Page 1

ZyWALL 2
Internet Security Gateway
Compact Guide
Version 3.62
April 2004
Page 2

ZyWALL 2
Table of Contents
1 Introducing the ZyWALL ............................................................................................................. 4
2 Hardware ........................................................................................................................................ 4
2.1 Rear Panel ................................................................................................................................. 5
2.2 The Front Panel LEDs............................................................................................................... 5
3 Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address..................................................................................... 7
3.1 Windows 2000/NT/XP.............................................................................................................. 7
4 Configuring Your ZyWALL ......................................................................................................... 9
4.1 Accessing Your ZyWALL Via Web Configurator.................................................................... 9
4.2 Internet Access Using the Wizard ........................................................................................... 11
4.3 Test Your Internet Connection ................................................................................................ 14
4.4 Check Your WAN Setup......................................................................................................... 15
4.5 Common Screen Command Buttons ....................................................................................... 15
5 Advanced Configuration.............................................................................................................. 16
5.1 Network Address Translation Overview ................................................................................. 16
5.2 Configuring SUA Server......................................................................................................... 16
5.3 Firewall Overview................................................................................................................... 18
5.4 Configuring Firewall............................................................................................................... 19
5.5 Procedure for Configuring Firewall Rules .............................................................................. 21
5.6 Configuring Source and Destination Addresses ...................................................................... 23
5.7 Content Filtering Overview..................................................................................................... 24
5.7.1 Restrict Web Features.................................................................................................... 24
5.7.2 Create a Filter List......................................................................................................... 24
5.7.3 Customize Web Site Access.......................................................................................... 25
5.7.4 General Content Filter Configuration............................................................................ 25
5.8 Content Filtering with an External Server............................................................................... 26
5.9 A Procedure to Enable External Database Content Filtering................................................... 26
5.10 Registering and Configuring for Category-based Filtering ....Error! Bookmark not defined.
5.11 Configuring Customization ................................................................................................... 28
5.12 VPN Overview ...................................................................................................................... 29
5.13 Summary Screen.................................................................................................................... 30
2
Page 3

ZyWALL 2
5.14 Configuring VPN Policies..................................................................................................... 32
5.14.1 X-Auth (Extended Authentication)................................................................................ 32
5.14.2 Certificates..................................................................................................................... 32
5.15 Viewing SA Monitor............................................................................................................. 40
5.16 Remote Management............................................................................................................. 40
5.16.1 HTTPS...........................................................................................................................41
5.16.2 SSH................................................................................................................................ 41
5.17 UPnP Overview..................................................................................................................... 41
5.18 Configuring UPnP ................................................................................................................. 41
6 Troubleshooting............................................................................................................................ 43
3
Page 4

ZyWALL 2
1 Introducing the ZyWALL
The ZyWALL 2 is the ideal secure gateway for all data passing between the Internet and the LAN.
By integrating NAT, firewall and VPN capability, ZyXEL’s ZyWALL 2 is a complete security
solution that protects your Intranet and efficiently manages data traffic on your network. The
embedded web configurator is easy to operate and totally independent of the operating system
platform you use.
You should have an Internet account already set up and have been given most of the following
information.
Internet Account Information
Your device’s WAN IP Address (if given): __________________
DNS Server IP Address (if given): Primary __________________, Secondary _________________
Encapsulation:
Ethernet
PPTP
PPPoE (PPPoE) Service Name: ____________
Service Type: _______________________
Login Server IP Address: ______________
User Name: ____________ Password: ____________
User Name: ____________ Password: ____________
Your WAN IP Address: ____________ PPTP Server IP Address: ___________
Connection ID (if required): ____________
User Name: ____________ Password: ____________
2 Hardware
This section provides details on hardware specifications.
4
Page 5

ZyWALL 2
2.1 Rear Panel
LABEL DESCRIPTION
1. LAN 10/100M 1-4 Connect a computer to one of these ports with an Ethernet cable. These ports are auto-
2. WAN 10/100M Connect your cable/DSL modem to this port with the cable that came with your modem.
3. POWER 12
VDC
After you’ve made the connections, connect the power cable to a power supply and look at the front panel LEDs.
CON/AUX switch
CON/AUX port
RESET You only need to use this button if you’ve forgotten the ZyWALL’s password. It returns
negotiating (can connect at 10 or 100Mbps) and auto-sensing (automatically adjust to
the type of Ethernet cable you use (straight-through or crossover).
Connect the included power adaptor (use only this adapter) to this power socket.
Only connect this port if you want to configure the ZyWALL using the SMT via console
port or set up a backup WAN connection; see your User’s Guide for details.
Set this switch to the “CON” side to use the CON/AUX port as a console port for local
device configuration and management. Connect the 9-pin male end of the console
cable to the console port of the ZyWALL and the other end to a serial port (COM1,
COM2 or other COM port) on your computer. Your computer should have a terminal
emulation communications program (such as HyperTerminal) set to VT100 terminal
emulation, no parity, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no flow control and 9600 bps port speed.
Set this switch to the “AUX” side to use the CON/AUX port as an auxiliary dial-up WAN
connection. Use the included CON/AUX converter, with the console cable to connect
the CON/AUX port to your modem or TA.
the ZyWALL to the factory defaults (password is 1234, LAN IP address 192.168.1.1,
terminal emulation settings as described above etc.; see your User’s Guide for details).
2.2 The Front Panel LEDs
The PWR LED turns on when you connect the power. The SYS LED blinks while performing
system testing and then stays on if the testing is successful. The CON/AUX, LAN, and WAN LEDs
turn on if the ports are properly connected.
5
Page 6

ZyWALL 2
LED COLOR STATUS MEANING
On The ZyWALL is turned on. PWR Green
Off The ZyWALL is turned off.
SYS Green Off The ZyWALL is not ready or failed.
LAN
10/100M
1-4
10/100M
WAN
CON/AUX Off The CON/AUX link is not ready, or has failed.
Orange Off The CON/AUX link is not ready, or has failed.
On The CON/AUX switch is set to AUX and the CON/AUX port has an
Flashing The CON/AUX switch is set to AUX and the CON/AUX port is
On The ZyWALL is ready and running.
Flashing The ZyWALL is rebooting.
Red On The power to the ZyWALL is too low.
Green
Orange
Green
Orange
Green
On
On
Flashing
Off
On
On
Flashing
Off
On The CON/AUX switch is set to CON and the CON/AUX port is
The ZyWALL has a LAN connection of 10Mbps.
The ZyWALL has a LAN connection of 100Mbps.
The ZyWALL is sending/receiving packets.
The ZyWALL does not have an Ethernet connection.
The WAN link is connected at 10Mbps.
The WAN link is connected at 100Mbps.
The WAN link is sending/receiving packets.
The WAN link is not ready, or has failed.
connected to a management computer.
Internet connection through a dial-up modem.
sending or receiving data through a dial-up modem.
6
Page 7

ZyWALL 2
3 Setting Up Your Computer’s IP Address
Skip this section if your computer is already set up to accept a dynamic IP
address. This is the default for most new computers.
The ZyWALL is already set up to assign your computer an IP address. Use this section to set up
your computer to receive an IP address or assign it a static IP address in the 192.168.1.2 to
192.168.1.254 range with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. This is necessary to ensure that your
computer can communicate with your ZyWALL.
Your computer must have an Ethernet card and TCP/IP installed. TCP/IP should already be installed
on computers using Windows NT/2000/XP, Macintosh OS 7 and later operating systems.
3.1 Windows 2000/NT/XP
1. In Windows XP, click start, Control Panel. In Windows 2000/NT, click Start, Settings, Control Panel.
2. In Windows XP, click Network Connections.
In Windows 2000/NT, click Network and Dial-up Connections.
3. Right-click Local Area Connection and then click Properties.
4. Select Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) (under the General tab in Win XP) and click Properties.
7
Page 8
ZyWALL 2
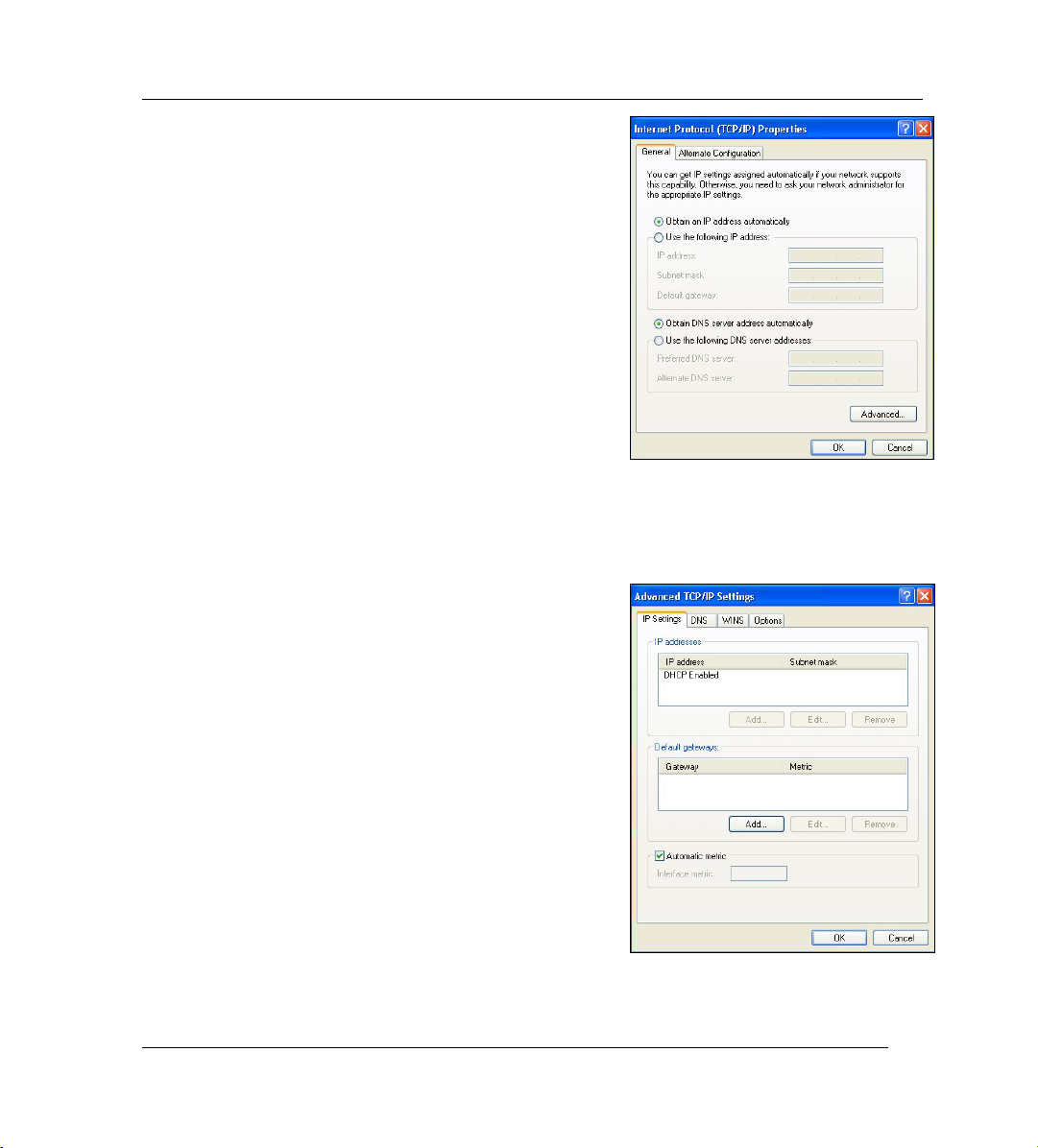
5. The Internet Protocol TCP/IP Properties screen opens (the
General tab in Windows XP).
- To have your computer assigned a dynamic IP address,
click Obtain an IP address automatically.
-To configure a static IP address, click Use the following IP
Address and fill in the IP address (choose one
from192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.254), Subnet mask
(255.255.255.0), and Default gateway (192.168.1.1) fields.
6. Click Advanced. Remove any previously installed gateways
in the IP Settings tab and click OK to go back to the Internet
Protocol TCP/IP Properties screen.
7. Click Obtain DNS server address automatically if you do
not know your DNS server IP address(es).
If you know your DNS server IP address(es), click Use the
following DNS server addresses, and type them in the
Preferred DNS server and Alternate DNS server fields.
If you have more than two DNS servers, click Advanced, the
DNS tab and then configure them using Add.
8. Click OK to close the Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) Properties
window.
9. Click OK to close the Local Area Connection Properties
window.
8
Page 9

ZyWALL 2
Checking Your Computer’s IP Address
1. In the computer, click Start, (All) Programs, Accessories and then Command Prompt.
2. In the Command Prompt window, type "ipconfig" and then press ENTER. Your computer’s IP address
must be in the correct range (192.168.1.2 to 192.168.1.254) with subnet mask 255.255.255.0 in order to
communicate with the ZyWALL.
Refer to your User’s Guide for detailed IP address configuration for other Windows and Macintosh
computer operating systems.
4 Configuring Your ZyWALL
This Compact Guide shows you how to use the web configurator wizard
only. See your User’s Guide for background information on all ZyWALL
features and System Management Terminal (SMT) configuration.
Web Configurator
4.1 Accessing Your ZyWALL Via Web Configurator
Step 1. Make sure your ZyWALL hardware is properly connected and prepare your
computer/computer network to connect to the ZyWALL (refer to the Quick Start
Guide).
Step 2. Launch your web browser.
Step 3. Type "192.168.1.1" as the URL.
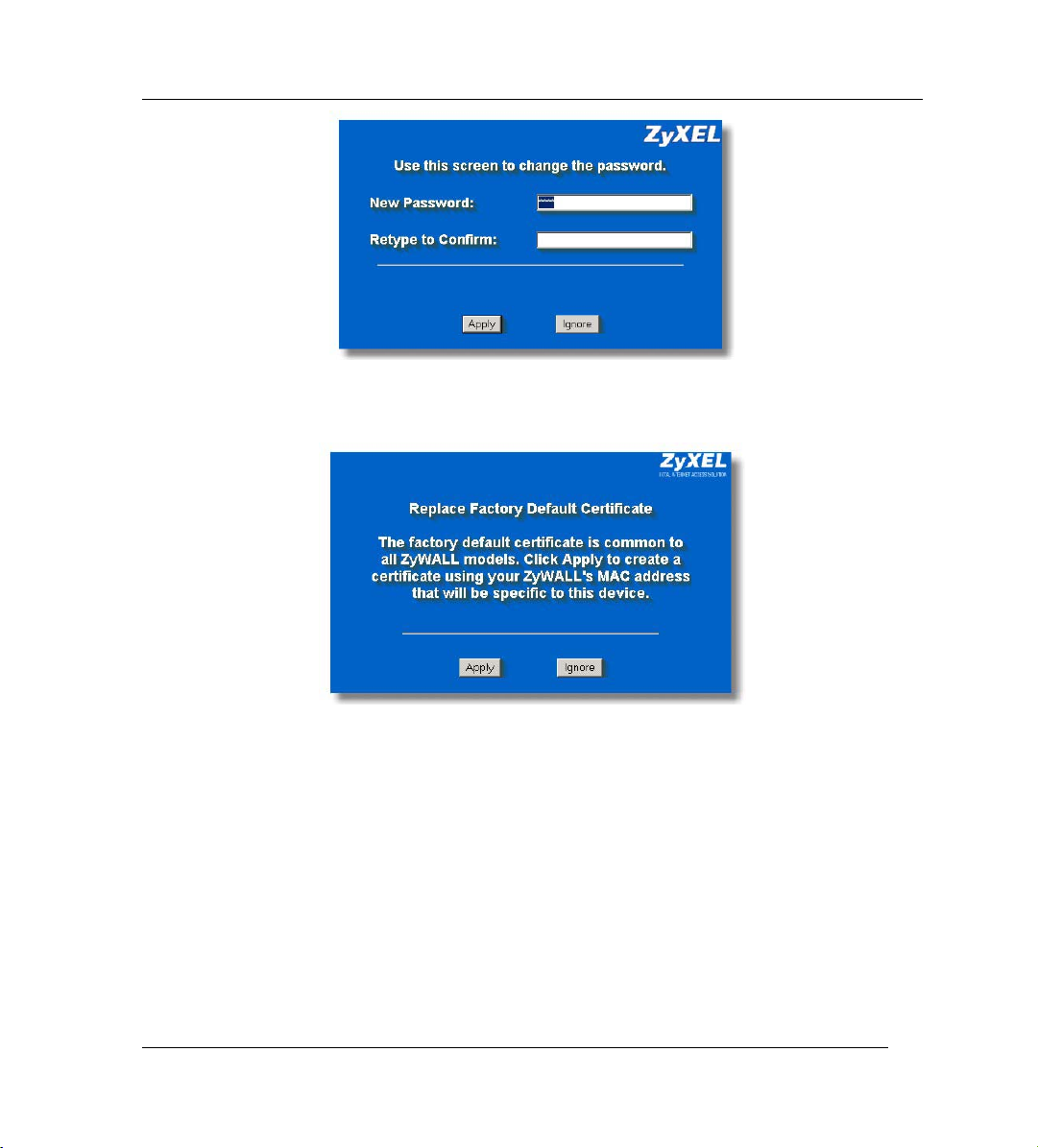
Step 4. Type "1234" (default) as the password and click Login. In some versions, the default
password appears automatically - if this is the case, click Login.
Step 5. You should see a screen asking you to change your password (highly recommended)
as shown next. Type a new password (and retype it to confirm) and click Apply or
click Ignore.
9
Page 10
ZyWALL 2
Step 6. Click Apply in the Replace Certificate screen to create a certificate using your
ZyWALL’s MAC address that will be specific to this device. This feature is not
available on the ZyWALL 2WE.
Step 7. You should now see the web configurator MAIN MENU screen.
Click WIZARD to begin a series of screens to help you configure your ZyWALL for the
first time.
Click MAINTENANCE in the navigation panel to see ZyWALL performance statistics,
upload firmware and back up, restore or upload a configuration file.
Click LOGOUT when you have finished a ZyWALL management session. The ZyWALL
automatically logs you out if it is left idle for five minutes; press ENTER to display the
Login screen again and then log back in.
10
Page 11

ZyWALL 2
Click WIZARD for initial configuration including general
setup, ISP Parameters for Internet Access and WAN
IP/DNS/MAC Address Assignment.
Use the submenus to
configure ZyWALL
features.
Click LOGOUT at any
time to exit the web
configurator.
Click MAINTENANCE to view information about your ZyWALL or
upgrade configuration/firmware files. Maintenance includes Status
(Statistics), DHCP Table, F/W (firmware) Upload, Configuration
(Backup, Restore Default) and Restart.
4.2 Internet Access Using the Wizard
Step 1. Click Wizard Setup in the main menu to display the first wizard screen.
11
Page 12

ZyWALL 2
System Name is for identification
purposes. Enter your computer's
"Computer Name".
The Domain Name entry is what is
propagated to the DHCP clients on
the LAN. If you leave this blank, the
domain name obtained by DHCP
from the ISP is used.
Click Next to continue.
Step 2. The second wizard screen has three variations depending on what encapsulation type you
use. Use the information in Internet Account Information to fill in fields.
Choose Ethernet when the WAN
port is used as a regular Ethernet.
Choose from Standard or a
RoadRunner version. You’ll need
User Name, Password and Login
Server IP Address for some
Roadrunner versions.
Click Next to continue.
12
Page 13

ZyWALL 2
Point-to-Point Protocol over
Ethernet (PPPoE) functions as a
dial-up connection. Therefore you’ll
also need a username and
password and possibly the PPPoE
service name. Your ISP will give
you all needed information.
Select Nailed Up Connection if
you do not want the connection to
the PPPoE server to time out.
Otherwise, enter the number of
seconds to elapse before the
ZyWALL disconnects from the
server in the Idle Timeout field.
The default value is 100 seconds.
Enter “0” to prevent the connection
from timing out.
Click Next to continue.
Choose PPTP if your service
provider uses a DSL terminator
with PPTP login. The ZyWALL
must have a static IP address (My
IP Address) in this case, and
possibly a subnet mask (My IP
Subnet Mask) if provided by your
ISP.
You’ll also need a username,
associated password, and the DSL
terminator IP address (Server IP
Address). If your ISP has provided
a connection ID name, enter it in
the Connection ID/Name field.
See the PPPoE encapsulation
above for information on the
Nailed Up Connection and Idle
Timeout fields.
Click Next to continue.
Step 3. Fill in the fields and click Finish to save and complete the wizard setup.
13
Page 14

ZyWALL 2
WAN IP Address
Assignment
Select Get automatically
from ISP if your ISP did not
assign you a fixed IP
address. Select Use fixed
IP address if the ISP
assigned a fixed IP address
and then enter your IP
address and subnet mask
in the next two fields. Enter
the gateway IP address in
this field (if provided) when
you select Use Fixed IP
Address.
DNS Server Assignment
Select From ISP if your ISP
dynamically assigns DNS
server information (and the
ZyWALL's WAN IP
address).
Select User-Defined if you
have the IP address of a
DNS server.
Select None if you do not
want to configure DNS
servers.
WAN MAC Address
Select Factory Default to use the factory assigned default MAC address. Alternatively, select Spoof this
Computer's MAC address - IP Address and enter the IP address of the computer on the LAN whose MAC address
you are cloning.
4.3 Test Your Internet Connection
Launch your web browser and navigate to www.zyxel.com. You don’t need a dial-up program such
as Dial Up Networking. Internet access is just the beginning. Refer to the User’s Guide for more
detailed information on the complete range of ZyWALL features. If you cannot access the Internet,
open the web configurator again to confirm that the WAN settings you configured in the Wizard
Setup are correct.
Refer to the Troubleshooting section if you have trouble logging in.
14
Page 15

4.4 Check Your WAN Setup
ZyWALL 2
Click WAN and then the WAN
ISP and WAN IP tabs.
The screens look very similar to
screens 2 and 3 in the Wizard
Setup. If the information is
incorrect, make changes and click
Apply. Click Reset to begin
configuring this screen afresh.
4.5 Common Screen Command Buttons
The following table shows common command buttons found on many web configurator screens.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the ZyWALL.
Reset Click Reset to begin configuring this screen afresh.
Cancel Click Cancel to go to the previous screen.
15
Page 16

ZyWALL 2
5 Advanced Configuration
This section shows you how to configure some of the advanced features of the ZyWALL.
5.1 Network Address Translation Overview
NAT (Network Address Translation - NAT, RFC 1631) is the translation of the IP address of a host
in a packet. For example, the source address of an outgoing packet, used within one network is
changed to a different IP address known within another network.
If you have a single public IP address then choose SUA Only in the Network Address
Translation field of the WAN ISP screen (see section 4.4). If you have multiple public IP
addresses then you may use full feature mapping types (see the User’s Guide for more details).
NAT supports five types of IP/port mapping. They are:
1. One-to-One: One-to-one mode maps one local IP address to one global IP address. Note
that port numbers do not change for One-to-One NAT mapping type.
2. Many-to-One: Many-to-One mode maps multiple local IP addresses to one global IP
address. This is equivalent to SUA (that is, PAT, port address translation), ZyXEL's Single
User Account feature.
3. Many-to-Many Overload: Many-to-Many Overload mode maps multiple local IP
addresses to shared global IP addresses.
4. Many One-to-One: Many One-to-One mode maps each local IP address to unique global
IP addresses.
5. Server: This type allows you to specify inside servers of different services behind the NAT
to be accessible to the outside world.
5.2 Configuring SUA Server
A SUA server set is a list of inside (behind NAT on the LAN) servers, for example, web or FTP,
that you can make visible to the outside world even though SUA makes your whole inside network
appear as a single computer to the outside world.
Click SUA/NAT to open the SUA Server screen.
16
Page 17

ZyWALL 2
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Default Server In addition to the servers for specified services, NAT supports a default server. A default
server receives packets from ports that are not specified in this screen. If you do not
assign a default server IP address, then all packets received for ports not specified in this
screen will be discarded.
# This is the number of an individual SUA server entry.
Active Select this check box to enable the SUA server entry. Clear this checkbox to disallow
forwarding of these ports to an inside server without having to delete the entry.
Name Enter a name to identify this port-forwarding rule.
Start Port Type a port number in this field. To forward only one port, type the port number again in
the End Port field. To forward a series of ports, type the start port number here and the
end port number in the End Port field.
End Port Type a port number in this field. To forward only one port, type the port number in the
Start Port field above and then type it again in this field. To forward a series of ports, type
the last port number in a series that begins with the port number in the Start Port field
above.
17
Page 18

ZyWALL 2
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server IP
Address
Enter the inside IP address of the server here.
5.3 Firewall Overview
The ZyWALL firewall is a stateful inspection firewall and is designed to protect against Denial of
Service attacks when activated. The ZyWALL’s purpose is to allow a private Local Area Network
(LAN) to be securely connected to the Internet. The ZyWALL can be used to prevent theft,
destruction and modification of data, as well as log events, which may be important to the security
of your network. The ZyWALL also has packet-filtering capabilities.
When activated, the firewall allows all traffic to the Internet that originates from the LAN, and
blocks all traffic to the LAN that originates from the Internet. In other words the ZyWALL will:
Allow all sessions originating from the LAN to the WAN
Deny all sessions originating from the WAN to the LAN
LAN-to-WAN rules are local network to Internet firewall rules. The default is to forward all traffic
from your local network to the Internet.
The following figure illustrates a ZyWALL firewall application.
18
Page 19

ZyWALL 2
5.4 Configuring Firewall
Click FIREWALL to open the Summary screen. Enable (or activate) the firewall by selecting the
Enable Firewall check box as seen in the following screen.
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Enable Firewall Select this check box to activate the firewall. The ZyWALL performs access control and
Bypass Triangle
Route
protects against Denial of Service (DoS) attacks when the firewall is activated.
Select this check box to have the ZyWALL firewall ignore the use of triangle route
topology on the network. See your User’s Guide- Appendices for more on triangle route
topology.
19
Page 20

ZyWALL 2
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Firewall Rules
Storage Space in
Use
Packet Direction Use the drop-down list box to select a direction of travel of packets (LAN to
Block/
Forward
Log Select the check box to create a log (when the above action is taken) for packets that are
The following read-only fields summarize the rules you have created that apply to traffic traveling in the selected
packet direction. The firewall rules that you configure (summarized below) take priority over the general firewall
action settings above.
# This is your firewall rule number. The ordering of your rules is important as rules are
Status This field displays whether a firewall is turned on (Active) or not (Inactive). Rules that
Source Address This drop-down list box displays the source addresses or ranges of addresses to which
Destination
Address
Service Type This drop-down list box displays the services to which this firewall rule applies. Please
Action This is the specified action for that rule, either Block or Forward. Note that Block means
Schedule This field tells you whether a schedule is specified (Yes) or not (No).
Log This field shows you if a log is created for packets that match the rule (Match), don't
Alert This field tells you whether this rule generates an alert (Yes) or not (No) when the rule is
Insert Type the index number for where you want to put a rule. For example, if you type “6”, your
This read-only bar shows how much of the ZyWALL's memory for recording firewall rules
it is currently using. When you are using 80% or less of the storage space, the bar is
green. When the amount of space used is over 80%, the bar is red.
LAN/ZyWALL, LAN to WAN, WAN to LAN, WAN to WAN/ZyWALL) for which you want
to configure firewall rules.
Use the option buttons to select whether to Block (silently discard) or Forward (allow the
passage of) packets that are traveling in the selected direction.
traveling in the selected direction and do not match any of the rules below.
applied in turn. The Move field below allows you to reorder your rules.
have not been configured display Empty.
this firewall rule applies. Please note that a blank source or destination address is
equivalent to Any.
This drop-down list box displays the destination addresses or ranges of addresses to
which this firewall rule applies. Please note that a blank source or destination address is
equivalent to Any.
note that a blank service type is equivalent to Any.
the firewall silently discards the packet.
match the rule (Not Match), both (Both) or no log is created (None).
matched.
new rule becomes number 6 and the previous rule 6 (if there is one) becomes rule 7.
Click Insert to display this screen and refer to the following table for information on the
fields.
20
Page 21

ZyWALL 2
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Move Select a rule’s Index option button and type a number for where you want to put that rule.
Edit Click Edit to create or edit a rule.
Delete Click Delete to delete an existing firewall rule. Note that subsequent firewall rules move
Click Move to move the rule to the number that you typed. The ordering of your rules is
important as they are applied in order of their numbering.
up by one when you take this action.
5.5 Procedure for Configuring Firewall Rules
Follow these directions to create a new rule.
Step 1. In the Summary screen, click the Insert button and enter the Rule Number before which
you want the new rule to be located.
Step 2. In the Available Services text box, select the services you want. Configure customized
ports for services not predefined by the ZyWALL by clicking the Add or Edit buttons
under Custom Port. For a comprehensive list of port numbers and services, visit the
IANA (Internet Assigned Number Authority) web site.
Step 3. Configure the Source Address and Destination Address for the rule.
21
Page 22

ZyWALL 2
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active Check the Active check box to have the ZyWALL use this rule. Leave it unchecked if
Packet Direction Use the drop-down list box to select the direction of packet travel to which you want
you do not want the ZyWALL to use the rule after you apply it
to apply this firewall rule.
22
Page 23

ZyWALL 2
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Source Address Click SrcAdd to add a new address, SrcEdit to edit an existing one or SrcDelete to
Destination
Address
Available/
Selected
Services
Custom Port
Delete Select a custom service (denoted by an “*”) from the Available Services list and
Block Services according to this schedule :
Day to Block Select everyday or the day(s) of the week to activate blocking.
Time of Day to
Block (24-Hour
Format)
Action for
Matched Packets
Log This field determines if a log is created for packets that match the rule (Match), don't
Alert Check the Alert check box to determine that this rule generates an alert when the
delete one.
Click DestAdd to add a new address, DestEdit to edit an existing one or DestDelete
to delete one.
Highlight a service from the Available Services box on the left, then click >> to add it
to the Selected Services box on the right. To remove a service, highlight it in the
Selected Services box on the right, then click <<.
Add Click this button to bring up the screen that you use to configure a new custom
service that is not in the predefined list of services.
Edit Select a custom service (denoted by an “*”) from the Available Services list and
click this button to edit the service.
click this button to remove the service.
Select All Day or enter the start and end times in the hour-minute format to activate
blocking.
Use the drop down list box to select whether to discard (Block) or allow the passage
of (Forward) packets that match this rule.
match the rule (Not Match), both (Both) or no log is created (None). Go to the Log
Settings page and select the Access Control logs category to have the ZyWALL
record these logs.
rule is matched.
5.6 Configuring Source and Destination Addresses
To add a new source or destination address, click SrcAdd or DestAdd from the previous screen. To
edit an existing source or destination address, select it from the box and click SrcEdit or DestEdit
from the previous screen. Either action displays the following screen.
23
Page 24

ZyWALL 2
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Address Type Do you want your rule to apply to packets with a particular (single) IP address, a range of
IP addresses (e.g., 192.168.1.10 to 192.169.1.50), a subnet or any IP address? Select an
option from the drop down list box
Start IP Address Enter the single IP address or the starting IP address in a range here.
End IP Address Enter the ending IP address in a range here.
Subnet Mask Enter the subnet mask here, if applicable.
5.7 Content Filtering Overview
Content filtering allows you to block certain web features, such as Cookies, and/or restrict specific
websites. With content filtering, you can do the following:
5.7.1 Restrict Web Features
The ZyWALL can block web features such as ActiveX controls, Java applets, cookies and
disable web proxies.
5.7.2 Create a Filter List
You can select categories, such as pornography or racial intolerance, to block from a predefined list.
24
Page 25

ZyWALL 2
5.7.3 Customize Web Site Access
You can specify URLs to which the ZyWALL blocks access. You can alternatively block access to
all URLs except ones that you specify. You can also have the ZyWALL block access to URLs that
contain key words that you specify.
5.7.4 General Content Filter Configuration
Click CONTENT FILTER to open the CONTENT FILTERING screen. The General tab
displays as shown. Use this screen to enable content filtering, configure a schedule, and create a
denial message. You can also choose specific computers to be included in or excluded from the
content filtering configuration.
25
Page 26

ZyWALL 2
5.8 Content Filtering with an External Server
Your ZyWALL uses an application services company that provides outsourced content filtering. If
you enable the content filter, your ZyWALL will have access to an external database, which
contains dynamically updated ratings of millions of web sites. The content filtering lookup process
is described below.
5.9 A Procedure to Enable External Database Content
Filtering
The following is an example procedure for using external database content filtering.
Step 1. Enable content filtering in the Content Filtering General screen.
Step 2. In the Content Filtering Categories screen, register for external database content
filtering.
Step 3. In the Content Filtering Categories screen, select Enable External Database Content
Filtering.
Step 4. In the Content Filtering Categories screen, select Block Matched Web Pages.
Step 5. In the Content Filtering Categories screen, select categories to block.
5.10 Configuring for Registering and Categories
To register for and configure category-based content filtering, click CONTENT FILTER, and then
the Categories tab. The screen appears as shown.
26
Page 27

ZyWALL 2
Click Register to go to a web site where you can register for category-based content filtering (using
an external database). You can use a trial application or register your iCard’s PIN. Refer to the web
site’s on-line help for details.
27
Page 28

ZyWALL 2
The web site displays a registration successful web page. It may take up to
another ten minutes for content filtering to be activated.
You can manage your registration status or view content filtering reports after you register this
device.
You may not be able to access the web site if you have enabled content filtering in the Content
Filter General screen and blocked access to web pages that use Java and/or cookies.
Do not close the Web Configurator’s window during the registration
process.
5.11 Configuring Customization
To customize the content filter list by adding or removing specific sites from the filter list on your
ZyWALL, click CONTENT FILTER, then the Customization tab. The screen appears as shown.
28
Page 29

ZyWALL 2
5.12 VPN Overview
A VPN (Virtual Private Network) provides secure communications between sites without the
expense of leased site-to-site lines. A secure VPN is a combination of tunneling, encryption,
authentication, access control and auditing technologies/services used to transport traffic over the
Internet or any insecure network that uses the TCP/IP protocol suite for communication.
29
Page 30

ZyWALL 2
5.13 Summary Screen
The following figure provides an example of a VPN application.
Local and remote IP addresses must be static.
Click VPN to open the Summary screen. This is a read-only menu of your IPSec rules (tunnels).
Edit or create an IPSec rule by selecting an index number and then clicking Edit to configure the
associated submenus.
30
Page 31

ZyWALL 2
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This field displays the VPN rule number.
Name This field displays the identification name for this VPN policy.
Active Y signifies that this VPN rule is active.
Local IP
Address
Remote IP
Address
Encap. This field displays Tunnel or Transport mode (Tunnel is the default selection).
This is the IP address(es) of computer(s) on your local network behind your ZyWALL.
The same (static) IP address is displayed twice when the Local Address Type field in the
Edit VPN Rule (or Manual Key) screen is configured to Single Address.
The beginning and ending (static) IP addresses, in a range of computers are displayed when
the Local Address Type field in the Edit VPN Rule (or Manual Key) screen is configured to
Range Address.
A (static) IP address and a subnet mask are displayed when the Local Address Type field
in the Edit VPN Rule (or Manual Key) screen is configured to Subnet Address.
This is the IP address(es) of computer(s) on the remote network behind the remote IPSec
router.
This field displays N/A when the Secure Gateway Address field displays 0.0.0.0. In this
case only the remote IPSec router can initiate the VPN.
The same (static) IP address is displayed twice when the Remote Address Type field in the
Edit VPN Rule (or Manual Key) screen is configured to Single Address.
The beginning and ending (static) IP addresses, in a range of computers are displayed when
the Remote Address Type field in the Edit VPN Rule (or Manual Key) screen is configured
to Range Address.
A (static) IP address and a subnet mask are displayed when the Remote Address Type
field in the Edit VPN Rule (or Manual Key) screen is configured to Subnet Address.
31
Page 32

ZyWALL 2
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IPSec
Algorithm
This field displays the security protocols used for an SA.
Both AH and ESP increase ZyWALL processing requirements and communications latency
(delay).
Secure
Gateway
Address
Edit Click Edit to edit the VPN policy.
Delete Click Delete to remove the VPN policy.
This is the static WAN IP address or URL of the remote IPSec router. This field displays
0.0.0.0 when you configure the Secure Gateway Address field in the Edit VPN Rule screen
to 0.0.0.0.
5.14 Configuring VPN Policies
5.14.1 X-Auth (Extended Authentication)
Extended authentication provides added security by allowing you to use usernames and passwords
for VPN connections. This is especially helpful when multiple ZyWALLs use one VPN rule to
connect to a single ZyWALL. An attacker cannot make a VPN connection without a valid username
and password.
The extended authentication server checks the user names and passwords of the extended
authentication clients before completing the IPSec connection.
A ZyWALL can be an extended authentication server for some VPN connections and an extended
authentication client for other VPN connections.
5.14.2 Certificates
The ZyWALL can use certificates (also called digital IDs) to authenticate users. Certificates are
based on public-private key pairs. Certificates provide a way to exchange public keys for use in
authentication.
32
Page 33

ZyWALL 2
Click Edit on the Summary screen to edit VPN policies.
33
Page 34

ZyWALL 2
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Active
Keep Alive
NAT Traversal Select this check box to enable NAT traversal. NAT traversal allows you to set up a VPN connection
Name Type up to 32 characters to identify this VPN policy. You may use any character, including spaces,
Key Management
(or IPSec Keying
Mode)
Negotiation Mode Select Main or Aggressive from the drop-down list box. Multiple SAs connecting through a secure
Enable Extended
Authentication
Select this check box to activate this VPN tunnel. This option determines whether a VPN rule is
applied before a packet leaves the firewall.
Select this check box to turn on the keep alive feature for this SA.
Turn on Keep Alive to have the ZyWALL automatically reinitiate the SA after the SA lifetime times out,
even if there is no traffic. The remote IPSec router must also have keep alive enabled in order for this
feature to work.
when there are NAT routers between the two IPSec routers.
The remote IPSec router must also have NAT traversal enabled.
You can use NAT traversal with ESP protocol using Transport or Tunnel mode, but not with AH
protocol nor with manual key management. In order for an IPSec router behind a NAT router to
receive an initiating IPSec packet, set the NAT router to forward UDP port 500 to the IPSec router
behind the NAT router.
but the ZyWALL drops trailing spaces.
Select IKE or Manual Key from the drop-down list box. IKE provides more protection so it is generally
recommended. Manual Key is a useful option for troubleshooting.
gateway must have the same negotiation mode.
Select this check box to activate extended authentication.
Server Mode Select Server Mode to have this ZyWALL authenticate extended authentication clients that request
this VPN connection.
You must also configure the extended authentication clients’ usernames and passwords in the auth
server’s local user database or a RADIUS server.
Click Local User to go to the Local User Database screen where you can view and/or edit the list of
users and passwords. Click RADIUS to go to the RADIUS screen where you can configure the
ZyWALL to check an external RADIUS server.
During authentication, if the extended authentication server does not find the extended authentication
clients’ user name in its internal user database and an external RADIUS server has been enabled, it
attempts to authenticate the client through the RADIUS server.
34
Page 35

ZyWALL 2
Client Mode Select Client Mode to have your ZyWALL use a username and password when initiating this VPN
User Name Enter a user name for your ZyWALL to be authenticated by the external extended authentication
Password Enter the corresponding password for the above user name. The password can be up to 31 case-
Local:
Local IP addresses must be static and correspond to the remote IPSec router's configured remote IP addresses.
Two active SAs can have the same configured local or remote IP address, but not both. You can configure multiple SAs
between the same local and remote IP addresses, as long as only one is active at any time.
In order to have more than one active rule with the Secure Gateway Address field set to 0.0.0.0, the ranges of the local IP
addresses cannot overlap between rules.
If you configure an active rule with 0.0.0.0 in the Secure Gateway Address field and the LAN’s full IP address range as the
local IP address, then you cannot configure any other active rules with the Secure Gateway Address field set to 0.0.0.0.
Client to Site Select this radio button to build a client to site VPN connection.
Local IP Address Enter a static local IP address. The local IP address must correspond to the remote IPSec router's
Site to Site Select this radio button to establish a VPN between two sites (groups of IP addresses).
Address Type Use the drop-down menu to choose Range Address or Subnet Address. Select Range Address for
connection to the extended authentication server ZyWALL. Only a VPN extended authentication client
can initiate this VPN connection.
server. The user name can be up to 31 case-sensitive ASCII characters, but spaces are not allowed.
You must enter a user name and password when you select client mode.
sensitive ASCII characters, but spaces are not allowed.
configured remote IP addresses.
a specific range of IP addresses. Select Subnet Address to specify IP addresses on a network by
their subnet mask.
Starting IP Address When the Address Type field is configured to Range Address, enter the beginning (static) IP
Ending IP Address/
Subnet Mask
address, in a range of computers on your LAN behind your ZyWALL. When the Address Type field is
configured to Subnet Address, this is a (static) IP address on the LAN behind your ZyWALL.
When the Address Type field is configured to Range Address, enter the end (static) IP address, in a
range of computers on the LAN behind your ZyWALL. When the Address Type field is configured to
Subnet Address, this is a subnet mask on the LAN behind your ZyWALL.
35
Page 36

ZyWALL 2
Remote:
Remote IP addresses must be static and correspond to the remote IPSec router's configured local IP addresses. The
remote fields do not apply when the Secure Gateway Address field is configured to 0.0.0.0. In this case only the remote
IPSec router can initiate the VPN.
Two active SAs cannot have the local and remote IP address(es) both the same. Two active SAs can have the same local
or remote IP address, but not both. You can configure multiple SAs between the same local and remote IP addresses, as
long as only one is active at any time.
Address Type Use the drop-down menu to choose Single Address, Range Address, or Subnet Address. Select
Starting IP Address When the Address Type field is configured to Single Address, enter a (static) IP address on the
Ending IP Address/
Subnet Mask
DNS Server (for
IPSec VPN)
Authentication Key
Pre-Shared Key Select the Pre-Shared Key radio button and type your pre-shared key in this field. A pre-shared key
Single Address with a single IP address. Select Range Address for a specific range of IP
addresses. Select Subnet Address to specify IP addresses on a network by their subnet mask.
network behind the remote IPSec router. When the Addr Type field is configured to Range Address,
enter the beginning (static) IP address, in a range of computers on the network behind the remote
IPSec router. When the Address Type field is configured to Subnet Address, enter a (static) IP
address on the network behind the remote IPSec router.
When the Address Type field is configured to Single Address, this field is N/A. When the Address
Type field is configured to Range Address, enter the end (static) IP address, in a range of computers
on the network behind the remote IPSec router. When the Address Type field is configured to
Subnet Address, enter a subnet mask on the network behind the remote IPSec router.
If there is a private DNS server that services the VPN, type its IP address here. The ZyWALL assigns
this additional DNS server to the ZyWALL's DHCP clients that have IP addresses in this IPSec rule's
range of local addresses.
A DNS server allows clients on the VPN to find other computers and servers on the VPN by their
(private) domain names.
identifies a communicating party during a phase 1 IKE negotiation. It is called "pre-shared" because
you have to share it with another party before you can communicate with them over a secure
connection.
Type from 8 to 31 case-sensitive ASCII characters or from 16 to 62 hexadecimal ("0-9", "A-F")
characters. You must precede a hexadecimal key with a "0x” (zero x), which is not counted as part of
the 16 to 62 character range for the key. For example, in "0x0123456789ABCDEF", “0x” denotes that
the key is hexadecimal and “0123456789ABCDEF” is the key itself.
Both ends of the VPN tunnel must use the same pre-shared key. You will receive a
“PYLD_MALFORMED” (payload malformed) packet if the same pre-shared key is not used on both
ends.
36
Page 37

ZyWALL 2
Certificate Select the Certificate radio button to identify the ZyWALL by a certificate.
Use the drop-down list box to select the certificate to use for this VPN tunnel. You must have
certificates already configured in the My Certificates screen. Click My Certificates to go to the My
Certificates screen where you can view the ZyWALL's list of certificates.
Local ID Type Select IP to identify this ZyWALL by its IP address.
Content When you select IP in the Local ID Type field, type the IP address of your computer in the local
Peer ID Type Select from the following when you set Authentication Method to Pre-shared Key.
Select DNS to identify this ZyWALL by a domain name.
Select E-mail to identify this ZyWALL by an e-mail address.
You do not configure the local ID type and content when you set Authentication Method to
Certificate. The ZyWALL takes them from the certificate you select.
Content field. The ZyWALL automatically uses the IP address in the My IP Address field (refer to the
My IP Address field description) if you configure the local Content field to 0.0.0.0 or leave it blank.
It is recommended that you type an IP address other than 0.0.0.0 in the local Content field or use the
DNS or E-mail ID type in the following situations.
When there is a NAT router between the two IPSec routers.
When you want the remote IPSec router to be able to distinguish between VPN connection
requests that come in from IPSec routers with dynamic WAN IP addresses.
When you select DNS or E-mail in the Local ID Type field, type a domain name or e-mail address by
which to identify this ZyWALL in the local Content field. Use up to 31 ASCII characters including
spaces, although trailing spaces are truncated. The domain name or e-mail address is for
identification purposes only and can be any string.
Select IP to identify the remote IPSec router by its IP address.
Select DNS to identify the remote IPSec router by a domain name.
Select E-mail to identify the remote IPSec router by an e-mail address.
Select from the following when you set Authentication Method to Certificate.
Select IP to identify the remote IPSec router by the IP address in the subject alternative
name field of the certificate it uses for this VPN connection.
Select DNS to identify the remote IPSec router by the domain name in the subject
alternative name field of the certificate it uses for this VPN connection.
Select E-mail to identify the remote IPSec router by the e-mail address in the subject
alternative name field of the certificate it uses for this VPN connection.
Select Subject Name to identify the remote IPSec router by the subject name of the
certificate it uses for this VPN connection.
Select Any to have the ZyWALL not check the remote IPSec router's ID.
37
Page 38

ZyWALL 2
Content The configuration of the peer content depends on the peer ID type.
Do the following when you set Authentication Method to Pre-shared Key.
For IP, type the IP address of the computer with which you will make the VPN connection. If
you configure this field to 0.0.0.0 or leave it blank, the ZyWALL will use the address in the
Secure Gateway Address field (refer to the Secure Gateway Address field description).
For DNS or E-mail, type a domain name or e-mail address by which to identify the remote
IPSec router. Use up to 31 ASCII characters including spaces, although trailing spaces are
truncated. The domain name or e-mail address is for identification purposes only and can
be any string.
It is recommended that you type an IP address other than 0.0.0.0 or use the DNS or E-mail ID type in
the following situations:
When there is a NAT router between the two IPSec routers.
When you want the ZyWALL to distinguish between VPN connection requests that come in
from remote IPSec routers with dynamic WAN IP addresses.
Do the following when you set Authentication Method to Certificate.
For IP, type the IP address from the subject alternative name field of the certificate the
remote IPSec router will use for this VPN connection. If you configure this field to 0.0.0.0 or
leave it blank, the ZyWALL will use the address in the Secure Gateway Address field
(refer to the Secure Gateway Address field description).
For DNS or E-mail, type the domain name or e-mail address from the subject alternative
name field of the certificate the remote IPSec router will use for this VPN connection.
For Subject Name, type the subject name of the certificate the remote IPSec router will use
for this VPN connection.
For Any, the peer Content field is not available.
Regardless of how you configure the ID Type and Content fields, two active SAs cannot have both
the local and remote IP address ranges overlap between rules.
My IP Address Enter the WAN IP address of your ZyWALL. The VPN tunnel has to be rebuilt if this IP address
changes.
The following applies if this field is configured as 0.0.0.0:
The ZyWALL uses the current ZyWALL WAN IP address (static or dynamic) to set up the VPN
tunnel.
If the WAN connection goes down, the ZyWALL uses the dial backup IP address for the VPN
tunnel when using dial backup or the LAN IP address when using traffic redirect. See the User’s
Guide for details on dial backup and traffic redirect.
38
Page 39

ZyWALL 2
Secure Gateway
Address
Encapsulation Mode Select Tunnel mode or Transport mode from the drop-down list box.
ESP Select ESP if you want to use ESP (Encapsulation Security Payload). The ESP protocol (RFC 2406)
Encryption Algorithm Select DES, 3DES, AES or NULL from the drop-down list box.
Authentication
Algorithm
Type the WAN IP address or the URL (up to 31 characters) of the IPSec router with which you're
making the VPN connection. Set this field to 0.0.0.0 if the remote IPSec router has a dynamic WAN IP
address (the Key Management (or IPSec Keying Mode) field must be set to IKE).
In order to have more than one active rule with the Secure Gateway Address field set to 0.0.0.0, the
ranges of the local IP addresses cannot overlap between rules.
If you configure an active rule with 0.0.0.0 in the Secure Gateway Address field and the LAN’s full IP
address range as the local IP address, then you cannot configure any other active rules with the
Secure Gateway Address field set to 0.0.0.0.
provides encryption as well as some of the services offered by AH. If you select ESP here, you must
select options from the Encryption Algorithm and Authentication Algorithm fields (described
below).
When you use one of these encryption algorithms for data communications, both the sending device
and the receiving device must use the same secret key, which can be used to encrypt and decrypt the
message or to generate and verify a message authentication code. The DES encryption algorithm
uses a 56-bit key. Triple DES (3DES) is a variation on DES that uses a 168-bit key. As a result, 3DES
is more secure than DES. It also requires more processing power, resulting in increased latency and
decreased throughput. This implementation of AES uses a 128-bit key. AES is faster than 3DES.
Select NULL to set up a tunnel without encryption. When you select NULL, you do not enter an
encryption key.
Select SHA1 or MD5 from the drop-down list box. MD5 (Message Digest 5) and SHA1 (Secure Hash
Algorithm) are hash algorithms used to authenticate packet data. The SHA1 algorithm is generally
considered stronger than MD5, but is slower. Select MD5 for minimal security and SHA-1 for
maximum security.
AH Select AH if you want to use AH (Authentication Header Protocol). The AH protocol (RFC 2402) was
Authentication
Algorithm
Advanced Click Advanced to configure more detailed settings of your IKE key management.
designed for integrity, authentication, sequence integrity (replay resistance), and non-repudiation but
not for confidentiality, for which the ESP was designed. If you select AH here, you must select options
from the Authentication Algorithm field (described below).
Select SHA1 or MD5 from the drop-down list box. MD5 (Message Digest 5) and SHA1 (Secure Hash
Algorithm) are hash algorithms used to authenticate packet data. The SHA1 algorithm is generally
considered stronger than MD5, but is slower. Select MD5 for minimal security and SHA-1 for
maximum security.
39
Page 40

ZyWALL 2
5.15 Viewing SA Monitor
A Security Association (SA) is the group of security settings related to a specific VPN tunnel. This
screen displays active VPN connections. Use Refresh to display active VPN connections. This
screen is read-only.
In the web configurator, click VPN and the SA Monitor tab to view Security Associations.
When there is outbound traffic but no inbound traffic, the SA times out
automatically after two minutes. A tunnel with no outbound or inbound
traffic is "idle" and does not timeout until the SA lifetime period expires.
5.16 Remote Management
Remote management allows you to determine which services/protocols can access which ZyWALL
interface (if any) from which computers.
When you configure remote management to allow management from the
WAN, you still need to configure a firewall rule to allow access. See the
firewall chapters for details on configuring firewall rules.
You may manage your ZyWALL from a remote location via:
Internet (WAN only) ALL (LAN and WAN)
LAN only, Neither (Disable).
When you Choose WAN only or ALL (LAN & WAN), you still need to
configure a firewall rule to allow access.
To disable remote management of a service, select Disable in the corresponding Server Access
field.
You may only have one remote management session running at a time. The ZyWALL automatically
disconnects a remote management session of lower priority when another remote management
session of higher priority starts. The priorities for the different types of remote management sessions
are as follows.
1. Console port
2. SSH
3. Telnet
4. HTTPS and HTTP
40
Page 41

ZyWALL 2
5.16.1 HTTPS
HTTPS (HyperText Transfer Protocol over Secure Socket Layer, or HTTP over SSL) is a web
protocol that encrypts and decrypts web sessions. Secure Socket Layer (SSL) is an application-level
protocol that enables secure transactions of data by ensuring confidentiality (an unauthorized party
cannot read the transferred data), authentication (one party can identify the other party) and data
integrity (you know if data has been changed).
HTTPS on the ZyWALL relies upon certificates, public keys, and private keys to securely access
the ZyWALL using the web configurator. The SSL protocol specifies that the SSL server (the
ZyWALL) must always authenticate itself to the SSL client (the computer which requests the
HTTPS connection with the ZyWALL), whereas the SSL client only should authenticate itself when
the SSL server requires it to do so (select Authenticate Client Certificates in the Remote Mngt,
WWW screen). Authenticate Client Certificates is optional and if selected means the SSL-client
must send the ZyWALL a certificate. You must apply for a certificate for the browser from a CA
that is a trusted CA on the ZyWALL.
5.16.2 SSH
SSH (Secure Shell) is a secure communication protocol that combines authentication and data
encryption to provide secure encrypted communication between two hosts over an unsecured
network.
5.17 UPnP Overview
Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a distributed, open networking standard that uses TCP/IP for
simple peer-to-peer network connectivity between devices. A UPnP device can dynamically join a
network, obtain an IP address, convey its capabilities and learn about other devices on the network.
In turn, a device can leave a network smoothly and automatically when it is no longer in use.
All UPnP-enabled devices may communicate freely with each other without additional
configuration. Disable UPnP if this is not your intention.
Windows ME and Windows XP support UPnP. See the Microsoft website for information about
other Microsoft operating systems.
5.18 Configuring UPnP
Click UPnP to open the UPnP screen.
41
Page 42

ZyWALL 2
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device Name This identifies the device in UPnP applications.
Enable the Universal Plug
and Play (UPnP) feature
Allow users to make
configuration changes
through UPnP
Allow UPnP to pass through
Firewall
Select this checkbox to activate UPnP. Be aware that anyone could use a UPnP
application to open the web configurator's login screen without entering the
ZyWALL's IP address (although you must still enter the password to access the
web configurator).
Select this check box to allow UPnP-enabled applications to automatically
configure the ZyWALL so that they can communicate through the ZyWALL, for
example by using NAT traversal, UPnP applications automatically reserve a NAT
forwarding port in order to communicate with another UPnP enabled device; this
eliminates the need to manually configure port forwarding for the UPnP enabled
application.
Select this check box to allow traffic from UPnP-enabled applications to bypass
the firewall.
Clear this check box to have the firewall block all UPnP application packets (for
example, MSN packets).
42
Page 43

ZyWALL 2
6 Troubleshooting
For advanced troubleshooting help, see the Logs section in the User’s Guide.
PROBLEM CORRECTIVE ACTION
None of the LEDs turn
on when you turn on
the ZyWALL.
Cannot access the
ZyWALL from the LAN.
Cannot ping any
computer on the LAN.
Cannot get a WAN IP
address from the ISP.
Cannot access the
Internet.
Make sure that you have the correct power adaptor connected to the ZyWALL and
plugged in to an appropriate power source. Check all cable connections.
If the LEDs still do not turn on, you may have a hardware problem. In this case, you
should contact your local vendor.
Check the cable connection between the ZyWALL and your computer or hub. Refer
to the Rear Panel section for details.
Ping the ZyWALL from a LAN computer. Make sure your computer Ethernet card is
installed and functioning properly.
If the 10/100M LAN LEDs are off, check the cable connections between the ZyWALL
and your LAN computers.
Verify that the IP address and subnet mask of the ZyWALL and the LAN computers
are in the same IP address range.
The WAN IP is provided after the ISP verifies the MAC address, host name or user
ID.
Find out the verification method used by your ISP and configure the corresponding
fields.
If the ISP checks the WAN MAC address, you should clone the MAC address from a
LAN computer. Click WAN and then the MAC tab, select Spoof this Computer's
MAC address - IP Address and enter the IP address of the computer on the LAN
whose MAC address you are cloning.
If the ISP checks the host name, enter your computer’s name (refer to the Wizard
Setup section in the User’s Guide) in the System Name field in the first screen of the
WIZARD.
If the ISP checks the user ID, click WAN and then the ISP tab. Check your service
type, user name, and password.
Check the ZyWALL’s connection to the cable/DSL device.
Check whether your cable/DSL device requires a crossover or straight-through cable.
Click WAN to verify your settings.
Check that you entered the password correctly. Some ISPs may lock you out after
several unsuccessful attempts.
43
 Loading...
Loading...