6: Velocity Mode Motion .............................................. 38
Figure 4-7: Trapezoidal Motion .................................................. 39
Figure 4-8: Encoder Diagram..................................................... 41
Figure 4-9: S-curve Profile Motion ............................................. 42
Figure 4-10: Automatic Velocity Decrease................................... 43
List of Figures v
Page 10

Figure 4-11: 2 Axes Linear Interpolation ...................................... 45
Figure 4-12: 3-Axis Linear Interpolation ....................................... 46
Figure 4-13: Circular interpolation for 2 axes ............................... 48
Figure 4-14: Circular Interpolation with Acc/dec Time ................. 50
Figure 4-15: Velocity and Acceleration Time A ............................ 51
Figure 4-16: Velocity and Acceleration Time B ............................ 52
Figure 4-17: home_mode=0......................................................... 54
Figure 4-18: home_mode=1......................................................... 55
Figure 4-19: home_mode=3......................................................... 55
Figure 4-20: home_mode=4......................................................... 56
Figure 4-21: home_mode=5......................................................... 57
Figure 4-22: home_mode=6......................................................... 57
Figure 4-23: home_mode=7......................................................... 57
Figure 4-24: home_mode=8......................................................... 58
Figure 4-25: home_mode=9......................................................... 58
Figure 4-26: home_mode=10....................................................... 59
Figure 4-27: home_mode=11....................................................... 60
Figure 4-28: home_mode=12....................................................... 60
Figure 4-29: Home Search Example............................................ 61
Figure 4-30: 90° Phase Difference Signals .................................. 70
Figure 4-31: Change Speed on the Fly ........................................ 74
Figure 4-32: HSL_M_v_change() Theory..................................... 76
Figure 4-33: Velocity Suggestions A ............................................ 77
Figure 4-34: Velocity Suggestions B ............................................ 78
Figure 4-35: Velocity Example ..................................................... 78
Figure 4-36: Velocity Profile Example .......................................... 79
Figure 4-37: Change Position on the Fly...................................... 80
Figure 4-38: Theory of HSL_M_p_change() ................................ 81
Figure 4-39: Continuously Comparison with Trigger Output........ 84
Figure 4-40: Vibration Suppression.............................................. 86
Figure 5-1: HSL Master Utility .................................................... 90
Figure 5-2: Main Menu ............................................................... 91
Figure 5-3: Interface I/O Configuration Menu............................. 92
Figure 5-4: Pulse IO Configuration Menu................................... 94
Figure 5-5: Operation Menu ....................................................... 96
Figure 5-6: Show Velocity Curve................................................ 97
Figure 5-7: Home Mode Configuration....................................... 98
vi List of Figures
Page 11

1 Introduction
The HSL-4XMO is a 4-axis motion controller module for HSL system. It can generate high frequency pulses (6.55MHz) to drive
stepper or servomotors. As a motion controller, it can provide 2axis circular interpolation, 4-axis linear interpolation, or continuous
interpolation for continual velocity. Also, changing position/speed
on the fly is available with a single axis operation.
Multiple HSL-4XMO modules can be used in one HSL system.
Incremental encoder interface on all four axes provide the ability to
correct positioning errors generated by inaccurate mechanical
transmissions. With the aid of on board DSP, the HSL-4XMO can
also perform many real-time applications without compromising
CPU resources. In addition, a mechanical sensor interface, servo
motor interface, and general-purposed I/O signals are provided for
easy system integration.
The HSL-4XMO uses one ASIC (PCL6045) to perform all 4 axes
motion controls and one DSP to communicate with Host PC and
HSL protocol. The motion control functions include linear and Scurve acceleration/deceleration, circular interpolation between two
axes, linear interpolation between 2~4 axes, continuous motion
positioning, and 13 home return modes. All these functions and
complex computations are performed internally by the ASIC, thus
limiting the impact on the PC’s CPU usage. The DSP can perform
as a motion path-loading manager without consuming Host PC’s
resource. It is more powerful than traditional ASIC-based motion
control card.
Introduction 1
Page 12

1.1 Features
X High Speed Link (HSL) protocol compatible
X 3M/6M/12M data transfer rate selectable
X Support dual and half duplex modes
X On board DSP (TMS320C6711)
X 4-axis stepper or servo motor control by pulse signal com-
mand
X Maximum pulse output frequency: 6.55 MPPS
X Pulse output types: OUT/DIR (single pulse), CW/CCW (dual
pulse)
X Support up to 63 axes in one HSL network
X Motion point table management
X Motion script download for precision timing motion control
X Any 2 of 4 axes circular interpolation in one module
X Any 2-4 of 4 axes linear interpolation in one module
X Continuous interpolation for contour following motion
X 3 Command buffers for special speed profile motion
X Change position and speed on the fly
X Change speed by condition comparing
X 13 home return modes with auto searching
X 2 ways software end-limits of each axis
X 28-bit up/down incremental encoder interface of each axis
X Dedicated motion I/O : home (DOG), index signal (EZ), end
limit, servo on, INP, ERC, ALM, motion interface of each
axis
X 4 general-purpose DI/DO channels
X One Emergency input with hardware motion stop function
X High-speed position counter latch input for each axis
X Continuous position compare with trigger pulse output of
each axis
X All digital input and output signals are 2500Vrms isolated
X Includes Motion Creator, a Microsoft Windows-based appli-
cation development software built in LinkMaster Utility
2Introduction
Page 13

X User-friendly function libraries and utilities for DOS and
Windows 9x/NT/2000/XP. Also supported under Linux
1.2 Specifications
Command Response Time
X Half Duplex: 240us for one module under 6Mhz data trans-
fer rate
X Full Duplex: 240us for two modules under 6Mhz data trans-
fer rate
Motion Control
X Maximum controllable axes in one module: 4
X Internal reference clock: 19.66MHz
X Position counter range: –134,217,728 to +134,217,727 (28-
bit)
X Command counter setting range: -134,217,728 to
+134,217,728 (28-bit)
X Pulse rate setting range: 1~ 65,535 (16-bit)
X Pulse rate multiplier setting range: 0.1~100
Pulse Output
X Line driver output
X Max. Speed: 6.55 Mhz
X Output Voltage:
Z Logic H: 2.5V min.
Z Logic L: 0.5V max.
X Isolated voltage: 500Vrms
Encoder Input
X Incremental Encoder Input
X Max. Speed: 5 Mhz
X Input Voltage:
Z Logic H: 3~5V
Z Logic L: 0~2.4V
X Input resistor: 220Ω @ 0.125W
X Isolated voltage: 500Vrms
Introduction 3
Page 14

Digital Input
X Sink or source type can be selected via ICOM
X Switching capability: 10K Hz
X Input voltage range:
Z Logic H: 14.4~24V
Z Logic L: 0~5V
X Input resistor: 4.7KΩ @ 0.5W
X Isolated voltage: 500Vrms
Digital Output
X Output type: Open-collector (PC3H7C)
X Sink Current: 4mA max.
X Switching capability: 10KHz @ 24V, load = 4.7KΩ
X Isolated voltage: 500Vrms
General Purpose Output
X Output type: NPN sinking type for –N module; PNP sourcing
type for –P module
X Sink Current: 90 mA max.
X Switching capability: 2 KHz @ 24V, load = 300Ω
X Isolated voltage: 500 Vrms
General Specifications
X Operating Temperature: 0°C – 60°C
X Storage Temperature: -20°C – 80°C
X Humidity: 0% – 90%, non-condensing
Power Consumption
X 5 Watts max. @ 24Vin
Dimensions
X 163.5mm (W) × 74.9mm (D) × 52.7mm (H)
4Introduction
Page 15

1.3 Supported Software
Programming Library
The Library supports Borland C/C++ (Version: 3.1) and Windows
95/98/NT/2000/XP. These function libraries are shipped with the
module. Users can check ADLINK website for latest update.
This module supports DOS/Windows 98/NT/2000/XP. For other
OS, please contact the local vendors.
Motion Creator on LinkMaster Utility
This Windows-based utility is used to setup cards, motors, and
systems. It can also aid in debugging hardware and software problems. It allows users to set I/O logic parameters to be loaded in
their own program. This product is also bundled with the card.
Introduction 5
Page 16

6Introduction
Page 17

2 Installation
This chapter describes how to install the HSL-4XMO series.
Please follow these steps below:
X Check what you have (section 2.1)
X Check the PCB (section 2.2)
X Install the hardware (section 2.3)
X Install the software driver (section 2.4)
X Understanding the I/O signal connections (chapter 3) and
their operation (chapter 4)
X Understanding the connector pin assignments (the remain-
ing sections) and wiring the connections
2.1 Package Contents
In addition to this User’s Guide, the package also includes the following items:
X HSL-4XMO: Advanced 4-Axis Servo / Stepper Motion Con-
trol Card (HSL-4XMO-CG-N/P, HSL-4XMO-CD-N/P)
X ADLINK All-in-one Compact Disc
If any of these items are missing or damaged, contact the dealer
from whom you purchased the product. Save the shipping materials and carton to ship or store the product in the future.
Installation 7
Page 18
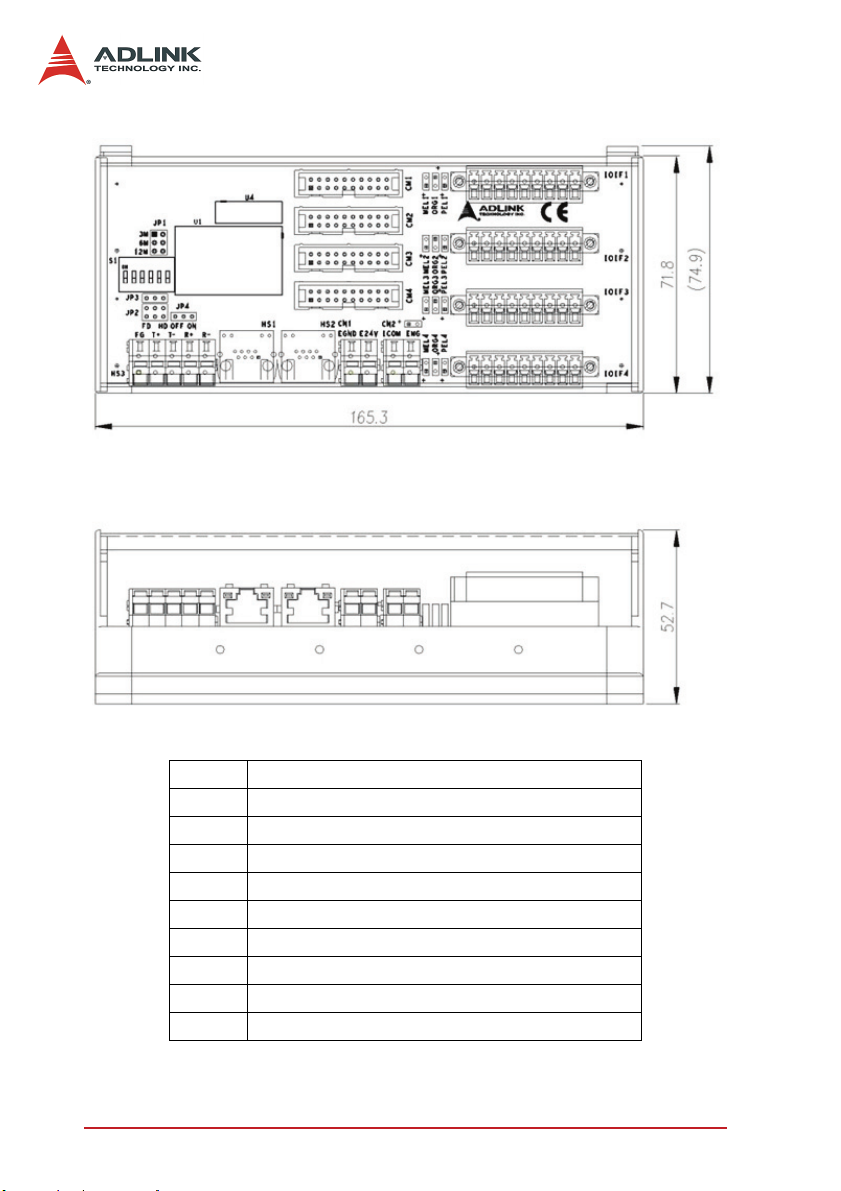
2.2 HSL-4XMO-CG-N/P Mechanical Drawing
Figure 2-1: HSL-4XMO-CG-N/P Mechanical Drawing
CN1: External Power Input Connector (+24V)
CN2: Digital Input Common and Emergency Input Pin
HS1-2: HSL Communication Signal Connector (RJ45)
HS3: HSL Communication Signal Connector (WAGO)
CM1-4: Servo Interface Signal Connector
IOIF1-4: Mechanical I/O and GPIO Signal Connector
S1: Slave ID Switch
JP1: Communication Speed Selection Jumper
JP2-3: Full Duplex / Half Duplex Selection Jumper
JP4: HSL Termination Resistor Jumper
8Installation
Page 19
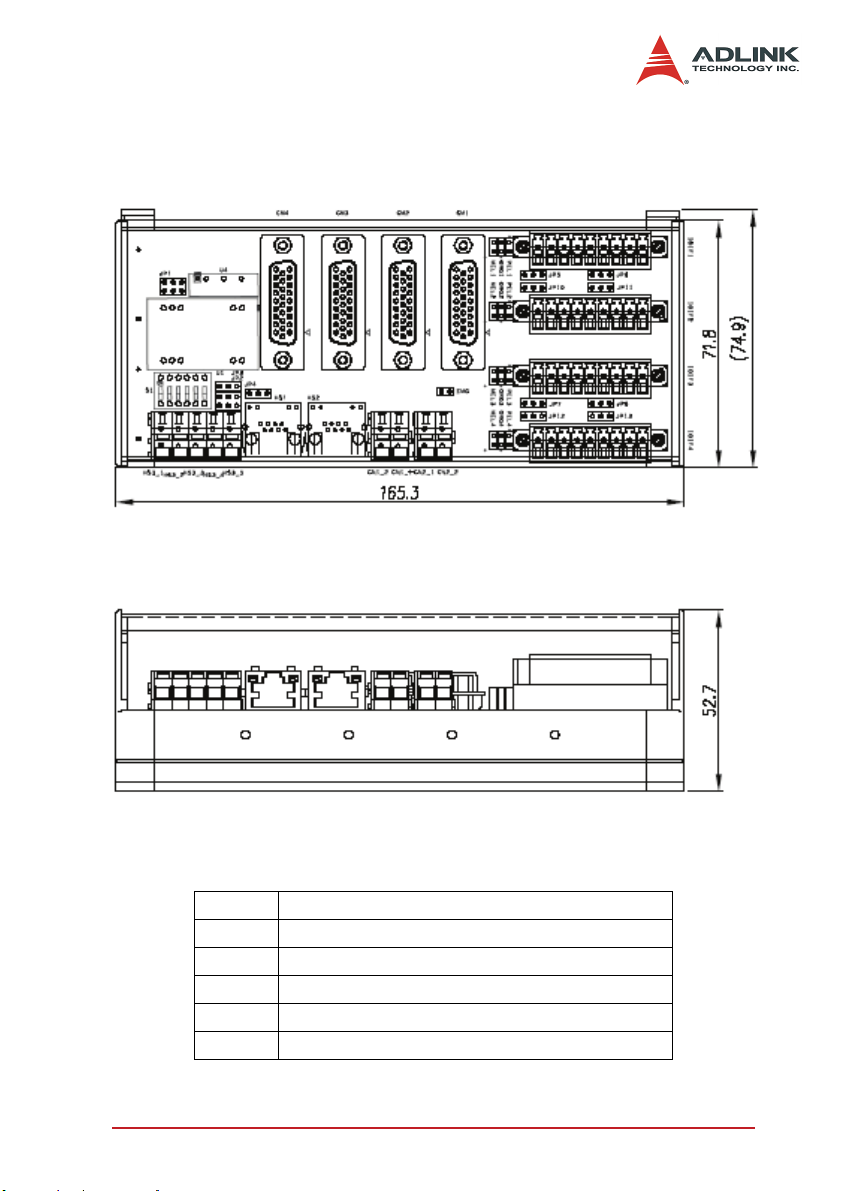
2.3 HSL-4XMO-CD-N/P Mechanical Drawing
Figure 2-2: HSL-4XMO-CD-N/P Mechanical Drawing
CN1: External Power Input Connector (+24V)
CN2: Digital Input Common and Emergency Input Pin
HS1-2: HSL Communication Signal Connector (RJ45)
HS3: HSL Communication Signal Connector (WAGO)
CM1-4: Servo Interface Signal Connector
IOIF1-4: Mechanical I/O and GPIO Signal Connector
Installation 9
Page 20

S1: Slave ID Switch
JP1: Communication Speed Selection Jumper
JP2-3: Full Duplex/Half Duplex Jumper
JP4: Termination Resistor Jumper
JP5-8: Enable/Disable DO to reset servo driver
JP9: NPN/PNP setting of EMG signal
JP10-13: NPN/PNP setting of DO signal
2.4 CN1 Pin Assignments: External Power Input
CN1 Pin Name Description
EGND External power ground
E24V
Table 2-1: CN1 Pin Assignments: External Power Input
+24VDC ±5% External power supply
2.5 CN2 Pin Assignment: Emergency Input and General Input
Common
CN2 Pin Name Description
ICOM Mechanical Input and General Input Common
EMG Emergency Stop Input
Table 2-2: CN2 Pin Assignments: Emergency Input and General Input
Common
Note: ICOM should be connected to either EGND or E24V
10 Installation
Page 21
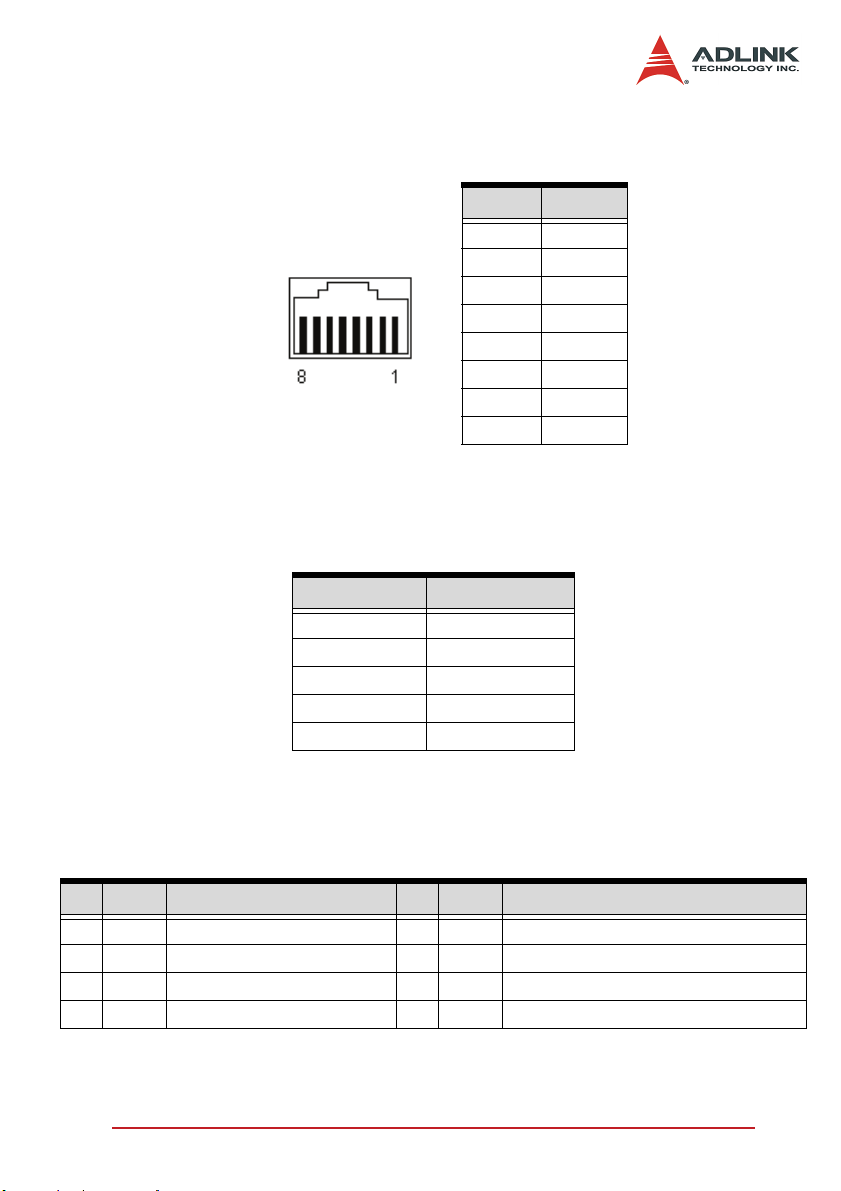
2.6 HS1,2 Pin Assignments: HSL Communication Signal (RJ-45).
PIN NO. PIN OUT
PIN 1 NC
PIN 2 NC
PIN 3 TXD+
PIN 4 RXD-
PIN 5 RXD+
PIN 6 TXD-
PIN 7 NC
RJ45 Female Connector PIN 8 NC
Table 2-3: HS1-HS2 Pin Assignments: HSL Communication Signal (RJ-45)
2.7 HS3 Pin Assignments: HSL Communication Signal (WAGO Type)
HS3 Pin Name Description
FG Shielding ground
T+ TXD+
T- TXD -
R+ RXD+
R- RXD-
Table 2-4: HS3 Pin Assignments: HSL Communication Signal (WAGO type)
2.8 CM1-CM4 Pin Assignments: For HSL-4XMO-CGN/P
No. Name Function No. Name Function
1 EA+ Encoder A-phase (+) 2 EA- Encoder A-phase (-)
3 EB+ Encoder B-phase (+) 4 EB- Encoder B-phase (-)
5 EZ+ Encoder Z-phase (+) 6 EZ- Encoder Z-phase (-)
7 PGND Ground of pulse I/O signals 8 PGND Ground of pulse I/O signals
Table 2-5: CM1-CM4 Pin Assignments: Servo Interface
Installation 11
Page 22

No. Name Function No. Name Function
9 OUT+ Pulse signal (+) 10 OUT- Pulse signal (-)
11 DIR+ Direction signal (+) 12 DIR- Direction signal (-)
13 EGND Ext. power ground 14 SVON Servo on output signal
15 INP In-position input signal 16 ERC Deviation counter clear output signal
17 EGND External power ground 18 E24V External power supply, +24V
19 RDY Ready input signal 20 ALM Alarm input signal
Table 2-5: CM1-CM4 Pin Assignments: Servo Interface
12 Installation
Page 23
2.9 CM1-CM4 Pin Assignments: For HSL-4XMO-CDN/P
No. Name Function No. Name Function
1 SVON Servo on output signal 2 INP In-position input signal
3 ERC Deviation counter clear output signal 4 RDY Ready input signal
5 OUT- Pulse signal (-) 6 OUT+ Pulse signal (+)
7 EA- Encoder A-phase (-) 8 EA+ Encoder A-phase (+)
9 N.C. Not Connected 10 RST Alarm reset output signal
11 ALM Alarm input signal 12 E24V External power supply, +24V
13 EGND Ext. power ground 14 N.C. Not Connected
15 PGND Ground of pulse I/O signals 16 EB- Encoder B-phase (-)
17 EB+ Encoder B-phase (+) 18 PGND Ground of pulse I/O signals
19 EMG Emergency stop output signal 20 EGND External power ground
21 EGND External power ground 22 EGND External power ground
23 DIR- Direction signal (-) 24 DIR+ Direction signal (+)
25 EZ- Encoder Z-phase (-) 26 EZ+ Direction signal (+)
Table 2-6: CM1-CM4 Pin Assignments: For HSL-4XMO-CD-N/P
2.10 IOIF1-4 Pin Assignments: Mechanical I/O and GPIO Signal Con-
nector
Pin No. Pin Name Description
1 E24V External power supply, +24V
2 MEL End limit input signal (-)
3 ORG Origin input signal
4 PEL End limit input signal (+)
5 LTC/SD Ramp-down/position latch input signal (default for LTC)
6 DI/EZ General purposed input/Index Input
7 DO General purposed output
8 CMP Position compare output
9 EGND External power ground
Table 2-7: IOIF1-4 Pin Assignments: Mechanical I/O and GPIO Signal
Connector
Installation 13
Page 24
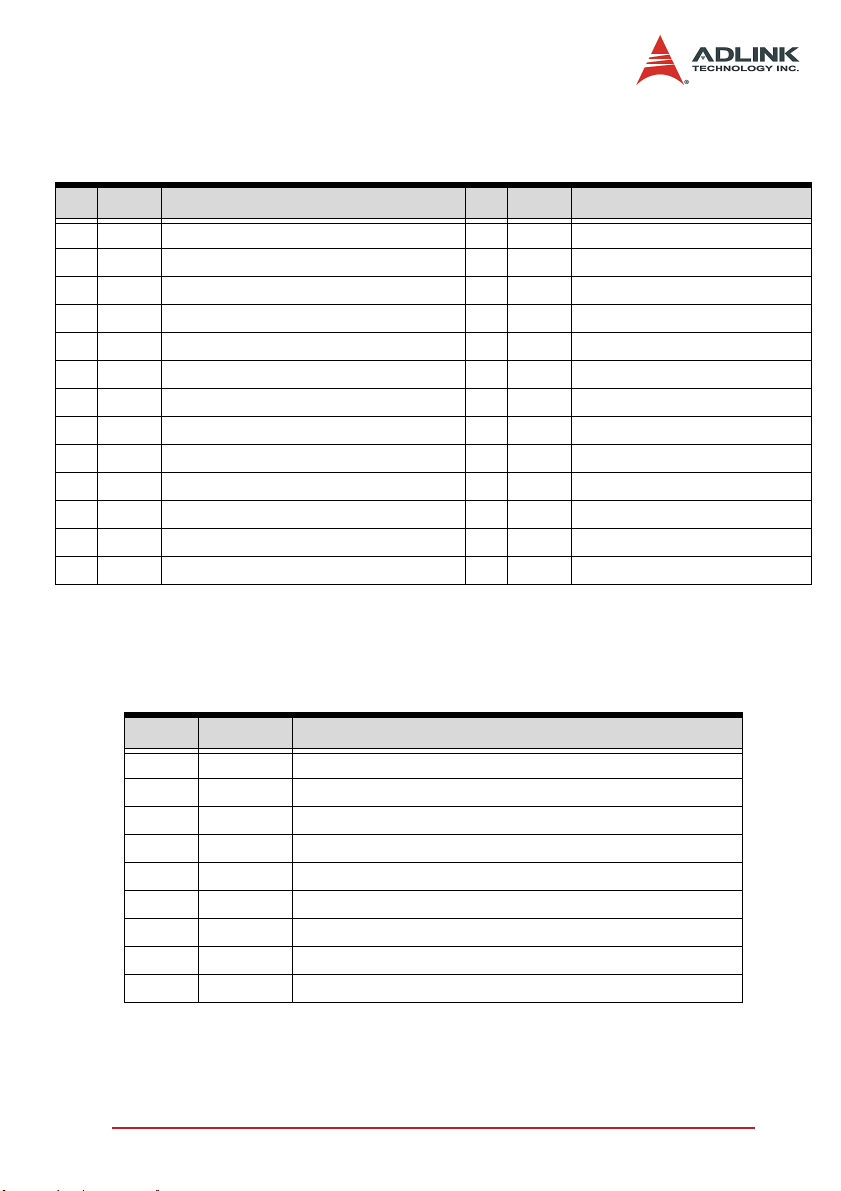
2.11 S1: Switch Setting for HSL Slave ID
Figure 2-3: S1: Switch Setting for HSL Slave ID
Note: Each HSL-4XMO occupies 4 HSL IDs. If using half duplex
mode, the occupied ID will be continuously from this setting.
For example, if you set the ID=1 then the occupied IDs will
be 1, 2, 3, 4. If using full duplex mode, the occupied ID will
be two ID steps in order. For example, if you set the ID=1
then the occupied IDs will be 1, 3, 5, 7.
2.12 JP1: Jumper Setting for HSL Communication Speed Selection
Figure 2-4: JP1: HSL Communication Speed Selection Jumper Setting
14 Installation
Page 25
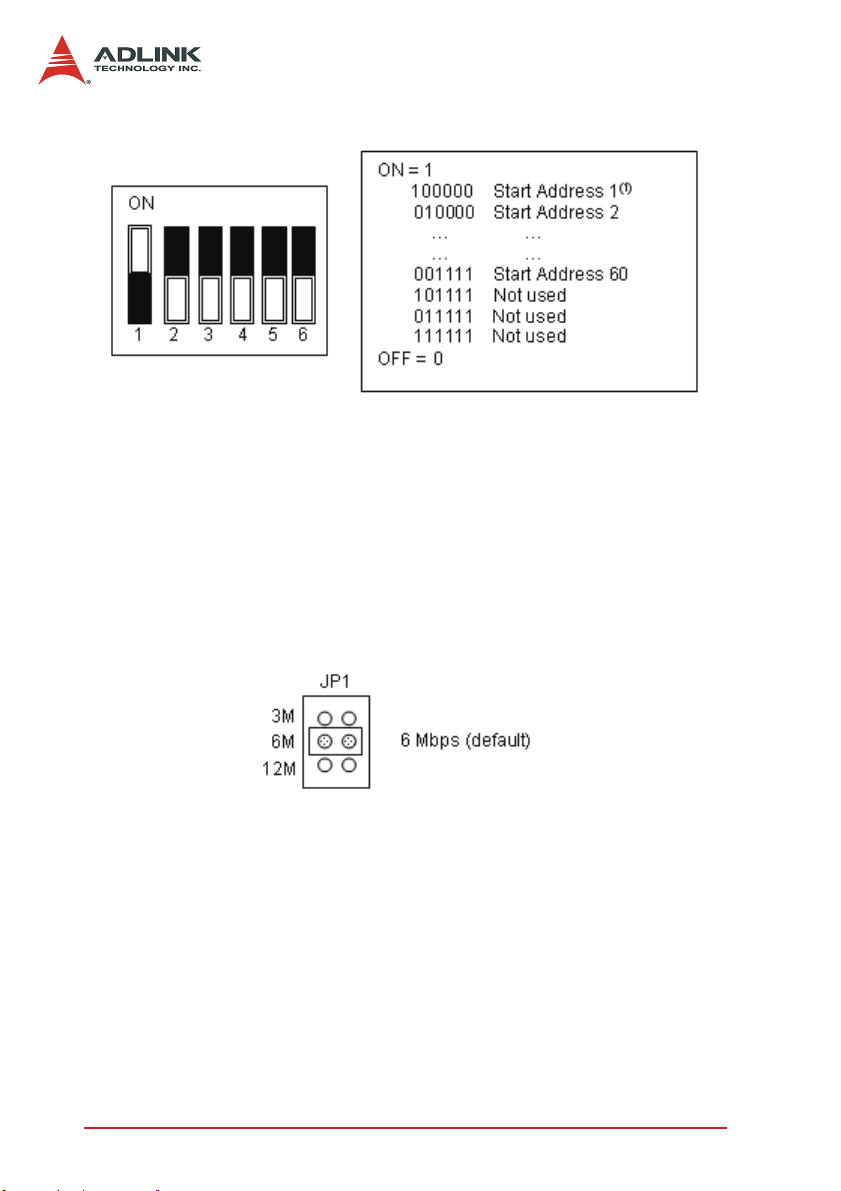
2.13 JP2 - 3: Jumper Setting for HSL Transmission Mode
Figure 2-5: JP2 - 3: Jumper Setting for HSL Transmission Mode
2.14 JP4: Jumper Setting for HSL Termination Resistor
Figure 2-6: JP4: HSL Termination Resistor Jumper Setting
Installation 15
Page 26
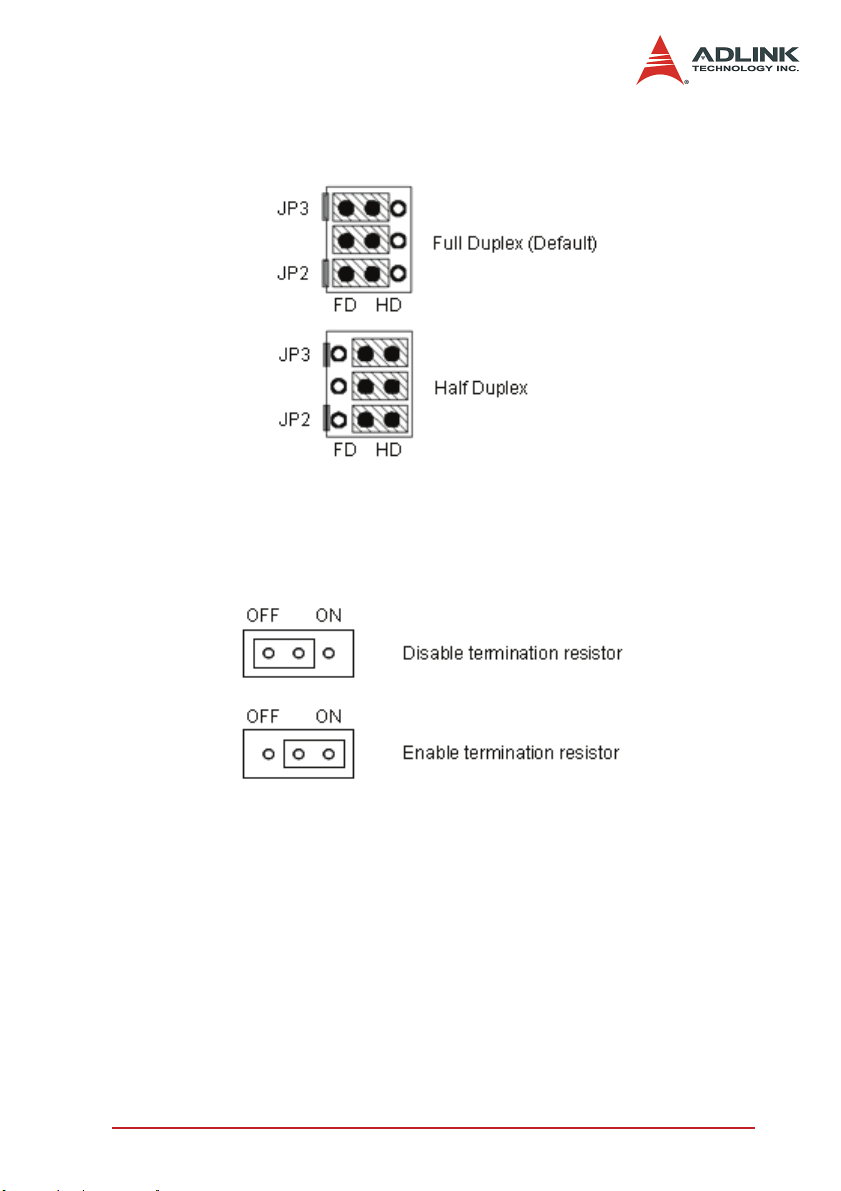
2.15 JP5-8, JP10-13: Enable/Disable DO to reset servo driver
Figure 2-7: JP5-8, JP10-13: Enable/Disable DO to reset servo driver
2.16 JP9: NPN/PNP setting of EMG signal
Figure 2-8: JP9: NPN/PNP setting of EMG signal
16 Installation
Page 27

3 Signal Connections
Signal connections of all I/O’s are described in this chapter. Refer
to the contents of this chapter before wiring any cables between
the HSL-4XMO and any motor drivers.
This chapter contains the following sections:
X Section 3.1 Pulse Output Signals OUT and DIR
X Section 3.2 Encoder Feedback Signals EA, EB and EZ
X Section 3.3 Origin Signal ORG
X Section 3.4 End-Limit Signals PEL and MEL
X Section 3.5 Ramping-down & Position latch signals
X Section 3.6 In-position signals INP
X Section 3.7 Alarm signal ALM
X Section 3.8 Deviation counter clear signal ERC
X Section 3.9 General-purpose signals SVON
X Section 3.10 General-purpose signal RDY
X Section 3.11 Position compare output pin: CMP
X Section 3.12 General-purpose DI
X Section 3.13 General-purpose DO
Signal Connections 17
Page 28

3.1 Pulse Output Signals OUT and DIR
There are 4 axis pulse output signals on the HSL-4XMO. For each
axis, two pairs of OUT and DIR signals are used to transmit the
pulse train and to indicate the direction. The OUT and DIR signals
can also be programmed as CW and CCW signal pairs. In this
section, the electrical characteristics of the OUT and DIR signals
are detailed. Each signal consists of a pair of differential signals.
For example, OUT2 consists of OUT2+ and OUT2- signals.
The following wiring diagram is for OUT and DIR signals on the 4
axes.
Figure 3-1: OUT and DIR Signals on the 4 Axes
Non-differential type wiring example:
Choose one of OUT/DIR+ and OUT/DIR- to connect to driver’s
OUT/DIR
18 Signal Connections
Page 29
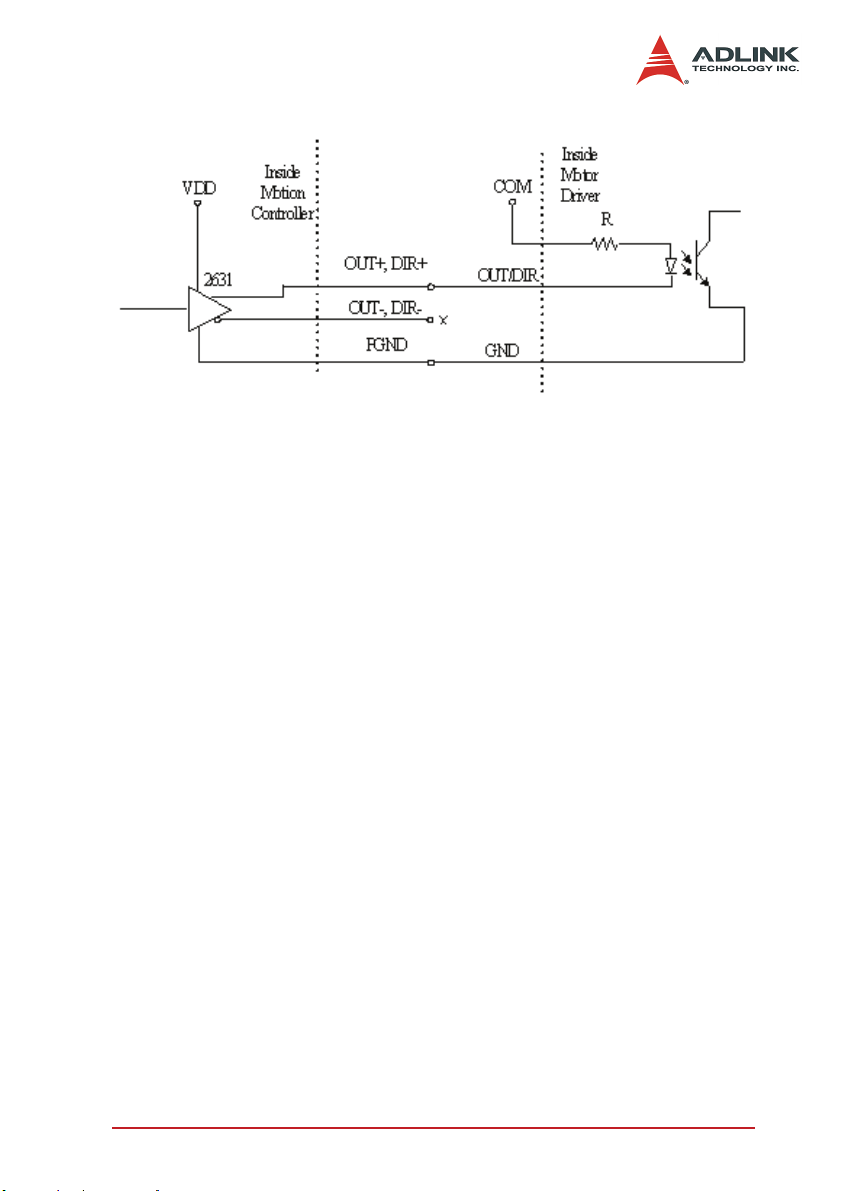
Figure 3-2: Non-differential Type Wiring Example
Warning: The sink current must not exceed 20mA or the 2631 will
be damaged!
Signal Connections 19
Page 30
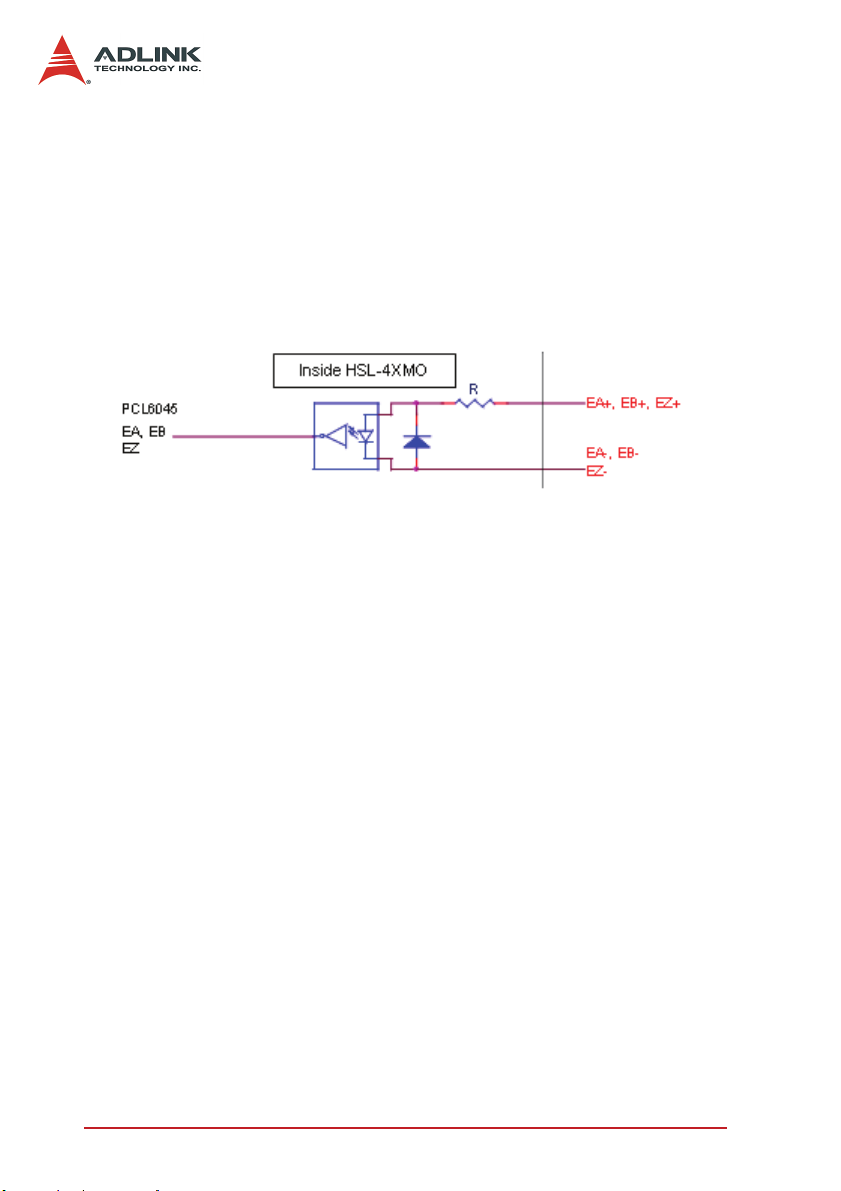
3.2 Encoder Feedback Signals EA, EB and EZ
The encoder feedback signals include EA, EB, and EZ. Every axis
has six pins for three differential pairs of phase-A (EA), phase-B
(EB), and index (EZ) inputs. EA and EB are used for position
counting, and EZ is used for zero position indexing.
The input circuit of the EA, EB, and EZ signals is shown as follows:
Figure 3-3: EA, EB, and EZ signals
Please note that the voltage across each differential pair of
encoder input signals (EA+, EA-), (EB+, EB-), and (EZ+, EZ-)
should be at least 3.5V. Therefore, the output current must be
observed when connecting to the encoder feedback or motor
driver feedback as not to over drive the source. The differential
signal pairs are converted to digital signals EA, EB, and EZ; then
feed to the PCL6045 ASIC (R=220ohm).
Below are examples of connecting the input signals with an external circuit. The input circuit can be connected to an encoder or
motor driver if it is equipped with: (1) a differential line driver or (2)
an open collector output.
Connection to Line Driver Output
To drive the HSL-4XMO encoder input, the driver output must provide at least 3.5V across the differential pairs with at least 6mA
driving capacity. The grounds of both sides must be tied together.
The maximum frequency will be 4Mhz or more depends on wiring
distance and signal conditioning.
20 Signal Connections
Page 31

Figure 3-4: Connection to Line Driver Output
Connection to Open Collector Output
To connect with an open collector output, an external power supply is necessary. Some motor drivers can provide the power
source. The connection between the HSL-4XMO, encoder, and
the power supply is shown in the diagram below. Note that an
external current limiting resistor R is necessary to protect the HSL4XMO input circuit. The following table lists the suggested resistor
values according to the encoder power supply.
Encoder Power (VDD) External Resistor R
+5V
+12V
+24V
Table 3-1: Encoder Power / External Resistor
X I
= 6mA max.
f
Signal Connections 21
0
Ω (None)
1.8kΩ
4.3kΩ
Page 32

Figure 3-5: Connection to Open Collector Output
For more operation information on the encoder feedback signals,
refer to section 4.9.
3.3 Origin Signal ORG
The origin signals (ORG1-ORG4) are used as input signals for the
origin of the mechanism.
The input circuit of the ORG signals is shown below. Usually, a
limit switch is used to indicate the origin on one axis. The specifications of the limit switch should have contact capacity of +24V @
6mA minimum. An internal filter circuit is used to filter out any high
frequency spikes, which may cause errors in the operation.
Figure 3-6: Origin Signal ORG
When the motion controller is operated in the home return mode,
the ORG signal is used to inhibit the control output signals (OUT
22 Signal Connections
Page 33

and DIR). For detailed operations of the ORG signal, refer to section 4.8.
3.4 End-Limit Signals PEL and MEL
There are two end-limit signals PEL and MEL for each axis. PEL
indicates the end limit signal is in the plus direction and MEL indicates the end limit signal is in the minus direction.
A circuit diagram is shown in the diagram below. The external limit
switch should have a contact capacity of +24V @ 6mA minimum.
Either ‘A-type’ (normal open) contact or ‘B-type’ (normal closed)
contact switches can be used. The type of switch can be configured by software. For more details on EL operation, refer to section 4.8.
Figure 3-7: End-Limit Signals PEL and MEL
3.5 Ramping-down & Position Latch
There is a SD/LTC signal for each of the 4 axes. A circuit diagram
is shown below. Typically, the limit switch is used to generate a
slow-down signal to drive motors operating at slower speeds.
While act as the LTC signal, it will trigger the counter-value-capturing functions, which provides a precise position determination. For
more details on SD/LTC operation, refer to section 4.8.
Signal Connections 23
Page 34

Figure 3-8: Ramping-down & Position Latch
3.6 In-position Signal INP
The in-position signal INP from a servo motor driver indicates its
deviation error. If there is no deviation error then the servo’s position indicates zero. The input circuit of the INP signals is shown in
the diagram below:
Figure 3-9: In-position Signal INP
The in-position signal is usually generated by the servomotor
driver and is ordinarily an open collector output signal. An external
circuit must provide at least 6mA current sink capabilities to drive
the INP signal. For more details of INP signal operations, refer to
section 4.7.
24 Signal Connections
Page 35

3.7 Alarm Signal ALM
The alarm signal ALM is used to indicate the alarm status from the
servo driver. The input alarm circuit is shown below. The ALM signal usually is generated by the servomotor driver and is ordinarily
an open collector output signal. An external circuit must provide at
least 6mA current sink capabilities to drive the ALM signal. For
more details of ALM signal operations, refer to section 4.7.
Figure 3-10: Alarm Signal ALM
3.8 Deviation Counter Clear Signal (ERC)
The deviation counter clear signal (ERC) is active in the following
4 situations:
1. Home return is complete
2. End-limit switch is active
3. An alarm signal stops OUT and DIR signals
4. An emergency stop command is issued by software
(operator)
The ERC signal is used to clear the deviation counter of the servomotor driver. The ERC output circuit is an open collector with a
maximum of 35V at 6mA driving capacity. For more details of ERC
operation, refer to section 4.7.
Signal Connections 25
Page 36

Figure 3-11: Deviation Counter Clear Signal (ERC)
3.9 General-purpose Signal SVON
The SVON signal can be used as a servomotor-on control or general- purposed output signal. The output circuit for the SVON signal is shown below:
Figure 3-12: General-purpose Signal SVON
3.10 General-purpose Signal RDY
The RDY signals can be used as motor driver ready input or general purpose input signals. The input circuit of RDY signal is
shown in the following diagram:
26 Signal Connections
Page 37

Figure 3-13: General-purpose Signal RDY
3.11 Position Compare Output CMP
The HSL-4XMO provides 4 comparison output channels. The
comparison output channel will generate a pulse signal when the
encoder counter reaches a pre-set value set by the user.
The following wiring diagram is of the CMP signals:
Figure 3-14: Position Compare Output CMP
Note: CMP trigger type can be set as normal low (rising edge) or
normal high (falling edge). Default setting is normal high.
3.12 Emergency Stop Input EMG
There is emergency stop input pin for this module. When EMG is
active, all the motion pulse output command will be rejected until
the EMG is deactive.
A circuit diagram is shown in the diagram below. The emergency
stop switch should have a contact capacity of +24V @ 6mA minimum. Either ‘A-type’ (normal open) contact or ‘B-type’ (normal
Signal Connections 27
Page 38

closed) contact switches can be used. The type of switch can be
configured by software.
Figure 3-15: Emergency Stop Input EMG
3.13 General-purpose Input
HSL-4XMO has 4 opto-isolated digital inputs for general-purposed
use. The following wiring diagrams are of these signals
Figure 3-16: General-purpose Input
3.14 General-purpose Output
HSL-4XMO has 4 opto-isolated digital outputs for general-purposed use. The following wiring diagrams are of these signals
28 Signal Connections
Page 39

NPN type general purpose Output (available in –N modules):
Figure 3-17: NPN Type General Purpose Output
PNP type general purpose Output (available in –P modules):
Figure 3-18: PNP Type General Purpose Output
Signal Connections 29
Page 40

30 Signal Connections
Page 41

4 Operation Theory
4.1 Communication Block Diagram
Figure 4-1: Communication Block Diagram
4.2 Host Command
Inside the HSL system, those remote modules communicate with
each other with HSL network packets. Actually, users do not have
to understand what the content of the packet is. Instead, we provide many kinds of API functions for controlling this module. They
are very easy to understand and to use.
Those APIs can analyze the parameters from user’s command
and pack them as HSL network packets. Next, the packets are
passed to the remote modules. Then, the remote modules will
interpret those packets and execute the commands correctly.
Before launching the packet, all the commands issued by users
are written into the dual port RAM and transferred on HSL network. Consequently, the dual port RAM is the bridge between HSL
master controller and host PC. The accessing time of dual port
RAM for one packet is about 600ns. It is quiet fast on host PC.
Furthermore, the delivering time of one command on network
depends on the number of modules and operating clock rate. A
complete command delivering time depends on the number of
HSL packets. Some APIs, which have much more parameters,
would need more packets and time for delivering. One packet
command could be delivered in one HSL scan (cycle) time.
Operation Theory 31
Page 42

4.3 Command Delivering Time
HSL-4XMO supports both full duplex and half duplex mode. In full
duplex mode, one module occupies 4 HSL slave IDs by two ID
number steps. For example, if the module start ID=1, then it occupies ID 1, 3, 5, 7. If having two slave modules, we suggest that the
second ID can be set at 2. Then, the second module would occupy
ID 2, 4, 6, 8.
In half duplex mode, the module occupies 4 HSL slave IDs by one
ID number step. For example, if the module start ID=1, then it
occupies ID 1, 2, 3, 4. If having two slave modules, we suggest
that the second ID can be set at 5. Then, the seoncd module occupies ID 5, 6, 7, 8.
Host command on PC is transferring via HSL protocol. The base
time for one ID at 6Mbps data transder rate is 30us. The more IDs
exist in HSL system, the more scan time is needed. For example,
one HSL-4XMO module occupies 4 IDs at full duplex mode. The
total scan (cycle) time would be 7 times base time (30.4us × 8).
Because it occupies ID1, 3, 5, and 7, it need time to scan from ID1
to ID7. Consequently, it would take 243.2 us.
The following figures show the timing of single command.
32 Operation Theory
Page 43

Figure 4-2: Single Command Timing
The base scan time table is as follows, N is the range of total IDs.
Half Duplex Full Duplex Maximum Length
3M 118 us x N 60.7 us x N 400 meters
6M 59 us x N 30.4 us x N 200 meters
12M 29.5 us x N 15.2 us x N 100 meters
Table 4-1: Base Scan Times
Operation Theory 33
Page 44

4.4 Command Dispatching in DSP
Command-dispatching task is executed by the DSP on the module. Once the DSP receives a new command, it will process this
command within the time less than the HSL scan time. The dispatching task includes the motion ASIC command, data downloading command, point table command and script program
downloading command.
The command-dispatching task is executed every HSL scan cycle.
It is real-time. While the DSP in idling, the other tasks, such as
position compare, point table motion, script motion, special speed
profile control and data monitoring are running at lower priority
than command dispatching.
The timing block diagram as follows shows the multi-tasks working
in DSP.
Figure 4-3: DSP Multi-Tasks
34 Operation Theory
Page 45

4.5 The role of DSP and motion ASIC
Motion control is executed by motion ASIC. DSP acts as a role to
execute the command dispatching, data management and motion
command sequecing. Motion ASIC is used for generating pulse
trains, position control, dedicated motion I/O control and so on.
There is no motion I/O scan time problem because the ASIC will
take care all of them.
4.6 Motion Control Modes
In this section, the pulse output signal configuration and the following motion control modes are described.
Pulse Command Output
The HSL-4XMO uses pulse commands to control servo/stepper
motors via the drivers. A pulse command consists of two signals:
OUT and DIR. There are two command types: (1) single pulse output mode (OUT/DIR), and (2) dual pulse output mode (CW/CCW
type pulse output). The software function,
HSL_M_set_pls_outmode(), is used to program the pulse command mode. The modes vs. signal type of OUT and DIR pins are
listed in the table below:
Mode Output of OUT pin Output of DIR pin
Dual pulse output (CW/CCW)
Single pulse output (OUT/DIR) Pulse signal
Pulse signal in plus
(or CW) direction
Pulse signal in minus
(or CCW) direction
Direction signal (level)
Table 4-2: Pulse Command Output
The interface characteristics of these signals can be differential
line driver or open collector output. Please refer to section 3.1 for
the jumper setting for different signal types.
Single Pulse Output Mode (OUT/DIR Mode)
In this mode, the OUT signal is for the command pulse (position or
velocity) chain. The numbers of OUT pulse represent the relative
“distance” or “position.” The frequency of the OUT pulse represents the command for “speed” or “velocity.” The DIR signal repre-
Operation Theory 35
Page 46

sents direction command of positive (+) or negative (-). This mode
is most commonly used. The diagrams below show the output
waveform. It is possible to set the polarity of the pulse chain.
Figure 4-4: Single Pulse Output Mode (OUT/DIR Mode)
Dual Pulse Output Mode (CW/CCW Mode)
In this mode, the waveform of the OUT and DIR pins represent
CW (clockwise) and CCW (counter clockwise) pulse output
respectively. Pulses output from the CW pin makes the motor
move in positive direction, whereas pulse output from the CCW
pin makes the motor move in negative direction. The following
diagram shows the output waveform of positive (+) commands
and negative (-) commands.
36 Operation Theory
Page 47

Figure 4-5: Dual Pulse Output Mode (CW/CCW Mode)
X Relative Function:
HSL_M_set_pls_outmode()
Velocity Mode Motion
This mode is used to operate a one-axis motor with Velocity mode
motion. The output pulse accelerates from a starting velocity
(StrVel) to a specified maximum velocity (MaxVel). The
HSL_M_tv_move() function is used for constant linear acceleration while the HSL_M_sv_move() function is use for acceleration
according to the S-curve. The pulse output rate is kept at maximum velocity until another velocity command is set or a stop command is issued. The HSL_M_v_change() is used to change the
speed during an operation. Before this function is applied, be sure
to call HSL_M_fix_speed_range(). Please refer to section 4.6 for
more detail explanation. The HSL_M_sd_stop() function is used to
decelerate the motion until it stops. The HSL_M_emg_stop() function is used to immediately stop the motion. These change or stop
functions follow the same velocity profile as its original move func-
Operation Theory 37
Page 48

tions, tv_move or sv_move. The velocity profile is shown as follows:
Note: The v_change and stop functions can also be applied to Pre-
set Mode or Home Mode (refer to 4.1).
Figure 4-6: Velocity Mode Motion
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_tv_move()
HSL_M_sv_move()
HSL_M_v_change()
HSL_M_sd_stop()
HSL_M_emg_stop()
HSL_M_fix_speed_range()
HSL_M_unfix_speed_range()
Trapezoidal Motion
This mode is used to move a singe axis motor to a specified position (or distance) with a trapezoidal velocity profile. The single axis
is controlled from point to point. An absolute or relative motion can
be performed. In absolute mode, the target position is assigned. In
relative mode, the target displacement is assigned. In both cases,
the acceleration and deceleration can be different. The function
HSL_M_motion_done() is used to check whether the movement is
complete.
The following diagram shows the trapezoidal profile:
38 Operation Theory
Page 49

Figure 4-7: Trapezoidal Motion
There are 2 trapezoidal point-to-point functions supported by the
HSL-4XMO. In the HSL_M_start_ta_move() function, the absolute
target position must be given in units of pulses. The physical
length or angle of one movement is dependent on the motor driver
and mechanism (including the motor). Since absolute move mode
needs the information of current actual position, the “External
encoder feedback (EA, EB pins)” should be set in
HSL_M_set_feedback_src() function. The ratio between command pulses and external feedback pulse input must be appropriately set by the HSL_M_set_move_ratio() function.
In the HSL_M_start_tr_move() function, the relative displacement
must be given in units of pulses. Unsymmetrical trapezoidal velocity profile (Tacc is not equal Tdec) can be specified with both
HSL_M_start_ta_move() and HSL_M_start_tr_move() functions.
The StrVel and MaxVel parameters are given in units of pulses per
second (PPS). The Tacc and Tdec parameters are in units of second to represent accel./decel. time respectively. Users need to
know the physical meaning of “one pulse” to calculate the physical
value of the relative velocity or acceleration parameters. The following formula gives the basic relationship between these parameters:
MaxVel = StrVel + accel*Tacc;
Operation Theory 39
Page 50

StrVel = MaxVel + decel *Tdec;
Where accel/decel represents the acceleration/deceleration rate in
units of pps/sec^2. The area inside the trapezoidal profile represents the moving distance.
Units of velocity setting are pulses per second (PPS). Usually,
units of velocity of the manual of motor or driver are in rounds per
minute (RPM). A simple conversion is necessary to match
between these two units. Here we use an example to illustrate the
conversion:
Example:
A servomotor with an AB phase encoder is used in a X-Y table.
The resolution of encoder is 2000 counts per phase. The maximum rotating speed of motor is designed to be 3600 RPM. What is
the maximum pulse command output frequency that you have to
set on HSL-4XMO?
Answer:
MaxVel = 3600/60*2000*4 = 480000 PPS
Multiplying by 4 is necessary because there are four states per AB
phase (See Figures in Section 4.4).
Usually, the axes need to set the move ratio if their mechanical
resolution is different from the resolution of command pulse. For
example, if an incremental encoder is mounted on the working
table to measure the actual position of moving part. A servomotor
is used to drive the moving part through a gear mechanism. The
gear mechanism is used to convert the rotating motion of the
motor into linear motion (see the following diagram). If the resolution of the motor is 8000 pulses/round, then the resolution of the
gear mechanism is 100 mm/round (i.e., part moves 100 mm if the
motor turns one round). Then, the resolution of the command
pulse will be 80 pulses/mm. If the resolution of the encoder mounting on the table is 200 pulses/mm, then users have to set the
move ratio to 200/80=2.5 using the function
HSL_M_set_move_ratio (axis, 2.5).
40 Operation Theory
Page 51

Figure 4-8: Encoder Diagram
If this ratio is not set before issuing the start moving command, it
will cause problems when running in “Absolute Mode” because the
HSL-4XMO won’t recognize the actual absolute position during
motion.
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_start_ta_move()
HSL_M_start_tr_move()
HSL_M_motion_done()
HSL_M_set_feedback_src()
HSL_M_set_move_ratio()
S-curve Profile Motion
This mode is used to move a single-axis motor to a specified position (or distance) with a S-curve velocity profile. S-curve acceleration profiles are useful for both stepper and servomotors. The
smooth transitions between the start of the acceleration ramp and
transition to constant velocity produce less wear and tear than a
trapezoidal profile motion. The smoother performance increases
the life of the motor and the mechanics of the system.
Operation Theory 41
Page 52

There are several parameters that need to be set in order to make
a S-curve move. They are:
X Pos: target position in absolute mode, in units of pulses
X Dist: moving distance in relative mode, in units of pulses
X StrVel: start velocity, in units of PPS
X MaxVel: maximum velocity, in units of PPS
X Tacc: time for acceleration (StrVel -> MaxVel), in units of
seconds
X Tdec: time for deceleration (MaxVel -> StrVel), in units of
seconds
X VSacc: S-curve region during acceleration, in units of PPS
X VSdec: S-curve region during deceleration, in units of PPS
Figure 4-9: S-curve Profile Motion
Normally, the accel/decel period consists of three regions, two
VSacc/VSdec curves and one linear. During VSacc/VSdec, the
jerk (second derivative of velocity) is constant, and, during the linear region, the acceleration (first derivative of velocity) is constant.
In the first constant jerk region during acceleration, the velocity
goes from StrVel to (StrVel + VSacc). In the second constant jerk
region during acceleration, the velocity goes from (MaxVel –
StrVel) to MaxVel. Between them, the linear region accelerates
42 Operation Theory
Page 53

velocity from (StrVel + VSacc) to (MaxVel - VSacc) constantly. The
deceleration period is similar in fashion.
Note: If user wants to disable the linear region, the VSacc/VSdec
must be assigned “0” rather than “0.5” (MaxVel-StrVel).
Remember that the VSacc/VSdec is in units of PPS and it should
always keep in the range of [0 to (MaxVel - Strvel)/2 ], where “0”
means no linear region.
The S-curve profile motion functions are designed to always produce smooth motion. If the time for acceleration parameters combined with the final position don’t allow an axis to reach the
maximum velocity (i.e. the moving distance is too small to reach
MaxVel), then the maximum velocity is automatically lowered (see
the following figure).
The rule is to lower the value of MaxVel and the Tacc, Tdec,
VSacc, VSdec automatically, and keep StrVel, acceleration, and
jerk unchanged. This is also applicable to Trapezoidal profile
motion.
Figure 4-10: Automatic Velocity Decrease
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_start_sr_move()
HSL_M_start_sa_move()
HSL_M_motion_done()
HSL_M_set_feedback_src()
HSL_M_set_move_ratio()
Operation Theory 43
Page 54

The Following table shows the differences between all single axis
motion functions, including preset mode (both trapezoidal and Scurve motion) and constant velocity mode.
Velocity Profile
Trapezoidal S-Curve Relative Absolute
HSL_M_tv_move Y ----------- -----------
HSL_M_sv_move Y ----------- -----------
HSL_M_v_change Y Y ----------- -----------
HSL_M_sd_stop Y Y ----------- -----------
HSL_M_emg_stop() ----------- ------------ ----------- -----------
HSL_M_start_ta_move Y Y
HSL_M_start_sa_move Y Y
HSL_M_start_tr_move Y Y
HSL_M_start_sr_move Y Y
Table 4-3: Single Axis Motion Functions
Linear interpolation for 2-4 axes
In this mode, any 2 of the 4, 3 of the 4, or all 4 axes may be chosen to perform linear interpolation. “Interpolation between multiaxes” means these axes start simultaneously, and reach their ending points at the same time. Linear means the ratio of speed of
every axis is a constant value.
Note that you cannot use 2 groups of 2 axes for linear interpolation
on a single card at the same time. You can however, use one 2axis linear and one 2-axis circular interpolation at the same time. If
you want to stop an interpolation group, the function
HSL_M_sd_stop() or HSL_M_emg_stop() can be used.
2 Axes Linear Interpolation
As in the diagram below, 2-axis linear interpolation means to move
the XY position (or any 2 of the 4 axis) from P0 to P1. The 2 axes
start and stop simultaneously, and the path is a straight line.
44 Operation Theory
Page 55

Figure 4-11: 2 Axes Linear Interpolation
The speed ratio along X-axis and Y-axis is (ΔX: ΔY), respectively,
and the vector speed is:
When calling 2-axis linear interpolation functions, the vector speed
needs to define the start velocity, StrVel, and maximum velocity,
MaxVel. Both trapezoidal and S-curve profiles are available.
Example:
HSL_M_start_tr_move_xy(0, 30000.0, 40000.0, 1000.0, 5000.0,
0.1, 0.2) will cause the XY axes (axes 0 & 1) of Card 0 to perform
a linear interpolation movement, in which:
ΔX = 30000 pulses; ΔY = 40000 pulses
Start vector speed = 1000pps, X speed=600pps, Y
speed = 800pps
Max. vector speed = 5000pps, X speed=3000pps, Y
speed = 4000pps
Acceleration time = 0.1sec; Deceleration time =
0.2sec
There are two groups of functions that provide 2-axis linear interpolation. The first group divides the 4 axes into XY (axis 0 & axis
1) and ZU (axis 2 & axis 3). By calling these functions, the target
axes are already assigned.
HSL_M_start_tr_move_xy()
HSL_M_start_tr_move_zu()
HSL_M_start_ta_move_xy(
Operation Theory 45
Page 56

HSL_M_start_ta_move_zu()
HSL_M_start_sr_move_xy()
HSL_M_start_sr_move_zu()
HSL_M_start_sa_move_xy()
HSL_M_start_sa_move_zu()
The second group allows user to freely assign the 2 target axes.
HSL_M_start_tr_line2()
HSL_M_start_sr_line2()
HSL_M_start_ta_line2()
HSL_M_start_sa_line2()
The characters “t”, “s”, “r”, and “a” after HSL_M_start mean:
X t – Trapezoidal profile
X s – S-Curve profile
X r – Relative motion
X a – Absolute motion
3-Axis Linear Interpolation
Any 3 of the 4 axes of the HSL-4XMO may perform 3-axis linear
interpolation. As shown the figure below, 3-axis linear interpolation
means to move the XYZ (if axes 0, 1, 2 are selected and assigned
to be X, Y, Z respectively) position from P0 to P1, starting and
stopping simultaneously. The path is a straight line in space.
Figure 4-12: 3-Axis Linear Interpolation
46 Operation Theory
Page 57

The speed ratio along X-axis, Y-axis, and Z-axis is (ΔX: ΔY: ΔZ),
respectively, and the vector speed is:
When calling 3-axis linear interpolation functions, the vector speed
is needed to define the start velocity, StrVel, and maximum velocity, MaxVel. Both trapezoidal and S-curve profiles are available.
Example:
HSL_M_start_tr_line3(….,1000.0 /*ΔX */ , 2000.0/
ΔY */, 3000.0 /*DistZ*/, 100.0 /*StrVel*/,
*
5000.0 /* MaxVel*/, 0.1/*sec*/, 0.2 /*sec*/)
ΔX = 1000 pulse; ΔY = 2000 pulse; ΔZ = 3000 pulse
Start vector speed=100pps,X speed = 100/ =
26.7pps
Y speed = 2*100/ = 53.3pps
Z speed = 3*100/ = 80.1pps
Max. vector speed =5000pps,X speed= 5000/ =
1336pps
Y speed = 2*5000/ = 2672pps
Z speed = 3*5000/ = 4008pps
The following functions are used for 3-axis linear interpolation:
HSL_M_start_tr_line3()
HSL_M_start_sr_line3()
HSL_M_start_ta_line3()
HSL_M_start_sa_line3()
The characters “t”, “s”, “r”, and “a” after HSL_M_start mean:
X t – Trapezoidal profile
X s – S-Curve profile
X r – Relative motion
X a – Absolute motion
4-axis Linear Interpolation
With 4-axis linear interpolation, the speed ratio along X-axis, Yaxis, Z-axis and U-axis is (
vector speed is:
ΔX: ΔY: ΔZ: ΔU), respectively, and the
Operation Theory 47
Page 58

The following functions are used for 4-axis linear interpolation:
HSL_M_start_tr_line4()
HSL_M_start_sr_line4()
HSL_M_start_ta_line4()
HSL_M_start_sa_line4()
The characters “t”, “s”, “r”, and “a” after HSL_M_start mean:
X t – Trapezoidal profile
X s – S-Curve profile
X r – Relative motion
X a – Absolute motion
Circular interpolation for 2 axes
Any 2 of the 4 axes of the HSL-4XMO can perform circular interpolation. In the example below, circular interpolation means XY (if
axes 0, 1 are selected and assigned to be X, Y respectively) axes
simultaneously start from initial point, (0,0) and stop at end
point,(1800,600). The path between them is an arc, and the MaxVel is the tangential speed.
Figure 4-13: Circular interpolation for 2 axes
Example:
HSL_M_start_a_arc_xy(0 /*card No*/, 1000,0 /
*center X*/, 0 /*center Y*/, 1800.0 /* End X
*/, 600.0 /*End Y */ ,1000.0 /* MaxVel */)
48 Operation Theory
Page 59

To specify a circular interpolation path, the following parameters
must be clearly defined:
X Center point: The coordinate of the center of arc (In abso-
lute mode) or the off_set distance to the center of arc (In relative mode)
X End point: The coordinate of end point of arc (In absolute
mode) or the off_set distance to center of arc (In relative
mode)
X Direction: The moving direction, either CW or CCW.
It is not necessary to set radius or angle of arc, since the information above gives enough constrains. The arc motion is stopped
when either of the 2 axes reached end point.
There are two groups of functions that provide 2-axis circular interpolation. The first group divides the 4 axes into XY (axis 0 & axis
1) and ZU (axis 2 & axis 3). By calling these functions, the target
axes are already assigned.
HSL_M_start_r_arc_xy()
HSL_M_start_r_ arc _zu()
HSL_M_start_a_ arc _xy()
HSL_M_start_a_ arc _zu()
The second group allows user to freely assign any targeted 2
axes.
HSL_M_start_r_arc2()
HSL_M_start_a_arc2()
Circular Interpolation with Acc/dec Time
In section 4.1, the circular interpolation functions do not support
acceleration and deceleration parameters; therefore, they cannot
perform a T or S curve speed profile during operation. However,
sometimes the need for an Acc/Dec time speed profile will help a
machine to make more accurate circular interpolation. The HSL4XMO has another group of circular interpolation functions to perform this type of interpolation, but requires the use of Axis3 as an
aided axis, which means that Axis3 cannot be used for other purposes while running these functions. For example, to perform a
circular interpolation with a T-curve speed profile, the function
HSL_M_start_tr_arc_xyu() is used. This function will used Axis0
Operation Theory 49
Page 60

and Axis1, and also Axis3 (Axis0=x, Axis1=y, Axis2=z, Axis3=u).
For the full lists of functions.
To check if the board supports these functions use the
HSL_M_version_info() function. If hardware information for the
card returns a value with the 4th digit greater then 0, for example
'1003', users can use this group of circular interpolation to perform
S or T-curve speed profiles. If the hardware version returns a
value with the 4th digit being 0, then that board does not support
these functions.
Figure 4-14: Circular Interpolation with Acc/dec Time
Relationship between Velocity and Acceleration Time
The maximum velocity parameter of a motion function will eventually have a minimum acceleration value. This means that there is a
range for acceleration time over one velocity value. Under this
relationship, to obtain a small acceleration time, a higher maximum velocity value to match the smaller acceleration time is
required. Function HSL_M_fix_speed_range() will provide such
operation. This function will raise the maximum velocity value,
which in turn results in a smaller acceleration time. Note it does
not affect the actual end velocity. For example, to have a 1ms
acceleration time from a velocity of 0 to 5000(pps), the function
can be inserted before the motion function as shown.
HSL_M_fix_speed_range(AxisNo,OverVelocity);
HSL_M_start_tr_move(AxisNo,5000,0,5000,0.001,0.0
01);
50 Operation Theory
Page 61

Figure 4-15: Velocity and Acceleration Time A
How do users decide an optimum value for “OverVelocity” in the
HSL_M_fix_speed_range() function? The HSL_M_verify_speed()
function is provided to calculate such value. The inputs to this
function are the start velocity, maximum velocity and over velocity
values. The output value will be the minimum and maximum values of the acceleration time.
For example, if the original acceleration range for the command is:
HSL_M_start_tr_move(AxisNo,5000,0,5000,0.001,0.0
01),
then use the following function:
HSL_M_verify_speed(0,5000,&minAccT,
&maxAccT,5000);
The value miniAccT will be 0.0267sec and maxAccT will be
873.587sec. This minimum acceleration time does not meet the
requirement of 1mS. To achieve such a low acceleration time the
over speed value must be used.
By changing the OverVelocity value to 140000,
Operation Theory 51
Page 62

HSL_M_verify_speed(0,5000,&minAccT,
&maxAccT,140000);
The value miniAccT will be 0.000948sec and maxAccT will be
31.08sec. This minimum acceleration time meets the requirements. So, the motion command can be changed to:
HSL_M_fix_speed_range(AxisNo,140000);
HSL_M_start_tr_move(AxisNo,5000,0,5000,0.001,0.0
01);
Note: The return value of HSL_M_verify_speed() is the minimum
velocity of motion command, it does not always equal to your
start velocity setting. In the above example, it will be 3pps
more than the 0pps setting.
To disable the fix speed function HSL_M_fix_speed_range()
use HSL_M_unfix_speed_range()
Minimize the use of the OverVelocity operation. The more it
is used, the coarser the speed interval is.
Figure 4-16: Velocity and Acceleration Time B
Example:
User’s Desired Profile: (MaxV2, Target T) is not possible under
MaxV2 according to the (MaxV, MiniT) relationship. So one must
52 Operation Theory
Page 63

change the (MaxV, MiniT) relationship to a higher value, (MaxV1,
MiniT1). Finally, the command would be:
HSL_M_fix_speed_range(AxisNo, MaxV1);
HSL_M_start_tr_move(AxisNo,Distance, 0 , MaxV2 ,
Target T, Target T);
Relative Functions:
HSL_M_fix_speed_range()
HSL_M_unfix_speed_range()
HSL_M_verify_speed()
Home Return Mode
In this mode, the HSL-4XMO is allowed to continuously output
pulses until the condition to complete the home return is satisfied
after writing the command HSL_M_home_move(). There are 13
home moving modes provided by the HSL-4XMO. The
“home_mode” of function HSL_M_set_home_config() is used to
select whichever mode is preferred.
After completion of home move, it is necessary to keep in mind
that all related position information should be reset to be “0.” The
HSL-4XMO has 4 counters and 1 software-maintained position
recorder. They are:
X Command position counter: counts the number of pulse out-
puts
X Feedback position counter: counts the number of pulse
inputs
X Position error counter: counts the error between command
and feedback pulse numbers.
X General-Purpose counter: can be configured as pulse out-
put, feedback pulse, manual pulse, or CLK/2.
X Target position recorder: records the target position.
Refer to section 4.4 for a more detailed explanation about position
counters.
After home move is complete, the first four counters will be cleared
to “0” automatically, however, the target position recorder will not.
Because it is software maintained, it is necessary to manually set
Operation Theory 53
Page 64

the target position to “0” by calling the function
HSL_M_reset_target_pos().
The following figures show the various home modes and the reset
points, when the counter is cleared to “0.”
home_mode=0: ORG -> Slow down -> Stop
X When SD (Ramp-down signal) is inactive.
Figure 4-17: home_mode=0
home_mode=1: ORG -> Slow down -> Stop at end of ORG
X When SD (Ramp-down signal) is active.
54 Operation Theory
Page 65

Figure 4-18: home_mode=1
home_mode=3: ORG -> EZ -> Slow down -> Stop
Figure 4-19: home_mode=3
Operation Theory 55
Page 66

home_mode=4: ORG -> Slow down -> Go back at FA speed ->
EZ -> Stop
Figure 4-20: home_mode=4
home_mode=5: ORG -> Slow down -> Go back ->? Accelerate
to MaxVel -> EZ -> Slow down -> Stop
56 Operation Theory
Page 67

Figure 4-21: home_mode=5
home_mode=6: EL only
Figure 4-22: home_mode=6
home_mode=7: EL -> Go back -> Stop on EZ signal
Figure 4-23: home_mode=7
Operation Theory 57
Page 68

home_mode=8: EL -> Go back -> Accelerate to MaxVel -> EZ > Slow down -> Stop
Figure 4-24: home_mode=8
home_mode=9: ORG -> Slow down -> Go back -> Stop at
beginning edge of ORG
Figure 4-25: home_mode=9
58 Operation Theory
Page 69

home_mode=10: ORG -> EZ -> Slow down -> Go back -> Stop
at beginning edge of EZ
Figure 4-26: home_mode=10
home_mode=11: ORG -> Slow down -> Go back (backward) ->
Accelerate to MaxVel -> EZ -> Slow down -> Go back again
(forward) -> Stop at beginning edge of EZ
Operation Theory 59
Page 70

Figure 4-27: home_mode=11
home_mode=12: EL -> Stop -> Go back (backward) -> Accelerate to MaxVel -> EZ -> Slow down -> Go back again (forward) -> Stop at beginning edge of EZ
Figure 4-28: home_mode=12
60 Operation Theory
Page 71

Home Search Example (Home mode=1)
Figure 4-29: Home Search Example
Operation Theory 61
Page 72

Moving Steps
1. Home searching start (-)
2. –EL touches, slow down and reverse moving (+)
3. ORG touches, slow down
4. Escape from ORG according to ORG offset
5. Start searching again (-)
6. ORG touches, slow down then using searching speed to
escape ORG (+)
7. After escape ORG, search ORG with search speed
again (-)
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_home_config()
HSL_M_home_move()
HSL_M_home_search()
62 Operation Theory
Page 73

4.7 The Motor Driver Interface
The HSL-4XMO provides the INP, ALM, ERC, SVON, and RDY
signals for a servomotor driver control interface. The INP and ALM
are used for feedback of the servo driver status, ERC is used to
reset the servo driver’s deviation counter under special conditions,
VON is a general purpose output signal, and RDY is a general
purpose input signal. The meaning of “general purpose” is that the
processing of the signal is not a build-in procedure of the hardware. The hardware processes INP, ALM, and ERC signals
according to pre-defined rules. For example, when receiving ALM
signal, the HSL-4XMO stops or decelerate to stop output pulses
automatically. However, SVON and RDY are not the case, they
actually act like common I/O’s.
INP
The processing of the INP signal is a hardware build-in procedure,
and it is designed to cooperate with the in-position signal of the
servomotor driver.
Usually, servomotor drivers with a pulse train input has a deviation
(position error) counter to detect the deviations between the input
pulse command and feedback counter. The driver controls the
motion of the servomotor to minimize the deviation until it
becomes 0. Theoretically, the servomotor operates with some time
delay from the command pulses. Likewise, when the pulse generator stops outputting pulses, the servomotor does not stop immediately but keeps running until the deviation counter is zero. Only
after stopping does the servo driver send out the in-position signal
(INP) to the pulse generator to indicate the motor has stopped running.
Normally the HSL-4XMO stops outputting pulses upon completion
of outputting designated pulses. However, by setting parameter
inp_enable with the HSL_M_set_inp() function, the delay in completion of the motion to the time the INP signal is issued can be
adjusted, i.e., the motor arrives at the target position. Status of
HSL_M_motion_done() and INT signal are also delayed. That is,
when performing under position control mode, the completion of
HSL_M_start_ta_move(), HSL_M_start_sr_move(), etc, is delayed
until the INP signal is issued.
Operation Theory 63
Page 74

The in-position function can be enabled or disabled, and the input
logic polarity is also programmable by the “inp_logic” parameter of
HSL_M_set_inp(). The INP signal status can be monitored by
software with the function: HSL_M_get_io_status().
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_inp()
HSL_M_get_io_status()
HSL_M_motion_done()
ALM
The processing of the ALM signal is a hardware build-in procedure, and it is designed to interact with the alarm signal of the servomotor driver.
The ALM signal is an output signal from servomotor driver. Usually, it is designated to indicate when something is wrong with the
driver or motor.
The ALM pin receives the alarm signal output from the servo
driver. The signal immediately stops the HSL-4XMO from generating any further pulses or stops it after deceleration. If the ALM signal is in the ON status at the start of an operation, the HSL-4XMO
will generate the INT signal and thus not generate any command
pulses. The ALM signal may be a pulse signal with a minimum
time width of 5 microseconds.
Setting the parameters “alm_logic” and “alm_mode” of the
HSL_M_set_alm function can alter the input logic of the ALM.
Whether or not the HSL-4XMO is generating pulses, the ALM signal allows the generation of the INT signal. The ALM status can
be monitored by using the software function:
HSL_M_get_io_status().
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_alm()
HSL_M_get_io_status()
ERC
The ERC signal is an output from the HSL-4XMO. The processing
of the ERC signal is a hardware build-in procedure, and it is
64 Operation Theory
Page 75

designed to interact with the deviation counter clear signal of the
servomotor driver.
The deviation counter clear signal is inserted in the following 4 situations:
1. Home return is complete
2. The end-limit switch is active
3. An alarm signal stops the OUT and DIR signals
4. The software operator issues an emergency stop com-
mand
Since the servomotor operates with some delay from the pulse
generated from the HSL-4XMO, it continues to move until the
deviation counter of the driver is zero even if the HSL-4XMO has
stopped outputting pulses because of the ?EL signal or the completion of home return. The ERC signal allows immediate stopping
of the servomotor by resetting the deviation counter to zero. The
ERC signal is outputted as a one-shot signal. The pulse width is of
time length defined by the function call HSL_M_set_erc(). The
ERC signal will automatically be generated when the ?EL and
ALM signal are turned on and the servomotor is stopped immediately.
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_erc()
SVON and RDY
All axes of the HSL-4XMO are equipped with SVON and RDY signals, which are general purpose output and input channels,
respectively. Usually, the SVON is used to interact with the servomotor drivers as a Servo ON command, and RDY to receive the
Servo Ready signal. There are no built-in procedures for SVON
and RDY.
The SVON signal is controlled by the software function
HSL_M_Set_Servo().
RDY pins are dedicated for digital input usage. The status of this
signal can be monitored using the software function
HSL_M_get_io_status().
Operation Theory 65
Page 76

X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_Set_Servo()
HSL_M_get_io_status()
4.8 The Limit Switch Interface and I/O Status
In this section, the following I/O signal operations are described.
X SD/PCS: Ramping Down & Position Change sensor
X ±EL: End-limit sensor
X ORG: Origin position
In any operation mode, if an ?EL signal is active during any moving condition, it will cause the HSL-4XMO to stop automatically
outputting pulses. If an SD signal is active during moving conditions, it will cause the HSL-4XMO to decelerate. If operating in a
multi-axis mode, it automatically applies to all related axes.
SD/LTC
SD/LTC signal pins are available for each axis and acts as the
input channel. It can be connected to a SD (Slow Down) or Position Latch (LTC).
This input pin is inside connected to both slow down function and
latch function. Users can control the slow down function to be
active or not. But the latch function is always turned on without any
problem. Care must be taken with the logic attributes of the signal
not being used.
The slow-down signals are used to force the output pulse (OUT
and DIR) to decelerate to and then maintain the StrVel when it is
active. The StrVel is usually smaller than MaxVel. This signal is
useful in protecting a mechanism moving under high speeds
toward the mechanism’s limit. SD signal is effective for both plus
and minus directions.
The ramping-down function can be enabled or disabled using the
software function HSL_M_set_sd(). The input logic polarity, level
operation mode, or latched input mode can also be set by this
function. The signal status can be monitored using
HSL_M_get_io_status().
66 Operation Theory
Page 77

The latch function is used to capture values on all 4 counters (refer
to section 4.4) at the instant the latch signal is activated.
The latched data can be read by the function
HSL_M_get_latch_data(). The latch logic can be set by the function HSL_M_set_ltc_logic().
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_sd()
HSL_M_get_io_status()
HSL_M_set_ltc_logic()
HSL_M_get_latch_data()
EL
The end-limit signal is used to stop the control output signals (OUT
and DIR) when the end-limit is active. There are two possible stop
modes, “stop immediately” and “decelerate to StrVel then stop.” To
select either mode use HSL_M_set_el().
The PEL signal indicates the end-limit in the positive (plus) direction. MEL signal indicates the end-limit in negative (minus) direction. When the output pulse signals (OUT and DIR) is towards the
positive direction, the pulse train will be immediately stopped when
the PEL signal is asserted, where the MEL signal is meaningless,
and vise versa. When the PEL is asserted, only a negative
(minus) direction output pulse can be generated when moving the
motor in a negative (minus) direction.
The logic of EL is programmable. You can use
HSL_M_set_el_logic() to set is as normal open or normal close
mode. The signal status can be monitored using the software function HSL_M_get_io_status().
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_el():
HSL_M_get_io_status()
HSL_M_set_el_logic()
ORG
The ORG signal is used when the motion controller is operating in
the home return mode. There are 13 home return modes (Refer to
section 4.1.8), any one of 13 modes cam be selected using
Operation Theory 67
Page 78

“home_mode” argument in the function
HSL_M_set_home_config(). The logic polarity of the ORG signal
level or latched input mode is also selectable using this function as
well.
After setting the configuration for the home return mode with
HSL_M_set_home_config(), the HSL_M_home_move() command can perform the home return function.
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_home_config(), HSL_M_home_move()
4.9 The Counters
There are four counters for each axis of the HSL-4XMO. They are
described in this section:
X Command position counter: counts the number of output
pulses
X Feedback position counter: counts the number of input
pulses
X Position error counter: counts the error between command
and feedback pulse numbers.
X General-purpose counter: The source can be configured as
pulse output, feedback pulse, manual pulse, or CLK/2.
Also, the target position recorder, a software-maintained position
recorder, is discussed.
Command Position Counter
The command position counter is a 28-bit binary up/down counter.
its input source is the output pulse from the HSL-4XMO, thus, it
provides accurate information of the current position. Note: the
command position is different from target position. The command
position increases or decreases according to the pulse output,
while the target position changes only when a new motion command has been executed. The target position is recorded by the
software, and needs manually resetting after a home move is completed.
The command position counter will clear (reset to “0”) automatically after a home move has completed. The function
68 Operation Theory
Page 79

HSL_M_set_command() can be executed at any time to set a new
command position value. To read current command position use
HSL_M_get_command().
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_command(), HSL_M_get_command():
Feedback Position Counter
The HSL-4XMO has a 28-bit binary up/down counter managing
the present position feedback for each axis. The counter counts
signal inputs from the EA and EB pins.
It accepts 2 kinds of pulse inputs: (1). Plus and minus pulse inputs
(CW/CCW mode). (2). 90° phase shifted signals (AB phase
mode). 90° phase shifted signals maybe multiplied by a factor of 1,
2 or 4. 4x AB phase mode is the most commonly used in incremental encoder inputs. For example, if a rotary encoder has 2000
pulses per phase (A or B phase), then the value read from the
counter will be 8000 pulses per turn or –8000 pulses per turn
depending on its rotating direction. These input modes can be
selected using the HSL_M_set_pls_iptmode() function.
In cases where the application has not implemented an encoder, it
is possible to set the feedback counter source to generate the output pulses, just as with the command counter. Thus, the feedback
counter and the command counter will have the same value. To
enable the counters to count the number of pulses inputted, set
the “Src” parameter of the software function
HSL_M_set_feedback_src() to “1.”
Plus and Minus Pulses Input Mode (CW/CCW Mode)
The pattern of pulses in this mode is the same as the Dual Pulse
Output Mode in the Pulse Command Output section; except that
the input pins are EA and EB.
In this mode, pulses from EA cause the counter to count up,
whereas EB caused the counter to count down.
90° Phase Difference Signals Input Mode (AB phase Mode)
In this mode, the EA signal is a 90° phase leading or lagging in
comparison with the EB signal. “Lead” or “lag” of phase difference
between two signals is caused by the turning direction of the
Operation Theory 69
Page 80

motor. The up/down counter counts up when the phase of EA signal leads the phase of EB signal.
The following diagram shows the waveform.
Figure 4-30: 90° Phase Difference Signals
The index input (EZ) signals of the encoders are used as the
“ZERO” reference. This signal is common on most rotational
motors. EZ can be used to define the absolute position of the
mechanism. The input logic polarity of the EZ signals is programmable using software function HSL_M_set_home_config(). The
EZ signals status of the four axes can be monitored by
get_io_status().
The feedback position counter will be automatically cleared to “0”
after a home move is complete. Besides setting a position with the
function call, HSL_M_set_position(), it can also be executed at
any time to set a new position value. To read the current command
position use HSL_M_get_position().
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_pls_iptmode()
HSL_M_set_feedback_src()
HSL_M_set_position()
HSL_M_get_position()
HSL_M_set_home_config()
70 Operation Theory
Page 81

Position Error Counter
The position error counter is used to calculate the error between
the command position and the feedback position. It will add one
count when the HSL-4XMO outputs one pulse and subtracts one
count when the HSL-4XMO receives one pulse (from EA, EB). It is
useful in detecting step-loses (stalls) in situations of a stepping
motor when an encoder is applied.
Since the position error counter automatically calculates the difference between pulses outputted and pulses fed back, it is inevitable to get an error if the motion ratio is not equal to “1.”
To obtain a position error reading, use the function call
HSL_M_get_error_counter(). To reset the position error counter,
use the function call HSL_M_reset_error_counter(). The position
error counter will automatically clear to “0” after home move is
complete.
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_get_error_counter()
HSL_M_reset_error_counter():
General Purpose Counter
The general purpose counter is very versatile. It can be any of the
following:
1. Pulse output – as a command position counter
2. Pulse input – as a feedback position counter
3. Manual Pulse input – Default status.
4. Clock – an accurate timer (9.8 MHz)
The default setting of the general purpose counter is set to manual
pulse. (Refer to section 4.1.9 for a detailed explanation of manual
pulsing). To change the source type, use the function
HSL_M_set_general_counter(). To obtain the counter status, use
the function HSL_M_get_general_counter().
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_general_counter()
HSL_M_get_general_counter()
Operation Theory 71
Page 82

The table below summarizes all functions used for the different
counter types
Counter Description
Counts the
Command
Feedback
Position error
General Purpose
number of
output pulses
Counts the
number of
input pulses
Counts the
error between
command
and feedback
pulse
General pur-
pose counter
Target Position Recorder
Counter
Source
Pulse output
EA/EB or
Pulse output
EA/EB and
Pulse output
Pulse output EA/EB
manual
pulse CLK/2
HSL_M_reset_error_counter
HSL_M_set_general_counter
HSL_M_get_general_counter
Function
HSL_M_set_command
HSL_M_get_command
HSL_M_set_pls_iptmode
HSL_M_set_feedback_src
HSL_M_set_position
HSL_M_get_position
HSL_M_get_error_counter
Table 4-4: Counter Summary
Function
Description
Set a new value for com-
mand position
Read current command
position
Select the input modes
of EA/EB
Set the counters input
source
Set a new value for feed-
back position
Read current feedback
position:
Gets the position error
Resets the position error
counter
Set a new counter value
Read current counter
value
The target position recorder is used for providing target position
information. For example, if the HSL-4XMO is operating in continuous motion with absolute mode, the target position lets the next
absolute motion know the target position of previous one.
It is very important to understand how the software handles the
target position recorder. Every time a new motion command is
executed, the displacement is automatically added to the target
position recorder. To ensure the correctness of the target position
recorder, users need to manually maintain it in the following two
situations using the function HSL_M_reset_target_pos():
72 Operation Theory
Page 83

1. After a home move completes
2. After a new feedback position is set
X Relative Function:
HSL_M_reset_target_pos()
4.10 Multiple HSL-4XMO Operations
The software function library can support a maximum of 16 HSL4XMO modules in one HSL set. This means up to 63 motors(maximum axes) can be connected.
When multiple modules are used, the order of axes number is
from low to high and each module takes four axis number.
Table 4-5: Multiple HSL-4XMO Operations
Example:
To accelerate CM3 of module 2 from 0 to 10000pps in 0.5sec for
Constant Velocity Mode operation, the axis number is 6, and the
code for the program will be:
HSL_M_start_tv_move(6, 0, 10000, 0.5);
Operation Theory 73
Page 84

4.11 Change Position Or Speed On The Fly
The HSL-4XMO provides the ability to change position or speed
while an axis is moving. Changing speed/position on the fly means
that the target speed/position can be altered after the motion has
started. However, certain limitations do exist. Carefully study all
constraints before implementing the on-the-fly function.
Change Speed on the Fly
Figure 4-31: Change Speed on the Fly
The change speed on the fly function is applicable on single axis
motion only. Both velocity mode motion and position mode motion
are acceptable. The graph above shows the basic operating theory.
The following functions are related to changing speed on the fly.
HSL_M_v_change() – change the MaxVel on the fly
HSL_M_cmp_v_change() –change velocity when the
general comparator comes into existence
HSL_M_sd_stop() – slow down to stop
HSL_M_emg_stop() – immediately stop
HSL_M_fix_speed_range() – define the speed range
HSL_M_unfix_speed_range() – release the speed
range constrain
74 Operation Theory
Page 85

The first 4 functions can be used for changing speed during a single axis motion. Functions HSL_M_sd_stop() and
HSL_M_emg_stop() are used to decelerate the axis speed to “0.”
HSL_M_fix_speed_range() is necessary before any
HSL_M_v_change() function, and HSL_M_unfix_speed_range()
releases the speed range constrained by
HSL_M_fix_speed_range().
The function HSL_M_cmp_v_change() almost has the same function as HSL_M_v_change(), except HSL_M_cmp_v_change() acts
only when a general comparator comes into existence. Refer to
section 4.4.4 for more details about the general comparator.
The last 4 functions are relatively easy to understand and use. So,
the discussion below will be focused on HSL_M_v_change().
Theory behind HSL_M_v_change():
The HSL_M_v_change() function is used to change MaxVel on the
fly. In a normal motion operation, the axis starts at StrVel speed,
accelerates to MaxVel, and then maintains MaxVel until it enters
the deceleration region. If MaxVel is change during this time, it will
force the axis to accelerate or decelerate to a new MaxVel in the
time period defined by the user. Both Trapezoidal and S-curve profiles are applicable. The speed changes at a constant acceleration
for a Trapezoidal and constant jerk for a S-curve profile.
Operation Theory 75
Page 86

Figure 4-32: HSL_M_v_change() Theory
Constraints of HSL_M_v_change()
In a single axis preset mode, there must be enough remaining
pulses to reach the new velocity, else the HSL_M_v_change() will
return an error and the velocity remains unchanged.
Example:
A trapezoidal relative motion is applied:
HSL_M_start_tr_move(0,10000,0,1000,0.1,0.1).
It cause axis 0 to move for 10000 pulses, and the maximum velocity is 1000 PPS.
At 5000 pulses, HSL_M_v_change(0,NewVel,Tacc) is applied
76 Operation Theory
Page 87

.
NewVel (PPS) Tacc (Sec) Necessary remaining pulses OK / Error
Acceleration Deceleration Total
5000 0.1 300 313 613 OK
5000 1 3000 3125 6125 Error
10000 0.1 550 556 1106 OK
50000 0.1 2550 2551 5101 Error
Table 4-6:
HSL_M_v_change() Example
1. To set the maximum velocity, the function
HSL_M_fix_speed_range() must be used in order for the
function HSL_M_v_change() to work correctly. If
HSL_M_fix_speed_range() is not applied, MaxVel set by
HSL_M_v_move() or HSL_M_start_ta_move() automatically becomes the maximum velocity, where
HSL_M_v_change() can not be exceeded.
Figure 4-33: Velocity Suggestions A
2. During the acceleration or deceleration period, using
HSL_M_v_change() is not suggested, although it does
work in most cases, the acceleration and deceleration
time is not guaranteed.
Operation Theory 77
Page 88

Figure 4-34: Velocity Suggestions B
Example:
There are 3 speed change sensors during an absolute move for
200000 pulses. Initial maximum speed is 10000pps. Change to
25000pps if Sensor 1 is touched. Change to 50000pps if Sensor 2
is touched. Change to 100000pps if Sensor 3 is touched. Then the
code for this application and the resulting velocity profiles are
shown below.
Figure 4-35: Velocity Example
#include “pci_HSL-4XMO.h”
HSL_M_fix_speed_range(axis, 100000.0);
HSL_M_start_ta_move(axis, 200000.0, 1000, 10000,
0.02,0.01);
while(!HSL_M_motion_done(axis))
{
// Get sensor’s information from another I/O
card
78 Operation Theory
Page 89

if((Sensor1==High) && (Sensor2==Low) &&
(Sensor3 == Low))
HSL_M_v_change(axis, 25000, 0.02);
else if((Sensor1==Low) && (Sensor2==High) &&
(Sensor3 == Low))
HSL_M_v_change(axis, 50000, 0.02);
else if((Sensor1==Low) && (Sensor2==Low) &&
(Sensor3 == High))
HSL_M_v_change(axis, 100000, 0.02);
}
The information of the three sensors is acquired from another I/O
card, and the resulting velocity profile from experiment is shown
below:
Figure 4-36: Velocity Profile Example
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_v_change()
HSL_M_sd_stop()
HSL_M_emg_stop()
HSL_M_fix_speed_range()
HSL_M_unfix_speed_range()
HSL_M_get_currebt_speed()
Operation Theory 79
Page 90

Change Position on the Fly
When operating in single-axis absolute pre-set motion, it is possible to change the target position during moving by using the function HSL_M_p_change().
Figure 4-37: Change Position on the Fly
Theory of HSL_M_p_change():
The HSL_M_p_change() is applicable to the
HSL_M_start_ta_move(), and HSL_M_start_sa_move() functions
only. It is used to change the target position, defined originally by
these two functions. After changing position, the axis will move to
the new target position and totally disregard the original position. If
the new position is in the passed path, it will cause the axis to
decelerate and eventually stop, then reverse, as shown in the
chart. The acceleration and deceleration rate, and StrVel and MaxVel are kept the same as the original setting.
80 Operation Theory
Page 91

Figure 4-38: Theory of HSL_M_p_change()
HSL_M_p_change() Constraints:
1. HSL_M_p_change() is only applicable on single-axis
absolute pre-set motion, i.e., HSL_M_start_ta_move(),
and HSL_M_start_sa_move() only.
2. Position change during the deceleration period is not
allowed.
3. There must be enough distance between the new target
position and current position where HSL_M_p_change()
is executed because the HSL-4XMO needs enough
space to finish deceleration.
Example:
A trapezoidal absolute motion is applied:
HSL_M_start_ta_move(0,10000,0,1000,0.5,1).
It cause axis 0 to move to pulse 10000 position with a maximum
velocity of 1000 PPS. The necessary number of pulses to decelerate is 0.5*1000*1 = 500.
Operation Theory 81
Page 92

At position “CurrentPos,” HSL_M_p_change(0, NewPos) is
applied.
NewPos CurrentPos OK / Error Note
5000 4000 OK
5000 4501 Error
5000 5000 Error
5000 5499 Error
5000 6000 OK Go back
5000 9499 OK Go back
5000 9500 Error
5000 9999 Error
Table 4-7: HSL_M_p_change() Constraints
X Relative Function:
HSL_M_p_change()
4.12 Position Compare
The HSL-4XMO provides position comparison functions for all
axes. The comparison function is used to output a trigger pulse
when the counter reaches a preset value set by the user.
CMP1~CMP4 are used as a comparison trigger.
Comparators of the HSL-4XMO
There are 5 comparators for each axis of the HSL-4XMO. Each
comparator has its unique functionality. Below is a table for comparison:
Compare Source Description Function Related
Comparator 1
Comparator 2
Comparator 3
82 Operation Theory
Command posi-
tion counter
Command posi-
tion counter
Position error
counter
Table 4-8: HSL-4XMO Comparators
Soft Limit (+)
(Refer to section 4.9)
Soft Limit (-)
(Refer to section 4.9)
Step-losing detection HSL_M_error_counter_check
HSL_M_set_softlimit
HSL_M_enable_softlimit
HSL_M_diable_softlimit
Page 93

Comparator 4 Any counters General-purpose HSL_M_set_general_comparator
HSL_M_set_trigger_comparator
Comparator 5
(Only Axes 0 & 1)
Feedback posi-
tion counter
Table 4-8: HSL-4XMO Comparators
Position compare
function (Trigger)
HSL_M_build_compare_function
HSL_M_build_compare_table
HSL_M_set_auto_compare
Note: Only comparator 5 has the ability to trigger an output pulse
via the CMP.
Comparators 1 and 2 are used for soft limits. Refer to section 4.9.
Comparator 3 is used to compare with the position error counter. It
is useful for detecting if a stepping motor has lost any pulses. To
enable/disable the step-losing detection, or set the allowable tolerance use HSL_M_set_error_counter_check()
Comparator 4 is a general purpose comparator. The comparing
source counter can be any counter. The compared value, source
counter, comparing method, and reaction are set by the function
HSL_M_set_general_comparator().
Position Compare
The 5th comparator, whose comparing source is the feedback
position counter, performs the position compare function. Only the
first 2 axes (0 and 1) can do a position comparison. The position
comparison function triggers a pulse output via the CMP, when the
comparing condition comes into existence.
The comparing condition consists of 2 parts, the first is the value to
be compared, and the second is the comparing mode. Comparing
mode can be “>“, “=“ or “<“. The easiest way to use the position
comparison function is to call the function:
HSL_M_set_trigger_comparator (AxisNo, CmpSrc,
Method, Data)
The second parameter, “Method,” indicates the comparing
method, while the third parameter, “Data,” is for the value to be
compared. In continuous comparison, this data will be ignored
automatically since the compare data is built by other functions.
Operation Theory 83
Page 94

Continuously Comparison with Trigger Output
To compare multiple data continuously, functions for building comparison tables are provided and are shown below:
HSL_M_build_comp_function(AxisNo, Start, End,
Interval)
HSL_M_build_comp_table(AxisNo, tableArray, Size)
HSL_M_set_auto_compare(AxisNo, SelectSource)
The first function builds a comparison list using start and end
points and constant intervals. The second function builds on an
arbitrary comparison table (data array). The third function is a
source comparing selection function. Users can check current values used for comparison using the function
HSL_M_check_compare_data():
Example:
Using the continuous position comparison function.
Figure 4-39: Continuously Comparison with Trigger Output
In this application, the table is controlled by the motion command,
and the CCD Camera is controlled by the position comparison out-
84 Operation Theory
Page 95

put of the HSL-4XMO. An image of the moving object is easily
obtained.
X Working Spec: 34000 triggering points per stroke, trigger
speed is 6000 pts/sec )
X Program Settings:
Z Table starts moving from 0 to 36000
Z Compare points are on 1001 35000, total 34000 pts,
points to points interval=1pulse
Z Moving Speed is 6000 pps
Z Compare condition is “=“
X Program codes:
HSL_M_set_trigger_comparator(0, 1, 1, 1001);
HSL_M_build_compare_function(0, 1001, 35000, 1,
1);
HSL_M_set_auto_compare(0, 1);
HSL_M_start_tr_move(0, 36000, 0, 6000, 0.01,
0.01);
X Monitoring or Check the current compare data:
HSL_M_check_compare_data(0, 5, *CurrentData);
Users can use this function to check if auto-trigger is running.
The “Value” block in this figure is the position where the comparison occurs, and where the data can be checked by using
HSL_M_check_compare_data().
Note that at the final compared point will still load an “After-final”
point into the “Value” block. Fill a dummy point into the comparison
table array at the final position. This value must be far enough
from the table’s stroke.
If using _build_compare_function(), a dummy “after-final” point is
automatically loaded. This value is equal to (End point + Interval x
Total counts) x moving ratio.
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_trigger_comparator(),
HSL_M_build_comp_function()
HSL_M_build_comp_table()
HSL_M_set_auto_compare()
HSL_M_check_compare_data()
Operation Theory 85
Page 96

HSL_M_set_trigger_type ()
4.13 Backlash Compensator and Vibration Suppression
Whenever direction change has occurred, the HSL-4XMO outputs
a backlash corrective pulse before sending the next command.
The function HSL_M_backlash_comp() is used to set the pulse
number.
In order to minimize vibration when a motor stops, the HSL-4XMO
can output a single pulse for a negative direction and then single
pulse for a positive direction right after completion of a command
movement. Refer to the timing chart below, the
HSL_M_suppress_vibration() function is used to set T1 & T2.
Figure 4-40: Vibration Suppression
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_backlash_comp()
HSL_M_suppress_vibration()
86 Operation Theory
Page 97

4.14 Software Limit Function
The HSL-4XMO provides 2 software limits for each axis. The soft
limit is extremely useful in protecting a mechanical system as it
works like a physical limit switch when correctly set.
The soft limits are built on comparators 1 and 2 (Refer to section
4.7), and the comparing source is the command position counter.
A preset limit value is set in comparators 1 and 2, then, when the
command position counter reaches the set limit value, the HSL4XMO reacts by generating the stop immediately or decelerates to
stop pulse output.
X To set the soft limit: HSL_M_set_softlimit();
X To enable soft limit: HSL_M_enable_softlimit();
X To disable soft limit: HSL_M_diable_softlimit();
Note: The soft limit is only applied to the command position and not
the feedback position (Refer to 4.4). In cases where the moving ratio is not equal to “1,” it is necessary to manually calculate its corresponding command position where the soft limit
would be, when using HSL_M_set_softlimit().
X Relative Functions:
HSL_M_set_softlimit()
HSL_M_enable_softlimit()
HSL_M_diable_softlimit()
4.15 Point Table Management
For rapid and multiple point-to-point motion application, it would
take much more time to do communucation between host PC and
HSL-4XMO module. Consequently, we design a series of functions for users to build definite points inside the modules, named
“Point Table”. Therefore, users can assign a point number of the
table to save transmission time in order to get a better response.
Before using this feature, users must know and plan the points of
their applications, download the point table into the module and
call them at any time. It will send out the pulse train to let the motor
run to the assigned position in a shortest time with the predefined
speed profile and acceleration parameters.
Operation Theory 87
Page 98

4.16 Motion Script Download
For time-critical applications or specific motion sequences, users
can pre-define a motion squence with simple script file. HSL4XMO will interpret the motion script command line-by-line and
realize the motion sequence as what users want.
This feature is much more useful because the module plays as a
standalone system and execute the motion commands by itself.
Windows context switching would not interrupt the module. Consequently, it has a better timing performance than non-standalone
system.
The motion script supports standard “G” code, and many traditional users are familiar with it. Users can use any text editor program to define their motion sequence and download it into the
HSL-4XMO. At any moment, you may want to execute it by issuing
a run command or run it cyclically by a repeat command.
88 Operation Theory
Page 99

5 Motion Creator in LinkMaster
After installing the hardware (Chapters 2 and 3), it is necessary to
correctly configure all modules and double check the system
before running. This chapter gives the guidelines for establishing a
control system and manually testing the HSL-4XMO module to
verify correct operation. The Motion Creator software provides a
simple and powerful way to setup, configure, test, and debug a
motion control system that uses HSL-4XMO module.
Note: Motion Creator is only available for Windows OS with a
screen resolution higher than 800x600.
5.1 Execute Motion Creator in LinkMaster
After installing the software drivers for the HSL-4XMO in Windows,
the motion creator program can be located at <chosen path
>\LinkMaster. To execute the program, double click on the executable file or use Start->Program Files->HSL->LinkMaster.
5.2 About Motion Creator in LinkMaster
Before Running Motion Creator, the following issues should be
kept in mind.
1. Motion Creator is available only for Windows system
with a screen resolution higher than 800x600. It cannot
be run under DOS.
2. Motion Creator allows users to save settings and configurations for HSL-4XMO modules. Saved configurations
will be automatically loaded the next time Motion Creator
is executed. Two files, HSL-4XMO.ini and HSL4XMOMC.ini, in the windows root directory are used to
save all settings and configurations.
3. To duplicate configurations from one system to another,
copy HSL-4XMO.ini and HSL-4XMOMC.ini into the windows root directory.
4. If multiple HSL-4XMO modules use the same Motion
Creator saved configuration files, the DLL function call
HSL_M_config_from_file() can be invoked within a user
Motion Creator in LinkMaster 89
Page 100

developed program. This function is available in a DOS
environment as well.
Figure 5-1: HSL Master Utility
90 Motion Creator in LinkMaster
 Loading...
Loading...