Page 1

Quick Start Guide
VMG5313-B10A / VMG5313B30A
Wireless N VDSL2 VoIP IAD with USB
Version 1.00
Edition 3, 09/2014
User’s Guide
Default Login Details
LAN IP Address http://192.168.1.1
Login admin, zyuser
Password 1234, 1234
Default URL http://192.168.1.1
www.zyxel.com
Copyright © 2014 ZyXEL Communications Corporation
Page 2

IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
Screenshots and graphics in this book may differ slightly from your product due to differences in
your product firmware or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure
that the information in this manual is accurate.
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide shows how to connect the VMG and get up and running right away.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
2
Page 3

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
User’s Guide .......................................................................................................................................15
Introducing the VMG ...............................................................................................................................17
The Web Configurator .............................................................................................................................23
Quick Start ...............................................................................................................................................33
Tutorials ..................................................................................................................................................35
Technical Reference ..........................................................................................................................71
Network Map and Status Screens ...........................................................................................................73
Broadband ...............................................................................................................................................79
Wireless ................................................................................................................................................107
Home Networking ..................................................................................................................................139
Routing ..................................................................................................................................................155
Quality of Service (QoS) .......................................................................................................................163
Network Address Translation (NAT) ......................................................................................................181
Dynamic DNS Setup .............................................................................................................................199
Vlan Group ............................................................................................................................................203
Interface Group ..................................................................................................................................... 205
USB Service .......................................................................................................................................... 211
Power Management .............................................................................................................................. 219
Firewall ..................................................................................................................................................223
MAC Filter .............................................................................................................................................233
Parental Control .................................................................................................................................... 235
Scheduler Rule ......................................................................................................................................241
Certificates ............................................................................................................................................243
VPN ....................................................................................................................................................... 251
Voice .....................................................................................................................................................265
Log .......................................................................................................................................................297
Traffic Status ........................................................................................................................................301
VoIP Status ...........................................................................................................................................305
xDSL Statistics ......................................................................................................................................307
3G Statistics ......................................................................................................................................... 311
User Account .........................................................................................................................................313
Remote Management ............................................................................................................................315
TR-069 Client ........................................................................................................................................ 319
TR-064 ..................................................................................................................................................321
SNMP ....................................................................................................................................................323
Time Settings ........................................................................................................................................325
E-mail Notification .................................................................................................................................327
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
3
Page 4

Contents Overview
Log Setting ........................................................................................................................................... 329
Firmware Upgrade ................................................................................................................................333
Configuration .........................................................................................................................................337
Diagnostic .............................................................................................................................................340
Troubleshooting .................................................................................................................................... 345
Appendices ......................................................................................................................................353
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
4
Page 5

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Contents Overview ..............................................................................................................................3
Table of Contents .................................................................................................................................5
Part I: User’s Guide .........................................................................................15
Chapter 1
Introducing the VMG ..........................................................................................................................17
1.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................17
1.2 Ways to Manage the VMG ................................................................................................................ 17
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the VMG .................................................................................................17
1.4 Applications for the VMG .................................................................................................................18
1.4.1 Internet Access ........................................................................................................................ 18
1.5 VMG’s USB Support .........................................................................................................................19
1.6 LEDs (Lights) .................................................................................................................................... 20
1.7 The RESET Button ............................................................................................................................21
1.8 Wireless Access ................................................................................................................................22
1.8.1 Using the Wi-Fi and WPS Buttons ...........................................................................................22
Chapter 2
The Web Configurator........................................................................................................................23
2.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................23
2.1.1 Accessing the Web Configurator .............................................................................................23
2.2 Web Configurator Layout ..................................................................................................................25
2.2.1 Title Bar ...................................................................................................................................25
2.2.2 Main Window ........................................................................................................................... 26
2.2.3 Navigation Panel .....................................................................................................................27
Chapter 3
Quick Start...........................................................................................................................................33
3.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................33
3.2 Quick Start Setup ..............................................................................................................................33
Chapter 4
Tutorials...............................................................................................................................................35
4.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................35
4.2 Setting Up an Ethernet WAN Connection .........................................................................................35
4.3 Setting Up an ADSL PPPoE Connection ..........................................................................................37
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Table of Contents
4.4 Setting Up a Secure Wireless Network .............................................................................................41
4.4.1 Configuring the Wireless Network Settings ............................................................................. 41
4.4.2 Using WPS ..............................................................................................................................42
4.4.3 Without WPS ...........................................................................................................................46
4.5 Setting Up Multiple Wireless Groups ................................................................................................47
4.6 Configuring Static Route for Routing to Another Network .................................................................50
4.7 Configuring QoS Queue and Class Setup ........................................................................................53
4.8 Access the VMG Using DDNS ..........................................................................................................56
4.8.1 Registering a DDNS Account on www.dyndns.org .................................................................. 56
4.8.2 Configuring DDNS on Your VMG .............................................................................................57
4.8.3 Testing the DDNS Setting ........................................................................................................ 57
4.9 Configuring the MAC Address Filter .................................................................................................. 57
4.10 Access Your Shared Files From a Computer ..................................................................................58
4.11 Using the Media Server Feature ....................................................................................................60
4.11.1 Configuring the VMG .............................................................................................................60
4.11.2 Using Windows Media Player ................................................................................................60
4.11.3 Using a Digital Media Adapter ...............................................................................................63
4.12 Using the Print Server Feature ........................................................................................................65
Part II: Technical Reference............................................................................71
Chapter 5
Network Map and Status Screens.....................................................................................................73
5.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................73
5.2 The Network Map Screen .................................................................................................................73
5.3 The Status Screen ............................................................................................................................. 74
Chapter 6
Broadband...........................................................................................................................................79
6.1 Overview ...........................................................................................................................................79
6.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ............................................................................................79
6.1.2 What You Need to Know .......................................................................................................... 80
6.1.3 Before You Begin ..................................................................................................................... 82
6.2 The Broadband Screen ..................................................................................................................... 83
6.2.1 Add/Edit Internet Connection ...................................................................................................85
6.3 The 3G Backup Screen ..................................................................................................................... 91
6.4 The Advanced Screen .......................................................................................................................95
6.5 The 802.1x Screen ............................................................................................................................98
6.5.1 Modify 802.1X Settings ............................................................................................................ 99
6.6 Ethernet WAN ...................................................................................................................................99
6.7 Technical Reference ........................................................................................................................100
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
6
Page 7

Table of Contents
Chapter 7
Wireless.............................................................................................................................................107
7.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................107
7.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................107
7.1.2 What You Need to Know ........................................................................................................108
7.2 The General Screen ....................................................................................................................... 108
7.2.1 No Security ............................................................................................................................ 110
7.2.2 Basic (WEP Encryption) ........................................................................................................ 111
7.2.3 More Secure (WPA(2)-PSK) .................................................................................................. 113
7.3 The Guest / More AP Screen .......................................................................................................... 114
7.3.1 Edit Guest / More AP ............................................................................................................ 115
7.4 MAC Authentication ........................................................................................................................ 117
7.5 The WPS Screen ............................................................................................................................ 118
7.6 The WMM Screen ........................................................................................................................... 119
7.7 The WDS Screen ............................................................................................................................ 120
7.7.1 WDS Scan .............................................................................................................................122
7.8 The Others Screen ..........................................................................................................................122
7.9 The Channel Status Screen ............................................................................................................124
7.10 Technical Reference ...................................................................................................................... 125
7.10.1 Wireless Network Overview .................................................................................................125
7.10.2 Additional Wireless Terms ...................................................................................................127
7.10.3 Wireless Security Overview .................................................................................................127
7.10.4 Signal Problems ..................................................................................................................129
7.10.5 BSS .....................................................................................................................................130
7.10.6 MBSSID ...............................................................................................................................130
7.10.7 Preamble Type ....................................................................................................................131
7.10.8 Wireless Distribution System (WDS) ...................................................................................131
7.10.9 WiFi Protected Setup (WPS) ...............................................................................................131
Chapter 8
Home Networking.............................................................................................................................139
8.1 Overview .........................................................................................................................................139
8.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................139
8.1.2 What You Need To Know .......................................................................................................140
8.1.3 Before You Begin ...................................................................................................................141
8.2 The LAN Setup Screen ...................................................................................................................141
8.3 The Static DHCP Screen ................................................................................................................. 144
8.4 The UPnP Screen ...........................................................................................................................146
8.4.1 Turning On UPnP in Windows 7 Example .............................................................................147
8.5 The Additional Subnet Screen ........................................................................................................148
8.6 The STB Vendor ID Screen .............................................................................................................150
8.7 The Wake on LAN Screen ..............................................................................................................150
8.8 The TFTP Server Name Screen .....................................................................................................151
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Table of Contents
8.9 Technical Reference ........................................................................................................................152
8.9.1 LANs, WANs and the VMG ....................................................................................................152
8.9.2 DHCP Setup ..........................................................................................................................152
8.9.3 DNS Server Addresses .........................................................................................................153
8.9.4 LAN TCP/IP ...........................................................................................................................153
Chapter 9
Routing ..............................................................................................................................................155
9.1 Overview ........................................................................................................................................155
9.2 The Routing Screen ........................................................................................................................ 155
9.2.1 Add/Edit Static Route .............................................................................................................156
9.3 The DNS Route Screen ..................................................................................................................157
9.3.1 The DNS Route Add Screen .................................................................................................158
9.4 The Policy Forwarding Screen ........................................................................................................158
9.4.1 Add/Edit Policy Forwarding ...................................................................................................160
9.5 RIP ..............................................................................................................................................160
9.5.1 The RIP Screen .....................................................................................................................161
Chapter 10
Quality of Service (QoS)...................................................................................................................163
10.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................163
10.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................163
10.2 What You Need to Know ...............................................................................................................163
10.3 The Quality of Service General Screen ........................................................................................165
10.4 The Queue Setup Screen .............................................................................................................166
10.4.1 Adding a QoS Queue .........................................................................................................167
10.5 The Class Setup Screen ...............................................................................................................168
10.5.1 Add/Edit QoS Class ............................................................................................................169
10.6 The QoS Policer Setup Screen ..................................................................................................... 173
10.6.1 Add/Edit a QoS Policer .......................................................................................................174
10.7 Technical Reference ......................................................................................................................175
Chapter 11
Network Address Translation (NAT)................................................................................................181
11.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................181
11.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................181
11.1.2 What You Need To Know .....................................................................................................181
11.2 The Port Forwarding Screen ........................................................................................................182
11.2.1 Add/Edit Port Forwarding .................................................................................................... 184
11.3 The Applications Screen ...............................................................................................................185
11.3.1 Add New Application ............................................................................................................ 186
11.4 The Port Triggering Screen ...........................................................................................................187
11.4.1 Add/Edit Port Triggering Rule .............................................................................................188
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
8
Page 9

Table of Contents
11.5 The DMZ Screen ...........................................................................................................................189
11.6 The ALG Screen ............................................................................................................................190
11.7 The Address Mapping Screen .......................................................................................................191
11.7.1 Add/Edit Address Mapping Rule ..........................................................................................192
11.8 The Sessions Screen .................................................................................................................... 193
11.9 Technical Reference ...................................................................................................................... 193
11.9.1 NAT Definitions .................................................................................................................... 194
11.9.2 What NAT Does ................................................................................................................... 194
11.9.3 How NAT Works ...................................................................................................................195
11.9.4 NAT Application ................................................................................................................... 195
Chapter 12
Dynamic DNS Setup .........................................................................................................................199
12.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................199
12.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................199
12.1.2 What You Need To Know .....................................................................................................200
12.2 The DNS Entry Screen .................................................................................................................. 200
12.2.1 Add/Edit DNS Entry .............................................................................................................200
12.3 The Dynamic DNS Screen ............................................................................................................201
Chapter 13
Vlan Group ........................................................................................................................................203
13.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................203
13.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................203
13.2 The Vlan Group Screen ................................................................................................................203
13.2.1 Add/Edit a VLAN Group .......................................................................................................204
Chapter 14
Interface Group.................................................................................................................................205
14.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................205
14.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................205
14.2 The Interface Group Screen .......................................................................................................... 205
14.2.1 Interface Group Configuration .............................................................................................206
14.2.2 Interface Grouping Criteria .................................................................................................208
Chapter 15
USB Service ......................................................................................................................................211
15.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 211
15.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................ 211
15.1.2 What You Need To Know ..................................................................................................... 211
15.1.3 Before You Begin ................................................................................................................. 213
15.2 The File Sharing Screen ...............................................................................................................213
15.2.1 The Add New User Screen ..................................................................................................214
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Table of Contents
15.3 The Media Server Screen .............................................................................................................215
15.4 Print Server ..................................................................................................................................216
15.4.1 Before You Begin ................................................................................................................. 216
15.4.2 The Print Server Screen ......................................................................................................217
Chapter 16
Power Management..........................................................................................................................219
16.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................219
16.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................219
16.1.2 What You Need To Know .....................................................................................................219
16.2 The Power Management Screen ..................................................................................................219
16.3 The Auto Switch Off Screen .......................................................................................................... 220
16.3.1 The Auto Switch Off Add or Modify Screen .........................................................................221
16.3.2 The Add/Edit Rule Screen ...................................................................................................222
Chapter 17
Firewall ..............................................................................................................................................223
17.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................223
17.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................223
17.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................224
17.2 The Firewall Screen ......................................................................................................................225
17.3 The Protocol Screen ....................................................................................................................225
17.3.1 Add/Edit a Service ..............................................................................................................226
17.4 The Access Control Screen ..........................................................................................................228
17.4.1 Add/Edit an ACL Rule ........................................................................................................228
17.5 The DoS Screen ............................................................................................................................230
Chapter 18
MAC Filter..........................................................................................................................................233
18.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................233
18.2 The MAC Filter Screen ..................................................................................................................233
Chapter 19
Parental Control................................................................................................................................235
19.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................235
19.2 The Parental Control Screen ......................................................................................................... 235
19.2.1 Add/Edit a Parental Control Profile ......................................................................................236
Chapter 20
Scheduler Rule..................................................................................................................................241
20.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................241
20.2 The Scheduler Rule Screen ..........................................................................................................241
20.2.1 Add/Edit a Schedule ............................................................................................................242
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
10
Page 11

Table of Contents
Chapter 21
Certificates........................................................................................................................................243
21.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................243
21.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................243
21.2 What You Need to Know ...............................................................................................................243
21.3 The Local Certificates Screen ....................................................................................................... 243
21.3.1 Create Certificate Request ................................................................................................. 244
21.3.2 Load Signed Certificate ......................................................................................................246
21.4 The Trusted CA Screen ................................................................................................................247
21.4.1 View Trusted CA Certificate .................................................................................................248
21.4.2 Import Trusted CA Certificate ..............................................................................................248
Chapter 22
VPN ....................................................................................................................................................251
22.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................251
22.2 The IPSec VPN Setup Screen ......................................................................................................251
22.2.1 The IPSec VPN Add/Edit Screen ........................................................................................252
22.3 The IPSec VPN Monitor Screen ....................................................................................................258
22.4 Technical Reference ......................................................................................................................258
22.4.1 IPSec Architecture ...............................................................................................................258
22.4.2 Encapsulation ......................................................................................................................259
22.4.3 IKE Phases .........................................................................................................................260
22.4.4 Negotiation Mode ................................................................................................................261
22.4.5 IPSec and NAT ....................................................................................................................262
22.4.6 VPN, NAT, and NAT Traversal .............................................................................................262
22.4.7 ID Type and Content ............................................................................................................263
22.4.8 Pre-Shared Key ...................................................................................................................264
22.4.9 Diffie-Hellman (DH) Key Groups ..........................................................................................264
Chapter 23
Voice ..................................................................................................................................................265
23.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................265
23.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................265
23.1.2 What You Need to Know About VoIP ...................................................................................266
23.2 Before You Begin ..........................................................................................................................266
23.3 The SIP Account Screen ..............................................................................................................266
23.3.1 The SIP Account Add/Edit Screen ......................................................................................267
23.4 The SIP Service Provider Screen ................................................................................................271
23.4.1 The SIP Service Provider Add/Edit Screen ........................................................................272
23.5 The Phone Screen .......................................................................................................................279
23.6 The Call Rule Screen ....................................................................................................................279
23.7 The Call History Summary Screen ................................................................................................280
23.8 The Call History Outgoing Calls Screen ........................................................................................281
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
11
Page 12

Table of Contents
23.9 The Call History Incoming Calls Screen ........................................................................................ 282
23.10 Technical Reference ....................................................................................................................282
23.10.1 Quality of Service (QoS) ....................................................................................................290
23.10.2 Phone Services Overview .................................................................................................291
Chapter 24
Log ....................................................................................................................................................297
24.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................297
24.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................297
24.1.2 What You Need To Know .....................................................................................................297
24.2 The System Log Screen ................................................................................................................298
24.3 The Security Log Screen ...............................................................................................................299
Chapter 25
Traffic Status ....................................................................................................................................301
25.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................301
25.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................301
25.2 The WAN Status Screen ............................................................................................................... 301
25.3 The LAN Status Screen .................................................................................................................302
25.4 The NAT Status Screen .................................................................................................................303
Chapter 26
VoIP Status.......................................................................................................................................305
26.1 The VoIP Status Screen ................................................................................................................305
Chapter 27
xDSL Statistics..................................................................................................................................307
27.1 The xDSL Statistics Screen ...........................................................................................................307
Chapter 28
3G Statistics .....................................................................................................................................311
28.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................... 311
28.2 The 3G Statistics Screen ............................................................................................................... 311
Chapter 29
User Account ....................................................................................................................................313
29.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................313
29.2 The User Account Screen .............................................................................................................313
29.2.1 The User Account Add/Edit Screen .....................................................................................314
Chapter 30
Remote Management........................................................................................................................315
30.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................315
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
12
Page 13

Table of Contents
30.2 The Remote MGMT Screen ..........................................................................................................315
30.3 The Trust Domain Screen .............................................................................................................316
30.4 The Add Trust Domain Screen ......................................................................................................317
Chapter 31
TR-069 Client.....................................................................................................................................319
31.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................319
31.2 The TR-069 Client Screen ............................................................................................................319
Chapter 32
TR-064................................................................................................................................................321
32.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................321
32.2 The TR-064 Screen .......................................................................................................................321
Chapter 33
SNMP .................................................................................................................................................323
33.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................323
33.2 The SNMP Screen ........................................................................................................................ 323
Chapter 34
Time Settings....................................................................................................................................325
34.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................325
34.2 The Time Screen ..........................................................................................................................325
Chapter 35
E-mail Notification............................................................................................................................327
35.1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................327
35.2 The Email Notification Screen ....................................................................................................... 327
35.2.1 Email Notification Edit ........................................................................................................328
Chapter 36
Log Setting .......................................................................................................................................329
36.1 Overview ......................................................................................................................................329
36.2 The Log Settings Screen ...............................................................................................................329
36.2.1 Example E-mail Log ............................................................................................................330
Chapter 37
Firmware Upgrade ............................................................................................................................333
37.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................333
37.2 The Firmware Screen .................................................................................................................... 333
Chapter 38
Configuration ....................................................................................................................................337
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
13
Page 14

Table of Contents
38.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................337
38.2 The Configuration Screen .............................................................................................................337
38.3 The Reboot Screen ....................................................................................................................... 339
Chapter 39
Diagnostic .........................................................................................................................................340
39.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................340
39.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................340
39.2 What You Need to Know ...............................................................................................................340
39.3 Ping & TraceRoute & NsLookup ...................................................................................................341
39.4 802.1ag .........................................................................................................................................341
39.5 OAM Ping ......................................................................................................................................342
Chapter 40
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................345
40.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs ....................................................................................345
40.2 VMG Access and Login .................................................................................................................346
40.3 Internet Access .............................................................................................................................348
40.4 Wireless Internet Access ...............................................................................................................349
40.5 USB Device Connection ................................................................................................................350
40.6 UPnP .............................................................................................................................................350
Part III: Appendices.......................................................................................353
Appendix A Customer Support ........................................................................................................355
Appendix B Wireless LANs..............................................................................................................361
Appendix C IPv6 ..............................................................................................................................375
Appendix D Services .......................................................................................................................383
Appendix E Legal Information..........................................................................................................387
............................................................................................................................................................391
Index ..................................................................................................................................................392
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
14
Page 15

PART I
User’s Guide
15
Page 16

16
Page 17

1.1 Overview
In this guide we refer to all models in the series as the VMG. The exact model name is
used for explicit references.
The VMG is a combo WAN (DSL, Ethernet and 3G in order of priority) gateway with V oIP capabilities
and high speed LAN and WAN access for business users. It is equipped with four LAN ports, of
which port number four can be converted into a WAN port, two phone ports that can be connected
to make VoIP calls and one USB 2.0 port for file sharing. It is backward compatible with ADSL,
ADSL2 and ADSL2+ in case VDSL is not available. The VMG is also a wireless access point and is
compatible with IEEE 802.11b/g/n wireless standard.
• The VMG5313-B10A works over the analog telephone system, POTS (Plain Old Telephone
Service).
• The VMG5313-B30A works over ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network) or T-ISDN (UR-2).
CHAPTER 1
Introducing the VMG
Only use firmware for your VMG’s specific model. Refer to the label on
the bottom of your VMG.
1.2 Ways to Manage the VMG
Use any of the following methods to manage the VMG.
• Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the VMG using a
(supported) web browser.
• TR-069. This is an auto-configuration server used to remotely configure your device.
1.3 Good Habits for Managing the VMG
Do the following things regularly to make the VMG more secure and to manage the VMG more
effectively.
• Change the password. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that consists of different
types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
17
Page 18

Chapter 1 Introducing the VMG
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an earlier
working configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even crashes. If you
forget your password, you will have to reset the VMG to its factory default settings. If you backed
up an earlier configuration file, you would not have to totally re-configure the VMG. You could
simply restore your last configuration.
1.4 Applications for the VMG
Here are some example uses for which the VMG is well suited.
1.4.1 Internet Access
Your VMG provides shared Internet access by connecting the DSL port to the DSL or MODEM jack
on a splitter or your telephone jack. You can have multiple WAN services over one ADSL, VDSL or
Ethernet connection at the same time. However, the VMG cannot work in ADSL and VDSL mode
simultaneously. The ADSL and VDSL lines share the same WAN (layer-2) interfaces that you
configure in the VMG. Refer to Section 6.2 on page 83 for the Network Setting > Broadband
screen. Computers can connect to the VMG’s LAN ports (or wirelessly).
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
18
Page 19
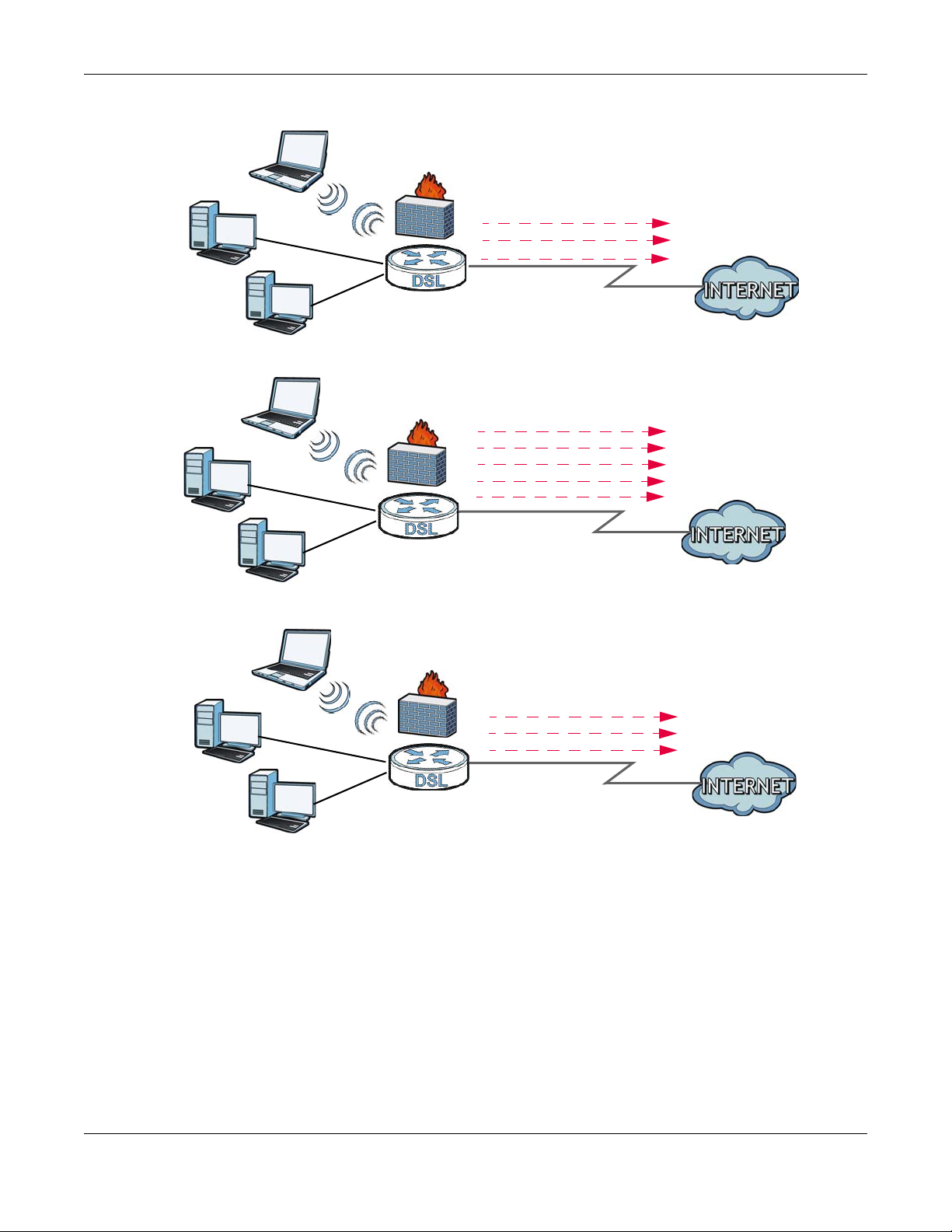
Chapter 1 Introducing the VMG
ADSL / VDSL
WLAN
PPPoE
IPoA
Bridging
WAN
ADSL
IPoE
WAN
LAN
LAN
WLAN
A
A
PPPoA
IPoE
PPPoE
Bridging
Ethernet
WAN
LAN
WLAN
A
IPoE
PPPoE
Bridging
Figure 1 VMG’s Internet Access Application
You can also configure IP filtering on the VMG for secure Internet access. Click Security > MAC
Filter to set the IP Filtering. When the IP filter is on, all incoming traffic from the Internet to your
network is blocked by default unless it is initiated from your network. This means that probes from
the outside to your network are not allowed, but you can safely browse the Internet and download
files.
1.5 VMG’s USB Support
The USB port of the VMG is used for file-sharing.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
19
Page 20

Chapter 1 Introducing the VMG
B
A
File Sharing
Use the built-in USB 2.0 port to share files on a USB memory stick or a USB hard drive (B). You can
connect one USB hard drive to the VMG at a time. Use FTP to access the files on the USB device.
Figure 2 USB File Sharing Application
1.6 LEDs (Lights)
The following graphic displays the labels of the LEDs.
PWR/
SYS
None of the LEDs are on if the VMG is not receiving power.
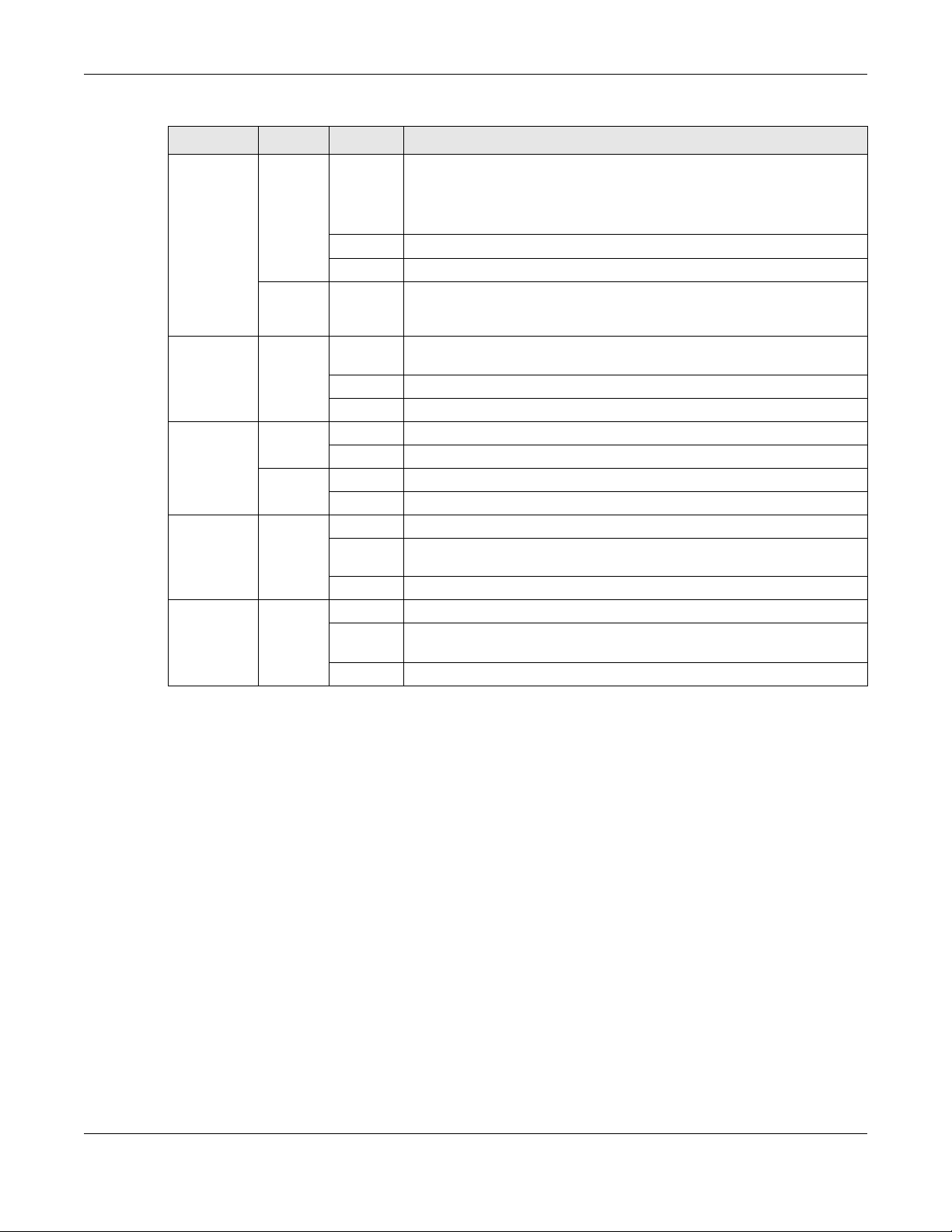
Table 1 LED Descriptions
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR/SYS Green On The VMG is receiving power and ready for use.
DSL Green On The ADSL line is up.
DSL INTERNET
Red On The VMG detected an error while self-testing, or there is a device
Orange On The VDSL line is up.
LAN1 LAN2 LAN3 LAN4
Blinking The VMG is self-testing.
malfunction.
Off The VMG is not receiving power.
Blinking The VMG is initializing the ADSL line.
Blinking The VMG is initializing the VDSL line.
Off The DSL line is down.
Wi-Fi
PHONE1 PHONE2
USB
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
20
Page 21
Chapter 1 Introducing the VMG
Table 1 LED Descriptions (continued)
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
INTERNET Green On The VMG has an IP connection but no traffic.
Your device has a WAN IP address (either static or assigned by a DHCP
server), PPP negotiation was successfully completed (if used) and the
DSL connection is up.
Blinking The VMG is sending or receiving IP traffic.
Off There is no Internet connection or the gateway is in bridged mode.
Red On The VMG attempted to make an IP connection but failed. Possible
causes are no response from a DHCP server, no PPPoE response, PPPoE
authentication failed.
LAN Green On The VMG has a successful 100 Mbps Ethernet connection with a device
on the Local Area Network (LAN).
Blinking The VMG is sending or receiving data to/from the LAN at 100 Mbps.
Off The VMG does not have an Ethernet connection with the LAN.
WiFi 2.4G Green On The 2.4 GHz wireless network is activated.
Blinking The VMG is communicating with other wireless clients.
Orange Blinking The VMG is setting up a WPS connection.
Off The 2.4 GHz wireless network is not activated.
Phone1,
Phone2
USB Green On The VMG recognizes a USB connection through the USB1 slot.
Green On A SIP account is registered for the phone port.
Blinking A telephone connected to the phone port has its receiver off of the hook
or there is an incoming call.
Off The phone port does not have a SIP account registered.
Blinking The VMG is sending/receiving data to /from the USB device connected
to it.
Off The VMG does not detect a USB connection through the USB1 slot.
1.7 The RESET Button
If you forget your password or cannot access the W eb Configurator, you will need to use the RESET
button at the back of the device to reload the factory-default configuration file. This means that y ou
will lose all configurations that you had previously and the default login names and passwords will
be reset (see the cover page).
1 Make sure the PWR/SYS LED is on (not blinking).
2 To set the device back to the factory default settings, press the RESET button for five seconds or
until the PWR/SYS LED begins to blink and then release it. When the PWR/SYS LED begins to
blink, the defaults have been restored and the device restarts.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
21
Page 22

1.8 Wireless Access
The VMG is a wireless Access Point (AP) for wireless clients, such as notebook computers or PDAs
and iPads. It allows them to connect to the Internet without having to rely on inconvenient Ethernet
cables.
You can configure your wireless network in either the built-in Web Configurator, or using the WPS
button.
Figure 3 Wireless Access Example
Chapter 1 Introducing the VMG
1.8.1 Using the Wi-Fi and WPS Buttons
If the wireless network is turned off, press the Wi-Fi button for one second. Once the WiFi LED
turns green, the wireless network is active.
You can also use the WPS button to quickly set up a secure wireless connection between the VMG
and a WPS-compatible client by adding one device at a time.
To activate WPS:
1 Make sure the PWR/SYS LED is on and not blinking.
2 Press the WPS button for five seconds and release it.
3 Press the WPS button on another WPS-enabled device within range of the VMG. The WiFi LED
flashes orange while the VMG sets up a WPS connection with the other wireless device.
4 Once the connection is successfully made, the WiFi LED shines green.
To turn off the wireless network, press the Wi-Fi button for one to five seconds. The WiFi LED
turns off when the wireless network is off.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
22
Page 23
2.1 Overview
The web configurator is an HTML-based management interface that allows easy VMG setup and
management via Internet browser. Use Internet Explorer 8.0 and later versions or Mozilla Firefox 3
and later versions or Safari 2.0 and later versions. The recommended screen resolution is 1024 by
768 pixels.
In order to use the web configurator you need to allow:
CHAPTER 2
The Web Configurator
• Web browser pop-up windows from your
Windows XP SP (Service Pack) 2.
• JavaScript (enabled by default).
• Java permissions (enabled by default).
See Appendix D on page 399 if you need to make sure these functions are allowed in Internet
Explorer.
2.1.1 Accessing the Web Configurator
1 Make sure your VMG hardware is properly connected (refer to the Quick Start Guide).
2 Launch your web browser. If the VMG does not automatically re-direct you to the login screen, go to
http://192.168.1.1.
3 A password screen displays. To access the administrative web configurator and manage the VMG,
type the default username admin and password 1234 in the password screen and click Login. If
advanced account security is enabled (see Section 29.2 on page 313) the number of dots that
appears when you type the password changes randomly to prevent anyone watching the password
field from knowing the length of your password. If you have changed the password, enter your
password and click Login.
Figure 4 Password Screen
VMG. Web pop-up blocking is enabled by default in
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
23
Page 24

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
4 The following screen displays if you have not yet changed your password. It is strongly
recommended you change the default password. Enter a new password, retype it to confirm and
click Apply; alternatively click Skip to proceed to the main menu if you do not want to change the
password now.
Figure 5 Change Password Screen
5 The Quick Start Wizard screen appears. You can configure the VMG’s time zone, basic Internet
access, and wireless settings. See Chapter 3 on page 33 for more information.
6 After you finished or closed the Quick Start Wizard screen, the Network Map page appears.
Figure 6 Network Map
7 Click Status to display the Status screen, where you can view the VMG’s interface and system
information.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
24
Page 25

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
C
A
B
2.2 Web Configurator Layout
Figure 7 Screen Layout
As illustrated above, the main screen is divided into these parts:
• A - title bar
• B - main window
• C - navigation panel
2.2.1 Title Bar
The title bar provides some icons in the upper right corner.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
25
Page 26
The icons provide the following functions.
Table 2 Web Configurator Icons in the Title Bar
ICON DESCRIPTION
2.2.2 Main Window
The main window displays information and configuration fields. It is discussed in the rest of this
document.
After you click Status on the Connection Status page, the Status screen is displayed. See
Chapter 5 on page 74 for more information about the Status screen.
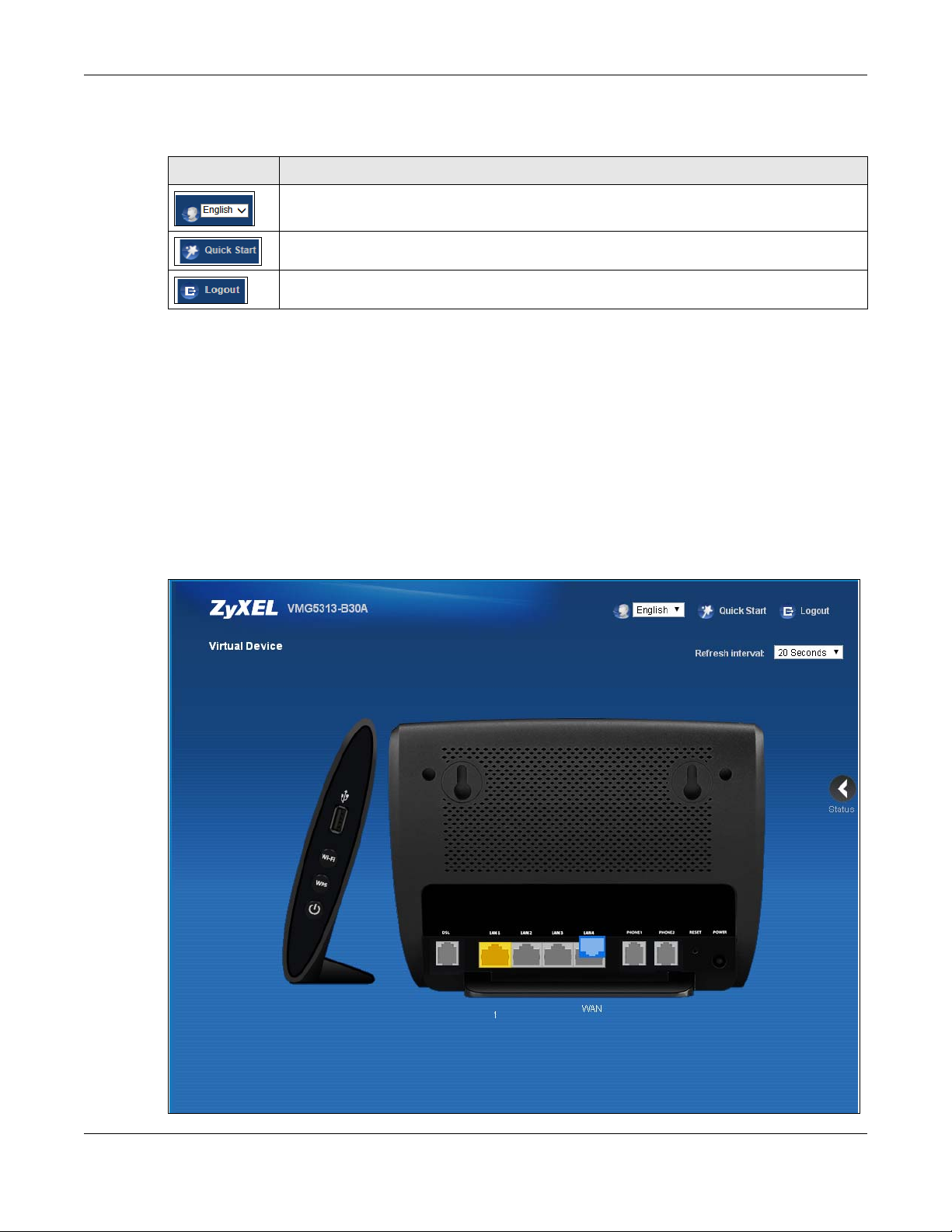
If you click Virtual Device on the System Info screen, a visual graphic appears, showing the
connection status of the VMG’s ports. The connected ports are in color and disconnected ports are
gray.
Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Language: Select the language you prefer.
Quick Start: Click this icon to open screens where you can configure the VMG’s time zone
Internet access, and wireless settings.
Logout: Click this icon to log out of the web configurator.
Figure 8 Virtual Device
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
26
Page 27

2.2.3 Navigation Panel
Use the menu items on the navigation panel to open screens to configure VMG features. The
following tables describe each menu ite m.
Table 3 Navigation Panel Summary
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Connection Status This screen shows the network status of the VMG and computers/
Network Setting
Broadband Broadband Use this screen to view and configure ISP parameters, WAN IP
3G Backup Use this screen to configure 3G WAN connection.
Advanced Use this screen to enable or disable PTM over ADSL, Annex M/Annex
802.1x Use this screen to view and configure the IEEE 802.1x settings on the
Ethernet WAN Use this screen to convert Ethernet LAN 4 port as WAN port, or
Wireless General Use this screen to configure the wireless LAN settings and WLAN
Guest/More AP Use this screen to configure multiple BSSs on the VMG.
MAC
Authentication
WPS Use this screen to configure and view your WPS (Wi-Fi Protected
WMM Use this screen to enable or disable Wi-Fi MultiMedia (WMM).
WDS Use this screen to set up Wireless Distribution System (WDS) links to
Others Use this screen to configure advanced wireless settings.
Channel Status Use this screen to scan wireless LAN channel noises and view the
Home
Networking
LAN Setup Use this screen to configure LAN TCP/IP settings, and other advanced
Static DHCP Use this screen to assign specific IP addresses to individual MAC
UPnP Use this screen to turn UPnP and UPnP NAT-T on or off.
Additional
Subnet
STB Vendor ID Use this screen to have the VMG automatically create static DHCP
Wake on Lan Use this screen to remotely turn on a device on the local network.
TFTP Server
Name
Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
devices connected to it.
address assignment, and other advanced properties. Y ou can also add
new WAN connections.
J, and DSL PhyR functions.
VMG.
restore the WAN port to LAN port.
authentication/security settings.
Use this screen to block or allow wireless traffic from wireless devices
of certain SSIDs and MAC addresses to the VMG.
Setup) settings.
other access points.
results.
properties.
addresses.
Use this screen to configure IP alias and public static IP.
entries for Set Top Box (STB) devices when they request IP
addresses.
Use DHCP option 66 to identify a TFTP server name.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
27
Page 28
Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Table 3 Navigation Panel Summary (continued)
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Routing Static Route Use this screen to view and set up static routes on the VMG.
DNS Route
Policy
Forwarding
RIP
QoS General Use this screen to enable QoS and traffic prioritizing. You can also
Queue Setup Use this screen to configure QoS queues.
Class Setup Use this screen to define a classifier.
Policer Setup Use these screens to configure QoS policers.
NAT Port Forwarding Use this screen to make your local servers visible to the outside
Applications
Port Triggering Use this screen to change your VMG’s port triggering settings.
DMZ Use this screen to configure a default server which receives packets
ALG Use this screen to enable or disable SIP ALG.
Address Mapping Use this screen to change your Device’s address mapping settings.
Sessions Use this screen to configure the maximum number of NAT sessions
DDNS DNS Entry Use this screen to view and configure DNS routes.
Dynamic DNS Use this screen to allow a static hostname alias for a dynamic IP
Vlan Group Vlan Group Use this screen to group and tag VLAN IDs to outgoing traffic from
Interface
Grouping
USB Service File Sharing Use this screen to enable file sharing via the VMG.
Power
Management
Security Settings
Interface
Grouping
Media Server Use this screen to use the VMG as a media server.
Print Server Use this screen to enable the print server on the VMG and get the
Power
Management
Auto Switch Off This screen is only available for administrators. Use this screen to
Use this screen to forward DNS queries for certain domain names
through a specific WAN interface to its DNS server(s).
Use this screen to configure policy routing on the VMG.
Use this screen to configure Routing Information Protocol to
exchange routing information with other routers.
configure the QoS rules and actions.
world.
Use this screen to configure servers behind the VMG.
from ports that are not specified in the Port Forwarding screen.
each client host is allowed to have through the VMG.
address.
the specified interface.
Use this screen to map a port to a PVC or bridge group.
model name of the associated printer.
This screen is only available for administrators. Use this screen to
manually turn on/off specific interface(s) and/or all LEDs
immediately.
configure schedules to have the VMG automatically turn on/off
specific interface(s) and/or all LEDs.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
28
Page 29

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Table 3 Navigation Panel Summary (continued)
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Firewall General Use this screen to configure the security level of your firewall.
Protocol Use this screen to add Internet services and configure firewall rules.
Access Control Use this screen to enable specific traffic directions for network
services.
DoS Use this screen to activate protection against De nial of Service ( DoS)
attacks.
MAC Filter MAC Filter Use this screen to block or allow traffic from devices of certain MAC
Parental
Control
Scheduler
Rules
Certificates Local Certificates Use this screen to view a summary list of certificates and manage
IPSec VPN Setup Use this screen to add or edit VPN policies.
VoIP
SIP SIP Account
Phone Phone
Call Rule Call Rule
Call History Call History
System Monitor
Parental Control Use this screen to block web sites with the specific URL.
Scheduler Rules Use this screen to configure the days and times when a configured
Trusted CA
Monitor Use this screen to view the status of all IPSec VPN tunnels. You can
SIP Service
Provider
Summary
Call History
Outgoing
Call History
Incoming
addresses to the VMG.
restriction (such as parental control) is enforced.
certificates and certification requests.
Use this screen to view and manage the list of the trusted CAs.
also manually initiate a tunnel in this screen.
Use this screen to set up information about your SIP account and
configure audio settings such as volume levels for the phones
connected to the VMG.
Use this screen to configure your VMG’s Voice over IP settings.
Use this screen to select your location and a call service mode.
Use this screen to view a call history list.
Use this screen to view detailed information for each outgoing call
you made.
Use this screen to view detailed information for each incoming call
from someone calling you.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
29
Page 30

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Table 3 Navigation Panel Summary (continued)
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Log System Log Use this screen to view the status of events that occurred to the VMG.
You can export or e-mail the logs.
Security Log Use this screen to view all security related events. You can select
level and category of the security events in their proper drop-down
list window.
Levels include:
•Emergency
•Alert
•Critical
•Error
•Warning
•Notice
• Informational
• Debugging
Category include:
• Account
•Attack
•Firewall
•MAC Filter
Traffic Status WAN Use this screen to view th e status of all netw ork tr affic going through
the WAN port of the VMG.
LAN Use this screen to view the status of all network traffic going through
NAT Use this screen to view NAT statistics for connected hosts.
VoIP Statu s VoIP Status Use this screen to view VoIP registration, current call status and
ARP table ARP table Use this screen to view the ARP table. It displays the IP and MAC
Routing Table Routing Table Use this screen to view the routing table on the VMG.
IGMP/MLD
Group Status
xDSL Statistics xDSL Statistics Use this screen to view the Device’s xDSL traffic statistics.
3G Statistics 3G Statistics Use this screen to look at 3G Internet connection status.
Maintenance
User Account User Account Use this screen to change user password on the VMG.
Remote MGMT
TR-069 Client TR-069 Client Use this screen to configure the VMG to be managed by an Auto
TR-064 TR-064 Use this screen to enable management via TR-064 on the LAN.
SNMP SNMP Use this screen to configure SNMP (Simple Network Management
Time Time Use this screen to change your VMG’s time and date.
IGMP/MLD
Group Status
Remote MGMT Use this screen to enable specific traffic directions for network
Trust Domain Use this screen to grant access to local management service by
the LAN ports of the VMG.
phone numbers for the phone ports.
address of each DHCP connection.
Use this screen to view the status of all IGMP settings on the VMG.
services.
adding IP address.
Configuration Server (ACS).
Protocol) settings.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
30
Page 31

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
Table 3 Navigation Panel Summary (continued)
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Email
Notification
Log Setting Log Setting Use this screen to change your VMG’s log settings.
Firmware
Upgrade
Configuration Configuration Use this screen to backup and restore your VMG’s configuration
Reboot Reboot Use this screen to reboot the VMG without turning the power off.
Diagnostic Ping&Traceroute
Email
Notification
Firmware
Upgrade
&Nslookup
802.1ag Use this screen to configure CFM (Connectivity Fault Management)
OAM Ping Use this screen to view information to help you ident ify problems with
Use this screen to configure up to two mail servers and sender
addresses on the VMG.
Use this screen to upload firmware to your VMG.
(settings) or reset the factory default settings.
Use this screen to identify problems with the DSL connection. You can
use Ping, TraceRoute, or Nslookup to help you identify problems.
MD (maintenance domain) and MA (maintenance association),
perform connectivity tests and view test reports.
the DSL connection.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 2 The Web Configurator
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
32
Page 33

3.1 Overview
Use the Quick Start screens to configure the VMG’s time zone, basic Internet access, and wireless
settings.
Note: See the technical reference chapters (starting on Chapter 4 on page 35) for
background information on the features in this chapter.
3.2 Quick Start Setup
1 The Quick Start Wizard appears automatically after login. Or you can click the Click Start icon in
the top right corner of the web configurator to open the quick start screens. Select the time zone of
the VMG’s location and click Next.
Figure 9 Quick Start - Welcome
CHAPTER 3
Quick Start
2 Enter your Internet connection information in this screen. The screen and field s to enter may vary
depending on your current connection type. Click Next. Click Next.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 3 Quick Start
Figure 10 Quick Start - Internet Connection
3 Turn the wireless LAN on or off . If you k eep it on, record the security settings so y ou can configure
your wireless clients to connect to the VMG. Click Save.
Figure 11 Quick Start - Wireless
4 Your VMG saves your settings and attempts to connect to the Internet.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
34
Page 35

4.1 Overview
This chapter shows you how to use the VMG’s various features.
• Setting Up an Ethernet WAN Connection, see page 35
• Configure the Broadband screen as follows., see page 35
• Setting Up a Secure Wireless Network, see page 41
• Setting Up Multiple Wireless Groups, see page 47
• Configuring Static Route for Routing to Another Network, see page 50
• Configuring QoS Queue and Class Setup, see page 53
• Access the VMG Using DDNS, see page 56
• Configuring the MAC Address Filter, see page 57
• Access Your Shared Files From a Computer, see page 58
• Using the Media Server Feature, see page 60
• Using the Print Server Feature, see page 65
CHAPTER 4
Tutorials
4.2 Setting Up an Ethernet WAN Connection
This tutorial shows you how to use LAN port 4 as an alternativ e or backup Internet connection using
the Web Configurator.
1 Click Network Setting > Broadband to open the following screen. Click Add New WAN
Interface.
2 Configure the Broadband screen as follows.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 4 Tutorials
3 The Broadband summary screen then appears as follows.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
36
Page 37

Chapter 4 Tutorials
4 Next, go to Broadband > Ethernet WAN, select Enable and then click Apply.
5 After the connection is set up, connect LAN port 4 to a broadband router or modem for Internet
access.
Note: The DSL Internet connection and the Ethernet Internet connection cannot operate
at the same time.
4.3 Setting Up an ADSL PPPoE Connection
This tutorial shows you how to set up an ADSL Internet connection using the Web Configurator.
If you connect to the Internet through an ADSL connection, use the information from your Internet
Service Provider (ISP) to configure the VMG. Be sure to contact your service provider for any
information you need to configure the Broadband screens.
1 Click Network Setting > Broadband to open the following screen. Click Add New WAN
Interface.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
37
Page 38

Chapter 4 Tutorials
2 In this example, the DSL connection has the following information.
General
Name MyDSLConnection
Type ADSL
Connection Mode Routing
Encapsulation PPPoE
IPv6/IPv4 Mode IPv4
ATM PVC Configuration
VPI/VCI 36/48
Encapsulation Mode LLC/SNAP-Bridging
Service Category UBR without PCR
Account Information
PPP User Name 1234@DSL-Ex.com
PPP Password ABCDEF!
PPPoE Service Name MyDSL
Static IP Address 192.168.1.32
Others PPPoE Passthrough: Disabled
NAT: Enabled
IGMP Multicast Proxy: Enabled
Apply as Default Gateway: Enabled
3 Select the Active check box. Enter the General and ATM PVC Configuration settings as provided
above.
Set the Type to ADSL over ATM.
Choose the Encapsulation specified by your DSL service provider. For this example, the service
provider requires a username and password to establish Internet connection. Therefore, select
PPPoE as the WAN encapsulation type.
Set the IPv6/IPv4 Mode to IPv4 Only.
4 Enter the account information provided to you by your DSL service provider.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
38
Page 39

Chapter 4 Tutorials
5 Configure this rule as your default Internet connection by selecting the Apply as Default Gateway
check box. Then select DNS as Static and enter the DNS server addresses pro vided to you, such as
192.168.5.2
6 Leave the rest of the fields to the default settings.
7 Click Apply to save your settings.
(DNS server1)/192.168.5.1 (DNS server2).
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 4 Tutorials
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
40
Page 41

Chapter 4 Tutorials
8 You should see a summary of your new DSL connection setup in the Broadband screen as follows.
Try to connect to a website to see if you have correctly set up your Internet connection. Be sure to
contact your service provider for any information you need to configure the WAN screens.
4.4 Setting Up a Secure Wireless Network
Thomas wants to set up a wireless network so that he can use his notebook to access the Internet.
In this wireless network, the VMG serves as an access point (AP), and the notebook is the wireless
client. The wireless client can access the Internet through the AP.
Thomas has to configure the wireless network settings on the VMG. Then he can set up a wireless
network using WPS (Section 4.4.2 on page 42 ) or manual configuration (Section 4.4.3 on page 46).
4.4.1 Configuring the Wireless Network Settings
This example uses the following parameters to set up a wireless network.
SSID Example
Security Mode WPA2-PSK
Pre-Shared Key DoNotStealMyWirelessNetwork
802.11 Mode 802.11b/g/n Mixed
1 Click Network Setting > Wireless to open the General screen. Select More Secure as the
security level and WPA2-PSK as the security mode. Configure the screen using the provided
parameters (see page 41). Click Apply.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 4 Tutorials
2 Go to the Wireless > Others screen and select 802.11b/g/n Mixed in the 802.11 Mode field.
Click Apply.
Thomas can now use the WPS feature to establish a wireless connection between his notebook and
the VMG (see Section 4.4.2 on page 42). He can also use the notebook’s wireless client to search
for the VMG (see Section 4.4.3 on page 46).
4.4.2 Using WPS
This section shows you how to set up a wireless network using WPS. It uses the VMG as the AP and
ZyXEL NWD210N as the wireless client which connects to the notebook.
Note: The wireless client must be a WPS-aware device (for example, a WPS USB adapter
or PCMCIA card).
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
42
Page 43

Chapter 4 Tutorials
There are two WPS methods to set up the wireless client settings:
• Push Button Configuration (PBC) - simply press a button. This is the easier of the two
methods.
• PIN Configuration - configure a Personal Identification Number (PIN) on the VMG. A wireless
client must also use the same PIN in order to download the wireless network settings from the
VMG.
Push Button Configuration (PBC)
1 Make sure that your VMG is turned on and your notebook is within the cover range of the wireless
signal.
2 Make sure that you have installed the wireless client driver and utility in your notebook.
3 In the wireless client utility, go to the WPS setting page. Enable WPS and press the WPS button
(Start or WPS button).
4 Push and hold the WPS button located on the VMG’s front panel for more than 5 seconds.
Alternatively, you may log into VMG’s web configurator and go to the Network Setting >
Wireless > WPS screen. Enable the WPS function and click Apply. Then click the Connect button.
Note: Y our VMG has a WPS button located on its front panel as well as a WPS button in it s
configuration utility. Both buttons have exactly the same funct ion: you can use one
or the other.
Note: It doesn’t matter which button is pressed first. You must press the second button
within two minutes of pressing the fi rs t one.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
43
Page 44

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Wireless Client
Device
SECURITY INFO
COMMUNICATION
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
Press and hold for
5 seconds
WLAN/
WPS
The VMG sends the proper configuration settings to the wireless client. This may take up to two
minutes. The wireless client is then able to communicate with the VMG securely.
The following figure shows you an example of how to set up a wireless network and its security by
pressing a button on both VMG and wireless client.
Example WPS Process: PBC Method
PIN Configuration
When you use the PIN configuration method, you need to use both the VMG’ s web configur ator and
the wireless client’s utility.
1 Launch your wireless client’s configuration utility. Go to the WPS settings and select the PIN method
to get a PIN number.
2 Log into VMG’s web configurator and go to the Network Setting > Wireless > WPS screen.
Enable the WPS function and click Apply.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
44
Page 45

Chapter 4 Tutorials
3 Enter the PIN number of the wireless client and click the Register button. Activate WPS function on
the wireless client utility screen within two minutes.
The VMG authenticates the wireless client and sends the proper configuration settings to the
wireless client. This may take up to two minutes. The wireless client is then able to communicate
with the VMG securely.
The following figure shows you how to set up a wireless network and its security on a VMG and a
wireless client by using PIN method.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Example WPS Process: PIN Method
Authentication by PIN
SECURITY INFO
WITHIN 2 MINUTES
Wireless Client
ZyXEL Device
COMMUNICATION
Chapter 4 Tutorials
4.4.3 Without WPS
Use the wireless adapter’s utility installed on the notebook to search for the “Example” SSID. Then
enter the “DoNotStealMyWirelessNetwork” pre-shared key to establish an wireless Internet
connection.
Note: The VMG supports IEEE 802.11b and IEEE 802.11g wireless clients. Make sure that
your notebook or computer’s wireless adapter supports one of these standards.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
46
Page 47

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Company
VIP
Guest
4.5 Setting Up Multiple Wireless Groups
Company A wants to create different wireless network groups for different types of users as shown
in the following figure. Each group has its own SSID and security mode.
• Employees in Company A will use a general Company wireless network group.
• Higher management level and important visitors will use the VIP group.
• Visiting guests will use the Guest group, which has a different SSID and password.
Company A will use the following parameters to set up the wireless network groups.
COMPANY VIP GUEST
SSID Company VIP Guest
Security Level More Secure More Secure More Secure
Security Mode WPA2-PSK WPA2-PSK WPA2-PSK
Pre-Shared Key ForCompanyOnly 123456789 guest123
1 Click Network Setting > Wireless to open the General screen. Use this screen to set up the
company’s general wireless network group. Configure the screen using the provided parameters
and click Apply.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
47
Page 48

Chapter 4 Tutorials
2 Click Network Setting > Wireless > Guest/More AP to open the following screen. Click the
Edit icon to configure the second wireless network group.
3 Configure the screen using the provided parameters and click Apply.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
48
Page 49

Chapter 4 Tutorials
4 In the Guest/More AP screen, click the Edit icon to configure the third wireless network
group.Configure the screen using the provided parameters and click Apply.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Chapter 4 Tutorials
5 Check the status of VIP and Guest in the Guest/More AP screen. The yellow bulbs signify that the
SSIDs are active and ready for wireless access.
4.6 Configuring Static Route for Routing to Another Network
In order to extend your Intranet and control traffic flowing directions, you may connect a router to
the VMG’s LAN. The router may be used to separate two department networks. This tutorial shows
how to configure a static routing rule for two network routings.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
50
Page 51

Chapter 4 Tutorials
N2
B
N1
A
R
N2
B
N1
A
R
In the following figure, router R is connected to the VMG’s LAN. R connects to two networks, N1
(192.168.1.x/24) and N2 (192.168.10.x/24). If you want to send traffic from computer A (in N1
network) to computer B (in N2 network), the traffic is sent to the VMG’s WAN default gateway by
default. In this case, B will never receive the traffic.
You need to specify a static routing rule on the VMG to specify R as the router in charge of
forwarding traffic to N2. In this case, the VMG routes traffic from A to R and then R routes the
traffic to B.
This tutorial uses the following example IP settings:
Table 4 IP Settings in this Tutorial
DEVICE / COMPUTER IP ADDRESS
The VMG’s WAN 172.16.1.1
The VMG’s LAN 192.168.1.1
IP Type IPv4
Use Interface VDSL/ppp1.1
A 192.168.1.34
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Table 4 IP Settings in this Tutorial
DEVICE / COMPUTER IP ADDRESS
R’s N1 192.168.1.253
R’s N2 192.168.10.2
B 192.168.10.33
To configure a static route to route traffic from N1 to N2:
1 Log into the VMG’s Web Configurator in advanced mode.
2 Click Network Setting > Routing.
3 Click Add new static route in the Static Route screen.
4 Configure the Static Route Setup screen using the following settings:
4a Select the Active check box. Enter the Route Name as R.
4b Set IP Type to IPv4.
4c Type 192.168.10.0 and subnet mask 255.255.255.0 for the destination, N2.
4d Select Enable in the Use Gateway IP Address field. T ype 192.168.1.253 (R’ s N1 address)
in the Gateway IP Address field.
4e Select VDSL/ppp1.1 as the Use Interface.
4a Click OK.
Now B should be able to receive traffic from A. You may need to additionally configure B’s firewall
settings to allow specific traffic to pass through.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
52
Page 53

Chapter 4 Tutorials
10,000 kbps
DSL
Your computer
IP=192.168.1.23
A colleague’s computer
Other traffic: Automatic classifier
and/or
MAC=AA:FF:AA:FF:AA:FF
Email traffic: Highest priority
4.7 Configuring QoS Queue and Class Setup
This section contains tutorials on how you can configure the QoS screen.
Let’s say you are a team leader of a small sales branch office. You want to prioritize e-mail traffic
because your task includes sending urgent updates to clients at least twice every hour. You also
upload data files (such as logs and e-mail archives) to the FTP server throughout the day. Your
colleagues use the Internet for research, as well as chat applications for communicating with other
branch offices.
In the following figure, your Internet connection has an upstream transmission bandwidth of
10,000 kbps. For this example, you want to configure QoS so that e-mail traffic gets the highest
priority with at least 5,000 kbps. You can do the following:
• Configure a queue to assign the highest priority queue (1) to e-mail traffic going to the WAN
interface, so that e-mail traffic would not get delayed when there is network congestion.
• Note the IP address (192.168.1.23 for example) and/or MAC address (AA:FF:AA:FF:AA:FF for
example) of your computer and map it to queue 7.
Note: QoS is applied to traffic flowing out of the VMG.
Traffic that does not match this class is assigned a priority queue based on the internal QoS
mapping table on the VMG.
QoS Example
1 Click Network Setting > QoS > General and select Enable. Set your WAN Managed Upstream
Bandwidth to 10,000 kbps (or leave this blank to have the VMG automatically determine this
figure). Click Apply.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
53
Page 54

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Tutorial: Advanced > QoS
2 Click Queue Setup > Add new Queue to cr
3 eate a new queue. In the screen that opens, ch eck Active and enter or select the following values:
• Name: E-mail
• Interface: WAN
• Priority: 1 (High)
• Weight: 8
• Rate Limit: 5,000 (kbps)
Tutorial: Advanced > QoS > Queue Setup
4 Click Class Setup > Add new Classifier to create a new class. Check Active and follow the
settings as shown in the screen below.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
54
Page 55

Tutorial: Advanced > QoS > Class Setup
Chapter 4 Tutorials
Class Name Give a class name to this traffic, such as E-mail in this example.
From
Interface
Ether Type Select IP to identify the traffic source by its IP address or MAC address.
IP Address Type the IP address of your computer - 192.168.1.23. Type the IP Subne t Mask if you
MAC Address Type the MAC address of your computer - AA:FF:AA:FF:AA:FF. Type the MAC Mask if you
To Queue
Index
This is the interface from which the traffic will be coming from. Select LAN1 for this
example.
know it.
know it.
Link this to an item in the Network Setting > QoS > Queue Setup screen, which is the E-
mail queue created in this example.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 4 Tutorials
w.x.y.z
a.b.c.d
http://zyxelrouter.dyndns.org
A
This maps e-mail traffic coming from port 25 to the highest priority, which you have created in the
previous screen (see the IP Protocol field). This also maps your computer’s IP address and MAC
address to the E-mail queue (see the Source fields).
5 Verify that the queue setup works by checking Network Setting > QoS > Monitor. This shows
the bandwidth allotted to e-mail traffic compared to other network traffic.
4.8 Access the VMG Using DDNS
If you connect your VMG to the Internet and it uses a dynamic WAN IP address, it is inconvenient
for you to manage the device from the Internet. The VMG’s WAN IP address changes dynamically.
Dynamic DNS (DDNS) allows you to access the VMG using a domain name.
To use this feature, you have to apply for DDNS service at www.dyndns.org.
This tutorial covers:
• Registering a DDNS Account on www.dyndns.org
• Configuring DDNS on Your VMG
• Testing the DDNS Setting
Note: If you have a private WAN IP address, then you cannot use DDNS.
4.8.1 Registering a DDNS Account on www.dyndns.org
1 Open a browser and type http://www.dyndns.org.
2 Apply for a user account. This tutorial uses UserName1 and 12345 as the username and
password.
3 Log into www.dyndns.org using your account.
4 Add a new DDNS host name. This tutorial uses the following settings as an example.
•Hostname: zyxelrouter.dyndns.org
•Service Type: Host with IP address
• IP Address: Enter the WAN IP address that your VMG is currently using. You can find the IP
address on the VMG’s Web Configurator Status page.
Then you will need to configure the same account and host name on the VMG later.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
56
Page 57

Chapter 4 Tutorials
4.8.2 Configuring DDNS on Your VMG
Configure the following settings in the Network Setting > DNS > Dynamic DNS screen.
•Select Enable Dynamic DNS.
•Select www.DynDNS.com as the service provider.
•Type zyxelrouter.dyndns.org in the Host Name field.
• Enter the user name (UserName1) and password (12345).
Click Apply.
4.8.3 Testing the DDNS Setting
Now you should be able to access the VMG from the Internet. To test this:
1 Open a web browser on the computer (using the IP address a.b.c.d) that is connected to the
Internet.
2 Type http://zyxelrouter.dyndns.org and press [Enter].
3 The VMG’s login page should appear. You can then log into the VMG and manage it.
4.9 Configuring the MAC Address Filter
Thomas noticed that his daughter Josephine spends too much time surfing the web and
downloading media files. He decided to prevent Josephine from accessing the Internet so that she
can concentrate on preparing for her final exams.
Josephine’s computer connects wirelessly to the Internet through the VMG. Thomas decides to use
the Security > MAC Filter screen to grant wireless network access to his computer but not to
Josephine’s computer.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Thomas
Josephine
1 Click Security > MAC Filter to open the MAC Filter screen. Select the Enable check box to
activate MAC filter function.
2 Select Allow. Then enter the host name and MAC address of Thomas’ computer in this screen. Click
Apply.
Thomas can also grant access to the computers of other members of his family and friends.
However, Josephine and others not listed in this screen will no longer be able to access the Internet
through the VMG.
4.10 Access Your Shared Files From a Computer
Here is how to use an FTP program to access a file storage device connected to the VMG’s USB port.
Note: This example uses the FileZilla FTP program to browse your shared files.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
58
Page 59

Chapter 4 Tutorials
1 In FileZilla enter the IP address of the VMG (the default is 192.168.1.1), your account’s user name
and password and port 21 and click Quickconnect. A screen asking for password authentication
appears.
File Sharing via Windows Explore r
2 Once you log in the USB device displays in the mnt folder.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
59
Page 60

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Computer with
ZyXEL Device
USB Storage Device
Windows Media Player
4.11 Using the Media Server Feature
Use the media server feature to play files on a computer or on your television (using DMA-2500).
This section shows you how the media server feature works using the following media clients:
• Microsoft (MS) Windows Media Player
Media Server works with Windows Vista and Windows 7. Make sure your computer is able to play
media files (music, videos and pictures).
• ZyXEL DMA-2500, a digital media adapter
You need to set up the DMA-2500 to work with your television (TV). R efer to the DMA-2500 Quick
Start Guide for the correct hardware connections.
Before you begin, connect the USB storage device containing the media files you want to play to the
USB port of your VMG.
4.11.1 Configuring the VMG
Note: The Media Server feature is enabled by default.
To use your VMG as a media server, click Network Setting > Home Networking > Media
Server.
Tutorial: USB Services > Me dia Server
Check Enable Media Server and click Apply . This enables DLNA-compliant media clients to play
the video, music and image files in your USB storage device.
4.11.2 Using Windows Media Player
This section shows you how to play the media files on the USB storage device connected to your
VMG using Windows Media Player.
Tutorial: Media Server Setup (Using Windows Media Player)
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
60
Page 61

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Windows Vista
1 Open Windows Media Player and click Library > Media Sharing as follows.
Tutorial: Media Sharing using Windows Vista
2 Check Find media that others are sharing in the following screen and click OK.
Tutorial: Media Sharing using Windows Vista (2)
3 In the Library screen, check the left panel. The Windows Media Player should detect the VMG.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
61
Page 62

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Tutorial: Media Sharing using Windows Vista (3)
The VMG displays as a playlist. Clicking on the category icons in the right panel shows you the
media files in the USB storage device attached to your VMG.
Windows 7
1 Open Windows Media Player. It should automatically detect the VMG.
Tutorial: Media Sharing using Windows 7 (1)
If you cannot see the VMG in the left panel as shown above, right-click Other Libraries > Refresh
Other Libraries.
2 Select a category in the left panel and wait for Windows Media Player to connect to the VMG.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
62
Page 63

Chapter 4 Tutorials
Tutorial: Media Sharing using Windows 7 (2)
3 In the right panel, you should see a list of files available in the USB storage device.
Tutorial: Media Sharing using Windows 7 (2)
4.11.3 Using a Digital Media Adapter
This section shows you how you can use the VMG with a Z yXEL DMA-2500 to play media files stored
in the USB storage device in your TV screen.
Note: For this tutorial, your DMA-2500 should already be set up with the TV according to
the instructions in the DMA-2500 Quick Start Guide.
1 Connect the DMA-2500 to an available LAN port in your VMG.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
63
Page 64

Chapter 4 Tutorials
DMA-2500
ZyXEL Device
USB Storage Device
Tutorial: Media Server Setup (Using DMA)
2 Turn on the TV and wait for the DMA-2500 Home screen to appear. Using the remote control, go to
MyMedia to open the following screen. Select the VMG as your media server.
Tutorial: Media Sharing using DMA-2500
3 The screen shows you the list of available media files in the USB storage device. Select the file you
want to open and push the Play button in the remote control.
Tutorial: Media Sharing using DMA-2500 (2)
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
64
Page 65

Chapter 4 Tutorials
4.12 Using the Print Server Feature
The VMG allows you to share a USB printer on your LAN. You can do this by connecting a USB
printer to one of the USB ports on the VMG and then adding the printer on the computers
connected to your network.
In this section you can:
• Add a New Printer Using Windows
• Add a New Printer Using Macintosh OS X
Add a New Printer Using Windows
This example shows how to connect a printer to your VMG using the Windows 7 operating system.
Some menu items may look different on your operating system.
1 Click Start > Control Panel > Devices and Printers to open the Devices and Printers screen.
Click Add a printer.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Tutorial: Printers Folder
Chapter 4 Tutorials
2 The Add Printer wizard screen displays. Click Add a network, wireless or Bluetooth printer.
Tutorial: Add Printer Wizard: Welcome
3 Click The printer that I want isn’t listed.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
66
Page 67

Tutorial: Add Printer Wizard: Welcome
Chapter 4 Tutorials
4 Select the Select a shared printer by name option. Enter the URL for your printer, http://
192.168.1.1:631/printers/USB_PRINTER, in this example. This URL can be found in the VMG’s
Web Configurator on the Network Setting > USB Service > Printer Server screen. Click Next.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
67
Page 68

Tutorial: Add Printer Wizard: Welcome
Chapter 4 Tutorials
5 Install the printer driver. Please check the Windows CD if it includes the printer driver . If not, please
install the driver from the CD included with your printer or by downloading it from the printer
vendor’s website.
6 After the printer driver installs successfully, choose if you want to set this printer to be the default.
Add a New Printer Using Macintosh OS X
Complete the following steps to set up a print server driver on your Macintosh computer.
1 Click the Print Center icon located in the Macintosh Dock (a place holding a series of icons/
shortcuts at the bottom of the desktop). Proceed to step 6 to continue. If the Print Center icon is
not in the Macintosh Dock, proceed to the next step.
2 On your desktop, double-click the Macintosh HD icon to open the Macintosh HD window.
Tutorial: Macintosh HD
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
68
Page 69

Chapter 4 Tutorials
3 Double-click the Applications folder.
Tutorial: Macintosh HD folder
4 Double-click the Utilities folder.
Tutorial: Applications Fold er
5 Double-click the Print Center icon.
Tutorial: Utilities Folder
6 Click the Add icon at the top of the screen.
Tutorial: Printer List Folder
7 Set up your printer in the Printer List configuration screen. Select IP Printing from the drop-
down list box.
8 In the Printer’s Address field, type the IP address of your VMG.
9 Deselect the Use default queue on server check box.
10 Type LP1 in the Queue Name field.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 4 Tutorials
11 Select your Printer Model from the drop-down list box. If the printer's model is not listed, select
Generic.
Tutorial: Printer Configuration
12 Click Add to select a printer model, save and close the Printer List configuration screen.
Tutorial: Printer Model
13 The Name LP1 on 192.168.1.1 displays in the Printer List field. The default printer Name
displays in bold type.
Tutorial: Print Server
Your Macintosh print server driver setup is complete. You can now use the VMG’s print server to
print from a Macintosh computer.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
70
Page 71

PART II
Technical Reference
71
Page 72

72
Page 73

Network Map and Status Screens
5.1 Overview
After you log into the Web Configur ator, the Network Map screen appears. This shows the network
connection status of the Device and clients connected to it.
You can use the Status screen to look at the current status of the Device, system resources, and
interfaces (LAN, WAN, and WLAN).
5.2 The Network Map Screen
Use this screen to view the network connection status of the device and its clients. A warning
message appears if there is a connection problem.
CHAPTER 5
Figure 12 Network Map: Icon View Mode
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 5 Network Map and Status Screens
If you want to view information about a client, click the client’s name and Info. Click the IP address
if you want to change it. If you want to change the name or icon of the client, click Change name/
icon.
If you prefer to view the status in a list, click List View in the Viewing mode selection box. You
can configure how often you want the Device to update this screen in Refresh interval.
Figure 13 Network Map: List View Mode
5.3 The Status Screen
Use this screen to view the status of the VMG. Click Status to open this screen.
Figure 14 Status Screen
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
74
Page 75

Chapter 5 Network Map and Status Screens
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 5 Status Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh Interval Select how often you want the VM G to update this screen.
Device Information
Host Name This field displays the VMG system name. It is used for identification.
Model Number This shows the model number of your VMG.
Serial Number This shows the unique serial number of your VMG.
Firmware
Version
WAN Information (These fields display when you have a WAN connection.)
WAN Type This shows wherther it’s a DSL, Ethernet or 3G WAN connection..
WAN Name This is the namke of the interface.
MAC Address This shows the WAN Ethernet adapter MAC (Media Access Control) Address of your VMG.
IP v4 Address This field displays the current IP address of the VMG in the WAN. Click Release to
IPv4 Subnet
Mask
IPv4 Uptime This shows how long the VMG has had the IP address.
Primary DNS
server
Secondary DNS
server
Encapsulation This field displays the current encapsulation method.
LAN Information
IPv4 Address This is the current IP address of the VMG in the LAN.
IPv4 Subnet
Mask
DHCP This field displays what DHCP services the VMG is providing to the LAN. Choices are:
This is the current versio n of the firmware inside the VMG.
release your IP address to 0.0.0.0. If you want to renew your IP address, click Renew.
This field displays the current subnet mask in the WAN.
This shows the primary DNS server IP address.
This shows the secondary DNS server IP address.
This is the current subnet mask in the LAN.
Server - The VMG is a DHCP server in the LAN. It assigns IP addresses to other
computers in the LAN.
Relay - The VMG acts as a surrogate DHCP server and relays DHCP requests and
responses between the remote server and the clients.
None - The VMG is not providing any DHCP services to the LAN.
MAC Address This shows the LAN Ethernet adapter MAC (Media Access Control) Address of your VMG.
WLAN Information
MAC Address This shows th e wireless adapter MAC (Media Access Control) Address of your VMG.
Status This displays whether WLAN is activated.
SSID This is the descriptive name used to identify the VMG in a wireless LAN.
Channel This is the channel number used by the VMG now.
Security This displays the type of security mode the VMG is using in the wireless LAN.
802.11 Mode This displays the type of 802.11 mode the VMG is using in the wireless LAN.
WPS This displays whether WPS is activated.
Security
Firewall This displays the firewall’s current security level.
System Status
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
75
Page 76

Chapter 5 Network Map and Status Screens
Table 5 Status Screen (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
System Up
Time
Current Date/
Time
System Resource
CPU Usage This field displays what percentage of the VMG’s processing ability is currently used.
Memory Usage This field displays what percentage of the VMG’s memory is currently used. Usually, this
NAT Session
Usage
Interface Status
Interface This column displays each interface the VMG has.
Status This field indicates the interface’s use status.
Rate For the Ethernet WAN and LAN interface, this displays the port speed and duplex setting.
This field displays how long the V MG has been running since it last started up. The VMG
starts up when you plug it in, when you restart it (Maintenance > Reboot), or when
you reset it.
This field displays the current date and time in the VMG. You can change this in
Maintenance> Time Setting.
When this percentage is close to 100%, the VMG is running at full load, and the
throughput is not going to improve anymore. If you want some applications to have
more throughput, you should turn off other applications (for example, using QoS; see
Chapter 10 on page 163).
percentage should not increase much. If memory usage does get close to 100%, the
VMG is probably becoming unstable, and you should restart the device. See Section 38.2
on page 337, or turn off the device (unplug the power) for a few seconds.
This field displays what percentage of the VMG supported NAT sessions are currently
being used.
For the DSL interface, this field displays Down (line down), Up (line up or connected)
and Drop (dropping a call) if you're using PPPoE encapsulation.
For the Ethernet WAN and LAN interface, this field displays Up when using the interface
and NoLink when not using the interface.
For the WLAN interface, this field displays the enabled (Active) or disabled (InActive)
state of the interface.
For the 3G USB interface, this field displays Up when using the interface and NoDevice
when no device is detected in any USB slot.
For the DSL interface, it displays the downstream and upstream transmission rate.
For the WLAN interface, it displays the maximum transmission rate or N/A with WLAN
disabled.
For the 3G USB interface, this field displays Up when a 3G USB device is installed in a
USB slot and NoDevice when no device is detected in any USB slot.
Registration Status
Account This column displays each SIP account in the VMG.
Action If the SIP account is already registered with the SIP server, the Account Status field
displays Registered.
Click Unregister to delete the SIP account’s registrat ion in the SIP s erver. This does not
cancel your SIP account, but it deletes the mapping between your SIP identity and your
IP address or domain name.
If the SIP account is not registered with the SIP server, the Account Status field
displays Not Registered.
Click Register to have the VMG attempt to register the SIP acc oun t with th e SIP se rv e r.
The button is grayed out if the SIP account is disabled.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
76
Page 77

Chapter 5 Network Map and Status Screens
Table 5 Status Screen (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Account Status This field displays the curr ent registr ation status of the SI P account. Y o u have to r egister
SIP accounts with a SIP server to use VoIP.
Inactive - The SIP account is not active. You can activate it in VoIP > SIP > SIP
Account.
Not Registered - The last time the VMG tried to register the SIP account with the SIP
server, the attempt failed. Use the Register button to register the account again. The
VMG automatically tries to register the SIP account when you turn on the VMG or when
you activate it.
Registered - The SIP account is already registered with the SIP server. You can use it
to make a VoIP call.
Service-Provider This column displays the service provider name and SIP number for each SIP account.
URI This field displays the account number and service domain of the SIP account. You can
change these in the VoIP > SIP screens.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
77
Page 78

Chapter 5 Network Map and Status Screens
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
78
Page 79

6.1 Overview
WAN
This chapter discusses the VMG’s Broadband screens. Use these screens to configure your VMG for
Internet access.
A WAN (Wide Area Network) connection is an outside connection to another network or the
Internet. It connects your private networks, such as a LAN (Local Area Network) and other
networks, so that a computer in one location can communicate with computers in other locations.
Figure 15 LAN and WAN
CHAPTER 6
Broadband
6.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
•Use the Broadband screen to view, remove or add a WAN interface. You can also configure the
WAN settings on the VMG for Internet access (Section 6.2 on page 83).
•Use the Advanced screen to enable or disable PTM over ADSL, Annex M/Annex J, and DSL PhyR
functions (Section 6.4 on page 95).
•Use the Ethernet WAN screen to convert LAN port number four as a WAN port or restore the
WAN to a LAN port. This is for Ethernet connection.
Table 6 WAN Setup Overview
LAYER-2 INTERFACE INTERNET CONNECTION
CONNECTION
ADSL/VDSL
over PTM
DSL LINK
TYPE
N/A Routing PPPoE PPP information, IPv4/IPv6 IP
MODE ENCAPSULATION CONNECTION SETTINGS
Bridge N/A VLAN and QoS
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
address, routing feature, DNS
server, VLAN, QoS, and MTU
IPoE IPv4/IPv6 IP address, routing
feature, DNS server, VLAN, QoS,
and MTU
79
Page 80

Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 6 WAN Setup Overview
LAYER-2 INTERFACE INTERNET CONNECTION
CONNECTION
ADSL over ATM EoA Routing PPPoE/PPP0A ATM PVC configuration, PPP
Ethernet
DSL LINK
TYPE
N/A
6.1.2 What Yo u Need to Know
The following terms and concepts may help as you read this chapter.
WAN IP Address
The WAN IP address is an IP address for the VMG, which makes it accessible from an outside
network. It is used by the VMG to communicate with other devices in other networks. It can be
static (fixed) or dynamically assigned by the ISP each time the VMG tries to access the Internet.
MODE ENCAPSULATION CONNECTION SETTINGS
information, IPv4/IPv6 IP address,
routing feature, DNS server, VLAN,
QoS, and MTU
IPoE/IPoA ATM PVC configuration, IPv4/IPv6
IP address, routing feature, DNS
server, VLAN, QoS, and MTU
Bridge N/A ATM PVC configuration, and QoS
Routing IPoE/PPPoE PPP information, IPv4/IPv6 IP
address, routing feature, DNS
server, VLAN, QoS, and MTU
Bridge N/A VLAN and QoS
If your ISP assigns you a static WAN IP address, they should also assign you the subnet mask and
DNS server IP address(es).
ATM
Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) is a WAN networking technology that provides high-speed data
transfer. ATM uses fixed-size packets of information called cells. With ATM, a high QoS (Quality of
Service) can be guaranteed. ATM uses a connection-oriented model and establishes a virtual circuit
(VC) between Finding Out More
PTM
Packet Transfer Mode (PTM) is packet-oriented and supported by the VDSL2 standard. In PTM,
packets are encapsulated directly in the High-level Data Link Control (HDLC) frames. It is designed
to provide a low-overhead, transparent way of transporting packets over DSL links, as an
alternative to ATM.
IPv6 Introduction
IPv6 (Internet Protocol version 6), is designed to enhance IP address size and features. The
increase in IPv6 address size to 128 bits (from the 32-bit IPv4 address) allows up to 3.4 x 10
addresses. The VMG can use IPv4/IPv6 dual stack to connect to IPv4 and IPv6 networks, and
supports IPv6 rapid deployment (6RD).
38
IP
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
80
Page 81

Chapter 6 Broadband
IPv6 Addressing
The 128-bit IPv6 address is written as eight 16-bit hexadecimal blocks separated by colons (:). This
is an example IPv6 address 2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000.
IPv6 addresses can be abbreviated in two ways:
• Leading zeros in a block can be omitted. So
2001:0db8:1a2b:0015:0000:0000:1a2f:0000 can be written as
2001:db8:1a2b:15:0:0:1a2f:0.
• Any number of consecutive blocks of ze ros can be replaced by a double colon. A double
colon can only appear once in an IPv6 address. So
2001:0db8:0000:0000:1a2f:0000:0000:0015 can be written as
2001:0db8::1a2f:0000:0000:0015, 2001:0db8:0000:0000:1a2f::0015,
2001:db8::1a2f:0:0:15 or 2001:db8:0:0:1a2f::15.
IPv6 Prefix and Prefix Length
Similar to an IPv4 subnet mask, IPv6 uses an address prefix to represent the network address. An
IPv6 prefix length specifies how many most significant bits (start from the left) in the address
compose the network address. The prefix length is written as “/x” where x is a number. For
example,
2001:db8:1a2b:15::1a2f:0/32
means that the first 32 bits (2001:db8) is the subnet prefix.
IPv6 Subnet Masking
Both an IPv6 address and IPv6 subnet mask compose of 128-bit binary digits, which are divided
into eight 16-bit blocks and written in hexadecimal notation. Hexadecimal uses four bits for each
character (1 ~ 10, A ~ F). Each block’s 16 bits are then represented by four hexadecimal
characters. For example, FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FFFF:FC00:0000:0000:0000.
IPv6 Rapid Deployment
Use IPv6 Rapid Deployment (6rd) when the local network uses IPv6 and the ISP has an IPv4
network. When the VMG has an IPv4 WAN address and you set IPv6/IPv4 Mode to IPv4 Only,
you can enable 6rd to encapsulate IPv6 packets in IPv4 packets to cross the ISP’s IPv4 network.
The VMG generates a global IPv6 prefix from its IPv4 WAN address and tunnels IPv6 traffic to the
ISP’s Border Relay router (BR in the figure) to connect to the native IPv6 Internet. The local
network can also use IPv4 services. The VMG uses it’s configured IPv4 WAN IP to route IPv4 traffic
to the IPv4 Internet.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 6 Broadband
ISP (IPv4)
IPv6 Internet
IPv4
IPv6
BR
IPv6 in IPv4
IPv4 Internet
IPv4
+
LAN
- IPv6
- IPv4
WAN
- IPv4
- IPv6 in IPv4
ISP (IPv6)
IPv6 Internet
IPv6
AFTR
IPv4 in IPv6
IPv4 Internet
IPv6
IPv4
+
LAN
- IPv6
- IPv4
WAN
- IPv6
- IPv4 in IPv6
Figure 16 IPv6 Rapid Deployment
Dual Stack Lite
Use Dual Stack Lite when local network computers use IPv4 and the ISP has an IPv6 network.
When the VMG has an IPv6 WAN address and you set IPv6/IPv4 Mode to IPv6 Only, you can
enable Dual Stack Lite to use IPv4 computers and services.
The VMG tunnels IPv4 packets inside IPv6 encapsulation packets to the ISP’s Address Family
Transition Router (AFTR in the graphic) to connect to the IPv4 Internet. The local network can also
use IPv6 services. The VMG uses it’s configured IPv6 WAN IP to route IPv6 traffic to the IPv6
Internet.
Figure 17 Dual Stack Lite
6.1.3 Before You Begin
You need to know your Internet access settings such as encapsulation and W AN IP address. Get this
information from your ISP.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
82
Page 83

Chapter 6 Broadband
6.2 The Broadband Screen
Use this screen to change your VMG’s Internet access settings. Click Network Setting >
Broadband from the menu. The summary table shows you the configured WAN services
(connections) on the VMG.
Figure 18 Network Setting > Broadband
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
83
Page 84

Chapter 6 Broadband
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 7 Network Setting > Broadband
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add New WAN
Interface
# This is the index number of the entry.
Name This is the service name of the connection.
Type This shows whether it is an ATM, Ethernet or a PTM connection.
Mode This shows whether the connection is in routing or bridge mode.
Encapsulation This is the method of encapsulation used by this connection.
802.1p This indicates the 802.1p priority level assigned to traffi c sent through this connec tion. This
802.1q This indicates the VLAN ID number assigned to traffic sent through this connection. This
IGMP Proxy This shows whether the VMG act as an IGMP proxy on this connection.
NAT This shows whether NAT is activated or not for this connection.
Default
Gateway
IPv6 This shows whether IPv6 is activated or not for this connection. IPv6 is not available when
MLD Proxy This shows whether Multicast Listener Discovery (MLD) is activated or not for this
Modify Click the Edit icon to configure the WAN connection.
Click this button to create a new connection.
displays N/A when there is no priority level assigned.
displays N/A when there is no VLAN ID number assigned.
This shows whether the VMG use the WAN interface of this connection as the system default
gateway.
the connection uses the bridging service.
connection. MLD is not available when the connection uses the bridging service.
Click the Delete icon to remove the WAN connection.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
84
Page 85

Chapter 6 Broadband
6.2.1 Add/Edit Internet Connection
Click Add New WAN Interface in the Broadband screen or the Edit icon next to an existing WAN
interface to configure a WAN connection. The screen varies depending on the interface type, mode,
encapsulation, and IPv6/IPv4 mode you select.
6.2.1.1 Routing Mode
Use Routing mode if your ISP give you one IP address only and you want multiple computers to
share an Internet account.
The following example screen displays when you select the ADSL/VDSL over ATM connection
type, Routing mode, and PPPoE encapsulation. The screen varies when you select other interface
type, encapsulation, and IPv6/IPv4 mode.
Figure 19 Network Setting > Broadband > Add New WAN Interface/Edit (Routing Mode)
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 6 Broadband
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 Network Setting > Broadband > Add New WAN Interface/Edit (Routing Mode)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General
Active Select this to enable the interface.
Name Specify a descriptive name for this connection.
Type Select whether it is an ADSL/VDSL over PTM, ADSL over ATM connection or Ethernet.
Mode Select Routing if your ISP give you one IP address only and you w ant multiple computers to
Encapsulation Select the method of encapsulation used by your ISP from the drop-down list box. This
IPv6/IPv4 Mode Select IPv4 Only if you want the Device to run IPv4 only.
ATM PVC Configuration (These fields appear when the Type is set to ADSL over ATM.)
VPI The valid range for the VPI is 0 to 255. Enter the VPI assigned to you.
VCI The valid range for the VCI is 32 to 65535 ( 0 to 31 is reserv ed for local management of ATM
DSL Link Type The choices in this field change according to the Encapsulation method chosen above. This
share an Internet account.
option is available only when you select Routing in the Mode field.
The choices depend on the connection type you select ed. If your connection type is ADSL/
VDSL over PTM, the choices are PPPoE and IPoE. If your connection type is ADSL over
ATM, the choices are PPPoE, PPPoA, IPoE and IPoA.
Select IPv6/IPv4 DualStack to allow the Device to run IPv4 and IPv6 at the same time.
Select IPv6 Only if you want the Device to run IPv6 only.
traffic). Enter the VCI assigned to you.
field is not editable. PPPoA and IPoA encapsulation use the same named DSL Link Type.
Ethernet-over-ATM (EoA) is used for PPPoE, and IPoE encapsulation.
EoA a protocol for data transfer between Ethernet LAN and WAN over the ATM protocol. It
creates a bridged connection between the VMG and the ISP. It uses an Ethernet header in
the packet, so that you can have multiple services/connections over one PVC. You can set
each connection to have its own MAC address or all connections share one MAC address but
use different VLAN IDs for different services. EoA supports ENET ENCAP (IPoE), PPPoE and
RFC1483/2684 bridging encapsulation methods.
Encapsulation
Mode
PPPoA (PPP over ATM) allows just one PPPoA connection over a PVC.
IPoA (IP over ATM) allows just one RFC 1483 routing connection over a PVC.
Select the method of multiplexing used by your ISP from the drop-down list box. Choices
are:
• LLC/SNAP-BRIDGING: In LCC encapsulation, bridged PDUs are encapsulated by
identifying the type of the bridged media in the SNAP header. This is available only when
you select IPoE or PPPoE in the Select DSL Link Type field.
• VC/MUX: In VC multiplexing, each protocol is carried on a single ATM virtual circuit
(VC). To transport multiple protocols, the VMG needs separate VCs. There is a binding
between a VC and the type of the network protocol carried on the VC. This reduces
payload overhead since there is no need to carry protocol information in each Protocol
Data Unit (PDU) payload.
• LLC/ENCAPSULATION: More than one protocol can be carried over the same VC. This
is available only when you select PPPoA in the Encapsulation field.
• LLC/SNAP-ROUTING: In LCC encapsulation, an IEEE 802.2 Logical Link Control (LLC)
header is prefixed to each routed PDU to identify the PDUs. The LCC header can be
followed by an IEEE 802.1a SubNetwork Attachment Point (SNAP) header. This is
available only when you select IPoA in the Encapsulation field.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
86
Page 87

Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 8 Network Setting > Broadband > Add New WAN Interface/Edit (Routing Mode) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Service
Category
PPP Information (This is available only when you select PPPoE or PPPoA in the Mode field.)
PPP User Name Ente r the user name exactly as your ISP assigned. If assigned a name in the form
PPP Password Enter the password associated with the user name above. Select password unmask to
PPP Trigger
Type
Idle Timeout This value specifies the time in minutes that elapses before the router automatically
PPPoE
Passthrough
Select UBR Without PCR or UBR With PCR for applications that are non-time sensitive,
such as e-mail.
Select CBR (Continuous Bit Rate) to specify fixed (always-on) bandwidth for voice or data
traffic.
Select Non Realtime VBR (non real-time Variable Bit Rate) for connections that do not
require closely controlled delay and delay variation.
Select Realtime VBR (real-time Variable Bit Rate) for applications with bursty connections
that require closely controlled delay and delay variation.
user@domain where domain identifies a service name, then enter both components exactly
as given.
show your entered password in plain text.
Select when to have the VMG establish the PPP connection.
Auto Connect - select this to not let the connecti on time out.
Connect on Demand - select this to automatically bring up the connection when the
Device receives packets destined for the Internet.Manual - select this if you want to
manually trigger the connection up.
disconnects from the PPPoE server.
This field is not configurable if you select Auto Connect in the PPP Trigger Type field.
This field is available when you select PPPoE encapsulation.
In addition to the VMG’s built-in PPPoE client, you can enable PPPoE pass through to allow up
to ten hosts on the LAN to use PPPoE client software on their computers to connect to the
ISP via the VMG. Each host can have a separate account and a public WAN IP address.
PPPoE pass through is an alternative to NAT for application where NAT is not appropriate.
Disable PPPoE pass through if you do not need to allow hosts on the LAN to use PPPoE client
software on their computers to connect to the ISP.
PPPoE Service
Name
PPPoE
Passthrough
IP Address (This is available only when you select IPv4 Only or IPv6/IPv4 DualStack in the IPv6/IPv4
Mode field.)
Obtain an IP
Address
Automatically
DHCP
option 60/
Vendor ID
Enter the name of your PPPoE service here.
This field is available when you select PPPoE encapsulation.
In addition to the VMG’s built-in PPPoE client, you can enable PPPoE pass through to allow up
to ten hosts on the LAN to use PPPoE client software on their computers to connect to the
ISP via the VMG. Each host can have a separate account and a public WAN IP address.
PPPoE pass through is an alternative to NAT for application where NAT is not appropriate.
Disable PPPoE pass through if you do not need to allow hosts on the LAN to use PPPoE client
software on their computers to connect to the ISP.
A static IP address is a fixed IP that your ISP gives you. A dynamic IP address is not fixed;
the ISP assigns you a different one each time you connect to the Internet. Select this if you
have a dynamic IP address.
This field displays when editing an existing WAN interface. Type the class vender ID you
want the VMG to add in the DHCP Discovery packets that go to the DHCP server.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
87
Page 88

Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 8 Network Setting > Broadband > Add New WAN Interface/Edit (Routing Mode) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
DHCP
option 43
Enable
Static IP
Address
IP Address Enter the static IP address provided by your ISP.
Subnet
Mask
Gateway IP
Address
Routing Feature (This is available only when you select IPv4 Only or IPv6/IPv4 DualStack in the IPv6/
IPv4 Mode field.)
NAT Enable Select this option to activate NAT on this connection.
Full cone NAT
enable
IGMP Proxy
Enable
Apply as
Default
Gateway
DNS Server (This is available only when you select IPv4 Only or IPv6/IPv4 DualStack in the IPv6/IPv4
Mode field.)
DNS Select Obtain DNS Info Automically if you want the VMG to use the DNS server
This field displays when editing an existing WAN interface. Type the vender specific
information you want the VMG to add in the DHCP Offer packets. The information is used,
for example, for configuring an ACS’s (Auto Configuration Server) URL.
Select this option If the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
Enter the subnet mask provided by your ISP.
Enter the gateway IP address provided by your ISP.
Select this option to enable full cone NA T on this connection. This field is available only when
you activate NAT. In full cone NAT, the VMG maps all outgoing packets from an internal IP
address and port to a single IP address and port on the external network. The VMG also
maps packets coming to that external IP address and port to the internal IP address and
port.
Internet Group Multicast Protocol (IGMP) is a network-layer protocol used to establish
membership in a Multicast group - it is not used to carry user data.
Select this option to have the VMG act as an IGMP proxy on this connection. This allows the
VMG to get subscribing information and ma intain a joined member list for each multicast
group. It can reduce multicast traffic significantly.
Select this option to have the VMG use the WAN interface of this connection as the system
default gateway.
addresses assigned by your ISP.
Select Use Following Static DNS Address if you want the VMG to use the DNS server
addresses you configure manually.
DNS server1 Enter the first DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
DNS server 2 Enter the second DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
Tunnel (This is available only when you select IPv4 Only or IPv6 Only in the IPv6/IPv4 Mode field.)
The DS-Lite (Dual Stack Lite) fields display when you set the IPv6/IPv4 Mode field to IPv6 Only.
Enable Dual Stack Lite to let local computers use IPv4 through an ISP’s IPv6 network. See Dual Stack Lite on
page 82 for more information.
The 6RD (IPv6 rapid deployment) fields display when you set the IPv6/IPv4 Mode field to IPv4 Only. See
IPv6 Rapid Deployment on page 81 for more information.
Enable DS-Lite This is available only when you select IPv6 Only in the IPv6/IPv4 Mode field. Select
Enable to let local computers use IPv4 through an ISP’s IPv6 network.
DS-Lite Relay
Server IP
Enable 6RD This is available only when you select IPv4 Only in the IPv6/IPv4 Mode field. Select
6RD Type Select Static if you have the IPv4 address of the relay server, otherwise select DHCP to
Specify the transition router’s IPv6 address.
Enable to tunnel IPv6 traffic from the local network through the ISP’s IPv4 network.
have the Device detect it automatically through DHCP.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
88
Page 89

Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 8 Network Setting > Broadband > Add New WAN Interface/Edit (Routing Mode) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPv4 Mask
Length
6RD Border
Relay Server IP
6RD IPv6 Prefix Enter an IPv6 prefix for tunneling IPv6 traffic to the ISP’s border relay router and connecting
IPv6 Address (This is available only when you select IPv6/IPv4 DualStack or IPv6 Onl y in the IPv6/IPv4
Mode field.)
IPv6 Address Select Automatic if you want to have the VMG use the IPv6 prefix from the connected
Prefix
Length
Next Hop Enter the IP address of the next-hop gateway. The gateway is a router or switch on the
IPv6 Routing Feature (This is available only when you select IPv6/IPv4 DualStack or IPv6 Only in the
IPv6/IPv4 Mode field. You can enable IPv6 routing features in the following section.)
MLD Proxy
Enable
Apply as
Default
Gateway
IPv6 DNS
Server
IPv6 DNS Select Dynamic to have the VMG get the IPv6 DNS server addresses from the ISP
IPv6 DNS
Server 1
IPv6 DNS
Server 2
VLAN (These fields appear when the Type is set to ADSL/VDSL over PTM.)
802.1p IEEE 802.1p defines up to 8 separate traffic types by inserting a tag into a MAC-layer frame
802.1q Type the VLAN ID number (from 1 to 4094) for traffic through this connection.
QoS
Enter the subnet mask number (1~32) for the IPv4 network.
When you set the 6RD Type to Static, specify the relay server’s IPv4 address in this field.
to the native IPv6 Internet.
router’s Router Advertisement (RA) to generate an IPv6 address.
• Select Get IPv6 Address From DHCPv6 Server(IA_NA) if you want to obtain an IPv6
address from a DHCPv6 server. The IP address assigned by a DHCPv6 server has priority
over the IP address automatically generated by the VMG using the IPv6 prefi x from an
RA. This option is available only when you choose to get your IPv6 address
automatically.
• Select Prefix Delegation(IA_PD) to use DHCP PD (Prefix Delegation) which enables
the Device to pass the IPv6 prefix information to its LAN hosts. The hosts can then use
the prefix to generate their IPv6 addresses.
Select Static if you have a fixed IPv6 address assigned by your ISP.
Select None to not assign any IPv6 address to this WAN connection.
Enter the address prefix length to specify how many most significant bits in an IPv6 address
compose the network address.
same segment as your VMG's interface(s). The gateway helps forward packets to their
destinations.
Select this checkbox to have the VMG act as an MLD proxy on this connection. This allows
the VMG to get subscription information and maintain a joined member list for each
multicast group. It can reduce multicast traffic significantly.
Select this option to have the VMG use the WAN interface of this connection as the system
default gateway.
Configure the IPv6 DNS server in the following section.
automatically.
Select Static to have the VMG use the IPv6 DNS server addresses you configure manually.
Enter the first IPv6 DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
Enter the second IPv6 DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
that contains bits to define class of service.
Select the IEEE 802.1p priority level (from 0 to 7) to add to traffic through this connection.
The greater the number, the higher the priority level.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 8 Network Setting > Broadband > Add New WAN Interface/Edit (Routing Mode) (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Rate L imit Enter the rate limit for the connection. This is the maximum transmission rate allowed for
traffic on this connection.
WAN Outgoing
Default Tag
DSCP If you enable Select WAN Outgoing Default Tag, enter a DSCP (DiffServ Code Point)
MTU
MTU Size Enter the MTU (Maximum Transfer Unit) size for this traffic.
Bridging and
Routing in the
same WAN
Enable Concurrent WAN
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the VMG.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving.
Select Enable and enter a DSCP (DiffServ Code Point) value to have the VMG add it in the
packets sent by this WAN interface.
value to have the VMG add it in the packets sent by this WAN interface.
Use this feature to bridge a LAN port(s) with the WAN interface. Traffic to/from LAN ports
not in the bridge is routed from the WAN interface.
ADSL use same VPI/VCI in Bridge and Route modes.
VDSL use same VLAN in Bridge and Route modes.
Enable this if you want to use the same VP I/VCI s ett ings in different WAN interfaces. Select
this and then choose the ports to bridge with the WAN interface. \
• ADSL concurrent WAN uses the same VCI/PVI in both routing and bridge modes.
• VDSL concurrent WAN uses same VLAN in both routing and bridge mode.
6.2.1.2 Bridge Mode
Click the Add new WAN Interface in the Network Setting > Broadband screen or the Edit icon
next to the connection you want to configure. Select Bridge as the encapsulation mode. The screen
varies depending on the interface type you select.
If you select ADSL/VDSL over PTM as the interface type, the following screen appears.
Figure 20 Network Setting > Broadband > Add New WAN Interface/Edit (Bridge Mode)
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
90
Page 91

Chapter 6 Broadband
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 9 Network Setting > Broadband > Add New WAN Interface/Edit (Bridge Mode)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General
Active Select this to enable the interface.
Name Enter a service name of the connection.
Type Select ADSL/VDSL over PTM as the interface that you want to configure. The VMG uses
Mode Select Bridge when your ISP provides you more than one IP address and you want the
VLAN This section is available only when you select ADSL/VDSL over PTM in the Type field.
802.1p IEEE 802.1p defines up to 8 separate traffic types by insertin g a tag into a MAC-la y er frame
802.1q Type the VLAN ID number (from 0 to 4094) for traffic through this connection.
QoS
Rate L imit Enter the rate limit for the connection. This is the maximum transmission rate allowed for
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving.
the VDSL technology for data transmission over the DSL port.
connected computers to get individual IP address from ISP’s DHCP server directly. If you
select Bridge, you cannot use routing functions, such as QoS, Firewall, DHCP server and
NAT on traffic from the selected LAN port(s).
that contains bits to define class of service.
Select the IEEE 802.1p priority level (from 0 to 7) to add to traffic through this connection.
The greater the number, the higher the priority level.
traffic on this connection.
6.3 The 3G Backup Screen
The USB ports (at the left side panel of the VMG) allow you to attach a 3G dongle to wirelessly
connect to a 3G network for Internet access. You can ha ve the VMG use the 3G W AN connection as
a backup. Disconnect the DSL and Ethernet WAN ports to use the 3G dongle as your primary WAN
connection. The VMG automatically uses a wired WAN connection when available.
Note: This VMG supports connecting one 3G dongle at a time.
Figure 21 Internet Access Application: 3G WAN
Use this screen to configure your 3G settings. Click Network Setting > Broadband > 3G
Backup.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
91
Page 92

Chapter 6 Broadband
Note: The actual data rate you obtain varies depending the 3G card you use, the signal
strength to the service provider’s base station, and so on.
Figure 22 Network Setting > Broadband > 3G Backup
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 10 Network Setting > Broadband > 3G Backup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
General
3G Backup Select Enable to have the VMG use the 3G connection as your WAN or a backup when the
Ping Check Select Enable if you want the VMG to ping check the connection status of your WAN. You
Check Cycle Enter the frequency of the ping check in this field.
Consecutive
PING Fail
Ping Default
Gateway
Ping the Host Select this to have the VMG ping the particular host name or IP address you typed in this
3G Connection Settings
Card
description
wired WAN connection fails.
can configure the frequency of the ping check and number of consecutive failures before
triggering 3G backup.
Enter how many consecutive failures are required before 3G backup is triggered.
Select this to have the VMG ping the WAN interface’s default gateway IP address.
field.
This field displays the manufacturer and model name of your 3G card if you inserted one in
the VMG. Otherwise, it displays N/A.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
92
Page 93

Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 10 Network Setting > Broadband > 3G Backup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Username Type the user name (of up to 64 ASCII printable characters) given to you by your service
provider.
Password Type the password (of up to 64 ASCII printable characters) associated with the user name
above.
PIN A PIN (Personal Identification Number) code is a key to a 3G card. Without the PIN code,
Dial string Enter the phone number (dial string) used to dial up a connect ion to y our se rvice pro vider’s
APN Enter the APN (Access Point Name) provided by your service provider. Connections with
Connection Select Nailed UP if you do not want the connection to time out.
you cannot use the 3G card.
If your ISP enabled PIN code authentication, enter the 4-digit PIN code (0000 for example)
provided by your ISP. If you enter the PIN code incorrectly, the 3G card may be blocked by
your ISP and you cannot use the account to access the Internet.
If your ISP disabled PIN code authentication, leave this field blank.
base station. Your ISP should provide the phone number.
For example, *99# is the dial string to establish a GPRS or 3G connection in Taiwan.
different APNs may provide different services (such as Internet access or MMS (Multi-Media
Messaging Service)) and charge method.
You can enter up to 32 ASCII printable characters. Spaces are allowed.
Select on Demand if you do not want the connection up all the time and specify an idle
time-out in the Max Idle Timeout field.
Max Idle
Timeout
Obtain an IP
Address
Automatically
Use the
following static
IP address
IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use the following static IP
Obtain DNS
info
dynamically
Use the
following static
DNS IP address
Primary
DNS server
Secondary
DNS server
Enable Email
Notification
Mail Server Select a mail server for the e-mail address specified below.
This value specifies the time in minutes that elapses b efore the VMG automatically
disconnects from the ISP.
Select this option if your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
Select this option if the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
address.
Select this to have the VMG get the DNS server addresses from the ISP automatically.
Select this to have the VMG use the DNS server addresses you configure manually.
Enter the first DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
Enter the second DNS server address assigned by the ISP.
Select this to enable the e-mail notification function. The VMG will e-mail you a notification
when the 3G connection is up.
3G backup
Send Email
Title
If you do not select a mail server, e-mail notifications cannot be sent via e-ma il. You must
have configured a mail server already in the Maintenance > Email Notification screen.
Type a title that you want to be in the subject line of the e-mail notifications that the VMG
sends.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
93
Page 94

Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 10 Network Setting > Broadband > 3G Backup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Send
Notification to
Email
Advanced Click this to sho w the advanced 3G backup settings.
Budget Setup
Enable Budget
Control
Time Budget Select this and specify the amount of time (in hours) that the 3G connection can be used
Data Budget
(Mbytes)
Data Budget
(kPackets)
Notifications are sent to the e-mail address specified in this field. If this field is left blank,
notifications cannot be sent via e-mail.
Select Enable to set a monthly limit for the user account of the installed 3G card. You can
set a limit on the total traffic and/or call time. The VMG takes the actions you specified when
a limit is exceeded during the month.
within one month. If you change the value after you configure and enable budget control,
the VMG resets the statistics.
Select this and specify how much downstream and/or upstream data (in Mega bytes) can be
transmitted via the 3G connection within one month.
Select Download/Upload to set a limit on the total traffic in both directions.
Select Download to set a limit on the downstream traffic (from the ISP to the VMG).
Select Upload to set a limit on the upstream traffic (from the VMG to the ISP).
If you change the value after you configure and enable budget control, the VMG resets the
statistics.
Select this and specify how much downstream and/or upstream data (in k Packets) can be
transmitted via the 3G connection within one month.
Select Download/Upload to set a limit on the total traffic in both directions.
Reset all
budget
counters on
Reset time and
data budget
counters
Actions before
over budget
Enable % of
time budget/
data budget
(Mbytes)/data
budget
(kPackets)
Actions when
over budget
Current 3G
connection
Actions
Enable Email
Notification
Select Download to set a limit on the downstream traffic (from the ISP to the VMG).
Select Upload to set a limit on the upstream traffic (from the VMG to the ISP).
If you change the value after you configure and enable budget control, the VMG resets the
statistics.
Select the date on which the VMG resets the budget every month. Select last if you want
the VMG to reset the budget on the last day of the mo nth. Select specific and enter the
number of the date you want the VMG to reset the budget
Click this button to reset the time and data budgets immediately. The count starts over with
the 3G connection’s full configured monthly time and data budgets. This does not affect the
normal monthly budget restart; so if you configured the time and data bud g et counters to
reset on the second day of the month and you use this button on the first, th e time and data
budget counters will still reset on the second.
Specify the actions the VMG takes before the time or data limit exceeds.
Select Enable and enter a number from 1 to 99 in the percentage fields. If you change the
value after you configure and enable budget control, the VMG resets the statistics.
Specify the actions the VMG takes when the time or data limit is exce eded.
Select Keep to maintain an existing 3G connection or Drop to disconnect it.
Select this to enable the e-mail notification function. The VMG will e-mail you a notification
when there over budget occurs.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
94
Page 95

Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 10 Network Setting > Broadband > 3G Backup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Mail Server Select a mail server for the e-mail address specified below.
If you do not select a mail server, e-mail notifications cannot be sent via e-ma il. You must
have configured a mail server already in the Maintenance > Email Notification screen.
Over Budget
Email Title
Send
Notification to
Email
Interval Enter the interval of how many minutes you want the VMG to e-mail you.
Enable Log Select this to activate the logging function at the interval you set in this field.
Basic Click this to hide the advanced settings of 3G backup.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the VMG.
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the previous configuration.
Type a title that you want to be in the subject line of the e-mail notifications that the VMG
sends.
Notifications are sent to the e-mail address specified in this field. If this field is left blank,
notifications cannot be sent via e-mail.
6.4 The Advanced Screen
Use the Advanced screen to enable or disable ADSL over PTM, Annex M, DSL PhyR, and SRA
(Seamless Rate Adaptation) functions. The VMG supports the PhyR retr ansmission scheme. PhyR is
a retransmission scheme designed to provide protection against noise on the DSL line. It improves
voice, video and data transmission resilience by utilizing a retransmission buffer.
ITU-T G.993.2 standard defines a wide range of settings for various par ameters, some of which are
encompassed in profiles as shown in the next table.
Table 11 VDSL Profiles
PROFILE
8a 8.832 2048 4.3125 17.5 50
8b 8.832 2048 4.3125 20.5 50
8c 8.5 1972 4.3125 11.5 50
8d 8.832 2048 4.3125 14.5 50
12a 12 2783 4.3125 14.5 68
12b 12 2783 4.3125 14.5 68
17a 17.664 4096 4.3125 14.5 100
30a 30 3479 8.625 14.5 200
BANDWIDTH
(MHZ)
NUMBER OF
DOWNSTREAM
CARRIERS
CARRIER
BANDWIDTH
(KHZ)
POWER (DBM)
MAX.
DOWNSTREAM
THROUGHPUT
(MBIT/S)
Click Network Setting > Broadband > Advanced to display the following screen.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 6 Broadband
Figure 23 Network Setting > Broadband > Advanced
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 Network Setting > Broadband > Advanced
LABEL DESCRIPTION
PhyR US Enable or disable PhyR US (upstream) for upstream transmission to the WAN. PhyR US
PhyR DS Enable or disable PhyR DS (downstream) for downstream transmission from the WAN.
Bitswap
SRA Enable or disable Seamless Rate Adaption (SRA). Select Enable to have the VMG
ADSL
Modulation
PTM over
ADSL:
G.Dmt: ITU G.992.1 (better known as G.dmt) is an ITU standard for ADSL using discrete multitone
should be enabled if data being transmitted upstream is sensitive to noise. However,
enabling PhyR US can decrease the US line rate. Enabling or disabling PhyR will require the
CPE to retrain. For PhyR to function, the DSLAM must also support PhyR and have it
enabled.
PhyR DS should be enabled if data being transmitted downstream is sensitive to noise.
However, enabling PhyR DS can decrease the DS line rate. Enabling or disabling PhyR will
require the CPE to retrain. For PhyR to function, the DSLAM must also support PhyR and
have it enabled.
automatically adjust the connection’s data rate according to line conditions without
interrupting service.
Select Enable to use PTM over ADSL. Since PTM has less overhead than ATM, some ISPs
use this for better performance.
modulation. G.dmt full-rate ADSL expands the usable bandwidth of existing copper
telephone lines, delivering high-speed data communications at rates up to 8 Mbit/s
downstream and 1.3 Mbit/s upstream.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
96
Page 97

Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 12 Network Setting > Broadband > Advanced (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
G.lite : ITU G.992.2 (better known as G.lite) is an ITU standard for ADSL using discrete multitone
modulation. G.lite does not strictly require the use of DSL filters, but like all variants of
ADSL generally functions better with splitters.
T1.413 : ANSI T1.413 is a technical standard that defines the requirements for the single asymmetric
ADSL2 : It optionally extends the capability of basic ADSL in data rates to 12 Mbit/s downstream
AnnexL : Annex L is an optional specification in the ITU-T ADSL2 recommendation G.992.3 titled
ADSL2+ : ADSL2+ extends the capability of basic ADSL by doubling the number of downstream
AnnexM : Annex M is an optional specification in ITU-T recommendations G.992.3 (ADSL2) and
VDSL Profile VDSL2 profiles differ in the width of the frequency band used to transmit the broadband
8a, 8b, 8c, 8d,
12a, 12b, 17a,
US0
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the VMG.
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the previous configuration.
digital subscriber line (ADSL) for the interface between the telecommunications network and
the customer installation in terms o f their interaction and electrical characteristics.
and, depending on Annex version, up to 3.5 Mbit/s upstream (with a mandatory capability
of ADSL2 transceivers of 8 Mbit/s downstream and 800 kbit/s upstream).
Specific requirements for a Reach Extended ADSL2 (READSL2) system operating in the
frequency band above POTS, therefore it is often referred to as Reach Extended ADSL2 or
READSL2.The main difference between this specification and commonly deployed Annex A is
the maximum distance that can be used. The power of the lower frequencies used for
transmitting data is boosted up to increase the reach of this signal up to 7 kilometers
(23,000 ft).
channels. The data rates can be as high as 24 Mbit/s downstream and up to 1.4 Mbit/s
upstream depending on the distance from the DSLAM to the customer's premises.
G.992.5 (ADSL2+), also referred to as ADSL2 M and ADSL2+ M. This specification extends
the capability of commonly deployed Annex A by more than doubling the number of
upstream bits. The data rates can be as high as 12 or 24 Mbit/s downstream and 3 Mbit/s
upstream depending on the distance from the DSLAM to the customer's premises.
signal. Profiles that use a wider frequency band can deliver higher maximum speeds.
The G.993.2 VDSL standard defines a wide range of profiles that can be used in different
VDSL deployment settings, such as in a central office, a street cabinet or a building.
The VMG must comply with at least one profile specified in G.993.2. but compliance with
more than one profile is allowed.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
97
Page 98

6.5 The 802.1x Screen
You can view and configure the 802.1X authentication settings in the 802.1x screen. Click
Network Setting > Broadband > 802.1x to display the following screen.
Figure 24 Network Setting > Broadband > 802.1x
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Chapter 6 Broadband
Table 13 Network Setting > Network Setting > 802.1x
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This is the index number of the entry.
Status This field displays whether the authentication is active or not. A yellow bulb signifies that
this authentication is active. A gray bulb signifies tha t this authentication is not active.
Interface This is the interface that uses the authentication. This displays N/A when there is no
EAP Identity This shows the EAP identity of the authentication. This displays N/A when there is no EAP
EAP method This shows the EAP method used in the authenti cation. This displays N/A when there is no
Bidirectional
Authentication
Certificate This shows the certificate used for this authentication. This displays N/A when there is no
Trusted CA This shows the Trusted CA used for this authentication. This displays N/A when there is no
Modify Click t h is icon to edit an item.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the VMG.
Cancel Click Cancel to return to the previous configuration.
interface assigned.
identity assigned.
EAP method assigned.
This shows whether bidirectional authentication is allowed.
certificate assigned.
Trusted CA assigned.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
98
Page 99

6.5.1 Modify 802.1X Settings
Use this screen to edit 802.1X authentication settings. Click the Edit icon next to the rule you want
to edit. The screen shown next appears.
Figure 25 Network Setting > Broadband > 802.1x > Modify
Chapter 6 Broadband
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 Network Setting > Broadband > 802.1x: Edit
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active This field allows you to activate/deactivate the authentication.
Select this to enable the authenti cation. Clear this to disable this authentication without
having to delete the entry.
Interface Select an interface to which the authentication applies.
EAP Identity Enter the EAP identity of the authentication.
EAP method This is the EAP method used for this authentication.
Enable
Bidirectional
Authentication
Certificate Select the certifica te you want to assign to the authentication. You need to import the
Trusted CA Select the Trusted CA you want to assign to the authenticatio n. You need to import the
Apply Click Apply to save your changes.
Cancel Click Cancel to exit this screen without saving.
Select this to allow bidirectional authentication.
certificate in the Security > Certificates > Local Certificates screen.
certificate in the Security > Certificates > Trusted CA screen.
6.6 Ethernet WAN
Use the Ethernet WAN screen to convert LAN port number four as a WAN port and to restore it
back from a WAN to a LAN port for Ethernet Internet access.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
99
Page 100

Chapter 6 Broadband
It’s not enough to just enable LAN 4 as a WAN connection here. You must also go to Network
Setting > Broadband > Add New WAN Interface screen and create a new interface for it with
the Type as Ethernet and Encapsulation as IPoE, and it’s advisable to enable NAT.
You cannot have DSL Ethernet and 3G WAN connections working at the same time. The order of
priority for the WAN connections are:
1 DSL
2 Ethernet
3 3G
Click Network Setting > Broadband > Ethernet WAN to display the following screen.
Figure 26 Network Setting > Broadband > Ethernet WAN
The following table describes the fields in the above screen.
Table 15 Network Setting > Broadband > Ethernet WAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable Click the radio button to convert LAN port number four to a WAN port.
Disable Click the radio button to restore LAN port number four to a LAN port.
6.7 Technical Reference
The following section contains additional technical information about the VMG features described in
this chapter.
Encapsulation
Be sure to use the encapsulation method required by your ISP. The VMG can work in bridge mode
or routing mode. When the VMG is in routing mode, it supports the following methods.
VMG5313-B10A/-B30A Series User’s Guide
100
 Loading...
Loading...