Page 1

V300 Series
IP Phone
User’s Guide
Version 1.00
11/2 007
Edition 2
www.zyxel.com
Page 2

Page 3

About This User's Guide
About This User's Guide
Intended Audience
This manual is intended for people who want to configure the V300 using the LCD screen and/
or web configurator. You should have at least a basic knowledge of TCP/IP networking
concepts and topology.
Related Documentation
• Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide is designed to help you get up and running right away. It contains
information on setting up and configuring the V300.
• Web Configurator Online Help
Embedded web help for descriptions of individual screens and supplementary
information.
• Supporting Disk
Refer to the included CD for support documents.
• ZyXEL Web Site
Please refer to www.zyxel.com
certifications.
for additional support documentation and product
User’s Guide Feedback
Help us help you. Send all User’s Guide-related comments, questions or suggestions for
improvement to the following address, or use e-mail instead. Thank you!
The Technical Writing Team,
ZyXEL Communications Corp.,
6 Innovation Road II,
Science-Based Industrial Park,
Hsinchu, 300, Taiwan.
E-mail: techwriters@zyxel.com.tw
V300 User’s Guide
3
Page 4
Document Conventions
Document Conventions
Warnings and Notes
These are how warnings and notes are shown in this User’s Guide.
1 Warnings tell you about things that could harm you or your device.
" Notes tell you other important information (for example, other things you may
need to configure or helpful tips) or recommendations.
Syntax Conventions
• The V300 or V301 may be referred to as the “V300”, the “device”, the “system” or the
“product” in this User’s Guide.
• Product labels, screen names, field labels and field choices are all in bold font.
• A key stroke is denoted by square brackets and uppercase text, for example, [ENTER]
means the “enter” or “return” key on your keyboard.
• “Enter” means for you to type one or more characters and then press the [ENTER] key.
“Select” or “choose” means for you to use one of the predefined choices.
• A right angle bracket ( > ) within a screen name denotes a mouse click. For example,
Maintenance > Log > Log Setting means you first click Maintenance in the navigation
panel, then the Log sub menu and finally the Log Setting tab to get to that screen.
• Units of measurement may denote the “metric” value or the “scientific” value. For
example, “k” for kilo may denote “1000” or “1024”, “M” for mega may denote “1000000”
or “1048576” and so on.
• “e.g.,” is a shorthand for “for instance”, and “i.e.,” means “that is” or “in other words”.
4
V300 User’s Guide
Page 5

Document Conventions
Icons Used in Figures
Figures in this User’s Guide may use the following generic icons. The V300 icon is not an
exact representation of your device.
V300 Computer Notebook computer
Server DSLAM Firewall
Telephone Switch Router
V300 User’s Guide
5
Page 6

Safety Warnings
Safety Warnings
1 For your safety, be sure to read and follow all warning notices and instructions.
• Do NOT use this product near water, for example, in a wet basement or near a swimming
pool.
• Do NOT expose your device to dampness, dust or corrosive liquids.
• Do NOT store things on the device.
• Do NOT install, use, or service this device during a thunderstorm. There is a remote risk
of electric shock from lightning.
• Connect ONLY suitable accessories to the device.
• Do NOT open the device or unit. Opening or removing covers can expose you to
dangerous high voltage points or other risks. ONLY qualified service personnel should
service or disassemble this device. Please contact your vendor for further information.
• Make sure to connect the cables to the correct ports.
• Place connecting cables carefully so that no one will step on them or stumble over them.
• Always disconnect all cables from this device before servicing or disassembling.
• Use ONLY an appropriate power adaptor or cord for your device. Connect it to the right
supply voltage (for example, 110V AC in North America or 230V AC in Europe).
• Do NOT allow anything to rest on the power adaptor or cord and do NOT place the
product where anyone can walk on the power adaptor or cord.
• Do NOT use the device if the power adaptor or cord is damaged as it might cause
electrocution.
• If the power adaptor or cord is damaged, remove it from the device and the power source.
• Do NOT attempt to repair the power adaptor or cord. Contact your local vendor to order a
new one.
• Do not use the device outside, and make sure all the connections are indoors. There is a
remote risk of electric shock from lightning.
• Do NOT obstruct the device ventilation slots, as insufficient airflow may harm your
device.
• If you wall mount your device, make sure that no electrical lines, gas or water pipes will
be damaged.
• The PoE (Power over Ethernet) devices that supply or receive power and their connected
Ethernet cables must all be completely indoors.
6
This product is recyclable. Dispose of it properly.
V300 User’s Guide
Page 7
Safety Warnings
V300 User’s Guide
7
Page 8

Safety Warnings
8
V300 User’s Guide
Page 9

Contents Overview
Contents Overview
Introduction ............................................................................................................................ 23
Introducing the V300 ................................................................................................................. 25
Hardware ................................................................................................................................... 29
LCD Screen Menus ................................................................................................................ 37
Using the LCD Screen ............................................................................................................... 39
The Phonebook ......................................................................................................................... 43
LCD Menus: Basic Settings ....................................................................................................... 45
LCD Menus: Advanced .............................................................................................................. 49
The Web Configurator ...........................................................................................................61
Introducing the Web Configurator .............................................................................................. 63
Status Screens .......................................................................................................................... 69
Network Setup ........................................................................................................................... 75
SIP Account Setup .................................................................................................................... 79
Phone Setup .............................................................................................................................. 93
The Phone Book ........................................................................................................................ 97
Maintenance and Troubleshooting .....................................................................................107
System ..................................................................................................................................... 109
Logs ..........................................................................................................................................113
Tools .........................................................................................................................................115
Troubleshooting ....................................................................................................................... 121
Appendices and Index ......................................................................................................... 127
V300 User’s Guide
9
Page 10

Contents Overview
10
V300 User’s Guide
Page 11

Table of Contents
Table of Contents
About This User's Guide ..........................................................................................................3
Document Conventions............................................................................................................4
Safety Warnings........................................................................................................................6
Contents Overview ...................................................................................................................9
Table of Contents....................................................................................................................11
List of Figures ......................................................................................................................... 17
List of Tables...........................................................................................................................21
Part I: Introduction................................................................................. 23
Chapter 1
Introducing the V300 .............................................................................................................. 25
1.1 Overview .............................................................................................................................. 25
1.2 Applications ......................................................................................................................... 25
1.2.1 Make Calls via Internet Telephony Service Provider .................................................. 26
1.2.2 Make Calls via IP-PBX ............................................................................................... 26
1.2.3 Make Peer-to-peer Calls ............................................................................................ 27
1.3 Ways to Manage the V300 .................................................................................................. 27
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the V300 ................................................................................... 28
Chapter 2
Hardware..................................................................................................................................29
2.1 Physical Features ................................................................................................................ 29
2.1.1 The LCD Screen ........................................................................................................ 33
2.1.2 Resetting the V300 ..................................................................................................... 33
2.2 Phone Functions .................................................................................................................. 33
2.2.1 Making a Call ............................................................................................................. 33
2.2.2 Receiving a Call .........................................................................................................34
2.2.3 Ending a Call .............................................................................................................. 34
2.2.4 Changing the Volume ................................................................................................. 34
2.2.5 Muting a Call .............................................................................................................. 34
2.2.6 Placing a Call on Hold ................................................................................................ 35
2.2.7 Using Voicemail ..........................................................................................................35
V300 User’s Guide
11
Page 12

Table of Contents
2.2.8 Making Conference Calls ........................................................................................... 35
2.2.9 Transferring a Call ......................................................................................................35
Part II: LCD Screen Menus .................................................................... 37
Chapter 3
Using the LCD Screen ............................................................................................................39
3.1 Navigation ............................................................................................................................ 39
3.2 Enabling and Disabling Features ......................................................................................... 39
3.3 Entering Numbers, Letters and Symbols ............................................................................. 40
3.4 LCD Menu Overview ........................................................................................................... 41
3.5 The LCD Status Screen ....................................................................................................... 42
Chapter 4
The Phonebook....................................................................................................................... 43
4.1 Add a Phonebook Entry ....................................................................................................... 43
4.2 Call a Phonebook Contact ...................................................................................................43
4.3 Calling a Number Not in the Phonebook ............................................................................. 44
Chapter 5
LCD Menus: Basic Settings ...................................................................................................45
5.1 Entering the Menu System .................................................................................................. 45
5.2 The Phonebook Menu .........................................................................................................45
5.3 The Volume Setting Menu ................................................................................................... 46
5.3.1 Volume Screen ........................................................................................................... 46
5.4 The System Info Menu ........................................................................................................ 46
5.5 The Advanced Setting Menu ............................................................................................... 47
5.6 The Reset Menu .................................................................................................................. 47
5.6.1 System Restart ...........................................................................................................47
5.6.2 Load Factory Default .................................................................................................. 48
Chapter 6
LCD Menus: Advanced...........................................................................................................49
6.1 The Advanced Setting Menu ............................................................................................... 49
6.2 The VoIP Menus .................................................................................................................. 49
6.2.1 SIP Active ................................................................................................................... 50
6.2.2 SIP Number ................................................................................................................ 50
6.2.3 SIP Server Address .................................................................................................... 51
6.2.4 SIP Server Port ..........................................................................................................52
6.2.5 SIP Register Server ................................................................................................... 52
6.2.6 SIP Register Port ....................................................................................................... 53
12
V300 User’s Guide
Page 13

Table of Contents
6.2.7 SIP Service Domain ................................................................................................... 54
6.2.8 SIP User ID ................................................................................................................ 54
6.2.9 SIP Password .............................................................................................................55
6.3 DHCP .................................................................................................................................. 55
6.4 Static IP ............................................................................................................................... 56
6.4.1 IP Address .................................................................................................................. 56
6.4.2 Gateway ..................................................................................................................... 57
6.4.3 Subnet Mask ..............................................................................................................57
6.4.4 First and Second DNS Servers .................................................................................. 58
6.5 The PPPoE Menu ................................................................................................................ 58
6.5.1 PPPoE Username ...................................................................................................... 59
6.5.2 PPPoE Password ....................................................................................................... 59
Part III: The Web Configurator .............................................................. 61
Chapter 7
Introducing the Web Configurator ........................................................................................63
7.1 Accessing the Web Configurator ......................................................................................... 63
7.1.1 Title Bar ...................................................................................................................... 65
7.1.2 Navigation Panel ........................................................................................................ 66
7.1.3 Main Window ..............................................................................................................66
7.1.4 Status Bar ................................................................................................................... 67
Chapter 8
Status Screens........................................................................................................................ 69
8.1 Status Screen ...................................................................................................................... 69
8.2 Packet Statistics .................................................................................................................. 71
8.3 VoIP Statistics ...................................................................................................................... 72
Chapter 9
Network Setup.........................................................................................................................75
9.1 TCP/IP Parameters ............................................................................................................. 75
9.1.1 IP Address Assignment .............................................................................................. 75
9.1.2 IP Address and Subnet Mask ..................................................................................... 75
9.1.3 PPPoE Encapsulation ................................................................................................ 76
9.2 Internet Connection ............................................................................................................. 76
9.3 Management Port ................................................................................................................ 77
Chapter 10
SIP Account Setup..................................................................................................................79
10.1 SIP Overview ..................................................................................................................... 79
V300 User’s Guide
13
Page 14

Table of Contents
10.1.1 Introduction to VoIP .................................................................................................. 79
10.1.2 Introduction to SIP .................................................................................................... 79
10.1.3 SIP Identities ............................................................................................................ 79
10.1.4 SIP Call Progression ................................................................................................ 80
10.1.5 SIP Client Server ...................................................................................................... 80
10.1.6 RTP .......................................................................................................................... 82
10.1.7 NAT and SIP ............................................................................................................ 82
10.1.8 Voice Coding ............................................................................................................83
10.1.9 MWI (Message Waiting Indication) ........................................................................... 84
10.1.10 Quality of Service (QoS) ........................................................................................ 84
10.2 SIP Screens ....................................................................................................................... 85
10.2.1 SIP Settings Screen ................................................................................................. 85
10.2.2 Advanced SIP Setup Screen .................................................................................... 88
10.3 SIP QoS Screen ................................................................................................................ 91
Chapter 11
Phone Setup............................................................................................................................ 93
11.1 Phone Settings Screen ...................................................................................................... 93
11.1.1 Voice Activity Detection/Silence Suppression .......................................................... 94
11.1.2 Comfort Noise Generation ........................................................................................ 94
11.1.3 Echo Cancellation .................................................................................................... 94
11.2 Phone Region Screen ....................................................................................................... 94
11.3 Speed Dial Settings Screen .............................................................................................. 95
Chapter 12
The Phone Book...................................................................................................................... 97
12.1 Call Forward Screen .......................................................................................................... 97
12.2 Contact List Screen ......................................................................................................... 100
12.3 Group List Screen ............................................................................................................ 101
12.4 Block List Screen ............................................................................................................. 102
12.5 DND White List Screen .................................................................................................... 104
Part IV: Maintenance and Troubleshooting ....................................... 107
Chapter 13
System ...................................................................................................................................109
13.1 System General Screen ................................................................................................. 109
13.2 Time Setting Screen .........................................................................................................110
Chapter 14
Logs ....................................................................................................................................... 113
14
V300 User’s Guide
Page 15

Table of Contents
14.1 Logs Screen ....................................................................................................................113
Chapter 15
Tools....................................................................................................................................... 115
15.1 Firmware Upload Screen ..................................................................................................115
15.2 Configuration Screen ........................................................................................................117
15.2.1 Backup Configuration ..............................................................................................117
15.2.2 Restore Configuration .............................................................................................118
15.2.3 Back to Factory Defaults .........................................................................................119
15.3 Restart Screen ..................................................................................................................119
Chapter 16
Troubleshooting....................................................................................................................121
16.1 Power, Hardware Connections, and LEDs ...................................................................... 121
16.2 Internet Access ................................................................................................................ 123
16.3 Phone Calls and VoIP ......................................................................................................124
Part V: Appendices and Index ............................................................ 127
Appendix A Product Specifications.......................................................................................129
Appendix B Setting up Your Computer’s IP Address............................................................135
Appendix C Pop-up Windows, JavaScripts and Java Permissions ...................................... 151
Appendix D IP Addresses and Subnetting ...........................................................................157
Appendix E Legal Information ..............................................................................................165
Appendix F Customer Support .............................................................................................169
Index....................................................................................................................................... 175
V300 User’s Guide
15
Page 16

Table of Contents
16
V300 User’s Guide
Page 17

List of Figures
List of Figures
Figure 1 Internet Telephony Service Provider Application ...................................................................... 26
Figure 2 IP-PBX Application .................................................................................................................. 27
Figure 3 Peer-to-peer Calling ................................................................................................................. 27
Figure 4 Front Panel Hardware ............................................................................................................. 29
Figure 5 Side Panel ................................................................................................................................ 31
Figure 6 Rear Panel ............................................................................................................................... 32
Figure 7 Base Panel Hardware ............................................................................................................. 32
Figure 8 Example: DHCP ....................................................................................................................... 40
Figure 9 LCD Status Screen ................................................................................................................... 42
Figure 10 LCD Contact Record .............................................................................................................. 43
Figure 11 LCD Contact Record: Save .................................................................................................... 43
Figure 12 LCD Dial Screen .................................................................................................................... 43
Figure 13 LCD Contact List Screen ....................................................................................................... 44
Figure 14 LCD Menu Setting .................................................................................................................. 45
Figure 15 LCD Menu: Phonebook .......................................................................................................... 45
Figure 16 LCD Menu: Volume Setting ................................................................................................... 46
Figure 17 LCD Menu: Volume Screen ................................................................................................... 46
Figure 18 LCD Menu: System Info ........................................................................................................ 46
Figure 19 LCD Menu: Reset .................................................................................................................. 47
Figure 20 LCD Menu: Reset: System Restart ........................................................................................ 47
Figure 21 LCD Menu: Reset: System Restart: Confirm ......................................................................... 48
Figure 22 LCD Menu: Reset: Reset Default ........................................................................................... 48
Figure 23 LCD Menu: Reset: Reset Default: Confirm ........................................................................... 48
Figure 24 LCD Menu: Advanced Setting ................................................................................................ 49
Figure 25 LCD Menu: VoIP..................................................................................................................... 50
Figure 26 LCD Menu: SIP Number......................................................................................................... 51
Figure 27 LCD Menu: SIP Number - Edit ............................................................................................... 51
Figure 28 LCD Menu: SIP Server Address............................................................................................. 51
Figure 29 LCD Menu: SIP Server Address - Edit ................................................................................... 51
Figure 30 LCD Menu: SIP Server Port ................................................................................................... 52
Figure 31 LCD Menu: SIP Server Port - Edit .......................................................................................... 52
Figure 32 LCD Menu: SIP Register Server ............................................................................................ 52
Figure 33 LCD Menu: SIP Register Server Address - Edit ..................................................................... 53
Figure 34 LCD Menu: SIP Register Port ................................................................................................ 53
Figure 35 LCD Menu: SIP Register Port - Edit ....................................................................................... 53
Figure 36 LCD Menu: SIP Service Domain ............................................................................................ 54
Figure 37 LCD Menu: SIP Service Domain - Edit................................................................................... 54
Figure 38 LCD Menu: SIP User ID ........................................................................................................ 54
V300 User’s Guide
17
Page 18

List of Figures
Figure 39 LCD Menu: SIP User ID - Edit ................................................................................................ 55
Figure 40 LCD Menu: Authentication Password..................................................................................... 55
Figure 41 LCD Menu: Authentication Password - Edit ........................................................................... 55
Figure 42 LCD Menu: DHCP ................................................................................................................ 55
Figure 43 LCD Menu: Static IP............................................................................................................... 56
Figure 44 LCD Menu: IP Address........................................................................................................... 56
Figure 45 LCD Menu: IP Address - Edit ................................................................................................. 57
Figure 46 LCD Menu: Gateway ............................................................................................................. 57
Figure 47 LCD Menu: Gateway - Edit..................................................................................................... 57
Figure 48 LCD Menu: Subnet Mask ....................................................................................................... 57
Figure 49 LCD Menu: Subnet Mask - Edit ............................................................................................. 58
Figure 50 LCD Menu: First / Second DNS ............................................................................................. 58
Figure 51 LCD Menu: First / Second DNS - Edit .................................................................................... 58
Figure 52 LCD Menu: PPPoE ................................................................................................................ 58
Figure 53 LCD Menu: PPPoE Username ............................................................................................... 59
Figure 54 LCD Menu: PPPoE Username - Edit .....................................................................................59
Figure 55 LCD Menu: PPPoE Password................................................................................................ 59
Figure 56 LCD Menu: PPPoE Password - Edit .....................................................................................59
Figure 57 Password Screen .................................................................................................................. 63
Figure 58 Change Password Screen ...................................................................................................... 64
Figure 59 The Status Screen ................................................................................................................. 65
Figure 60 Status Screen ......................................................................................................................... 69
Figure 61 Packet Statistics ..................................................................................................................... 71
Figure 62 VoIP Statistics ......................................................................................................................... 72
Figure 63 Network > Internet Connection ............................................................................................... 77
Figure 64 Network > Mgnt Port ............................................................................................................... 78
Figure 65 SIP User Agent ....................................................................................................................... 81
Figure 66 SIP Proxy Server .................................................................................................................... 81
Figure 67 SIP Redirect Server ................................................................................................................ 82
Figure 68 STUN ...................................................................................................................................... 83
Figure 69 DiffServ: Differentiated Service Field ...................................................................................... 85
Figure 70 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings ...................................................................................................... 86
Figure 71 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings > Advanced .................................................................................. 88
Figure 72 VoIP > SIP > QoS ................................................................................................................... 91
Figure 73 VoIP > Phone > Phone Settings ............................................................................................. 93
Figure 74 VoIP > Phone > Region .......................................................................................................... 95
Figure 75 Phone Book > Speed Dial ...................................................................................................... 96
Figure 76 VoIP > Phone Book > Call Forward ........................................................................................ 98
Figure 77 VoIP > Phone Book > Contact List ....................................................................................... 100
Figure 78 VoIP > Phone Book > Group List ......................................................................................... 101
Figure 79 VoIP > Phone Book > Block List .......................................................................................... 103
Figure 80 VoIP > Phone Book > DND White List ................................................................................. 104
Figure 81 Maintenance > System > General ........................................................................................ 109
18
V300 User’s Guide
Page 19

List of Figures
Figure 82 Maintenance > Time Setting .................................................................................................. 111
Figure 83 Maintenance > Logs ..............................................................................................................113
Figure 84 Maintenance > Tools > Firmware Upload ..............................................................................115
Figure 85 Upload Warning .....................................................................................................................116
Figure 86 Network Temporarily Disconnected .......................................................................................116
Figure 87 Upload Error Message ..........................................................................................................117
Figure 88 Maintenance > Tools > Configuration ....................................................................................117
Figure 89 Configuration Upload Successful ..........................................................................................118
Figure 90 Temporarily Disconnected .....................................................................................................118
Figure 91 Configuration Restore Error ..................................................................................................119
Figure 92 Maintenance > Tools > Restart ..............................................................................................119
Figure 93 Wall-mounting Example ........................................................................................................ 133
Figure 94 Masonry Plug and M4 Tap Screw ......................................................................................... 133
Figure 95 WIndows 95/98/Me: Network: Configuration ........................................................................ 136
Figure 96 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: IP Address ............................................................ 137
Figure 97 Windows 95/98/Me: TCP/IP Properties: DNS Configuration ................................................ 138
Figure 98 Windows XP: Start Menu ...................................................................................................... 139
Figure 99 Windows XP: Control Panel ................................................................................................. 139
Figure 100 Windows XP: Control Panel: Network Connections: Properties ......................................... 140
Figure 101 Windows XP: Local Area Connection Properties ............................................................... 140
Figure 102 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties .......................................................... 141
Figure 103 Windows XP: Advanced TCP/IP Properties ....................................................................... 142
Figure 104 Windows XP: Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties .......................................................... 143
Figure 105 Macintosh OS 8/9: Apple Menu .......................................................................................... 144
Figure 106 Macintosh OS 8/9: TCP/IP ................................................................................................. 144
Figure 107 Macintosh OS X: Apple Menu ............................................................................................ 145
Figure 108 Macintosh OS X: Network .................................................................................................. 146
Figure 109 Red Hat 9.0: KDE: Network Configuration: Devices ......................................................... 147
Figure 110 Red Hat 9.0: KDE: Ethernet Device: General ................................................................... 147
Figure 111 Red Hat 9.0: KDE: Network Configuration: DNS ............................................................... 148
Figure 112 Red Hat 9.0: KDE: Network Configuration: Activate ......................................................... 148
Figure 113 Red Hat 9.0: Dynamic IP Address Setting in ifconfig-eth0 ............................................... 149
Figure 114 Red Hat 9.0: Static IP Address Setting in ifconfig-eth0 .................................................... 149
Figure 115 Red Hat 9.0: DNS Settings in resolv.conf ........................................................................ 149
Figure 116 Red Hat 9.0: Restart Ethernet Card .................................................................................. 149
Figure 117 Red Hat 9.0: Checking TCP/IP Properties ....................................................................... 150
Figure 118 Pop-up Blocker ................................................................................................................... 151
Figure 119 Internet Options: Privacy .................................................................................................... 152
Figure 120 Internet Options: Privacy .................................................................................................... 153
Figure 121 Pop-up Blocker Settings ..................................................................................................... 153
Figure 122 Internet Options: Security ................................................................................................... 154
Figure 123 Security Settings - Java Scripting ....................................................................................... 155
Figure 124 Security Settings - Java ...................................................................................................... 155
V300 User’s Guide
19
Page 20

List of Figures
Figure 125 Java (Sun) .......................................................................................................................... 156
Figure 126 Network Number and Host ID ............................................................................................ 158
Figure 127 Subnetting Example: Before Subnetting ............................................................................ 160
Figure 128 Subnetting Example: After Subnetting ............................................................................... 161
20
V300 User’s Guide
Page 21

List of Tables
List of Tables
Table 1 Models Covered ........................................................................................................................ 25
Table 2 Front Panel Hardware ............................................................................................................... 30
Table 3 Side Panel Hardware ................................................................................................................ 31
Table 4 Rear Panel Hardware ............................................................................................................... 32
Table 5 Base Panel Hardware ............................................................................................................... 33
Table 6 Keypad Characters ................................................................................................................... 40
Table 7 LCD Menu Overview ................................................................................................................. 41
Table 8 LCD Menu: Volume Setting ....................................................................................................... 46
Table 9 LCD Menu: System Info ............................................................................................................ 47
Table 10 Advanced Setting Menu .......................................................................................................... 49
Table 11 LCD Menu: SIP Account Configuration ................................................................................... 50
Table 12 LCD Menu: Static IP ................................................................................................................ 56
Table 13 LCD Menu: PPPoE ................................................................................................................. 59
Table 14 Web Configurator Icons in the Title Bar .................................................................................. 65
Table 15 Navigation Panel Summary .................................................................................................... 66
Table 16 Status Screen .......................................................................................................................... 69
Table 17 Packet Statistics ...................................................................................................................... 71
Table 18 VoIP Statistics ......................................................................................................................... 72
Table 19 Private IP Address Ranges ..................................................................................................... 75
Table 20 Network > Internet Connection ............................................................................................... 77
Table 21 Network > Mgnt Port ............................................................................................................... 78
Table 22 SIP Call Progression ............................................................................................................... 80
Table 23 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings ....................................................................................................... 86
Table 24 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings > Advanced Setup ........................................................................ 89
Table 25 VoIP > SIP > QoS ................................................................................................................... 91
Table 26 VoIP > Phone > Phone Settings ............................................................................................. 93
Table 27 VoIP > Phone > Region .......................................................................................................... 95
Table 28 Phone Book > Speed Dial ....................................................................................................... 96
Table 29 VoIP > Phone Book > Call Forward ........................................................................................ 98
Table 30 VoIP > Phone Book > Contact List ........................................................................................ 100
Table 31 VoIP > Phone Book > Group List .......................................................................................... 102
Table 32 VoIP > Phone Book > Block List ........................................................................................... 103
Table 33 VoIP > Phone Book > DND White List .................................................................................. 104
Table 34 Maintenance > System > General .........................................................................................110
Table 35 Maintenance > Time Setting ..................................................................................................111
Table 36 Maintenance > Logs ..............................................................................................................113
Table 37 Maintenance > Tools > Firmware Upload ..............................................................................116
Table 38 Maintenance > Tools > Configuration > Restore ....................................................................118
V300 User’s Guide
21
Page 22

List of Tables
Table 39 Hardware Specifications ....................................................................................................... 129
Table 40 Firmware Specifications ........................................................................................................ 130
Table 41 Standards Supported ............................................................................................................ 131
Table 42 Power over Ethernet Injector Specifications ........................................................................ 132
Table 43 Power over Ethernet Injector RJ-45 Port Pin Assignments .................................................. 132
Table 44 IP Address Network Number and Host ID Example ............................................................. 158
Table 45 Subnet Masks ....................................................................................................................... 159
Table 46 Maximum Host Numbers ...................................................................................................... 159
Table 47 Alternative Subnet Mask Notation ......................................................................................... 159
Table 48 Subnet 1 ................................................................................................................................ 161
Table 49 Subnet 2 ................................................................................................................................ 162
Table 50 Subnet 3 ................................................................................................................................ 162
Table 51 Subnet 4 ................................................................................................................................ 162
Table 52 Eight Subnets ........................................................................................................................ 162
Table 53 24-bit Network Number Subnet Planning .............................................................................. 163
Table 54 16-bit Network Number Subnet Planning .............................................................................. 163
22
V300 User’s Guide
Page 23

PART I
Introduction
Introducing the V300 (25)
Hardware (29)
23
Page 24

24
Page 25
CHAPTER 1
Introducing the V300
This chapter introduces the main applications and features of the V300. It also introduces the
ways you can manage the V300.
1.1 Overview
The V300 is an IP phone that allows you to make phone calls over the Internet.
Sending voice signals over the Internet is called Voice over IP (VoIP). VoIP allows you to call
other IP phones, mobile phones or landlines all over the world.
The V300 is packed with features - including multiple lines, phonebook, conference calls, call
transfer, call hold, and many more.
You can configure and manage the V300 directly, using its multi-function keypad and LCD
screen. Alternatively, access the internal web configurator using a computer connected to the
network for remote administrative configuration.
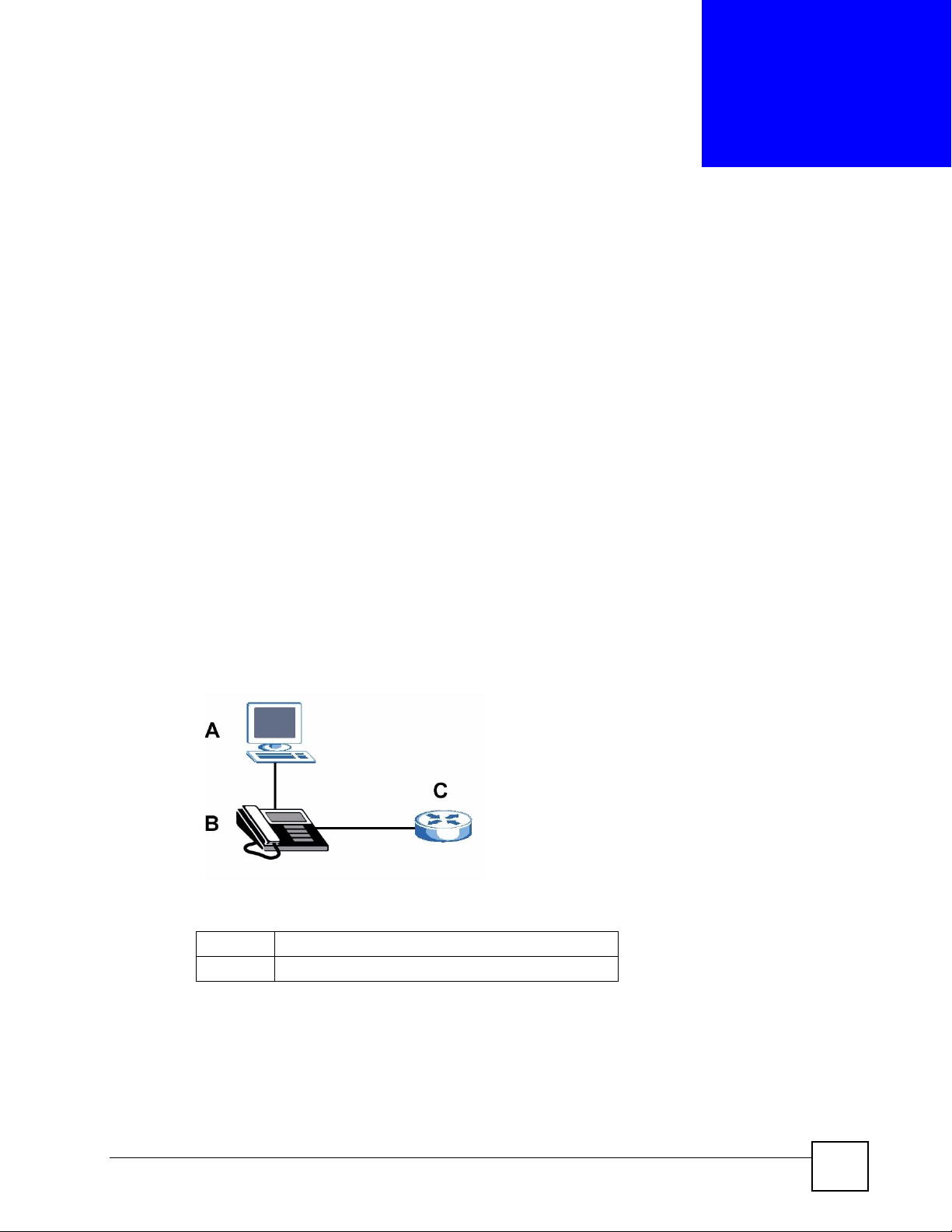
The V300’s Ethernet ports allow you to connect it to your Local Area Network (LAN) and
your computer. Your computer can access the LAN through the V300, as shown in the
following figure. A is your computer, B is your V300 and C is your modem or router.
At the time of writing, this User’s Guide covers the following models.
Table 1 Models Covered
V300 IP phone.
V301 IP phone with Power over Ethernet (PoE) capability.
1.2 Applications
Here are some examples of how you can use your V300.
V300 User’s Guide
25
Page 26
Chapter 1 Introducing the V300
1.2.1 Make Calls via Internet Telephony Service Provider
In a home or small office environment, you can use the V300 to make and receive VoIP
telephone calls through an Internet Telephony Service Provider (ITSP).
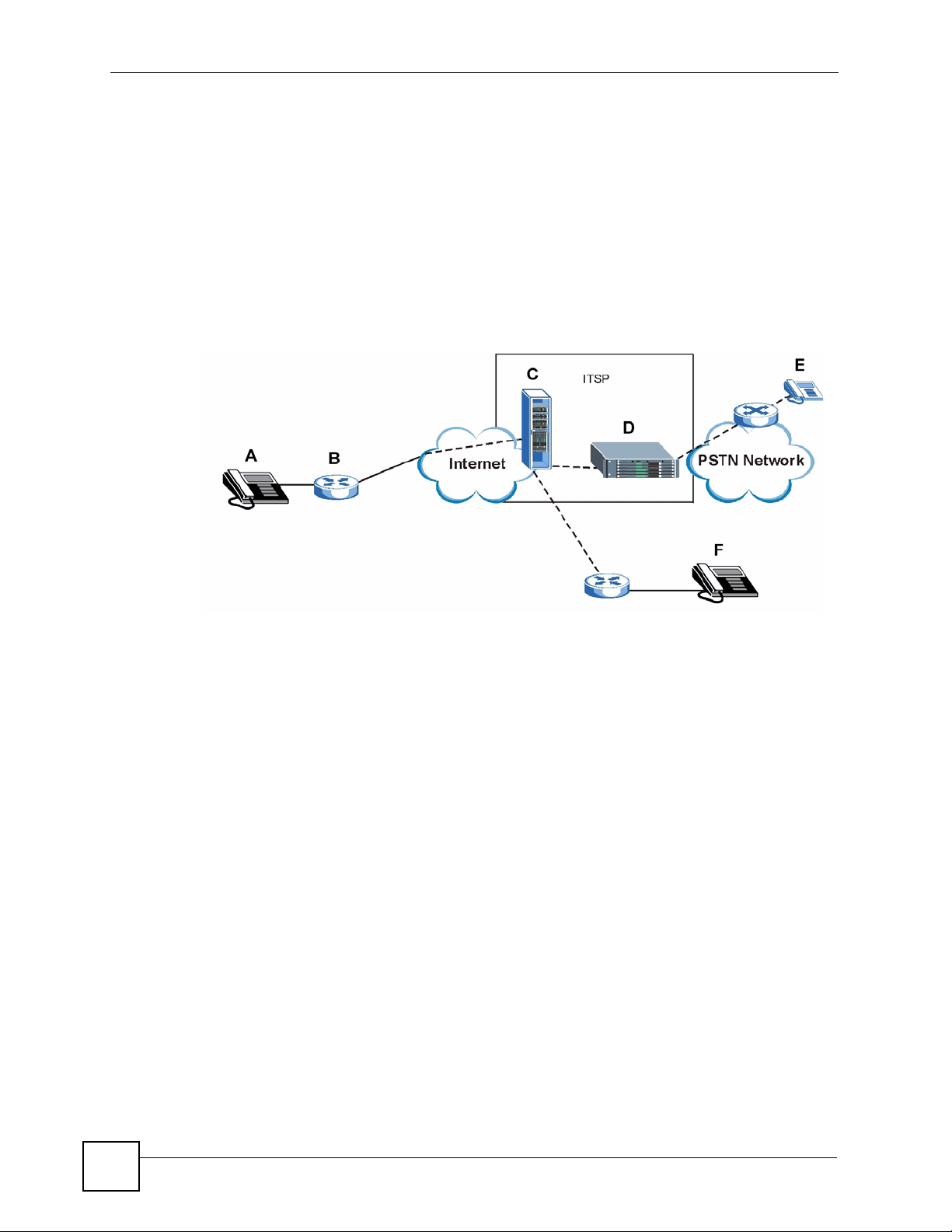
The following figure shows a basic example of how you make a VoIP call through an ITSP. In
this example, you make a call from your V300 (A in the figure), which sends the call through
your modem or router (B) to the Internet and the ITSP’s SIP server (C). The VoIP call server
forwards calls to PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) phones through a trunking
gateway (D) to phones on the PSTN network (E). The VoIP call server also forwards calls to
IP phones (F) through the Internet.
Figure 1 Internet Telephony Service Provider Application
1.2.2 Make Calls via IP-PBX
If your company has an IP-PBX (Internet Protocol Private Branch Exchange), you can use the
V300 to make and receive VoIP telephone calls through it.
In this example, you make a call from your V300 (A in the figure), which sends it to the IPPBX. The IP-PBX forwards calls to PSTN phones (B) on the PSTN network. The IP-PBX also
forwards calls to IP phones (C) through an IP network (this could include the Internet).
26
V300 User’s Guide
Page 27
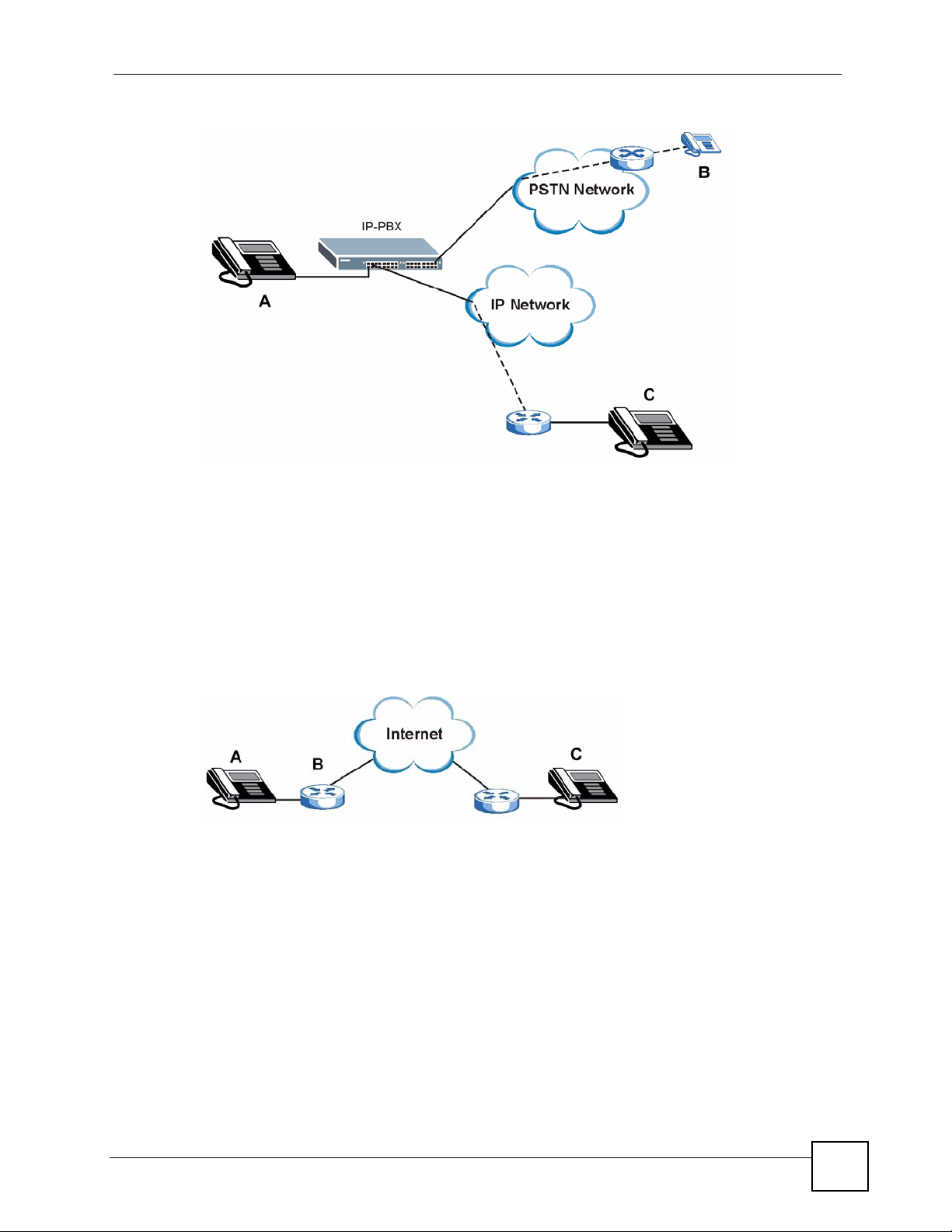
Figure 2 IP-PBX Application
1.2.3 Make Peer-to-peer Calls
Chapter 1 Introducing the V300
Use the V300 to make a call to the recipient’s IP address without using a SIP server. Peer-topeer calls are also called “Point to Point” or “IP-to-IP” calls. You must know the peer’s IP
address in order to do this.
The following figure shows a basic example of how you would make a peer-to-peer VoIP call.
You make a call on your V300 (A), which sends your call through your modem or router (B)
and the Internet to the peer VoIP device (C).
Figure 3 Peer-to-peer Calling
1.3 Ways to Manage the V300
Use any of the following methods to manage the V300.
• Hardware keys. Use the control keys and LCD menus on the V300 for basic configuration.
• Web Configurator. This is recommended for everyday management of the V300 using a
(supported) web browser.
• FTP. Use File Transfer Protocol for firmware upgrades and configuration backup/restore.
• SPTGEN. SPTGEN is a text configuration file that you can edit and upload to the device.
This is especially convenient if you need to configure many devices of the same type.
V300 User’s Guide
27
Page 28

Chapter 1 Introducing the V300
1.4 Good Habits for Managing the V300
Do the following things regularly to make the V300 more secure and to manage the V300
more effectively.
• Change the web configurator password. Use a password that’s not easy to guess and that
consists of different types of characters, such as numbers and letters.
• Write down the password and put it in a safe place.
• Keep the V300 in a safe place. The LCD menus are not password-protected, so anyone
using the phone can access your phonebook, SIP account information, etc.
• Back up the configuration (and make sure you know how to restore it). Restoring an
earlier working configuration may be useful if the device becomes unstable or even
crashes. If you forget your password, you will have to reset the V300 to its factory default
settings to access the web configurator. If you backed up an earlier configuration file, you
would not have to totally re-configure the V300. You could simply restore your last
configuration.
28
V300 User’s Guide
Page 29
CHAPTER 2
Hardware
This chapter describes the V300’s physical features, and how to use the V300’s phone
functions.
2.1 Physical Features
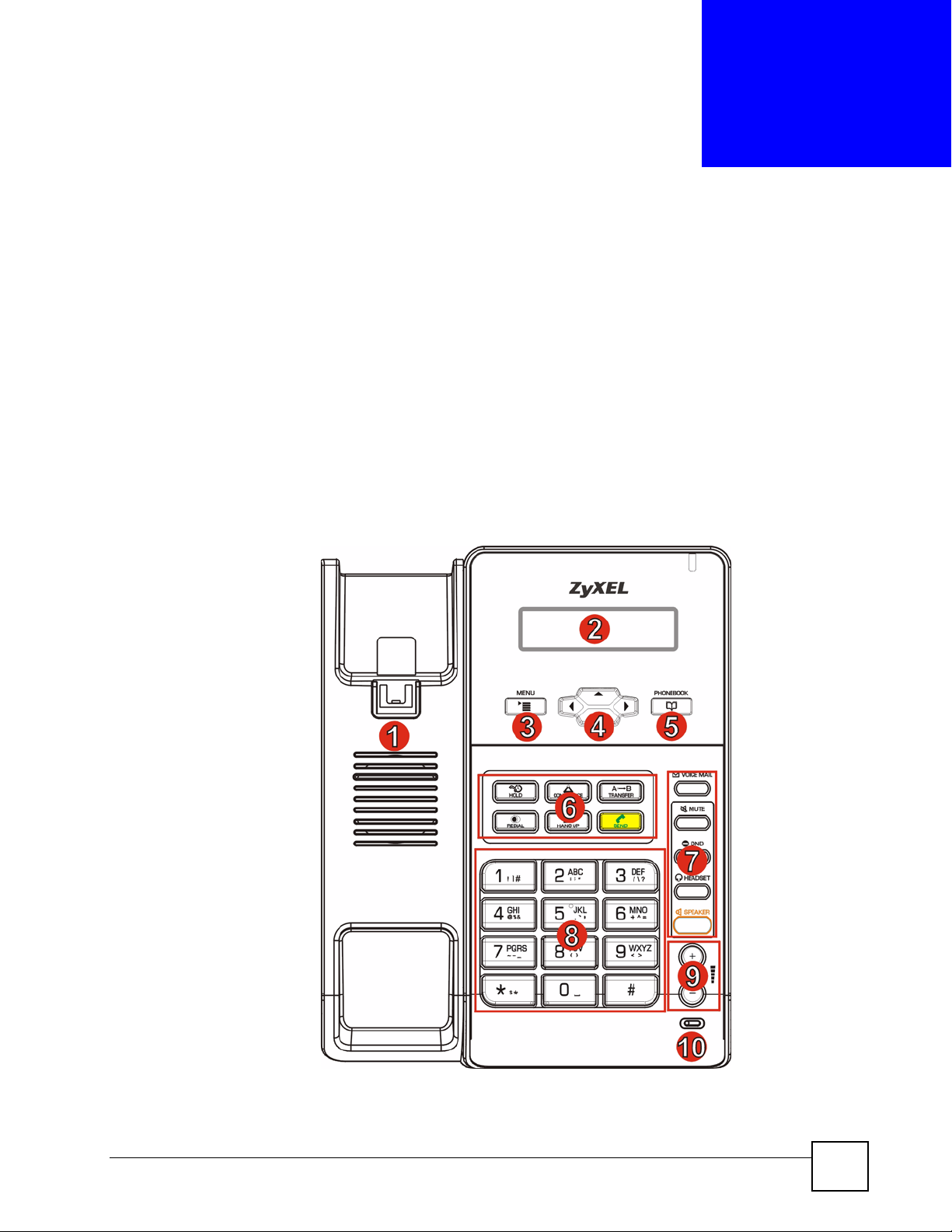
This section discusses the V300’s front, side, rear and base panel hardware features. See your
Quick Start Guide for descriptions of how to set up the V300’s hardware and network
connections.
Figure 4 Front Panel Hardware
V300 User’s Guide
29
Page 30
Chapter 2 Hardware
The following table describes the front panel hardware.
Table 2 Front Panel Hardware
LABEL DESCRIPTION
1 Handset cradle.
2 LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screen.
3 Menu Press this to display the V300’s configuration menu. When the menu
4 Navigator Use this to move around the V300’s screens. Press to go up one line
5 Phonebook Use this to display the list of contacts stored in the V300. If there is no
6 Action keys HOLD Use this to put a call on hold. Press it a second time
displays, you can press this key again to exit the menu. The menu is not
accessible when a call is in progress.
in a menu, and press to go down one line. In the configuration menu,
press to enter a menu or continue to the next menu, and press to
go back to the previous menu. When the V300 is not in the configuration
menu, you can press or to view the previous calls and use to
delete the records or save them as the contacts in your phone book.
When the V300 is connected to the Internet and not in the configuration
menu, use or to select the SIP account you want to use to make
calls.
contact stored in the V300, the message “Phonebook is empty” displays.
To add, edit or remove an entry in the phonebook, use the web
configurator. See Chapter 12 on page 97 for more information. In a
menu, use this to clear the previous settings.
to take the call off hold.
CONFERENCE Use this to set up a conference call between the
V300 and two other phones, or to split a
conference call you set up into two separate calls.
TRANSFER Use this to transfer a call to another phone.
HANG UP Use this to end a call.
REDIAL Use this to dial the last number that was called from
SEND Use this to start a call, once you have entered the
the V300.
phone number.
30
V300 User’s Guide
Page 31

Chapter 2 Hardware
Table 2 Front Panel Hardware (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
7 Function keys The LEDs (lights) in these keys illuminate when they are active.
VOICEMAIL Use this to check your voicemail messages, once
the voicemail number is configured in the V300.
MUTE Use this to mute the current call. The V300 no
DND Use this to toggle the Do Not Disturb function on or
HEADSET Use this to activate a line using the headset, or to
SPEAKER Use this to activate a line using the speakerphone,
8 Alphanumeric
keypad
9 Volume keys Use the + key to increase the volume, and use the - key to decrease it.
10 Microphone The microphone is active when the V300 is in speakerphone mode.
Use this to enter numbers, letters and symbols. Use the # key to switch
between Number mode, Uppercase mode, Lowercase mode and
Symbol mode. In the configuration menu, use a numeric key (from 1 to
5) to go to a specific menu directly.
• When you use the handset, these keys control the handset’s
listening volume.
• When you use the headset, these keys control the listening volume
on the headphone ( ) port on the V300.
• When you use the speakerphone, these keys control the internal
speaker volume.
longer transmits a signal, but you can still hear the
incoming signal.
off.
transfer a call to the headset when using the
handset or the speakerphone.
When a line is active and you are using the
headset, press this key to hang up.
or to transfer a call to the speakerphone when
using the handset or the headset.
When a line is active and you are using the
speakerphone, press this key to hang up.
Figure 5 Side Panel
The following table describes the side panel hardware.
Table 3 Side Panel Hardware
LABEL DESCRIPTION
1 Headphone socket Use this to connect a headset’s earphone jack, headphones, or
2 Microphone socket Use this to connect a headset’s microphone jack, or an external
V300 User’s Guide
an external loudspeaker.
microphone.
31
Page 32

Chapter 2 Hardware
Figure 6 Rear Panel
The following table describes the rear panel hardware.
Table 4 Rear Panel Hardware
LABEL DESCRIPTION
1 Power socket Attach the included power adaptor, if you are not using Power
2 LAN port Use an Ethernet cable to connect to your network.
3 PC port Use an Ethernet cable to connect a computer for configuration,
over Ethernet (V301 only). See the product specifications
appendix for power supply specifications.
Note: Use only the power adaptor and cable that
came with your V300.
or to access the Internet.
Figure 7 Base Panel Hardware
32
V300 User’s Guide
Page 33

The following table describes the rear panel hardware.
Table 5 Base Panel Hardware
LABEL DESCRIPTION
1 Wall-mounting holes Use these to hang the V300 on a wall. See the wall-mounting
2 Handset port Use this to attach the included handset cable’s RJ-11
3 Reset button Use this to return the V300 to its factory default settings. See
4 Cable channel Clip the V300’s handset cable into this.
2.1.1 The LCD Screen
When the V300 is on, the LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) screen shows either the status screen,
a phonebook screen, or a configuration menu.
Chapter 2 Hardware
appendix for details.
connector.
the appendix on product specifications for the default settings.
Note: If you do this, all configuration changes and
data on the V300 are lost, including
phonebook records.
The LCD menus allow you to configure and control the V300. See Chapter 3 on page 39 for
details on configuring the V300 via the LCD menus.
2.1.2 Resetting the V300
If you want to reset the V300 to its factory defaults (if you forgot the web configurator
password, for example) press and hold the RESET button for approximately ten seconds. The
V300 restarts automatically.
" If you reset the V300, all settings return to their factory defaults. All data stored
in the V300 (phonebook entries, for example) will be lost.
2.2 Phone Functions
This section describes how to use your V300’s basic telephone functions. See Chapter 3 on
page 39 for information on the using the V300’s LCD screen menus and Chapter 4 on page 43
for information on how to use the V300’s phonebook.
2.2.1 Making a Call
1 Start the call:
• If you want to use the handset:
Lift the handset.
• If you want to use the speakerphone:
V300 User’s Guide
33
Page 34

Chapter 2 Hardware
Press the SPEAKER key.
• If you want to use a headset:
Press the HEADSET key.
2 Check that you can hear a dial tone.
3 Enter the number you want to call. If you have numbers stored in the V300’s phone
book, you can use the navigator to select from the list of entries.
4 Press the yellow SEND key.
During the call:
• If you are using the headset or the speakerphone, you can switch to the handset by
lifting it off the hook.
• If you are using the handset or the speakerphone, you can switch to the headset by
pressing the HEADSET key.
• If you are using the handset or a headset, you can switch to the V300’s speakerphone
by pressing the SPEAKER key.
Note that the call ends if you are using the speakerphone and press the SPEAKER key,
or if you are using the headset and press the HEADSET key.
2.2.2 Receiving a Call
When the phone rings, do one of the following:
• Pick up the handset to receive the call using the handset.
• Press the SPEAKER key to receive the call using the internal speakerphone.
• Press the HEADSET key to receive the call using an external headset.
2.2.3 Ending a Call
When you want to end a call, press the HANG UP key. Alternatively, do one of the following:
• If you are using the handset, replace it in the cradle.
• If you are using the internal speakerphone, press the SPEAKER key.
• If you are using an external headset, press the HEADSET key.
2.2.4 Changing the Volume
Use the VOLUME + key to increase the volume, and use the VOLUME - key to decrease it.
• When there is no line active on the V300, the volume keys control the ringing volume.
• When the handset is off hook, the keys control the handset’s speaker volume.
• When the speakerphone is active, the keys control the speaker volume.
• When the headset is active, the keys control the headset’s speaker (earpiece) volume.
2.2.5 Muting a Call
When you mute a call on the V300 you can hear the incoming signal (the sound from the other
end of the line) but you do not transmit a signal (the person on the other end of the line cannot
hear you). It does not matter whether you are using the handset, the internal speakerphone or
an external headset.
34
V300 User’s Guide
Page 35

Press the MUTE key once to mute a call. Press it a second time to return to the call.
2.2.6 Placing a Call on Hold
When you place a call on hold, you neither receive nor transmit a signal. If your phone system
is configured to use the Music on Hold feature, the person on the other end of the line hears the
preconfigured music (or other audio). Otherwise, they hear nothing.
Press the HOLD key once to place a call on hold. Press it a second time to return to the call.
2.2.7 Using Voicemail
Once you have configured your SIP account’s voicemail number on the V300, you can press
the VOICEMAIL key to check your messages.
Use the VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings screen to set the voicemail account number. See Section
10.2.1 on page 85 for more information.
2.2.8 Making Conference Calls
Take the following steps to make a three-way conference call.
Chapter 2 Hardware
1 Either start a call, or receive a call. Make sure you know which line the call is using.
2 Ensure the call is active (you can talk with the other person). Press the Conference key.
This “marks” the first call you want to mix into the conference call.
3 Select another line. You can either receive an incoming call, make another outgoing call,
or resume an existing call that you previously put on hold.
4 Ensure the call is active and press the Conference key again. The three-way conference
call begins. All three parties can talk with one another.
" Do not press any other keys between step 2 and step 3. If you do, you will
have to start again.
" You cannot have a conference call and a transferred call ongoing at the same
time.
2.2.9 Transferring a Call
Take the following steps to transfer an ongoing call to another phone number.
1 During the ongoing call, press the Transfer key.
2 The next available line automatically activates. Ensure you can hear a dial tone.
3 Dial the number to which you want to transfer the call.
4 To transfer the call, either:
V300 User’s Guide
35
Page 36

Chapter 2 Hardware
• Wait until you hear the ringing tone, then simply put down the handset, press the
• Wait for the other person to answer, then end the call. This is known as a consultant or
Speaker key or the Headset key (depending on which you are using) to end the call.
The call is transferred. This is known as a blind or unsupervised transfer.
supervised transfer, and allows you to ask the other person whether they want to
receive the call or not.
36
V300 User’s Guide
Page 37

PART II
LCD Screen Menus
Using the LCD Screen (39)
The Phonebook (43)
LCD Menus: Basic Settings (45)
LCD Menus: Advanced (49)
37
Page 38

38
Page 39

CHAPTER 3
Using the LCD Screen
This chapter shows how to use and configure the V300 via the LCD screen menu system.
" See the web configurator section of this guide for background information on
the V300’s features.
3.1 Navigation
Use the following keys to move around the V300’s LCD screen menu system.
• The navigator.
Use this to move the cursor up and down (when selecting a menu item) or left and right
(when editing a field).
• The alphanumeric keypad.
Enter a menu item’s number to jump to that item (single-digit numbers only).
•The MENU key.
Use this to access the V300's configuration menu or exit the menu.
•The PHONEBOOK key.
Use this to return to view the stored contacts, or delete a character when editing a field.
" When there is more than one entry in a menu, one or two arrows display on
the right side of the LCD screen. If you can scroll down to see other entries
displays, if you can scroll up to see other entries displays, and if you can
scroll up or down to see other entries displays. These arrows are not
shown in this User’s Guide.
3.2 Enabling and Disabling Features
Many of the V300’s LCD screen menus allow you check a feature’s settings and then edit the
setting. Take the following steps to check a feature’s current setting and then enable or disable
the feature. This example uses the DHCP feature.
V300 User’s Guide
39
Page 40

Chapter 3 Using the LCD Screen
1 Select the feature you want to configure. In this example, press MENU to enter the menu
system, then select Adv Setting. In the Adv Setting menu, select DHCP. The following
screen displays.
Figure 8 Example: DHCP
1. DHCP
On
If On appears, the feature is enabled. If Off appears, the feature is disabled.
2 To change the setting, press .
3.3 Entering Numbers, Letters and Symbols
When you enter information into the V300 (when setting up a phonebook entry, for example)
you may need to enter different kinds of characters. The alphanumeric keypad has four input
modes:
• Number mode
• Uppercase mode
• Lowercase mode
• Symbol mode
Use the # key to cycle between modes.
" Not all modes are available in all screens.
When you press a key to enter a character, wait a short time until the cursor moves on to the
next space. Press a key multiple times to access the different characters. For example, in
Uppercase mode press 9 four times to enter “Z”.
The following table shows the numbers, letters and symbols you can enter.
Table 6 Keypad Characters
MODE
Number Uppercase Lowercase Symbol
40
V300 User’s Guide
Page 41

Table 6 Keypad Characters
KEY
1 1 [NONE] [NONE] ! | #
22 A B C a b c : ; “
3 3D E Fd e f / \ ?
4 4 G H I g h i @ % &
5 5 J K L j k l . ‘ ,
6 6 M N O m n o + ^ =
7 7 P Q R S p q r s ~ - _
8 8 T U V t u v ( )
9 9 W X Y Z w x y z < >
* . .. $ *
0 0 [NONE] [NONE] [SPACE]
# [CYCLE MODE]
3.4 LCD Menu Overview
Chapter 3 Using the LCD Screen
This section shows the LCD menus, and describes what you can do with each.
Press the Navigator up or down to access the V300’s LCD menu system.
Table 7 LCD Menu Overview
MENU DESCRIPTION
Phonebook Use this menu to view details of your contacts.
Volume Setting Speaker Volume Use this menu to set the loudness of the internal speaker.
Phone Volume Use this menu to set the loudness of the V300’s handset.
Ring Volume Use this menu to set the loudness of the V300’s ringtone.
Headset Volume Use this menu to set the loudness of an external headset you
plug into the V300.
System Info IP Address Use this to see the IP address, subnet mask, gateway and
Subnet Mask
Gateway
1st DNS
2nd DNS
F/W Version Use this to see the version number of the firmware the V300 is
Advanced Setting VoIP1 Use this to set up the first Voice over Internet (VoIP) account.
VoIP2 Use this to set up the second Voice over Internet (VoIP)
DHCP Use this menu to have the V300 get an IP address
Static IP Use this menu to give your V300 an IP address.
PPPoE Use this menu to configure your PPPoE username and
DNS settings currently assigned to the V300.
currently using.
account.
automatically.
password, if provided by your Internet Service Provider or
network administrator.
V300 User’s Guide
41
Page 42

Chapter 3 Using the LCD Screen
Table 7 LCD Menu Overview (continued)
MENU DESCRIPTION
Reset Restart Phone Use this to restart the V300.
Reset Default Use this to return the V300 to its factory defaults.
3.5 The LCD Status Screen
When you first turn on the V300 or make a call, the status screen displays. The status screen is
divided into two main sections, as shown below.
Figure 9 LCD Status Screen
09:45 2007-03-20
1234
In the status screen, the upper line displays the time and date configured on the V300, and the
lower line displays information about the SIP account. The SIP account’s name displays if it is
successfully registered. If it has tried to register but failed, NoReg displays. If the SIP account
is not enabled (see Section 6.2.1 on page 50) NoUse displays.
Using this feature does NOT return the V300 to its factory
defaults.
42
V300 User’s Guide
Page 43

CHAPTER 4
The Phonebook
Use the V300’s phonebook to view or store the names and phone numbers of your contacts.
The following sections describe how to add and use phonebook entries.
4.1 Add a Phonebook Entry
Take the following steps to add a call record to the V300’s phonebook.
1 Press the Navigator up or down to display the previous called numbers.
Figure 10 LCD Contact Record
1. 889763
15:30 2007-11-08
2 Press , select Save to Phone and press again to store this record as a contact entry in
your phone book
Figure 11 LCD Contact Record: Save
889763
Save to Phone
" You can view the stored contact entry by pressing the PHONEBOOK key.
4.2 Call a Phonebook Contact
In order to call a number you previously entered into the V300’s phonebook, first activate a
line (lift the handset, or press the SPEAKER or HEADSET key). The following screen
displays. Ensure you can hear a dial tone.
Figure 12 LCD Dial Screen
Line 1 Dial:
_
V300 User’s Guide
43
Page 44

Chapter 4 The Phonebook
Press the PHONEBOOK key. The Contact List screen displays.
Figure 13 LCD Contact List Screen
1. Ann
1234
Scroll to the contact name or number you want to call, then press the SEND key to dial the
number.
" The numbers that display to the left of a contact’s name in this screen are
index numbers only - you cannot use them to select an entry to call.
4.3 Calling a Number Not in the Phonebook
When you want to call a number that is not in your V300’s phonebook, activate a line, dial the
number and press the SEND key to start the call.
44
V300 User’s Guide
Page 45

CHAPTER 5
LCD Menus: Basic Settings
This chapter discusses how to set up your V300 using the internal configuration menus.
5.1 Entering the Menu System
Press MENU to enter the menu system. The Menu Setting screen displays as shown below.
Figure 14 LCD Menu Setting
Menu Setting:
1. Phonebook
See the rest of this chapter for details on configuring each menu. For background information,
see the relevant chapter in the web configurator section of this User’s Guide.
" When a menu has more than one option, only the first option can be seen on
the LCD screen. Use the navigator to scroll down to the other options.
5.2 The Phonebook Menu
Use the phonebook to view a list of your contacts.
Select Menu Setting > Phonebook. The following screen displays.
Figure 15 LCD Menu: Phonebook
1. Ann
1234
If you want to add, edit or remove an entry in the phonebook, use the web configurator. See
Chapter 7 on page 63 for more information.
If you want to add a call record in the phonebook or call a phonebook contact, see Chapter 4
on page 43.
V300 User’s Guide
45
Page 46

Chapter 5 LCD Menus: Basic Settings
5.3 The Volume Setting Menu
Use these menus to set the loudness of the V300’s audio equipment.
Figure 16 LCD Menu: Volume Setting
2. Vol Control
1. Speaker Volume
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 8 LCD Menu: Volume Setting
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Speaker Volume Select this to set the internal speakerphone volume. This controls both the
internal speaker and the internal microphone.
Phone Vol Select this to set the handset volume. This controls both the handset’s
speaker and its microphone.
Ring Volume Select this to set the volume of the V300’s ringtone. This setting applies to
all configured group rings.
Headset Volume Select this to set the volume of an attached headset (or any device
connected to the external speaker and/or microphone sockets). This
controls both the handset’s speaker (earpiece) and its microphone.
5.3.1 Volume Screen
When you select one of the options in the Volume Setting menu, a screen similar to the
following displays. This example uses the Speaker Volume screen.
Figure 17 LCD Menu: Volume Screen
Speaker Vol:-+
Use the VOLUME keys to increase or decrease the volume. Press or to go back to the
previous menu when you are done.
5.4 The System Info Menu
The System Info menu allows you to quickly check some of your V300’s settings. These
settings are read-only. Press MENU > System Info. The following screen displays.
Press
Figure 18 LCD Menu: System Info
to enter the System Info menu and use the arrows to view the system settings.
Menu Setting:
46
3. System Info
V300 User’s Guide
Page 47

The following table describes the labels in this menu.
Table 9 LCD Menu: System Info
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Address This is the IP address currently assigned to the V300. This displays 0.0.0.0
if DHCP is disabled.
Subnet Mask This is the subnet mask currently configured on the V300. This displays
0.0.0.0 if DHCP is disabled.
Gateway This is the IP address of the device on the network your V300 uses to
access the Internet. This displays 0.0.0.0 if DHCP is disabled.
1st DNS This is the primary DNS (Domain Name System) server your V300 uses.
This displays 0.0.0.0 if DHCP is disabled.
2nd DNS This is the secondary (backup) DNS server your V300 uses. This displays
0.0.0.0 if DHCP is disabled.
F/w Version This is the version number of the firmware currently running on the V300.
You can upload new firmware using the web configurator.
5.5 The Advanced Setting Menu
Chapter 5 LCD Menus: Basic Settings
Use this menu to configure network and SIP account settings. See Chapter 6 on page 49 for
information on the Advanced Setting menu.
5.6 The Reset Menu
Use this menu to restart the V300 or reset the V300 to the factory defaults. Press MENU >
Reset and then to access the Reset menu. The following screen displays.
Figure 19 LCD Menu: Reset
Menu Setting:
5. Reset
5.6.1 System Restart
Use this screen to restart the V300 without turning the power off.
1 Select RestartPhone.
Figure 20 LCD Menu: Reset: System Restart
5. Reset
1. RestartPhone
2 Press .and the following screen displays. Press the 1 key to restart the V300 or press
V300 User’s Guide
the 2 key to return to the previous menu without restarting the V300.
47
Page 48

Chapter 5 LCD Menus: Basic Settings
Figure 21 LCD Menu: Reset: System Restart: Confirm
Yes ->Press 1
No ->Press 2
5.6.2 Load Factory Default
Use this screen to reset the V300 back to the factory defaults.
1 Select ResetDefault.
Figure 22 LCD Menu: Reset: Reset Default
5. Reset
2. ResetDefault
2 Press .and the following screen displays. Press the 1 key to clear all user-entered
information and return to the factory defaults. Otherwise, press the 2 key to go back to
the previous menu without resetting the V300.
Figure 23 LCD Menu: Reset: Reset Default: Confirm
Yes ->Press 1
No ->Press 2
48
V300 User’s Guide
Page 49

CHAPTER 6
LCD Menus: Advanced
This chapter discusses using the V300’s LCD menus to do the following things:
• Set up your VoIP (SIP) account on the V300 - see Section 6.2 on page 49.
• Set up your V300’s IP address - see Section 6.4 on page 56 and Section 6.3 on page 55.
• Set up PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet) - see Section 6.5 on page 58.
6.1 The Advanced Setting Menu
Press MENU to access the LCD screen menu system, select Advanced Setting and press .
The following screen displays.
Figure 24 LCD Menu: Advanced Setting
4. Setting
1. VoIP1
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 10 Advanced Setting Menu
LABEL DESCRIPTION
VoIP1 Use this to set up the first VoIP (SIP) account.
VoIP2 Use this to set up the second VoIP (SIP) account.
DHCP Use this to enable DHCP if you do not have an IP address to use for the
Static IP Use this if you have an IP address to use for the V300.
PPPoE Use this to configure the V300’s PPPoE username and password, if it is a
See the rest of this chapter for information on each of these menus. For background
information, see the relevant chapter in the web configurator section of this User’s Guide.
6.2 The VoIP Menus
Use these menus to set up your V300 to set up and use a Voice over Internet (VoIP) account.
V300. The V300 obtains an address automatically from a DHCP server on
the network.
PPPoE client.
V300 User’s Guide
49
Page 50

Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
" Once you have configured the fields in these menus with the correct
information, the V300 must register with the SIP server. You may need to
restart the V300 to do this.
" Enter information in these menus exactly as you received it from your VoIP
service provider. If you were not given information for any menu or field, leave
it at its default setting.
Select Adv Setting > VoIP1 or VoIP2 and press . The following screen displays.
Figure 25 LCD Menu: VoIP
1. SIP1 Active
On
See the following sections for more information on each menu in this screen.
Tabl e 11 LCD Menu: SIP Account Configuration
SIP Active see Section 6.2.1 on page 50
SIP Number see Section 6.2.2 on page 50
Serv Addr see Section 6.2.3 on page 51
Serv Port see Section 6.2.4 on page 52
Reg Addr see Section 6.2.5 on page 52
Reg Port see Section 6.2.6 on page 53
Domain see Section 6.2.7 on page 54
User ID see Section 6.2.8 on page 54
Password see Section 6.2.9 on page 55
6.2.1 SIP Active
Select this to see whether the SIP account is turned on (On) or off (Off). Press again to
change the setting.
When the account is not active, you cannot use it to make or receive calls on the V300.
6.2.2 SIP Number
50
Use this to see and edit the SIP number for your SIP account.
V300 User’s Guide
Page 51

Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
" If you have a SIP account like “1234567@voip-provider.com”, the SIP Number
is “1234567”.
Select Adv Setting > VoIP1 or VoIP2 > SIP Num. The following screen displays.
Figure 26 LCD Menu: SIP Number
2. SIP Num
If a SIP account number is already configured, it displays. Otherwise, no SIP number displays.
Press to edit the SIP number, or press to return to the previous screen.
6.2.2.1 SIP Number - Edit
Press in the SIP Num screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 27 LCD Menu: SIP Number - Edit
2 SIP Num
_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new SIP account
number and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous screen.
6.2.3 SIP Server Address
Use this menu to see and edit the IP address of the SIP server for your account. Select Adv
Setting > VoIP1 or VoIP2 > Serv Addr. The following screen displays.
Figure 28 LCD Menu: SIP Server Address
3. Serv Addr
The IP address of the SIP server already configured on the V300 displays. If no IP address is
already configured, none displays. Press to edit the SIP server address, or press to return
to the previous screen.
6.2.3.1 SIP Server Address - Edit
Press in the Serv Addr screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 29 LCD Menu: SIP Server Address - Edit
3. Serv Addr
_
V300 User’s Guide
51
Page 52

Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new SIP server
address and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous screen.
6.2.4 SIP Server Port
Use this screen to see and edit the port on the this account’s SIP server used for SIP calls.
Select Advanced Setting > VoIP1 or Vo IP2 > Serv Port. The following screen displays.
Figure 30 LCD Menu: SIP Server Port
4. Serv Port
5060
This screen displays the SIP server port number on the V300. The default is 5060. Press to
edit the SIP server port number, or press to return to the previous screen.
" Make no changes in this screen unless your service provider told you to.
6.2.4.1 SIP Server Port - Edit
Press in the Serv Port screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 31 LCD Menu: SIP Server Port - Edit
4. Serv Port
5060_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new SIP server
port number (from 1024 to 65535) and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to
return to the previous screen.
" The port number can consist of numerals (0 ~ 9) only.
6.2.5 SIP Register Server
Use this menu to see and edit the IP address of the server your SIP service provider uses to
register the V300. Select Adv Setting > VoIP1 or VoIP2 > Reg Addr. The following screen
displays.
52
Figure 32 LCD Menu: SIP Register Server
5. Reg Addr
V300 User’s Guide
Page 53

The IP address of the SIP register server already configured on the V300 displays. If no IP
address is already configured, none displays. Press to edit the SIP register server address, or
press to return to the previous screen.
6.2.5.1 SIP Register Server - Edit
Press in the Reg Addr screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 33 LCD Menu: SIP Register Server Address - Edit
5. Reg Addr
_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new SIP register
server address and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous
screen.
6.2.6 SIP Register Port
Use this screen to see and edit the listening port on the SIP register server for calls from this
account. Select Adv Setting > VoIP1 or VoIP2 > Reg Port. The following screen displays.
Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
Figure 34 LCD Menu: SIP Register Port
6. Reg Port
5060
This screen displays the SIP register server port number on the V300. The default is 5060.
Press to edit the SIP register server port number, or press to return to the previous screen.
" Make no changes in this screen unless your service provider told you to.
6.2.6.1 SIP Register Port - Edit
Press in the Reg Port screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 35 LCD Menu: SIP Register Port - Edit
6. Reg Port
5060_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new SIP server
port number (from 1024 to 65535) and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to
return to the previous screen.
" The port number can consist of numerals (0 ~ 9) only.
V300 User’s Guide
53
Page 54

Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
6.2.7 SIP Service Domain
Use this to see and edit the SIP service domain configured for your SIP account. The SIP
service domain of the VoIP service provider (the company that lets you make phonecalls over
the Internet) is the domain name in a SIP URI. For example, if the SIP address is
“1122334455@voip-provider.com”, then “voip-provider.com” is the SIP service domain.
Select Adv Setting > VoIP1 or Vo I P 2 > Domain. The following screen displays.
Figure 36 LCD Menu: SIP Service Domain
7. Domain
If a SIP domain is already configured on the V300, it displays in this screen. If no SIP domain
is already configured, none displays. Press to edit the SIP domain, or press to return to the
previous screen.
6.2.7.1 SIP Service Domain - Edit
Press in the Domain screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 37 LCD Menu: SIP Service Domain - Edit
7. Domain
_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new SIP service
domain. If you have a SIP account like “1234567@voip-provider.com”, the SIP service
domain is “voip-provider.com”. Press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to
the previous screen.
6.2.8 SIP User ID
A SIP account’s user ID is its username. Select Adv Setting > VoIP1 or VoIP2 > User ID to
see and edit the SIP user name for your SIP account. The following screen displays.
Figure 38 LCD Menu: SIP User ID
8. User ID
If a SIP authentication ID is already configured on the V300, it displays in this screen. If no
SIP authentication ID is already configured, none displays. Press to edit the SIP
authentication ID, or press to return to the previous screen.
6.2.8.1 SIP Authentication ID - Edit
Press in the User ID screen. The following screen displays.
54
V300 User’s Guide
Page 55

Figure 39 LCD Menu: SIP User ID - Edit
8. User ID
_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new SIP
authentication ID. Press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous
screen.
6.2.9 SIP Password
Use this screen to see and edit the password for your SIP account. Select Adv Setting > VoIP1
or VoIP2 > Password. The following screen displays.
Figure 40 LCD Menu: Authentication Password
9. Password
If a SIP authentication password is already configured on the V300, it displays in this screen as
a row of asterisks (*). If no SIP authentication password is already configured, no asterisks
display. Each asterisk represents one character of the password configured on the V300. Press
to edit the SIP authentication password, or press to return to the previous screen.
Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
6.2.9.1 Authentication Password - Edit
Press in the Password screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 41 LCD Menu: Authentication Password - Edit
9. Password
_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new SIP
authentication password. Press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the
previous screen.
6.3 DHCP
Use DHCP to have the V300 get an IP address automatically from a DHCP server on the
network.
Select Adv Setting > DHCP. The following screen displays.
Figure 42 LCD Menu: DHCP
3 DHCP (On)
V300 User’s Guide
55
Page 56

Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
Check whether DHCP is enabled on the V300 or not. If DHCP is disabled (Off), press to
enter the DHCP screen and press again to change the configuration (turn DHCP on).
Alternatively press to return to the previous screen.
" If static IP or PPPoE is enabled, DHCP will be disabled automatically.
6.4 Static IP
Use this menu to manually configure your V300’s IP address, subnet mask and gateway
settings. Enter the settings exactly as your ISP or network administrator gave them to you.
Select Adv Setting > Static IP. The following screen displays.
Figure 43 LCD Menu: Static IP
4. Static IP (Off)
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 LCD Menu: Static IP
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Static IP Select this to turn on static IP. Your V300 uses the IP settings you configure
IP Address Select this to set the static IP address you want the V300 to use.
Gateway Select this to set the IP address of the device your V300 uses to access the
Subnet Mask Select this to enter the subnet mask your V300 uses.
1st DNS Select this to enter the primary DNS (Domain Name System) server’s IP
2nd DNS Select this to enter the secondary (backup) DNS server’s IP address.
6.4.1 IP Address
Select Adv Setting > Static IP > IP Address. The following screen displays.
Figure 44 LCD Menu: IP Address
2. IP Address
0.0.0.0
in this menu. If DHCP or PPPoE is enabled, static IP will be disabled
automatically.
Internet.
address.
56
The number that displays is the static IP address currently configured on the V300. Press to
edit the static IP address, or press to return to the previous screen.
V300 User’s Guide
Page 57

6.4.1.1 IP Address - Edit
Press in the IP Address screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 45 LCD Menu: IP Address - Edit
2. IP Address
0.0.0.0_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter your static IP address
and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous screen.
6.4.2 Gateway
Select Adv Setting > Static IP > Gateway. The following screen displays.
Figure 46 LCD Menu: Gateway
3. Gateway
0.0.0.0
Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
The number that displays is the static IP address of the device your V300 uses to access the
Internet. Press to edit the static IP address, or press to return to the previous screen.
6.4.2.1 Default Gateway - Edit
Press in the Gateway screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 47 LCD Menu: Gateway - Edit
3. Gateway
0.0.0.0_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new gateway IP
address and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous screen.
6.4.3 Subnet Mask
Select Adv Setting > Static IP > Subnet Mask. The following screen displays.
Figure 48 LCD Menu: Subnet Mask
4. Subnet Mask
0.0.0.0
The number that displays is the subnet mask your V300 is currently set to use. Press to edit
the subnet mask, or press to return to the previous screen.
6.4.3.1 Subnet Mask - Edit
Press in the Subnet Mask screen. The following screen displays.
V300 User’s Guide
57
Page 58

Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
Figure 49 LCD Menu: Subnet Mask - Edit
4 Subnet Mask
0.0.0.0_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new subnet mask
and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous screen.
6.4.4 First and Second DNS Servers
Use these screens to enter the IP address(es) of DNS (Domain Name System) servers on your
network. Use 1st DNS for the primary (main) server, and use 2nd DNS if you have
information about a secondary (backup) server.
Select 1st DNS or 2nd DNS in the Advanced Setting > Static IP menu. A screen similar to
the following displays (this example uses the 1st DNS screen).
Figure 50 LCD Menu: First / Second DNS
5. 1st DNS:
0.0.0.0
If a DNS server is already configured, its IP address displays. Otherwise, no IP address
displays. Press to edit the DNS server settings, or press to return to the previous screen.
6.4.4.1 First / Second DNS - Edit
Press in the 1st DNS or 2nd DNS screen. A screen similar to the following displays (this
example uses the 1st DNS screen).
Figure 51 LCD Menu: First / Second DNS - Edit
5 1st DNS:
0.0.0.0_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter the new DNS server
IP address and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous
screen.
6.5 The PPPoE Menu
Use this menu to configure your V300’s PPPoE username and password, if it is a PPPoE
client. Enter your details exactly as your ISP or network administrator gave them to you.
Select Adv Setting > PPPoE. The following screen displays.
58
Figure 52 LCD Menu: PPPoE
1. PPPoE
On
V300 User’s Guide
Page 59

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 LCD Menu: PPPoE
LABEL DESCRIPTION
PPPoE Use this to turn PPPoE on.
Username Enter your PPPoE username.
Password Enter your PPPoE password.
6.5.1 PPPoE Username
Select Adv Setting > PPPoE > Username. The following screen displays.
Figure 53 LCD Menu: PPPoE Username
2. Username
Press to edit the PPPoE username, or press to return to the previous screen.
Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
If DHCP or static IP is enabled, PPPoE will be disabled automatically.
6.5.1.1 PPPoE Username - Edit
If you press in the Username screen, the following screen displays.
Figure 54 LCD Menu: PPPoE Username - Edit
2. Username
_
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter your PPPoE username
and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous screen.
6.5.2 PPPoE Password
Select Adv Setting > PPPoE > Password. The following screen displays.
Figure 55 LCD Menu: PPPoE Password
3. Password
Press to edit the PPPoE password, or press to return to the previous screen.
6.5.2.1 PPPoE Password - Edit
Press in the PPPoE > Password screen. The following screen displays.
Figure 56 LCD Menu: PPPoE Password - Edit
3. Password
_
V300 User’s Guide
59
Page 60

Chapter 6 LCD Menus: Advanced
Use PHONEBOOK to clear the previously-saved settings if any. Enter your PPPoE username
and press to save the change. Alternatively, press to return to the previous screen.
60
V300 User’s Guide
Page 61

PART III
The Web
Configurator
Introducing the Web Configurator (63)
Status Screens (69)
Network Setup (75)
SIP Account Setup (79)
Phone Setup (93)
The Phone Book (97)
61
Page 62

62
Page 63

CHAPTER 7
Introducing the Web
Configurator
This chapter describes how to access the V300’s web configurator and provides an overview
of its screens.
7.1 Accessing the Web Configurator
1 Make sure your hardware is properly connected and prepare your computer or computer
network to connect to the V300 (refer to the Quick Start Guide).
2
Launch your web browser.
3 Enter the V300’s IP address as the URL. The V300 is set to get an IP address
automatically. Use the System Info > IP Address LCD screen to find it out (see Section
5.4 on page 46).
" If the V300 is not connected to a network, use the management IP address.
The default management IP address is 192.168.5.1.
The following screen displays.
Figure 57 Password Screen
4 Type "1234" (default) as the password and click Login.
V300 User’s Guide
63
Page 64

Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator
5 It is strongly recommended that you change your password in the screen that displays
next.
" If you do not change your password, anyone who knows the default password
can access your phonebook and SIP account information over the network.
6 Type a new password (and retype it to confirm) then click Apply. Alternatively, click
Ignore.
" If you do not change the password, the following screen appears every time
you log in.
Figure 58 Change Password Screen
64
The Status screen displays.
V300 User’s Guide
Page 65

B
Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator
Figure 59 The Status Screen
A
C
As illustrated above, the web configurator screen is divided into four parts.
• A - title bar
• B - navigation panel
• C - main window
• D - status bar
7.1.1 Title Bar
The title bar has some icons in the upper right corner.
The icons have the following functions.
Table 14 Web Configurator Icons in the Title Bar
ICON DESCRIPTION
D
Language: At the time of writing, only English is supported.
Help: Click this to see online help related to the current screen.
Logout: Click this icon to log out of the web configurator.
V300 User’s Guide
65
Page 66

Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator
7.1.2 Navigation Panel
Use the menu items on the navigation panel to open screens and configure the V300’s features.
The following table describes the menu items.
Table 15 Navigation Panel Summary
LINK TAB FUNCTION
Status This screen contains administrative and system-related information.
Network
Ethernet Internet
Connection
Mgnt Port Use this screen to set the V300’s management IP address.
VoIP
SIP SIP Settings Use this screen to configure your V300’s Voice over IP settings.
QoS Use this screen to configure your V300’s Quality of Service settings for
Phone Phone Settings Use this screen to configure general phone settings, including volume
Region Use this screen to select your location.
Speed Dial
Settings
Phone Book Call Forward Use this screen to redirect incoming calls to other phone numbers.
Contact List Use this screen to view, edit and add to your list of phonebook entries.
Group List Use this screen to view and edit the groups to which your phonebook
Block List Use this screen to view and edit the phone numbers that you prevent from
DND White List Use this screen to view and edit the list of people who can call you even
Maintenance
System General This screen contains administrative and system-related information and
Time Setting Use this screen to change your V300’s time and date.
Logs View Log Use this screen to display your device’s logs.
To ol s Firmware Use this screen to upload firmware to your device.
Configuration Use this screen to backup and restore your device’s configuration (settings)
Restart This screen allows you to reboot the V300 without turning the power off.
Use this screen to configure ISP parameters, WAN IP address assignment
and other advanced properties.
VoIP.
levels and ringtone selection.
Use this screen to configure speed dial for phone numbers that you call
often.
entries belong.
calling you.
when DND (Do Not Disturb) is turned on.
also allows you to change your password.
or reset the factory default settings.
7.1.3 Main Window
The main window displays information and configuration fields. It is discussed in the rest of
this document.
Right after you log in, the Status screen is displayed. See Chapter 8 on page 69 for more
information about the Status screen.
66
V300 User’s Guide
Page 67

7.1.4 Status Bar
Check the status bar when you click Apply or OK to verify that the configuration has been
updated.
Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator
V300 User’s Guide
67
Page 68

Chapter 7 Introducing the Web Configurator
68
V300 User’s Guide
Page 69

CHAPTER 8
Status Screens
Use the Status screens to see the current status of the V300, its system resources, interfaces,
and SIP accounts. You can also register and unregister SIP accounts.
The Status screen also provides detailed traffic and VoIP statistics.
8.1 Status Screen
Click Status to open this screen.
Figure 60 Status Screen
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 16 Status Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh Interval Enter how often you want the V300 to update this screen.
Refresh Now Click this to update this screen immediately.
V300 User’s Guide
69
Page 70

Chapter 8 Status Screens
Table 16 Status Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Information
System Name This field displays the V300’s system name. It is used for identification. You
Firmware Version This field displays the current version of the firmware inside the device. It also
IP Address This field displays the current IP address of the V300 on the LAN.
IP Subnet Mask This field displays the current subnet mask on the LAN.
DHCP This field displays what DHCP services the V300 is receiving from the LAN.
System Status
System Uptime This field displays how long the V300 has been running since it last started up.
Current Date/
Time
CPU Usage This field displays what percentage of the V300’s processing ability is currently
Memory Usage This field displays what percentage of the V300’s memory is currently in use. If
Interface Status
Interface This column displays each interface of the V300.
Status This field indicates whether or not the V300 is using the interface.
Rate This displays the port speed and duplex setting. Ethernet port connections can
VoIP Status
Account This column displays each SIP account in the V300.
Registration This field displays the current registration status of the SIP account. You have
can change this in the Maintenance > System > General screen’s System
Name field.
shows the date the firmware version was created. You can change the
firmware version by uploading new firmware in Maintenance > Tools >
Firmware.
Choices are:
Client - The V300 is a DHCP client. It is receiving DHCP services.
None - The V300 is not receiving DHCP services.
You can change this in the Network > Ethernet > Internet Connection
screen.
This field displays the current date and time in the V300. You can change this
in Maintenance > System > Time Setting.
in use. If this nears 100%, the V300 may slow down.
this nears 100%, the V300 may slow down. Some memory is required just to
start the V300 and to run the web configurator. You can reduce the memory
usage by deleting rules in functions such as call forwarding, speed dial entries,
and contact list entries.
This field displays Up when the V300 is using the interface and Down when
the V300 is not using the interface.
be in half-duplex or full-duplex mode. Full-duplex refers to a device's ability to
send and receive simultaneously, while half-duplex indicates that traffic can
flow in only one direction at a time. The Ethernet port must use the same
speed or duplex mode setting as the peer Ethernet port in order to connect.
to register a SIP account with a SIP server to use VoIP.
If the SIP account is already registered with the SIP server,
Click Unregister to delete the SIP account’s registration in the SIP server.
This does not cancel your SIP account, but it deletes the mapping between
your SIP identity and your IP address or domain name.
The second field displays Registered.
If the SIP account is not registered with the SIP server,
Click Register to have the V300 attempt to register the SIP account with
the SIP server.
The second field displays Unregister.
70
V300 User’s Guide
Page 71

Table 16 Status Screen
LABEL DESCRIPTION
URI This field displays the account number and service domain of the SIP account.
Summary
VoIP Statistics Click this link to view statistics about your VoIP usage.
Packet Statistics Click this link to view port status and packet specific statistics.
8.2 Packet Statistics
To access this screen, open the Status screen (see Section 8.1 on page 69), and click
(Details...) next to Packet Statistics. Read-only information here includes port status and
packet specific statistics. Also provided are "system up time" and "poll interval(s)". The Poll
Interval(s) field is configurable.
Figure 61 Packet Statistics
Chapter 8 Status Screens
You can change these in VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings.
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 17 Packet Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Packet Statistics
Port This column displays each interface of the V300.
Status This displays the port speed and duplex setting.
TxPkts This field displays the number of packets transmitted on this interface.
RxPkts This field displays the number of packets received on this interface.
Collisions This field displays the number of collisions on this port.
Tx B/s This field displays the number of bytes transmitted in the last second.
Rx B/s This field displays the number of bytes received in the last second.
Up Time This field displays the elapsed time this interface has been connected.
System up Time This is the elapsed time the system has been on.
Poll Interval(s) Type the time interval (in seconds) for the browser to refresh system statistics.
V300 User’s Guide
71
Page 72

Chapter 8 Status Screens
Table 17 Packet Statistics (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Set Interval Click this button to apply the new poll interval you entered in the Poll Interval
Stop Click this button to halt the refreshing of the system statistics.
8.3 VoIP Statistics
This screen displays SIP registration information, status of calls and VoIP traffic statistics. To
access this screen, open the Status screen (see Section 8.1 on page 69), and click (Details...)
next to VoIP Statistics.
Figure 62 VoIP Statistics
field.
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 18 VoIP Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SIP Status
Account This column displays each SIP account in the V300.
Registration This field displays the current registration status of the SIP account. You can
Last
Registration
URI This field displays the account number and service domain of the SIP account.
Protocol This field displays the transport protocol the SIP account uses. SIP accounts
Message
Waiting
Last Incoming
Number
change this in the Status screen.
Registered - The SIP account is registered with a SIP server.
Unregister - The SIP account has failed to register with a SIP server, or is not
active.
This field displays the last time you successfully registered the SIP account. It
displays N/A if you never successfully registered this account.
You can change these in VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings.
always use UDP.
This field indicates whether or not there are any messages waiting for the SIP
account.
This field displays the last number that called the SIP account. It displays N/A if no
number has ever dialed the SIP account.
72
V300 User’s Guide
Page 73

Chapter 8 Status Screens
Table 18 VoIP Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Last Outgoing
Number
Call Statistics
Call This field displays the V300’s line number.
Status This field indicates whether the line is active or not.
Codec This field displays what voice codec (coder/decoder) is being used for a current
Peer Number This field displays the SIP number of the person on the other end of the line, when
Duration This field displays how long the current call has lasted.
Packets Sent This field displays the number of packets the V300 has transmitted in the current
Packets Recv This field displays the number of packets the V300 has received in the current call.
Tx Rate B/s This field displays how quickly the V300 has transmitted packets in the current
Rx Rate B/s This field displays how quickly the V300 has received packets in the current call.
Poll Interval(s) Enter how often you want the V300 to update this screen, and click Set Interval.
Set Interval Click this to make the V300 update the screen based on the amount of time you
Stop Click this to make the V300 stop updating the screen.
This field displays the last number the SIP account called. It displays N/A if the
SIP account has never dialed a number.
Idle - The line is not active.
Dial - the line is active and a connection to a SIP server has been made, but a call
is not in progress.
Dialing - the V300 is initiating a call on this line.
Ringing - the V300 has initiated a call, and the phone at the other end is ringing.
Connected - a call is in progress on this line.
Disconnect - the line is active, but the connection with the SIP server has been
terminated.
Hold - a call on this line is on hold.
Waiting - another line is active, and this line has an incoming call that has not
been answered.
Transfer - a call on this line is waiting to be transferred.
Transferred - a call on this line has been transferred to another number, and is
still ongoing.
Incoming - an incoming call on this line is waiting to be answered.
Busy - the V300 has tried to initiate a call, but the phone at the other end is
engaged.
VoIP call.
a call is in progress.
call.
call. The rate is the average number of bytes transmitted per second.
The rate is the average number of bytes transmitted per second.
specified in the Poll Interval field.
V300 User’s Guide
73
Page 74

Chapter 8 Status Screens
74
V300 User’s Guide
Page 75

CHAPTER 9
Network Setup
This chapter discusses how to configure the V300’s network settings.
9.1 TCP/IP Parameters
9.1.1 IP Address Assignment
Every computer on the Internet must have a unique IP address. If your networks are isolated
from the Internet (for instance, only between your two branch offices) you can assign any IP
addresses to the hosts without problems. However, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority
(IANA) has reserved the following three blocks of IP addresses specifically for private
networks.
Table 19 Private IP Address Ranges
10.0.0.0 - 10.255.255.255
172.16.0.0 - 172.31.255.255
192.168.0.0 - 192.168.255.255
You can obtain your IP address from the IANA, from an ISP or have it assigned by a private
network. If you belong to a small organization and your Internet access is through an ISP, the
ISP can provide you with the Internet addresses for your local networks. On the other hand, if
you are part of a much larger organization, you should consult your network administrator for
the appropriate IP addresses.
" Regardless of your particular situation, do not create an arbitrary IP address;
always follow the guidelines above. For more information on address
assignment, please refer to RFC 1597, Address Allocation for Private Internets
and RFC 1466, Guidelines for Management of IP Address Space.
9.1.2 IP Address and Subnet Mask
Similar to the way houses on a street share a common street name, computers on a LAN share
one common network number.
V300 User’s Guide
75
Page 76

Chapter 9 Network Setup
Where you obtain your network number depends on your particular situation. If the ISP or
your network administrator assigns you a block of registered IP addresses, follow their
instructions in selecting the IP addresses and the subnet mask.
If the ISP did not explicitly give you an IP network number, then most likely you have a single
user account and the ISP will assign you a dynamic IP address when the connection is
established. The Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) reserved this block of addresses
specifically for private use; please do not use any other number unless you are told otherwise.
Let's say you select 192.168.1.0 as the network number; which covers 254 individual
addresses, from 192.168.1.1 to 192.168.1.254 (zero and 255 are reserved). In other words, the
first three numbers specify the network number while the last number identifies an individual
computer on that network.
Once you have decided on the network number, pick an IP address that is easy to remember,
for instance, 192.168.1.2, for your device, but make sure that no other device on your network
is using that IP address.
The subnet mask specifies the network number portion of an IP address. Your device will
compute the subnet mask automatically based on the IP address that you entered. You don't
need to change the subnet mask computed by the device unless you are instructed to do
otherwise.
9.1.3 PPPoE Encapsulation
The V300 supports PPPoE (Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet). PPPoE is an IETF standard
(RFC 2516) specifying how a personal computer (PC) interacts with a broadband modem
(DSL, cable, wireless, etc.) connection.
For the service provider, PPPoE offers an access and authentication method that works with
existing access control systems (for example Radius).
One of the benefits of PPPoE is the ability to let you access one of multiple network services,
a function known as dynamic service selection. This enables the service provider to easily
create and offer new IP services for individuals.
Operationally, PPPoE saves significant effort for both you and the ISP or carrier, as it requires
no specific configuration of the broadband modem at the customer site.
By implementing PPPoE directly on the V300 (rather than individual computers), the
computers on the LAN do not need PPPoE software installed, since the V300 does that part of
the task. Furthermore, with NAT, all of the LANs’ computers will have access.
9.2 Internet Connection
Use this screen to change your V300’s Internet access settings. Click Network > Internet
Connection.
76
V300 User’s Guide
Page 77

Chapter 9 Network Setup
Figure 63 Network > Internet Connection
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 20 Network > Internet Connection
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ethernet TCP/IP Settings
Get
automatically
from DHCP
Use Fixed IP
Address
IP Address Enter your WAN IP address in this field if you selected Use Fixed IP Address.
IP Subnet Mask Enter the IP Subnet Mask in this field.
Gateway IP
Address
Primary DNS
Secondary DNS
PPPoE
Use PPPoE
Client
PPPoE User
Name
Password Type the password associated with the user name above.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Reset Click this to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
Select this option if your ISP did not give you an IP address.
Select this option If your ISP assigned a fixed IP address. Enter the address
information in the following fields.
Enter a Gateway IP Address (if your ISP gave you one) in this field.
Enter the DNS (Domain Name Service) servers, if provided by your ISP.
Select this if your V300 is a PPPoE client.
Type the user name given to you by your ISP.
9.3 Management Port
Use this screen to configure the management IP address of the V300. You can use this IP
address to connect to the V300 even when its WAN IP address is in a different subnet. Your
computer must be in the same subnet as the management IP address to use it.
V300 User’s Guide
77
Page 78

Chapter 9 Network Setup
Click Network > Ethernet > Mgnt Port. The following screen displays.
Figure 64 Network > Mgnt Port
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 21 Network > Mgnt Port
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Management IP Address
IP Address Enter the new management IP address you want the V300 to use.
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Reset Click this to reload the previous configuration for this screen.
78
V300 User’s Guide
Page 79

CHAPTER 10
SIP Account Setup
This chapter discusses the V300’s VoI P > SIP screens.
10.1 SIP Overview
10.1.1 Introduction to VoIP
VoIP (Voice over IP) is the sending of voice signals over the Internet Protocol. This allows you
to make phone calls and send faxes over the Internet at a fraction of the cost of using the
traditional circuit-switched telephone network. You can also use servers to run telephone
service applications like PBX services and voice mail. Internet Telephony Service Provider
(ITSP) companies provide VoIP service. A company could alternatively set up an IP-PBX and
provide its own VoIP service.
Circuit-switched telephone networks require 64 kilobits per second (kbps) in each direction to
handle a telephone call. VoIP can use advanced voice coding techniques with compression to
reduce the required bandwidth.
10.1.2 Introduction to SIP
The Session Initiation Protocol (SIP) is an application-layer control (signaling) protocol that
handles the setting up, altering and tearing down of voice and multimedia sessions over the
Internet.
SIP signaling is separate from the media for which it handles sessions. The media that is
exchanged during the session can use a different path from that of the signaling. SIP handles
telephone calls and can interface with traditional circuit-switched telephone networks.
10.1.3 SIP Identities
A SIP account uses an identity (sometimes referred to as a SIP address). A complete SIP
identity is called a SIP URI (Uniform Resource Identifier). A SIP account's URI identifies the
SIP account in a way similar to the way an e-mail address identifies an e-mail account. The
format of a SIP identity is SIP-Number@SIP-Service-Domain.
10.1.3.1 SIP Number
The SIP number is the part of the SIP URI that comes before the “@” symbol. A SIP number
can use letters like in an e-mail address (johndoe@your-ITSP.com for example) or numbers
like a telephone number (1122334455@VoIP-provider.com for example).
V300 User’s Guide
79
Page 80

Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
10.1.3.2 SIP Service Domain
The SIP service domain of the VoIP service provider (the company that lets you make phone
calls over the Internet) is the domain name in a SIP URI. For example, if the SIP address is
1122334455@VoIP-provider.com
10.1.4 SIP Call Progression
The following figure displays the basic steps in the setup and tear down of a SIP call. A calls
B.
Table 22 SIP Call Progression
A B
1. INVITE
4. ACK
5.Dialogue (voice traffic)
6. BYE
, then “VoIP-provider.com” is the SIP service domain.
2. Ringing
3. OK
7. OK
1 A sends a SIP INVITE request to B. This message is an invitation for B to participate in
a SIP telephone call.
2 B sends a response indicating that the telephone is ringing.
3 B sends an OK response after the call is answered.
4 A then sends an ACK message to acknowledge that B has answered the call.
5 Now A and B exchange voice media (talk).
6 After talking, A hangs up and sends a BYE request.
7 B replies with an OK response confirming receipt of the BYE request and the call is
terminated.
10.1.5 SIP Client Server
SIP is a client-server protocol. A SIP client is an application program or device that sends SIP
requests. A SIP server responds to the SIP requests.
When you use SIP to make a VoIP call, it originates at a client and terminates at a server. A
SIP client could be a computer or a SIP phone. One device can act as both a SIP client and a
SIP server.
10.1.5.1 SIP User Agent
A SIP user agent can make and receive VoIP telephone calls. This means that SIP can be used
for peer-to-peer communications even though it is a client-server protocol. In the following
figure, either A or B can act as a SIP user agent client to initiate a call. A and B can also both
act as a SIP user agent to receive the call.
80
V300 User’s Guide
Page 81

Figure 65 SIP User Agent
10.1.5.2 SIP Proxy Server
A SIP proxy server receives requests from clients and forwards them to another server.
In the following example, you want to use client device A to call someone who is using client
device C.
1 The client device (A in the figure) sends a call invitation to the SIP proxy server (B).
2 The SIP proxy server forwards the call invitation to C.
Figure 66 SIP Proxy Server
Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
10.1.5.3 SIP Redirect Server
A SIP redirect server accepts SIP requests, translates the destination address to an IP address
and sends the translated IP address back to the device that sent the request. Then the client
device that originally sent the request can send requests to the IP address that it received back
from the redirect server. Redirect servers do not initiate SIP requests.
In the following example, you want to use client device A to call someone who is using client
device C.
1 Client device A sends a call invitation for C to the SIP redirect server (B).
2 The SIP redirect server sends the invitation back to A with C’s IP address (or domain
name).
3 Client device A then sends the call invitation to client device C.
V300 User’s Guide
81
Page 82

Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
Figure 67 SIP Redirect Server
10.1.5.4 SIP Register Server
A SIP register server maintains a database of SIP identity-to-IP address (or domain name)
mapping. The register server checks your user name and password when you register.
10.1.6 RTP
When you make a VoIP call using SIP, the RTP (Real time Transport Protocol) is used to
handle voice data transfer. See RFC 1889 for details on RTP.
10.1.7 NAT and SIP
NAT (Network Address Translation - NAT, RFC 1631) is the translation of the IP address of a
host in a packet, for example, the source address of an outgoing packet, used within one
network to a different IP address known within another network.
The V300 must register its public IP address with a SIP register server. If there is a NAT router
between the V300 and the SIP register server, the V300 probably has a private IP address. The
V300 lists its IP address in the SIP message that it sends to the SIP register server. NAT does
not translate this IP address in the SIP message. The SIP register server gets the V300’s IP
address from inside the SIP message and maps it to your SIP identity. If the V300 has a private
IP address listed in the SIP message, the SIP server cannot map it to your SIP identity.
Use STUN or outbound proxy to allow the V300 to list its public IP address in the SIP
messages.
82
V300 User’s Guide
Page 83

10.1.7.1 STUN
STUN (Simple Traversal of User Datagram Protocol (UDP) through Network Address
Translators) allows the V300 to find the presence and types of NAT routers and/or firewalls
between it and the public Internet. STUN also allows the V300 to find the public IP address
that NAT assigned, so the V300 can embed it in the SIP data stream. STUN does not work
with symmetric NAT routers or firewalls. See RFC 3489 for details on STUN.
The following figure shows how STUN works.
1 The V300 (A) sends SIP packets to the STUN server (B).
2 The STUN server (B) finds the public IP address and port number that the NAT router
3 The V300 uses the public IP address and port number in the SIP packets that it sends to
Figure 68 STUN
Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
used on the V300’s SIP packets and sends them to the V300.
the SIP server (C).
10.1.7.2 Outbound Proxy
Your VoIP service provider may host a SIP outbound proxy server to handle all of the V300’s
VoIP traffic. This allows the V300 to work with any type of NAT router and eliminates the
need for STUN or a SIP ALG. Turn off a SIP ALG on a NAT router in front of the V300 to
keep it from retranslating the IP address (since this is already handled by the outbound proxy
server).
10.1.8 Voice Coding
A codec (coder/decoder) codes analog voice signals into digital signals and decodes the digital
signals back into voice signals. The V300 supports the following codecs.
• G. 7 11 is a Pulse Code Modulation (PCM) waveform codec. PCM measures analog signal
amplitudes at regular time intervals (sampling) and converts them into digital bits
(quantization). Quantization “reads” the analog signal and then “writes” it to the nearest
digital value. For this reason, a digital sample is usually slightly different from its analog
original (this difference is known as “quantization noise”).
G.711 provides excellent sound quality but requires 64kbps of bandwidth.
• G. 7 2 2 is an Adaptive Differential Pulse Code Modulation (ADPCM) waveform codec.
Differential (or Delta) PCM is similar to PCM, but encodes the audio signal based on the
difference between one sample and a prediction based on previous samples, rather than
encoding the sample’s actual quantized value. Many thousands of samples are taken each
second, and the differences between consecutive samples are usually quite small, so this
saves space and reduces the bandwidth necessary.
V300 User’s Guide
83
Page 84

Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
However, DPCM produces a high quality signal (high signal-to-noise ratio or SNR) for
high difference signals (where the actual signal is very different from what was predicted)
but a poor quality signal (low SNR) for low difference signals (where the actual signal is
very similar to what was predicted). This is because the level of quantization noise is the
same at all signal levels. Adaptive DPCM solves this problem by adapting the difference
signal’s level of quantization according to the audio signal’s difference level. A low
difference signal is given a higher quantization level, increasing its signal-to-noise ratio.
This provides a similar sound quality at all signal levels.
G.722 samples audio at 16 kHz; twice the traditional rate of 8 kHz. G.722 provides
excellent quality audio and requires 48 to 64 kbps.
• G.722.2 is similar to G.722, but with a lower compression rate that can vary according to
the amount of available bandwidth. When there is plenty of bandwidth, the compression
ratio decreases, and when there is network congestion the compression ratio increases.
G.722.2 is also known as Adaptive Multi Rate - WideBand (AMR-WB).
• G.723.1 is a Code Excited Linear Prediction (CELP) codec that compresses voice audio in
30 ms frames. G.723.1 operates at two bitrates: 6.3 kbps when sampling at 24 bytes or 5.3
kbps when sampling at 20 bytes per 30 ms frame.
• G. 7 2 6 is an ADPCM waveform codec that uses a lower bitrate than standard PCM
conversion. G.726 operates at 16, 24, 32 or 40 kbps.
• G. 7 2 9 is an Analysis-by-Synthesis (AbS) hybrid waveform codec. It uses a filter based on
information about how the human vocal tract produces sounds. The codec analyzes the
incoming voice signal and attempts to synthesize it using its list of voice elements. It tests
the synthesized signal against the original and, if it is acceptable, transmits details of the
voice elements it used to make the synthesis. Because the codec at the receiving end has
the same list, it can exactly recreate the synthesized audio signal.
G.729 provides good sound quality and reduces the required bandwidth to 8kbps.
10.1.9 MWI (Message Waiting Indication)
Enable Message Waiting Indication (MWI) enables your phone to give you a message–waiting
(beeping) dial tone when you have one or more voice messages. Your VoIP service provider
must have a messaging system that sends message-waiting-status SIP packets as defined in
RFC 3842.
10.1.10 Quality of Service (QoS)
Quality of Service (QoS) refers to both a network's ability to deliver data with minimum delay
and the networking methods used to provide bandwidth for real-time multimedia applications.
10.1.10.1 Type Of Service (ToS)
Network traffic can be classified by setting the ToS (Type Of Service) values at the data source
(for example, at the V300) so a server can decide the best method of delivery, that is the least
cost, fastest route and so on.
84
V300 User’s Guide
Page 85

10.1.10.2 DiffServ
DiffServ is a class of service (CoS) model that marks packets so that they receive specific perhop treatment at DiffServ-compliant network devices along the route based on the application
types and traffic flow. Packets are marked with DiffServ Code Points (DSCPs) indicating the
level of service desired. This allows the intermediary DiffServ-compliant network devices to
handle the packets differently depending on the code points without the need to negotiate paths
or remember state information for every flow. In addition, applications do not have to request
a particular service or give advanced notice of where the traffic is going.
10.1.10.3 DSCP and Per-Hop Behavior
DiffServ defines a new DS (Differentiated Services) field to replace the Type of Service (TOS)
field in the IP header. The DS field contains a 2-bit unused field and a 6-bit DSCP field which
can define up to 64 service levels. The following figure illustrates the DS field.
Figure 69 DiffServ: Differentiated Service Field
Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
1
DSCP
(6-bit)
DSCP is backward compatible with the three precedence bits in the ToS octet so that nonDiffServ compliant, ToS-enabled network device will not conflict with the DSCP mapping.
The DSCP value determines the forwarding behavior, the PHB (Per-Hop Behavior), that each
packet gets across the DiffServ network. Based on the marking rule, different kinds of traffic
can be marked for different priorities of forwarding. Resources can then be allocated
according to the DSCP values and the configured policies.
10.1.10.4 VLAN
Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) allows a physical network to be partitioned into multiple
logical networks. Only stations within the same group can communicate with each other.
Your V300 can add IEEE 802.1Q VLAN ID tags to voice frames that it sends to the network.
This allows the V300 to communicate with a SIP server that is a member of the same VLAN
group. Some ISPs use the VLAN tag to identify voice traffic and give it priority over other
traffic.
10.2 SIP Screens
Unused
(2-bit)
This section describes the VoIP > SIP screens.
10.2.1 SIP Settings Screen
Use this screen to maintain basic information about each SIP account. Your VoIP service
provider (the company that lets you make phone calls over the Internet) should provide this.
You can also enable and disable each SIP account. To access this screen, click VoIP > SIP >
SIP Settings.
1. The V300 does not support DiffServ at the time of writing.
V300 User’s Guide
85
Page 86

Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
Figure 70 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings
86
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 23 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SIP Settings
SIP Account Select the SIP account you want to see in this screen. At the time of writing, the
V300 supports two SIP accounts.
Active Select this if you want the V300 to use this account. Clear it if you do not want the
Account
Name
Number Enter your SIP number. In the full SIP URI, this is the part before the @ symbol.
V300 to use this account.
Enter your SIP account name, if supplied by your SIP service provider.
You can use up to 50 printable English keyboard characters.
V300 User’s Guide
Page 87

Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
Table 23 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SIP Local Port Enter the V300’s listening port number, if your VoIP service provider gave you one.
Otherwise, keep the default value.
SIP Server
Address
SIP Server
Port
REGISTER
Server
Address
REGISTER
Server Port
SIP Service
Domain
Send Caller ID Select this if you want to send identification when you make VoIP phone calls.
Voice Mail
Number
DNS SRV Select this to use the DNS server(s) you configured in the Network > Ethernet >
Backup SIP
Server
1st / 2nd
Backup SIP
Server
SIP Service
Address
SIP Service
Port
Register
Service
Address
Register
Service Port
Authentication
User Name Enter the user name for registering this SIP account, exactly as it was given to
Password Enter the user name for registering this SIP account, exactly as it was given to
Apply
Advanced Setup
Enter the IP address or domain name of the SIP server provided by your VoIP
service provider. You can use up to 32 printable English keyboard characters. It
does not matter whether the SIP server is a proxy, redirect or register server.
Enter the SIP server’s listening port number, if your VoIP service provider gave
you one. Otherwise, keep the default value.
Enter the IP address or domain name of the SIP register server, if your VoIP
service provider gave you one. Otherwise, enter the same address you entered in
the SIP Server Address field. You can use up to 32 printable English keyboard
characters.
Enter the SIP register server’s listening port number, if your VoIP service provider
gave you one. Otherwise, enter the same port number you entered in the SIP
Server Port field.
Enter the SIP service domain name. In the full SIP URI, this is the part after the @
symbol. You can use up to 32 printable English keyboard characters.
Clear this if you do not want to send identification.
Enter the voicemail number associated with this SIP account.
Internet Connection screen.
Select the check box to have the V300 use the backup SIP server(s) you
configure. If the V300 cannot use the server you configured in the SIP Settings
section of this screen, it tries to use the backup server(s). It tries to use the 1st
Backup SIP Server and, if it cannot connect, then tries to use the 2nd Backup
SIP Server.
Enter the IP address or domain name of the backup SIP server provided by your
VoIP service provider. You can use up to 32 printable English keyboard
characters. It does not matter whether the SIP server is a proxy, redirect or
register server.
Enter the backup SIP server’s listening port number, if your VoIP service provider
gave you one. Otherwise, keep the default value.
Enter the IP address or domain name of the backup SIP register server, if your
VoIP service provider gave you one. Otherwise, enter the same address you
entered in the SIP Service Address field for this backup server. You can use up to
32 printable English keyboard characters.
Enter the backup SIP register server’s listening port number, if your VoIP service
provider gave you one. Otherwise, enter the same port number you entered in the
SIP Service Port field for this backup server.
you. You can use up to 20 printable English keyboard characters.
you. You can use up to 20 printable English keyboard characters.
Click this to save your changes.
Click this to edit the advanced settings for this SIP account. The Advanced SIP
Setup screen appears.
V300 User’s Guide
87
Page 88

Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
10.2.2 Advanced SIP Setup Screen
Use this screen to maintain advanced settings for each SIP account. Click Advanced Setup in
VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings. The following screen displays.
Figure 71 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings > Advanced
88
V300 User’s Guide
Page 89

Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 24 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings > Advanced Setup
LABEL DESCRIPTION
SIP Server
Settings
URL Type Select whether or not to include the SIP service domain name when the V300
sends the SIP number.
SIP - include the SIP service domain name
TEL - do not include the SIP service domain name
Expiration
Duration
Register Resend timer
Session
Expires Active
Session
Expires
Min-SE Enter the minimum number of seconds the V300 accepts for a session expiration
RTP Port Range
Start Port
End Port
Voice
Compression
Primary
Compression
Type
Secondary
Compression
Type
Third
Compression
Type
Enter the number of seconds your SIP account is registered with the SIP register
server before it is deleted. The V300 automatically tries to re-register your SIP
account when one-half of this time has passed. (The SIP register server might
have a different expiration.)
Enter the number of seconds the V300 waits before it tries again to register the
SIP account, if the first try failed or if there is no response.
Select this to have the V300 use the setting you configure in the Session Expire
field. If you do not select this, the V300 does not automatically disconnect calls.
Enter the number of seconds the conversation can last before the call is
automatically disconnected. Usually, when one-half of this time has passed, the
V300 or the other party updates this timer to prevent this from happening.
time when it receives a request to start a SIP session. If the request has a shorter
time, the V300 rejects it.
Enter the listening port number(s) for RTP traffic, if your VoIP service provider
gave you this information. Otherwise, keep the default values.
To enter one port number, enter the port number in the Start Port and End Port
fields.
To enter a range of ports,
• enter the port number at the beginning of the range in the Start Port field
• enter the port number at the end of the range in the End Port field.
Select the type of voice coder/decoder (codec) that you want the V300 to use.
G.711 provides high voice quality but requires more bandwidth (64 kbps).
• G. 7 11 A is typically used in Europe.
• G. 7 11 u is typically used in North America and Japan.
• G.722 provides excellent sound quality and operates at 48 ~ 64 kbps.
• G.722.2 is similar to G.722 but allows for greater voiceband compression when
the network is congested.
• G. 7 26 operates at 16, 24, 32 or 40 kbps.
• By contrast, G.729 requires only 8 kbps.
• G. 7 23 refers to G.723.1, which uses 5.3 or 6.4 kbps.
The V300 must use the same codec as the peer. When two SIP devices start a
SIP session, they must agree on a codec.
Select the V300’s first choice for voice coder/decoder.
Select the V300’s second choice for voice coder/decoder.
Select the V300’s third choice for voice coder/decoder.
V300 User’s Guide
89
Page 90

Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
Table 24 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings > Advanced Setup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
DTMF Mode Control how the V300 handles the alphanumeric keypad tones. You should use
STUN
Enable Select this if all of the following conditions are satisfied.
Server
Address
Server Port Enter the STUN server’s listening port, if your VoIP service provider gave you one.
Outbound Proxy
Enable Select this if your service provider has a SIP outbound server to handle voice
Server
address
Server Port Enter the outbound proxy server’s listening port, if your VoIP service provider gave
NAT Keep Alive
Active Select this to stop NAT routers between the V300 and SIP server (a SIP proxy
Keep Alive
Interval
MWI (Message
Waiting
Indication)
Enable Select this if you want to hear a waiting (beeping) dial tone on your phone when
Expiration
Time
Call Forward
Enable Select this if you want the V300 to use the call forwarding rules you set up in the
RingBack Active
the same mode your VoIP service provider uses.
RFC 2833 - send the DTMF tones in RTP packets
PCM - send the DTMF tones in the voice data stream. This method works best
when you are using a codec that does not use compression (like G.711). Codecs
that use compression (like G.729) can distort the tones.
SIP INFO - send the DTMF tones in SIP messages.
RFC 2833 like - send the information in SIP messages but with an RTP payload.
• There is a NAT router between the V300 and the SIP server.
• The NAT router is not a SIP ALG.
• Your VoIP service provider gave you an IP address or domain name for a
STUN server.
Otherwise, clear this field.
Enter the IP address or domain name of the STUN server provided by your VoIP
service provider.
Otherwise, keep the default value.
calls. This allows the V300 to work with any type of NAT router and eliminates the
need for STUN or a SIP ALG. Turn off any SIP ALG on a NAT router in front of the
V300 to keep it from retranslating the IP address (since this is already handled by
the outbound proxy server.
Enter the IP address or domain name of the SIP outbound proxy server.
you one. Otherwise, keep the default value.
server or outbound proxy server) from dropping the SIP session. The V300 does
this by sending SIP notify messages to the SIP server based on the specified
interval.
Enter how often (in seconds) the V300 should send SIP notify messages to the
SIP server.
you have at least one voice message. Your VoIP service provider must support
this feature.
Keep the default value, unless your VoIP service provider tells you to change it.
Enter the number of seconds the SIP server should provide the message waiting
service each time the V300 subscribes to the service. Before this time passes, the
V300 automatically subscribes again.
VoIP > Phone Book > Call Forward screen.
90
V300 User’s Guide
Page 91

Table 24 VoIP > SIP > SIP Settings > Advanced Setup (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable Select this to turn the RingBack function on. When someone calls you, and the
line is busy, the caller is given the option to set an automatic RingBack. When you
finish your call, the V300 automatically calls the person who called you, and then
rings to alert you once the caller picks up.
MusicOnHold
Active
Enable Check this box if you want people to hear a customized recording when you put
them on hold. This function depends on your service provider.
Apply
Back Click this to return to the SIP Settings screen without saving your changes.
Click this to save your changes.
10.3 SIP QoS Screen
Use this screen to maintain ToS and VLAN settings for the V300. Click VoIP > SIP > QoS.
The following screen displays.
Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
Figure 72 VoIP > SIP > QoS
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 25 VoIP > SIP > QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
TOS
SIPTOS Enter the priority for SIP voice transmissions. The V300 creates Type of Service
priority tags with this priority to voice traffic that it transmits.
RTPTOS Enter the priority for RTP voice transmissions. The V300 creates Type of Service
VLAN Tagging
Enable VLAN
Ta g
Voice VL AN IDEnter the VLAN ID provided by your network administrator. Your LAN and gateway
priority tags with this priority to RTP traffic that it transmits.
Select this if the V300 has to be a member of a VLAN to communicate with the SIP
server. Ask your network administrator if you are unsure.
Otherwise, clear this field.
must be configured to use VLAN tags.
V300 User’s Guide
91
Page 92

Chapter 10 SIP Account Setup
Table 25 VoIP > SIP > QoS
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click this to save your changes.
Reset Click this to set every field in this screen to its last-saved value.
92
V300 User’s Guide
Page 93

CHAPTER 11
Phone Setup
This chapter discusses the V300’s Phone screens.
11.1 Phone Settings Screen
Use this screen to configure basic phone settings like volume levels.
Click VoIP > Phone > Phone Settings. The following screen displays.
Figure 73 VoIP > Phone > Phone Settings
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 26 VoIP > Phone > Phone Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Volume Control
Speaker
Volum e
Phone Volume Select this to set the handset volume. This controls both the handset’s speaker
V300 User’s Guide
Select this to set the internal speakerphone volume. This controls both the internal
speaker and the internal microphone.
0 is the quietest and 12 is the loudest.
and its microphone.
0 is the quietest and 12 is the loudest.
93
Page 94

Chapter 11 Phone Setup
Table 26 VoIP > Phone > Phone Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Ring Volume Select this to set the volume of the V300’s ringtone.
0 is the quietest and 12 is the loudest.
Headset
Volum e
Echo Cancellation
G.168 Active Select this if you want to eliminate the echo caused by the sound of your voice
Voice Active
Detection
VAD Support Select this if the V300 should stop transmitting when you are not speaking. This
Apply
Reset
Select this to set the volume of an attached headset (or any device connected to
the external speaker and/or microphone sockets). This controls both the handset’s
speaker (earpiece) and its microphone.
0 is the quietest and 12 is the loudest.
reverberating in the telephone receiver while you talk.
reduces the bandwidth the V300 uses.
Click this to save your changes and to apply them to the V300.
Click this to set every field in this screen to its last-saved value.
11.1.1 Voice Activity Detection/Silence Suppression
Voice Activity Detection (VAD) detects whether or not speech is present. This lets the V300
reduce the bandwidth that a call uses by not transmitting “silent packets” when you are not
speaking.
11.1.2 Comfort Noise Generation
When using VAD, the V300 generates comfort noise when the other party is not speaking. The
comfort noise lets you know that the line is still connected as total silence could easily be
mistaken for a lost connection.
11.1.3 Echo Cancellation
G.168 is an ITU-T standard for eliminating the echo caused by the sound of your voice
reverberating in the telephone receiver while you talk.
11.2 Phone Region Screen
Use this screen to maintain settings that depend on which region of the world the V300 is in.
To access this screen, click VoIP > Phone > Region.
94
V300 User’s Guide
Page 95

Figure 74 VoIP > Phone > Region
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 27 VoIP > Phone > Region
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Region Setting
Region
Settings
Apply
Reset Click this to set this screen to its last-saved value.
Select the place in which the V300 is located.
Click this to save your changes.
Chapter 11 Phone Setup
11.3 Speed Dial Settings Screen
Speed dial provides shortcuts for dialing frequently used phone numbers. You can map a
phone number to an alphanumeric keypad key (0 to 9) and then use that keypad key to call the
phone number (press and hold the key for one second or longer). Use this screen to add, edit,
or remove speed-dial numbers for outgoing calls.
You also have to create speed-dial entries if you want to make peer-to-peer calls or call SIP
numbers that use letters.
In peer-to-peer calls, you call another VoIP device directly without going through a SIP server.
Enter the callee’s IP address or domain name. The V300 sends SIP INVITE requests to the
peer VoIP device when you use the speed dial entry.
You do not need to configure a SIP account in order to make a peer-to-peer VoIP call.
Click VoIP > Phone > Speed Dial Settings. The following screen displays.
V300 User’s Guide
95
Page 96

Chapter 11 Phone Setup
Figure 75 Phone Book > Speed Dial
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 28 Phone Book > Speed Dial
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Speed Dial
Settings
Speed Dial Key 0
~ 9
Apply
Reset
Enter the phone number you want the V300 to call when you use this speed dial
key.
Click this to save your settings.
Click this to set every field in this screen to its last-saved value.
96
V300 User’s Guide
Page 97

CHAPTER 12
The Phone Book
This chapter discusses the Phone Book screens.
12.1 Call Forward Screen
Use this screen to configure call forwarding for incoming calls. When call forwarding is
active, incoming calls are redirected to other phone numbers. You can set up rules for all
incoming calls, or have the V300 forward calls from specific numbers only.
Click VoIP > Phone Book > Call Forward. The following screen displays.
V300 User’s Guide
97
Page 98

Chapter 12 The Phone Book
Figure 76 VoIP > Phone Book > Call Forward
98
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 29 VoIP > Phone Book > Call Forward
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Call Forward
Setup
Active
Allow
Anonymous
Call
Conditional
Forward
The V300 checks these rules, in the order in which they appear, after it checks the
rules in the Advanced Setup section.
Select this to turn call forwarding on. This setting applies to all call forwarding on
the V300.
Select this to allow incoming calls that do not carry caller ID.
If this is not selected, the phone does not ring when someone tries to call you with
caller ID deactivated.
Select this to forward all incoming calls under certain circumstances (if the phone
is in use, if you do not answer, or if you have the Do Not Disturb function turned
on).
V300 User’s Guide
Page 99

Chapter 12 The Phone Book
Table 29 VoIP > Phone Book > Call Forward (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Busy Forward
to Number
No Answer
Forward to
Number
DND Forward
Unconditional
Forward to
Number
Forward
Number
No Answer
Time
Specific Active
List Table
Group List Select this to see the phonebook entries belonging to each group.
Block List Select this to see the phone numbers that are prevented from calling the V300.
DND White
List
Advanced Setup
#
Activate
Incoming Call
Number
Forward to
Number
Uncondition
Select this if you want the V300 to forward incoming calls to the specified phone
number if the phone is busy (it does not matter which line is being used). Specify
the phone number in the field on the right. If you have call waiting, the incoming
call is forwarded to the specified phone number if you reject or ignore the second
incoming call.
Select this to forward all incoming calls if you do not answer the phone within the
time you set in the No Answer Time field.
Select this to forward all incoming calls if you have DND (Do Not Disturb) turned
on.
Select this if you want the V300 to forward all incoming calls to the specified phone
number, regardless of other rules in the Forward to Number section. Specify the
phone number in the Forward Number field.
Enter the phone number to which you want to forward incoming calls.
This field is used by the No Answer Forward to Number feature and No Answer
conditions.
Enter the number of seconds the V300 should wait for you to answer an incoming
call before it considers the call is unanswered.
Select this to turn on the specific call forwarding rules you set up in the Advanced
Setup section of this screen.
If you have Conditional Forwarding or Unconditional Forwarding turned on as
well as specific call forwarding, the V300 applies the specific call forwarding rules
first. If the incoming number does not match a specific call forwarding rule, the
V300 applies the conditional or unconditional forwarding rule.
Select this to see which contacts (phonebook entries) are allowed to call the V300
even when DND (Do Not Disturb) is turned on.
The V300 checks these rules before it checks the rules in the Call Forward Setup
section.
This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with a specific rule. The
sequence is important, however. The V300 checks each rule in order, and it only
follows the first one that applies.
Select this to have the V300 use the specific call forwarding rule. Deselect it to
ignore the rule.
Enter the incoming phone number to which you want this rule to apply.
Enter the phone number to which you want to forward calls from this number
Select this to always forward incoming calls from this number.
NoAnswer
Busy
DND
V300 User’s Guide
Select this to forward incoming calls from this number if you do not answer the
phone within the time you set in the No Answer Time field.
Select this to forward incoming calls from this number if the V300 is in use. It does
not matter which line is being used.
Select this to forward incoming calls from this number if you have DND (Do Not
Disturb) turned on.
99
Page 100

Chapter 12 The Phone Book
Table 29 VoIP > Phone Book > Call Forward (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Apply Click this to save your settings.
Reset Click this to set every field in this screen to its last-saved value.
12.2 Contact List Screen
Use this screen to see, add and edit details of your contacts. Click VoIP > Phone Book >
Contact List. The following screen displays.
Figure 77 VoIP > Phone Book > Contact List
100
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 30 VoIP > Phone Book > Contact List
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Phone Book
Item This shows the index number of the list entry. The V300 supports up to 200
phonebook entries.
Number
Name
Group
Assign
Account
Block Select this if you want to prevent this contact from calling you.
DND White Select this if you want this contact to be able to call you even when DND (Do Not
Modify
Phone Book Table
Enter the contact’s phone number.
Enter the contact’s name.
Select the group to which you want the contact to belong. Alternatively, leave
Default selected if you do not wish to assign the contact to a group.
At the time of writing, the V300 supports a single SIP account.
Disturb) is turned on.
Click the Add button to include the new entry in the phonebook, or to save the
changes you made to an existing entry.
V300 User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...