Page 1

EAP110 V1.10
Enterprise Access Point
Page 2

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Copyright & Disclaimer
Copyright
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, stored,
transcribed in an information retrieval system, translated into any language, or transmitted in any
form or by any means, mechanical, magnetic, electronic, optical, photocopying, manual, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of 4IPNET, INC.
Disclaimer
4IPNET, INC. does not assume any liability arising out the application or use of any products, or
software described herein. Neither does it convey any license under its parent rights not the parent
rights of others. 4IPNET further reserves the right to make changes in any products described herein
without notice. The publication is subject to change without notice.
Trademarks
4IPNET (4ipnet) is a registered trademark of 4IPNET, INC. Other trademarks mentioned in this
publication are used for identification purposes only and may be properties of their respective
owners.
1
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 3

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Table of Contents
1. Before You Start ..................................................................................................................................4
1.1 Preface.................................................................................................................................................4
1.2 Document Conventions....................................................................................................................4
1.3 Package Content................................................................................................................................5
2. System Overview and Getting Started .............................................................................................6
2.1 Introduction of 4ipnet EAP110 .......................................................................................................6
2.2 Deployment Topology......................................................................................................................7
2.3 Hardware Description......................................................................................................................8
2.4 Hardware Installation....................................................................................................................10
2.5 Access Web Management Interface .............................................................................................11
3. Connect your AP to your Network..................................................................................................15
4. Adding Virtual Access Points ..........................................................................................................21
5. Secure Your AP ..................................................................................................................................22
6. Create a WDS Bridge between two APs .........................................................................................30
7. Web Management Interface Configuration...................................................................................32
7.1 System...............................................................................................................................................34
7.1.1 System Information .................................................................................................................34
7.1.2 Network Interface ....................................................................................................................36
7.1.3 Management .............................................................................................................................37
7.1.4 GRE Tunnel ..............................................................................................................................39
7.1.5 CAPWAP....................................................................................................................................40
7.1.6 QoS Classification ....................................................................................................................42
7.2 Wireless............................................................................................................................................43
7.2.1 VAP Overview...........................................................................................................................43
7.2.2 General......................................................................................................................................46
7.2.3 VAP Configuration ..................................................................................................................48
7.2.4 Security .....................................................................................................................................49
7.2.5 Repeater....................................................................................................................................53
7.2.6 Advanced ..................................................................................................................................54
7.2.7 Access Control..........................................................................................................................55
7.3 Firewall.............................................................................................................................................58
7.3.1 Firewall List ..............................................................................................................................58
7.3.2 Service .......................................................................................................................................63
7.3.3 Advanced ..................................................................................................................................64
7.4 Utilities.............................................................................................................................................65
7.4.1 Change Password .....................................................................................................................65
2
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 4

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.4.2 Network Utilities .....................................................................................................................66
7.4.3 Save & Restore .........................................................................................................................67
7.4.4 System Upgrade.......................................................................................................................68
7.4.5 Reboot .......................................................................................................................................69
7.4.6 Upload Certificate....................................................................................................................70
7.5 Status ................................................................................................................................................71
7.5.1 Overview....................................................................................................................................71
7.5.2 Clients........................................................................................................................................73
7.5.3 Repeater....................................................................................................................................74
7.5.4 Event Log ..................................................................................................................................75
7.6 Online Help......................................................................................................................................76
3
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 5

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
1. Before You Start
1.1 Preface
This manual is intended for system integrators, field engineers, and network administrators to set up
4ipnet’s EAP110 802.11n/b/g 2.4GHz MIMO Access Point in their network environments. It contains stepby-step procedures and visual examples to guide MIS staff or individuals with basic network system
knowledge to complete the installation.
1.2 Document Conventions
Note: Contains related information that corresponds to a topic.
Represents essential steps, actions, or messages that should not be ignored.
Indicates that clicking this button will save the changes you made, but you must reboot
the system upon the completion of all configuration settings for the changes to take effect.
Indicates that clicking this button will clear what you have set before the settings are
applied.
4
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 6
1.3 Package Content
The standard package of EAP110 includes:
• 4ipnet EAP110 x1
• Quick Installation Guide (QIG) x1
• CD-ROM (with User’s Manual and QIG) x1
• Power Adapter (DC 5V) x1
• Antenna x2
It is recommended to keep the original packing materials for possible future shipment when repair or
maintenance is required. Any returned product should be packed in its original packaging to prevent
damage during delivery.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
5
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 7

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
2. System Overview and Getting Started
2.1 Introduction of 4ipnet EAP110
The 4ipnet EAP110 Enterprise Access Point embedded with 802.11 n/b/g 2.4GHz MIMO radio in dustproof metal housing is designed for wireless connectivity in enterprise or industrial environments of all
dimensions. EAP110 makes the wireless communication fast, secure and easy. It supports business
grade security such as 802.1X, and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA and WPA2).
EAP110 also features multiple ESSIDs with VLAN tags and multiple Virtual APs, great for enterprise
applications, such as separating the traffics of different departments using different ESSIDs. The PoE
LAN port can receive power from Power over Ethernet (PoE) sourcing device. Its metal case is IP50 antidust compliant, which means that EAP110 is well suited to WLAN deployment in industrial environments.
6
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 8
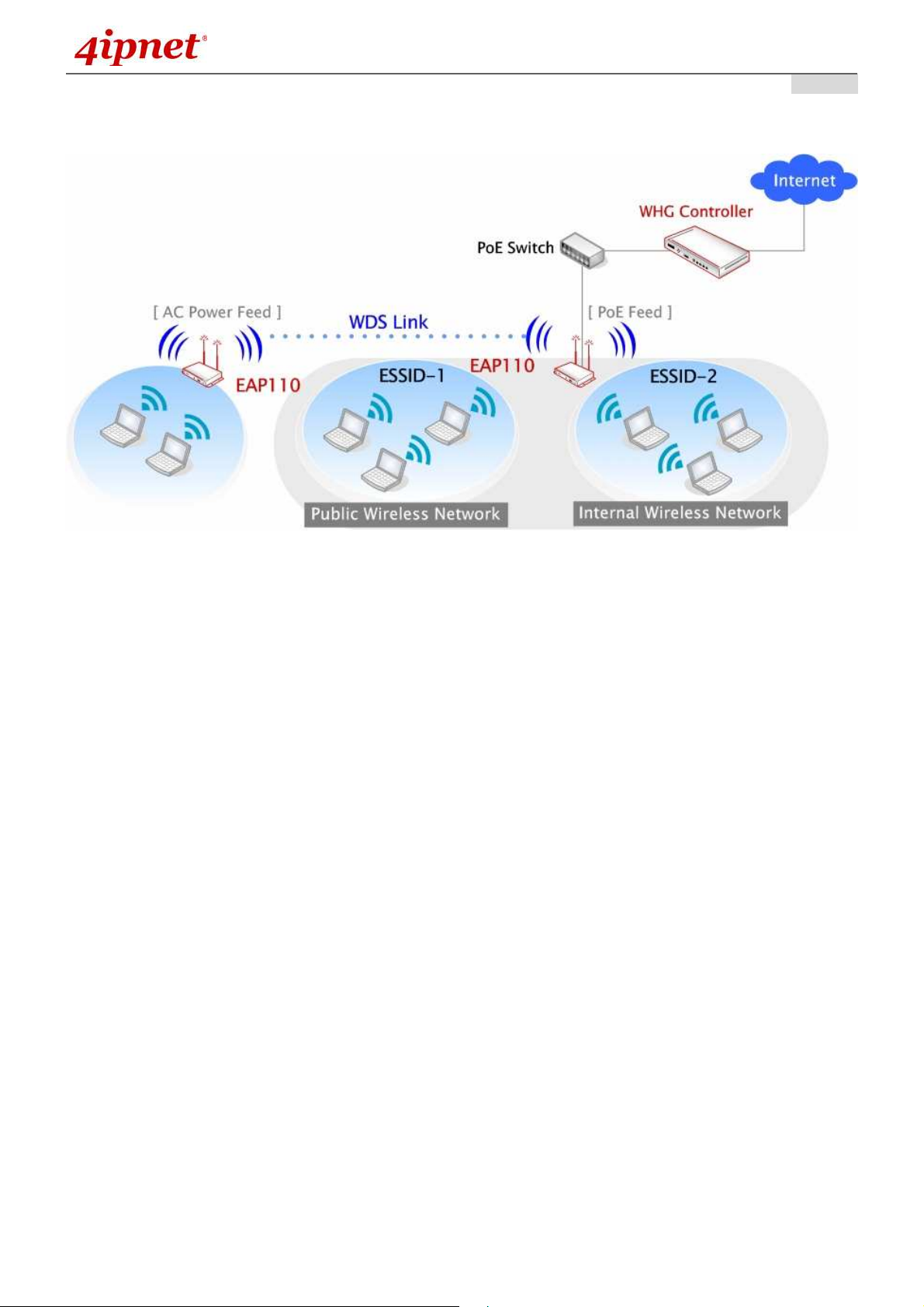
2.2 Deployment Topology
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Network Layout with EAP110s
This above deployment scenario illustrates a deployment example using these access points.
• Three EAP110 systems construct a network comprising of wireless segments.
• AP plays the role of a wireless bridge.
• All devices share the same DHCP server 192.168.1.1.
7
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 9
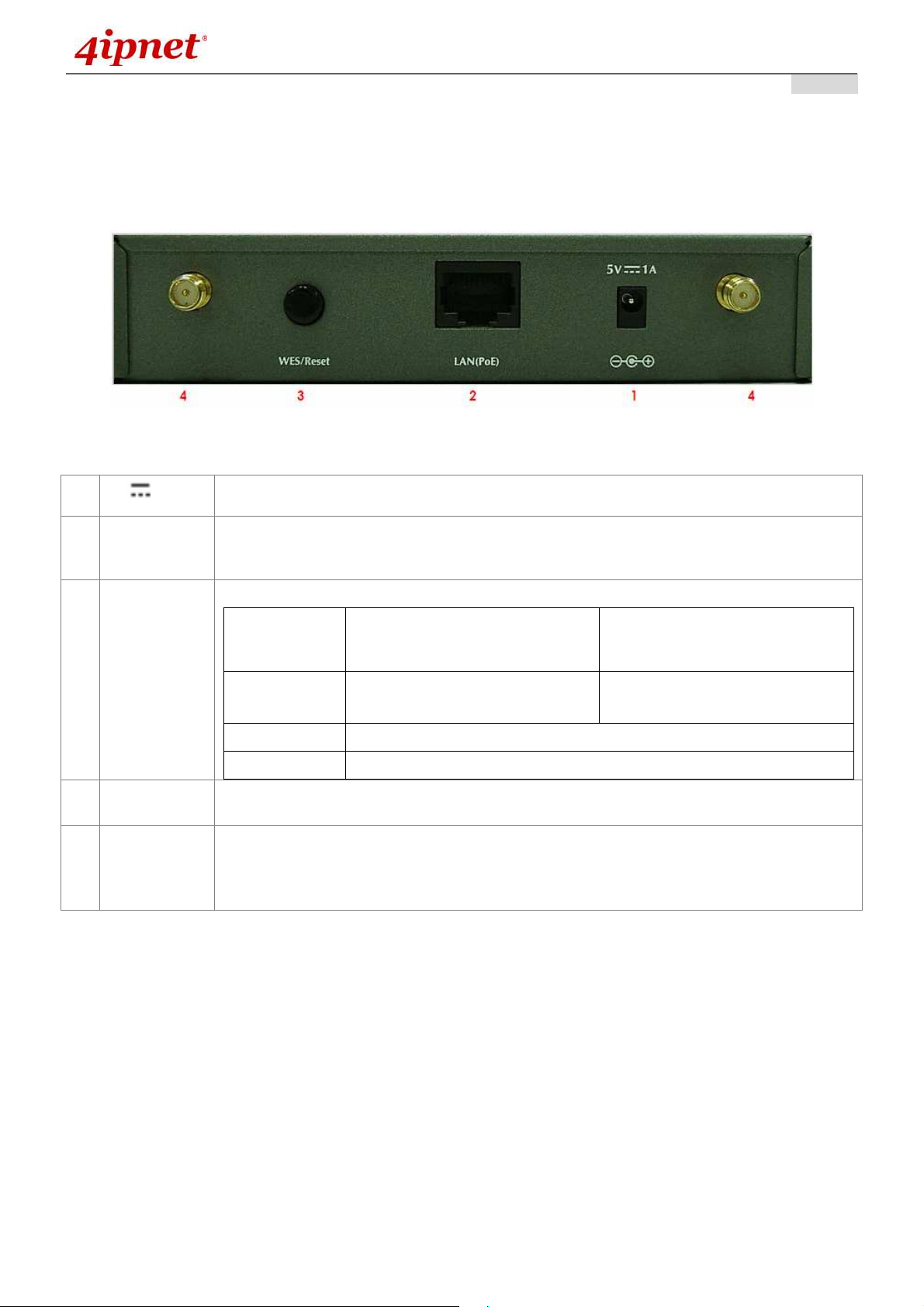
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
2.3 Hardware Description
This section depicts the hardware information including all panel description.
Connector Panel
EAP110 Connector Panel
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
1
5V 1A
2 LAN(PoE)
3 WES
3 Reset
Antenna
4
Connector
Attach the power adapter here.
Attach the Ethernet cable here for connecting to wired local network. This port supports
PoE as well which can be connected to a PSE (power sourcing equipment) as an
alternative power sourcing.
Press to start running WES process.
Master (Press for more than 3
WES
WES Start WLAN LED BLINKING SLOWLY WLAN LED BLINKING QUICKLY
WES Success WLAN LED ON constantly for 5 seconds
WES Fail WLAN LED OFF for 5 seconds
Press and hold the button for more than 10 seconds until WLAN LED OFF. WLAN ON while
reset is successful.
Attach the antennas here. The system supports one RF interface with two SMA connectors.
seconds until the WLAN LED
blinks twice and then release)
Slave (Press once until the WLAN
LED starts blinking and then
release right away)
8
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 10
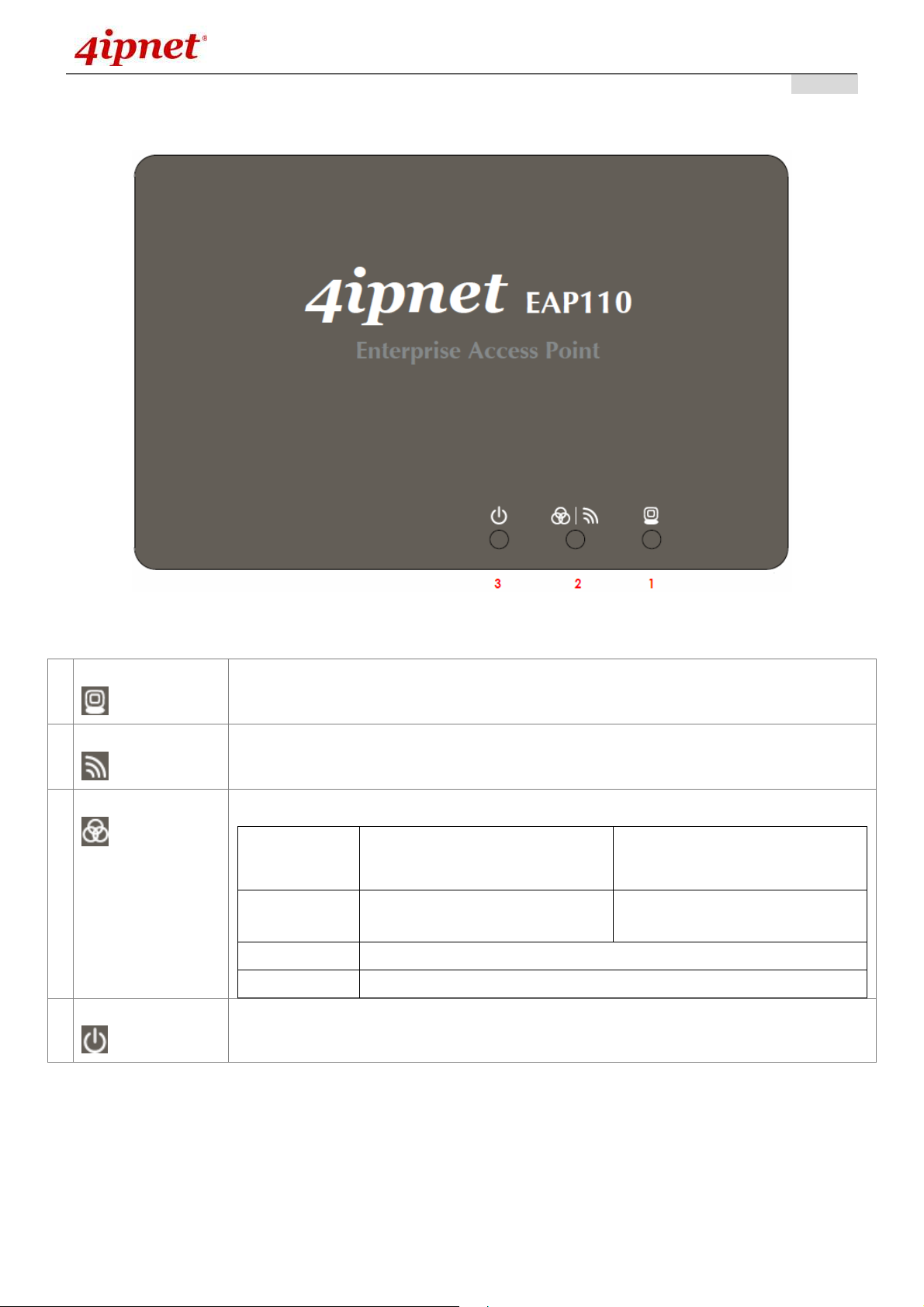
LED Panel
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
1 LAN LED
2 WLAN LED
2 WES LED
3 Power LED
EAP110 LED Panel
LED ON indicates LAN cable is connected; OFF indicates no connection; BLINKING
indicates transmitting data.
LED ON indicates wireless is ready.
To indicate WES status.
Master (Press for more than 3
WES
WES Start WLAN LED BLINKING SLOWLY WLAN LED BLINKING QUICKLY
WES Success WLAN LED ON constantly for 5 seconds
WES Fail WLAN LED OFF for 5 seconds
LED ON indicates power on; OFF indicates power off.
seconds until the WLAN LED
blinks twice and then release)
Slave (Press once until the WLAN
LED starts blinking and then
release right away)
9
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 11

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
2.4 Hardware Installation
Please follow the steps mentioned below to install the hardware of EAP110:
1. Place the EAP110 at the best location.
The best location for EAP110 is usually at the center of your intended wireless network.
2. Connect the EAP110 to your network device.
Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to LAN port of EAP110 and the other end of the cable to a
switch, a router, or a hub. EAP110 is then connected to your existing wired LAN network.
3. There are two ways to supply power over to EAP110.
a) Connect the DC power adapter to the EAP110 power socket.
b) EAP110 LAN port is capable of transmitting DC currents. Connect an IEEE 802.3af-compliant
PSE device (e.g. a PoE-switch) to the LAN port of EAP110 with the Ethernet cable.
Now, the Hardware Installation is complete.
• Please only use the power adapter supplied with the EAP110 package. Using a different
power adapter may damage this system.
• To double verify the wired connection between EAP110 and you switch / router / hub, please
also check the LED status indicator of the respective network devices.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
10
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 12
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
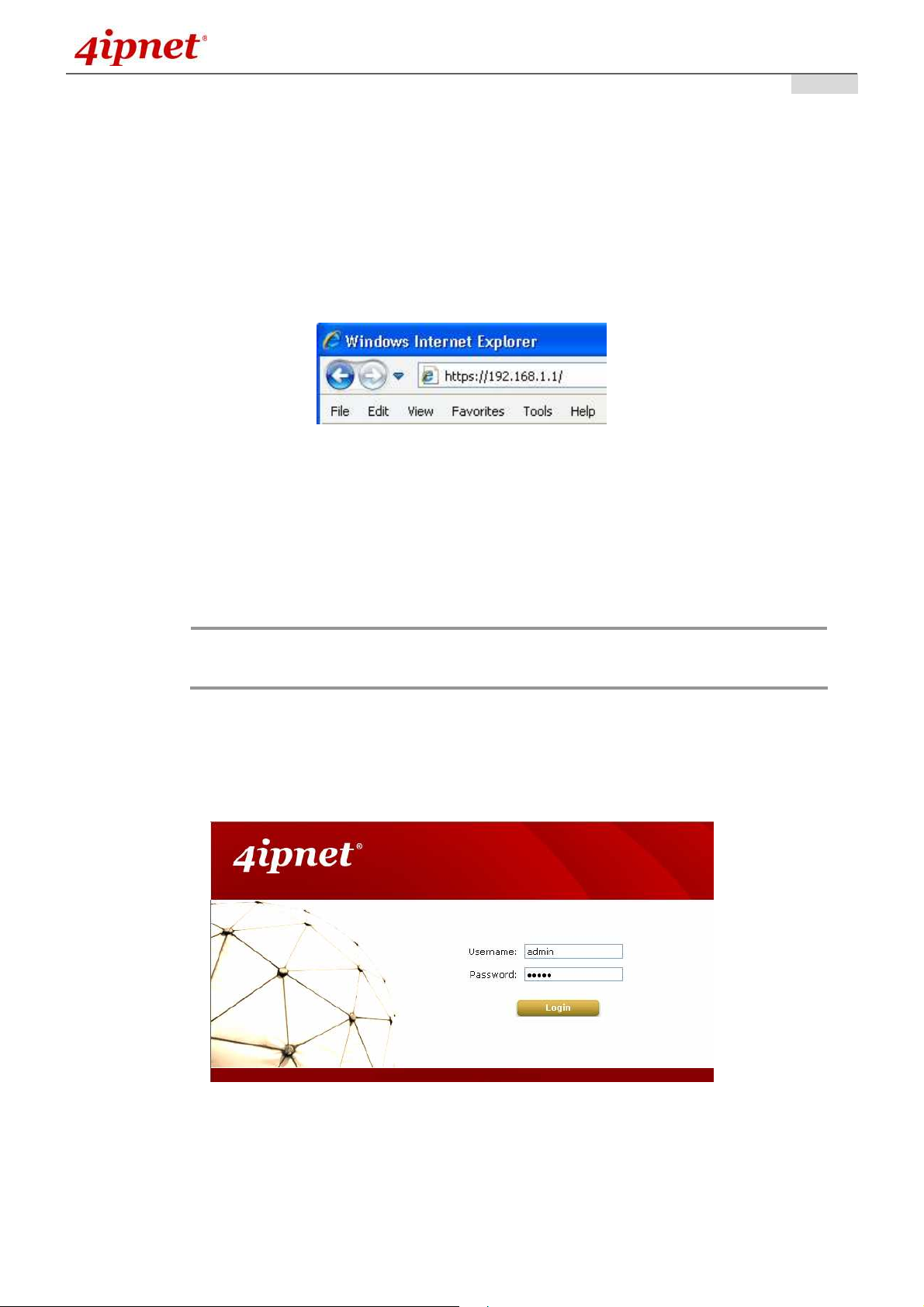
2.5 Access Web Management Interface
4ipnet EAP110 supports web-based configuration. Upon the completion of hardware installation, EAP110
can be configured through a PC by using its web browser such as Mozilla Firefox 2.0 (and higher) or Internet
Explorer version 6.0 (and higher).
The default values of the EAP110’s LAN IP Address and Subnet Mask are:
IP Address: 192.168.1.1
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Example of entering EAP110's default IP Address into a web browser
• To access the web management interface (WMI), connect the administrator PC to the LAN port of
EAP110 via an Ethernet cable. Then, set a static IP Address on the same subnet mask as the
EAP110 in TCP/IP settings of your PC, such as the following example:
IP Address: 192.168.1.100
Subnet Mask: 255.255.255.0
Note:
• Launch the web browser on your PC and enter the IP Address of the EAP110 (192.168.1.1) at the
address field, and then press Enter. The following Administrator Login Page will then appear. Enter
“admin” for both the Username and Password fields, and then click Login.
Please note that the IP Address used should not overlap with the IP Addresses of
any other device within the same network.
Administrator Login Page
11
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 13
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
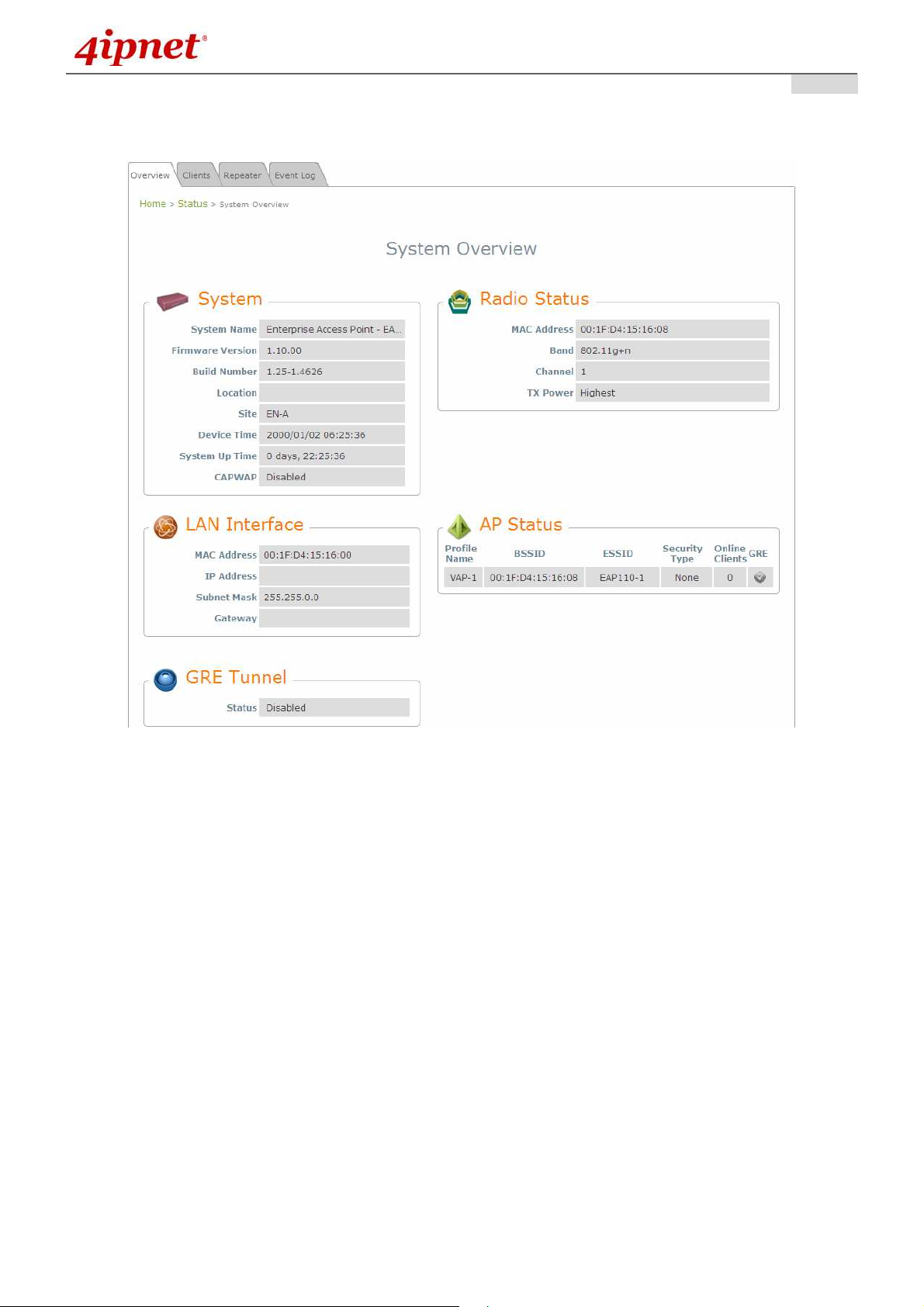
• After a successful login into EAP110, a System Overview page of the Web Management Interface
(WMI) will appear.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
The Web Management Interface - System Overview Page
12
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 14
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
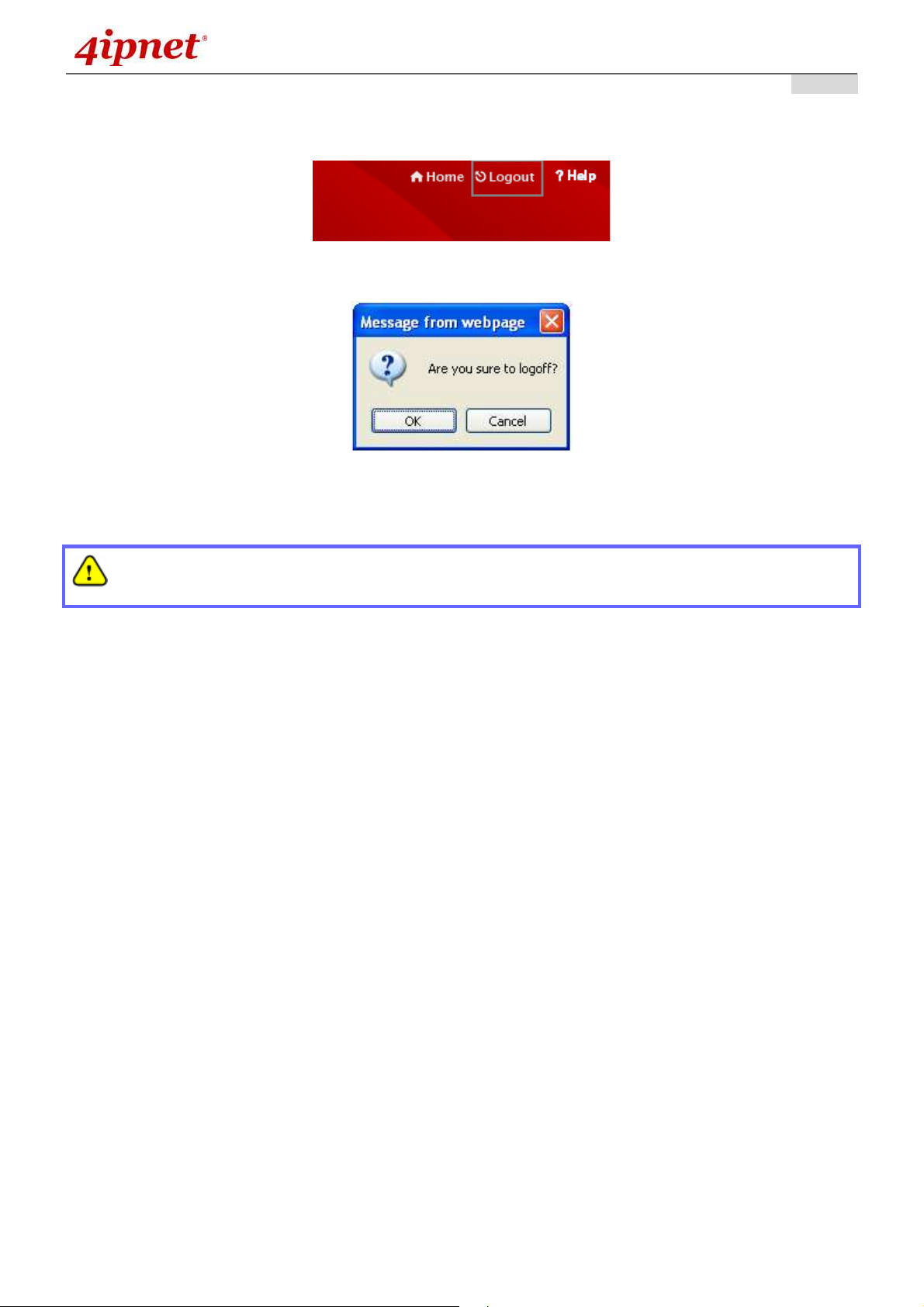
• To logout, simply click on the Logout button at the upper right hand corner of the interface to return to
the Administrator Login Page. Click OK to logout.
Logout
Logout Prompt
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
For security reasons, it is strongly recommended to change the administrator’s password upon the
completion of all configuration settings
13
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 15
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
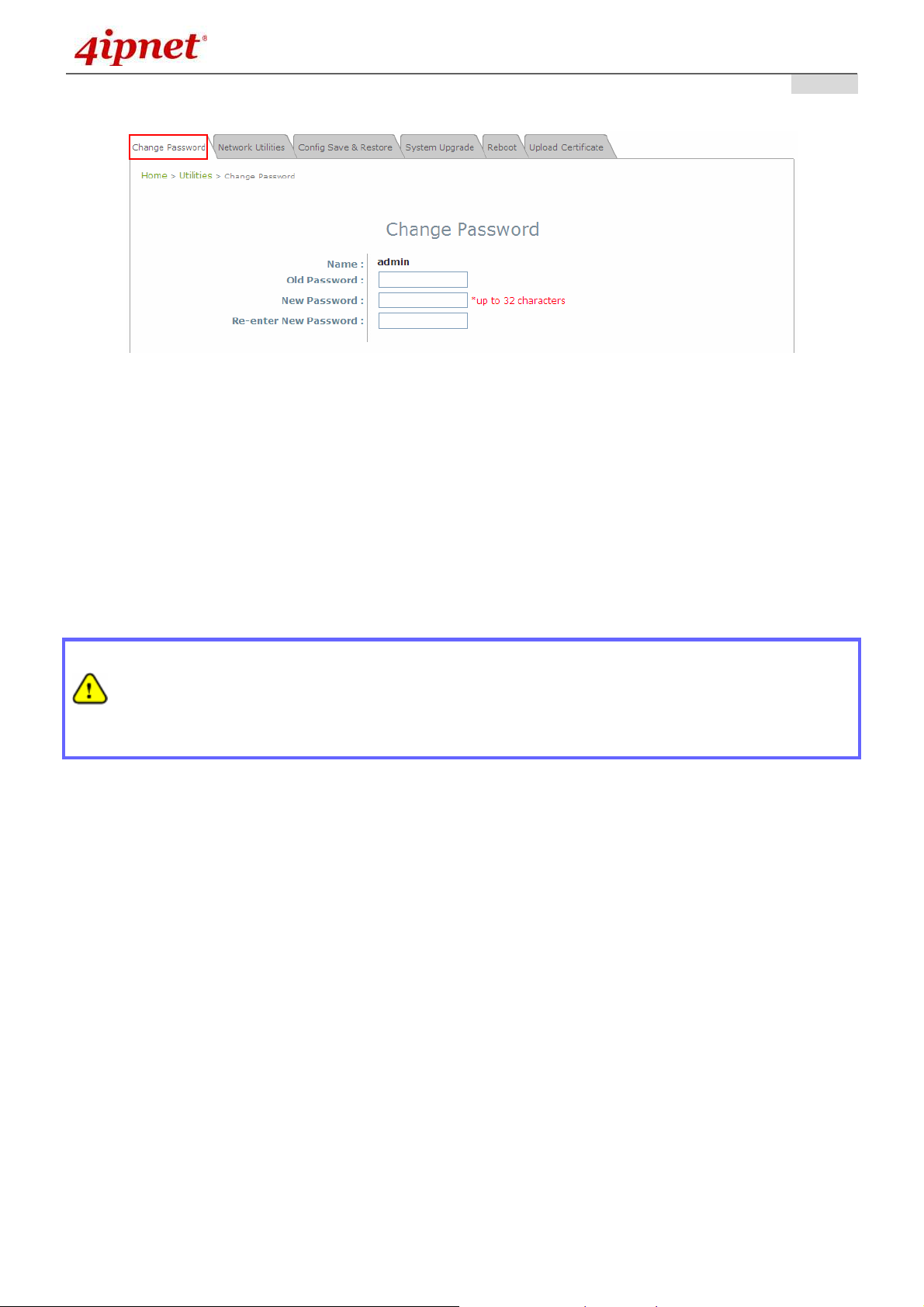
Please follow the following steps to change the administrator’s password:
Change Password Page
Click on the Utilities main menu button, and then select the Change Password tab.
Enter the old password and then a new password with a length of up to 32 characters, and retype it in
the Re-enter New Password field.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Congratulations!
Now, 4ipnet’s EAP110 is installed and configured successfully.
• It is strongly recommended to make a backup copy of configuration settings.
• After the EAP110’s network configuration is completed, please remember to change the IP
Address of your PC Connection Properties back to its original settings in order to ensure that
your PC functions properly in its real network environments.
14
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 16
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
3. Connect your AP to your Network
The following instructions depict how to establish the wireless coverage of your network. The AP will
connect to the network through its LAN port and provide wireless access to your network.
After having prepared the EAP110’s hardware for configuration, set the TCP/IP settings of administrator’s
computer to have a static IP Address of 192.168.1.10 and Subnet Mask of 255.255.255.0.
Step 1: Configuring the AP’s System Information
Enter the AP’s default IP Address (192.168.1.1) into the URL of a web browser.
Login via using Username: admin and Password: admin.
The WMI appears as shown below.
Web Management Interface Main Page (System Overview)
From here, click on the System icon to arrive at the following page. On this Page you can make
entries to the Name, Description, and Location fields as well as set the device’s time.
15
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 17
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
System Information Page
There are two methods of setting up the time: Manual (indicated by the option Set Date & Time) and
NTP.
The default is Manual and requires individual setup every time the system starts up. Simply choose a
time zone and set the time accordingly. When finished, click SAVE.
Manually Time Setup
The alternative is NTP. Upon selecting NTP under the Time field, the configuration changes to allow
up to two NTP servers. Simply enter a local NTP server’s IP Address (if available) or search online for
an NTP server nearest you. Set the time zone and click SAVE.
NTP Setup
16
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 18
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Step 2: Configuring the AP’s Network Settings
While still on this Page, click on the Network Interface tab to begin configuration of the network
settings.
Network Settings Page
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
If the deployment decides the AP will be getting dynamic IP Addresses from the connected network,
set Mode to DHCP; otherwise, set Mode to Static and fill in the required fields marked with a red
asterisk (IP Address, Netmask, Gateway, and Primary DNS Server) with the appropriate values for
the network. Click SAVE when you are finished to save changes that have been made.
17
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 19
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Step 3: Configure the AP’s Wireless General Settings
Click on the Wireless icon followed by the General tab. On this page we only need to choose the
Band and Channel that we wish to use.
Wireless General Settings Page
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
On this page, select the Band with which the AP is to broadcast its signal. The rest of the fields are
optional and can be configured at another time. Click SAVE if any changes have been made.
18
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 20
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
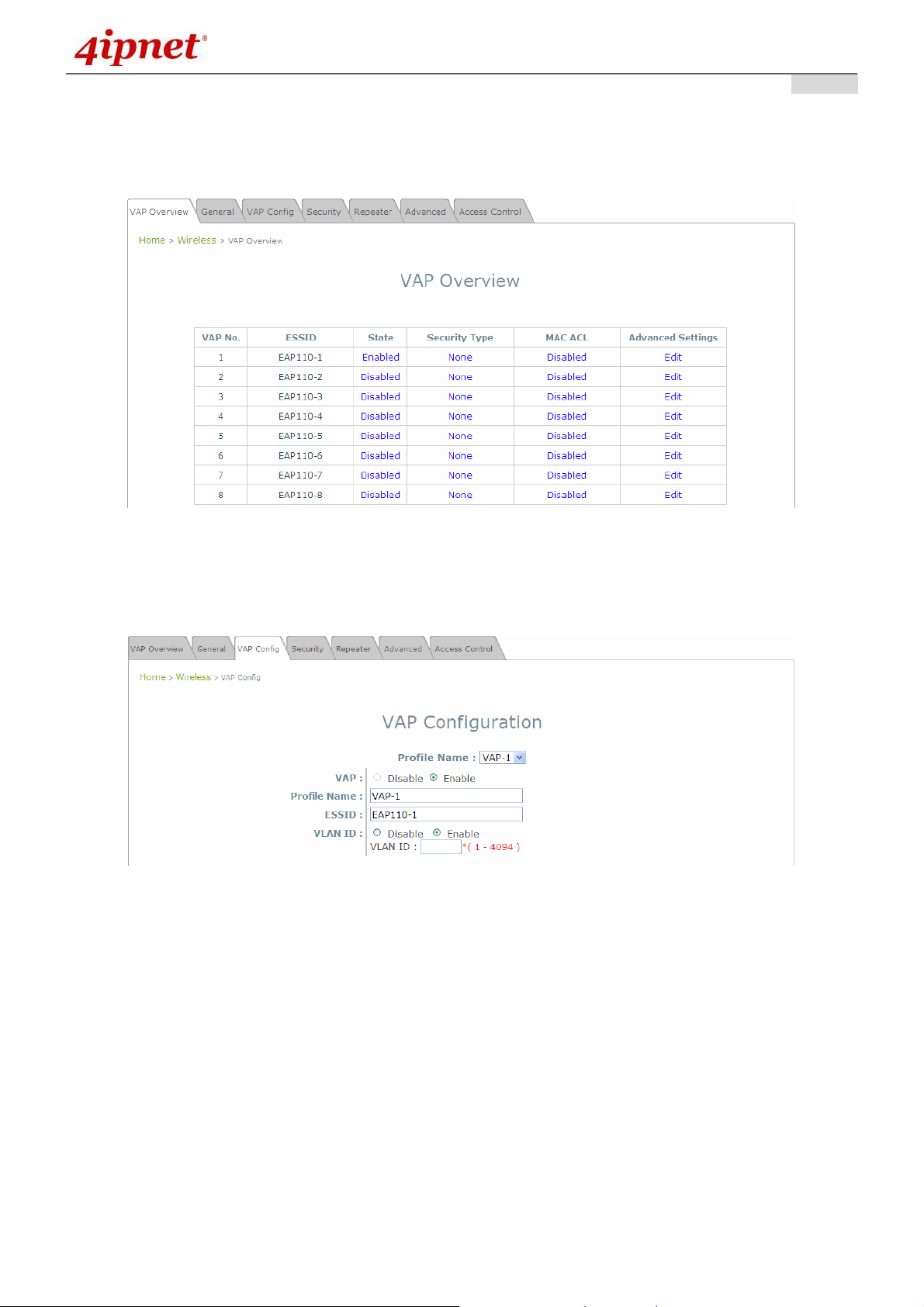
Step 4: Configuring Wireless Coverage (VAP-1)
To setup the AP’s wireless access, refer to the following VAP-1 configuration (other VAP configuration
can refer to the same setup steps as done for VAP-1). Click on the Overview tab to proceed.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Virtual AP Overview Page
On this page click the hyperlink in the row and column that corresponds with VAP-1’s State. This will
bring up the following page.
VAP Configuration Page (VAP-1 shown)
19
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 21

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
The desired VAP profile can be selected from the drop-down menu of Profile Name and VAP-1
configuration will serve as an example for all other VAPs. Before proceeding further, please make
sure that the VAP field is Enable; afterwards, enter an ESSID to represent the WLAN associated with
AP’s VAP-1. It is suggested that Profile Name is used to describe what this particular VAP will be
used for; otherwise, leave it as default. VLAN ID can be chosen at another time. Click SAVE to save
all changes up to this point and Reboot the system to apply these revised settings.
Congratulations!
After reboot, the AP can start to work with these revised settings.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
20
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 22
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
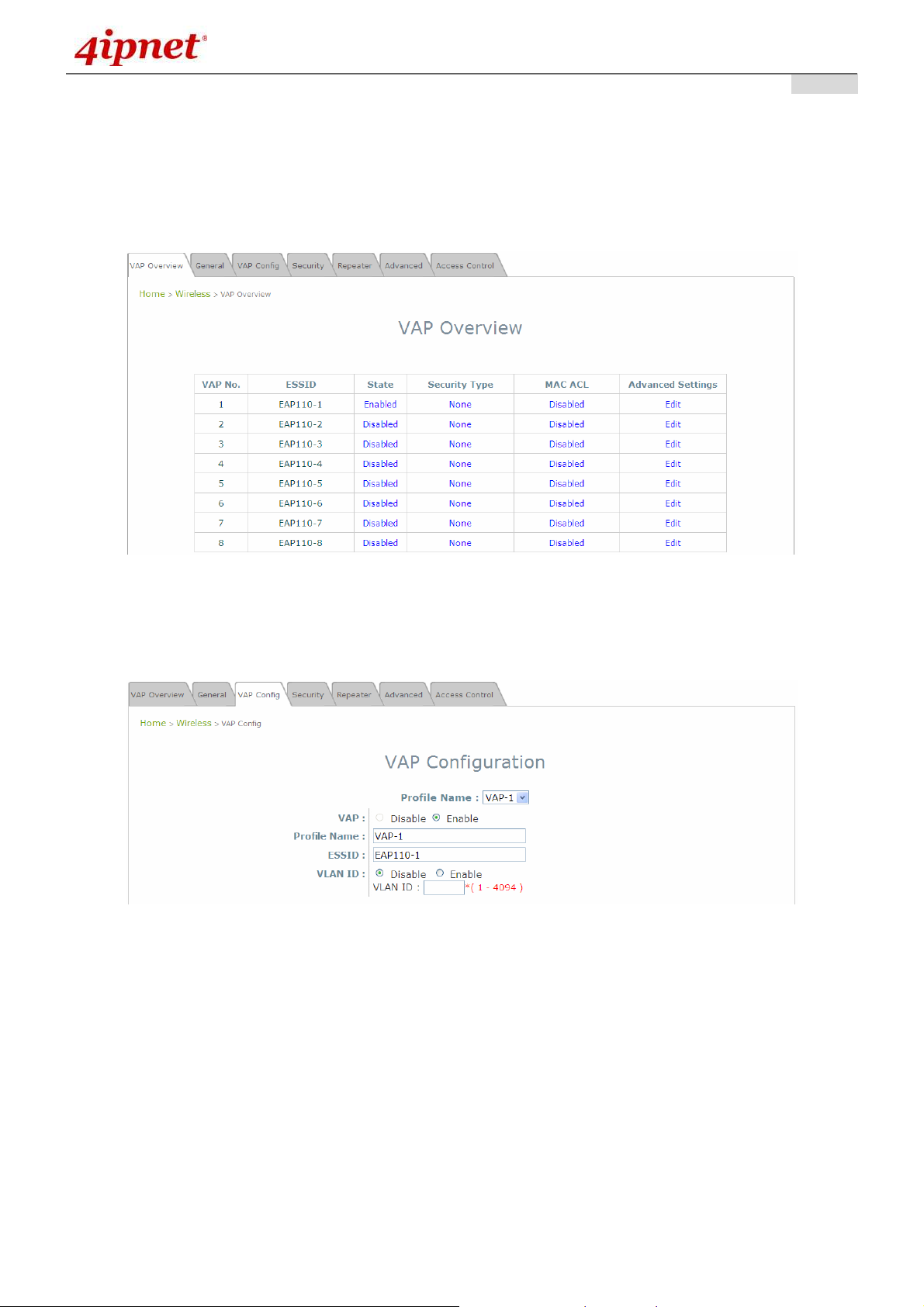
4. Adding Virtual Access Points
EAP110 possesses the feature of multi-ESSID; namely, it can behave as multiple virtual access points,
providing different levels of services from the same physical AP device.
Please click on the AP icon to review the VAP Overview page.
VAP Overview Page
To proceed with specific VAP configuration, click on the corresponding cell in the State column and
the row of the VAP; the particular VAP’s Configuration page will then appear for further configuration.
VAP Configuration Page (VAP-1 shown)
Please select the desired VAP profile from the drop-down menu of Profile Name. Choose Enable for
the VAP field. Pick a descriptive Profile Name and an appropriate ESSID for clients to associate to. A
VLAN ID can be provided to indicate the traffics through this particular VAP. It may allow further
management/control (e.g. access rights and Internet usage, etc) of each VAP with a management
gateway. Click SAVE and then Reboot for the changes to take effect.
21
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 23
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
5. Secure Your AP
Different VAP may require different level of security. These instructions will guide the user through setting
up different types of security for a particular VAP. Simply repeat the following steps for other VAP with
security requirement.
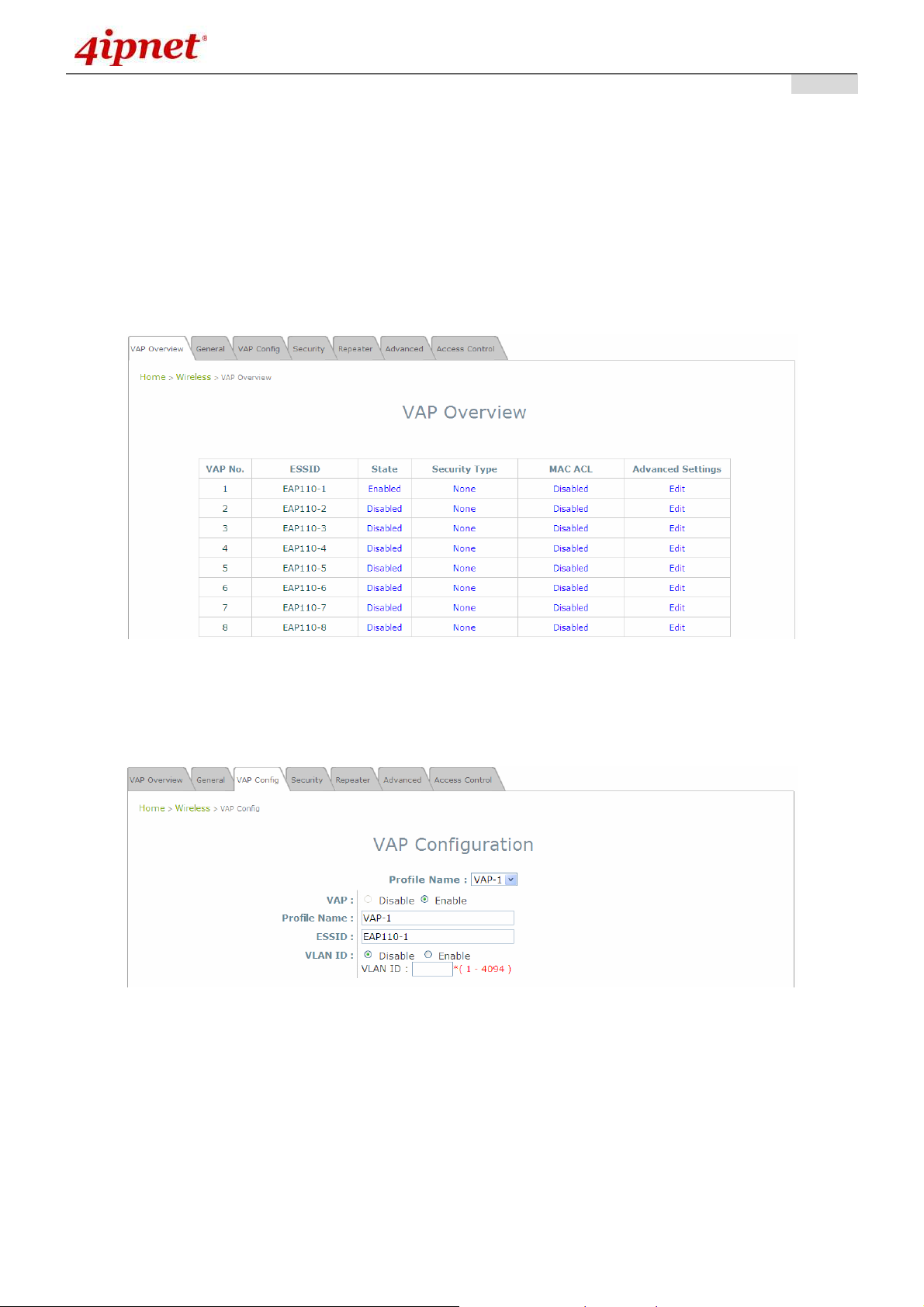
Step 1: Ensure the intended VAP is Enabled
VAP Overview Page
On the VAP Overview page, check the table to confirm the VAP State. If it is Enabled, skip to Step 2.
If not, click on to proceed with VAP Configuration for that particular VAP.
VAP Configuration Page (VAP-1 as shown for example)
Select Enable for the VAP field, and click SAVE. Click the Overview tab to return to the previous
table to begin the next step.
22
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 24
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Step 2: Configure Security Settings for your VAP
The following instructions will guide the user to set up wireless security with a specific VAP. If only
restricted access of certain MAC addresses is desired, skip to the Step3. MAC restriction can be
coupled with wireless security to provide extra protection.
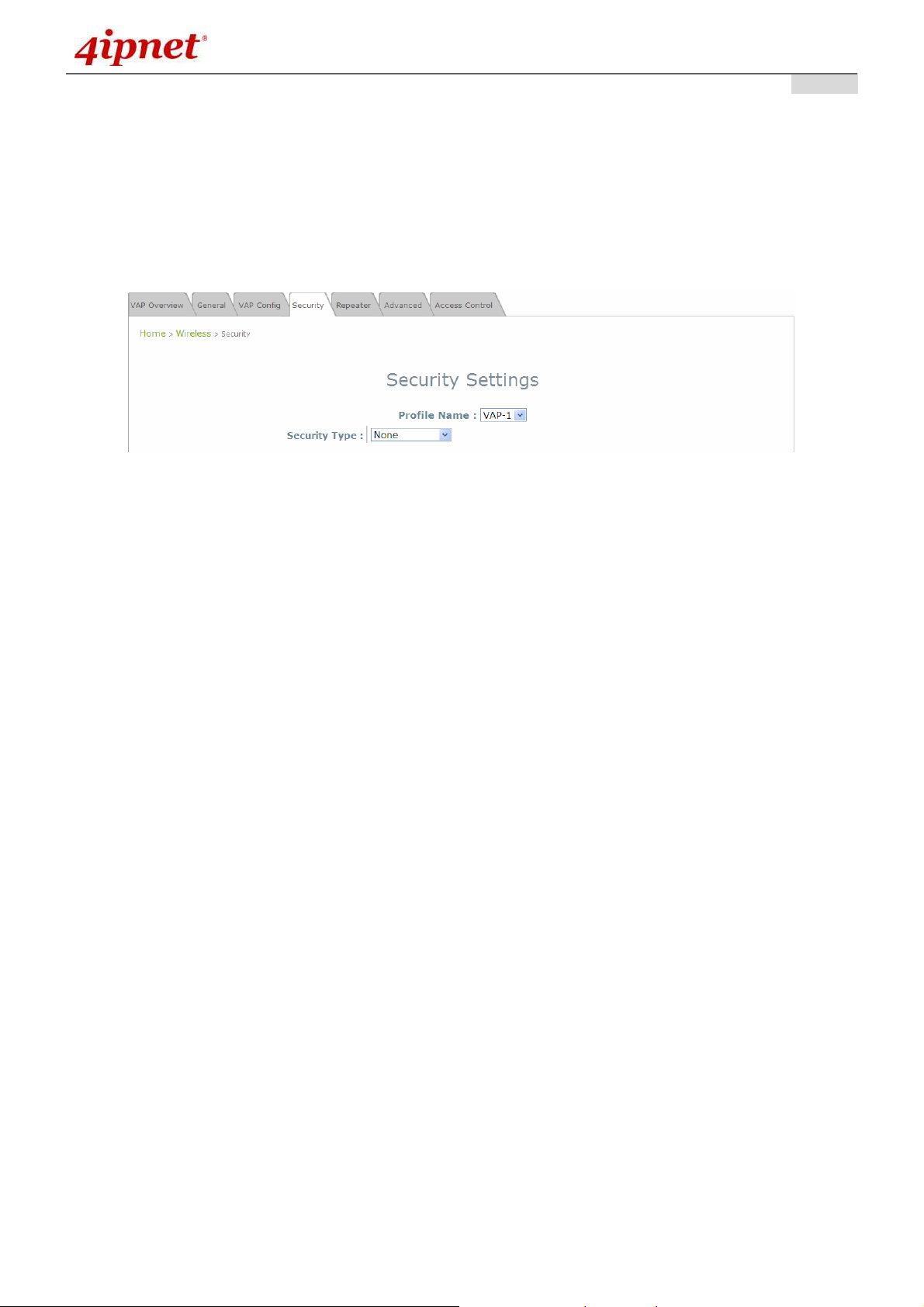
First, click on the corresponding cell in the column labeled Security Type. This hyperlink will direct
the user to the following Security Settings page.
Security Settings Page (VAP-1 as shown for example)
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Select the desired Security Type from the drop-down menu, which includes None, WEP, 802.1X,
WPA-PSK, and WPA-RADIUS.
23
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 25

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
• None: Authentication is not required and data is not encrypted during transmission when this option is
selected. This is the default setting as shown in the following figure.
Security Settings: None
• WEP: WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a data encryption mechanism with key length selected from
64-bit, or 128-bit.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Security Settings: WEP
802.11 Authentication: Select from Open System, Shared Key, or Auto.
WEP Key Length: Select from 64-bit, 128-bit key length.
WEP Key Format: Select from ASCII or Hex format for the WEP key.
WEP Key Index: Select a key index from 1 through 4. The WEP key index is a number that
specifies which WEP key is used for the encryption of wireless frames during data transmission.
WEP Keys: Provide the pre-defined WEP key value; the system supports up to 4 sets of WEP
keys.
24
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 26

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
• 802.1X: When 802.1X Authentication is selected, RADIUS authentication and enhanced dynamic
WEP are provided.
Security Settings: 802.1X Authentication
Dynamic WEP Settings:
o
Dynamic WEP: For 802.1X security type, Dynamic WEP is always enabled to automatically
generate WEP keys for encryption.
o
WEP Key Length: Select from 64-bit or 128-bit key length.
o
Rekeying Period: The time interval for the dynamic WEP key to be updated; the time unit is in
second.
RADIUS Server Settings:
o
Host: Enter the IP address or domain name of the RADIUS server.
o
Authentication Port: The port number used by the RADIUS server. Specify a port number or
use the default, 1812.
o
Secret Key: The secret key for the system to communicate with the RADIUS server.
25
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 27

• WPA-PSK:
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Provide shared key authenticaiton in WPA data encryption.
Security Settings: WPA-PSK
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Cipher Suite: Select an encryption method from TKIP (WPA), AES (WPA), TKIP (WAP2), AES
(WAP2), or Mixed.
Pre-shared Key Type: Select a pre-shared key type: PSK (Hex) or Passphrase.
Pre-shared Key: Enter the key value for the pre-shared key; the format of the key value depends
on the key type selected.
Group Key Update Period: The time interval for the Group Key to be renewed; the time unit is in
seconds.
26
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 28

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
• WPA-RADIUS:
WPA Settings:
o Cipher Suite: Select an encryption method from TKIP (WPA), AES (WPA), TKIP (WAP2), AES
Authenticate users by RADIUS and provide WPA data encryption.
Security Settings: WPA-RADIUS
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
(WAP2), or Mixed.
o Group Key Update Period: The time interval for the Group Key to be renewed; the time unit is
in seconds.
RADIUS Server Settings:
o Host: Enter the IP address or domain name of the RADIUS server.
o Authentication Port: The port number used by the RADIUS server. Specify a port number or
use the default, 1812.
o Secret Key: The secret key for the system to communicate with the RADIUS server.
When these configurations are finished and MAC restriction is not needed, click SAVE and then
Reboot the system. Otherwise, click on the Overview tab and proceed with the next step.
27
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 29

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Step 3: Configuring MAC ACL (Access Control List)
Clicking on the hyperlink corresponding with intended VAP in the MAC ACL column, the user will be
brought to the Access Control Settings page.
Access Control Settings Page
Please choose among Disable, Allow, and Deny from the drop-down menu of Access Control Type.
1) Disable Access Control: This means that there is no restriction for client devices to access the
system.
2) MAC ACL Allow List: This means that only the client devices (identified by their MAC addresses)
listed in the Allow List (“allowed MAC addresses”) are granted with access to the system. The
administrator can temporarily block any allowed MAC address by checking Disable, until the
administrator re-Enables the listed MAC.
MAC ACL Allow List
An empty Allow List means that there are no allowed MAC addresses. Make sure at least the MAC
of the modifying system is included (e.g. network administrator’s computer)
3) MAC ACL Deny List: This means that all client devices are granted with access to the system
except those listed in the Deny List (“denied MAC addresses”). The administrator can allow any
denied MAC address to connect to the system temporarily by checking Enable.
28
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 30

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
MAC ACL Deny List
Click SAVE and Reboot upon completing the related configurations to take effect.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
29
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 31

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
6. Create a WDS Bridge between two APs
WDS link creation will assist to extend network coverage where running wires is not an option, effectively
transferring the traffics to the other end of WLAN/LAN through the EAP110. Since this is a peer to peer
connection, both EAP110s will be configured by the same way.
Step 1: Make sure the Band and Channel are matched between the WDS peers
In order to create a valid WDS link, the two EAP110s must be configured to use the same channel
and band for their wireless settings. Click the AP icon and then General tab to go to the following
page.
Wireless General Settings Page
Please make sure both APs are using the same Band and Channel in order to establish a successful
WDS link. Click SAVE if any changes have been made.
30
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 32

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Step 2: Prevent Loops if Connecting Many APs
When many APs are linked in this manner, undesired loops may form to lower overall WLAN
performance. To prevent such occurrence, please make sure Layer 2 STP is enabled.
To turn on this feature, please click on the System and then Network Interface tab.
Network Settings Page
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Please select Enable in the field labeled Layer2 STP. This will prevent data from looping or a broadcast
storm. Click SAVE when completed, and then Reboot to allow updated settings to take effect.
31
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 33

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7. Web Management Interface Configuration
This chapter will guide the user through the EAP110’s detailed settings. The following table shows all the
User Interface (UI) functions of 4ipnet’s EAP110 Enterprise Access Point. The Web Management
Interface (WMI) is the page where the status is displayed, control is issued and parameters are configured.
The management functions are grouped into branches: System, Wireless, Firewall, Utilities, and Status.
Table 1 EAP110's Function Organization
OPTION FUNCTION
System Information
Network
System
Wireless
Firewall
Management
GRE Tunnel
CAPWAP
QoS Classification
VAP Overview
General
VAP Configuration
Security
Repeater
Advanced
Access Control
Firewall List
Service
Advanced
Change Password
Network Utilities
Utilities
Status
Save & Restore
System Upgrade
Reboot
Upload Certificate
Overview
Clients
Repeater
Event Log
32
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 34

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Click SAVE to save the changes, but the user must reboot the system upon the completion of all
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Note:
configurations for the changes to take effect. Upon clicking SAVE, the following message will
appear: “Some modification has been saved and will take effect after Reboot.”
All online users will be disconnected during reboot or restart.
33
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 35

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.1 System
Upon clicking on the System button, users can work on this section for general configurations of the
devices (e.g. Time Setup, Network Configurations, and System Logs). This section includes the following
functions: Information, Network, Management, GRE Tunnel, CAPWAP and QoS Classification.
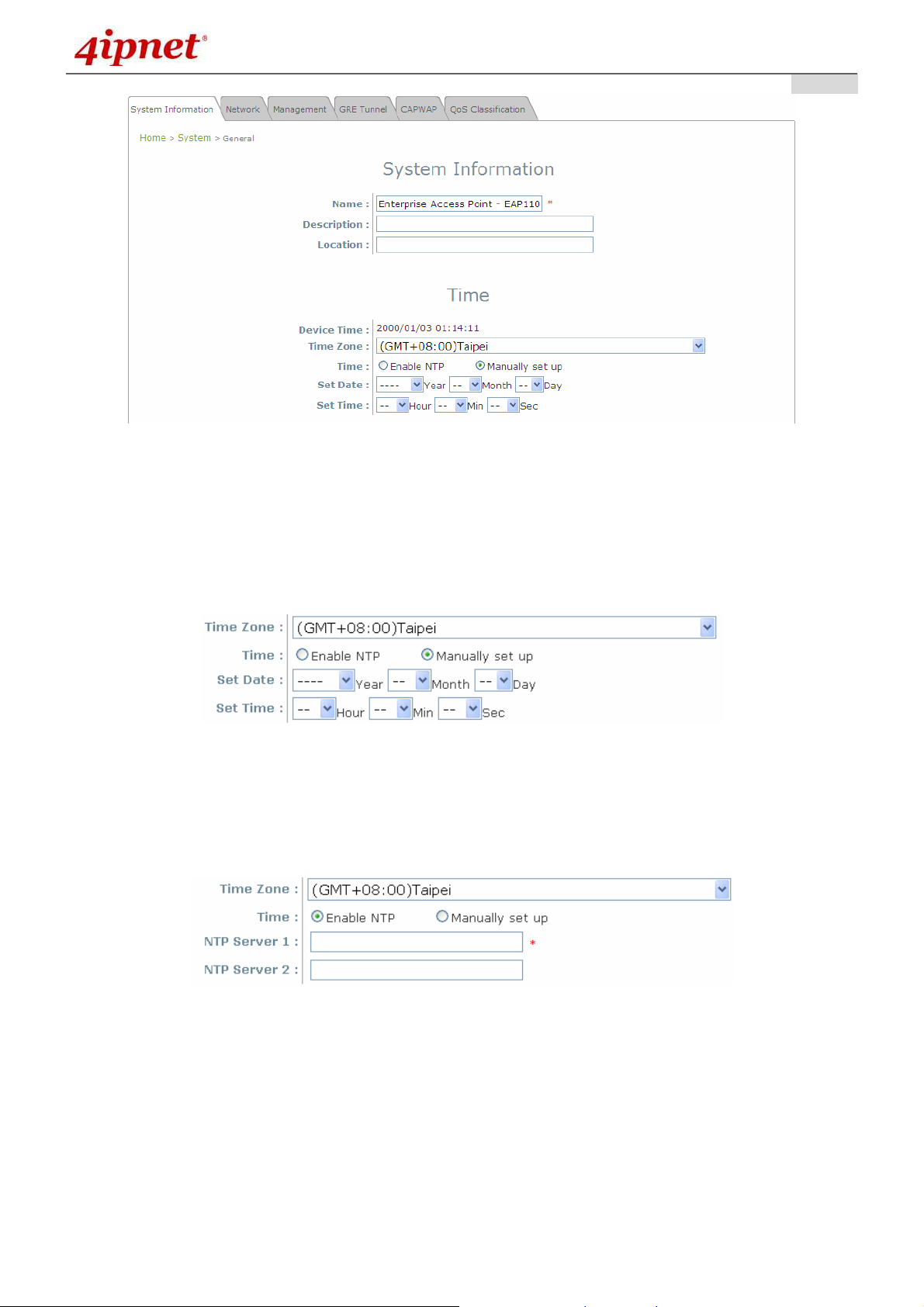
7.1.1 System Information
System Information Page
System Information
For maintenance purpose, it is highly recommended to have the following information stated as clearly
as possible:
Name: The system name used to identify this system.
Description: Further information about the system (e.g. device model, firmware version, and
active date).
Location: The information on geographical location of the system for the administrator to locate the
system easily.
Time
Device Time: Display the current time of the system.
Time Zone: Select an appropriate time zone from the drop-down list box.
Time: Synchronize the system time by NTP server or manual setup.
34
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 36

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
1) Enable NTP:
By selecting Enabled NTP, EAP110 can synchronize its system time with the NTP server
automatically. While this method is chosen, at least one NTP server's IP address or domain
name must be provided.
NTP Time Configuration Fields
Generally networks would have a common NTP server (internal or external). If there is, use that one,
otherwise locate a nearby NTP server on the web.
2) Manually set up:
By selecting Manually set up, the administrator can manually set the system date and time.
Manual Time Configuration Fields
▬
Set Date: Select the appropriate Year, Month, and Day from the drop-down menu.
▬
Set Time: Select the appropriate Hour, Min, and Sec from the drop-down menu.
Unless either Internet connection or NTP server may become unavailable, it is recommended to use
NTP server for time synchronization because system time needs to be reconfigured upon reboot.
35
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 37

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
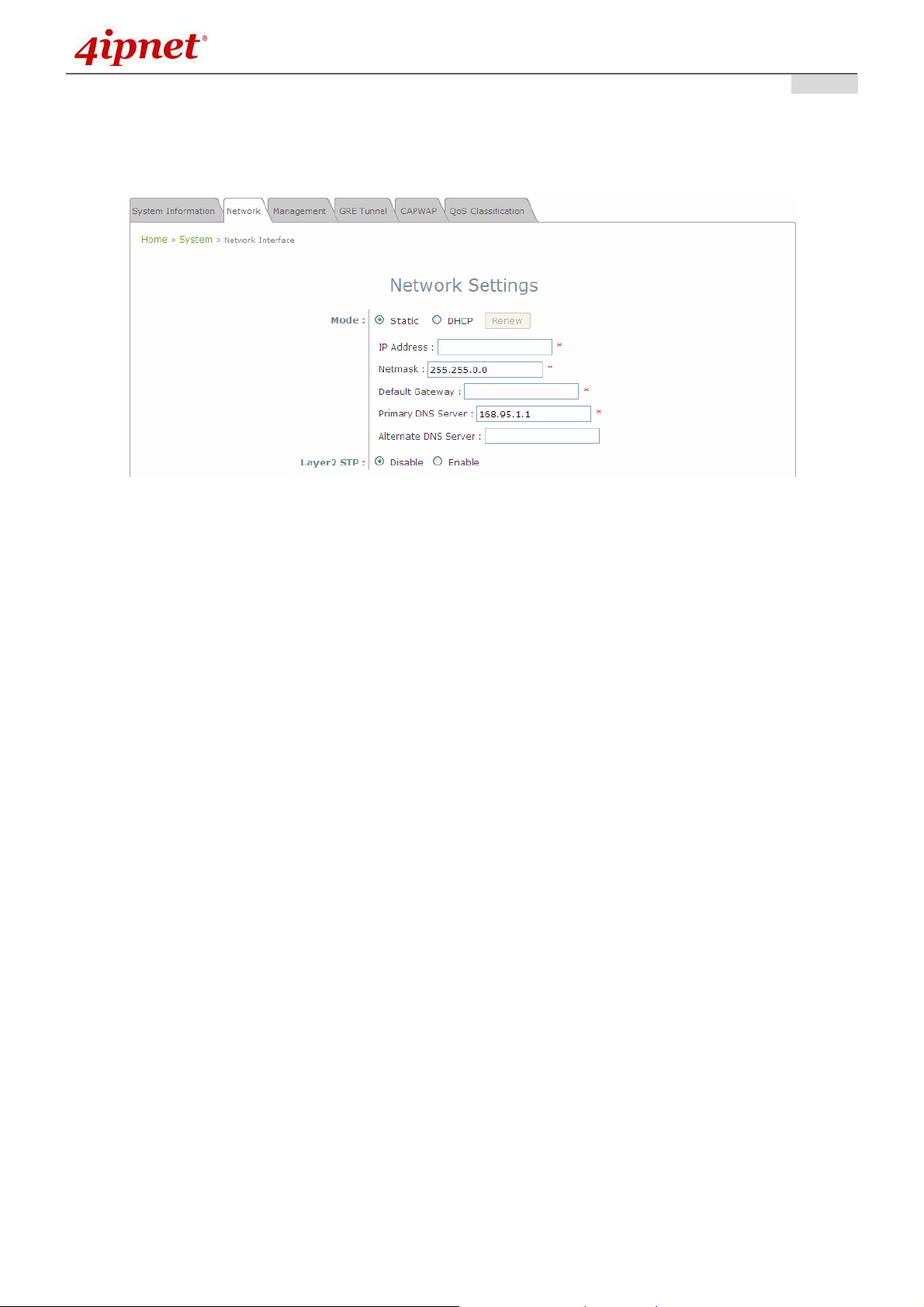
7.1.2 Network Interface
On this page, the network settings of the device can be configured; fields with a red asterisk (i.e. IP
Address, Netmask, Gateway, and Primary DNS Server) are mandatory.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Network Settings Page
• Mode: Determine the way to obtain the IP address, by DHCP or Static.
Static: The administrator can manually set up the static LAN IP address. All required fields are
marked with a red asterisk.
o IP Address: The IP address of the LAN port.
o Netmask: The Subnet mask of the LAN port.
o Default Gateway: The Gateway IP address of the LAN port.
o Primary DNS Server: The IP address of the primary DNS (Domain Name System) server.
o Alternate DNS Server: The IP address of the substitute DNS server.
DHCP: This configuration type is applicable when the system is connected to a network with the
presence of a DHCP server; all related IP information required will be provided by the DHCP server
automatically.
• Layer 2 STP: If the EAP110 is set up to bridge other network components, this option can be enabled to
prevent undesired loops because broadcasting storm may occur in a multi-switch environment where
broadcast packets are forwarded in an endless loop between switches. Moreover, a broadcast storm may
consume most of available system resources in addition to available bandwidth. Thus, enabling the Layer
2 STP can lower such undesired occurrence and derive the best available data path for network
communication.
36
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 38

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.1.3 Management
The management services (e.g. VLAN for Management, SNMP, and System log) can be configured
here.
Management Services Page
• VLAN for Management: When it is enabled, management traffics from the system will be tagged with a
VLAN ID. In other words, administrator who wants to access the WMI must send management traffics
with the same VLAN ID such as connecting to a specific VAP with the same VLAN ID. Enter a value
between 1 and 4094 for the VLAN ID if the option is enabled.
37
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 39

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
• SNMP Configuration: By enabling SNMP function, the administrator can obtain the system information
remotely.
SNMP Configuration Fields
Enable/ Disable: Enable or Disable this function.
Community String: The community string is required when accessing the Management Information
Base (MIB) of the system.
o Read: Enter the community string to access the MIB with Read privilege.
o Write: Enter the community string to access the MIB with Write privilege.
Trap: When enabled, events on Cold Start, Interface UP & Down, and Association & Disassociation
can be reported to an assigned server.
o Enable/ Disable: Enable or Disable this function.
o Server IP Address: Enter the IP address of the assigned server for receiving the trap report.
• System Log: By enabling this function, specify an external SYSLOG server to accept SYSLOG
messages from the system remotely.
System Log Fields
Enable/ Disable: Enable or Disable this function.
Server IP: The IP address of the Syslog server that will receive the reported events.
Server Port: The port number of the Syslog server.
Syslog Level: Select the desired level of received events from the drop-down menu.
38
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 40

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.1.4 GRE Tunnel
When GRE tunnel is created between EAP200 and the controller, EAP200 can be logically deployed into the
Controller’s managed network regardless of its physical location. If the tunnel is created from WHG series
controllers, all of the configuration should be performed on the Controller side. It is meaningless to configure
GRE tunnel settings from the EAP200 side. Once the settings are applied from the Controller side, the applied
settings such as Key string will be passed to the corresponding EAP200 and its WMI page will automatically
open to confirm the changes. Click Restart link and EAP200 will restart to activate the tunnel. A new window
will automatically open and display the tunnel settings from the AP side which is passed from the Controller.
Click the Reboot link to apply and activate the settings to AP. Please refer to your WHG manual for more
information regarding AP management with tunnels.
• GRE Tunnel: To enable, click Enable of GRE Tunnel.
Remote IP: Enter the IP address of the Controller.
Key: Set up a password for the connection.
• Interface: Select a VAP or WDS that its traffic will pass through the GRE Tunnel between APs and
controller. For how to enable VAP items, please refer the section 7.2.3 VAP Configuration for reference.
39
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 41

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.1.5 CAPWAP
CAPWAP is a standard interoperable protocol that enables a controller to manage a collection of wireless
access points. There are 5 ways of discovery, DNS SRV, DHCP option, Broadcast, Multicast, and Static.
Certificate Date Check: To enable this item, select Enable and click Manage Certificates to enter the
page of Upload Certificate. Please refer to the section 7.4.4. Upload Certificate.
DNS SRV Discovery: The way of using DNS SRV to discover acess controller.
Domain Name Suffix: Enter the suffix of the access controller, such as example.com.
DHCP Option Discovery: The way of using DHCP option to discover access controller.
Broadcast Discovery: The way of using Broadcast to discover access controller.
Multicast Discovery: The way of using muticast to discover access controller.
Static Discovery: The way of using Static approach to discover access controller.
AC Address: The IP address of access controller. If it can not discover the first AC, it will try to
discover the second AC.
40
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 42

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Manage Certificates
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
41
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 43

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
7.1.6 QoS Classification
Network Administrator can assign different traffic priorities in this page.
• Status: Check Enable to use QoS feature.
A total of 9 different VLAN IDs can be assigned a QoS class (voice, video, best effort,
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
background). AP will decide the traffic forwarding priorities based on the VLAN tag on the traffic
packet and its corresponding QoS class.
42
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 44

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.2 Wireless
This section includes the following functions: VAP Overview, General, VAP Configuration, Security,
Repeater, Advanced, and Access Control. EAP110 supports up to eight Virtual Access Points (VAPs).
Each VAP can have its own settings (e.g. ESSID, VLAN ID, security settings, etc.). With such VAP
capabilities, different levels of service can be configured to meet network requirements.
7.2.1 VAP Overview
An overall status is collected on this page, including ESSID, State, Security Type, MAC ACL, and
Advanced Settings, where EAP110 features 8 VAPs with respective settings. In this table, please click
on the hyperlink to further configure each individual VAP.
VAP Overview Page
43
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 45

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
• State: The hyperlink showing Enable or Disable connects to the VAP Configuration page.
VAP Overview Page – State
• Security Type: The hyperlink showing the security type connects to the Security Settings Page.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
VAP Overview Page – Security Type
44
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 46

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
• MAC ACL: The hyperlink showing Allow or Disable connects to the Access Control Settings Page.
VAP Overview Page – MAC ACL
• Advanced Settings: The advanced settings hyperlink connects to the Advanced Wireless Settings
Page.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
VAP Overview Page – Advanced Settings
45
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 47

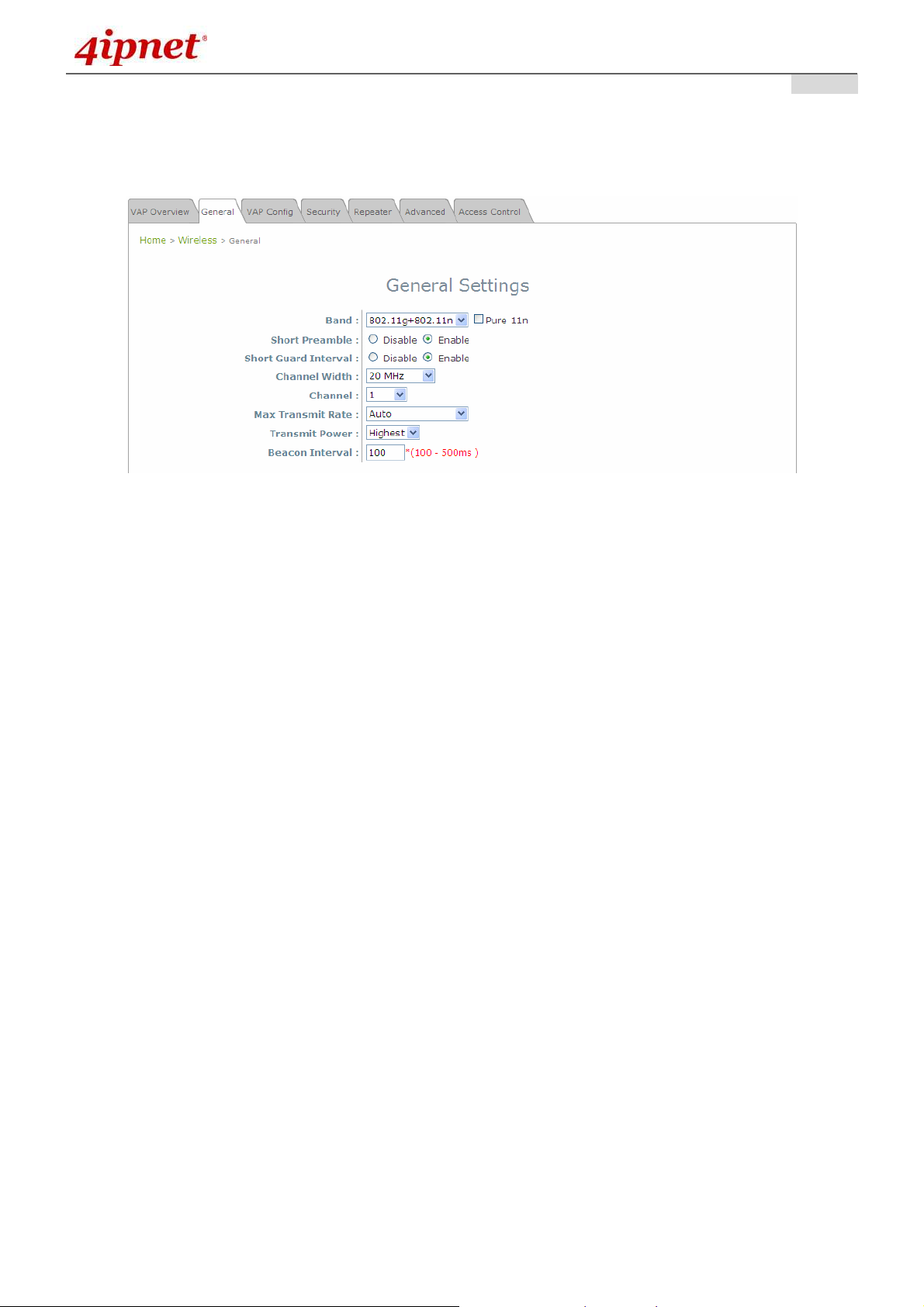
7.2.2 General
AP’s general wireless settings can be configured here:
AP General Settings Page
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
• Band: Select an appropriate wireless band: 802.11b, 802.11g, 802.11b+802.11g, 802.11g+802.11n
or select Disable if the wireless function is not required.
Pure 11n: When this option is checked, only clients with 802.11n capable device can
associate successfully with this AP.
• Short Preamble: The short preamble with a 56-bit synchronization field can improve WLAN
transmission efficiency. Select Enable to use Short Preamble or Disable to use Long Preamble with a
128-bit synchronization field.
• Short Guard Interval (available when Band is 802.11g+802.11n): The guard interval is the space
between symbols (characters) being transmitted to eliminate inter-symbol interference. In order to
further boost throughput with 802.11n, short guard interval is half of what it used to be; please select
Enable to use Short Guard Interval or Disable to use normal Guard Interval.
• Channel Width (available when Band is 802.11g+802.11n): Double channel bandwidth to 40 MHz
is supported to enhance throughput.
• Channel: Select the appropriate channel from the drop-down menu to correspond with your network
settings, for example, Channel 1-11 is available in North American and Channel 1-13 in Europe, or
choose the default Auto.
• Max Transmit Rate: The maximum wireless transmit rate can be selected from the drop-down menu.
The system will use the highest possible rate when Auto is selected.
• Transmit Power: The signal strength transmitted from the system can be selected among Auto,
Highest, High, Medium, Low, and Lowest from the drop-down menu.
• Beacon Interval (ms): Enter the desired time interval for the access point to send beacon signal.
46
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 48

Table 2 RF Configurations
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Band SSID
Disable N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A
802.11b
802.11g
802.11b+
802.11g
Associated
AP’s SSID
Associated
AP’s SSID
Associated
AP’s SSID
Short
Channel
Preamble
Auto, 1~11, 13
Disable/Enable
or 14
Auto, 1~11 or
Disable/Enable
13
Auto, 1~11, 13
Disable/Enable
or 14
Max Transmit
Rate
1M, 2M, 5.5M,
11M
6M, 9M, 12M,
18M, 24M,
36M, 48M, 54M
1M, 2M, 5.5M,
6M, 9M, 11M,
12M, 18M,
24M, 36M,
48M, 54M
1M, 2M, 5.5M,
Transmit
Power
Auto, Lowest,
Low, Medium,
High, Highest
6M, 9M, 11M,
802.11g+
802.11n
Note: Please note that available values above will vary depending on the regulation of the country.
Associated
AP’s SSID
Disable/Enable
Auto, 1~11, or
13
12M, 18M,
24M, 36M,
48M, 54M,
MCS0~15
47
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 49

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.2.3 VAP Configuration
This section provides configuration of each Virtual Access Point with settings such as Profile Name,
ESSID, and VLAN ID.
VAP Configuration Page
To enable specific VAP, select the VAP from the drop-down list of Profile Name. The basic settings of
each VAP are collected in the profile as follows:
• VAP: Enable or Disable this VAP.
• Profile Name: The profile name of specific VAP for identity / management purposes.
• ESSID: ESSID (Extended Service Set ID) serves as an identifier for clients to associate with the
specific VAP. It can be coupled with different service level like a variety of wireless security types.
• VLAN ID: EAP110 supports tagged VLANs (virtual LANs). To enable VLAN function, each VAP shall
be given a unique VLAN ID with valid values ranging from 1 to 4094.
48
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 50

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.2.4 Security
EAP110 supports various wireless authentication and data encryption methods in each VAP profile. With
this, the administrator can provide different service levels to clients. The security type includes None,
WEP, 802.1X, WPA-PSK, and WPA-RADIUS.
• None: Authentication is not required and data is not encrypted during transmission when this option is
selected. This is the default setting as shown in the following figure.
Security Settings: None
• WEP: WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy) is a data encryption mechanism based on a 64-bit, or 128-bit,
shared key algorithm.
Security Settings: WEP
49
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 51

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
802.11 Authentication: Select from Open System, Shared Key, or Auto.
WEP Key Length: Select from 64-bit, 128-bit key length.
WEP Key Format: Select from ASCII or Hex format for the WEP key.
WEP Key Index: Select a key index from 1~4. The WEP key index is a number that specifies
which WEP key will be used for the encryption of wireless frames during data transmission.
WEP Keys: Provide the pre-defined WEP key value; the system supports up to 4 sets of WEP
keys.
• 802.1X: When 802.1X Authentication is selected, RADIUS authentication and Dynamic WEP are
provided.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Security Settings: 802.1X Authentication
50
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 52

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Dynamic WEP Settings:
o
Dynamic WEP: For 802.1X security type, Dynamic WEP is always enabled to automatically
generate WEP keys for encryption.
o
WEP Key Length: Select from 64-bit or 128-bit key length.
o
Re-keying Period: The time interval for the dynamic WEP key to be updated; the time unit is in
second.
RADIUS Server Settings (Primary/Secondary):
o
Host: Enter the IP address or domain name of the RADIUS server.
o
Authentication Port: The port number used by the RADIUS server. Specify a port number or
use the default, 1812.
o
Secret Key: The secret key for the system to communicate with the RADIUS server.
• WPA-PSK: WPA-PSK (Wi-Fi Protected Access Pre-shared Key) is a pre-shared key authentication
method, a special mode of WPA.
Security Settings: WPA-PSK
Cipher Suite: Select an encryption method from TKIP (WPA), AES (WPA), TKIP (WAP2), AES
(WAP2), or Mixed.
Pre-shared Key Type: Select a pre-shared key type: PSK (Hex) or Passphrase.
Pre-shared Key: Enter the key value for the pre-shared key; the format of the key value depends
on the key type selected.
Group Key Update Period: The time interval for the Group Key to be renewed; the time unit is in
seconds.
51
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 53

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
WPA-RADIUS: If this option is selected, the RADIUS authentication and data encryption will be
both enabled.
Security Settings: WPA-RADIUS
WPA Settings:
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
o Cipher Suite: Select an encryption method from TKIP (WPA), AES (WPA), TKIP(WAP2), AES
(WAP2), or Mixed.
o Group Key Update Period: The time interval for the Group Key to be renewed; the time unit is
in seconds.
RADIUS Server Settings (Primary/Secondary):
o Host: Enter the IP address or domain name of the RADIUS server.
o Authentication Port: The port number used by the RADIUS server. Specify a port number or
use the default, 1812.
o Secret Key: The secret key for the system to communicate with the RADIUS server.
52
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 54

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.2.5 Repeater
To extend wireless network coverage, EAP110 supports either WDS or None as options of repeater
types; selecting None will turn off this function.
WDS
If WDS is selected, EAP110 can support up to 4 WDS links to its peer APs. Security Type (None,
WEP, or WPA/PSK) can be configured to decide which encryption to be used for WDS connections
respectively. Please fill in remote peer’s MAC address and click SAVE to proceed; if setting revision is
necessary, CLEAR button is used to clear the contents in the above WDS connection list.
Repeater Settings: WDS
53
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 55

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.2.6 Advanced
The advanced wireless settings for the EAP110’s VAP (Virtual Access Point) profiles allow customization
of data transmission settings. The administrator can tune the following parameters to improve network
communication performance if a poor connection occurs.
Advanced Wireless Settings Page
• RTS Threshold: Enter a value between 1 and 2346. RTS (Request to Send) Threshold determines
the packet size at which the system issues a request to send (RTS) before sending the fragment to
prevent the hidden node problem. The RTS mechanism will be activated if the data size exceeds the
value provided. A lower RTS Threshold setting can be useful in areas where many client devices are
associating with EAP110 or in areas where the clients are far apart and can detect only EAP110 but
not each other.
• Fragmentation Threshold: Enter a value between 256 and 2346. The default is 2346. A packet size
larger than this threshold will be fragmented (sent with several pieces instead of one chunk) before
transmission. A smaller value results in smaller frames but allows a larger number of frames in
transmission. A lower Fragment Threshold setting can be useful in areas where communication is
poor or disturbed by a serious amount of radio interference.
• Broadcast SSID: Disabling this function will prevent the system from broadcasting its SSID. If
broadcast of the SSID is disabled, only devices that have the correct SSID can connect to the system.
• Wireless Station Isolation: By enabling this function, all stations associated with the system are
isolated and can only communicate with the system.
• WMM: The default is Disable. Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) is a Quality of Service (QoS) feature that
prioritizes wireless data packets based on four access categories: voice, video, best effort, and
background. Applications without WMM and applications that do not require QoS are assigned to the
best-effort category, which receives a lower priority than that of voice and video. Therefore, WMM
decides which data streams are more important and assigns them a higher traffic priority. This option
works with WMM-capable clients only.
54
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 56

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.2.7 Access Control
On this page, the network administrator can restrict the total number of clients connected to the EAP110,
as well as specify particular MAC addresses that can or cannot access the device.
Access Control Settings Page
• Maximum Number of Clients
EAP110 supports various methods of authenticating clients for wireless LAN access. The default
policy is unlimited access without any authentication required. To restrict the station number of
wireless connections, simply change the Maximum Number of Stations to a desired number. For
example, while the number of stations is set to 20, only 20 stations are allowed to connect to the
specified VAP. The maximum number of clients supported by the system is up to 128.
55
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 57

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
• Access Control Type
The administrator can restrict the wireless access of client devices based on their MAC addresses.
Disable Access Control: When Disable is selected, there is no restriction for client devices to
access the system.
MAC ACL Allow List: When selecting MAC ACL Allow List, only the client devices (identified by
their MAC addresses) listed in the Allow List (“allowed MAC addresses”)are granted with access to
the system. The administrator can temporarily block any allowed MAC address by checking
Disable, until the administrator re-Enables the listed MAC.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Note:
MAC Allow List
An empty Allow List means that there is no allowed MAC address. Make sure at least the MAC
of the management system is included (e.g. network administrator’s computer)
56
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 58

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
MAC ACL Deny List: When selecting MAC ACL Deny List, all client devices are granted with
access to the system except those listed in the Deny List (“denied MAC addresses”). The
administrator can allow any denied MAC address to connect to the system temporarily by checking
Disable.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
Deny List
57
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 59

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.3 Firewall
The system provides an added security feature, Layer2 Firewall, in addition to typical AP security. Layer2
Firewall offers a firewall function that is tailored specifically for Layer2 traffics, providing another choice of
shield against possible security threats coming from/going to WLAN (AP interfaces); hence, besides
firewall policies configured on gateways, this extra security feature will assist to mitigate possible security
breach. This section provides information in the following functions: Firewall Settings, Service and
Advanced Firewall Settings.
7.3.1 Firewall List
It provides an overview of firewall rules in the system; 6 default rules with up to total 20 firewall rules are
available for configuration.
Firewall List Page
58
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 60

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
From the overview table, each rule is designated with the following field;
No.: The numbering will decide the priority to let system carry out the available firewall rules in the
tables.
State: The check marks will enable the respective rules.
Action: DROP denotes a block rule; ACCEPT denotes a pass rule.
Name: It shows the name of rule.
EtherType: It denotes the type of traffics subject to this rule.
Remark: It shows the note of this rule.
Setting: 4 actions are available; Del denotes to delete the rule, Ed denotes to edit the rule, In
denotes to insert a rule, and Mv denotes to move the rule.
>>To delete a specific rule,
Del in Setting column of firewall list will lead to the following page for removal confirmation. After SAVE
button is clicked and system reboot, the rule will be removed.
>>To edit a specific rule,
Ed in Setting column of firewall list will lead to the following page for detail configuration. From this page,
the rule can be edited from scratch or an existing rule for revision.
Rule ID: The numbering of this specific rule will decide its priority among available firewall rules in
the table.
59
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 61

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Rule name: The rule name can be specified here.
EtherType: The drop-down list will provide the available types of traffics subject to this rule.
Interface: It can indicate inbound/outbound direction with desired interfaces.
Service (when EtherType is IPv4): Select the available upper layer protocols/services from the drop-
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
down list.
DSAP/SSAP (when EtherType is IEEE 802.3): The value can be further specified for the fields in
802.2 LLC frame header.
Type (when EtherType is IEEE802.3): The field can be used to indicate the type of encapsulated
traffics.
VLAN ID (when EtherType is 802.1 Q): The VLAN ID is provided to associate with certain VLANtagging traffics.
Priority (when EtherType is 802.1 Q): It denotes the priority level with associated VLAN traffics.
Encapsulated Type (when EtherType is 802.1 Q): It can be used to indicate the type of
encapsulated traffics.
Opcode (when EtherType is ARP/RARP): This list can be used to specify the ARP Opcode in ARP
header.
Source: MAC Address/Mask indicates the source MAC; IP Address/Mask indicates the source IP
address (when EtherType is IPv4); ARP IP/MAC & MASK indicate the ARP payload fields.
Destination: MAC Address/Mask indicates the destination MAC; IP Address/Mask indicates the
destination IP address (when EtherType is IPv4); ARP IP/MAC & MASK indicate the ARP payload
fields.
Action: The rule can be chosen to be Block or Pass.
Remark: The note of this rule can be specified here.
When the configuration for firewall rule is provided; please click SAVE and Reboot system to let the
firewall rule take effort.
60
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 62

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
>>To insert a specific rule,
In in Setting column of firewall list will lead to the following page for detail configuration with rule ID for
the current inserted rule.
From this page, the rule can be edited form scratch or from an existing rule for revision.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
>>To move a specific rule,
MV in Setting column of firewall list will lead to the following page for reordering confirmation. After SAVE
button is clicked and system reboot, the order of rules will be updated.
Please make sure all desired rules (state of rule) are checked and saved in overview page; the rule will be
enforced upon system reboot.
61
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 63

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
62
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 64

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.3.2 Service
The administrator can add or delete firewall service here; the services in this list will become options to
choose in firewall rule (when EtherType is IPv4).
EAP110 provides a list of rules to block or pass traffics of layer-3 or above protocols. These services are
available to choose from drop-down list of layer2 firewall rule edit page with Ether Type to be IPv4. The first
28 entries are default services and the administrator can add/delete any extra desired services.
There are 28 firewall services available in default settings; these default services cannot be deleted but can
be disabled. If changes are made, please click SAVE to save the settings before leaving this page.
Firewall Service Page
63
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 65

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.3.3 Advanced
Advanced firewall settings are used to supplement the firewall rules, providing extra security enhancement
against DHCP and ARP traffics traversing the available interfaces of system.
Trust Interface: Each VAP interface can be checked individually to mark as trusted interfaces;
security enforcements on DHCP/ARP like DHCP snooping and ARP inspection will be carried out on
non-trusted interfaces.
DHCP Snooping: When enabled, DHCP packets will be validated against possible threats like
DHCP starvation attack; in addition, the trusted DHCP server (IP/MAC) can be specified to prevent
rouge DHCP server.
ARP Inspection: When enabled, ARP packets will be validated against ARP spoofing.
Force DHCP option when enabled, the AP only learns MAC/IP pair information through
DHCP packets. Since devices configured with static IP address does not send DHCP
traffic, therefore any clients with static IP address will be blocked from internet access
unless its MAC/IP pair is listed and enabled on the Static Trust List.
Trust List Broadcast can be enabled to let other AP (with L2 firewall feature) learn the
trusted MAC/IP pairs to issue ARP requests.
Static Trust List can be used to add MAC or MAC/IP pairs of devices that are trusted to
issue ARP request. Other network nodes can still send their ARP requests; however, if
their IP appears in the static list (with different MAC), their ARP requests will be dropped
to prevent eavesdropping.
If any settings are made, please click SAVE to save the configuration before leaving this page.
64
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 66

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.4 Utilities
The administrator can maintain the system on this page: Change Password, Network Utilities, Config
Save & Restore, System Upgrade, Reboot, and Upload Certificate.
7.4.1 Change Password
To protect the Web Management Interface from unauthorized access, it is highly recommended to change
the administrator’s password to a secure password. Only alpha-numeric characters are allowed, and it is
also recommended to make use of a combination of both numeric and alphabetic characters.
Change Password Page
The administrator can change password on this page. Enter the original password (“admin”) and new
password, and then re-enter the new password in the Re-enter New Password field. Click SAVE to save
the new password.
65
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 67

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.4.2 Network Utilities
This page provides to ping external hosts from the AP. The result will be displayed in the windows below.
Network Utilities Page
66
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 68

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.4.3 Save & Restore
This function is used to backup and restore the EAP110 settings. The EAP110 can also be restored to
factory defaults using this function. It can be used to duplicate settings to other access points (backup
settings of this system and then restore on another AP).
Backup & Restore Page
• Reset to Default:
Click Reset to load the factory default settings of EAP110. A pop-up Page will appear to reconfirm
the request to reboot the system. Click OK to proceed.
Reboot Confirmation Prompt
A warning message as displayed below will appear during the reboot period. The system power
must be kept turn on before the completion of the reboot process.
The System Overview page will appear upon the completion of reboot.
• Backup System Settings: Click Backup to save the current system settings to a local disk such as
the hard disk drive (HDD) of a local computer or a compact disc (CD).
• Restore System Settings: Click Browse to search for a previously saved backup file, and then click
Upload to restore the settings. The backup file will replace the active configuration file currently
running on the system.
After network parameters have been reset / restored, the network settings of the administrator PC
may need to be changed to ensure that the IP address of the administrator PC is on the same
subnet mask as the EAP110.
67
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 69

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.4.4 System Upgrade
The EAP110 provides a web firmware upload / upgrade feature. The administrator can download the
latest firmware from the website and save it on the administrator’s PC. To upgrade the system firmware,
click Browse to choose the new firmware file you downloaded onto your PC and then click Upload to
execute the process. There will be a prompt confirmation message appearing to notify the administrator to
restart the system after a successful firmware upgrade. Please restart the system after upgrading the
firmware.
Note:
System Upgrade Page
• It is recommended to check the firmware version number before proceeding further.
Please make sure you have the correct firmware file.
• Firmware upgrade may sometimes result in the loss of some data. Please ensure that all
necessary settings are written down before upgrading the firmware.
• During firmware upgrade, please do not turn off the power. This may permanently
damage the system.
68
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 70

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.4.5 Reboot
This function allows the administrator to restart the EAP110 safely. The process shall take about three
minutes. Click Reboot to restart the system. Please wait for the blinking timer to complete its countdown
before accessing the system’s Web Management Interface again. The System Overview page will appear
after reboot successfully.
Occasionally, it is necessary to reboot the EAP110 to ensure that parameter changes are submitted.
Reboot Page
69
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 71

7.4.6 Upload Certificate
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
Upload Certificate Page
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
AP’s Certificate can be managed under this tab page.
Upload Private Key: Upload the private key for decryption.
Upload Certificate: Network Administrator can upload other certificates for SSL verification.
Upload Trusted Certificate: Network Administrator can upload other trusted certificates for SSL
verification.
Use Default Certificate: When the network administrator wishes to use AP’s default certificate and
key, click this button and restart the AP.
70
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 72

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
7.5 Status
This page is used to view the current condition and state of the system and includes the following
functions: Overview, Clients, Repeater and Event Log.
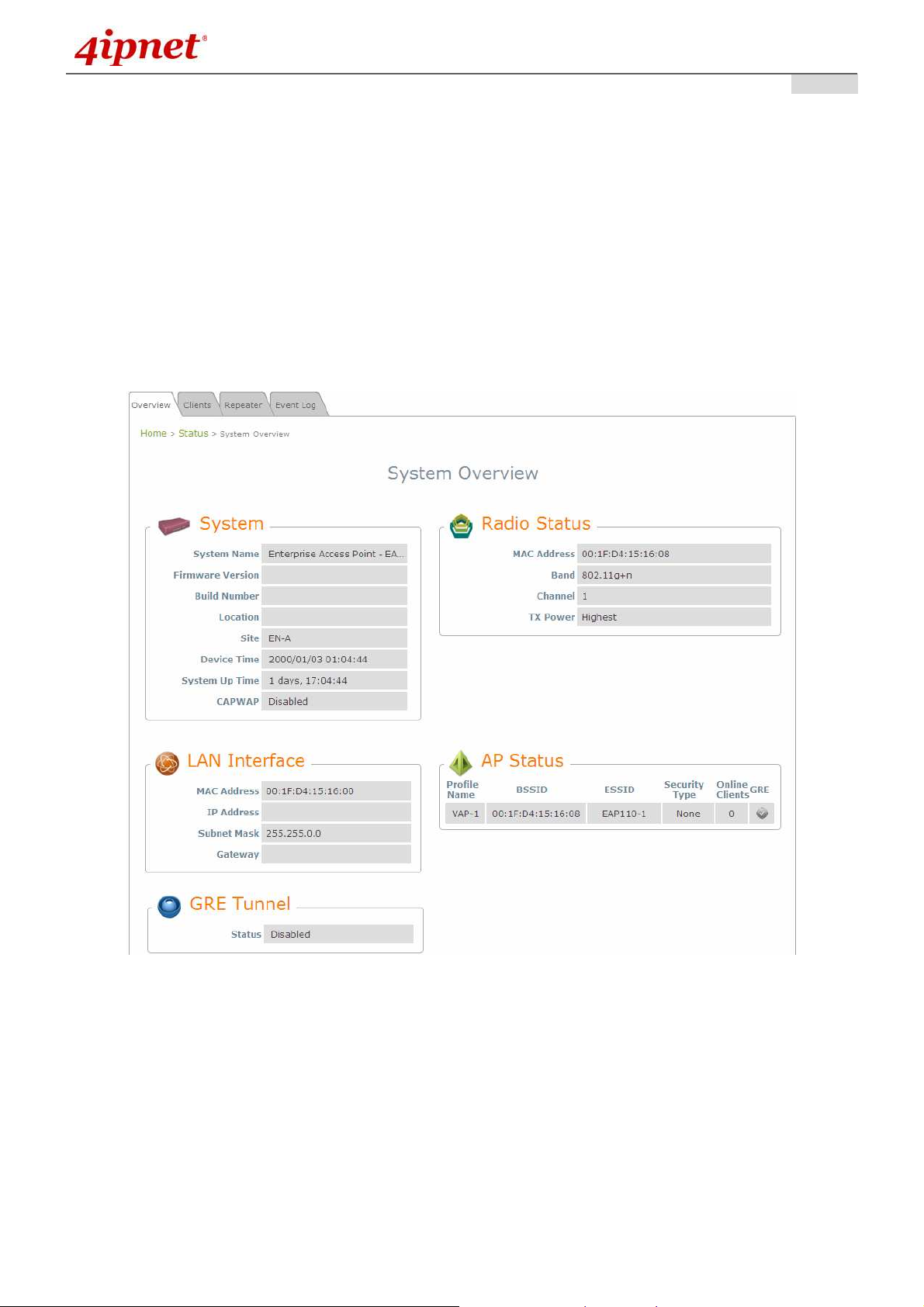
7.5.1 Overview
The System Overview page provides an overview of the system status for the administrator.
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
System Overview Page
71
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 73

Table 3 Status Page's Organizational Layout
Item Description
System Name The system name of the EAP110.
Firmware Version The present firmware version of the EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
System
LAN Interface
Radio Status
Build Number
The present firmware build number of the
EAP110
Location The location of the EAP110.
Site The site of the EAP110
Device Time The system time of the EAP110.
The time that the system has been rebooted in
System Up Time
operation.
MAC Address The MAC address of the LAN Interface.
IP Address The IP address of the LAN Interface.
Subnet Mask The Subnet Mask of the LAN Interface.
Gateway The Gateway of the LAN Interface.
MAC Address The MAC address of the RF Card.
Band The RF band in use.
Channel The channel specified.
Tx Power Transmit Power level of RF card.
Profile Name The profile name of AP
BSSID Basic Service Set ID
AP Status
ESSID Extended Service Set ID
Security Type Security type of the Virtual AP.
Online Clients The number of online clients.
72
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 74

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.5.2 Clients
The administrator can remotely oversee the status of all associated clients on this page. When a low SNR
is found here, the administrator can tune the corresponding parameters or investigate the settings of
associated clients to improve network communication performance.
Associated Client Status Page
• Associated VAP: The name of a VAP (Virtual Access Point) that the client is associated with.
• ESSID: The Extended Service Set ID which the client is associated with.
• MAC Address: The MAC address of associated clients.
• SNR: The Signal to Noise Ratio of respective client’s association.
• Idle Time: Time period that the associated client is inactive; the time unit is in second.
• Disconnect: Upon clicking Kick, the client will be disconnected with the system.
73
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 75

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.5.3 Repeater
The system supports 3 options of Repeater types including status of MAC Address, SNR, TX Rate, TX
Count and TX Errors.
WDS Link Status Page
• WDS Link Status: The table will indicate the link status of all WDS interfaces.
Status: The status of the WDS link either Enabled or Disabled.
MAC Address: The MAC Address of the WDS peer.
RSSI: Received Signal Strength Indication, a measurement of received radio signal over WDS link.
TX Rate: The transmit rate of the WDS link.
TX Count: The accumulative number of transmission counts.
TX Errors: The accumulative number of transmission errors.
74
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 76

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.5.4 Event Log
The Event Log provides the records of system activities. The administrator can monitor the system status
by checking this log.
Event Log Page
In the log each line represents an event record; in each line, there are 4 fields:
• Date / Time: The time & date when the event happened.
• Hostname: Indicates which host recorded this event. Note that all events on this page are local
events, so the hostname in this field is always the same. However, in remote SYSLOG service, this
field will help the administrator identify which event is from this EAP110.
• Process name: Indicate the event generated by the running instance.
• Description: Description of the event.
To save the file locally, click SAVE LOG; to clear all of the records, click CLEAR.
75
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
Page 77

EAP110
EAP110 Enterprise Access Point ENGLISH
EAP110EAP110
User’s Manual
User’s Manual
User’s ManualUser’s Manual
7.6 Online Help
The Help button is at the upper right corner of the display screen.
Click Help for the Online Help window, and then click the hyperlink of the relevant information needed.
Online Help Corner
Online Help Page
P/N: V11020110818
76
Copyright © 4IPNET, INC.
 Loading...
Loading...