Page 1

VLC1324G
VDSL2 Line Card
User’s Guide
Version 3.95
4/2010
Edition 1
www.zyxel.com
Page 2

Page 3

About This User's Guide
About This User's Guide
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for users of the VLC1324G VDSL2 Line Card and the VSC1224-41
Splitter Card. It describes detailed information about the cards’ features and hardware.
Related Documentation
• IES-5000 and IES-6000 User’s Guides
Refer to the IES-5000 or the IES-6000 User’s Guide for directions on installation,
connections, maintenance, hardware trouble shooting and safety warnings.
• MSC1000G and MSC1024G Management Switch Card User’s Guides
These user’s guides cover the configuration of your IES-50 00 or IES-60 00. Refer to these
user’s guides for information on your VLC’s default settings.
• ZyXEL Web Site
Please refer to www.zyxel.com
certifications.
for additional support documentation and product
Documentation Feedback
Send your comments, questions or suggestions to: techwriters@zyxel.com.tw
Thank you!
The Technical Writing Team, ZyXEL Communications Corp.,
6 Innovation Road II, Science-Based Industrial Park, Hsinchu, 30099, Taiwan.
Need More Help?
More help is available at www.zyxel.com.
• Download Library
Search for the latest product updates and documentation from this link. Read the T ech Doc
Overview to find out how to efficiently use the documentation in order to better
understand how to use your product.
• Knowledge Base
VLC1324G User’s Guide
3
Page 4

About This User's Guide
If you have a specific question about your product, the answer may be here. This is a
collection of answers to previously asked questions about ZyXEL products.
•Forum
This contains discussions on ZyXEL products. Learn from others who use ZyXEL
products and share your experiences as well.
Customer Support
Should problems arise that cannot be solved by the methods listed above, you should contact
your vendor. If you cannot contact your vendor, then con tact a ZyXEL o ffice for the region in
which you bought the device.
See http://www.zyxel.com/web/contact_us.php for contact information. Please have the
following information ready when you contact an office.
• Product model and serial number.
• Warranty Information.
• Date that you received your device.
• Brief description of the problem and the steps you took to solve it.
4
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 5
Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this User’s Guide.
1 Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
" Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may
need to configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• The VLC1324G may be referred to as the “line card”, the “VLC”, the “device” or the
“system” in this User’s Guide.
• The “VLC1324G”, the “VLC”, the “device” and the “line card” refer to the VLC1324G51 for VDSL over POTS (Annex A). They also refer to the VLC1324G-53 for VDSL over
ISDN (Annex B). Differentiation is made where needed.
• “IES” refers to the IES-5000 or IES-6000 system, including the main chassis and all
associated cards.
• “MSC” refers to the MSC1000GA management switch card.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A key stroke is denoted by square brackets and uppercase text, for example, [ENTER]
means the “enter” or “return” key on your keyboard.
• “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters and then press the [ENTER] key.
“Select” or “choose” means for you to use one of the predefined choices.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example,
Maintenance > Log > Log Setting means you first click Maintenance in the navigation
panel, then the Log sub menu and finally the Log Setting tab to get to that screen.
• Units of measurement may denote the “metric” value or the “scientific” value. For
example, “k” for kilo may denote “1000” or “1024”, “M” for mega may denote “1000000”
or “1048576” and so on.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
5
Page 6
Safety Warnings
Safety Warnings
1 For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
• Do NOT use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming
pool.
• Do NOT expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do NOT store things on the device.
• Do NOT install, use, or service this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk
of electric shock from lightning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• Do NOT open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to
dangerous high voltage points or other risks. ONLY qualified service personnel should
service or disassemble this device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
• Always disconnect all cables from this device before servicing or disassembling.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a
remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Do NOT obstruct the device ventilation slots, as insufficient airflow may harm your
device.
• Warning! To avoid risk of electric shock, remove only one card at a time and do not place
fingers or objects inside the chassis. Cover empty slots with slot covers.
6
This product is recyclable. Dispose of it properly.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 7

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
About This User's Guide..........................................................................................................3
Document Conventions............................................................................................................5
Safety Warnings ........................................................................................................................6
Table of Contents......................................................................................................................7
List of Figures...........................................................................................................................9
List of Tables...........................................................................................................................11
Chapter 1
VLC Overview..........................................................................................................................13
1.1 VLC Overview ........ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................................... ... ... .... ... ... .............13
1.2 VDSL2 Profiles Overview ................ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ..........................................................13
1.3 Key Features ......................... .......................................................... .... ... ... ... .... ...................13
1.4 Front Panel of VLC ................... ... ... ... ... .... .......................................................... ... ... ... ....... 20
1.5 Ports and LEDs of VLC .......................................................................................................20
1.5.1 Ports ................................................. ... ... .......................................................... .......... 20
1.5.2 LEDs . .... ... ... ... .... .......................................................... ... ... ....................................... 20
1.6 VSC1224-41 POTS Splitter ....... ... ... ... ... .............................................................. ... ... ..........20
Chapter 2
VLC Specifications .................................................................................................................23
2.1 VLC Product Specifications .................................................................................................23
2.2 VLC Firmware Naming Conventions ...................................................................................25
2.3 Telco-50 Connector Pin Assignments ..................................... ... .......................................... 26
2.4 Wire Gauge Specifications ................. ... .... ... ... ... .......................................................... .... ...29
2.5 Console Cable Pin Assignments ......................................................................................... 29
2.6 VSC1224-41 .......... ... .... .......................................................... ... ... ... .... ... ............................. 30
2.7 VSC1224-43U ........................................... .......................................................... ... ... ... ....... 30
Chapter 3
VLC Troubleshooting..............................................................................................................31
3.1 The SYS or PWR LED Does Not Turn On ........................................................................... 31
3.2 The ALM LED Is On ............................................................................................................31
3.3 VDSL2 Data Transmission ........................... .......................................................................32
3.4 Local Server .............................................. ... ... ....................................................................32
3.5 Data Rate ........................................ ... ... .... .......................................................... ... .............32
VLC1324G User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Table of Contents
3.6 The Line Card is Not Manageable ....................................................................................... 33
3.6.1 Uploading the Default Configuration File via Boot Commands ........... ....................... 33
3.6.2 Uploading the Firmware via Boot Commands .................. ............. ............. ............. ... 34
Appendix A Legal Information ................................................................................................37
Index.........................................................................................................................................41
8
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 9

List of Figures
List of Figures
Figure 1 Front Panel ...............................................................................................................................20
Figure 2 Front Panel of VSC1224-41 .....................................................................................................20
Figure 3 VLC Ports 1-24 Telco-50 Connector Pin Assignments ...........................................................26
Figure 4 IES-5000/5005 Cable Telco-50 Pin Assignments (VLC End) ................................................... 27
Figure 5 IES-5000/5005 Cable Telco-50 Pin Assignments (Splitter Card End) ...................................... 27
Figure 6 IES-6000 Cable Telco-50 Pin Assignments (VLC End) ............................................................28
Figure 7 IES-6000 Cable Telco-50 Pin Assignments (Splitter End) ........................................................29
Figure 8 Console Cable Mini RJ-11 Male Connector ............................................................................. 30
Figure 9 Example Xmodem Upload ........................................................................................................ 33
Figure 10 Example Xmodem Upload ......................................................................................................35
VLC1324G User’s Guide
9
Page 10

List of Figures
10
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 11

List of Tables
List of Tables
Table 1 VDSL2 Profile Maximum Transfer Rates ..................................................................................13
Table 2 Front Panel Ports ...................................................................................................................... 20
Table 3 LED Descriptions ...................................................................................................................... 20
Table 4 VLC Specifications .................................................................................................................... 23
Table 5 VLC Telco-50 Connector Pin Assignments ............................................................................... 26
Table 6 Wire Gauge Specifications ........................................................................................................ 29
Table 7 Console Cable Connector Pin Assignments ............................................................................. 30
Table 8 VSC1224-41 CO Impedance Splitter Card Specifications ........................................................ 30
Table 9 SYS LED Troubleshooting ........................................................................................................ 31
Table 10 ALM LED Troubleshooting ...................................................................................................... 31
Table 11 VDSL2 Data Transmission Troubleshooting .... ... ... .... ... .......................................................... 32
Table 12 Local Server Troubleshooting .................................................................................................32
Table 13 SYNC-rate Troubleshooting .................................................................................................... 32
VLC1324G User’s Guide
11
Page 12

List of Tables
12
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 13
CHAPTER 1
VLC Overview
This chapter introduces the VDSL2 line card's general features, default settings and hardware.
1.1 VLC Overview
The VLC VDSL2 Line Card is perfect for ISPs or large building applications seeking to
provide high bandwidth broadband services to subscribers while minimizing costs. One VLC
provides VDSL2 service for 24 subscribers over existing telephone wiring, thus avoiding the
cost and hassle of installing new wiring.
The line from the user carries both the VDSL2 and the voice signals. For each line, the splitter
card separates the high frequency VDSL2 signal from the voice band signal and feeds the
VDSL2 signal to the line card, while the voice band signal is diverted to the central office
switch or PBX (Private Branch Exchange).
Use the Telco-50 connector pin assignments in Section 2.3 on page 26 along with the
directions and safety warnings in the IES User’s Guide to install the line card and make the
necessary connections.
1.2 VDSL2 Profiles Overview
Here are the VDSL2 maximum transmission rates that the VLC supports at the time of writing.
The actual transfer rates will vary depending on what the subscriber’s device supports, the line
conditions and the connection distance.
Table 1 VDSL2 Profile Maximum Transfer Rates
VDSL2 PROFILE MAXIMUM DOWNSTREAM MAXIMUM UPSTREAM
8a/b/c/d 85 Mbps 18 Mbps
12a/b 85 Mbps 50 Mbps
17a 100 Mbps 50 Mbps
1.3 Key Features
Here is a partial list of the VLC’s features.
1
1. These are the highest link rates attained in testing. Actual data transfer rates will vary. These rates are for a
single port. The ports cannot all simultaneously link up at these rates.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
13
Page 14

Chapter 1 VLC Overview
VDSL2 Compliance
•ITU-T
-G.993.2
-G.994.1
Discrete Multi-Tone (DMT) Modulation
The VLC is a DMT-based VDSL2 solution which dynamically adapts the bit transfer rate to
conditions on the local loop. This allows the line card to sustain high performance even over
noisy lines.
Transmit PSD Notches
The VLC supports the transmission of PSD (Power Spectral Density) notches at RFI (Radio
Frequency Interference) bands. This reduces the effects of strong radio sources nearby.
Upstream Power Backoff
Upstream Power Backoff (UPBO) methods can be applied to VDSL2 networks, in order to
solve FEXT (Far End Cross (X) Talk) noise effects in distributed environments.
Downstream Power Back-Off
The VLC1324G-51 supports the downstream power back-off (DPBO) in ITU-T G.997.1 to
reduce far-end crosstalk.
Band Plan Support
The VLC supports the band plans defined in ITU-T G.993.2.
Alarm Profiles
The system allows you to customize the priority levels of individual alarms and the alarm
severity threshold for recording alarms on an individual port(s). The VLC also includes a DSL
error (ES, SES, UAS) monitoring and alarm reporting mechanism.
VDSL2 Profiles
Profiles allow you to configure VDSL2 ports efficiently. You can configure all of the VDSL2
ports with the same profile, thus removing the need to configure the VDSL2 ports one-by-one.
You can also change an individual VDSL2 port by assigning it a different profile. The VLC
supports the following VDSL2 profiles:
•8a •8b
•8c •8d
• 12a • 12b
• 17a
14
• The DS1 frequency band of the 17a profile starts at 138 kHz and the edge frequency of the
upper band of the 17a profile is 17.664 MHz.
• The VDSL2 profiles are programmable and automatically adapt according to the line
condition of each VDSL2 line.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 15

Chapter 1 VLC Overview
VDSL2 to ADSL2+ Fallback
The VLC can automatically use ADSL2+ for connections where VDSL2 training fails. This
allows a longer connection distance.
Spectral Mask
PSD (Power Spectral Density) defines the distribution of a VDSL line’s power in the
frequency domain. A PSD mask is a template that specifies the maximum allowable PSD for a
line. The VLC transmitter signal complies with the Power Spectrum Density (PSD) mask
specified in ITU-T G.993.2 and supports masks EU32_D32, EU36_D48, and EU40_D48.
Latency Mode
The VLC supports the latency path function specified in ITU-T G.993.2 and you can manually
configure the payload transfer delay for interleaved transmissions.
Rate Adaption
Rate adaption lets the VLC adjust from the configured transmission rate to the attainable
transmission rate automatically depending on the line quality. The VDSL transmission rate
then stays at the new rate or adjusts if line quality improves or deteriorates.
The rate adaptation conforms to ITU-T G.993.2 and G.997.1 and is manually configurable and
can adjust automatically based on the line quality as determined by the Signal-to-Noise Ratio
(SNR).
Trellis Coding
The VLCuses Trellis coding (as specified in ITU-T G.993.2) to help reduce the noise in VDSL
transmissions.
Impulse Noise Protection (INP)
Short impulses from external sources may cause bursts of errors which could impact
multimedia (ex. voice, video, or picture) quality. The VLC’s VDSL2 supports Impulse Noise
Protection (INP) as defined ITU-T G.993.2. The VLC’s impulse noise protection provides the
ability to correct errors regardless of the number of errors in an errored DMT (Discrete MultiTone) symbol. You can configure the minimum impulse noise protection to provide up to 16
DMT symbols protection.
Loop Diagnostic
The VLC supports the loop diagnostic function specified in ITU-T G.993.2. The test
parameters include quiet line noise, signal-to-noise ratio, loop attenuation, signal attenuation,
signal-to-noise ratio margin, attainable net data rate, and far-end actual aggregate transmit
power. After completing the loop diagnostic function, the VLC displays the test results and
automatically returns to the normal state to be ready for initialization.
System Monitoring
• System status (link status, rates, statistics counters)
• Configurable temperature and voltage monitoring thresholds and alarm reports.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
15
Page 16

Chapter 1 VLC Overview
Alarm LED
An ALM (alarm) LED lights when the VLC is overheated or the voltage readings are outside
the tolerance levels and turns off when the temperature or voltage has returned to a normal
level.
CFM
The IEEE 802.1ag Connectivity Fault Management (CFM) specification allows network
administrators to identify and manage connection faults. Through discovery and verification
of the path, CFM can detect, analyze and isolate connectivity faults in bridged LANs. This is
especially helpful when the route between a CO VDSL switch and one of its CPE goes
through switches owned by independent organizations .
IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN
Your VLC uses the IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN (Virtual Local Area Network), which allows
it to deliver tagged/untagged frames to and from its ports.
Subnet Based VLAN
Subnet based VLAN allows you to group traffic into logical VLANs based on the source IP
subnet you specify. When a frame is received on a port, the VLC checks if a tag is added
already and the IP subnet it came from. The untagged packets from the same IP subnet are then
placed in the same subnet based VLAN. One advantage of using subnet based VLANs is that
priority can be assigned to traffic from the same IP subnet.
xVLAN
xVLAN translates (changes) the VLAN IDs (VIDs) of subscriber traffic before sending it to
the service provider’s network. This lets you use unique VLANs for each subscriber but still
deploy all the CPE devices with the same VLAN configuration. xVLAN also supports
translating single-tagged frames to double-tagged frames.
Port Isolation
The VLC's port isolation feature allows each port to communicate with the uplink port but not
communicate with each other.
Isolation (per-VLAN)
Use isolation to block the VDSL2 subscribers in a specific VLAN from sending traffic directly
to each other.
IEEE 802.1x Port-based Authentication
The VLC supports the IEEE 802.1x standard for centralized user authentication and
accounting management through an optional netw ork authentication (RADIUS) server.
Packet Filter
The VLC supports packet filtering based on protocol. You can configure the VLC to accept all
packets, accept PPPoE packets only or block any combination of the following protocols: IP,
ARP, DHCP, EAPOL, PPPoE, NetBios or IGMP.
16
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 17

Chapter 1 VLC Overview
MAC (Media Access Control) Filter
Use the MAC filter to deny or accept incoming frames based on MAC (Media Access Control)
address(es) or OUI (Organizational Unit Identifier) that you specify. You may enable/disable
the MAC filter on specific ports. You may specify up to ten MAC addresses per port.
Upstream Broadcast Storm Control
Broadcast storm control lets you set limits for how many broadcast, multicast and destination
lookup failure (DLF) packets a port receives per second from the subscriber.
Downstream Broadcast VLAN Control
Downstream broadcast VLAN control allows you to block downstream broadcast packets
from being sent to specified VLANs on specified ports. This helps to reduce downstream
bandwidth requirements on a subscriber line.
MAC Count Limit
You can limit the number of MAC addresses that may be dynamically learned on a port. You
may enable/disable the MAC count filter on individual ports.
IGMP Snooping
The VLC supports IGMP snooping enabling group multicast traffic to be only forwarded to
ports that are members of that group; thus allowing you to significantly reduce multicast traffic
passing through your VLC.
IGMP Filter
The IGMP filter defines multicast groups a port can join. You can create IGMP filter profiles
which allow access to a multicast group, then assign the IGMP filter to a specific VDSL2 port.
Multicast Group Limit
You can limit the number of multicast groups a subscriber on a port can join. You may enable/
disable the multicast group limit on individual ports.
Discarding of IGMP Query Messages
The VLC discards IGMP query messages received from subscriber ports. This prevents
subscribers from hosting IGMP multicast servers.
IGMP Statistics
The VLC records the number of active users in an IGMP multicast channel (multicast group).
The VLC also records IGMP message statistics on a per port basis to ease management and
troubleshooting.
IGMP Message Rate Limiting
The VLC can limit how many IGMP message packets a subscriber can send per second. This
prevents subscribers from flooding the multicast server.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
17
Page 18

Chapter 1 VLC Overview
Static Multicast
Use static multicast to allow incoming frames based on multicast MAC address(es) that you
specify . This feature can be used in conjunction with IGMP snooping to allow multicast MAC
address(es) that are not learned by IGMP snooping. You can use static multicast to pass
routing protocols, such as RIP and OSPF.
Multicast VLAN
Multicast VLAN is designed for applications (such as Media-on-Demand (MoD)) using
multicast traffic across an Ethernet ring-based service provider network. Multicast VLAN
allows one single multicast VLAN to be shared among different subscriber VLANs on the
network. This improves bandwidth utilization by reducing multicast traffic in the subscriber
VLANs and simplifies multicast group management.
Multicast Bandwidth Control
The VLC supports static bandwidth control for multicast traffic. Bandwidth limits can be
assigned to multicast channels. During IGMP snooping, the system checks the total bandwidth
usage to see if it exceeds the specified limit. If the specified limits are reached, the system
restricts the joining of multicast groups on a per port basis.
DHCP Relay
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol RFC 2131 and RFC 2132) allows individual
computers to obtain TCP/IP configuration at start-up from a server. You can configure the
system as a DHCP relay agent to have another DHCP server provide TCP/IP configuration for
the clients. In addition, you can set the system to forward client DHCP requests to specific
DHCP servers based on the VLAN ID. You can also specify up to two DHCP servers for each
VLAN to provide failover protection.
Rate Limiting
Rate limiting on the subscriber ports allows service providers to offer tiered service in
increments of 64 Kbps. This service differentiation is not only to fulfill the needs of different
customers, but also to provide a network infrastructure that combines guaranteed performance
and flexibility in service provisioning.
DHCP Relay Option 82
The system supports DHCP relay agent82 (RFC 3046) that adds additional information to
client DHCP requests that the MSC relays to a DHCP server. It also supports adding the suboption 2 (Remote ID) with additional information.
PPPoE Intermediate Agent Information
Similar to DHCP relay option82, you can set the system to insert line information into client
PPPoE Active Discovery Initialization (PADI), PPPoE Active Discovery Request (PADR),
and upstream PPPoE Active Discovery Terminate (PADT) packets. This allows a PPPoE
termination server to identify and authenticate a PPPoE client.
18
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 19

Chapter 1 VLC Overview
DHCP Snooping
DHCP snooping allows the system to identify packets with DHCP server assigned IP
address(es) and block access of devices using unknown IP addresses on a subscriber port. You
can also manually add static IP addresses to the DHCP snooping table.
LAN 2 LAN
LAN 2 LAN allows you to control whether or not a DHCP server connected to a subscriber
port is permitted to receive and send traffic through the IES.
Anti-IP Address Spoofing
With DHCP snooping, a line card records which IP addresses are assigned on each port. The
line card drops packets from a device using a different IP address.
Anti-MAC Address Spoofing
The VLC checks to make sure the MAC addresses of the devices connected to the DSL ports
are not the same as MAC addresses of devices connected to the Ethernet network. This
protects the network from disruptions of service caused by subscriber devices spoofing the
MAC address of ISP servers.
ARP Inspection
ARP inspection drops ARP packets if the MAC address to IP address binding does not match
that of a learned or manually added trusted client. This prevents many common man-in-themiddle attacks.
Transparent LAN Service (TLS)
Use TLS (also known as VLAN stacking) to add an outer VLAN tag to the inner IEEE 802.1Q
tagged frames that enter the network. This allows a service provider to provide different
services based on specific VLANs, for many different customers.
VDSL Double-Tag VLAN
DT VLAN (Double-Tag VLAN) adds two VLAN tags to untagged frames received on a
VDSL port. These two VLAN tags consist of an inner c-tag (customer tag) and an outer s-tag
(service provider tag). These double VLAN tags consist of an inner c-tag (c ustomer tag) and
an outer s-tag (service provider tag). The line card drops any tagged frames it receives from a
subscriber.
Double-Tag PVC (DTPVC)
For VDSL2 ports operating in ADSL2+ connection mode, DTPVCs (Double-Tag Permanent
Virtual Circuits) add double VLAN tags to untagged frames received from a DSL subscriber
on the specified PVC. These double VLAN tags consist of an inner c-tag (customer tag) and an
outer s-tag (service provider tag). The line card drops any tagged frames received on the
DTPVC. DTPVCs support DHCP relay, IGMP, IEEE 802.1x and PPPoE agent.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
19
Page 20

Chapter 1 VLC Overview
1.4 Front Panel of VLC
The figure below shows the front panel of the VLC.
Figure 1 Front Panel
1.5 Ports and LEDs of VLC
These are the details of the VLC ports and LEDs.
1.5.1 Ports
The following table describes the port labels on the front panel.
Table 2 Front Panel Ports
LABEL DESCRIPTION
CONSOLE For troubleshooting purposes, this mini RJ-11port connects to a computer
when the line card is not manageable from the MSC.
1-24 These Telco-50 connectors are for connecting the VLC to the splitter cards.
1.5.2 LEDs
The following table describes the LED indicators on the front panel of the VLC.
Table 3 LED Descriptions
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR Green On The line card is turned on.
Off The line card is off.
SYS Green Blinking The line card is rebooting and performing self-diagnostic
On The line card is on and functioning properly.
Off The power is off or the line card is malfunctioning.
ALM Red On There is a hardware failure or alarm.
Off The line card is functioning normally.
1.6 VSC1224-41 POTS Splitter
Figure 2 Front Panel of VSC1224-41
tests.
20
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 21

Chapter 1 VLC Overview
A 24 port POTS splitter is used to differentiate analog signal from the VDSL2 band. The
VLC1324G-51 uses the VSC1224-41 and the VLC1324G-53 uses the VSC1224 - 43U. The
splitter is installed in the splitter chassis. See the IES User’s Guide for installation instructions.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
21
Page 22

Chapter 1 VLC Overview
22
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 23

CHAPTER 2
VLC Specifications
This chapter gives details about the line card hardware and features.
2.1 VLC Product Specifications
Table 4 VLC Specifications
Dimensions 390.6 mm (W) x 240.0 mm (D) x 13.8 mm (H)
Weight 1 kg
Interface • One Telco-50 connector: 24 VDSL2 Ports
• One mini RJ11 console port for local management
Operation Temperature -40º C ~ 65º C
Storage Temperature -40º C ~ 70º C
Operation Humidity 10% ~ 90% RH (non-condensing)
Storage Humidity 10% ~ 95% RH (non-condensing)
Power Consumption Less than 70 Watts
Power Input -36~-72 VDC (typical -48 VDC)
Fuse Rating Number of fuses: 1
Type: T
Amps: 4
Volts AC: 250
Dimensions: 5mm (D) x 20mm (L)
VDSL2 Compliance ITU-T VDSL2 Standard
• G.993.2
• G.994.1
MAC Address Table 4 K entries
Max. Number of IGMP
Filter Profiles
Supported VDSL2
Profiles
Number of VLANs per
card
External Splitter Details The VLC1324G-51 uses the VSC1224-41 splitter.
Supported Band Plans ITU-T G.993.2 Annex A
128
8a, 8b, 8c, 8d, 12a, 12b, 17a
Up to 1 K individual VLANs
The VLC1324G-53 uses the VSC1224-43U splitter.
The splitter has a front panel Te lco-50 connector for connecting to the VLC.
ITU-T G.993.2 Annex B (bandplans 997 and 998)
VLC1324G User’s Guide
23
Page 24

Chapter 2 VLC Specifications
Table 4 VLC Specifications
Certifications RoHS & WEEE compliant
Network Management • Local debug function through a RS-232 port
NEBS compliant
ETSI 300-019
K.20
Safety
EN60950-1
EN41003-1
ETSI300-386
CSA60950-1
UL60950-1
IEC60950-1
EMC
FCC Part 15 Class A
EN55022 Class A
EN55024 Class A
ETSI 300 386
• Web-based configurator through MSC
• SNMP v1, v2c and v3 based support through MSC
• Remote debug through MSC (Telnet)
• Status display and event report
• Multi-level login through MSC
24
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 25

Table 4 VLC Specifications
MIB • RFC1213 SNMP MIB II
• RFC1493 Bridge MIB·
• RFC1643 Ethernet MIB·
• RFC2674 Q MIB·
• VDSL2 Line MIB (RFC3728)·
• RFC1757 RMON MIB, group 1, 2, 3, 9
• ZyXEL proprietary MIB.
- MIB for VDSL2 uplink/downlink SNR
- MIB for VDSL2 interface Tx/Rx power
- MIB for IGMP statistics per subscriber interface and per multicast
VLAN basis, which at least include counters of IGMP join, IGMP leave
and active multicast group(s)
- MIB for counters of active users on a per-multicast group basis
- MIB for VDSL2 line includes far-end and near-end Error Second (ES),
Severely Error Second (SES) and Unavailable Second (UAS) at VTUO, and near-end ES, SES and UAS at VTU-R
- MIB for VDSL2 port includes the far-end and near-end Code Violation
(incorrect Cyclic Redundancy Check, CRC) at VTU-O, and near-end
Code Violation at VTU-R
Other Features • Anti-IP Address Spoofing
• Anti-MAC Address Spoofing
• MAC Filtering
• MAC Count Limiting
• Hardware-based Multicasting
• Multicast Group Limit
• IGMP Message Rate Limiting
• IEEE 802.1Q VLAN Tagging
• IEEE 802.1p CoS with Priority Queuing
• IGMP v1, v2, and v3 Snooping
• DHCP Snooping
• IEEE 802.1x Port-based Authentication
• ACL profile
• IEEE 802.1p Priority Mapping Sets
• Transmit PSD
• Upstream Broadcast Storm Control
• Downstream Broadcast VLAN Control
• PPPoE Intermediate Agent Information
• Subnet Based VLAN
• xVLAN
Chapter 2 VLC Specifications
2.2 VLC Firmware Naming Conventions
A firmware version includes the model code and release number as shown in the following
examples:
Firmware Version: V3.95(AYL.0), V3.95(BBW.0)
“AYL” or “BBW” is the model code.
• "AYL" denotes the VLC1324G-51 for VDSL over POTS (Annex A).
• "BBW" denotes the VLC1324G-53 for VDSL over ISDN (Annex B).
“0” is the firmware’s release number . This varies as new firmware is released. Your firmware’ s
release number may not match what is displayed in this User’s Guide.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
25
Page 26
Chapter 2 VLC Specifications
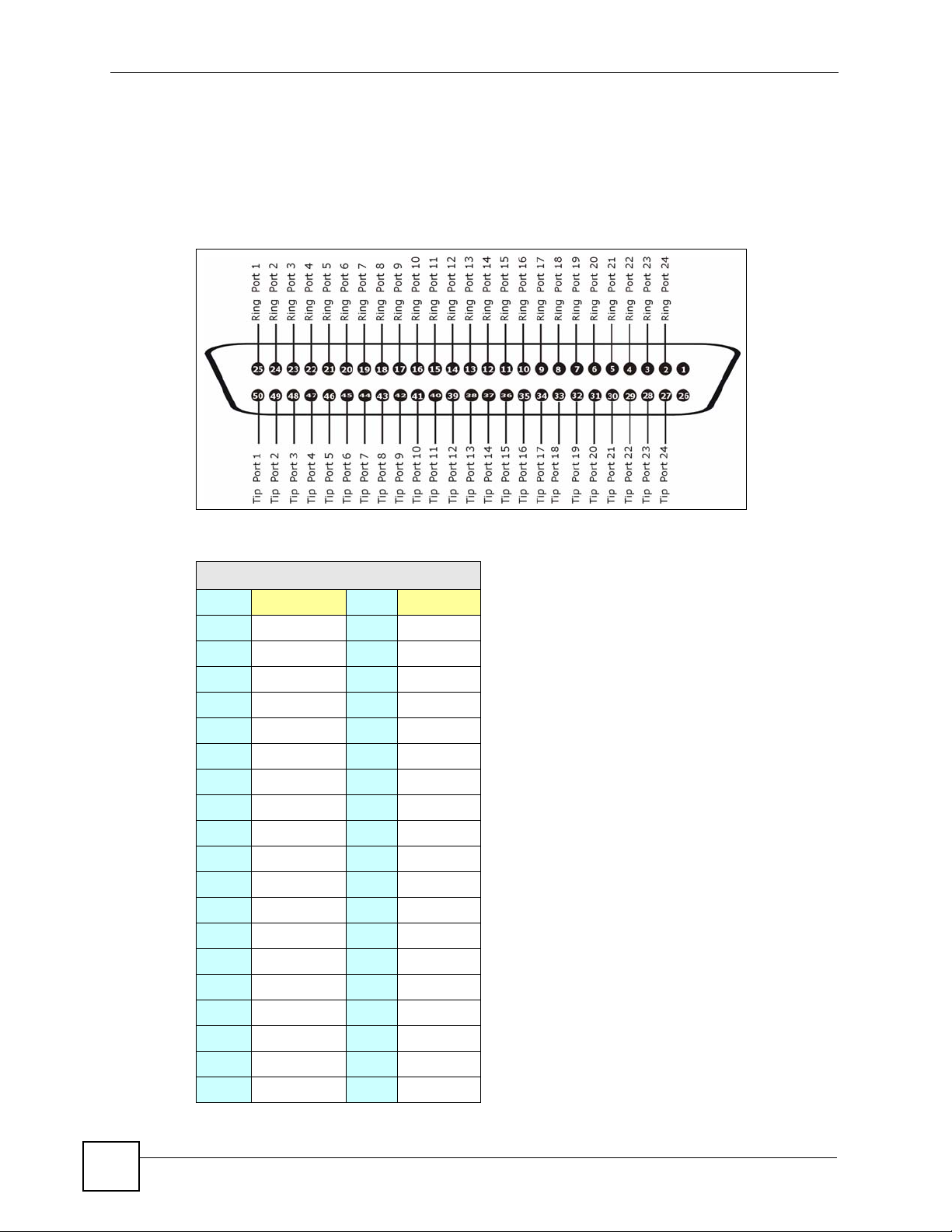
2.3 Telco-50 Connector Pin Assignments
The following figures and table describe the pin assignments for the VLC’s Telco-50
connector. The splitter card’s Telco-50 connector and the USER and CO hardware Telco-50
connectors on the rear panel of the splitter chassis also use the same pin assignments.
Figure 3 VLC Ports 1-24 Telco-50 Connector Pin Assignments
Table 5 VLC Telco-50 Connector Pin Assignments
PORTS 1-24
Pin 1 NULL Pin 26 NULL
Pin 2 Ring Port 24 Pin 27 Tip Port 24
Pin 3 Ring Port 23 Pin 28 Tip Port 23
Pin 4 Ring Port 22 Pin 29 Tip Port 22
Pin 5 Ring Port 21 Pin 30 Tip Port 21
Pin 6 Ring Port 20 Pin 31 Tip Port 20
Pin 7 Ring Port 19 Pin 32 Tip Port 19
Pin 8 Ring Port 18 Pin 33 Tip Port 18
Pin 9 Ring Port 17 Pin 34 Tip Port 17
Pin 10 Ring Port 16 Pin 35 Ti p Port 16
Pin 11 Ring Port 15 Pin 36 Ti p Port 15
Pin 12 Ring Port 14 Pin 37 Ti p Port 14
Pin 13 Ring Port 13 Pin 38 Ti p Port 13
Pin 14 Ring Port 12 Pin 39 Ti p Port 12
Pin 15 Ring Port 11 Pin 40 Tip Port 11
Pin 16 Ring Port 10 Pin 41 Ti p Port 10
Pin 17 Ring Port 9 Pin 42 Ti p Port 9
Pin 18 Ring Port 8 Pin 43 Ti p Port 8
Pin 19 Ring Port 7 Pin 44 Ti p Port 7
Pin 20 Ring Port 6 Pin 45 Ti p Port 6
26
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 27

Chapter 2 VLC Specifications
Table 5 VLC Telco-50 Connector Pin Assignments (continued)
PORTS 1-24
Pin 21 Ring Port 5 Pin 46 Ti p Port 5
Pin 22 Ring Port 4 Pin 47 Ti p Port 4
Pin 23 Ring Port 3 Pin 48 Ti p Port 3
Pin 24 Ring Port 2 Pin 49 Ti p Port 2
Pin 25 Ring Port 1 Pin 50 Ti p Port 1
The following graphics show pin assignments for the Telco-50 connectors on the cables that
connect the VLC to a splitter card in the splitter chassis.
Figure 4 IES-5000/5005 Cable Telco-50 Pin Assignments (VLC End)
Figure 5 IES-5000/5005 Cable Telco-50 Pin Assignments (Splitter Card End)
VLC1324G User’s Guide
27
Page 28

Chapter 2 VLC Specifications
Figure 6 IES-6000 Cable Telco-50 Pin Assignments (VLC End)
28
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 29

Chapter 2 VLC Specifications
Figure 7 IES-6000 Cable Telco-50 Pin Assignments (Splitter End)
2.4 Wire Gauge Specifications
AWG (American Wire Gauge) is a measurement system for wire that specifies its thickness.
As the thickness of the wire increases, the AWG number decreases.
Table 6 Wire Gauge Specifications
WIRE TYPE REQUIRED AWG NO. (DIAMETER)
Telephone Wire 26 or larger
2.5 Console Cable Pin Assignments
The following diagram and chart show the pin assignments of the console cable.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
29
Page 30

Chapter 2 VLC Specifications
Figure 8 Console Cable Mini RJ-11 Male Connector
Table 7 Console Cable Connector Pin Assignments
MINI RJ-11 MALE
Pin 2: TXD
Pin 3: RXD
Pin 4: GND
2.6 VSC1224-41
The following table lists the splitter card specifications.
Table 8 VSC1224-41 CO Impedance Splitter Card Specifications
COUNTRY POTS
Taiwan 900 Ω
Others 600 Ω
2.7 VSC1224-43U
The VSC1224-43U provides an impedance of 135 ohms and 150 ohms for ISDN.
30
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 31

CHAPTER 3
VLC Troubleshooting
This chapter covers potential problems and possible remedies. After each problem description,
some steps are provided to help you to diagnose and solve the problem.
3.1 The SYS or PWR LED Does Not Turn On
Table 9 SYS LED Troubleshooting
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Make sure the power wires are properly connected to the power supply and the power
2 Make sure the power wires are connected properly.
3 Make sure the line card is properly installed.
4 The LED itself or the unit may be faulty; contact your vendor.
supply is operating normally. Make sure you are using the correct power source (refer to
the IES User’s Guide for details).
3.2 The ALM LED Is On
The ALM (alarm) LED lights when the line card is overheated or the voltage readings are
outside the tolerance levels.
Table 10 ALM LED Troubleshooting
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1Use the sys monitor show command to verify the cause of the alarm. See step 2 if the
unit is overheated, and step 3 if the voltages are out of the allowed ranges.
2 Ensure that the IES is installed in a well-ventilated area and that normal operation of the
fans is not inhibited. Keep the bottom, top and all sides clear of obstructions and away from
the exhaust of other equipment.
3 If the voltage levels are outside the allowed range, take a screen shot of the
monitor show command display and contact your vendor.
sys
VLC1324G User’s Guide
31
Page 32

Chapter 3 VLC Troubleshooting
3.3 VDSL2 Data Transmission
The VDSL2 link is up, but data cannot be transmitted.
Table 11 VDSL2 Data Transmission Troubleshooting
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Check the line card’s port isolation settings.
If the subscriber is having problems with video or other high-bandwidth services, make
sure the line card’s VDSL2 port’s data rates are set high enough.
2 Check the VLAN configuration.
3 Ping the MSC from the computer behind the VDSL2 modem or router.
If you cannot ping, connect a VDSL2 modem to a VDSL2 port (that is known to work).
If the VDSL2 modem or router works with a different VDSL2 port, there may be a problem
with the original port. Contact the distributor.
If using a different port does not work, try a different VDSL2 modem or router with the
original port.
3.4 Local Server
The computer behind a VDSL2 modem or router cannot access a local server connected to the
line card.
Table 12 Local Server Troubleshooting
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Refer to Section 3.3 on page 32 to make sure that the subscriber is able to transmit to the
2 Make sure the computer behind the DS L de vi ce has the correct gateway IP address
3 Check the VLAN configuration.
4 Check the cable and connections between the line card and the local server.
5 Try to access another local server.
3.5 Data Rate
The SYNC-rate is not the same as the configured rate.
Table 13 SYNC-rate Troubleshooting
STEPS CORRECTIVE ACTION
1 Connect the VDSL2 modem or router directly to the VDSL2 port using a different telephone
2 If the rates match, the quality of the telephone wiring that connects the subscriber to the
line card.
configured.
If data can be transmitted to a different local server, the local server that could not be
accessed may have a problem.
wire.
VDSL2 port may be limiting the speed to a certain rate.
If they do not match when a good wire is used, contact the distributor.
32
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 33

Chapter 3 VLC Troubleshooting
3.6 The Line Card is Not Manageable
The line card always uses the default configuration. Any changes you did to the line card are
stored on the MSC. By default, the MSC is allowed to manage every line card. Use the
command on the MSC to see a line card’s connection status. If you still cannot manage
show
the line card from the MSC, the line card’ s configu ration file may be damaged or the firmware
may be old, you may need to restore the default configuration file or upload new firmware
using the line card’s console port.
lcman
1 The MSC resets the line card after a period of inactivity on the line card. This
may damage the line card if you are uploading the default configuration file or
new firmware to the line card. Use the
the MSC to prevent the MSC from managing the line card.
lcman disable <slot> command on
1 After you upload the file successfully , use the lcman enable <slot> command
on the MSC to allow the MSC to manage the line card again.
3.6.1 Uploading the Default Configuration File via Boot Commands
Obtain the default configuration file, unzip it and save it in a folder. Use a console cable to
connect a computer with terminal emulation software to the line card’s console port. Pull out
the line card and push it back in, you will see the initial screen. When you see the message
Press any key to enter Debug Mode within 3 seconds press any key to enter
debug mode.
To upload the configuration file, do the following:
1 Type atlc after the Enter Debug Mode message.
2 Wait for the Starting XMODEM upload message before activating XMODEM
upload on your terminal.
3 This is an example Xmodem configuration upload using HyperTerminal. Click
Transfer, then Send File to display the following screen.
Figure 9 Example Xmodem Upload
Type the configuration file's
location, or click Browse to
search for it.
Choose the 1K Xmodem
protocol.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Then click Send.
33
Page 34

Chapter 3 VLC Troubleshooting
4 After a successful configuration file upload, type atgo to restart the line card.
Bootbase Version: V1.00 | 03/23/2005 16:10:06
FLASH: AMD 32M
Hardware Version:
Serial Number:
RAM: Size = 133120 Kbytes
ZyNOS Version: V3.94(AYL.0)c0 | 1/01/2008 20:50:26
Press any key to enter debug mode within 3 seconds.
...........
Enter Debug Mode
atlc
Starting XMODEM upload (CRC mode)....
CCCC
Total 393216 bytes received.
Erasing...
...........................................................................
.....OK
atgo
3.6.2 Uploading the Firmware via Boot Commands
Usually you should use FTP or HTTP with the MSC to upload the line card’s firmware. If you
cannot manage the line card from the MSC, use the following procedure to upload firmware to
the line card.
1 Obtain the firmware file, unzip it and save it in a folder on your computer.
2 Connect your computer to the console port and use terminal emulation software
configured to the following parameters:
• VT100 termi nal emulation • 9600 bps
• No parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit • No flow control
3 Pull out the line card and push it back in to restart it and begin a session.
4 When you see the
message, press a key to enter debug mode.
5 Type
atba5 after the Enter Debug Mode message (this changes the console port
speed to 115200 bps).
6 Change the configuration of your terminal emulation software to use 115200 bps and
reconnect to the line card.
7 Type
atur after the Enter Debug Mode message.
8 Wait for the
on your terminal.
9 This is an example Xmodem configuration upload using HyperTerminal. Click
Transfer, then Send File to display the following screen.
Press any key to enter Debug Mode within 3 seconds
Starting XMODEM upload message before activating XMODEM upload
34
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 35

Chapter 3 VLC Troubleshooting
Figure 10 Example Xmodem Upload
Type the firmware file's
location, or click Browse to
search for it.
Choose the 1K Xmodem
protocol.
Then click Send.
10After a successful firmware upload, the line card re starts. The console port speed
automatically changes back to 9600 bps when the line card restarts.
Bootbase Version: V1.00 | 03/23/2005 16:10:06
FLASH: AMD 32M
Hardware Version:
Serial Number:
RAM: Size = 133120 Kbytes
ZyNOS Version: V3.94(AYL.0)c0 | 1/01/2008 20:50:26
Press any key to enter debug mode within 3 seconds.
...........
Enter Debug Mode
atba5
Now, console speed will be changed to 115200 bps
OK
atur
Starting XMODEM upload (CRC mode)....
CCCCCCCC
Total 2003968 bytes received.
Erasing...............................
...........................................................................
...........................................................................
...........................................................................
...........................................................................
...........................................................................
...........................................................................
.........
OK
System Reboot...
Console speed will be changed to 9600 bps
VLC1324G User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 3 VLC Troubleshooting
36
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 37

APPENDIX A
Legal Information
Copyright
Copyright © 2010 by ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
The contents of this publication may not be reproduced in any part or as a whole, transcribed,
stored in a retrieval system, translated into any language, or transmitted in any form or by any
means, electronic, mechanical, magnetic, optical, chemical, photocopying, manual, or
otherwise, without the prior written permission of ZyXEL Communications Corporation.
Published by ZyXEL Communications Corporation. All rights reserved.
Disclaimers
ZyXEL does not assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any products, or
software described herein. Neither does it convey any license under its patent rights nor the
patent rights of others. ZyXEL further reserves the right to make changes in any products
described herein without notice. This publication is subject to change without notice.
Trademarks
ZyNOS (ZyXEL Network Operating System) is a registered trademark of ZyXEL
Communications, Inc. Other trademarks mentioned in this publication are used for
identification purposes only and may be properties of their respective owners.
Certifications
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) Interference Statement
This device complies with Part 15 of FCC rules. Operation is subject to the following two
conditions:
• This device may not cause harmful interference.
• This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operations.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
37
Page 38

Appendix A Legal Information
FCC Warning
This device has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital switch,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a commercial environment. This device generates,
uses, and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of
this device in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference in which case the user
will be required to correct the interference at his own expense.
CE Mark Warning:
This is a class A product. In a domestic environment this product may cause radio interference
in which case the user may be required to take adequate measures.
Taiwanese BSMI (Bureau of Standards, Metrology and Inspection) A Warning:
Notices
Changes or modifications not expressly approved by the party responsible for compliance
could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
This Class A digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Cet appareil numérique de la classe A est conforme à la norme NMB-003 du Canada.
Viewing Certifications
1 Go to http://www.zyxel.com
2 Select your product on the ZyXEL home page to go to that product's page.
3 Select the certification you wish to view from this page.
ZyXEL Limited Warranty
ZyXEL warrants to the original end user (purchaser) that this product is free from any defects
in materials or workmanship for a period of up to two years from the date of purchase. During
the warranty period, and upon proof of purchase, should the product have indications of fai lure
due to faulty workmanship and/or materials, ZyXEL will, at its discretion, repair or replace the
defective products or components without charge for either parts or labor, and to whatever
extent it shall deem necessary to restore the product or components to proper operating
condition. Any replacement will consist of a new or re-manufactured functionally equivalent
product of equal or higher value, and will be solely at the discretion of ZyXEL. This warranty
shall not apply if the product has been modified, misused, tampered with, damaged by an act
of God, or subjected to abnormal working conditions.
.
38
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 39

Appendix A Legal Information
Note
Repair or replacement, as provided under this warranty, is the exclusive remedy of the
purchaser. This warranty is in lieu of all other warranties, express or implied, including any
implied warranty of merchantability or fitness for a particular use or purpose. ZyXEL shall in
no event be held liable for indirect or consequential damages of any kind to the purchaser.
To obtain the services of this warranty, contact your vendor. You may also refer to the
warranty policy for the region in which you bought the device at http://www.zyxel.com/web/
support_warranty_info.php.
Registration
Register your product online to receive e-mail notices of firmware upgrades and information
at www.zyxel.com.
VLC1324G User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Appendix A Legal Information
40
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 41

Index
Index
A
alarm LED 16
Alarm profile 14
ALM LED 16, 31
AWG (American Wire Gauge) 29
B
bandwidth control 18
C
certifications 24, 37
notices 38
viewing 38
CFM
Connectivity Fault 16
console cable pin assignments 29
console port 20, 34
copyright 37
F
FCC interference statem en t 37
features 13
other supported 25
filter protocols 16
filter, packet 16
front panel 20
H
hardware 20
I
IEEE 802.1Q Tagged VLAN 16
IEEE 802.1x Port-based Authentication 16
Impulse Noise Protection 15
INP 15
isolation 16
D
DHCP 18
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) 18
DHCP Relay Option 82 18
DHCP snooping 19
dimensions 23
disclaimer 37
Discrete Multi-Tone 15
DMT 15
E
error logging 15
VLC1324G User’s Guide
L
LED
ALM 16
description 20
LED problems 31
lockout 33
logging errors 15
M
MAC (Media Access Control) Filter 17
MAC count limit 17
MIBs 25
monitoring, system 15
multicast bandwidth control 18
41
Page 42

Index
multicast group limit 17
multicast static 18
multicast VLAN 18
MVLAN 18
N
network management 24
P
packet filter 16
pin assignments 26
port description 20
port isolation 16
Power Spectral Density See PSD
PPPoE intermediate agent 18
product registration 39
product specifications 23
profile
VDSL 18
profiles 14
Alarm 14
VDSL2 14
protocol filter 16
PSD 15
PWR LED 31
R
supported features 25
syntax conventions 5
SYS LED 31
system error logging 15
system monitoring 15
T
Telco-50 connector 20
Telco-50 pin assignments 26
telephone wire 29
terminal emulation 34
trademarks 37
Transparent LAN Service (TLS) 19
troubleshooting 31
U
USER Telco-50 connectors 29
V
VDSL profile 18
VDSL2 profile 14
VDSL2 standards 13
VLAN 32
VLAN stacking 19
VLAN, multicast 18
VT100 34
rate adaption 15
recovering firmware 34
registration
product 39
related documentation 3
S
safety warnings 6
Signal-to-Noise Ratio See SNR
SNR 15
standards, VDSL2 13
static multicast 18
42
W
warranty 38
note 39
weight 23
wire gauge 29
X
XMODEM upload 33, 34
xVLAN 16
VLC1324G User’s Guide
Page 43

Index
VLC1324G User’s Guide
43
Page 44

Index
44
VLC1324G User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...