Page 1

Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
User’s guide
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 2

Copyright © SWsoft, 2002. All rights reserved.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
OS/2 is a registered trademarks of IBM Corporation.
UNIX is a registered trademarks of The Open Group.
Windows and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and copyrights referred to are the property of their
respective owners.
Distribution of substantively modified versions of this document is prohibited
without the explicit permission of the copyright holder.
Distribution of the work or derivative work in any standard (paper) book form
for commercial purposes is prohibited unless prior permission is obtained
from the copyright holder.
DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED «AS IS» AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED
CONDITIONS, REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES, INCLUDING ANY
IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT, ARE DISCLAIMED, EXCEPT TO THE
EXTENT THAT SUCH DISCLAIMERS ARE HELD TO BE LEGALLY INVALID.
Page 3

Table of Contents
INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................... 5
1. INSTALLING AND STARTING WORK WITH ..................................................
A
CRONIS TRUEIMAGE DELUXE ............................................................... 14
1.1 ACRONIS TRUEIMAGE DELUXE SYSTEM PACKAGE ................................... 14
1.2 INSTALLATION ........................................................................................... 14
1.3 REPAIRING ACRONIS TRUEIMAGE DELUXE .............................................. 23
1.4 REMOVING THE SOFTWARE ....................................................................... 24
1.5 USER INTERFACE ....................................................................................... 24
1.5.1 TERMINOLOGY ...................................................................................................24
1.5.2 USER INTERFACE BASICS ....................................................................................24
1.5.3 WINDOWS........................................................................................................... 25
1.5.4 DIALOGS AND CONTROLS...................................................................................27
1.5.5 INFORMATIVE ELEMENTS ...................................................................................33
1.5.6 SPECIAL DIALOG TYPES .....................................................................................34
1.6 RUNNING ACRONIS TRUEIMAGE DELUXE SOFTWARE .............................. 35
1.7 FINISHING THE WORK WITH ACRONIS TRUEIMAGE DELUXE SOFTWARE .. 35
2. CREATING DISK/PARTITION IMAGES ....................................................... 36
2.1 CREATING A DISK/PARTITION IMAGE ON A HARD DISK ............................. 36
2.1.1 WELCOME PAGE .................................................................................................36
2.1.2 SELECTING AN OPERATION .................................................................................37
2.1.3 SELECTING PARTITIONS FOR IMAGE CREATION ...................................................38
2.1.4 IMAGE DEVICE TYPE ...........................................................................................39
2.1.5 A PARTITION/DISK ARCHIVE FILE........................................................................ 40
2.1.6 IMAGE’S DATA COMPRESSION LEVEL ..................................................................43
2.1.7 CREATING ARCHIVE VOLUMES ........................................................................... 43
2.1.8 PROTECTING AN ARCHIVE FILE WITH A PASSWORD............................................. 45
2.1.9 COMMENTING AN ARCHIVE FILE .........................................................................46
2.1.10 IMAGE CREATION SCRIPT ..................................................................................47
2.1.11 CREATING AN IMAGE ........................................................................................48
2.1.12 FINISHING IMAGE CREATION.............................................................................49
2.2 CREATING A DISK/PARTITION IMAGE ON REMOVABLE MEDIA................... 49
2.2.1 SELECTING A PARTITION AND AN OPERATION .....................................................49
2.2.2 SELECTING A REMOVABLE DISK DRIVE ...............................................................49
2.2.3 THE FOLLOWING ACTIONS ..................................................................................50
2.2.4 THE SCRIPT WINDOW ..........................................................................................52
2.2.5 THE SCRIPT PROGRESS ........................................................................................52
3. RESTORING A DISK/PARTITION FROM AN IMAGE .................................... 54
3.1 RESTORING A PARTITION (DISK) ................................................................ 54
3.1.1 SELECTING AN ACTION: RESTORE A PARTITION/DISK.......................................... 54
3.1.2 SELECTING AN ARCHIVE FILE.............................................................................. 55
3.1.3 ENTERING A PASSWORD...................................................................................... 57
3.1.4 ARCHIVE FILE PARTITIONS..................................................................................57
3.1.5 DESTINATION PARTITION ....................................................................................58
3.1.6 EXCLUSIVE PARTITION ACCESS........................................................................... 59
3.1.7 PARTITION TYPE (PRIMARY/LOGICAL) ................................................................60
3.1.8 FILE SYSTEM....................................................................................................... 61
3.1.9 CHANGING SIZE OF A PARTITION TO BE RESTORED.............................................. 62
3.1.10 SELECTING A LETTER FOR A PARTITION TO BE RESTORED .................................64
3.1.11 THE NEXT PARTITION/DISK TO BE RESTORED ....................................................65
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
3
Page 4

3.1.12 RESTORATION SCRIPT .......................................................................................66
3.2 PARTITION RESTORATION PECULIARITIES ................................................. 67
3.3 PECULIARITIES OF RESTORATION FROM REMOVABLE MEDIA.................... 69
3.4 RESTORING SEPARATE FILES ..................................................................... 70
3.4.1 CONNECTING A DRIVE FROM A PARTITION IMAGE ...............................................70
3.4.2 SELECTING AN ARCHIVE FILE.............................................................................. 71
3.4.3 DISCONNECTING A DRIVE ...................................................................................75
CONCLUSION .................................................................................................. 78
APPENDIX A. GENERAL INFORMATION. HARD DISKS ................................ 80
A.1 HARD DISK ORGANIZATION ...................................................................... 80
A.2 OPERATING SYSTEM AND HARD DISKS ..................................................... 81
A.3 HARD DISK PARTITIONS ............................................................................ 82
A.4 CREATING PARTITIONS FOR OTHER OSES ................................................. 83
A.5 PRIMARY AND LOGICAL PARTITIONS ........................................................ 83
A.6 FORMATTING HARD DISKS........................................................................ 84
A.7 FILE SYSTEMS ............................................................................................ 85
APPENDIX B. GLOSSARY ............................................................................... 86
4 Table of Contents
Page 5

Introduction
What is Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe is the first title in a new generation of software
for creating exact images of hard disks (and partitions). It will let you store an
image of your disk in an archive file on a hard disk or on one of numerous
removable media, such as Iomega Zip or Jaz, CD-R(W) or DVD-R(W) disc.
Having an exact copy of your hard disk, you will be able to restore its data at
anytime – in case of a system error, virus infection, or even disk malfunction.
With the help of a hard disk image and the Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
software, you will be able to deploy a system on a new PC hard disk, i.e.
install all operatings systems, applications without using installation
disks/discs, and thus avoiding the re-set of all those system and program
parameters.
Having created an exact hard disk image, you can be assured that all your
data, operating systems, and applications (along with all their related
settings!) are safe. In case of an operating system error or a virus attack,
you will be able to easily restore the content of your PC hard disk, having
created its exact image with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe. If you need to
restore only several files, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will let you connect the
stored file as a logical drive and copy all the files you need from it.
The unique technology developed by Acronis Inc., and used in the TrueImage
Deluxe software, will let you create exact disk images and restore your PC
disk contents under Windows without rebooting.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe makes image creation and hard disk content
restoration easy for users of any level. Irrespective of their qualification and
PC experience, every user can truly use this software.
The TRUE differences between Acronis TrueImage Deluxe and other back-up
software:
• The opportunity to create images of disks (and partitions), including
system partitions, under Windows, without rebooting your computer. No
other software for storing images of partitions (and disks) in archive files
allows you to perform these functions under Windows!
• The opportunity to restore partitions under Windows (with the except of
system partitions or those containing swap files).
At the point of partition restoration, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will let you
change its size and location on a disk, as well as its type and file system.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 5
Page 6

• Convenient tools for restoration of separate files and folders from an archive
file: you can connect a logical drive from an archived image and simply
copying files.
Connecting a logical drive from an image file means that you will be able
to browse stored and encoded partition contents like any real disk
partition in Windows or in a Windows Explorer window. (see Figure 3.24
below).
• Unlike per-file back-up software, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe allows you to
restore partitions even if they were deleted, formatted, had its Partition
Table erased, or its disk bootsector infected by a virus!
The software combines a convenient graphical user interface with
exceptional simplicity and user availability. Back-up and restoration
operations can be performed in several easy steps!
Archive file
An archive file is a file containing images of partitions and disks. The images
contain both data of partitions and/or disks and information, allowing you to
restore a partition (disk) from the image.
Partition images include all its files and folders, irrespective of their attributes
(hidden, system, etc.), Master Boot Record (MBR), File Allocation Table
(FAT), and a root directory (Root).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software stores only the data sectors of a hard
disk in its partition image.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software creates an archive file with a ’.tib’
extension. The .tib file can contain images of several partitions and/or disks.
An archive file of large disk partitions or several partitions (and disks) can
become quite large. In this case Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will split the
image into more than one archive volume or archive volume files. Splitting an
archive into separate volumes may also be required for writing to removable
media.
Computer errors
Unfortunately personal computers are not 100% reliable or foolproof –
operating systems (OS) are subject to failures; application and hardware
drivers can cause errors as well. The Internet brings additional information
security problems such as the threat of virus infection and the computer’s
future inoperability. A hard disk also accumulates various «garbage» as a
result of installing and removing software as well as decreases in the
perfomance of your PC from continuous Internet access.
PC hard disks can encounter critical errors when executable files and
applications cannot be run and operating system cannot be loaded. In many
6 Introduction
Page 7

cases this means that some system or data files are corrupt or newly
updated driver are inoperable. Quite often it is extremely difficult to fix such
problems, or even determine the exact software component that is causing
the problem.
The necessity of software back-ups
Data files are the most critical and valuable files on your PC hard disk as they
contain information of a «personal» nature. Operating system and
applications can be reinstalled with disks/discs. Information in data files are
unique, so it is vital to keep back-up copies of the most important on a hard
disk as well as on other back-up removable media.
The restoration of operating system and applications with their diskettes or
CD-ROMs usually takes a considerable amount of time. And do not forget the
need to restore all those settings! It should be obvious that this is not the
best way to restore your PC hard disk drive.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software offers you the most effective way to
restore your PC’s operability. You can quickly and easily restore system or
data partitions or even whole hard disks from a previously created partition
(disk) image. Acronis TrueImage Deluxe offers back-up copying of whole hard
disks and their partitions, with separate partition (and disk) images stored in
archive files.
General information on back-up copying
The need for system and data files back-up was realized long ago. The
majority of industrial systems still feature bulky tape back-up. This type of
back-up is usually performed by qualified specialists with the help of rather
complex and time consuming devices.
With widespread PC use, the variety and volume of back-up data grew
exponentially. At same time the need for simple back-up devices and
software to help even inexperienced users became apparent.
There are two groups of software for back-up copying of individual PC users’
data. They differ most in the level of work and the type of back-up copies
they allow one to make. These programs back-up:
• (group 1) Separate files and folders,
• (group 2) Partitions and whole disks data.
Both groups have benefits as well as some disadvantages. But as hard disks
and removable media capacity grew, and their cost decreased, it turned out
that back-up copying of whole disk partitions became more effective and
simple. Back-up copying of hard disk system partitions became largely
available to new users. Performing back-up copying and restoration of
system files and folders by means of the first group’s software assumed that
the user had great system and PC operating knowledge.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 7
Page 8

g
The usage of partition and disk back-up copying software turned out to be
simpler as well as more visual. Such programs allow the user to work by
means of a simple and user-friendly interface, while minimizing storing and
restoring operations to several easy steps.
The purpose and capabilities of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe system
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software is used to create exact images of hard
disks (and disk partitions) that can be used to restore disk contents, deploy
hard drive on new PCs, or to replace a hard disk. A disk image is stored in an
archive file on a hard disk or any removable media. This file may contain
images of several disks (and partitions) at once.
Restoring a disk/partition from an archive file, a user can easily select the
image of a needed disk/partition; select a disk/partition to restore to, and
change its size, location, and other parameters. A user can restore whole
disk/partition as well as separate files from a disk image.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software works under Windows 9x/Me, Windows
NT/2000/XP and supports FAT16/32 and NTFS as well as the Linux ext2, ext3,
ReiserFS file systems.
You can install the software only under Windows, but you will be able to run Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe from a bootable diskette or CD-R(W) under any other OS includin
Linux.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software works with any disks connected to your
PC (including IDE, SCSI, USB, FireWire, and/or PCMCIA interfaces). An
archive file can be created on a hard disk as well as on any other recording
device running under an OS, such as Iomega Zip, CD-R(W) or DVD-R(W)
drives, magneto-optical disk, and other media.
The software has a user-friendly graphical user interface that allows you to
work with both the mouse and keyboard.
Working with the software is performed through our easy image creation and
restoration wizard.
It takes just a few simple steps to start the disk/partition image creation
procedure:
• Select the operation of partition (disk) image creation;
• Select partition(s) and/or disk(s) to create images of (store data in an
archive file);
• Select type of a device for image creation (storing image in an archive
file): fixed or removable. For example, a hard disk, magneto-optical disk,
CD-R(W), DVD-R(W), etc.;
• Enter archive file name and specify its path;
8 Introduction
Page 9

• Select the disk/partition data compression level for archive file creation;
• Specify if you need a single file or the one split into several volumes of
fixed size (for example, for creating a large disk/partition archive file on a
CD-RW);
• Protect an archive file with a password if needed;
• Enter a comment for your archive file with information about stored
images of disks/partitions, their data files, OS version, or any other
information if needed;
• Execute the disk/partition image creation script, you created while working
with the software wizard.
It takes a few simple steps as well to start disk/partition restoration from an
image stored in archive file, or to deploy disk/partition contents onto a new
PC hard disk:
• Select the operation of disk/partition restoration from a disk/partition
image;
• Select an archive file on a hard disk (or removable media) that contains
the image of a disk/partition to be restored;
• Select a disk and/or partition to be restored in the archive file;
• Select a partition (disk and free space) to restore a disk/partition image,
stored in an archive file, to;
• Select the type of a disk/partition to be restored;
• Select the disk/partition file system;
• Change partition size and/or location as needed;
• Select the next partition to be restored to change its size and/or location
as needed;
• Execute restoration script.
Procedures of disk image creation (restoration) on a hard disk (from a hard
disk) and removable media (from removable media) slightly differ (these
differences will be described below).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software runs either under Windows from the Start
menu, or from a specially created bootable diskette or CD.
Disk operations are delayed in Acronis TrueImage Deluxe. It means that a
partition or disk image creation (or restoration) script is created first, and
then executed only when you are ready. Until a script is executed you can
return one or a few steps back to select another disk and/or partition and
image creation parameters.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 9
Page 10

Opportunities for Acronis TrueImage Deluxe usage
There are several variants of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software usage:
1. Creating images of and restoring your PC’s information.
You can use Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software to create images of
separate partitions of your PC hard disk, or the whole drive in an archive
file on another disk or removable media. You can use our software to
regularly create images of your information, applications and your
operating system update.
If new drivers, new applications, or an operating upgrade or change leads
to instability of your PC, you can easily revert back to its previous state. In
the same easy way you will be able to restore your system in case of a
serious error or accidental destruction or deletion of files. The more you
use Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software to create disk images, the higher
the possibility of restoring the newest version of your data, applications,
and operating systems.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software can be used not only to restore system in case
of a critical error, but also to revert the system back to its previous state. For
example, you may wish to restore after a perfomance falloff or instability caused by
a driver update.
Disk/partition image creation and data restoration from disk/partition
images are the main function of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe. However you
may want to use it for other purposes . . .
2. Deploying the system on identical PCs (disk cloning).
If you have to regularly set-up many identical PCs (install and set-up the
same operating systems and applications), you can utilize the disk-cloning
feature implemented in Acronis TrueImage Deluxe. All you have to do is:
Install and set-up an operating system and applications to a hard disk of
one of identical PCs. Create a disk (system partition) image in an archive
file. Boot the next PC up with a diskette containing Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe, and restore the hard disk contents from the image stored in the
archive file.
If you already have a PC with installed system and applications, you will
be able to clone another in just a few minutes! Create an image of the
first PC’s disk on any media (hard disk, CD-RW, DVD-RW), connect it to
the second PC, boot it from Acronis TrueImage Deluxe diskette or CD, and
restore disk contents from the image. You will save considerable time and
effort with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe!
3. Replacing a hard disk of your PC.
If you want to install a new higher capacity hard disk on your PC, and do
not want to spend all the day re-installing operating system and
10 Introduction
Page 11

applications, and restoring their settings, simply use Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe! Create an image of your hard disk in an archive file on any media,
be it another hard disk or CD-R, CD-RW. Install a new disk, boot with a CD
(or diskette) containing Acronis TrueImage Deluxe, and restore the old disk
contents from the image to a new disk. You can also change disk partition
size and location along with their type and operating system if needed.
Who Acronis TrueImage Deluxe is intended for
As everybody faces possible hardware or software failures, Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe software can help the widest circle of users.
PC users get software with simple and user-friendly interfaces that will
guarantee data will not be lost in case of any PC failures. And after serious
malfunctions with their system, they will be able to restore in no time without
help of an outside IT specialists.
More experienced users who test all new software on their PCs, will be able to
restore back to an original stable operating state any time should they
encounter an unsuccessful application or driver version or after any experiments
with their OS settings.
Administrators in small companies will get a simple, effective, and
inexpensive tool for creating images of disks (workstation and server system
partitions, user data partitions). PC assemblers can use Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe for quickly equipping whole PC consignments with software. The
simplicity and convenience of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe allows all users, to
take advantage of its unique technology and utility.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 11
Page 12
How to find the necessary information in this guide
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe user’s guide contains the following main chapters:
• 1. «Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe» - this
describes how to install, run, and remove the software;
• 2. «Creating a disk/partition image on a hard disk» - this describes how to
store an exact disk/partition image on a hard disk or removable media;
• 3. «Restoring a disk/partition from an image» - this describes how to
restore partitions with an image stored in an archive file, and how to
restore separate partition files;
• Appendix A. «General Information. Hard Disks» - this describes the
construction of hard disks, installation into a PC, disk file structures, and
interaction with an operating system;
• Appendix B. «Glossary» - contain a dictionary of technical terms to help
you to better understand this Guide.
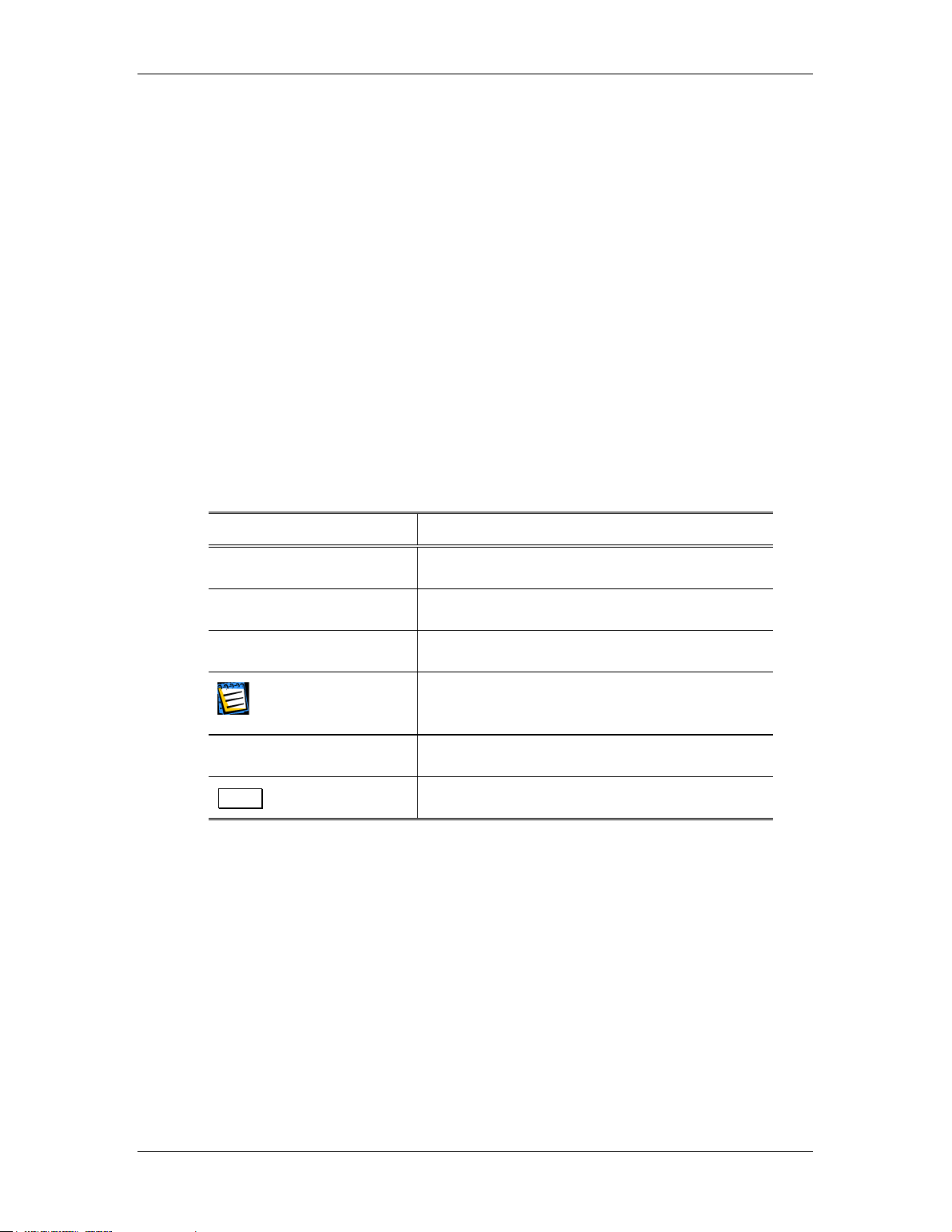
Legend
Designation Meaning
Courier New font
• Enumeration
1. Press a button...
Strings displayed or entered by a user.
Enumeration item.
A procedure step performed by a user.
Information we recommend you pay very
Operation selection
Quit
close attention to.
Dialog boxes and their element names.
Button and key names.
12 Introduction
Page 13

Hardware and software requirements
To take full advantage of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe one should have:
• A PC-compatible computer with a Pentium CPU or similar,
• 32 MB RAM,
• A floppy or a CD-RW drive,
• VGA monitor,
• A mouse (recommended),
• Free disk space for archive files.
Software usage conditions
The conditions for Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software usage are described
in the «License agreement», included with this package. The supplied
registration card is the confirmation of your legal purchase and usage of
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe on your system. Each registration card has its
own unique registration number.
Under current legislation the «License agreement» is considered a contract
between a user (you) and a software manufacturer (Acronis Inc.). The
contract has legal effect and its violation may entail a court examination.
Illegal use and/or distribution of this software will be prosecuted.
Technical support
Users of legally purchased and registered copies of Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe receive free technical support from Acronis Inc. In case you have
problems with installation or use that cannot be solved with this guide or
read-me file, please visit our support web-site or e-mail our support
department at the addresses shown below. You must also send us the
registration number of your Acronis TrueImage Deluxe copy. This number is
written on a registration card supplied with this product.
Support URL: http://www.acronis.com/support/
E-mail: support@acronis.com
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 13
Page 14

1. Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
1.1 Acronis TrueImage Deluxe system package
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe system package includes:
• An installation disc,
• This guide,
• License agreement,
• Registration card,
• Advertising materials.
1.2 Installation
You can purchase the Acronis TrueImage Deluxe program on a compact disc
(CD-ROM) or download it from the Internet.
The CD-ROM contains an installer that can be run in Windows 9x/ and
Windows NT/2000/XP operating systems.
If you purchased TrueImage Deluxe on CD-ROM, to run it do the following:
1. Insert the compact disc into CD-ROM drive.
If you have the Windows operating system installed, run the Windows
Explorer and click the CD-ROM drive with the mouse. You will now see the
set-up.exe executable on the compact disc. Double-click it to run the
installation program.
14 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 15

The executable will then be loaded into the computer memory and the
following window will appear on the screen:
Next button to continue.
Click
2. To continue working with the software you will need to accept the
conditions of the license agreement between you (the user) and the
software developer.
For this purpose set the switch in the lower part of the window to I accept
this agreement position.
Click the
Next button to continue.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 15
Page 16

3. If you disagree with the agreement conditions, set the switch to I decline
this agreement position and click the
Next button. In this case you will be
thanked for the interest in the software, and the program will terminate.
4. In the next window you will need to enter the product serial number that
you will find on the Acronis TrueImage Deluxe registration form – AND
DON’T FORGET TO REGISTER YOUR SOFTWARE TOO!
Click the
16 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Next button after entering the serial number.
Page 17

5. In the next page you should specify a folder to install TrueImage Deluxe
program to. The default folder is C:\Program Files\Acronis\TrueImage. If
you agree with it, click
Next. If you want to install the program to a
different folder, enter its name and path into the appropriate field. If there
is no such folder on a disk, it will be created during installation.
You can choose a folder for program installation by clicking
Browse…. You
will see a folder tree of your hard disk. Select a folder with mouse and
click
OK. (You can select any computer disk for installation.)
After selecting a folder, click
Next to continue.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 17
Page 18

6. On the next page you will be offered to make TrueImage Deluxe available
to all users of the computer or only to the current user. If you want to
make the program available to all users, check the Yes, I want to install
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe for all users box. (This page of InstallationWizard
is specificial for Windows NT/2000/XP operating systems.)
If you use Windows 9x/Me family operating system the above page of the
wizard will be omitted.
Click
Next to continue.
18 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 19

7. In the next page you will be offered to create a new program group for
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe program or to select an existing. If you agree
to create a new group just click
Next. If you want to use one of the
existing program groups, select it by clicking it with the mouse.
After selecting a program group, click
Next to continue.
8. After selecting program group the installation program will show you the
generated installation script. Before you click the
Proceed button you can
change any of its parameters: disk and folder, program group, or for
example, make the program accessible only for yourself.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 19
Page 20

9. If you are sure all installation parameters are correct, click the Proceed
button. The process of copying of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe files on your
computer will be executed and shown in a special window.
10. On the next page you will be asked to create a bootable diskette or
CD-R(W) for Acronis TrueImage Deluxe. This is very important as the disk
partition data restoration software can only be run from a bootable
diskette or CD-R(W). Therefore it is strongly recommended you create
either of them. You can also create the bootable diskette or CD-R(W)
when the set-up process is finished.
If you wish to create a bootable disk/disc, check the Yes, I would like to
create bootable rescue media box and press
20 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Next.
Page 21

In next window you will select a device for bootable media creation.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe allows you to create either a bootable diskette
or a CD-R(W) disc. Select the preferred device from the list.
Having chosen a device and pressed
Next, you will see the next window
asking you to insert a diskette or a disc into the appropriate device.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 21
Page 22

Having prepared a diskette or CD-R(W) and inserted it into the
appropriate device, press
Proceed. It will take some time to copy the
necessary files to load Acronis TrueImage Deluxe. The copying process
will be shown in the following window:
11. The installation process will be completed and you will be offered the
opportunity to read the README file.
22 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 23

After installation of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe is completed, you should
restart your computer.
12. Having opened Programs menu, you will find the Acronis program group
containing the Acronis TrueImage Deluxe program. This menu will look like:
1.3 Repairing Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
If a bootable diskette or compact disc is spoiled, please create a new one. If
you get an error message on trying to create a diskette or compact disc by
selecting the Bootable Rescue Media Builder menu item, start the TrueImage
Deluxe installation program again. It will determine that TrueImage Deluxe
was already installed on your computer and will ask you if you want to
restore (update) the program or completely remove it from disk.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 23
Page 24

1.4 Removing the software
To remove the software select Acronis -> TrueImage -> Uninstall Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe from the Programs menu. You will see a dialog box asking
if you really want to remove the software from your PC hard disk.
Press
Yes to confirm removal. Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software will be
completely removed.
1.5 User Interface
1.5.1 Terminology
In these paragraphs you will find information about the Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe user interface, its main features and controls.
If you work with Windows, X Window, or OS/2 applications on a regular basis, you will
have no problems understanding and using Acronis TrueImage Deluxe interface.
However, for the sake of users that are not accustomed to standard user interfaces and
for the fullness of description, here we provide a relatively detailed description of it.
1.5.2 User interface basics
Managing Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software works under the Windows operating
system. It has a graphical user interface, controlled by mouse or
Shift+Tab, Left, Right ,Up ,Down, Space , Enter , and Escape keys, and
represents an application of a Wizard type, widespread in this OS
environment.
Tab,
While working with a partition store and restore wizard, a user sees a
sequence of Wizard pages, on each of which he (she) selects from several
available actions, and thus sets switches to the desired state.
The switches can be set with the mouse or keyboard.
Each dialog box contains detailed text comments for the dialog’s purpose and
switches (control elements) as well as for each switch state.
User interface elements and use are described further.
24 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 25

Using the Mouse
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe window interface performs best when using a
mouse. Of course it is possible to do everything without one, but it is
much less convenient.
In this guide we use «click the … button» expression instead of «place the
mouse pointer on the button (object) and click the left mouse button (press
and release the left mouse button)».
The mouse is used to check checkboxes, press buttons, select items (lines)
from a list, etc.
Using the Keyboard
Everything that can be done with the help of a mouse can also be performed
with the keyboard.
Switching between controls is done with
control that has focus at the moment is marked with a dash line around it or
along its perimeter (for screen buttons).
(Un)checking a checkbox (or selecting a radio button position) is done with
the
Space key.
Switching between dialog pages is done by pressing the Next (switching to
the next page) and Back (to the previous one) buttons.
To quit the program press the Escape key or the Cancel button.
1.5.3 Windows
All actions that the user performs in Acronis TrueImage Deluxe are displayed
in windows. A window is a rectangle screen area that has a title and a
border.
Window border
A border is a line confining the rectangle of a window. All the contents of the
window lie within this line.
Tab or Shift+Tab keys. The active
If a window is resizable, you can resize it using its border. Point the mouse
cursor at the border so that it changes to a double-headed arrow, press and
hold the left mouse button, move the mouse until you get the desired
window size, and then release the button. The lower border is used to
change the height of a window, and the left and right borders allow changing
its width.
You can change the position of dialogs on the screen with help of their
borders. Point the mouse cursor at the border so that it changes to a hand,
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 25
Page 26

press and hold the left mouse button, move the mouse until you are satisfied
with the position of the dialog, and release the button.
Window Titlebar
Titlebar is located on the top of a window and contains a text string that
describes the window (the title itself) and minimize/maximize and close
buttons.
The titlebar can also be used to change the position of a window on the
screen. Point the mouse cursor at the titlebar so that it changes to a
hand, press and hold the left mouse button, move the mouse until you
are satisfied with the position of the dialog, and release the button.
Double-clicking the titlebar of a resizable window maximizes the window or
reverts the maximized window to its original size.
Window Purpose Bar
Window purpose bar is right below the titlebar and is supposed to inform the
user about what action he/she has to perform on the given upgrade Wizard
page, for example, check a checkbox, select an item from a list, or enter a
value into a field.
Controls are located below the purpose bar.
System Menu
Clicking the
, button in the upper left corner of a window opens the system
menu for the window.
The system menu of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe windows contains the
following items:
• Move – moves window along with mouse cursor;
• Close – closes the window.
26 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 27

Same result can be obtained by pressing the .
1.5.4 Dialogs and Controls
A dialog box (dialog window, dialog) is a window that allows browsing and
editing various information. Size of a dialog is usually fixed.
The user interacts with a dialog via controls. There can be the following
controls in a dialog:
• Checkbox;
• Radio button;
• Edit field;
• Spinner – a special type of edit field: ;
• List;
• Memo field;
• Slider;
• Button.
All these controls can be accessed both via the mouse and via the keyboard.
All controls of a dialog are grouped in a looped list. One of the controls is
current (has focus) and reacts to the keyboard. Focus can be cyclically
moved along the list forward (
Tab key) and backward (Shift+Tab keys).
Arrow keys also move the focus if they are not allocated in the current
control for other purposes; they move the focus not cyclically, but according
to actual position in the dialog.
Some controls can be blocked. In this case they are grayed and cannot be
accessed either via the mouse or via the keyboard.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 27
Page 28

Checkbox
A checkbox is a control that can be in two states: on or off. If it is off, it is a
blank square, if it is on, it has a tick (or a cross in text mode) inside it. To the
right from the square there is a description of the checkbox. You can toggle
the state of a checkbox either by clicking the square or its description, or by
pressing the
Space key when the checkbox has focus.
The description of a checkbox sometimes has an underlined letter in it. In
this case pressing the underlined letter (if it is not allocated in the current
control for other purposes) or pressing it together with the
Alt key moves
focus to the checkbox and toggles it.
Radio button
Like a checkbox, a radio button is a control with two possible states. If it is
on the circle is filled, otherwise it is empty. Unlike checkboxes, radio buttons
are arranged in groups, and one and only one radio button can be on in each
group. Clicking the circle or the description of the radio button or pressing
Space key when the radio button has focus turns it on (and turns off all
the
the radio buttons in the same group).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software uses radio buttons for:
• Selecting operations (creating, restoring images, etc.);
• Selecting a device for image creation (a hard disk or removable media);
• Selecting a type of partition (disk) image creation: as a single file or split
into separate volumes;
• Selecting a type of a partition to be restored (primary / logical);
• Selecting a file system of a partition to be restored (FAT16 / FAT32).
28 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 29

Edit Field
The purpose of an edit field is to browse and edit information in the form of
a text string.
A text string can be edited only via the keyboard. Clicking the mouse moves
the focus to the edit field. When an edit field gets the focus, the string in it
becomes highlighted. Typing anything over a highlighted string removes the
old contents of the field and replaces it with newly typed characters. You can
cancel highlighting by pressing the
Left or Right arrow keys, and then you
can edit the contents of the field. Current editing position is marked with a
rectangular cursor. Aside from
Left and Right arrow keys and the mouse
you can use the following keys when editing a string:
Home moves the cursor to the beginning of the string;
•
• End moves the cursor to the end of the string;
• Backspace deletes a character to the left from the cursor;
• Del deletes the character under the cursor.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software uses edit field for:
• Entering an archive filename as well as its full path;
• Entering a password and its confirmation.
Spinner
A spinner is a special type of field:
Its special feature is that you can either enter the desired value manually or
use the up and down arrows in the right part of the spinner to scroll the
value of the field. While you keep one of these buttons pressed (by holding
the left mouse button pressed above the arrow) the contents of the field will
either decrease or increase.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software uses spinners for:
• Entering volume size of an archive file,
• Changing partition size and location at its restoration.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 29
Page 30

List
Lists are used in dialogs to select one item from a group (which can be quite
large) or to perform some actions with the item (delete it from the group,
edit it, etc) or with the group itself (add an item, change the order of items,
etc).
A list is a rectangle with several lines, each designated to one item. If the
items do not fit into the rectangle horizontally or vertically, horizontal and/or
vertical scrollbar appears.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software uses lists for presenting available
removable media connected to your PC, and also for selecting certain media
for back-up copying.
The following keys are active in a list:
•
Up and Down keys move the cursor one line up or down respectively;
• Left and Right keys scroll the contents of the list left or right if the list
does not fit into the rectangle horizontally;
PgUp and PgDn keys move the cursor one page up or down respectively;
•
• Home and End keys move the cursor to the beginning or the end of the
list respectively;
•
Enter key can be allocated to perform some action with the selected
item, e.g. opening the properties dialog for example.
Same actions can be performed on the list with the help of the
mouse. Clicking an item moves the cursor to it. Vertical (one
line/page up or down)/horizontal scrolling is done with the
vertical/horizontal scrollbars. Double-clicking an item is usually
equivalent to pressing the
Enter key on it.
Memo Field
A memo field is a rectangle in which a text is displayed. If the text does not
fit into the rectangle, scrollbars appear.
30 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 31

The following keys are active in a memo field:
•
Up and Down keys scroll the text one line up or down respectively;
• Left and Right keys scroll the text left or right if it does not fit into the
rectangle horizontally;
PgUp and PgDn keys move the cursor one page up or down respectively;
•
• Home and End keys move the cursor to the beginning or the end of the
text respectively.
Some actions can be performed on the memo field with the help of the
mouse. Vertical (one line/page up or down)/horizontal scrolling is done with
the vertical /horizontal scrollbars.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe uses view fields for viewing generated image
creation or partition restoration script as well as for representing a script in
back-up copying and restoration processes.
Slider
A slider is a graphic interface element for setting software parameters that
change from the minimum to maximum continuously or stepwise (for
example, a sound volume slider under the Windows OS). Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe software uses sliders for setting partition data compression level of an
image.
Button, Default Button
A button is a control that is most frequently used in dialogs. One can tell
from its name that the main action one can perform with a button is press it.
You can press a button either with the mouse by clicking it or with the
keyboard (by pressing
Enter or Space key when the button has focus, or by
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 31
Page 32

pressing the Alt key together with the letter that is underlined on the
button).
A dialog usually has a default button. It differs from usual buttons, because
double-clicking the mouse or pressing the
Enter key (if they are not
allocated for other purposes in the current control) is equivalent to pressing
the default button. Unlike other buttons, the default button is highlighted.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software uses buttons for transitions between image
creation and restoration wizard pages, exiting the program, and also for
executing scripts.
Resizing and Positioning a Partition Graphically
A special graphical control that is shown below is used to graphically resize
and position partitions on the hard disk.
This control is a rectangle that represents a partition of a hard disk. You can
«grab» the left or right side of this rectangle and move/resize the rectangle.
Point the mouse at the vertical «engraved» line on the right side of the
rectangle, and the mouse cursor will change to two vertical lines with two
arrows (left and right) around them. Click and hold the left mouse button
and move it to the left. You will see that the right side of the rectangle also
moves to the left, and the size of the rectangle changes.
The same is true for the left side of the rectangle, and you can change its
position with respect to the left side of the window.
Finally, you can change the position on the disk (move it as a whole). Click
and hold the left mouse button on the rectangle symbolizing the partition
(the mouse pointer changes to a hand), and move it to the left or to the
right. The rectangle will move along with the pointer.
32 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 33

The program will remember the position and the size of the partition that you
have entered this way and will use them when creating the transformation
scenario.
1.5.5 Informative Elements
Aside from controls TrueImage Deluxe uses elements that inform you about
some parameters of hard disk structure and the actions the program
performs.
Hard Disk and Partition Parameters
On the picture you can see the parameters of a hard disk as they are
displayed by the TrueImage Deluxe program.
Here you can see the structure of hard disk #1; its capacity is 27.96 GB.
There is one primary partition on the disk (yellow; color codes are explained
in the bottom part of the picture) with FAT32 file system and SYSTEM
partition label and set of logical partitions. Some disk space is unallocated.
The above-described presentation of hard disk structures is used in Wizard
pages that prompt you to select source and destination disks.
The colors that show primary and extended partitions, and unallocated disk
space can be changed. Click the desired element (or move focus to it by
pressing the
Tab or Shift+Tab keys, and press the Enter key afterwards).
Color setting dialog opens. Here you can either select the desired color from
the samples in the lower part of the window by clicking the color you like and
pressing the
Accept button (you can also select the desired sample by
moving focus to it with Tab or Shift+Tab keys and pressing the Enter
key), or create your own color by moving the Red, Green, and Blue sliders in
the upper part of the window until the color in the rectangle to the right suits
you. Press the
Accept button to finish color selection.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 33
Page 34

g
g
Progress Bar
A progress bar is a purely informative dialog element (it is not a control). It is used
to display the current state of some lengthy process (copying a partition etc.).
1.5.6 Special Dialog Types
Wizard
A Wizard is a dialog that allows displaying and editing information in several
pages, like the properties dialog. Unlike the latter you can move along the
Wizard’s pages only in a one-after-another fashion. This makes it possible to
make the contents of later pages not fixed, but adjustable to the actions you
perform on earlier pages.
In the lower part of a Wizard page there always are 3 buttons:
•
<Back moves you to the previous page. This button is disabled on the
first page.
Next> takes you to the next page. On some pages this button can have
•
other names. On the last page this button finishes the Wizard and starts
the actions that you have chosen in it.
Cancel exits the Wizard and negates all actions you were going to
•
perform. On some pages this button can have other names.
There is no Help button on Wizard pages. It is unnecessary because on each pa
there is detailed information about the purpose of the page and its controls.
Moreover, there is detailed information about what possibilities you
any of controls in any possible state.
et if you select
e
Almost all Acronis TrueImage Deluxe windows are Wizard pages.
34 1 : Installing and Starting Work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Page 35

1.6 Running Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software
Acronis TrueImage software runs in different modes during disk/partition
image creation or restoration, in case of a serious system malfunction or disk
filing structure damage.
To create a disk/partition image under Windows, select Start -> Programs ->
Acronis -> TrueImage -> Acronis TrueImage Deluxe. You will immediately
see a welcome window containing the partition (disk) image creation and
restoration wizard.
If your system is damaged and you are unable to boot the PC from its
system partition, you should use the bootable diskette or CD-R(W) that you
previously created, selecting Start -> Program -> Acronis -> TrueImage ->
Bootable Rescue Media Builder.
1.7 Finishing the work with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software
You can exit Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software anytime simply by clicking
Cancel or pressing Escape.
Clicking window close button, selecting Close in the window’s system
menu, or pressing Alt+F4 will produce the same result.
In any of these cases, the program will always ask if you really want to quit,
as shown in the following dialog box:
Yes to quit the program.
Press
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 35
Page 36

2. Creating disk/partition images
2.1 Creating a disk/partition image on a hard disk
2.1.1 Welcome page
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software starts with the welcome page (Figure
2.1). It enumerates all the main software capabilities, described in the
Introduction.
Let’s shortly revise them once again. The software allows to create images of
hard disk partitions or the whole disks and store them in an archive file. This
file can be created on any hard disk or removable media (Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe software allows to create archive files using CD-R, CD-RW, Iomega
Zip, an other devices). Any partition can be further restored from an image,
stored in an archive file.
While working with whole partitions and hard disks, Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe software still allows to restore separate files from an image. For this
purpose Acronis TrueImage Deluxe has image contents viewing tools for
representing partition images as usual logical drives. You can work with this
connected drive with any file manager like with a usual hard disk. Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe allows to disconnect the disk after necessary files and/or
folders are restored from it by simple copying.
All above functions allow to organize data back-up copying and restoration
(or to revert a system back) on a PC or several PCs in a small office. Besides,
an archive file can be used for deploying systems on identical computers
(hard disk cloning), and also for replacing PC hard disks.
36 2 : Creating disk/partition images
Page 37

g
Figure 2.1. Wizard Welcome window
Press Next to begin working with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software.
2.1.2 Selecting an action
The next wizard window will offer you to select an action to perform with the
help of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe (Figure 2.2). There are three actions
available:
• Create an image of a disk partition and/or the whole hard disk drive (a
group of partitions, several partitions);
• Restore a partition (disk) from an image file, stored in an archive file;
• Connect an image, stored in an archive file, as a temporary logical drive to
restore separate files and/or folders.
A connected disk can be unplugged by calling
from Acronis TrueImage Deluxe itself. Runnin
causes the additional
Selection
the disk, as it will automatically disappear after reboot.
window (see 3.4.3 «Disconnecting a drive»). Still it’s not necessary to unplug
Unplug function from its context menu or
the software with a disk connected
Unplug back-up archive logical drives switch to appear in the Action
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 37
Page 38

Figure 2.2. Action Selection window
Set the switch to Create an image of a partition or the whole hard disk drive
position. Click
Next to continue.
2.1.3 Selecting partitions for image creation
In the next Selecting Partitions to Image window (Figure 2.3) you will see the
structure of the disks connected to your PC. Click a rectangle representing a
partition to select it. As a result this rectangle will become underlined red.
You’ll be able to consequently select several hard disk partitions and/or
different disks. Click a rectangle representing the whole hard disk (with an
icon, disk number and capacity) to select it for image creation. As a result all
disk’s partitions will become underlined red. You’ll be able to select one or
several disks as well as a random serie of partition and disks for image
creation.
38 2 : Creating disk/partition images
Page 39

g
Figure 2.3. Selecting Partitions to Image window
Having chosen the partitions and/or disks, click Next to continue. Have in
mind that this button will be disabled until none of partitions and disks is
selected.
2.1.4 Image archive location
In the next Image Archive Location window you’ll need to select a type of a
device to create a disk/partition image on (Figure 2.4). Acronis TrueImage
supports only two device types:
• Any hard disks,
• Removable media – CD-R, CD-RW, Iomega Zip, Iomega Jaz, magneto-
optical, and other drives.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software is intended for individual PC users and small
offices, therefore this
consumers.
uide describes only drives available to these categories of
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 39
Page 40

g
Figure 2.4. Selecting Image Archive location
Let’s assume you have chosen a hard disk as an image creation device. Click
Next to continue.
Creatin
chapter; see 2.2 «Creating a disk/partition image on removable media».
an image on a removable media will be described in the next section of this
2.1.5 A disk/partition archive file
In the next Image Archive Creation window you’ll need to provide an archive
filename to store images of chosen partitions (disks) to as well as its full path
(Figure 2.5). Enter a filename to the File name field.
You can also use a connected disks tree in the left part of the window to find
archive files (if previously created) and their locations.
40 2 : Creating disk/partition images
Page 41

Figure 2.5. The list of devices, connected to the PC
Select a hard disk and click the “+” sign to the left of its icon to browse a list of
files and folders of this disk (Figure 2.6). Select a necessary file from the list.
Figure 2.6. Selecting a folder and an archive file name
You can assign a filename along with its path in the appropriate field, for
example, F:\backup\backup1.tib. The disks and folders tree will be set to
correspond the entered filename and the path, i.e. this file will become a
current selection on the figure.
A filename on a hard disk can contain up to 255 symbols. If the F:\backup
folder is already exists on the F:\ disk, an archive file will be created inside it.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 41
Page 42

g
g
g
If there’s no F:\backup folder on the F: disk, it will be created along with an
archive file inside it.
If an archive file with the entered filename already exists in the chosen
folder, you’ll be prompted about it by Acronis TrueImage with a question if
you want to create a new file with the same name, that is to delete an old
archive file and create a new one instead (Figure 2.7).
Figure 2.7. An archive file with the filename entered is already exist.
If you click Yes, an old archive file will be deleted and replaced by a new one.
You can store images of several partitions or even disks in a single archive file, but you
can’t append ima
an image of the partition (disk) on the same partition (disk), included into an archive, if
there’s enough free space.
An archive file can be created on a network disk. You mi
ima
es of a partition with an accounting database, for example. It’s most efficient to
keep partition images on a server or to create an image library on a CD-R(W). To
speed up the process you can create a multivolume archive on a hard disk and then
move archive volumes to a CD-R(W).
es to an existing archive file. You can also create an archive file with
ht need to regularly create
Having chosen (or entered) a filename and its path, click Next to continue.
42 2 : Creating disk/partition images
Page 43

2.1.6 Image’s data compression level
In the next Compression level window you’ll need to select a data
compression level of a partition image. A compression level can be selected
by moving the slider (Figure 2.8). If you select zero compression, files will be
obviously moved to an archive file without any compression, which is
inefficient. On the other hand the work speed might drop and image creation
time might increase, if you select the maximal compression. Certainly, the
optimal compression level depends on the type of files, stored on a
disk/partition, and can only be determined empirically.
For example, we chose the primary hard disk partition with the Windows 98
operating system installed. The partition size was 3.89 GB, actually occupied
space – 683 MB, so the largest part of the partition was free. We chose the
rd
3
compression level for image creation. The resulting file turned out to be
267 MB. As you can see, the given partitions were actually compressed by
2.6 times, but you shouldn’t highlight it much, as these values are very
rough, because different files are differently compressed.
Figure 2.8. Image’s data compression level
Having chosen the compression level, click Next to continue.
2.1.7 Creating archive volumes
In the next Image Archive Splitting window you’ll be able to select if the
software should create a single archive file or split it into a number of
volumes. If you set the switch to Automatic, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will
try to determine settings for certain situations itself. If there’s enough space
on a hard disk that you’ve chosen for locating an image on, the software will
create a single archive file. If there’s not enough space, Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe will prompt you a warning and wait for your actions. You’ll be able to
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 43
Page 44

g
g
try to and free some additional space on the partition, where an archive file
is being created, and then continue the image creation. But you will also be
able to terminate Acronis TrueImage Deluxe, prepare a partition for image
creation, and run the process anew.
FAT16 and FAT32 limit file sizes. In particular, the maximal file size of FAT16 and
FAT32 is 4 GB. FAT32 file system is currently the most widespread in individual users’
PCs. At the same time modern hard disks have 20 GB, 40 GB, and hi
Hence the maximal file size can be easily exceeded at creating an archive file. In this
case Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will automatically split an archive file into separate
volumes.
her capacities!
If you are creating an archive file on CD-R, CD-RW disks in Automatic mode,
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will simply pause and prompt you to insert a new
disk into the drive, if the current disk space is fully occupied.
If you set the switch to Fixed Size and set the volume size in megabytes
(MB), then, for example, having 4 GB partition size, 3.2 GB of which are
actually occupied with data, and 600 MB volume size, it will be possible to
create backup.tib, backup1.tib,... backup4.tib volumes on a hard disk. The
actual quantity of volumes depends on data files, stored on a partition, and
their possible compression level. If there are mostly text files, they will be
compressed very well, and you’ll get some three or four archive volumes, for
example. But if there are graphic files, they’ll be compressed to a lesser
degree, and you’ll get some five volumes, for example.
Splittin
on a hard disk as well, as you’ll be able to move archive volumes to CD-R, CD-RW
disks in the future. Creating an archive file directly on a CD-R, CD-RW disk would
have taken much longer time then in case of a hard disk.
an archive file into separate fixed size volumes makes sense when storing it
44 2 : Creating disk/partition images
Page 45

Figure 2.9. Splitting an archive file into separate volumes
Having set the image creation mode (Automatic or Fixed size) and entered an
archive volume size if needed, click
Next to continue.
2.1.8 Protecting an archive file with a password
An archive file with a partition (disk) image can be protected with a
password. If you think a partition (disk), you create an image of, shouldn’t
be restored by anybody except you, enter a password and its confirmation
into the text fields of the next Image Archive Protection window (Figure 2.10).
A password should consist of at least 8 symbols and contain both letters (in
the upper and lower cases desirably), and numbers. (So it would be harder
to hack it.)
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 45
Page 46

Figure 2.10. Protecting an archive file with a password
When you try to restore a password protected partition (disk) from an image,
stored in an archive file, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will prompt you to enter
it into the appropriate window and won’t allow restoring it by a person
without this password.
Click
Next to continue.
2.1.9 Commenting an archive file
In the next window you’ll be able to provide an archive file with any
comment that may include any information on the PC and its user, the hard
disk, partition data, image creation time, and any peculiarities and conditions
(Figure 2.11). For example:
True Image of Primary Partition HDD1.
OS:
Windows 98SE.
Applications:
Office 97 (Word, Excel, Outlook);
Adobe Photoshop
Adobe PageMaker
Adobe Acrobat
True Image of Primary Partition HDD2.
Financial Database.
24.02.2002
46 2 : Creating disk/partition images
Page 47

Figure 2.11. Commenting an archive file
Click Next to continue.
2.1.10 Image creation script
In the next window you’ll see a partition (disk) image creation script (several
images, perhaps). It will contain a list of operations to be performed on
partitions (disks) along with their main features.
Figure 2.12. An archive file creation script
All operations of a partition (disk) image creation in an archive file are
delayed in Acronis TrueImage Deluxe. A partition (disk) image creation script
is created first, and then it’s executed.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 47
Page 48

Script creation includes the following steps, as you’ve seen before:
• Selecting partitions (one or several) and/or disks,
• Selecting a device type to create an archive file with a partition and/or
disk image on,
• Selecting a file or entering an archive file name,
• Selecting a data compression level of an archive file,
• Selecting an archive type (single or multivolume),
• Protecting an archive file with a password,
• Commenting a partition and/or disk archive file.
Now Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software is ready to perform a procedure of
image creation in an archive file. If you click
Back, you’ll be able to select
other partitions and/or disks for image creation, other compression level, etc.
You will be able to change any image creation parameters until you click
Proceed. By clicking this button, you execute an image creation script.
Click Proceed to execute a partition and/or disk image creation script.
2.1.11 Creating an image
You will see the image (several images, perhaps) creation script progress
window.
Figure 2.13. Image creation process
This window will contain the estimated time of image creation in addition to
the main partition (disk) features, which image is being created.
48 2 : Creating disk/partition images
Page 49

2.1.12 Finishing image creation
Image creation procedure finishes by way of such a message:
Figure 2.14. Finishing image creation
Clicking Exit closes Acronis TrueImage Deluxe.
In this certain case a partition with 689 MB of data was compressed to a 267
MB archive file. It took 3 minutes to create it. (We remind that these values
are very rough, as files of different types can be compressed very
differently.)
2.2 Creating a disk/partition image on removable media
2.2.1 Selecting a partition and an action
The initial stages of working with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software, when
creating a partition and/or disk image on removable media, are the same as
when creating it on a hard disk. It is started with the welcome window
(Figure 2.1); then you select an action to be performed (Create image of a
partition or the whole hard disk drive; Figure 2.2); then you select partition(s)
and/or disk(s) to create images of (Figure 2.3). Now you should set the switch
to Removable disk drive in the Image Archive Location window (Figure 2.4).
2.2.2 Selecting a removable disk drive
Having clicked
Next, you’ll see a list of removable media drives, connected
to your PC, in the next window (Figure 2.15). The most popular devices of
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 49
Page 50

this type include Iomega Zip, CD-R, CD-RW drives, DVD-R, DVD-RW,
magneto-optical drives, and some other. Anyway, all removable media
drives, connected to your PC, will be enumerated in this list. In the given
case there’s only LG CD-RW 8080B (8x/4x/32x) recorder in it, except a usual
3.5’’ floppy drive.
Figure 2.15. Available removable media drives
Click a drive you want to create a partition and/or disk image on. Click Next
to continue.
2.2.3 The following actions
In the next window you’ll be asked an archive file name (Figure 2.16). It’s
completely the same as the window on the figure above. However, creating
images in archive files on a CD-R or CD-RW differs from creating images in
archive files on a hard disk:
• A filename length can’t exceed 24 symbols (including a dot and three
extension symbols);
• A file is created in the root of a CD;
• No need to enter a file path, i.e. a filename isn’t entered like, for example,
G:\back-up1.tib (where G: is a recorder drive), but simply like backup1.tib, as you have chosen a drive in the previous window;
• If Acronis TrueImage will find a file with the entered name on a CD-RW
disk, it will replace it with a new one.
50 2 : Creating disk/partition images
Page 51

T
g
Figure 2.16. An archive file name for CD-R(W) recording
If a CD-RW disk already has an archive file, created earlier by Acronis
Deluxe, the software will be able to append one (or several) more archive files to the
disk, having enough free space. If a CD has been recorded by another software,
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe won’t be able to record an archive file to it, even havin
enough free space.
rueImage
Click Next to continue.
All the following pages of the partition (disk) image creation wizard are
completely the same as the above (Figure 2.8 – Figure 2.11) including:
• Selecting a compression level,
• Splitting an archive file into volumes,
• Protecting an archive file with a password,
• Commenting an archive file,
and finish with the script window.
When creating an image in an archive file on removable media (CD-RW), you
can leave the default Automatic setting in the Image Archive Splitting window.
Working with removable media, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software will
automatically determine the number of CD-RW disks, needed to create an
image, and will prompt you to insert a new disk into the drive if needed.
CD-R, CD-RW recording begins with a prompt to insert the first disk into the
drive (Figure 2.18).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 51
Page 52

2.2.4 The script window
Having commented an archive file, you’ll get to the script window of image
creation in an archive file on removable media (Figure 2.17).
Figure 2.17. The script window of image creation in an archive file on
removable media
As you can see, the script window of image creation in an archive file on
removable media is the same as the script window of image creation in an
archive file on a hard disk (Figure 2.12).
We’ll remind that has been already said about creating an image on a hard
disk: now Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software is ready to execute the
partition image creation procedure. If you click
other partitions and/or disks for image(s) creation, etc. You’ll be able to
change any image creation parameters, until you click
it, you’ll execute the image creation script.
So, click
Proceed to continue.
2.2.5 The script progress
Having clicked
Proceed, you’ll see the script progress window. As the image
is being created in an archive file on removable media, you’ll be prompted to
insert a new disk into the drive.
Back, you’ll be able to select
Proceed. By clicking
52 2 : Creating disk/partition images
Page 53

Figure 2.18. Insert a disk into the recorder
Having inserted a disk, click OK. The procedure of recording an archive file to
CD-R or CD-RW recorder will begin.
Figure 2.19. Image creation progress
If an archive file can’t be recorded to a single CD-R (or CD-RW) disk, Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe software will pause image creation and prompt you to
insert another disk into the drive.
The image creation procedure finishes with a message window completely
the same as on the figure above (Figure 2.14).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 53
Page 54

3. Restoring a disk/partition from an image
3.1 Restoring a partition (disk)
Partition or disk restoration from an image is a more complex procedure than
storing. When you store a partition, you can do it directly under Windows or
from a bootable CD. But your system is assumed inoperable in general.
If your data partition files are corrupt, you’ll be able to restore the partition
with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe directly under Windows.
However, if your system or a system partition (usually the primary one) is
damaged, it gets more complex. In this situation there’s only way to restore
everything: booting from a diskette, created with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe,
or from a bootable CD with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe.
You can run Acronis TrueImage Deluxe from a CD and then replace a
bootable disk with an archive file CD, containing the image of a partition to
be restored. But an archive file can be possibly stored on a special back-up
hard disk. In this case you’ll have to connect it to PC.
There’s a simple rule: do not store archive files with partition images on the
same hard disk you create back-up copies of. As in case of filing structures
(for example, Partition Table) damage, you’ll just not be able to access these
images!
So, the main thing for partition restoration is the availability of a bootable media
(a diskette or CD), created with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe, and also the access
to an archive file with a partition image (on a hard disk or removable media).
After you ran the software from a diskette or a CD and got to Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe welcome window, the further steps should not be of any
difficulty to you.
3.1.1 Selecting an action: restore a disk/partition
To restore a disk/partition from an archive file you must set the switch to
Restore a partition or the whole hard disk drive or deploy a new PC in the Action
Selection window.
54 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 55

Figure 3.1. Selecting an action: restore a partition
Click Next to continue.
3.1.2 Selecting an archive file
In the next window Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will show you the complete list of
storage devices connected to your PC, including hard disks as well as any other
storage drives (Figure 3.2).
Figure 3.2. The list of storage devices
You’ll be able to navigate the files and folders tree, using standard Windows
controls, to find the archive file with the image of a partition to be restored
and select it by clicking (Figure 3.3).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 55
Page 56

Figure 3.3. Selecting an archive file
If you commented the archive file when creating it, the description will help
you understand if you selected the right archive file or the partition image is
located in some other file. Your comment will be shown in the right part of
the Image Archive Selection window. Notice that a comment is available
without entering a password that protects an archive file. However, you
won’t be able to either restore, or browse archive file contents without a
password (see Figure 3.4 – contents of a password unprotected archive file).
Figure 3.4. Contents of a password unprotected archive file
The more detailed is your comment, the more assured your actions would
be. In particular, you can store several system partition configurations in
archive files, if working intensively with your operating system,
56 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 57

experimenting with various applications or device drivers, to restore one of
them if needed.
Having made sure that you are to restore a partition from the right archive
file, click
Next to continue.
3.1.3 Entering a password
So, if an archive file is protected with a password, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
will prompt you for it in the next window. You won’t be able to move to the
next wizard page, i.e. to continue the restoration without entering a
password, as the
Next key will be disabled. If you enter the right password,
you’ll be able to move to the page of selecting a partition to be restored.
Figure 3.5. Entering a password to an archive file during the restoration
Having entered a password, click Next to continue.
3.1.4 Archive file partitions
One archive file may contain images of several disk partitions or the whole disks.
Therefore the next window will offer you the contents of the selected archive file
(Figure 3.6). The main level that Acronis TrueImage Deluxe works at is the hard
disk partitions and the whole disks level, so you’ll see all the partitions and disks,
stored in the archive file.
As you’ll see further, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software can work with separate
files as well during the restoration (see 3.4 «Restoring separate files»).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 57
Page 58

Select a partition for restoration by clicking the appropriate rectangle. It will
become underlined red (by default).
Figure 3.6. Selecting a partition to be restored from an archive file
You can select several partitions and/or disks for restoration during a session
of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe, but you’ll have to do it in turns (see 3.1.11
«The next partition/disk to be restored»), i.e. select one partition (disk) and
set restoration parameters for it first, and then repeat this for all other. You’ll
be able to return to the Source Partition Selection window if needed after
setting the partition restoration parameters and mark another partition (disk)
for restoration. A partition you set restoration parameters of will be marked
with an icon in the upper right corner.
Click
Next to continue.
3.1.5 Destination partition
As it has been said above, you can restore a partition image, stored in an
archive file, to a new hard disk. In the same way you can restore contents of
a stored partition to another partition. For example, you could have stored
logical drive D: data in an archive file. You would like this data to be restored
to the logical drive E: on a new hard disk. Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
software allows to do this as well. In the Restored Partition Location window
click a partition, to which you’d like to restore the data to (Figure 3.7). This
partition will become underlined red.
58 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 59

Figure 3.7. Selecting a destination partition
Click Next to continue.
3.1.6 Exclusive partition access
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software must obtain exclusive access to a
partition to restore an image from an archive file to. It means no other
software must work with this partition during the restoration. Therefore it’s
recommended to close all applications for the restoration period (for more
information see 3.2 «Partition restoration peculiarities»). However, it’s not
enough for some cases, in particular if you restore a partition the operating
system was booted from. You can receive a message such as shown below
(Figure 3.8).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 59
Page 60

g
g
Figure 3.8. Unavailability of exclusive access to a partition
We’ll discuss this situation later (see 3.2 «Partition restoration peculiarities»). It may
appear at system partition restoration (the one PC is currently booted from).
So, having selected the destination to restore a partition from an archive file,
Next to continue.
click
3.1.7 Partition type (primary/logical)
You can change the type of a partition from an archive file, while restoring it
(Figure 3.9).
Read more about partition types in the Appendix: see Appendix A «General
Information. Hard Disks». We also note that an operatin
a primary partition, and lo
files.
ical drives of an extended partition are used for storing data
You can imagine the following example situation to understand what you
might have to change partition type for. Both system, and data files were
stored on a single damaged primary partition. Now you need to restore a
partition from a back-up copy to another hard disk with several partitions
and an operating system installed.
You need only the data of a stored partition, and need not another system
partition. In this case you can restore the partition as a logical to use its
data.
system is usually installed to
In case you are restoring a system partition, you should select the primary
type for it.
60 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 61

Figure 3.9. Selecting the restored partition type
Having selected partition type, click Next to continue.
3.1.8 File system
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software allows to similarly change a partition file system at restoration (Figure 3.10).
Let’s assume you are restoring a partition from a low capacity disk with the
FAT16 file system to a new higher capacity hard disk. It would be ineffective
(and just impossible in some cases) to use the FAT16 file system on a high
capacity hard disk. The fact is that FAT16 limits partition size to 4 GB, so you
won’t be able to restore a 4 GB FAT16 partition to a new disk of higher
capacity, as you’ll have to change the file system.
It would be logical to change FAT16 to FAT32 in the given case. Set the
switch to the appropriate position in the Restored Partition File System window
to do this.
You should also remember that not all operating systems can boot from a
FAT32 partition. MS-DOS, Windows 95 Original, Windows NT 3.x, 4.x does
not support FAT32 and won’t work after restoration with a file system
change, i.e. they can be restored to a FAT16 partition only.
But you can freely convert a FAT16 partition with newer operating systems to
FAT32.
You can find file system comparatives in the Appendix A «General Information. Hard
Disks» section.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 61
Page 62

Figure 3.10. Selecting the restored partition file system
Click Next to continue.
3.1.9 Changing size of a partition to be restored
So, you are to restore a hard disk partition. The reasons can be very
different: you might have just installed a bad device driver, causing system
instability; or Windows registry is damaged. The question might be a hard
disk: there have appeared many bad sectors; file read/write errors have
become regular. Finally, the File Allocation Table (FAT) or the Root is
damaged, or the Bootsector is infected with a still incurable virus.
If your PC health was ruined due to one of these reasons, you might like to
restore a partition to a new disk and change the partition configuration and
size comparing to what you had before. Acronis TrueImage software is
flexible enough to let you do this. You’ll be able to change the size and disk
location of a partition to be restored in the following window (Figure 3.11).
The information on a stored partition is kept in its image. The window shows
exactly this information. You can resize a partition to make it larger or
smaller (not smaller than the space occupied with its data.)
62 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 63

Figure 3.11. Changed partition: initial size
The figure below shows the initial 3.907 GB partition size changed to the
2.007 GB.
Figure 3.12. Resizing a partition
The next figure (Figure 3.13) demonstrates changing partition location.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 63
Page 64

Figure 3.13. Changing partition location
Having changed partition size and location if needed, click Next to continue.
3.1.10 Selecting a letter for a partition to be restored
Having restored a partition, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will «map» its
contents, stored in an archive file, to a logical drive.
Windows operating system uses Roman alphabet letters for disk and partition
identification. Letters are automatically assigned during OS boot process.
Acronis TrueImage software lets you assign any unoccupied letter to a
partition (logical drive) to be restored under Windows NT/2000/XP. To do
this, set the switch to Yes, I want to assign a logical drive letter to the restored
partition on the following page and select a letter from the drop-down list. If
you do not set this switch, a logical drive will have its letter automatically assigned
by the operating system. This page will be omitted under Windows 9x/Me.
64 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 65

Figure 3.14. Selecting a partition letter
3.1.11 The next partition/disk to be restored
You can restore several partitions at one session in the same way as you can
store several images. To do this, set the switch to Yes, I want to restore
another partition or hard disk drive in the Next Selection window.
Figure 3.15. Selecting the next partition to be restored
Having clicked Next, you’ll see the Source Partition Selection window again
(Figure 3.6). This time the upper right corner of a rectangle representing the
partition, which you have already worked with, will be ticked off. You’ll be
able to select the next partition to be restored and to perform actions,
described above, in the following windows:
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 65
Page 66

• Select a destination partition (Figure 3.7),
• Select a partition type (primary/logical; Figure 3.9),
• Select a file system (Figure 3.10),
• Change partition size and disk location if needed (Figure 3.11 - Figure 3.13).
If you restore the only partition, you don’t need to set the switch to Yes, I
want to restore another partition or hard disk drive. In this case you’ll get to the
restoration script window at once, having clicked
3.1.12 Restoration script
So, you’ll finally get a script again, but this time for restoring a partition from an
image instead of creating an image in an archive file (Figure 3.16).
Next.
Figure 3.16. Partition restoration script window
All said about an image creation script is basically true regarding a restoration
script (see Figure 2.12 above), including:
As you have seen before, restoration script creation includes the following
stages:
• Selecting restoration (Restore a partition or the whole hard disk drive or deploy
a new PC),
• Selecting an archive file with a partition (disk) image on a hard disk (or
removable media; see below),
• Selecting a partition and/or disk to be restored,
• Selecting a destination partition (disk) to restore a partition from an
archive file to,
66 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 67

• Selecting a type of a partition to be restored,
• Selecting a partition file system,
• Changing partition size and/or location,
• Moving to the next partition to be restored or to the restoration script.
Now Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software is ready for partition restoration. If
you click
Back, you’ll be able to select other partitions and/or disks for
restoration, rethink partition size changes, its type and file system selection, in
other words to change any restoration parameters. You can execute the
partition restoration script by clicking
Proceed.
So, click Proceed to execute the partition restoration script.
Restoration progress will be shown in the special window.
3.2 Partition restoration peculiarities
There may be several general cases of partition restoration:
• Data partition restoration,
• System partition restoration.
Restoring a data partition
If, for example, you find your accounting database damaged on a logical
drive and decide to restore it from a previously created image in an archive
file to the same partition, you might receive this warning:
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 67
Page 68

Figure 3.17. Warning of unavailability of exclusive access to a logical drive at
partition restoration
This means the following. Operating system blocks logical drives for some
low-level operations that Acronis TrueImage tries to perform to restore a
partition. In particular, some application might work with this partition data.
It can be MS Word, MS Excel, or Norton Utilities. Therefore, it is necessary to
close all applications before restoring a partition.
In some cases Acronis TrueImage Deluxe can unplug a logical drive, perform
restoration, and connect it again. (In the given situation
Reboot is replaced
by Dismount.) Sometimes it’s impossible to unplug a logical drive. Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe then prompts you to reboot the PC. So, in the situation
above you can:
• Close applications and click
Retry – retry to restore a partition from an
archive file,
• Click
Dismount to force logical drive disconnection,
• Click Reboot to reboot the PC.
You should remember that you can’t force any drive disconnection. For
example, an attempt to unplug a logical drive with an operating system or a
swap file would cause OS to crash.
You can unplug a logical drive in case of a data partition restoration.
If you have free space on a disk, you can use it to restore a partition (for
example, if you decided to enlarge the data partition). You won’t have any
problems with it: Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will restore a partition and
connect a new logical drive.
68 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 69

Restoring a system partition
System partition restoration is different. There are two possible situations:
• System shows off failure signs, but still boots; you also succeed to run
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe directly from the Windows Start menu;
• System doesn’t boot, or it’s impossible to run applications, including
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe, under it after booting.
If you succeeded to boot Windows and run Acronis TrueImage Deluxe, you
should do the following:
1. Set the switch to Restore a partition or the whole hard disk drive or deploy a
new PC in the Action Selection window;
2. Find an archive file on a hard disk or removable media;
3. Select a partition (the system one) to be restored from this archive file;
4. Select a partition, to which you want to restore the previously selected
partition, from the list of hard disks connected to the PC;
5. Having clicked
Next, you receive a message such as shown on the figure
above (Figure 3.17).
You reboot your PC, clicking
Reboot. As a result Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe will run before Windows, restore the system partition and
terminate, allowing Windows OS to boot.
If the operating system doesn’t boot or applications (particularly Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe) do not run, you should have a bootable diskette or CD for
this situation. Acronis TrueImage Deluxe lets you create it by clicking
Acronis -> TrueImage -> Bootable Rescue Media Builder. Such a diskette
(CD) will contain everything necessary to run Acronis TrueImage Deluxe and
access hard disks and other drives, connected to your PC. Having run Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe, you should act the same as described above to restore
the system partition. Having restored the partition, you should remove the
diskette from the drive and reboot your PC.
3.3 Peculiarities of restoration from removable media
Restoring a partition (disk) from removable media shouldn’t be of any
additional difficulties than restoring it from a hard disk. But you should
remember that it (as well as back-up copying to removable media) will take
much longer time.
Moreover, you will usually need several CD-R, CD-RW disks to create a backup copy of a partition and, especially, the whole disk on removable media,
that you’ll have to insert into drive in turns.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 69
Page 70

3.4 Restoring separate files
As it has been said before, Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software works with
both hard disk partitions, and the whole disks (see Introduction). In particular,
you can store images of several partitions or even disks in an archive file.
However, if you have only one or several files damaged (or accidentally
deleted!) on the partition, it would be inefficient to entirely restore it. A disk
partition may already contain many newer file versions than stored in the last
image in an archive file along with new files and folders. So, how to restore a
separate file on a partition? Acronis TrueImage Deluxe is flexible enough to
help you in this situation as well.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe features temporary logical drive connection from an
image for separate files restoration. Having connected a drive, you’ll be able
to access it as a usual hard disk. It means that:
• The list of your PC drives will be updated with a new one with a letter
assigned to it;
• You’ll be able to browse the files and folders tree of a partition, stored in
an archive file, with the Windows file managing tools (Explore, etc.), as in
case of a usual hard disk (or its partition);
• You’ll be able to use any file manager to find and copy any file (files
and/or folders) needed from a connected drive to a real one.
You’ll have the read access only to a connected drive, and won’t be able to
change it somehow.
3.4.1 Connecting a drive from a partition image
So, you’ll need to connect a temporary logical drive to restore a separate file
(a group of files, folders) from an image. To do this, set the switch to Explore
an image archive (Figure 3.18) in the Action Selection window of Acronis
TrueImage Deluxe.
70 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 71

Figure 3.18. Exploring a partition image in an archive file
Click Next to continue.
3.4.2 Selecting an archive file
As in case of the whole disk partition (disk) restoration (Figure 3.2), the next
window of Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will offer you the full list of storage
devices, connected to your PC, which you will have to browse for the archive
file with the necessary partition image (Figure 3.19).
Figure 3.19. Selecting an archive file to connect a logical drive
If this archive file isn’t protected with a password, selecting it you’ll see the
previously created comment along with the list of stored partitions, as shown
on the Figure 3.19. If the file is protected with a password, you’ll see the
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 71
Page 72

comment only. Having clicked Next, you’ll get to the window with a prompt
to enter the archive file password.
Figure 3.20. Entering an archive file password
Click Next to continue, having entered password if needed.
In the next window you’ll be able to select one of the partition (disk) images
to connect as a temporary logical drive (Figure 3.21).
Figure 3.21. Selecting a partition and letter for a drive to be connected
A partition is selected by clicking the appropriate rectangle representing it. As
a result, the selected partition (rectangle) will become underlined red.
Another click will deselect the partition. You can select to connect several
72 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 73

partitions simultaneously. Each of them will be represented as a separate
logical drive with a letter assigned to it.
The same window will also allow to select a letter to assign to a drive to be
connected (Drive letter for the selected partition drop-down list).
If you want to change the letter assigned by default, you should select a
partition first by clicking it and then select a letter. (You can then select
another partition and letter if needed, etc.)
Having selected a partition (disk) and a letter, click
Next to continue.
In the next window you’ll see the temporary logical drive connection script.
Figure 3.22. The drive connection script window
If you do not have any doubts regarding the selected partitions (and its
letter), click
Proceed to continue.
The connection of a temporary logical drive will finish a message about
successful connection script execution (Figure 3.23).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 73
Page 74

Figure 3.23. The successful drive connection message window
Having clicked Exit, you’ll find out a Windows window opened right after
the message window, with the contents of the connected drive (partition,
stored in an archive file; Figure 3.24).
Figure 3.24. The Windows window with the temporary connected logical drive
Now you can easily copy any file (or file folder) from the connected logical
drive to replace the damaged one on your real hard disk.
74 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 75

3.4.3 Disconnecting a drive
You should unplug a temporary logical drive after restoring separate files and
folders. If you do not do this, it will disappear after reboot.
Disconnecting with the context menu
Select Unplug in the context menu of a connected drive, invoked by right-
clicking the disk icon in the Windows window. As a result this disk will
disappear.
Disconnecting from Acronis TrueImage Deluxe
Having run Acronis TrueImage Deluxe after connection, you’ll find out
another button in the operation selection window – Unplug temporary logical
drives (Figure 3.25).
Figure 3.25. A new operation in the Action Selection window
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 75
Page 76

After selecting this operation and clicking Next, you’ll see the list of
connected temporary logical drives (Figure 3.26). Use it to select a drive to
unplug.
Figure 3.26. The list of connected drives
Click Next to continue. Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software will show you
the temporary logical drive disconnection script (Figure 3.27).
Figure 3.27. The drive disconnection script window
76 3 : Restoring a disk/partition from an image
Page 77

By clicking Proceed, you’ll execute the script. Drive unplugging will finish
with a standard message about the operation success (Figure 3.28).
Figure 3.28. The successful drive unplugging window
By clicking Exit you’ll finish the session of separate partition files and
folders restoration from an archive file.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 77
Page 78

Conclusion
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software allows to create exact image of a disk
(disk partition) in an archive file on a hard disk or any removable media. At
creating a disk/partition image Acronis TrueImage Deluxe compresses the
data. An archive file can be commented and protected with a password.
A disk image can be used to restore your hard disk data, or deploy a system
on another PC, or revert a system back on a small office PCs, as well as on a
school computer room, a club, an Internet café.
In all these cases Acronis TrueImage Deluxe offers effective tools for
creating images and restoring both the whole disks, and separate partitions.
Moreover, it lets you restore separate files and folders.
To restore separate files from an archive, a partition image, stored in an
archive file, is connected to the system as a temporary logical drive, allowing
to copy any files and folders to a real hard disk with any file manager. The
connected disk is unplugged after separate files restoration.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe offers effective tools for creating images of both
data, and system partitions to restore them in the most complex cases. The
software allows to create bootable diskettes and CDs to restore the system in
case of its full inoperability.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software is flexible enough to allow not only to
restore a partition, but also to change its type, file system, size, and location
during its restoration.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe software features a user-friendly graphic
interface, is intuitive. Back-up and restoration operations require user to
answer literally a few simple questions. The software is available to every,
even the most inexperienced PC user who needs to keep his personal data
safe and the system operable.
The regular back-up copying with Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will make a user
confident in his work, and guarantee that his personal data won’t be lost in
any circumstances.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe will be very useful for both common users, and
small company and office system administrators, managers of computer
classes and clubs, where user actions often lead to necessity of timeconsuming operating system (Windows) re-installation. Acronis TrueImage
Deluxe allows to restore system and applications literally in minutes.
78 Conclusion
Page 79

In conclusion we thank you for choosing our products! We are always ready
to render you qualified assistance. Wherever you are, whatever tasks and
problems you face, you can always find an answer to any question about our
products and their running on these pages or by contacting our technical
support.
If you have any questions concerning the installation and running of Acronis
software, please carefully follow the instructions below:
• Try to find answers to your questions in the guide supplied with the
software package. You can also download user’s guides from our site at
http://www.acronis.com/download/docs/
frequently asked questions (http://www.acronis.com/support/faq.html
. Please, look through the
),
where you can possibly find an answer to your question.
• Make sure you use the latest build of Acronis software. The current build
number of Acronis products is at http://www.acronis.com/
support/updates/
. You can learn the version of installed software by
running it and opening the «About» window. Registered users can use
this link to update their software: http://www.acronis.com/
support/updates/
version from http://www.acronis.com/download/
. If you use a demo version, please download the latest
.
• If you couldn’t find answers to your questions contact our technical
support at support@acronis.com.
• Please provide the product name, version, and build in your letter along
with the product registration information – the serial number and e-mail
used at the registration.
Do not forget to register purchased software (http://www.acronis.com/
registration/)! We guarantee an answer in 48 hours to registered users only.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 79
Page 80

Appendix A. General Information. Hard Disks
The Appendices below provide you with extra information on the hard disk
organization, how information is stored on disks, how disks should be installed
in the computer and plugged into motherboard, configuring disks with BIOS,
partitions, file systems, and how operating systems interact with disks.
A.1 Hard Disk Organization
All hard disks, or hard disk drives, have basically the same structure,
however diverse they are in size. Inside the case there are several disks with
magnetic coating set on a single axis (spindle). A special motor provides the
necessary rotation speed to the spindle, e.g. 5400 rpm, 7200 rpm, or
10000 rpm.
Information on disks resides on concentric tracks. Each track has its
number. The outermost track is number 0, and the numbers grow
inwards.
Each of the tracks is divided into sectors that contain minimal information
blocks that can be written to disk or read from it. Sectors also have numbers.
On every disk there is a marker that indicates the beginning of sector
enumeration. The sector that is the closest to this marker is number 1.
Usually sector size is 571 bytes. At the beginning of a sector there is a
header (prefix portion) that marks the beginning of the sector and its
number. At the end of a sector, in the suffix portion, there is the checksum
that is used to check data integrity. Data area between the prefix and suffix
portions is 512 bytes large.
Both upper and lower sides of each disk on the spindle are used to store
data. All tracks that have the same number on all the surfaces of all disks
comprise a cylinder. For each work surface of a disk in the drive there is a
head that enables reading and writing data to/from the disk. Heads are
assembled into a block and are enumerated, starting with 0.
To perform an elementary read or write operation the head block must be
positioned at the necessary cylinder. When the necessary sector (with the
necessary number in the service area) of the rotating disks approaches the head,
data is exchanged between the head and the electronic board of the drive.
Sector structure of a hard disk is created via low-level formatting during which
each of the tracks of the disk is marked up.
Modern disk drives usually contain relatively few magnetic disks (1-2) to
make the head block lighter and speed up access to sectors (a drive like this
has 2-4 heads respectively).
80 Appendix A : General Information. Hard Disks
Page 81

There can be up to several tens of thousands of cylinders per disk. The
higher the write density on the disk, the more cylinders can be created on it
and the larger the capacity of the disk.
This design has many technical implementation peculiarities, but we will not
discussing those here.
A.2 Operating System and Hard Disks
You know that hard disks are used to store information. You also know (see
A.1 «Hard Disk Organization») that information is stored in sectors, and the
sectors appear on disks by way of low-level formatting. Each sector contains
the smallest possible 512-byte data block.
Data blocks of larger size are stored in chains of such sectors. Each sector of
a chain contains the address of the next sector in the chain or the marker
telling that this sector is the last one in its service area. Chains of sectors
make a file. The address (number) of the first sector of a file is stored in the
file allocation table (FAT).
All applications you are familiar with – office applications (text and graphical
editors, spreadsheet processors) – and documents, tables, images, e-mail clients
and Internet access software, and games – are stored on hard disks as files.
Files are grouped into folders to make working with them more convenient.
Among various software the most important one is the operating system.
An operating system provides all other applications running under its control
with basic input/output access to all the resources of the PC, be that the
CPU, memory, or external devices (monitor, hard disks, floppy disks,
CD-ROM, DVD, printer). All applications are loaded into memory from a hard
disk and are executed under the control of the operating system.
It would have been very inconvenient for a user to use data on disks if
he/she had to deal only with addresses (numbers) of sectors comprising a
file. That is why every file in the file system has its name. In DOS and
Windows 3.x operating systems the name of the file contained 8 characters
followed by a dot (.), which, in its turn, was followed by three more
characters of the extension (or the type of the file). There could be fewer
characters in the name and/or extension, and there were limitations as to
what characters could be included in names and extensions.
Windows NT and newer OS versions allow files names that are up to 255
characters long. Full file name (including the disk letter and the name of the
folder containing the file) can be up to 260 characters long, however it is not
recommended using file names longer than 50-70 characters.
Other operating systems, like Linux, have never had such strict limitations on
file names as did DOS or Windows. The name of the file in Linux can be up
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 81
Page 82

to 256 characters long and have not one, but several extensions (or none at
all). The path to the file in Linux can be up to 4096 characters long.
To provide access to data organized in files and folders each operating
system, for example, MS-DOS, Windows 95/98/Me/NT/2000, Linux, has its
own characteristic way to create and manage hard disk space, which is
generally non-compatible with other OSes. However, it would be inefficient if
one hard disk could be used by only one operating system. That is why a
mechanism was created allowing several operating systems to use the hard
disk. This mechanism breaks the hard disk space into partitions.
A.3 Hard Disk Partitions
Partitioning Hard Disks in DOS/Windows
Partitioning hard disk is done by special applications. In MS-DOS and
Windows the widely known FDISK program is used for this purpose. It allows
creating partitions, setting their size and labels. FDISK allows allocating
either all hard disk space or part of it for MS-DOS or Windows, and leave
some part of it for other operating systems.
FDISK can perform the following functions:
• create a primary DOS partition containing one logical disk;
• create an Extended Partition that can be broken into any number of
logical disks;
• mark a partition as active (only one primary partition can be active).
The structure of partitions on the hard disk can be shown as follows:
MBR.
Primary partition 1-1.
System logical disk C:.
Extended partition 1-2.
Logical partition 1-5.
Logical disk D:.
Logical disk E:.
Logical disk F:.
…………………………
82 Appendix A : General Information. Hard Disks
Page 83

g
g
g
Information about partitions on a hard disk is stored in a special disk area – in the 1
sector of the 0th cylinder, header 0, which is called a Partition Table. This sector is
called the Master Boot Record, MBR.
A physical hard disk can contain up to 4 primary partitions. This limitation is due only
to the capacity of the Partition Table, which itself consists of only four partitions.
However, this does not mean that you can install only 4 different operatin
Modern software disk mana
systems. For example, the Acronis OS Selector 5.0 Deluxe disk mana
to install up to 100 operating systems on one hard disk!
ers allows the installation of many more operating
Partitioning hard disks is a feature that is available in all operating systems.
A.4 Creating Partitions for Other OSes
In this part of the Guide we have described the way to partition a hard disk
by the FDISK program for the DOS/Windows operating system. As it has
been said above, the FDISK program creates primary and possibly (but
necessarily so) extended DOS partitions and logical partitions (disks) on
them, and can also leave disk space unallocated to be used by other
operating systems. However, the Windows operating system, while being a
very widely distributed operating system for PCs, is not the only operating
system.
st
systems.
er, allows a user
You can configure the hard disk of your computer to used with the Linux
operating system. In this case you do not need to create either primary nor
extended DOS partitions (if you are not going to use DOS/Windows).
For example, the installation program from the ASPLinux operating system
includes a disk manager that allows partitioning a disk into partitions that can
be used by this OS.
A.5 Primary and Logical Partitions
Many operating systems, including DOS and Windows 95, can only be booted
from primary partitions.
Some operating systems do not see primary partitions except those they
were booted from (OS/2).
Knowing these limitations allows you to decide what partitions are better to
use and for what purposes. Primary partitions are better used for booting
operating systems and storing system folders and files.
Logical partitions can keep all the other information, since they are accessible
from most operating systems.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 83
Page 84

If you are going to keep several operating systems on your computer, it is
better to install those that can be booted from logical partitions onto logical
partitions, so that they do not use up extra primary partition space.
A.6 Formatting Hard Disks
Within each of the partitions information has to be organized in a way
understandable for the operating system that uses the partition. This
organization is the file system. Format and location of information (the logical
structure of a partition) for MS-DOS and Windows is created by the FORMAT
program.
FORMAT program performs the following functions:
• It creates the boot record;
• It creates the file allocation table (FAT);
• It marks bad clusters so they are not used.
After formatting, logical disks created by the FDISK program are organized
as follows:
• Logical disks start with the boot sector;
• One or several copies of file allocation table (FAT) are placed after the
boot sector;
• Next goes the root folder;
• Then the data area.
Each logical disk has to be formatted with FORMAT separately.
Formatting a partition is done by issuing a DOS command:
FORMAT C:
To create a system (bootable) logical disk, it has to be formatted with
FORMAT with /S parameter:
FORMAT C: /S
Another way is to transfer the system to the partition that has been
formatted with /B parameter is booting the computer from a system diskette
and issuing the command
SYS C:
IO.SYS, MSDOS.SYS, COMMAND.COM files that are necessary for the
operating system to be booted are copied from the diskette to the disk.
Initial loader code is written to the boot sector.
84 Appendix A : General Information. Hard Disks
Page 85

Other operating systems provide hard disk formatting means to create file systems
that are recognizable by these OSes.
A.7 File Systems
The logical structure that has been created on the hard disk is supported by
means of operating system. The file system itself presents the information on
the disk as an ensemble of files and folders.
From the user’s point of view a file is a unit of storage of logically connected
information: text, graphics, and sound. As for data storage organization, a file is
a chain of connected sectors or clusters. A cluster is a unit of several sectors.
(Sectors are characteristic for file systems supported by various versions of
Windows.)
Operating systems support file systems on hard disks (or disk partitions) by
allowing to create, copy, and delete files and folders.
At present, the most widely spread file systems for PCs are the following two:
• FAT (File Allocation Table) for DOS, OS/2, Windows 95/ 98/Me/NT/2000;
• NTFS (Windows NT File System) for Windows NT/2000.
However, there are many more other file systems. The Linux operating
system, for example, uses three different file systems:
• Ext2 is a common file system used on desktop PCs running Linux;
• Ext3 is the default file system used by Red Hat Linux;
• ReiserFS is a more secure (with respect to data integrity) file system that
is used on many Linux data servers.
• For details on file systems see Appendix A. «General Information. Hard
Disks».
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 85
Page 86

Appendix B. Glossary
Active partition. One of the primary partitions of a hard disk is usually active.
Default MBR code tries to boot an operating system from the active partition
of the first hard disk. Letter assignment in Microsoft operating systems
depends on what partitions are active.
Bad cluster. A cluster that contains bad sectors. Such cluster cannot store
useful information.
Bad sector. A sector that cannot store the information written, for instance
due to defects or aging of the magnetic surface.
BIOS extension. BIOS versions that were released before 1994 could only
support hard disks that were less than 8 gigabytes. Extended hard disk
management functions were added to BIOS versions to solve this problem,
and now the maximum supported hard disk capacity is 2
75
bytes.
Boot partition of an operating system is a partition from which the initial stage
of operating system booting is done (boot sector is read and executed, first
file of the operating system is read and executed).
Boot record. The initial part of a partition that contains code and data
necessary for booting an operating system. May consist of one or several
sectors. First sector of a boot record must end with the boot sector signature
(0AA55h).
Boot sector is the first sector of a disk or a partition that contains the initial code
for the operation system booting. Boot sector must end with 0AA55h signature.
Bootable disk is a disk from which an operating system may be booted. A
bootable disk must contain the boot sector of an operating system and the
necessary system and configuration files. The «Bootable disk» term usually
refers to diskettes and CD-ROMs.
Bootable partition. A partition that can host an operating system. In the
beginning of such a partition, there must be a boot record.
Booting an operating system is initialized by reading its boot sector to the
memory at 0:7C00h and passing control to it. Since each operating system
has its own boot sector, it is able to perform the required actions on loading
and initializing system and configuration files.
86 Appendix B : Glossary
Page 87

Booting the computer is a procedure that is executed every time a computer
is turned on or an operating system finishes its work or when the reset
button is pressed. Booting consists of the following stages:
• Hardware diagnostics;
• Memory check;
• Built-in BIOS initialization;
• Initialization of additional hardware components and their BIOS versions
(video, SCSI etc.);
• Booting an operation system.
Cluster. Information storage unit in such file systems as FAT and NTFS. Every
file occupies a certain number of whole clusters, so the larger the cluster size
the higher the losses are that are due to file size adjustment; and conversely,
the smaller the cluster the larger the cluster distribution tables.
Cylinder. A group of all the tracks on all the magnetic platters of a hard disk
that can be accessed without moving the magnetic head. Access to the data
inside one cylinder is much faster than moving the head from one cylinder to
the other.
Disk. It is a general term that can mean both a data storage media (floppy
disk, compact disk), and a data-reading device (hard disk), and a partition
that is accessible from some operating system (logical disk).
Diskette. Floppy disk. A removable storage media that consists of a flexible
magnetic platter enclosed in a protective envelope. The most common are
3.5” diskettes with 1.44 megabyte capacity.
File. A file is named information storage in the file system. In different file
systems files can be stored in different ways, differences may also exist in
storing file names and writing the full path of the file in the folder tree.
File system. Data structure that is necessary to store and manage files. File
system does the following functions: tracks free and occupied space,
supports folders and file names, tracks the physical positions of files on the
disk. Each partition may be formatted with its own file system.
Floppy disk drive. A device that reads and writes data to diskettes.
Folder. A table in the file system that contains description of files and other
folders. Such structure allows creating folder tree that begins with the root
folder.
Formatting. The process of creating service structure on the disk. There are
three levels of hard disk formatting: low-level (marking the magnetic surface
with tracks and sectors), partitioning and high-level (creation of file system
on a partition).
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 87
Page 88

Hard disk. Fixed storage media along with integrated electronics that consists
of several magnetic platters that rotate synchronously on one spindle. Hard
disks have relatively high capacity and high read/write speed.
Hard disk geometry. A set of hard disk parameters that usually includes the
number of cylinders, heads and sectors per track.
Head (magnetic head, read/write head). A hard disk consists of several magnetic
platters, for each side of each platter there is a head that is used to read and
write information on it.
Hidden partition. A partition that is made invisible to the operating system.
Usually partitions are hidden by changing their type.
Label. An optional name that can be assigned to a partition to simplify its
identification. Usually has the same limitation as file names. For example,
FAT partitions have labels up to 11 characters long, but may contain spaces.
Large hard disk support software. Some BIOS versions have troubles
supporting large (larger than 8 gigabytes) hard disks. That is why some hard
disk manufacturers provide special software that is installed in the beginning
of the hard disk, is loaded before any operating systems, and substitutes
hard disk access BIOS functions.
Letter (of a drive, partition). All operating systems that are somehow
DOS-compatible use Latin letters to identify drives and partitions. Letters A:
and B: are usually reserved for floppy drives. Starting with C: letters are
assigned to hard disk partitions that can be recognized by the operating
system. Separate letters may be assigned to CD-ROMs, to DVD drives, or to
network drives.
Logical disk is a partition whose file system is recognized by the operating
system. Usually each logical disk is assigned with a letter that uniquely
identifies it.
Logical partition. Partition information which is located not in MBR, but in the
extended partition table. The number of logical partitions on a disk is
unlimited.
Master Boot Record (MBR) is a special place in the very first sector of the hard
disk to store information about the hard disk partitioning and code to be
loaded with BIOS. All the actions that follow depend on the contents of this
code.
Operating system is a set of programs that usually includes kernel, drivers,
shell, and system programs that are used for centralized hardware
management and hiding the details of hardware management from the user
and applications.
88 Appendix B : Glossary
Page 89

Operating system installation is a process during which its system folders are
created, system files are copied and boot sector are created.
Partition. An independent area on a hard disk where a file system can be
located. A partition can be either primary or logical, depending on its position
in the partition structure. One of the primary partitions of a hard disk may be
active. A partition has the following attributes: type, beginning and size.
Some partition managing software and boot managers allow hiding
partitions. Information about partitions is stored in the partition table.
Partition structure. All the partitions on a hard disk make a tree with the root
in the MBR partition table. Many operating systems and programs assume
that any partition table, but MBR, may contain not more than one partition
entry and one table entry, and it simplifies the partition structure greatly – all
the logical partitions form one chain.
Partition table. It is the table that contains the information about partitions
and links to other partition tables. A partition table cannot have more than
four entries. The main partition table is located in the hard disk MBR. Other
partition tables are called extended. Partition tables are usually stored in the
first sector of a cylinder.
Partitioning. The process of creating the partition logical structure on a hard
disk. Partitioning is usually done with programs like FDISK.
Primary partition. The partition, information about which is contained in the
MBR partition table. The majority of operating systems can be booted only
from the primary partition of the first hard disk, and the number of primary
partitions is limited.
Physical disk. A disk that is physically a separate device. Thus, a floppy disk,
hard disk, CD-ROM, and DVD drives are considered physical disks.
Root folder. The folder where the folder tree of a file system begins. Starting
from the root folder one can uniquely describe the file position on the folder
tree by sequentially naming all the intermediate nested folders, e.g.:
\WINDOWS\SYSTEM\VMM32.VXD. Here the WINDOWS folder is a subfolder
of the root folder, SYSTEM folder – of the WINDOWS folder, and the
VMM32.VXD file is located in the SYSTEM folder.
Sector. It is the minimal information unit on a disk that is transferred in single
read or write operation. Usually a sector is 512 bytes large. A sector on a
disk can be addressed two ways: via the absolute number or via cylinder,
head, and sector number on a track.
Status. A flag that shows if a partition is active. This flag is stored in the
partition table and has no meaning for logical partitions.
Acronis TrueImage Deluxe 89
Page 90

System disk/partition is a disk/partition from which an operating system may
be booted. This disk usually contains the boot sector and system files of the
operating system.
System file is a file that contains the code and constant data for an operating
system. Each operating system has its own system file set.
System folder. Some operating systems keep most of their files in a special
folder on a partition that may be different from the system one. For example
for Windows 95/98/ME operating systems IO.SYS system file resides on the
system partition, while other system files are located in the system folder
which is usually called WINDOWS. Program Files folder can also be treated
as system since it resides on the same partition as WINDOWS and also
contains files that are relevant to the operating system.
Track. Disks are divided into concentric circles called tracks. Information from
one track can be accessed without moving the head.
User interface is a set of principles, concepts, and means by which programs
interact with the user. For example, in the window user interface, all input
and output is done in windows with control via a mouse.
90 Appendix B : Glossary
 Loading...
Loading...