Page 1

3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Absolut-Drucksensor U11320
Bedienungsanleitung
10/08 Hh
1. Sicherheitshinweise
• Um dauerhafte Beschädigungen des eingebau-
ten Halbleitersensors zu vermeiden, den maximalen Grenzdruck von 1000 kPa keinesfalls
überschreiten!
• Nur für nicht-korrodierende Gase wie Luft,
Helium und Stickstoff geeignet!
• Das Sensorelement nicht mit Wasser in Berüh-
rung bringen!
2. Beschreibung
Absolut-Drucksensor mit weitem Messbereich geeignet für Experimente zum Boyle-Mariott’schen
Gesetz und zur Messung des Kolbendrucks (pVDiagramm) im Stirlingmotor sowie zur Erfassung
der O2-Produktion bei der Fotosynthese und für
Transpirationsversuche in abgeschlossenen System.
Zweitor-Messverfahren des Sensors: Anschluss 1 via
Anschlussstutzen mit dem Aussendruck verbunden,
Anschluss 2 mit einem gekappselten Referenzvakuum verschlossen.
Die Sensorbox besitzt eine automatische Erkennung
durch das Interface.
3. Lieferumfang
1 Sensorbox
1 MiniDIN-Anschlusskabel 8-pin, 60 cm lang
1 Silikonschlauch, Øinnen 2 mm, 1 m lang
1 Kunststoffspritze 20 ml
4. Technische Daten
Messbereich: 0 bis 250 kPa
Sensortyp: Halbleitersensor
Genauigkeit: ± 1 %
Auflösung: 0,1 Pa
Anschluss: Schlauchwelle 4,8 mm Ø
5. Bedienung
• Den Silikonschlauch in der Gesamtlänge ver-
wenden oder auf die erforderliche Länge kürzen.
• Die Druckquelle mittels des Schlauchstücks an
der Schlauchwelle des Sensors anschließen.
• Beim Experiment die Elastizität des Schlauches
berücksichtigen – dies führt ggfs. zu einer Verfälschung des Messwertes.
1
Page 2
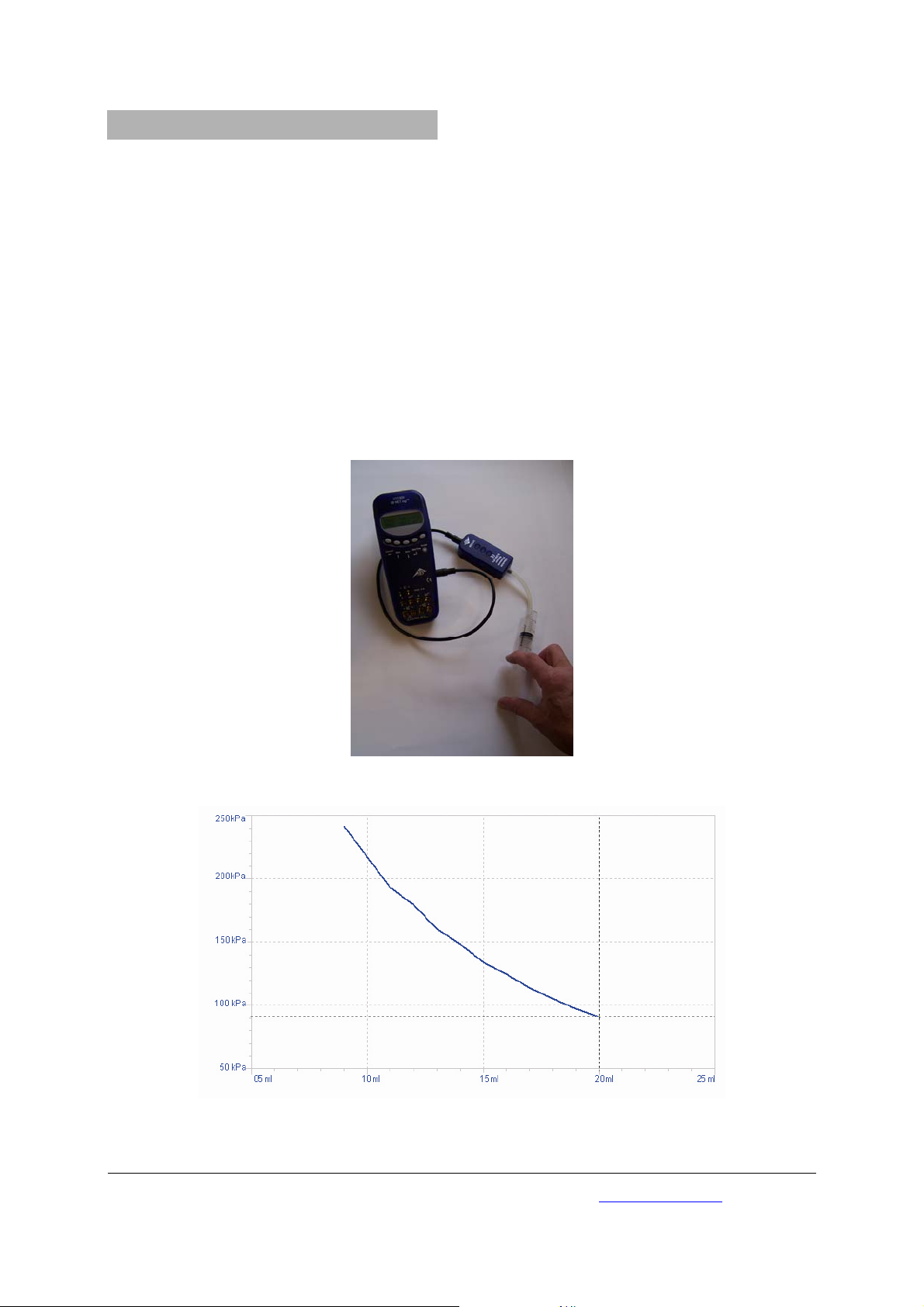
6. Versuchsbeispiel
6.1 Messung des absoluten Drucks in Abhängigkeit vom Volumen (Boyle-Mariott’sches Gesetz)
Benötigte Geräte:
1 3B NETlog
TM
-Interface U11300
1 Absolut-Drucksensor U11320
• Versuchsaufbau gemäß Fig. 1.
• Kunststoffspritze mit einem ca. 2 cm langen
Schlauchstück versehen.
• Spritzenvolumen auf 20 ml Umgebungsluft
aufziehen.
• Das freie Ende des Schlauchstücks auf die
Schlauchwelle des Drucksensors aufschieben.
• ACHTUNG: Dabei das Spritzenvolumen mög-
lichst nicht verändern!
TM
• Den Absolut-Drucksensor an das 3B NETlog
Interface anschließen und die Sensorerkennung abwarten.
• Im Interface-Display erscheint der erste Mess-
wert.
• Im Manuell-Modus der 3B NETlab
TM
-Software zu
jedem Volumenwert in 1 ml-Schritten diese
Messwerte aufnehmen und die Volumenwerte
manuell eintragen.
• Die Kennlinie grafisch darstellen.
Fig. 1 Messung des absoluten Drucks in Abhängigkeit vom Volumen
Fig. 2 Druck in Abhängigkeit vom Volumen
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Deutschland • www.3bscientific.com
Technische Änderungen vorbehalten
© Copyright 2008 3B Scientific GmbH
Page 3

3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Absolute Pressure Sensor U11320
Instruction Sheet
10/08 Hh
1. Safety instructions
• To avoid permanent damage to the built-in
semiconductor sensor, never exceed the maximum threshold pressure of 1000 kPa.
• Suitable only for non-corrosive gases such as
air, helium and nitrogen.
• Do not allow the sensor element to come into
contact with water.
2. Description
The absolute pressure sensor with its extensive
measurement range is particularly suitable for
experiments to demonstrate Boyle’s law and for
measuring the piston pressure (PV diagram) in a
Stirling engine. In addition, the absolute pressure
sensor can also be used to record and measure the
production of oxygen during photosynthesis and
for transpiration experiments in a closed system.
Two-port measurement procedure for the pressure
sensor: nozzle 1 is connected to the external pressure via a connecting nipple, and nozzle 2 is connected to a sealed reference vacuum.
The sensor box is automatically recognised via the
interface.
3. Equipment supplied
1 Sensor box
1 8-pin mini DIN connection lead, length: 60 cm
1 Silicone tube, inner dia.: 2 mm, length: 1 m
1 Plastic syringe 20ml
4. Technical data
Measurement range: 0 to 250 kPa
Sensor type: Semiconductor sensor
Accuracy: ±1%
Resolution: 0.1 Pa
Connections: Serrated nozzle 4.8 mm dia.
5. Operation
• Use the full length of the silicone tube or shor-
ten it to the length desired.
• Use the silicone tube to connect the pressure
source to the nozzle of the sensor.
• During the experiment, the elasticity of the
tube should be taken into account – this could
possibly lead to an error in readings.
1
Page 4
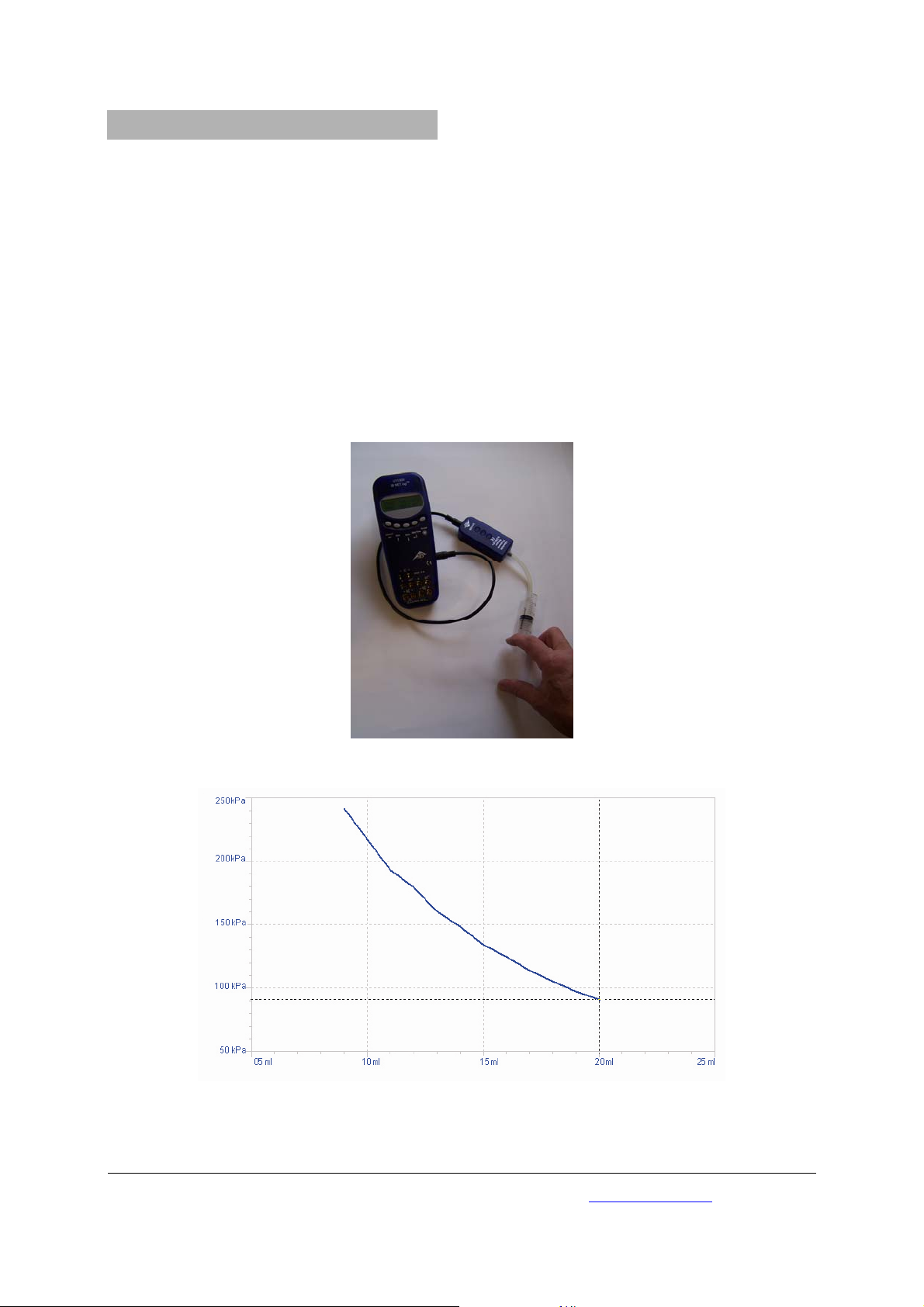
6. Sample experiment
6.1 Measuring the absolute pressure in relation
to the volume (Boyle’s law)
Apparatus required:
1 3B NETlog
TM
interface U11300
1 Absolute pressure sensor U11320
• Set-up the experiment according to Fig. 1.
• Fit the plastic syringe with an approx. 2-cm
long hose.
• Fill the syringe with 20 ml of ordinary air.
• Push the free end of the silicone tube onto the
nozzle of the pressure sensor.
• CAUTION: as far as possible, do not alter the
volume in the syringe!
• Connect the absolute pressure sensor to the
3B NETlog
TM
interface and wait for the interface
to recognise the sensor.
• The first reading appears on the interface dis-
play.
• In the 3B NETlab
TM
software’s manual mode,
enter the readings for the volume by hand in
steps of 1 ml at a time.
• Plot the graph of the characteristic.
Fig. 1: Measuring the absolute pressure in relation to the volume
Fig. 2: Pressure against volume
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Germany • www.3bscientific.com
Subject to technical amendments
© Copyright 2008 3B Scientific GmbH
Page 5

3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Capteur de pression absolue U11320
Instructions d’utilisation
10/08 Hh
1. Consignes de sécurité
• Pour éviter des dommages durables du capteur
intégré à semiconducteurs, il est interdit de
dépasser la pression maximale de 1 000 kPa !
• Convient uniquement à des gaz non corrodants
comme l'air, l'hélium et l'azote !
• Ne pas mettre la sonde du capteur en contact
avec de l'eau !
2. Description
Le capteur de pression absolue de grande gamme
de mesure convient aux expériences sur la loi de
Boyle-Mariotte et à la mesure de la pression de
piston (diagramme pV) dans le moteur Stirling ainsi
qu'à la saisie de production de O
synthèse et aux expériences de transpiration dans
un système fermé.
Procédé de mesure à deux portes du capteur :
connexion 1 reliée via tubulure de raccord à la
pression extérieure, connexion 2 fermée avec un
vide de référence étanche.
La boîte du capteur possède une détection automatique par l'interface.
lors de la photo-
2
3. Matériel fourni
1 boîte de capteur
1 câble de connexion mini-Din à 8 broches, 60
cm de long
1 tuyau en silicone, Ø intérieur 2 mm, 1 m de long
1 seringue en plastique 20 ml
4. Caractéristiques techniques
Plage de mesure : 0 à 250 kPa
Type de capteur : capteur à semiconducteurs
Précision : ± 1 %
Résolution : 0,1 Pa
Connexion : arbre de tuyau Ø 4,8 mm
5. Manipulation
• Utilisez toute la longueur du tuyau en silicone
ou raccourcissez-le.
• Branchez la source de pression à l'arbre du
capteur via la pièce du tuyau.
• Au cours de l'expérience, tenez compte de
l'élasticité du tuyau – la valeur de mesure risque éventuellement d'être faussée.
1
Page 6

6. Exemple d'expérience
6.1 Mesure de la pression absolue en fonction
du volume (loi de Boyle-Mariotte)
Appareils requis :
1 interface 3B NETlog
TM
U11300
1 capteur de pression absolue U11320
• Montez l'expérience comme le montre la fig. 1.
• Pourvoyez la seringue en plastique d'une pièce
de tuyau d'environ 2 cm de long.
• Remplissez la seringue avec 20 ml d'air am-
biant.
• Glissez l'extrémité libre de la pièce de tuyau
sur l'arbre du capteur de pression.
• ATTENTION : ne modifiez pas le volume de la
seringue !
• Branchez le capteur de pression absolue à
l'interface 3B NETlog
TM
et attendez que le cap-
teur soit reconnu.
• L'écran de l'interface affiche la première valeur
de mesure.
• En mode manuel du logiciel 3B NETlab
TM
, relevez ces valeurs de mesure en pas de 1 ml pour
chaque valeur de volume et saisissez manuellement les valeurs de volume.
• Représentez la courbe sous forme graphique.
Fig. 1 Mesure de la pression absolue en fonction du volume
Fig. 2 Pression en fonction du volume
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Allemagne • www.3bscientific.com
Sous réserve de modifications techniques
© Copyright 2008 3B Scientific GmbH
Page 7

FISICA 3B SCIENTIFIC®
Sensore di pressione assoluta U11320
Istruzioni per l'uso
10/08 Hh
1. Norme di sicurezza
• Per evitare danni permanenti del sensore a
semiconduttore incorporato, non superare la
pressione di collasso massima di 1000 kPa!
• Adatto solo per gas non corrosivi come aria,
elio e azoto!
• Non portare il sensore a contatto con acqua!
2. Descrizione
Sensore di pressione assoluto con ampio range di
misura adatto per esperimenti sulla legge di Boyle
e Mariotte, per la misurazione della pressione dei
pistoni (diagramma pV) nel motore Stirling, per il
rilevamento della produzione di O
fotosintesi e per esperimenti sulla traspirazione in
sistemi chiusi.
Metodo di misurazione doppio bipolo del sensore:
collegamento 1 collegato tramite raccordo con la
pressione esterna, collegamento 2 chiuso con un
vuoto di riferimento incapsulato.
La scatola del sensore viene riconosciuta
automaticamente dall’interfaccia.
durante la
2
3. Dotazione
1 scatola del sensore
1 cavo di collegamento Mini DIN a 8 pin, lungo
60 cm
1 tubo di silicone, Øinterno 2 mm, lungo 1 m
1 siringa di plastica 20 m
4. Dati tecnici
Range di misura: da 0 a 250 kPa
Tipo sensore: sensore a semiconduttore
Precisione: ± 1 %
Risoluzione: 0,1 Pa
Allacciamento: albero tubo flessibile 4,8 mm Ø
5. Comandi
• Utilizzare il tubo di silicone nella sua
lunghezza complessiva o ridurlo alla lunghezza
necessaria.
• Collegare il dispositivo di pressione all’albero
flessibile tramite
• il tubo flessibile.
l
1
Page 8

• Durante l’esperimento tenere in
considerazione l’elasticità del tubo – potrebbe
provocare un’alterazione del valore misurato.
6. Esempi di esperimenti
6.1 Misurazione della pressione assoluta in
funzione del volume (legge di Boyle e
Mariotte)
Apparecchi necessari:
1 interfaccia 3B NETlog
TM
U11300
1 sensore di pressione assoluta U11320
• Struttura di prova come da fig. 1.
• Siringa di plastica dotata di un tubo flessibile
lungo 2 cm circa.
• Aspirare un volume di iniezione di 20 ml di
aria ambiente.
• Collegare l’estremità libera del tubo flessibile
all’albero flessibile del sensore di pressione.
• ATTENZIONE: durante questa operazione non
modificare il volume di iniezione!
• Collegare il sensore di pressione all’interfaccia
3B NETlog
TM
e attendere il riconoscimento del
sensore.
• Sul display dell’interfaccia appare il primo
valore misurato.
• Nella modalità manuale del software
3B NETlab
TM
, per ogni valore del volume,
registrare questi valori di misurazione in stadi
da 1 ml.
• Rappresentare graficamente la caratteristica.
Fig. 1 Misurazione della pressione assoluta in funzione del volume
Fig. 2 Pressione in funzione del volume
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburg • Germania • www.3bscientific.com
Con riserva di modifiche tecniche
© Copyright 2008 3B Scientific GmbH
Page 9

3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Sensor de presión absoluta U11320
Instrucciones de uso
10/08 Hh
1. Aviso de seguridad
• ¡Para evitar daños duraderos del sensor semi-
conductor incorporado no se debe exceder bajo ningún concepto la máxima presión límite
de 1000 kPa!
• ¡Apropiado solamente para gases no corrosivos
como aire, helio y nitrógeno!
• ¡El elemento sensor no debe entrar en contac-
to con el agua!
2. Descripción
El sensor de presión absoluta, dado su amplio
rango de medición, es apropiado para experimentos relacionados con la ley de Boyle y Mariotte, o
para mediciones de la presión que ejerce el pistón
(diagrama pV) en el motor Stirling. También es
apropiada para la detección de la producción de
O2 en la fotosíntesis y para ensayos de transpiración en un sistema cerrado.
Procedimiento de medición de dos puertas del
sensor: Conexión 1 vía tomas de contacto conectadas con la presión externa, conexión 2 cerrada con
vacío de referencia encapsu-lado.
La caja sensora está equipada de manera que sea
reconocida automáticamente por la interfaz.
3. Volumen de suministro
1 caja sensora
1 cable de conexión MiniDIN de 8 pins,
60 cm largo
1 manguera de silicona, diámetro interior
2 mm, 1 m largo
1 jeringa plástica de 20 ml
4. Datos técnicos
Rango de medición: 0 a 250 kPa
Tipo de sensor: semiconductor
Precisión: ± 1 %
Resolución: 0,1 Pa
Conexión: conector de manguera
de 4,8 mm Ø
5. Servicio
• Usar el tubo de silicona en la longitud total o
cortarlo de acuerdo con la longitud requerida.
• Conectar la fuente de presión por medio del
segmento de manguera al conector de manguera del sensor.
1
Page 10

• Durante el experimento se debe tener en cuen-
ta la elasticidad del tubo – esto conduce, dado
el caso, a una adulteración del valor medido.
6. Ejemplo de experimento
6.1 Medición de la presión absoluta en función
del volumen (ley de Boyle y Mariotte)
Equipo requerido:
1 Interfaz 3B NETlog
TM
U11300
1 Sensor de presión absoluta U11320
• Montaje del experimento según Fig. 1.
• Jeringa plástica provista de una manguera de
aprox. 2 cm. de largo.
• Llenar la jeringa con un volumen de 20 ml de
aire ambiental.
• Encajar la punta libre de la manguera en el
conector de manguera del sensor de presión.
• ATENCIÓN: ¡En lo posible, no se debe variar el
volumen de la jeringa durante esta maniobra!
• Conectar el sensor de presión absoluta a la
interfaz 3B NETlog
TM
y esperar el reconocimien-
to del sensor.
• En el display de la interfaz aparece el primer
valor de medición.
TM
• En el modo manual del software 3B NETlab
,
registrar cada valor de volumen, en pasos de
1 ml, y anotar manualmente estos valores.
• Representar gráficamente la curva
característica.
Fig. 1 Medición de la presión absoluta en función del volumen
Fig. 2 Presión en función del volumen
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburgo • Alemania • www.3bscientific.com
Se reservan las modificaciones técnicas
© Copyright 2008 3B Scientific GmbH
Page 11

3B SCIENTIFIC® PHYSICS
Sensor de pressão absoluta U11320
Instruções para o uso
10/08 Hh
1. Indicações de segurança
• Para evitar danos permanentes no sensor se-
micondutor integrado, nunca ultrapassar o limite máximo de pressão de 1000 kPa!
• Este aparelho só é adequado para gases não
corrosivos como ar, hélio e hidrogênio!
• Nunca ponha o elemento sensor em contato
com água!
2. Descrição
Sensor de pressão absoluta com faixa de
medição ampla adequado para experiências
sobre a lei de Boyle-Mariott e para a medição
da pressão de pistões (diagrama pV) em
motores de Stirling assim como para o
registro da produção de O2 durante a
fotossíntese e para experiências de
transpiração em sistemas fechados.
Método de medição de dois portais do
sensor: conector 1 conectado com a pressão
externa por meio de pontos de contato,
conector 2 fechado com vácuo de referência
encapsulado.
O sensorbox está equipado com um
reconhecimento automático pela interface.
3. Fornecimento
1 sensorbox
1 cabo de conexão MiniDIN de 8 pin, 60 cm de
comprimento
1 Mangueira de silicone, Øinterior 2 mm, 1 m
de comprimento
1 Seringa de plástico de 20 ml
4. Dados técnicos
Faixa de medição: 0 a 250 kPa
Tipo de sensor: sensor semicondutor
Precisão: ± 1 %
Resolução: 0,1 Pa
Conexão: conector de mangueira Ø 4,8 mm
5. Utilização
• Utilizar a mangueira de silicone no seu
comprimento total ou cortar no comprimento
necessário.
• Conectar a fonte de pressão com o conector de
mangueira do sensor por meio do pedaço de
mangueira.
1
Page 12

• Levar em conta a elasticidade da mangueira
durante a experiência, esta pode em certos casos levar a desvios no valor de medição.
6. Exemplo de experiência
6.1 Medição da pressão absoluta em função do
volume (lei de Boyle-Mariott)
Aparelhos necessários:
1 interface 3B NETlog
TM
U11300
1 sensor de pressão absoluta U11320
• Montagem da experiência conforme fig. 1.
• Colocar um pedaço de mangueira de aproxi-
madamente 2 cm de comprimento na seringa.
• Levar o volume da seringa a 20 ml de ar ambi-
ente.
• Encaixar a ponta livre do pedaço de mangueira
no conector de mangueira do sensor de pressão.
• ATENÇÃO: na medida do possível, ao fazê-lo,
não alterar o volume da seringa!
• Conectar o sensor de pressão absoluta na
interface 3B NETlog
TM
e aguardar o
reconhecimento do sensor.
• O primeiro valor de medição aparece no dis-
play da interface.
• Registrar no modo manual do software 3B
NETlab
TM
o valor de medição para cada valor de
volume em passos de 1 ml e introduzir manualmente os valores de volume.
• Representar graficamente as linhas de recon-
hecimento.
Fig. 1 Medição da pressão absoluta em função do volume
Fig. 2 Pressão em função do volume
3B Scientific GmbH • Rudorffweg 8 • 21031 Hamburgo • Alemanha • www.3bscientific.com
Sob reserva de alterações técnicas
© Copyright 2008 3B Scientific GmbH
 Loading...
Loading...