Page 1

Copyright and Warranty Notice
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and does not
represent a commitment on part of the vendor, who assumes no liability or responsibility
for any errors that may appear in this manual.
No warranty or representation, either expressed or implied, is made with respect to the
quality, accuracy or fitness for any particular part of this document. In no event shall the
manufacturer be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages
arising from any defect or error in this manual or product.
Product names appearing in this manual are for identification purpose only and
trademarks and product names or brand names appearing in this document are the
property of their respective owners.
This document contains materials protected under International Copyright Laws. All
rights reserved. No part of this manual may be reproduced, transmitted or transcribed
without the expressed written permission of the manufacturer and authors of this manual.
If you do not properly set the motherboard settings, causing the motherboard to
malfunction or fail, we cannot guarantee any responsibility.
Page 2

Page 3

NV7m Motherboard User’s Manual
Index
CHAPTER 1.
1-1. F
1-2. S
1-3. I
1-4. L
EATURES OF
PECIFICATION S
TEM CHECKLIS T
AYOUT DIAGRAM FOR
CHAPTER 2.
2-1. I
2-2. I
2-3. I
2-4. C
NSTALLATION OF THE
NSTALLING THE MOTHERBOARD TO THE CHASSIS
NSTALLING SYSTEM MEMORY
ONNECTORS
CHAPTER 3.
3-1. S
3-2. A
3-3. A
3-4. I
3-5. P
3-6. PNP/PCI C
3-7. PC H
3-8. L
3-9. L
3-10. S
3-11. S
3-12. S
3-13. E
TANDARD
DVANCED
DVANCED CHIPSET FEATURES SETUP MENU
NTEGRATED PERIPHERALS
OWER MANAGEMENT SETUP MENU
OAD FAIL-SAFE DEFAULTS
OAD OPTIMIZED DEFAULTS
ET SUPERVISOR PASSWORD
ET USER PASSWORD
AVE
XIT WITHOUT SAVING
APPENDIX A. NVIDIA NFORCE CHIPSET DRIVERS INSTALLATION
INTRODUCTION OF NV7M FEATURES ........................1-1
NV7M M
INSTALLING THE MOTHERBOARD.............................. 2-1
, H
INTRODUCING THE BIOS ................................................3-1
CMOS F
BIOS F
ONFIGURATIONS SETUP MENU
EALTH STATUS
& E
XIT SETUP
OTHERBOARD
....................................................................................................1-1
..................................................................................................1-3
NV7M.............................................................................1-4
AMD A
EADERS AND SWITCHES
EATURES SETUP MENU
EATURES SETUP MENU
.................................................................................3-10
...........................................................................................3-20
...............................................................................3-21
.........................................................................................3-21
...........................................................................................3-22
......................................................................................3-22
FOR WINDOWS
...................................................................1-1
THLON™
.............................................................................2-6
..............................................................................3-21
..............................................................................3-21
®
XP, A
THLON™ AND DURON™
................................................2-5
...............................................................2-7
.........................................................3-3
...........................................................3-6
.......................................................3-8
..................................................................3-14
...........................................................3-17
2000......................................................... A-1
CPU .........2-2
APPENDIX B. NVIDIA VGA DRIVERS INSTALLATION FOR WINDOWS®
2000 ........................................................................................ B-1
APPENDIX C. INSTALLING THE WINBOND HARDWARE MONITOR
SYSTEM................................................................................. C-1
APPENDIX D. BIOS UPDATE GUIDE ........................................................ D-1
APPENDIX E. TROUBLESHOOTING (NEED ASSISTANCE?) ............... E-1
APPENDIX F. HOW TO GET TECHNICAL SUPPORT ............................. F-1
4200-0253-02 Rev. 1.01
Page 4

NV7m Motherboard
Page 5
Introduction of NV7m Features
1-1
Chapter 1. Introduction of NV7m Features
1-1. Features of NV7m Motherboard
This motherboard is designed for AMD Socket A Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ processors. It
supports the AMD Socket-A structure, with up to 1 GB (Unbuffered & Non-ECC) of memory, super I/O.
and Green PC functions. The ABIT NV7m is an excellent computer motherboard based on the innovative
nForce 420D chipset, which supports powerful Geforce 2 3D graphics, AC3 audio and LAN for an all in
one Micro ATX form factor solution with high performance value.
The NVIDIA nForce 420D chipset used in this motherboard supports two DDR DIMMs up to 1 GB
maximun. The memory controller can support Non-ECC DDR (up to DDR PC 2100 it running on 133
MHz) memory and support twin bank memory architecture for up to 4.2GB/s bandwidth. The AGP
interface can support external AGP slot with AGP 1X/2X/4X (1.5V graphics card only) capability and
Fast Write Transactions.
The NV7m has a built in Ultra DMA 100 function. This means that it provides speedier HDD throughput
boosting overall system performance. Ultra DMA 100 is the new standard for IDE devices. It enhances
existing Ultra DMA 33 technology by increasing both performance and data integrity. This new
high-speed interface almost doubles the Ultra DMA 66 burst data transfer rate to 100 Mbytes/sec. The
result is maximum disc performance using the current PCI local bus environment. Another benefit is you
can connect four IDE devices in your system through either Ultra DMA 66 or Ultra DMA 100. You will
have more flexibility to expand your computer system.
This motherboard also supports three PCI slots and one AGP slot. This motherboard has built-in hardware
monitoring functions that monitors and protects your computer, insuring a safe computing environment. It
equips the Realtek ALC201A 2-channel audio and 8201L 10/100 Mbps LAN controller.
The NV7m optional SPDIF out module turns your computer into a high-end entertainment system with
optical and coaxial connectivity to powerful speaker system (CA-21).
1-2. Specifications
1. Processor
! Supports AMD Athlon™ XP 1500+ ~ 2000+ or future Socket A processors based on 200 MHz/266
MHz (100 MHz/133 MHz Double Data Rate)
! Supports AMD Athlon
MHz (100 MHz/133 MHz Double Data Rate)
! Supports AMD Duron
MHz Double Data Rate)
! Supports 200 MHz Alpha EV6 bus for the AMD Athlon
User’s Manual
™
700 MHz ~ 1.4 GHz or future Socket A processors based on 200 MHz/266
™
600 MHz ~ 1.2 GHz or future Socket A processors based on 200 MHz (100
™
XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ processors
Page 6

Chapter 1
1-2
2. Chipset (nVIDIA Crush 12 & MCP-D)
! Integrates 128-bit memory controller (Dual independent 64-bit memory controllers)
! 4.2 GB/Sec total maximum memory bandwidth
! Supports Advanced Configuration and Power Management Interface (ACPI)
! Supports AGP 2X/4X only 1.5V
3. Memory (System Memory)
! Two 184-pin DIMM slots support PC 1600 and PC 2100 DDR SDRAM modules
! Supports up to 1 GB maximun memory capacity. (64, 128, 256, 512MB DDR SDRAM)
! Supports unbuffered Non-ECC type DDR DIMM
4. Graphics
! Chipset integrated nVIDIA 256-bit 3D/2D graphics accelerator
! Second generation transform and lighting engine
5. Audio
! nVIDIA MCP-1 built-in Audio processing unit w/ 256 total voices
! Support AC3 encode purpose
! Professional digital audio interface supporting SPDIF out (Optional)
! AC’ 97 Audio CODEC onboard
! Audio driver included
6. LAN
! Onboard Realtek 8201L physical layer interface
! 10/100 Mb Operation
! User friendly driver included
7. System BIOS
! Award Plug and Play BIOS supports APM and DMI
! Write-Protect Anti-Virus function by AWARD BIOS
8. Multi I/O Functions
! One floppy port connector (up to 2.88MB)
! Two channels of bus master IDE ports supporting up to four ultra DMA 33/66/100 devices
! One PS/2 keyboard and PS/2 mouse connector
! One parallel port connector (Standard/EPP/ECP)
! One serial ports connectors
! One VGA port connectors
! Two USB connectors
! One 10/100 Mb port
! One audio connector (Line-in, Line-out, Mic-in, and MIDI/Game port)
NV7m Motherboard
Page 7
Introduction of NV7m Features
1-3
9. Miscellaneous
! Micro ATX form factor
! One AGP slot, three PCI slots
! One built-in IrDA TX/RX header
! One built-in SM-Bus header
! One USB header for two extra USB channels
! One CD audio input connector
! One AUX audio input connector
! One SPDIF header for digital signal connection (Optional)
! TV/DVI output interface card (Optional)
! Hardware monitoring:Included fan speed, voltages, processor and system environment temperature
! Board size: 245 * 245mm
# Your ATX power supply 5V standby power must be able to provide at least a 720mA current
capacity.
# This motherboard supports the standard bus speeds of 66 MHz/100 MHz/133 MHz that are
used by specific PCI, processor and chipset specifications. Exceeding these standard bus speeds
is not guaranteed due to the specific component specifications.
# Specifications and information contained in this manual are subject to change without notice.
Note
All brand names and trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
1-3. Item Checklist
Check that your package is complete. If you discover any damaged or missing items, please contact your
retailer or dealer.
$ One ABIT NV7m Motherboard
$ One 80-wire/40-pin ribbon cable for master and slave Ultra DMA 100, Ultra DMA 66 or Ultra DMA
33 IDE devices
$ One ribbon cable for 3.5” floppy disk devices
$ One compact disc for support drivers and utilities
$ One USB cable
$ One I/O shield (CA-21, optional)
$ One user’s manual for the motherboard
User’s Manual
Page 8
Chapter 1
1-4
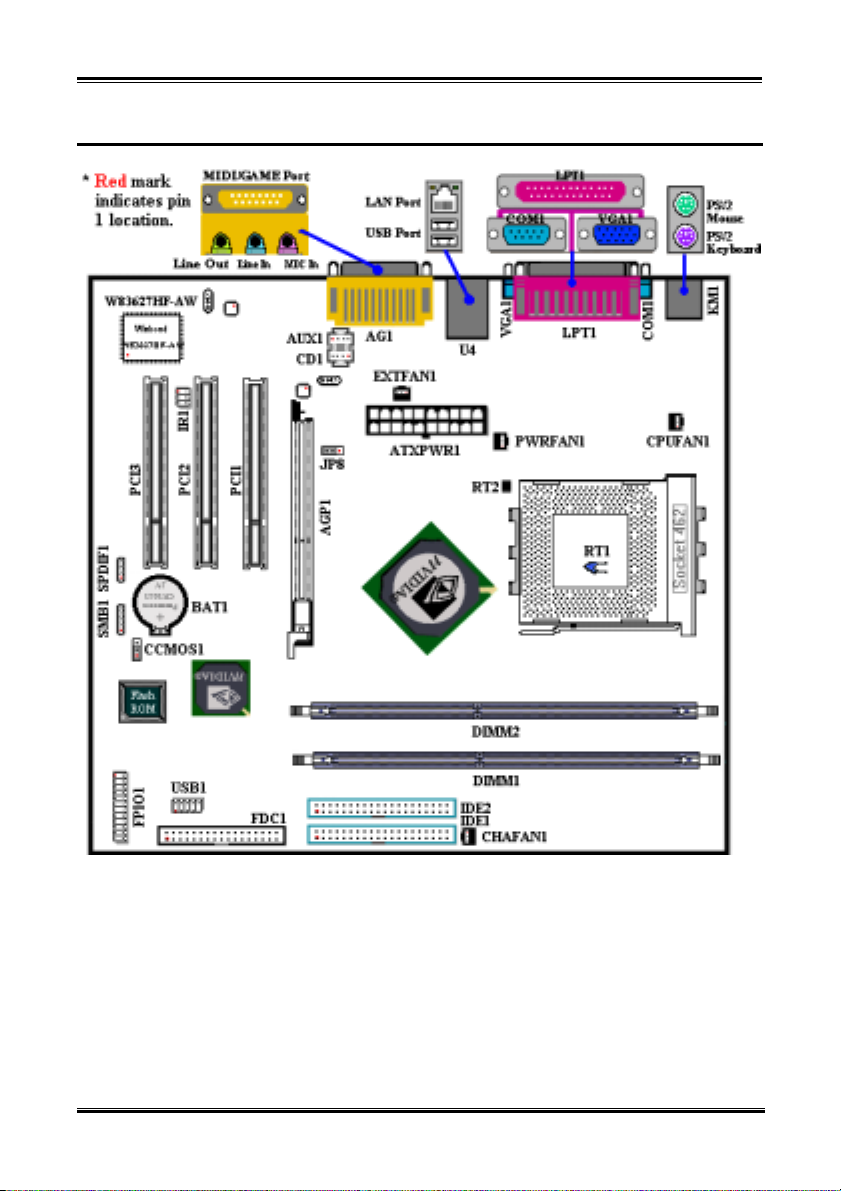
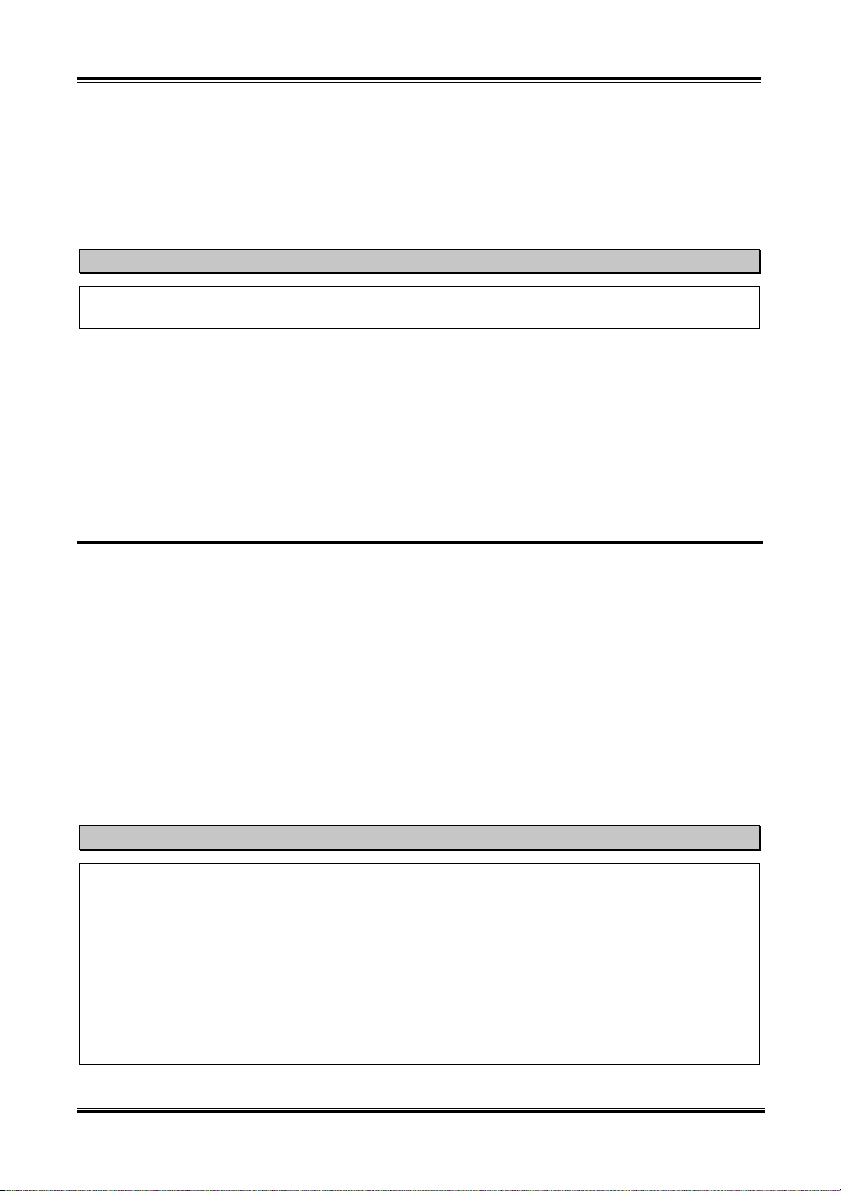
1-4. Layout Diagram for NV7m
NV7m Motherboard
Figure 1-1. NV7m motherboard component location
Page 9
Installing the Motherboard
2-1
Chapter 2. Installing the Motherboard
This NV7m motherboard not only provides all standard equipment for classic personal computers, but
also provides great flexibility for meeting future upgrade demands. This chapter will introduce step by
step all of the standard equipment and will also present, as completely as possible, future upgrade
capabilities. This motherboard is able to supports all AMD Socket A Athlon
processors now on the market. (For details, see specifications in Chapter 1.)
This chapter is organized according the following features:
™
2-1 Installation of the AMD Athlon
2-2 Install The Motherboard
2-3 Install System Memory
2-4 Connectors, Headers and Switches
XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ CPU
™
XP, Athlon™ and Duron™
%%%%
Before you install or unplug any connectors or add-on cards, please remember to turn the ATX power
supply switch off (fully turn the +5V standby power off), or take the power cord off. Otherwise, you may
cause the motherboard components or add-on cards to malfunction or be damaged.
&
Please read our instructions carefully and follow them step-by-step. Our objective is to enable the novice
computer user to perform the installation by himself. We have attempted to write this document in a very
clear, concise and descriptive manner to help overcome any obstacles you may face during installation.
This chapter contains many color drawings, diagrams and photos, we strongly recommend you read this
chapter use the PDF file that is stored on the CD-Title. Color improves the clarity and quality of the
diagrams. For the downloadable edition, as files larger than 3 MB are difficult to download, we will cut
the graphics and photo resolution to reduce the manual file size. In such this case, if your manual is
downloaded from our WEB site and not from a CD-ROM, enlarging graphics or photos will distort the
image.
Before Proceeding with the Installation
User Friendly Instructions
Diagram and Photos
%%%%
User’s Manual
Page 10
Chapter 2
2-2
2-1. Installation of the AMD Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™
CPU
Note
! Installing a heatsink and cooling fan is necessary for heat to dissipate from your processor. Failing
to install these items may result in overheating and processor damage.
! The AMD Socket A processor will produce a lot of heat while operating, so you need to use a large
heat sink that is especially designed for the AMD socket A processor. Otherwise, it may result in
overheating and processor damage.
! If your processor fan and its power cable are not installed properly, never plug the ATX power
cable into the motherboard. This can prevent possible processor damage.
! Please refer to your processor installation manual or other documentation with your processor for
detailed installation instructions.
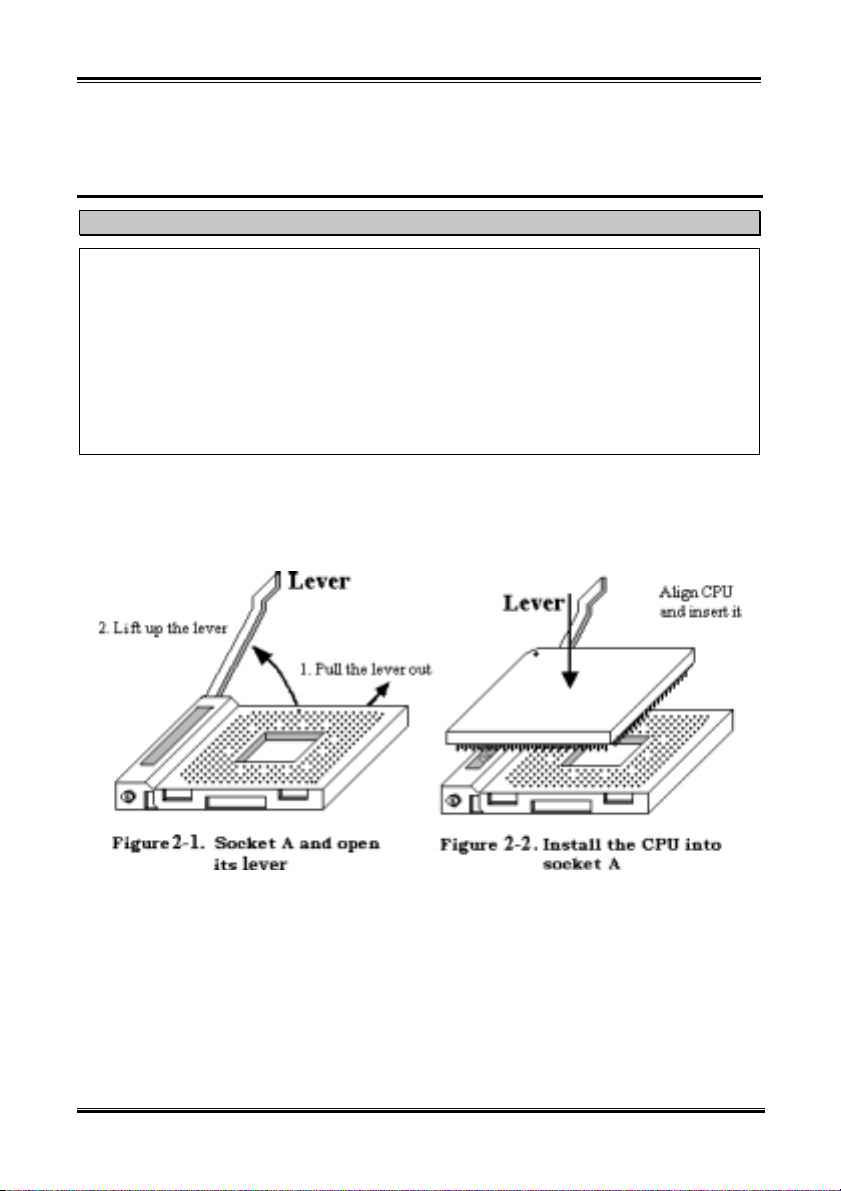
The AMD Socket A Athlon™ XP, Athlon™ and Duron™ processor installation is easy, like Socket 7
®
Pentium
easily fix the processor firmly into position. Figure 2-1 shows you what the socket A looks like, and how
to open the lever. The socket A has more pins than the socket 7. Therefore, a Pentium level processor
cannot be inserted into a socket A.
processors before. Because it uses the “Socket A” ZIF (Zero Insertion Force) socket, you can
When you raise the lever, you have to loosen the socket lock. Please raise the lever to the end, and
prepare to insert the processor. Next, you need to align the processor pin 1 to the socket pin 1. If you put
it in the wrong direction, you will not be able to insert the processor easily, and processor pins will not
fully go into the socket. If this is the case, please change the direction, until it easily and fully inserts into
the socket A. See Figure 2-2 at the same time check the processor temperature detection thermistor height
(if your motherboard has this component), then you can slowly insert the processor into the Scoket A.
Finally, you need to check that the processor edge and the Socket A edge is parallel. It should be parallel
and not tilted.
When you finish the above, push the lever down to its original position, you should feel the lever lock the
socket A. You have then finished the processor installation.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 11
Installing the Motherboard
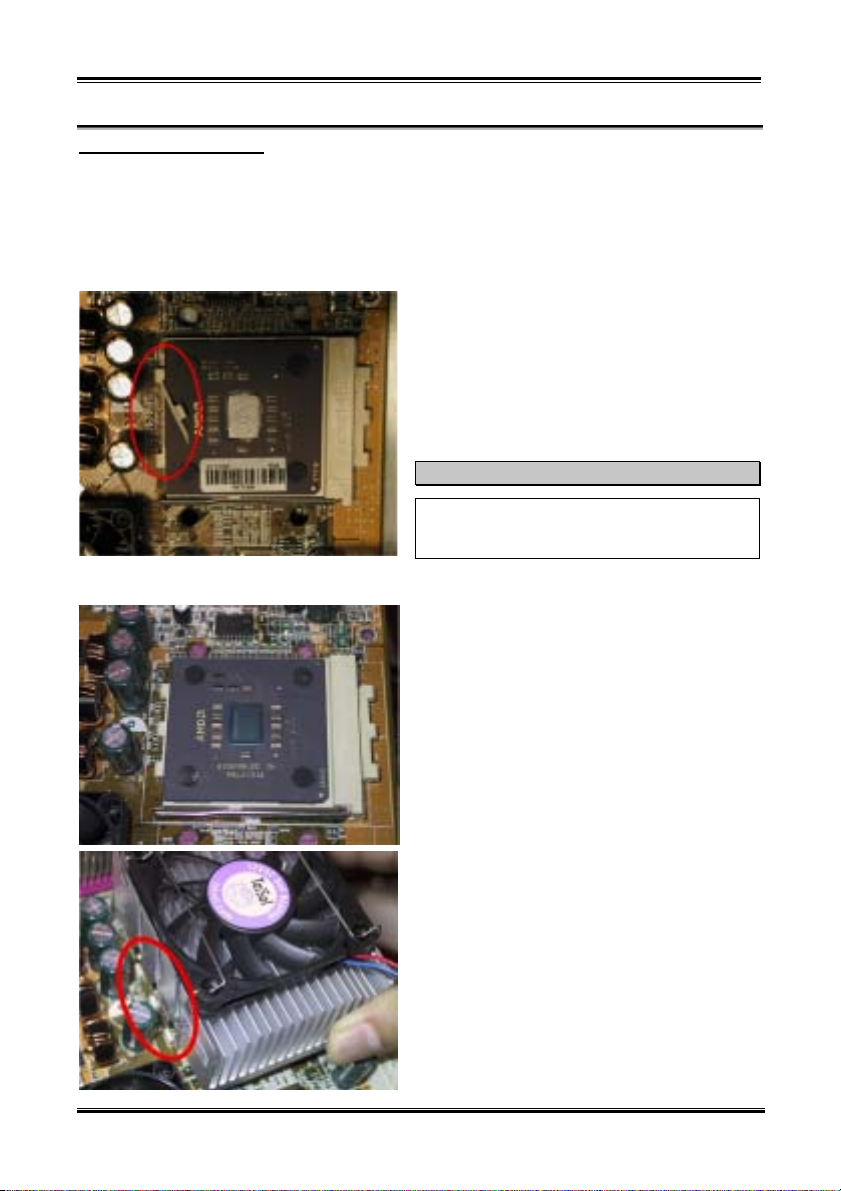
Heatsink Installation Hints
Because the processor will produce a lot of heat while operating, we suggest you use a heatsink approved
by AMD to be safe and to keep the processor temperature within normal operation temperatures. The
heatsink will be large and heavy, so the fixing plate has a strong tension. When you install the heatsink on
to the processor and its socket, you have to very carefully fix the fixing plate to the processor socket hook
on both sides. If you do not pay attention to this, you may make the fixing plate scratch the PCB surface
and cause circuit damage, break socket hooks or damage the die on the top of processor.
Please follow the sequence metioned below, Do Not
inverse the sequence. Otherwise, you may have a
situation like the photo on the left. Because of the
design of the CPU socket, the left side hooks are not
as strong as the right side hooks. If you follow our
suggestions you will prevent your processor and
socket from damage.
Note
Considering the chassis structure problem, please
always take off the motherboard from chassis,
before adding or removing a heatsink kit.
The proper procedure to install the heatsink kit:
First, install the processor into the processor socket.
Insert the heatsink left side fix plate into the
processor socket left side fix hooks. Make sure the fit
is very tight. Check the photo on the left.
2-3
User’s Manual
Page 12

Chapter 2
2-4
Insert a flat screwdriver into the middle slot of the
right side fix plate and push down. Then you can
push the fix plate over the socket hooks on the right
side. Check the photo on the left.
Check the photo on the left. You have finished the
heatsink installation.
Now hold the whole heatsink and slightly shake it,
make sure the buttom right side of the heaksink does
not contact the right side of the Socket (see bottom
picture). Otherwise, the processor die does not have
proper contact with the heatsink. This situation may
cause processor damage.
Remember to install the heatsink fan power cable to
the CPU fan header on the motherboard.
Now you can reinstall the motherboard back into the
chassis.
When all above procedures done, you can connect
the ATX power cable to the motherboard.
If you have different types of heatsink kit, please
refer to the manual that came with the heatsink kit.
The left photo shows another type of heatsink fix
plate design. The install sequences are still the same,
from right side to left side. Just remember that.
We strongly recommand you to buy a heatsink
with three holes in the fix plate. This will provide
the best stabability and won’t cause the Socket fix
hooks to be broken or damaged.
The left photo shows the bottom right side of the
heaksink in contact with the right side of the Socket.
In this situation, the processor die does not properly
contact the heatsink. If you start the computer at this
monent, it will immediately cause the processor
damage. Always check this place when you finish the
heatsink installation.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 13
Installing the Motherboard
2-5
2-2. Installing the Motherboard to the Chassis
After you install the processor to the motherboard, you can start to fix the motherboard into the chassis.
Most computer chassis will have a base on which there will be many mounting holes that allows the
motherboard to be securely attached and at the same time, prevents short circuits. There are two ways to
attach the motherboard to the base of chassis:
! With studs
! With spacers
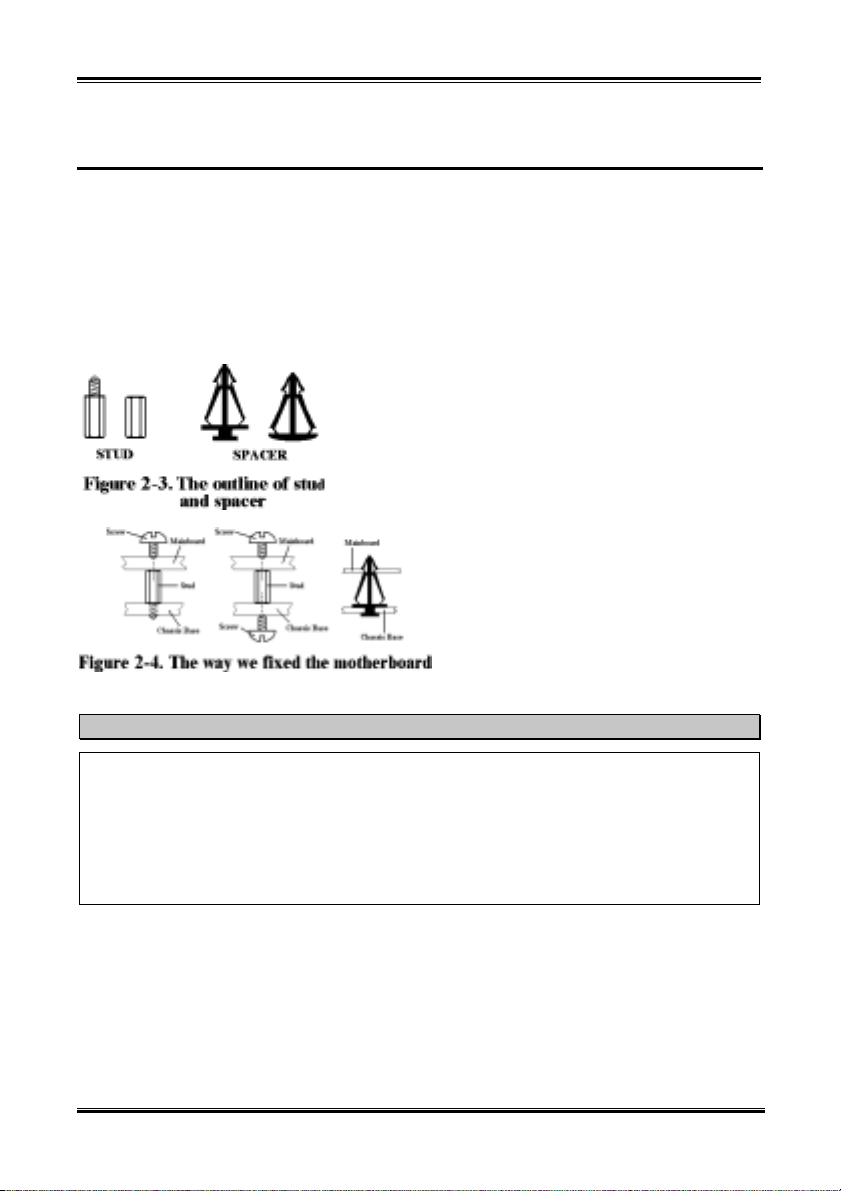
Please refer to figure 2-3, which shows the studs and spacers. There may be several types, but all look
like the figures below:
In principle, the best way to attach the motherboard is with studs.
Only if you are unable to do this should you attach the board
with spacers. Take a careful look at the motherboard and you
will see many mounting holes on it. Line these holes up with the
mounting holes on the base. If the holes line up and there are
screw holes this means you can attach the motherboard with
studs. If the holes line up and there are only slots, this means
you can only attach the motherboard with spacers. Take the tip
of the spacers and insert them into the slots.
After doing this to all the slots, you can slide
the motherboard into position aligned with the
slots. After the motherboard has been
positioned, check to make sure everything is
OK before putting the casing back on.
Figure 2-4 shows you the way to affix the
motherboard using studs or spacers.
Note
If the motherboard has mounting holes, but they don’t line up with the holes on the base and there are
no slots to attach the spacers, don’t worry, you can still attach the spacers to the mounting holes. Just
cut the bottom portion of spacers (the spacer they may be a little hard to cut, so be careful with your
hands). In this way you can still attach the motherboard to the base without worrying about short
circuits. Sometimes you may need to use the plastic springs to isolate the screw from the motherboard
PCB surface, because the circuit wire may be near by the hole. Be careful, don’t let the screw contact
any the printed circuit wire or parts on the PCB that are near the fixing hole, otherwise it may damage
the board or cause board malfunctioning.
User’s Manual
Page 14
Chapter 2
2-6
2-3. Installing System Memory
This motherboard provides two 184-pin DDR DIMM sites for memory expansion. The DDR DIMM
sockets support 8 M x 64 (64 MB), 16M x 64 (128 MB), 32 M x 64 (256 MB) and 64 M x 64 (512 MB)
or double density DDR DIMM modules. Minimum memory is 64 MB and the maximum memory is 1 GB
DDR SDRAM. There are two memory module sockets on the system board (for a total of four banks). In
order to create a memory array, following rules must be followed.
! The memory array is 64 or 72 bits wide. (Depending on with or without parity)
! For those modules, we suggest that you be populate DIMM1 to DIMM2 in order.
! Supports single and double density DDR DIMMs.
Table 2-1. Valid Memory Configurations
Bank Memory Module Total Memory
Bank 0, 1
(DDR DIMM1)
Bank 2, 3
(DDR DIMM2)
Total System Memory for Unbuffered and Non-ECC DDR
SDRAM DIMM (PC1600/PC2100)
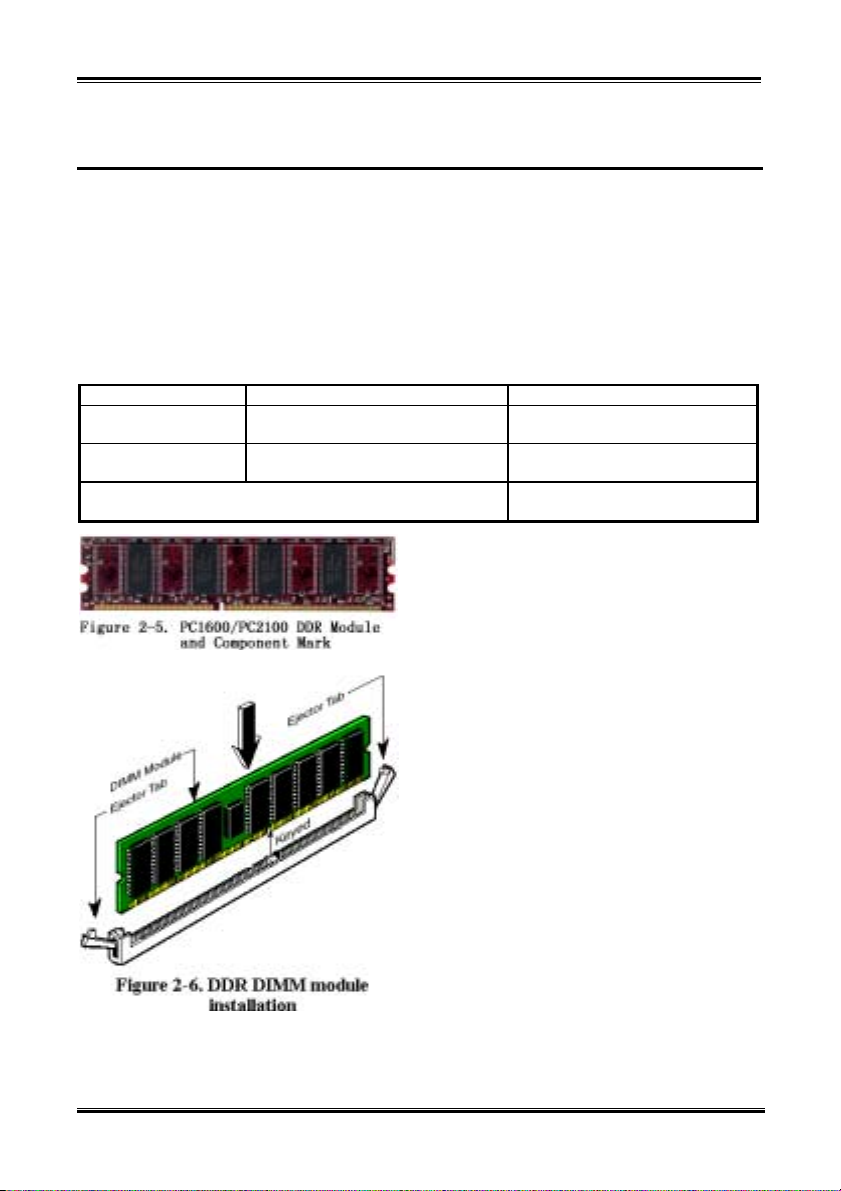
Step 4. Locate your computer’s 184-pin memory expansion DDR DIMM socket.
Step 5. Insert the DDR DIMM module into the expansion socket as shown in the illustration. Note how
the module is keyed to the socket. You can refer to Figure 2-6 for the details. This insures the
64 MB, 128 MB,
256 MB, 512 MB
64 MB, 128 MB,
256 MB, 512 MB
Generally, installing DDR SDRAM modules to your
motherboard is an easy thing to do. You can refer to
Figure 2-5 to see what a 184-pin PC 1600 and PC
2100 DDR SDRAM module looks like.
Unlike installing SIMMs, DIMMs may be
“snapped” directly into the socket. Note: Certain
DDR DIMM sockets have minor physical differences.
If your module doesn't seem to fit, please do not
force it into the socket as you may damaged your
memory module or DDR DIMM socket.
The following procedure will show you how to
install a DDR DIMM module into a DDR DIMM
socket.
Step 1. Before you install the memory module,
Step 2. Remove the computer’s chassis cover.
Step 3. Before touching any electronic components,
64 MB ~ 512 MB
64 MB ~ 512 MB
64 MB ~ 1 GB
please place the computer power switch in
the off position and disconnect the AC
power cord from your computer.
make sure you first touch an unpainted,
grounded metal object to discharge any
static electricity stored on your clothing or
body.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 15
Installing the Motherboard
DDR DIMM module will be plugged into the socket in one way only. Firmly press the DDR
DIMM module into DDR DIMM socket, making certain the module is completely seated in the
DDR DIMM socket.
Step 6. Once the DDR DIMM module has been installed, the installation is complete and the computer’s
cover can be replaced. Or you can continue to install other devices and add-on cards that are
mentioned in the following section.
Note
When you install a DDR DIMM module fully into the DDR DIMM socket, the eject tab should be
locked into the DDR DIMM module very firmly and fit into its indention on the both sides.
It is difficult to differentiate between the PC 1600 and PC 2100 DDR SDRAM modules from the exterior.
The only way you can identify them is to look at the sticker on the DDR SDRAM module. The sticker
will tell you which kind of structure module the DDR SDRAM is.
2-7
2-4. Connectors, Headers and Switches
Inside the case of any computer several cables and plugs have to be connected. These cables and plugs are
usually connected one-by-one to connectors located on the motherboard. You need to carefully pay
attention to any connection orientation the cables may have and, if any, notice the position of the first pin
of the connector. In the explanations that follow, we will describe the significance of the first pin.
We will show you all of the connectors, headers and switches here, and tell you how to connect them.
Please pay attention and read the entire section for necessary information before attempting to finish all of
the hardware installation inside the computer chassis.
Figure 2-7 shows you all of the connectors and headers that we’ll discuss in the next section, you can use
this diagram to visually locate each connector and header we describe.
All connectors, headers and switches mentioned here, will depend on your system configuration. Some
features you may (or may not) have and need to connect or configure depending on the peripheral. If your
system doesn't have such add-on cards or switches you can ignore some special feature connectors.
Warning!!!
NVIDIA nForce chipset supports AGP 1.5V only, wrongfully plug an AGP 3.3V only AGP
graphic card on NV7m motherboard will burn the Crush 12 chipset and cause your NV7m
motherboard damaged.
Explaination: Most of the AGP cards golden finger is with a notch to identify AGP 3.3V or AGP
1.5V, an AGP graphic card without the notch means AGP 1.5V not compatible and can’t be inserted
into AGP slot fully. Very few AGP graphic cards it’s a 3.3V only AGP graphic card but with “1.5V
identify notch” golden finger! Such kind of abnormal golden finger will permit AGP graphic card
plug into NV7m motherboard then burn the chipset and cause motherboard damaged. Some AGP
graphic cards are with jumpers for switches to AGP 1.5V or 3.3V. Please DO MAKE SURE it’s
jumpers setting at 1.5V position before you insert it into NV7m motherboard.
User’s Manual
Page 16
Chapter 2
2-8
Figure 2-7. All Connectors and Headers for the NV7m
First, let’s see the headers that NV7m uses, and what their functions are. We will show you all the
connectors and headers.
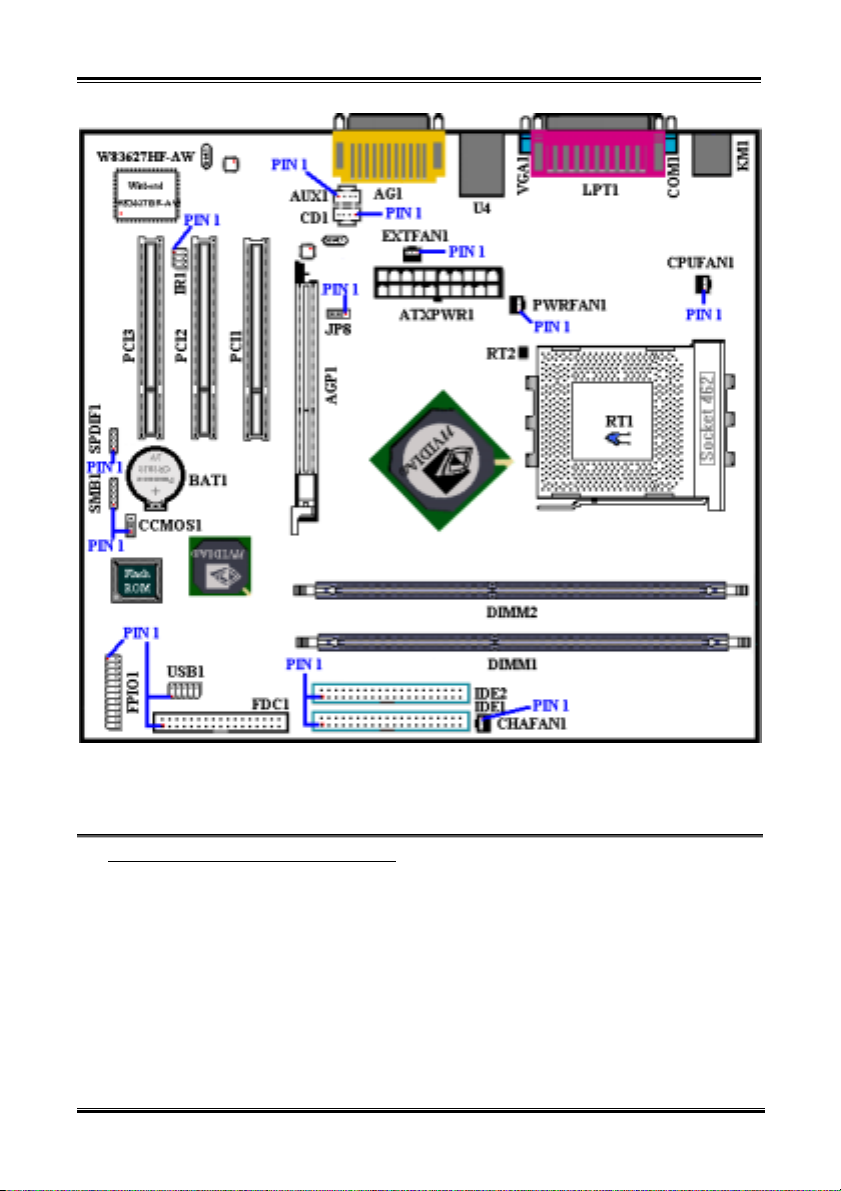
(1). ATXPWR1: ATX Power Input Connector
Attach the connector from the power supply to the ATXPWR1 connector here. Remember you have to
push the connector from the ATX power supply firmly to the end with the ATXPWR1 connector,
insuring that you have a good connection.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 17
Installing the Motherboard
Caution
If the power supply connectors are not properly attached to the ATX power supply, the power supply
or add-on cards may be damaged.
One end of AC power core connects to ATX power supply, and the other end (AC plug) will plug into
the wall outlet. Be aware that when facing the wall outlet, the round hole is in the middle. The right
side slot is called ground wire slot. It has a longer slot length than the left side slot. The left side slot is
called the live wire slot. You can use an electroscope to detect its polarity or you can use a voltage
meter to measure the voltage of both slot sides. If you insert an electroscope into the live wire slot, the
electroscope will light up. Using a voltage meter, you will find that the live wire slot will register a
higher voltage.
If you reverse the polarity of AC plug, it may affect the life of computer equipment, or cause an
electric shock when you touch the computer chassis. We suggest that you plug the computer AC plug
to a three-hole wall outlet for better safety and to avoid electric shock.
2-9
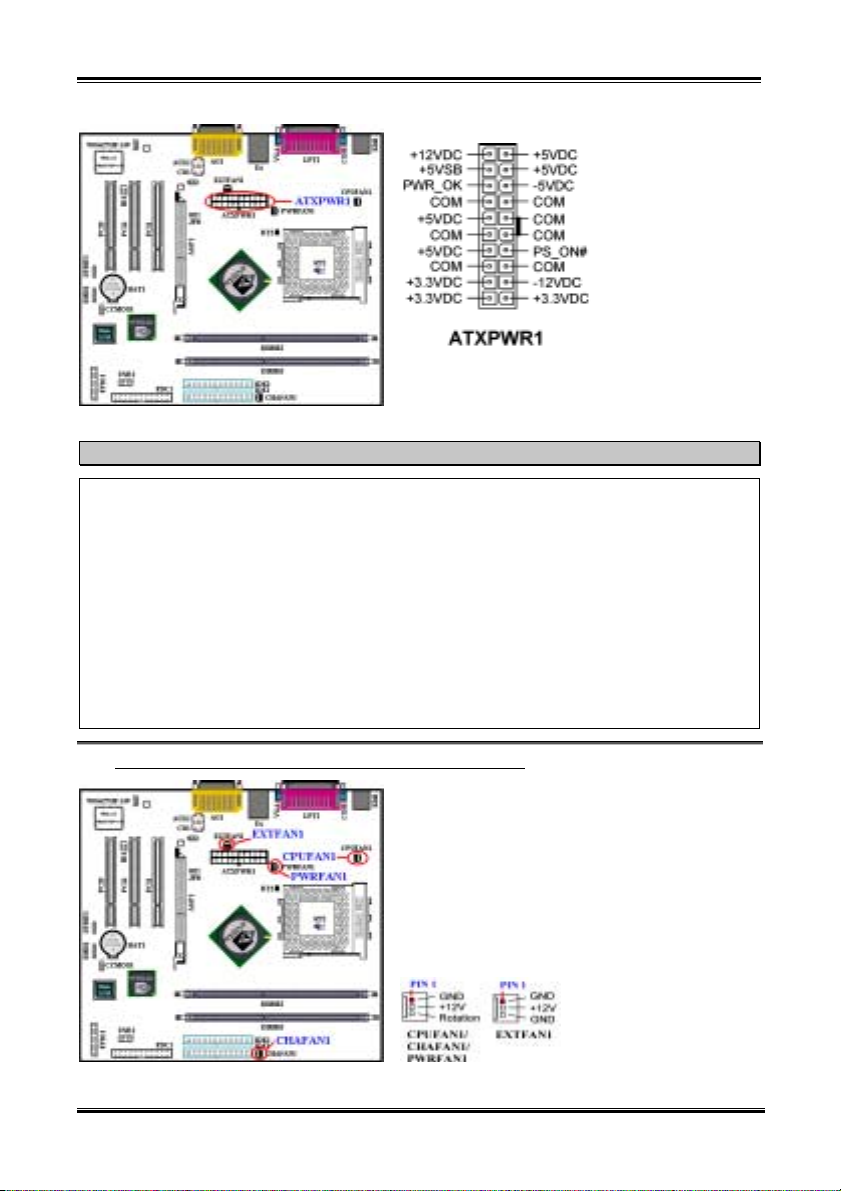
(2). CPUFAN1, CHAFAN1, PWRFAN1 and EXTFAN1 headers
Attach the connector from the processor fan to the
header named CPUFAN1 and connector from the front
chassis fan to the header CHAFAN1. Attach the
connector from the power fan to PWRFAN1 header
and connector from the back chassis fan to the header
EXTFAN1. You must attach the processor fan to the
processor, or your processor will work abnormally or
may be damaged by overheating. To prevent the
computer chassis internal temperature from getting too
high, also connect the chassis fan.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
User’s Manual
Page 18
Chapter 2
2-10
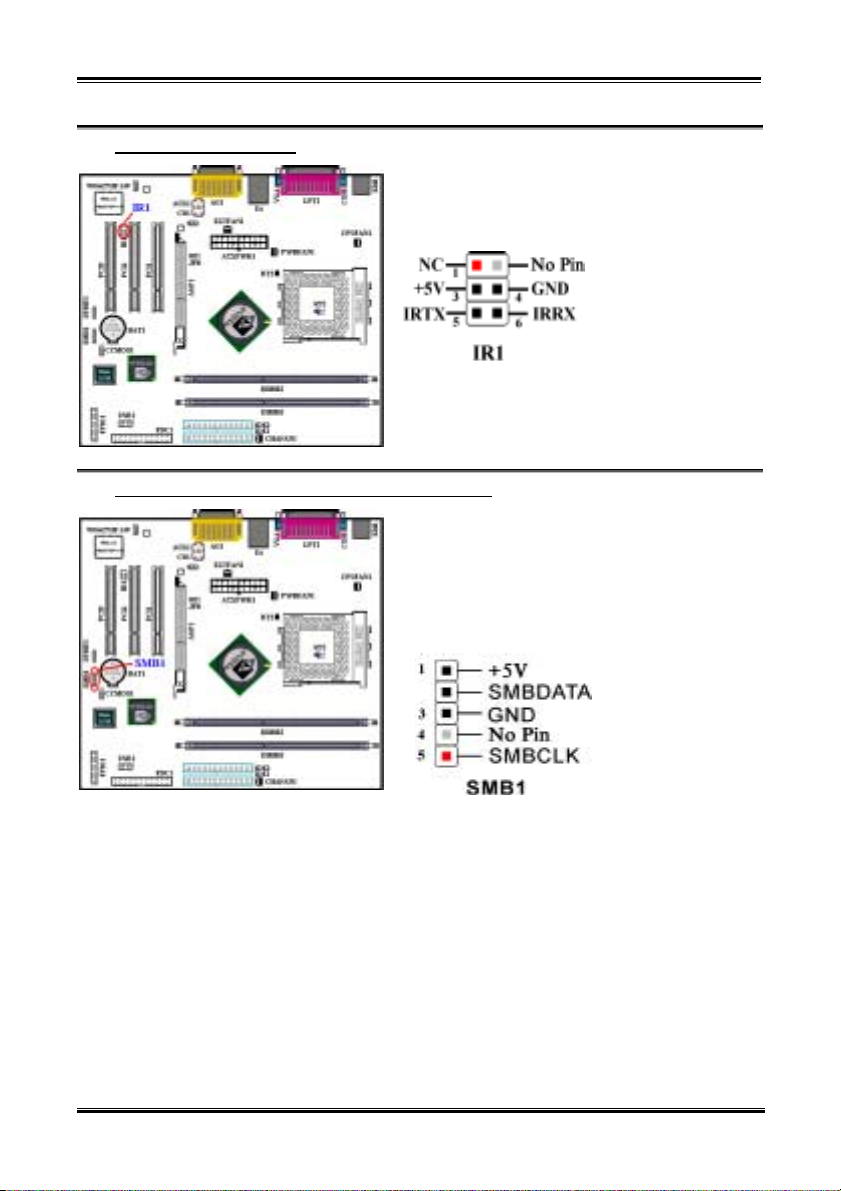
(3). IR1: IR Header (Infrared)
There is a specific orientation for pins 1 through 6,
attach the connector from the IR KIT or IR device to
the IR1 header. This motherboard supports standard IR
transfer rates.
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
(4). SMB1: System Management Bus (SM-Bus) Connectors
This connector is reserved for the system management
bus (SM-Bus). The SM-Bus is a specific
implementation of an I
this means that multiple chips can be connected to the
same bus and each one can act as a master by initiating
a data transfer. If more than one master simultaneously
tries to control the bus, an arbitration procedure decides
Note: Watch the pin position and the orientation
2
C bus. I2C is a multi-master bus,
which master gets
priority. You can
connect the devices
which utilizes the
SM-Bus.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 19
Installing the Motherboard
(5). RT1 & RT2: Processor & System Temperature Thermistor
The RT1 is used to detect the processor temperature.
The RT2 is used to detect the system environment
temperature. You can see the readings in the BIOS or in
the hardware monitoring application main screen.
2-11
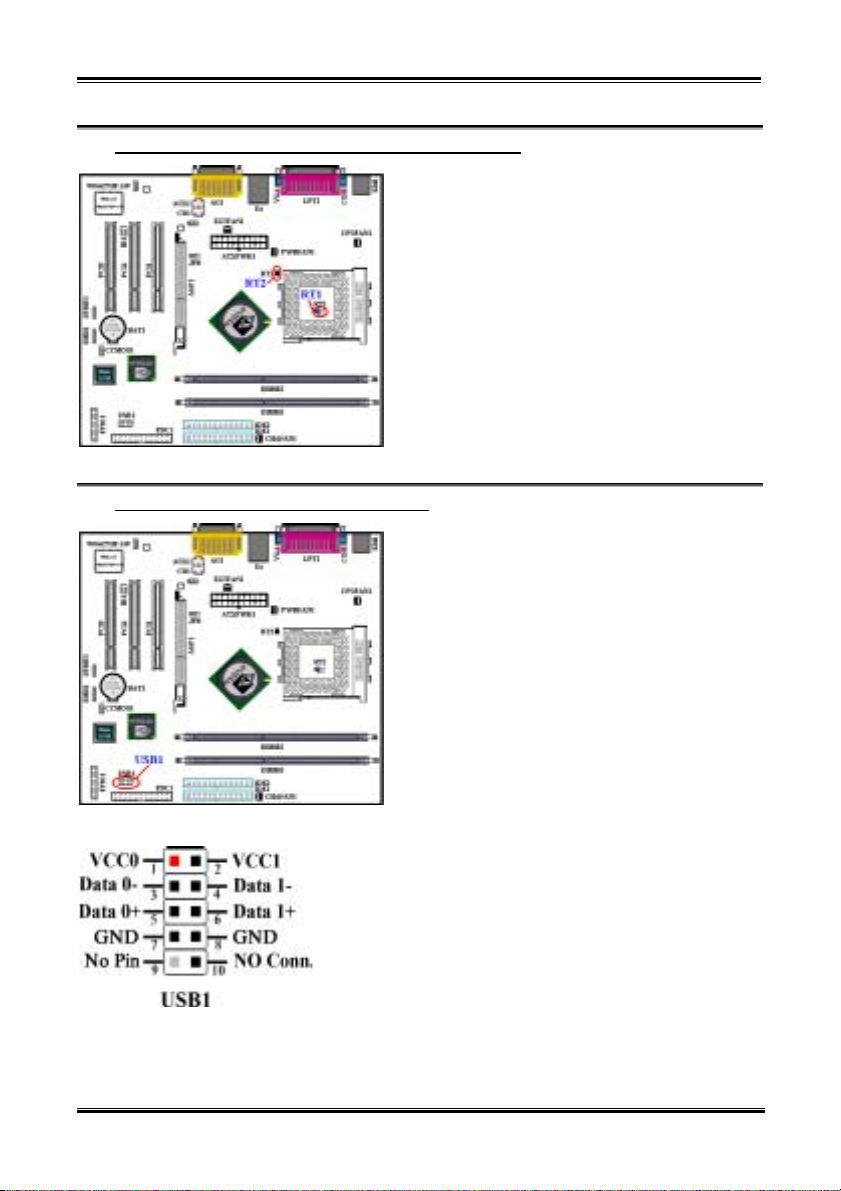
(6). USB1 Headers: Additional USB Plugs Header
This header is for connecting the additional USB port
plugs. This connector can provides two additional USB
plugs. Which means, total you can get two additional
USB plugs. You can use the special USB port
expansion cable to connect it (the cable come with the
metal plate can fixed on the back panel of computer
chassis).
User’s Manual
Page 20
Chapter 2
2-12
(7). CCMOS1 Header: CMOS Discharge Jumper
Jumper CCMOS1 used to discharge CMOS memory.
When you install the motherboard, make sure this
jumper is set for normal operation (pin 1 and 2 shorted).
See figure below.
Note
Before you clear the CMOS, you have to first turn the power off (including the +5V standby power).
Otherwise, your system may work abnormally.
After updating your BIOS and before boot up, please clear the CMOS first. Then put the jumper to its
default position. After that, you can reboot your system and ensure that your system is working fine.
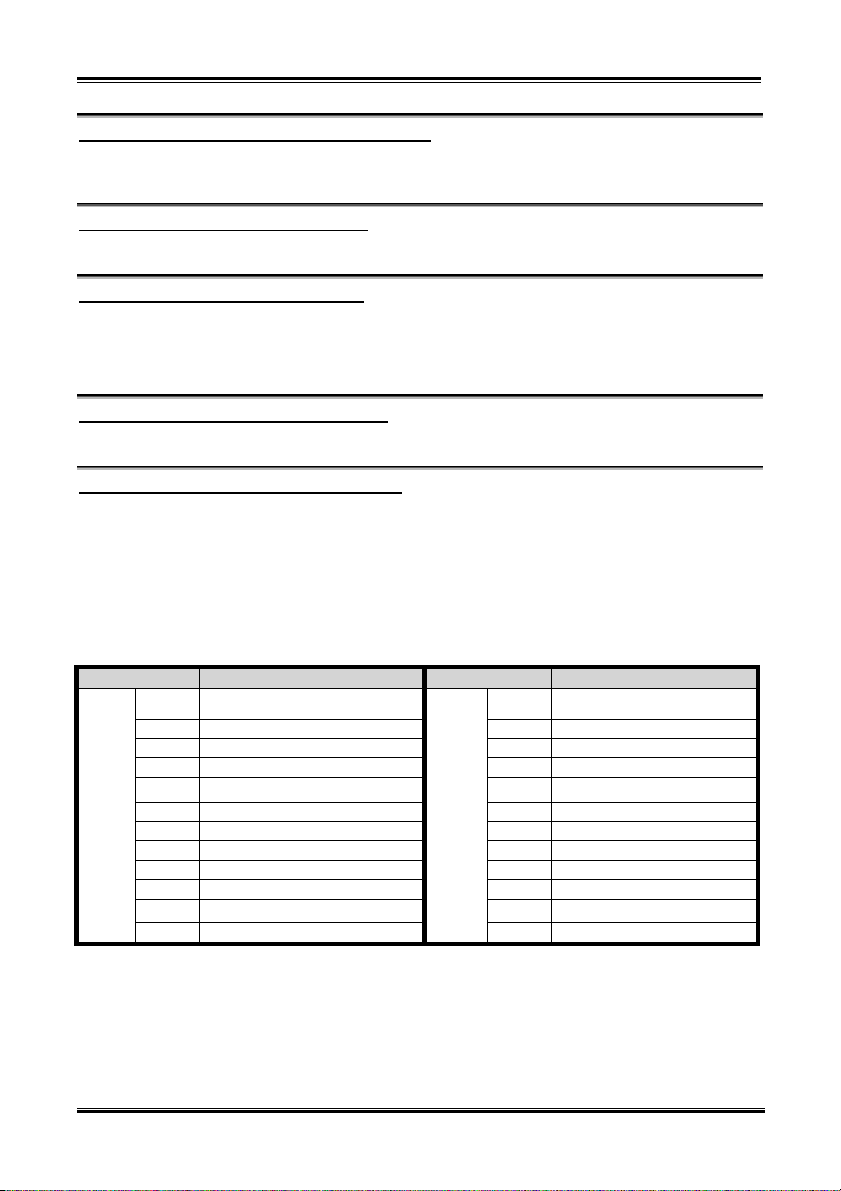
(8). FPIO1 Headers: The Headers for Chassis’s Front Panel Indicators and Switches
FPIO1 are for switches and indicators for the chassis’s
front panel, there are several functions that come from
this header. You have to watch the pin position and the
orientation, or you may cause LED do not light up.
Figure below shows you the FPIO1 functions of the
pins.
FPIO1 (Pin 1 & 3): HDD LED Header
Attach the cable from the case’s front panel HDD LED to this header. If you install it in the wrong
direction, the LED light will not illuminate correctly.
Note: Watch the HDD LED pin position and the orientation.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 21
Installing the Motherboard
FPIO1 (Pin 5 & 7): Hardware Reset Switch Header
Attach the cable from the case’s front panel Reset switch to this header. Press and hold the reset button
for at least one second to reset the system.
2-13
FPIO1 (Pin 15-17-19-21): Speaker Header
Attach the cable from the system speaker to this header.
FPIO1 (Pin 2 & 4): Suspend LED Header
Insert the two-threaded suspend LED cable into this header. If you install it in the wrong direction, the
LED light will not illuminate correctly.
Note: Watch the Suspend LED pin position and the orientation.
FPIO1 (Pin 6 & 8): Power On Switch Header
Attach the cable from the case’s front panel power on switch to this header.
FPIO1 (Pin 16-18-20): Power On LED Headers
There is a specific orientation for pins 1 through 3. Insert the three-threaded power on LED cable to this
header. Check to make sure the correct pins go to the correct connectors on the motherboard. If you
install them in the wrong direction, the power LED light will not illuminate correctly.
Note: Watch the power LED pin position and orientation.
For the PN1 and PN2 pin’s count-name list, please refer to table 2-2.
Table 2-2. FPIO1 pin count name list
PIN Name Significance of signal PIN Name Significance of signal
PIN 1 HDD LED (+) PIN 2 SP-LED (+)
PIN 3 HDD LED (-) PIN 4 SP-LED (-)
PIN 5 Reset SW (-) PIN 6 PWR-ON (+)
PIN 7 Reset SW (+) PIN 8 PWR-ON (-)
PIN 9 No Connection PIN 10
PIN 11 No Pin PIN 12 No Pin
FPIO1
PIN 13 No Pin PIN 14 No Pin
PIN 15 Speaker (+5V) PIN 16 PWR LED (+)
PIN 17 Speaker (GND) PIN 18 No Pin
PIN 19 Speaker (GND) PIN 20 PWR LED (-)
PIN 21 Speaker (Driver) PIN 22 No Connection
PIN 23 No Pin
FPIO1
PIN 24 No Connection
No Pin
User’s Manual
Page 22
Chapter 2
2-14
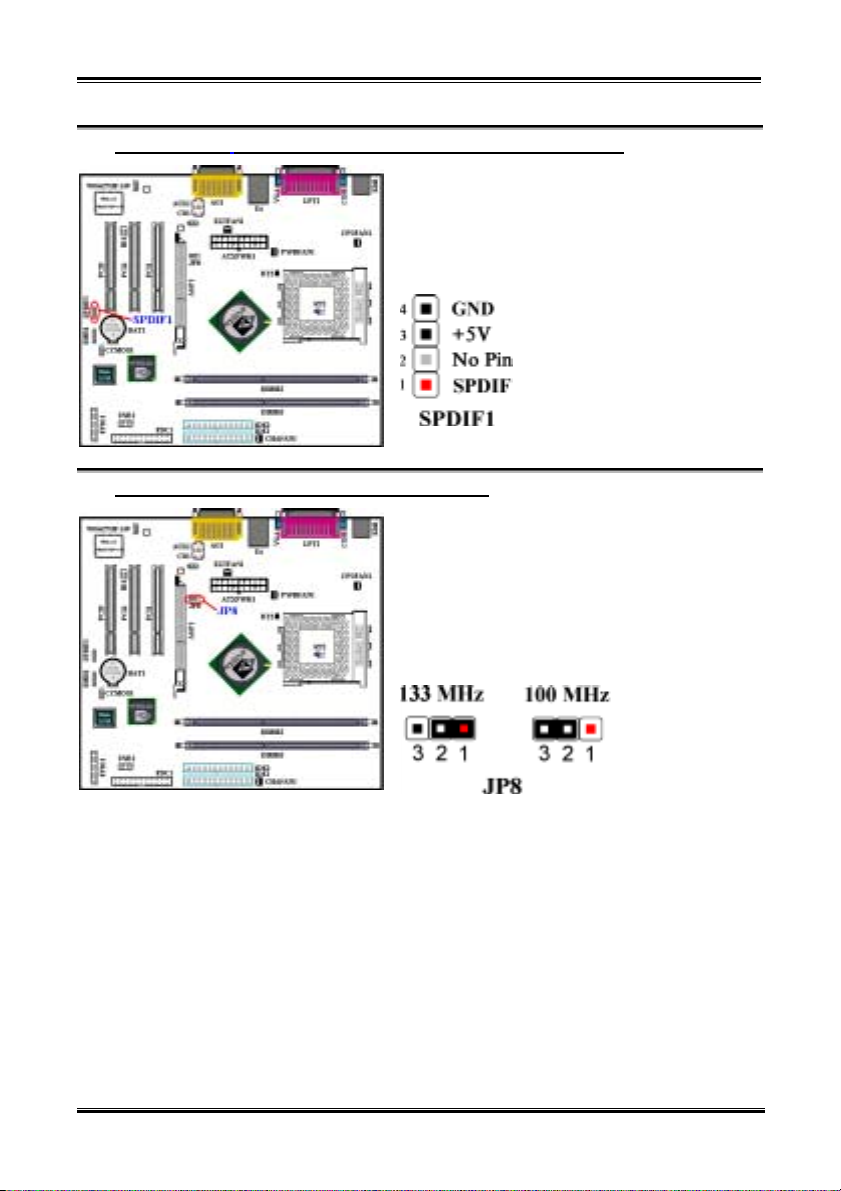
(9). SPDIF1 Header: Sony/Philips Digital InterFace Output Header (Optional)
This header is for SPDIF output signal use. This option
can let you output the digital SPDIF signal to the
external decode equipment. This function is optional.
(10). JP8 Header: Processor FSB Frequency Setting Header
Jumper JP8 used to select processor FSB frequency.
The default setting is 100 MHz (pin 2 and 3 shorted).
Please accord your processor FSB speed to set correct
FSB frequency.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 23

Installing the Motherboard
(11). CD1 and AUX1 Headers: CD Audio and Auxiliary audio signal input headers
These connectors connect to the audio output of
internal CD-ROM drive or add-on card.
2-15
(12). FDC1 Connector
A red mark on a wire typically designates the location of pin 1. You need to align the wire pin 1 to the
FDC1 connector pin 1, then insert the wire connector into the FDC1 connector.
This 34-pin connector is called the “floppy disk drive
connector”. You can connect a 360K, 5.25”, 1.2M,
5.25”, 720K, 3.5’’, 1.44M, 3.5” or 2.88M, 3.5” floppy
disk drive.
A floppy disk drive ribbon cable has 34 wires and two
connectors to provide the connection of two floppy disk
drives. After connecting the single end to the FDD1,
connect the two connectors on the other end to the
floppy disk drives. In general, people only install one
floppy disk drive on their computer system.
Note
User’s Manual
Page 24

Chapter 2
2-16
(13). IDE1and IDE2 Connectors
This motherboard provides two IDE ports (IDE1 &
IDE2) to connect up to four IDE devices in Ultra DMA
100 mode by Ultra DMA 66 ribbon cables. Each cable
has 40-pin 80-conductor and three connectors,
providing two hard drive connections with the
motherboard. Connect the single end (blue connector)
at the longer length of ribbon cable to the IDE port on
motherboard, and the other two ends (gray and black
connector) at the shorter length of the ribbon cable to
the connectors on hard drives.
If you want to connect two hard drives together through
one IDE channel, you must configure the second drive
to Slave mode after the first Master drive. Please refer
to the HDD documentation for jumper settings. The
first drive connected to IDE1 is usually referred to as
“Primary Master”, and the second drive as “Primary
Slave”. The first drive connected to IDE2 is referred to as
“Secondary Master” and the second drive as “Secondary
Slave”.
Keep away from connecting one legacy slow speed device,
like CD-ROM, together with another hard disk drive on
the same IDE channel; this will decrease your integral
system performance.
Figure 2-8. Ultra DMA 66
Ribbon Cable Outline
Note
! The Master or Slave status of the hard disk drive is set on the hard disk itself. Please refer to the
hard disk drive user’s manual.
! To connect Ultra DMA 100 devices on IDE1and IDE2, an Ultra DMA 66 cable is required.
! A red mark on a wire typically designates the location of pin 1. You need to align the wire pin 1 to
the IDE connector pin 1, before inserting the wire connector into the IDE connector.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 25

Installing the Motherboard
Figure 2-9. NV7m back panel connectors
Figure 2-9 shows the NV7m back panel connectors, these connectors are for connection to outside
devices to the motherboard. We will describe which devices will attach to these connectors below.
2-17
(14). PS/2 Keyboard Connector
(15). PS/2 Mouse Connector
Attach a PS/2 mouse to this 6-pin Din-connector.
(16). Serial Port COM1 Connector
This motherboard provides one COM port, you can connect an external modem, mouse or other devices
that support this communication protocol to these connectors.
You can decide which external devices you want to connect to COM1. The COM port can only have one
device connected at a time.
(17). VGA Port VGA1 Connector
This motherboard had built-in the nVIDIA 256-bit 3D/2D graphic accelerator, so you don’t need to buy
another AGP grapgic accelerator. This DIN 15 pin Female connector is for a VGA output signal to the
monitor or LCD display. You can connect the plug from the monitor to this connector. If you don't move
your system often, we suggest you fasten the two screws from the plug with this connector. It will assure
the quality of your display.
Attach a PS/2 keyboard connector to this 6-pin Din-connector.
If you use an AT keyboard, you can go to a computer store to
purchase an AT to ATX converter adapter, then you can
connect your AT keyboard to this connector. We suggest you
use a PS/2 keyboard for best compatibility.
User’s Manual
Page 26

Chapter 2
2-18
(18). Parallel Port Connector
This parallel port is also called an “LPT”
port, because it usually connects to the
printer. You can connect other devices that
support this communication protocol, like
an EPP/ECP scanner, etc.
(19). USB Port Connectors
This motherboard provides two USB ports. Attach the USB connector from the individual device to these
connectors.
You can attach USB devices such as a, scanner, digital speakers, monitor, mouse, keyboard, hub, digital
camera, joystick etc. to one of each
USB connector. You must make
sure your operating system supports
this feature and you may need to
install an additional driver for
individual devices. In Please refer to
your device user’s manual for
detailed information.
(20). 10/100 Mb LAN Port Connector
This motherboard provides built-in 10/100 Mb LAN port, this jack is for connecting the RJ-45 cable from
the local area network hub to your computer. We suggest you use the category 5 UPT (Unshielded
Twisted Pair) or STP (Shielded Twisted Pair) cable to make this connection. The connection length from
the hub to the computer is best to be kept under 100 meter.
The green LED shows the connection situation. If the network active well, this LED will light on. The
yellow LED shows if the data is active or not. If the computer is translating or receiving data from the
network, this LED will flicker.
(21). Line Out, Line In and Mic In Connector
Line Out connector: You can connect an external stereo speaker signal input plug to this connector, or
you can connect the plug from here to the stereo audio equipment AUX signal input socket. Remember,
the motherboard does not have a built in amplifier to drive the speaker, so you must use a speaker that has
a built in amplifier, or you may not hear any sound or only a small volume of sound from the speaker.
Line In Connector: You can connect the TV adapter audio output signal, or external audio sources, like
a CD walkman, video camcorder, VHS recorder audio output signal plug to this connector. Your audio
software can control the input level for the line-in signal.
Mic In Connector: You can connect the plug from the microphone to this connector. Do not connect
other audio (or signal) sources to this connector.
(22). MIDI/GAME Port Connector
You can connect your joystick, game pad, or other simulation hardware device DIN 15-pin plugs to this
connector. Please refer to the further connection notes of the device’s user's manual for further detailed
information.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 27

Installing the Motherboard
Note
This chapter contains many color drawing diagram and photos, we strongly recommend you to read
this chapter use the PDF file we gave you that store in the CD-Title. It will provide you the better look
and clearly color identify.
2-19
User’s Manual
Page 28

Chapter 2
2-20
NV7m Motherboard
Page 29

Introducing the BIOS
3-1
Chapter 3. Introducing the BIOS
The BIOS is a program located on a Flash Memory chip on the motherboard. This program will not be
lost when you turn the computer off. This program is also referred to as the boot program. It is the only
channel the hardware circuit has to communicate with the operating system. Its main function is to
manage the setup of the motherboard and interface card parameters, including simple parameters such as
time, date, hard disk drive, as well as more complex parameters such as hardware synchronization, device
operating mode. The computer will operate normally, or will operate at its best, only if all of these
parameters are correctly configured through the BIOS.
Don’t change the parameters inside the BIOS unless you fully understand the meanings
'
and consequences
The parameters inside the BIOS are used to setup the hardware synchronization or the
device-operating mode. If the parameters are not correct, they will produce errors, the computer will
crash, and sometimes you will even not be able to boot the computer after it has crashed. We
recommend that you do not change the parameters inside the BIOS unless you are very familiar with
them. If you are not able to boot your computer anymore, please refer to the section “CCMOS1
Header” in Chapter 2 to see how to discharge the CMOS date.
When you start the computer, the BIOS program controls it. The BIOS first operates an auto-diagnostic
test called POST (Power On Self Test) for all of the necessary hardware. It then configures the
parameters of the hardware synchronization, and detects all of the hardware. Only when these tasks are
completed does it give up control of the computer to the program to the next level, which is the operating
system (OS). Since the BIOS is the only channel for hardware and software to communicate, it is the key
factor for system stability, and in insuring that your system performs at its best. After the BIOS has
achieved the auto-diagnostic and auto-detection operations, it will display the following message:
PRESS DEL TO ENTER SETUP
The message will be displayed for three to five seconds, if you press the Del key, you will access the
BIOS Setup menu. At that moment, the BIOS will display the following message:
Figure 3-1. CMOS Setup Utility Screen Shot
User’s Manual
Page 30

Chapter 3
3-2
In the BIOS Setup main menu of Figure 3-1, you can see several options. We will explain these options
step by step in the following pages of this chapter, but let us first see a short description of the function
keys you may use here:
! Press Esc to quit the BIOS Setup.
! Press ↑↓←→ (up, down, left, right) to choose, in the main menu, the option you want to confirm
or to modify.
! Press F10 when you have completed the setup of BIOS parameters to save these parameters and to
exit the BIOS Setup menu.
! Press Page Up/Page Down or +/- keys when you want to modify the BIOS parameters for the active
option.
Note
You only can use the “awdflash.exe” attached in NV7m product CD-ROM, DO NOT USE the others
Award flash program to flash your NV7m BIOS.
Note
Parts of the screenshot may not same as you see on your screen, because the BIOS version may
change periodically. However, most of the functions covered in this manual will work. We suggest
that you go to our WEB site often to see if there are new manual releases. Then you can check the
newly updated BIOS items.
Computer Knowledge: CMOS Data
Maybe you have heard somebody saying that his or her CMOS DATA was lost. What is the CMOS?
Is it important? The CMOS is the memory used to store the BIOS parameters that you have
configured. This memory is passive. You can read its data, and you can also store data in it. But this
memory has to be powered by a battery, in order to avoid any loss of its data when the computer is
turned off. Since you may have to change the CMOS battery when it is out of power and if doing so,
you will loose all CMOS data, therefore, we recommend that you write down all the parameters of
your hardware, or to put a label with these parameters on your hard disk.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 31

Introducing the BIOS
3-3
3-1. Standard CMOS Features Setup Menu
This contains the basic configuration parameters of the BIOS. These parameters include date, hour, VGA
card, floppy disk and HDD settings.
Figure 3-2A. Standard CMOS Features Screen Shot
Date (mm:dd:yy):
You can set the date in this item: month (mm), date (dd) and year (yy).
Time (hh:mm:ss):
You can set the time in this item: hour (hh), minute (mm) and second (ss).
IDE Primary Master / Slave and IDE Secondary Master / Slave:
These items have a sub-menu to let you choose further options. You can refer to figure 3-3B to check
what options are available.
Figure 3-2B. IDE Primary Master Screen Shot
User’s Manual
Page 32

Chapter 3
3-4
IDE HDD Auto-Detection:
Press the Enter key for the BIOS to auto detect all detailed parameters of the hard disk drivers (HDD). If
auto detection is successful, the correct values will be shown in the remaining items of this menu.
Note
( A new IDE HDD must be first formatted, otherwise it can’t do the read/write. The basic step in
using a HDD is to run FDISK, and then FORMAT the drive. Most current HDDs have already
been subjected to low-level format at the factory, so you can probably skip this operation.
Remember though, the primary IDE HDD must have its partition set to active within the FDISK
procedure.
) If you are using an old HDD that is already formatted, auto detection can’t detect the correct
parameters. You may need to do a low-level format or set the parameters manually, and then
check if the HDD is working.
IDE Primary Master:
Three settings are available: None * Auto * Manual, The default setting is Auto. If you choose Auto,
the BIOS will automatically check what kind hard disk you are using. If you want to set the HDD
parameters yourself, make sure you fully understand the meaning of the parameters, and be sure to refer
to the manual provided by the HDD manufacture to get the settings right.
Access Mode:
Since old operating systems were only able to support HDDs with capacities no bigger than 528MB, any
hard disk with more than 528MB was unusable. AWARD BIOS features a solution to this problem: you
can, according to your operating system, choose four operating modes: CHS * LBA * Large *Auto.
The HDD auto detection option in the sub-menu will automatically detect the parameters of your hard
disk and the mode supported.
CHS (Normal mode):
!
Standard normal mode supports hard disks of up to 528MB or less. This mode directly uses positions
indicated by Cylinders (CYLS), Heads, and Sectors to access data.
LBA (Logical Block Addressing) mode:
!
The earlier LBA mode can support HDD capacities of up to 8.4GB, and this mode uses a different
method to calculate the position of disk data to be accessed. It translates Cylinders (CYLS), Heads
and Sectors into a logical address where data is located. The Cylinders, Heads, and Sectors displayed
in this menu do not reflect the actual structure of the hard disk, they are just reference values used to
calculate actual positions. Currently, all high capacity hard disks support this mode, that’s why we
recommend you use this mode. Currently, the BIOS can support the INT 13h extension function,
enabling the LBA mode to support hard disk drive capacities exceeding 8.4GB.
Large Mode:
!
When the number of cylinders (CYLs) of the hard disk exceeds 1024 and DOS is not able to support it,
or if your operating system does not support LBA mode, you should select this mode.
Auto:
!
Just let the BIOS detect your HDD access mode and make the decisions.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 33
Introducing the BIOS
Capacity:
"
This item auto displays your HDD size. Note that this size is usually slightly greater than the size
given by a disk checking program of a formatted disk.
Note
All the items below are available when you set the item Primary IDE Master to Manual.
Cylinder:
"
When disks are placed directly above one another along the shaft, the circular vertical “slice”
consisting of all the tracks located in a particular position is called a cylinder. You can set the number
of cylinders for a HDD. The minimum number you can enter is 0, the maximum number you can
enter is 65536.
Head:
"
This is the tiny electromagnetic coil and metal pole used to create and read back the magnetic patterns
on the disk (also called the read/write head). You can configure the number of read/write heads. The
minimum number you can enter is 0, the maximum number you can enter is 255.
Precomp:
"
The minimum number you can enter is 0, the maximum number you can enter is 65536.
Wa rn in g
Setting a value of 65536 means no hard disk exists.
Landing Zone:
"
This is a non-data area on the disk's inner cylinder where the heads can rest when the power is turned
off. The minimum number you can enter is 0, the maximum number you can enter is 65536.
Sector:
"
The minimum segment of track length that can be assigned to stored data. Sectors usually are grouped
into blocks or logical blocks that function as the smallest units of data permit. You can configure this
item to sectors per track. The minimum number you can enter is 0, the maximum number you can
enter is 255.
3-5
Driver A & Driver B:
If you have installed the floppy disk drive here, then you can select the type of floppy drive it can support.
Six options are available: None * 360K, 5.25 in. * 1.2M, 5.25in. * 720K, 3.5 in. * 1.44M, 3.5 in. *
2.88M, 3.5 in.
Floppy 3 Mode Support:
Four options are available: Disabled * Driver A * Driver B * Both. The default setting is Disabled. 3
Mode floppy disk drives (FDD) are 3 1/2” drives used in Japanese computer systems. If you need to
access data stored in this kind of floppy, you must select this mode, and of course you must have a 3
Mode floppy drive.
User’s Manual
Page 34

Chapter 3
3-6
Video:
You can select the VGA modes for your video adapter, four options are available: EGA/VGA ! CGA 40
! CGA 80 ! MONO. The default setting is EGA/VGA.
Halt On:
You can select which type of error will cause the system to halt. Five options are available: All Errors !
No Errors ! All, But Keyboard ! All, But Diskette ! All, But Disk/Key.
You can see your system memory list in the lower right box, it shows the Base Memory, Extended
Memory and total Memory size configurations in your system. It is detected by the system during boot-up
procedure.
3-2. Advanced BIOS Features Setup Menu
In each item, you can press <Enter> at any time to display all the options for this item.
Attention
Advanced BIOS Features Setup Menu has already been set for maximum operation. If you do not
really understand each of the options in this menu, we recommend you use the default values.
NV7m Motherboard
Figure 3-3. Advanced BIOS Features Screen Shot
Page 35

Introducing the BIOS
3-7
Quick Power On Self Test:
Two options are available: Disabled or Enabled. The default setting is Enabled. After the computer has
been powered on, the BIOS of the motherboard will run a series of tests in order to check the system and
its peripherals. If the Quick Power on Self-Test feature is enable, the BIOS will simplify the test
procedures in order to speed up the boot process.
First Boot Device:
When the computer boots up, the BIOS attempts to load the operating system from the devices in the
sequence selected in these items: floppy disk drive A, LS120, ZIP100 devices, hard drive C, SCSI hard
disk drive or CD-ROM. There are ten options for the boot sequence that you can choose (The default
setting is Floppy.):
Floppy * LS120 * HDD-0 * SCSI * CDROM * HDD-1 * HDD-2 * HDD-3 * ZIP100 * LAN
* Disabled * Back to Floppy.
Second Boot Device:
Description is the same as the First Boot Device, the default setting is CDROM.
Third Boot Device:
Description is same as the First Boot Device, the default setting is HDD-0.
Boot Other Device:
Two options are available: Disabled or Enabled. The default setting is Enabled. This setting allows the
BIOS to try to boot devices other than the three which are listed in the above First, Second and Third
Boot Devices. If you set to Disabled, the BIOS will boot from only the three kinds of boot devices that
are set above.
Swap Floppy Drive:
This item can be set as Disabled or Enabled. The default setting is Disabled. When this feature is enabled,
you don’t need to open the computer case to swap the position of floppy disk drive connectors. Drive A
can be set as drive B and drive B can be set as drive A.
Boot Up Floppy Seek:
Two options are available: Disabled or Enabled. The default setting is Disabled. When the computer
boots up, the BIOS detects if the system has a FDD or not. When this item is set to “Enabled”, if the
BIOS detects no floppy drive, it will display a floppy disk drive error message. If this item is disabled, the
BIOS will skip this test.
Security Option:
This option can be set to Setup or System. The default setting is Setup. After you have created a password
through PASSWORD SETTING, this option will deny access to your system (System) or modification of
computer setup (BIOS Setup) by unauthorized users.
!SETUP: When you choose Setup, a password is required only when accessing the BIOS Setup. If
the correct password is not given, you can’t enter the BIOS setup menu.
User’s Manual
Page 36

Chapter 3
3-8
!SYSTEM: When you choose System, a password is required each time the computer boots up. If the
To disable security, select Set Supervisor Password at main menu and then you will be asked to enter
password. Do not type anything and just press the Enter key and it will disable security. Once security is
disabled, the system will boot and you can enter the BIOS setup menu freely.
Don’t forget your password. If you forget the password, you will have to open the computer case and
clear all information in the CMOS before you can start up the system. But by doing this, you will have
to reset all previously set options.
correct password is not given, the system will not start.
Notice
3-3. Advanced Chipset Features Setup Menu
The Chipset Features Setup Menu is used to modify the contents of the buffers in the chipset on the
motherboard. Since the parameters of the buffers are closely related to hardware, if the setup is not correct
or is false, the motherboard will become unstable or you will not be able to boot up. If you don’t know the
hardware very well, use default values (i.e. use the LOAD SETUP DEFAULTS option).
NV7m Motherboard
Figure 3-4. Advanced Chipset Features Screen Shot
Page 37

Introducing the BIOS
You can use the arrow keys to move between the items. Use PgUP, PgDn, + or - key to change the values.
When you have finished setting up the chipset, press ESC to go back to the main menu.
Note
The parameters in this screen are for system designers, service personnel, and technically competent
users only. Do not reset these values unless you understand the consequences of your changes.
AGP Aperture Size:
Five options are available: 32MB ! 64MB ! 128MB ! 256MB ! 512MB !Back to 32MB. The
default setting is 64MB. This option specifies the amount of system memory that can be used by the AGP
device. The aperture is a portion of the PCI memory address range dedicated for graphics memory
address space. Host cycles that hit the aperture range are forwarded to the AGP without any translation.
See http://www.agpforum.org
for AGP information.
3-9
Frame Buffer Size:
Four options are available: 8MB ! 16MB ! 32MB ! Disabled !Back to 8MB. The default setting is
32MB. This item can let you select the frame buffer memory size for onboard VGA accelerator.
Memory Timings:
Two options are available: Aggressive ! Optimal. The default setting is Optimal. Choose Aggressive for
better memory performance, choose Optimal for better memory compability.
CAS Latency Override:
Three options are available: 2 Clocks ! 2.5 Clocks ! Auto. The default setting is 2.5 Clocks. You can
select SDRAM CAS (Column Address Strobe) latency time according your SDRAM specification.
Clock Spread Spectrum:
Four options are available: 0.50% ! 1.00% ! 2.00% ! Disabled, the default setting is Disabled. For
EMC (Electro-Magnetic Compatibility Test) testing you may need to adjust these options for optimal
results, we do not recommend you change the default, except for special reasons. Some values you select
may cause system instability under some situations, please be careful.
CPU/MEM/AGP’s Freq:
Four options are available: 100/100/66 ! 100/133/66 ! 133/100/66 ! 133/133/66. The default setting
is 100/100/66. This item lets you set the processor Front Side Bus, DDR SDRAM and AGP clock. It
correlates with the processor FSB clock you set. Many of options are available, you can choose the
frequency ratio you want. The default setting is 100/100/66. In this case, the processor clock will be the
100 MHz. Memory clock will be the 100 MHz. The AGP clock will be the 66 MHz.
User’s Manual
Page 38

Chapter 3
3-10
3-4. Integrated Peripherals
In this menu, you can change the onboard I/O device, I/O port address and other hardware settings.
Figure 3-5A. Integrated Peripherals Upper Screen Shot
Figure 3-5B. Integrated Peripherals Lower Screen Shot
This item can let you sets several items concerning the SIS OnChip IDE device parameters.
Onboard IDE-1 Controller:
The onboard IDE 1 controller can be set as Enabled or Disabled. The default setting is Enabled. Of course
you can disable this item as well. The enable items will show as white color and disabled items will show
blue green color.
Master Drive PIO Mode:
"
!Auto: The BIOS can auto-detect the transfer mode of the IDE devices in order to set its data
NV7m Motherboard
Page 39

Introducing the BIOS
transfer rate (Default). You can select the PIO mode from 0 to 4 of the IDE devices in order
to set its data transfer rate.
This field does not available to enter when the “Onboard IDE-1 Controller” field is Disabled.
Slave Drive PIO Mode:
"
!Auto: The BIOS can auto-detect the transfer mode of the IDE devices in order to set its data
transfer rate (Default). You can select the PIO mode from 0 to 4 of the IDE devices in order
to set its data transfer rate.
This field does not available to enter when the “Onboard IDE-1 Controller” field is Disabled.
Master Drive Ultra DMA:
"
Ultra DMA is a DMA data transfer protocol that utilizes ATA commands and the ATA bus to allow
DMA commands to transfer data at a maximum burst rate of 100 MB/sec.
!Disable: If you encounter the problem of using Ultra DMA devices, you can try to set this item to
!Auto: When you select Auto, the system automatically determines the optimal data transfer rate
This field does not available to enter when the “Onboard IDE-1 Controller” field is Disabled.
Slave Drive Ultra DMA:
"
!Disable: If you encounter the problem of using Ultra DMA devices, you can try to set this item to
!Auto: When you select Auto, the system automatically determines the optimal data transfer rate
This field does not available to enter when the “Onboard IDE-1 Controller” field is Disabled.
Disabled.
for each IDE device. (Default)
Disabled.
for each IDE device. (Default)
3-11
Onboard IDE-2 Controller:
The onboard IDE 2 controller can be set as Enabled or Disabled. Description is the same as the item
“Onboard IDE-1 Controller”. You can refer the above description.
PIO MODE 0~4 reflects the IDE device data transfer rate. The higher the MODE value is, the better the
IDE device data transfer rate. However, it does not mean that the highest MODE value can be selected.
You first have to be sure that your IDE device supports this MODE. Otherwise, the hard disk will not be
able to operate normally.
USB Controller:
Two options are available: Disabled * Enabled. The default setting is Enabled. This should be enabled if
your system has a USB device installed on the system board and you wish to use it. If you add a higher
performance controller, you will need to disable this feature. If you choose disable this item, the “USB
Keyboard Support” and “USB Mouse Support” items will disappear in Integrated Peripherals menu.
USB Keyboard Support:
"
Two options are available: OS * BIOS. The default setting is OS. If your operating system supports a
USB keyboard, please set it to OS. Only in some situations, such as in a pure DOS environment that
does not support a USB keyboard, should you set it to BIOS.
User’s Manual
Page 40

Chapter 3
3-12
USB Mouse Support:
!
Two options are available: OS ! BIOS. The default setting is OS. If your operating system supports a
USB mouse, please set it to OS. Only in some situations, such as in a pure DOS environment that does
not support a USB mouse, should you set it to BIOS.
AC97 Audio:
Two options are available: Disabled ! Enabled. The default setting is Enabled. This item can let you
enable or disable the onboard AC97 CODEC functions.
AC97 APU:
Two options are available: Disabled ! Enabled. The default setting is Enabled. This item can let you
enable or disable the APU (Audio Processor Unit) function of south bridge.
MAC Lan:
Two options are available: Disabled ! Enabled. The default setting is Enabled. This item can let you
enable or disable the onboard LAN chip functions.
Power ON Function:
Six options are available: Password ! Hot KEY ! Mouse Left ! Mouse Right ! Any KEY !
BUTTON ONLY ! Keyboard 98. The default setting is Enabled.
KB Power ON Password:
!
This item let you set the password for keypad wakeup. After you set the password, any event affecting
keypad will awaken a system that has powered down.
Hot Key Power ON:
!
Twelve options are available: Ctrl-F1 ! Ctrl-F2 ! Ctrl-F3 ! Ctrl-F4 ! Ctrl-F5 ! Ctrl-F6 !
Ctrl-F7 ! Ctrl-F8 ! Ctrl-F9 ! Ctrl-F10 ! Ctrl-F11 ! Ctrl-F12. The default setting is Ctrl-F1.
Onboard FDD Controller:
Two options are available: Disabled or Enabled. The default setting is Enabled. This is used to enable or
disable the Onboard FDD Controller. If you add a higher performance controller, you will need to
Disable this feature.
Onboard Serial Port 1:
This item allows you to determine which I/O address the onboard serial port 1 controller will access. Six
options are available: Disabled ! 3F8/IRQ4 ! 2F8/IRQ3 ! 3E8/IRQ4 ! 2E8/IRQ3 ! Auto ! Back
to Disabled. The default setting is 3F8/IRQ4.
Onboard IR Function:
Three options are available: IrDA ! ASKIR (Amplitude Shift Keyed IR) ! Disabled. The default
setting is Disabled.
RxD , TxD Active:
!
Four options are available: Hi, Hi ! Hi, Lo ! Lo, Hi ! Lo, Lo. The default setting is Hi, Lo. Set IR
NV7m Motherboard
Page 41

Introducing the BIOS
transmission/reception polarity as High or Low.
IR Transmission Delay:
!
Two options are available: Disabled or Enabled. The default setting is Enabled. Set IR transmission
delays 4 character-time (40 bit-time) when SIR is changed from RX mode to TX mode.
UR2 Duplex Mode:
!
Two options are available: Full or Half. The default setting is Half.
Select the value required by the IR device connected to the IR port. Full-duplex mode permits
simultaneous two-direction transmission. Half-duplex mode permits transmission in only one
direction at a time.
Use IR Pins:
!
Two options are available: RxD2, TxD2 or IR-Rx2Tx2. The default setting is IR-Rx2Tx2. If you
choose RxD2, TxD2, your motherboard must support a COM port IR KIT connection. Otherwise, you
can only choose the IR-Rx2Tx2 to use the IR header on your motherboard to connect your IR KIT.
Please use the default setting.
Note
The setting for item “RxD, TxD Active”, also called “TX, RX inverting”, allows you to
determine the activity of RxD and TxD. We set it to “Hi, Lo”. If your motherboard BIOS uses
“No” and “Yes” to represent this item, you should set it to the same setting as the NV7m. This
means that you should set it to “No, Yes” in order to match the transfer and receiving speed. If
you fail to do so, you will not get an IR connection between the NV7m and the other computer.
Onboard Parallel Port:
Four options are available: Disabled ! 378/IRQ7 ! 278/IRQ5 ! 3BC/IRQ7. The default setting is
378/IRQ7. Select a logical LPT port name and matching address for the physical parallel (printer) port.
Parallel Port Mode:
!
Five options are available: SPP ! EPP ! ECP ! ECP+EPP ! Normal. Default is ECP+EPP
mode. Select an operating mode for the onboard parallel (printer) port. SPP (Standard Parallel Port),
EPP (Extended Parallel Port), ECP (Extended Capabilities Port), Normal or ECP plus EPP.
Select SPP unless you are certain your hardware and software supports both EPP or ECP mode.
According to your selection, the following items will appear.
EPP Mode Select:
!
Two options are available: EPP1.9 ! EPP1.7. The default setting is EPP1.9. When the mode selected
for the parallel port mode is EPP, the two EPP mode options are available.
ECP Mode Use DMA:
!
Two options are available: 1 ! 3. The default setting is 3. When the mode selected for the onboard
parallel port is ECP or ECP+EPP, the DMA channel selected can be 1 (Channel 1) or 3 (Channel 3).
3-13
Game Port Address:
Three options are available: Disabled ! 201 ! 209. Default setting is 201. You can choose the game
port I/O base address in this item to meet the need for game requirement.
User’s Manual
Page 42

Chapter 3
3-14
Midi Port Address
Four options are available: Disabled ! 330 ! 300 ! 290. Default setting is 330. You can choose the
MPU-401 I/O address in this item to meet the need for MIDI device requirement.
Midi Port IRQ:
!
Two options are available: 5 ! 10. The default setting is 10. You can choose the MIDI port IRQ in
this item to meet the need for game requirement.
3-5. Power Management Setup Menu
The difference between Green PCs and traditional computers is that Green PCs have a power
management feature. With this feature, when the computer is powered on but inactive, the power
consumption is reduced in order to save energy. When the computer operates normally, it is in Normal
mode. In this mode, the Power Management Program will control the access to video, parallel ports, serial
ports and drives, and the operating status of the keyboard, mouse and other device. These are referred to
as Power Management Events. In cases where none of these events occur, the system enters the power
saving mode. When one of the controlled events occurs, the system immediately returns to normal mode
and operates at its maximum speed. Power saving modes can be divided into three modes according to
their power consumption: Doze Mode, Standby Mode, and Suspend Mode. The four modes proceed in the
following sequence:
Normal Mode ===> Doze Mode ===> Standby Mode ===> Suspend Mode
The system consumption is reduced according the following sequence:
Normal > Doze > Standby > Suspend
1. In the Main Menu, select “Power Management Setup” and press “Enter”. The following screen is
displayed:
NV7m Motherboard
Figure 3-6. Power Management Setup Screen Shot
Page 43
Introducing the BIOS
3-15
2. You can use the arrow keys to move between the items. Use PgUP, PgDn, + or - key to change the
values. When you have finished setting up the chipset, press ESC to go back to the main menu.
3. After you have configured the Power Management feature, press Esc to go back to the Main Menu.
We are now going to briefly explain the options in this menu:
ACPI Function (Advanced Configuration and Power Interface):
ACPI gives the operating system direct control over the power management and Plug and Play functions
of a computer. The ACPI functions are always “Enabled”. If you want ACPI functions to work normally,
you should notice two things. One is your operating system must support ACPI, as of now only
Microsoft
devices and add-on cards in your system must fully support ACPI, both hardware and software (drivers).
If you want to know if your devices or add-on cards support ACPI or not, please contact the device or
add-on card manufacture for more information. If you want to know more about ACPI specifications,
please go to the address below for more detailed information:
http://www.teleport.com/~acpi/acpihtml/home.htm
Note: If you enable the ACPI function in the BIOS setup, the SMI function will not work.
ACPI requires an ACPI-aware operating system. ACPI features include:
! Plug and Play (including bus and device enumeration) and APM functionality normally contained in
! Power management control of individual devices, add-in cards (some add-in cards may require an
! A Soft-off feature that enables the operating system to power off the computer.
! Support for multiple wake-up events (see Table 3-5-1).
! Support for a front panel power and sleep mode switch. Table 3-5-2 describes the system states based
®
Windows® 98 SE and Windows® 2000 supports these functions. The second thing is that all
the BIOS.
ACPI-aware driver), video displays, and hard disk drives.
on how long the power switch is pressed, depending on how ACPI is configured with an ACPI-aware
operating system.
Note
If you enable the ACPI function in the BIOS setup, the SMI switch function will not work.
System States and Power States
Under ACPI, the operating system directs all system and device power state transitions. The operating
system puts devices in and out of low-power states based on user preferences and knowledge of how
devices are being used by applications. Devices that are not being used can be turned off. The operating
system uses information from applications and user settings to put the system as a whole into a low-power
state.
The table below describes which devices or specific events can wake the computer from specific states.
User’s Manual
Page 44

Chapter 3
3-16
Table 3-5-1: Wake Up Device and Events
These device/events can wake up the
computer……
……from this state
Power switch Sleeping mode or power off mode
RTC alarm Sleeping mode
LAN Sleeping mode
Modem Sleeping mode
IR command Sleeping mode
USB Sleeping mode
PS/2 keyboard Sleeping mode
PS/2 mouse Sleeping mode
Table 3-5-2: Effect of Pressing the Power Switch
If the system is in this
state……
……and the power switch is
pressed for
……the system enters this
state
Off Less than four seconds Power on
On More than four seconds Soft off/Suspend
On Less than four seconds Fail safe power off
Sleep Less than four seconds Wake up
ACPI Suspend Type:
Three options are available: S1 (POS) * S3 (STR) * S1&S3. The default setting is S3 (STR). POS is
“PowerOn-Suspend”, and STR is “Suspend-To-RAM”. Generally, ACPI has six states: System S0 state,
S1 state, S2 state, S3 state, S4 state, S5 state. S1 and S3 states are described below:
The S1 (POS) State (POS means Power On Suspend):
While the system is in the S1 sleeping state, its behavior is as described below:
! The processor is not executing instructions. The processor’s complex context is maintained.
! Dynamic RAM context is maintained.
! Power Resources are in a state compatible with the system S1 state. All Power Resources that supply a
System Level reference of S0 are in the OFF state.
! Devices states are compatible with the current Power Resource states. Only devices which solely
reference Power Resources which are in the ON state for a given device state can be in that device state.
In all other cases, the device is in the D3 (off) state.
! Devices that are enabled to wake the system and that can do so from their current device state can
initiate a hardware event which transitions the system state to S0. This transition causes the processor
to continue execution where it left off.
To transition into the S1 state, the operating software does not have to flush the processor's cache.
The S3 (STR) State (STR means Suspend to RAM):
The S3 state is logically lower then the S2 state and is assumed to conserve more power. The behavior of
this state is defined as follows:
! Processor is not executing instructions. The processor complex context is not maintained.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 45

Introducing the BIOS
! Dynamic RAM context is maintained.
! Power Resources are in a state compatible with the system S3 state. All Power Resources that supply a
System Level reference of S0, S1, or S2 are in the OFF state.
! Devices states are compatible with the current Power Resource states. Only devices which solely
reference Power Resources which are in the ON state for a given device state can be in that device state.
In all other cases, the device is in the D3 (off) state.
! Devices that are enabled to wake the system and that can do so from their current device state can
initiate a hardware event which transitions the system state to S0. This transition causes the processor
to begin execution at its boot location. The BIOS performs initialization of core functions as required to
exit an S3 state and passes control to the firmware resume vector. Please see the ACPI Specification
Rev. 1.0 book section 9.3.2 for more details on BIOS initialization.
From the software point of view, this state is functionally the same as the S2 state. The operational
difference can be that some Power Resources that could be left ON in the S2 state might not be available
to the S3 state. As such, additional devices can be required to be in logically lower D0, D1, D2, or D3
state for S3 than S2. Similarly, some device wake events can function in S2 but not S3.
Because the processor context can be lost while in the S3 state, the transition to the S3 state requires that
the operating software flush all dirty cache to DRAM.
Above information for system S1 were refer to ACPI Specification Rev. 1.0.
+
3-17
3-6. PnP/PCI Configurations Setup Menu
In this menu, you can change the INT# and IRQ# of the PCI bus and other hardware settings.
Figure 3-7A. PnP/PCI Configurations Screen Shot
User’s Manual
Page 46
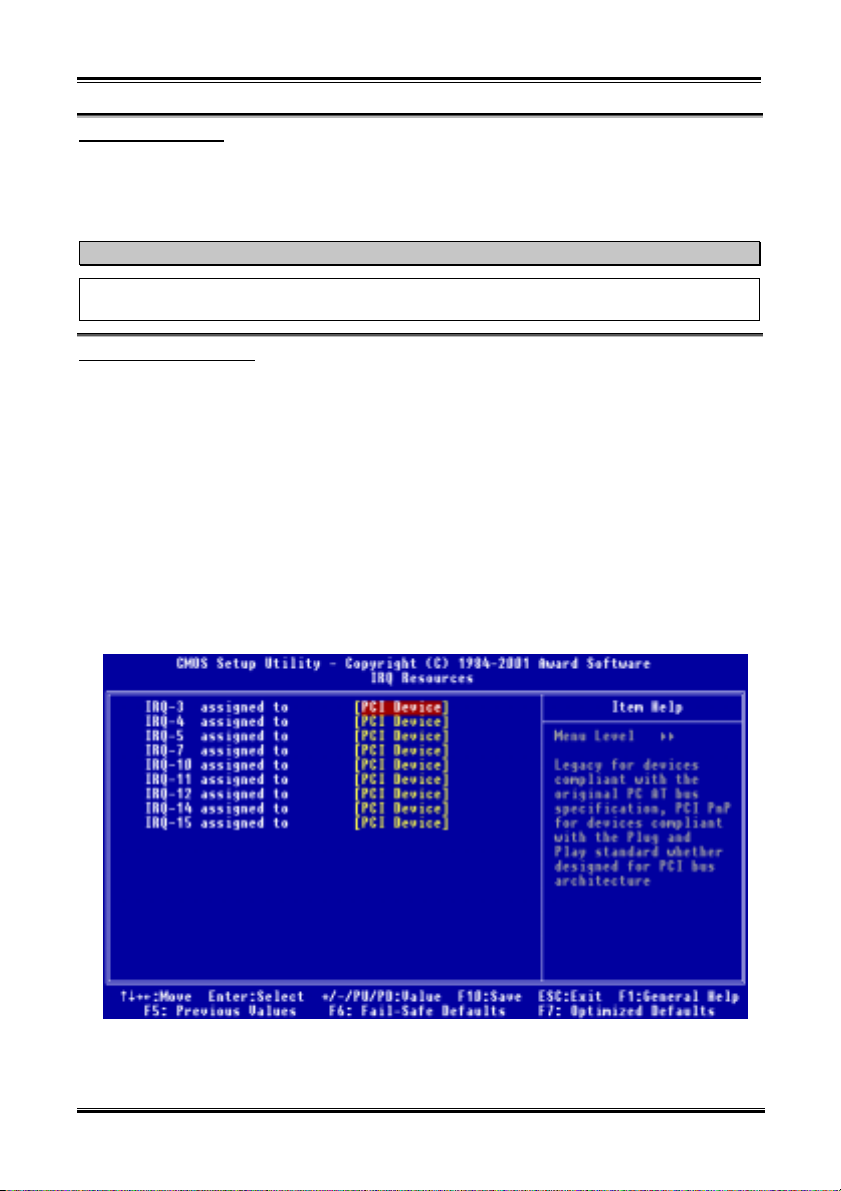
Chapter 3
3-18
Force Update ESCD:
Two options are available: Disabled or Enabled. The default setting is Disabled. Normally, you should
leave this field Disabled. Select Enabled to reset Extended System Configuration Data (ESCD) when you
exit Setup if you have installed a new add-on and the system reconfiguration has caused a serious conflict
that prevents the operating system from booting.
Computer Knowledge: ESCD (Extended System Configuration Data)
The ESCD contains the IRQ, DMA, I/O port, memory information of the system. This is a
specification and a feature specific to the Plug & Play BIOS.
Resources Controlled By:
When resources are controlled manually, assign each system interrupt as one of the following types,
depending on the type of device using the interrupt:
Legacy devices compliant with the original PC AT bus specification require a specific interrupt (such as
IRQ4 for serial port 1). PCI PnP devices comply with the Plug and Play standard, whether designed for
the PCI or legacy bus architecture.
Two options are available: Auto (ESCD) or Manual. The default setting is Auto (ESCD). The Award Plug
and Play BIOS has the capability to automatically configure all boot and Plug and Play compatible
devices. If you select Auto (ESCD), all of the interrupt request (IRQ) fields become unselectable, as the
BIOS automatically assigns them.
IRQ Resources:
"
If you have trouble in assigning the interrupt resources automatically, you can select Manual to set
which IRQis assigned to which PCI Device or Reserved it. See the screen shot below.
NV7m Motherboard
Figure 3-7B. IRQ Resources Screen Shot
Page 47

Introducing the BIOS
Memory Resources:
!
Figure 3-7C. Memory Resources Screen Shot
3-19
Reserved Memory Base:
Seven options are available: N/A ! C800 ! CC00 ! D000 ! D400 ! D800 ! DC00. The default
setting is N/A.
Reserved Memory Length:
!
Seven options are available: 8K ! 16K ! 32K ! 64K. The default setting is 8K. This item can let
you select a base address and length for the memory area used by any peripheral that requires high
memory.
" PCI slot 1 shares IRQ signals with the AGP slot.
" If you want to install two PCI cards into those PCI slots that share IRQ with one another at the
same time, you must make sure that your OS and PCI devices’ driver supports the IRQ sharing
function.
User’s Manual
Note
Page 48

Chapter 3
3-20
3-7. PC Health Status
You can set the warning and shutdown temperatures for your computer system, and you can check the fan
speeds and power supply voltages of your computer system. The features are useful for monitoring all the
important parameters within your computer system. We call it the PC Health Status.
Figure 3-8. PC Health Status Screen Shot
CPU Warning Temperature:
Eight options are available: Disabled ! 50℃/122℉ ! 53℃/127℉ ! 56℃/133℉ ! 60℃/140℉ !
63℃/145℉ ! 66℃/151℉ ! 70℃/158℉. The default setting is 70
processor warning temperature here. If the processor temperature exceeds the settings value, the system
will give you an alarm message or sound to remind you that the processor is overheating.
All Voltages, Fans Speed and Thermal Monitoring:
These items list the current states of the processor and environment (using RT1 and RT2 to detect them.)
temperatures as well as fan speeds (processor fan and chassis fan). It cann’t be changed by the user.
The following items list all the voltage states of the system power. It is also unchangeable.
The hardware monitoring features for temperatures, fans and voltages will occupy the I/O address
from 294H to 297H. If you have a network adapter, sound card or other add-on cards that might use
those I/O addresses, please adjust your add-on card I/O address, to avoid the use of those addresses.
NV7m Motherboard
/158℉. You can set the
℃
Note
Page 49

Introducing the BIOS
3-21
3-8. Load Fail-Safe Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item you get a confirmation dialog box with a message similar to:
Load Fail-Safe Defaults (Y/N)? N
Pressing “Y” loads the BIOS default values for the most stable, minimal-performance system operations.
3-9. Load Optimized Defaults
When you press <Enter> on this item you get a confirmation dialog box with a message similar to:
Load Optimized Defaults (Y/N)? N
Pressing “Y” loads the default values that are factory settings for optimal performance system operations.
3-10. Set Supervisor Password
Can let you enter and change the options of the setup menus.
3-11. Set User Password
Set Password: Can enter but do not have the right to change the options of the setup menus. When you
Type the password, up to eight characters in length, and press <Enter>. The password typed now will
clear any previously entered password from CMOS memory. You will be asked to confirm the password.
Type the password again and press <Enter>. You may also press <Esc> to abort the selection and not
enter a password.
To disable a password, just press <Enter> when you are prompted to enter the password. A message will
confirm the password will be disabled. Once the password is disabled, the system will boot and you can
enter Setup freely.
User’s Manual
select this function, the following message will appear at the center of the screen to
assist you in creating a password.
ENTER PASSWORD:
PASSWORD DISABLED.
Page 50

Chapter 3
3-22
When a password has been enabled, you will be prompted to enter it every time you try to enter Setup.
This prevents an unauthorized person from changing any part of your system configuration. Additionally,
when a password is enabled, you can also require the BIOS to request a password every time your system
is rebooted. This would prevent unauthorized use of your computer. You determine when the password is
required within the BIOS Features Setup Menu and its Security option. If the Security option is set to
System, the password will be required both at boot and at entry to Setup. If you set to Setup, prompting
only occurs when trying to enter Setup.
3-12. Save & Exit Setup
Pressing <Enter> on this item asks for confirmation:
Save to CMOS and EXIT (Y/N)? Y
Pressing “Y” stores the selections made in the menus in CMOS - a special section of memory that stays
on after you turn your system off. The next time you boot your computer, the BIOS configures your
system according to the Setup selections stored in CMOS. After saving the values the system is restarted
again.
3-13. Exit Without Saving
Pressing <Enter> on this item asks for confirmation:
Quit without saving (Y/N)? Y
This allows you to exit Setup without storing in CMOS any change. The previous selections remain in
effect. This exits the Setup utility and restarts your computer.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 51

NVIDIA nForce Chipset Drivers Installation for Windows® 2000
A-1
Appendix A. NVIDIA nForce Chipset Drivers
Installation for Windows
After you’ve installed Windows® 2000, you will need to install the NVIDIA nForce chipset drivers. Step
by step instructions on how to do this are found in the following section.
Note
After installingWindows® 2000, the quality of your display will be poor because it will be set to
640*480 and 16 colors. For the best screen capture quality, install the VGA drivers and set the
desktop to 800*600 using True Color.
Note
Under Windows® 2000 operating system you have to install the service pack 2 (SP2) or latest service
pack to get the best system performance. You can download SP2 at Microsoft® WEB site.
Note
Details of the Windows® 2000 operating system will not be mentioned in this manual. If you have any
problems with Windows® 2000 installation, operations, or settings, please refer to your Windows®
2000 user's manual or other databases provided by Microsoft® Corporation.
Insert the nForce series CD into your CD-ROM drive, it should execute the program automatically. If not,
you can go to the CD location and execute the execution file at the main directory of the CD. After it has
been executed you will see the screen below.
®
2000
Step 1: Move the cursor to “NVIDIA nForce
Chipset Driver” and click on it. You will go to
the next screen.
User’s Manual
Step 2: The nForce driver setup InstallShield
wizard shows up, and it will go to the next screen
for a while.
®
Page 52

Appendix A
A-2
Step 5: the “Digital Signature Not Found”
screen show up, click “Yes” to go on.
Step 3: You will now see the welcome screen
and its dialogue box. Click “N
ext>” to go on.
Step 6: When the installation is complete, the
installer will ask you to restart your computer.
We suggest that you choose “Yes, I want to
restart my computer now.” then click the
“Finish” button to restart your computer to finish
the driver updates.
Step 4: Program will start to install all drivers the
system needs. The installer will show the install
progress percentage.
Note
The version you see will be change, because
we may change the drivers or change the CD
version. If happened, the version may
different with this picture, but the install
process won’t be change at all.
NV7m Motherboard
Step 7: When OS restart, the “Digital Signature
Not Found” screen show up, click “Yes” to go
on.
Step 8: System found new hardware (NVIDIA
®
Page 53

NVIDIA nForce Chipset Drivers Installation for Windows® 2000
A-3
nForce™ Audio), click “Finish” to go on.
Step 9: System will ask you to restart your
computer. We suggest that you choose “Yes” to
Step 10: When OS restart, you can then check the “Device Manager” to see that the devices are properly
installed.
restart your computer.
User’s Manual
Page 54

Appendix A
A-4
NV7m Motherboard
Page 55

NVIDIA VGA Drivers Installation for Windows® 2000 B-1
Appendix B. NVIDIA VGA Drivers Installation for
Windows
After you’ve installed Windows® 2000 and NVIDIA nForce chipset drivers, you will need to install the
NVIDIA VGA drivers. Step by step instructions on how to do this are found in the following section.
The following description will tell you how to install the Winbond hardware monitor system and use it.
Insert the nForce series CD into your CD-ROM drive. It should execute the program automatically. If not,
you can go to the CD location and execute the execution file from the main directory of this CD. After it
is executed, you will see the screen below.
Step 1: Click “NVIDIA VGA Driver” button.
®
2000
Step 3: The welcome screen and its dialogue box
will appear. Click the “Next>” button to go on.
®
Step 2: The nForce driver setup InstallShield
wizard shows up, and it will go to the next screen
for a while.
User’s Manual
Step 4: Program will start to install drivers the
system needs. The installer will show the install
progress percentage.
Page 56

B-2 Appendix B
Step 5: When the installation is complete, the
installer will ask you to restart your computer.
We suggest that you choose “Yes, I want to
restart my computer now.” then click the
“Finish” button to restart your computer to finish
the driver update.
Step 6: When OS restart, you can then check the
“Device Manager” to see that the VGA device
are properly installed.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 57

Installing The Winbond Hardware Monitor System C-1
Appendix C. Installing The Winbond Hardware
Monitor System
The Winbond hardware monitor system is a self-diagnostic system for PCs. It will protect PC hardware
by monitoring several critical items including power supply voltage, processor and system fan speeds,
and processor and system temperatures. These items are important for the operation of the system; errors
may result in permanent damage to the PC. Once any item is out of its normal range, a warning message
will pop up and remind the user to take proper measures.
The following description will tell you how to install the Winbond hardware monitor system and use it.
Insert the nForce series CD into your CD-ROM drive. It should execute the program automatically. If not,
you can go to the CD location and execute the execution file from the main directory of this CD. After it
is executed, you will see the screen below.
Step 1: Click “Utility” button.
Step 2: Click “Windbond Hardware Doctor”
button to start install the hardware monitor
system utility.
User’s Manual
Step 3: Then hardware doctor setup program is
preparing the InstallShield
to the rest of the setup process.
Step 4: The welcome screen and its dialogue box
will appear. Click the “N
®
wizard to guide you
ext>” button to go on.
Page 58

C-2 Appendix C
Step 7: Program will start to install drivers the
system needs. The installer will show the install
progress percentage.
Step 5: Now you can choose the destination
location where you want to install the drivers.
We suggest that you use the default folder as the
destination location. After checking the folder
ext>” button.
click “N
Step 8: When the installation is complete, the
installer will ask you to restart your computer.
We suggest that you choose “Yes, I want to
restart my computer now.” then click the
“Finish” button to restart your computer to finish
the driver update.
Step 6: You can choose the name of the program
folder. We suggest you use the default program
folder name. After checking the program folder
name then click “Next>” button.
NV7m Motherboard
Step 9: You can select the program from Start
toolbar, and then choose “Programs”. You will
see the item called “winbond” * “Hardware
Doctor”. Click it, and you will be able to see the
screen below.
Page 59

Installing The Winbond Hardware Monitor System C-3
Step 10: This screen shows the hardware monitor system screen. It shows information about system
temperature, voltages and fan speed. Some items can let you set the warning range; you can optimize
values by setting them in accordance your system.
User’s Manual
Page 60

C-4 Appendix C
NV7m Motherboard
Page 61

BIOS Update Guide
D-1
Appendix D. BIOS Update Guide
We will use the SE6 motherboard as an example. All other models follow the same process. First, know
your motherboard’s model name and version number. You can find it on one slot or at the back of the
motherboard. Each motherboard always has the label at the same place as shown in the photo below.
You will find the model name and version on the white sticker.
2. Know the current BIOS ID.
For example, in this case, the current BIOS ID is “00”. If you already have the latest BIOS, no any update
action is necessary. If your BIOS is not the latest BIOS, go on to the next step.
User’s Manual
Page 62

Appendix D
D-2
3. Download the correct BIOS file from our Web site.
Go to our Web site and choose the correct BIOS file and download it.
4. Double click the download file, it will self-extract to .bin file.
5. Make a bootable floppy disk and copy the necessary files onto it.
You may make a floppy disk bootable either in Explorer or in the DOS prompt mode.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 63

BIOS Update Guide
After formatting and transferring the system to the floppy disk, copy two files into it. One is the BIOS
flash utility “awdflash.exe” and the other is the decompressed BIOS binary file.
6. Boot off floppy disk.
D-3
User’s Manual
Page 64

Appendix D
D-4
Please set the first boot sequence as “floppy” in BIOS and boot off the floppy disk.
7. Flash the BIOS in pure DOS mode. After successfully booting off of the floppy, execute the flash
utility according to these instructions show below:
A:\awdflash se6_sw.bin /cc /py /sn /r
Note
We strongly recommend you use the above parameters following “awdflash” to flash your BIOS. DO
NOT just type “awdflash se6_sw.bin” without the above parameters following the .bin file. You only
can use the “awdflash.exe” attached in NV7m product CD-ROM, DO NOT USE the others Award
flash program to flash your NV7m BIOS.
Note
The Award flash utility can’t be completed under a Windows® 95/98 or Windows® NT, Windows®
2000, Windows® XP, Windows® ME environment, you must be in a pure DOS environment.
You should check which BIOS file is to be used with your motherboard, don't flash with the wrong
BIOS file. Otherwise, you may cause system malfunctions.
Note
During the updating, the progress will be measured by white blocks. The last four blue blocks of the
flash update process represent the “BIOS boot block”. The BIOS boot block is used to prevent the
BIOS from becoming corrupt during programming. It should not be programmed every time. If this
“BIOS boot block” remains intact when the BIOS becomes corrupt during programming, then you
can boot from a bootable floppy next time you boot your computer. This allows you to flash your
BIOS again without the need for technical support from the dealer.
NV7m Motherboard
Page 65

Troubleshooting (Need Assistance?) E-1
Appendix E. Troubleshooting (Need Assistance?)
Motherboard Troubleshooting:
Q & A:
Q: Do I need to clear the CMOS before I use a new motherboard to assemble my new computer
system?
A: Yes, we highly recommend that you clear the CMOS before installing a new motherboard. Please
move the CMOS jumper from its default 1-2 position to 2-3 for a few seconds, and then back. When
you boot up your system for the first time, follow the instructions in the user's manual to load the
optimized defaults.
Q: If my systems hang when I update the BIOS or set the wrong processor parameters, what
should I do?
A: Whenever you update the BIOS or if the system hangs due to wrong processor parameters setting,
always clear CMOS jumper before booting up again.
Q: How can I get a quick response to my request for technical support?
A: Be sure to follow the guidelines as stated in the “Technical Support Form” section of this manual.
If you have a problem during operation, in order to help our technical support personnel quickly
determine the problem with your motherboard and give you the answers you need, before filling in the
technical support form, eliminate any peripheral that is not related to the problem, and indicate it on
the form. Fax this form to your dealer or to the company where you bought the hardware in order to
benefit from our technical support. (You can refer to the examples given below)
,
Example 1: With a system including: motherboard (with processor, DDR DRAM, etc.) HDD,
CD-ROM, FDD, graphic adapter, MPEG-2 card, SCSI adapter, audio card, etc. After the
system is assembled, if you cannot boot up, check the key components of the system
using the procedure described below. First remove all interface cards except the VGA
card and try to reboot.
- If you still cannot boot up:
Try installing another brand/model VGA card and see if the system will start. If it still
does not start, note the VGA card model, motherboard model, Bios identification
number, processor on the technical support form (refer to main instructions), and
describe the problem in the problem description space provided.
- If you can boot up:
Insert the interface cards you have removed back into the system, one by one and try
to start the system each time you insert a card, until the system will not start. Keep the
VGA card and the interface card that caused the problem inserted on the motherboard,
remove any other cards or peripheral, and start again. If you still cannot start, note the
information related to both cards in the add-on card space provided, and don’t forget
to indicate the motherboard model, version, BIOS identification number, processor
(refer to main instructions), and give a description of the problem.
User’s Manual
Page 66

E-2 Appendix E
,
Example 2: With a system including: motherboard (with processor, DDR DRAM, etc.) HDD,
We will show you how to fill the “Technical Support Form” right now.
CD-ROM, FDD, graphic adapter, MPEG-2 card, SCSI adapter, audio card, etc. After
assembly and after having installed the audio card driver, when you restart the system,
when it runs the audio card driver, it resets automatically. This problem may be due to the
audio card driver. During the starting DOS… procedure, press SHIFT (BY-PASS) key, to
skip CONFIG.SYS and AUTOEXEC.BAT; edit CONFIG.SYS with a text editor, and in
function the line that loads the audio card driver, add a remark REM, in order to disable
the audio card driver. See the example below.
CONFIG.SYS:
DEVICE=C:\DOS\HIMEM.SYS
DEVICE=C:\DOS\EMM386.EXE HIGHSCAN
DOS=HIGH, UMB
FILES=40
BUFFERS=36
REM DEVICEHIGH=C:\PLUGPLAY\DWCFGMG.SYS
LASTDRIVE=Z
Restart the system. If the system starts and does not reset, you can be sure that the
problem is due to the Sound Card Driver. Write down the Sound Card model,
motherboard model, BIOS identification number on the technical support file (refer to
main instructions), and describe the problem in the space provided.
. Instructions .
To fill in this “Technical Support Form”, refer to the step-by-step instructions given below:
*
. Model Name: Note the model number given in your user’s manual.
1
For example: NV7m, SD7-533, KR7A-133, KR7A-133R, etc.
*
2
. Motherboard PCB Version: Note the motherboard PCB version labeled on the motherboard slot or
back side as “Rev:*.**”.
For example: REV: 1.01
*
. BIOS ID & Part Number: See Appendix D for detialed information.
3
4. DriverVersion: Note the driver version number indicated on the device driver disk or CD-ROM (if
have) as “Release *.**” (or Rev. *.**, Version *.**). For example:
NV7m Motherboard
Page 67

Troubleshooting (Need Assistance?) E-3
5*. OS/Applications: Indicate the operating system and the applications you are running on the system.
For example: Windows
*
. Processor Type: Indicate the brand and the speed (MHz) of your CPU.
6
Example: (A) In the “Brand” space, write “AMD”, in the “Specifications” space, write “ Athlon
®
98 SE, Windows® 2000, Windows® XP, etc.
™
1
GHz”。
7. Hard Disk Drive: Indicate the brand and specifications of your HDD(s), specify if the HDD is using
/IDE1 or /IDE2. If you know the disk capacity, indicate it and check (“0”) “
”; in case you give
no indication, we will consider that your HDD is “$IDE1” Master.
For example: In the “Hard Disk Drive” space, check the box, in the “Brand” space, write
“SEAGATE”, in the “Specifications” space, write “Darracuda ATA2 ST330631A
(30 GB)”.
8. CD-ROM Drive: Indicate the brand and specifications of your CD-ROM drive. Specify if it uses
/ IDE1 or /IDE2, and check (“0”) “
”; in case you give no indication, we will consider that
your CD-ROM is “$IDE2” Master.
For example: In the “CD-ROM Drive” space, check the box, in the “Brand” space, write
“Pioneer”, in the “Specifications” space, write “DVD-16”.
9. System Memory (DDR SDRAM): Indicate the brand and specifications (DDR DIMM) of your
system memory. Examples: Density, Description, Module Components, Module Part Number, CAS
Latency, Speed (MHz). For example:
In the “Brand” space, write “Micron”, in the “Specifications” space, write:
Density: 128MB, Description: SS 16 Megx72 2.5V ECC Gold, Module Components: (9) 16 Megx
8, Module Part Number: MT9VDDT1672AG, CAS Latency: 2, Speed (MHz): 200 MHz.
Please give us the detailed information of your DDR DIMM module, as it will help us to simulate
the problems you met.
10. Add-On Card: Indicate which add-on cards you are absolutely sure are related to the problem.
If you can’t identify the problem’s origin, indicate all the add-on cards inserted into your system.
Remember to identify which card insert on which slot.
For example: Creative SB Value sound card insert on PCI slot 3.
11. Problem Description: Please tell us problem you met. The more detailed, the better as our engineers
can help to find the solution more quickly. If the problem is random occurance, it may be hard to
simulate the problem and may take more time to find a solution.
Note
Items between the “*” are absolutely necessary.
User’s Manual
Page 68

E-4 Appendix E
Technical Support Form
! Company Name: 1 Phone Number:
" Contact Person: # Fax Number:
2 E-mail Address:
IDE1
IDE2
IDE1
IDE2
*
BIOS ID & Part Number
Driver Version
*
*
Model Name
Motherboard PCB Version
OS/Applications
Hardware Name Brand Specifications
Processor Type
Hard Disk Drive
CD-ROM Drive
System Memory
(DDRDRAM)
Add-On Card
Problem Description:
*
NV7m Motherboard
Page 69

How to Get Technical Support F-1
Appendix F. How to Get Technical Support
(From our website) http://www.abit.com.tw
(In North America) http://www.abit-usa.com
(In Europe) http://www.abit.nl
Thank you for choosing ABIT products. ABIT sells all our products through distributors, resellers and
system integrators, we have no direct sales to end-users. Before sending email for tech support please
check with your resellers or integrators if you need any services, they are the ones who sold you your
system and they should know best as to what can be done, how they serve you is a good reference for
future purchases.
We appreciate every customer and would like to provide the best service to you. Providing fast service to
our customers is our top priority. However we receive many phone calls and a huge amount of email from
all over the world. At the present time it is impossible for us to respond to every single inquiry. Therefore
it is quite possible that if you send an email to us that you may not receive a response.
We have done many compatibility tests and reliability tests to make sure our products have the best
quality and compatibility. In case you need service or technical support, please understand the constraint
we have and always check with the reseller who sold the product to you first.
To expedite service, we recommend that you follow the procedures outlined below before contacting us.
With your help, we can meet our commitment to provide the best service to the greatest number of
ABIT customers:
1. Check the Manual. It sounds simple, but we have taken a lot of care in making a well-written and
thorough manual. It is full of information that doesn't only pertain to motherboards. The CD-ROM
included with your board will have the manual as well as drivers. If you don't have either one, go to
the Program Download Area of our website or FTP server.
2. Download latest BIOS, software or drivers. Please go to our Program Download area on our
website to check to see if you have the latest BIOS. They are developed over periods of time to fix
bugs or incompatibilities. Also please make sure you have the latest drivers from your peripheral
cards makers!
3. Check the ABIT Technical Terms Guide and FAQ on our website. We are trying to expand and
make the FAQs more helpful and information rich. Let us know if you have any suggestions. For hot
topics check out our HOT FAQ!
4. Internet Newsgroups. They are a great source of information and many people there can offer help.
ABIT's Internet News group, alt.comp.periphs.mainboard.abit, is an ideal forum for the public to
exchange information and discuss experiences they have had with ABIT products. Many times you
will see that your question has already been asked before. This is a public Internet news group and it
is reserved for free discussions, Here is a list of some of the more popular ones:
alt.comp.periphs.mainboard.abit
comp.sys.ibm.pc.hardware.chips
alt.comp.hardware.overclocking
alt.comp.hardware.homebuilt
alt.comp.hardware.pc-homebuilt
Ask your reseller. Your ABIT authorized distributor should be able to provide the fastest solution to
your technical problem. We sell our products through distributors who sell to resellers and stores.
Your reseller should be very familiar with your system configuration and should be able to solve your
problem much more efficiently than we could. After all, your reseller regards you as an important
User’s Manual
Page 70

F-2 Appendix F
customer who may purchase more products and who can urge your friends to buy from him or her as
well. They integrated and sold the system to you. They should know best what your system
configuration is and your problem. They should have reasonable return or refund policies. How they
serve you is also a good reference for your next purchase.
5. Contacting ABIT. If you feel that you need to contact ABIT directly you can send email to the ABIT
technical support department. First, please contact the support team for the branch office closest to
you. They will be more familiar with local conditions and problems and will have better insight as to
which resellers offer what products and services. Due to the huge number of emails coming in every
day and other reasons, such as the time required for problem reproduction, we will not be able to reply
to every email. Please understand that we are selling through distribution channels and don't have the
resources to serve every end-user. However, we will try to do our best to help every customer. Please
also remember that for many of our technical support team English is a second language, you will
have a better chance of getting a helpful answer if your question can be understood in the first place.
Be sure to use very, simple, concise language that clearly states the problem, avoid rambling or
flowery language and always list your system components. Here is the contact information for our
branch offices:
In North America and South America please contact:
ABIT Computer (USA) Corporation
46808 Lakeview Blvd.
Fremont, California 94538, U.S.A.
sales@abit-usa.com
technical@abit-usa.com
Tel: 1-510-623-0500
Fax: 1-510-623-1092
In the UK and Ireland:
ABIT Computer Corporation Ltd.
Unit 3, 24-26 Boulton Road
Stevenage, Herts
SG1 4QX, UK
abituksales@compuserve.com
abituktech@compuserve.com
Tel: 44-1438-228888
Fax: 44-1438-226333
In Germany and Benelux (Belgium, Netherlands, Luxembourg) countries:
AMOR Computer B.V. (ABIT's European Office)
Van Coehoornstraat 7,
5916 PH Venlo, The Netherlands
sales@abit.nl
technical@abit.nl
Tel: 31-77-3204428
Fax: 31-77-3204420
NV7m Motherboard
Page 71

How to Get Technical Support F-3
All other territories not covered above please contact:
Taiwan Head Office
When contacting our headquarters please note we are located in Taiwan and we are 8+ GMT time. In
addition, we have holidays that may be different from those in your country.
ABIT Computer Corporation
3F-7, No. 79, Sec. 1, Hsin Tai Wu Rd.
Hsi Chi, Taipei Hsien, Taiwan
sales@abit.com.tw
market@abit.com.tw
technical@abit.com.tw
Tel: 886-2-2698-1888
Fax: 886-2-2698-1811
RMA Service. If your system has been working but it just stopped, but you have not installed any
new software or hardware recently, it is likely that you have a defective component. Please contact the
reseller from whom you bought the product. You should be able to get RMA service there.
6. Reporting Compatibility Problems to ABIT. Because of tremendous number of email messages we
receive every day, we are forced to give greater weight to certain types of messages than to others.
For this reason, any compatibility problem that is reported to us, giving detailed system configuration
information and error symptoms, will receive the highest priority. For the other questions, we regret
that we may not be able to reply directly. But your questions may be posted to the internet news group
in order that a larger number of users can have the benefit of the information. Please check the news
group from time to time.
7. Listed below are some chipset vendors’ WEB site addresses for your reference:
ALi’s WEB site: http://www.ali.com.tw/
AMD’s WEB site: http://www.amd.com/
Highpoint Technology Inc.’s WEB site: http://www.highpoint-tech.com/
Intel’s WEB site: http://www.intel.com/
SiS’ WEB site: http://www.sis.com.tw/
VIA’s WEB site: http://www.via.com.tw/
Thank you, ABIT Computer Corporation
http://www.abit.com.tw
User’s Manual
Page 72

F-4 Appendix F
NV7m Motherboard
 Loading...
Loading...