Acer VERITON M661 User Manual

Intel Matrix Storage Manager Quick Guide for Acer Selected Veriton PC V1.1
Acer RAID Ready Systems
With Intel Matrix storage Manager
User's Guide
Acer Incorporated
Version: v1.1
Date: August, 2007
This document contains proprietary technical information, which is the property
of the Acer Incorporated and shall not be disclosed to others in whole or in
part, reproduced, copied, or used as the basis for design, manufacturing, or
sale of apparatus without written permission of Acer Incorporated.
1/21
Intel Matrix Storage Manager Quick Guide for Acer Selected Veriton PC V1.1
Revision History
Rev. # Date Explanation of Change Approved by
1.0 2007/08/15 First release
1.1 2007/8/22 Format and spelling enhancement
2/21

Intel Matrix Storage Manager Quick Guide for Acer Selected Veriton PC V1.1
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................................................... 4
2. RAID TECHNOLOGY AND SELECTION .................................................................................. 5
RAID0 (STRIPING) .............................................................................................................................. 5
RAID1 (MIRRORING) ............................................................................................................................ 6
RAID5 (STRIPING WITH PARITY) ....................................................................................................... 6
RAID10 (RAID1+0: STRIPING + MIRRORING) ............................................................................... 7
3. WARNINGS AND REMINDERS ................................................................................................... 9
4. ENABLING THE RAID FUNCTION WITH INTEL MATRIX STORAGE MANAGER CONSOLE
10
5. CONFIGURING RAID0 OR RAID1 ON YOUR RAID READY ACER PC ...................... 17
6. CONFIGURING AN EXISTING HDD AS A RAID0 OR RAID1 VOLUME .................... 18
7. MIGRATING FROM RAID0/1/10 TO RAID5 SYSTEM ................................................... 19
8. PRE-INSTALLATION OF THE INTEL® MATRIX STORAGE MANAGER DRIVER ...... 20
8.1 BUILD THE RAID DRIVER ON A FLOPPY DISK .......................................................................... 20
8.2 PRE-INSTALLATION USING THE "F6" PROCESS ...................................................................... 20
3/21

Intel Matrix Storage Manager Quick Guide for Acer Selected Veriton PC V1.1
1. Introduction
This document will assist customers in evaluating, configuring and enabling
RAID functionality on Acer RAID Ready platforms using the Intel® Matrix Storage
Manager software.
This document also describes RAID volume management such as creating, deleting,
and modifying volumes, common usage models, and any special notes necessary to
enable customers to develop their RAID-compatible products.
Selected high-end Acer desktop systems are configured as Intel RAID Ready
systems. A "RAID Ready" system can be upgraded to RAID0, RAID1, RAID5 or RAID10
using the RAID migration feature built into Intel Matrix Storage Manager 7.5.
This technology enables you to install additional SATA hard drives, and then
migrate a RAID Ready configuration to a RAID0, RAID1, RAID5 or RAID10
configuration.
Before you start to build your RAID system, please do check Section 3 "Warnings
and Reminders" for more detailed information. You can also check the on-line
user's manual for the Intel Matrix Storage manager in Windows for detailed RAID
function execution.
4/21

Intel Matrix Storage Manager Quick Guide for Acer Selected Veriton PC V1.1
2. RAID Technology and Selection
RAID (a redundant array of inexpensive disks, also later known as a redundant
array of independent disks) is a system that uses multiple hard drives to share
or replicate data among the drives. Depending on the version chosen, the benefits
of RAID are one or more of the following: greater capacity, reliability,
protection of data, and/or speed compared to a single drive.
RAID0 (striping)
• RAID0 splits data evenly across two or more disks with no parity information
for redundancy.
• Multiple files can be read (and written) simultaneously and transfer time
is improved dramatically, thus increasing throughput.
• RAID0 volume capacity = number of (HDDs) x (capacity of smallest HDD)
• RAID0 can be created with disks of differing sizes, but the storage space
added to the array by each disk is limited to the size of the smallest disk.
For example, if a 120 GB disk is striped together with a 100 GB disk, the
size of the array will be 200 GB.
Disk 1
Block 1
Block 3
Block 5
Block 7
Disk 2
Block 2
Block 4
Block 6
Block 8
Physicaldisks
Physicaldisk
120 GB
RAID 0
Physical disk
120 GB
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Block 4
Block 5
Block 6
Block 7
Block 8
Logicaldisks
Logical disk
240 GB
5/21

Intel Matrix Storage Manager Quick Guide for Acer Selected Veriton PC V1.1
RAID1 (mirroring)
• RAID1 creates an exact copy (or mirror) of a set of data on two or more
disks when reliability is more important than data capacity.
• A classic RAID1 mirrored pair contains two disks, which increases
reliability exponentially over a single disk.
o Mirroring allows continued operation of the system in the event of
one drive or array failing.
o Restoration can be performed using the mirrored copy.
o I/O performance may suffer during reconstruction due to the increased
activity between locations.
• RAID1 volume capacity = capacity of smallest HDD
• Such an array can only be as large as the smallest member disk.
Di sk 1
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Block 4
Di sk 2
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Block 4
Physicaldisks
Physical
disks
120 GB
RAID 1
Physical
disks
120 GB
Block 1
Block 2
Block 3
Block 4
Logicaldisk
Logical disks
120 GB
RAID5 (striping with parity)
• RAID5 uses block-level striping with parity data distributed across all
member disks.
• A RAID5 array can withstand a single disk failure without losing data or
access to data.
• RAID5 is a good all-round system that combines efficient storage with
excellent security and decent performance. It is ideal for file and
application servers.
• RAID5 volume capacity = [(number of HDDs) - 1] x (capacity of smallest HDD)
6/21
Intel Matrix Storage Manager Quick Guide for Acer Selected Veriton PC V1.1
Disk 1 Disk 2 Disk 3
Block A1
Block B1
Block Cp
Block A2
Block Bp
Block C1
Block Ap
Block B2
Block C2
Physical
disks
120 GB
Physical
disk
120 GB
Physical
disk
120 GB
Logical disks
240 GB
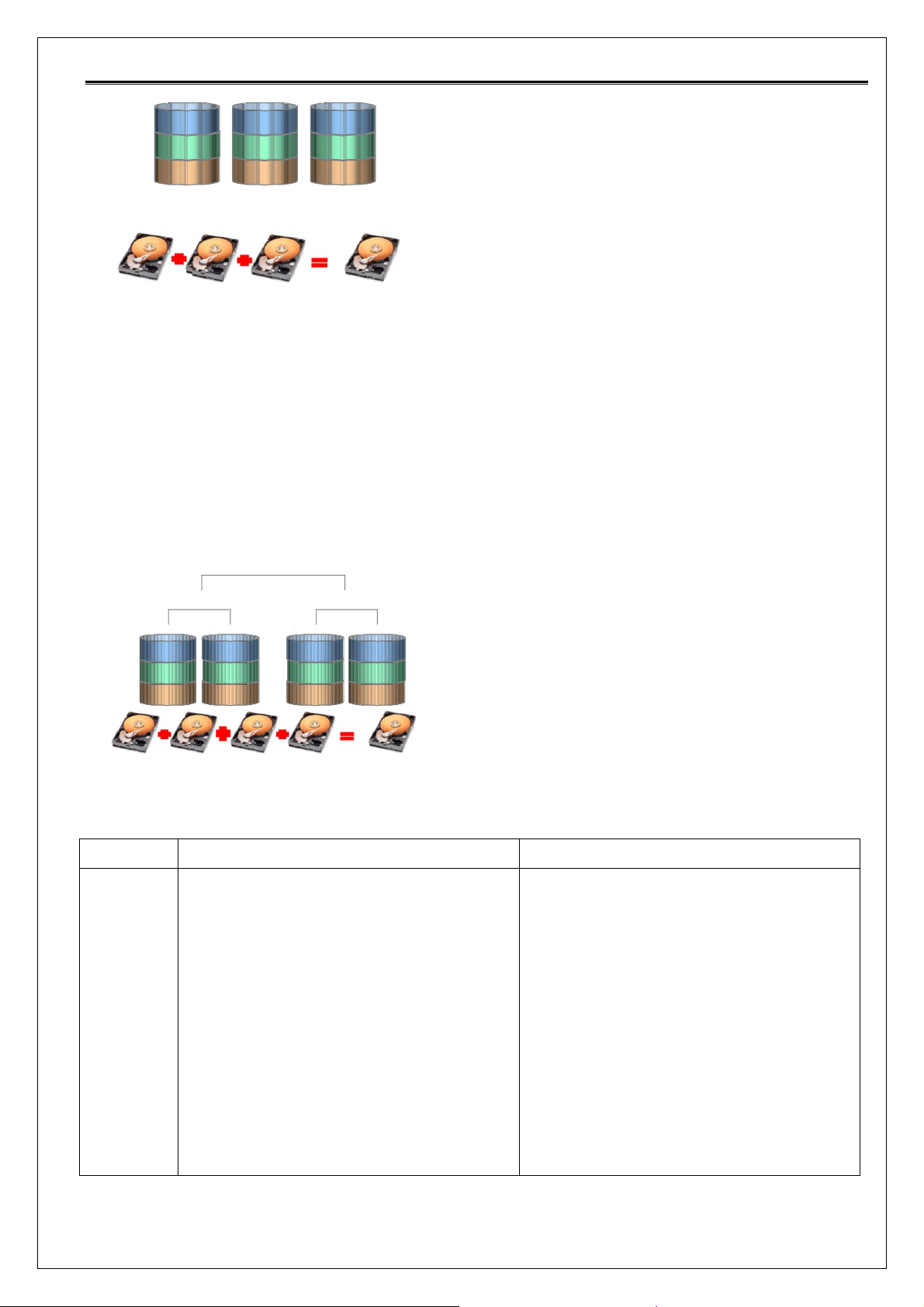
RAID10 (RAID1+0: striping + mirroring)
• A combination of RAID1 and RAID0 — mirroring and striping, but without
parity.
• RAID10 is used for both replicating and sharing data among disks.
• RAID10 is often the primary choice for high-load databases, because the
lack of parity to calculate gives it faster write speeds.
• RAID10 volume capacity = 2 x (capacity of smallest HDD)
RAID 0
RAID 1 RAID 1
Disk 1 Disk 2 Disk 3
Block A1
Block A3
Block A5
Block A1
Block A3
Block A5
Block A2
Block A4
Block A6
Disk 4
Block A2
Block A4
Block A6
Physical
disks
120 GB
RAID0
Physical
disks
120 GB
Physical
disks
120 GB
Physical
disks
120 GB
Logical disks
240 GB
Characteristics/Advantages Disadvantages
¾ RAID0 implements a striped
disk array, the data is broken
down into blocks and each
block is written to a separate
disk drive
¾ I/O performance is greatly
improved by spreading the I/O
load across many channels and
¾ Not a "True" RAID because it is
NOT fault-tolerant
¾ The failure of just one drive
will result in all data in an
array being lost
¾ Should never be used in
mission-critical
environments
drives
¾ Best performance is achieved
when data is striped across
7/21
 Loading...
Loading...