Page 1

Table of Contents
Chapter 1 Introduction of PD5N Features
¬ PD5N..........................................................................................1-2
l Specifications.........................................................................1-2
l Layout diagram......................................................................1-4
¯ System block diagram................................................................ 1-11
Chapter 2 Installing the Mainboard
¬ Standard External Connectors...................................................... 2-3
- Jumpers and Switches................................................................ 2-10
® Presentation and Installation of the CPU....................................2-11
¯ Installing System Memory
¡i
Chapter 3 Introduction of BIOS
¬ Standard CMOS Setup Menu.......................................................3-4
- BIOS Features Setup Menu .........................................................3-6
® Chipset Features Setup Menu.....................................................3-12
¯ Power Management Setup Menu................................................3-14
° PCI & Onboard I/O Setup..........................................................3-18
± Load BIOS Defaults ..................................................................3-23
² Load Setup Defaults ..................................................................3-23
³ Password Setting.......................................................................3-24
´ IDE HDD Auto Detection .........................................................3-35
Chapter 4 VGA Installation
Appendix A Quick Installation
DRAM Memory
¡j
.........2-21
Appendix B Intel Pentium CPUs
Appendix C AMD-K5 CPUs
Page 2

Chapter 1 -2
Appendix DCyrix 6x86 CPUs
Appendix EGeneral Discussion about HDD Installation
Appendix F Technical Support
Appendix GFlash BIOS User Instructions
Page 3

Introduction of PD5N Features 1-1
Chapter 1 Introduction of PD5N
Features
The PD5N have been especially designed for File server, Workstation and
Professional users. It can support a wide range of processors, including all
Intel CPUs (P54C) and Intel CPUs with MMX (P55C), as well as all AMDK5/K6 and Cyrix 6x86/6x86L/6x86MX CPUs. It also takes into account, as
much as possible, all future CPUs.
The PD5N uses DIP switches or jumpers.
The PD5N uses SIS 5598 series chipsets, and has 512K Level-2 Pipeline
Burst SRAM on board.
72-pin SIMM slots meet the requirements for all memory configurations
required by high level computing. The 72-pin SIMM slots support
traditional Fast Page and EDO DRAM as a memory standard for next
generation 64-bit systems. The 72-pin SIMM slots have been reserved to meet
requirements for both present and future upgrades.
The PD5N provides two Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports and meets the
Concurrent PCI Rev. 2.1 standard. It also supports IDE interface for Fast
HDD (Mode 0~4) and Ultra DMA/33, as well as IDE Bus Master. These
features also meet present and future interface standards and needs.
The PD5N Built-in high-performance 64 bit GUI accelerator. High
resolution modes including 1024 ¡Ñ 768 ¡Ñ 64K Hi colors and 1600 ¡Ñ
1200 ¡Ñ 256 colors. It also supports MPEG and live video playback.
System BIOS features include Plug-and-Play (PnP), Advanced
Configuration Power Interface (ACPI), the newest Desktop Management
Interface (DMI), as well as PD5N’s unique CPU operating frequency and
voltage setup feature in order to meet modern computing demands.
Page 4

1-2 Chapter 1
¬
Specifications
1. Support AT/ATX power supply
2. Adjustment for Frequency and Voltage
Using DIP switch or jumper wires to adjust the frequency and voltage
on the mainboard
3. Uses ZIF CPU Socket 7 for easy CPU installation
l Support switching power for CPU to get more stable environment
l Supports Intel Pentium CPUs:75~200MHz and P55C CPUs with
MMX (166~233MHz)
l Supports all AMD sixth generation AMD-K5™ CPUs:
75~166MHz, AMD-K6™ CPUs:166MHz, 200MHz , 233MHz
l Supports all Cyrix sixth generation 6x86™ CPUs: P120+, P133+,
P150+, P166+, P166+L, P200+, P200+L and 6x86MX
l Reserved circuitry supports future sixth generation CPUs
4. Chipset
l SIS 5598 chipset
l Supports standard version PCI 2.1
5. L2 Cache Memory
l 256K or 512K of cache memory (Pipeline Burst SRAM)
6. System DRAM
l Four 72-pin SIMM sockets: support FP and EDO DRAM
l Up to 384MB memory configuration possible
7. System BIOS
l AWARD BIOS
l Supports Plug-and-Play (PnP)
l Supports Advanced Configuration Power Interface (ACPI)
l Supports Desktop Management Interface (DMI)
8. Graphic and video Accelerator
l Built-in 64 bit GUI accelerator
l Supports video scaling, overlap and color space conversion
l Supports DDC1 and DDC2B Specification
l Video memory: shared system memory
9. Multi I/O features
Page 5

Introduction of PD5N Features 1-3
l
Two Universal Serial Bus (USB) ports
l
Four fast IDE channels (PIO mode 0~4, Ultra “DMA/33” and Bus
Master)
l One EPP/ECP parallel port and two 16550A serial ports
l
Two floppy disk drive connectors (FDD) (360K, 720K, 1.2M,
1.44M and 2.88M)
l
Support PS/2 type mouse
10. Other features
l
Standard AT architecture dimensions
l
Four ISA bus slots and four PCI bus slots
l
Supports 3-MODE for a special Japanese floppy disk drive
l
Supports two bootable hard disks--able to run two different
operating systems
l
Supports IDE interface CDROM and LS-120 type floppy disk drive
(Boot only)
l PD5N is using DIP switch to configure mainboard , the RED DIP
switch is using to setup the CPU voltage-VCORE and VIO. The
BLUE DIP switch is using to setup the CPU Frequency and Rating.
Note: All brand names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
Page 6
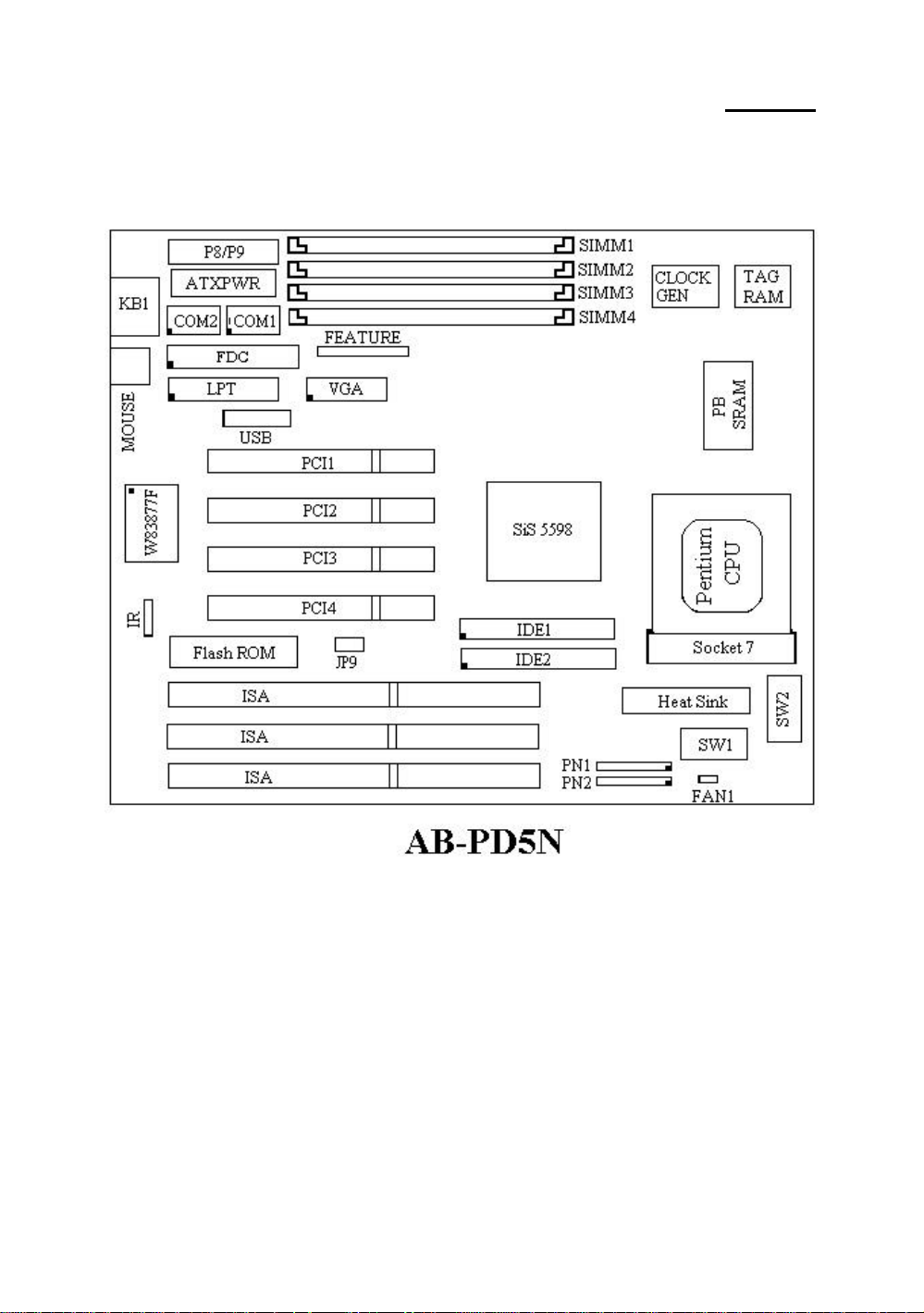
1-4 Chapter 1
-
Layout diagram
Fig 1-1 Layout diagram
Page 7
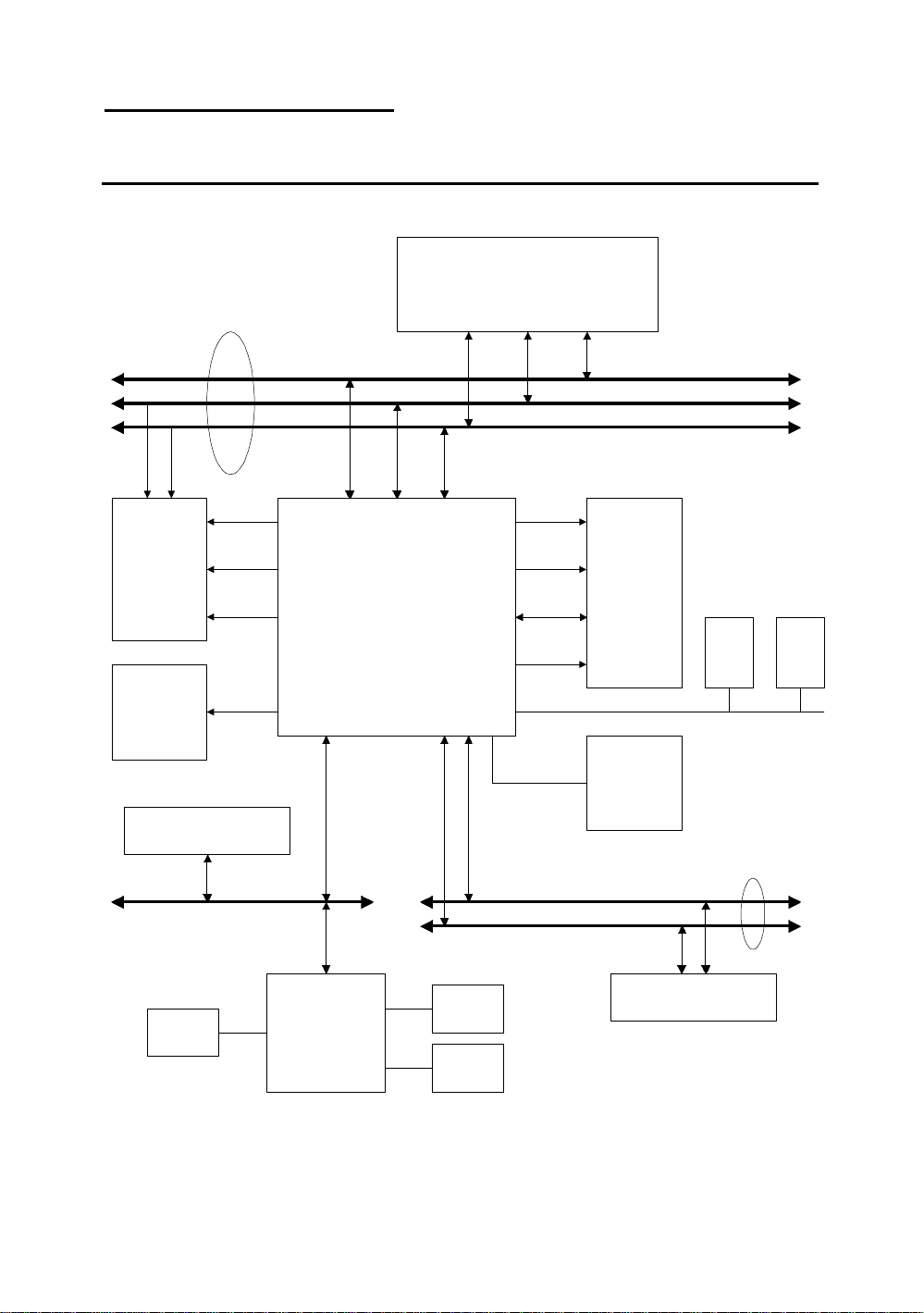
Introduction of PD5N Features 1-5
®
System block diagram
TM
Pentium Processor
3.3v
Host BUS
Control
Address
Data
CACHE
(SRAM)
TAG
CD ROM&
Hark Disk
ISA Device(s)
ISA BUS
Serial
Cntrl
Tag Cntrl
TIO[0..7]
Winbond
w83877f
SiS 5598
LPT
FDC
Addr
Cntrl
ECC
Data
Control
Address/Data
Main
Memory
(DRAM)
VGA
USB
Universal Serial Bus
PCI Device(s)
1
PCI BUS
USB
2
Fig. 1-4 System block diagram
Page 8

Page 9
Installing the Mainboard 2-1
Chapter 2 Installing the
Mainboard
This PD5N mainboard not only provides all standard equipment for classic
personal computers, but also provides great flexibility for meeting future
upgrade demands. This chapter will introduce step by step all the standard
equipment and will also present, as completely as possible future upgrade
capabilities. This mainboard is able to support all Intel Pentium including
P55C with MMX, Cyrix 6x86, 6x86L, 6x86MX and AMD-K5/K6 processors
now on the market. (For details, see specifications in Chapter 1.)
However, we cannot guarantee that the description given in this manual on the
circuitry of your mainboard will work for processors not listed in Chapter 1.
For example, the operating voltage of Cyrix’s next generation CPUs is unknown
at the present time. Thus we were not able to include these specifications in
your motherboard. We will supply further information about CPU support
when new CPUs arrive on the market.
This chapter is organized according the following features:
ΠStandard external connectors
• Jumpers and switches
Ž Presentation and Installing of the CPU.
• Installing the system memory.
NNNN
Before proceeding with the installation
Before installing the mainboard please be sure to turn off or disconnect the
power supply unit. Before making any modifications to the hardware
configuration of the mainboard, the power supply to any areas of the mainboard
you plan to modify should be turned off to avoid unnecessary damage to the
hardware.
Page 10

2-2 Chapter 2
&
User friendly instructions
Our objective is to enable the novice computer user to perform the
installation by themselves. We have attempted to write this document in a
very clear, concise and descriptive manner to help overcome any obstacles you
may face during installation. Please read our instructions carefully and
follow them carefully step-by-step.
Page 11
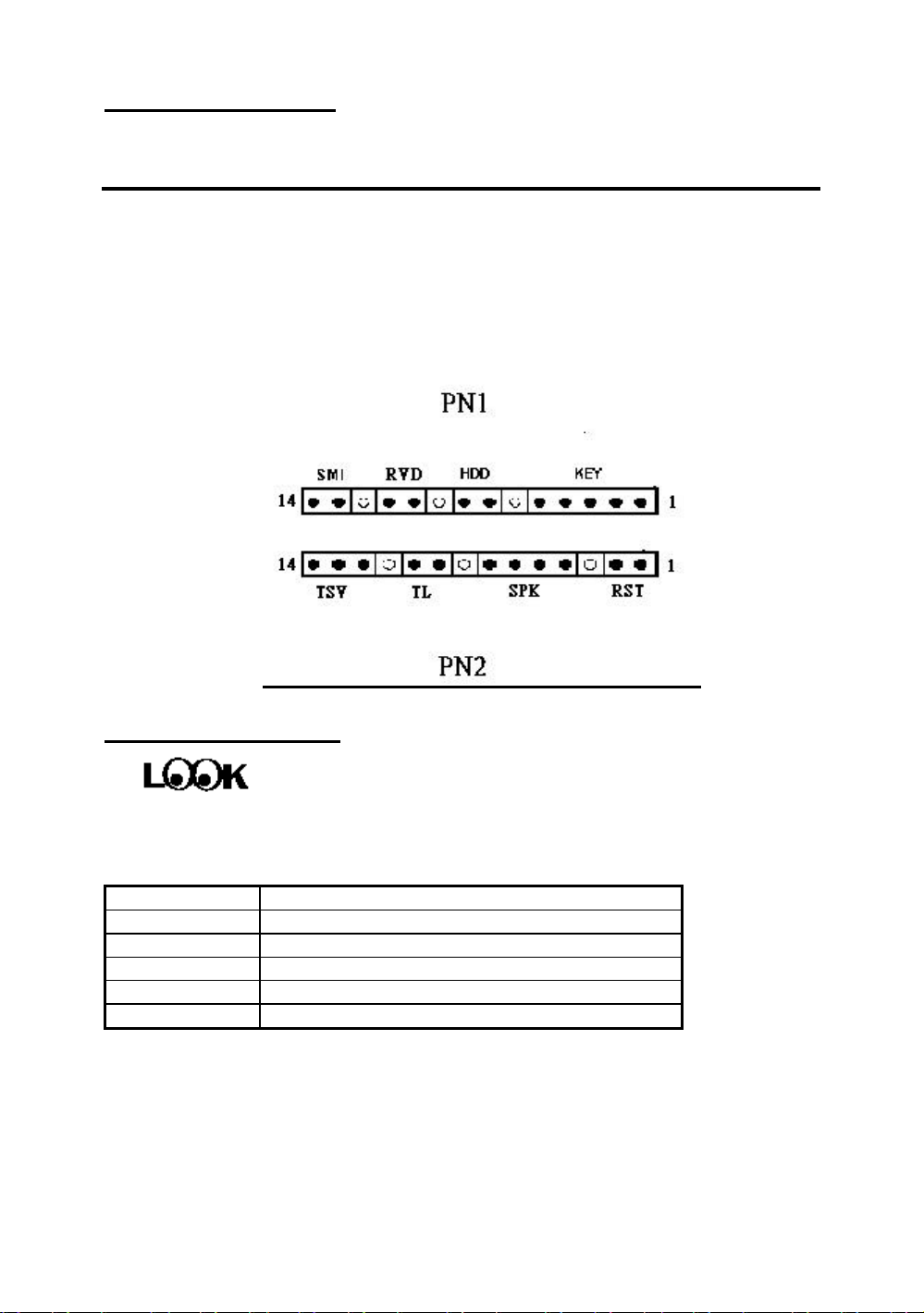
Installing the Mainboard 2-3
Knowledge
¬
Standard External Connectors
Inside the case of any computer several cables and plugs have to be
connected. These cables and plugs are usually connected one-by-one to
connectors located on the mainboard. You need to carefully pay attention to
any connection orientation the cables may have and, if any, notice the position of
the first pin of the connector. In the explanations that follow, we will
describe the significance of the first pin.
PN1 - Keylock connector Please pay attention to pin position and orientation
This connector has a specific orientation. Connect the five-thread keylock
connector cable to the PN1 connector pins on the mainboard.
Pin number Name or significance of signal
1 +5VDC
2 No connection
3 Ground
4 Keyboard inhibit Signal
5 Ground
Computer
The “keylock switch” is used to lock the computer’s keyboard.
This disables the keyboard so that unauthorized persons cannot
use it. When this function is in use, you will need to use
the unlock key to activate the keyboard.
Page 12
2-4 Chapter 2
PN1 - Power ON/OFF switch
There is no specific orientation. Since most cases do not support this feature,
most of you ignore this instruction.
Pin number Name or significance of the signal
10 Power on/off
11 Ground
PN1 - SMI Switch
There is no specific orientation. Connect the two-thread cable to the PN1
connector pins on the mainboard. Since most cases do not support this
feature, most of you ignore this instruction. Furthermore, this feature is not
necessary as it is already a part of the mainboard.
Pin number Name or significance of the signal
13 +5VDC
14 Ground
PN1 - HDD LED connector
This connector has a specific orientation. Connect the two-thread IDE LED
connector cable attached to the case to the IDE LED connector on the
mainboard.
Pin number Name or significance of signal
7 LED’s Cathode
8 LED’s Anode
PN2 - Speaker connector
There is no specific orientation. Connect the four-thread speaker cable to
the PN2 connector pins on the mainboard.
Pin number Name or significance of signal
4 +5VDC
5 Ground
6 Ground
7 Sound Signal
Page 13
Installing the Mainboard 2-5
PN2 - Hardware Reset connectors
There is no specific orientation. Connect the two-thread hardware reset
cable to the PN2 connector pins on the mainboard.
Pin number Name or significance of signal
1 Hardware reset signal
2 Ground
FAN1 - CPU Fan power connector
This has a specific orientation. Connect the three-threads CPU fan cable to the
FAN1 connector.
Pin number Name of the signal or signification
1 Ground
2 +12V
3 Ground
IR - Infrared remote Connectors (JP10)
Watch the pin number and the orientation.
This has a specific orientation. Your mainboard supports this feature, but you
must buy the infrared remote device as an option.
Pin number Name of the signal or signification
1 +5VDC
2 No connection
3 Receive data
4 Ground
5 Transmit data
ATXPWR - ATX Power input Connectors
These have a specific orientation. The three warning marks indicate that if you
make a mistake in pin number or connection orientation, you could destroy your
equipment. During installation, you just need to connect to the correct pins and
Page 14
2-6 Chapter 2
in the correct orientation, and to connect connector of the power supply unit to
the connector on the mainboard.
Pin number
1 +3.3VDC 11 +3.3VDC
2 +3.3VDC 12 -12VDC
3 Ground 13 Ground
4 +5VDC 14 PS_ON
5 Ground 15 Ground
6 +5VDC 16 Ground
7 Ground 17 Ground
8 POWERGOOD 18 -5VDC
9 +5VDC 19 +5VDC
10 +12VDC 20 +5VDC
Name of the signal or
signification
Pin number
Name of the signal or
signification
P8/P9 - AT Power input Connectors
These have a specific orientation. The three warning marks indicate that if you
make a mistake in pin number or connection orientation, you could destroy your
equipment. During installation, you just need to connect to the correct pins and
in the correct orientation, and to connect connectors P8 and P9 of the power
supply unit to the connectors on the mainboard.
Pin number
1 POWERGOOD 7 Ground
2 +5VDC 8 Ground
3 +12VDC 9 -5VDC
4 -12VDC 10 +5VDC
5 Ground 11 +5VDC
6 Ground 12 +5VDC
Name of the signal or
signification
Pin number
Name of the signal or
signification
Page 15
Installing the Mainboard 2-7
Mouse - PS/2 Mouse connector(J4)
Watch the pin number and the orientation
This has a specific orientation. Connect the six-threads PS/2 Mouse cable
provided to the connector on the mainboard.
Pin number Name of the signal or signification
1 Mouse data
2 No connection
3 Ground
4 +5VDC
Computer
5 Ground
6 Mouse clock
knowledge
The “PS/2 Mouse Port” is different from COM1 or COM2 serial
ports to which you can also connect a Mouse. This mainboard
features an extra PS/2 Mouse port, so when you buy a mouse,
be sure that it is a PS/2 Mouse before connecting it to this port.
But if you cannot find any PS/2 Mouse, you can still use COM1
or COM2 to connect a serial mouse to your computer.
KB1 - Keyboard Connector
This has an orientation pin. Connect your keyboard connector to the connector
on the mainboard.
Pin number Name of the signal or signification
1 Keyboard clock
2 Keyboard data
3 No connection
4 Ground
5 +5VDC
I/O Port connectors
Watch the pin number and the orientation
Connector name Pin number Name of the peripheral connected
IDE 1 40 IDE Channel 1
Page 16
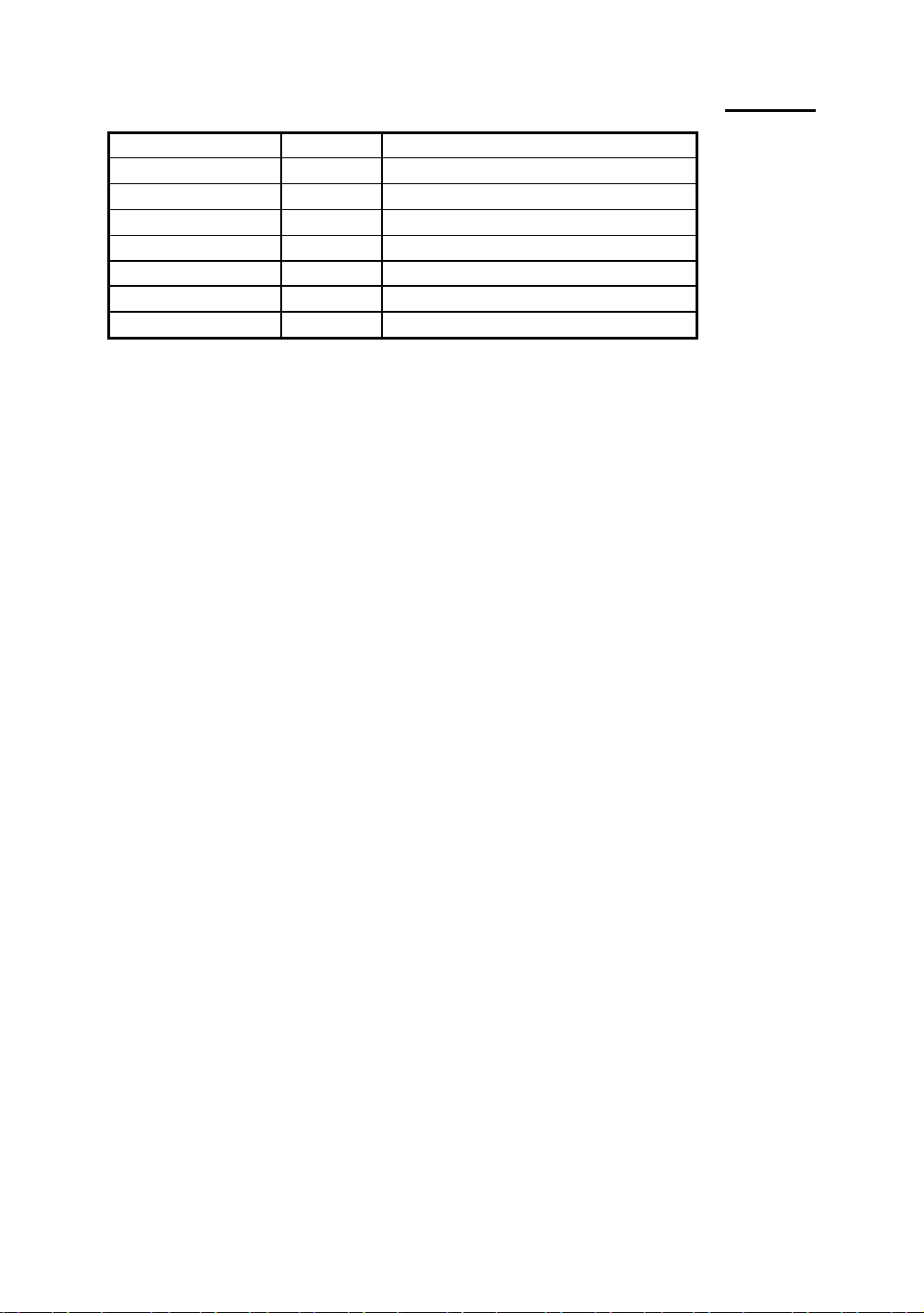
2-8 Chapter 2
IDE 2 40 IDE Channel 2
FDC 34 Floppy Disk connector
LPT 26 Parallel port connector
COM1 10 Serial port COM1connector
COM2 10 Serial port COM2connector
VGA 16 VGA connector
Feature 26 FEATURE connector
USB 16 Universal Serial Bus connector
Page 17

Installing the Mainboard 2-9
-
Jumpers and Switches
CCMOS(JP9) : Delete the contents of the CMOS
This jumper is set on pins 1 and 2 at the factory, in order for the
computer to function normally, so please do not change this setting.
The main feature of this jumper is to solve situations where the
computer crashes due to improper usage. For instance:
l You have forgotten the password you set.
l You have changed inappropriately the settings in the BIOS
menu.
l You want to change the version of flash BIOS.
All these errors are very serious, you must avoid them. But if you
have made one of these errors, this jumper can save your life. First
turn off the power supply and open the computer case, than place the
jumper on pins 2 and 3 in order to save your computer. But if you use
your computer normally, you should not need to use this feature.
After you have deleted the CMOS information, the computer is saved, but
you still have to go back to the BIOS Setup menu, and reset one by one all
the specifications: CPU, date, hour, FDD and HDD parameters. etc., before
your computer will get back into normal operation.
Page 18

2-10 Chapter 2
®
Presentation and Installation of the CPU
Since 1996, every two or three months, Intel adds new models to the
Pentium CPU series. That is why the CPU market is filled with a lot of different
models and brands. All CPUs have different electrical specifications. That’s why
installing a CPU is becoming more and more complex. You can’t help that,
because everybody wants to be able to upgrade its hardware. So, you have to
take a bit of time to read this section, in order to be able to install a cheaper and
better processor.
The PD5N mainboard does not only support all the CPUs listed in the
specifications, but also has reserved several circuits in order to be able to
support future processors. But before we go further in our presentation, we
must clarify that “we have only tested the CPUs listed in Chapter 1”, we cannot
guarantee that this board will be able to support future products, because we
cannot forecast future developments. But we will do our best to support any
possible CPU.
Related terminology :
External clock
Also referred to as the external CPU clock, or “Bus clock”, it is the input
clock of the CPU. For instance, Intel Pentium P90, P120 and P150 all have
a 60MHz external CPU clock, but have different internal clock multiplier
factors.
Clock multiplier factor
The real operation clock within the CPU is the multiple of the external
clock. We refer to this factor as the clock multiplier factor. The four
factors possible are 1.5, 2, 2.5 and 3. The factor differs from one CPU to
another. For instance, the Intel Pentium 166 CPU has a 66MHz external
clock, with a multiplier factor of 2.5, so that the speed of the internal clock
is 66MHz x 2.5.
Page 19

Installing the Mainboard 2-11
Internal clock
Also referred to as the real internal CPU clock, it is the actual internal
operating clock of the CPU. The Internal Clock is a multiple of the external
clock and of the clock multiplier factor. For instance, the Intel Pentium 90
CPU has a 60MHz external clock and its clock multiplier factor is 1.5; the
Intel Pentium P133 CPU has a 66MHz external clock and its clock
multiplier factor is 2.
Internal CPU clock = clock multiplier factor * external CPU clock
AT Bus clock
Also referred to as ISA SPEED, or AT CLOCK, or even ISA Bus clock.
Ten years ago, the original specification of AT Bus clock installed in the
first generation PC/AT computers was 8MHz, this means that there are
some interface cards which can only work at 8MHz. In order to guarantee
compatibility with older hardware, we still support 8MHz AT Bus clock,
but if your interface card is newer or faster, you can choose a higher speed
for the AT Bus clock, in order to increase the transmission rate of the
interface cards. But we recommend you not to be too ambitious. An 8MHz
setup ensures maximum compatibility.
CPU Voltage - Vcore and Vio
From the voltage point of view, 586 series CPU can be divided into two
categories: single voltage CPU and dual voltage CPUs. Single voltage
CPUs include: Intel Pentium P54C series, AMD-K5 and Cyrix 6x86, etc.
Dual voltage CPUs include: Intel P55C with MMX, future AMD-K6 CPUs,
Cyrix 6x86L and 6x86MX.
The voltage of dual voltage CPUs has two components: Vcore and Vio.
Vcore provides all the power for internal processing, and its power
consumption is quite important. Vio provides the power necessary for the
external interface of the CPU.
Page 20
2-12 Chapter 2
External ClockDS6DS7DS8
50MHZ
55MHZ
60MHZ
66MHZ
75MHZ
83MHZ
P-Rating
The P-Rating was defined by some manufacturers other than Intel to rate
the performance of their CPU in comparison with Intel Pentium CPUs. For
instance, Cyrix 6x86 P166+ has a higher actual speed compared with Intel
Pentium P166, its internal clock needs only 133MHz versus 166MHz for
Intel’s product. The main reason is that Cyrix has improved the internal
architecture of the 6x86 CPU, which means that with the same internal
clock speed, the actual clock speed will be different.
Having read the related terminology above, please refer to the information in
appendices B, C or D for the type and specifications of your own CPU. We
suggest that you note down these specifications, which will help you when you
install the CPU.
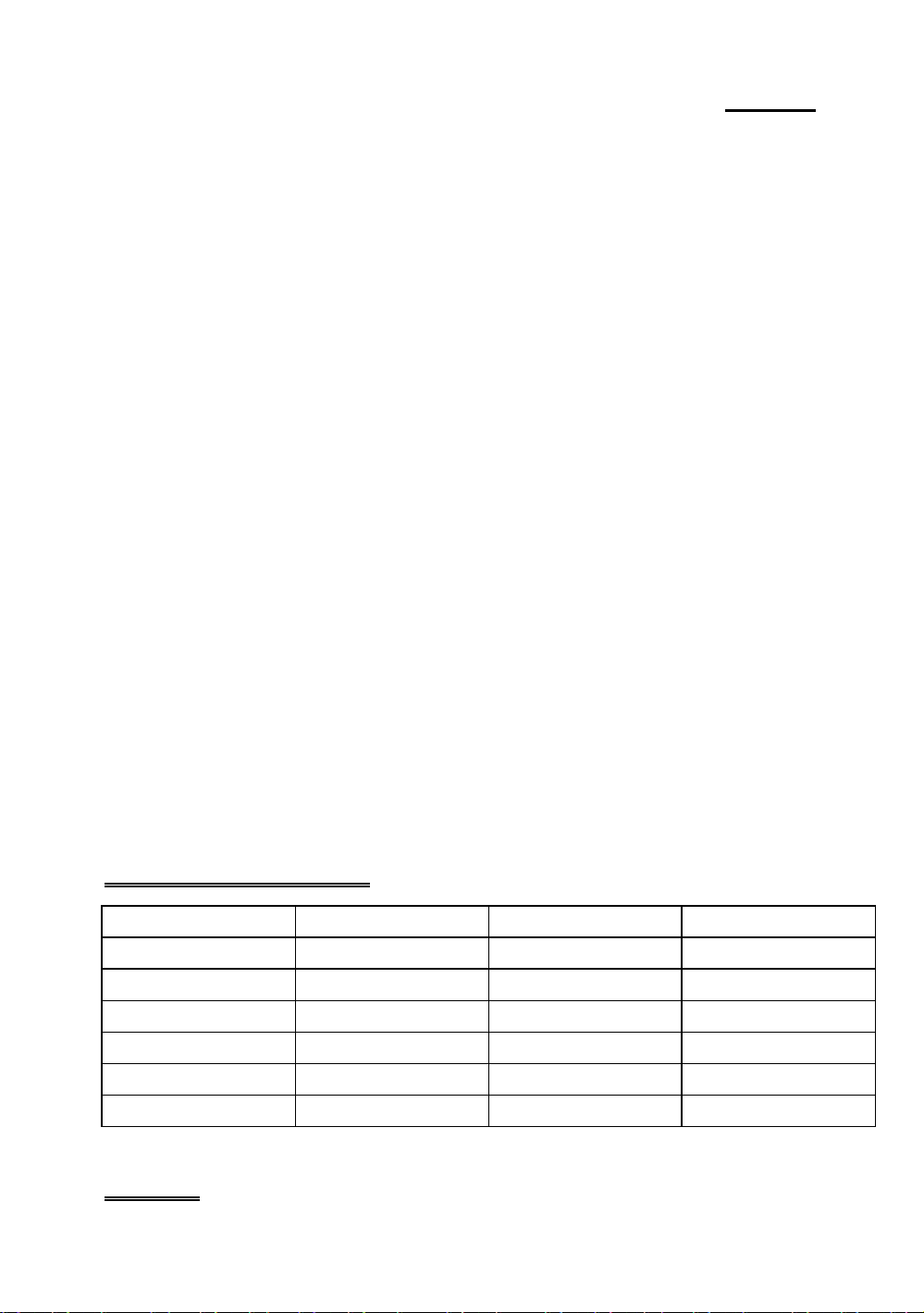
Voltage and Frequency Setup
PD5N are using DIP switches to setup the CPU Frequency and voltage
please make sure which kind of CPU and its frequency and voltage before
you setup.
There are two DIP switches on the mainboard, one is using to setup CPU
frequency (including external clock and rating parameter) which is called
SW2, another one is SW1 which is using to setup the CPU voltage.
1. PD5N CPU frequency setting (SW2)
The following tables will present the adjustment for all serials of 586 CPU,
Please setup the correct adjustment regarding the CPU type and brand.
Clock Chip:PLL52C61-01H
ON ON OFF
OFF OFF OFF
ON OFF OFF
OFF ON OFF
ON OFF ON
OFF ON ON
Intel CPU
Page 21
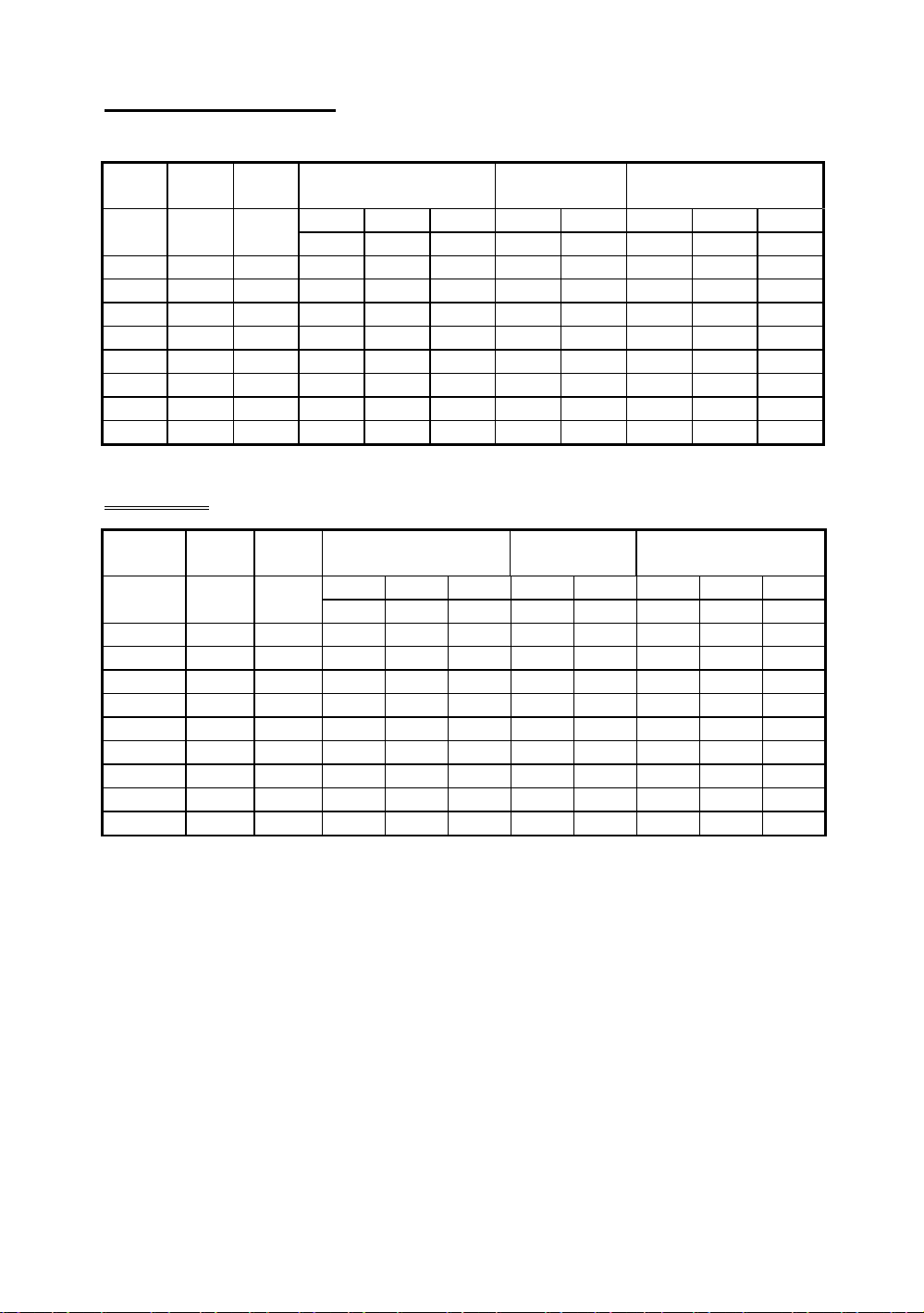
Installing the Mainboard 2-13
Intel Pentium
/ with MMX
External
clock
Internal
clock
External clock Factor Reserve External clock Frequency
DS1 DS2 DS3 DS4 DS5 DS6 DS7 DS8
P75 50MHz 75MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON OFF
P90 60MHz 90MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
P100 66MHz 100MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
P120 60MHz 120MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
P133 66MHz 133MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
P150 60MHz 150MHz ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
P166 66MHz 166MHz ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
P200 66MHz 200MHz OFF ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
P233 66MHz 233MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
AMD CPU
AMD
K5/K6
K5-PR75 50MHz 75MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON OFF
K5-PR90 60MHz 90MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
K5-PR100 66MHz 100MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
K5-PR120 60MHz 90MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
K5-PR133 66MHz 100MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
K5-PR150 60MHz 105MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
K5-PR166 66MHz 117MHz ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
K6-166 66MHz 166MHz ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
K6-200 66MHz 200MHz OFF ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
K6-233 66MHz 233MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
External
clock
Internal
clock
External clock Factor Reserve External clock Frequency
DS1 DS2 DS3 DS4 DS5 DS6 DS7 DS8
Page 22
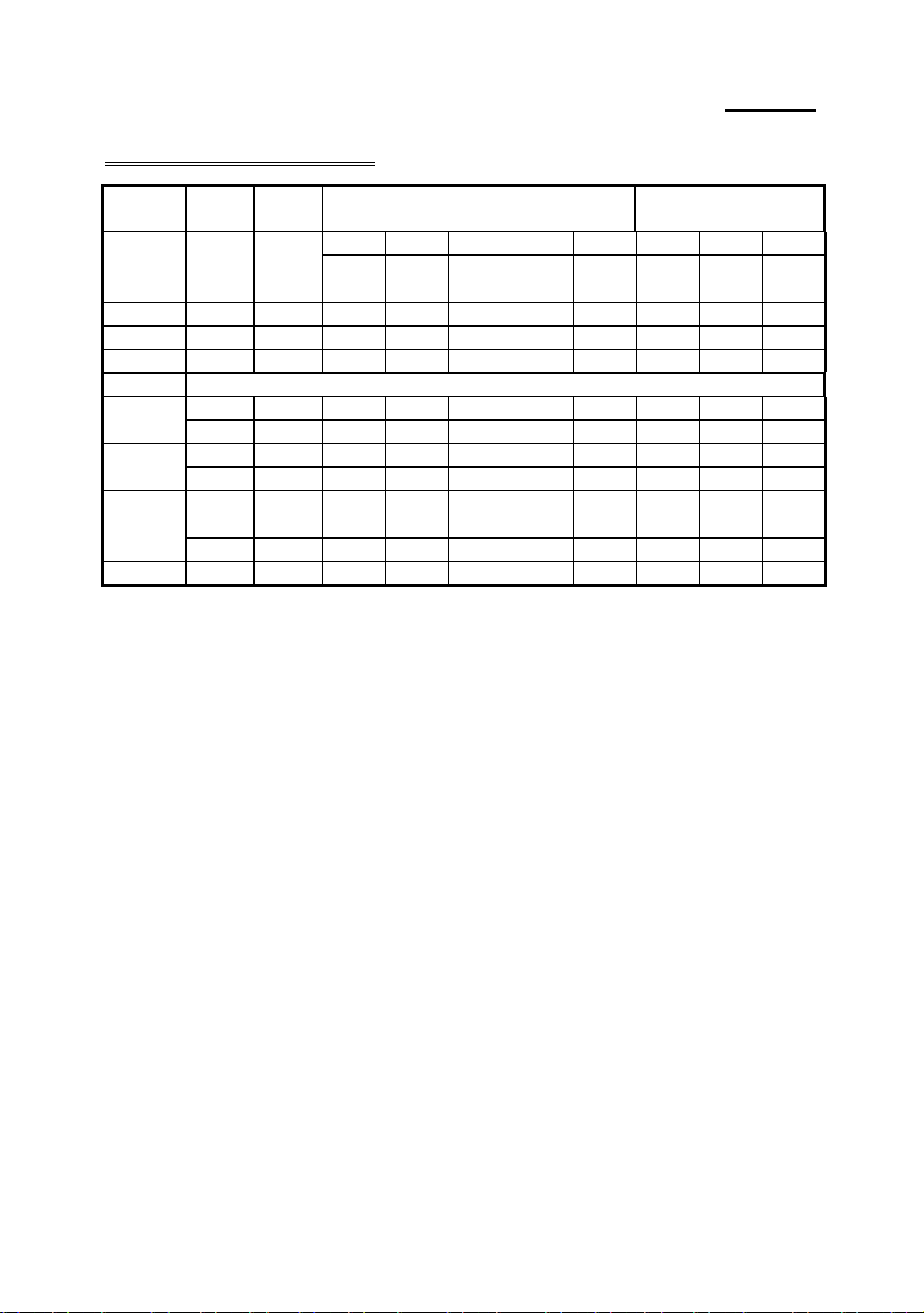
2-14 Chapter 2
Cyrix/IBM 6x86/6x86L CPU
Cyrix / IBM
6x86/6x86L
PR120+ 50MHz 100MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON OFF
PR133+ 55MHz 110MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF
PR150+ 60MHz 120MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
PR166+ 66MHz 133MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
PR200+ 75MHz 150MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF ON
6x86MX
PR166 66MHz 133MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
PR200 66MHz 166MHz ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
PR233 66MHz 200MHz OFF ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
PR266 66MHz 233MHz OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
External
clock
60MHz 150MHz ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON OFF OFF
75MHz 150MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON OFF ON
75MHz 188MHz ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON OFF ON
83MHz 166MHz ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON ON
Internal
clock
External clock Factor Reserve External clock Frequency
DS1 DS2 DS3 DS4 DS5 DS6 DS7 DS8
There are eight switches at SW2, DS1-DS3 is using to setup the rating
parameter, DS6-DS8 is using to setup the external clock, the following
table presents all of the adjustments for the setup combinations of CPU.
Page 23
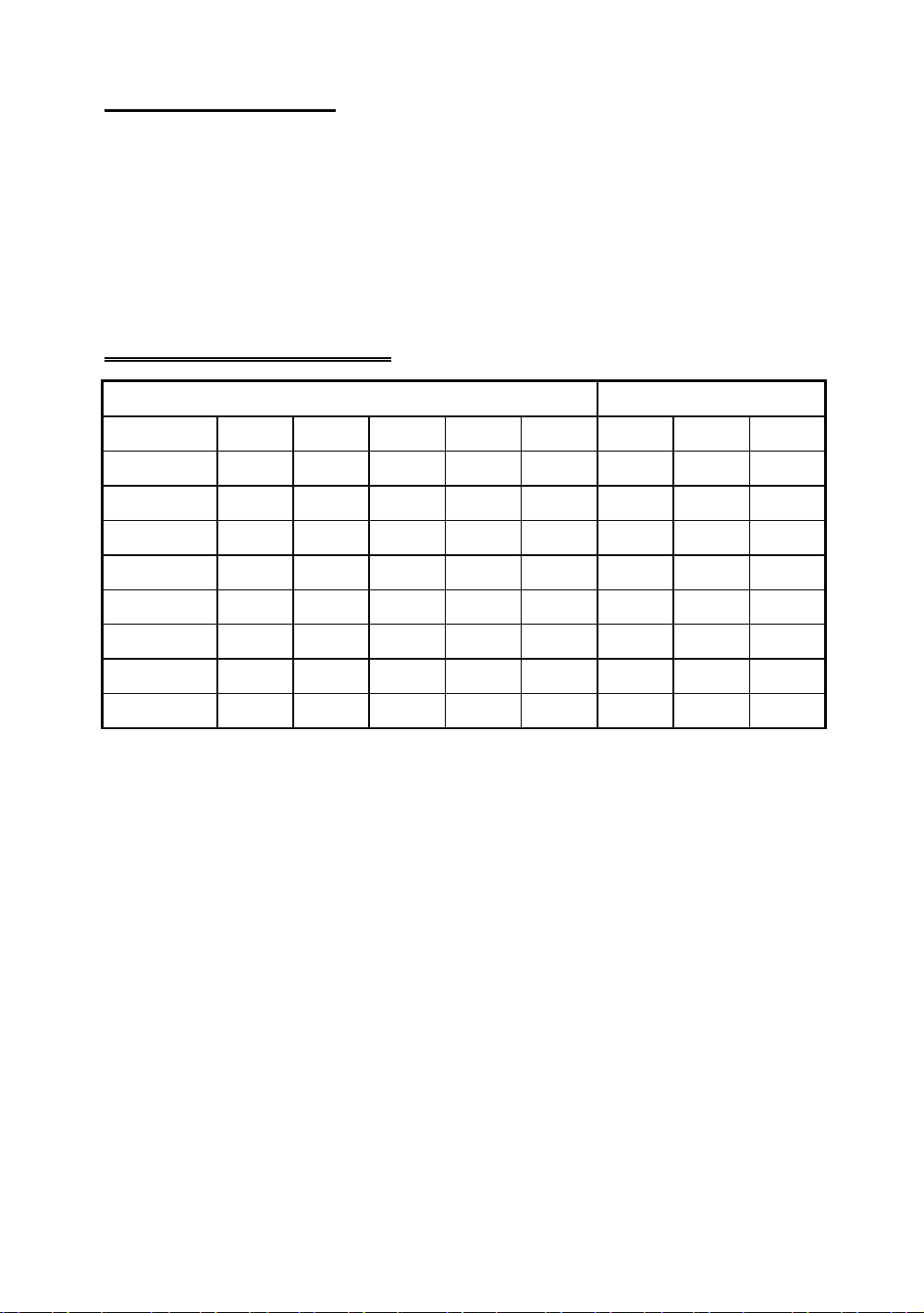
Installing the Mainboard 2-15
2.CPU Voltage and Setup (SW2)
For the voltage of 586 serials of CPU, there are two kinds of operation
mode depend different CPUs, single voltage and dual voltage. Please
make sure which kind of CPU and the working voltage that you used
before you install. The following table presents all of the adjustments
of voltage for all serials of 586 CPUs, Please setup the Vcore voltage if
the CPU you are using is single voltage.
SW1 CPU Vcore / Vio settings
VCORE VIO
Vcore/Vio VC1 VC2 VC3 VC4 VC5 VC6 VC7 VC8
3.5/3.3
3.4/3.3
3.3/3.3
3.2/3.38
2.9/3.38
2.8/3.38
2.7/3.38
2.6/3.38
¡i Note ¡j The Vcore of CPU voltage is design using switching power
ON ON ON ON OFF OFF ON OFF
ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON OFF
ON ON OFF ON OFF OFF ON OFF
ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON
ON OFF OFF ON OFF OFF OFF ON
ON OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF OFF ON
OFF ON ON ON OFF OFF OFF ON
OFF ON ON OFF OFF OFF OFF ON
supply, the Vio of CPU voltage is design using linear regulator
power supply. That is Vcore can provide more current and
voltage drop without occure more heat and high temperature.
The linear power supply will occure more heat and temperature.
Please setup the Vio voltage smaller than Vcore voltage if the single
voltage CPU is installed, it is using to make sure the CPU voltage is
provided by Vcore (Switching Power Supply), and make the CPU
more stable.
Page 24

2-16 Chapter 2
¯
Installing System Memory
¡i
DRAM
Memory
When this mainboard was designed, we not only have taken into account
the present needs, but we have also tried to care about demands for future
upgrades:
2. 72-pin SIMM sockets:
PD5N support four 72 pin SIMM sockets
3. Easy installation
Besides the features mentioned above, you can use simultaneously 72-pin
SIMM modules, but you will rarely encounter this kind of configuration. Before
you proceed with installation, be patient, first read what follows:
1. Factory default setting of the mainboard is for 60ns FP or EDO
¡j
You just need to insert the modules, without the help of God. Isn’t it
great?
modules.
If your memory modules are faster than 60ns, say 45ns, you can modify
the BIOS settings in order to speed up the operating speed of the
system. But if you don’t want to modify these settings, or if you don’t
know how to modify them, it’s no big deal.
But if you set the external CPU clock at 66MHz or more, we
recommend you use 60ns or even faster DRAM modules.
2. Memory error check and correction do not support this feature on
this mainboard.
The SIS 5598 chipset does not support this feature, since the memory
error check and correction feature may not be effective, and since you
cannot easily find memory modules with memory check and correction
feature, this mainboard does not support it.
Page 25

Installing the Mainboard 2-17
3. Maximum memory capacity 384M bytes supported by this
mainboard.
¡i
Computer
knowledge
Relationships between memory modules and Pentium
CPUs
Pentium, Cyrix 6x86 and AMD-K5/K6 are all 64 bit CPUs, but
72-pin SIMM modules are only 32-bit. That’s why they have to
be used in pairs, because the CPU will always be only able to see
64 bits. This means that 72-pin SIMM modules have to be
installed in pairs. For instance, SIMM1 and SIMM2 must form a
pair, and SIMM3 and SIMM4 must form another pair. Of
course, the two members of a pair must be of the same kind
¡i EDO or FP DRAM ¡j , and you cannot use pairs from
different “species”.
But the PD5N support different “pairs” and use different type of
memory modules, notice:
¡j
l ¡i SIMM1 and SIMM2 ¡j must use the same
memory type, as well as ¡i SIMM3 and
SIMM4 ¡j .
l ¡i SIMM1 and SIMM2 ¡j use the same memory
type, and ¡i SIMM3 and SIMM4 ¡j can use
the same type, or a different type, in order to permit you
to obtain the best speed configuration for each “single”
pair, and to make the system work at its maximum
capacity. If one memory pair is slower, it will have no
influence on the pair whose speed is higher.
After installing the DRAM, the BIOS of the mainboard will
automatically detect the size of the memory installed on the
mainboard. Below is a list of all the possible situations:
You use 72-pin SIMM modules:
l
The maximum memory size is 256M bytes.
l
Support possible for single density or double density memory
modules.
l Memory modules supported: 1Mx32 ¡i 4M ¡j , 2Mx32
¡i 8M ¡j, 4Mx32 ¡i 16M ¡j, 8Mx32 ¡i 32M ¡j
or 16Mx32 ¡i 64M ¡j .
Page 26

2-18 Chapter 2
l
You can also directly refer to table 2-1.
Page 27
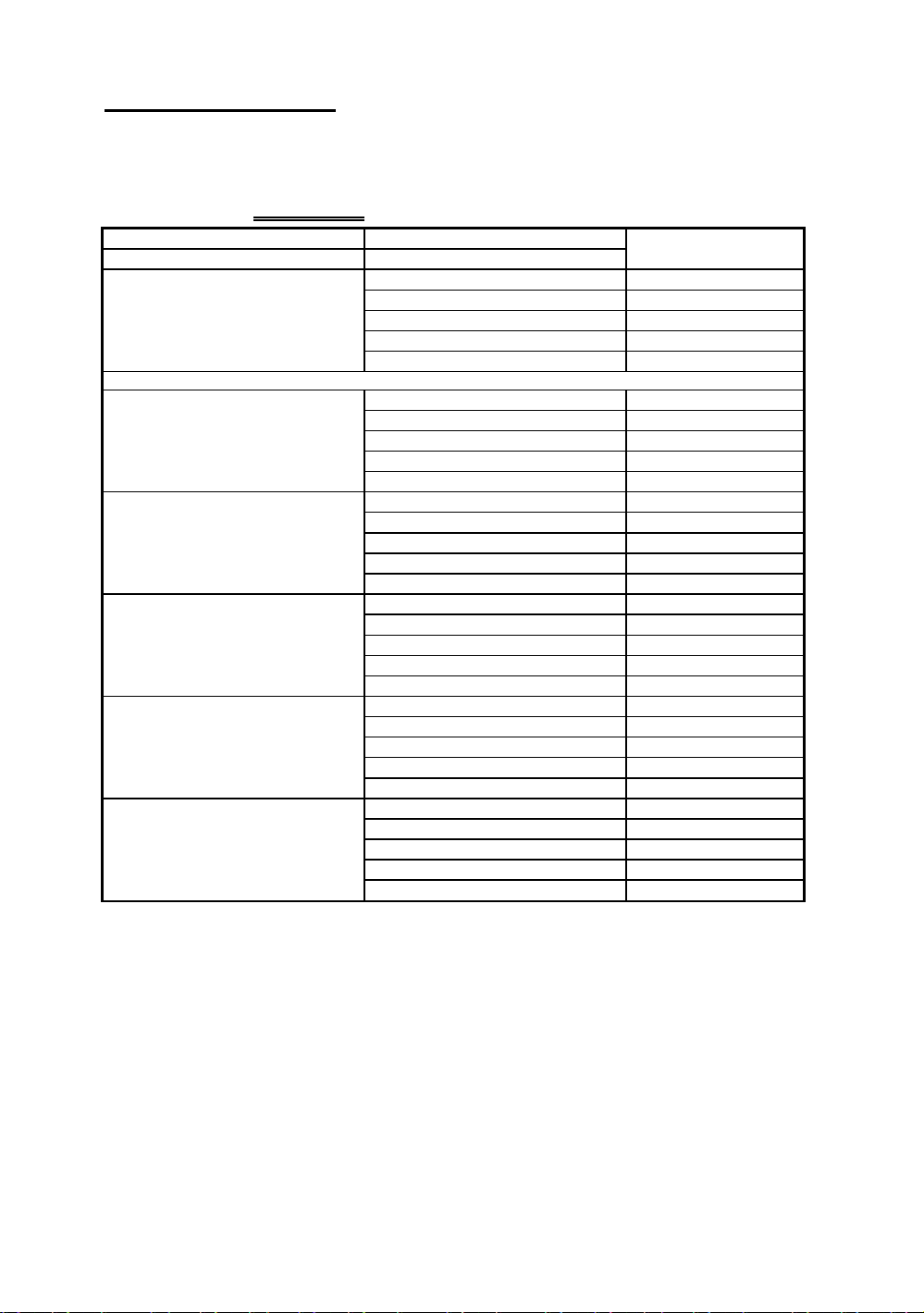
Installing the Mainboard 2-19
Table 2-1 72-pin SIMM Module Installation
¡i SIMM1, SIMM2 ¡j ¡i SIMM3, SIMM4 ¡j
1st¡i 2nd pair ¡j 2nd¡i 1
1Mx32 ¡i 4Mx2 ¡j
2Mx32 ¡i 8Mx2 ¡j
NO MODULE INSERTED
Since the installation described above is valid for the first pair as well as for the second pair, it will not be repeated.
1Mx32 ¡i 4Mx2 ¡j 4Mx32 ¡i 16Mx2 ¡j
2Mx32 ¡i 8Mx2 ¡j 4Mx32 ¡i 16Mx2 ¡j
4Mx32 ¡i 16Mx2 ¡j 4Mx32 ¡i 16Mx2 ¡j
8Mx32 ¡i 32Mx2 ¡j 4Mx32 ¡i 16Mx2 ¡j
16Mx32 ¡i 64Mx2 ¡j 4Mx32 ¡i 16Mx2 ¡j
4Mx32 ¡i 16Mx2 ¡j
8Mx32 ¡i 32Mx2 ¡j
16Mx32 ¡i 64Mx2 ¡j
1Mx32 ¡i 4Mx2 ¡j
2Mx32 ¡i 8Mx2 ¡j
8Mx32 ¡i 32Mx2 ¡j
16Mx32 ¡i 64Mx2 ¡j
1Mx32 ¡i 4Mx2 ¡j
2Mx32 ¡i 8Mx2 ¡j
8Mx32 ¡i 32Mx2 ¡j
16Mx32 ¡i 64Mx2 ¡j
1Mx32 ¡i 4Mx2 ¡j
2Mx32 ¡i 8Mx2 ¡j
8Mx32 ¡i 32Mx2 ¡j
16Mx32 ¡i 64Mx2 ¡j
1Mx32 ¡i 4Mx2 ¡j
2Mx32 ¡i 8Mx2 ¡j
8Mx32 ¡i 32Mx2 ¡j
16Mx32 ¡i 64Mx2 ¡j
1Mx32 ¡i 4Mx2 ¡j
2Mx32 ¡i 8Mx2 ¡j
8Mx32 ¡i 32Mx2 ¡j
16Mx32 ¡i 64Mx2 ¡j
st
pair ¡j
Total memory size
8MB
16MB
32MB
64MB
128MB
16MB
24MB
40MB
72MB
136MB
24MB
32MB
48MB
80MB
144MB
40MB
48MB
64MB
96MB
160MB
72MB
80MB
96MB
128MB
192MB
136MB
144MB
160MB
192MB
256MB
Perhaps you have already found out the rules from the table above. This table,
we belive, contains all possible configurations. In fact, you just need to insert
two or four 72-pin SIMM modules in the socket to complete the installation.
Page 28

Page 29
Interuction of BIOS 3-1
Chapter 3 Introduction of BIOS
The BIOS is a program located on a Read-Only Memory chip on the
mainboard. This program will not be lost when you turn the computer off. This
program is also referred to as the boot program. It is the only channel for the
hardware circuit to communicate with the operating system. Its main function is
to manage the setup of the mainboard and interface cards parameters, including
simple parameters such as time, date, hard disk drive, as well as more complex
parameters such as hardware synchronization, device operating mode, CPU
SOFT MENU™ techniques, setup of CPU voltage and speed. The computer
will operate normally, or will operate at its best, only if all these parameters are
correctly configured through the BIOS.
M
Don’t change the parameters inside the BIOS unless you know what
you are doing
The parameters inside the BIOS are used to setup the hardware
synchronization or the device operating mode. If the parameters are not
correct, they will produce errors, the computer will crash, and sometimes you
will even not be able to boot the computer after it has crashed. We recommend
that you do not change the parameters inside the BIOS unless you are familiar
with them. If you are not able to boot your computer anymore, please refer to
the section “Erase CMOS data” in Chapter 2.
When you start the computer, it is controlled by the BIOS program. The
BIOS first operates an auto-diagnostic for all the necessary hardware,
configurates the parameters of the hardware synchronization, and detects all the
hardware. Only when these tasks are completed does it give up control of the
computer to the program of the next level, which is the operating system. Since
the BIOS is the only channel for hardware and software to communicate, it will
be the key factor to system stability, and to ensure that your system performs at
its best. After the BIOS has achieved the auto-diagnostic and auto-detection
operations, it will display the following message:
PRESS DEL TO ENTER SETUP
Page 30

3-2 Chapter 3
Three to five seconds after the message is displayed, if you press the Del
key, or if you press simultaneously the Ctrl Alt Esc keys, you will access the
BIOS Setup menu. At that moment, the BIOS will display the following
message:
Fig 3 BIOS Setup main menu
In the BIOS Setup main menu of Figure 3, you can see several options. We
will explain these options step by step in the following pages of this chapter, but
let us first see a short description of the function keys you may use here:
l Press Esc to quit the BIOS Setup.
l Press ¡ô¡õ¡÷¡ö (up, down, left, right) to choose, in the
main menu, the option you want to confirm or to modify.
l Press F10 when you have completed the setup of BIOS parameters to
save these parameters and to exit the BIOS Setup menu.
l Press Page Up/Page Down or +/- keys when you want to modify the
BIOS parameters for the active option.
Page 31

Interuction of BIOS 3-3
Computer
knowledge
CMOS DATA
Maybe you have heard somebody saying that their CMOS
DATA was lost. What is the CMOS? Is it important? The
CMOS is the memory used to store the BIOS parameters that
you have configured. This memory is passive. You can read its
data, and you can also store data in it. But this memory has to
be powered by a battery, in order to avoid any loss of its data
when the computer is turned off. Since you may have to
change the CMOS battery when it is out of power and indoing
so, you will loose all CMOS data, therefore, we recommend
that you write down all the parameters of your hardware, or to
put a label with these parameters on your hard disk.
Page 32

3-4 Chapter 3
¬
Standard CMOS Setup Menu
It is the basic configuration parameters of the BIOS. These parameters
include the settings of date, hour, VGA card, FDD and HDD.
Fig 3-2 Standard CMOS Setup Menu
l
Set up of HDD operating mode
LARGE
Since old operating systems were only able to support HDD whose capacity
was not bigger than 528MB, any hard disk with more than 528MB was
unusable. AWARD BIOS features a solution to this problem: you can,
according to your operating system, choose three operating modes:
NORMAL, LBA or LARGE.
ä Normal mode:
¡j
Standard normal mode supports hard disks of 528MB or less.
This mode directly uses positions indicated by Cylinders
(CYLS), Heads, and Sectors to access data.
¡i
NORMAL, LBA,
Page 33

Interuction of BIOS 3-5
ä LBA (Logical Block Addressing) mode:
LBA mode supports hard disk drives up to 8.4Giga. This mode
uses a different method to calculate the position of disk data to
be accessed. It translates Cylinders (CYLS), Heads and Sectors
into a logical address where data are located. The Cylinders,
Heads, and Sectors displayed in this menu do not reflect the
actual structure of the hard disk, they are just reference values
used to calculate actual positions. Currently, all high capacity
hard disks support this mode, that’s why we recommend you
use this mode. The HDD AUTODETECTION option in the
Main Menu will automatically detect the parameters of your
hard disk and the mode supported.
ä LARGE Mode:
When the number of cylinders (CYLs) of the hard disk exceeds
1024 and DOS is not able to support it, or if your operating
system does not support LBA mode, you should select this
mode.
l FDD supporting 3 Mode:
3 Mode floppy disk drives (FDD) are 3 1/2” drives used in Japanese
computer systems. If you need to access data stored in this kind of floppy,
you must select this mode, and of course you must have a 3 Mode floppy
drive.
2 For further information about HDD installation, refer to Appendix E.
Page 34

3-6 Chapter 3
-
BIOS Features Setup Menu
BIOS Features Setup Menu has already been set for maximum operation. If
you do not really understand each of the options in this menu, we recommend
you use default values.
In each item, you can press <F1> at any time to display all the options for
this item.
Fig 3-3 BIOS Features Setup
Virus Warning:
This item can be set as Enable or Disable.
When this feature is enabled, if there is any attempt from a software or an
application to access the boot sector or the partition table, the BIOS will
warn you that a boot virus is attempting to access to the hard disk.
CPU Internal Cache:
This item is used to Enable or to Disable the CPU internal cache. When the
cache is set at Disable, it is much slower, so the default setting for this item
is Enable. Some old and very bad programs will make the computer
malfunction or crash if the system speed is to high. In that case, you should
Disable this feature.
Page 35

Interuction of BIOS 3-7
CPU External Cache:
This item is used to enable or to disable the CPU external cache. When the
external cache is enabled, the system works faster. The default is Enable.
Quick power on self test:
After the computer has been powered on, the BIOS of the mainboard will
run a series of tests in order to check the system and its peripherals. If the
Quick power on self test feature is Enable, the BIOS will simplify the test
procedures in order to speed up the boot process. The default is Enable.
Boot Sequence:
When the computer boots up, it can load the operating system from floppy
drive A:, hard disk drive C:, SCSI disk drive or CD-ROM. There are many
options for the boot sequence:
ä A, C, SCSI
ä C, A, SCSI
ä C, CD-ROM, A
ä CD-ROM, C, A
ä D, A, SCSI (at least 2 IDE HDD can be used)
ä E, A, SCSI (at least 3 IDE HDD can be used)
ä F, A, SCSI (at least 4 IDE HDD can be used)
ä SCSI, A, C
ä SCSI, C, A
ä A, SCSI, C
ä LS120, C
Swap Floppy Drive:
This item can be set as Enable or Disable.
When this feature is enabled, you don’t need to open the computer case to
swap the position of floppy disk drive connectors. Drive A: can be set as
drive B:, and drive B: can be set as drive A:.
Boot Up Floppy Seek:
When computer boots up, the BIOS detects if the system has FDD or not.
When this item is enabled, if the BIOS detects no floppy drive, it will
display a floppy disk drive error message. If this item is disabled, the BIOS
will skip this test.
Boot Up NumLock Status:
Page 36

3-8 Chapter 3
ä On: At boot up, the Numeric Keypad is in numeric mode.
ä Off: At boot up, the Numeric Keypad is in cursor control mode.
IDE HDD Block Mode:
This item can be set as Enable or Disable.
Most of new hard disk drives (IDE drives) support multi-sector transfers.
This feature speeds up hard disk drive access performance and reduces the
time necessary to access data. When this item is enabled, the BIOS will
automatically detect if your hard disk drive supports this feature or not, and
will choose the right settings for you.
2 For further details about hard disk drive installation, refer to appendix E.
Typematic Rate Setting:
This item allows you to adjust the keystroke repeat rate. When enabled,
you can set the two keyboard typematic control that follow (Typematic
Rate and Typematic Rate Delay). If this item is disabled, the BIOS will use
the default setting.
Typematic Rate (Chars/Sec):
When you press a key continuously, the keyboard will repeat the keystroke
according to the rate you have set. (Unit: characters/second ¡^
Typematic Rate Delay (Msec):
When you press a key continuously, if you exceed the delay you have set
here, the keyboard will automatically repeat the keystroke according a
certain rate. (Unit: milliseconds)
Page 37

Interuction of BIOS 3-9
Security Option:
This option can be set to System or to Setup.
After you have created a password through PASSWORD SETTING, this
option will deny access to your system (System) or modification of
computer setup (BIOS Setup) by unauthorized users.
ä SYSTEM: When you choose System, a password is required each time
the computer boots up. If the correct password is not given, the system
will not start.
ä SETUP: When you choose Setup, a password is required only when
accessing the BIOS Setup. If you have not set a password in the
PASSWORD SETTING option, this option is not available.
Notice: Don’t forget your password. If you forget the password, you will
have to open the computer case and clear all information in the
CMOS before you can start up the system. But doing this, you
have to reset all the options you had set up before.
PCI /VGA Palette Snoop:
This option allows the BIOS to preview VGA Status, and to modify the
information delivered from the Feature Connector of the VGA card to the
MPEG Card. This option can solve the display inversion to black after you
have used the MPEG card.
Delay IDE Initial:
This item is using for support some old model or special type of hard disks
or CDROMs . Because the BIOS may not detect those kinds of
devices during system booting .
OS Select For DRAM > 64MB:
When the system memory is bigger than 64MB, the communication method
between the BIOS and the operating system will differ from one operating
system to another. If you use OS/2, select OS2; if you choose another
operating system, select Non-OS2.
Page 38

3-10 Chapter 3
Video BIOS Shadow:
This option is used to define whether the BIOS on the video card uses
shadow feature or not. You should set this option to Enable, otherwise the
display performance of the system will greatly decrease.
Shadowing address ranges (C8000-CBFFF Shadow):
This option allows you to decide if the memory block (BIOS) of an
interface card at the address C8000-CBFFF uses the shadow feature or not.
If you have no interface card using this memory block, don’t enable this
option.
Shadowing address ranges (CC000-CFFFF Shadow):
This option allows you to decide if the memory block (BIOS) of an
interface card at the address CC000-CFFFF uses the shadow feature or not.
If you have no interface card using this memory block, don’t enable this
option.
Shadowing address ranges (D0000-D3FFF Shadow):
This option allows you to decide if the memory block (BIOS) of an
interface card at the address D0000-D3FFF uses the shadow feature or not.
If you have no interface card using this memory block, don’t enable this
option.
Shadowing address ranges (D4000-D7FFF Shadow):
This option allows you to decide if the memory block (BIOS) of an
interface card at the address D4000-D7FFF uses the shadow feature or not.
If you have no interface card using this memory block, don’t enable this
option.
Shadowing address ranges (D8000-DBFFF Shadow):
This option allows you to decide if the memory block (BIOS) of an
interface card at the address D8000-DBFFF uses the shadow feature or not.
If you have no interface card using this memory block, don’t enable this
option.
Shadowing address ranges (DC000-DFFFF Shadow):
Page 39

Interuction of BIOS 3-11
This option allows you to decide if the memory block (BIOS) of an
interface card at the address DC000-DFFFF uses the shadow feature or not.
If you have no interface card using this memory block, don’t enable this
option.
SHADOW
Computer
knowledge
What is the SHADOW? The BIOS of standard video or
interface cards is stored in ROM, and it is often very slow.
With the Shadow feature, the CPU reads the BIOS on the
VGA card and copies it into RAM. When the CPU runs this
BIOS, the operation is speeded up.
Page 40

3-12 Chapter 3
®
Chipset Features Setup Menu
The Chipset Features Setup Menu is used to modify the contents of the
buffers in the chipset on the mainboard. Since the parameters of the buffers are
closely related to hardware, if the setup is not correct or false, the mainboard
will become unstable or you will not be able to boot up. If you don’t know the
hardware very well, use default values (use the LOAD SETUP DEFAULTS
option).
Fig 3-4 Chipset Features Setup
You can use the arrow keys to move between the items. Use "PgUP",
"PgDn", "+" and "-" to change the values. When you have finished setting up the
chipset, press "ESC" to go back to the main menu.
Auto Configuration:
This option allows (Enable) or prevents (Disable) the BIOS from using
default values for Auto Configuration. The BIOS default is Enable.
ä When you select Enable, the BIOS will automatically use the values
related to DRAM. You will not be able to set up the following options.
ä When you select Disable, you can manually set up DRAM options.
Attention:Unless you are very familiar with your computer and with the
DRAM configuration and speed, we recommend you not
change the DRAM options but enable this option.
Page 41

Interuction of BIOS 3-13
DRAM settings:
The other DRAM settings are all closely related to hardware. If you do not
understand this very well, don’t make any changes. Our BIOS is able to
autodetect the characteristics of your DRAM and to choose the best
settings.
Memory Hole At 15M-16M:
This option is used to free up the 15M-16M memory block. Some special
peripherals need to use a memory bloc located between 15M and 16M, and
this memory block has a size of 1M. We recommend that you disable this
option.
VGA Shared Memory Size:
This option is used to choose VGA Memory by shared system Memory and
at least need 1MB Memory for showing higher resolution. The setting buffer
allocated from 0.5/1/1.5/2/2.5/3/3.5/4MB.
There are small differences in the chipset feature setup according to
different mainboard models, but this has no influence upon performance. Our
default setup should be the best one. That is the reason why we do not describe
all the features of this menu.
Page 42

3-14 Chapter 3
¯
Power Management Setup Menu
The difference between Green PCs and traditional computers is that Green PCs
have a power management feature. With this feature, when the computer is powered on
but inactive, the power consumption is reduced in order to save energy. When the
computer operates normally, it is in Normal mode. In this mode, the Power Management
Program will control the access to video, parallel ports, serial ports and drives, and the
operating status of the keyboard, mouse and other device. These are referred to as
Power Management Events. In cases where none of these events occur, the system
enters the power saving mode. When one of the controlled events occurs, the system
immediately returns to normal mode and operates at its maximum speed. Power saving
modes can be divided into three modes according to their power consumption: Doze
Mode, Standby Mode , and Suspend Mode. The four modes proceed in the following
sequence:
Normal Mode===> Doze Mode===> Standby Mode===> Suspend Mode
The system consumption is reduced according the following sequence:
Normal > Doze > Standby > Suspend
1. In the Main Menu, select "Power Management Setup" and press "Enter". The
following screen is displayed:
Fig 3-5 Power Management Setup Menu
2. Use arrow keys to go to the item you want to configure. To change the
settings, use "PgUP", "PgDn", "+" and "-".
3. After you have configured the Power Management feature, press “Esc” to go
Page 43

Interuction of BIOS 3-15
back to the Main Menu.
We are now going to briefly explain the options in this menu:
Power Management:
Four options:
ä User Define
User Define defines the delay for accessing the power modes.
ä Disable
Disable Power Management features.
ä Min Saving
When the three saving modes are enabled, the system is set up for
minimum power savings.
Doze = 40 minutes
Standby = 40 minutes
Suspend = 40 minutes
ä Max Saving
When the three saving modes are enabled, the system is set up for
maximum power savings.
Doze = 20 seconds
Standby = 20 seconds
Suspend = 20 seconds
PM Control by APM:
Power Management is completely controlled by the APM.
APM stands for Advanced Power Mangement, it is a power management
standard set by Microsoft, Intel and other major manufacturers.
Video Off Method:
Three video off methods are available: "Blank", "V/H SYNC+Blank" and
"DPMS".
If this setting does not shut off the screen, select “Blank”. If your monitor
and video card support DMPS standard, select “DPMS”.
Page 44

3-16 Chapter 3
Video Off After:
Select the saving mode in which the video is switched off.
ä Always On
The video will never be switched off in no saving mode.
ä All Modes Off
The video will be switched off in all saving modes.
ä Standby
The video will only be switched off in Standby or Suspend mode.
ä Suspend
The video will only be switched off in Suspend mode.
CPU Fan Off In Suspend:
CPU fan can be turn off in suspend mode.
Power Up by Ring:
Special function supports by ATX power supply. To connect a external
EODEM with the build-in serial port, the system will be turned on when
telephone ring-up.
IDE HDD Power Down:
If the system has not accessed data on the hard disk drive during the
specified time period, the engine of the HDD will stop in order to save
electricity.
You can set 1 to 15 minutes or select Disable according to your use of the
HDD.
Doze Mode:
When the setting selected for "Power Management" is "User Define", you
can define for this mode any delay from 1 minute to 1 hour. If no power
management event occurs during this time period, meaning that computer is
inactive during this period, the system will enter the Doze power saving
mode.
If this mode is disabled, the system will enter the next mode in the sequence
(Standby or Suspend mode).
Standby Mode:
When the setting selected for "Power Management" is "User Define", you
Page 45

Interuction of BIOS 3-17
can define for this mode any delay from 1 minute to 1 hour. If no power
management event occurs during this time period, meaning the computer is
inactive during this period, the system will enter the Standby power saving
mode.
If this mode is disabled, the system will enter the next mode in the sequence
(Suspend mode).
Page 46

3-18 Chapter 3
Suspend Mode:
When the setting selected for "Power Management" is "User Define", you
can define for this mode any delay from 1 minute to 1 hour. If no power
management event occurs during this time period, meaning the computer is
inactive during this period, the system will enter the Suspend power saving
mode. The CPU stops working completely.
If this mode is disabled, the system will not enter the Suspend mode.
Power Management Setup Menu
When one of the speficied occurs, the count down made for entry in power
saving mode goes back to zero.
Since the computer will enter a power saving mode only after an inactivity
delay specified (time speficied for Doze, Standby and Suspend modes) and
after it has no activity, during this time period, any event will cause the
computer to re-count the time elapsed. Resume events are operations or
signals that cause the computer to resume time counting.
Page 47

Interuction of BIOS 3-19
±
PnP, PCI & Onboard I/O Setup
In this menu, you can change the INT# and IRQ of the PCI bus and the
onboard I/O device, I/O port address and other hardware settings.
Fig 3-6 PCI & Onboard I/O Setup
Force Update ESCD:
If you want to clear ESCD data next time you boot up, and ask the BIOS to
reset the settings for the Plug & Play ISA Card and the PCI Card, select
Enabled. But the next time you boot up, this option will automatically be set
as Disabled.
Computer
Knowledge
ESCD (Extended System Configuration Data)
The ESCD contains the IRQ, DMA, I/O Port, Memory
information of the system. This is a specification and a feature
specific to Plug & Play BIOS.
Resources Controlled By:
When you select Auto, the BIOS will automatically assign the IRQ and
DMA to PCI / ISA PnP . When this option is Manual, you can choose which
IRQ or DMA can assign to PCI / ISA PnP .
Page 48

3-20 Chapter 3
PCI IDE Card 2nd Channel:
This option can be enabled or disabled. BIOS default is Enable.
Since this channel uses IRQ15, if you want to use this channel, you have to
enable this option to make the BIOS assign IRQ15 to this channel.
PCI IDE Card IRQ Map to:
Three options are available for this item: PCI Auto, PCI-slotX and ISA.
ä PCI-Auto: The onboard BIOS auto-detects which PCI slot has an IDE
card inserted in.
ä PCI-slotX: Some old PCI IDE cards cannot be detected by the BIOS. If
the onboard BIOS cannot detect a PCE IDE card, you have to specify
on which PCI slot the IDE card is inserted, to make the BIOS assign
IRQ14 for use by the interrupt number (INT#) of this PCI slot.
ä ISA: If you select ISA, it means that your PCI IDE card features a
“paddleboard” and a cable that can be connected to IRQ on the ISA slot,
because the BIOS will not assign any IRQ to this PCI slot.
Attention:Primary Channel and Secondary Channel : The BIOS needs two
independent interrupt number (INT#) lines to be allocated to the
PCI IDE card. Be careful not to choose twice the same interrupt
number (INT#).
On Board FDD Controller:
This is to Enable or Disable the Onboard FDD Controller.
On board Serial Port 1:
This is used to specify the I/O address and IRQ of Serial Port 1. Five
options are available: Disable, 3F8h/IRQ4, 2F8h/IRQ3, 3E8h/IRQ4 or
2E8h/IRQ3.
On board Serial Port 2:
This is used to specify the I/O address and IRQ of Serial Port 2. Five
options are available: Disable, 3F8h/IRQ4, 2F8h/IRQ3, 3E8h/IRQ4 or
2E8h/IRQ3.
Page 49

Interuction of BIOS 3-21
Attention:Do not select the same I/O address and IRQ for the two serial
ports, otherwise the serial ports will not be able to operate
normally.
/ Onboard IR Function:
Onboard serial port 2 can support IR (Infrared) function. Three
options are available:
ä Disable: No support for IR function.
ä IrDA (HPSIR) mode.
ä ASK IR (Amplitude Shift Keyed IR) mode.
/
IR Function Duplex:
Set the IR mode as Half or Full. Default is Half.
/
RxD , TxD Active:
Set IR transmission/reception polarity as High or Low.
On board parallel Port:
Set the I/O address and IRQ of the onboard parallel port. Four options are
available: Disable, 3BCh/IRQ7, 278h/IRQ5 and 378h/IRQ7. Default is
378h/IRQ7.
/
Parallel Port Mode:
Can be set as ECP, ECP+EPP, or Normal (SPP) mode. Default is
Normal (SPP) mode.
/ ECP Mode Use DMA:
When the mode selected for the onboard parallel port is ECP, the
DMA channel selected can be Channel 1 or Channel 3.
/ EPP Mode Select:
When the mode selected for the onboard parallel port is EPP, two
EPP version options are available: EPP1.7 or EPP1.9 .
Page 50

3-22 Chapter 3
On board IDE Controller:
Onboard PCI IDE controller can be set as IDE-1, IDE-2, Both or Disable.
/ Master drive PIO Mode:
ä Auto: the BIOS can auto-detect the PIO mode of the HDD in
order to set its data transfer rate. (Default)
ä Mode 0~Mode 4: User can specify the PIO mode of the HDD in
order to set its data transfer rate.
/
Slave drive PIO Mode:
ä Auto: the BIOS can auto-detect the PIO mode of the HDD in
order to set its data transfer rate. (Default)
ä Mode 0~Mode 4: User can specify the PIO mode of the HDD in
order to set its data transfer rate.
MODE 0~4 reflects the HDD data transfer rate. The higher the
Computer
knowledge
MODE value is, the better is the HDD data transfer rate. But it
does not mean that you can select the highest MODE value
just as you like, you first have to be sure that your HDD
supports this MODE, otherwise the hard disk will not be able
to operate normally.
2 For further information about HDD installation, refer to Appendix E.
Page 51

Interuction of BIOS 3-23
±
Load BIOS Defaults
BIOS defaults are the reference settings that allow your system to work at
a comparatively low performance. When you choose the option, the following
message is displayed:
“Load BIOS Defaults (Y/N)? N”
If you want to use BIOS default values, press “Y”, than <Enter>.
²
Load Setup Defaults
Setup defaults are the settings that allow your system to operate at its
highest performance. When you choose this option, the following message is
displayed:
“Load Setup Defaults (Y/N)? N”
If you want to use BIOS Setup default values, press “Y”, than <Enter> to
complete the loading of the settings for best performance.
You should first load the best settings, than enter the CPU Soft Menu to
set up CPU parameters, otherwise the BIOS will replace set parameters by
default parameters.
Page 52

3-24 Chapter 3
³
Password Setting
This option allows you to set a password required to start the system
(System) or to access to the BIOS (Setup).
After you have set a password through the PASSWORD SETTING option,
you can enter the Security Option in the “BIOS Features Setup Menu” to select
the security level in order to prevent any unauthorized access.
Password setting procedure:
When you choose the Password setting option, the following message
is displayed:
“Enter Password:“
Type your password. When complete, press <Enter>. The following
message is displayed:
“Confirm Password:“
Type your password again. When complete, press <Enter>. The password
setting is completed.
Password clearing procedure:
When you select the Password setting option, the following message is
displayed:
“Enter Password:“
Press <Enter>, the message “Password Disable” is displayed. Press a key.
The password clearing procedure is completed.
Notice: Do not forget your password. If you forget it, you will have to
open the computer case, clear the contents of the CMOS, and
boot the system up again. But doing this, you must reset all your
settings.
Page 53

Interuction of BIOS 3-25
´
IDE HDD Auto Detection
After you have installed the hard disk, in old systems, you had to know the
hard disk specifications, such as the number of cylinders, heads and sectors, and
to enter the relevant information into the hard disk information section. If the
CMOS data were erased, and you had forgotten the hard disk specifications, it
was a great problem. But now, you can use this option to autodetect the hard
disk type and specifications, and the BIOS will automatically detect all the
relevant information and place them in the Hard Disk data section of the
Standard CMOS Setup Menu, in order to allow you to use your hard disk.
Page 54

Page 55

VGA Driver Setup 4-1
Chapter 4 VGA Driver Setup
DOS Utility
1.1. SVGAUTL.EXE
1.1.1 General Description
SVGAUTL.EXE is one of the utilities of PD5N. It supports three functions:
(1) Video Mode Setting
(2) Frame Rate Setting
(3) Power Saving Setting
You can use SVGAUTL.EXE to select the desired video mode. For 640x480,
800x600, 1024x768, and 1280x1024 resolutions, PD5N supports multiple frame
rates. If your monitor could synchronize with these frame rates, you can use
SVGAUTL.EXE to get advantage. PD5N also supports VESA DPMS Power
Saving Modes. SVGAUTL.EXE can help you to set the capability.
1.1.2 How to Use?
To use SVGAUTL.EXE,
(1) Type “SVGAUTL” in the directory where it resides.
For example:
A:\> SVGAUTL <Enter> (suppose SVGAUTL.EXE resides in Diskette
#1 ) or
D:\> MM\DOS\SVGAUTL <Enter> (suppose SVGAUTL.EXE resides in
CD-ROM )
(2) The Main Menu would appear and direct you to configure PD5/PD5N.
(3) When you complete configuration, you may save your preferences to
"AUTOEXEC.BAT” file and use it as your power-on (or hardware reset)
default environment.
Page 56

4-2 Chapter 4
1.1.3 What the Parameters Stand for?
The meaning of parameters used by SVGAUTL.EXE are explained below:
Syntax:
>SVGAUTL [/D:mode_no] [/F0:n0] [/F1:n1] [/F2:n2] [/F3:n3] [/PA:ta] [/PB:tb]
where
/D: Set the Video Mode to be mode_no which is a hex number.
For example:Set 1024x768 256 color graphic mode.
>SVGAUTL /D:38 <Enter>
/F0: For 640x480, set frame rate to be n0 Hz.
Three available frame rates are 60, 72, and 75 Hz.
For example:Set 640x480 graphic mode with 60Hz frame rate
>SVGAUTL /F0:60 <Enter>
/F1: For 800x600, set frame rate to be n1 Hz.
Four available frame rates are 56, 60, 72, and 75 Hz.
For example:Set 800x600 graphic mode with 72Hz frame rate.
>SVGAUTL /F1:72 <Enter>
/F2: For 1024x768, set frame rate to be n2 Hz.
Four available frame rates are 87 (Interlace), 60, 70, and 75 Hz.
For example:Set 1024x768 graphic mode with 60Hz frame rate.
>SVGAUTL /F2:60 <Enter>
/F3: For 1280x1024, set frame rate to be n3 Hz.
Two available frame rates are 87 (Interlace) and 60 Hz.
For example:Set 1280x1024 graphic mode with 60Hz frame rate.
>SVGAUTL /F3:60 <Enter>
/PA: Set Standby Timer to be ta minutes. (0 < ta < 15 min.)
For example:Set Standby Timer be 5 minutes.
>SVGAUTL /PA:5 <Enter>
/PB: Set Suspend Timer to be tb minutes. (0 < tb < 15 min.)
For example:Set Suspend Timer be 5 minutes.
>SVGAUTL /PB:5 <Enter>
Note:
(1) Suspend Time would be "ta + tb". (i.e. standby time + suspend time)
(2) The timers will not be very accurate and would just be around the time.
Page 57

VGA Driver Setup 4-3
1.2 Autodesk ADI 4.2 -Protected Mode
1.2.1.1 Unpack & Copy
To unpack and copy drivers to where they should resides, please follow the
following procedures:
(1) Run "INSTDRV.EXE" where it resides.
For example,
A:\> INSTDRV <Enter> (suppose INSTDRV.EXE resides in
Driver Disk #1 ) or
D:\> MM\DOS\INSTDRV <Enter> (suppose INSTDRV.EXE resides in
CD-ROM )
(2) In "SiS Super VGA Drivers Installation" menu, select "A. ADI 4.2" to
unpack and copy drivers.
(To select, type "A".)
(3) In "Unpack & Copy ADI 4.2 Drivers" screen,
keying the "drive:\directory" where these drivers would reside
(default C:\ADI42).
Program would unpack & copy all related driver files to where you assign.
(4) After "unpack and copy" completed, exit the INSTDRV.EXE program.
(5) Refer to Sec. 1.2.2 to Sec. 1.2.5 for the real installation procedures for each
program.
1.2.2 AutoCAD R11 Setup
(1) The following procedures assume that
1 - You have complete "unpack & copy" procedure.
2 - Your ADI 4.2 drivers are located in C:\ADI42.
(2) Add the following setting to your own batch file for AutoCAD R11 (say
ACADR11.BAT) or to your "AUTOEXEC.BAT" file:
SET DSPADI=\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP <Enter>
(3) Delete the configure file ACAD.CFG resides in \ACAD directory.
(4) Type
ACADR11 <Enter>
to configure your AutoCAD R11 system.
(5) In "Select Display Device:" item, choose "ADI P386 V4.0/4.1 display.".
(6) In "Select Display Resolution" screen, choose which display driver you want
to use.
(7) Go through the whole instructions, and the system would start with the
desired display setting.
Page 58

4-4 Chapter 4
1.2.3 AutoCAD R12 Setup
(1) The following procedures assume that
1 - You have complete "unpack & copy" procedure.
2 - Your SiS ADI 4.2 drivers are located in C:\ADI42.
3 - Your AutoCAD R12 program is located in C:\ACADR12.
4 - Your AutoCAD R12 default drivers are located in C:\ACADR12\DRV.
5 - Your AutoCAD R12 configure file ACAD.CFG is located in
C:\ACADR12.
(2) Copy the following driver file to C:\ACADR12\DRV:
RCPSIS.EXP
.
You may complete this step by
COPY C:\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP C:\ACADR12\DRV
(3) Delete your original ACAD.CFG file.
You may complete this step by
DEL C:\ACADR12\ACAD.CFG
(4) Restart your AutoCAD R12 program as usual.
(5) AutoCAD R12 will ask you to complete the configuration procedures since it
can't find the configure file ACAD.CFG.
(6) Follow the instructions of AutoCAD R12 to proceed configuration.
(7) In "Available Video Displays:" item, choose the "SiS Super VGA ADI V4.2
Display and Rendering driver" item.
(8) In "Select Display Resolution" screen, choose which display driver you want
to use.
(9) Go through the whole instructions, and the system would start with the
selected display setting.
Page 59

VGA Driver Setup 4-5
1.2.4 AutoShade R2.0 Setup
(1) The following procedures assume that
(a) You have complete "unpack & copy" procedure.
(b) Your ADI 4.2 drivers are located in C:\ADI42.
(2) Add the following settings to your batch file for AutoShade R2.0 (say
SHADE2.BAT) or to your "AUTOEXEC.BAT" file.
(a) For display driver setting,
SET DSPADI=\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP
(b) For rendering driver setting,
SET RDPADI=\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP
(3) Delete the configure file SHADE.CFG.
(4) Type
SHADE2 <Enter>
to re-configure the AutoShade.
(5) While prompting "Select display device:", choose "P386 AutoDesk Device
Interface display driver.".
(6) While prompting "Select rendering display driver:", choose "P386 AutoDesk
Device Interface rendering driver.".
(7) Go through all the instructions, the system would start with the desired
display setting.
Page 60

4-6 Chapter 4
1.2.5 3D Studio Version 3.0 Setup
(1) The following procedures assume that
1 - You have complete "unpack & copy" procedure.
2 - Your ADI 4.2 drivers are located in C:\ADI42.
(2) Create your own 3D Studio V3.0 batch file (say 3DS3.BAT) and add the
following settings to it, or
add the following settings to your "AUTOEXEC.BAT" file.
1 - SET RCPADI=C:\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP
2 - SET RDPADI=C:\ADI42\RCPSIS.EXP
(3) Execute the new 3DS batch file or reboot the computer using the new
"AUTOEXEC.BAT" as to make the new settings effective.
(4) Change your current working directory to \3DS3 (where your 3D Studio
V3.0 usually resides).
(5) Delete original configuration file "3DADI.CFG".
(6) Type
3DS VIBCFG<Enter>
to configure your display environment.
(7) After the "Company Register Screen" appears,
press <Enter>
to continue.
(8) The "Video Environment Configuration Screen" will appear.
Please follow the following procedures to configure your video display
environment.
1 - In "Main-Display" item,
(a) Press <Enter>
The selection menu will appear.
(b) In selection menu,
move cursor to "RCPADI".
Press <Enter> to select.
2 - In "Material-Display" item,
(a) Press <Enter>
The selection menu will appear.
(b) In selection menu,
move cursor to "RCPADI".
Press <Enter>
to select.
3 - In "Render-Display" item,
(a) Press <Enter>
The selection menu will appear.
(b) In selection menu,
Page 61

VGA Driver Setup 4-7
move cursor to "RCPADI" or "RDPADI".
Press <Enter>
to select.
4 - Complete the other selections and exit configuration.
(9) After exit configure,
3DS will boot automatically
using the environment you just select.
(10) If your previous configuration is OK, 3DS will ask you to make detail
configuration for SiS 5597/5598 drivers.
If this didn't happen, please check your previous procedures or contact the
technical support people.
(11) In the detail configuration for PD5N drivers,
just follow the instructions appear on the screen and make your own choice.
If you are confused in anything, contact the technical support people for
solution.
(12) After detail configuration,
you will enter the 3DS main display screen and
you may begin your 3D Studio work
in the environment you make before.
(13) Once completing the detail configuration,
you may enter 3D Studio in the same configuration simply by type
\3DS3\3DS <Enter>
next time.
(14) If you want to change your video configuration,
just follow the procedures mentioned before to re-configure
Page 62

4-8 Chapter 4
2. Windows NT 3.5 & 3.51
2.1 Installation
(1) Select Control Panel from Main group.
(2) Select Display icon.
(3) Select Change Display Type from Display Settings.
(4) Select Change from Display Type.
(5) Select Other from Select Device.
(6) Place the Windows NT 3.51 Installation Disk (Diskette #1) into Floppy
Drive
(7) When the "Install from Disk" dialog box appears, type the directory
storing the drivers and click "OK".
The directory in Diskette #1 is at "A:\WINNT35".
The directory in CD-Title is at "D:\MM\WINNT\WINNT35".
(8) Select Install and click "Yes" when the "Installing Driver" dialog box
appears.
(9) Select New when the "Windows NT Setup" dialog box appears.
(10) Click "Continue".
A message will appear stating that the drivers were successfully installed.
Click "OK". You must now restart Windows NT 3.51.
2.2 Selecting resolution and color depth
(1) Select Control Panel from Main group.
(2) Select Display icon.
(3) Select Color Palette to change between 16 colors, 256 colors, 32768 colors,
65536 colors, and 16777216 colors.
(4) To select desktop resolution size, go to the Desktop area and use the slide
bar to change resolution from 640x480, 800x600, 1024x768, and
1280x1024.
(5) Select Test to test the resolution.
If the display test screen was good then select "Yes" when the "Testing
Mode" dialog box appears. If the display test screen was bad then select
"No". Windows NT will give you an error message.
(6) If the display test screen was good and you select "Yes", Windows
NT 3.51 will prompt you to restart Windows NT 3.51.
Page 63

VGA Driver Setup 4-9
3. Windows NT 4.0
3.1 Installation
(1) Click "Start" menu and select Control Panel from Settings group.
(2) Select Display icon.
(3) Select Settings of Display Properties.
(4) Select Display Type.
(5) Select Change from the Adapter Type area.
(6) Select Have Disk of Change Display.
(7) Place the Windows NT 4.0 Installation Disk (Diskette #1) into Floppy Drive
(8) When the "Install from Disk" dialog box appears, type the directory storing
the drivers and click "OK".
The directory in Diskette #1 is at "A:\WINNT40".
The directory in CD-Title is at "D:\MM\WINNT\WINNT40".
(9) When the "Change Display" dialog box appears, click "OK".
(10) When the "Third-party Drivers" dialog box appears, click "Yes".
A message will appear stating that the drivers were successfully installed. Click
"OK". You must now restart Windows NT 4.0.
3.2 Selecting resolution and color depth
(1) Click "Start" menu and select Control Panel from Settings group.
(2) Select Display icon.
(3) Select Settings.
(4) Select Color Palette to change between 16 colors, 256 colors, 32768 colors,
65536 colors, and 16777216 colors.
(5) To select desktop resolution size, go to the Desktop area and use the slide
bar to change resolution from 640x480, 800x600, 1024x768, and
1280x1024.
(6) Select Test to test the resolution. If the display test screen was good then
select "Yes" when the
"Testing Mode" dialog box appears. If the display test screen was bad then
select "No". Windows NT 4.0 will give you an error message.
(7) Click "OK". If the display test screen was good and you select "Yes",
Windows NT 4.0 will change the mode without restarting Windows NT 4.0.
Page 64

4-10 Chapter 4
4. Windows 95
4.1 Installation
(1) Click "Start" menu and select Control Panel from Settings group.
(2) Select "Display" icon.
(3) Select "Settings" index in the display properties sheet.
(4) Select "Advanced Properties" button.
Page 65

VGA Driver Setup 4-11
(5) Select "Change..." button in "Adapter Type" group.
Page 66

4-12 Chapter 4
(6) Select "Have Disk" button.
Page 67

VGA Driver Setup 4-13
(7) Place the Windows 95 Installation Disk (Diskette #2) into Floppy Drive
The directory in CD-Title is at "D:\MM\WIN95".
(8) When the "Install from Disk" dialog box appears, type the directory
storing the drivers and click "OK".
The directory in Diskette #2 is at "A:\".
(9) When the "Change Display" dialog box appears, click "Close".
(10)Select "Close" or "Apply" button from display properties sheet.
(11)A message will appear stating you must restart the windows 95 system, select
"yes" to restart.
(12)After restarting, windows 95 will run on 640x480x256 color, 75NI.
4.2 Selecting resolution, color depth and refresh rate
(1) Click "Start" menu and select Control Panel from Settings group.
(2) Select Display icon.
(3) Select Settings.
(4) Select Color Palette to change between 16 color, 256 color, Hi color, and
True color.
(5) To select desktop resolution size, go to the Desktop area and use the slide bar
to change resolution from 640x480, 800x600, 1024x768, and 1280x1024.
(6) Select Refresh rate list box to change the screen refresh rate.
(7) Click "OK" or "Apply".
Page 68

4-14 Chapter 4
4.3 Utilities
(1) Place the Windows 95 Installation Disk into Floppy Drive or Place the PD5N
CD-Title Disk into CD-ROM Drive.
(2) Click "Start" menu and select "Run..." menu item.
(3) In "Run" dialog, typing the source execution file then press "OK".
The execution file in Diskette #2 is at "A:\SETUP.EXE".
The execution file in CD-Title is at "D:\MM\WIN95\SETUP.EXE".
(4) Setup procedure will create a "SiS Multimedia Vx.xx" program group, there
would be contained
3 items:
-- Multimedia Manager
-- SiS MMPlayer
-- Center Screen
(5) A setup successful dialog will appear when setup complete, user can choose
restart system now or restart later.
Page 69

VGA Driver Setup 4-15
5. Windows 3.1
5.1 Installation
5.1.1 Installation Procedures
(1) Click "File" menu and select "Run..." menu item.
(2) In "Run" dialog, typing the source execution file then press "OK".
The execution file in Diskette#5 is at "A:\SETUP.EXE".
The execution file in CD-Title is at "D:\MM\WIN31\SETUP.EXE".
(3) Follow the setup program's on-screen instructions.
(4) Setup procedure will create a "SiS Multimedia Vx.xx" program group, there
would be contained
5 items:
-- Multimedia Manager
-- SiS MMPlayer
-- SVGA Setup
-- Center Screen
-- Uninstall
(5) A setup successful dialog will apear when setup complete, user can choose
restart system now or restart later.
5.1.2 Graphics Setup
(1) In "SiS Multimedia Vx.xx" program group, choose "SVGA Setup" icon to
enter "SiS VGA Configuration System" screen.
(2) In "SiS VGA Configuration System" Screen, choose which options you
would like to use.
(3) After completing your selections, choose "OK" to make all your selections
effective.
(4) Choose "Restart Windows" to re-boot Windows using new settings.
Or, choose "Continue" to continue your current Windows processes.
(But when you re-boot Windows, the new settings would take effect.)
5.2.3 Power Saving Setup in Windows
(1) In "SiS VGA Configuration System" screen, choose "power saver" item to
enter "Power Saver" screen.
(2) In "Power Saver" Screen, choose which options you would like to use.
(3) After completing the selections, choose "OK" to make all your selections
effective.
(4) After complete setup, the power_saver would take effect as you request
when time up and you may continue your normal process.
5.1.4 Zoom_Key Setup
Page 70

4-16 Chapter 4
(1) In "SiS VGA Configuration System" screen, choose "zooming" item to
define "hot keys" for zoom-in or zoom-out screen without entering setup
program.
The operation principles of zoom-in and zoom-out are as follow:
1-The resolution change sequence for zoom-in is
1024x768 ===> 800x600 ===> 640x480 .
2-The resolution change sequence for zoom-out is
640x480 ===> 800x600 ===> 1024x768 .
3-But you must first be able to zoom-in before you may zoom-out,
that means you can not get a resolution larger than that you setup.
To use this feature, please follow the following procedures.
(2) In "SiS VGA Configuration System" screen, choose "zooming" item to enter
"Zooming Hotkey" screen.
(3) In "Zooming Hotkey" Screen, choose which "hot key" you would like to use
and enable it.
(4) After completing the selections, choose "OK" to make all your selections
effective.
(5) After complete setup, you may use your own defined hot key to zoom-in
or zoom-out screen.
5.1.5 Notes
(1) The power saver's timer settings would be effective even exit Windows back
to DOS.
Page 71

VGA Driver Setup 4-17
5.2 Video Operations
5.2.1 DCI Function
SiS 5597/5598 supports DCI driver for software MPEG playback and other media
player programs which could take advantage of DCI.
The SiS 5597/5598 DCI driver is automatically loaded during "Windows Driver
Unpack & Copy" process. Therefore it should be transparent to the end-user
and any media players could take advantage of it.
5.2.2 SiS MMPlay (SW MPEG)
To make SW MPEG playback more friendly than original SW MPEG player
supplier provided, SiS provide an MMPlayer application program to provide an
VCP-like (Video Cassette Player) interface.
To take advantage of the SiS MMPlayer, you must first install "SW MPEG
Player". All the SiS provided is just an interface but not a SW MPEG
Player at present. If the SW MPEG Player does not exist, the SiS
MMPlayer will not work. (Xing or Mediamatics SW MPEG Player
supported)
To use the SiS MMPlayer, you just follow the procedures below:
(1) In "SiS Multimedia Vx.xx" program group, choose "SiS MMPlayer" icon
and SiS MMPlayer VCP-like icon would appear.
(2) Enjoy the SW MPEG playback as you like.
Page 72

4-18 Chapter 4
5.2.3 Note on DCI & MMPlay
MMPLAY.EXE Button Description
: Power On/Off
: Open File & Type Control
: Minimize This Application
: Eject CD Title(Not implemented yet.)
: Fast Backward
: Fast Forward
: Mark in
: Mark out
: Pause
: Play
: Stop
: End
: Home
: Volume increase(Not implemented yet.)
: Volume decrease(Not implemented yet.)
Page 73

Quick Installation A-1
Appendix A Quick Installation
Appendix A will give you a simplified installation procedure, in order to
allow you to install tour mainboard quickly and correctly.
If you need further information or if you need to change some other settings,
read from Chapters 1.
Installing the CPU:
on the socket, and lower the lever back in position. Don’t worry, if you don’t
respect the correct orientation, you will not be able to insert the CPU.
Adjusting CPU voltage and speed:
Lift up the lever of the CPU socket, insert your CPU
.
Installing DRAM:
SIMM4 ~ SIMM1
Installing FDD:
with the drive to the FDD connector, and the other end of the cable to the FDC
pin connector on the mainboard.
Note: Be sure that the red line on the cable connects to the first pin of the
connectors.
FDC- Connect one end of the 34-pin cable that comes
Page 74

A-2 Appendix A
Installing HDD:
IDE1- Connect one end of the 40-pin cable that comes
with the drive to the HDD connector, and the other end to IDE1 pin connector on
the mainboard.
Note: Be sure that the red line on the cable connects to the first pin of the
connectors.
Installing CD-ROM Drive:
IDE2- Connect one end of the 40-pin
cable that comes with the drive to the CD-ROM connector, and the other end to
the IDE2 pin connector on the mainboard.
Note: Be sure that the red line on the cable connects to the first pin of the
connectors.
Installing parallel port:
LPT- Connect the 26-pin cable that comes
with the hardware to the LPT connector on the mainboard.
Installing serial port:
COM1- Connect the 10-pin cable that comes
with the hardware to connector COM1 on the mainboard.
COM2- Connect the other 10-pin cable to connector COM2 on the mainboard.
Attach the bracket of Parallel Port, Serial Port and PS2 Mouse on the computer
case.
Installing Keylock connector:
Watch the pin position and the
orientation
PN1 - There is a specific orientation for pin 1 to pin 5. Insert the five-threads
keylock cable into correct pins of connector on the mainboard.
Pin number Name of the signal or signification
1 +5VDC
2 No connection
3 Ground
4 Keyboard inhibit Signal
5 Ground
Page 75

Page 76

A-4 Appendix A
Installing speaker connector:
PN2 - There is no specific orientation
for pin 4 to pin 7. Connect the four-threads speaker cable to the PN2 connector
pins on the mainboard.
Pin number Name of the signal or signification
4 +5VDC
5 Ground
6 Ground
7 Sound Signal
Installing ATX Power input connector:
Watch the pin position and
the orientation
ATXPWR - Connect the power supply unit to the correct connectors on the
mainboard.
Pin number
1 +3.3VDC 11 +3.3VDC
2 +3.3VDC 12 -12VDC
3 Ground 13 Ground
4 +5VDC 14 PS_ON
5 Ground 15 Ground
6 +5VDC 16 Ground
7 Ground 17 Ground
8 POWERGOOD 18 -5VDC
9 +5VDC 19 +5VDC
10 +12VDC 20 +5VDC
Name of the signal or
signification
Pin number
Name of the signal or
signification
Watch the pin position and
Installing AT Power input connector:
the orientation
Connect connectors P8 and P9 or the power supply unit to the correct connectors
on the mainboard.
Page 77

Quick Installation A-5
Pin number Name of the signal or
signification
1 POWERGOOD 7 Ground
2 +5VDC 8 Ground
3 +12VDC 9 -5VDC
4 -12VDC 10 +5VDC
5 Ground 11 +5VDC
6 Ground 12 +5VDC
Installing Keyboard connector:
Pin number Name of the signal or
signification
KB1 - There is an orientation pin.
Connect your keyboard connector to
connector on the mainboard.
Installing PS2 Mouse:
Mouse - Connect the six-threads PS/2 Mouse
cable that comes with the hardware to the connector on the mainboard. Install the
bracket located on the other end of the computer case. When you buy a Mouse, it
has to be a PS/2 Mouse for it to be connected to this port.
Attach the bracket of Parallel Port, Serial Port and PS2 Mouse on the computer
case.
Installing CPU Fan Power connector:
FAN1 - There is a specific
orientation. Connect the three-threads CPU Fan power cable to the Fan connector
on the mainboard.
FAN1
Pin number Name of the signal or signification
1 Ground
2 +12V
3 Ground
Page 78

A-6 Appendix A
Adjusting other jumpers:
functions or are not to be adjusted in normal operation. Adjust them according to
the following recommendations.
CCMOS ¡G Put jumper on pin 1 and pin 2.
BIOS Setup:
steps described above and completed the installation, when you power the
computer on, you will see the following message displayed:
Press immediately Del key to enter BIOS Setup. Select Load Setup Defaults, than
enter CPU Soft Menu to set CPU parameters.
Parameters and CPU settings After you have followed the
PRESS DEL TO ENTER SETUP
Some jumpers are reserved for future
Page 79

Intel Pentium CPUs B-1
Appendix B Intel Pentium CPUs
Pentium 75MHz
CPU CPU Internal Bus External
Speed Spec. Clock Factor Clock Vcore VIO Timing Supp. Note
P54CS Q0649 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Sx753 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C SX961 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C 75 MHz SX969 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Q0700/S 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Q0749/S 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Q0837 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C SY005 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Q0540 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Q0541 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Q0666 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C SX961 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C SZ977 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Q0700 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Q0749 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C SX998 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C SZ994 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C SU070 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C Q0689 75MHz 1.5 50MHz 2.9V 3.3V Yes
P54C SK091 75MHz 1.5 50MHz 2.9V 3.3V Yes
P54C Q0851 75MHz 1.5 50MHz 2.9V 3.3V Yes
P54C SK122 75MHz 1.5 50MHz 2.9V 3.3V Yes
P54C SU097 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
P54C SU098 75MHz 1.5 50MHz
CPU DP
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
MD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
MD Yes
MD Yes
MD Yes
MD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
Page 80

B-2 Appendix B
Pentium 90MHz
CPU CPU Internal Bus External
Speed Spec Clock Factor Clock Vcore VIO Timing Supp. Note
P54C Sx653 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx957 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0654 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx958 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C 90 MHz Q0655 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx959 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0699/S 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx968 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx969 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0783 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sy006 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0542 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0613 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0543 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx879 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx885 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx909 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0628 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0611 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0612 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx923 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx922 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sx921 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sz951 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0653 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0654 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sz978 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0699 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Sz995 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C SU031 90MHz 1.5 60MHz
P54C Q0695 90MHz 1.5 60MHz 2.9V 3.3V Yes
P54C SK092 90MHz 1.5 60MHz 2.9V 3.3V Yes
P54C Q0852 90MHz 1.5 60MHz 2.9V 3.3V Yes
P54C SK123 90MHz 1.5 60MHz 2.9V 3.3V Yes
CPU DP
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
MD Yes
MD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
DP Yes
STD Yes
MD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
MD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
Page 81

Intel Pentium CPUs B-3
Pentium 100MHz
CPU CPU Internal Bus External
Speed Spec Clock Factor Clock Vcore VIO Timing Supp. Note
P54C Sx886 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Sx910 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C 100 MHz Sx956 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Sx960 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0657 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0658 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Sx962 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0698/S 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0697/S 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Sx963 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Sx970 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0784 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C SY007 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0563 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0587 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0614 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0677 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0656 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0698 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0697 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C SZ996 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C SU032 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C Q0853 100MHz 1.5 66MHz 2.9V 3.3V MD Yes
P54C SK124 100MHz 1.5 66MHz 2.9V 3.3V MD Yes
P54C SY046 100MHz 1.5 66MHz Yes
P54C Q0784 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C SU110 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
P54C SU099 100MHz 1.5 66MHz
CPU DP
MD No
MD No
STD No
MD No
MD No
MD Yes
MD Yes
MD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
MD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
MD Yes
MD Yes
MD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
Page 82

B-4 Appendix B
Pentium120MHz
CPU CPU Internal Bus External
Speed Spec. Clock Factor Clock Vcore VIO Timing Supp. Note
P54CQS Q0708 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54CQS 120 MHz Q0711 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54CQS Q0730 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54CQS Sk084 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54CQS Sk086 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C Sx994 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C Q0732/S 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C Q0785 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C SY008 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C SY033 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C Q0707 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C Q0732 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C SU033 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C Q0776 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C SK110 120MHz 2 60MHz
CPU DP
STD Yes
MD Yes Convert to P54C
MD Yes
MD Yes
MD Yes Convert to P54C
MD No
MD No
STD No
STD No
STD No
STD No
MD No
MD No
Yes
Yes
P54C Q0808 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C SX999 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C SY030 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54C SU100 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54CS Q031 120MHz 2 60MHz
P54CS SY062 120MHz 2 60MHz
Yes
Yes
Yes
STD No
KIT Yes
KIT Yes
Page 83

Intel Pentium CPUs B-5
Pentium 133MHz
CPU CPU Internal Bus External
Speed Spec Clock Factor Clock Vcore VIO Timing Supp. Note
P54CS Q0772 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS Q0773 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS Q0774 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS Q0877 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS Sk106 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS S106J 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS Sk107 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS Q0843 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS SY022 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS Q0844 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS SY023 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS 133 MHz SU038 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS SU073 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CS Q0882 133MHz 2 66MHz Yes
P54CS SY082 133MHz 2 66MHz Yes
P54CQS Q0733 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CQS Sk098 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CQS Q0751 133MHz 2 66MHz
P54CQS Q0775 133MHz 2 66MHz
CPU DP
STD Yes
Kit Yes
MD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes
MD Yes Convert to P54CS
MD Yes Convert to P54CS
MD Yes
MD Yes Convert to P54CS
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Page 84

B-6 Appendix B
Pentium 150MHz
CPU CPU Internal Bus External
Speed Spec Clock Factor Clock Vcore VIO Timing Supp. Note
P54CS Q0835 150MHz 2.5 60MHz
P54CS SY015 150MHz 2.5 60MHz
P54CS Q0878 150MHz 2.5 60MHz
P54CS SU071 150MHz 2.5 60MHz
P55C 150 MHz Q0939 150MHz 2.5 60MHz 2.9V 3.3V CPGA
P55C Q0941 150MHz 2.5 60MHz 2.9V 3.3V PPGA
P55C Q974 150MHz 2.5 60MHz 2.8V 3.3V CPGA
P55C Q977 150MHz 2.5 60MHz 2.8V 3.3V PPGA
CPU DP
STD Yes
STD Yes
STD Yes PPGA
STD Yes
Pentium 166MHz
CPU CPU Internal Bus External
Speed Spec Clock Factor Clock Vcore VIO Timing Supp. Note
P54CS SY016 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS Q0841 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS SY017 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS Q0949 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS SY037 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS 166MHz Q0951F 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS SY044 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS Q0836 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS Q0886 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS Q0890 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
P54CS SY072 166MHz 2.5 66MHz
CPU DP
Yes
Yes
Yes
Kit No PPGA up
No PPGA up
Kit Yes PPGA
Kit Yes PPGA
Yes
Yes PPGA
Yes PPGA
Yes
P55C Q0940 166MHz 2.5 66MHz 2.9V 3.3V CPGA
P55C Q0942 166MHz 2.5 66MHz 2.9V 3.3V PPGA
P55C Q975 166MHz 2.5 66MHz 2.8V 3.3V CPGA
P55C Q978 166MHz 2.5 66MHz 2.8V 3.3V PPGA
P55C Q019 166MHz 2.5 66MHz 2.8V 3.3V PPGA
Page 85

Intel Pentium CPUs B-7
Pentium 200MHz
CPU CPU Internal Bus External
Speed Spec Clock Factor Clock Vcore VIO Timing Supp. Note
P54CS Q0951 200MHz 3 66MHz
P54CS SY045 200MHz 3 66MHz
P54CS 200 MHz Q0951F 200MHz 3 66MHz
P54CS SY044 200MHz 3 66MHz
P55C Q018 200MHz 3 66MHz 2.8V 3.3V PPGA
CPU DP
No PPGA up
Kit No PPGA up
Kit Yes PPGA
Yes PPGA
Pentium 233MHz
CPU CPU Internal Bus External CPU DIP
Speed Speed Clock Factor Cclock Vcore VIO Timing Supp Note
P55C 200MHz SY060 200MHz 3 66MHz 2.8V 3.3V PPGA
P55C 233MHz SL2BM 233MHz 3 66MHz 2.8V 3.3V PPGA
Page 86

B-8 Appendix B
Y
Bus Factor
Power STD
VR
VRE
Timing STD
MD
Kit
P54C
1. Beginning with the P54C E-Step, standard timings have been replaced by
existing Min Delay timing.
P54CS
1. P54CS PPGA UP:No DP,No APIC,No FRC
2. Beginning with the P54C E-Step, standard timings have been replaced by
existing Min Delay timing.
P55C
1. P55C A-Step is NOT production stepping
2. A-1 step: Vcc and timing on initial samples is 2.9V +/- 0.1V
3. A-2 Step and B step: Vcc and timing on production stepping is 2.8V +/- 0.1V
3.15V~3.465V (Recommended voltage is 3.38V)
3.300V~3.465V (Recommended voltage is 3.38V)
3.450V~3.6V (Recommended voltage is 3.52V)
Standard Timing
Min. Delay (denoting shorter minimum valid delay AC
timing for some signal)
Supports timing for C55/C88 cache chipsets & design
Page 87

AMD-K5 CPUs C-1
Appendix C AMD-K5 CPUs
Recognizing AMD CPU speed, voltage and package:
AMD-K5-PR100 A B Q xx
Processor name
K5
K6
P-Rating
PR75 ,PR90 ,PR100,
PR120 ,PR133 ,PR150 ,
PR166 ,166 ,200 ,233
Package Type
A=SPGA (296 pin)
Reserved
Case Temperature
Q= 60 ¢J
R= 70 ¢J
W=55 ¢J
X= 65 ¢J
Y= 75 ¢J
Z= 85 ¢J
Operating Voltage
B= 3.45V-3.60V
C= 3.30V-3.465V
F= 3.135V-3.465V
G= x/y
H=2.86V-3.00V / 3.30V-
3.465V
J= 2.57V-2.84V / 3.30V-
3.465V
K= 2.38V-2.63V / 3.30V-
3.465V
x = Vcore ; y= Vio
Page 88

C-2 Appendix C
Page 89

Cyrix 6x86 CPUs
Appendix D Cyrix 6x86 CPUs
Recognizing Cyrix CPU speed and voltage:
Name of the
D-1
processor
6x86, 6x86L
6x86MX
P-Rating
90+,120+,133+,
150+,166+,200+
6x86-P166+ GP
133 MHz
3.52V (028)
VCC Specification
Center of Core
Voltage
3.3V
Full spec.: 3.15V-3.70V
C-spec. (016): 3.15V-3.45V
C-spec. (028): 3.40V-3.70V
CPU Core Frequency
100,110,120,
133,150
3.52V
2.9V
Page 90

D-2
Appendix D
Page 91

Page 92

Appendix FF-4
4. DRIVER REV: Note the driver version number indicated on the
DEVICE DRIVER disk as “Release *.**”.
Example:< IDE Device Driver
Drivers Diskette Release 1.09A
Release 1.09A
*5. OS/APPLICATION: Indicate what are the operating system and
the applications your are running on the system.
Example: MS-DOS 6.22, Windows 3.1....
*6. CPU: Indicate the brand and the speed (MHz) of your CPU.
Example: (A) In the “Brand” space, write “Intel”, in the “Specifications”
space, write “150MHz”¡C
(B) In the “Brand” space, write “Cyrix”, in the
“Specifications” space, write “P166+”¡C
(C) In the “Brand” space, write “AMD”, in the
“Specifications” space, write “P75”.
7. HDD: Indicate the brand and specifications of your HDD(s), specify if
the HDD is using ¨IDE1 or ¨IDE2. If you know the disk capacity,
indicate it and check (“ü”) “ ”; in case you give no indication, we will
consider that your HDD is “þIDE1” Master.
Example: In the “HDD” space, check the box, in the Brand space, write
“Seagate”, in the Specifications space, write “ST31621A
(1.6GB)”.
8. CD-ROM Drive: Indicate the brand and specifications of your CD-
ROM drive, specify if it uses ¨ IDE1 or ¨IDE2 ¡A and check (“ü”)
“ ”; in case you give no indication, we will consider that your CD-
ROM is “þIDE2” Master.
Example: In the “CD-ROM drive” space, check the box, in the Brand
space, write “Mitsumi”, in the Specifications space, write “FX-
400D”.
Page 93

Technical Support F-5
9. System Memory (DRAM): Indicate the brand and specifications (SIMM/DIMM)
of your system memory.
Examples:
In the Brand space, write “Panasonic”, in the Specifications space, write
“SIMM-FP DRAM 4MB-06”.
Or, in the Brand, write “NPNX”, in the Specifications space, write “SIMM-
EDO DRAM 8MB-06”.
Or, in the Brand space, write “SEC”, in the Specifications space, write “DIMM-
S DRAM 8MB-G12”.
10. COAST: Indicate the brand and specifications of your COAST.
Example: In the Brand space, write “Winbond”, in the Specifications space, write
“256KB” or “W25P010AF-8”¡C
11. ADD-ON CARD: Indicate which add-on cards you are “absolutely sure” are related
to the problem.
If you cannot identify the problem origin, indicate all the add-on cards inserted into
your system.
Note: Items between the “*” are absolutely necessary.
Page 94

&
Technical Support Form
Company name: ( Phone #:
J Contact: /Fax #:
Model * BIOS ID # *
Mainboard model no. DRIVER REV
OS/Application *
Hardware name Brand Specifications
C.P.U *
HDD IDE1
IDE2
CD-ROM Drive IDE1
IDE2
Appendix FF-6
System Memory
(DRAM)
COAST
ADD-ON CARD
?
Problem Description:
Page 95

Flash BIOS User Instructions G-1
Appendix G Flash BIOS User
Instructions
Example 1 To update BIOS and create a backup of the current system BIOS
execute this command:
AWDFLASH NEWBIOS /Py SAVEBIOS
/Sy
Example 2 To update BIOS, create a backup of current system BIOS, and
clear the CMOS, execute this command:
AWDFLASH NEWBIOS SAVEBIOS /CC
Example 3 To update BIOS and clear PnP settings execute this command:
AWDFLASH NEWBIOS /Sn /CP
Example 4 To make a backup of the current system BIOS execute the
following command:
AWDFLASH NEWBIOS /Pn SAVEBIOS
Notes: “NEWBIOS” indicates file name for the new BIOS which can be
downloaded from our website at http://www.abit.com.tw (user can
choose a different file name in place of NEWBIOS).
“SAVEBIOS” indicates the filename of the old system BIOS (user
can choose a different file name in place of SAVEBIOS).
Page 96

G-2 Appendix G
Explanation of parameter names:
/CC: Clears CMOS data
/CP: Clears PnP data
Remarks:
¬ When executing AWDFLASH.EXE, do not run HIMEM.SYS and
EMM386.EXE in the CONFIG.SYS.
- Please take the following actions to solve problems caused by
power shortage or other other unpreventable malfunctions during
BIOS update that lead to update failure. First, it is strongly
suggested that you format a disk that can boot your computer
before you update your BIOS. If the above mentioned
problem occurs during BIOS update you will be able to use this disk
to automatically execute a BIOS update. The content of the disk
should be the following:
a. Startup system files (COMMAND.COM, MSDOS.SYS,
IO.SYS...)
b. AWDFLSH.EXE
c. The NEWBIOS file which can be downloaded from ABIT’s
website.
d. AUTOEXEC.BAT, which has the following content:
A:\AWDFLASH NEWBIOS /Py /Sn /CC
® When a version of BIOS that is for the incorrect mainboard
model the following message will appear:
“The program file’s part number does not match with your
system!”
Page 97

Super VGA User’ s Manual H-1
Appendix H 5597/5598 Super VGA
User’s Manual
Appendix:
H1. Video Modes
H1.1 Standard VGA Modes
MODE TYPE DISPLAY
SIZE
0 A/N 320x200 16 40x25 B800 8x8 8
0* A/N 320x350 16 40x25 B800 8x14 8
0+ A/N 360x400 16 40x25 B800 9x16 8
1 A/N 320x200 16 40x25 B800 8x8 8
1* A/N 320x350 16 40x25 B800 8x14 8
1+ A/N 360x400 16 40x25 B800 9x16 8
2 A/N 640x200 16 80x25 B800 8x8 8
2* A/N 640x350 16 80x25 B800 8x14 8
2+ A/N 720x400 16 80x25 B800 9x16 8
3 A/N 640x200 16 80x25 B800 8x8 8
3* A/N 640x350 16 80x25 B800 8x14 8
3+ A/N 720x400 16 80x25 B800 9x16 8
4 APA 320x200 4 40x25 B800 8x8 1
5 APA 320x200 4 40x25 B800 8x8 1
6 APA 640x200 2 80x25 B800 8x8 1
7 A/N 720x350 4 80x25 B000 9x14 8
7+ A/N 720x400 4 80x25 B000 9x16 8
0D APA 320x200 16 40x25 A000 8x8 8
0E APA 640x200 16 80x25 A000 8x8 4
0F APA 640x350 2 80x25 B000 8x14 2
10 APA 640x350 16 80x25 A000 8x14 2
11 APA 640x480 2 80x30 A000 8x16 1
12 APA 640x480 16 80x30 A000 8x16 1
13 APA 320x200 256 40x25 A000 8x8 1
COLORS
SHADES
ALPHA
FORMAT
BUFFER
START
BOX
SIZE
MAX.
PAGES
NOTE: 1. A/N: Alpha/Numeric
2. APA: All Point Addressable (Graphics)
Page 98

H-2 Appendix H
MODE DISPLAY
SIZE
0 320x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
0* 320x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
0+ 360x400 16 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
1 320x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
1* 320x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
1+ 360x400 16 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
2 640x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
2* 640x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
2+ 720x400 16 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
3 640x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
3* 640x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
3+ 720x400 16 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
4 320x200 4 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
5 320x200 4 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
COLORS
SHADES
FRAME
RATE.
H-SYNC. VIDEO
FREQ.
6 640x200 2 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
7* 720x350 4 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
7+ 720x400 4 70 31.5 K 28.3 M
0D 320x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
0E 640x200 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
0F 640x350 2 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
10 640x350 16 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
11 640x480 2 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
12 640x480 16 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
13 320x200 256 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
NOTE: i - interlaced mode
n - noninterlaced mode
Page 99

Super VGA User’ s Manual H-3
H1.2 Enhanced Video Modes
MODE TYPE DISPLAY
SIZE
COLORS
SHADES
ALPHA
FORMAT
BUFFER
START
BOX
SIZE
22 A/N 1056x352 16 132x44 B800 8x8 2
23 A/N 1056x350 16 132x25 B800 8x14 4
24 A/N 1056x364 16 132x28 B800 8x13 4
25 APA 640x480 16 80x60 A000 8x8 1
26 A/N 720x480 16 80x60 B800 9x8 3
29 APA 800x600 16 100x37 A000 8x16 1
2A A/N 800x600 16 100x40 B800 8x15 4
2D APA 640x350 256 80x25 A000 8x14 1
2E APA 640x480 256 80x30 A000 8x16 1
2F APA 640x400 256 80x25 A000 8x16 1
30 APA 800x600 256 100x37 A000 8x16 1
37 APA 1024x768 16 128x48 A000 8x16 1
38 APA 1024x768 256 128x48 A000 8x16 1
39 APA 1280x1024 16 160x64 A000 8x16 1
3A APA 1280x1024 256 160x64 A000 8x16 1
40 APA 320x200 32K 40x25 A000 8x8 1
41 APA 320x200 64K 40x25 A000 8x8 1
42 APA 320x200 16.8M 40x25 A000 8x8 1
43 APA 640x480 32K 80x30 A000 8x16 1
44 APA 640x480 64K 80x30 A000 8x16 1
45 APA 640x480 16.8M 80x30 A000 8x16 1
46 APA 800x600 32K 100x37 A000 8x16 1
47 APA 800x600 64K 100x37 A000 8x16 1
48 APA 800x600 16.8M 100x37 A000 8x16 1
49 APA 1024x768 32K 128x48 A000 8x16 1
4A APA 1024x768 64K 128x48 A000 8x16 1
4B APA 1024x768 16.8M 128x48 A000 8x16 1
4C APA 1280x1024 32K 160x64 A000 8x16 1
4D APA 1280x1024 64K 160x64 A000 8x16 1
MAX.
PAGES
NOTE: 1. A/N: Alpha/Numeric
2. APA: All Point Addressable (Graphics)
Page 100

H-4 Appendix H
MODE DISPLAY
SIZE
22 1056x352 16 70 30.5 K 40.0 M
23 1056x350 16 70 30.5 K 40.0 M
24 1056x364 16 70 30.5 K 40.0 M
25 640x480 16 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
26 720x480 16 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
29 800x600 16 56 35.1 K 30.0 M
29* 800x600 16 60 37.9 K 40.0 M
29+ 800x600 16 72 48.0 K 50.0 M
29# 800x600 16 75 46.8 K 50.0 M
29## 800x600 16 85 53.7 K 56.3 M
2A 800x600 16 56 35.1 K 36.0 M
2D 640x350 256 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
2E 640x480 256 60 31.5 K 25.1 M
2E* 640x480 256 72 37.9 K 31.5 M
2E+ 640x480 256 75 37.5 K 31.5 M
2E++ 640x480 256 85 43.4 K 36.0 M
2F 640x400 256 70 31.5 K 25.1 M
30 800x600 256 56 35.1 K 36.0 M
30* 800x600 256 60 37.9 K 40.0 M
30+ 800x600 256 72 48.0 K 50.0 M
30# 800x600 256 75 46.8 K 50.0 M
30## 800x600 256 85 53.7 K 56.3 M
37i 1024x768 16 87 35.5 K 44.9 M
37n 1024x768 16 60 48.4 K 65.0 M
37n+ 1024x768 16 70 56.5 K 75.0 M
37n# 1024x768 16 75 60.2 K 80.0 M
37n## 1024x768 16 85 68.7 K 94.5 M
38i 1024x768 256 87 35.5 K 44.9 M
COLORS
SHADES
FRAME
RATE.
H-SYNC. VIDEO
FREQ.
38n 1024x768 256 60 48.4 K 65.0 M
38n+ 1024x768 256 70 56.5 K 75.0 M
38n# 1024x768 256 75 60.2 K 80.0 M
38n## 1024x768 256 85 68.7 K 94.5 M
39i 1280x1024 16 87 48.8 K 80.0 M
39n 1280x1024 16 60 65.0 K 110.0 M
39n+ 1280x1024 16 75 80.0 K 135.0 M
 Loading...
Loading...