Page 1

1000 Series Pipe Shredder
Models Covered:
APS, CPS, MPS, EPS, SPS
Part Number: MAN-EPS-0001
Bulletin Number: GRN4-610
Effective: August 1, 2012
Page 2

GRN4-610 ii
Write Down Your Serial Numbers Here For Future Reference:
_________________________ _________________________
_________________________ _________________________
_________________________ _________________________
We are committed to a continuing program of product improvement.
Specifications, appearance, and dimensions described in this manual are subject to change without notice.
DCN No. ____________
© Copyright 2013
All rights reserved.
Page 3

GRN4-610 iii
Shipping Info
Unpacking and Inspection
You should inspect your granulator for possible shipping damage.
Thoroughly check the equipment for any damage that might have occurred in transit, such as
broken or loose wiring and components, loose hardware and mounting screws, etc.
In the Event of Shipping Damage
According to the contract terms and conditions of the Carrier, the responsibility of the
Shipper ends at the time and place of shipment.
Notify the transportation company’s local agent if you discover damage.
Hold the damaged goods and packing material for the examining agent’s inspection. Do not
return any goods before the transportation company’s inspection and authorization.
File a claim with the transportation company. Substantiate the claim by referring to the
agent’s report. A certified copy of our invoice is available upon request. The original Bill of
Lading is attached to our original invoice. If the shipment was prepaid, write us for a
receipted transportation bill.
Advise customer service regarding your wish for assistance and to obtain an RMA (return
material authorization) number.
If the Shipment is Not Complete
Check the packing list as back-ordered items are noted on the packing list. You should have:
! Granulator
! Bill of lading
! Packing list
! Operating and Installation packet
! Electrical schematic and panel layout drawings
! Component instruction manuals
Re-inspect the container and packing material to see if you missed any smaller items during
unpacking.
If the Shipment is Not Correct
If the shipment is not what you ordered, contact the shipping department immediately. For
immediate assistance, please contact the correct facility located in the technical assistance
section of this manual. Have the order number and item number available. Hold the items
until you receive shipping instructions.
Page 4

GRN4-610 iv
Returns
Do not return any damaged or incorrect items until you receive shipping instructions from the
shipping department.
Credit Returns
Prior to the return of any material, authorization must be given by the manufacturer. A
RMA number will be assigned for the equipment to be returned.
Reason for requesting the return must be given.
ALL returned material purchased from the manufacturer returned is subject to 15% ($75.00
minimum) restocking charge.
ALL returns are to be shipped prepaid.
The invoice number and date or purchase order number and date must be supplied.
No credit will be issued for material that is not within the manufacturer’s warranty period
and/or in new and unused condition, suitable for resale.
Warranty Returns
Prior to the return of any material, authorization must be given by the manufacturer. A
RMA number will be assigned for the equipment to be returned.
Reason for requesting the return must be given.
All returns are to be shipped prepaid.
The invoice number and date or purchase order number and date must be supplied.
After inspecting the material, a replacement or credit will be given at the manufacturer’s
discretion. If the item is found to be defective in materials or workmanship, and it was
manufactured by our company, purchased components are covered under their specific
warranty terms.
Page 5

GRN4-610 v
Table of Contents
CHAPTER 1:! SAFETY ................................................................ 6!
1-1! How to Use This Manual ............................................................................................. 6!
Safety Symbols Used in this Manual ..................................................................... 6!
General Safety Regulations ................................................................................................... 9!
1-2! Responsibility .............................................................................................................. 9!
1-3! Warnings and Precautions ........................................................................................ 10!
CHAPTER 2:! FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION ........................... 15!
2-1! Models Covered in This Manual ................................................................................ 15!
2-2! General Description & Typical Features ................................................................... 15!
2-3! Safety Features ......................................................................................................... 30!
CHAPTER 3:! INSTALLATION .................................................. 34!
3-1! Uncrating the Equipment ........................................................................................... 34!
3-1! Electrical Connections ............................................................................................... 35!
3-2! Initial Start-up ............................................................................................................ 36!
CHAPTER 4:! OPERATION ....................................................... 38!
4-1! Start-up ..................................................................................................................... 38!
4-2! Operation Procedures ............................................................................................... 38!
4-3! Shut-down ................................................................................................................. 39!
CHAPTER 5:! MAINTENANCE ................................................. 40!
5-1! Preventative Maintenance Schedule ......................................................................... 40!
5-2! Preventative & Corrective Maintenance ................................................................... 41!
CHAPTER 6:! TROUBLESHOOTING ....................................... 59!
6-1! Introduction ............................................................................................................... 59!
CHAPTER 7:! APPENDIX .......................................................... 61!
7-1! Technical Specifications ............................................................................................ 61!
7-3! Drawings and Diagrams ............................................................................................ 62!
7-4! Spare Parts List ......................................................................................................... 69!
7-5! Technical Assistance ................................................................................................ 72!
Parts and Service Department ............................................................................ 72!
Sales and Contracting Department ..................................................................... 72!
Page 6

GRN4-610 Chapter 1: Safety 6 of 73
Chapter 1: Safety
1-1 How to Use This Manual
Use this manual as a guide and reference for installing, operating, and maintaining your
granulator. The purpose is to assist you in applying efficient, proven techniques that enhance
equipment productivity.
This manual covers only light corrective maintenance. No other maintenance should be
undertaken without first contacting a service engineer.
The Functional Description section outlines models covered, standard features, and safety
features. Additional sections within the manual provide instructions for installation, preoperational procedures, operation, preventive maintenance, and corrective maintenance.
The Installation chapter includes required data for receiving, unpacking, inspecting, and setup
of the granulator. We can also provide the assistance of a factory-trained technician to help
train your operator(s) for a nominal charge. This section includes instructions, checks, and
adjustments that should be followed before commencing with operation of the granulator.
These instructions are intended to supplement standard shop procedures performed at shift,
daily, and weekly intervals.
The Operation chapter includes a description of electrical and mechanical controls, in
addition to information for operating the granulator safely and efficiently.
The Maintenance chapter is intended to serve as a source of detailed assembly and
disassembly instructions for those areas of the equipment requiring service. Preventive
maintenance sections are included to ensure that your granulator provides excellent, long
service.
The Troubleshooting chapter serves as a guide for identification of most common problems.
Potential problems are listed, along with possible causes and related solutions.
The Appendix contains technical specifications, drawings, schematics, parts lists, and
available options. A spare parts list with part numbers specific to your machine is provided
with your shipping paperwork package. Refer to this section for a listing of spare parts for
purchase. Have your serial number and model number ready when ordering.
Safety Symbols Used in this Manual
The following safety alert symbols are used to alert you to potential personal injury hazards.
Obey all safety messages that follow these symbols to avoid possible injury or death.
DANGER indicates an imminently hazardous situation that, if not avoided,
will result in death or serious injury.
WARNING indicates a potentially hazardous situation or practice that, if
not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION indicates a potentially hazardous situation or practice that, if
not avoided, may result in minor or moderate injury or in property damage.
Page 7

GRN4-610 Chapter 1: Safety 7 of 73
Figure 1: Safety Tags and warning features
Hazard Alert Symbol
Description/Explanation
Preventative Maintenance
High Voltage Hazard. The electrical
enclosure is supplied with 3-phase
electrical power. Use caution when
using or maintaining this product.
Every six months inspect all
electrical connections for secure
attachment. For further
information see the Maintenance
Chapter in this manual
Hands could be exposed to a
crushing movement.
Every month inspect the
shears/blades for any type of
wear. For further information see
the Maintenance Chapter in this
manual.
When equipped with belts and
sheaves, hands could become
entangled.
Every month inspect the belt(s)
for any type of wear. For further
information see the Maintenance
Chapter in this manual.
Hands can become entangled
or cut if they enter the danger
zone of gears or cutting shears
Every month inspect the
shears/blades for any type of
wear. For further information see
the Maintenance Chapter in this
manual.
The unit can produce
continuous noise above 85 dBA
and/or produce projectiles
under normal operating
conditions.
Always wear eye and ear
protection when the machine is in
operation or performing
maintenance.
A person could be exposed to a
crushing movement if walking
around or under machine that is
open/suspended for moving.
Always be aware of your
surroundings and do not walk
underneath a suspended machine.
Page 8
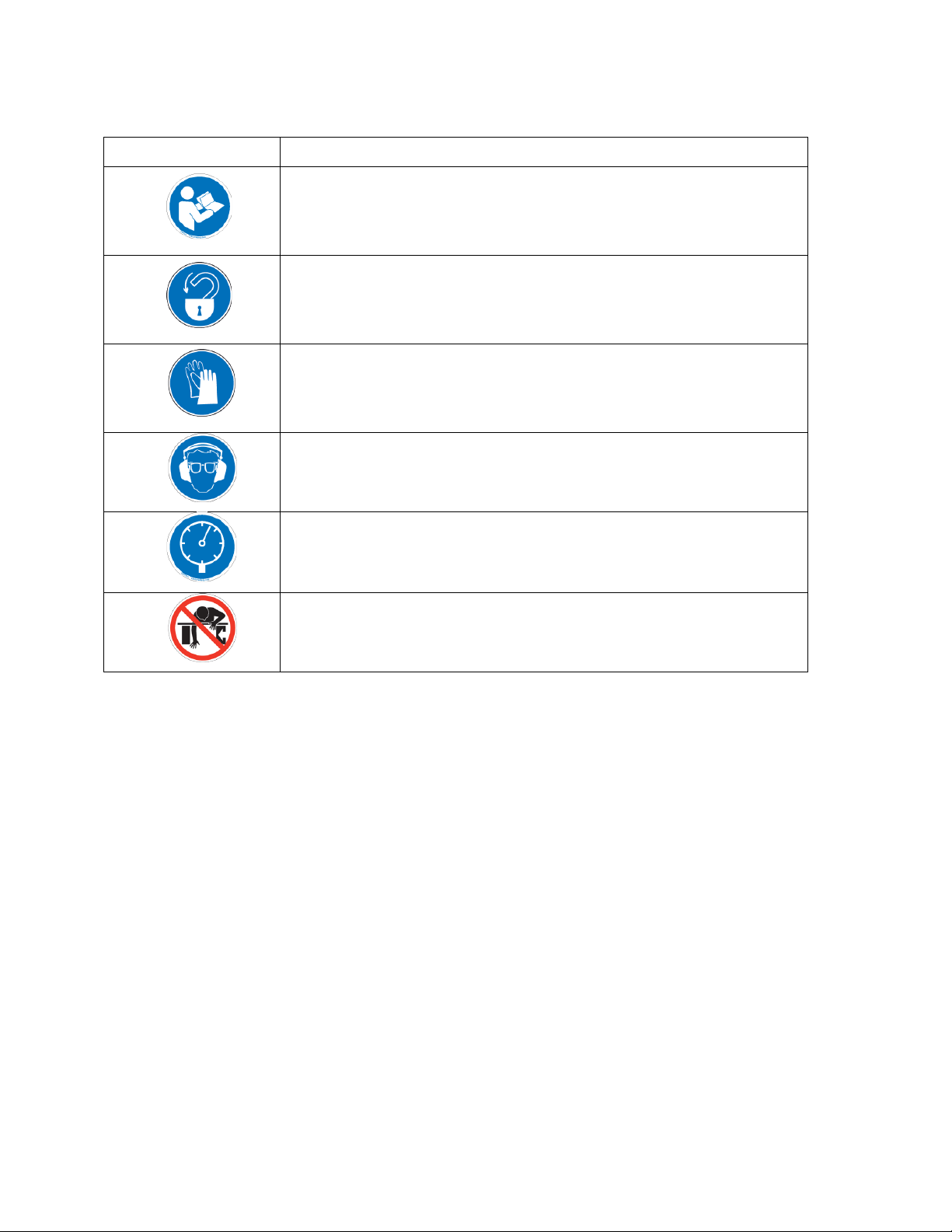
GRN4-610 Chapter 1: Safety 8 of 73
Mandatory Symbol
Description/Explanation
Read Operators Manual. This equipment must be operated and
maintained by properly trained personnel. The information
contained within this manual must be read and understood prior to
operating this equipment.
Lock Out. This equipment is operated with 3-phase electrical
power. Therefore, when performing any maintenance operations
we recommend following the local standards for performing a
lock-out/tag-out procedure.
Wear Safety Gloves. This equipment operates with sharp blades
and rotors. We recommend that technicians use safety gloves
while performing maintenance to protect hands from being
exposed to these sharp surfaces.
Wear ear and eye protection. This unit may produce loud and
continuous noise and may produce projectiles.
Pneumatic or hydraulic equipment. Pneumatic or hydraulic
equipment must be kept at a safe pressure.
Do not reach into unit. Reaching into a unit is prohibited while the
unit is in operation and may cause serious injury.
Page 9

GRN4-610 Chapter 1: Safety 9 of 73
General Safety Regulations
This machine uses knives for the performance of its intended use. Consequently, it can be a
dangerous machine to operate and maintain unless these safety regulations are followed.
These regulations should be read, understood and periodically reviewed by all personnel
involved in any way with this machine.
Never operate or remove any machine components that are secured by wrench-type fasteners
unless the motor is electrically locked out and the rotor is motionless.
Never operate the machine or jog the rotor unless the cutting chamber covers, discharge
chute, or any guards or covers are in place and secure. Do not circumvent the safety
interlocks.
Prior to clearing a jam or performing any maintenance, the motor should be turned off and
electrically locked out. Be sure that the rotor has come to a stop. Hands must not be inserted
into the machine to clear the jam.
Do not extend any part of the body into feed roll openings or discharge area unless the motors
are electrically locked out and the rotor and feed rolls are motionless.
Never extend fingers through holes in screen.
Be sure that the v-belts are properly aligned and that tension is at its maximum.
Extreme care should be taken to see that all bolts are properly tightened at all times. During
the operation of the machine, rotor knife bolts may come loose. Although fine threads are
used on the rotor knife bolts because vibration does not easily loosen them, you should
inspect the tightness of the bolts frequently.
This machine is designed for the granulation of plastic materials. Do not feed any other
materials into the machine.
1-2 Responsibility
These machines are constructed for maximum operator safety when used under standard
operating conditions and when recommended instructions are followed in the maintenance
and operation of the machine.
All personnel engaged in the use of the machine should become familiar with its operation as
described in this manual.
Proper operation of the machine promotes safety for the operator and all workers in its
vicinity.
Becoming familiar with materials, inspection, speed limitations, screens, and guard
maintenance and total user responsibility will assist you in learning potential areas in need of
observation for danger.
Each individual must take responsibility for observing the prescribed safety rules as outlined.
All caution, warning and danger signs must be observed and obeyed. All actual or potential
danger areas must be reported to your immediate supervisor.
Page 10
GRN4-610 Chapter 1: Safety 10 of 73
1-3 Warnings and Precautions
Our granulators are designed to provide safe and reliable operation when installed and
operated within design specifications, following national and local safety codes.
To avoid possible personal injury or equipment damage when installing, operating, or
maintaining this granulator, use good judgment and follow these safe practices:
! LEARN AND OBEY your company’s safety policy regarding granulating
equipment.
! MOVING OR LIFTING THE GRANULATOR: Although our equipment is built
and engineered for great ruggedness in operation, care must be taken when moving
the machine along the floor or lifting it. Damage may occur to sheet metal covers,
electrical cabinets, or small brackets if pressure is applied to them when moving the
granulator. When lifting the granulator, be certain of total machine weight and the
capability of the lifting equipment. (See the Granulator Specification Sheets for
machine weights and dimensions.)
! GRANULATOR LOCATION: Adequate area for routine maintenance should be
provided in order to open the machine for knife, screen, or cleanout service. Proper
service area clearances also should allow people who are working on the machine to
be clearly visible to others, thereby reducing the potential safety hazards.
! SAFE HOUSEKEEPING: The work area must be kept clean and uncluttered during
periods of operation or maintenance. No hand tools or other metal objects should be
left on or around the machine. Any tools or other metal objects that mistakenly fall
into the hopper feed opening can cause severe damage to internal cutting chamber,
rotor and screen components.
! SAFETY GLASSES OR A FACE SHIELD MUST ALWAYS BE WORN when
servicing or operating the machine. Although our machines are designed for the
maximum in flyback control, caution must be used when operating near the hopper
feed opening in order to guard against unexpected material flyback.
! EAR PROTECTION may be required when operating the machine during
granulation of very hard or noisy materials. The Occupational Safety and Health Act
of 1970 has established guidelines for Permissible Noise Exposures (OSHA 1910.95)
that should be followed.
! NEVER attempt to operate the granulator unless it is fully assembled with all guards
and interlocks in place and functional.
! OBSERVE all danger, warning, caution and safety labels on the equipment.
! Upon completion of any machine maintenance, be certain ALL SAFETY GUARDS
AND COVERS are securely and properly fastened prior to resuming machine
operation. All fasteners must be in place and properly tightened. ANY
SHORTCUTS MAY RESULT IN INJURY TO PERSONNEL OR DAMAGE
TO EQUIPMENT.
! NEVER wear any loose fitting clothes, neckties, or dangling items such as earrings,
belts, or shoestrings. Jewelry, such as wristwatches, bracelets, or rings should
NEVER be worn. Long hair must be tied back or placed in a tight fitting hairnet.
NEVER lean against or rest hands or feet on the granulator when it is in operation or
open for maintenance. NEVER stand on the granulator when it is in operation.
Page 11

GRN4-610 Chapter 1: Safety 11 of 73
! ROTATION OF MOTORS: The correct rotating direction for the granulator motor
is clearly marked on the machine. Always check for proper rotation of motors.
Incorrect rotation direction can cause severe damage.
! ELECTRICAL GROUNDING: All electrical equipment on the granulator must be
grounded in accordance to all local codes and Article 250 of the National Electric
Code.
! ALWAYS DISCONNECT AND LOCKOUT the main electrical power to the
granulator before performing any service.
! SAFETY INTERLOCKS MUST NOT BE BYPASSED. The mechanical and
electrical safety interlocks ensure the safety of personnel. They should never be
tampered with or removed for ANY reason. They should be checked frequently by a
qualified mechanic for proper operation.
! NEVER modify the machine configuration or any individual component without
written notice from the factory.
Page 12
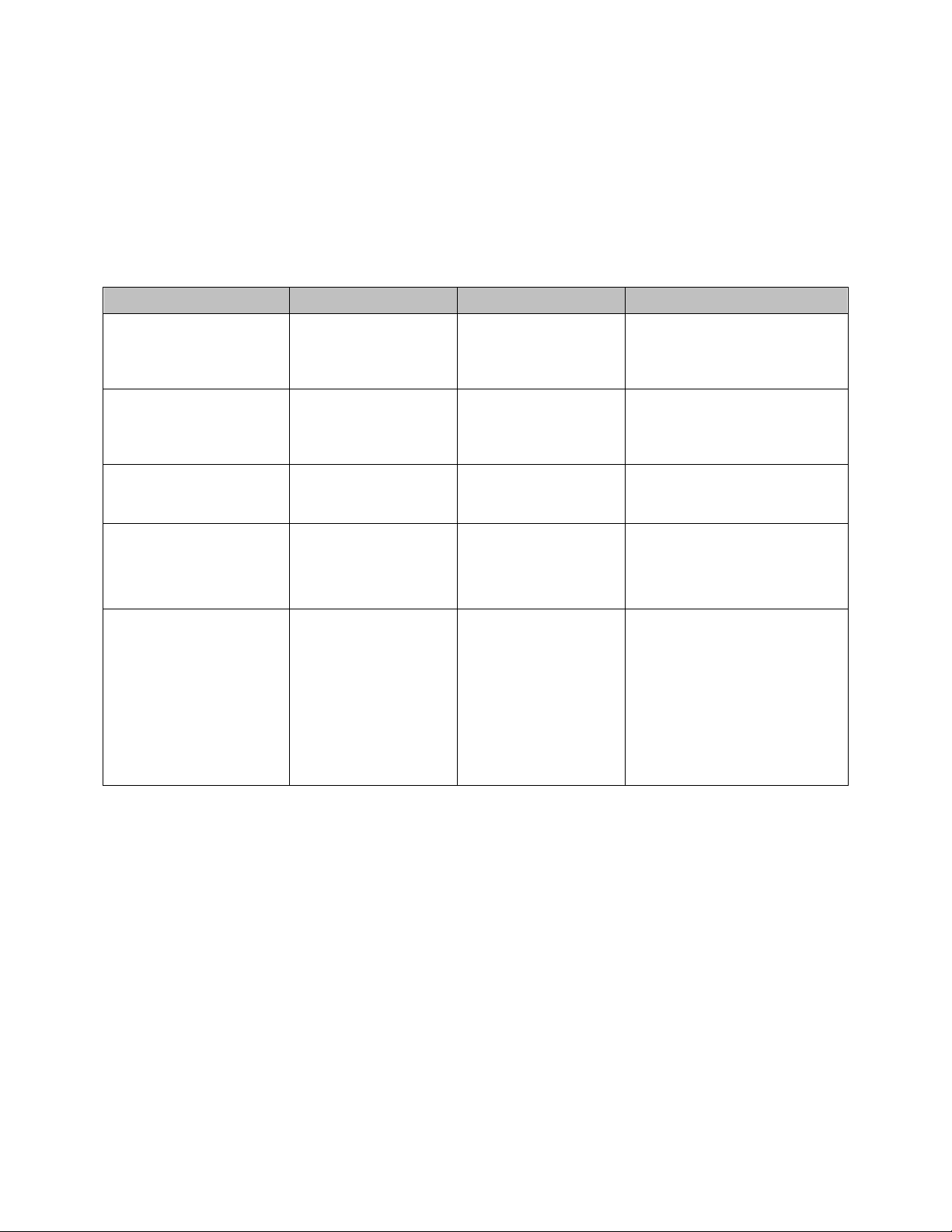
GRN4-610 Chapter 1: Safety 12 of 73
Remaining Risks
The machine is constructed so that you are able to operate it safely. Non-avoidable dangers are
prevented as greatly as possible by the protective devices. Remaining risks always exist. Please
be aware of the risks described below as this will help operators/staff avoid accidents. To further
avoid danger, please adhere to all advice provided in the operational manual.
Mechanical Dangers
Type of Danger
Activity
Possible Consequences
Preventative Measures
Crushing due to heavy
parts falling down or over.
Unloading/transporting
the machine and/or
components.
Serious injury.
• Wear personal protective gear
and follow the instructions
provided in the operational
manual.
Cutting caused by sharp
knives—even when the
rotor is stationary.
Knife replacement, knife
setting, knife
sharpening, and other
maintenance.
Serious injury—
particularly to the hands
and fingers.
• Wear personal protective gear
and follow the instructions
provided in the operational
manual.
Crushing when
opening/closing the doors
on front side of machine.
Maintenance.
Serious injury.
• Ensure no persons are in the
danger area while closing the
door.
Tripping over cables and
other surrounding objects.
All activities.
Serious injury.
• Lay cables in accordance with
regulations.
• Keep work station clean and
tidy.
Crushing, cutting,
amputation caused by rundown of the rotor.
Maintenance.
Serious injury or death.
• The maintenance doors must
always be tightly locked during
operation.
• DO NOT make the run-down
safety devices ineffective by
using technical aids or other
manipulations.
• NEVER use hands to check if
the rotor has stopped.
Page 13
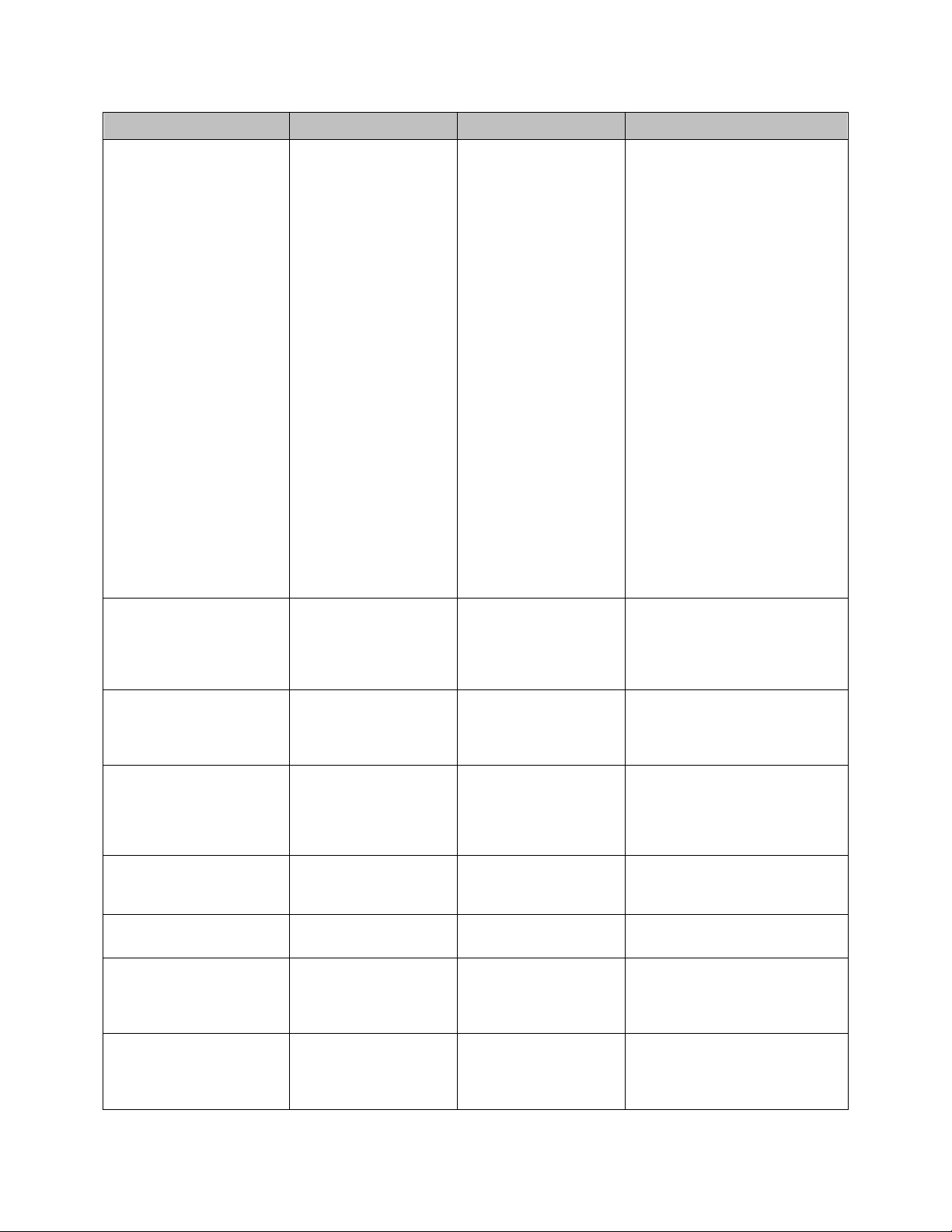
GRN4-610 Chapter 1: Safety 13 of 73
Type of Danger
Activity
Possible Consequences
• Preventative Measures
Direct/indirect contact with
live parts in terminal box.
Maintenance; start-up.
Serious injury or death.
• Only trained electricians may
carry out work on the electrical
equipment.
• If work is necessary on parts
that could conduct dangerous
voltage, a second person
should be present to break the
power supply in case of an
emergency.
• The yellow-marked lines
conduct voltage even when the
machine is switched OFF.
• Only use original safety fuses
with stipulated intensity of
current.
• Faulty electrical components
must be replaced immediately.
• If faults occur in electrical
energy supply, switch the
machine OFF immediately.
• The terminal box must be
locked during operation.
Before opening the terminal
box turn main switch to 0.
Failure of the Emergency
Stop Function.
All activities.
Serious injury or death.
• There must be a guarantee
that the machine will be
stopped immediately upon
failure of an Emergency Stop
button.
Fire/explosion caused by
throwing dangerous
objects (i.e. spray cans)
into the shredder.
Grinding.
Serious injury or death.
• Only grind material that
corresponds to the agreed
customer-specific
specifications.
Damage to hearing.
All activities.
Diminished hearing,
headaches, impaired
balance, and
deterioration of
concentration.
• Reduce noise levels by taking
suitable measures and wear
ear protection.
Instable machine due to
vibration.
All activities.
Serious injury.
• Install the machine according
to the instructions in the
operational manual.
Loose cutter/bed knife
mountings due to vibration.
All activities.
Serious injury.
• Check the cutter/bed knife
mountings regularly.
Inhalation of grinding dust.
All activities.
Respirator disease, etc.
• Mount a suitable air suction
device. DO NOT blow out
grinding dust when cleaning
the machine.
Crushing, cutting,
amputation caused by
manipulation of protective
devices.
All activities.
Serous injury or death.
• Never make the protective
devices ineffective; check the
devices regularly for proper
function.
Page 14

GRN4-610 Chapter 1: Safety 14 of 73
For further information on granulator safety, installation, and operation, see the American
National Standard for Plastics Machinery!Granulators, Pelletizers, and Dicers Used for
Size Reduction of Plastics!Construction, Care, and Use. ANSI B151.11-1982.
We have long recognized the importance of safety and have designed and manufactured our
equipment with operator safety as a prime consideration. We expect you, as a user, to abide
by the foregoing recommendations in order to make operator safety a reality.
Page 15

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 15 of 73
Chapter 2: Functional Description
2-1 Models Covered in This Manual
This manual covers the1000 Series pipe shredder which includes models APS, CPS, MPS,
EPS and SPS. The 1000 Series pipe shredder is designed for size-reduction of plastic pipes
made of PE, PP, and PVC etc. The user is responsible for consequences resulting from
incorrect operation: This will lead to the loss of the warranty as well as any compensation
claims.
2-2 General Description & Typical Features
Mechanical section
After the machine has been switched on, a hydraulically controlled feeding unit pushes
the pipe onto the slow-running rotor. The in feed is controlled according to the load of the
motor.
The pipes can be fed horizontally and without precutting into the feeding trough of the
pipe shredder by a forklift or optionally with a loading device. The feeding trough has a
hydraulically operated cover, which is closed after it is filled with material. A hydraulic
ram system is than pushing the material towards the rotor. The ram consists of a doubleacting telescopic cylinder and the pusher itself, which is a heavy durable welding
construction. The pusher is moving on 3 sets of high performance guide roller skids.
Those adjustable skids are running on 3 independent guide rails. The trough is built with
tough steel profiles and all safety features are according latest CE-standards for work
safety. The pipe should be placed horizontally in the feeding trough mounted next to the
cutting chamber. Attention must be paid that this material does not contain any metal
parts. The guarantee does not cover any damage to the machine as a result of metal parts
being fed into the machine. The pipe in the feeding trough is shredded by the rotating
knives on the rotor. This shredding process is finished when the hydraulic cylinder has
reached its full stroke and the pusher is at the end position. The 1000 series shredder is
equipped with an E style rotor using a standard square, concave cutter blocks. These
cutters make light work of the heaviest pieces. Importantly, the design allows efficient
cutting of material, rather than hammering as well as reduced heat build-up and
degradation of material. The cutter blocks have four corners so they can be easily turned
once a corner has worn away. The projection of the cutter can be easily adjusted to match
the aggressiveness of the shredder with the customer’s material by adding or removing
thin shims on the cutters holder. The housing is a rigid welded and very compact
construction. Upper and lower part of the housing are bolted together and this makes
maintenance work very convenient. The housing is sitting on a base frame, which allows
easy installation of a discharge conveyor.
Due to the compact design this machine can only be used for screen-less operations!
The heavy-duty outboard bearings mounted on the 1000 series shredders minimize the
risk of contamination of the recycled materials and also minimize the risk of dust
penetrating the bearings and make a rotor change easier. Power is transmitted from the
electromotor by V-belts to the gearboxes, which are mounted directly on the shaft end on
either side of the rotor. In combination with the elastically supported torque arm this
construction will reduce stress to both motor and gear. The dual drive will further ensure
that all loads are evenly distributed into the rotor.
Page 16

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 16 of 73
Control
The pusher feeds the rotor with as much material as it is able to process. Upon reaching
70-90 % of rated current, the feeding of the pusher will be stopped and automatically
started again after the power consumption has fallen by 20 % in comparison with rated
current. If the high current is applied for longer than 0.7 - 1.5 sec., the main drive motor
switches off and runs back after about 3 sec. standstill time. The pusher plate also runs
back whilst the rotor runs back. The drive motor then stops for another 3 sec. before
starting again. The position of the pusher is controlled by an optical distance sensor. The
in feed is controlled according to load. Duration of pauses and return as well as the
current settings can be adjusted. Any alterations, however, should only be carried out
after consulting the manufacturer.
Grinding Material In-feed
The grinding material can be fed into the shredder using the following methods:
• Manual in-feed of the grinding material directly into the feeding trough.
• Manual in-feed of the grinding material with the help of an additional in-feed
device (i.e. hydraulic feeding unit).
In-feed Hopper
The grinding material in-feed ensues via a feeding trough. The pipe can be placed easily
in the feeding trough by a forklift.
Illustration:
Feeding trough
The feeding trough has a hydraulically operated cover, which is
closed after it is filled with material.
A hydraulic ram system is than pushing the material towards the rotor.
Page 17

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 17 of 73
Illustration:
(1) Stage cylinder
(2) Cover
(3) Lock
(4) Pusher
Optional (not included in standard machine) the feeding trough can
be equipped with a hydraulic feeding device.
Illustration:
(1) Base frame
(2) Lower housing flap
(3) Upper housing flap
(4)Gear box
(5) Drive motor
(6) V-belt protection
(7) Discharge conveyor
The machine housing is mounted on the base frame and the drive
motor and the gear box are mounted on the machine housing. This
design makes the machine compact.
3
1
4
1 2 7
3 4 6
5
Page 18

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 18 of 73
Drive
The drive of the rotor ensues by means of an electric motor via "V"-belts. The motor,
which is mounted on sliding rails or a motor plate, can be adjusted for regulating the
tension of the "V"-belts by means of tensioning screws. The "V"-belt pulley is attached
with a special tensioning element to the motor shaft.
Illustration:
Drive
Please observe the operation manual from the manufacturer!
Page 19
GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 19 of 73
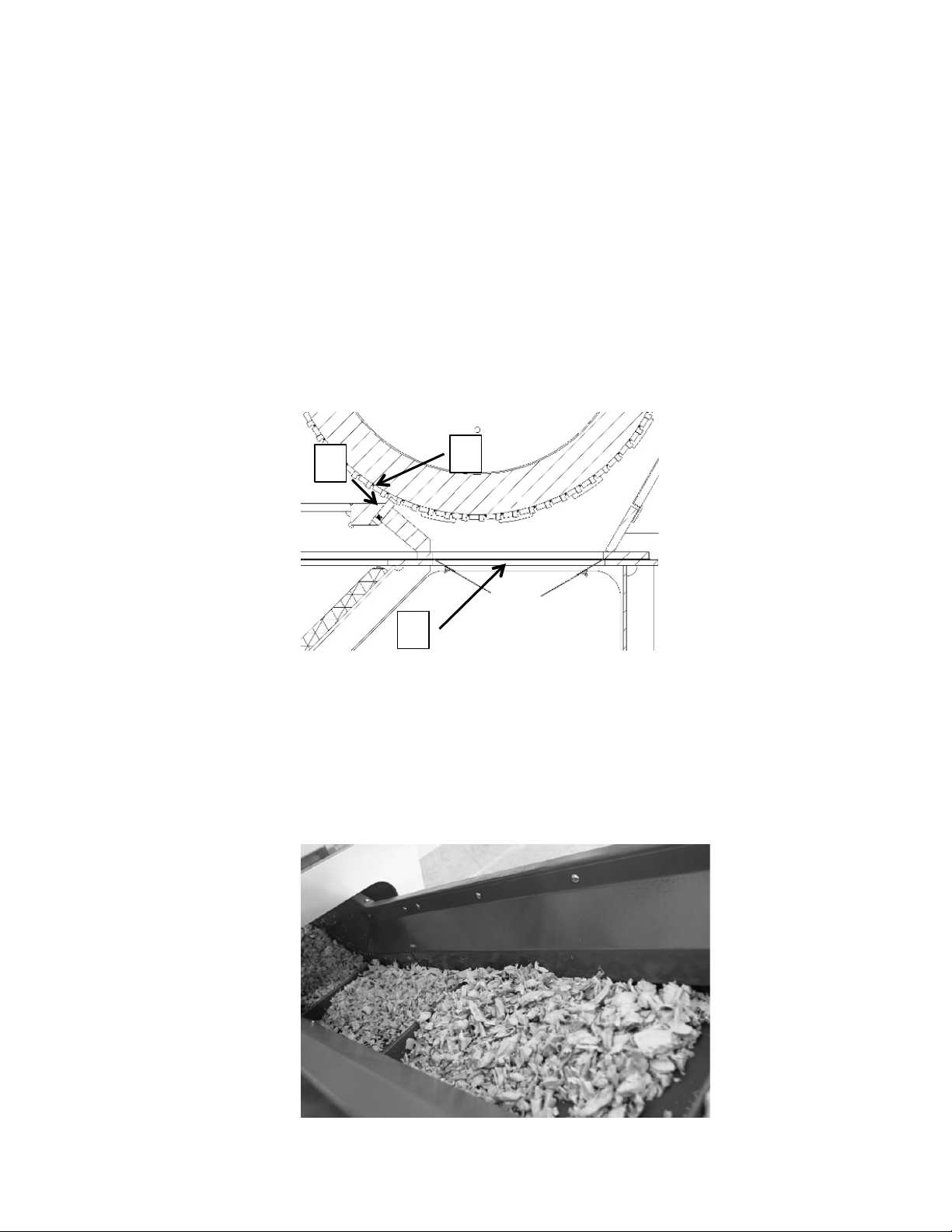
Rotor and Cutters
The material is ground between the knives assembled on the rotor and the stator knives
which are mounted in a fixed position in the machine lower section. All rotors are
equipped with square knives. These knives make light work of the heaviest pieces. The
knives have four corners, so that they can be easily turned once a comer has worn off.
The design of the rotor has a significant influence on the quality of the grinding process
and its results. The rotor construction, the type of knife mounting and the number of
knives have all been exactly matched to your task allocation.
Illustration:
(1) Rotor knife
(2) Stator knife
(3) Discharge area
Due to the compact design this machine can only be used for screen-less operations!
The rotor is accessible after opening the lower housing flap or the upper housing flap.
The rotor is arranged on roller bearings, which are situated outside the housing. The "V"belt pulley is attached by means of a taper bush to the rotor axis. The rotor is dynamically
counter balanced and has vibration-free concentricity.
Discharge of grinding material
Illustration:
Conveyor belt discharge
2 1 3
Page 20

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 20 of 73
The ground material will be discharged by a conveyor belt.
Hydraulic pusher
The ram consists of a double-acting telescopic cylinder and the pusher itself, which is a
heavy durable welding construction. The pusher is moving on 3 sets of high performance
guide roller skids. Those adjustable skids are running on 3 independent guide rails. The
position of the pusher is controlled by an optical distance sensor.
Illustration:
(1) Hydraulic stage
cylinder
(2) Guide roller
(3) Guide rail
(4) Pusher
Illustration:
(1) Pusher front plate
(2) Guide rail
1
3 2 4 1 2
Page 21
GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 21 of 73
Illustration:
(1) Distance sensor
(2) Reflecting area
Control Panel
Illustration:
Control panel
(1) Emergency STOP
(2) Ampere meters
(3) Elapsed hour counter
(4) Part 1
(5) Part 2
1
2 2 3
4
1
5
Page 22

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 22 of 73
Illustration:
Part 1
(1) Error lights
(2) Control lights
(3) Start buttons
(4) Stop buttons
(5) Control light hydraulic
(6) Start/Stop switch hydraulic
Illustration:
Part 2
(1) Error lights
(2) Control lights
(3) Star buttons
(4) Stop buttons
(5) Overload light shredder
(6) Oil filter jam
(7) Overload light Ram
(8) Reset
1 5 6 2 7 3 8 4 1 2 3 4 5
6
Page 23

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 23 of 73
Operator panel
Illustration:
Control panel
(1) Part 1
(2)Part 2
(3)HMI operator panel
(4)Emergency STOP
Illustration:
Part 1
(1) System ON
(2) Automatic/Manual switch
(3) Error light Ram
(4) System OFF
(5) Half stroke
(6) Manual rotor move
(7) Reset
(8) Pulse-push switch
(9) Manual push button for Rotor move
1 2 3
4 5 6 7 8 9 1 4 3
2
Page 24

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 24 of 73
Illustration:
Part 2
(1) Control light Overload reverse
(2) Control light Ram PUSH
(3) Control light Ram PULL
(4) Lid open
(5) Lock open
(6) Ram PUSH
(7) Lid close
(8) Lock close
(9) Ram PULL
Illustration:
HMI operator panel
1 2 3
4 5 6 7 8
9
Page 25

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 25 of 73
Machine HMI operation manual
Start menu
Illustration:
Operation panel start menu
You can select the second menu what you want to read.
F1: ram running status,
F2: the timer what you want to modify when you operate this machine,
F3: the ram position where you want to modify,
F4: alarm information,
K1: go back to start menu,
K4: stop HMI
Page 26

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 26 of 73
Machine running status
Illustration:
Operation panel running status
You can read the ram position when the machine running.
End holding time: When the ram reach end position, it will has 20
seconds delay, this time could be modified
Page 27

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 27 of 73
Time setting menu
Illustration:
Operation panel time setting menu
End holding: the ram reaches end position and delay time
Standard push: When the ram pushes, this action lasts 30 seconds and
then will has a 1 second pull action. So the 30 seconds is standard push
time and the 1 second is standard pull.
Standard pull: See above.
Pulse push: When the ram moves to 700mm point before end position, it
will act as this rule, pushes 3 seconds and stop 1 second, so the 3 seconds
is pulse push and 1 second is pulse stop.
Pulse stop: See above.
Page 28

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 28 of 73
Position setting menu
Illustration:
Operation panel
position setting menu
Half position: the whole length of ram stroke is 7200mm, our setting is 3600mm,
but it could be modified. Pulse position: to avoid current peak and motor
overload, this setting is 6700mm, it could be modified.
Page 29

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 29 of 73
Information menu
Illustration:
Operation panel
position setting menu
You can read information when the machine has alarm or stops automatically.
When machine has 3 times overload in 2 minutes or 3 times hydraulic overload
in 2 minutes, rotor will stop running automatically, and also has a message on the
HNI, meanwhile the red LED will flash. Press down “ACK” which on the HMI
at first, use up and down moves the wire frame to “reset”, then press “ENTER”
button, the ram will goes back to start position, and the cover will open, after that
could restart the machine again.
Page 30

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 30 of 73
Pulse/Push function
In normal process mode the pusher pushes forward continuously till the pusher arm reaches the
proximity switch which reverses the function and the pusher moves backwards. By changing the
switch (9) to “Pulse push” function on the main control board the pusher moves forward in steps.
This means, after each step the pusher remains in his position for a small while before it moves
forward again. This function should be used for very heavy applications and in case of danger to
overload the system
2-3 Safety Features
Protective Devices
The machine may under no circumstances be operated without these protective devices or
with faulty or manipulated protective devices.
Safety device for housing flap
Illustration:
(1) Safety device for lower
housing flap
(2) Safety device for
upper housing flap
The shredder can only be operated if the housing flap is closed and thus
deactivating the safety switch. If the housing flap is opened, the contact is
2
1
Page 31

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 31 of 73
broken. If the housing flap will be opened during operation, the safety switch is
activated, thus switching off the machine.
"V"-belts and pusher protector
"V"-belt and pusher protection are fixedly connected to the machine. They can be
dismounted for installation and maintenance work. However, this may only then be
carried out when all rotating parts have come to a complete standstill.
Illustration:
V-belt cover
Pusher cover
If machines are delivered on the request of the customer without drive motors,
the operator is obliged to fit and mount the protective devices delivered together
with the machine himself in line with the current legal safety regulations.
Page 32

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 32 of 73
Safety Light grid
The feeding trough in feed is safeguarded by a light grid. During opening and closing of
the cover it is activated. If somebody walks inside this light grid, the hydraulic will be
stopped. After the cover is opened or closed the light grid is deactivated.
Illustration:
Safety Light Grid
Safety markings
Safety markings are attached to the machine. If one of these markings becomes detached
or is no longer recognizable, it must be replaced. You can order new markings at
specialist shops or from us.
Page 33

GRN4-610 Chapter 2: Functional Description 33 of 73
Personal Protective Gear
The following protective gear must be worn when carrying out the outlined tasks. Use
breathing equipment before inhaling substances that may be harmful to your health if
necessary.
Task
Safety
Helmet
Safety
Boots
Safety
Gloves
Safety
Goggles
Ear Muffs
Unloading machine
X X X
Connecting machine
X
Operation.
X X X X
Cleaning.
X X X
Maintenance of bearings
X
Maintenance of gearbox
motor
X
Maintenance of cutters/bed
knives
X X
Knife sharpening
X X X X
Page 34

GRN4-610 Chapter 3: Installation 34 of 73
Chapter 3: Installation
3-1 Uncrating the Equipment
Choosing Application Site
The location of the machine and site of application must exhibit the characteristics listed
below.
• Enclosed space.
• Sufficient load-bearing capacity. (Find the machine weight in Chapter 7:
Technical Specifications.)
• Machine must be freely accessible from all sides.
• Sufficient available room for operating and service personnel.
• Spatial requirements—refer to the assembly drawing. All hinged parts must be
able to be completely opened.
• Vibration-free surroundings.
• Sufficient lighting.
• Machine may not be exposed to direct radiation of any kind.
• Room temperature must range from 40°F (5°C) to 104°F (40°C).
• Relative atmospheric humidity according to DIN 40040: 15 to 70% (indoor). (In
humidity levels of higher than 70%, apply an anti-corrosive agent to the metallicfinished machine parts. Insulation for the tropics is also necessary.)
• The machine may not be operated within range of static discharges or strong
magnetic fields—this could lead to faults in the machine’s control system.
Unloading and Installing the Machine
The machine and/or components are packed so they will arrive safely. Use a suitable
crane or forklift for unloading the packaged machine and/or components.
• After unloading the equipment, remove the packaging material and all
transportation safety devices.
• In the case that the shredder and its accessory components have been delivered as
individual items, mount these at the site of application in accordance with the
assembly drawing.
• Align the machine horizontally using a suitable spirit level.
• Do not use blocks to place underneath the machine; use metal strips in order to
prevent buckling of the base frame. Make sure that an even distribution of
weight is achieved on all the points of support.
Page 35

GRN4-610 Chapter 3: Installation 35 of 73
Suspended load! Falling loads can cause serious injury or death! Only use
a crane or forklift appropriate for the weight and dimensions of the load.
Use suitable means to stop and pay attention to the center of gravity. Do
NOT step under the suspended load. Wear a safety helmet in addition to
the basic protective gear.
Overturning or falling machine! Serious injury or death can result! In case
that the granulation will be placed erect over a pit, on a frame, or on a
platform, the machine MUST be secured by placing mounting screws
though the holes on the mounting pads (see assembly drawing).
3-1 Electrical Connections
Electrical connections should only be made by qualified electricians!
Voltage, current, frequency, and protection are marked on the type plate. The voltage
tolerance is +/- 10%.
For machines that are not pre-wired, the electrical connection is to be carried out in
accordance with the enclosed wiring diagram in the terminal box. When performing this
task, it is important to follow the regulations of the local electricity authority. The
required cable cross-section is determined according to the rated capacity of the units.
The wiring schematics are located in the control panel.
NOTE: Alterations to the wiring diagrams require the approval of the
manufacturer. Failure to obtain approval will result in the termination of
all guaranteed claims.
Dangerous voltage. Touching live parts can lead to serious injury or death!
All work relating to the electricity of the machine may only be carried out
by trained electricians. Observe the currently effective EMC regulations.
Caution must be taken to prevent electrical shock when operating certain
equipment. Installation, service, alterations, and/or modifications must
only be done by qualified personnel and with a high regard for safety.
Failing to conform to the requirements could result in bodily injury, costly
damage, or death!
Page 36

GRN4-610 Chapter 3: Installation 36 of 73
Connection of Emergency Stop Button
The machine must only be operated with installed Emergency Stop buttons. If the
Emergency Stop buttons are not installed prior to delivery, one Emergency Stop button
must be installed at the control cabinet and a second one at the grinding material in-feed.
NOTE: The control panel with the switches and Emergency Stop button should be
installed near the machine; the distance should not exceed 16 ft (5 m). The
connecting cables between the control panel and machine must be protected
against damage. If the control panel cannot be installed according to these
rules, an additional Emergency Stop button must be installed on the
machine
3-2 Initial Start-up
General Advice
All work related to the start-up of the machine must be carried out by trained and
specialized personnel.
Check the oil level of the gearbox before operating the machine!
Fill hydraulic tank with oil. Please observe the instructions in the
operational manual!
Checking the Rotational Direction
Rotational direction of the motors must be checked before initial start-up. The following
steps must be completed.
• Switch the machine on and immediately off again.
• Observe whether the discharge air fan in the drive motor is rotating in the
direction of the directional arrow.
NOTE: If running in the wrong direction, re-connect the motor connection
immediately. Damage to the machine will result from operating in the
wrong direction.
Page 37

GRN4-610 Chapter 3: Installation 37 of 73
Start-up Checklist
! When the housing panel is opened, check the cutter mounting screws using a
torque wrench.
! Search the grinding chamber for foreign matter.
! Check oil level of the gearbox motor.
! Examine in-feed device for foreign matter.
! Check that they Emergency Stop buttons are unlocked.
! Check all safety devices for proper function.
! Switch ON the machine for a short time to check the rotational direction—can be
seen at the discharge air fan of the drive motor—observe the running direction
arrow.
! Allow machine to run approximately 10 minutes without grinding material.
! Connect material discharge and in-feed device; check rotational direction drives.
! Feed grinding material uniformly; too much material can cause the machine to
overload.
! Check the temperature of ground material if necessary.
! Monitor the ammeter. This displays the present current consumption and
provides information on the load of the machine.
Page 38

GRN4-610 Chapter 4: Operation 38 of 73
Chapter 4: Operation
4-1 Start-up
Machine Checks Prior to Start-up
! The cutters are properly set and the screws are tightened with the specified
torque.
! The grinding chamber is free of foreign matter.
! The housing panel is closed.
! All safety devices, including devices for the grinding material in-feed and
discharge devices, are checked for proper function.
Switching Machine ON
1. Switch on the grinding material discharge device.
2. Switch on the hydraulics
3. Switch on the machine (main switch to 1)
4. Set to automatic on the control board
5. After cover is opened put in the pipe
6. Press cycle start button
7. Machine will operate automatically
4-2 Operation Procedures
Manual In-feed of Material
• Throw the grinding material into the feeding trough than start the cycle.
• The material should be fed into the front of the machine.
• During opening and closing of the cover, the safety light grid is activated. The
hydraulic will stop when somebody reaches in this light grid.
Rotating knives can cause serious injuries and death! Do NOT
reach into the in-feed hopper or lean in while the rotor is operating.
Use only approved grinding material!
DO NOT climb into the in-feed hopper while operating the machine.
Death will result!
Page 39

GRN4-610 Chapter 4: Operation 39 of 73
4-3 Shut-down
Switching Machine OFF
1. Wait until the cycle is finished and the cover has opened.
2. Then switch off the shredder, (main switch to 0).
3. If you want to close the cover of the feeding trough, close it manually by pressing
the button cover close.
4. Switch off the grinding material discharge device.
Page 40

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 40 of 73
Chapter 5: Maintenance
5-1 Preventative Maintenance Schedule
Only trained personnel may perform maintenance on the machine. The maintenance
must be performed within the specified time and also documented for records. Regular
maintenance is important to the continued effectiveness and efficiency of the machine.
Electrical voltage causes danger while starting the machine for
maintenance—the main switch MUST be turned to 0, the machine
must be safeguarded with a padlock, and a warning sign must be
attached.
Maintenance Plan
The following maintenance must be completed after every 8 operation hours:
• Check protective devices for proper function.
• Check mountings of cutters and bed knives.
• Check the condition of the cutters and bed knives.
The following maintenance must be completed after every 40 operation hours:
• Check that all screws are tightened.
• Check all wearing parts.
• Check hydraulic oil level and consistence.
The following maintenance must be completed after every 2000 operation hours:
• Check the oil level in the gearbox motor.
The following maintenance must be completed when necessary:
• Clean the machine.
• Check the main bearings (bearing clearance, lubricant renewal).
Yearly Maintenance:
• The purpose of yearly maintenance is to check the general condition of the
machine and to arrange for the arrival of any necessary replacement parts in good
time. A service engineer can assist in performing this task.
Page 41

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 41 of 73
5-2 Preventative & Corrective Maintenance
Checking the Protective Devices
Check all safety devices for stipulated condition, location, and function; verify they have
safe mountings.
Danger results from non-functioning protective devices! Serious
injury or death can result. Eliminate all defects before you put the
machine into operation! If defects occur during operation, stop the
machine immediately and eliminate the defect! Do NOT change or
remove any protective devices. Do NOT modify the protective
devices
Cleaning the Machine
To clean the machine, follow the steps below.
1. Switch OFF the shredder at main switch.
2. Safeguard main switch with a padlock.
3. Open the housing panel.
4. Safeguard the housing panel.
5. Pre-clean the grinding chamber with a hand brush.
6. Evacuate the remaining grinding material residue with a suitable suction device.
7. Remove any clinging residue with a wooden scraper.
8. Close the housing panel.
9. Machine can be started again.
Danger of cutting caused by sharp knives even while the rotor is
stationary. Serious injury may result—especially to the hands and
fingers—wear protective gloves.
Inhalation of dust can be hazardous and can result in respiratory
injury—never blow out the residue and use breathing protection if
necessary.
Replacing the Gearbox Motor
The gearbox motor’s dimensions make replacing the gearbox necessary only in
exceptional cases. Dismounting and mounting the gearbox requires specialized
knowledge. Please observe the installation requirements of the gearbox manufacturer.
Page 42

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 42 of 73
Replacing the Rotor
The rotor has a heavy-duty design, which makes replacement necessary only after a
crash, i.e. a hammer falls inside the machine. Dismounting and mounting the rotor
requires specialized knowledge.
Dismounting the rotor
Follow the steps below to dismount the rotor.
1. Dismount the gearbox motor.
2. Remove the rotor mounting slot cover plates from the housing.
3. Screw in hooks on both shaft ends.
4. Remove the bearing housing mounting bolt.
5. Carefully lift the rotor out of the housing using suitable lifting equipment.
6. Place the rotor in a safe location (appropriately-sized timber beams are suitable
for this).
Mounting the rotor
Clean the bearing seat surfaces and check the key before proceeding as follows to mount
the rotor.
1. Lift the rotor using suitable lifting/stopping equipment and place the rotor
carefully into the bearing seats.
2. Attach the bearing housing (Pos) to the bearing seats with screws.
3. Place the gearbox motor onto the rotor axis.
4. Return the rotor mounting slot cover plates.
5. Carry out a test run.
Replacing the Main Bearings
The dimensions of the main bearings make a replacement necessary only in exceptional
cases. Dismounting and mounting the bearings requires specialized knowledge;
therefore, please observe all instructions provided by the manufacturer or call customer
service for assistance.
The bearings mounting in this machine are indicated in the spare parts list. A
requirement for dismounting and mounting the bearings is a suitable pulling-off device.
Page 43

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 43 of 73
Dismounting the main bearings
Follow the steps below to dismount the main bearings.
1. Dismount the gearbox motor.
2. Pull the distance sleeve from the rotor axis.
3. Remove the rotor cover plates from the housing.
4. Screw in hooks/eye bolts on both shaft ends.
5. Hang the rotor from hooks/eye bolts on both shaft ends.
6. Remove the bearing housing mounting bolt.
7. Carefully lift out the complete rotor using suitable lifting equipment.
8. Place the rotor in a safe location (timber beams are recommended).
9. Loosen the bearings cover mounting screws and take off the bearing cover.
10. Pull the bearing housing off using a pulling-off device.
11. Pull the bearing off the rotor axis using a pulling-off device.
Mounting the main bearings
Thoroughly clean the bearing surfaces and the shaft surfaces and grease them lightly
before following the steps below to mount the main bearings.
1. Mount the bearing in bearing housing.
2. Attach the bearing with the bearing housing to the rotor axis.
3. Lift the rotor using suitable equipment; carefully place the rotor into the bearing
seats.
4. Attach the bearing housing to the bearing seats with screws.
5. Return the distance sleeve to the rotor axis.
6. Return the gearbox motor to the rotor axis.
7. Return the rotor cover plates.
8. Carry out a test run.
NOTE: The mounting forces must always engage the inner-ring or roller body
damage will result. The hardened bearing rings are sensitive to stressed
impact; never hit the rings directly with a hammer. It is recommended to
use a brass arbor or piping piece made from soft material. The bearing
should be put onto the shaft using light blows. When performing this task,
the force of pressure must be evenly distributed on the circumference of the
bearing ring.
Page 44

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 44 of 73
Lubricating the Main Bearings
A correct lubricant supply is an important requirement for operational safety and long
service life of bearings. Every machine is greased and test runs are performed before
delivery.
NOTE: Unsuitable lubricant, lubricant deficiency, excessive lubricant, or impurities
in the lubricant lead to overheating and extreme wear of the bearings.
Lubrication intervals
Use the following table to determine when to check and replace the lubricant.
Shift Operation
When to Replace
When to Check
One shift operation.
Every 18 months.
Monthly.
Two shift operation.
Every 9 months.
Monthly.
Three shift operation.
Every 6 months.
Monthly.
Checking lubricant quality
When determining whether a lubricant needs to be replaced, check for the following:
• Change in consistency.
• Discoloration.
• Degree of soiling.
Replacing or refilling lubricant
• Fill the bearings uniformly with grease until all operating surfaces are well-
greased.
• A lubricant quantity of 1/3 to 1/2 of the bearing volume per bearing is
required. If too much grease is used, the lubricant will become unusable due
to excessive temperature.
• Only one type of grease must be used. Mixing different types of grease
together is prohibited. The bearings are filled at the factory with lithium
base saponification roller bearing grease F3.
• Use the “List of lubricants” to determine which lubricants from which
manufacturers to use.
Page 45

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 45 of 73
Refilling lubricant
The grease travels through the circulating grooves and bores via lubrication nipples into
the interior of the bearing. The greasing quantity is 2 oz. (60g) to 3.5 oz. (100g) roller
bearing grease F3 per bearing.
Replacing lubricant
Renewing the lubricant between the specified intervals is only necessary when unusual
bearing noises or overheating occurs. Mounting and dismounting the bearings must be
performed according to the instruction in the operation manual.
Follow the steps below to replace the lubricant.
1. Open the bearing.
2. Remove the bearing housing and the bearing cover.
3. Carefully clean the bearing with petroleum ether. (Petroleum ether, petroleum,
spirit, aqueous neutral, or alkaline cleaning agents may be used to clean the
bearings.) The bearing must be immediately preserved with the lubricant after
cleaning in order to avoid corrosion.
4. Fill the bearing with an approved lubricant (see “list of lubricants”).
Grease
nipple
Page 46

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 46 of 73
List of lubricants
Name/ Country of Manufacturer
Roller Bearing Grease
ARAL
ARAL Grease HL 3
BP
BP ENERGREASE LS 3
CASTROL
CASTROL SPHEEROL AP 3
ESSO
Beacon 3
FUCHS
FUCHS Grease 1200; FUCHS Grease FWA 220
SHELL
SHELL Alvania Grease 3
MOBIL-OIL
MOBILUX 3
WISURA
WISURA Liba L 3
Zeller & Gmelin
ZET GE Grease M 50
FAG
FAG L 71
ANTAR Petroles de l’Antantique
ROLEXA
Holland, Beverol
Beverol Multi-Purpose Grease
Italy, Agip
AGIP Grease 33 FD
Sweden, NYNAS
Nynas FI 3-42
Page 47

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 47 of 73
Mounting and dismounting TAPER-LOCK tensioning element
The motor- and the gear-"V"-belt pulleys are attached onto the shaft by means of a
TAPER-LOCK tensioning element. The disks must be dismounted for certain
maintenance work.
Table for the tightening torque of the screws
Tensioning element
(Type)
Screws-Tightening
torque in Nm
Screw details
Number
Size (BSW)
3535
60 3 ½”
Page 48

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 48 of 73
Mounting the TAPER-LOCK tensioning element
Proceed as follows:
• Remove the protective coating from the bore and outside of bushing, and
bore of hub. After ensuring that the mating tapered surfaces are
completely clean and free from oil or dirt. Insert bushing in hub so that
holes line up.
• Sparingly oil thread and point of grub screws, or thread and under head
on cap screws. Place screws loosely in holes threaded in hub, shown thus
◎ in.
• Clean shaft and fit hub to shaft as one unit and locate in position desired,
remembering that bushing will hip the shaft first and then will be
slighting drawn on the bush.
• Using a hexagon wrench tighten screws gradually and alternately to
certain torque.
• Hammer against large-end of bushing, using a block or sleeve to prevent
damage. (This will ensure that the bushing is seated squarely in the bore).
Screws will now turn a little more. Repeat this alternate hammering and
screw tightening once or twice to achieve maximum grip on the shaft.
• If a key is to be fitted, place it in the shaft keyway before fitting the
bushing. It is essential that it is a parallel key and side fitting only and
has TOP CLEARANCE.
• After drive has been running under load for a short time stop and check
tightness of screws.
• Fill empty holes with grease to exclude dirt.
Dismounting the TAPER-LOCK tensioning element
Proceed as follows:
• Slacken all screws by several turns, remove one or two according to
number of jacking off holes shown thus • in the illustration. Insert screws
in jacking off holes after oiling thread and point of grub screws or thread
and under head of cap screws.
• Tighten screws alternately until bushing is loosened in hub and assembly
is free on the shaft.
• Remove assembly from shaft.
Work on the “V” belts
"V"-belts are wearing parts, which stretch and must be re-tensioned. In order to guarantee a
long service life of the "V"- belts, regular checks on the tension force of the "V"-belts and the
condition of the "V"-belts are necessary.
Checking the tension force of the “V” belt
Page 49

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 49 of 73
1. Verify that the alignment of the pulley is correct. Utilizing a straightedge of
sufficient length to span from one pulley to the other, place it along the sides of
both pulleys. The entire face of each pulley should fully contact the straightedge.
2. Measure the belt SPAN with a measuring tape. Record this dimension in your
note book.
3. Using the deflection tester, apply a perpendicular force at the midpoint of any
one of the belts to deflect the belt 1/64th of an inch.
4. Calculate the deflection force:
FORCE[Lb]= SPAN[IN] X (1/64)[Lb/IN]
5. Identify the belt type and measure the small sheave diameter. Look up the proper
model belt deflection force table and find out what the force is supposed to be.
6. The motor position should be adjusted until the actual deflection force matches
the force listed in the table.
7. In no case should the belts be over tensioned, as this can significantly reduce belt
and/or bearing life
Page 50

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 50 of 73
!"#$%&'())%
)*+##%
),"+-"%
."/#"&$0(1%
/('&"%
!"#$%&'(
)%*+"$",(,*'-"(
./012(
)2+%
%%
3456748%
%%%%745%
)2+%
%%
7476945%
%%%%949%
)2!%
%%
:486;45%
%%%%<<%
)2!%
%%
5486<84=%
%%%%<=43%
)2&%
%%
;4;6<=4>%
%%%%<54;%
)2&%
%%
<=496884>%
%%%%8:4=%
?2!%
%%
;4;654;=%
%%%%949%
Checking “V” belt condition, replacing “V” belt
Serious injury can result by running “V” belt. Never dismount the
“V” belt cover and window during operation. Hair, jewelry etc. can
be pulled into the machine.
Working on the Cutters
The correct grinding properties, the correct setting, and the correct mounting of the
cutters are all important factures to ensure proper function and economic operation of the
shredder.
Replacing and checking the cutter mountings
• Certain machine parts are subject to stress while operating due to vibrations,
which can lead to the loosening of screw connections. It is very important to
check the cutter mounting screws according to the intervals in the maintenance
plan.
• Tighten the mounting screws on the cutters using a torque wrench set to the
required torque for the screw size. The required torque for the cutter mounting
bolts is 120 Nm.
• Use the table below to determine torque values. The tightening capacity
decreases on screws that have been loosened and tightened several times. New
screws of the same material must replace the cutter mounting screws after they
have been loosened and tightened several times.
Page 51

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 51 of 73
Torque Value Table
Bolt Type
Grade 8.8
Grade 10.9
Grade 12.9
Nm
lb. ft.
Nm
lb. ft.
Nm
lb. ft.
M8
25
18.4
35
25.8
41
30.2
M10
49
36
69
60
83
61.2
M12
86
63.4
120
88.5
145
106
M16
210
154
295
271
355
261
M20
410
302
580
428
690
508
M24
710
523
1000
737
1200
885
Checking the condition of the cutters
The cutters become blunt after a certain number of operation hours. They need to be
checked regularly. Using blunt knives has several consequences including decreased
grinding capacity, increased current consumption of the drive motor, inexact cuts, and
overheating of the material.
Sharp knives are dangerous even while the rotor is at standstill.
Serious injury can result—especially to the hands and fingers—wear
protective gloves!
Dismounting the cutters
Follow the steps below to dismount the cutters. (See image below.)
1. Switch OFF the shredder at the main switch.
2. Safeguard the main switch with a padlock.
3. Open the lower housing panel.
4. Safeguard the housing panel.
5. Clean the hexagon head socket of the cutter mounting bolt (2).
6. Loosen the bolt using a high quality Allen key (.4 in./10 mm). Lightly knock the
Allen key with a hammer to loosen if necessary.
7. Take out the cutter mounting bolt, the washer, and the cutter.
Page 52

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 52 of 73
NOTE: It is possible to reach the cutting shaft by climbing into the feeding chamber;
however, it is strongly recommended that the cutters are accessed through the front
size door. The shaft can be rotated manually by turning the motor V-belt pulley.
Sharp knives are dangerous even while the rotor is at standstill.
Serious injury can result—especially to the hands and fingers—wear
protective gloves!
Dismounting the cutter holders
Follow the steps below to dismount the cutter holders. (See previous image.)
1. Switch OFF the shredder at main switch.
2. Safeguard the main switch with a padlock.
3. Open the lower housing panel.
4. Safeguard the housing panel.
5. Clean the hexagon head socket of the cutter mounting (2).
6. Loosen the bolt using a high quality Allen key (.4 in./10 mm). Light knock the
Allen key with a hammer to loosen if necessary.
7. Take out the cutter holder mounting bolts.
8. Remove the cutter holder with the delivered Extractor.
NOTE: It is possible to reach the cutting shaft by climbing into the feeding chamber;
however, it is strongly recommended that the cutters are accessed through the front
size door. The shaft can be rotated manually by turning the motor V-belt pulley.
4
1 2 3
(1) Cutter
(2) Cutter mounting screw
(3) Cutter holder
(4) Cutter mounting
screws
Page 53

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 53 of 73
Sharp knives are dangerous even while the rotor is at standstill.
Serious injury can result—especially to the hands and fingers—wear
protective gloves!
Dismounting the bed knives
Follow the steps below to dismount the bed knives. (See image below.)
1. Switch OFF the shredder at the main switch.
2. Safeguard main switch with padlock.
3. Open the upper housing panel.
4. Safeguard the housing panel.
5. Clean the hexagon head socket of the knife mounting bolts (2) and the cover
plates mounting bolts.
6. Loosen the cover plate mounting bolts with Allen key; lightly knock with a
hammer if necessary.
7. Take out the bolts and cover plates.
8. Loosen the knife adjusting screws for pulling and take them out. Loosen the
knife mounting bolts using an Allen key; knock lightly with a hammer if
necessary.
9. Take out the knife mounting bolt and the knife.
Page 54

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 54 of 73
Mounting the cutter holders
Follow the steps below to mount the cutter holders.
1. Clean the knife pocket and the cutter holder.
2. Insert the cutter holder into the pocket.
NOTE: Cutter holder must slide in easily. Do NOT damage the cutter holder surfaces
with a hammer.
3. Attach the cutter holder mounting bolts (DIN912 – M8x25 – 12.9) and add some
Loctite.
4. Make sure that the cutter holder fits properly.
5. Tight the cutter mounting bolts using a torque wrench. The required torque for
the cutter holder mounting bolts is 39 Nm. (Refer to torque values table.)
6 7 3 5 4 1 6
(1) Bed knife
(2) Bed knife mounting
screws
(3) Bed knife holder
(4) Cover plates
(5) Bed knife adjusting
screw
(6) Cover plate holder
(7) Cover plate mounting
screws
Page 55

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 55 of 73
Mounting the cutters
NOTE: The cutters and bed knives—especially the cutters—should only be
sharpened or replaced in sets. There is a danger of balance error if a combination
of cutters from different sets is used.
Follow the steps below to mount the cutters.
1. Clean the knife support surface and the hole on the cutter holder.
2. Insert sharp cutter or turn old cutter and push against the cutter holder surface.
3. Attach the cutter mounting bolt (DIN912 – M12x40 – 12.9), and the washer
(DIN433 – 13 – 300HV).
4. Screw in the mounting screws and tighten lightly first. Make sure the cutter
fits planar in the seat!
5. Tighten the cutter mounting bolts using a torque wrench. The required torque for
all cutter mounting bolts is 120 Nm (refer to the torque values table).
6. Make sure the cutting gap is correct and also that the cutters and bed knives do
not collide as the rotor turns.
7. Remove tools and other objects from the cutter chamber.
8. Switch ON the shredder for a brief time without grinding material; listen for
noises. If unusual noises are present, determine the cause and eliminate it.
NOTE: Cutters are reversible and have four symmetrical cutting edges, which
makes it possible to turn the cutters and only to sharpen after every fourth cutter
change.
Sharp knives are dangerous even while the rotor is at standstill.
Serious injury can result—especially to the hands and fingers—wear
protective gloves!
Page 56

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 56 of 73
Mounting the bed knives
Follow the steps below to mount the bed knives.
1. Clean the knife supporting surface and the holes on the knife holder.
2. Insert sharp knife or turn old knife.
3. Attach the knife adjusting bolts.
4. Attach the knife mounting bolts (DIN912 – M12x55 – 12.9) and tighten lightly at
first.
5. Adjust the gap between the cutters and bed knives to 0.03 in. to 0.04 in. (.8 –
1mm).
6. Tighten the knife mounting bolts using a torque wrench. The required torque for
all knife mounting bolts is 120 Nm (refer to the torque values table).
7. Turn the rotor by hand.
8. Make sure the cutting gap is correct and that the cutters and bed knives do not
collide as the rotor turns.
9. Return the cover plates and mount them with the bolts.
10. Remove tools and other objects from the cutting chamber.
11. Switch ON the shredder for a brief time without grinding material; listen for
noises. If unusual noises are present, determine the cause and eliminate it.
Page 57

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 57 of 73
Sharpening cutters and bed knives
Shredder cutters have four cutting edges, which means they can be turned three times.
After the third turn, they should be replaced with new ones. Bed knives can be turned
two times and can be re-sharpened for as long as they can be mounted with the long hole.
NOTE: Specialist sharpening of the cutters and bed knives is available through customer
service.
NOTE: The cutters and bed knives—especially the cutters—should only be sharpened or
replaced in sets. There is danger of balance error if a combination of cutters from
different sets is used.
Follow the steps below to sharpen the cutters and bed knives.
1. Dismount the cutters.
2. Sharpen the cutters. A specialist should use the sharpening plan to uniformly
sharpen the cutting knives mechanically. It is important to make sure that
sharpening takes places with small grinding allowance and sufficient coolant
supply. The sharpening process is finished when the cutting edge is sharply cut.
Not all indentations must be worked out, or the number of possibilities for
sharpening is reduced. For the sharpening process, use soft grinding wheels
(40H or 46K). Knives with grinding cracks should not be re-used due to danger
or breakage during operation.
3. Whet the cutting edges of the cutters and bed knives with a whetstone.
4. Set the cutters and bed knives.
5. Mount the cutters and bed knives.
Sharp knives are dangerous even while the rotor is at standstill.
Serious injury can result—especially to the hands and fingers—wear
protective gloves!
Page 58

GRN4-610 Chapter 5: Maintenance 58 of 73
Setting the cutters and bed knives
Rotor knives used in this machine don’t have to be adjusted. All adjustments have to be
done with the bed knives. To simplify knife setting and shorten the standstill, the bed
knives have four adjusting screws—two for pulling and two for pushing the knife.
Standstill needs to be avoided/reduced if there are multiple cutter sets. Setting the gap
between the cutters and bed knives carefully and correctly is an important requirement
for the productivity of the shredder. Factors for the size of the gap include the size and
design of the rotor and the material to be ground.
Follow the steps below to set the cutters and bed knives.
1. Remove old knives.
2. Insert sharp knife or turn old knife.
3. Attach the knife adjusting bolts and adjust them roughly. Attach the knife
mounting bolts (DIN912 – M12x55 – 12.9) and tighten lightly first.
4. Adjust the gap between the cutter and bed knife to 0.3 in. to 0.4 in. (0.8 to 1 mm).
5. Tighten the knife mounting bolts using a torque wrench. The required torque for
all knife mounting bolts is 120 Nm (refer to torque values table).
6. Turn the rotor by hand.
7. Make sure the cutting gap is correct and also that the cutters and bed knives do
not collide as the rotor turns.
8. Mount the knife cover plates.
Transporting and storing the cutters and bed knives
Sharp knives present danger of cutting! Serious injury can result—
especially to the hands and fingers—wear protective gloves!
• Only transport and store the packaged cutters and bed knives.
• Grease the cutters and bed knives to avoid rust.
• Protect the cutting edges with doubled cardboard, and use adhesive
tape to safeguard the cutters and bed knives from slipping out of the
sides.
• After unpacking, the cutters and bed knives MUST be de-greased in
order to promote a safe grip!
Page 59

GRN4-610 Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 59 of 73
Chapter 6: Troubleshooting
6-1 Introduction
The utmost in safety precautions should be observed at all times when working on or around
the machine and the electrical components. All normal trouble-shooting must be
accomplished with the power off, line fuses removed, and with the machine tagged as out of
service.
The use of good quality test equipment cannot be over-emphasized when troubleshooting is
indicated. Use a good ammeter that can measure at least twice the AC and DC current that
can be encountered for the machine. Be sure that the voltmeter has at least minimum
impedance of 5,000 OHMS-per-volt on AC and 20,000 OHMS-per-volt on DC scales.
Popular combination meters, VOM and VTVM can be selected to provide the necessary
functions.
Before making haphazard substitutions and repairs when defective electrical components are
malfunctioning, we recommend that you check the associated circuitry and assemblies for
other defective devices. It is common to replace the obviously damaged component without
actually locating the real cause of the trouble. Such hasty substitutions will only destroy the
new component. Refer to wiring diagrams and schematics.
Locating mechanical problems, should they occur, is relatively straightforward. When
necessary, refer to the parts catalog section.
Page 60

GRN4-610 Chapter 6: Troubleshooting 60 of 73
Problem
Possible Cause
Possible Remedy
Motor doesn’t work
Electric source
Motor damage
Correct wire connection
Replace motor
Oil pump doesn’t work
Motor not working
Pump damage
Correct wire connection
Replace pump
Oil pump noise
Filter jam
Hydraulic oil to thick
Poor hydraulic oil quality
Pipe leaking
Pump damage
Motor and pump
misalignment
Clean the filter
Change hydraulic oil
Change hydraulic oil
Tighten pipe connectors
Change pump
Working pressure abnormal
Spillover valve and sequence
valve jam
Pump damage
Clean spill over valve and
sequence valve
Change pump
Pressure maintain abnormal
Sealing broken
Pipe leak
Single direction valve jam
Change sealing
Check and solve the leak
Clean the valve
Work abnormal
Pressure abnormal
Magnetic valve abnormal
Electrical problem
Clean spill over valve and
sequence valve
If the valve jams, clean it. If
it is broken, change it
Check and change the
broken electrical parts
Page 61

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 61 of 73
Chapter 7: Appendix
7-1 Technical Specifications
Feeding chamber opening:
Data in mm:
6720x840
Rotor dimension:
Diameter in mm:
Width of cut in mm:
980
1210
Rotor type E
Rotor knives:
No. of rotor knives:
108
Stator knives:
No. of stator knives:
4
Rows of stator knives:
1x4
Rotor speed (50Hz):
rpm
36
Width:
Data in mm:
2820
Length:
Data in mm:
11770
Height:
Data in mm:
2590
Drive motor:
Power in kW:
2x45
Motor hydraulic unit
Power in kW:
15
Range of stage cylinder:
Data in mm:
7000
Machine weigh:
In kg
Approx. 20
Electrical connection data:
Markings are attached to the maching
Noise level:
Depends on plant location
and type of grinding
material!
Without noise equipment, in
dB(A):
Approx. 95
With noise equipment in
dB(A):
Depends on type of
soundproof
Page 62

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 62 of 73
7-3 Drawings and Diagrams
(See corresponding spare parts lists)
Rotor knife fixing
Page 63

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 63 of 73
Stator knife fixing
604
602
607
603
605
606
601
Page 64

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 64 of 73
Rotor assembly
Page 65

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 65 of 73
Drive
410
Page 66

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 66 of 73
Guidance
Page 67

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 67 of 73
Hydraulic Diagram
Page 68

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 68 of 73
Hydraulic Pump
Page 69

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 69 of 73
7-4 Spare Parts List
Pos.
Pc
Description/Standard
Part number/SAP
100
Machine complete
101
2
Side cover
ZRS1000-01-06-00
102
1
Lower door
ZRS1000-01-07-00
103
1
Upper door
ZRS1000-01-08-00
104
1
Top cover
ZRS1000-01-09-00
105
1
Scraper top
ZRS1000-01-03
106
12
Anti-vibrating foot
80050273
200
1
Feeding trough
201
3
Bolt (I) for cylinder for cover
ZRS1000-04-02-00
202
3
Bolt (II) for cylinder for cover
ZRS1000-04-03-00
203
3
Bolt (III) for cylinder for cover
ZRS1000-04-04-00
204
10
Anti-vibrating foot
80050273
205
2
Pneumatic cylinder SI-63x160-S-CB
80040369
206
2
Lock GH72425
207
2
Bolt (I)
ZRS1500-11-07
208
2
Bolt (II)
ZRS1500-11-08
209
8
Circlip DIN471 – 16
210
2
Safety grid
ZRS1500-16-00
211
2
Safety bar for cover
ZRS1500-18-00
300
2
Bearing
301
2
Bearing housing SN236
302
2
Bearing 22236/W33
303
3
Bearing Cover A
GSH80120-021-03-
304
1
Bearing Cover B
GSH80120-021-03-
305
0
Bearing Cover C
306
4
Sealing DIN3760 D200 x 230 x 15
307
2
Key 308
2
Distance bush
ZRS1000-06-02
309
32
Fixing bolt DIN912 – M12 x 30 8.8
310
2
Washer DIN125 – 25
311
2
Fixing bolt DIN912 – M24 x 70 8.8
312
2
Spring washer DIN127 – 24
313
8
Washer DIN125 – A24
314
8
Fixing bolt DIN912 – M24 x 11- 8.8
315
8
Spring washer DIN127 – B24
400
2
Drive 45 kW
401
2
Motor 45 kW
Page 70

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 70 of 73
402
2
Gear pulley SPC375-4
403
2
Gear pulley taper bush TB 3535 - 48
80002370
404
2
Key 405
8
V-Belt SPC3350
406
2
Motor pulley SPC375-4
407
2
Motor pulley taper bush TB 3535 - 60
80002350
408
2
Key 409
2
Pulley cover + support
ZRS1000-15-01-00
410
1
Base frame for motor
ZRS1000-07-01-00
411
1
Gear box SEW MC3PLHF06SD – 14 (i=41)
1
Gear box SEW MC3PLHF05SD – 23 (i-41)
412
2
Torque arm plate
ZRS1000-07-04-01-00
413
8
Bolt DIN933 – M24x140 – 12.9
414
16
Washer DIN433 – 25 – 300HV
415
8
Nut DIN934 – M24
416
2
Torque arm bolt
ZRS1500-07-05
417
40
Disc spring DIN2093 – A71
418
2
Hard washer
ZRS1000-07-06-04
419
2
Nut DIN934 – M36 – 10
420
2
Nut DIN935 – M36 – 10
80040180
421
6
Hard washer
ZRS1000-07-06-06
422
2
Fixing bolt
ZRS1500-07-03-00
423
2
Bolt DIN933 – M10x30 – 8.8
424
2
Washer DIN125 – A10
425
2
Spring washer DIN127 – 10
426
2
Distance sleeve
ZRS1000-07-07
427
2
Cover
ZRS1000-07-08
428
2
Bolt DIN933 – M16x45
429
2
Spring washer DIN127 - 17
500
1
E-knife rotor 1482x1410
501
204
Rotor knife 34x34x20
80001002
502
204
Rotor knife fixing Bolt DIN912 – M12x40 – 12.9
80040034
503
204
Washer GB/T1230-12
80040029
504
204
Rotor knife holder
21660700
505
408
Knife holder fixing bolt M8x25 DIN912/12.9
80011090
506
204
Underlay plate t=2
ZRS1500-06-01-05
600
1
Stator knife complete
601
4
Stator knife 279x80x30
80001202
602
8
Prism fixing Bolt DIN912 – M12x65 – 12.9
603
8
Bolt for pushing DIN912 – M12x65 – 12.9
80011290
604
8
Bolt for pulling DIN912 – M16x50 – 12.9
605
8
Knife holder fixing bolt DIN912 – M16x45 – 12.9
80011290
606
4
Knife holder plate
ZRS1500-01-01-03-03
607
4
Prism
ZRS1500-01-01-03-02
Page 71

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 71 of 73
Pos.
Pc
Description/Standard
Partnumber/SAP
700
1
Pusher complete
701
1
Stage cylinder 100x140x180x225-7000
702
6
Support roller NATV40PPA
703
6
Shaft for bearing
ZRS1500-05-01-02-01
704
12
Lock washer DIN5406 – MB8
705
12
Slotted nut DIN981 – KM8
706
12
Fixing bolt support roller DIN933 – M16 –
707
12
Washer DIN125 – 16 – 300HV
708
18
Support roller KR80PPA
709
18
Nut DIN934 – M30x1.5 – 10
710
18
Washer DIN125 – 31 – 300HV
711
3
Scraper
712
1
Bolt for cylinder
ZRS1500-12-03-00
800
Hydraulic
801
3
Cylinder for cover 63 x 35 x 280
802
1
Hydraulic unit SCH-412-00-2 F 15 kW
803
6
Pipe holder
80050784
804
Connectors
900
Electrical parts
901
3
Safety switch AZ15zvrk
902
5
Small control box
903
1
Control panel
904
1
Control cabinet
905
3
Proximity switch II0297
906
3
Cable for Proximity switch E10200
907
1
Laser distance sensor 01D1000
908
3
Light barrier YM-T10
Page 72

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 72 of 73
7-5 Technical Assistance
Parts and Service Department
The ACS Customer Service Group will provide your company with genuine OEM quality parts
manufactured to engineering design specifications, which will maximize your equipment’s performance and
efficiency. To assist in expediting your phone or fax order, please have the model and serial number of
your unit when you contact us. A customer replacement parts list is included in this manual for your
convenience. ACS welcomes inquiries on all your parts needs and is dedicated to providing excellent
customer service.
For immediate assistance, please contact:
• North, Central and South America, 8am – 5pm CST +1 (800) 483-3919 for drying, conveying,
heating and cooling and automation. For size reduction: +1 (800) 229-2919.
North America, emergencies after 5pm CST (847) 439-5855
North America email: acsuscanadacustserv@corpemail.com
• Mexico, Central & South America
Email: acslatinamericacustserv@corpemail.com
• Europe, Middle East & Africa +48 22 390 9720
Email: acseuropecustserv@corpemail.com
• India +91 21 35329112
Email: acsindiacustserv@corpemail.com
• Asia/Australia +86 512 8717 1919
Email: acsasiacustserv@corpemail.com
Sales and Contracting Department
Our products are sold by a worldwide network of independent sales representatives. Contact our Sales
Department for the name of the sales representative nearest you.
Let us install your system. The Contract Department offers any or all of these services: project planning;
system packages including drawings; equipment, labor, and construction materials; and union or non-union
installations.
For assistance with your sales or system contracting needs please Call:
North, Central and South America +1 (262) 641-8600 or +1 (847) 273-7700
Monday–Friday, 8am–5pm CST
• Europe/Middle East/Africa +48 22 390 9720
• India +91 21 35329112
• Asia/Australia +86 512 8717 1919
Facilities:
ACS offers facilities around the world to service you no matter where you are located. For more
information, please visit us at www.acscorporate.com
Asia/Australia:
ACS Suzhou
109 Xingpu Road SIP
Suzhou, China 215126
Phone: + 86 8717 1919
Fax: +86 512 8717 1916
Europe/Middle East/Africa:
ACS Warsaw
Ul. Działkowa 115
02-234 Warszawa
Phone: + 48 22 390 9720
Fax: +48 22 390 9724
India
ACS India
Gat No. 191/1, Sandbhor Complex
Mhalunge, Chakan, Tal Khed,
Dist. Pune 410501, India
Phone: +91 21 35329112
Fax: + 91 20 40147576
United States:
ACS Schaumburg- Corporate Facility
1100 E. Woodfield Road
Suite 588
Schaumburg, IL 60173
Phone: + 1 847 273 7700
Fax: + 1 847 273 7804
ACS New Berlin- Manufacturing Facility
2900 S. 160th Street
New Berlin, WI 53151
Phone : +1 262 641 8600
Fax: + 1 262 641 8653
Page 73

GRN4-610 Chapter 7: Appendix 73 of 73
 Loading...
Loading...