Page 1

ABBYY FormReader
Enterprise Edition
User`s Guide
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
1
Page 2

Contents
Introducing ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition ....................................................... 6
About ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition....................................................................................................................................................................6
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition process overview.......................................................................................................................................... 6
Administration Station............................................................................................................................................ 7
Scanning Station ..................................................................................................................................................... 7
Registration Station................................................................................................................................................. 7
Recognition Station ................................................................................................................................................. 7
Verification Station (optional)................................................................................................................................ 7
Correction Station................................................................................................................................................... 8
Export and Monitoring Station ............................................................................................................................... 8
Technical Support..................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
Installing, Uninstalling and Starting the Form Capture System....................................... 9
Software and hardware requirements........................................................................................................................................................................................ 9
Installing and uninstalling the form capture system........................................................................................................................................................ 9
Type of protection................................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Starting the form capture system................................................................................................................................................................................................11
Administration Station.................................................................................................. 12
Administration Station Interface................................................................................................................................................................................................. 12
Administration Station main window................................................................................................................... 12
Administration Station toolbar ............................................................................................................................. 12
Typical actions of the administrator......................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition Settings............................................................................................................................................................. 13
Project settings .......................................................................................................................................................13
Document template................................................................................................................................................13
Batch type ............................................................................................................................................................. 15
Page template library............................................................................................................................................ 15
Batch type structure.............................................................................................................................................. 16
Registration parameters........................................................................................................................................ 16
Batch type rules..................................................................................................................................................... 16
Setting up a Batch Type ........................................................................................................................................ 17
Export settings....................................................................................................................................................... 18
Image Export......................................................................................................................................................... 19
Batch type status................................................................................................................................................... 19
List of Form Identifiers .......................................................................................................................................... 19
Rules...................................................................................................................................................................... 20
Automated registration settings............................................................................................................................. 21
Saving a batch type definition .............................................................................................................................. 22
Saving documents and their images ..................................................................................................................... 22
Operator management....................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 23
Operator roles........................................................................................................................................................23
Operator permissions............................................................................................................................................ 24
Workstations..............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................24
License............................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 24
Working with problem batches................................................................................................................................................................................................... 24
Scanning Station............................................................................................................ 25
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
2
Page 3

Introducing the Scanning Station............................................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Scanning Station Interface............................................................................................................................................................................................................... 25
Scanning Station main window............................................................................................................................ 25
Scanning Station toolbar....................................................................................................................................... 25
Typical actions of the scanning operator.............................................................................................................................................................................. 26
Additional capabilities of Scanning Station......................................................................................................................................................................... 26
Registration Station....................................................................................................... 28
Introducing Registration Station................................................................................................................................................................................................. 28
Registration Station Interface........................................................................................................................................................................................................ 28
Registration Station: main window....................................................................................................................... 28
Registration Station: toolbar .................................................................................................................................28
Typical use scenario.............................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 29
Additional capabilities of Registration Station................................................................................................................................................................... 29
Recognition Station....................................................................................................... 31
Introducing the Recognition Station........................................................................................................................................................................................ 31
Recognition Station Interface........................................................................................................................................................................................................31
Recognition Station main window.........................................................................................................................31
Recognition Station toolbar....................................................................................................................................31
Typical actions of the recognition operator....................................................................................................................................................................... 32
Additional capabilities of the Recognition Station.........................................................................................................................................................32
Verification Station ....................................................................................................... 33
Introducing the Verification Station......................................................................................................................................................................................... 33
Verification Station Interface.........................................................................................................................................................................................................33
Verification Station main window .........................................................................................................................33
Verification Station toolbar....................................................................................................................................33
Typical actions of the verification operator........................................................................................................................................................................ 34
Additional Capabilities of the Verification Station.........................................................................................................................................................34
Correction Station......................................................................................................... 35
Introducing the Correction Station...........................................................................................................................................................................................35
Correction Station Interface........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 35
Correction Station main window...........................................................................................................................35
Correction Station toolbar......................................................................................................................................36
Typical actions of the correction operator.......................................................................................................................................................................... 36
Additional Capabilities of the Correction Station........................................................................................................................................................... 37
Status of pages and documents..............................................................................................................................38
Export and Monitoring Station...................................................................................... 39
Introducing the Export and Monitoring Station ............................................................................................................................................................. 39
Export and Monitoring Station Interface.............................................................................................................................................................................. 39
Export and Monitoring Station main window .......................................................................................................39
Export and Monitoring Station toolbar................................................................................................................. 41
Typical actions of the export and monitoring operator............................................................................................................................................42
Additional capabilities of Export and Monitoring station........................................................................................................................................ 42
Appendix ....................................................................................................................... 46
Supported image formats.................................................................................................................................................................................................................. 46
Structure description language.....................................................................................................................................................................................................46
Annex component................................................................................................................................................. 46
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
3
Page 4

Page component ................................................................................................................................................... 46
Variant component............................................................................................................................................... 47
Repetition component........................................................................................................................................... 47
Optional component ............................................................................................................................................. 47
Document component........................................................................................................................................... 47
Descriptive multipage rule language ........................................................................................................................................................................................ 48
The Value of a multipage rule............................................................................................................................... 48
The verity of a multipage rule............................................................................................................................... 48
One–dimensional constant................................................................................................................................... 48
Multi–dimensional constant ................................................................................................................................. 49
Page field reference............................................................................................................................................... 49
MR document reference ........................................................................................................................................ 49
Dimension matching............................................................................................................................................. 49
Type conversion ...................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 50
Binary operators: + , – , / , * , ^ , & , Or , And , = , < , <= , > , >= , <> , In , Like , Mod.................................. 50
Unary operators: – , ! ........................................................................................................................................... 51
Zero–argument operators: Now, Date.................................................................................................................. 51
Type conversion operators: CDbl, CBool, CStr, CLng, CDate................................................................................ 51
Packing operators: Sum, Prod, Avg, Max, Min, Count, First, Last, NumMax, NumMin, Same, Unique................ 51
String processing operators: UCase, LCase, Len, Trim ..........................................................................................52
Part–of–date operators: Year, Month, Day.......................................................................................................... 52
IsError operator .................................................................................................................................................... 52
Error operator....................................................................................................................................................... 52
Abs operator.......................................................................................................................................................... 52
Formatting operator: Format ................................................................................................................................53
Progression operators: Inc, Dec, Mult ....................................................................................................................53
Cut operator: SubArray..........................................................................................................................................53
Substring cut operator: SubStr ...............................................................................................................................53
Selection operator: IIf............................................................................................................................................ 54
Substring replace operator: Replace ..................................................................................................................... 54
Data creation operator: DateSerial ...................................................................................................................... 54
Glue operator: Array............................................................................................................................................. 54
VBScript for ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition................................................................................................................................................... 54
General scope........................................................................................................................................................ 54
Creating custom functions by using the Form Page Access API............................................................................. 54
Support for custom verification rules and error messages.................................................................................... 58
Sequence of calculating the form field values .......................................................................................................58
Peculiarities of the script....................................................................................................................................... 58
Auxiliary function library .....................................................................................................................................58
Example of using the Form Data Access API ......................................................................................................... 59
How to modify the script ....................................................................................................................................... 59
Automation Export................................................................................................................................................................................................................................ 59
Export procedure.................................................................................................................................................. 60
ExportData argument........................................................................................................................................... 60
Glossary.......................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 64
Hotkeys........................................................................................................................................................................................................................................................... 65
Scanning Station hotkeys ...................................................................................................................................... 65
Verification Station hotkeys................................................................................................................................... 66
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
4
Page 5

Correction Station hotkeys ....................................................................................................................................66
Export and Monitoring Station hotkeys................................................................................................................. 66
Frequently Asked Questions ........................................................................................................................................................................................................... 67
How to buy ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition.................................................................................................................................................... 67
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
5
Page 6
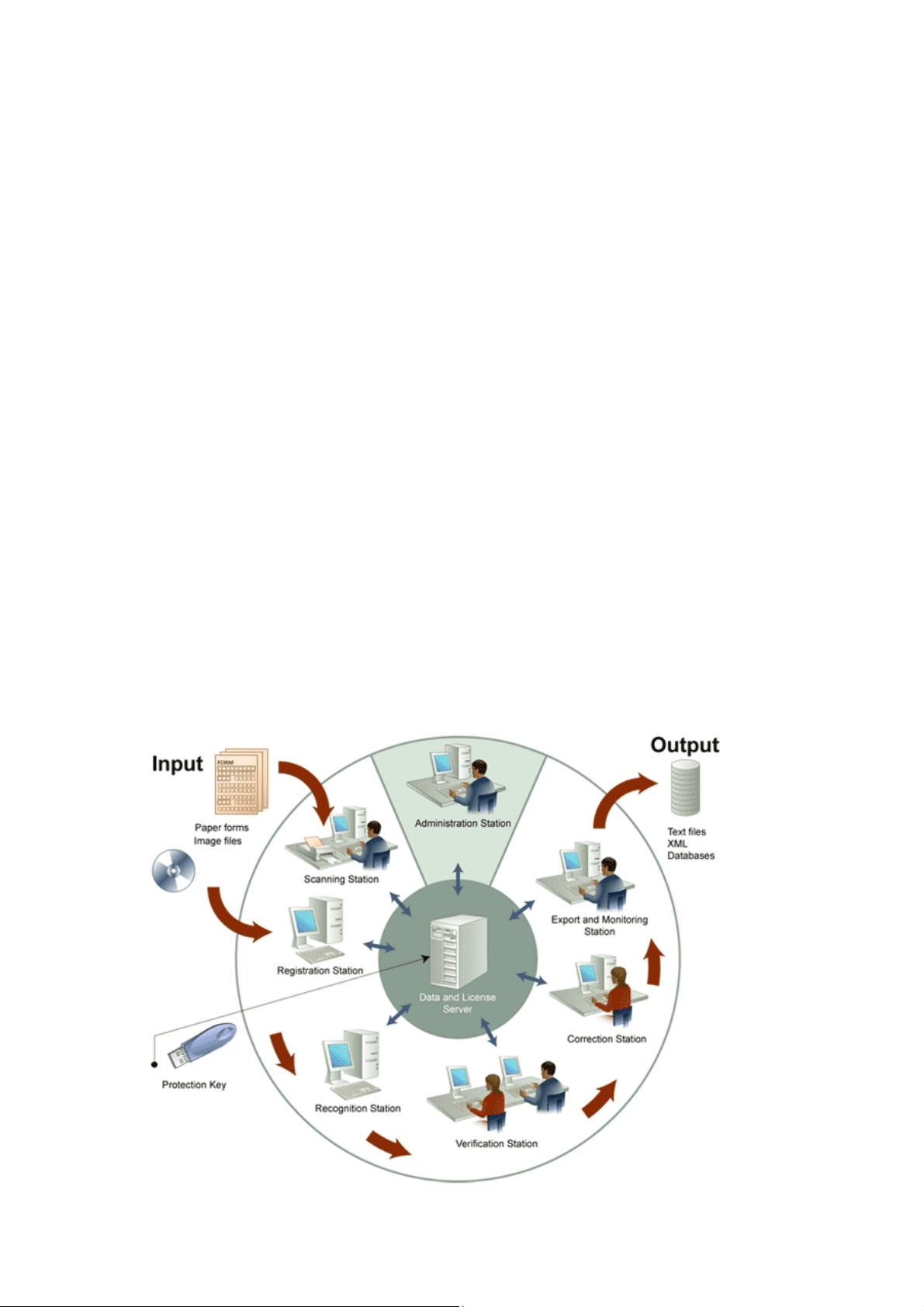
Introducing ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition
About ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition is a form capture system that is a distributed client–server application built on ABBYY
FormReader and Microsoft SQL Server/MSDE technologies.
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition includes a Data and License Server and the following specialized stations:
• Administration Station
• Scanning Station
• Registration Station
• Recognition Station
• Verification Station
• Correction Station
• Export and Monitoring Station
All stations can be installed on different PCs.
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition is highly scalable (i.e. the number of workstations can be easily changed to suit the user’s
needs) and can be used to process unlimited numbers of forms.
Main features:
• System setup precedes form capture
• Scanning paper documents and image cleanup
• Automated recognition of typographical and hand–printed text (OCR, ICR), barcodes and checkmarks (OMR)
• Validating data using validation rules
• Checking document integrity
• Exporting data into CSV or XML formats or into a database; exporting images into external information systems
• Controlling the form capture process
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition process overview
The scheme of the ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition form capture process...
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition includes a set of stations and a Data and License Server. Each station performs single–type
operations providing effective setup and continuous streaming of form capture. The Data Server is a connecting link between the
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
6
Page 7

stations. The stations transfer data via the Data Server, and the only protection key for the entire system is installed on the Data and
License Server.
System setup is separated from the form capture process and is performed on a special station – the Administration Station.
The form capture process, which converts paper forms (or image files) into editable data, is consecutively performed on the following
stations: Scanning Station or the Registration Station, Recognition Station, Verification Station (optional), Correction Station and
Export and Monitoring Station. The above processing order is determined by the architecture of ABBYY FormReader Enterprise
Edition and cannot be changed.ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition is a scalable solution, i.e. the number of stations involved in
form processing can be changed to suit the user’s needs. The maximum number of stations of each type that can be run within the
form capture system at one time is determined by the license that is written in the protection key.
The first station where the forms are sent for processing is either a Scanning Station or a Registration Station. Either station adds the
incoming images to a batch, supplies the batch with certain user information about the batch, and sends it on to other stations for
further processing. The choice between a Scanning Station and a Registration Station depends on the task to be solved:
• A Scanning Station provides greater control over the images that are being added to the batch: image defects can
be repaired (images can be despeckled, their orientation can be corrected, etc.), images can be added to the batch
in a particular order, and each batch can be manually supplied with user information. All these features will
ensure high capture quality for complex forms which differ greatly from one another.
• A Registration Station performs all the above actions automatically in accordance with user presets. This ensures
fast processing of large numbers of sametype forms (e.g. forms scanned by means of a batch scanner).
Both stations can be used simultaneously to process different sets of forms.
Below follows a brief overview of each station:
Administration Station
The Administration Station is used to prepare the form capture system for operation.
The operator of the Administration Station plans the overall form capture process and sets up each station: adds batch types to the
project and sets them up, allocates duties to the operators and gives them the necessary permissions.
Additionally, the operator of the Administration Station can view the license parameters of the form capture system and the list of
network computers on which the system stations are installed and which are currently running.
Once the system has been set up, form processing can start.
Scanning Station
The Scanning Station is the first station to process forms. A stack of paper forms or image files of previously scanned paper forms are
fed into the Scanning Station.
The operator of the Scanning Station creates a new batch for storing and further processing the images of the paper forms, registers
the batch, scans the paper forms and/or adds ready image files to the batch and then sends the batch to the Recognition Station.
If required, processing of any batch can be suspended. The suspended batch is not sent for further processing. The operator of the
Scanning Station can resume its processing later.
Registration Station
A Registration Station automatically adds incoming images from a particular folder to a batch, registers the batch, and sends it to a
Recognition Station. A Registration Station may be more preferable than a Scanning Station when there is no need to enter
registration parameters manually and to control the order in which the images are added to the batch. The operator simply launches
the registration process, and the program automatically extracts mages from a userdefined folder, adds them to a batch, and provides
the batch with a name and registration parameters. The program will repeat this process every 60 seconds until the operator stops the
registration process.
Recognition Station
The Recognition Station automatically recognizes batches. All the operator of the Recognition Station needs to do is to start the
recognition process, and the Recognition Station will recognize the batches. When batch recognition is completed, the batches are
automatically sent to the Verification Station or, if the form capture system does not include the Verification Station, to the Correction
Station.
Verification Station (optional)
The Verification Station is used to edit recognition results and, optionally, to validate data. The operator of the Verification Station is
guided by program prompts and consecutively verifies uncertainly recognized characters and validates data using one–page rules.
Once a batch is verified and validated, it is sent to the Correction Station.
If a problem occurred when processing a batch, the operator of the Verification Station can provide the batch with a comment and
send it to the Correction Station marked as a problem batch.
The Verification Station is optional. If the form capture system does not include the Verification Station, data are verified and
validated using one–page rules on the Correction Station.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
7
Page 8

Correction Station
The Correction Station is used to assemble batch documents and edit the results of multipage rules. The operator of the Correction
Station is guided by program prompts and consecutively assembles a batch and validates data using multipage rules. Once a batch is
verified and validated, it is sent to the Export and Monitoring Station.
If required, the operator of the Correction Station may scan or recognize some pages in the batch anew (using the same or adjusted
scanning or recognition settings), re–verify some pages in the batch, and correct errors detected by one–page rules.
Note. Changes made to the scanning or recognition settings are used to process only the current batch and are not applied to the
current batch type.
If a problem occurs when processing a batch, the operator of the Correction Station can provide the batch with a comment and send
it to the Export and Monitoring Station marked as a problem batch. If the form capture system does not include the Verification
Station, all data are verified and validated using one–page rules on the Correction Station.
Export and Monitoring Station
The Export and Monitoring Station is used to export batches, monitor the operation of the form capture system and process problem
batches.
Data can be exported either automatically or manually. In the first case, once export has started, all batches put into the Export queue
are exported automatically. In the latter case, the operator selects from the Export queue batches to be exported and then exports the
selected batches.
While monitoring the operation of the form capture system, the operator can view:
• Batch processing statistics;
• Station sessions statistics;
• Event log.
While processing problem batches, the operator can:
• Assign a batch to a specific operator;
• Delete a batch form the database;
• Stop any station;
• Block/unblock processing of a batch;
• Return a batch to a previous processing stage or to an operator if required.
Technical Support
Should you have any questions regarding the way in which ABBYY FormReader works, first of all consult the documentation supplied
with the software (User’s Guide and Help). You may also browse the technical support section on our Web site www.abbyy.com.
Our technical support service experts will need the following information to answer your question competently:
• your first and last name
• your organization’s name
• your telephone number (or fax, or e–mail)
• serial number of your ABBYY FormReader package
• build number (see Help/About.../Build)
• general description of your problem and the full error message text (if there was one)
• your computer and processor type
• the version of your Windows operating system
• you may supply us with any other information you consider important.
You can get some information automatically by clicking the System Info button in the About ABBYY FormReader dialog box
(menu Help).
Important!
Only registered users are eligible for technical support. You can register your copy of the application at our Web site.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
8
Page 9

Installing, Uninstalling and Starting the Form Capture
System
Software and hardware requirements
Server requirements:
• PC with Pentium 300MHz processor (Windows Server 2003, XP); Pentium 200MHz processor (Windows 2000)
• Microsoft Windows Vista, Microsoft Windows Server 2003, 2000 Server (SP2 or higher), XP, 2000 Professional (SP2 or
higher).
• 128 MB RAM (Windows Server 2003, XP); 64 MB RAM (Windows 2000)
• 15 MB of hard disk space for Server, 75 MB for MSDE, 375 MB if installation files are copied onto server for remote
installation, additional disk space to store batches
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher
• Mouse or other pointing device
• CD–ROM drive
• SVGA monitor (resolution 800x600 or higher)
• USB port for hardware protection key
Station requirements:
• PC with Pentium 350MHz processor (MS Windows Server 2003, XP); Pentium 200MHz processor (MS Windows 2000,
Me, 98)
• Microsoft Windows Vista, Microsoft Windows Server 2003, XP, Server 2000 (SP2 or higher), 2000 Professional (SP2 or
higher), Me, 98
• 128 MB RAM (Windows Server 2003, XP); 64 MB RAM (Windows 2000, Server 2000, Me, 98)
• 170 MB of hard disk space for minimal installation; 5 MB of hard disk space for minimal installation of each additional
station; additional hard disk space to create local batch copies
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.0 or higher
• Mouse or other pointing device
• CD–ROM drive (in case of CD–ROM installation)
• SVGA monitor (resolution 800x600 or higher)
• 100% TWAIN compatible scanner (for Scanning Station)
Installing and uninstalling the form capture system
The ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition form capture system consists of the following components:
1. Data and License Server
2. Administration station
3. Registration Station
4. Scanning Station
5. Recognition Station
6. Verification Station
7. Correction Station
8. Export and Monitoring Station
Important!
• We recommend closing all the running applications (MS Outlook, MS Word, etc.) before installing ABBYY FormReader
Enterprise Edition.
• You must have the local administrator’s permissions to install the program.
In order to install the program, you must have read and write permissions for the Server destination folder. If the Stations are installed
from the CD–ROM, it is enough to have read and write permissions for the LicenseBase subfolder of the Server destination folder.
• Uninstall FormReader 6.5 Desktop/Developer Edition if this program is installed on your computer.
• If your computer is running under Microsoft Windows Server 2000 or Windows Server 2003, the computers on which
the Server and the Stations will be installed must be in the same domain.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
9
Page 10

Installing the Server and Stations from the installation CD–ROM
1. Insert the ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition installation CD–ROM into your CD–ROM drive.
2. Select the ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition item from the
of the installation CD–ROM. Then follow the installation program’s instructions.
3. In the
Select Network Components dialog box:
Autorun program’s menu or run setup.exe from the root folder
• If you wish to install the Data and License Server only, select the Install Server option.
• If you wish to install the Data and License Server and one or several Stations, select both Install Server and
Install Stations options
• If you have already installed the Data and License Server and wish to install one or several Stations, select the
Install Stations option and specify the path to the LicenseBase subfolder of the Server installation folder.
If the Install Server option is selected, the following options become available:
• Copy distribution files onto network server – select this option if you wish to install the Stations from the Data and
License Server over the local area network.
• Interface Language Specifies the interface language for all the stations of the complex.
Note: We recommend selecting the same language for the setup process and for the user interface.
4. In the
Important!
This dialog box is not displayed if:
5. In the
Important!
Server Installation (MSDE) dialog box, specify the path to the folder where the MSDE (Microsoft SQL Server 2000
Desktop Engine) executable files will be installed and the path to the folder where data will be stored.
• The Data and License Server is not installed
• An MSDE version required for operation of ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition has already been installed on your
computer.
Server Installation (Database) dialog box, specify the database installation parameters.
• This dialog box will not be displayed if the Server is not installed.
• The network folder where new batches will be stored must be empty and accessible for reading and writing in the local
area network. The path to the folder must be in UNC format.
6. In the
Important!
When you install the Administration Station for the first time, you will not be able to deselect the Administration Station option.
If you install only the Stations, make sure that the protection key is installed on the computer where the Server is installed and
that the Server operates properly.
This dialog box is not displayed if you have chosen not to install the Stations.
Select Stations dialog box, select the Stations to be installed.
7. In the Setup Type dialog box, select a setup type:
• Standard. The default components will be installed in this mode. The default components are determined by the
Administration Station installation components if the Administration Station has already been installed.
• Custom. The default components and the components selected from the Custom Setup dialog box will be installed.
This dialog box is not displayed if you have chosen not to install the Stations.
8. In the Installation folder dialog box, specify:
• The path to the folder where the program files will be installed,
• The path to the local folder where batch copies will be stored (if the Stations are being installed).
Important!
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
10
Page 11

The ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition destination folder must be located on the same computer where you are
running the setup program.
9. Once the Server is installed, connect the hardware protection key to the USB port of your computer.
Installing a Station remotely from the Server
From the computer on which you wish to install the Station, run setup.exe located in the Server destination folder on the computer
where the Server is installed. Then follow the installation program’s instructions.
Uninstalling the form capture system
To uninstall the program, select Start>Settings>Control Panel>Add or Remove Programs>ABBYY FormReader Enterprise
Edition.
Important!
MSDE must be uninstalled separately. To uninstall MSDE, select Start>Settings>Control Panel>Add or Remove Programs
>Microsoft SQL Server Desktop Engine (FRE6ENTERPRISE).
Type of protection
To install ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition, you need a protection key.
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition may be supplied with one of the two types of protection key:
• hardware protection key
• software protection key
Hardware protection key
The hardware protection key is plugged into a USB port.
For the correct operation of the hardware protection key, you need to install the corresponding drivers. This can be done either from
within the installation program or from within the License Manager utility.
Software protection key
A software protection key is a license file.
For the correct operation of ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition, you need to activate the software protection key via the ABBYY
activation server. This can be done either from within the installation program or from within the License Manager utility. Your
activated license file will be sent to you by email. Once you have received your activated license file, you will need to specify the path
to this file in the License Manager utility.
Warning!
1. To be able to run the program, place the license file on the same computer where the License Manager is installed (the License
Manager is automatically installed on the same computer where the Data and License Server is installed).
2. A license file that has been activated for one computer will not work on another computer because it includes specific parameters
of the computer for which it has been activated.
Starting the form capture system
To start ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition, select Start/Programs and then select the desired Station in the ABBYY
FormReader Enterprise Edition group.
Important!
• When you run the Administration Station for the first time, specify the following information in the Login dialog box:
Operator: FRE6Admin
Password: 555555
• Before running other Stations, set up the appropriate operator roles on the Administration Station.
Important!
You must have read/write permissions for:
• The Server destination folder. If the Stations are installed from the CD–ROM, it is enough to have read and write
permissions for the LicenseBase subfolder of the Server destination folder.
• The folder where batches will be stored.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
11
Page 12

Administration Station
Administration Station Interface
Administration Station main window
The main window of the Administration Station is divided into two panes. The left–hand part contains the project itself – the settings
for batch types, operators and stations. The settings are displayed in a tree–view format. When you select a tree object in the left–
hand pane, its “contents” are displayed in the right–hand pane.
The project tree includes the following objects that are shown below together with their nested objects:
• Project
• Batch types
• Page template library
• Document templates
o Document template rules
• Batch type rules
• Registration parameters
• Operators
• Stations
The main window of the Administration Station provides all the available information about all the settings of ABBYY FormReader
Enterprise Edition.
Administration Station toolbar
The Administration Station toolbar contains the buttons which provide shortcuts to the standard menu commands, such as going to
the previously selected object, editing or deleting an object, etc.
Toolbar buttons:
Button Description
Back Allows you to go to the previous object.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
12
Page 13

Forward Allows you to go the next object.
Up Allows you to move up one level in the project tree.
Edit Edits the selected object (if editing is enabled for this object).
Delete Deletes the selected object.
Typical actions of the administrator
The sequence of actions typically performed by the administrator of ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition to prepare the system for
operation:
1. Creating a new batch type,
2. Setting up the created batch type,
3. Setting up the scanning and recognition processes,
4. Making operators’ settings (specifying operators’ roles and permissions).
Creating a new batch type
1. Create a new batch type using the Batch Type Creation Wizard. To start the Batch Type Creation Wizard, select the
Batch Types object in the project tree, then in the Action menu, select the appropriate item:
o If you wish to create a batch type by using the ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition features, select
New/Blank....
o If you wish to create a new batch type on the base of an existing batch type definition, select New/Based
on Definition...
o select the Новый/из MXFD... command to create a batch type based on an *.mxfd file, which contains
information about a document, the templates in the document, their number, and order
2. If required, edit the batch type structure, add a new document template or edit the structure of the existing document
templates, add a new page template to the page template library or edit the existing page templates.
3. Specify rules for the batch type and document templates.
4. Specify registration parameters.
Setting up a new batch type
• In the Batch Type Settings dialog box, make the required batch type settings.
Setting up scanning and recognition
• Use the page template library to make scanning and recognition settings.
Create operators that will work with the new batch type, assign roles and permissions to the operators.
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition Settings
Before you run ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition, you must set up the system. The Administration Station is controlled by the
operator of the Administration Station who sets up the other stations, allocates tasks to them, gives permissions to station operators,
sets up the project, batch types, etc.
Project settings
A project in ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition is a collection of all the batches to be processed by the system together with all the
settings required for their processing.
The project settings are as follows: the project name, the SQL server name, and the path to the network folder where new batches will
be stored. All project settings are located in the Project Settings dialog box, and almost all of them are specified when installing
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition. Once the system has been installed, only the Path to network folder for storing new
batches option is available for editing.
Document template
A document template is a description of a sequence of page templates and rules required for data validation.
Creating, editing and deleting a document template
To create a document template:
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
13
Page 14

1. Select the Document Templates object in the required batch type.
2. In the
3. The
4. If required, edit the structure of the document template.
5. Specify document template rules.
You can edit the name, structure and rules of the template.
Action menu, select the New... item.
Document Template Creation Wizard will be launched. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
To edit the name of a document template:
1. Select the required document template.
2. In the
3. In the dialog box that appears, edit the template name.
Action menu, select Edit Name...
To edit the structure of a document template:
1. Select the required document template.
2. In the
3. In the
Action menu, select Edit Structure...
Edit Document Template Structure dialog box, edit the structure of the document template.
To delete a document template:
1. Select the required document template.
2. In the
Action menu, select Delete.
The structure of a document template
The structure of a document template is a description of a sequence of page templates written in a special language.
There are four types of document template structure:
• One–page document,
• Two–page document,
• Document with a predefined page order,
• Custom structure.
A one–page document is the structure of a document consisting of one page.
A two–page document is the structure of a document consisting of two pages. The order of pages can be either arbitrary or
predefined.
A document with a predefined page order is the structure of a document consisting of several pages that go in a predefined order.
The structure types mentioned above are standard and do not require a special description. All you need to do is enter the information
requested by the program.
A custom structure is used to describe the structure of a document template in the structure description language.
Specifying and editing the structure of a document template
The structure of a document template is specified when creating the document template in the Document Template Creation Wizard.
After the structure has been created, you can edit it or change its type. Use the Edit Document Template Structure dialog box to
edit the structure.
Document template rules
When creating a new document template, you can specify multipage rules for the template. Multipage rules of a document template
establish relations between data and are used to validate the data in the document.
Creating, editing and deleting document template rules
To create a rule for a document template:
1. Select the Rules object in the required document template.
2. In the
3. In the
Action menu, select New...
Create New Rule dialog box that appears, enter the required information and write the rule in the descriptive
rule language.
To edit a rule of a document template:
1. Select the required rule.
2. In the
Action menu, select Edit...
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
14
Page 15

3. In the Edit Rule dialog box, edit the rule.
To delete a rule from a document template:
1. Select the required rule.
2. In the
Action menu, select Delete.
Document template export settings
Document template export settings are specified in the Batch Type Setting dialog box when you specify export settings for the
batch containing the selected template (see Batch Type Setting for more details).
You can see or edit some of the document template export settings in the Docxument template export setting dialog box. To
open this dialog box, select the necessary template in the project tree and click Export Settings... in the local menu.
Batch type
A batch type is a description of page templates, document templates and their sequence, registration parameters, and settings and
rules required for batch recognition and data validation. Each batch to be processed is associated with a certain batch type. The batch
will be processed in accordance with the settings of its batch type.
Creating, editing and deleting a batch type
You can create a batch type, set up the created batch type, set validation rules and specify registration parameters.
To create a batch type:
1. Select the Batch Types object in the project tree;
Then, in the Action menu, select the appropriate item:
• If you wish to create a batch type by using the ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition features, select
New/Blank...
• If you wish to create a new batch type on the base of an existing batch type definition, select New/Based
on Definition...
Importatnt!
You cannot create a new batch type on the base of any batch type existing in your form capture system. In
order to do this you have to rename or delete the batch type.
2. The
3. If required, edit the structure of the batch type, add a new document template or edit the structure of the existing
4. Specify batch type rules and document template rules.
5. Specify registration parameters.
6. Set up the batch type.
You can edit the name, structure, registration parameters, settings and rules of your batch type.
To edit the name of a batch type:
To edit the structure of a batch type:
Batch Type Creation Wizard will be displayed. Follow the instructions of the wizard.
templates, add a new page template to the page template library or edit the existing templates.
1. Select the required batch type.
2. In the
3. In the dialog box that appears, edit the name of the batch type.
1. Select the required batch type.
2. In the
3. In the
Action menu, select Edit Name...
Action menu, select Edit Structure...
Batch Type Structure dialog box, edit the structure of the batch type.
To delete a batch type:
1. Select the required batch type.
2. In the
Action menu, select Delete.
Page template library
A page template library is a set of page templates used in a certain batch type.
A page template library is a ABBYY FormReader (*.frm) batch, and it is created in the Batch Type Creation Wizard.
Note. When creating a new batch type, you can create a new library or use an existing one.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
15
Page 16

You can edit (i.e. add, edit or delete page templates), replace or set up a page template library. You can view the list of blocks and
one–page rules specified for a given page template library. To do this, select a page template in the project tree, and then select
Action>Properties... The Page Template Properties dialog box will appear.
Batch type structure
A batch type structure is a description of document templates in a special structure description language.
There are two types of document template structure:
1. Set of documents,
2. Custom structure.
A set of documents is the standard type of structure. A batch type of this structure can include all the documents specified for the
batch type in any number or order. If you use the standard structure, you do not have to create rules manually.
A custom structure is used to describe the structure of a batch type in the structure description language.
Creating and editing a batch type structure
The structure of a batch type is created when creating a batch type in the Batch Type Creation Wizard.
Once the structure has been created, you can edit it or change its type. To edit the structure, use the Batch Type Structure dialog
box.
Registration parameters
Registration parameters are specified for a batch type and are used to enter user information when registering a batch of this type on
the Scanning Station.
For example, suppose that stacks of questionnaires have been sorted by city from which they came and you need to enter this
information into your database. When setting up the batch type, you can specify “City” as the registration parameter. In this case the
scanning operator will be prompted to fill out the field corresponding to this registration parameter, and the entered information will
be saved in the database.
Creating, editing and deleting registration parameters
To create a registration parameter:
1. Select the Registration Parameters object in the required batch type.
2. In the
3. In the
Action menu, select New...
Registration Parameters dialog box that appears, specify the code and name of the registration parameter.
To edit a registration parameter:
1. Select the required parameter.
2. In the
3. In the
Action menu, select Edit...
Registration Parameters dialog box that appears, edit the registration parameter.
To delete a registration parameter:
1. Select the required parameter.
2. In the
Action menu, select Delete.
Batch type rules
When creating a new batch type, you can create multipage rules for it.
Multipage rules of a batch type establish relations between various data in a batch and are used to validate these data. In contrast to
multipage rules of a document, batch type rules can establish relations between data located in different documents of the batch.
Creating, editing and deleting batch type rules
To create a batch type rule:
1. Select the Rules object in the required batch type.
2. In the
3. In the
Action menu, select New...
Create New Rule dialog box that appears, enter the required information and write the rule in the descriptive
rule language.
To edit a batch type rule:
1. Select the required rule.
2. In the
Action menu, select Edit...
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
16
Page 17

3. In the Edit Rule dialog box that appears, edit the rule.
To delete a batch type rule:
1. Select the required rule.
2. In the
Action menu, select Delete.
Setting up a Batch Type
When creating or editing a batch type you should set up the options for processing and exporting all batches belonging to the batch
type. In order to set up or edit the batch type settings, open the Batch Type Settings (select the batch type in the project tree, and
then go to Action>Settings...).
In the dialog box that appears you can specify the following:
• General batch type settings;
• Batch processing settings;
• Export settings.
General batch type settings
The general batch type settings include: the batch type name, the path to the page template library, and the path to a network folder
where new batches will be stored. In order to set up or edit these settings, go to the General tab of the Batch Type Settings dialog
box.
Batch processing settings
The batch processing settings allows the user to select the way for processing batches on the input system stations. In order to set up
or edit these settings, go to the Processing tab of the Batch Type Settings dialog box.
Scanning Station. The following options are available for this station:
• Name batches automatically. If this option is selected the input system will automatically name all new batches. The
batch ID assigned to the batch when registering is used for naming the batch.
• Get local copy for scanning. This option will help to speed up batch processing due to creating local copies of the
processed batches and processing them on the station rather over your LAN.
Registration Station
The settings of this station determine the automated creation of batches of a specific type from images arriving into a userdefined
folder. The batches are registered and sent on to the Recognition Station.
• Include Registration Station. A Registration Station need not be included for a particular batch type. In this case, each
batch is created and registered manually on the Scanning Station. In some cases this method proves inefficient (for
example, if batches of this type include only onepage documents and their registration parameters need not be entered
manually). Besides, you may need to add batches acquired from other sources as soon as they arrive into a certain folder.
The work of the scanning operator can be considerable simplified by means of a Registration Station. The Registration
Station will automatically from batches from images arriving into the specified folder, register the batches and queue them
for scanning.
• Select the method of the Hot Folder processing. The Hot Folder can be processed with the help of the standard
method (at the Registration Station) or with the help of a custom module. Regardless of the selected Hot Folder processing
method, such operation as creation and registration of batches, adding images from the Hot Folder to a batch, and sending
batches to the recognition queue, are always performed at the Registration Station. If you want to process the Hot Folder at
the Registration Station, select Standard from the dropdown list. If you want to use a custom module, select the name of
the necessary module.
Note. If no custom import modules have been registered in the system, the dropdown list will have only one item,
Standard. Custom import modules must be installed on the computer where the Registration Station is installed, and the
modules must be registered in the system. To register an import module, click Add... and in the dialog box that opens,
specify the module name and identifier (ProgID). Alternatively, you can register a module by selecting the Import
Modules... item in the Tools menu. Then specify the registration parameters.
• Registration Settings... Opens a dialog box where you can set up the registration process for batches of a specific type.
You can specify a folder where images to be processed will arrive and select a method of creating batches and assigning
registration parameters. For details about setting up the Registration Station, please refer to Automated registration settings.
Recognition Station.
The settings of this station provide additional processing functionality:
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
17
Page 18

• Delete blank pages. This option allows you to reduce the size of your batches due to removing blank pages included into
the batch by mistake.
• Get local copy for recognition. This option will help to speed up batch processing due to creating local copies of the
processed batches and processing them on the station rather over your LAN.
Verification and Correction Stations.
validated, how documents will be assembled, and how errors detected at recognition and verification will be corrected.
The settings of these two stations determines how recognized data will be verified and
• Use the Verification Station. The Verification Station can be excluded from the form capturing system, because the
Correction Station allows the user not only to correct various errors which might hinder batch processing but also to check the
data with the help of onepage and multipage rules. However, the Verification Station is often necessary when you need to
process large volumes of information.
If you wish to process batches of a certain batch type at the Verification Station (i.e. the Use the Verification Station option is
selected), you must specify the operations that will be performed at the Verification Station. Select one of the following options:
• For verification, if you would like to use the verification Station for verification only.
• For verification and onepage rule check, if you would like to run both the types of data check at the Verification
Station: verification (recognized data check by an operator) and onepage rules check (automatic recognized data check with
the help of rules).
Verification is a complicated procedure which might be rather timeconsuming. If the recognized data do not have many errors and
absolute accuracy of recognition is not required, the Verification station can be excluded from the processing sequence for batches of
this batch type.
• Do not verify batches if the number of uncertain characters is less than. This option allows you to skip the
verification stage and send a batch directly to the Export and Monitoring Station if the percentage of uncertainly recognized
characters in the batch data does not exceed the threshold which is specified in the corresponding filed of this option.
• The number of pages sent simultaneously to verification. Group verification is a convenient way to check
recognition results. This option allows you to specify the number of pages which will be sent simultaneously to group
verification. This number must not exceed 50.
• Skip Correction Station for batches without errors. This option allows you start the process of batch assembly and
multipage rules check (if any) automatically when onepage rules check is complete. If this process is successful, the batch is
sent directly to the export queue and skips the Correction Station. If an error occurred during the assembly or multipage rules
check, the batch is sent to the Correction Station.
• Use local batch copies. These options allow you to speed up batch processing with the help of a copy of the batch which
is created and processed at the station. If you want to use a batch copy during batch processing at the Verification or Correction
Station, select the corresponding option.
Export settings
To specify data export settings, you must select the batch export folder and the export type on the Batch Export tab in the Batch
Type Settings dialog box, and to select the necessary options on the Images & Documents Export tab.
The following export types are available:
• Export to XML
This option allows you to export recognized data to XML format. You can also export the blocks coordinates.
• Export to CSV
This option allows you to export recognized data to CSV format. You can select the column separator that will be used
when exporting the recognized data. The Save tables to a separate file option allows you to export tables to a separate
file retaining the table structure.
• Export to OLE DB
This option allows you to export recognized data to a database. In order to set up this type of export, click the Settings
button and, in the OLE DB Export Setup dialog box that appears, specify the database source and associate batch
documents with the database tables.
• Automation export
This option allows you to export recognized data by using Automation. Specify the Automation export procedure (prog ID)
that will be used for exporting the batches of this batch type.
• Export to Content Management System
The recognition results will be exported to a Content Management System (CMS). Export settings must be specified
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
18
Page 19
separately for each of the document templates of the selected batch type. To do this, select the necessary template in the list
and click Settings...
Note. You can use custom export modules during export to content management systems (CMS). Custom export modules
must be installed on the computer where the Export and Monitoring Station is installed, and the modules must be
registered in the system. If you want to use a custom export module, select the necessary module in the Select an export
module dropdown list.
If the necessary module has not been registered, its name will be missing from the dropdown list. To register a custom
export module, click Add... and in the dialog box that opens, specify the module name and identifier (ProgID).
Alternatively, you can register a module by selecting the Export Modules… item in the Tools menu. Then specify the export
parameters.
Image Export
To export the document as its scanned image or editable copy (for example, in the text format), click on the Images & Documents
Export tab in the Batch Type Settings dialog box. Select the documents to be exported as images and/or editable copies and
specify the necessary export settings: document format and language, export file name format.
Export file name format is specified in the File Names dialog box. The following prefixes can be added to the standard export file
name:
• Export file name prefix. Enter a prefix of your choice;
• Batch level prefix. Select this option to add one of the batch parameters to file names: the batch name, batch ID or
registration number;
• Block name one of the document template blocks is selected. Its recognized data will be added to the filename at the
image export.
Batch type status
A batch type always has a certain status. When you create a batch type, it is automatically assigned Editable status. The status of a batch
type can be changed in the Batch Type Status dialog box.
In this dialog box, select one of the available batch type statuses:
• Editable
Editable status is assigned to a batch type that has to be set up (a new batch type is assigned Editable status automatically).
A batch type with
change its status to
Editable status has the icon in the batch types list. To be able to change the settings of any batch type,
Editable.
• Published
Published status is assigned to a batch type once the batch type has been set up. Batches associated with this batch type will
be processed by the system. A batch type with
batch type is changed to
document structures and validation rules.
Published, the program checks all the required settings and the accuracy of the batch and
Published status has the icon in the batch types list. If the status of a
• Reserved
Reserved status is assigned to a batch type whose batches will not be processed by the system unless you change the status
of the batch to
type is color–marked. A batch type can be assigned
being processed at the moment.
Published. A batch type with Reserved status has the icon in the batch types list, and the name of the
Reserved status only if no batches associated with the batch type are
List of Form Identifiers
Form identifier is a unique number that is assigned to a form when you publish it in ABBYY FormFiller Template Designer. If you
edit and republish a form, its identifier will be changed (see ABBYY FormFiller Template Designer Help for details). Form identifiers
are stored in *.mxfd files.
One form may be compatible with several *.mxfd files, each storing its own identifier. ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition can
process very similar forms (i.e. several *.mxfd files which are compatible with one and the same form) in one batch, but you need to
specify the list of their identifiers first. In particular, ffdata of compatible forms will be checked by using one and the same batch type.
The administrator must ensure the correct processing of the differences between the forms by making the necessary batch type
settings.
Note: If you use an *.mxfd file to create a batch type, the list of form identifiers will consist of the form identifier stored in
this file.
To create a list of form identifiers:
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
19
Page 20

1. Run the Administration Station.
2. Select the required document type in the project tree.
3. Then in the Action menu, select Edit Form Identifiers...
4. In the dialog box that opens, add or remove the required form identifiers.
Important! If you use an *.mxfd file to create a batch type, its list of identifiers must contain at least one identifier.
Rules
A rule is a formalized description that applies certain restrictions to data as well as establishing relations between data in a batch.
Rules are divided into:
• One– page r ules that establish relations between data in the same document page. For more information about one–
page rules, refer to the ABBYY FormReader User’s Guide, Creating a Batch/Using Validation Rules.
• Multipage rules establish relations between data located on different pages. They are used to validate the data in a
batch. A multipage rule for a document template establishes relations between data in the same document, while a rule
for a batch type establishes relations between data in different documents included in a batch.
Important!
Multipage rules should refer to exportable blocks only. When creating a multipage rule, make sure that the Export block option on the
Block tab in the Properties dialog box is selected for all blocks mentioned in the rule.
There are the following types of multipage rules:
• Assembly rules validated during assembly are rules stating restrictions on the structure of a document or a
batch. If errors are detected by such rules, the batch cannot be assembled. When you add a page during assembly, the
program checks all the rules of this type. If one of the rules reports an error, the batch will not be assembled.
Important!
Use rules of this type only if absolutely necessary, as they greatly slow down batch assembly. It is recommended to describe all the
restrictions on the structure of a document or a batch either in the structure or in assembly rules checked after batch assembly.
• Assembly rules validated after assembly are rules stating restrictions on the structure of a document or batch.
These rules are checked after batch assembly. The values returned by these rules are either TRUE or FALSE.
If the program detects errors by using required multipage rules, and these errors cannot be corrected for some reason, in
order to finish processing of the document it must be assigned 'Multipage rule error' status.
• Required rules are rules associating the values of fields in document (batch) pages. The values returned by these rules
are either TRUE or FALSE.
If the program detects errors by using required multipage rules, and these errors cannot be corrected for some reason, in order to
finish processing of the document it must be assigned 'Multipage rule error' status.
• Value rules are rules connecting the values of page fields in a document or in a batch. In contrast to all the above rules,
the value returned by these rules should be a number.
Example: Suppose the first page of a document is a questionnaire with the personal data about a respondent, and the
other pages are the respondent’s bank accounts. In this case you can create a multipage rule that will count the balance
of all the respondent’s accounts and use this value in other rules.
• Wa rn in g is a rule connecting the values of page fields in a document or in a batch. The value returned by these rules
should be a number.
If the program detects errors by using Warning multipage rules, and these errors cannot be corrected, in order to finish
processing of the document it must be assigned
There are two ways of creating rules:
'Multipage rule warning' status.
• By using descriptive rule language.
• By using VB Script.
Rules are created and edited in the Create/Edit Rule dialog box. In this dialog box, besides the name and the expression of the rule,
you can specify the order in which the rules will be run and enable/disable rules.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
20
Page 21

Automated registration settings
Batch registration is the first step in forms processing and consists in creating a new batch, entering its registration parameters, and
adding images to the batch. Batch registration can be performed manually by the operator of the Scanning Station or automatically by
the Registration Station.
In the case of automated registration, the program will check the userdefined "Hot Folder" for new images every 60 seconds. Any
images detected in this folder are formed into a batch. A name and registration parameters are then assigned to the batch. Automated
registration is convenient when you need to process a large number of sametype forms, or when batches must be created as images
are added to a particular folder.
Automated registration of batches of a certain type becomes available after the Include Registration Station option is selected
(Batch Type Settings dialog box) and the required settings have been made. The main settings to be made are the path to the Hot
Folder and the method of batch creation.
Important! If you set up automated registration for several batch types, you need to specify a separate Hot Folder for each batch
type.
Batch creation methods
When selecting a batch creation method, you need to take into account how images will be acquired and i what format. Below
follows a description of the possible batch creation methods:
1. One batch for every file
Creates a batch from images grouped into one multipage image file in PDF or TIFF format. Each such file arriving into the Hot Folder
is formed into a batch by the Registration Station. Depending on the settings, the name and the registration parameters of the batch
may be set based on the name and/or date and time of creation of the multipage file. This batch creation method can be used for
batch types consisting both of onepage and multipage documents.
2. One batch for several file
Creates a batch from individual batches continuously arriving into the Hot Folder (e.g. as a result of scanning). This method can be
used when the batch consists of onepage documents or of documents with a fixed number of pages. In this case you need to specify
the total number of pages in the batch (or provide a range of pages). The batch will be formed from the stated number of images (or
from all the available images if their number is within the range). If images arrive to the Hot Folder not quickly enough, you can
specify how long the program must wait until the required number of images has accumulated in the Hot Folder. Once this time
period has elapsed, the program will create a batch from the available number of images (even of this number is smaller than the
required number).
3. According to description file
Creates a batch from images (either onepage or multipage files) obtains from a batch scanner. Programs used in conjunction with
such scanners can automatically divide images into groups and create an index file (socalled description file) for each group. The
description file contains information about the images in the group. The Registration Station will form a separate batch from each
group of images. The name and registration parameters of the batch can be assigned based on the values of the index fields and the
properties of the corresponding description file. The format of the description file depends on which scanning program is used.
You can select from among the following formats:
• Kodak Capture Software Batch Index File if you scan with Kodak Capture Software. In this case you need to set up the
scanning program so that a separate folder is created for each description file (i.e. for each batch). We recommend using
the firstlevel subfolder of the Hot Folder. When creating a batch, the program will add to it all the images from the folder
specified in the corresponding description file in alphabetical order;
• Captiva QuickScan Batch File if you scan with Captiva QuickScan. We recommend setting up the scanning program so
that scanned images are placed into the Hot Folder itself or into its firstlevel subfolders. When creating a batch, the
program will add to it all the images listed in the corresponding description file. The images will be added in the order in
which they are arranged in the description file;
• ABBYY FormReader Index File (*.xml) if your scanning program creates XML files of the following structure:
ABBYY FormReader Index File (*.xml)
A ABBYY FormReader Index File (*.xml) must contain a root element Batch with child elements Images and
IndexFields (the IndexFields element is optional).
The Images element, in turn, must include Image elements, whose number corresponds to the number of pages in the
batch that is being created. Each Image element must contain a UNC path to the corresponding image file. The path to the
folder containing the image must be the same for all Image elements.
The IndexFields element may include one or more child Field elements corresponding to the index fields of the batch.
Each Field element must have a required attribute Name, which defines the name of the index field and the value
corresponding to the value of this field.
– <Batch>
...
– <Images>
<Image>\\HotFolder\Page1.tif</Image>
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
21
Page 22

<Image>\\HotFolder\Page2.tif</Image>
<Image>\\HotFolder\Page3.tif</Image>
</Images>
– <IndexFields>
<Field Name="Field1">Field1_Value</Field>
<Field Name="Field2">Field2_Value</Field>
</IndexFields>
</Batch>
In the case, we recommend setting up the scanning program so that scanned images are placed into the Hot Folder itself or
into its firstlevel subfolders. When creating a batch, the program will add to it all the images listed in the Image elements of
the corresponding description file. The images will be added in the order in which they are arranged in the description file;
• Empty Index File if your scanning program creates files of a format other than any of the above. In this case, all the
images and the description file must be placed in the Hot Folder itself. The information contained in the Empty
Index File cannot be taken into account during automated registration. When creating a batch, the program sorts the
files in the Hot Folder by name and then adds to the batch those files located above the description file.
Important! When setting up your scanning program, remember that:
• The program starts creating a batch as soon as it detects a description file of the specified format. Therefore you need to
make sure that a description file is created only after all the images of the corresponding batch have been scanned;
• Description files must be created either in the Hot Folder or in its firstlevel subfolders, i.e. description files from the folder
\\HotFolder\Batch\Batch1 will not be detected.
Saving a batch type definition
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition allows the user to save a batch type definition.
A batch type definition is a set of batch type settings that can be used when creating a new batch type.
The saved batch type definition can be used for creating a new batch type with the same settings at another form capture system.
To create a batch type with the same settings at another form capture system:
1. Select the required batch type in the first form capture system;
2. In the
3. In the dialog box that appears, specify an empty folder where your batch type definition will be saved;
4. In the second form capture system, create a new batch type on the base of the existing definition.
Action menu, select Save Batch type Definition...;
Saving documents and their images
The final stage of batch processing in FormReader 6.5 Enterprise Edition is exporting the recognized data to file, database or a
Content Management System. But sometimes you might need to save the document as the image and to create an editable copy of the
document (for example, in the text format). In such cases FormReader 6.5 Enterprise Edition allows you to:
• save the image of the scanned form in the selected graphical format;
• create an editable document copy of the selected format (PDF, TXT, RTF, HTML).
Image Saving
To save the processed document as image, you have to select the Image option for the template of the corresponding document on
the Images & Documents Export tab in the Batch Type Settings dialog box and specify the necessary settings there:
• select the format for the saved image (TIFF, JPEG etc.);
• specify resolution for the saved object;
• select filename format for the saved image;
• if necessary, specify advanced processing settings.
Document Copy Creation
To create an editable document copy, you have to select the Document option for the template of the corresponding document on
the Images & Documents Export tab in the Batch Type Settings dialog box and specify the necessary settings there:
• select the language(s) for the electronic document;
• select the format of the electronic document (PDF, TXT, RTF or HTML) and specify format properties;
• select filename format for the electronic document to be created;
• if necessary, specify advanced settings of the electronic document to be created.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
22
Page 23

Operator management
An operator is a user of the system who has been assigned roles and permissions to process certain batch types.
Creating, editing and deleting operators
To create a new operator:
1. In the project tree, select the Operators object.
2. In the
3. In the
To change the login of an operator:
1. In the project tree, select the Operators object.
2. Select the required operator from the list.
3. In the
4. In the dialog box that appears, specify the login.
To change the password of an operator:
1. In the project tree, select the Operators object.
2. Select the required operator from the list.
3. In the Action menu, select Change Password...
4. In the
Action menu, select New...
Operator dialog box that appears, specify the operator’s login, password, roles and batch types (separately for
each role) that the operator will be allowed to process.
Important! Operators’ names are not casesensitive.
Action menu, select Change Name...
Change Password dialog box that appears, specify the new password and confirm it.
To change operator roles and batch type permissions:
1. In the project tree, select the Operators object.
2. Select the required operator from the list.
3. In the
4. In the
To delete an operator:
1. In the project tree, select the Operators object.
2. Select the required operator from the list.
3. In the
Important!
Only an operator who did not perform any action in the form capture system (including login on any station) can be deleted.
Tip:
If you wish that an operator could not work in the form capture system, cancel all the roles and permissions specified to the operator.
Action menu, select Properties...
Operator dialog box that appears, make the necessary changes.
Action menu, select Delete.
Operator roles
There are the following operator roles in the form capture system:
• “Scanning operator” is the role of an operator working on the Scanning Station and on the Registration Station;
• “Recognition operator” is the role of an operator working on the Recognition Station;
• “Export and Monitoring operator” is the role of an operator working on the Export and Monitoring Station;
• “Verification operator” is the role of an operator working on the Verification Station;
• “Correction operator” is the role of an operator working on the Correction Station;
• “Administrator” is the role of an operator working on the Administration Station.
Each operator should be assigned a role. If a role is not assigned to an operator, the operator will not be able to work on the station
corresponding to the role.
For example, if an operator is not assigned the role of Recognition operator, he will not be able to work on any of the Recognition
Stations of the system.
Important!
To be able to assign a role to an operator, you must have at least one batch type in the project.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
23
Page 24

Operator permissions
You must specify batch type processing permissions for each operator. If an operator has no permissions for processing a batch type,
the batches associated with this type will not be sent to this operator.
Use the Operator dialog box, to specify and edit operator permissions. To open this dialog box, select Operators in the project tree,
select the required operator, and then select Action>Properties...
Workstations
The operator of the Administration Station can view the list of the workstations (computers) on which the form capture system
stations are installed as well as the settings of the stations.
To view the list of the computers, select the Stations objects in the project tree.
To view the settings of a workstation:
1. From the project tree, select Stations.
2. From the workstations list, select the desired workstation.
3. From the
4. In the
Action menu, select Settings...
Workstation dialog box that appears, view and/or specify the required settings.
License
The operator of the Administration Station can view information about the ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition license:
• The license parameters and their current status,
• The workstations which are working at the moment.
To view the information about your license, select Tools>License... The license parameters will be displayed in the License dialog
box that appears.
Working with problem batches
If by some reason the processing of a batch cannot be completed (for example, the operator cannot determine why the batch has not
been assembled or there are some rule errors that he cannot correct, etc.), the operator of the Correction Station can mark the batch
as a "problem batch". Such batches are routed to the Problem Batches queue.
Use the Problem Batches dialog box to view problem batches on the Administration Station. In this dialog box, you can view batch
comments, open a problem batch and edit it. The administrator can perform any operations with problem batches that are allowed by
ABBYY FormReader with the exception of export.
To open the Problem Batches dialog box:
1. Select the Project object in the project tree;
2. In the
Action menu, select Problem Batches...
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
24
Page 25

Scanning Station
Introducing the Scanning Station
The Scanning Station is the first station to process forms in the form capture system. The Scanning Station is controlled by a scanning
operator whose tasks include:
• Batch registration: The operator creates a new batch, enters its registration parameters, and scans paper forms (the
images will be added to the batch automatically) or adds to the batch form images obtained from other sources.
• Editing images: the operator despeckles images, adjusts image orientation, renumbers pages and deletes pages (if
required).
Once the forms have been scanned and edited, the operator sends the batch into the Recognition queue.
If the processing of a batch cannot be completed, the batch can be suspended (the batch will be assigned "Suspended" status). The
operator can resume the processing of the suspended batch by selecting it in the Select Next Batch dialog box.
Scanning Station Interface
Scanning Station main window
Title bar. Displays the names of the form capture system, the station and the currently processed batch.
Menu bar. Contains the station menus: Scan, Image, Batch and Help.
To ol b ar . Contains the most frequently used station commands.
Batch window. Contains the list of batch pages. For each page, its number and the login of the operator who opened the page are
displayed. The main window displays only one batch at a time.
Status bar. Provides information on the current status of the station.
Scanning Station toolbar
The Scanning Station toolbar contains the buttons which provide shortcuts to the standard menu commands, such as scanning pages,
adding images to the batch, etc.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
25
Page 26

Toolbar buttons:
Button Description
Scan (multi–functional
button)
Send Opens the Batch Registration Parameters dialog box where you can check the
Scan Scans a batch page.
Scan Multiple
Pages
Add Adds images stored in the image folder to the batch. The image folder is specified when
Add from... Adds images stored in any folder to the batch. When selecting this item, specify the path to
Scans several batch pages.
setting up the station.
the folder.
correctness of the registration parameters you entered.
Typical actions of the scanning operator
1. Start the station (select Start>All Programs*>ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition>Scanning Station).
2. In the
3. If there is an unfinished batch on the station, resume its processing. If there are no such batches, the
4. If you choose:
5. If you choose
6. Scan the form pages: either
7. Edit the images if required. Use the
8. Send the processed batch to the next station (
9. The
10. If you need to close the station while a batch is still being processed, select
Login dialog box, type in your login and password, then click OK.
Select Next Batch dialog
box will be displayed. In this dialog box, select a batch. The following options are available:
o New,
o Suspended.
o New – specify the type of the new batch.
o Suspended – select a batch from the list. If required, view the comments for the batch.
New, the Batch Registration Parameters dialog box will be displayed. In this dialog box, enter the registration
parameters for your batch.
Scan or click on the arrow to the right of the Scan button and select a mode.
Image menu to edit images. (For more about editing images, refer to Introducing ABBYY
FormReader/ABBYY FormReader Interface/Page
Select Next Batch dialog box will be displayed. In this dialog box, choose a batch to be processed or click Close Station if
you wish to exit the station.
in the ABBYY FormReader Help.)
Batch>Send).
Scan>Close Station.
* – For the Windows operating systems lower than XP, select Start>Programs.
Additional capabilities of Scanning Station
The Scanning Station provides the following additional capabilities:
• Entering and viewing batch comments
• Renumbering pages
• Viewing and editing batch registration parameters
• Suspending batches
Entering and viewing batch comments
You can view the comments for the opened batch or add your own comments to the batch.
To view or add comments, open the Batch Comments dialog box (select Batch>Comments).
Renumbering pages
To renumber a page, select it and choose Image>Renumber Page... The Renumber Page dialog box will be displayed. In this
dialog box, enter the new page number. If you choose a page number that already exists, some pages in the batch will also be
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
26
Page 27

renumbered. If the current page number is less than the new one, the numbers of the pages between the current number and the new
number will be incremented by 1. If the current page number is bigger than the new one, the numbers of the pages between the
current number and the new number will be reduced by 1. If you select several pages, the program will renumber only the page that
has the smallest number (and the adjoining pages if there is already a page that has the same number).
Viewing and editing batch registration parameters
To view or edit batch registration parameters, open the Batch Registration Parameters dialog box (select Batch>Edit
Registration Parameters...). In this dialog box, you can view the parameters and change them if required.
Suspending batches
If you cannot complete the processing of a batch, you can suspend it. The batch will be routed to the Suspended batches queue.
To suspend a batch that is being processed at the moment, select Batch>Suspend.
To view the list of suspended batches, open the Suspended Batches dialog box (select Batch>View Suspended Batches).
To resume the processing of a suspended batch, select the Suspended option in the Select Next Batch dialog box.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
27
Page 28

Registration Station
Introducing Registration Station
ABBYY FormReader 6.5 Enterprise Edition can be set up to monitor a userdefined folder for new images, add the detected images to
a batch of a specified type, and send the batch to the Recognition Station for further processing. Each batch is automatically provided
with a name and registration parameters as specified by the user in the preliminary settings.
Batches are formed and provided with registration parameters on a Registration Station, which is supervised by the operator of the
Scanning Station. Automated registration is available for batches of a particular type if one of its settings is set to Include
Registration Station and the following station properties have been set: the path to the folder containing incoming images, folder
processing methods, registration parameters, etc. The operator of the Scanning Station will only need to launch the Registration
Station. Multiple Registration Stations can run simultaneously on different computers.
Important! The Registration Station does not require constant operator control. We recommend locking the station commands to
prevent unauthorized access to the station in the absence of the operator.
Registration Station Interface
Registration Station: main window
Window title displays the name of the complex and the name of the station.
Menu bar contains the Registration and Help menus.
Toolbar contains the buttons for the most frequently used commands.
Process Log displays events in the current session: launch time, start of batch registration start, end of batch registration, number of
pages in the created batch, operations, errors, etc.
Process pane displays the name of the current batch and the total number of batches created during the session.
Status line displays the current station status: Running, Stopped, Locked.
Registration Station: toolbar
The toolbar of the Registration Station contains buttons for the standard batch registration commands and station maintenance.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
28
Page 29

Toolbar buttons:
Button Description
Start Launches the registration process.
Stop Stops the registration process.
Lock
Unlock Unlocks the commands of the Registration Station.
Locks all the commands of the Registration Station except the Unlock command
Typical use scenario
The Registration Station runs in automatic mode and does not require constant operator involvement. (The Registration Station is
supervised by the operator of the Scanning Station.)
1. Launch the station (Start>All Programs>ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition>Registration Station).
Important! The station will be launched only if the following conditions are met:
• There is at least one batch with the Include Registration Station option selected for which Registration Station
settings have been made;
• The type of this batch has Published status;
• The operator of the Scanning Station has permissions for processing this batch type.
2. In the Login dialog box that opens, enter the scanning operator login and password.
3. Once the station has been launched it will immediately start checking the folders of all the batch types for which automated
registration was allowed. Any images detected in such folders will be extracted and formed into batches. depending on the
batch type settings, the images may be either deleted from the checked folder or moved to another folder. All the events,
starting from the launch of the station, are logged in the Process Log. The name of the current batch and the number of
created batches are displayed in the Process pane of the main window. Once all the images from all the folders have been
extracted, the station switches into standby mode, which lasts 60 seconds, following which the station will check the
folders again. All the created batches are queued for recognition.
Important! We recommend locking the station commands while the station is running (Registration>Lock). To
unlock the station, use Registration>Unlock.
4. To end the registration process, select Stop on the Registration menu.
5. To quit the station, select Close Station on the Registration menu.
6.
* If you use an operating system lower than Windows XP, this menu item is called Programs.
Additional capabilities of Registration Station
The Registration Station provides the following additional capabilities:
• Stopping registration
To stop the registration process, click the Stop button (or select Registration>Stop on the menu).
• Locking the Registration Station
To lock the station commands, click the Lock button (or select Registration>Lock).
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
29
Page 30

• Unlocking the Registration Station
To unlock the station commands, click the Unlock button (or select Registration>Unlock) and in the dialog box that
opens, enter the operator login and password.
Important!
If the station has been locked by another operator, once you enter your login the registration process will stop (after the registration
of the current batch has completed) and the station will close down. To resume the process, you need to relaunch the station.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
30
Page 31

Recognition Station
Introducing the Recognition Station
The Recognition Station is intended for automated recognition. The station runs in unattended mode. The recognition operator only
starts the recognition process. Batches from the Recognition queue are automatically processed and sent to the Verification or
Correction queue.
The recognition operator can monitor the recognition process: current processing results are shown in the batch recognition statistics
pane, and the recognition process is logged in the event log.
Important!
The station does not require permanent control by the operator. Therefore we recommend that you lock the station commands to
prevent unauthorized access to the station in your absence.
Recognition Station Interface
Recognition Station main window
Title bar. Displays the name of the form capture system and the name of the station.
Menu bar. Contains the station menus: Recognition, Locking and Help.
To ol b ar . Contains the most frequently used station commands.
Batch recognition statistics. This pane displays information about the batch that is being processed on the station at the moment:
the name of the batch, the number of pages in the batch, the number of blank pages detected in the batch, the number of recognized
pages, the number of pages that were not matched with the template, and the number of uncertainly recognized characters (average
percentage). This pane also includes a progress bar that displays the percentage of processing that has been completed.
Event log. Logs the events of the current session: the time when the Recognition Station is launched and closed, the time when
recognition starts and stops, the time when batch processing starts and ends, the statistics for each processed batch, operations, errors,
etc.
Status bar. Provides information on the current status of the station.
Recognition Station toolbar
The Recognition Station toolbar contains the buttons which provide shortcuts to the standard menu commands, such as starting and
stopping the recognition process, etc.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
31
Page 32

Toolbar buttons:
Button Description
Start Starts the recognition process.
Stop Stops the recognition process.
Lock Locks all the station commands, except for the Unlock command.
Unlock Opens the Unlock Recognition Station dialog box where you can unlock the station commands.
Typical actions of the recognition operator
1. Start the station (select Start>All Programs*>ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition>Recognition Station).
2. In the
3. When the station starts, you will be prompted to start recognition. Recognition is performed automatically. If there is a batch that
Important!
It is recommended to lock the station commands during the operation of the station.
1. To exit the station, select Recognition>Close Station.
Login dialog box, type in your login and password.
has not been recognized, recognition of this batch will be resumed when you click Start. If there are no unfinished batches, the
Recognition Station will start recognizing the batches from the Recognition queue. Recognition ends when there are no more
waiting batches in the Recognition queue.
* – For the Windows operating systems lower than XP, select Start>Programs.
Additional capabilities of the Recognition Station
The Recognition Station provides the following additional capabilities:
• Stopping recognition
• Locking the Recognition Station
• Unlocking the Recognition Station
Stopping recognition
To stop recognition, click the Stop button or select Recognition>Stop. The recognition process can be stopped either after the
station completes processing a batch or during processing.
Locking the Recognition Station
To lock the station commands, click the Lock button or select Lock Commands>Lock.
Unlocking the Recognition Station
To unlock the station commands, click the Unlock button or select Lock Commands>Unlock. In the Unlock Recognition
Station dialog box that opens, enter your login and password and click OK.
Important!
If the Recognition Station was locked by another operator, recognition will be stopped and the station closed after you enter your
login and password (first, the station will finish processing the current batch). Run the station again if you wish to resume recognizing
batches.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
32
Page 33

Verification Station
Introducing the Verification Station
The Verification Station is used to verify uncertain characters and characters explicitly marked for verification and to validate data by
using one–page rules (see ABBYY FormReader Help: Working with application/Checking recognition results). The Verification Station is
controlled by a verification operator who verifies and validates data following the program’s prompts.
Once verification is completed, all uncertain characters must be edited, and one–page rule errors must be corrected. In this case all
the pages in the batch are automatically assigned '(No errors)' status, and the batch can be sent to the Correction queue.
If for some reason the verification operator fails to edit the uncertain characters and/or correct the errors detected by required one–
page rules on some pages, the operator can send this batch to the correction operator marked as a "problem batch".
If for some reason the verification operator fails to edit the uncertain characters and/or correct the errors detected by optional one–
page rules on some pages, the operator can accept these pages with 'One–page rule warning' status.
The Verification Station is optional. If the system does not include the Verification Station, all verification and validation operations
are carried out on the Correction Station.
Verification Station Interface
Verification Station main window
Title bar. Displays the names of the form capture system, the station and the current batch.
Menu bar. Contains the station menus: Verify, Page, Batch and Help.
To ol b ar . Contains the most frequently used station commands.
Batch window. Contains the list of batch pages. For each page its properties are displayed: the page number, the login of the
operator who opened the page, the availability of the page image, the name of the template matched with the page, the results of
recognition, verification and validation, the presence of a barcode on the page, the page status and the results of document assembly.
To sort the pages, click on the name of the required parameter. Only one batch is displayed in the main window at a time.
Status bar. Provides information on the current station status.
Verification Station toolbar
The Verification Station toolbar contains the buttons which provide shortcuts to the standard menu commands, such as verifying
batch pages, validating data using one–page rules, etc.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
33
Page 34

Toolbar buttons:
Button Description
Verify Verifies unverified pages.
Validate 1
(multi–functional button)
Send Allows the operator to send the batch to the next station.
Validate Data Using One–Page Rules Starts validating data by using one–page rules.
Continue Validation Allows the operator to go to the next page with one–page rule errors.
Stop Validation Stops validating data by using one–page rules.
Typical actions of the verification operator
1. Start the station (select Start>All Programs*>ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition>Verification Station).
2. In the
3. If there is an unsent batch on the station, you will be prompted to resume its processing. If there are no such batches, the program
4. Start processing the batch and follow the program’s prompts.
Login dialog box that appears, type in your login and password, then click OK.
will prompt you to get one of the batches from the Verification queue.
4.1. Verify the batch (for more information on the verification process, refer to the ABBYY FormReader Help file).
4.2. Validate the data by using one–page rules:
• Correct invalid data on the current batch page (the fields containing invalid data are color–marked),
• Go to the next page with incorrect data by using the
Va li d at io n) or press Alt+A.
Continue Validation command (select Ve r i f y> C o n t i n ue
4.3 Once you have processed the batch (verified it and validated its data by using one–page rules), send the batch to the
next station (select Batch>Send). Add comments to the batch if required.
5. Once you have finished processing batches, close the station (select Verify>Close Station).
* – For the Windows operating systems lower than XP, select Start>Programs.
Additional Capabilities of the Verification Station
The Recognition Station provides the following additional capabilities:
• Stopping verification
• Stopping data validation by one–page rules
• Resuming batch processing
• Assigning and changing page status
• Sending a problem batch
• Viewing and adding batch comments
Stopping verification
To stop verification, close the Verification dialog box.
Stopping data validation by one–page rules
To stop validating data by using one–page rules, select Verify>Stop Validation.
Resuming batch processing
To resume processing a batch, select one of the commands of the Verification menu: Ver i f y or Validate Data by Using One–page
Rules (the choice depends on the processing stage at which you stopped).
Assigning and changing page status
If for some reason the operator cannot correct the errors detected by optional one–page rules on the batch pages the operator can
accept the pages with 'One–page rule warning' status.
In order to accept the page with 'One–page rule warning' status, select Page>Accept with Status 'One–page rule warning'.
To reset the status for the selected pages, select Page>Reset Status for Selected Pages.
Sending a problem batch
If you cannot finish processing a batch on the Verification Station, you can send the batch to the Correction Station. To do this,
select the Send to Correction Operator command in the Batch menu.
Viewing and adding batch comments
The verification operator can view the comments to the current batch or add his own comments.
To view or add comments, open the Batch Comments dialog box (select Batch>Comments).
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
34
Page 35

Correction Station
Introducing the Correction Station
The Correction Station is used to assemble batches and validate data. If there is no Verification Station in the system, data are verified
and validated on the Correction Station using multipage and one–page rules. One–page rules are also used to validate data if the
administrator has made the corresponding batch type settings.
The Correction Station is controlled by a correction operator who assembles batches and validates data following the program’s
prompts. Once a batch has been assembled and validated, the operator sends it from the Correction Station to the Export queue.
The correction operator also processes problem batches: scans paper documents anew, recognizes, verifies and validates data by using
one–page rules. Problem batches come from the Verification Station and from the Export and Monitoring Station.
After processing a problem batch, the correction operator can:
• Send the batch to the Export queue (if all problems have been solved and the operator has successfully assembled the
batch and validated its data);
• Send the batch to the verification operator (if all problems have been solved but the batch has not been verified and
validated by one–page rules);
• Send the batch to the Export and Monitoring Station marked as a problem batch (if the problems have not been solved).
Correction Station Interface
Correction Station main window
Once you have launched the Correction Station, the Correction Station main window will open.
Title bar. Displays the names of the form capture system, the station and the current batch.
Menu bar. Contains the station menus: Processes, Image, Page, Batch and Help.
To ol b ar . Contains the most frequently used station commands.
Batch window. Contains the list of batch pages. For each page its properties are displayed: the page number, the login of the
operator who opened the page, the availability of the page image, the name of the template matched with the page, the results of
recognition, verification and validation, the presence of a barcode on the page, the page status and the results of document assembly.
To sort the pages, click on the name of the required parameter. Only one batch is displayed in the main window at a time.
Status bar. Provides information on the current station status.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
35
Page 36

Correction Station toolbar
The Correction Station toolbar contains the buttons which provide shortcuts to the standard menu commands, such as verifying
batch pages, validating data using one–page and multipage rules, etc.
Button Description
Verify Verifies unverified pages.
Validate 1 (multi–functional
button)
Validate Data Using One–Page
Rules
Starts validating data by using one–page rules.
Continue Validation Allows the operator to go to the next page with one–page rule
errors.
Stop Validation Stops validating data by using one–page rules.
Assemble Starts assembling batch documents.
Validate 2 Starts validating data by using multipage rules.
Send Sends a processed batch to the next station for processing.
Typical actions of the correction operator
1. Start the station (select Start>All Programs*>ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition>Correction Station).
2. In the
3. If there is an unsent batch on the station, you will be prompted to resume its processing. If there are no such batches, the program
4. Process the batch by following the program’s prompts.
Login dialog box that appears, type in your login and password.
will prompt you to get one of the batches from the Correction queue. If there are no batches in the Correction queue, the station
goes into stand–by mode.
4.1 Verify the batch (for more information about the verification process, refer to the ABBYY FormReader Help file).
4.2 Correct data containing one–page rule errors, if there are some:
• In the opened page, select the first one–page rule that has detected invalid data (these rules are listed in the right lower
corner of the window). When you select a rule from the list, the fields containing invalid data will be marked in red in
the
Data window.
• Edit the field values.
• Correct all the invalid data that have been detected on the page by one–page rules.
• Go to the next page with invalid data by clicking the
Continue button on the toolbar or by selecting
Processes>Continue Validation.
4.3 Monitor the process of batch assembly (batch assembly starts automatically once the data have been validated by using
multipage rules if validation has been performed on the Correction Station or when the batch has been opened if the data
have been validated by using one–page rules on the Verification Station). If necessary, correct errors that occurred at batch
assembly.
To start batch assembly manually, click the Assemble button on the toolbar or select Processes>Assemble.
4.4 Correct multipage rule errors, if any. To do so:
• In the Rule Validation dialog box that appears, select the first rule which detected incorrect data (these rules are
color–marked and have the
• Double–click on the selected rule.
• In the list that opens, edit the field values to be validated by the rule. To do this, double–click on the field and type in
the new value in the
• Continue editing the field values until the value of the multipage rule changes to
• Go to the next rule with the
• Once you have validated the data by using multipage rules, close the
False value).
New Field Value dialog box that appears.
Tru e.
False value.
Rule Validation dialog box.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
36
Page 37

To start validating the data by using multipage rules manually, click the Validate 2 button on the toolbar or select
Processes>Validate Data Using Multipage Rules.
5. Send the ready batch to the next station (select Batch>Send).
6. Once you have finished working with batches, close the station (select
* – For the Windows operating systems lower than XP, select Start>Programs.
Processes>Close Station).
Additional Capabilities of the Correction Station
Scanning
To start scanning, select Processes>Scan: Scan, Scan Multiple Pages.
Adding images to the batch
To add images to the batch, select Processes>Scan>Add from... In the dialog box that appears, specify the folder where the images
are stored.
Editing images
To edit images, use the Image menu commands (for more information about image editing, refer to the ABBYY FormReader Help file:
Introducing ABBYY FormReader/ABBYY FormReader interface/Page window).
Template matching
To match a page with its template, select Page>Match Template Named... In the Select Template dialog box, select the required
template.
Recognition
To start recognition, select Processes>Recognize: Recognize All Unrecognized Pages, Recognize Selected Pages.
Verification
To start verification, select Processes>Verify: Verify, Verify Selected Pages (for more information about verification, refer to the
ABBYY FormReader Help file).
Validating data by using one–page rules
To validate data by using one–page rules:
1. Start validating data by using one–page rules: select Processes>Validate Data Using One–Page Rules.
2. Correct the invalid data on the page. The list shows the rules that have detected errors and the description of each error.
When you select a rule from the list, the error field will be marked in red.
3. Go to the next page with incorrect data by selecting
Renumbering a page
To renumber a page, select the required page and then select the Renumber Page... command in the Page menu. In the Renumber
Page dialog box that appears, type in the new page number (for more information about page renumbering, refer to the ABBYY
FormReader Help file).
Getting a barcode
If no barcode has been found on the page during recognition, you can get barcodes automatically (Page>Get Barcode
Automatically) or you can enter the missing barcode manually (Page>Enter Barcode Manually).
Assigning and changing the page status
A batch can be exported only if all of its pages have one of the following statuses: '(no errors)', 'Loose page', 'Verification error',
'One–page rule error', 'One–page rule warning'.
To assign 'Loose page' status to a page, select Page>Accept with Status>'Loose page'.
To assign 'Verification error' status to a page, select Page>Accept with Status>'Verification error'.
To assign 'One–page rule error' status to a page, select Page>Accept with Status>'One–page rule error'.
To assign 'One–page rule warning' status to a page, select Page>Accept with Status>'One–page rule warning'.
To reset the assigned status, select Page>Reset Status for Selected Pages.
Assigning and changing the document status
If multipage rules detect some errors and the operator fails to correct them, the document can be accepted with the errors. If the
document has errors of required multipage rules, it will be accepted with 'Multipage rule error' status. If the document has errors of
optional multipage rules, it will be accepted with 'Multipage rule warning' status.
If you wish to accept a document with errors when validating data by using multipage rules (in the Rule Validation dialog box),
select Document>Accept with Errors.
If you wish to reset the status of a document when validating data by using multipage rules (in the Rule Validation dialog box),
select Document>Reset Document Status.
In order to reset the status of a document from the main window of the Correction Station, select Page>Reset Document Status.
Deleting a page
To delete a page form the batch, select the required page and then select the Delete Selected Pages command in the Page menu.
Deleting blocks and data from a page
Verify>Continue Validation or by pressing ALT+A.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
37
Page 38

To delete the template matching results and page data, select the required page, and then select the Delete Blocks and Data
command in the Page menu.
Changing the scanning and recognition settings
To change the scanning and recognition settings, select Batch>Options... In the Options dialog box that appears, open the
Scanning/Opening tab or the Recognition tab and change the settings, if necessary. (For more information about the scanning
and recognition options, refer to the ABBYY FormReader Help file.)
Note: The changes the correction operator makes to the scanning or recognition options will be applied only to the batch that is
being processed on the Correction Station at the moment and will not affect the batch type settings.
Return a batch to verification
To return a batch to verification, select Batch>Return to Verification.
Sending a problem batch to the next station
If the correction operator cannot correct all the errors and finish processing a batch, the operator can send the batch to the Export
and Monitoring Station marked as a “problem batch” (Batch>Send Problem Batch).
Viewing and adding batch comments
The correction operator can view the comments to the current batch or provide the batch with his own comments.
To view or add the comments, open the Batch Comments dialog box (select Batch>Comments).
Status of pages and documents
Status of pages and documents displays information about documents and pages such as the presence or absence on a document or a
page of invalid data that is not subject to correction.
All forms processed in the system are exported on the Export and Monitoring Station but with different status assigned during
processing.
The only exception is documents containing assembly rule errors: they cannot be assigned any status and exported.
Important!
A batch can be exported only after all assembly rule errors have been corrected.
There are 5 page statuses and 6 document statuses.
Page statuses
'(No errors)' status is assigned to a page on which the program has not detected verification or one–page rule errors or all the
detected errors have been corrected.
The status is assigned automatically.
'Loose page' status is assigned to a page that should be excluded from the entire further processing. For example, this status is
assigned to a page included into a batch by mistake.
A page with 'Loose page' status is automatically assembled into a special one–page document with 'Loose page' status.
This page status is assigned manually by the correction operator.
'Verification error' status is assigned to a page on which the program has detected errors during verification and these verification
errors cannot be corrected for some reason.
The status is assigned manually by the correction operator, and it can be reset by both the correction operator and the verification
operator.
'One–page rule error' status is assigned to a page on which during validating data by using one–page rules the program has detected
errors of required one–page rules (one–page rules with 'Error' status) and these errors could not be corrected for some reason.
The status is assigned manually by the correction operator, and it can be reset by both the correction operator and the verification
operator.
'One–page rule warning' status is assigned to a page on which during validating data by using one–page rules the program has
detected errors of optional one–page rules (one–page rule with 'Warning' status), and these errors cannot be corrected for some
reason.
The status is assigned manually by the correction operator, and it can be reset by both the correction operator and the verification
operator (if data are validated by using one–page rules on the Verification Station).
Document statuses
'Loose page' status is assigned to a document consisting of one page with 'Loose page' status.
The status is assigned to the document automatically.
'Verification error' status is assigned to a document if it contains at least one page with 'Verification error'.
The status is assigned to the document automatically.
'One–page rule error' status is assigned to a document containing at least one page with 'One–page rule error' status.
The status is assigned to the document automatically.
'Multipage rule error' status is assigned to a document if, when validating data by using multipage rules, the program has detected
errors of required multipage rules ('Required' or 'Assembly' rules) on the document pages, and these errors could not be corrected
for some reason.
The status is assigned and reset manually by the correction operator.
'One–page rule warning' status is assigned to a document if it contains at least one page with 'One–page rule warning' status.
The status is assigned to the document automatically.
'Multipage rule warning' status is assigned to a document if, when validating data by using multipage rules, the program has
detected errors of optional multipage rules ('Warning' multipage rules), and these errors could not be corrected for some reason.
The status is assigned and reset manually by the correction operator.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
38
Page 39

Export and Monitoring Station
Introducing the Export and Monitoring Station
The Export and Monitoring Station is the last station used to process forms. This station is used to export completely processed
batches. Additionally, the station is used to monitor and control the operation of ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition.
The station is controlled by an export and monitoring operator.
Batches can be exported in automated or manual mode.
When exporting batches automatically, the export and monitoring operator only has to start the export process: the batches coming
to the Export queue will be exported automatically. If the manual export mode has been selected, only the selected batches will be
exported.
When export is started, the Batch Export dialog box will be displayed. Use this dialog to view batch export statistics. If you close the
Batch Export dialog box, you can re–open it by double–clicking on the status bar.
Data are exported to text files in CSV and XML formats. Image export is also available.
The user can create custom export procedures and connect them via the API.
The export and monitoring operator can also do the following:
• Send batches from one processing queue to another,
• Assign a batch to a given operator,
• Delete batches,
• Lock and unlock batches,
• Terminate the sessions on other stations,
• Track the batch processing statistics and the work of other operators,
• Create reports on the operation of the entire form capture system, stations, operators, etc.,
• Control the database contents,
• View batches.
Export and Monitoring Station Interface
Export and Monitoring Station main window
Title bar. Displays the name of the form capture system and the name of the station.
Menu bar. Contains the station menus: Export, Action, Tools and Help.
To ol b ar . Contains the most frequently used station commands.
The status bar displays the current status of the station.
The main window is divided into two panes. The left–hand pane of the window displays the project tree that is used to monitor and
control the operation of ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition.
The project tree includes the following objects organized as shown below:
• Project
• Statistics
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
39
Page 40

• Batches
• Tasks
• Sessions
• Event Log
• Reports
• Operators
• Registration Parameters
• Rules
When you selecting an object in the left–hand pane of the window, its “contents” will be displayed in the right–hand pane.
Object Information displayed in the right–hand pane of the main window:
Project The list of the objects included into the project.
Statistics
Batches The list of all batches that are present in the database at the moment (except for batches
associated with batch types with 'Reserved' status). Batches associated with batch types with
'Editable' status are displayed in grey. For each batch its properties are displayed:
• number,
• name,
• type,
• date of creation,
• page number,
• queue,
• the name of the computer where the station is installed and the login and role of the
operator who is processing the batch if the batch is being processed on some station.
To sort the batches, click on the name of a column.
Tasks The list of the tasks executed by the operators during a certain period. The following
information is shown for each operator:
• login,
• the name of the workstation on which the operator executed the task,
• the name and number of the processed batch,
• queue,
• time when the task was started and finished.
Tasks are always assigned one of the following statuses:
• 'Under execution' status is assigned to a task that is performed at the moment. This task
is displayed with the icon.
• 'Interrupt task' status is assigned to a task that was interrupted by the export and
monitoring operator. This task is displayed with the icon.
• 'Completed' status is assigned to a task that was implemented. This task is displayed with
the icon.
To sort the tasks, click on the name of a column.
Sessions The list of all workstation sessions running in the form capture system at the moment. The
following information is shown for each station:
• station type,
• name of the workstation (the network name of the computer),
• login of the operator working on the station,
• role of the operator,
• name and type of the batch processed on the station,
• time when the station was launched.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
40
Page 41

Object Information displayed in the right–hand pane of the main window:
Event log The list of all events in the system:
• login and logoff,
• operation execution,
• information,
• opening and closing batch processing sessions on the Verification and Correction Stations,
• errors and warnings that occurred during batch processing,
• batch passing through the processing queues,
• batch creation,
• batch deletion,
• batch export completion.
The following information is displayed for each event:
• event type,
• time, operator login, workstation,
• operator role,
• batch number,
• comments.
To sort the events, click on the name of a column.
Reports The list of reports that can be created in the form capture system.
Operators The list of operators registered in the form capture system. To sort the operators, click on the
name of a column.
Registration Parameters
Display
The list of registration parameters. The following information is shown for each parameter:
• enabled/disabled,
• parameter code,
• parameter name,
• batch type.
If a registration parameter is enabled and the filter is set up for displaying one batch type only,
the values of the registration parameters will be displayed in a separate column in the batch list
(the Batches object).
To sort the registration parameters, click on the name of a column.
Rules The list of multipage rules. The following information is shown for each rule:
• enabled/disabled,
• batch type to which the rule is applies and the document template (if the rule applies to a
document template).
To sort the rules, click on the name of a column.
Export and Monitoring Station toolbar
The Export and Monitoring Station toolbar contains buttons which provide shortcuts to the standard menu commands such as batch
export.
Toolbar buttons:
Button Description
Export Selected Batches Starts exporting the selected batches.
Export
Export Automatically Starts exporting batches in automated mode.
Stop Export Stops the export process.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
41
Page 42

Typical actions of the export and monitoring operator
1. Start the station (select Start>All Programs*>ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition>Export and Monitoring
Station)
2. In the
3. Start the export process.
To export selected batches:
To export batches from the Export queue in automated mode:
You can stop the export process at any moment.
To stop the export process:
Login dialog box that appears, enter your login and password.
1. In the project tree, select Batches.
2. In the batch list, select the batches you wish to export.
3. In the
1. In the project tree, select Batches.
2. In the
1. In the project tree, select Batches.
2. In the
Export menu, select Export Selected Batches.
Export menu, select Export Automatically.
Export menu, select Stop Export.
Once you have finished working with batches, close the station (select
Export>Close Station).
* – For the Windows operating systems lower than XP, select Start>Programs.
Additional capabilities of Export and Monitoring station
Locking a batch
The operator of the Export and Monitoring Station can lock a batch, i.e. exclude it from processing.
To lock a batch:
1. In the project tree, select Batches.
2. In the batch list, select the batch you wish to lock.
3. In the
Important!
A batch can be locked only if it is not being processed on any of the stations at the moment.
To resume processing the batch, use the Unlock Batch command.
Returning a batch
The operator of the Export and Monitoring Station can return a batch to a previous processing stage specifying (if required) the
operator who will process the batch at the indicated stage.
To return a batch to a previous processing stage:
1. In the project tree, select Batches.
2. In the batch list, select the batch you wish to return.
3. In the
4. In the
Action menu, select Lock Batch.
Action menu, select Return.
Return Batch dialog box that appears, make the necessary settings and click OK.
Important!
A batch can be return to a previous processing stage only starting from the Verification queue.
Assigning a batch to a operator
The operator of the Export and Monitoring Station can assign a certain batch in the current queue to a specific operator.
To assign a batch in the current queue to a specific operator:
1. In the project tree, select Batches.
2. In the batch list, select the batch you wish to assign.
3. In the
Action menu, select Assign to Operator.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
42
Page 43

4. In the Assign to Operator dialog box that appears, enter the operator login.
Important!
You can only assign a batch to an operator within the same queue.
Deleting a batch
The export and monitoring operator can delete a batch from the database.
To delete a batch from the database:
1. In the project tree, select Batches.
2. In the batch list, select the batch you wish to delete.
3. In the
Action menu, select Delete.
Adding and viewing comments
The export and monitoring operator can view the comments to a batch.
To view batch comments:
1. In the project tree, select Batches.
2. In the batch list, select the required batch.
3. In the
4. The
Action menu, select Comments...
Batch Comments dialog box that appears displays the comments to the selected batch.
The export and monitoring operator can add new comments to a batch only when the batch is being moved from one queue to
another.
Filter
The export and monitoring operator can set up and apply a filter to each list of objects (Batches, Tasks and Event log) of the
Statistics object. Setting up the filter consists of specifying the sorting conditions for the list (for example, by batch name, batch
type, operator login, etc.). When you apply the filter, the objects meeting the specified sorting conditions will be displayed.
To apply the filter:
1. In the project tree, select an object: Batches, Tasks or Event log.
2. In the
3. The
4. In the
Action menu, select Set up Filter...
Filter Setup dialog box corresponding to the selected object (Batch Filter Setup, Task Filter Setup, Event
Filter Setup)
will be displayed.
Filter Setup dialog box that appears, specify the sorting conditions.
To apply/cancel the filter:
1. In the project tree, select an object: Batches, Tasks or Event log.
2. In the
Action menu, select Apply Filter/Cancel Filter.
Viewing a batch
Batches can be viewed on the Export and Monitoring Station. Information about batches is displayed in the View Batch dialog box.
This information depends on the current processing stage of a particular batch. For example, for a scanned, recognized, verified,
validated and assembled batch you can view the number of pages in the batch, the number of documents and the number of pages in
the document, and the names and values of the page fields.
To view a batch:
1. In the project tree, select Batches.
2. In the batch list, select the batch you wish to view.
3. In the
Action menu, select View... Information about the batch will be displayed in the View Batch dialog box.
Important!
Only batches from the queues following the Recognition queue can be viewed on the Export and Monitoring Station.
Terminating a session
The export and monitoring operator can terminate any workstation session. This may be necessary if the operation of a station ended
abnormally.
To terminate a workstation session:
1. In the project tree, select the Sessions object.
2. In the list, select the session you wish to terminate.
3. In the Action menu, select Terminate Session.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
43
Page 44

Creating, editing and deleting an operator
The export and monitoring operator can create new operators and change the settings of the existing operators.
To create an operator:
1. In the project tree, select Operators.
2. In the
3. In the
Action menu, select New...
Operator dialog box that appears, specify the operator’s login, password and roles and the batch types
(separately for each role) which the operator will be able to process.
To change the operator’s password:
1. In the project tree, select Operators.
2. Select the required operator from the list.
3. In the
4. In the
Action menu, select Change Password...
Change Password dialog box that appears, specify the new password and confirm it.
To change the operator’s roles and batch processing permissions:
1. In the project tree, select Operators.
2. Select the required operator from the list.
3. In the
4. In the
Action menu, select Properties...
Operator dialog box that appears, make all necessary changes.
To change the operator’s login:
1. In the project tree, select Operators.
2. Select the required operator from the list.
3. In the
4. In the dialog box that appears, type in the operator’s new login.
Action menu, select Change Login...
To delete an operator:
1. In the project tree, select Operators.
2. Select the required operator from the list.
3. In the
Action menu, select Delete.
Important!
Only an operator who did not perform any actions in ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition (including logging into any station) can
be deleted.
Tip:
If you wish to prevent an operator from working in ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition, cancel the operator’s roles and
permissions.
Clearing the database
The export and monitoring operator can clear the database by deleting processed batches and information about these batches
(processing statistics and event log).
To clear the database:
1. Select Tools>Clear Database....
2. In the
Clear Database dialog box that appears, select the necessary options and click OK.
Clearing the Event Log
All events taking place during form input system operation are registered in the Event Log. Information about the registered events is
stored in the data base. If necessary, you can delete events that took place during a given period from the Event Log. At the same time
the information about deleted events is deleting from the database and saved in a convenient format.
To clear the Event Log:
1. Select Event Log>Archive.
2. In the dialog box that appears, specify:
• the path to the folder into which the file with information on the deleted events will be saved,
• the dates of the beginning and end of the time period during which the deleted events took place.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
44
Page 45

3. Click Move.
Important!
All the events that took place during the specified period will be deleted from the data base. Information about these
events will be saved in a CSV file located in the specified folder.
Viewing the license parameters
The export and monitoring operator can view the following information about the license:
• the license parameters and their current status,
• the workstations that are working at the moment.
To view information about the license:
1. Select Tools>License...
2. Information about the license will be displayed in the
License dialog box that appears.
Reports
The export and monitoring operator can create and print reports about the operation of ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition.
Reports can be created either for one or for all the batch types.
The following types of report are available:
• Batch processing report
The report contains information on the batch number, batch name, queue (in which the batch is located at the moment
when the report is created), total number of documents and pages in the batch, number of pages with
status, 'Verification error' status, number of documents (pages) with 'One–page rule error' status, 'One–page
'Loose page'
rule warning' status, 'Multipage rule error' status, 'Multipage rule warning' status, and date and time when
the batch was processed in each processing queue.
• Full verification report
The report provides the following information on each verification operator and each batch processed by the operator:
the batch number, batch name, total batch processing time, total number of pages in the batch, number of pages with
'One–page rule warning' status, and average processing speed.
• Brief verification report
The report provides the following information on each verification operator: the number of batches processed by the
operator during the specified period of time, total working time, total number of pages, number of pages with
'One–
page rule warning' status, and average processing speed.
• Current status report
The report provides the following information on each batch type: the number of batches, documents and pages
processed at the moment, and processing queue where the batch is being processed at the moment.
• Full correction report
The report provides the following information on each operator and each batch processed by the operator: the batch
number, batch name, total batch processing time, total number of documents and pages, number of pages with
page'
status, number of documents (pages) with 'Verification error' status, 'One–page rule error' status, 'One–
page rule warning'
processing speed.
status, 'Multipage rule error' status, 'Multipage rule warning' status, and average
'Loose
• Brief correction report
The report provides the following information on each correction operator: the number of processed batches, total
working time, total number of documents and pages, number of pages with
documents (pages) with
status, 'Multipage rule error' status, 'Multipage rule warning' status, and average processing speed.
'Verification error' status, 'One–page rule error' status, 'One–page rule warning'
'Loose page'status, number of
• Station–by–station report
The report provides the following information: the batch number, batch name, queue (in which the batch is located at
the moment when the report is created), time and data when the batch was sent from the system stations.
To create a report:
1. In the project tree, select the Reports object.
2. In the report list, select the required report type.
3. In the
4. In the
Action menu, select Create Report...
Reports dialog box that appears, specify the parameters for your report.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
45
Page 46

Appendix
Supported image formats
Type Color
BMP Black–and–white, gray, color
PCX Black–and–white, gray
PNG Black–and–white, gray, color
JPEG Gray, color
TIFF Black–and–white – not compressed, CCITT3, CCITT4, Packbits;
gray – not compressed, Packbits, JPEG;
color – not compressed, JPEG
DCX Black–and–white, gray
PDF Files in PDF format
Structure description language
Custom batch type structure and custom document template structure are described in a special structure description language. The
structure description language has six components: annex component, page component, variant component, repetition component,
optional component, and document component.
The following components are used to describe the structure of a batch type:
• variant component
• repetition component
• optional component
• document component
The following components are used to describe the structure of a document template:
• annex component
• page component
• variant component
• repetition component
• optional component
• document component
Annex component
Use. The component is used to describe a sequence consisting of one page.
Syntax.
Annex([BarcodeCondition((False|True|"<Barcode value>"))])
Comments on syntax.
1. Annex – the name of the component
2. BarcodeCondition – indicates that the program will look for barcode on the page. It is an optional sign
3. False|True – indicates that the page has (True) or has not (False) barcode
4. "<Barcode value>" – the specified barcode value. This value is optional.
Definition: A page sequence meets the above description if it consists of one page, the page is annex, it meets the barcode
presence/absence condition (if it is specified), and the barcode value is equal to the required value if it is specified).
Examples:
Annex() – the program will not look for barcode on the page.
Annex(BarcodeCondition(False)) – the page is an annex without barcode
Annex(BarcodeCondition(True)) – the page is an annex with barcode
Annex(BarcodeCondition("21")) – the page is an annex with the barcode that should have the value of 21.
The component consists of:
Page component
Use. The component is used to describe a sequence consisting of one recognizable page corresponding to a given template.
Syntax. Page(“<Template name>”{, BlockCondition(“<Key field name>,” “<Key field value>”)})
Comments on syntax. The component consists of:
Page – the name of the component,
“<Template name>” – the name of the page template corresponding to the page,
BlockCondition – indicates that the program will check the key field values,
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
46
Page 47

“<Key field name>” – the name of the field which value is checked,
“<Key field value>” – the specified field value.
Definition: A page sequence meets the above description if it consists of one page, this page is recognizable and corresponds to the
required template, and the page field values are equal to the specified values (if they are specified).
Examples:
Page("А") – a recognizable page with the ‘A’ template.
Page("А",BlockCondition("Code","21")) – a recognizable page with the ‘A’ template and the Code field equal to 21.
Variant component
Use. The component is used if there are several variants of structure for the same part of a document.
Syntax.
Select(<Structure description1>{, <Structure descriptionN>})
Comments on syntax. The component consists of:
1. Select – the name of the component,
2. <Structure descriptionN> – the description of the structure of the N–th variant.
Definition: A page sequence meets the above description if it meets at least one of the structure description variants included in the
component.
Examples:
Select(Annex(BarcodeCondition("21")),Annex(BarcodeCondition("48"))) – non–recognizable pages containing barcode whose value
is equal to 21 or 48 meet this structure.
Select(Page("A",BlockCondition("Code", "21")), Page("B",BlockCondition("Code", "21"))) – recognizable pages that have the ‘A’ and ‘B’
templates and the Code field value equal to 21.
Repetition component
Use. The component is used when some part of a document may be repeated several times.
Syntax.
Repeat(<Structure definition>[, <Integer non–negative number N1>] [, < Integer non–negative number N2>])
Comments on syntax. The component consists of:
1. Repeat – the name of the component
2. <Structure definition> – the description of that part of a document that may be repeated
3. < Integer non–negative number N1> – a numeric parameter that indicates the minimum number of possible repetitions of the
document part
4. < Integer non–negative number N2> – a numeric parameter that indicates the minimum number of possible repetitions of the
document part.
Definition: A page sequence meets the above description if it consists of repeated parts each of which meets the structure definition.
The number of possible repetitions depends on the presence or absence of numeric parameters:
– If numeric parameters are absent, the structure definition can be repeated any number of times,
– If the component includes only the N1 numeric parameter, the structure definition can be repeated N1 times,
– If the component includes both N1 and N2 parameters, the structure definition can be repeated from N1 to N2 times.
Examples:
Repeat(Page("А")) – a recognizable page corresponding to the ‘A’ template can be repeated any number of times.
Repeat(Page("А"),2) – a recognizable page corresponding to the ‘A’ template must be repeated twice.
Repeat(Page("А"),3,5) – a recognizable page corresponding to the ‘A’ template must be repeated from 3 to 5 times.
Optional component
Note: An optional component is a particular case of a repetition component.
Use.
The component is used when some part of a document can be present or absent.
Syntax. Repeat(<Structure definition>, 0,1)
Examples:
Repeat(Page("А"),0,1) – a recognizable page corresponding to the ‘A’ template can be included into the document once or be absent.
Document component
Use. The component is used when describing a sequence consisting of one document that corresponds to a certain template.
Syntax.
Document(“<Template name>”)
Comments on syntax.
The component consists of:
1. Document – the name of the component,
2. <Template name> – the name of the corresponding document template.
Definition: a page sequence meets the above description if it consists of a document corresponding to the required template.
Example:
Document("Help") – a document corresponding to the ‘Help’ template.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
47
Page 48

Descriptive multipage rule language
Multipage rules (MRs) are written in а special descriptive multipage rule language.
Below follows а formalized description of the multipage rule language in terms of the meta–linguistic formulas. Terminal symbols are
boldfaced.
<Rule description>::= ( <MR> | < Operator calling automation–rule > (`<String>`) )
<MR>::= ( <Elementary expression> |
( <MR> ) |
<MR> <Binary operator> <MR>|
<Unary operator> <MR>|
<Zero–argument operator> () |
< Single–argument operator > (<MR>) |
< Formatting operator > (<MR> , <MR>) |
< Binary or ternary operator > (<MR> , <MR> [, <MR> ] ) |
< Ternary operator > (<MR> , <MR> , <MR>) |
< Glue operator > (<MR> { , <MR> } ) )
<Elementary expression>::=(<Reference to field> | <Reference to document MR> | <One–dimensional constant> | <Multi–
dimensional constant>)
<Reference to field>::= # ( <Template name> | * ) ! <Field name> #
<Reference to document MR>::= #^ ( <Document type name> | * | me ) ! <MR name>#
<One–dimensional constant>::= ( <Number> | `<String>` | False | True )
<Multi–dimensional constant>::= { <One–dimensional constant> { , <One–dimensional constant>} }
<Binary operator>::=( + | – | / | * | ^ | & | Or | And | = | < | <= | > | >= | <>| In | Like | Mod)
<Unary operator>::=( – | !)
< Zero–argument operator > ::= ( Now | Date )
< Single–argument operator > ::= (<Type conversion operator> | <String processing operator>| < Packing operator > |<Part–of–date
operator> | IsError | Error | Abs )
<Type conversion operator>::=( CDbl | CBool | CStr | CLng | CDate)
<Packing operator>::= ( Sum | Prod | Avg | Max | Min | Count | First | Last| NumMax | NumMin | Same | Unique)
< String processing operator > ::= ( UCase | LCase | Len | Trim )
< Part–of–date operator> ::=( Year | Month | Day )
<Formatting operator> ::= Format
<Binary or ternary operator>::=( < Progression operator > | <Cut operator>| < Substring cut operator >)
<Progression operator>::=( Inc | Dec | Mult )
<Cut operator>::= SubArray
<Substring cut operator>::= SubStr
<Ternary operator > ::= ( < Select operator > | <Substring replace operator> | <Data creation operator> )
<Select operator>::= IIf
< Substring replace operator > ::= Replace
<Data creation operator> ::= DateSerial
<Glue operator>::= Array
< Operator calling automation–rule > ::= AutoRule
A multipage rule is a function that depends on the page field values and the document parameter values and returns a value.
The Value of a multipage rule
The value of a multipage rule can be a constant or a collection of constants. For example, if a multipage rule is a simple reference to
the “Number” field of the “Card” page template, then its value is a collection of the “Number” field values of all document pages that
correspond to the “Card” template (there may be more than one such page). In general, the value of a multipage rule is a collection of
constants that can consist of one or several elements or be empty (if, for example, there are no pages with the given template in the
batch). The dimension of the multipage rule value is the number of elements it contains. The dimension of an empty collection is 0.
There are standard value types – long, real, string, Boolean, data – and a special Error type. The cases when an error value is returned
are described below.
The verity of a multipage rule
A multipage rule is executed successfully if its value is an empty collection or a collection all elements of which are either logical
constants True or string constants “true.”
Let us now consider several types of multipage rule and how their values are calculated. For each type of rule the following
information is provided: rule syntax, its meaning, sample rules, and examples of use (in complicated cases).
Note: The command words are not case–sensitive. A multipage rule may be enclosed in brackets; in this case its meaning will not
change.
Elementary multipage rules:
One–dimensional constant
Syntax. ( <Number> | `<String>` | False | True )
Comments on syntax
Value
. The value of this simple expression is a collection containing a single element – a numeric, string or Boolean constant.
Sample expression. 32.43
. String constants are enclosed in single quotes «`». Number constants are separated by a full stop.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
48
Page 49

Multi–dimensional constant
Syntax. { <One–dimensional constant> { , <One–dimensional constant>} }
Value. The expression value is a collection consisting of one–dimensional constant values.
Sample expression.
{5, `Name`, 4.5, true}
Page field reference
Syntax. # ( <Template name> | * ) ! <Field name> #
Meaning.
If the template name is specified, the expression value is a collection containing the values of fields with the specified name located
on all the document pages corresponding to the specified template. The order of values in the collection corresponds to the order of
the pages in the document. If there are no pages matched with the specified template or there are no fields of the specified name, the
value is an empty collection. If the «*» character is used instead of the template name, the collection includes the fields with the
specified name located on all document pages regardless of their template.
Sample expression.
The “visibility scope” of a document is the pages directly contained in it; the pages contained in its children are not “visible.”
#Reference !Surname#
MR document reference
Syntax. #^ (<Document type name> | * | me ) ! <MR name> #
Comments on syntax.
opening «#» character. If this character is lacking, the reference is considered to be a page field reference.
Meaning.
“visible.” There are three variants of reference syntax:
Variant 1. Reference to the MR of a certain document template.
The value is a collection containing the values of the MR with the specified name of all the nearest document children corresponding
to the specified template. Note that the value of each MR may also be a collection, so that the value of the reference will be a
collection containing all the elements of the corresponding collections in the order of the respective subdocuments in the document.
If there are no subdocuments corresponding to the specified template, or they do not contain MR with the specified name, the
expression value will be an empty collection.
The arguments may be any document MRs, including rules.
Example.
Variant 2. The character «*» is used instead of the document template.
The expression value is a collection including all subdocuments regardless of their templates.
Example.
Variant 3. The word “me” is used instead of a document template.
Only the document’s MRs are searched, not the ones of its children. Thus, you can select a frequently repeated expression and then
include it as a separate multipage parameter in other document MRs by using the #^me!MR name# reference.
Example.
Now let us consider multipage rules that contain various operators. The value of such rules depends on the values of the operands that
are multipage expressions themselves. Therefore, the values of the operands are always calculated first, and then the value of the
multipage expression is calculated. The operations are quite various, but they all share two common properties: dimension matching
and type conversion.
The “visibility scope” of a document is the documents directly contained in it; the pages contained in its children are not
#^ UserCard !IsNumberCorrect#
# ^* ! Number #
# ^me !ResultSum #
Note that in contrast to a reference to a page field, the «^» character specifying the reference type follows the
Dimension matching
As has already been said, the value of a multipage expression is a collection of constants. So the values of the expression operands may
have different dimensions. In some cases it does not contradict the meaning of the expression, whilst in other cases the operands’
dimensions must be the same. In the latter case dimension matching is performed.
The input values are the operand values, and each value itself may be a collection of constants. During matching, the program checks
if the dimensions of the given operand values can be matched, and if they can, the positive result is returned and the values are
corrected so that their dimensions will be the same. If they cannot be matched, the negative result is returned. The matching rules are
as follows:
1. If there is a single value of the zero dimension, all the values are assigned zero dimension, i.e. they become empty collections.
2. If there are two values with the dimensions more than 1 and not the same, the negative result is returned – the dimensions cannot
be matched.
3. Any value’s dimension is either equal to 1 or coincides with the maximum dimension (if the maximum is more than 1). In this case
all the dimensions are carried to the maximum: the values having the dimension of 1 are supplied with the necessary number of
additional constants that duplicate the first one.
So, if the matching is successful, all the operands will have the same dimension.
The process is best illustrated by the following examples:
Examples.
If the input values are {2,1,`dc`,0,4}, {2,3}, {}, the output values will be {}, {}, {}.
If the input values are {2,1,`dc`,0,4}, {2,3}, {1}, the result will be negative – the dimensions cannot be matched.
If the input values are {2,1,`dc`,0,4}, {2}, {1}, the output values will be {2,1,`dc`,0,4}, {2,2,2,2,2}, {1,1,1,1,1}.
If the input values are {2,1,`dc`,0,4}, {2,3,1,4,2}, {1}, the output values will be {2,1,`dc`,0,4}, {2,3,1,4,2}, {1,1,1,1,1}.
Use examples.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
49
Page 50

1. Suppose we have the following expression: #A!Summa#>5
• If there are no pages corresponding to the «À» template in the document, the result will be an empty collection.
• If there is only one page corresponding to the «À» template, the value will be True if the value of the «Summa» field of the
page is more than 5, and False otherwise.
• If there is more than one page corresponding to the «À» template, the second operand (5) will be supplied with the
additional constants of 5 until the necessary dimension is reached. The value of the expression will be a collection with
the dimension equal to the number of pages corresponding to the «À» template, and each element of the collection will
be True if the value of the «Summa» field of the respective page is more than 5, and False otherwise.
2. Suppose we have the following expression: #A!Number# >{3,5}
• If the document has no pages corresponding to the «À» template, the result will be an empty collection.
• If the document has only one page corresponding to the «À» template, the value of the first operand will be
complemented to the dimension of the second operand (i.e. to 2). The value of the expression will be a collection with
2 elements. The first one will be True if the value of the «Number» field of the page is more than 3, and False otherwise.
The second will be True if the value of the «Number» field of the page is more than 5, and False otherwise.
• If the document has two pages corresponding to the «À» template, the value of the expression will be a collection with
2 elements. The first one will be True if the value of the «Number» field of the first page is more than 3, and False
otherwise. The second element will be True, if the value of the «Number» field of the second page is more than 5, and
False otherwise.
• If the document includes more than two pages corresponding to the «À» template, the result will be an expression
containing a single Error constant – the dimensions of operands cannot be matched. To avoid the dimension matching
error, you may use the cut operator (SubArray): SubArray(#A!Number#,1,2)>{3,5} – the pages will be taken two by two
starting from the first page, and then the program will check if the value of the «Number» field on the first page is more
than three, and on the second page is more than five.
Type conversion
Many operations require that the operands be of a certain type. Type conversion is performed to ensure that the operands meet this
requirement. An operand may be converted to one of the four types: long, real, string, and Boolean. If a value is converted to a certain
type, it means that every element of the value will be converted to the type:
• If there are elements that cannot be converted to the required type, they are converted to the Error type (type
conversion error).
• If you try to convert an element into the long, real or Boolean types, and the source element is an empty string, no error
will occur, and the element will be converted to 0 and False, respectively.
Example. Suppose we have the expression: #A!Summa#*10.
Let us consider a document that has 5 pages corresponding to the «А» template, and the values of the «Summa» fields on them are
equal to 1, 23, 4^^, , and 4, respectively (the «Summa» field of the third page contains uncertain characters, while the same field of the
fourth page is empty). Then the value of the expression will be a collection of five elements the values of which will be as follows: 10,
230, #Error, 0, 40.
Binary operators: + , – , / , * , ^ , & , Or , And , = , < , <= ,
> , >= , <> , In , Like , Mod
Syntax. <ME>::= ( … | <MR1> <Binary operator> <MR2>| … )
<Binary operator>::= ( + | – | / | * | ^ | & | Or | And | = | < | <= | > | >= | <> | In | Like | Mod)
Meaning. Once the values of the MR1 and MR2 operands have been calculated, dimension matching is performed for both (in all
cases, except for the In operation). If matching fails, the expression value will be a single Error constant (the text will be ‘The
dimensions of the operands cannot be matched.’).
Then the operands are converted to the required type (depending on the operator type):
• To the real type in the case of + , – , / , * , ^ , < , > , <= , >=, and MOD,
• To the Boolean type in the case of Or and And,
• To the string type in the case of Like and &.
No type matching is performed for In, = and <>.
Then the specified operation is performed for each element (if an element is of the Error type, the respective element of the resulting
collection will also be of the Error type). The dimension of the result will be equal to the maximum dimension of the operands (for all
operations, except for In).
Descriptions of the operations follow:
1. + , – , / ,* are the arithmetical operations of addition, subtraction, multiplication and division,
^ is the involution operation,
2.
3.
Mod is integer division,
& is string concatenation,
4.
And and Or are the Boolean operations “AND” and “OR.”,
5.
6.
< , <= , > , >= , = and <> are comparison operations,
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
50
Page 51

7. Like is string comparison operation,
In is occurrence indicator: the dimension of the result is the dimension of the first operand. Each result element is True if the
8.
respective element of the first operand is present in the second one; otherwise the result is False.
Examples.
{`My`,`Your`} & {` name`,` age`} is {`My name`,`Your age`}
{2,–1} In {3,5,1,2} is {True, False}.
{`F`,`F`, `aBBBa`, `aM5b`} Like {`[A–Z]`,`[!A–Z]`,`a*a`,`a[L–P]#[!c–e]`} is {True, False, True, True}
Binary operators priority
As any expression can contain several binary operators (for example, 3+4*5), the calculation priority for the operators must be
defined. Of course, if a subexpression is enclosed in brackets, it is calculated first. The following is the list of operators in order of
calculation. Operators of the same priority are calculated in order of appearance:
1. ^,
2. / , *,
3. + , –,
4. &,
5. Like,
6. In,
7. , < , <= , >=,
8. = , <>,
9. Or , And.
Unary operators: – , !
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | <Unary operator> <MR1> | … )
<Unary operator>::= ( – | !)
Meaning.
· Real for the “–” operation,
· Boolean for the “!” operation.
The required operation is performed element by element, so that the dimension of the result is the same as the operand’s.
Before the operation begins, the MR1 operand is converted to the following type:
1. “–“ – arithmetical operation of multiplication by (–1).
2. “!” – Boolean «NOT» operation.
Zero–argument operators: Now, Date
Syntax. <ME>::= ( … | <Zero–argument operator> () | … )
<Zero–argument operator> ::= ( Now | Date )
Meaning.
and current date and time for Now() (for example, 02.03.2001 12:48:46).
The Date() and Now() operators return a one–dimensional Date value. The result is the current date for the Date() operator,
Type conversion operators: CDbl, CBool, CStr, CLng, CDate
Syntax. <МE>::= ( … | <Type conversion operator> (<MR1>)| … )
<Type conversion operator>::=( CDbl | CBool | CStr | CLng | CDate)
Meaning.
string, CLng – long, CDate – date). For more information, refer to the “Type conversion” section.
Example.
Use examples.
«А» template is equal to the value of the «ResultSum» field of the page corresponding to the «А» template. If we specify a rule like this:
#A!Sum#=#B!ResultSum#, then, if the values of these fields are 2 and 2.00 respectively, the result will be False, as the string values do
not match. But if we specify the same rule as: CDbl(#A!Sum#)=CDbl(#B!ResultSum#), then the rule will be calculated correctly.
Note that if an expression is used, for example, 1* #A!Sum#=1*#B!ResultSum#, there will be no need to use a type conversion operator,
as the operands are automatically converted to the required type before the arithmetical operation begins.
The value returned is the result of converting the operand into the respective type (CDbl – real, CBool – Boolean, CStr –
CDbl({``, `2.0`, `d4f`}) is {0, 2, #Error}
Let us assume we need to specify the following rule: the value of the «Summa» field on the page corresponding to the
Packing operators: Sum, Prod, Avg, Max, Min, Count, First, Last, NumMax, NumMin, Same,
Unique
Syntax. <ME>::= ( … |<Packing operator > (<MR1>) | … )
<Packing operator >::= ( Sum | Prod | Avg | Max | Min | Count | First| Last | NumMax | NumMin | Same | Unique )
Meaning.
several elements, but returning a value containing only one element. Before a packing operation begins, the following types of
conversion are performed: to the real type for all operations, except for Same, Unique, First, Last, and Count (there is no conversion
for these). If any result value contains at least one Error element, the result of the operation will also be Error. If the type conversion is
performed successfully, the only result element is calculated as follows:
The value of a packing operator is a single element, i.e. a packing operator is a function with an input value consisting of
1. For Sum, Prod and Avg , the result is the sum, multiplication and arithmetic mean of the input elements respectively.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
51
Page 52

2. For Max and Min, the result is the maximum and minimum element respectively.
3. For
4. For
5. For
6. For
7. For
Examples. Let the value of the #A!Sum# reference be a multidimensional constant {2, 1, 4, 4.6, 0, 4}, then
Sum(#A!Sum#) is {12.6}
Prod(#A!Sum#) is {0}
Avg(#A!Sum#) is {2.1}
Max(#A!Sum#) is {4.6}
Min(#A!Sum#) is {0}
NumMax(#A!Sum#) is {4}
NumMin(#A!Sum#) is {5}
First(#A!Sum#) is {2}
Last(#A!Sum#) is {4}
Count(#A!Sum#) is {6}
Same(#A!Sum#) is {False}
Unique(#A!Sum#) is {False}
NumMax and NumMin, the result is the number of maximum and minimum element (in the operand value).
First and Last, the result is the first and the last element respectively.
Count, the result is the dimension of the operand’s value.
Same, the result is True if all elements of the operand are the same, and False otherwise.
Unique, the result is True if all elements of the operand are different (no repetitions), and False otherwise.
String processing operators: UCase, LCase, Len, Trim
Syntax. <ME>::= ( … | <String processing operator> (<МE1>) | … )
<String processing operator> ::= ( UCase | LCase | Len | Trim )
Meaning.
element by element, so that the result dimension will be the dimension of the operand:
Before the operation begins, the value of the МE1 operand is converted to a string. The required operation is performed
• UCase and LСase – the string is converted to upper or lower case, respectively,
• Len – returns the string length (the number of characters),
• Tr im – cuts the left and right spaces.
Examples.
LCase({`i SaId tHe RoOk `,`5+3 EQUALS 8`}) is {`i said the rook`,`5+3 equals 8`}
Len ({` fghj jk `, `2`}) is {9 , 1}
Trim ({` fghj jk `, ` 2 1`}) is {`fghj jk`, `2 1`}
Part–of–date operators: Year, Month, Day
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | <Part–of–date operator> (<MR1>) | … )
<Part–of–date operator> ::=( Year | Month | Day )
Meaning.
performed element by element, so that the result dimension will be the dimension of the operand. The Year, Month, and Day
operators return the year, month, and day of the provided date respectively.
Examples.
Year(`20/1/1`) is 2001
Month(`20.02.01`) is 2
Day({`2.22.1`,`31/1/20`}) is {22,31}
Before performing the operation, the value of the МE1 operand is converted to the Date type. The required operation is
IsError operator
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | IsError (<MR1>) | … )
Meaning. The result dimension is the dimension of the operand MR1. Each element is True if the respective element of the operand is
Error, and False otherwise.
Example.
IsError (Array (2+3, 2/0, `3a` – 2)) is { False, True, True }
Error operator
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | Error (<MR1>) | … )
Meaning. The MR1 dimension must be 1; its value must be able to be converted to a string. The result will be a single Error element;
the description of the error will be the string in the MR1 operand.
Abs operator
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | Abs (<MR1>) | … )
Meaning.
value of each element. The result dimension will be the dimension of the operand MR1.
Example.
Before the operation begins, the value of the МE1 operand is converted to the Real type. The operation gets the absolute
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
52
Page 53

Abs ({–2,`3.0`,`4b`}) is {2, 3, #Error}
Formatting operator: Format
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | Format (<MR1> , <MR2>) | … )
Meaning. Before the operation begins, the value of the МE1 operand is converted to the string type. Then dimension matching is
performed. If it is successful, the result dimension is the maximum of the dimensions of the involved operands. The result itself will be
a string. Each element of the result value will be equal to the result of calling the VB Format function for the corresponding elements
of the operand values.
Example.
Format(Array(5459.4,`HELLO`,Now()), {`##,##0.00`,`<`,`h:m:s`}) is {5 459.40,`hello`, 17:16:52}
Progression operators: Inc, Dec, Mult
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | <Progression operator> (<MR1> , <MR2> [, <MR3> ]) | … )
<Progression operator>::=( Inc | Dec | Mult )
Meaning.
whilst progression operators return a progression similar to an arithmetic or geometric progression for a single element. The first
operand serves as the first term of the progression, the second serves as the number of iterations, and the third is the common
difference. Before the operation begins, the type conversion is performed: the first and the third argument are converted to the real
type, the second – to the long type. If there is a third operand, the dimensions of the first and the third operand are matched. If all
these operations are performed successfully, the result will be calculated as follows:
Step 0: The value got at the zero step is the value of the first operand.
Step k:
Progression operators are, in a sense, the reverse of packing operators: packing operators return a single value for a value set,
1. All elements got at the previous step are added to the resulting collection.
2. If there is no third operand, the value got at this step is the value got at the previous step. If there is a third operand, the
value got at this step is the result of the binary operation of addition (for the
operation) and multiplication (for the Mult operation) over the values of the first and the third operands.
Inc operation), subtraction (for the Dec
The number of steps is equal to the first element of the second operand value (i.e. the second operand should be one–dimensional,
but if it is not, no error will occur, as the program takes only the first element).
Examples.
Inc(1,{3,4,–1},6) is {1, 7, 13}
Dec({2,20},5,1) is {2, 20, 3, 21, 4, 22, 5, 23, 6, 24}
Mult({1,4,5},{3,1},{–1,–2,2}) is {1, 4, 5, –1, –8, 10, 1, 16, 20}
Use examples.
starting from 1. You can specify the following rule: #*!Page number #=Inc(1, Count(#*!Page number#), 1).
Let all the document pages have the ‘Page number’ field, and the values of these fields must form the natural sequence
Cut operator: SubArray
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … |SubArray ( <MR1> , <MR2> [ , <MR3> ] ) | … )
Meaning.
elements from the third to the fifth one. Before the operation begins, the second and the third operands are converted to the integer
type. The second and the third operands should be one–dimensional, but if they are not so, no error occurs – the program only takes
their first elements. The result of the operation will be a value that contains the MR1 value of elements with numbers from N1 to N2,
inclusive, where N1 is the first element of the MR2 value, and N2 is the first element of the MR3 value if there is such operand, and the
number of the MR1 elements if there is no MR3. If N2<N1, or N1 is more than the number of elements, or N2<1, the result will be an
empty collection.
Examples.
SubArray({2,3,`ddf`,–1,3,45}, {2,1}, 3) is {3,`ddf`}
SubArray({2,3,`ddf`,–1,3,45}, –1, {3,–2}) is {2,3,`ddf`}
SubArray({2,3,`ddf`,–1,3,45}, 4, 4) is {–1}
SubArray({2,3,`ddf`,–1,3,45}, 4) is {–1,3,45}
SubArray({2,3,`ddf`,–1,3,45}, 7) is {} (empty collection)
Use examples.
sum of the «RevenueSum» fields of the third and fourth pages corresponding to the same template. You can specify the following rule:
CDbl(SubArray(#A!Summa#,2,2))=Sum(SubArray(#A!RevenueSum,3,4)).
The cut operator gets a range of elements form a collection. You can get, for example, only the second element, or all
Suppose we have a rule: the «Summa» field on the second page corresponding to the «А» template must be equal to the
Substring cut operator: SubStr
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | SubStr (<MR1> , <MR2> [ , <MR3>])| … )
Meaning. Before the operation begins, the first operand is converted to the string type, and the second and the third are converted to
the long type. Then the dimensions of all the three operands are matched. If all these operations are performed successfully, the
element–by–element operation of substring cutting is performed; this operation is similar to the Visual Basic Mid operation. It works
as follows: let the respective operands’ values equal s, n1 [, n2]. A substring is cut from the string; this substring begins with the n1–th
character of the source string inclusive and has the n2 length (if there is a third operand) or stretches to the end of the source string
otherwise. The substring is added to the resulting value.
Examples.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
53
Page 54

SubStr({`Olga`, 23, `ffe`, `Mary`}, 1, 1) is {`O`, `2`, `f`, `M`}
SubStr({`Olga`, 23, `ffe`, `Mary`}, {1, 2, 3, 4}, 1) is {`O`, `3`, `e`, `y`}
Use examples. If you want all the ‘DocCode’ fields of all pages corresponding to the ‘A’ template to begin with the prefix ‘_D’, specify
the following rule: SubStr (#A!DocCode#,1,2) = `_D`.
Selection operator: IIf
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | IIf (<MR1> , <MR2> , <MR3>)| … )
Meaning.
will be MR2; if it is False, the result will be MR3. The IIf operation can be performed in two ways: element–by–element or over the
entire values depending on the dimension of the first operand:
The meaning of the operator is as follows: the MR1 operand is a selection condition. If its value is True, the resulting value
• If the value of the first operand is a single element, then the select operator affects the entire values. If this single element is True,
the resulting value will be the second operand value, otherwise – the third operand value.
• If the value of the first operand contains more than one element, the select operation is performed element–by–element. Before
the operation begins, the dimensions of all the three operands are matched. The resulting value is a collection of elements. Each
element is got as follows: if the first element is True, the respective element of the second operand will be the result, otherwise the
third one.
Examples.
IIf(1, {23,`Fg`, 0, 87}, {0,True}) is {23,`Fg`, 0, 87}
IIf(False, {1,2,3,4}, {5,6,7,8}) is {5,6,7,8}
IIf({1, False, 0, 2}, {1,2,3,4}, {5,6,7,8}) is {1,6,7,4}
IIf({1,0,True,False}, 1, 5) is {1,5,1,5}
Substring replace operator: Replace
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | Replace ( <MR1> , <MR2> , <MR3>) | … )
Meaning. Before the operation begins, all the operands are converted to the string type. Then the dimensions of all the three operands
are matched. If this operation is performed successfully, the resulting dimension will be the maximum of the operand dimensions (the
result itself is a string). The first operand is the string in which the search is performed, the second is what is being searched, snd the
third is the substring with which the search pattern will be replaced. The result will be the first operand with all the occurrences of the
search pattern replaced with the specified substring.
Example.
Replace ({`ghsko22fghj2`,`222`}, `22`, `0`) is {`ghsko0fghj2`,`02`}
Data creation operator: DateSerial
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | DateSerial ( <MR1> , <MR2> , <MR3> ) | … )
Meaning. Before the operation begins, all the operands are converted to the real type. Then the dimensions of all the three operands
are matched. If this operation is performed successfully, the result dimension will be the maximum of the operand dimensions; the
result itself will be of the Date type. Each element will be a date made up of three parts: the first operand element is the day, the
second operand element is the month, and the third operand element is the year.
Example.
DateSerial (2001, {2,3}, {20,21}) is { 20.2.01, 21.3.01}
Glue operator: Array
Syntax. <MR>::= ( … | Array (<MR1> , <MR2> , ... , <MRN> ) | … )
Meaning.
the dimensions of the operands.
Examples.
Array({1, 23, `ffe`, True}, {0,1}, {}, {True}) is {1, 23, `ffe`, True, 0,1, True}
Use examples.
following rule: Same(Array(#A!DocType#, #B!DocType#))
The glue operator “glues” all the values of all operands in a single resulting value. The dimension of this value is the sum of
Let the ‘DocType’ fields on all pages corresponding to the ‘А’ and ‘В’ templates be the same. You can specify the
VBScript for ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition
General scope
A VBScript–rule is a program written in the VBScript language. It can use the values of the other form fields, ABBYY FormReader
Enterprise Edition predefined functions as well as any standard VBScript functions. Besides that, the user can define global constants
and functions and use formulae for calculating expressions.
In order to create custom functions, the Form Page Access API is available.
Creating custom functions by using the Form Page Access API
The API consists of primary types (enumerations) and five classes:
• FormDocument
• FormPage
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
54
Page 55

• FormPages
• Field
• Fields
The form data are accessible through the global object Form of the FormDocument type.
Enumerations
Enum TErrorLevel
Enum TErrorLevel
EL_Warning
EL_Error
EL_CriticalError
End Enum
Determines the level of an error:
EL_Warning corresponds to a warning, a form data error. The form data with these warnings and errors can be exported.
EL_Error means a form data error. Data with this error can be exported.
EL_CriticalError refers to a critical error. Data with these errors can be exported. In particularly, all run time errors of the VB script
belong to this level.
Enum TDateFormat
Enum TDateFormat
DF_DayMonthYear
DF_MonthDayYear
DF_YearMonthDay
End Enum
Specifies the date format (the sequence of its parts)
Enum TYearLength
Enum TYearLength
YL_TwoDigits
YL_FourDigits
End Enum
Specifies the number of digits used for the year:
YL_TwoDigits means that two digits will be used for the year (“YY”)
YL_FourDigits means that four digits will be used for the year (“YYYY”)
FormDocument class
IDString property
IDString As String is a read–only property. It returns the unique ID of the form.
Pages property
Pages As FormPages is a read–only property. It returns the collection of all form pages.
GetPagesForTemplate method
The GetPagesForTemplate( TemplateName As String ) As FormPages returns all the form pages matched with the specified
template.
SetError method
For the description of the SetError( ByVal ErrorMessage, Optional ByVal ErrorFields, Optional ByVal ErrorLevel ) method, refer to the
"Check support" section.
SetDefaultDateFormat method
The SetDefaultDateFormat( ByVal DateType As TDateFormat, ByVal YearLength As TYearLength, ByRef DateSeparator As String )
method sets the default format date parameters for the execution period or until the method is called next time. The values of these
parameters are used by the Field.ToDate() function when it is called without one or two parameters.
Parameters:
• DateType specifies the date format (see Enum TDateFormat).
• YearLength specifies the number of digits in the year (see Enum TYearLength).
• DateSeparator specifies the date delimiter. The delimiter should be one character only, for example, a full stop (“.”).
SetDefaultDecimalSeparator method
The SetDefaultDecimalSeparator( ByRef DecimalSeparator As String ) method sets the default number delimiter for the
execution period or till the method is called next time. The values of these parameters are used by the Field.ToDecimal() method
when it is called without the parameter.
Parameters:
• DecimalSeparator specifies the decimal number delimiter. The delimiter should be one character only, for example, a full stop
(“.”).
FormatDate method
Function FormatDate( ByRef DateValue As Date, ByVal Optional DateType As TDateFormat, ByVal Optional YearLength As
TYearLength, ByRef Optional DateSeparator As String ) As String
Converts DateValue to a string of the specified format.
Parameters:
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
55
Page 56

• DateValue specifies the date value to be converted to the string.
• DateType specifies the date format (see Enum TDateFormat).
• YearLength specifies the number of digits in the year (see Enum TYearLength).
• DateSeparator specifies the delimiter of the date parts. It should consist of one character only.
If the method is called without one or several default parameters, the default parameters specified for the form will be used (see
SetDefaultDateFormat). If the default parameters have not been predefined, a run time error will occur.
Note. It is recommended to use this method before writing the date by using the SetCheckValue function.
FormatDecimal method
Function FormatDecimal( ByRef DecimalValue As Currency, Optional ByRef DecimalSeparator As String ) As String
Converts the DecimalValue number to a string of the specified format.
Parameters:
• DecimalValue specifies the value.
• DecimalSeparator contains the decimal delimiter (one character only) that will be used for converting the number to
text.
If the method is called without the DecimalSeparator value, the default decimal delimiter specified for the form will be used (see
SetDefaultDecimalSeparator). If the default decimal delimiter has not been specified for the form, a run time error will occur.
Note; It is recommended to use this method before writing the number by using the SetCheckValue function.
FormPages collection
Count property
Count As Long is a read–only property. It returns the number of the pages in the collection.
Item method
Item( Index As Long ) As FormPage returns the collection element with the specified index.
FormPage class
TemplateName property
TemplateName As String is a read–only property.
Fields property
Fields As Fields is a read–only property.
Fields collection
Count property
Count As Long is a read–only property. It returns the number of the fields on the page.
Item method
The Item( Index As Long ) As Field method returns the object of the field with the specified index.
ItemByName method
The ItemByName( FieldName As String ) As Field method returns the object of the field with specified name.
Note: If a checkmark is a member of a checkmark group, it cannot be an independent object and it is absent in the field collection.
Field class
The object corresponds to a field in the form page.
Name property
Name is a read–only property. It returns the field name.
Value property
Value As Varian t (vbSt ring) is a read–only property. It returns the field value (text).
The value of the Va lu e property for different field types:
Field type Return values
Text
Date
Number
Checkmark
Type: Variant(vbString)
Text string.
Type: Variant(vbString)
Text string.
Note: The field can contain both the correct and incorrect date (arbitrary text). The incorrect date can be entered
when editing the form in ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition or it can be exported from the *. ffdata file. In this case
the Value property returns the text "as it is". If the field is not filled, the method returns “”.
Type: Variant(vbString)
Text string.
Note: The field can contain both the correct and incorrect number (arbitrary text). The incorrect number can be
entered when editing the form in ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition or it can be exported from the *. ffdata file. In
this case the Value property returns the text "as it is". If the field is not filled, the method returns “”.
Type: Variant(vbString)
If the check mark is not selected, the property returns “0”; otherwise it returns “1”.
Any other data are regarded as invalid.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
56
Page 57

Field type Return values
Type: Variant(vbString)
If the case of multiple selection the property returns “–2”.
If no check mark was selected, the property returns “–1”.
Check mark
group
CheckValue property
CheckValue As Variant is a read–only property. It returns the field value.
SetCheckValue method
The Sub SetCheckValue( ByVal Value As String, Optional ByVal ErrorLevel, Optional ByVal Precision, Optional ByVal ErrorFields )
method sets CheckValue for the field as well as the error level for Enterprise check.
Parameters:
If the first check mark in the group was selected, the property returns “1”.
If the second check mark in the group was selected, the property returns “2”.
...
If the last check mark in the group was selected, the property returns
“number_of_the_last_check_mark_in_the_group".
Any other data are regarded as invalid.
• Value specifies the new value for the attribute of the CheckValue field.
• ErrorLevel specifies the error level (see Enum TErrorLevel). The default level is EL_Error.
• Precision specifies the accuracy of the Va lu e number. ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition uses it to compare the
attribute values of the
Va lu e and CheckValue fields.
• ErrorFields is the array of the references to error fields. These fields will be shown to the user if an error occurs in the
field. To form this parameter, use the standard VBScript function Array(). If the field for which the SetCheckValue is
called contains an error, the filed will be listed in the error fields list and will be the first item of the list. If the ErrorFields
parameter is omitted, the error fields list will contain only one field for which the SetCheckValue function is called.
Field.Value vs. Field.CheckValue
How do Va lu e and CheckValue differ from each other? The difference is as follows:
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise
Field.Value
Field.CheckValue
Field.SetCheckValue()
ToDate method
The ToDate( ByVal Optional DateType As TDateFormat, ByRef Optional DateSeparator As String ) converts the string value
of the filed to the Date format by using the specified parameters:
read–only
Returns the field value
read–only
Returns the field value to be checked
See the comment to the Field.SetCheckValue() method
Sets the filed value to checked and the error level. When Enterprise checks the form data, this value will be
compared with the filed value recognized (or entered) in ABBYY FormReader (i. e. with the value of the Va lu e
property). In the case of mismatch the error message will be displayed. Comparison accuracy is specified by
using the Precision parameter. The error level is specified by using the ErrorLevel parameter.
If the value of the CheckValue filed is not specified (Empty), check is not performed.
• DateType specifies the date format (sequence of its part); see Enum TDateFormat.
• DateSeparator specifies the date delimiter. It should contain one character, for example, a full stop (“.”).
If the method is called without one or several default parameters, the default parameters specified for the form will be used (see
SetDefaultDateFormat). If the default parameters have not been predefined, a run time error will occur.
If the filed contains incorrect data, the method returns Variant(vbNull).
Note: It is recommended to use this method for converting the field text to the date instead of the standard VB Script method
Cdate, as the standard method uses the system date format, which can vary on different computers.
ToDecimal method
Function ToDecimal( ByRef Optional DecimalSeparator As String ) As Variant
Converts the string filed value to the Currency format by using the specified parameter:
• DecimalSeparator specifies the delimiter (one character only) that will be used for converting the filed text into a
number (Currency).
If the method is called without the default parameters, the decimal delimiter specified for the form will be used (see
SetDefaultDateFormat). If the decimal delimiter has not been predefined, a run time error will occur.
If the filed contains incorrect data, the method returns Variant(vbNull).
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
57
Page 58

Note: It is recommended to use this method for converting the field text to the number instead of the standard VB Script methods
CCur, CInt, CDb, as the standard methods use the system number format, which can vary on different computers.
Global objects
The users have access to the Form global object. This object belongs to the FormDocument type and represents the document of
the current form.
Support for custom verification rules and error messages
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition provides access to a special function of the FormDocument type that is intended for providing
detailed error messages for custom verifications created using the VBScript language:
Sub SetError( ByVal ErrorMessage, ByVal Optional ErrorFields, Optional ByVal Level )
• When ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition executes this function, the appropriate error will be added to the error level list of
the document (no dialog box is displayed).
The Level parameter allows the user to set the error level (see Enum TErrorLevel)
The error codes are not supported.
The ErrorFileds parameter is of the Variant (vbArray) type. It contains the array references to the Field objects. To form
errorFileds, use the Array function (predefined VB Script function).
For example:
Sub CheckSumOfNumbers
Dim sum, fields, fld1, fld2, fld3
Set fields = Form.GetPagesForTemplate( "Page 1" ).Item(1).Fields
Set fld1 = fields.ItemByName( "Number1" )
Set fld2 = fields.ItemByName( "Number2" )
Set fld3 = fields.ItemByName( "Number3" )
sum = 0
sum = sum + fld1.ToDecimal
sum = sum + fld2.ToDecimal
sum = sum + fld3.ToDecimal
If sum < 10000 Then
form.SetError "The total amount is less than 10,000.00", Array( fld1, fld2, fld3 ), EL_Error
End If
End Sub
Sequence of calculating the form field values
Sequence of calculating the form field values is specified by the user while the script is executed.
The entry point is Sub Main().
Peculiarities of the script
MsgBox function
The MsgBox function should not be used. This ensures the operation of the script on the server in the unattended mode. Error and
warning messages are displayed to the user by using the SetError function.
Accuracy of the field values
When the VBScript is executed in ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition and the Field.SetCheckValue() function assigns the value
to the field, the value is rounded up to the decimal digit specified in the Precision parameter.
The programs use the standard round algorithm corresponding to the VB Script function:
Round(expression[, numdecimalplaces])
The algorithm should be modified explicitly in the expression used for the field value calculation.
Auxiliary function library
The auxiliary function library includes aggregation functions:
• ASum
• ASumProduct
• ACount
• ACountNotEmpty
• AMin
• AMax
• AFirst
• ALast
The “A” prefix in the function names means “Aggregate”.
Note. The auxiliary function library was written by using the Form Data Access API.
ASum
Function ASum(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
58
Page 59

The pageDefName and fieldName arguments specify the field array (the fieldName field for each page matched with the
pageDefName template in the form document).
The function returns the sum of the array elements.
Empty summands are regarded as 0.
ASumProduct
Function ASumProduct(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName1, ByVal fieldName2)
The pageDefName, fieldName1 and fieldName2 specify two arrays of the same dimension (the array dimension is equal to the
number of the pages matched with the pageDefName template in the form document).
The function returns the cum of the element–by–elements products of the fieldName1 and filedName2 arays.
Empty fields (array elements) are regarded as 0.
ACount
Function ACount(ByVal pageDefName)
The function returns the number of pages matched with the pageDefName templates in the form document.
ACountNotEmpty
Function ACountNotEmpty(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
The function returns the number of the fieldName fields that were filled in the pages matched with the pageDefName template in
the form document.
AMin*/AMax*
Function AMinNum(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
Function AMinDate(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
Function AMinText(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
Function AMaxNum(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
Function AMaxDate(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
Function AMaxText(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
The function returns the minimal (maximal) value of the corresponding type for the fieldName fields of all the pages matched with
the pageDefName template.
The empty fields are not compared
If the fieldName fields of all the pages matched with the pageDefName template are empty, the function returns Variant(Empty).
When calculating the field values, the program checks that each field has the value of the appropriate type (IsNumeric(Variant),
IsDate(Variant)) or is empty (IsEmpty()).
AFirst/ALast
Function AFirst(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
Function ALast(ByVal pageDefName, ByVal fieldName)
AFirst returns the fields value of the first document page of the specified type.
ALast returns the fields value of the last document page of the specified type.
Example of using the Form Data Access API
Option Explicit
' Sums the values of the fieldName field on all pageDefName pages
Function ASum( pageDefName, fieldName )
Dim sum, pages, i
sum = 0
Set pages = Form.GetPagesForTemplate( pageDefName )
For i = 1 To pages.Count
Dim fieldValue
fieldValue = pages.Item( i ).Fields.ItemByName( fieldName ).ToDecimal()
If Not IsNull( fieldValue ) Then
sum = sum + fieldValue
End If
Next
ASum = sum
End Function
How to modify the script
The scripts cannot be modified automatically in ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition.
When renaming fields and pages in the ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition interface, the user must change the name of these
objects in the script.
Automation Export
Automation export (or custom export) is a custom export procedure development kit that provides software control over data export
via an Automation interface (Automation API).
Custom export procedure
An example of a custom export procedure is installed together with the Administration and Correction Stations (refer to
<Installation folder>\Enterprise\Samples\CustomExport).
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
59
Page 60

Export procedure
In order to implement a custom export procedure, you must create an ActiveX component and implement in it a method with the
following signature:
Function ExportBatch( _
ByVal ExportData As String, _
Optional ByRef ResultReport As String _
) As Long
The first argument, ExportData, contains the export settings and batch data in the XML format. The specification for these data is
given below in the ExportData argument section.
The second argument, ResultReport, can return a message about the results of batch export.
If a batch was exported successfully the message can contain the name of the final output file. This message will be listed in the event
log together with the message about successful export.
If the batches cannot be exported, the ResultReport argument must return an error message. It will also be listed in the event log.
The ExportBatch method must return export results and have one of the following values:
Value Description
0 The batch has been exported successfully. The batch is routed to the processed batches queue.
Batch export has been canceled/interrupted by the user. This batch is not routed to the problem batches queue and can be
–1
exported again. The other batches can be exported.
Batch export error. The other batches can be exported. The problem batch is routed to the problem batches queue. In order to
–2
export this batch, it should be returned to the Export queue (this can be done on the Export and Monitoring Station).
The export procedure has been canceled/interrupted by the user. No error message is displayed. The current batch is not
–3
routed to the problem batches queue and can be exported again.
Export procedure fatal error (for example, an error in the settings or database connection error). The export procedure is
–4
interrupted. An error message is displayed. The current batch is routed to the problem batches queue. In order to export this
batch, it should be returned to the Export queue (this can be done on the Export and Monitoring Station).
ExportData argument
Data are transferred as a string in XML format. You must parse the string by using the MSXML.dll library (the
MSXML.DOMDocument.loadXML method), read the data iterating them by elements and attributes, and export the data as required.
General data hierarchy
The hierarchy of the elements is as follows:
root
exportSettings
exportSetting
...
exportSetting
batch
registrationParameters
registrationParameter
...
registrationParameter
document
page
block
...
block
...
page
document
...
document
page
...
document
For the description of each element, its attributes and nested elements, refer to the next pages.
"root" element
The "root" element is a root element.
It has the following attributes:
Attribute
name
version string Yes Format version. The current version is 1.0.
Type Required Description
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
60
Page 61

producer string Yes Product name and build number. For example, ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition (build 511).
The "root" element contains nested elements:
Element name Repetitions number Description
exportSettings 1 Export settings
batch 1 Batch data
"exportSettings" and "exportSetting" elements
The "exportSettings" element is a set of export settings: both standard, determined by the form capture system architecture, and
custom, added for processing a specific batch type.
The element contains nested "exportSetting" elements. The number of "exportSetting" elements is not limited. The set of export
settings includes all the settings of the "EXPORT_SETTINGS" section associated with the batch type as well as the settings that are not
associated with any batch type.
Each "exportSetting" element corresponds to one export setting.
The "exportSetting" element has the following attributes:
Attribute name Type Required? Description
settingName string Yes Setting name
isForAllBatchDefs Boolean Yes Notifies if the settings are specified for all batch types or only for the given batch.
The value of the element is the value of the setting.
The required standard settings are:
Setting name Description
"ExportFolder" Export folder
"ExportBlockCoordinates" Notifies if the output data include the coordinates of the blocks.
"batch" element
The "batch" element is a root element. It corresponds to the batch object.
The "batch" element has the following attributes:
Attribute name Type Required? Description
batchID integer Yes Batch ID in the database
batchName string Yes Batch name (specified when a batch is registered)
batchDefID integer Yes Batch type ID in the database
batchDefName string Yes Batch type name
batchPath string Yes Full path to the *.frm batch file
The "batch" element has the following nested elements:
Element name Repetitions number Description
registrationParameters 1 Registration parameters
FREParameters 1 FormReader parameters
document Unlimited Document
"registrationParameters" and "registrationParameter" elements
The "registrationParameters" element is a set of batch registration parameters (parameters specified when a batch is registered on the
Scanning Station).
The element contains nested "registrationParameter" elements. The number of "registrationParameter" elements is not limited.
Each "registrationParameter" element corresponds to one batch registration parameter.
The "registrationParameter" element has the following attributes:
Attribute name Type Required? Description
registrationParameterName string Yes
The value of the element is the value of the registration parameter.
"FREParameters" and "FREParameter" elements
The element is a collection of nested "FREParameter" elements. Each "FREParameter" corresponds to a FormReader paramter.
The name (heading) of a registration parameter. Specified when the parameter is set
up on the Administration Station.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
61
Page 62

The collection includes the following FormReader parameters:
• The time and date when the batch was created,
• The name of the computer on which the batch was scanned,
• The name of the computer on which the batch was verified,
• The name of the computer from which the batch was exported,
• The current time and date,
• The name of the operator who exported the batch,
• The name of the Windows user.
The "FREParameter" element has the following attributes:
Attribute name Type Required? Description
Name string Yes Parameter name
Code string Yes Parameter code
The value of the element is the value of the FormReader parameter.
"document" element
It corresponds to one document.
The "document" element has the following attributes:
Attribute name Type Required? Description
docDefID integer Yes Document template ID in the database.
docDefName string Yes Document template name in the database.
docNumber integer Yes
The sequence number of a document among the documents of the same level (child
documents of the same parent document).
docStatus enum Yes Document status. See the status list below
exportedImagePath string Yes The path to the file to which the document images are exported
exportedDataPath string Yes The path to the file to which the recognized document is exported
The "docStatus"attribute can have the following values:
Value Description
OPRuleWarning Accepted. All the document pages have the 'Accepted' status.
OPRuleError Rejected. The document contains pages with the 'Rejected' status.
LoosePage Loose page.
VerificationError Verification error. The documents contains pages with Verification error status.
MPRuleWarning Multipage rule warning. Multipage rules of Warning type have failed on the document.
MPRuleError Multipage rule warning. Required multipage rules have failed on the document.
Undefined Undefined status.
The "document" element contains nested elements:
Element name Repetitions number Description
Page Unlimited Page
Document Unlimited Document
Page and document elements can alternate.
"docDefUID" element
The value of the element is the identifier of the *.mxfd file (FormDefID) which was used to create the document definition in
FormReader Enterprise Edition, or the identifier of a compatible *.mxfd file.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
62
Page 63

"page" element
Corresponds to one page.
The "page" element has the following attributes:
Attribute name Type Required? Description
pageNumber integer Yes Batch page number.
pageTemplate string Yes
pageImagePath string Yes Full path to the page image file.
pageStatus enum Yes Page status. See the status list below.
annexBarcodeValue string No Barcode value. Required only for non–recognizable pages (annexes).
The "pageStatus" attribute can have the following values:
Value Description
OPRuleWarning Accepted.
OPRuleError Rejected. Manually assigned to pages containing one–page check rules.
LoosePage Loose page. Manually assigned to pages that cannot be identified as a part of a document.
VerificationError Verification error.
OK No errors. A page does not contain invalid data or all detected errors have been corrected.
Undefined Undefined status.
The "page" element contains nested "block" elements. The number of "block" elements is not limited.
"block" element
Corresponds to one exported page block.
The "block" element contains the following attributes:
Attribute
name
blockName string Yes The name of a block in the ABBYY FormReader template
l integer No
t integer No
r integer No
b integer No
The value of the element is the value of the exported page block.
If the "block" element corresponds to table it contains a "table" element.
"table" element
The element corresponds to an exported Table block. The "table" element contains nested "row" elements. The number of "row"
elements is not limited.
The "row" element corresponds to a table row and has the following attributes:
Attribute name Type Required? Description
rowNumber integer Yes The row number in the table (row numbers start from 1)
Type Required? Description
The name of the page template (if the page has not been recognized, the attribute value is
an empty string).
The left border coordinate of an image block, dpi. Required if the Export block coordinates
option is selected (the ExportBlockCoordinates setting is set to True).
The upper border coordinate of an image block. Required if the Export block coordinates
option is selected (the ExportBlockCoordinates setting is set to True).
The right border coordinate of an image block. Required if the Export block coordinates option
is selected (the ExportBlockCoordinates setting is set to True).
The lower border coordinate of an image block. Required if the Export block coordinates option
is selected (the ExportBlockCoordinates setting is set to True).
The "row" element contains nested "cell" elements. The number of "cell" elements is not limited.
The "cell" element corresponds to a cell of table block and has the following attributes:
Attribute name Type Required? Description
columnHeader string Yes The heading of the column in which the cell is located
The value of the element is the value of the table cell.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
63
Page 64

Glossary
A
Administration Station
Program used for setting up the form capture system: adding and setting up batch types, assigning roles and permissions to operators.
Annex
A batch page that has no template but takes part in batch assembly.
B
Batch assembly
Binding batch pages into documents according to the document templates and the batch structure.
Batch identification number (ID)
The unique number of a batch within the form capture system. The ID is assigned to the batch automatically when the batch is
registered.
Batch locking
Temporary exclusion of a batch from processing.
Batch Registration Parameters
The user information entered by the operator of the Scanning Station when registering the batch or assigned automatically by the
Registration Station.
Batch Registration
A process which includes the creation of a new batch, entry of certain user information (socalled registration parameters), and
adding images of scanned forms to the batch. Batch registration can be performed manually by the operator of the Scanning Station
or automatically by the Registration Station.
Batch type definition
Set of batch type settings that can be used when creating a new batch type.
Batch type rule
A multipage rule establishing relations between data in different documents included in a batch.
Batch type structure
Description of document template sequence written in a special structure description language.
Batch unlocking
Return a locked batch to processing
C
ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition
A distributed client–server application built on ABBYY FormReader and Microsoft SQL Server/MSDE technologies.
Correction Station
Program used to assembly batches and validate batch data by using rules.
D
Data and License Server
Program used to store and exchange data between the stations in the form capture system. The form capture system protection key is
installed on the Server.
Document
A set of batch pages corresponding to a paper form.
Document template
Description of page template sequence (document template structure) and rules required for validating the data of a document.
Document template rule
A multipage rule establishing relations between data in the same document.
Document template structure
A description of a sequence of page templates and rules required for data validation.
E
Export and Monitoring Station
Program used to export processed batches to an external information system as well as to monitor and control the entire ABBYY
FormReader Enterprise Edition form capture system.
F
Form capture
Automated conversion of paper document data into editable electronic data.
Form capture system
Program consisting of the Data and License Server and stations and intended for automated form capture.
L
'Loose page' (document status)
A status assigned to a document consisting of one page with 'Loose page' status.
'Loose page' (page status)
A status assigned to a page that should be excluded from the entire further processing. For example, this status is assigned to a page
included in a batch by mistake.
M
Multipage rule
A rule establishing relations between data located on different pages. Multipage rules are used to validate the data in a batch.
'Multipage rule error' (document status)
A status assigned to a document if, when validating data by using multipage rules, the program has detected errors of required
multipage rules (Required rules or Assembly rules) on the document pages and these errors could not be corrected for some reason.
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
64
Page 65

'Multipage rule warning' (document status)
A status assigned to a document if, when validating data by using multipage rules, the program has detected errors of optional
multipage rules ('Warning' multipage rules) and these errors could not be corrected for some reason.
N
'(No errors)' (page status)
A status assigned to a page on which the program has not detected verification or one–page rule errors or all the detected errors have
been corrected.
O
'One–page rule error' (document status)
A status assigned to a document containing at least one page with 'One–page rule error' status.
'One–page rule error' (page status)
A status is assigned to a page on which during validating data by using one–page rules the program has detected errors of required
one–page rules (one–page rules with 'Error' status) and these errors could not be corrected for some reason.
'One–page rule warning' (document status)
A status assigned to a document if it contains at least one page with 'One–page rule warning' status.
This status is assigned to the document automatically.
'One–page rule warning' (page status)
A status is assigned to a page on which during validating data by using one–page rules the program has detected errors of optional
one–page rules (one–page rule with 'Warning' status) and these errors could not be corrected for some reason.
P
Page template library
A page template library is a set of page templates used in a certain batch type.
Problem batch
A batch that cannot be processed in the present processing stage (for example, the operator fails to find out why the batch cannot be
assembled or he cannot correct rule errors, etc.)
Project
A collection of all the batches to be processed by the system together with all the settings required for their processing.
R
Recognition Station
Program used to recognize batch data.
Rule
A formalized description that applies certain restrictions to data as well as establishing relations between data in a batch.
S
Scanning Station
Program used to scan paper forms and add ready images to a batch.
V
'Verification error' (document status)
A status assigned to a document if it contains at least one page with 'Verification error'.
'Verification error' (page status)
A status assigned to a page on which the program has detected errors during verification and these verification errors could not be
corrected for some reason.
Verification Station
Program used to verify and validate data by using one–page rules.
W
Workstation
A computer on which the form capture system stations are installed.
Hotkeys
Scanning Station hotkeys
Menu To: Press:
Update batch page list F5
Scan Ctrl+K
Scan multiple pages Ctrl+Shift+K
Scan
Stop scanning Ctrl+T
Add Ctrl+P
Add from… Ctrl+O
Close station Ctrl+Shift+Q
Select all Ctrl+A
Image
Renumber pages... Alt+Shift+N
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
65
Page 66

Batch Send Ctrl+Shift+B
Verification Station hotkeys
Main window
Menu To: Press:
Verify Shift+F7
Update batch page list F5
Verify
Continue Validation Alt+A
Close Station Ctrl+Shift+Q
Assign with Status One–page Rule Warning Ctrl+Shift+Y
Page
Reset Status for Selected Pages Ctrl+Shift+Z
Batch Send Ctrl+Shift+В
Correction Station hotkeys
Main window
Menu To: Press:
Scan Ctrl+K
Scan Multiple Pages Ctrl+Shift+K
Stop Scanning Ctrl+T
Add from... Ctrl+O
Recognize All Unrecognized Pages Ctrl+Shift+R
Recognize Selected Pages Ctrl+R
Verify Shift+F7
Verify Selected Pages F7
'One–page Rule Error' Ctrl+Shift+W
'One–page Rule Warning' Ctrl+Shift+Y
'Verification Error' Ctrl+Shift+U
'Loose Page' Ctrl+Shift+J
Processes
Page
Batch
Scan
Recognize
Verify
Continue Validation Alt+A
Stop Validation Ctrl+Shift+I
Assemble Ctrl+Shift+A
Close Station Ctrl+Shift+Q
Accept with Status
Reset Status for Selected Pages Ctrl+Shift+Z
Delete Blocks and Data Alt+Del
Renumber… Alt+Shift+N
Match Template Named… Ctrl+Shift+E
Select All Ctrl+A
Option… Ctrl+Shift+O
Send Ctrl+Shift+B
Save Verification Results Ctrl+Shift+S
Export and Monitoring Station hotkeys
Main window
Menu To: Press:
Action Update List F5
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
66
Page 67

View Batch dialog box
Menu To: Press:
File Exit Ctrl + X
Edit Advanced Search... Ctrl + F
View Open Page... Ctrl + G
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it necessary to install the Data and License Server on a separate computer?
The Data and License Server is a database (MSDE or SQL), a file storage unit, and a license server. If the server workload is low, you
may install it not on a separate computer but, for example, together with one of the Stations.
How does network architecture (star connection, etc.) affect the speed of the system performance?
Network architecture affects FormReader Enterprise Edition performance just like it affects any other network task which requires
large file transfers via the network. The main data exchange takes place between workstations and the file storage unit (the project’s
shared folder). If possible, we recommend using a separate network fragment with its own router.
Are there any recommendations for the system architecture and network parameters?
Network data transfer rate – 100 Mbps
Installation of the workstations and the Data and License Server on separate computers
Operating system Win2000/XP
Use of NamedPipes as the network protocol in SQL Server.
What is “sending a batch to the server and among the Stations”?
Batch transfer is a change in the project database. Batch files may actually remain in the same location, but the record in the database
which denotes the next stage of batch processing changes. The operation of getting a batch for processing and returning a batch are
actually getting and releasing the batch by a user; the batch being processed is unavailable for other users.
What is the function of the "Use local batch copies for ..."option?
A batch is copied from the Server to a Station local disk for processing, and when the batch is processed it is copied back to the Server.
If this option is selected, a batch is opened from the Server. This ability allows you to reduce the Server load and to speed up the batch
processing due to its local (and not network) processing. But is processed batched are very large (hundreds of documents, large
dictionaries), copying an entire batch can occupy the network for a long time.
How to buy ABBYY FormReader Enterprise Edition
For detailed information about the FormReader family of products, please visit http://www.formreader.com/. This site is maintained
by ABBYY Software house. Here you can:
• Get all the information about FormReader products
• Read ABBYY's success stories
• Find an ABBYY office nearest to you or find you local reseller specializing in FormReader products
To order your copy of ABBYY FromReader 6.5 Enterprise Edition or to get additional information about the product please write to
sales@abbyy.com or call:
USA: +1 5102266717
Western Europe: +49 895111590
Eastern Europe: + 380 44 490 9999
Other regions: +7 495 7833700
© 2007 ABBYY. All rights reserved.
67
 Loading...
Loading...