Page 1

Acronis Backup Advanced
Version 11.7
USER GUIDE
APPLIES TO THE FOLLOWING PRODUCTS
Advanced for Windows Server
Advanced for Linux Server
Advanced for PC
Advanced for VMware / Hyper-V / RHEV / Citrix XenServer / Oracle VM
Advanced for Exchange
Advanced for SQL
Advanced for SharePoint
Advanced for Active Directory
For Windows Server Essentials
Page 2

Copyright Statement
Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016. All rights reserved.
“Acronis” and “Acronis Secure Zone” are registered trademarks of Acronis International GmbH.
"Acronis Compute with Confidence", “Acronis Startup Recovery Manager”, “Acronis Active Restore”,
“Acronis Instant Restore” and the Acronis logo are trademarks of Acronis International GmbH.
Linux is a registered trademark of Linus Torvalds.
VMware and VMware Ready are trademarks and/or registered trademarks of VMware, Inc. in the
United States and/or other jurisdictions.
Windows and MS-DOS are registered trademarks of Microsoft Corporation.
All other trademarks and copyrights referred to are the property of their respective owners.
Distribution of substantively modified versions of this document is prohibited without the explicit
permission of the copyright holder.
Distribution of this work or derivative work in any standard (paper) book form for commercial
purposes is prohibited unless prior permission is obtained from the copyright holder.
DOCUMENTATION IS PROVIDED "AS IS" AND ALL EXPRESS OR IMPLIED CONDITIONS,
REPRESENTATIONS AND WARRANTIES, INCLUDING ANY IMPLIED WARRANTY OF MERCHANTABILITY,
FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR NON-INFRINGEMENT, ARE DISCLAIMED, EXCEPT TO THE
EXTENT THAT SUCH DISCLAIMERS ARE HELD TO BE LEGALLY INVALID.
Third party code may be provided with the Software and/or Service. The license terms for such
third-parties are detailed in the license.txt file located in the root installation directory. You can
always find the latest up-to-date list of the third party code and the associated license terms used
with the Software and/or Service at http://kb.acronis.com/content/7696
Acronis patented technologies
Technologies, used in this product, are covered and protected by one or more U.S. Patent Numbers:
7,047,380; 7,275,139; 7,281,104; 7,318,135; 7,353,355; 7,366,859; 7,475,282; 7,603,533; 7,636,824;
7,650,473; 7,721,138; 7,779,221; 7,831,789; 7,886,120; 7,895,403; 7,934,064; 7,937,612; 7,949,635;
7,953,948; 7,979,690; 8,005,797; 8,051,044; 8,069,320; 8,073,815; 8,074,035; 8,145,607; 8,180,984;
8,225,133; 8,261,035; 8,296,264; 8,312,259; 8,347,137; 8,484,427; 8,645,748; 8,732,121 and patent
pending applications.
2 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 3

Table of contents
1 Introducing Acronis Backup ............................................................................................ 10
1.1 What's new in Acronis Backup 11.7 .........................................................................................10
1.2 Acronis Backup components ...................................................................................................11
1.2.1 Agent for Windows ....................................................................................................................................... 12
1.2.2 Agent for Linux .............................................................................................................................................. 12
1.2.3 Agent for VMware ......................................................................................................................................... 13
1.2.4 Agent for Hyper-V ......................................................................................................................................... 13
1.2.5 Agent for SQL ................................................................................................................................................. 13
1.2.6 Agent for Active Directory ............................................................................................................................ 13
1.2.7 Components for centralized management ................................................................................................. 13
1.2.8 Management Console ................................................................................................................................... 15
1.2.9 Bootable Media Builder ................................................................................................................................ 15
1.2.10 Acronis Wake-on-LAN Proxy ........................................................................................................................ 15
1.3 About using the product in the trial mode ..............................................................................15
1.4 Supported file systems ............................................................................................................16
1.5 Technical Support ....................................................................................................................16
2 Getting started .............................................................................................................. 18
2.1 Using the management console ..............................................................................................21
2.1.1 "Navigation" pane ......................................................................................................................................... 22
2.1.2 Main area, views and action pages .............................................................................................................. 24
2.1.3 Console options ............................................................................................................................................. 26
3 Understanding Acronis Backup ....................................................................................... 29
3.1 Owners .....................................................................................................................................29
3.2 Credentials used in backup plans and tasks ............................................................................29
3.3 User privileges on a managed machine ...................................................................................31
3.4 List of Acronis services .............................................................................................................31
3.5 Full, incremental and differential backups ..............................................................................34
3.6 What does a disk or volume backup store? .............................................................................35
3.7 About dynamic and logical volumes ........................................................................................36
3.7.1 Backup and recovery of dynamic volumes (Windows) .............................................................................. 36
3.7.2 Backup and recovery of logical volumes and MD devices (Linux) ............................................................. 38
3.8 Support for Advanced Format (4K-sector) hard disks .............................................................44
3.9 Support for UEFI-based machines ...........................................................................................45
3.10 Support for Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 ................................................................45
3.11 Compatibility with encryption software ..................................................................................47
3.12 Support for SNMP ....................................................................................................................48
4 Backup .......................................................................................................................... 50
4.1 Back up now .............................................................................................................................50
4.2 Creating a backup plan ............................................................................................................50
4.2.1 Selecting data to back up .............................................................................................................................. 52
4.2.2 Access credentials for source ....................................................................................................................... 54
4.2.3 Source files exclusion .................................................................................................................................... 55
3 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 4

4.2.4 Backup location selection ............................................................................................................................. 56
4.2.5 Access credentials for archive location ........................................................................................................ 59
4.2.6 Backup schemes ............................................................................................................................................ 60
4.2.7 Archive validation .......................................................................................................................................... 69
4.2.8 Backup plan's credentials ............................................................................................................................. 70
4.2.9 Label (Preserving machine properties in a backup) .................................................................................... 70
4.2.10 Sequence of operations in a backup plan ................................................................................................... 72
4.2.11 Why is the program asking for the password? ........................................................................................... 72
4.3 Simplified naming of backup files ............................................................................................72
4.3.1 The [DATE] variable ....................................................................................................................................... 73
4.3.2 Backup splitting and simplified file naming ................................................................................................. 74
4.3.3 Usage examples ............................................................................................................................................. 74
4.4 Scheduling ................................................................................................................................77
4.4.1 Daily schedule ................................................................................................................................................ 79
4.4.2 Weekly schedule ........................................................................................................................................... 81
4.4.3 Monthly schedule .......................................................................................................................................... 83
4.4.4 On Windows Event Log event ...................................................................................................................... 85
4.4.5 Advanced scheduling settings ...................................................................................................................... 87
4.4.6 Conditions ...................................................................................................................................................... 88
4.5 Replication and retention of backups ......................................................................................91
4.5.1 Supported locations ...................................................................................................................................... 93
4.5.2 Setting up replication of backups ................................................................................................................. 94
4.5.3 Setting up retention of backups ................................................................................................................... 94
4.5.4 Retention rules for the Custom scheme ...................................................................................................... 95
4.5.5 Usage examples ............................................................................................................................................. 97
4.6 How to disable backup cataloging .........................................................................................100
4.7 Default backup options ..........................................................................................................100
4.7.1 Additional settings....................................................................................................................................... 102
4.7.2 Archive protection ....................................................................................................................................... 104
4.7.3 Backup cataloging ....................................................................................................................................... 104
4.7.4 Backup performance ................................................................................................................................... 105
4.7.5 Backup splitting ........................................................................................................................................... 106
4.7.6 Compression level ....................................................................................................................................... 107
4.7.7 Disaster recovery plan (DRP) ...................................................................................................................... 108
4.7.8 E-mail notifications ...................................................................................................................................... 109
4.7.9 Error handling .............................................................................................................................................. 110
4.7.10 Event tracing ................................................................................................................................................ 111
4.7.11 Fast incremental/differential backup ........................................................................................................ 112
4.7.12 File-level backup snapshot ......................................................................................................................... 112
4.7.13 File-level security ......................................................................................................................................... 113
4.7.14 LVM snapshotting ....................................................................................................................................... 114
4.7.15 Media components ..................................................................................................................................... 115
4.7.16 Mount points ............................................................................................................................................... 115
4.7.17 Multi-volume snapshot ............................................................................................................................... 116
4.7.18 Pre/Post commands .................................................................................................................................... 116
4.7.19 Pre/Post data capture commands ............................................................................................................. 118
4.7.20 Replication/cleanup inactivity time ........................................................................................................... 120
4.7.21 Sector-by-sector backup ............................................................................................................................. 120
4.7.22 Tape management ...................................................................................................................................... 121
4.7.23 Task failure handling ................................................................................................................................... 122
4.7.24 Task start conditions ................................................................................................................................... 123
4.7.25 Volume Shadow Copy Service .................................................................................................................... 124
4 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 5

5 Recovery ..................................................................................................................... 127
5.1 Creating a recovery task ........................................................................................................127
5.1.1 What to recover .......................................................................................................................................... 129
5.1.2 Access credentials for location ................................................................................................................... 133
5.1.3 Access credentials for destination ............................................................................................................. 134
5.1.4 Where to recover ........................................................................................................................................ 134
5.1.5 When to recover ......................................................................................................................................... 142
5.1.6 Task credentials ........................................................................................................................................... 142
5.2 Recovering BIOS-based systems to UEFI-based and vice versa .............................................143
5.2.1 Recovering volumes .................................................................................................................................... 144
5.2.2 Recovering disks .......................................................................................................................................... 145
5.3 Acronis Active Restore ...........................................................................................................147
5.4 Bootability troubleshooting ...................................................................................................148
5.4.1 How to reactivate GRUB and change its configuration ............................................................................ 150
5.4.2 About Windows loaders ............................................................................................................................. 151
5.5 Reverting a Windows system to its factory settings ..............................................................151
5.6 Default recovery options .......................................................................................................152
5.6.1 Additional settings....................................................................................................................................... 153
5.6.2 E-mail notifications ...................................................................................................................................... 154
5.6.3 Error handling .............................................................................................................................................. 156
5.6.4 Event tracing ................................................................................................................................................ 156
5.6.5 File-level security ......................................................................................................................................... 157
5.6.6 Mount points ............................................................................................................................................... 158
5.6.7 Pre/Post commands .................................................................................................................................... 158
5.6.8 Recovery priority ......................................................................................................................................... 159
5.6.9 Tape management ...................................................................................................................................... 160
6 Conversion to a virtual machine ................................................................................... 161
6.1 Conversion methods ..............................................................................................................161
6.2 Conversion to an automatically created virtual machine ......................................................161
6.2.1 Considerations before conversion ............................................................................................................. 162
6.2.2 Setting up regular conversion to a virtual machine .................................................................................. 163
6.2.3 Recovery to the ''New virtual machine'' destination ................................................................................ 166
6.3 Recovery to a manually created virtual machine ..................................................................169
6.3.1 Considerations before conversion ............................................................................................................. 169
6.3.2 Steps to perform ......................................................................................................................................... 170
7 Storing the backed up data........................................................................................... 171
7.1 Vaults .....................................................................................................................................171
7.1.1 Working with vaults .................................................................................................................................... 172
7.1.2 Centralized vaults ........................................................................................................................................ 173
7.1.3 Personal vaults ............................................................................................................................................ 182
7.1.4 Changing the default cache folder for catalog files .................................................................................. 184
7.2 Acronis Secure Zone ..............................................................................................................185
7.2.1 Creating Acronis Secure Zone .................................................................................................................... 186
7.2.2 Managing Acronis Secure Zone .................................................................................................................. 188
7.3 Removable devices ................................................................................................................189
7.4 Tape devices ..........................................................................................................................190
7.4.1 What is a tape device? ................................................................................................................................ 190
7.4.2 Overview of tape support ........................................................................................................................... 190
7.4.3 Getting started with a tape device ............................................................................................................. 196
5 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 6

7.4.4 Tape management ...................................................................................................................................... 200
7.4.5 Vaults on tapes ............................................................................................................................................ 208
7.4.6 Usage examples ........................................................................................................................................... 208
7.5 Storage nodes ........................................................................................................................212
7.5.1 What is a storage node? ............................................................................................................................. 212
7.5.2 Supported types of storage ........................................................................................................................ 212
7.5.3 Operations performed by storage nodes .................................................................................................. 212
7.5.4 Getting started with a storage node .......................................................................................................... 213
7.5.5 User privileges on a storage node .............................................................................................................. 214
7.5.6 Operations with storage nodes .................................................................................................................. 215
7.5.7 Deduplication .............................................................................................................................................. 225
8 Operations with archives and backups.......................................................................... 232
8.1 Validating archives and backups ............................................................................................232
8.1.1 Archive selection ......................................................................................................................................... 233
8.1.2 Backup selection .......................................................................................................................................... 233
8.1.3 Vault selection ............................................................................................................................................. 233
8.1.4 Access credentials for source ..................................................................................................................... 234
8.1.5 When to validate ......................................................................................................................................... 235
8.1.6 Task credentials ........................................................................................................................................... 235
8.2 Exporting archives and backups ............................................................................................236
8.2.1 Archive selection ......................................................................................................................................... 238
8.2.2 Backup selection .......................................................................................................................................... 238
8.2.3 Access credentials for source ..................................................................................................................... 239
8.2.4 Destination selection .................................................................................................................................. 239
8.2.5 Access credentials for destination ............................................................................................................. 240
8.3 Mounting an image ................................................................................................................241
8.3.1 Archive selection ......................................................................................................................................... 242
8.3.2 Backup selection .......................................................................................................................................... 242
8.3.3 Access credentials ....................................................................................................................................... 242
8.3.4 Volume selection ......................................................................................................................................... 243
8.3.5 Managing mounted images........................................................................................................................ 243
8.4 Operations available in vaults ................................................................................................244
8.4.1 Operations with archives ............................................................................................................................ 244
8.4.2 Operations with backups ............................................................................................................................ 245
8.4.3 Converting a backup to full ......................................................................................................................... 246
8.4.4 Deleting archives and backups ................................................................................................................... 246
9 Bootable media ........................................................................................................... 248
9.1 How to create bootable media ..............................................................................................249
9.1.1 Linux-based bootable media ...................................................................................................................... 249
9.1.2 WinPE-based bootable media .................................................................................................................... 253
9.2 Connecting to a machine booted from media .......................................................................255
9.3 Working under bootable media.............................................................................................256
9.3.1 Setting up a display mode .......................................................................................................................... 257
9.3.2 Configuring iSCSI and NDAS devices .......................................................................................................... 257
9.4 List of commands and utilities available in Linux-based bootable media .............................258
9.5 Acronis Startup Recovery Manager .......................................................................................259
9.6 Acronis PXE Server .................................................................................................................260
9.6.1 Acronis PXE Server Installation ................................................................................................................... 260
9.6.2 Setting up a machine to boot from PXE .................................................................................................... 261
9.6.3 Work across subnets ................................................................................................................................... 261
6 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 7

10 Disk management .................................................................................................. 262
10.1 Supported file systems ..........................................................................................................262
10.2 Basic precautions ...................................................................................................................262
10.3 Running Acronis Disk Director Lite ........................................................................................263
10.4 Choosing the operating system for disk management ..........................................................263
10.5 "Disk management" view ......................................................................................................264
10.6 Disk operations ......................................................................................................................264
10.6.1 Disk initialization .......................................................................................................................................... 265
10.6.2 Basic disk cloning ......................................................................................................................................... 265
10.6.3 Disk conversion: MBR to GPT ..................................................................................................................... 267
10.6.4 Disk conversion: GPT to MBR ..................................................................................................................... 268
10.6.5 Disk conversion: basic to dynamic ............................................................................................................. 268
10.6.6 Disk conversion: dynamic to basic ............................................................................................................. 269
10.6.7 Changing disk status .................................................................................................................................... 270
10.7 Volume operations ................................................................................................................270
10.7.1 Creating a volume ....................................................................................................................................... 270
10.7.2 Delete volume ............................................................................................................................................. 274
10.7.3 Set active volume ........................................................................................................................................ 275
10.7.4 Change volume letter ................................................................................................................................. 275
10.7.5 Change volume label ................................................................................................................................... 275
10.7.6 Format volume ............................................................................................................................................ 276
10.8 Pending operations ................................................................................................................277
11 Protecting applications with disk-level backup ........................................................ 278
11.1 Backing up an application server ...........................................................................................278
11.1.1 Locating database files ................................................................................................................................ 280
11.1.2 Truncating transaction logs ........................................................................................................................ 283
11.1.3 Best practices when backing up application servers ................................................................................ 286
11.2 Recovering SQL Server data ...................................................................................................287
11.2.1 Recovering SQL Server databases from a disk backup ............................................................................. 288
11.2.2 Accessing SQL Server databases from a disk backup ............................................................................... 288
11.2.3 Attaching SQL Server databases ................................................................................................................ 289
11.3 Recovering Exchange Server data ..........................................................................................289
11.3.1 Recovering Exchange Server database files from a disk backup ............................................................. 290
11.3.2 Mounting Exchange Server databases ...................................................................................................... 290
11.3.3 Granular recovery of mailboxes ................................................................................................................. 291
11.4 Recovering Active Directory data ..........................................................................................291
11.4.1 Recovering a domain controller (other DCs are available) ...................................................................... 291
11.4.2 Recovering a domain controller (no other DCs are available) ................................................................. 292
11.4.3 Restoring the Active Directory database ................................................................................................... 293
11.4.4 Restoring accidentally deleted information .............................................................................................. 294
11.4.5 Avoiding a USN rollback .............................................................................................................................. 294
11.5 Recovering SharePoint data ..................................................................................................296
11.5.1 Recovering a content database .................................................................................................................. 296
11.5.2 Recovering configuration and service databases ..................................................................................... 298
11.5.3 Recovering individual items........................................................................................................................ 299
12 Protecting Microsoft SQL Server with single-pass backup ........................................ 301
12.1 General information ..............................................................................................................301
12.1.1 Agent for SQL ............................................................................................................................................... 301
12.1.2 Supported operating systems .................................................................................................................... 302
7 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 8

12.1.3 Supported Microsoft SQL Server versions ................................................................................................. 302
12.1.4 Permissions for SQL Server backup and recovery .................................................................................... 302
12.1.5 What else you need to know about single-pass backup .......................................................................... 303
12.2 Installation of Agent for SQL ..................................................................................................304
12.3 Backing up Microsoft SQL server ...........................................................................................304
12.3.1 Single-pass backup settings ........................................................................................................................ 305
12.4 Recovering Microsoft SQL Server data ..................................................................................306
12.4.1 Recovering SQL databases to instances .................................................................................................... 306
12.4.2 Extracting the database files to folders ..................................................................................................... 308
12.5 Mounting SQL Server databases from a single-pass backup .................................................309
12.5.1 Unmounting mounted SQL Server databases ........................................................................................... 309
12.6 Protecting clustered SQL Server instances and AAG .............................................................310
13 Protecting Microsoft Active Directory with single-pass backup ................................ 312
13.1 Agent for Active Directory .....................................................................................................312
13.2 Supported operating systems ................................................................................................312
13.3 Installation of Agent for Active Directory ..............................................................................312
13.4 Backing up Microsoft Active Directory ..................................................................................313
13.5 Recovering Microsoft Active Directory ..................................................................................313
13.5.1 Re-promoting the domain controller ........................................................................................................ 314
13.5.2 Recovering the Active Directory data from a single-pass backup ........................................................... 314
14 Administering a managed machine ......................................................................... 316
14.1 Backup plans and tasks ..........................................................................................................316
14.1.1 Actions on backup plans and tasks ............................................................................................................ 316
14.1.2 States and statuses of backup plans and tasks ......................................................................................... 318
14.1.3 Export and import of backup plans ............................................................................................................ 320
14.1.4 Deploying backup plans as files .................................................................................................................. 324
14.1.5 Backup plan details ..................................................................................................................................... 325
14.1.6 Task/activity details ..................................................................................................................................... 326
14.2 Log ..........................................................................................................................................326
14.2.1 Actions on log entries.................................................................................................................................. 327
14.2.2 Log entry details .......................................................................................................................................... 327
14.3 Alerts ......................................................................................................................................328
14.4 Changing a license .................................................................................................................329
14.5 Collecting system information ...............................................................................................330
14.6 Adjusting machine options ....................................................................................................330
14.6.1 Additional settings....................................................................................................................................... 330
14.6.2 Acronis Customer Experience Program ..................................................................................................... 331
14.6.3 Alerts ............................................................................................................................................................ 331
14.6.4 E-mail settings ............................................................................................................................................. 332
14.6.5 Event tracing ................................................................................................................................................ 333
14.6.6 Log cleanup rules ......................................................................................................................................... 335
14.6.7 Machine management................................................................................................................................ 336
14.6.8 Cloud backup proxy ..................................................................................................................................... 336
15 Centralized management ....................................................................................... 338
15.1 Understanding centralized management ..............................................................................338
15.1.1 Basic concepts ............................................................................................................................................. 338
15.1.2 Privileges for centralized management ..................................................................................................... 339
8 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 9

15.1.3 Communication between Acronis Backup components .......................................................................... 343
15.2 Back up now ...........................................................................................................................347
15.3 Creating a centralized backup plan ........................................................................................348
15.3.1 Selecting data to back up ............................................................................................................................ 348
15.3.2 Selection rules for files and folders ............................................................................................................ 350
15.3.3 Selection rules for volumes ........................................................................................................................ 352
15.3.4 Backup location selection ........................................................................................................................... 355
15.3.5 Centralized backup plan's credentials ....................................................................................................... 356
15.3.6 What if a machine does not have data meeting the selection rules ....................................................... 357
15.4 Administering Acronis Backup Management Server .............................................................357
15.4.1 Dashboard .................................................................................................................................................... 357
15.4.2 Machines with agents ................................................................................................................................. 359
15.4.3 Virtual machines .......................................................................................................................................... 371
15.4.4 Backup plans and tasks ............................................................................................................................... 372
15.4.5 Storage nodes .............................................................................................................................................. 375
15.4.6 Licenses ........................................................................................................................................................ 375
15.4.7 Alerts ............................................................................................................................................................ 377
15.4.8 Reporting ..................................................................................................................................................... 378
15.4.9 Log ................................................................................................................................................................ 383
15.4.10 Management server options ...................................................................................................................... 385
15.5 Configuring Acronis Backup components ..............................................................................391
15.5.1 Parameters set by using Acronis Administrative Template ..................................................................... 391
15.5.2 Parameters set by using Windows registry ............................................................................................... 406
16 Cloud backup ......................................................................................................... 407
16.1 Introduction to Acronis Cloud Backup ...................................................................................407
16.1.1 What is Acronis Cloud Backup? .................................................................................................................. 407
16.1.2 What data can I back up and recover? ...................................................................................................... 407
16.1.3 How long will my backups be kept in the cloud storage? ........................................................................ 407
16.1.4 How do I secure my data? .......................................................................................................................... 408
16.1.5 How do I back up virtual machines to the cloud storage? ....................................................................... 408
16.1.6 Supported operating systems and virtualization products ...................................................................... 409
16.1.7 Backup and recovery FAQ .......................................................................................................................... 410
16.1.8 Initial Seeding FAQ ...................................................................................................................................... 411
16.1.9 Large Scale Recovery FAQ .......................................................................................................................... 417
16.1.10 Subscription lifecycle FAQ .......................................................................................................................... 418
16.2 Where do I start? ...................................................................................................................421
16.3 Choosing a subscription .........................................................................................................421
16.4 Configuring proxy settings .....................................................................................................422
16.5 Checking the firewall settings ................................................................................................422
16.6 Activating cloud backup subscriptions ..................................................................................423
16.6.1 Activating subscriptions in Acronis Backup Advanced ............................................................................. 423
16.6.2 Reassigning an activated subscription ....................................................................................................... 423
16.7 Retrieving files from the cloud storage by using a web browser ..........................................425
16.8 Limitations of the cloud storage ............................................................................................426
16.9 Terminology reference ..........................................................................................................426
17 Glossary ................................................................................................................. 429
9 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 10

1 Introducing Acronis Backup
1.1 What's new in Acronis Backup 11.7
Installation
Microsoft SQL Server 2014 can be used to store the databases of Acronis Backup Management
Server.
Licensing
Support for the subscription licensing model. For more information, please refer to the Acronis
Backup Licensing FAQ.
Deduplication
128 MB of RAM per 1 TB of unique data are required, instead of 3 GB.
No need to allocate the deduplication database on expensive SSD disks. Regular HDD disks can be
used without performance degradation.
Recovery from a deduplicated backup is now 40 percent faster.
The backup speed does not reduce as the deduplication database size increases.
The Storage Node startup time on large data sets is reduced to 1-3 minutes.
Validating deduplicated backups and compacting the data store are now 2.5 times faster.
These improvements are effective when v11.7 agents back up to deduplicating vaults created on
v11.7 storage nodes. When a new agent backs up to an old vault or an old agent backs up to a new
vault, the old deduplication algorithm is used. To apply the new deduplication algorithm to old
backups, you need to import the backups into a newly created vault.
Tape support
Configurable block size (p. 192) for reading and writing to tapes. The default value is taken from
the tape device driver.
Hardware Compatibility List (HCL) and Hardware Compatibility Tool are introduced. Hardware
Compatibility List contains tape devices with confirmed support by Acronis Backup. To learn if
your specific device is supported, use the Hardware Compatibility Tool.
Full support for the LTO-7 technology. See the HCL for the exact names of the tested devices.
Centralized management
It is possible to specify a custom backup location (p. 355) for each machine that is included in a
centralized backup plan.
In addition to exporting licenses from the management server to an .xml file, you can export
them to a .txt file (p. 376).
Microsoft Exchange Server support
Agent for Exchange can back up and recover Microsoft Exchange Server 2016 databases. Backup
and recovery of Exchange 2016 mailboxes (including mailbox recovery from database backups)
are not supported.
Supported operating systems
Support for Windows Server 2016 Technical Preview 4.
Support for Linux kernel version 4.2, 4.3, and 4.4.
10 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 11

Support for Red Hat Enterprise Linux 7.2, Oracle Linux 7.2, ClearOS, Debian 8.2, Ubuntu 15.10,
and Fedora 23.
Support for Windows 2000 in Acronis Backup Advanced is limited. Components of v11.7 cannot
be installed in this operating system. To back up machines that run Windows 2000, use the
agents of v11.5. The v11.5 agents are compatible with the management components of v11.7.
Acronis Backup for Windows Server and Acronis Backup for PC cannot be installed in Windows
2000. To back up machines that run this operating system, use v11.5.
Acronis Backup v11.5 supports Windows 2000 SP4.
Other
It is possible to use compression in combination with third-party hardware or software
deduplication (for disk-level backups only). This effectively reduces the storage space occupied
by the backups.
More functionality is available via the command-line interface:
Generating management server reports
Deploying Agent for VMware (Virtual Appliance)
Agent for VMware does not back up independent disks and Raw Device Mapping (RDM) disks in
physical compatibility mode, regardless of the state of a virtual machine. This limitation is
introduced for better predictability of the product behavior.
32-bit Linux-based bootable media was optimized in size by removing the rarely used acrocmd
utility.
When a disk backup is mounted in the read/write mode, the respective incremental backup is
not created immediately, but after the disk backup is unmounted, instead. While the backup is
mounted, the changes are saved in the %Temp% folder.
1.2 Acronis Backup components
Acronis Backup includes the following main types of components.
Components for a managed machine (agents)
These are applications that perform data backup, recovery and other operations on the machines
managed with Acronis Backup. Agents require a license to perform operations on each managed
machine.
Components for centralized management
These components, included in Acronis Backup Advanced, provide centralized management
capability. Usage of these components is not licensed.
Console
The console provides Graphical User Interface to other Acronis Backup components. Usage of the
console is not licensed.
Bootable media builder
With bootable media builder, you can create bootable media in order to use the agents and other
rescue utilities in a rescue environment.
Bootable Media Builder does not require a license if installed together with an agent. To use a media
builder on a machine without an agent, you need to enter the license key or have at least one license
on the license server. The license may be either available or assigned.
11 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 12

1.2.1 Agent for Windows
This agent enables disk-level and file-level data protection under Windows.
Disk backup
Disk-level data protection is based on backing up either a disk or a volume file system as a whole,
along with all the information necessary for the operating system to boot; or all the disk sectors using
the sector-by-sector approach (raw mode). A backup that contains a copy of a disk or a volume in a
packaged form is called a disk (volume) backup or a disk (volume) image. It is possible to recover
disks or volumes as a whole from such backup, as well as individual folders or files.
File backup
File-level data protection is based on backing up files and folders residing on the machine where the
agent is installed or on a network share. Files can be recovered to their original location or to another
place. It is possible to recover all files and folders that were backed up or select which of them to
recover.
Conversion to a virtual machine
Agent for Windows performs the conversion by recovering a disk backup to a new virtual machine of
any of the following types: VMware Workstation, Microsoft Virtual PC, Citrix XenServer Open Virtual
Appliance (OVA) or Red Hat Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM). Files of the fully configured and
operational machine will be placed in the folder you select. You can start the machine using the
respective virtualization software or prepare the machine files for further usage.
Disk management
Agent for Windows includes Acronis Disk Director Lite - a handy disk management utility. Disk
management operations, such as cloning disks; converting disks; creating, formatting and deleting
volumes; changing a disk partitioning style between MBR and GPT or changing a disk label, can be
performed either in the operating system or using bootable media.
1.2.2 Agent for Linux
This agent enables disk-level and file-level data protection under Linux.
Disk backup
Disk-level data protection is based on backing up either a disk or a volume file system as a whole,
along with all information necessary for the operating system to boot; or all the disk sectors using the
sector-by-sector approach (raw mode.) A backup that contains a copy of a disk or a volume in a
packaged form is called a disk (volume) backup or a disk (volume) image. It is possible to recover
disks or volumes as a whole from such backup, as well as individual folders or files.
File backup
File-level data protection is based on backing up files and directories residing on the machine where
the agent is installed or on a network share accessed using the smb or nfs protocol. Files can be
recovered to their original location or to another place. It is possible to recover all files and
directories that were backed up or select which of them to recover.
12 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 13

Conversion to a virtual machine
Agent for Linux performs the conversion by recovering a disk backup to a new virtual machine of any
of the following types: VMware Workstation, Microsoft Virtual PC, Citrix XenServer Open Virtual
Appliance (OVA) or Red Hat Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM). Files of the fully configured and
operational machine will be placed in the directory you select. You can start the machine using the
respective virtualization software or prepare the machine files for further usage.
1.2.3 Agent for VMware
Acronis Backup Agent for VMware enables backup and recovery of ESX(i) virtual machines without
installing agents into the guest systems. This backup method is known as agent-less backup or
backup at a hypervisor level. The agent can be imported or deployed to a VMware ESX(i) host as a
virtual appliance.
1.2.4 Agent for Hyper-V
Acronis Backup Agent for Hyper-V protects virtual machines residing on a Hyper-V virtualization
server. The agent allows for backing up virtual machines from the host without having to install
agents on each virtual machine.
1.2.5 Agent for SQL
Acronis Backup Agent for SQL enables you to create single-pass disk and application backups and to
recover Microsoft SQL databases from them. The databases can be recovered directly to a running
SQL Server instance or extracted to a folder on a file system.
The agent uses Microsoft VSS to ensure the consistency of the backed-up databases. After a
successful backup, the agent can truncate the SQL Server transaction log.
The agent is included in the setup program of Acronis Backup Advanced.
The agent is installed with Agent for Windows (p. 12) or on a machine where Agent for Windows is
already installed.
1.2.6 Agent for Active Directory
Acronis Backup Agent for Active Directory enables you to create single-pass disk and application
backups and to extract Microsoft Active Directory data from them to a folder on a file system.
The agent uses Microsoft VSS to ensure the consistency of the backed-up data.
The agent is included in the setup program of Acronis Backup Advanced.
The agent is installed with Agent for Windows (p. 12) or on a machine where Agent for Windows is
already installed.
1.2.7 Components for centralized management
This section lists the components that are included in Acronis Backup Advanced and provide the
centralized management capability. Besides these components, Acronis Backup Agents have to be
installed on all machines that need data protection.
13 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 14

1.2.7.1 Management Server
Acronis Backup Management Server is the central server that drives data protection within the
enterprise network. The management server provides the administrator with:
a single entry point to the Acronis Backup infrastructure
an easy way to protect data on numerous machines (p. 438) using centralized backup plans and
grouping
integration with VMware vCenter to discover virtual machines for protection
enterprise-wide monitoring and reporting functionality
built-in license management
the ability to create centralized vaults (p. 432) for storing enterprise backup archives (p. 430)
the ability to manage storage nodes (p. 440)
the centralized catalog (p. 433) of all data stored on the storage nodes.
If there are multiple management servers on the network, they operate independently, manage
different machines and use different centralized vaults for storing archives.
1.2.7.2 Storage Node
Acronis Backup Storage Node is a server designed to optimize the usage of various resources (such as
the corporate storage capacity, the network bandwidth, or the managed machines' CPU load) which
are required to protect the enterprise data. This goal is achieved by organizing and managing the
locations that serve as dedicated storages of the enterprise backup archives (managed vaults).
The most important function of a storage node is deduplication (p. 225) of backups stored in its
vaults. This means that identical data will be backed up to this vault only once. This minimizes the
network usage during backup and storage space taken by the archives.
The storage nodes enable creating highly scalable and flexible, in terms of the hardware support,
storage infrastructure. Up to 50 storage nodes can be set up, each being able to manage up to 20
vaults.
The administrator controls the storage nodes centrally from the Acronis Backup Management Server
(p. 14). Direct console connection to a storage node is not possible.
1.2.7.3 Components for Remote Installation
These are Acronis component installation packages used by the management console (p. 15) for
installation on remote machines.
Components for Remote Installation need to be installed on the machine with the console or with
the management server (p. 14). During installation, the setup program saves the components in the
default location and saves this location path in the registry. As a result, the components are readily
available in the Remote Installation Wizard as "registered components".
1.2.7.4 PXE Server
Acronis PXE Server allows for booting machines into Acronis bootable components through the
network.
The network booting:
14 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 15

Eliminates the need to have a technician onsite to install the bootable media (p. 431) into the
system that has to be booted
During group operations, reduces the time required for booting multiple machines as compared
to using physical bootable media.
1.2.7.5 License Server
The server enables you to manage licenses of Acronis products and install the components that
require licenses.
You can install a license server as a separate component or use the one integrated into the
management server. The functionality of the license server (p. 375) is similar for both types of
installation.
1.2.8 Management Console
Acronis Backup Management Console is an administrative tool for access to Acronis Backup agents
and, in Acronis Backup Advanced, to Acronis Backup Management Server.
The console has two distributions: for installation on Windows and installation on Linux. While both
distributions enable connection to any Acronis Backup agent and Acronis Backup Management
Server, we recommend that you use the console for Windows if you have a choice between the two.
The console that installs on Linux has limited functionality:
Remote installation of Acronis Backup components is not available.
The Active Directory-related features, such as browsing the AD, are not available.
1.2.9 Bootable Media Builder
Acronis Bootable Media Builder is a dedicated tool for creating bootable media (p. 431). There are
two media builder distributions: for installation in Windows and installation in Linux.
The media builder that installs on Windows can create bootable media based on either Windows
Preinstallation Environment, or Linux kernel. The media builder that installs on Linux creates
bootable media based on Linux kernel.
1.2.10 Acronis Wake-on-LAN Proxy
Acronis Wake-on-LAN Proxy enables Acronis Backup Management Server to wake up for backup
machines located in another subnet. Acronis Wake-on-LAN Proxy installs on any server in the subnet
where the machines to be backed up are located.
1.3 About using the product in the trial mode
Before buying an Acronis Backup license, you may want to try the software. This can be done without
a license key.
To install the product in the trial mode, run the setup program locally or use the remote installation
functionality. Unattended installation and other ways of installation are not supported.
Limitations of the trial mode
When working under bootable media:
15 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 16

The disk management functionality is not available. You can try the user interface, but there is no
option to commit the changes.
The recovery functionality is available, but the backup functionality is not. To try the backup
functionality, install the software in the operating system.
Upgrading to the full mode
After the trial period expires, the product GUI displays a notification requesting you to specify or
obtain a license key.
To specify a license key, click Help > Change License (p. 329). Specifying the key by running the setup
program is not possible.
If you have activated a trial or purchased a subscription for the cloud backup service (p. 407), cloud
backup will be available until the subscription period expires, regardless of whether you specify a
license key.
1.4 Supported file systems
Acronis Backup can back up and recover the following file systems with the following limitations:
FAT16/32
NTFS
ReFS - volume recovery without the volume resize capability. Supported in Windows Server
2012/2012 R2 and Windows Server 2016 (p. 45) only.
Ext2/Ext3/Ext4
ReiserFS3 - particular files cannot be recovered from disk backups located on Acronis Backup
Storage Node
ReiserFS4 - volume recovery without the volume resize capability; particular files cannot be
recovered from disk backups located on Acronis Backup Storage Node
XFS - volume recovery without the volume resize capability; particular files cannot be recovered
from disk backups located on Acronis Backup Storage Node
JFS - particular files cannot be recovered from disk backups located on Acronis Backup Storage
Node
Linux SWAP
Acronis Backup can back up and recover corrupted or non-supported file systems using the
sector-by-sector approach.
1.5 Technical Support
Maintenance and Support Program
If you need assistance with your Acronis product, please go to
http://www.acronis.com/en-us/support/
Product Updates
You can download the latest updates for all your registered Acronis software products from our
website at any time after logging into your Account (http://www.acronis.com/en-us/my) and
registering the product. See Registering Acronis Products at the Website
16 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 17

(http://kb.acronis.com/content/4834) and Acronis Website User Guide
(http://kb.acronis.com/content/8128).
17 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 18

2 Getting started
Step 1. Installation
These brief installation instructions enable you to start using the product quickly. For the
complete description of installation methods and procedures, please refer to the Installation
documentation.
Before installation, make sure that:
Your hardware meets the system requirements.
You have license keys for the product of your choice.
You have the setup program. You can download it from the Acronis website.
Procedure
When following the instructions below, you can select more than one machine role.
1. Install the management server to be able to manage multiple machines.
a. Run the setup program and click Install Acronis Backup.
b. After accepting the terms of the license agreement, select the Centrally monitor and
configure the backing up of physical and virtual machines check box.
c. Type your license keys or import them from a text file.
d. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Details. The console will also be installed so that you can control the management server locally.
2. Install an agent on each machine you want to back up.
a. Run the setup program and click Install Acronis Backup.
b. After accepting the terms of the license agreement, select the Back up this machine's data
check box.
c. Select I purchased a license or a subscription.
d. Select the Use the following license server check box, and then enter the name or IP address
of the previously installed management server.
e. When prompted, register the machine on the management server.
f. Follow the on-screen instructions.
Details. The console will also be installed on each machine.
3. [Optional] Install the storage node on the machine that will serve as a storage for backups of
other machines.
a. Run the setup program and click Install Acronis Backup.
b. After accepting the terms of the license agreement, select the Store the backups of other
machines on this machine check box.
c. When prompted, register the storage node on the management server.
d. Follow the on-screen instructions.
4. [Optional] Install the console on a machine from which you prefer to operate, if this machine is
not the management server and does not have an agent.
a. Run the setup program and click Install Acronis Backup.
b. After accepting the terms of the license agreement, select the Connect to remote machines
check box.
18 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 19

c. Follow the on-screen instructions.
In Windows
Start the console by selecting Acronis Backup from the Start menu.
In Linux
Log in as root or log in as an ordinary user and then switch user as
required. Start the console with the command
/usr/sbin/acronis_console
1. Select Tools > Create bootable media in the menu.
2. Click Next in the welcome screen. Keep clicking Next until the list of components appears.
3. Proceed as described in "Linux-based bootable media" (p. 249).
Manage this machine
If the agent is installed on the same machine as the console.
Manage a remote machine
If the agent is installed on a remote machine.
Connect to a management server
To manage multiple physical and virtual machines.
Step 2. Running
Run Acronis Backup Management Console.
For understanding of the GUI elements see "Using the management console" (p. 21).
Step 3. Bootable media
To be able to recover an operating system that fails to start, or deploy it on bare metal, create
bootable media.
Step 4. Connection
Connect the console to the managed machine, or to the management server.
On the first page of the console, click one of the following:
Step 5. Backup
Back up now (p. 50)
Click Back up now to do a one-time backup in a few simple steps. The backup process will
start immediately after you perform the required steps.
To save your machine to a file:
Under Where to back up, click Location, and select the location where the backup will be
saved. Click OK to confirm your selection. Click OK at the bottom of the window to start the
backup.
19 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 20

Tip. Using the bootable media, you can do off-line ("cold") backups in the same way as in the
operating system.
Create backup plan (p. 50)
Create a backup plan if you need a long-term backup strategy including backup schemes,
schedules and conditions, timely deleting of backups, or moving them to different locations.
Notes for users of Acronis Backup Advanced: When creating a backup plan on the
management server, you can:
- Select entire machines or groups of machines.
- Select different data items on each machine.
- Use selection rules to select the same data items on different machines.
This way, you will create a centralized backup plan to be deployed to the selected machines.
For more information, please refer to "Creating a centralized backup plan" (p. 348).
Step 6. Recovery
Recover (p. 127)
To recover data, you need to select the backed-up data and the destination the data will be
recovered to. As a result, a recovery task will be created.
Recovery of a disk or volume over a volume locked by the operating system requires a reboot.
After the recovery is completed, the recovered operating system goes online automatically.
If the machine fails to boot or if you need to recover a system to bare metal, boot the
machine using the bootable media and configure the recovery operation in the same way as
the recovery task.
Notes for users of Acronis Backup Advanced: You cannot control operations under bootable
media by using the management server. But you can disconnect the console from the server
and connect it to the machine booted from the media.
Step 7. Management
The Navigation pane (at the left part of the console) enables you to navigate across the product
views that are used for different administering purposes.
Use the Backup plans and tasks view to manage backup plans and tasks: run, edit, stop and
delete plans and tasks, view their states and progress.
Use the Alerts view to rapidly identify and solve the problems.
Use the Log view to browse the operations log.
The location where you store backup archives is called a vault (p. 441). Navigate to the
Vaults (p. 171) view to obtain information about your vaults. Navigate further to the specific
vault to view backups and their contents. You can also select the data to recover and perform
manual operations with backups (mounting, validating, deleting).
Administering the management server
Use the Machines with agents view to manage machines registered on the management
server. To effectively work with a large number of machines, organize them into groups (p. 359).
Use the Virtual machines (p. 371) view to manage supported virtualization environments.
20 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 21

If you opt for storing all backup archives in a single or a few networked locations, create
Name
Description
Navigation pane
Contains the Navigation tree and the Shortcuts bar. Lets you navigate to the
different views. For details, see Navigation pane (p. 22).
Main area
Here you configure and monitor backup, recovery and other operations. The
main area displays views and action pages (p. 24) depending on the items
selected in the menu or Navigation tree.
centralized vaults in these locations. After a vault is created, you can view and administer its
content by selecting Vaults > Centralized > 'Vault name' in the Navigation pane.
The shortcut to the vault will be deployed to all the registered machines. The vault can be
specified as a backup destination in any backup plan created by you or by the registered
machines' users.
Create centralized managed vaults on the storage node (p. 213) to be able to:
Search the Data catalog (p. 131) for the required version of backed up data in all of the
managed vaults.
Back up multiple machines to tape devices (p. 190) attached to the storage node.
Use deduplication (p. 225) to minimize storage space taken by the data and reduce network
load during backup.
2.1 Using the management console
As soon as the console connects to a managed machine (p. 438) or to a management server (p. 439),
the respective items appear across the console's workspace (in the menu, in the main area with the
Welcome screen, or in the Navigation pane) enabling you to perform agent-specific or server-specific
operations.
Acronis Backup Management Console - Welcome screen
Key elements of the console workspace
21 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 22

Menu bar
Appears across the top of the program window. Lets you perform most of
operations available in Acronis Backup. The menu items change dynamically
depending on the item selected in the Navigation tree and the main area.
2.1.1 "Navigation" pane
The navigation pane includes the Navigation tree and the Shortcuts bar.
Navigation tree
The Navigation tree enables you to navigate across the program views. Views depend on whether
the console is connected to a managed machine or to the management server. In both cases, you can
choose between the Full list or the Short list of views. The Short list contains the most frequently
used views from the Full list.
Views for a managed machine
When the console is connected to a managed machine, the following views are available in the
navigation tree.
The Short list displays
[Machine name]. This is the root of the tree also called a Welcome screen. It displays the
name of the machine the console is currently connected to. Use this view for quick access to the
main operations, available on the managed machine.
Backup plans and tasks. Use this view to manage backup plans and tasks on the
managed machine: run, edit, stop and delete plans and tasks, view their progress.
Vaults. Use this view to manage personal vaults and archives stored in there, add new
vaults, rename and delete the existing ones, validate vaults, explore backup content, perform
operations on archives and backups, etc. If the machine is registered on the management
server, you can browse the centralized vaults and perform operations on the archives for
which you have the appropriate permissions.
Alerts. Use this view to examine warning messages for the managed machine.
The Full list additionally displays
Tape management. Use this view to perform operations with tapes.
Disk management. Use this view to perform operations on the machine's hard disk
drives.
Log. Use this view to examine information on operations performed by the program on
the managed machine.
Mounted images. This node is displayed if at least one volume is mounted. Use this view
to manage mounted images.
Views for a management server
When the console is connected to a management server, the following views are available in the
navigation tree.
The Short list displays
[Management server name]. This is the root of the tree also called a Welcome screen.
Displays the name of the management server the console is currently connected to. Use this view
for quick access to the main operations, available on the management server.
22 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 23

Dashboard. Use this view to estimate at a glance whether the data is successfully
protected on the machines registered on the management server.
Machines with agents. Use this view to manage machines registered on the
management server.
Backup plans and tasks. Use this view to manage centralized backup plans and tasks on
the management server.
Vaults. Use this view to manage centralized vaults and archives stored in there: create
new centralized vaults, rename and delete the existing ones, assign vault users and
administrators, perform operations on archives and backups.
Alerts. Use this view to examine warning messages for the management server and all
the registered machines.
The Full list additionally displays
Data catalog. Use this view for quick search of the required version of backed up data in
the centralized managed vaults.
Virtual machines. Use this view to manage supported virtualization environments.
Storage nodes. Use this view to manage storage nodes. Add a storage node to be able to
create centralized vaults that will be managed by the node.
Tape management. Use this view to perform operations with tapes.
Licenses. Use this view manage licenses.
Reports. Use this view to generate reports.
Log. Use this view to examine the history of centralized management operations, as well
as the history of operations logged in the local logs of the registered machines and the
storage nodes.
Shortcuts bar
The Shortcuts bar appears under the navigation tree. It offers you an easy and convenient way of
connection to the machines in demand by adding them as shortcuts.
To add a shortcut to a machine
1. Connect the console to a managed machine.
2. In the navigation tree, right-click the machine's name (a root element of the navigation tree), and
then select Create shortcut.
If the console and agent are installed on the same machine, the shortcut to this machine will be
added to the shortcuts bar automatically as Local machine [Machine name].
Operations with pane
How to expand/minimize panes
By default, the Navigation pane appears expanded. You might need to minimize the pane in order to
free some additional workspace. To do this, click the chevron ( ). The pane will be minimized and
the chevron changes its direction ( ). Click the chevron once again to expand the pane.
How to change the panes' borders
1. Point to the pane's border.
2. When the pointer becomes a double-headed arrow, drag the pointer to move the border.
23 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 24

2.1.2 Main area, views and action pages
The main area is a basic place where you work with the console. Here you create, edit and manage
backup plans, recovery tasks and perform other operations. The main area displays different views
and action pages according the items you select in the menu, or Navigation tree.
2.1.2.1 Views
A view appears on the main area when clicking any item in the Navigation tree in the Navigation
pane (p. 22).
"Log" view
Common way of working with views
Generally, every view contains a table of items, a table toolbar with buttons, and the Information
panel.
Use filtering and sorting (p. 24) capabilities to search the table for the item in question.
In the table, select the desired item.
In the information panel (collapsed by default), view the item's details. To expand the panel, click
the arrow mark ( ).
Perform actions on the selected item. There are several ways of performing the same action on
selected items:
By clicking the buttons on the table toolbar.
By selecting the items in the Actions menu.
By right-clicking the item and selecting the operation in the context menu.
Sorting, filtering and configuring table items
The following is a guideline to sort, filter and configure table items in any view.
24 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 25

To
Do the following
Sort items by any column
Click a column's header to sort items in ascending order.
Click it once again to sort items in descending order.
Filter items by predefined
column value
In a field below the corresponding column's header, select the required value
from the drop-down list.
Filter items by entered value
In a field below the corresponding column's header, type a value.
As a result you will see the list of values, fully or just partly coincide with the
entered value.
Filter items by predefined
parameters
Click the appropriate buttons above the table.
For example, in the Log view, you can filter the log entries by event type
(Error, Warning, Information) or by the period when the event occurred (For
last 24 hours, For last week, For last three months, or For custom period).
Show or hide table columns
By default, any table has a fixed number of columns that are shown, others
are hidden. If required, you can hide the shown columns and show the hidden
ones.
To show or hide columns
1. Right-click any column header to open the context menu.
2. Click the items you want to be displayed/hidden.
2.1.2.2 Action pages
An action page appears in the main area when clicking any action item in the Actions menu. It
contains steps you need to perform in order to create and launch any task or a backup plan.
Action page - Create backup plan
25 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 26
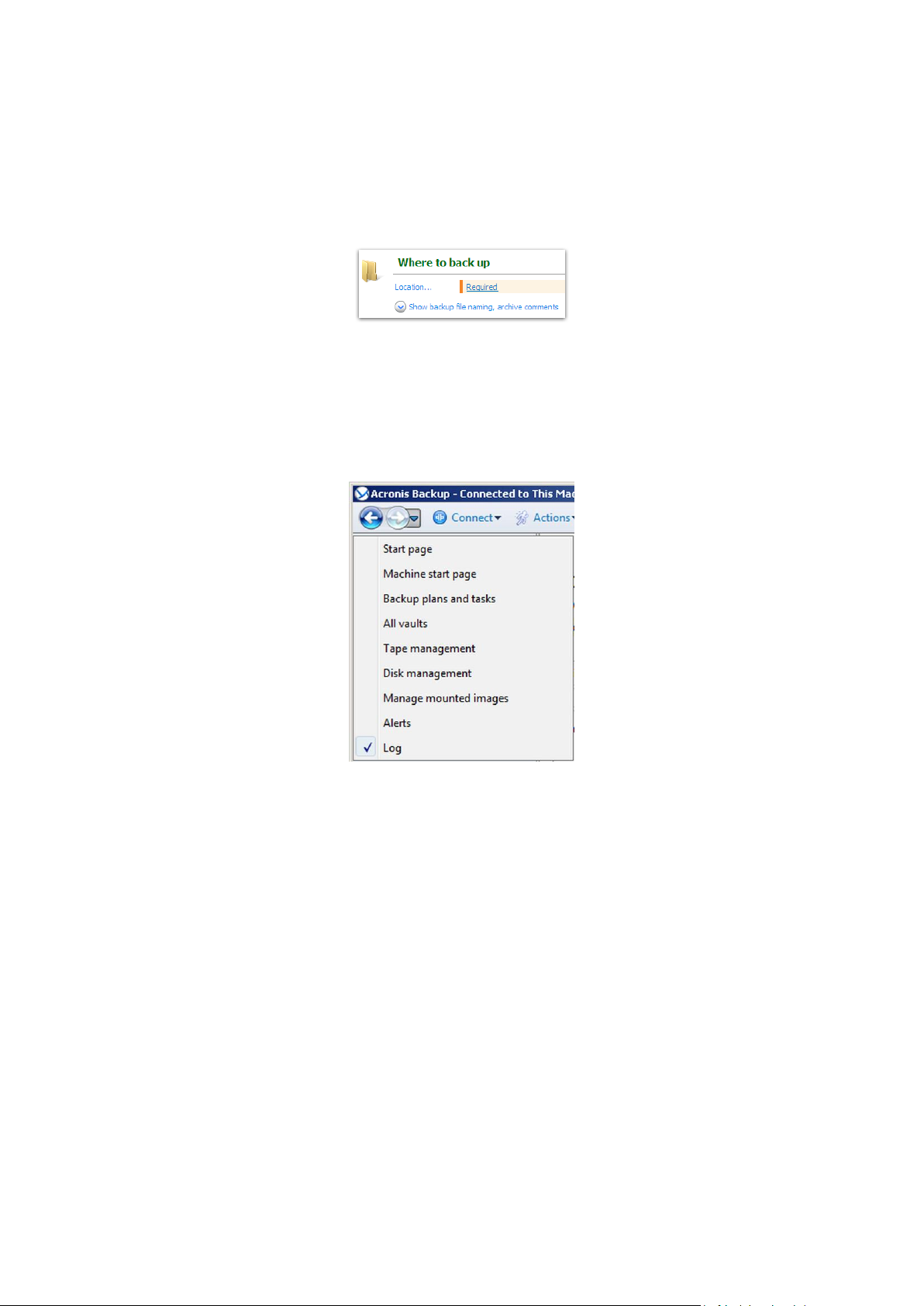
Using controls and specifying settings
Use active controls to specify a backup plan or recovery task settings and parameters. By default,
such fields as credentials, options, comments, and some others are hidden. Most settings are
configured by clicking the respective Show… links. Others are selected from the drop-down list, or
typed manually in the page's fields.
Action page - Controls
Acronis Backup remembers the changes you made on the action pages. For example, if you started to
create a backup plan, and then for any reason switched to another view without accomplishing the
plan creation, you can click the Back navigation button on the menu. Or, if you have passed several
steps forward, click the Down arrow and select the page where you started the plan creation from
the list. Thus, you can perform the remaining steps and accomplish the backup plan creation.
Navigation buttons
2.1.3 Console options
The console options define the way information is represented in the Graphical User Interface of
Acronis Backup.
To access the console options, select Options > Console options from the top menu.
2.1.3.1 Alert display options
The option specifies which alerts to show and which to hide in the Alerts view.
The preset is: All alerts.
To show (hide) alerts, select (clear) the check boxes next to the respective alert types.
2.1.3.2 Credentials cache
The option specifies whether to store the credentials entered while using the management console.
The preset is: Enabled.
26 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 27

If the option is enabled, the credentials for various locations that you enter during a console session
are saved for use during later sessions. In Windows, the credentials are stored in the Windows
Credential Manager. In Linux, the credentials are stored in a special encrypted file.
If the option is disabled, the credentials are stored only until the console is closed.
To clear the credentials cache for the current user account, click the Clear credentials cache button.
2.1.3.3 Fonts
The option defines the fonts to be used in the Graphical User Interface of Acronis Backup. The Menu
font setting affects the drop-down and context menus. The Application font setting affects all other
GUI elements.
The preset is: System Default font for both the menus and the application interface items.
To make a selection, choose the font from the respective combo-box and set the font's properties.
You can preview the font's appearance by clicking Browse to the right.
2.1.3.4 Pop-up messages
These options are effective when the console is connected to a managed machine or to the
management server.
The “Interaction Required” dialog
This option defines whether to display a pop-up window when one or more activities require user
interaction. This window enables you to specify your decision, such as to confirm reboot or to retry
after freeing-up the disk space, on all the activities in the same place. Until at least one activity
requires interaction, you can open this window at any time from the managed machine's welcome
screen. Alternatively, you can review the task execution states in the Backup plans and tasks view
and specify your decision on each task in the information panel.
The preset is: Enabled.
To make a selection, select or clear the The “Interaction Required” dialog check box.
The “Feedback Confirmation” dialog
This option defines whether to display a pop-up window with the information about your system
after an error occurs. You can send this information to Acronis technical support.
The preset is: Enabled.
To make a selection, select or clear the The “Feedback Confirmation” dialog check box.
Notify if bootable media is not created
This option defines whether to display a pop-up window when the management console is launched
on a machine and no bootable media has been created on that machine.
The preset is: Enabled.
To make a selection, select or clear the Notify if bootable media is not created check box.
27 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 28

Notify when the management console is connected to a component of a different
version
This option defines whether to display a pop-up window when a console is connected to an
agent/management server and their versions differ.
The preset is: Enabled.
To make a selection, select or clear the Notify when the management console is connected to a
component of a different version check box.
Request description when ejecting a tape
This option defines whether to display a prompt for you to describe a tape when you eject (p. 204) it
from a tape device by using Acronis Backup. For example, you may describe the physical location
where the tape will be kept (recommended). If a tape is ejected automatically according to the Eject
tapes after successful backups option (p. 121), no such prompt is displayed.
The preset is: Enabled.
To make a selection, select or clear the Request description when ejecting a tape check box.
Note Tape devices can only be used with Acronis Backup Advanced.
About the task execution results
This option is effective only when the console is connected to a managed machine.
The option defines whether to display the pop-up messages about task run results: successful
completion, failure or success with warnings. When the displaying of pop-up messages is disabled,
you can review the task execution states and results in the Backup plans and tasks view.
The preset is: Enabled for all results.
To make a setting for each result (successful completion, failure or success with warnings)
individually, select or clear the respective check box.
2.1.3.5 Startup page
This option defines whether to show the Welcome screen or the Dashboard view on the console
connection to the management server.
The preset is: the Welcome screen.
To make a selection, select or clear the check box for Show the "Dashboard" view.
This option can also be set on the Welcome screen. If you select the check box for At startup, show
the Dashboard instead of the current view on the Welcome screen, the setting mentioned above
will be updated accordingly.
28 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 29

3 Understanding Acronis Backup
This section attempts to give its readers a clear understanding of the product so that they can use
the product in various circumstances without step-by-step instructions.
3.1 Owners
This section explains the concept of a backup plan (task) owner and an archive owner.
Plan (task) owner
A local backup plan owner is the user who created or last modified the plan.
A centralized backup plan owner is the management server administrator who created or last
modified the centralized backup plan.
Tasks, belonging to a backup plan, either local or centralized, are owned by the backup plan owner.
Tasks that do not belong to a backup plan, such as the recovery task, are owned by the user who has
created or last modified the task.
Managing a plan (task) owned by another user
Having Administrator privileges on the machine, a user can modify local backup plans and tasks
owned by any user registered in the operating system.
When a user opens a plan or task for editing, which is owned by another user, all passwords set in
the task are cleared. This prevents the "modify settings, leave passwords" trick. The program displays
a warning each time you are trying to edit a plan (task) last modified by another user. On seeing the
warning, you have two options:
Click Cancel and create your own plan or task. The original task will remain intact.
Continue editing. You will have to enter all credentials required for the plan or task execution.
Archive owner
An archive owner is the user who saved the archive to the destination. To be more precise, this is the
user whose account was specified when creating the backup plan in the Where to back up step. By
default, the plan's credentials are used.
3.2 Credentials used in backup plans and tasks
This section explains the concept of access credentials, backup plan's credentials and task
credentials.
Access credentials
When browsing backup locations, setting up backups, or creating recovery tasks, you may need to
provide credentials for accessing various resources, such as the data you are going to back up or the
location where the backups are (or will be) stored.
If the Credentials cache (p. 26) option is enabled (it is enabled by default), the credentials which you
provide during a console session are saved for use during the later sessions. Thus, there is no need to
29 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 30

enter the credentials next time. The credentials are cached independently for each user who uses the
console on the machine.
Backup plan's credentials
Any backup plan running on a machine runs on behalf of a user.
In Windows
By default, the plan runs under the agent service account, if created by a user having administrative
privileges on the machine. If created by a regular user, such as a member of the Users group, the
plan runs under this user's account.
When creating a backup plan, you are only asked for credentials in specific cases. For example:
You are scheduling backups as a regular user and did not enter credentials when connecting the
console to the machine. This may be the case when the console is installed on the same machine
that you are backing up.
You are backing up a Microsoft Exchange cluster to a storage node.
Specifying the credentials explicitly
You have the option to explicitly specify a user account under which the backup plan will run. To do
this, on the backup plan creation page:
1. In the Plan parameters section, click Show plan's credentials, comments, label.
2. Click Plan's credentials.
3. Enter the credentials under which the plan will run. When entering the name of an Active
Directory user account, be sure to also specify the domain name (DOMAIN\Username or
Username@domain).
In Linux
You do not need to specify backup plan's credentials. In Linux, backup plans always run under the
root user account.
Task credentials
Like a backup plan, any task runs on behalf of a user.
In Windows
When creating a task, you have the option to explicitly specify an account under which the task will
run. Your choice depends on whether the task is intended for manual start or for executing on
schedule.
Manual start
Every time you manually start the task, the task will run under the credentials with which you are
currently logged on. Any person that has administrative privileges on the machine can also start
the task. The task will run under this person's credentials.
The task will always run under the same credentials, regardless of the user who actually starts
the task, if you specify the task credentials explicitly.
Scheduled or postponed start
The task credentials are mandatory. You cannot complete the task creation until you specify the
task credentials. Task credentials are specified on the task creation page in a similar manner as
the plan’s credentials are specified.
30 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 31

In Linux
You do not need to specify task credentials. In Linux, tasks always run under the root user account.
3.3 User privileges on a managed machine
Windows
When managing a machine running Windows, the scope of a user's management rights depends on
the user's privileges on the machine.
Regular users
A regular user, such as a member of the Users group, has the following management rights:
Perform file-level backup and recovery of the files that the user has permissions to access—but
without using a file-level backup snapshot (p. 112).
Create backup plans and tasks and manage them.
View—but not manage—backup plans and tasks created by other users.
View the local event log.
Backup operators
A user who is a member of the Backup Operators group, also has the following management right:
Back up and recover the entire machine or any data on the machine, with or without using a disk
snapshot. Using a hardware snapshot provider may still require administrative privileges.
Administrators
A user who is a member of the Administrators group, also has the following management right:
View and manage backup plans and tasks owned by any user on the machine.
Linux
When managing a machine running Linux, the user has or obtains the root privileges, and so can:
Back up and recover any data or the entire machine, having full control over all Acronis Backup
agent operations and log files on the machine.
Manage local backup plans and tasks owned by any user registered in the operating system.
To avoid routine logging on to the system as root, the root user can log on with the ordinary user
credentials and then switch user as required.
3.4 List of Acronis services
During installation, Acronis Backup creates several services.
Main services present the main components of Acronis Backup: the agent, the management
server, the storage node.
Auxiliary services enable certain functionalities of the main components.
Common services assist multiple Acronis Backup components and other Acronis products.
Services of Acronis Backup components
A main service can run under a dedicated account or under an account you specify during installation.
Either account is given privileges that are needed for the service to work. The privileges include a set
31 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 32
of user rights, membership in security groups, and the Full Control permissions on respective registry
Service name
Purpose
Account used
by the service
Privileges added to the account
User rights
Group
membership
Permissions on registry
keys
Services for Acronis Backup agents
Acronis
Managed
Machine Service
(Main service)
Backing up and
recovering data
on the machine
Acronis Agent
User (new
account) or
user-specified
account
Log on as a
service
Adjust memory
quotas for a
process
Replace a
process level
token
Modify
firmware
environment
values
Backup
Operators
(for any account)
Administrators
(for new account
only)
BackupAndRecovery
Encryption
Global
MMS
Acronis VSS
Provider
(Auxiliary
service; created
only for Agent
for Windows in a
Windows Server
operating
system)
Using a Volume
Shadow Copy
(VSS) provider
(p. 124) that
comes with
Acronis Backup
Local System
No additional privileges
Acronis
Removable
Storage
Management
Service
(Auxiliary
service)
Managing locally
attached tape
devices. Can be
also used by the
Storage Node
Service.
Local System
No additional privileges
Services for Acronis Backup Management Server
Acronis
Management
Server Service
(Main service)
Centrally
managing
backup
operations on
multiple
machines
AMS User
(new account)
or
user-specified
account
Log on as a
service
Acronis
Centralized
Admins
AMS
BackupAndRecovery
keys in the following key: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Acronis. There are no permissions
granted on other registry keys.
The following table lists the services of Acronis Backup components and the privileges for their
accounts.
32 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 33
Service name
Purpose
Account used
by the service
Privileges added to the account
User rights
Group
membership
Permissions on registry
keys
SQL Server
(ACRONIS)
(Auxiliary
service; created
only if a new SQL
server is
installed)
Running a
Microsoft SQL
Server that is
optionally
installed with
the management
server
Local System
No additional privileges
Acronis Web
Server Service
(Auxiliary
service)
Hosting the
management
server Web page
Same as for Acronis Management Server Service
Services for Acronis Backup Storage Node
Acronis Storage
Node Service
(Main service)
Managing and
deduplicating
backup archives,
maintaining the
centralized data
catalog
ASN User (new
account) or
user-specified
account
Log on as a
service
Backup
Operators
(for any account)
Administrators
(for new account
only)
ASN
BackupAndRecovery
Encryption
Acronis
Removable
Storage
Management
Service
(Auxiliary
service)
Managing locally
attached tape
devices. Can also
be used by the
Managed
Machine Service.
Local System
No additional privileges
Common services
Service name
Purpose
Account used by the service
Services for Acronis PXE Server
Acronis PXE
Server Service
Booting machines into Acronis bootable components over
the network
Local System
Acronis File
Server Service
Providing bootable components for Acronis PXE Server
Local System
Remote-access and scheduling services
Acronis Remote
Agent Service
Providing connectivity among Acronis components
Local System
(Windows Vista and later)
or
NetworkService
(earlier than Windows Vista)
The following services can be used by multiple components of Acronis Backup and by other Acronis
products. These services always run under a system account. No additional privileges are given to the
account.
33 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 34

Acronis
Scheduler2
Service
Providing scheduling for tasks performed by Acronis
components
Local System
Dependencies on other services
The main services depend on Acronis Scheduler2 Service and on the following standard Windows
services: Remote Procedure Call (RPC) and Protected Storage. Acronis Managed Machine Service
and Acronis Storage Node Service also depend on the Windows Management Instrumentation
standard service.
To view the list of dependencies for a service, do the following:
1. In the Services snap-in, double-click the name of the service.
2. On the Dependencies tab, examine the This service depends… field.
3.5 Full, incremental and differential backups
Acronis Backup provides the capability to use popular backup schemes, such as
Grandfather-Father-Son and Tower of Hanoi, as well as to create custom backup schemes. All backup
schemes are based on full, incremental and differential backup methods. The term "scheme" in fact
denotes the algorithm of applying these methods plus the algorithm of the archive cleanup.
Comparing backup methods with each other does not make much sense because the methods work
as a team in a backup scheme. Each method should play its specific role according to its advantages.
A competent backup scheme will benefit from the advantages of all backup methods and lessen the
influence of all the methods’ shortcomings. For example, weekly differential backup facilitates
archive cleanup because it can be easily deleted along with the weekly set of daily incremental
backups depending on it.
Backing up with the full, incremental or differential backup method results in a backup (p. 430) of the
corresponding type.
Full backup
A full backup stores all data selected for backup. A full backup underlies any archive and forms the
base for incremental and differential backups. An archive can contain multiple full backups or consist
of only full backups. A full backup is self-sufficient - you do not need access to any other backup to
recover data from a full backup.
It is widely accepted that a full backup is the slowest to do but the fastest to restore. With Acronis
technologies, recovery from an incremental backup may be not slower than recovery from a full one.
A full backup is most useful when:
you need to roll back the system to its initial state
this initial state does not change often, so there is no need for regular backup.
Example: An Internet cafe, school or university lab where the administrator often undoes changes
made by the students or guests but rarely updates the reference backup (in fact, after installing
software updates only). The backup time is not crucial in this case and the recovery time will be
minimal when recovering the systems from the full backup. The administrator can have several
copies of the full backup for additional reliability.
34 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 35
Incremental backup
Parameter
Full backup
Differential backup
Incremental backup
Storage space
Maximal
Medium
Minimal
Creation time
Maximal
Medium
Minimal
Recovery time
Minimal
Medium
Maximal
An incremental backup stores changes to the data against the latest backup. You need access to
other backups from the same archive to recover data from an incremental backup.
An incremental backup is most useful when:
you need the possibility to roll back to any one of multiple saved states
the data changes tend to be small as compared to the total data size.
It is widely accepted that incremental backups are less reliable than full ones because if one backup
in the "chain" is corrupted, the next ones can no longer be used. However, storing multiple full
backups is not an option when you need multiple prior versions of your data, because reliability of an
oversized archive is even more questionable.
Example: Backing up a database transaction log.
Differential backup
A differential backup stores changes to the data against the latest full backup. You need access to
the corresponding full backup to recover the data from a differential backup. A differential backup is
most useful when:
you are interested in saving only the most recent data state
the data changes tend to be small as compared to the total data size.
The typical conclusion is: "differential backups take longer to do and are faster to restore, while
incremental ones are quicker to do and take longer to restore." In fact, there is no physical difference
between an incremental backup appended to a full backup and a differential backup appended to
the same full backup at the same point of time. The above mentioned difference implies creating a
differential backup after (or instead of) creating multiple incremental backups.
An incremental or differential backup created after disk defragmentation might be considerably larger than
usual because defragmentation changes file locations on the disk and the backup reflects these changes. It is
recommended that you re-create a full backup after disk defragmentation.
The following table summarizes the advantages and shortcomings of each backup type as they
appear based on common knowledge. In real life, these parameters depend on numerous factors
such as the amount, speed and pattern of data changes; the nature of the data, the physical
specifications of the devices, the backup/recovery options you set, to name a few. Practice is the
best guide to selecting the optimal backup scheme.
3.6 What does a disk or volume backup store?
A disk or volume backup stores a disk or a volume file system as a whole and includes all of the
information necessary for the operating system to boot. It is possible to recover disks or volumes as a
whole from such backups as well as individual folders or files.
Windows
35 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 36
A volume backup stores all files and folders of the selected volume independent of their
attributes (including hidden and system files), the boot record, the file allocation table (FAT) if it
exists, the root and the zero track of the hard disk with the master boot record (MBR).
A disk backup stores all volumes of the selected disk (including hidden volumes such as the
vendor's maintenance partitions) and the zero track with the master boot record.
The following items are not included in a disk or volume backup (as well as in a file-level backup):
The swap file (pagefile.sys) and the file that keeps the RAM content when the machine goes
into hibernation (hiberfil.sys). After recovery, the files will be re-created in the appropriate
place with the zero size.
Windows shadow storage. The path to it is determined in the registry value VSS Default
Provider which can be found in the registry key
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\BackupRestore\FilesNotToBa
ckup. This means that in operating systems starting with Windows Vista, Windows Restore
Points are not backed up.
Linux
A volume backup stores all files and directories of the selected volume independent of their
attributes, a boot record, and the file system super block.
A disk backup stores all disk volumes as well as the zero track with the master boot record.
With the sector-by-sector (raw mode) option enabled, a disk backup stores all the disk sectors. The
sector-by-sector backup can be used for backing up disks with unrecognized or unsupported file
systems and other proprietary data formats.
3.7 About dynamic and logical volumes
3.7.1 Backup and recovery of dynamic volumes (Windows)
This section explains in brief how to back up and recover dynamic volumes (p. 436) using Acronis
Backup.
A dynamic volume is a volume located on dynamic disks (p. 435), or more exactly, on a disk group (p.
435). Acronis Backup supports the following dynamic volume types/RAID levels:
simple/spanned
striped (RAID 0)
mirrored (RAID 1)
a mirror of stripes (RAID 0+1)
RAID-5.
Backing up dynamic volumes
Dynamic volumes are backed up in the same way as basic volumes. When creating a backup plan
through the GUI, all types of volumes are available for selection as Items to back up. When using the
command line, specify the dynamic volumes with the DYN prefix.
Command line examples
acrocmd backup disk --volume=DYN1,DYN2 --loc=\\srv1\backups
--credentials=netuser1,pass1 --arc=dyn1_2_arc
This will back up volumes DYN1 and DYN2 to a network shared folder.
36 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 37

acrocmd backup disk --volume=DYN --loc=\\srv1\backups --credentials=netuser1,pass1
--arc=alldyn_arc
This will back up all dynamic volumes of the local machine to a network shared folder.
Recovering dynamic volumes
A dynamic volume can be recovered:
Over any type of existing volume.
To unallocated space of a disk group.
To unallocated space of a basic disk.
To a disk which has not been initialized.
Recovery over an existing volume
When a dynamic volume is recovered over an existing volume, either basic or dynamic, the
target volume’s data is overwritten with the backup content. The type of target volume (basic,
simple/spanned, striped, mirrored, RAID 0+1, RAID-5) will not change. The target volume size has
to be enough to accommodate the backup content.
Recovery to disk group unallocated space
When recovering a dynamic volume to disk group unallocated space, the software preserves the
volume's original type and size. If the disk group configuration does not allow for the original
volume type, the volume will be recovered as a simple or spanned volume. If this volume does
not fit the unallocated space, the volume will be resized by decreasing its free space.
Examples of when the disk group configuration does not allow the original type of the volume
Example 1. The group contains fewer disks than is required for the dynamic volume. Assume you
are going to recover an 80 GB RAID-5 volume that had resided on three disks, to a disk group
consisting of two disks. The total size of unallocated space is 100 GB: 40 GB on the first disk and
60 GB on the second. The RAID-5 volume will be recovered as a spanned volume across two
disks.
Example 2. Unallocated space distribution does not allow recovery of certain types of dynamic
volumes. Assume you are going to recover a 30 GB striped volume to a disk group consisting of
two disks. The total size of unallocated space is 50 GB: 10 GB on the first disk and 40 GB on the
second. The striped volume will be recovered to the second disk as simple.
Recovery to a disk that has not been initialized
In this case, the target disk will be automatically initialized to the MBR partitioning style. The
dynamic volumes will be recovered as basic ones. If the volumes cannot fit into unallocated
space, they will be proportionally resized (by decreasing their free space).
The table below demonstrates the resulting volume types depending on the backed-up source and
the recovery target.
37 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 38
Backup (source):
Recovered to:
Dynamic volume
Basic volume
Dynamic volume
Dynamic volume
Type as of the target
Dynamic volume
Type as of the target
Unallocated space (disk group)
Dynamic volume
Type as of the source
Dynamic volume
Simple
Basic volume or unallocated space on
a basic disk
Basic volume
Basic volume
Moving and resizing volumes during recovery
You can manually resize the resulting basic volume during recovery, or change the volume's
location on the disk. A resulting dynamic volume cannot be moved or resized manually.
Preparing disk groups and volumes
Before recovering dynamic volumes to bare metal you should create a disk group on the target
hardware.
You also might need to create or increase unallocated space on an existing disk group. This can be
done by deleting volumes or converting basic disks to dynamic.
You might want to change the target volume type (basic, simple/spanned, striped, mirrored, RAID
0+1, RAID 5). This can be done by deleting the target volume and creating a new volume on the
resulting unallocated space.
Acronis Backup includes a handy disk management utility which enables you to perform the above
operations both under the operating system and on bare metal. To find out more about Acronis Disk
Director Lite, see the Disk management (p. 262) section.
3.7.2 Backup and recovery of logical volumes and MD devices
(Linux)
This section explains how you would back up and recover volumes managed by Linux Logical Volume
Manager (LVM), called logical volumes; and multiple-disk (MD) devices, called Linux Software RAID.
To learn more about LVM please visit http://tldp.org/HOWTO/LVM-HOWTO/ or
http://www.centos.org/docs/5/html/5.1/Deployment_Guide/ch-lvm.html.
3.7.2.1 Backing up logical volumes
Acronis Backup Agent for Linux can access, back up, and recover logical volumes when running in
Linux starting with 2.6.x kernel or under Linux-based bootable media.
Backup
In Acronis Backup GUI, logical volumes appear under Dynamic volumes at the end of the list of
volumes available for backup. If you select logical volumes for backup, the logical volume structure
will be saved to the backup along with the volume contents. This structure can be automatically
recreated when you recover these volumes under a Linux-based bootable media.
To back up all available disks, specify all logical volumes plus basic volumes not belonging to them.
This is the default choice when you open the Create backup plan page.
38 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 39

Basic volumes included in logical volumes are shown in the list with None in the File system column.
If you select such volumes, the program will back them up sector-by-sector. Normally this is not
required.
Recovery
When recovering logical volumes, you have two options:
Recovering volume contents only. The type or other properties of the target volume will not
change.
This option is available both in the operating system and under bootable media.
This option is useful in the following cases:
When some data on the volume was lost, but no hard disks were replaced.
When recovering a logical volume over a basic disk or volume. You can resize the resulting
volume in this case.
A system, recovered from a logical volume backup to a basic disk, cannot boot because its kernel tries
to mount the root file system at the logical volume. To boot the system, change the loader
configuration and /etc/fstab so that LVM is not used and reactivate your boot loader (p. 150).
When recovering a basic or logical volume to an existing logical volume.
If the boot partition (/boot) was located on a basic volume, we recommend recovering it to a basic
volume, even if your boot loader supports booting from logical volumes.
Recovering both the structure of logical volumes and their contents.
Such is the case when recovering on bare metal or on a machine with different volume structure.
The structure of logical volumes can be automatically created at the time of recovery (p. 41).
This option is available only under bootable media.
For detailed instructions on how to recover logical volumes, see Recovering MD devices and logical
volumes (p. 40).
3.7.2.2 Backing up MD devices
MD devices, known as Linux Software RAID, combine several volumes and make solid block devices
(/dev/md0, /dev/md1, ..., /dev/md31). The information about MD devices is stored in /etc/raidtab
or in dedicated areas of those volumes.
You can back up active (mounted) MD devices in the same way as logical volumes. The MD devices
appear at the end of the list of volumes available for backup. If you select MD devices for backup, the
structure of the MD devices will be backed up along with their contents.
Backing up volumes included in MD devices does not make sense when an MD device is mounted, as
it won’t be possible to recover them.
When recovering MD devices under bootable media, the structure of MD devices can be recreated
automatically. For detailed information about recovering MD devices under bootable media, see
Recovering MD devices and logical volumes (p. 40).
For information about assembling MD devices when performing recovery in Linux, see Assembling
MD devices for recovery (Linux) (p. 40).
39 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 40

3.7.2.3 Backing up hardware RAID arrays (Linux)
Hardware RAID arrays under Linux combine several physical drives to create a single partitionable
disk. The special file related to a hardware RAID array is usually located in /dev/ataraid. You can back
up hardware RAID arrays in the same way as ordinary hard disks.
Physical drives that are part of hardware RAID arrays may be listed alongside other disks as if they
had a bad partition table or no partition table at all. Backing up such disks does not make sense as it
won’t be possible to recover them.
3.7.2.4 Assembling MD devices for recovery (Linux)
In Linux, when performing recovery from a disk backup to an existing MD device (also called Linux
Software RAID), make sure that this device is assembled at the time of recovery.
If the device is not assembled, assemble it by using the mdadm utility. Here are two examples:
Example 1. The following command assembles the device /dev/md0 combined from the volumes
/dev/sdb1 and /dev/sdc1:
mdadm --assemble /dev/md0 -ayes /dev/sdb1 /sdc1
Example 2. The following command assembles the device /dev/md0 combined from the disks
/dev/sdb and /dev/sdc:
mdadm --assemble /dev/md0 -ayes /dev/sdb /dev/sdc
If the recovery requires the machine to be rebooted (usually, when the volumes to recover include
the boot partition), follow these guidelines:
If all parts of the MD device are volumes (a typical case, such as in the first example), make sure
that each volume type—called partition type or system ID—is Linux raid automount; the
hexadecimal code of this partition type is 0xFD. This will guarantee that the device will be
automatically assembled following the reboot. To view or change the partition type, use a disk
partitioning utility such as fdisk.
Otherwise (such as in the second example), perform the recovery from bootable media. No
reboot will be required in that case. In bootable media, you may need to create the MD device
manually or automatically, as described in Recovering MD devices and logical volumes (p. 40).
3.7.2.5 Recovering MD devices and logical volumes
Recovering MD devices and/or volumes created by Logical Volume Manager (logical volumes)
assumes that the corresponding volume structure will be recreated.
In Linux-based bootable media, you can choose to recreate the volume structure automatically (p.
41).
This functionality is intended primarily for bare-metal recovery of an entire machine. The software
backs up and recreates the entire logical volume structure, even if not all MD devices or logical
volumes are being backed up or recovered. Therefore, you need at least as many disks as the original
volume structure used.
Do not try to recreate the volume structure automatically in any of the following cases:
The machine has data that must be preserved. The software will destroy all data on the disks
that it chooses to recreate the volume structure on.
40 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 41

The machine has fewer physical disks than the original volume structure used. The software will
fail to recreate the volume structure even if the capacity of the physical disks is enough to fit all
the data being recovered.
The backup does not contain the volume structure information. This information might be
absent in backups created by Acronis Backup & Recovery 10, because saving it was optional.
In these cases, create the volume structure manually (p. 41) prior to recovery. You can do this by
using the mdadm and lvm utilities, either in Linux-based bootable media or in Linux.
Creating the volume structure automatically
Use the following procedure to automatically recreate the logical volume structure on a machine.
Caution As a result of the following procedure, the current volume structure on the machine will be replaced
with the one stored in the backup. This will destroy the data that is currently stored on some or all of the
machine's hard disks.
If disk configuration has changed. An MD device or a logical volume resides on one or more disks. If
you replaced any of these disks between backup and recovery (or if you are recovering the volumes
to a different machine), ensure that the new disk configuration includes at least the same number of
disks as the original volume structure did. The capacity of the disks must be enough to fit all the data
being recovered.
To create the volume structure automatically
1. Boot the machine from a Linux-based bootable media.
2. Click Acronis Bootable Agent. Then, click Run management console.
3. In the management console, click Recover.
Under the archive contents, Acronis Backup will display a message saying that it detected
information about the volume structure.
4. Click Details in the area with that message.
5. Review the volume structure, and then click Apply RAID/LVM to create it.
Creating the volume structure manually
The following is a general procedure for recovering MD devices and logical volumes by using a
Linux-based bootable media, and an example of such recovery. You can use a similar procedure in
Linux.
To create the volume structure manually
1. Boot the machine from a Linux-based bootable media.
2. Click Acronis Backup. Then, click Run management console.
3. On the toolbar, click Actions, and then click Start shell. Alternatively, you can press
CTRL+ALT+F2.
4. If necessary, examine the structure of volumes which are stored in the archive, by using the
acrocmd utility. Also, you can use this utility to mount one or more of these volumes as if they
were regular volumes (see "Mounting backup volumes" later in this topic).
5. Create the volume structure according to that in the archive, by using the mdadm utility (for MD
devices), the lvm utility (for logical volumes), or both.
Note: Logical Volume Manager utilities such as pvcreate and vgcreate, which are normally available in
Linux, are not included in the bootable media environment, so you need to use the lvm utility with a
corresponding command. For example: lvm pvcreate, lvm vgcreate, and lvm lvcreate.
41 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 42

6. If you previously mounted the backup by using the acrocmd utility, use this utility again to
unmount the backup (see "Mounting backup volumes" later in this topic).
7. Return to the management console by pressing ALT+F1.
(Do not reboot the machine at this point. Otherwise, you will have to create the volume
structure again.)
8. Click Recover, then specify the path to the archive and any other required parameters, and then
click OK.
Note: This procedure will not work if you connect to Acronis Backup Bootable Agent remotely, because the
command shell is not available in this case.
Example
Suppose that you previously performed a disk-level backup of a machine with the following disk
configuration:
The machine has two 1-gigabyte and two 2-gigabyte SCSI hard disks, mounted on /dev/sda,
/dev/sdb, /dev/sdc, and /dev/sdd, respectively.
The first and second pairs of hard disks are configured as two MD devices; both are in the RAID-1
configuration, and are mounted on /dev/md0 and /dev/md1, respectively.
A logical volume is based on the two MD devices and is mounted on
/dev/my_volgroup/my_logvol.
The following picture illustrates this configuration.
Do the following to recover data from this archive.
Step 1: Creating the volume structure
1. Boot the machine from a Linux-based bootable media.
2. In the management console, press CTRL+ALT+F2.
3. Run the following commands to create the MD devices:
mdadm --create /dev/md0 --level=1 --raid-devices=2 /dev/sd[ab]
mdadm --create /dev/md1 --level=1 --raid-devices=2 /dev/sd[cd]
4. Run the following commands to create the logical volume group:
Caution: The pvcreate command destroys all data on the /dev/md0 and /dev/md1 devices.
42 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 43

lvm pvcreate /dev/md0 /dev/md1
lvm vgcreate my_volgroup /dev/md0 /dev/md1
lvm vgdisplay
The output of the lvm vgdisplay command will contain lines similar to the following:
--- Volume group --VG Name my_volgroup
...
VG Access read/write
VG Status resizable
...
VG Size 1.99 GB
...
VG UUID 0qoQ4l-Vk7W-yDG3-uF1l-Q2AL-C0z0-vMeACu
5. Run the following command to create the logical volume; in the -L parameter, specify the size
given by VG Size:
lvm lvcreate -L1.99G --name my_logvol my_volgroup
6. Activate the volume group by running the following command:
lvm vgchange -a y my_volgroup
7. Press ALT+F1 to return to the management console.
Step 2: Starting the recovery
1. In the management console, click Recover.
2. In Archive, click Change and then specify the name of the archive.
3. In Backup, click Change and then select the backup from which you want to recover data.
4. In Data type, select Volumes.
5. In Items to recover, select the check box next to my_volgroup-my_logvol.
6. Under Where to recover, click Change, and then select the logical volume that you created in
Step 1. Click the chevron buttons to expand the list of disks.
7. Click OK to start the recovery.
For a complete list of commands and utilities that you can use in the bootable media environment,
see List of commands and utilities available in Linux-based bootable media (p. 258). For detailed
descriptions of the acrocmd utility, see the Acronis Backup command-line reference.
Mounting backup volumes
You may want to mount a volume stored in a disk backup, for example, to view some files in it before
starting the recovery.
To mount a backup volume
1. Use the acrocmd list content command to list the disks and volumes that are stored in the
backup. For example, the following command lists the content of the latest backup of the
linux_machine archive:
acrocmd list content --loc=\\server\backups --credentials=user,MyPassWd
--arc=linux_machine
The output will contain lines similar to the following:
43 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 44

type: disk
Num Partition Flags Size Type GUID
---------- -------------------- ---------- ---------- ------------- ------
-Dyn1 my_volgroup-my_lo... 4 GB Ext 3
Dyn2 md0 2.007 GB Ext 2
Disk 1 sda 16 GB DT_FIXED
1-1 sda1 Act,Pri 203.9 MB Ext 2
1-2 sda2 Pri 11.72 GB Reiser
1-3 sda3 Pri 1.004 GB Linux swap
Disk 2 sdb 8 GB DT_FIXED
2-1 sdb1 Pri 2.007 GB Ext 2
2-2 sdb2 Pri 2.007 GB None
Disk 3 sdc 1 GB DT_FIXED
Disk 4 sdd 8 GB DT_FIXED
4-1 sdd1 Pri 2.007 GB Ext 2
4-2 sdd2 Pri 2.007 GB None
2. Use the acrocmd mount command, specifying the volume's name in the --volume parameter.
For example:
acrocmd mount --loc=\\server\backups --arc=linux_machine --mount_point=/mnt
--volume=DYN1
This command mounts the logical volume DYN1 on the mount point /mnt.
To unmount a backup volume
Use the acrocmd umount command, specifying the volume's mount point as a parameter. For
example:
acrocmd umount --mount_point=/mnt
3.8 Support for Advanced Format (4K-sector) hard disks
Acronis Backup can back up hard disks with a sector size of 4 KB (known as Advanced Format disks),
as well as traditional hard disks that have 512-byte sectors.
Acronis Backup can recover data from one disk to another as long as both disks have the same logical
sector size. (This is the sector size presented to the operating system.) Acronis Backup automatically
aligns the disk’s volumes (p. 140) if necessary. This way, the start of a cluster in the file system always
matches the start of a physical sector on the disk.
The disk management (p. 262) functionality of Acronis Backup is not available for disks with a 4-KB
logical sector size.
Determining the logical sector size
By disk specification
Development of the Advanced Format technology is coordinated by the International Disk Drive
Equipment and Materials Association (IDEMA). For more details, see
http://www.idema.org/?page_id=2.
In terms of the logical sector size, IDEMA specifies two types of Advanced Format disks:
512 Byte emulation (512e) disks have a 512-byte logical sector size. These disks are supported in
Windows starting with Windows Vista, and in modern Linux distributions. Microsoft and Western
Digital use the term “Advanced Format” exclusively for this type of disk.
44 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 45

4K native (4Kn) disks have a 4-KB logical sector size. Modern operating systems can store data on
these disks, but they generally cannot boot from these disks. These disks are commonly external
drives with USB connection.
By running the appropriate command
To find out the logical sector size of a disk, do the following.
In Windows:
1. Make sure that the disk contains an NTFS volume.
2. Run the following command as an administrator, specifying the drive letter of the NTFS
volume:
fsutil fsinfo ntfsinfo D:
3. Examine the value in the Bytes Per Sector line. For example, the output may be the
following:
Bytes Per Sector : 512
In Linux:
1. Determine the device name of the disk, such as /dev/sdb.
2. Run the following command as the root user, specifying the device name:
parted /dev/sdb print
3. Examine the first value in the Sector size (logical/physical) line. For example, the output may
be the following:
Sector size (logical/physical): 512B/4096B
3.9 Support for UEFI-based machines
Acronis Backup can back up and recover machines that use 64-bit Unified Extensible Firmware
Interface (UEFI) in the same way as it does for machines that use BIOS for booting.
This applies to both physical and virtual machines, no matter if the virtual machines are backed up at
a hypervisor level or from inside a guest OS.
Backup and recovery of devices that use 32-bit UEFI are not supported.
Limitations
WinPE-based bootable media of versions earlier than 4.0 and Acronis PXE Server do not support
UEFI booting.
Acronis Active Restore (p. 429) is not available on UEFI machines.
Acronis Startup Recovery Manager (ASRM) (p. 429) is not supported on UEFI machines running
Linux. On UEFI machines running Windows, activate ASRM in Windows rather than under
bootable media.
A machine running Linux cannot be transferred between UEFI and BIOS. For details about
transferring Windows machines, see "Recovering BIOS-based systems to UEFI-based or vice
versa" (p. 143).
3.10 Support for Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012
This section describes how Acronis Backup supports features that are introduced in the Windows 8
and Windows Server 2012 operating systems.
45 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 46

The information in this section also applies to Windows 8.1, Windows Server 2012 R2, Windows 10,
and Windows Server 2016.
Limitations
Acronis Disk Director Lite (p. 262) is not available under Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012.
Disk management operations under bootable media may work incorrectly if storage spaces are
configured on the machine.
The Windows To Go feature of Windows 8 is not supported.
WinPE 4.0 and WinPE 5.0
Acronis Media Builder can create bootable media based on these versions of Windows Preinstallation
Environment (WinPE).
These bootable media support new features of Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 (see later in
this section). They can boot on machines that use Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI).
To create bootable media based on these versions of WinPE, you need Windows Assessment and
Deployment Kit (ADK). For more details, see the “WinPE-based bootable media” (p. 253) section.
UEFI Secure Boot
On a machine that runs Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012 and uses UEFI, the Secure Boot feature
of UEFI may be turned on. Secure Boot ensures that only trusted boot loaders can boot the machine.
By using Acronis Media Builder, you can create a bootable media that has a trusted boot loader. To
do this, choose to create a 64-bit Linux-based media or a 64-bit media based on WinPE 4 or later.
Resilient file system (ReFS)
In Windows Server 2012, you can format a volume by using the ReFS file system. This file system
provides a more reliable way of storing data on the volume as compared with the NTFS file system.
In Windows Server 2012 and under a bootable media based on WinPE 4 or later, you can back up
and recover a ReFS volume. Resizing a ReFS volume during recovery is not supported.
Linux-based bootable media and bootable media based on WinPE version earlier than 4.0 cannot
write files to a ReFS volume. Therefore, you cannot recover files to a ReFS volume by using these
media; and you cannot select a ReFS volume as a backup destination.
Storage spaces
In Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012, you can combine several physical disks into a storage pool.
In this storage pool, you can create one or more logical disks, called storage spaces. As with ordinary
disks, storage spaces can have volumes.
In Windows 8, in Windows Server 2012, and under a bootable media based on WinPE 4 or later,
you can back up and recover storage spaces. In Windows Server 2012 and under a bootable media
based on WinPE 4 or later, you also can recover a storage space to an ordinary disk or vice versa.
Linux-based bootable media does not recognize storage spaces. It backs up the underlying disks
sector-by-sector. The same applies to Agent for VMware and Agent for Hyper-V. If you recover all of
the underlying disks to the original disks, the storage spaces will be recreated.
46 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 47

Data Deduplication
In Windows Server 2012, you can enable the Data Deduplication feature for an NTFS volume. Data
Deduplication reduces the used space on the volume by storing duplicate fragments of the volume's
files only once.
You can back up and recover a data deduplication–enabled volume at a disk level, without limitations.
File-level backup is supported, except when using Acronis VSS Provider. To recover files from a disk
backup, mount the backup (p. 241) on a machine running Windows Server 2012, and then copy the
files from the mounted volume.
The Data Deduplication feature of Windows Server 2012 is unrelated to the Acronis Backup
Deduplication feature.
3.11 Compatibility with encryption software
Acronis Backup fully retains its functionality when interacting with file-level encryption software.
Disk-level encryption software encrypts data on the fly. This is why data contained in the backup is
not encrypted. Disk-level encryption software often modifies system areas: boot records, or partition
tables, or file system tables. These factors affect disk-level backup and recovery, the ability of the
recovered system to boot and access to Acronis Secure Zone.
Under some conditions, Acronis Backup is compatible with the following disk-level encryption
software:
Microsoft BitLocker Drive Encryption
McAfee Endpoint Encryption
PGP Whole Disk Encryption.
To ensure reliable disk-level recovery, follow the common rules and software-specific
recommendations.
Common installation rule
The strong recommendation is to install the encryption software before installing Acronis Backup.
The way of using Acronis Secure Zone
Acronis Secure Zone must not be encrypted with disk-level encryption. This is the only way to use
Acronis Secure Zone:
1. Install encryption software; then, install Acronis Backup.
2. Create Acronis Secure Zone.
3. Exclude Acronis Secure Zone when encrypting the disk or its volumes.
Common backup rule
You can do a disk-level backup in the operating system. Do not try to back up using bootable media
or Acronis Startup Recovery Manager.
Software-specific recovery procedures
Microsoft BitLocker Drive Encryption
To recover a system that was encrypted by BitLocker:
1. Boot from the bootable media.
47 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 48

2. Recover the system. The recovered data will be unencrypted.
3. Reboot the recovered system.
4. Turn on BitLocker.
If you only need to recover one partition of a multi-partitioned disk, do so under the operating
system. Recovery under bootable media may make the recovered partition undetectable for
Windows.
McAfee Endpoint Encryption and PGP Whole Disk Encryption
You can recover an encrypted system partition by using bootable media only.
If the recovered system fails to boot, rebuild Master Boot Record as described in the following
Acronis knowledge base article: http://kb.acronis.com/content/1507 and reboot.
3.12 Support for SNMP
SNMP objects
Acronis Backup provides the following Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) objects to
SNMP management applications:
Type of event
Object identifier (OID): 1.3.6.1.4.1.24769.100.200.1.0
Syntax: OctetString
The value may be "Information", "Warning", 'Error" and "Unknown". "Unknown" is sent only in
the test message.
Text description of the event
Object identifier (OID): 1.3.6.1.4.1.24769.100.200.2.0
Syntax: OctetString
The value contains the text description of the event (it looks identical to messages published by
Acronis Backup in its log).
Example of varbind values:
1.3.6.1.4.1.24769.100.200.1.0:Information
1.3.6.1.4.1.24769.100.200.2.0:I0064000B
Supported operations
Acronis Backup supports only TRAP operations. It is not possible to manage Acronis Backup using
GET- and SET- requests. This means that you need to use an SNMP Trap receiver to receive
TRAP-messages.
About the management information base (MIB)
The MIB file acronis-abr.mib is located in the Acronis Backup installation directory. By
default: %ProgramFiles%\Acronis\BackupAndRecovery in Windows and
/usr/lib/Acronis/BackupAndRecovery in Linux.
This file can be read by a MIB browser or a simple text editor such as Notepad or vi.
48 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 49

About the test message
When configuring SNMP notifications, you can send a test message to check if your settings are
correct.
The parameters of the test message are as follows:
Type of event
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.24769.100.200.1.0
Value: "Unknown"
Text description of the event
OID: 1.3.6.1.4.1.24769.100.200.2.0
Value: "?00000000"
49 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 50

4 Backup
4.1 Back up now
Use the Back up now feature to configure and run a one-time backup in a few simple steps. The
backup process will start immediately after you perform the required steps and click OK.
For a long-time backup strategy that includes schedules and conditions, timely deleting of backups or
moving them to different locations, consider creating a backup plan.
Configuring immediate backup is similar to creating a backup plan (p. 50) except for the following:
There are no options to schedule backups and to set up retention rules.
Simplified naming of backup files (p. 72) is used, if the backup destination supports it. Otherwise,
the standard backup naming is used.
The following locations do not support simplified file naming: managed vaults, tape, Acronis
Secure Zone or Acronis Cloud Storage.
Due to simplified file naming, an RDX drive or USB flash drive can only be used in the removable
media (p. 189) mode.
Conversion of a disk-level backup to a virtual machine is not available as a part of the backup
operation. You can convert the resulting backup afterwards.
4.2 Creating a backup plan
Before creating your first backup plan (p. 430), please familiarize yourself with the basic concepts
used in Acronis Backup.
To create a backup plan, perform the following steps.
What to back up
Items to back up (p. 52)
Select the type of data to back up and specify the data items. The type of data depends on
the agents installed on the machine.
Access credentials, exclusions
To access these settings, click Show access credentials, exclusions.
Access credentials (p. 54)
Provide credentials for the source data if the plan's account does not have access
permissions to the data.
Exclusions (p. 55)
Set up exclusions for the specific types of files you do not wish to back up.
Where to back up
Location (p. 56)
Specify a path to the location where the backup archive will be stored and the archive name.
The archive name has to be unique within the location. Otherwise, backups of the newly
created backup plan will be placed to the existing archive that belongs to another backup
plan. The default archive name is Archive(N) where N is the sequence number of the archive
in the location you have selected.
50 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 51

Select the mode the removable device will be used in (p. 189)
If the specified location is an RDX drive or USB flash drive, select the device mode:
Removable media or Fixed drive.
Backup file naming, access credentials, archive comments
To access these settings, click Show backup file naming, access credentials, archive comments.
File naming (p. 72)
[Optional] Select the Name backup files using the archive name, as in Acronis True Image
Echo, rather than auto-generated names check box if you want to use simplified file naming
for the archive’s backups.
Not available when backing up to a managed vault, tape, Acronis Secure Zone, or Acronis
Cloud Storage. When backing up to an RDX drive or USB flash drive, the file naming scheme is
determined by the removable device mode (p. 189).
Access credentials (p. 59)
[Optional] Provide credentials for the location if the plan account does not have access
permissions to the location.
Archive comments
[Optional] Enter comments on the archive.
Single-pass disk and application backup (p. 305)
Applies only to machines that have a license for single-pass backup
Specify settings related to single-pass disk and application backup.
How to back up
Backup scheme (p. 60)
Specify when and how often to back up your data; define for how long to keep the created
backup archives in the selected location; set up schedule for the archive cleanup procedure
(see “Replication and retention settings” below).
Replication and retention settings (p. 91)
Not available for removable media or when simplified naming of backup files (p. 72) is
chosen.
Define whether to copy (replicate) the backups to another location, and whether to move or
delete them according to retention rules. The available settings depend on the backup
scheme.
2nd location
[Optional] To set up replication of backups, select the Replicate newly created backup to
another location check box. For more information about backup replication, see Setting up
replication of backups (p. 94).
Validation, convert to virtual machine
To access these settings, click Show validation, convert to virtual machine.
When to validate (p. 69)
[Optional] Depending on the selected backup scheme, define when and how often to
perform validation and whether to validate the entire archive or the latest backup in the
archive.
Convert to virtual machine (p. 163)
[Optional] Applies to: disk or volume backup, backup of entire virtual machines or volumes of
a virtual machine.
51 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 52

Set up a regular conversion of a disk or volume backup to a virtual machine.
Plan parameters
Plan name
[Optional] Enter a unique name for the backup plan. A conscious name lets you identify the
plan among others.
Backup options
[Optional] Configure parameters of the backup operation, such as pre/post backup
commands, maximum network bandwidth allocated for the backup stream or the backup
archive compression level. If you do nothing in this section, the default values (p. 100) will be
used.
After any of the settings is changed against the default value, a new line that displays the
newly set value appears. The setting status changes from Default to Reset to default. Should
you modify the setting again, the line will display the new value unless the new value is the
default one. When the default value is set, the line disappears. Therefore, in this section you
always see only the settings that differ from the default values.
To reset all the settings to the default values, click Reset to default.
Plan's credentials, comments, label
To access these settings, click Show plan's credentials, comments, label.
Plan's credentials (p. 70)
[Optional] Specify the credentials under which the plan will run.
Comments
[Optional] Type a description of the backup plan.
Label (p. 70)
[Optional] Type a text label for the machine you are going to back up. The label can be used
to identify the machine in various scenarios.
After you have performed all the required steps, click OK to create the backup plan.
After that, you might be prompted for the password (p. 72).
The plan you have created will be accessible for examination and managing in the Backup plans and
tasks (p. 316) view.
4.2.1 Selecting data to back up
To select the data to back up
1. In Data to back up section, select the type of data you want to be backed up. The list of available
data types depends on the agents running on the machine and the types of licenses:
Disks/volumes
To be able to back up this data, you must have Administrator or Backup operator privileges.
Select this option to back up:
Entire physical machines or their individual disks or volumes, if Acronis Backup Agent for
Windows or Acronis Backup Agent for Linux is installed.
A disk-level backup enables you to recover the entire system in case of severe data
damage or hardware failure. Also, you can individually recover files and folders. The
backup procedure is faster than copying files, and may significantly speed up the backup
process when backing up large volumes of data.
52 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 53

Microsoft SQL databases by means of single-pass disk and application backup, if Acronis
Backup Agent for SQL is installed.
Agent for SQL enables you to create application-aware disk backups and to recover
Microsoft SQL databases from such backups. For more information, see the "Protecting
Microsoft SQL Server..." (p. 301) section.
Microsoft Active Directory data by means of single-pass disk and application backup, if
Acronis Backup Agent for Active Directory is installed.
Agent for Active Directory enables you to create application-aware disk backups and to
recover Microsoft Active Directory data from such backups. For more information, see
the "Protecting Microsoft Active Directory ..." (p. 312) section.
Folders/files
Available if Acronis Backup Agent for Windows or Acronis Backup Agent for Linux is installed.
Select this option to back up specific files and folders.
A file-level backup is not sufficient for recovery of the operating system. Choose file backup if
you plan to keep safe only certain data (the current project, for example). This will reduce
the archive size, thus saving storage space.
In order to recover your operating system along with all the settings and applications, you
have to perform a disk backup.
Virtual machines
Available if Acronis Backup Agent for VMware or Acronis Backup Agent for Hyper-V is
installed.
Select this option to back up entire virtual machines residing on a virtualization server or
their disks or volumes.
Backing up an entire virtual machine, its disks, or volumes yields a standard disk backup (p.
434). In addition, this backup stores the virtual machine configuration. This configuration will
be suggested by default when recovering the backup content to a new virtual machine. For
more information about backing up virtual machines see "Backing up virtual machines".
Microsoft Exchange information store
Available if Acronis Backup Agent for Exchange is installed.
Select this option to back up information store, individual storage groups or databases of
Microsoft Exchange servers. In case of disaster, you will be able to recover lost or corrupted
databases or storage groups. Also, you can individually recover mailboxes, public
folders, single emails, contacts, calendar events, and other items.
To be able to back up Exchange data, a domain user account that has administrative
privileges on the Exchange server is required. In a cluster, the account must have
administrative privileges on each of the cluster’s nodes.
For more information about backing up Microsoft Exchange data see "Backing up Microsoft
Exchange Server data".
Microsoft Exchange mailboxes
Available if Acronis Backup Agent for Exchange is installed.
Select this option to back up individual mailboxes and public folders without backing up the
entire Microsoft Exchange database. By using the exclusion filters, you can specify items to
be skipped during mailbox backups.
To be able to back up Exchange data, a domain user account that has administrative
privileges on the Exchange server is required. In a cluster, the account must have
administrative privileges on each of the cluster’s nodes.
53 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 54

For more information about backing up Microsoft Exchange data see "Backing up Microsoft
Exchange Server data".
2. In the tree below Data to back up section, select the items to back up.
To back up all items of the selected data type present on a machine, select the check box next to
the machine. To back up individual data items, expand the machine and select check boxes next
to the required items.
Notes for Disks/volumes
If your operating system and its loader reside on different volumes, always include both
volumes in the backup. The volumes must also be recovered together; otherwise there is a
high risk that the operating system will not start.
Note for Linux users: Logical volumes and MD devices are shown under Dynamic volumes.
For more information about backing up such volumes and devices, see "Backup and recovery
of logical volumes and MD devices (Linux)" (p. 38).
Note for Linux users: We recommend that you unmount any volumes that contain
non-journaling file systems—such as the ext2 file system—before backing them up.
Otherwise, these volumes might contain corrupted files upon recovery; recovery of these
volumes with resize might fail.
Notes for Virtual machines
Backing up entire virtual machines comes in handy when having small (in terms of virtual
disks size) but numerous legacy servers such as those resulting from workload consolidation.
A separate archive will be created for each machine.
Backing up individual disks or volumes within a virtual machine comes in handy when the
operating system and applications, such as a database server, run on a virtual disk, but the
data, such as a database, is stored on a large capacity physical disk added to the same
machine. You will be able to use different backup strategies for the virtual disk and the
physical storage.
3. Having specified the data to back up, click OK.
4.2.2 Access credentials for source
Specify the credentials required for access to the data you are going to back up.
To specify credentials
1. Select one of the following:
Use the plan's credentials
The program will access the source data using the credentials of the backup plan account
specified in the Plan parameters section.
Use the following credentials
The program will access the source data using the credentials you specify.
Use this option if the plan's account does not have access permissions to the data.
Specify:
User name. When entering the name of an Active Directory user account, be sure to also
specify the domain name (DOMAIN\Username or Username@domain).
Password. The password for the account.
Confirm password. Re-enter the password.
2. Click OK.
54 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 55

4.2.3 Source files exclusion
This option is effective for Windows and Linux operating systems and bootable media.
This option is effective for disk-level backup of NTFS, FAT, Ext3, and Ext4 file systems only. This option
is effective for file-level backup of all supported file systems.
The option defines which files and folders to skip during the backup process and thus exclude from
the list of backed-up items.
Note: Exclusions override selection of data items to back up. For example, if you select to back up file
MyFile.tmp and to exclude all .tmp files, file MyFile.tmp will not be backed up.
To specify which files and folders to exclude, set up any of the following parameters.
Exclude all hidden files and folders
Select this check box to skip files and folders that have the Hidden attribute (for file systems that are
supported by Windows) or that start with a period (.) (for file systems in Linux such as Ext2 and Ext3).
If a folder is hidden, all of its contents (including files that are not hidden) will be excluded.
Exclude all system files and folders
This option is effective only for file systems that are supported by Windows. Select this check box to
skip files and folders with the System attribute. If a folder has the System attribute, all of its contents
(including files that do not have the System attribute) will be excluded.
Tip: You can view file or folder attributes in the file/folder properties or by using the attrib command. For more
information, refer to the Help and Support Center in Windows.
Exclude files matching the following criteria
Select this check box to skip files and folders matching any of the criteria. Use the Add, Edit, Remove
and Remove All buttons to create the list of criteria.
The criteria are not case-sensitive in Windows and Linux. For example, if you choose to exclude
all .tmp files and the C:\Temp folder, also excluded will be all .Tmp files, all .TMP files, and the
C:\TEMP folder.
Criteria: full path
Specify the full path to the file or folder, starting with the drive letter (when backing up Windows) or
the root directory (when backing up Linux).
Both in Windows and Linux, you can use a forward slash in the file or folder path (as in C:/Temp and
C:/Temp/File.tmp). In Windows, you can also use the traditional backslash (as in C:\Temp and
C:\Temp\File.tmp).
Under a Windows-style bootable media, a volume might have a different drive letter than in
Windows. For more information, see "Working under bootable media" (p. 256).
Criteria: name
Specify the name of the file or folder, such as Document.txt. All files and folders with that name will
be excluded.
55 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 56

Wildcard characters
Criterion
Example
Description
Windows and Linux
By name
F.log
F
Excludes all files named "F.log"
Excludes all folders named "F"
By mask (*)
*.log
F*
Excludes all files with the .log extension
Excludes all files and folders with names starting with "F"
(such as folders F, F1 and files F.log, F1.log)
By mask (?)
F???.log
Excludes all .log files with names consisting of four
symbols and starting with "F"
Windows
By file path
C:\Finance\F.log
Excludes the file named "F.log" located in the folder
C:\Finance
By folder path
C:\Finance\F
or
C:\Finance\F\
Excludes the folder C:\Finance\F
(be sure to specify the full path starting from the drive
letter)
Linux
By file path
/home/user/Finance/F.log
Excludes the file named "F.log" located in the folder
(directory) /home/user/Finance
By folder path
/home/user/Finance
or
/home/user/Finance/
Excludes the folder (directory) /home/user/Finance
You can use one or more wildcard characters * and ? in the criterion. These characters can be used
both within the full path and in the file or folder name.
The asterisk (*) substitutes for zero or more characters in a file name. For example, the criterion
Doc*.txt covers files such as Doc.txt and Document.txt
The question mark (?) substitutes for exactly one character in a file name. For example, the criterion
Doc?.txt covers files such as Doc1.txt and Docs.txt, but not the files Doc.txt or Doc11.txt
Exclusion examples
4.2.4 Backup location selection
Specify where the archive will be stored.
1. Selecting the destination
In the Path field, enter the full path to the destination, or select the desired destination in the
location tree as described in "Selecting backup destinations" (p. 57).
2. Using the archives table
To assist you with choosing the right destination, the table displays the names of the archives
contained in each location you select. While you are reviewing the location content, archives can be
56 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 57

added, deleted or modified by another user or by the program itself according to scheduled
operations. Use the Refresh button to refresh the list of archives.
3. Naming the new archive
Once you select the archive destination, the program generates a name for the new archive and
displays it in the Name field. The name commonly looks like Archive(N), where N is a sequence
number. The generated name is unique within the selected location. If you are satisfied with the
automatically generated name, click OK. Otherwise enter another unique name.
If the automatically generated name looks like [Machine Name]_Archive(N), this means that the
name contain variables. Such might be the case when you have selected virtual machines to back up.
The [Machine Name] stands for the virtual machine name. You can add suffixes to the name but
never delete the variables, since each virtual machine has to back up to a separate archive with the
unique name.
Backing up to an existing archive
You can configure the backup plan to back up to an existing archive. To do so, select the archive in
the archives table or type the archive name in the Name field. If the archive is protected with a
password, the program will ask for it in the pop-up window.
By selecting the existing archive, you are meddling in the area of another backup plan that uses the
archive. This is not an issue if the other plan is discontinued. However, you should generally follow
the rule: "one backup plan - one archive". Doing the opposite will not prevent the program from
functioning but is not practical or efficient, except for some specific cases.
Why two or more plans should not back up to the same archive
1. Backing up different sources to the same archive makes it difficult to use archive. When it comes
to recovery, every second counts, and you might be "lost" in the archive content.
Backup plans that operate with the same archive should back up the same data items (say, both
plans back up volume C.)
2. Applying multiple retention rules to an archive makes the archive content unpredictable. Since
each of the rules will be applied to the entire archive, the backups belonging to one backup plan
can be easily deleted along with the backups belonging to the other. You should not expect the
classic behavior of the GFS and Tower of Hanoi backup schemes.
Normally, each complex backup plan should back up to its own archive.
4.2.4.1 Selecting backup destinations
Acronis Backup lets you back up data to various physical storages.
57 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 58

Destination
Details
Cloud storage
To back up data to Acronis Cloud Storage, click Log in and specify the credentials to log in
to the cloud storage. Then, expand the Cloud storage group and select the account.
Prior to backing up to the cloud storage, you need to buy a subscription (p. 421) to the
cloud backup service and activate (p. 423) the subscription on the machine(s) you want to
back up.
Cloud backup is not available under bootable media.
Cloud backup of Microsoft Exchange Server data by using Agent for Exchange is not
possible.
Note Acronis Cloud Backup might be unavailable in your region. To find more information,
click here: http://www.acronis.com/en-us/my/cloud-backup/corporate
Personal
To back up data to a personal vault, expand the Vaults group and click the vault.
Acronis Secure Zone is considered as a personal vault available to all users that can log on
to the system.
Centralized
To back up data to a centralized vault, expand the Vaults group and click the vault.
Machine
Local machine
Local folders
To back up data to a local folder of the machine, expand the <Machine name> group and
select the required folder.
CD, DVD, BD
To back up data to optical media such as CD, DVD, or Blu-ray Discs (BD), expand the
<Machine name> group, then select the required drive.
RDX, USB
To back up data to an RDX drive or USB flash drive, expand the <Machine name> group,
then select the required drive. For information about using these drives, see the
"Removable devices" (p. 189) section.
Tape device
To back up data to a locally attached tape device, expand the <Machine name> group,
then click the required device.
Note Tape devices can only be used with Acronis Backup Advanced.
For information about using tapes, see the "Tape devices" (p. 190) section.
Network folders
To back up data to a network folder, expand the Network folders group, select the
required networked machine, and then click the shared folder.
If the network share requires access credentials, the program will ask for them.
Note for Linux users: To specify a Common Internet File System (CIFS) network share
which is mounted on a mount point such as /mnt/share, select this mount point instead of
the network share itself.
58 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 59

Destination
Details
FTP, SFTP
To back up data to FTP or SFTP, type the server name or address in the Path field as
follows:
ftp://ftp_server:port _number or sftp://sftp_server:port number
To establish an active mode FTP connection, use the following notation:
aftp://ftp_server:port _number
If the port number is not specified, port 21 is used for FTP and port 22 is used for SFTP.
After entering access credentials, the folders on the server become available. Click the
appropriate folder on the server.
You can access the server as an anonymous user if the server enables such access. To do
so, click Use anonymous access instead of entering credentials.
Note: According to the original FTP specification, credentials required for access to FTP
servers are transferred through a network as plaintext. This means that the user name and
password can be intercepted by an eavesdropper using a packet sniffer.
Storage nodes
When you need to back up data to a storage node that is not registered on the
management server, or when operating on a machine booted with bootable media:
To access a managed vault, type the following string in the Path field:
bsp://node_address/vault_name/
To access an unmanaged centralized vault, type the full path to the vault's folder.
NFS folders
To back up data to an NFS share, expand the NFS folders group and click the folder.
Available only in Linux and under Linux-based bootable media.
4.2.5 Access credentials for archive location
Specify credentials required for access to the location where the backup archive will be stored. The
user whose name is specified will be considered as the archive owner.
To specify credentials
1. Select one of the following:
Use the plan's credentials
The program will access the source data using the credentials of the backup plan account
specified in the Plan parameters section.
Use the following credentials
The program will access the source data using the credentials you specify.
Use this option if the plan account does not have access permissions to the location. You
2. Click OK.
59 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
might need to provide special credentials for a network share or a storage node vault.
Specify:
User name. When entering the name of an Active Directory user account, be sure to also
specify the domain name (DOMAIN\Username or Username@domain).
Password. The password for the account.
Confirm password. Re-enter the password.
Page 60

Warning: According to the original FTP specification, credentials required for access to FTP servers are
transferred through a network as plaintext. This means that the user name and password can be intercepted by
an eavesdropper using a packet sniffer.
4.2.6 Backup schemes
Choose one of the available backup schemes:
Simple – to schedule when and how often to backup data and specify retention rules.
Grandfather-Father-Son – to use the Grandfather-Father-Son backup scheme. The scheme does
not allow data to be backed up more than once a day. You set the days of week when the daily
backup will be performed and select from these days the day of weekly/monthly backup. Then
you set the retention periods for the daily (referred to as "sons"), weekly (referred to as
"fathers") and monthly (referred to as "grandfathers") backups. The expired backups will be
deleted automatically.
Tower of Hanoi – to use the Tower of Hanoi backup scheme. This scheme allows you to schedule
when and how often to back up (sessions) and select the number of backup levels (up to 16). The
data can be backed up more than once a day. By setting up the backup schedule and selecting
backup levels, you automatically obtain the rollback period – the guaranteed number of sessions
that you can go back at any time. The automatic cleanup mechanism maintains the required
rollback period by deleting the expired backups and keeping the most recent backups of each
level.
Custom – to create a custom scheme, where you are free to set up a backup strategy in the way
your enterprise needs it most: specify multiple schedules for different backup types, add
conditions and specify the retention rules.
Manual start – to create a backup task for manual start.
Initial seeding – to save locally a full backup whose final destination is Acronis Cloud Storage.
Note for Microsoft Exchange users: For information about backup schemes used when backing up Exchange
databases, storage groups or mailboxes, refer to the "Backup schemes" section of the "Backing up Microsoft
Exchange Server data" documentation.
4.2.6.1 Simple scheme
With the simple backup scheme, you just schedule when and how often to back up data. Other steps
are optional.
To set up the simple backup scheme, specify the appropriate settings as follows.
Schedule
Set up when and how often to back up the data. To learn more about setting up the schedule,
see the Scheduling (p. 77) section.
Retention rules
Specify how long to store backups in the location and whether to move or delete them afterward.
The retention rules are applied after creating a backup. The Keep backups indefinitely is set by
default, which means that no backups will be deleted automatically. For more information about
retention rules, see Setting up retention of backups (p. 94).
Backup type
To access this setting, click Show backup type, validation, convert to virtual machine.
Select the backup type.
60 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 61

Full - selected by default for all backup locations (except for Acronis Cloud Storage).
Mo
Tu
We
Th
Fr
Sa
Su
Jan 1—Jan 7
D D D D W - -
Jan 8—Jan 14
D D D D W - -
Jan 15—Jan 21
D D D D W - -
Jan 22—Jan 28
D D D D M - -
Jan 29—Feb 4
D D D D W - -
Feb 5—Feb 11
D D D D W - -
Feb 12—Feb 18
D D D D W - -
Feb 19—Feb 25
D D D D M - -
Feb 26—Mar 4
D D D D W - -
Start backup at
Specifies when to start a backup. The default value is 12:00 PM.
Back up on
Specifies the days of the week when a backup will be performed. The default value is
Workdays.
Weekly/Monthly
Specifies which day of the week (out of the days selected in the Back up on field) you
want to reserve for weekly and monthly backups.
The default value is Friday. With this value, a monthly backup will run on the last
Friday of each month. Weekly backups will run on all other Fridays. If you choose a
different day of week, these rules will apply to the day chosen.
Incremental. At the first time a full backup will be created. The next backups will be
incremental. Selected as the one and only backup type for Acronis Cloud Storage.
Note: When the Incremental backup type is selected along with retention rules, the archive will be
cleaned up using consolidation (p. 433), which is a more time-consuming and resource-intensive
operation.
4.2.6.2 Grandfather-Father-Son scheme
At a glance
Daily ("Son"), weekly ("Father"), and monthly ("Grandfather") backups
Custom day for weekly and monthly backups
Custom retention periods for backups of each type
Description
Let us suppose that we want to set up a backup plan that will regularly produce a series of daily (D),
weekly (W), and monthly (M) backups. Here is a natural way to do this: the following table shows a
sample two-month period for such a plan.
Daily backups run every workday except Friday, which is left for weekly and monthly backups.
Monthly backups run on the last Friday of each month, and weekly backups run on all other Fridays.
As a result, you will normally obtain 12 monthly backups over a full year.
Parameters
You can set up the following parameters of a Grandfather-Father-Son (GFS) scheme.
61 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 62

Keep backups
Specifies how long you want the backups to be stored in the archive. A term can be
set in hours, days, weeks, months, or years. For monthly backups, you can also select
Keep indefinitely if you want them to be saved forever.
The default values for each backup type are as follows.
Daily: 5 days (recommended minimum)
Weekly: 7 weeks
Monthly: indefinitely
The retention period for weekly backups must exceed that for daily backups; the
monthly backups' retention period must be greater than the weekly backups'
retention period.
We recommend setting a retention period of at least one week for daily backups.
Backup type
Specifies the types of daily, weekly and monthly backups
Always full - all the daily, weekly and monthly backups will always be full. This is
the default selection for cases when a tape drive is selected as a backup location.
Full/Differential/Incremental - daily backups are incremental, weekly backups
are differential, and monthly backups are full.
The first backup is always full. However, this does not mean that it is a monthly
backup. It will be kept as a daily, weekly or monthly backup, depending on the
day of week it is created.
Advanced settings
Available only in Acronis Backup Advanced when creating a centralized backup plan.
See the "Advanced scheduling settings" (p. 87) section for details.
A backup is not deleted until all backups that directly depend on it become subject to deletion as well. This is
why you might see a backup, marked with the icon, for a few days past its expected expiration date.
Examples
Each day of the past week, each week of the past month
Let us consider a GFS backup scheme that many may find useful.
Back up files every day, including weekends
Be able to recover files as of any date over the past seven days
Have access to weekly backups of the past month
Keep monthly backups indefinitely.
Backup scheme parameters can then be set up as follows.
Start backup at: 11:00 PM
Back up on: All days
Weekly/monthly: Saturday (for example)
Keep backups:
Daily: 1 week
Weekly: 1 month
Monthly: indefinitely
As a result, an archive of daily, weekly, and monthly backups will be created. Daily backups will be
available for seven days since creation. For instance, a daily backup of Sunday, January 1, will be
62 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 63

available through next Sunday, January 8; the first weekly backup, the one of Saturday, January 7,
will be stored on the system until February 7. Monthly backups will never be deleted.
Limited storage
If you do not want to arrange a vast amount of space to store a huge archive, you may set up a GFS
scheme so as to make your backups more short-lived, at the same time ensuring that your
information can be recovered in case of an accidental data loss.
Suppose that you need to:
Perform backups at the end of each working day
Be able to recover an accidentally deleted or inadvertently modified file if this has been
discovered relatively quickly
Have access to a weekly backup for 10 days after it was created
Keep monthly backups for half a year.
Backup scheme parameters can then be set up as follows.
Start backup at: 6:00 PM
Back up on: Workdays
Weekly/monthly: Friday
Keep backups:
Daily: 1 week
Weekly: 10 days
Monthly: 6 months
With this scheme, you will have a week to recover a previous version of a damaged file from a daily
backup; as well as 10-day access to weekly backups. Each monthly full backup will be available for six
months since the creation date.
Work schedule
Suppose you are a part-time financial consultant and work in a company on Tuesdays and Thursdays.
On these days, you often make changes to your financial documents, statements, and update the
spreadsheets etc. on your laptop. To back up this data, you may want to:
Track changes to the financial statements, spreadsheets, etc. performed on Tuesdays and
Thursdays (daily incremental backup).
Have a weekly summary of file changes since last month (Friday weekly differential backup).
Have a monthly full backup of your files.
Moreover, assume that you want to retain access to all backups, including the daily ones, for at least
six months.
The following GFS scheme suits such purposes:
Start backup at: 11:30 PM
Back up on: Tuesday, Thursday, Friday
Weekly/monthly: Friday
Keep backups:
Daily: 6 months
Weekly: 6 months
63 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 64
Monthly: 5 years
Parameter
Meaning
Full backup schedule
Specifies on what schedule and under which conditions to perform a full backup.
For example, the full backup can be set up to run every Sunday at 1:00 AM as
soon as all users are logged off.
Incremental backup
schedule
Specifies on what schedule and under which conditions to perform an
incremental backup.
If the archive contains no backups at the time of the task run, a full backup is
created instead of the incremental backup.
Differential backup schedule
Specifies on what schedule and under which conditions to perform a differential
backup.
If the archive contains no full backups at the time of the task run, a full backup is
created instead of the differential backup.
Here, daily incremental backups will be created on Tuesdays and Thursdays, with weekly and
monthly backups performed on Fridays. Note that, in order to choose Friday in the Weekly/monthly
field, you need to first select it in the Back up on field.
Such an archive would allow you to compare your financial documents as of the first and the last day
of work, and have a five-year history of all documents, etc.
No daily backups
Consider a more exotic GFS scheme:
Start backup at: 12:00 PM
Back up on: Friday
Weekly/monthly: Friday
Keep backups:
Daily: 1 week
Weekly: 1 month
Monthly: indefinitely
Backup is thus performed only on Fridays. This makes Friday the only choice for weekly and monthly
backups, leaving no other date for daily backups. The resulting “Grandfather-Father” archive will
hence consist only of weekly differential and monthly full backups.
Even though it is possible to use GFS to create such an archive, the Custom scheme is more flexible in
this situation.
4.2.6.3 Custom backup scheme
At a glance
Custom schedule and conditions for backups of each type
Custom schedule and retention rules
Parameters
64 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 65

Parameter
Meaning
Clean up archive
Specifies how to get rid of old backups: either to apply retention rules (p. 95)
regularly or clean up the archive during a backup when the destination location
runs out of space.
By default, the retention rules are not specified, which means older backups will
not be deleted automatically.
Using retention rules
Specify the retention rules and when to apply them.
This setting is recommended for backup destinations such as shared folders or
centralized vaults.
When there is insufficient space while backing up
The archive will be cleaned up only during backup and only if there is not enough
space to create a new backup. In this case, the software will act as follows:
Delete the oldest full backup with all dependent incremental/differential
backups
If there is only one full backup left and a full backup is in progress, then
delete the last full backup with all dependent incremental/differential
backups
If there is only one full backup left, and an incremental or differential backup
is in progress, an error occurs saying there is a lack of available space
This setting is recommended when backing up to a USB drive or Acronis Secure
Zone. This setting is not applicable to managed vaults, FTP and SFTP servers.
This setting enables deletion of the last backup in the archive, in case your
storage device cannot accommodate more than one backup. However, you
might end up with no backups if the program is not able to create the new
backup for some reason.
Apply retention rules
(only if the retention rules
are set)
Specifies when to apply the retention rules (p. 95).
For example, the cleanup procedure can be set up to run after each backup, and
also on schedule.
This option is available only if you have set at least one retention rule in
Retention rules.
Cleanup schedule
(only if On schedule is
selected)
Specifies a schedule for archive cleanup.
For example, the cleanup can be scheduled to start on the last day of each
month.
This option is available only if you selected On schedule in Apply retention rules.
2nd location, 3rd location,
and so on
Specifies where to copy or move (p. 91) the backups from the current location.
This option is available only if you selected either the Replicate newly created
backup to another location check box under How to back up, or Move the
oldest backups to another location in the Retention rules window.
Examples
Weekly full backup
The following scheme yields a full backup performed every Friday night.
Full backup: Schedule: Weekly, every Friday, at 10:00 PM
65 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 66

Here, all parameters except Schedule in Full backup are left empty. All backups in the archive are
kept indefinitely (no archive cleanup is performed).
Full and incremental backup plus cleanup
With the following scheme, the archive will consist of weekly full backups and daily incremental
backups. We further require that a full backup begin only after all users have logged off.
Full backup: Schedule: Weekly, every Friday, at 10:00 PM
Full backup: Conditions: User is logged off
Incremental: Schedule: Weekly, every workday, at 9:00 PM
Also, let all backups older than one year be deleted from the archive, and let the cleanup be
performed upon creating a new backup.
Retention rules: Delete backups older than 12 months
Apply the rules: After backing up
By default, a one-year-old full backup will not be deleted until all incremental backups that depend
on it become subject to deletion too. For more information, see Retention rules (p. 95).
Monthly full, weekly differential, and daily incremental backups plus cleanup
This example demonstrates the use of all options available in the Custom scheme.
Suppose that we need a scheme that will produce monthly full backups, weekly differential backups,
and daily incremental backups. Then the backup schedule can look as follows.
Full backup: Schedule: Monthly, every Last Sunday of the month, at 9:00 PM
Incremental: Schedule: Weekly, every workday, at 7:00 PM
Differential: Schedule: Weekly, every Saturday, at 8:00 PM
Further, we want to add conditions that have to be satisfied for a backup task to start. This is set up
in the Conditions fields for each backup type.
Full backup: Conditions: Location available
Incremental: Conditions: User is logged off
Differential: Conditions: User is idle
As a result, a full backup—originally scheduled at 9:00 PM—may actually start later: as soon as the
backup location becomes available. Likewise, backup tasks for incremental and differential backups
will wait until all users are logged off and users are idle, respectively.
Finally, we create retention rules for the archive: let us retain only backups that are no older than six
months, and let the cleanup be performed after each backup task and also on the last day of every
month.
Retention rules: Delete backups older than 6 months
Apply the rules: After backing up, On schedule
Cleanup schedule: Monthly, on the Last day of All months, at 10:00 PM
66 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 67
By default, a backup is not deleted as long as it has dependent backups that must be kept. For
Schedule
Set up a daily (p. 79), weekly (p. 81), or monthly (p. 83) schedule. Setting up schedule
parameters allows for the creation of simple schedules (example of a simple daily
schedule: a backup task will be run every 1 day at 10 AM) as well as more complex
schedules (example of a complex daily schedule: a task will be run every 3 days, starting
from January 15. During the specified days the task will be repeated every 2 hours from
10 AM to 10 PM). Thus, complex schedules specify the sessions on which the scheme
should run. In the discussion below, "days" can be replaced with "scheduled sessions".
Number of levels
Select from 2 to 16 backup levels. See the example stated below for details.
Roll-back period
The guaranteed number of sessions that one can go back in the archive at any time.
Calculated automatically, depending on the schedule parameters and the numbers of
levels you select. See the example below for details.
Backup type
Specifies what backup types the backup levels will have
Always full - all levels of backups will be full. This is the default selection for cases
when a tape drive is selected as a backup location.
Full/Differential/Incremental - backups of different levels will have different types:
- Last-level backups are full
- Backups of intermediate levels are differential
- First-level backups are incremental
example, if a full backup has become subject to deletion, but there are incremental or differential
backups that depend on it, the deletion is postponed until all the dependent backups can be deleted
as well.
For more information, see Retention rules (p. 95).
4.2.6.4 Tower of Hanoi scheme
At a glance
Up to 16 levels of full, differential, and incremental backups
Next-level backups are twice as rare as previous-level backups
One backup of each level is stored at a time
Higher density of more recent backups
Parameters
You can set up the following parameters of a Tower of Hanoi scheme.
Example
Schedule parameters are set as follows
Recur: Every 1 day
Frequency: Once at 6 PM
Number of levels: 4
Backup type: Full/Differential/Incremental
This is how the first 14 days (or 14 sessions) of this scheme's schedule look. Shaded numbers denote
backup levels.
67 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 68
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10
11
12
13
14
4 1 2 1 3 1 2 1 4 1 2 1 3
1
Backups of different levels have different types:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 4 1 2 1 3 1 2
1
Number of
levels
Full backup
every
On different
days, can go
back
Roll-back
period
2
2 days
1 to 2 days
1 day
3
4 days
2 to 5 days
2 days
4
8 days
4 to 11 days
4 days
5
16 days
8 to 23 days
8 days
6
32 days
16 to 47 days
16 days
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10
11
12 4 1 2 1 3 1 2 1 4 1 2 1
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10
11
12
13 4 1 2 1 3 1 2 1 4 1 2 1
3
Last-level (in this case, level 4) backups are full;
Backups of intermediate levels (2, 3) are differential;
First-level (1) backups are incremental.
A cleanup mechanism ensures that only the most recent backups of each level are kept. Here is how
the archive looks on day 8, a day before creating a new full backup.
The scheme allows for efficient data storage: more backups accumulate toward the current time.
Having four backups, we could recover data as of today, yesterday, half a week, or a week ago.
Roll-back period
The number of days we can go back in the archive is different on different days. The minimum
number of days we are guaranteed to have is called the roll-back period.
The following table shows full backup and roll-back periods for schemes of various levels.
Adding a level doubles the full backup and roll-back periods.
To see why the number of recovery days varies, let us return to the previous example.
Here are the backups we have on day 12 (numbers in gray denote deleted backups).
A new level 3 differential backup has not yet been created, so the backup of day five is still stored.
Since it depends on the full backup of day one, that backup is available as well. This enables us to go
as far back as 11 days, which is the best-case scenario.
The following day, however, a new third-level differential backup is created, and the old full backup is
deleted.
This gives us only a four day recovery interval, which turns out to be the worst-case scenario.
68 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 69

On day 14, the interval is five days. It increases on subsequent days before decreasing again, and so
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10
11
12
13
14 4 1 2 1 3 1 2 1 4 1 2 1 3 1
on.
The roll-back period shows how many days we are guaranteed to have even in the worst case. For a
four-level scheme, it is four days.
4.2.6.5 Manual start
With the Manual start scheme, you do not have to specify the backup schedule. You can run the
backup plan from the Plans and Tasks view manually at any time afterwards.
Specify the appropriate settings as follows.
Backup type
Select the type of backup
Full - selected by default for all backup locations (except for Acronis Cloud Storage).
Incremental. At the first time a full backup will be created. The next backups will be
incremental. Selected as the one and only backup type for Acronis Cloud Storage.
Differential. At the first time a full backup will be created. The next backups will be
differential.
4.2.6.6 Initial seeding
This backup scheme is available when Acronis Cloud Storage is selected as the backup destination. A
backup is only successful if you have an Initial Seeding license.
The Initial Seeding service might be unavailable in your region. To find more information, click here:
http://kb.acronis.com/content/15118.
Initial seeding enables you to transfer the first backup, which is full and usually the largest, to the
cloud storage on a hard drive instead of over the Internet. Subsequent backups, which are all
incremental and thus usually much smaller, can be transferred over the Internet after the full backup
has arrived in the cloud storage.
If you back up 500 GB of data or more, initial seeding ensures faster delivery of the backed-up data
and lower traffic costs.
Please refer to the "Initial Seeding FAQ (p. 411)" section for more details.
4.2.7 Archive validation
Set up the validation task to check if the backed-up data is recoverable. If the backup could not pass
the validation successfully, the validation task fails and the backup plan gets the Error status.
Validation of a file backup imitates recovery of all files from the backup to a dummy destination.
Validation of a volume backup calculates a checksum for every data block saved in the backup.
To set up validation, specify the following parameters
1. When to validate – select when to perform the validation. As the validation is a
resource-intensive operation, it makes sense to schedule the validation to the managed
machine's off-peak period. On the other hand, if the validation is a major part of your data
69 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 70

protection strategy and you prefer to be immediately informed whether the backed-up data is
not corrupted and can be successfully recovered, think of starting the validation right after
backup creation.
2. What to validate – select either to validate the entire archive or the latest backup in the archive.
Validation of the archive will validate all the archive’s backups and may take a long time and a lot
of system resources.
Validation of the latest backup may also take time, even if this backup is incremental or
differential, and small in size. This is because the operation validates not only the data physically
contained in the backup, but all of the data recoverable by selecting the backup. This requires
access to previously created backups.
3. Validation schedule (appears only if you have selected On schedule in step 1) - set the schedule
of validation. For more information see the Scheduling (p. 77) section.
4.2.8 Backup plan's credentials
Provide the credentials for the account under which the plan will run. By default, the plan runs under
the agent service account, if created by a user having administrative privileges on the machine. If
created by a regular user, such as a member of the Users group, the plan runs under this user's
account.
To specify credentials explicitly
1. If you have administrative privileges on the machine, select Use the following credentials.
Otherwise skip this step.
2. Specify:
User name. When entering the name of an Active Directory user account, be sure to also
specify the domain name (DOMAIN\Username or Username@domain).
Password. The password for the account.
Confirm password. Re-enter the password.
3. Click OK.
To learn more about operations available depending on the user privileges, see the Users' privileges
on a managed machine (p. 31) section.
4.2.9 Label (Preserving machine properties in a backup)
Any time data on a machine is backed up, information about the machine name, operating system,
Windows service pack and security identifier (SID) is added to the backup, along with the
user-defined text label. The label may include the department or machine owner's name or similar
information that can be used as a tag or a key.
If you recover (p. 127) the machine to a VMware ESX(i) using Agent for VMware, or convert (p. 163)
the backup to a ESX(i) virtual machine, these properties will be transferred to the virtual machine's
configuration. You can view them in the virtual machine settings: Edit settings > Options > Advanced
> General > Configuration parameters. You can select, sort and group the virtual machines with the
help of these custom parameters. This can be useful in various scenarios.
Example:
Let's assume you migrate your office or datacenter to a virtual environment. By using third-party
software that can access configuration parameters through VMware API, you can automatically apply
security policies to each machine even before powering it on.
70 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 71

To add a text label to a backup:
Parameter
Value
Description
acronisTag.label
<string>
A user-defined label.
The label can be set by a user when creating a backup
plan.
acronisTag.hostname
<string>
Host name (FQDN)
acronisTag.os.type
<string>
Operating system
acronisTag.os.servicepack
0, 1, 2...
The version of the Service Pack installed in the system.
For Windows OS only.
acronisTag.os.sid
<string>
Machine's SID.
For example:
S-1-5-21-874133492-782267321-3928949834.
For Windows OS only.
Windows XP All Editions
winXPProGuest
Windows XP All Editions (64 bit)
winXPPro64Guest
Windows Server 2003, All Editions
winNetStandardGuest
Windows Server 2003, All Editions (64 bit)
winNetStandard64Guest
Windows 2008
winLonghornGuest
Windows 2008 (64 bit)
winLonghorn64Guest
Windows Vista
winVistaGuest
Windows Vista (64 bit)
winVista64Guest
Windows 7
windows7Guest
Windows 7 (64 bit)
windows7_64Guest
Windows Server 2008 R2 (64 bit)
windows7Server64Guest
Linux
otherLinuxGuest
Linux (64 bit)
otherLinux64Guest
Other Operating System
otherGuest
Other Operating System (64 bit)
otherGuest64
1. On the Create backup plan (p. 50) page, click Show plan's credentials, comments, label.
2. In Label, enter the text label or select it from the drop-down menu.
Parameters specification
Values of the "acronisTag.os.type" parameter
Example
acronisTag.label = “DEPT:BUCH; COMP:SUPERSERVER; OWNER:EJONSON”
acronisTag.hostname = “superserver.corp.local”
acronisTag.os.type = “windows7Server64Guest”
acronisTag.os.servicepack = “1”
71 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
acronisTag.os.sid = “S-1-5-21-874133492-782267321-3928949834”
Page 72

4.2.10 Sequence of operations in a backup plan
If a backup plan contains multiple operations, Acronis Backup performs them in the following order:
1. Cleanup (if configured Before backup) and validation (if cleanup has been performed and
validation is configured to run After the retention rules are applied).
If a backup was moved to a different location during the cleanup, all the operations configured
for the subsequent locations are performed before continuing to the following steps in the
primary location.
2. Pre-backup command execution.
3. Backup:
a. Pre-data capture command execution
b. Snapshot creation
c. Post-data capture command execution
d. Backup process
4. Start of backup cataloging.
Backup cataloging can be a time-consuming process. It is performed in parallel with the following
steps.
5. Post-backup command execution.
6. Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP) creation.
7. Conversion to a virtual machine.
8. Backup replication.
9. Cleanup.
If the replication took place, or a backup was moved to a different location during the cleanup, all
the operations configured for the subsequent locations are performed before continuing to the
following steps in the primary location.
10. Validation.
11. Tape media ejection.
12. Sending e-mail notification.
4.2.11 Why is the program asking for the password?
A scheduled or postponed task has to run regardless of users being logged on. In case you have not
explicitly specified the credentials, under which the task(s) will run, the program proposes using your
account. Enter your password, specify another account or change the scheduled start to manual.
4.3 Simplified naming of backup files
To use simplified naming of backup files, do either of the following:
In the welcome screen, click Create backup plan (p. 50), expand Show backup file naming,
archive comments, and then select the Name backup files using the archive name… check box.
When you back up to a locally attached RDX drive or USB flash drive, the Name backup files
using the archive name... check box does not appear. Instead, the removable device mode (p.
189) determines whether the standard or simplified naming scheme will be used. In Linux, the
check box appears after you manually mount the device.
In the welcome screen, click Back up now (p. 50). Simplified naming will be used whenever the
backup destination supports it (see “Restrictions” below).
72 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 73

When you use simplified file naming
The file name of the first (full) backup in the archive will consist of the archive name; for
example: MyData.tib. The file names of subsequent (incremental or differential) backups will
have an index. For example: MyData2.tib, MyData3.tib, and so on.
This simple naming scheme enables you to create a portable image of a machine on a detachable
media or move the backups to a different location by using a script.
Before creating a new full backup, the software will delete the entire archive and start a new
one.
This behavior is useful when you rotate USB hard drives and want each drive to keep a single full
backup (p. 75) or all backups created during a week (p. 76). But you might end up with no
backups if a full backup to your only drive fails.
This behavior can be suppressed by adding the [Date] variable (p. 73) to the archive name.
When you use standard file naming
Each backup will have a unique file name with the exact time stamp and the backup type. For
example: MyData_2010_03_26_17_01_38_960D.tib. This standard file naming allows for a wider
range of backup destinations and backup schemes.
Restrictions
Simplified file naming is not available in the following cases:
Using a centralized backup plan.
Backing up to a managed vault, tape, Acronis Secure Zone, or Acronis Cloud Storage.
Backing up virtual machines by using Agent for VMware or Agent for Hyper-V.
Backing up Microsoft Exchange Server data by using Agent for Exchange.
When using simplified file naming, the following functionality is not available:
Setting up full, incremental and differential backups within a single backup plan. You need to
create separate backup plans for each type of backup.
Setting up replication of backups.
Setting up retention rules.
Setting up regular conversion of backups to a virtual machine.
Converting an incremental or differential backup into a full one.
Restrictions on archive names
The archive name cannot end with a number.
The FAT16, FAT32, and NTFS file systems do not allow the following characters in the file name:
backslash (\), slash (/), colon (:), asterisk (*), question mark (?), quotation mark ("), less than
sign (<), greater than sign (>), and pipe (|).
4.3.1 The [DATE] variable
If you specify the [DATE] variable in the archive name, the file name of each backup will include that
backup’s creation date.
When using this variable, the first backup of a new day will be a full backup. Before creating the next
full backup, the software deletes all backups taken earlier that day. Backups taken before that day
are kept. This means you can store multiple full backups with or without incremental ones, but no
73 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 74

more than one full backup per day. You can sort the backups by date. You can also use a script to
copy, move, or delete the older backups.
The value of this variable is the current date surrounded by brackets ([]). The date format depends on
the regional options on the machine. For example, if the date format is year-month-day, the value for
January 31, 2012, is [2012-01-31]. Characters that are not supported in a file name, such as slashes
(/), are replaced with underscores (_).
You can place this variable anywhere in the archive name. You can use both lowercase and
uppercase letters in this variable.
Examples
Example 1. Suppose that you perform incremental backups twice a day (at midnight and noon) for
two days, starting on January 31, 2012. The archive name is MyArchive-[DATE], the date format is
year-month-day. Here is the list of backup files after day two:
MyArchive-[2012-01-31].tib (full, created on January 31 at midnight)
MyArchive-[2012-01-31]2.tib (incremental, created on January 31 at noon)
MyArchive-[2012-02-01].tib (full, created on February 1 at midnight)
MyArchive-[2012-02-01]2.tib (incremental, created on February 1 at noon)
Example 2. Suppose that you perform full backups, with the same schedule, archive name, and date
format as in the previous example. Then, the list of backup files after day two is the following:
MyArchive-[2012-01-31].tib (full, created on January 31 at noon)
MyArchive-[2012-02-01].tib (full, created on February 1 at noon)
This is because the full backups created at midnight were replaced by new full backups of the same
day.
4.3.2 Backup splitting and simplified file naming
When a backup is split according to backup splitting (p. 106) settings, the same indexing is used to
also name parts of the backup. The file name for the next backup will have the next available index.
For example, suppose that the first backup of the archive MyData has been split in two parts. Then,
the file names for this backup are MyData1.tib and MyData2.tib. The second backup (supposing that
it is not split) will be named MyData3.tib.
4.3.3 Usage examples
This section provides examples of how you can use simplified file naming.
4.3.3.1 Example 1. Daily backup replacing the old one
Consider the following scenario:
You want to perform a daily full backup of your machine.
You want to store the backup on a locally attached USB hard drive in the file MyMachine.tib.
You want each new backup to replace the old one.
In this scenario, create a backup plan with a daily schedule. When creating the backup plan, specify
the USB hard drive as the archive location, specify MyMachine as the archive name, select the Name
backup files using the archive name... check box, and select Full as the backup type.
74 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 75

Result. The archive consists of a single file: MyMachine.tib. This file is deleted before creating a new
backup.
If you choose to back up to a locally attached RDX drive or USB flash drive, you will not see the Name
backup files using the archive name... check box. Instead, make sure that the removable device
mode (p. 189) is set to Removable media.
4.3.3.2 Example 2. Daily full backups with a date stamp
Consider the following scenario:
You want to perform a daily full backup of your machine.
You want to move older backups to a remote location by using a script.
In this scenario, create a backup plan with a daily schedule. When creating the backup plan, specify
MyMachine-[DATE] as the archive name, select the Name backup files using the archive name...
check box, and select Full as the backup type.
Result:
The backups of January 1, 2012, January 2, 2012, and so on, are stored respectively as
MyMachine-[2012-01-01].tib, MyMachine-[2012-01-02].tib, and so on.
Your script can move older backups based on the date stamp.
See also “The [Date] variable” (p. 73).
4.3.3.3 Example 3. Hourly backups within a day
Consider the following scenario:
You want to perform hourly backups of your server's critical files every day.
You want the first backup of each day to be full and to run at midnight; and the subsequent
backups of the day to be differential and to run at 01:00, 02:00, and so on.
You want to keep older backups in the archive.
In this scenario, create a backup plan with a daily schedule. When creating the backup plan, specify
ServerFiles[Date] as the archive name, select the Name backup files using the archive name… check
box, specify Differential as the backup type, and schedule the backups to run every hour from
midnight.
Result:
The 24 backups of January 1, 2012, will be stored as ServerFiles[2012-01-01].tib,
ServerFiles[2012-01-01]2.tib, and so on up to ServerFiles[2012-01-01]24.tib.
The following day, the backups will start with the full backup ServerFiles[2012-01-02].tib.
See also "The [Date] variable" (p. 73).
4.3.3.4 Example 4. Daily full backups with daily drive swaps
Consider the following scenario:
You want to perform a daily full backup of your machine.
You want to store the backup on a locally attached USB hard drive in the file MyMachine.tib.
You have two such drives. You want to swap them before each backup so that one drive contains
today’s backup and the other drive yesterday’s backup.
75 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 76

You want each new backup to replace the backup on the currently attached drive.
In this scenario, create a backup plan with a daily schedule. When creating the backup plan:
Specify MyMachine as the archive name.
In Windows, specify D:\ as the archive location, where D is the letter each of the drives has in the
operating system when attached to the machine.
In Linux, create a directory such as /mnt/backup and specify it as the archive location. Each time
you attach a drive, make sure to mount it to the mount point /mnt/backup.
Select the Name backup files using the archive name... check box.
Select Full as the backup type.
Result. Each hard disk drive will contain one full backup. While one drive is attached to the machine,
you can keep the other drive off-site for extra data protection.
In Windows, if you choose to back up to locally attached RDX drives or USB flash drives, the Name
backup files using the archive name... check box does not appear. Instead, make sure that the
removable device mode (p. 189) is set to Removable media.
4.3.3.5 Example 5. Daily backups with weekly drive swaps
Consider the following scenario:
You want to perform daily backups of your machine: a full backup each Monday and incremental
backups on Tuesday through Sunday.
You want to store the backups on a locally attached USB hard drive in the archive MyMachine.
You have two such drives. You want to swap them each Monday so that one drive contains
backups of the current week (Monday through Sunday), and the other drive those of the
previous week.
In this scenario, you need to create two backup plans as follows:
a) When creating the first backup plan:
Specify MyMachine as the archive name.
In Windows, specify D:\ as the archive location, where D is the letter either of the drives has
in the operating system when attached to the machine.
In Linux, create a directory such as /mnt/backup and specify it as the archive location. Each
time you attach a drive, make sure to mount it to the mount point /mnt/backup.
Select the Name backup files using the archive name... check box.
Select Full as the backup type.
Schedule the backups to run every week on Monday.
b) When creating the second backup plan, specify the same settings as in the first backup plan, but
select Incremental as the backup type and schedule the backups to run every week on Tuesday
through Sunday.
Result:
Before creating a Monday backup (by the first backup plan), all backups will be deleted from the
currently attached drive.
While one drive is attached to the machine, you can keep the other drive off-site for extra data
protection.
76 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 77

In Windows, if you choose to back up to locally attached RDX drives or USB flash drives, the Name
backup files using the archive name... check box does not appear. Instead, make sure that the
removable device mode (p. 189) is set to Removable media.
4.3.3.6 Example 6. Backups within working hours
Consider the following scenario:
You want to back up your server’s critical files every day.
You want the first backup of each day to be full and to run at 01:00 AM.
You want the backups during working hours to be differential and to run every hour from
8:00 AM through 5:00 PM.
You want to include a creation date in the name of each backup file.
In this scenario, you need to create two backup plans as follows:
a) When creating the first backup plan, specify ServerFiles[DATE] as the archive name, select the
Name backup files using the archive name… check box, select Full as the backup type, and
schedule the backups to run every day at 01:00:00 AM.
b) When creating the second backup plan, specify the same settings as in the first backup plan, but
select Differential as the backup type and schedule the backups as follows:
Run the task: Daily
Every: 1 Hour(s)
From: 08:00:00 AM
Until: 05:01:00 PM
Result:
The full backup of January 31, 2012, will be stored as ServerFiles[2012-01-31].tib.
The 10 differential backups of January 31, 2012, will be stored as ServerFiles[2012-01-31]2.tib,
ServerFiles[2012-01-31]3.tib, and so on up to ServerFiles[2012-01-31]11.tib.
The following day, February 1, the backups will start with the full backup
ServerFiles[2012-02-01].tib. The differential backups will start with ServerFiles[2012-02-01]2.tib.
See also “The [Date] variable” (p. 73).
4.4 Scheduling
Acronis scheduler helps the administrator adapt backup plans to the company’s daily routine and
each employee’s work style. The plans’ tasks will be launched systematically keeping the critical data
safely protected.
The scheduling is available when creating a backup plan (p. 50) with any of the following backup
schemes: Simple, Custom or Tower of Hanoi. The schedule also can be set for validation tasks (p.
232).
The scheduler uses local time of the machine the backup plan exists on. Before creating a schedule,
be sure the machine’s date and time settings are correct.
Schedule
To define when a task has to be executed, you need to specify an event or multiple events. The task
will be launched as soon as any of the events occurs. The table below lists the events available under
Windows and Linux operating systems.
77 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 78

Event
Windows
Linux
Time: Daily, Weekly, Monthly
+
+
Time since completion of the last successful backup within the same backup plan
(specify the length of time)
+
+
User logon
(any user, current user, specify the user’s account)
+
-
User logoff*
(any user, current user, specify the user’s account)
*Shutting down is not the same as logging off. The task will not run at a system
shutdown.
+
-
System startup
+
+
System shutdown
+
-
An event in Windows Event Log
(specify the parameters of the event)
+
-
Condition
Condition: run the task only if
Windows
Linux
User is idle (a screen saver is running or the machine is locked)
+
-
Location's host is available
+
+
The task run time is within the specified time interval
+
+
All users are logged off
+
-
The specified period of time has passed since the completion of the last successful
backup within the same backup plan
+
+
For backup operations only, you can specify a condition or multiple conditions in addition to the
events. Once any of the events occurs, the scheduler checks the condition and runs the task if the
condition is met. With multiple conditions, all of them must be met simultaneously to enable task
execution. The table below lists the conditions available under Windows and Linux operating
systems.
The scheduler behavior, in case the event occurs but the condition (or any of multiple conditions) is
not met is defined by the Task start conditions (p. 123) backup option.
What-ifs
What if an event occurs (and a condition, if any, is met) while the previous task run has not
completed?
The event will be ignored.
What if an event occurs while the scheduler is waiting for the condition required by the
previous event?
The event will be ignored.
What if the condition is not met for a very long time?
If delaying a backup is getting risky, you can force the condition (tell the users to log off) or run
the task manually. To automatically handle this situation, you can set the time interval after
which the task will run regardless of the condition.
78 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 79

4.4.1 Daily schedule
Every: <...> day(s)
Set up the certain number of days you want the task to be run. For example, if
you set Every 2 day(s), the task will be started on every other day.
Once at: <...>
Set up the time at which the task will be run once.
Every: <...>
From: <...> Until: <...>
Set up how many times the task will be run during the specified time interval.
For example, setting the task frequency to Every 1 hour From 10:00:00 AM
Until 10:00:00 PM allows the task to be run 13 times from 10 AM to 10 PM
during one day.
From: <...>
Set up a date when this schedule will be enabled (an effective date). If this
check box is cleared, the task will be started on the nearest day and time you
have specified above.
To: <...>
Set up a date when this schedule will be disabled. If this check box is cleared,
the task will be run for an indefinite number of days.
Daily schedule is effective in Windows and Linux operating systems.
To specify a daily schedule
In the Schedule area, select the appropriate parameter as follows:
In the During the day execute the task... area, select one of the following:
In the Effective... area, set the following settings:
If one or more task launches were missed while the machine was powered off, the software tries to
create a backup at the machine startup. If you do not need this extra backup, clear the If the
machine is turned off, run missed tasks at the machine startup check box.
Advanced scheduling settings (p. 87) are available only for machines registered on Acronis Backup
Management Server. To specify these settings, click Change in the Advanced settings area.
All the settings you made are displayed in the Result field at the bottom of the window.
Examples
"Simple" daily schedule
Run the task every day at 6PM.
The schedule's parameters are thus set up as follows.
1. Every: 1 day(s).
2. Once at: 06:00:00 PM.
3. Effective:
From: not set. The task will be started on the current day, if it has been created before 6PM. If
you have created the task after 6 PM, the task will be started for the first time on the next day at
6 PM.
To: not set. The task will be performed for an indefinite number of days.
"Three-hour time interval lasting for three months" schedule
Run the task every three hours. The task starts on a certain date (say, September 15, 2009), and ends
after three months.
The schedule's parameters are thus set up as follows.
79 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 80

1. Every: 1 day(s).
2. Every: 3 hours
From: 12:00:00 AM (midnight) Until: 09:00:00 PM - thus, the task will be performed 8 times a
day with a 3 hour time interval. After the last daily recurrence at 9 PM, the next day comes and
the task starts over again from midnight.
3. Effective:
From: 09/15/2009. If September 15, 2009 is the current date of the task's creation and, say,
01:15 PM is the task's creation time, the task will be started when the nearest time interval
comes: at 03:00 PM in our example.
To: 12/15/2009. On this date the task will be performed for the last time, but the task itself is still
available in the Tasks view.
Several daily schedules for one task
There are some cases when you might need the task to be run several times a day, or even several
times a day with different time intervals. For such cases, consider adding several schedules to a single
task.
For example, suppose that the task has to be run every 3rd day, starting from 09/20/2009, five times
a day:
first at 8 AM
second at 12 PM (noon)
third at 3 PM
fourth at 5 PM
fifth at 7 PM
The obvious way is to add five simple schedules. If you spend one minute for examination, you can
think out a more optimal way. As you can see, the time interval between the first and the second
task's recurrences is 4 hours, and between the third, fourth and fifth is 2 hours. In this case, the
optimal way is to add two schedules to the task.
First daily schedule
1. Every: 3 day(s).
2. Every: 4 hours.
From: 08:00:00 AM Until: 12:00:00 PM.
3. Effective:
From: 09/20/2009.
To: not set.
Second daily schedule
1. Every: 3 day(s).
2. Every: 2 hour(s).
From: 03:00:00 PM Until: 07:00:00 PM.
3. Effective:
From: 09/20/2009.
To: not set.
80 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 81

4.4.2 Weekly schedule
Every: <...> week(s) on: <...>
Specify a certain number of weeks and the days of the week you want the
task to be run. For example, with the Every 2 week(s) on Mon setting, the task
will be performed on Monday of every other week.
Once at: <...>
Set up the time at which the task will be run once.
Every: <...>
From: <...> Until: <...>
Set up how many times the task will be run during the specified time interval.
For example, setting the task frequency to Every 1 hour From 10:00:00 AM
Until 10:00:00 PM allows the task to be run 13 times from 10 AM to 10 PM
during one day.
From: <...>
Set up a date when this schedule will be enabled (an effective date). If this
check box is cleared, the task will be started on the nearest day and time you
have specified above.
To: <...>
Set up a date when this schedule will be disabled. If this check box is cleared,
the task will be run for an indefinite number of weeks.
Weekly schedule is effective in Windows and Linux operating systems.
To specify a weekly schedule
In the Schedule area, select the appropriate parameter as follows:
In the During the day execute the task... area, select one of the following:
In the Effective... area, set the following settings:
If one or more task launches were missed while the machine was powered off, the software tries to
create a backup at the machine startup. If you do not need this extra backup, clear the If the
machine is turned off, run missed tasks at the machine startup check box.
Advanced scheduling settings (p. 87) are available only for machines registered on Acronis Backup
Management Server. To specify these settings, click Change in the Advanced settings area.
All the settings you made are displayed in the Result field at the bottom of the window.
Examples
"One day in the week" schedule
Run the task every Friday at 10PM, starting from a certain date (say 05/14/2009) and ending after six
months.
The schedule's parameters are thus set up as follows.
1. Every: 1 week(s) on: Fri.
2. Once at: 10:00:00 PM.
3. Effective:
From: 05/13/2009. The task will be started on the nearest Friday at 10 PM.
To: 11/13/2009. The task will be performed for the last time on this date, but the task itself will
still be available in the Tasks view after this date. (If this date were not a Friday, the task would
be last performed on the last Friday preceding this date.)
This schedule is widely used when creating a custom backup scheme. The "One day in the week"-like
schedule is added to the full backups, while the incremental backups are scheduled to be performed
on workdays. For more details, see the Full and incremental backups plus cleanup example in the
Custom backup scheme (p. 64) section.
81 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 82

"Workdays" schedule
Run the task every week on workdays: from Monday through Friday. During a workday, the task
starts only once at 9 PM.
The schedule's parameters are thus set up as follows.
1. Every: 1 week(s) on: <Workdays> - selecting the <Workdays> check box automatically selects the
corresponding check boxes (Mon, Tue, Wed, Thu, and Fri), and leaves the remaining ones
unchanged.
2. Once at: 09:00:00 PM.
3. Effective:
From: empty. If you have created the task, say on Monday at 11:30 AM, the task will be started
on the same day at 9 PM. If the task was created, say on Friday after 9 PM, then it will be started
for the first time on the nearest workday (Monday in our example) at 9 PM.
End date: empty. The task will be restarted for an indefinite number of weeks.
This schedule is widely used when creating a custom backup scheme. The "Workdays"-like schedule
is added to the incremental backups, while the full backup is scheduled to be performed one day in
the week. For more details, see the Full and incremental backups plus cleanup example in the
Custom backup scheme (p. 64) section.
Several weekly schedules for one task
In the case when the task needs to be run on different days of the weeks with different time intervals,
consider adding a dedicated schedule to every desired day of the week, or to several days.
For example, you need the task to be run with the following schedule:
Monday: twice at 12 PM (noon) and 9 PM
Tuesday: every 3 hours from 9 AM until 9 PM
Wednesday: every 3 hours from 9 AM until 9 PM
Thursday: every 3 hours from 9 AM until 9 PM
Friday: twice at 12 PM and 9 PM (i.e. same as on Monday)
Saturday: once at 9 PM
Sunday: once at 9 PM
Combining the identical times, the following three schedules can be added to the task:
First schedule
1. Every: 1 week(s) on: Mon, Fri.
2. Every: 9 hours
From: 12:00:00 PM Until: 09:00:00 PM.
3. Effective:
From: not set.
To: not set.
Second schedule
1. Every 1 week(s) on: Tue, Wed, Thu.
2. Every 3 hours
From 09:00:00 AM until 09:00:00 PM.
82 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 83
3. Effective:
Months: <...>
Select a certain month(s) you want to run the task in.
Days: <...>
Select specific days of the month to run the task on. You can also select the
last day of the month, irrespective of its actual date.
On: <...> <...>
Select specific days of the weeks to run the task on.
Once at: <...>
Set up the time at which the task will be run once.
Every: <...>
From: <...> Until: <...>
Set up how many times the task will be run during the specified time interval.
For example, setting the task frequency to Every 1 hour From 10:00:00 AM
Until 10:00:00 PM allows the task to be run 13 times from 10 AM to 10 PM
during one day.
From: <...>
Set up a date when this schedule will be enabled (an effective date). If this
check box is cleared, the task will be started on the nearest day and time you
have specified above.
To: <...>
Set up a date when this schedule will be disabled. If this check box is cleared,
the task will be run for an indefinite number of months.
From: not set.
To: not set.
Third schedule
1. Every: 1 week(s) on: Sat, Sun.
2. Once at: 09:00:00 PM.
3. Effective:
From: not set.
To: not set.
4.4.3 Monthly schedule
Monthly schedule is effective in Windows and Linux operating systems.
To specify a monthly schedule
In the Schedule area, select the appropriate parameter as follows:
In the During the day execute the task... area, select one of the following:
In the Effective... area, set the following settings:
If one or more task launches were missed while the machine was powered off, the software tries to
create a backup at the machine startup. If you do not need this extra backup, clear the If the
machine is turned off, run missed tasks at the machine startup check box.
Advanced scheduling settings (p. 87) are available only for machines registered on Acronis Backup
Management Server. To specify these settings, click Change in the Advanced settings area.
All the settings you made are displayed in the Result field at the bottom of the window.
Examples
"Last day of every month" schedule
Run the task once at 10 PM on the last day of every month.
83 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 84

The schedule's parameters are set up as follows.
1. Months: <All months>.
2. Days: Last. The task will run on the last day of every month despite its actual date.
3. Once at: 10:00:00 PM.
4. Effective:
From: empty.
To: empty.
This schedule is widely used when creating a custom backup scheme. The "Last day of every month"
schedule is added to the full backups, while the differential backups are scheduled to be performed
once a week and incremental on workdays. For more details, see the Monthly full, weekly differential,
and daily incremental backups plus cleanup example in the Custom backup scheme (p. 64) section.
"Season" schedule
Run the task on all workdays during the northern autumn seasons of 2009 and 2010. During a
workday, the task is performed every 6 hours from 12 AM (midnight) until 6 PM.
The schedule's parameters are set up as follows.
1. Months: September, October, November.
2. On: <all> <workdays>.
3. Every: 6 hours.
From: 12:00:00 AM Until: 06:00:00 PM.
4. Effective:
From: 08/30/2009. Actually the task will be started on the first workday of September. By setting
up this date we just define that the task must be started in 2009.
To: 12/01/2010. Actually the task will end on the last workday of November. By setting up this
date we just define that the task must be discontinued in 2010, after autumn ends in the
northern hemisphere.
Several monthly schedules for one task
In the case when the task needs to be run on different days or weeks with different time intervals
depending on the month, consider adding a dedicated schedule to every desired month or several
months.
Suppose that the task goes into effect on 11/01/2009.
During northern winter, the task runs once at 10PM on every workday.
During northern spring and autumn, the task runs every 12 hours on all workdays.
During northern summer, the task runs every first and fifteenth of every month at 10 PM.
Thus, the following three schedules are added to the task.
First schedule
1. Months: December, January, February.
2. On: <All> <All workdays>
3. Once at: 10:00:00 PM.
4. Effective:
From: 11/01/2009.
84 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 85

To: not set.
Second schedule
1. Months: March, April, May, September, October, November.
2. On: <All> <All workdays>.
3. Every: 12 hours
From: 12:00:00 AM Until: 12:00:00 PM.
4. Effective:
From: 11/01/2009.
To: not set.
Third schedule
1. Months: June, July, August.
2. Days: 1, 15.
3. Once at: 10:00:00 PM.
4. Effective:
From: 11/01/2009.
To: not set.
4.4.4 On Windows Event Log event
This type of schedule is effective only in Windows operating systems.
You can schedule a backup task to start when a certain Windows event has been recorded in one of
the event logs such as the Application, Security, or System log.
For example, you may want to set up a backup plan that will automatically perform an emergency
full backup of your data as soon as Windows discovers that your hard disk drive is about to fail.
Parameters
Log name
Specifies the name of the log. Select the name of a standard log (Application, Security, or
System) from the list, or type a log name—for example: Microsoft Office Sessions
Event source
Specifies the event source, which typically indicates the program or the system component that
caused the event—for example: disk
Event type
Specifies the event type: Error, Warning, Information, Audit success, or Audit failure.
Event ID
Specifies the event number, which typically identifies the particular kind of events among events
from the same source.
For example, an Error event with Event source disk and Event ID 7 occurs when Windows
discovers a bad block on a disk, whereas an Error event with Event source disk and Event ID 15
occurs when a disk is not ready for access yet.
85 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 86
Examples
"Bad block" emergency backup
One or more bad blocks that have suddenly appeared on a hard disk usually indicate that the hard
disk drive will soon fail. Suppose that you want to create a backup plan that will back up hard disk
data as soon as such a situation occurs.
When Windows detects a bad block on a hard disk, it records an event with the event source disk
and the event number 7 into the System log; the type of this event is Error.
When creating the plan, type or select the following in the Schedule area:
Log name: System
Event source: disk
Event type: Error
Event ID: 7
Important: To ensure that such a task will complete despite the presence of bad blocks, you must make the task
ignore bad blocks. To do this, in Backup options, go to Error handling, and then select the Ignore bad sectors
check box.
Pre-update backup in Vista
Suppose that you want to create a backup plan that will automatically perform a backup of the
system—for example, by backing up the volume where Windows is installed—every time that
Windows is about to install updates.
Having downloaded one or more updates and scheduled their installation, the Microsoft Windows
Vista operating system records an event with the event source
Microsoft-Windows-WindowsUpdateClient and event number 18 into the System log; the type of
this event is Information.
When creating the plan, type or select the following in the Schedule area:
Log name: System
Event source: Microsoft-Windows-WindowsUpdateClient
Event type: Information
Event ID: 18
Tip: To set up a similar backup plan for machines running Microsoft Windows XP, replace the text in Event
source with Windows Update Agent and leave the remaining fields the same.
How to view events in Event Viewer
To open a log in Event Viewer
1. On the Desktop or in the Start menu, right-click My Computer, and then click Manage.
2. In the Computer Management console, expand System Tools, and then expand Event Viewer.
3. In Event Viewer, click the name of a log that you want to view—for example, Application.
Note: To be able to open the security log (Security), you must be a member of the Administrators group.
To view properties of an event, including the event source and event number
1. In Event Viewer, click the name of a log that you want to view—for example, Application.
Note: To be able to open the security log (Security), you must be a member of the Administrators group.
86 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 87

2. In the list of events in the right pane, double-click the name of an event whose properties you
want to view.
3. In the Event Properties dialog box, view the event's properties such as the event source, shown
in the Source field; and the event number, shown in the Event ID field.
When you are finished, click OK to close the Event Properties dialog box.
4.4.5 Advanced scheduling settings
The following advanced settings are available when setting up a daily, weekly, or monthly schedule in
a centralized backup plan.
Use Wake-on-LAN
When this setting is enabled, Acronis Backup Management Server will use the Wake-on-LAN
functionality to wake up turned-off registered machines when a backup, cleanup, or validation is
scheduled to start. If you start any of these operations manually, the Wake-on-LAN functionality will
not be used.
If the backup task on each machine starts with a delay (see the next setting), the management server
will wake up the machines according to those delays.
Before using this setting, ensure that you have enabled Wake-on-LAN on the registered machines.
The machine's basic input/output system (BIOS) configuration, network adapter configuration, and
the operating system configuration must allow waking up the machine from the powered-off state,
also known as the S5 or G2 power state.
Distribute start time within the time window
When this setting is enabled, the backup task on each registered machine will start with a specific
delay from the start time set in the backup plan. This distributes the tasks' actual start times within a
time interval.
You may want to use this setting when creating a centralized backup plan for backing up multiple
machines to a network location, to avoid excessive network load.
The delay values range from zero to the specified maximum delay value, and are determined
according to the chosen distribution method. The delay value for each machine is determined when
the backup plan is deployed to the machine, and remains the same until you edit the backup plan
and change the maximum delay value.
The conditions, if any, will be checked at the task's actual start time on each machine.
The following examples illustrate this setting.
Example 1
Suppose that you are deploying a centralized backup plan with the following schedule to three
machines:
Run the task: Daily
Once at: 09:00:00 AM
Distribute start time within the time window
Maximum delay: 1 Hour(s)
Distribution method: Random
87 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 88
In this case, the task's start time on each machine may be any time between 09:00:00 AM and
09:59:59 AM. For instance:
First machine: Every day at 09:30:03 AM
Second machine: Every day at 09:00:00 AM
Third machine: Every day at 09:59:59 AM
Example 2
Suppose that you are deploying a centralized backup plan with the following schedule to three
machines:
Run the task: Daily
Every: 2 Hour(s) From: 09:00:00 AM Until: 11:00:00 AM
Distribute start time within the time window
Maximum delay: 1 Hour(s)
Distribution method: Random
In this case, the time of the task's first run on each machine may be any time between
09:00:00 AM and 09:59:59 AM; the interval between the first and the second run is exactly two
hours. For instance:
First machine: Every day at 09:30:03 AM and at 11:30:03 AM
Second machine: Every day at 09:00:00 AM and at 11:00:00 AM
Third machine: Every day at 09:59:59 AM and at 11:59:59 AM
To specify advanced settings
1. Connect to the management server and then start creating a backup plan.
2. In How to back up, select the Simple, GFS (Grandfather-Father-Son), Tower of Hanoi, or Custom
backup scheme.
3. Depending on the backup scheme, do one of the following:
For the GFS (Grandfather-Father-Son) backup scheme, click Advanced settings.
For the Simple, Tower of Hanoi, or Custom backup scheme:
a. Click Schedule to specify a schedule for the scheme.
b. Under Run the task, select Daily, Weekly, or Monthly.
c. In the Advanced settings area, click Change.
4. To enable the use of the Wake-on-LAN functionality, select the Use Wake-on-LAN check box.
5. To distribute the centralized backup tasks' start times, select the Distribute start time within the
time window check box and then specify the maximum delay value and the distribution method.
4.4.6 Conditions
Conditions add more flexibility to the scheduler, enabling to execute backup tasks with respect to
certain conditions. Once a specified event occurs (see the "Scheduling (p. 77)" section for the list of
available events), the scheduler checks the specified condition and executes the task if the condition
is met.
Conditions are available only when the custom backup scheme (p. 64) is used. You can set conditions for full,
incremental and differential backup separately.
The scheduler behavior in case the event occurs but the condition (or any of multiple conditions) is
not met, is defined by the Task start conditions (p. 123) backup option. There, you can specify how
important the conditions are for the backup strategy:
88 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 89

conditions are obligatory - put the backup task run on hold until all the conditions are met.
conditions are preferable, but a backup task run has higher priority - put the task on hold for the
specified time interval. If the time interval lapses and the conditions are still not met, run the
task anyway. With this setting, the program will automatically handle the situation when the
conditions are not met for too long and further delaying the backup is undesirable.
backup task start time matters - skip the backup task if the conditions are not met at the time
when the task should be started. Skipping the task run makes sense when you need to back up
data strictly at the specified time, especially if the events are relatively often.
Adding multiple conditions
If two or more conditions are specified, the backup will start only when all of them are met.
4.4.6.1 User is idle
Applies to: Windows
"User is idle" means that a screen saver is running on the managed machine or the machine is locked.
Example:
Run the backup task on the managed machine every day at 9PM, preferably when the user is idle. If
the user is still active by 11PM, run the task anyway.
Event: Daily, every 1 day(s); Once at: 09:00:00 PM.
Condition: User is idle.
Task start conditions: Wait until the conditions are met, Run the task anyway after 2 hour(s).
As a result,
(1) If the user becomes idle before 9PM, the backup task will start at 9PM.
(2) If the user becomes idle between 9PM and 11PM, the backup task will start immediately after the
user becomes idle.
(3) If the user is still active at 11PM, the backup task starts anyway.
4.4.6.2 Location's host is available
Applies to: Windows, Linux
"Location's host is available" means that the machine hosting the destination for storing archives on
a networked drive is available.
Example:
Backing up data to the networked location is performed on workdays at 9:00 PM. If the location's
host is not available at that moment (for instance, due to maintenance work), skip the backup and
wait for the next workday to start the task. It is assumed that the backup task should not be started
at all rather than failed.
Event: Weekly, Every 1 week(s) on <workdays>; Once at 09:00:00 PM.
Condition: Location's host is available
Task start conditions: Skip the task execution.
As a result,
89 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 90

(1) If 9:00 PM comes and the location's host is available, the backup task starts right on time.
(2) If 9:00 PM comes but the host is unavailable at the moment, the backup task will start on the next
workday if the location's host is available.
(3) If the location's host will never be available on workdays at 9:00 PM, the task never starts.
4.4.6.3 Fits the time interval
Applies to: Windows, Linux
Restricts a backup task's start time to a specified interval.
Example
A company uses different locations on the same network-attached storage for backing up users data
and servers. The workday starts at 8AM and ends at 5 PM. Users' data should be backed up as soon
as the users log off, but not earlier than 4:30 PM and not later than 10 PM. Every day at 11 PM the
company's servers are backed up. So, all the users' data should be preferably backed up before this
time, in order to free network bandwidth. By specifying the upper limit as 10 PM, it is supposed that
the backing up of users' data does not take more than one hour. If a user is still logged on within the
specified time interval, or logs off at any other time – do not back up the users' data, i.e. skip task
execution.
Event: When logging off, The following user: Any user.
Condition: Fits the time interval, from 04:30:00 PM until 10:00:00 PM.
Task start conditions: Skip the task execution.
As a result,
(1) if the user logs off between 04:30:00 PM and 10:00:00 PM, the backup task will start immediately
following the logging off.
(2) if the user logs off at any other time, the task will be skipped.
What if...
What if a task is scheduled to be executed at a certain time and this time is outside the specified time
interval?
For example:
Event: Daily, Every 1 day(s); Once at 03:00:00 PM.
Condition: Fits the time interval, from 06:00:00 PM until 11:59:59 PM.
In this case, whether and when the task will run depends on the task start conditions:
If the task start conditions are Skip the task execution, the task will never run.
If the task start conditions are Wait until the conditions are met and the Run the task anyway
after check box is cleared, the task (scheduled to run at 3:00 PM) will start at 6:00 PM—the time
when the condition is met.
If the task start conditions are Wait until the conditions are met and the Run the task anyway
after check box is selected with, say, the 1 Hour waiting time, the task (scheduled to run at
3:00 PM) will start at 4:00 PM—the time when the waiting period ends.
90 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 91

4.4.6.4 Users logged off
Applies to: Windows
Enables to put a backup task run on hold until all users log off from Windows on the managed
machine.
Example
Run the backup task at 8 PM on the first and third Friday of every month, preferably when all users
are logged off. If one of the users is still logged on at 11 PM, run the task anyway.
Event: Monthly, Months: <All>; On: <First>, <Third> <Friday>; Once at 08:00:00 PM.
Condition: Users logged off.
Task start conditions: Wait until the conditions are met, Run the task anyway after 3 hour(s).
As a result,
(1) If all users are logged off at 8PM, the backup task will start at 8PM.
(2) If the last user logs off between 8PM and 11PM, the backup task will start immediately after the
user has logged off.
(3) If any of the users is still logged on at 11PM, the backup task starts anyway.
4.4.6.5 Time since last backup
Applies to: Windows, Linux
Postpones a backup until the specified time passes since the completion of the last successful backup
within the same backup plan.
Example:
Run the backup task at system startup, but only if more than 12 hours have passed since the last
successful backup.
Event: At startup, Start the task on machine startup.
Condition: Time since last backup, Time since the last backup: 12 hour(s).
Task start conditions: Wait until the conditions are met.
As a result,
(1) if the machine is restarted before 12 hours pass since the completion of the latest successful
backup, the scheduler will wait until 12 hours pass, and then will start the task.
(2) if the machine is restarted after 12 hours have passed since the completion of the latest
successful backup, the backup task will start immediately.
(3) if the machine is never restarted, the task will never start. You can start the backup manually, if
need be, in the Backup plans and tasks view.
4.5 Replication and retention of backups
When creating a backup plan (p. 50), you specify the primary location for the backups. In addition,
you can do the following:
91 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 92

Replicate (copy) each backup to a second location immediately after creation.
Backup scheme
Can copy
backups
Can move
backups
Can delete
backups
Manual start (p. 69)
Yes
No
No
Simple (p. 60)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Grandfather-Father-Son
(GFS) (p. 61)
Yes
No
Yes
Retain the backups according to the retention rules you specify, and then either move them to a
second location or delete them.
Similarly, you can copy or move backups from a second location to a third location and so on. Up to
five consecutive locations are supported (including the primary one).
Note: The replication feature replaces and enhances the Dual destination option, which was available in
Acronis Backup & Recovery 10.
Example. You back up your machine to a local folder. The backup is immediately copied to a network
folder. In the original local folder, the backup is stored for just one month.
The following picture illustrates this example.
Usage scenarios
Reliable disaster recovery (p. 97)
Store your backups both on-site (for immediate recovery) and off-site (to secure the backups
from local storage failure or a natural disaster).
Keeping only the latest recovery points (p. 97)
Delete older backups from a fast storage according to retention rules, in order to not overuse
expensive storage space.
Using Acronis Cloud Backup to protect data from a natural disaster (p. 98)
Replicate the archive to the cloud storage by transferring only the data changes outside working
hours.
Reduced costs of storing the backed-up data (p. 99)
Store your backups on a fast storage for as long as a need to access them is likely. Then, move
them to a lower-cost storage to keep them there for a longer term. This enables you to meet
legal requirements on data retention.
Backup to a slow device within a narrow backup window (p. 99)
Back up overnight to a managed vault on a fast storage, and then let Acronis Backup Storage
Node move the backups to tapes during the day.
Replication and retention in backup schemes
The following table shows availability of replication and retention rules in various backup schemes.
92 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 93

Tower of Hanoi (p. 67)
Yes
No
Yes
Custom (p. 64)
Yes
Yes
Yes
Initial seeding (p. 69)
No
No
No
Notes:
Setting up both copying and moving backups from the same location is not possible.
With simplified naming of backup files (p. 72), neither replication nor use of retention rules is
available.
4.5.1 Supported locations
You can copy or move a backup from any of these locations:
A local folder on a fixed drive
A network folder
An FTP or SFTP server
Acronis Backup Storage Node
Acronis Secure Zone
You can copy or move a backup to any of these locations:
A local folder on a fixed drive
A network folder
An FTP or SFTP server
Acronis Backup Storage Node
A tape device
Acronis Cloud Storage
A removable device (p. 189) used in the Fixed drive mode. (You select the removable device
mode when creating a backup plan.)
Backups that were copied or moved to the next location do not depend on the backups remaining in
the original location and vice versa. You can recover data from any backup without access to other
locations.
Restrictions
Copying or moving backups to and from optical discs (CD, DVD, Blu-ray discs) is not supported.
Copying or moving backups to and from removable devices used in the Removable media mode
is not supported.
Copying or moving backups from Acronis Backup Storage Node to a local folder is not supported.
A local folder means a folder on the machine with the agent that created the backup.
A tape device and Acronis Cloud Storage can only be the final locations. Further copying or
moving backups from them is not possible.
You cannot specify the same location more than once. For example, you cannot move a backup
from one folder to another and then back to the original folder.
Which machine performs the operation?
Copying, moving or deleting a backup from any location is initiated by the agent that created the
backup, and is performed:
93 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 94

By that agent, if the location is not a managed vault.
By the corresponding storage node, if the location is a managed vault. However, copying or
moving the backup from the managed vault to the cloud storage is performed by the agent that
created the backup.
As follows from the above description, the operation will be performed only if the machine with the
agent is powered on. If the operation is scheduled, the schedule will use that machine's date and
time.
Copying and moving backups between managed vaults
Copying or moving a backup from one managed vault to another managed vault is performed by the
storage node.
If the target vault is a deduplicating vault (p. 434) (possibly on a different storage node), the source
storage node sends only those blocks of data that are not present in the target vault. In other words,
like an agent, the storage node performs deduplication at source (p. 226). This saves network traffic
when you replicate data between geographically separated storage nodes.
4.5.2 Setting up replication of backups
Setting up replication of backups is available when creating a backup plan (p. 50).
To set up replication from the primary location, select the Replicate newly created backup to
another location check box.
To set up replication from the second or a further location, select the Replicate backups to
another location as soon as they appear in this location check box.
Next, select the location where to replicate the backups.
If allowed by the backup scheme, you can also specify when to automatically delete the backups
from each of the locations.
A backup is replicated to the next location as soon as it appears in the previous location. If earlier
backups were not replicated (for example, the network connection was lost), the software also
replicates all of the backups that appeared after the last successful replication.
4.5.3 Setting up retention of backups
You can set retention rules for backups when creating a backup plan (p. 50). The available retention
rules depend on the chosen backup scheme.
Applying retention rules can be restricted by the Replication/cleanup inactivity time (p. 120) option.
Simple scheme
Each backup is retained until its age exceeds a limit you specify. Then, it is either deleted or moved.
To set up deleting the backups:
In Retention rules, select Delete backups older than…, and then specify the retention period.
To set up moving the backups:
In Retention rules, select Move backups older than…, specify the retention period. Under Where
to replicate/move backups, specify the location.
94 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 95

The retention rules are applied after creating a backup. For the second and next locations, creating a
backup means copying or moving a backup there from the previous location.
Grandfather-Father-Son (GFS) scheme
Backups of each type (daily, weekly, and monthly) are retained for the periods you specify in Keep
backups, and then deleted.
The retention rules are applied after creating a backup. They are applied sequentially in the primary,
the second and all next locations.
Tower of Hanoi scheme
Each backup is retained based on its level (p. 67), and then deleted. You specify the number of levels
in Number of levels.
The retention rules are applied after creating a backup. They are applied sequentially in the primary,
the second and all next locations.
Custom scheme
Each backup is retained until the rules you specify are met. Then, it is either deleted or moved.
To set up deleting the backups:
In Clean up archive, select Using retention rules. In the Retention Rules window (p. 95), specify
the rules and select If the specified conditions are met: Delete the oldest backups.
In Apply retention rules, specify when to apply the rules.
To set up moving the backups:
In Clean up archive, select Using retention rules. In the Retention Rules window (p. 95), specify
the rules and select If the specified conditions are met: Move the oldest backups to another
location. Click OK and then specify the location under Where to replicate/move backups.
In Apply retention rules, specify when to apply the rules.
You can choose to apply the retention rules before creating a backup, after creating a backup, on a
schedule, or combine these options. For the second and next locations, creating a backup means
copying or moving a backup there from the previous location.
4.5.4 Retention rules for the Custom scheme
In the Retention Rules window, you can select how long to store backups in the location and
whether to move or delete them afterward.
The rules will be applied to all the backups taken on the specific machine and put in this specific
location by this specific backup plan. In Acronis Backup, such set of backups is called an archive.
To set up retention rules for backups:
1. Specify one of the following (options (a) and (b) are mutually exclusive):
a. Backups older than... and/or Archive size greater than....
A backup will be stored until the specified condition (or both of the conditions) are met.
Note: In a deduplicating vault (p. 434), almost all backed-up data is stored in a data store
outside the archive. Thus, the Archive size greater than condition is not effective and is
not displayed.
Example:
95 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 96

Backups older than 5 days
Archive size greater than 100 GB
With these settings, a backup will be stored until it is older than five days and the size of
the archive containing it exceeds 100 GB.
b. Number of backups in the archive exceeds...
If the number of backups exceeds the specified value, one or more of the oldest backups
will be moved or deleted. The minimal setting is 1.
2. Select whether to delete the backups or to move them to another location if the specified
conditions are met.
You will be able to specify the location where to move the backups and set up retention rules for
that location after you click OK.
Deleting the last backup in the archive
The retention rules are effective if the archive contains more than one backup. This means that the
last backup in the archive will be kept, even if a retention rule violation is detected. Please do not try
to delete the only backup you have by applying the retention rules before backup. This will not work.
Use the alternative setting Clean up archive > When there is insufficient space while backing up (p.
64) if you accept the risk of losing the last backup.
Deleting or moving backups with dependencies
To access this setting, click Show advanced settings in the Retention Rules window.
Retention rules presume deleting or moving some backups while retaining the others. What if the
archive contains incremental and differential backups that depend on each other and on the full
backups they are based on? You cannot, say, delete an outdated full backup and keep its incremental
“children”.
When deletion or movement of a backup affects other backups, one of the following rules is applied:
Retain the backup until all dependent backups become subject to deletion (movement)
The outdated backup (marked with the icon) will be kept until all backups that depend on it
also become outdated. Then, all the chain will be deleted at once during the regular cleanup. If
you chose moving outdated backups to the next location, the backup will be copied there
without delay. Only its deletion from the current location is postponed.
This mode helps to avoid the potentially time-consuming consolidation but requires extra space
for storing backups whose deletion is postponed. The archive size and/or the backup age or
number can exceed the values you specify.
This mode is not available for Acronis Cloud Storage when you copy or move backups there. In
the cloud storage, all backups are incremental except the first backup of an archive which is
always full. This chain cannot be entirely deleted because the most recent backup must always
be kept.
Consolidate these backups
The software will consolidate the backup that is subject to deletion or movement, with the next
dependent backup. For example, the retention rules require to delete a full backup but to retain
the next incremental one. The backups will be combined into a single full backup which will be
dated with the incremental backup date. When an incremental or differential backup from the
middle of the chain is deleted, the resulting backup type will be incremental.
This mode ensures that after each cleanup the archive size and the age or number of backups are
within the bounds you specify. The consolidation, however, may take a lot of time and system
96 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 97

resources. You still need some extra space in the vault for temporary files created during
consolidation.
This mode is not available if you selected the Archive size greater than rule for any archive
location except for Acronis Cloud Storage.
What you need to know about consolidation
Please be aware that consolidation is just a method of deletion but not an alternative to deletion.
The resulting backup will not contain data that was present in the deleted backup and was
absent from the retained incremental or differential backup.
4.5.5 Usage examples
This section provides examples of how you can replicate backups and set up retention rules for them.
4.5.5.1 Example 1. Replicating backups to a network folder
Consider the following scenario:
You want to perform a full backup of your machine manually.
You want to store the backups in Acronis Secure Zone (p. 185) on the machine.
You want to store a copy of the backups in a network folder.
In this scenario, create a backup plan with the Manual start scheme. When creating the backup plan,
specify Acronis Secure Zone in the Location field, select Full in the Backup type field, select the
Replicate newly created backup to another location check box, and then specify the network folder
in the 2nd location field.
Result:
You can recover the machine’s volumes or files from a readily available local backup, which is
stored in a dedicated area of the hard disk.
You can recover the machine from the network folder if the machine’s hard disk drive fails.
4.5.5.2 Example 2. Limiting the age and total size of stored backups
Consider the following scenario:
You want to perform a weekly full backup of your machine.
You want to keep all backups that are younger than a month.
You want to keep even older backups, as long as the total size of all backups stays below 200 GB.
In this scenario, create a backup plan with the Custom scheme. When creating the backup plan,
specify a weekly schedule for the full backup. In Clean up archive, select Using retention rules.
Click Retention rules, select the Backups older than and the Archive size greater than check boxes,
and specify respectively 1 month and 200 GB. In If the specified conditions are met, select Delete
the oldest backups.
Click OK. In Apply retention rules, select the After backup check box.
Result:
Backups that are younger than one month are kept, regardless of their total size.
97 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 98

Backups that are older than one month are kept only if the total size of all backups (older plus
younger) does not exceed 200 GB. Otherwise, the software deletes some or all of the older
backups, starting from the oldest one.
4.5.5.3 Example 3. Replicating backups to the cloud storage
This example assumes that you have activated (p. 423) a cloud backup subscription (p. 407) for the
machine that you are backing up.
The following scenario assumes that the amount of data you want to back up is relatively small. For
larger backups, see “Replicating large amounts of data to the cloud storage” later in this section.
Consider the following scenario:
You want to occasionally back up your machine to a local folder.
You want to keep a copy of the resulting archive off-site in Acronis Cloud Storage.
No matter when you start the backup, you want the replication to take place outside working
hours, when demand on the Internet connection is lower.
In this scenario, create a backup plan with the desired backup scheme. When creating the backup
plan, specify a local folder in the Location field. Select the Replicate newly created backup to
another location check box, and then specify the cloud storage in the 2nd location field.
In Backup options, go to Replication/cleanup inactivity time (p. 120), and specify the working hours
(for example, Monday through Friday from 8:00 until 17:00).
Result:
After the backup plan starts, the data is backed up to the local folder.
If the backup finishes outside the working hours, replication starts immediately. Otherwise,
replication is postponed until the end of the working hours.
Note: In the cloud storage, the second and further backups of an archive will always be incremental, no matter
what type they are in the original location. This leads to efficient use of storage space for your cloud backup
subscription.
Replicating large amounts of data to the cloud storage
If you are planning to back up 500 GB of data or more, you may want to send the first backup to the
cloud storage on a physical hard drive. This option is provided by the Initial Seeding service (p. 411)
which you can buy in addition to your cloud backup subscription.
The Initial Seeding service might be unavailable in your region. To find more information, click here:
http://kb.acronis.com/content/15118.
During the subsequent backups, only changes to the original data will be sent to the cloud storage
and will not affect network traffic as much.
In this scenario, create a backup plan with the Initial seeding scheme. When creating the backup plan,
specify a local folder in the Location field. This can be a folder on the hard drive that you are going to
send. For more details, see “How to perform initial seeding?” (p. 413).
After you have sent the hard drive and the order status becomes The data upload has been
completed, edit the backup plan. Change the backup scheme, destination, and replication settings to
those previously described in this section.
98 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 99

The updated backup plan will produce backups that will be replicated to the cloud storage outside
working hours.
4.5.5.4 Example 4. Moving older backups to tapes
Consider the following scenario:
You want to perform a daily backup of your machine.
You want to store the backups locally for one week.
You want to move the backups that are older than one week to a tape device.
Such scenario is sometimes called disk staging, or D2D2T (disk-to-disk-to-tape).
In this scenario, create a backup plan with the Simple scheme and a daily schedule. (All backups will
be full by default.) When creating the backup plan, specify a local folder or Acronis Secure Zone in
the Location field. Under Retention rules, select Move backups older than 1 week. Then, specify the
tape device in the 2nd location field.
Make sure that the tape device is ready to work. The preparation steps are described in the "Backing
up a machine to a directly attached tape device" (p. 196) section.
Result:
After a backup is completed, the agent checks for backups that need to be moved.
The agent moves the backups that are older than one week, by copying them to the tape device
and then deleting them from the original location.
You can eject tapes with backups and securely store them off-site. Once you select data for
recovery, Acronis Backup will prompt you which tapes to insert.
4.5.5.5 Example 5. Backing up to tapes within a narrow backup window
This example assumes that you are using Acronis Backup Advanced.
Consider the following scenario:
You want to back up servers every workday after working hours.
You want to do a monthly full backup on one of the workdays, and partial (incremental or
differential) backups on the other workdays.
You want to store the backups on a tape library.
The backup window for the servers is narrow, so they cannot be backed up to the tapes directly.
In this scenario, install Acronis Backup Storage Node and create two managed vaults: one on a hard
disk local to the storage node, and another on the tape library locally attached to it.
Create a centralized backup plan for all of the machines with the Grandfather-Father-Son (GFS)
scheme. When creating the backup plan, specify the vault on the hard disk in the Location field.
Under Backup type, select Full/Incremental/Differential.
For the primary location, in Keep backups, choose to keep monthly backups for one month (you
need to clear the Keep indefinitely check box). This way, the vault will serve as an intermediate,
short-term storage for the backups.
Select the Replicate newly created backup to another location check box, and then specify the vault
on the tape library in the 2nd location field. For the second location, select to keep monthly backups
indefinitely.
99 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
Page 100

Result:
Agents back up their machines to the vault on the hard disk.
The storage node copies the backups to the tape device. No CPU resource from the machines is
taken.
The lifetime of backups on the hard disk does not exceed one month. On the tape library, the
monthly backups are kept indefinitely.
4.6 How to disable backup cataloging
Cataloging a backup adds the contents of the backup to the data catalog as soon as the backup is
created. This process can be time-consuming, especially in environments with a large amount of
machines. Therefore, you may want to disable cataloging in the entire environment.
To disable backup cataloging
These steps can be performed in any order.
1. Modify the Windows registry (p. 406) on the management server.
2. Modify the Windows registry (p. 223) on storage nodes.
3. [On managed machines in an Active Directory domain] Load Acronis Administrative Template (p.
391) on the domain controller and configure the Cataloging setting in the Acronis Backup Agent
for Windows (p. 396) category of the template.
4. [On managed machines not included in an Active Directory domain] Connect the console to each
machine, go to Options > Machine options, and configure the Backup cataloging option.
4.7 Default backup options
Each Acronis agent has its own default backup options. Once an agent is installed, the default options
have pre-defined values, which are referred to as presets in the documentation. When creating a
backup plan, you can either use a default option, or override the default option with the custom
value that will be specific for this plan only.
You can also customize a default option itself by changing its value against the pre-defined one. The
new value will be used by default in all backup plans you will create later on this machine.
To view and change the default backup options, connect the console to the managed machine and
then select Options > Default backup and recovery options > Default backup options from the top
menu.
Availability of the backup options
The set of available backup options depends on:
The environment the agent operates in (Windows, Linux, bootable media).
The type of the data being backed up (disk, file).
The backup destination (networked location or local disk).
The backup scheme (manual start or using the scheduler).
The following table summarizes the availability of the backup options.
100 Copyright © Acronis International GmbH, 2002-2016
 Loading...
Loading...