
Quick Start Guide
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series
VPN Firewall
Version 3.10
Edition 4, 01/2014
User’s Guide
Default Login Details
LAN Port IP Address https://192.168.1.1
User Name admin
Password 1234
www.zyxel.com
Copyright © 2014 ZyXEL Communications Corporation

IMPORTANT!
READ CAREFULLY BEFORE USE.
KEEP THIS GUIDE FOR FUTURE REFERENCE.
This is a User’s Guide for a series of products. Not all products support all firmware features.
Screenshots and graphics in this book may differ slightly from your product due to differences in
your product firmware or your computer operating system. Every effort has been made to ensure
that the information in this manual is accurate.
Screen Identification Syntax Convention
The > symbol is used to identify a mouse click in a path to access a screen in the web configurator.
For example, Configuration > Network > Interface > Ethernet means first you click the
Configuration icon in the navigation panel, then click the Network menu item, then the
Interface submenu and finally the Ethernet tab in order to access the Ethernet interface screen.
Related Documentation
•Quick Start Guide
The Quick Start Guide shows how to connect the ZyWALL and access the Web Configurator
wizards. (See the wizard real time help for i n formation on configuring each screen.) It also
contains a connection diagram and package contents list.
• CLI Reference Guide
The CLI Reference Guide explains how to use the Command-Line Interface (CLI) to configure the
ZyWALL.
Note: It is recommended you use the Web Configurator to configure the ZyWALL.
• Web Configurator Online Help
Click the help icon in any screen for help in configuring that screen and supplementary
information.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide2

Part I: User’s Guide .........................................................................................16
Chapter 1
Introduction.........................................................................................................................................18
1.1 Overview ...................................................... .......................................... .... ... ....................................18
1.2 Management Overview ....................................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ..............................20
1.3 Web Configurator ................................................ ... .......................................... ... .... ..........................21
1.3.1 Web Configurator Access ........................................................................................................21
1.3.2 Web Configurator Screens Overview ......................................................................................22
1.3.3 Navigation Panel .......... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... .................................................................................26
1.3.4 Tables and Lists .. ... .... ... ... ... .......................................... .... .......................................................29
Chapter 2
Installation Setup Wizard...................................................................................................................33
2.1 Installation Setup Wizard Screens ...................................................................................................33
2.1.1 Internet Access Setup - WAN Interface ..................................................................................33
2.1.2 Internet Access: Ethernet .......................................................................................................34
2.1.3 Internet Access: PPPoE ............................ ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ..........34
2.1.4 Internet Access: PPTP .......................................... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ..........35
2.1.5 ISP Parameters ............................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ... ....................35
2.1.6 Internet Access - Finish ..........................................................................................................36
Chapter 3
Hardware Introduction .......................................................................................................................37
3.1 Default Zones, Interfaces, and Ports ............................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ...........................................37
3.2 Stopping the ZyWALL .......................................................................................................................38
3.3 Rack-mounting .......... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ..............................................................38
3.4 Wall-mounting .................................................. ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... .......................39
3.5 Front Panel LEDs ...... ... .......................................... ... .... ... ... ... ...........................................................39
3.5.1 Rear Panels ........................ .... .......................................... ... ... .................................................41
Chapter 4
Quick Setup Wizards..........................................................................................................................42
4.1 Quick Setup Overview ......................... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... .... ..........................42
4.2 WAN Interface Quick Setup ..............................................................................................................42
4.2.1 Choose an Ethernet Interface .......... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... .......................................43
4.2.2 Select WAN Type .......................... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... .......................43
4.2.3 Configure WAN Settings ..........................................................................................................44
4.2.4 WAN and ISP Connection Settings .........................................................................................44
4.2.5 Quick Setup Interface Wizard: Summary ................................................................................46
4.3 VPN Setup Wizard ............................................................................................................................47
4.3.1 Welcome ....... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................... ... .... .......................................................47
4.3.2 VPN Setup Wizard: Wizard Type .............................................................................................48
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
3

4.3.3 VPN Express Wizard - Scenario .............................................................................................49
4.3.4 VPN Express Wizard - Configuration ....................... ... .... ... ... ... .......................................... ... .50
4.3.5 VPN Express Wizard - Summary ....................... .......................................... ..........................50
4.3.6 VPN Express Wizard - Finish .................................................................................................51
4.3.7 VPN Advanced Wizard - Scenario .........................................................................................52
4.3.8 VPN Advanced Wizard - Phase 1 Settings .............................................................................53
4.3.9 VPN Advanced Wizard - Phase 2 ...........................................................................................55
4.3.10 VPN Advanced Wizard - Summary ......................................................................................56
4.3.11 VPN Advanced Wizard - Finish ...................................... ... ... .................................................56
4.4 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Wizard: Wizard Type .............................. ... .................57
4.4.1 Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard - VPN Settings ...................................................58
4.4.2 Configuration Provisioning VPN Express Wizard - Configuration ..........................................59
4.4.3 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard - Summary .............................60
4.4.4 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard - Finish ...................................61
4.4.5 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard - Scenario ...........................62
4.4.6 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard - Phase 1 Settings ..............63
4.4.7 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard - Phase 2 ............................64
4.4.8 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard - Summary ..........................65
4.4.9 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard- Finish .................................65
Chapter 5
Dashboard...........................................................................................................................................67
5.1 Overview ................ ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... .................................................................67
5.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ............................................................................................67
5.2 The Dashboard Screen .....................................................................................................................67
5.2.1 The CPU Usage Screen ..........................................................................................................72
5.2.2 The Memory Usage Screen ............... .... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... ... .... ... .......73
5.2.3 The Active Sessions Screen ....................................................................................................73
5.2.4 The VPN Status Screen .......................................... ... ... .......................................... ... .... ..........74
5.2.5 The DHCP Table Screen .........................................................................................................75
5.2.6 The Number of Login Users Screen .......................................................................................76
Part II: Technical Reference............................................................................77
Chapter 6
Monitor.................................................................................................................................................79
6.1 Overview ................ ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... .................................................................79
6.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ............................................................................................79
6.2 The Port Statistics Screen ................................................................................................................80
6.2.1 The Port Statistics Graph Screen ....................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... .......................................81
6.3 Interface Status Screen .....................................................................................................................82
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide4

6.4 The Traffic Statistics Screen ..............................................................................................................86
6.5 The Session Monitor Screen ........... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ............................................. ..............89
6.6 The DDNS Status Screen .................................................................................................................91
6.7 IP/MAC Binding Monitor .. .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... .... ..........................91
6.8 The Login Users Screen ..................................................................................................................92
6.9 Cellular Status Screen ......................................................... .......................................... . ...................93
6.9.1 More Information ... .... ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... ... .... .......................................95
6.10 USB Storage Screen .......................................................................................................................96
6.11 The IPSec Monitor Screen ..............................................................................................................97
6.11.1 Regular Expressions in Searching IPSec SAs .......................................................................98
6.12 The SSL Connection Monitor Screen ................................ ....... ...... ...... ....... ...... ....... ...... ....... ..........99
6.13 The L2TP over IPSec Session Monitor Screen ...............................................................................99
6.14 Log Screen ....................................................................................................................................100
Chapter 7
Interfaces...........................................................................................................................................103
7.1 Interface Overview ................. ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................... ... .... ... .....................103
7.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................103
7.1.2 What You Need to Know .................................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... .....................................103
7.1.3 What You Need to Do First ........................................................ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ............108
7.2 Port Role Screen .............................................................................................................................108
7.3 Ethernet Summary Screen .. ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...............................109
7.3.1 Ethernet Edit ...................... .... ... .......................................... ... ... ............................................110
7.3.2 Object References .............. .... ... ... .......................................... ... ... .........................................122
7.3.3 Add/Edit DHCPv6 Request/Release Options ............ ... .... ... ... .......................................... ... ..123
7.3.4 Add/Edit DHCP Extended Options ................................... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..124
7.4 PPP Interfaces ................................................................................................................................125
7.4.1 PPP Interface Summary ........................................................................................................126
7.4.2 PPP Interface Add or Edit .....................................................................................................127
7.5 Cellular Configuration Screen (3G) .................................................................................................132
7.5.1 Cellular Add/Edit Screen .......................................................................................................134
7.6 Tunnel Interfaces ...................... .......................................... ... .... .....................................................140
7.6.1 Configuring a Tunnel .............................. ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ..................................................142
7.6.2 Tunnel Add or Edit Screen .....................................................................................................143
7.7 VLAN Interfaces .............................................................................................................................147
7.7.1 VLAN Summary Screen ........................................................................................................148
7.7.2 VLAN Add/Edit ......................................................................................................................150
7.8 Bridge Interfaces ............................................................................................................................159
7.8.1 Bridge Summary ........................ ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..................160
7.8.2 Bridge Add/Edit .....................................................................................................................162
7.9 Virtual Interfaces ............................................................................................................................170
7.9.1 Virtual Interfaces Add/Edit ............... ... .... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ..................171
7.10 Interface Technical Reference .......................................................................................................172
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
5

Chapter 8
Trunk..................................................................................................................................................176
8.1 Overview ................ ... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ...............................................................176
8.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................176
8.1.2 What You Need to Know .................................. .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... .....................................176
8.2 The Trunk Summary Screen ...........................................................................................................179
8.2.1 Configuring a User-Defined Trunk ............. ............................................................................180
8.2.2 Configuring the System Default Trunk ..................................................................................182
Chapter 9
Policy and Static Routes..................................................................................................................185
9.1 Policy and Static Routes Overview .................................................................................................185
9.1.1 What Yo u Can Do in this Chapter ..........................................................................................185
9.1.2 What You Need to Know ............................................................................... ... ... ... ... .... ........186
9.2 Policy Route Screen ........................................................................................................................187
9.2.1 Policy Route Edit Screen .......................................................................................................189
9.3 IP Static Route Screen ....................................................................................................................193
9.3.1 Static Route Add/Edit Screen ................................................................................................194
9.4 Policy Routing Technical Reference .................................................... ... .... ... ..................................195
Chapter 10
Routing Protocols.............................................................................................................................197
10.1 Routing Protocols Overview ..........................................................................................................197
10.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................197
10.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............197
10.2 The RIP Screen ....................................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .........................................................197
10.3 The OSPF Screen ......... .... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ..................................199
10.3.1 Configuring the OSPF Screen .............................................................................................202
10.3.2 OSPF Area Add/Edit Screen ..............................................................................................204
10.3.3 Virtual Link Add/Edit Screen ...............................................................................................206
10.4 Routing Protocol Technical Reference ..........................................................................................206
Chapter 11
Zones.................................................................................................................................................208
11.1 Zones Overview ............................................................................................................................208
11.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter .. .......................................... ... .... .....................................208
11.1.2 What You Need to Know ......................................................................................................208
11.2 The Zone Screen ...........................................................................................................................209
11.3 Zone Edit .......................................................................................................................................210
Chapter 12
DDNS..................................................................................................................................................212
12.1 DDNS Overview ............................................................................................................................212
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide6

12.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................212
12.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............212
12.2 The DDNS Screen ........................................................................................................................213
12.2.1 The Dynamic DNS Add/Edit Screen ....................................................................................214
Chapter 13
NAT.....................................................................................................................................................217
13.1 NAT Overview ...............................................................................................................................217
13.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................217
13.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............217
13.2 The NAT Screen ............................. ... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ...............................218
13.2.1 The NAT Add/Edit Screen ....................................................................................................219
13.3 NAT Technical Reference ..............................................................................................................221
Chapter 14
HTTP Redirect...................................................................................................................................224
14.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................224
14.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................224
14.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............224
14.2 The HTTP Redirect Screen ...........................................................................................................225
14.2.1 The HTTP Redirect Edit Screen ..........................................................................................226
Chapter 15
ALG ....................................................................................................................................................228
15.1 ALG Overview ...............................................................................................................................228
15.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................228
15.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............228
15.1.3 Before You Begin .................................................................................................................231
15.2 The ALG Screen ...........................................................................................................................231
15.3 ALG Technical Reference .............................................................................................................233
Chapter 16
IP/MAC Binding.................................................................................................................................235
16.1 IP/MAC Binding Overview .............................................................................................................235
16.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................235
16.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............235
16.2 IP/MAC Binding Summary ............................................................................................................236
16.2.1 IP/MAC Binding Edit ............................................................................................................236
16.2.2 Static DHCP Edit .................................................................................................................237
16.3 IP/MAC Binding Exempt List .........................................................................................................238
Chapter 17
Inbound Load Balancing..................................................................................................................240
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
7

17.1 Inbound Load Balancing Overview ...............................................................................................240
17.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................240
17.2 The Inbound LB Screen ................................................................................................................241
17.2.1 The Inbound LB Add/Edit Screen ........................................................................................242
17.2.2 The Inbound LB Member Add/Edit Screen ..........................................................................244
Chapter 18
Authentication Policy.......................................................................................................................246
18.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................246
18.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................246
18.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............246
18.2 Authentication Policy Screen ........................................................................................................247
18.2.1 Creating/Editing an Authentication Policy ............................................................................249
18.3 User-aware Access Control Example ...........................................................................................251
18.3.1 Set Up User Accounts ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ...............................................................................251
18.3.2 Set Up User Groups ... .........................................................................................................252
18.3.3 Set Up User Authentication Using the RADIUS Server .......................................................252
18.3.4 User Group Authentication Using the RADIUS Server ........................................................254
Chapter 19
Firewall ..............................................................................................................................................256
19.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................256
19.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................256
19.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............256
19.2 The Firewall Screen ................... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... .......................................... ... ..................259
19.2.1 Configuring the Firewall Screen ..........................................................................................259
19.2.2 The Firewall Add/Edit Screen ..............................................................................................263
19.3 The Session Limit Screen .............................................................................................................264
19.3.1 The Session Limit Add/Edit Screen .....................................................................................266
19.4 Firewall Rule Configuration Example ............................................................................................267
19.5 Firewall Rule Example Applications ............................ ..................................................................269
Chapter 20
IPSec VPN..........................................................................................................................................272
20.1 Virtual Private Networks (VPN) Overview .....................................................................................272
20.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................273
20.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............274
20.1.3 Before You Begin .................................................................................................................275
20.2 The VPN Connection Screen ........................................................................................................276
20.2.1 The VPN Connection Add/Edit (IKE) Screen .......................................................................277
20.2.2 The VPN Connection Add/Edit Manual Key Screen ............................................................283
20.3 The VPN Gateway Screen ............................................................................................................285
20.3.1 The VPN Gateway Add/Edit Screen ....................................................................................286
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide8

20.4 VPN Concentrator ........................................................................................................................292
20.4.1 VPN Concentrator Requirements and Suggestions ............................................................293
20.4.2 VPN Concentrator Screen ...................................................................................................293
20.4.3 The VPN Concentrator Add/Edit Screen .............................. ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ........................293
20.5 ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client Configuration Provisioning ................................. ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..294
20.6 IPSec VPN Background Information ....................... ......................................................................296
Chapter 21
SSL VPN ............................................................................................................................................308
21.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................308
21.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................308
21.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............308
21.2 The SSL Access Privilege Screen ................................................................................................309
21.2.1 The SSL Access Policy Add/Edit Screen ...........................................................................310
21.3 The SSL Global Setting Screen ....................................................................................................313
21.3.1 How to Upload a Custom Logo ................................ ....................... ...................... ............... 314
21.4 SSL VPN Example ........................................................................................................................315
Chapter 22
SSL User Screens.............................................................................................................................318
22.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................318
22.1.1 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............318
22.2 Remote SSL User Login ...............................................................................................................319
22.3 The SSL VPN User Screens ................ ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ........322
22.4 Bookmarking the ZyWALL ............................................................................................................323
22.5 Logging Out of the SSL VPN User Screens ..................................................................................324
22.6 SSL User Application Screen ........................................................................................................324
22.7 SSL User File Sharing ...................................................................................................................325
22.7.1 The Main File Sharing Screen .............................................................................................325
22.7.2 Opening a File or Folder .................................... ...................................................... ............326
22.7.3 Downloading a File ..............................................................................................................327
22.7.4 Saving a File ........................................................................................................................327
22.7.5 Creating a New Folder .........................................................................................................328
22.7.6 Renaming a File or Folder ...................................................................................................328
22.7.7 Deleting a File or Folder ......................................................................................................329
22.7.8 Uploading a File ................................ ....................... ....................... ...................... ...............329
Chapter 23
ZyWALL SecuExtender ....................................................................................................................331
23.1 The ZyWALL SecuExtender Icon ..................................................................................................331
23.2 Status ............................................................................................................................................331
23.3 View Log .......................................................................................................................................332
23.4 Suspend and Resume the Connection .........................................................................................333
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
9

23.5 Stop the Connection ......................................................................................................................333
23.6 Uninstalling the ZyWALL SecuExtender .......................................................................................333
Chapter 24
L2TP VPN...........................................................................................................................................335
24.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................335
24.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................335
24.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............335
24.2 L2TP VPN Screen ......... .... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ..................................337
Chapter 25
Bandwidth Management.................................................................................................................339
25.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................339
25.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................339
25.1.2 What You Need to Know .....................................................................................................339
25.2 The Bandwidth Management Screen ................................... ............................................. ............343
25.2.1 The Bandwidth Management Add/Edit Screen ..... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..345
Chapter 26
Device HA..........................................................................................................................................349
26.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................349
26.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................349
26.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............349
26.1.3 Before You Begin .................................................................................................................350
26.2 Device HA General .......................................................................................................................350
26.3 The Active-Passive Mode Screen ..................... ................................................................ ............351
26.3.1 Configuring Active-Passive Mode Device HA ......................................................................353
26.4 Configuring an Active-Passive Mode Monitored Interface ............................................................355
26.5 Device HA Technical Reference ....................................................................................................356
Chapter 27
User/Group........................................................................................................................................361
27.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................361
27.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................361
27.1.2 What You Need To Know ............................................................ .........................................361
27.2 User Summary Screen ..................................................................................................................363
27.2.1 User Add/Edit Screen ..........................................................................................................364
27.3 User Group Summary Screen .......................................................................................................366
27.3.1 Group Add/Edit Screen ........................................................................................................367
27.4 The User/Group Setting Screen .......... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ..................................................368
27.4.1 Default User Authentication Timeout Settings Edit Screens ................................................370
27.4.2 User Aware Login Example .................................................................................................371
27.5 User /Group Technical Reference .................................................................................................372
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide10

Chapter 28
Addresses .........................................................................................................................................374
28.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................374
28.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................374
28.1.2 What You Need To Know ............................................................ .........................................374
28.2 Address Summary Screen ...................... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ...............................374
28.2.1 IPv4 Address Add/Edit Screen ............................................................................................376
28.2.2 IPv6 Address Add/Edit Screen ............................................................................................377
28.3 Address Group Summary Screen .................................................................................................378
28.3.1 Address Group Add/Edit Screen ...... .... .......................................... ... ... ... .... ... .....................379
Chapter 29
Services.............................................................................................................................................380
29.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................380
29.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................380
29.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............380
29.2 The Service Summary Screen ......................................................................................................381
29.2.1 The Service Add/Edit Screen ..............................................................................................382
29.3 The Service Group Summary Screen ........................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... .....383
29.3.1 The Service Group Add/Edit Screen ...................................................................................384
Chapter 30
Schedules..........................................................................................................................................386
30.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................386
30.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................386
30.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............386
30.2 The Schedule Summary Screen ...................................................................................................387
30.2.1 The One-Time Schedule Add/Edit Screen ...........................................................................388
30.2.2 The Recurring Schedule Add/Edit Screen .................. .........................................................389
Chapter 31
AAA Server........................................................................................................................................390
31.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................390
31.1.1 Directory Service (AD/LDAP) ..............................................................................................390
31.1.2 RADIUS Server ...................................................................................................................390
31.1.3 ASAS ...................................................................................................................................391
31.1.4 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................391
31.1.5 What You Need To Know ............................................................ .........................................391
31.2 Active Directory or LDAP Server Summary ..................................................................................393
31.2.1 Adding an Active Directory or LDAP Server ........................................................................ 393
31.3 RADIUS Server Summary .............................................................................................................396
31.3.1 Adding a RADIUS Server ...................................................................................................396
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
11

Chapter 32
Authentication Method.....................................................................................................................399
32.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................399
32.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................399
32.1.2 Before You Begin .................................................................................................................399
32.1.3 Example: Selecting a VPN Authentication Method ..............................................................399
32.2 Authentication Method Objects .....................................................................................................400
32.2.1 Creating an Authentication Method Object .................................................. ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..400
Chapter 33
Certificates........................................................................................................................................403
33.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................403
33.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................403
33.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............403
33.1.3 Verifying a Certificate ...........................................................................................................405
33.2 The My Certificates Screen .................. .................................... ................................ .....................406
33.2.1 The My Certificates Add Screen ..........................................................................................407
33.2.2 The My Certificates Edit Screen ................. ... .......................................... .... ... .....................409
33.2.3 The My Certificates Import Screen .....................................................................................412
33.3 The Trusted Certificates Screen ..................................................................................................413
33.3.1 The Trusted Certificates Edit Screen ..................................................................................414
33.3.2 The Trusted Certificates Import Screen ..............................................................................417
33.4 Certificates Technical Reference ...................................................................................................418
Chapter 34
ISP Accounts.....................................................................................................................................419
34.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................419
34.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................419
34.2 ISP Account Summary ..................................................................................................................419
34.2.1 ISP Account Edit .................................................................................................................420
Chapter 35
SSL Application................................................................................................................................422
35.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................422
35.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................422
35.1.2 What You Need to Know ....................................... ............. ............. ............. ............ ............422
35.1.3 Example: Specifying a Web Site for Access ............................................ ............................423
35.2 The SSL Application Screen ................................ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... ............424
35.2.1 Creating/Editing an SSL Application Object ........................................................................425
Chapter 36
DHCPv6..............................................................................................................................................428
36.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................428
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide12

36.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................428
36.2 The DHCPv6 Request Screen ................ ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ............................................428
36.2.1 DHCPv6 Request Add/Edit Screen .....................................................................................429
36.3 The DHCPv6 Lease Screen ........... ............................................. ... ... ... .... ... ..................................429
36.3.1 DHCPv6 Lease Add/Edit Screen .........................................................................................430
Chapter 37
System...............................................................................................................................................432
37.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................432
37.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................432
37.2 Host Name ....................................................................................................................................433
37.3 USB Storage .................................................................................................................................433
37.4 Date and Time ...............................................................................................................................434
37.4.1 Pre-defined NTP Time Servers List ......................................................... .... ... .....................437
37.4.2 Time Server Synchronization ............................................. ................ ................ ..................437
37.5 Console Port Speed ......................................................................................................................438
37.6 DNS Overview ...............................................................................................................................439
37.6.1 DNS Server Address Assignment .......................................................................................439
37.6.2 Configuring the DNS Screen ...............................................................................................439
37.6.3 Address Record ............................... ...................................................................................441
37.6.4 PTR Record .........................................................................................................................441
37.6.5 Adding an Address/PTR Record .........................................................................................442
37.6.6 Domain Zone Forwarder ......... .......................................... .......................................... ........442
37.6.7 Adding a Domain Zone Forwarder ......................................................................................442
37.6.8 MX Record ..........................................................................................................................443
37.6.9 Adding a MX Record ...........................................................................................................443
37.6.10 Adding a DNS Service Control Rule ................................ ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ... ..444
37.7 WWW Overview ............................................................................................................................445
37.7.1 Service Access Limitations ..................................................................................................445
37.7.2 System Timeout ...................................................................................................................445
37.7.3 HTTPS .................................................................................................................................445
37.7.4 Configuring WWW Service Control .....................................................................................446
37.7.5 Service Control Rules ........................... ....................................................... ........................449
37.7.6 Customizing the WWW Login Page ....................................................................................450
37.7.7 HTTPS Example ..................................................................................................................454
37.8 SSH ............................................................................................................................................461
37.8.1 How SSH Works ......................... ... ... .......................................... .... ... ... ... .... ........................462
37.8.2 SSH Implementation on the ZyWALL ..................................................................................463
37.8.3 Requirements for Using SSH ................................... ... .... ... ... ... ... .........................................463
37.8.4 Configuring SSH ..................................................................................................................463
37.8.5 Secure Telnet Using SSH Examples ...................................................................................464
37.9 Telnet ............................................................................................................................................465
37.9.1 Configuring Telnet ................................................................................................................465
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
13

37.10 FTP ............................................................................................................................................467
37.10.1 Configuring FTP ................................................................................................................467
37.11 SNMP ...... ... ... .... ... ... .......................................... ... .... .......................................... ........................468
37.11.1 Supported MIBs ..................... ... ... .......................................... ... .... ... ... ... ............................469
37.11.2 SNMP Traps .......................... ... ... ... .... .......................................... ... ... ... .... ... .....................470
37.11.3 Configuring SNMP ................. ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ...............................470
37.12 Language Screen ........................................................................................................................472
37.13 IPv6 Screen ..................................... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... ... ... ... .... .....................................................472
Chapter 38
Log and Report .................................................................................................................................474
38.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................474
38.1.1 What You Can Do In this Chapter ........................................................................................474
38.2 Email Daily Report ........................................................................................................................474
38.3 Log Setting Screens .....................................................................................................................476
38.3.1 Log Setting Summary ..........................................................................................................476
38.3.2 Edit System Log Settings ...................................................................................................478
38.3.3 Edit Log on USB Storage Setting . ... .......................................... .... ... ..................................480
38.3.4 Edit Remote Server Log Settings .......................................................................................482
38.3.5 Log Category Settings Screen .............................................................................................484
Chapter 39
File Manager......................................................................................................................................488
39.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................488
39.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................488
39.1.2 What you Need to Know ......................................................................................................488
39.2 The Configuration File Screen ......................................................................................................490
39.3 The Firmware Package Screen ....................................................................................................494
39.4 The Shell Script Screen ...............................................................................................................496
Chapter 40
Diagnostics ...................................................................................................................................... 499
40.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................499
40.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................499
40.2 The Diagnostic Screen ...... ... .......................................... ... ... .... ... ... ... ... .... ... ..................................499
40.2.1 The Diagnostics Files Screen ..............................................................................................500
40.3 The Packet Capture Screen ..........................................................................................................501
40.3.1 The Packet Capture Files Screen ........................................................................................503
40.4 Core Dump Screen .......................................................................................................................504
40.4.1 Core Dump Files Screen .....................................................................................................505
40.5 The System Log Screen ................................................................................................................505
Chapter 41
Packet Flow Explore.........................................................................................................................507
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide14

41.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................507
41.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter ........................................................................................507
41.2 The Routing Status Screen ...........................................................................................................507
41.3 The SNAT Status Screen ..............................................................................................................511
Chapter 42
Reboot ...............................................................................................................................................514
42.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................514
42.1.1 What You Need To Know ............................................................ .........................................514
42.2 The Reboot Screen .......................................................................................................................514
Chapter 43
Shutdown...........................................................................................................................................515
43.1 Overview .......................................................................................................................................515
43.1.1 What You Need To Know ............................................................ .........................................515
43.2 The Shutdown Screen ................................................................................................................. ..515
Chapter 44
Troubleshooting................................................................................................................................516
44.1 Resetting the ZyWALL ..................................................................................................................524
44.2 Getting More Troubleshooting Help ..............................................................................................525
Appendix A Legal Information..........................................................................................................526
Index ..................................................................................................................................................529
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
15

PART I
User’s Guide
16

17
1.1 Overview
Note: This help covers the fo llowing ZyWALL models and refers to them all as “ZyWALL”.
Features and interface names vary by model. Ke y fe ature d iffe re nces be tw ee n ZyWALL models are
as follows. Other features are common to all models although features may vary slightly by model.
See the specific product’s datasheet for detailed specifications.
Table 1 Model-Specific Features
Port Role (see Section 7.2 on page 108) 110
Compact Flash Card Slot (not supported at the time of writing) 110
CHAPTER 1
Introduction
FEATURE ZYWALL
Rack-mounting 110, 310, 1100
Wall-mounting 110
Here are some ZyWALL application scenarios.
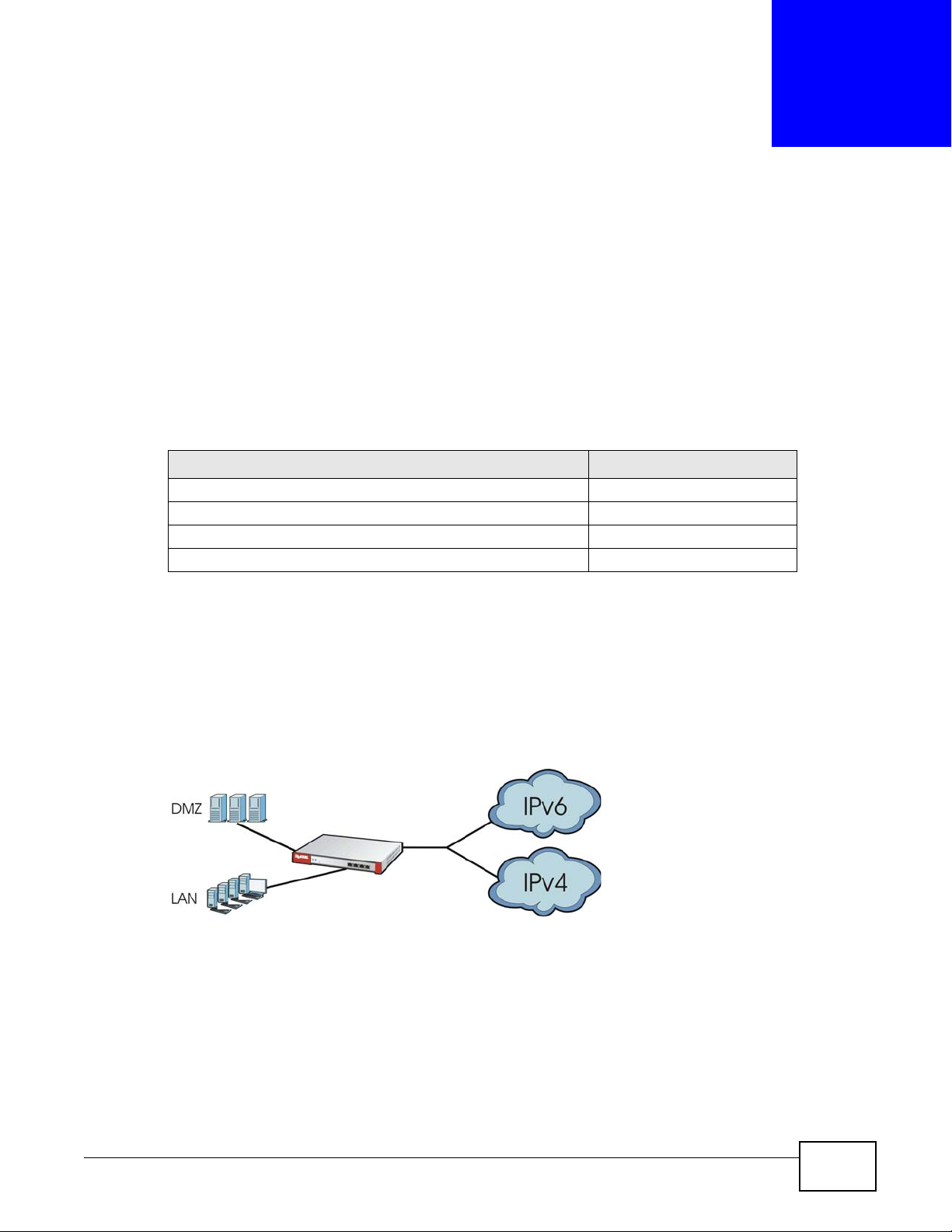
IPv6 Routing
The ZyWALL supports IPv6 Ethernet, PPP, VLAN, and bridge routing. You may also create IPv6
policy routes and IPv6 objects. The ZyWALL can also route IPv6 packets through IPv4 networks
using different tunneling methods.
Figure 1 Applications: IPv6 Routing
VPN Connectivity
Set up VPN tunnels with other companies, branch offices, telecommuters, and business travelers to
provide secure access to your network. You can also purchase the ZyWALL OTPv2 One-Time
Password System for strong two-factor authentication for Web Configurator, Web access, SSL VPN,
and ZyXEL IPSec VPN client user logins.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide 18
Chapter 1 Introduction
OTP PIN
SafeWord 2008
Authentication Server
File
Email
Web-based
Server
Server
Application
*****
Web Mail File Share
Web-based Application
https://
Application Server
Non-Web
LAN (192.168.1.X)
Figure 2 Applications: VPN Connectivity
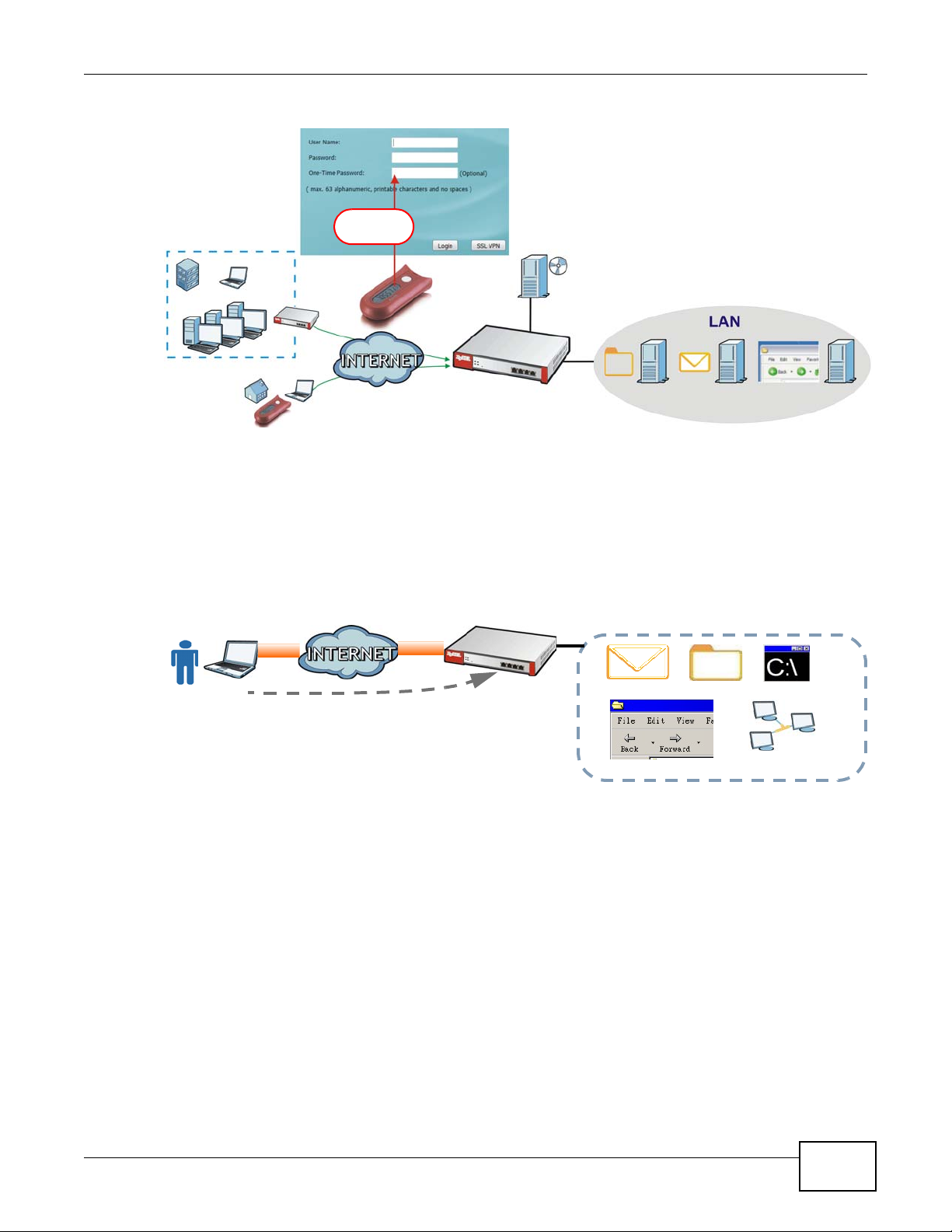
SSL VPN Network Access
SSL VPN lets remote users use their web browsers for a very easy-to-use VPN solution. A user just
browses to the ZyWALL’s web address and enters his user name and password to securely connect
to the ZyWALL’s network. Here full tunnel mode creates a virtual connection for a remote user and
gives him a private IP address in the same subnet as the local network so he can access network
resources in the same way as if he were part of the internal network.
Figure 3 SSL VPN With Full Tunnel Mode
User-Aware Access Control
Set up security policies to restrict access to sensitive information and shared resources based on
the user who is trying to access it. In the following figure user A can access both the Internet and
an internal file server. User B has a lower level of access and can only access the Internet. User C is
not even logged in and cannot access either.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
19
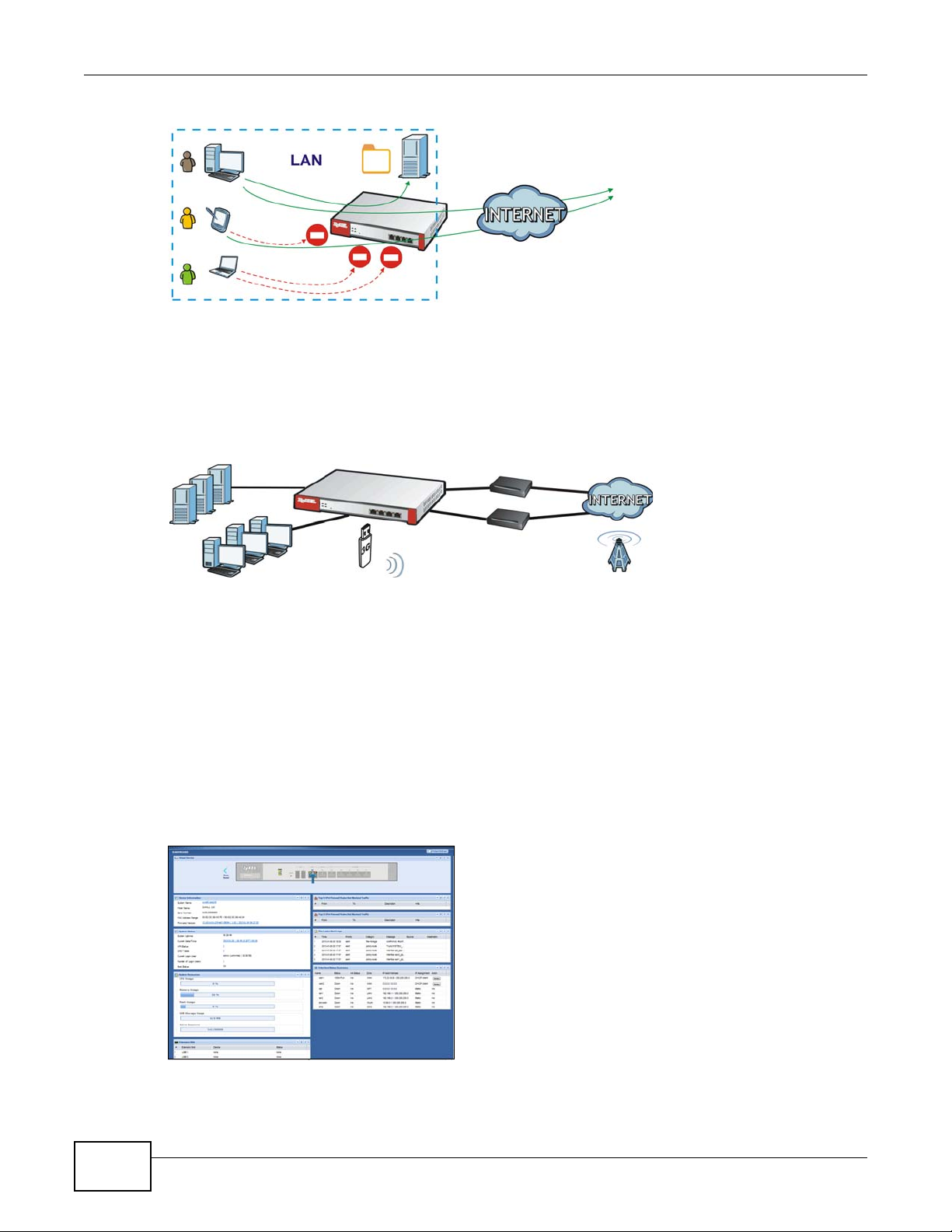
Chapter 1 Introduction
A
B
C
Figure 4 Applications: User-Aware Access Control
Load Balancing
Set up multiple connections to the Internet on the same port, or different ports, including cellular
interfaces. In either case, you can balance the traffic loads between them.
Figure 5 Applications: Multiple WAN Interfaces
1.2 Management Overview
You can manage the ZyWALL in the following ways.
Web Configurator
The Web Configur ator allows easy ZyWALL setup and management using an Internet browser. This
User’s Guide provides information about the Web Configurator.
Figure 6 Managing the ZyWALL: Web Configurator
20
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Command-Line Interface (CLI)
The CLI allows you to use text-based commands to configure the ZyWALL. Access it using remote
management (for example, SSH or Telnet) or via the physical or Web Configurator console port.
See the Command Reference Guide for CLI details. The default settings for the console port are:
Table 2 Console Port Default Settings
SETTING VALUE
Speed 115200 bps
Data Bits 8
Parity None
Stop Bit 1
Flow Control Off
1.3 Web Configurator
In order to use the Web Configurator, you must:
Chapter 1 Introduction
• Use one of the following web browser versions or later: Internet Explorer 7, Firefo x 3.5, Chr ome
9.0
• Allow pop-up windows (blocked by default in Windows XP Service Pack 2)
• Enable JavaScripts, Java permissions, and cookies
The recommended screen resolution is 1024 x 768 pixels.
1.3.1 Web Configurator Access
1 Make sure your ZyWALL hardware is properly connected. See the Quick Start Guide.
2 In your browser go to http://192.168.1.1. By default, the ZyWALL automatically routes this request
to its HTTPS server, and it is recommended to keep this setting. The Login screen appears.
3 Type the user name (default: “admin”) and password (default: “1234”).
If you have a OTP (One-Time Password) token generate a number and enter it in the One-Time
Password field. The number is only good for one login. You must use the token to generate a new
number the next time you log in.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
21
Chapter 1 Introduction
A
C
B
4 Click Login. If you logged in using the default user name and password, the Update Admin Info
screen appears. Otherwise, the dashboard appears.
5 Follow the directions in the Update Admin Info screen. If you change the default password, the
Login screen appears after you click Apply. If you click Ignore, the Installation Setup Wizard
opens if the ZyWALL is using its default configuration; otherwise the dashboard appears.
1.3.2 Web Configurator Screens Overview
The Web Configurator screen is divided into these parts (as illustrated on page 22):
• A - title bar
• B - navigation panel
• C - main window
Title Bar
Figure 7 Title Bar
22
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 1 Introduction
The title bar icons in the upper right corner provide the following functions.
Table 3 Title Bar: Web Configurator Icons
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Logout Click this to log out of the Web Configurator.
Help Click this to open the help page for the current screen.
About Click this to display basic information about the ZyWALL.
Site Map Click this to see an overview of links to the Web Config urator screens.
Object Reference Click this to check which configuration items reference an object.
Console Click this to open a Java-based console window from which you can run command line
CLI Click this to open a popup window that displays the CLI commands sent by the Web
interface (CLI) commands. You will be prompted to enter your user name and password.
See the Command Reference Guide for information about the commands.
Configurator to the ZyWALL.
About
Click About to display basic information about the ZyWALL.
Figure 8 About
Table 4 About
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Boot Module This shows the version number of the software that handles the booting process of the
ZyWALL.
Current Version This shows the firmware version of the ZyWALL.
Released Date This shows the date (yyyy-mm-dd) and time (hh:mm:ss) when the firmware is released.
OK Click this to close the screen.
Site Map
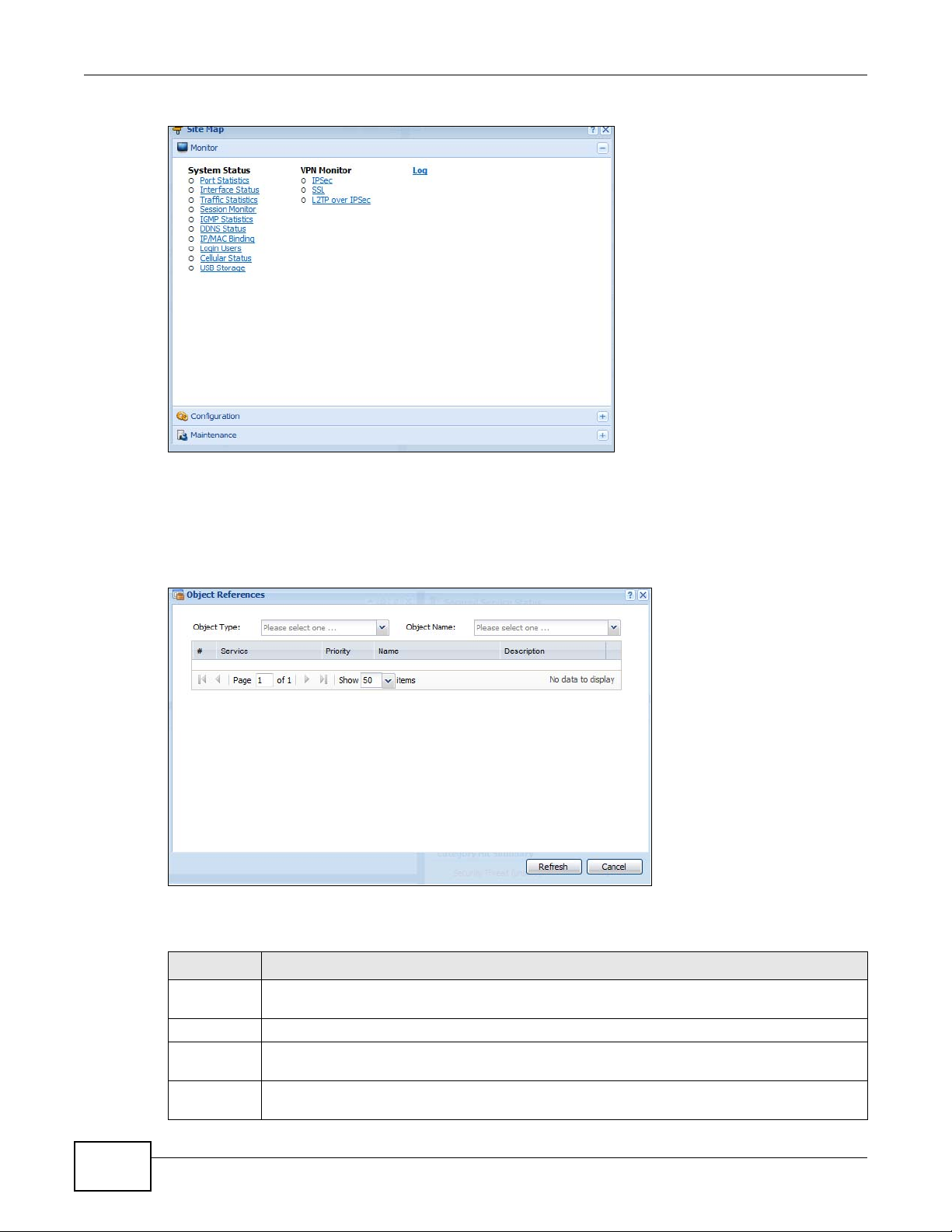
Click Site MAP to see an overview of links to the Web Configurator screens. Click a screen’ s link to
go to that screen.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
23
Chapter 1 Introduction
Figure 9 Site Map
Object Reference
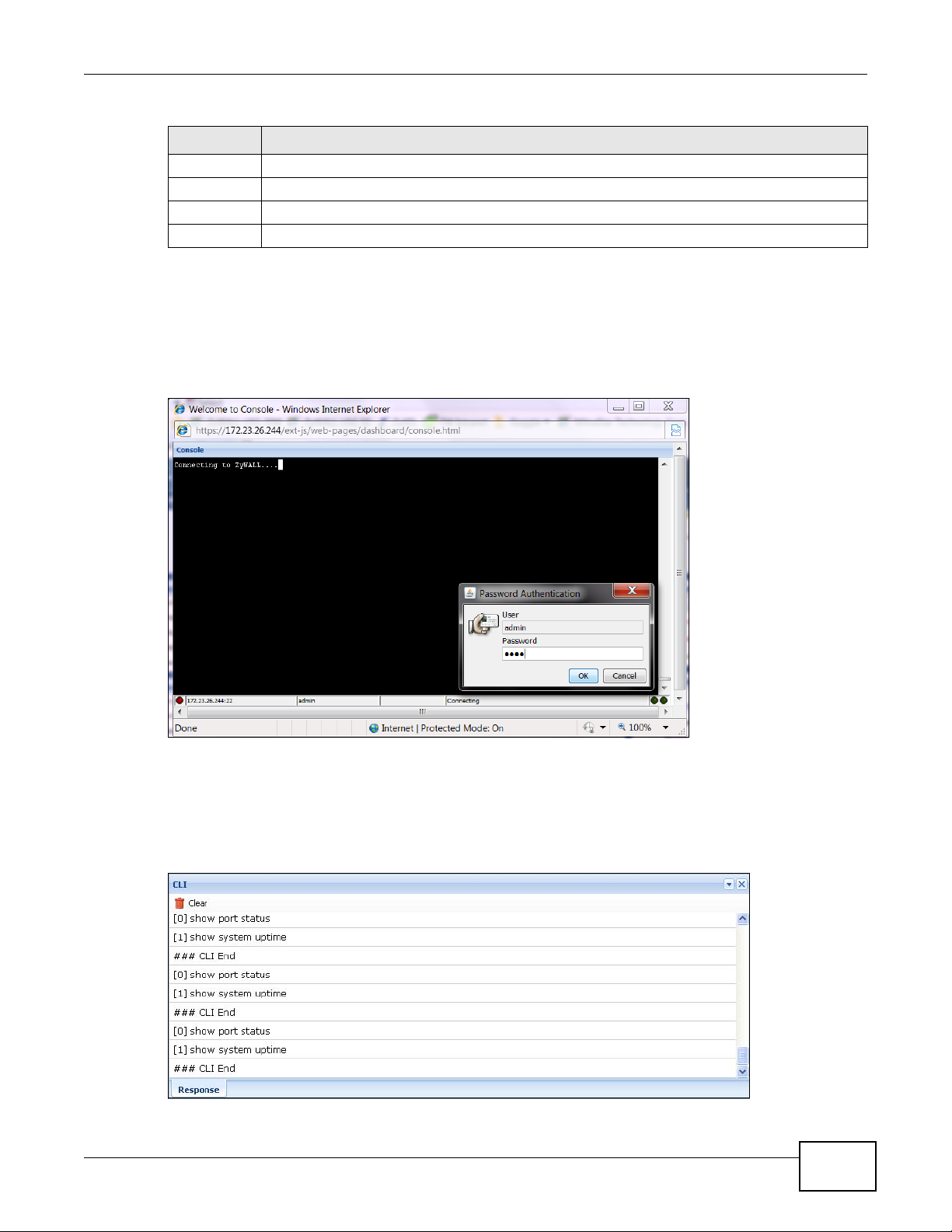
Click Object Reference to open the Object Reference screen. Select the type of object and the
individual object and click Refresh to show which configuration settings reference the object.
Figure 10 Object Reference
The fields vary with the type of object. This table describes labels that can appear in this screen.
Table 5 Object References
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Object Name This identifies the object for which the configuration settings t hat use it are disp layed. Clic k the
# This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with any entry.
Service This is the type of setting that references the selected object. Click a service’s name to display
Priority If it is applicable, this field lists the refe rencing configuration item’s position in its list,
object’s name to display the object’s configuration screen in the main window.
the service’s configuration screen in the main window.
otherwise N/A displays.
24
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 5 Object References (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name This field identifies the configuration item that references the object.
Description If the referencing configuration item has a description configured, it displays here.
Refresh Click this to update the information in this screen.
Cancel Click Cancel to close the screen.
Console
Click Console to open a Java-based console window from which you can run CLI commands. You
will be prompted to enter your user name and password. See the Command Reference Guide for
information about the commands.
Figure 11 Console Window
CLI Messages
Click CLI to look at the CLI commands sent by the W eb Configurator. Open the pop-up window and
then click some menus in the web configurator to dislay the corresponding commands.
Figure 12 CLI Messages
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
25

Chapter 1 Introduction
1.3.3 Navigation Panel
Use the navigation panel menu items to open status and configuration screens. Click the arrow in
the middle of the right edge of the navigation panel to hide the panel or drag to resize it. The
following sections introduce the ZyWALL’s navigation panel menus and their screens.
Figure 13 Navigation Panel
Dashboard
The dashboard displays general device information, system status, system resource usage,, and
interface status in widgets that you can re-arr ange to suit your needs. See the W eb Help for details
on the dashboard.
Monitor Menu
The monitor menu screens display status and statistics information.
Table 6 Monitor Menu Screens Summary
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
System Status
Port Statistics Displays packet statistics for each physical port.
Interface
Status
Traffic
Statistics
Session
Monitor
DDNS Status Displays the status of the ZyWALL’s DDNS domain names.
IP/MAC Binding Lists the devices that have received an IP address from ZyWALL interfaces
Login Users Lists the users currently logged into the ZyWALL.
Displays general interface information and packet statistics.
Collect and display traffic statistics.
Displays the status of all current sessions.
using IP/MAC binding.
26
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
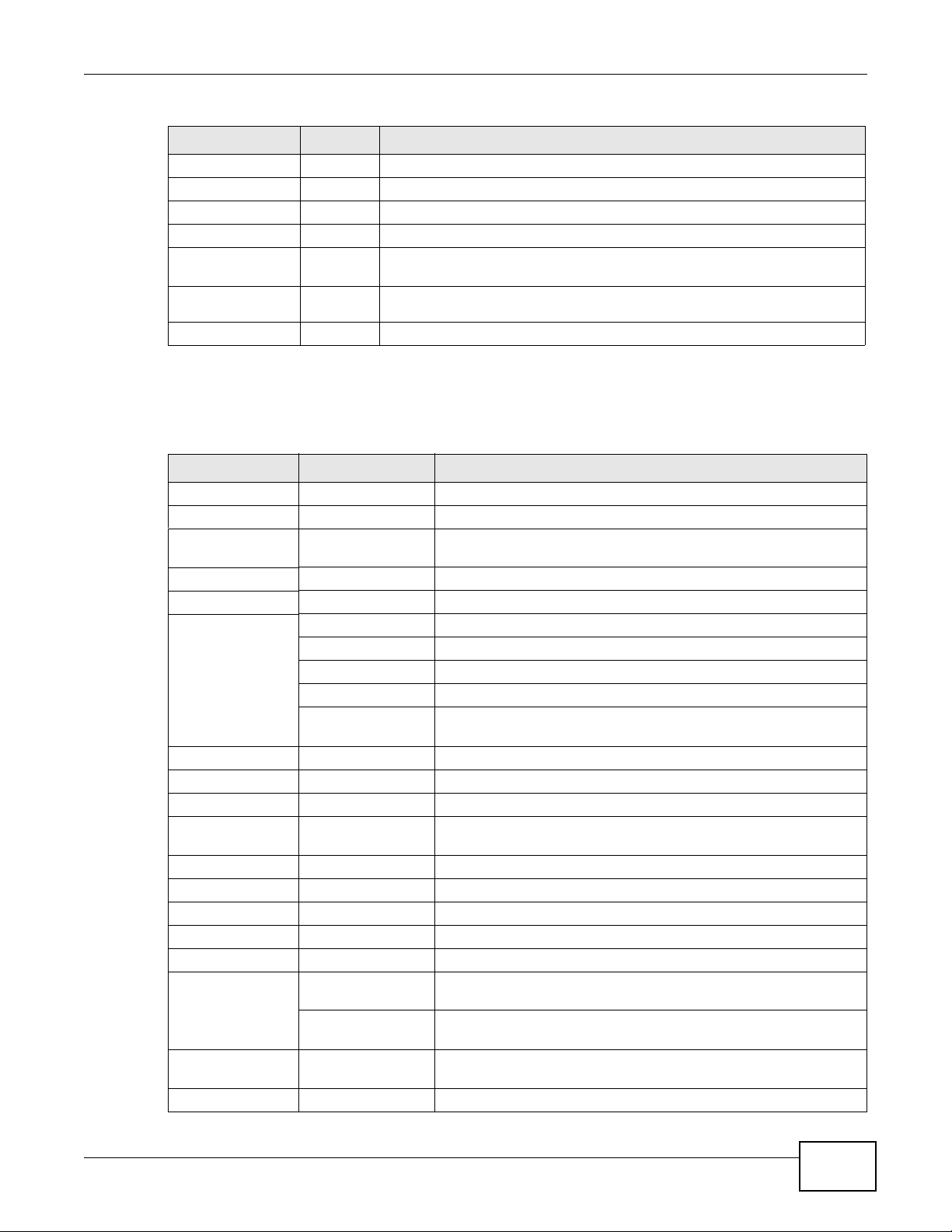
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 6 Monitor Menu Screens Summary (continued)
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Cellular Status Displays details about the ZyWALL’s 3G connection status.
USB Storage Displays details about USB device connected to the ZyWALL.
VPN Monitor
IPSec Displays and manages the active IPSec SAs.
SSL Lists users currently logged into the VPN SSL client portal. You can also log
out individual users and delete related session information.
L2TP over
IPSec
Log Lists log entries.
Displays details about current L2TP sessions.
Configuration Menu
Use the configuration menu screens to configure the ZyWALL’s features.
Table 7 Configuration Menu Screens Summary
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Quick Setup Quickly configure WAN interfaces or VPN connections.
Network
Interface Port Role Use this screen to set the ZyWALL’s flexible ports as LAN1, WLAN,
or DMZ.
Ethernet Manage Ethernet interfaces and virtual Ethernet interfaces.
PPP Create and manage PPPoE and PPTP interfaces.
Cellular Configure a cellular Internet connection for an installed 3G card.
Tunnel Configure tunneling between IPv4 and IPv6 networks.
VLAN Create and manage VLAN interfaces and virtual VLAN interfaces.
Bridge Create and manage bridges and virtual bridge interfaces.
Trunk Create and manage trunks (groups of interfaces) for load
balancing.
Routing Policy Route Create and manage routing policies.
Static Route Create and manage IP static routing information.
RIP Configure device-level RIP settings.
OSPF Configure device-level OSPF settings, including areas and virtual
Zone Configure zones used to define various policies.
DDNS DDNS Define and manage the ZyWALL’s DDNS domain names.
NAT Set up and manage port forwarding rules.
HTTP Redirect Set up and manage HTTP redirection rules.
ALG Configure SIP, H.323, and FTP pass-th rough settings.
IP/MAC
Binding
DNS Inbound LBDNS Load
Auth. Policy Define rules to force user authentication.
Summary Configure IP to MAC address bindings for devices connected to
Exempt List Configure ranges of IP addresses to which th e ZyWALL does not
Balancing
links.
each supported interface.
apply IP/MAC binding.
Configure DNS Load Balancing.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
27
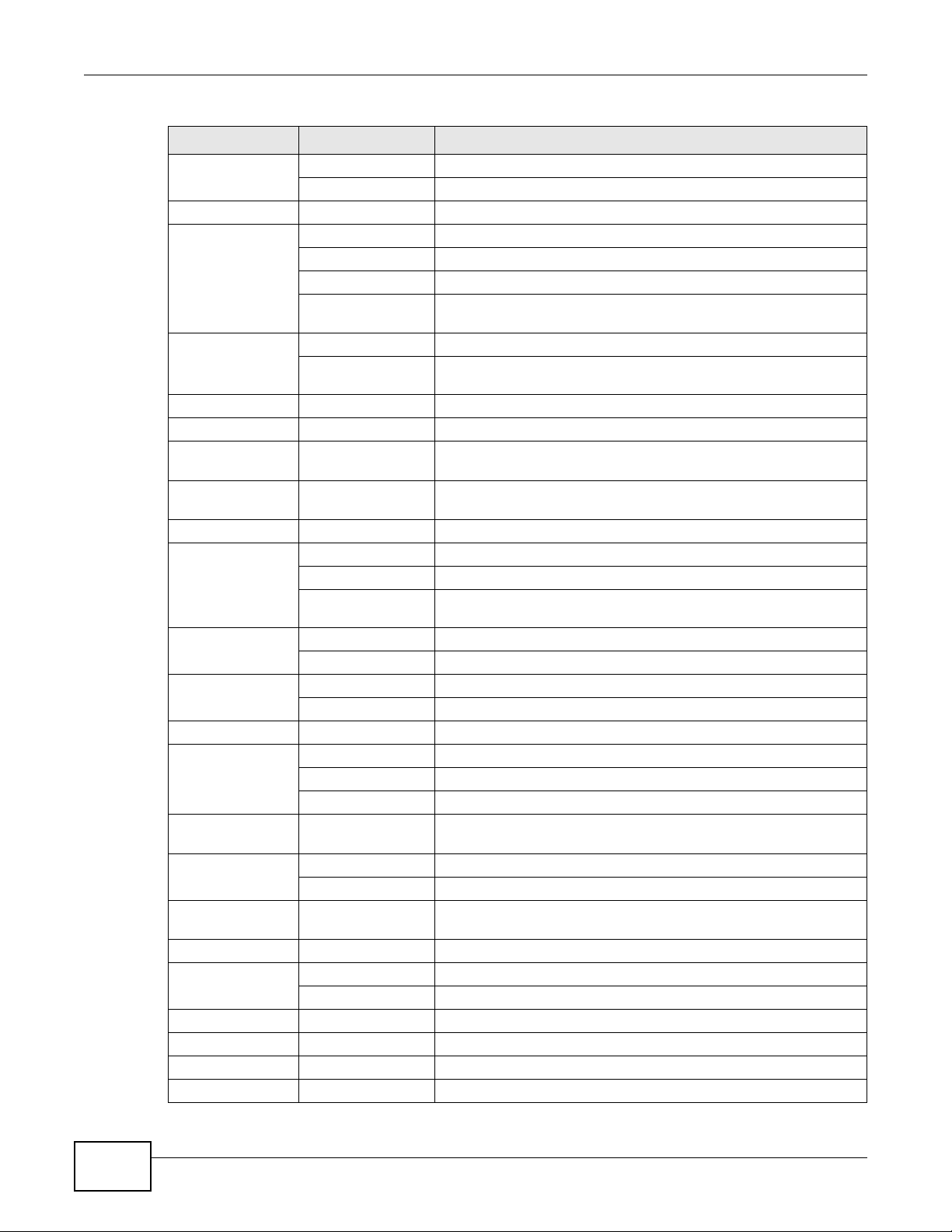
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 7 Configuration Menu Screens Summary (continued)
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Firewall Firewall Create and manage level-3 traffic rules.
VPN
IPSec VPN VPN Connection Configure IPSec tunnels.
SSL VPN Access Privilege Configure SSL VPN access rights for users and groups.
L2TP VPN L2TP VPN Configure L2TP over IPSec tunnels.
BWM BWM Enable and configure bandwidth management rules.
Device HA General Configure device HA global settings, and see the status of each
Object
User/Group User Create and manage users.
Address Address Create and manage host, range, and network (subnet) addresses.
Service Service Create and manage TCP and UDP services.
Schedule Schedule Create one-time and recurring schedules.
AAA Server Active Directory Configure the Active Directory settings.
Auth. Method Authentication
Certificate My Cer tificates Create and manage the ZyWALL’s certifica tes.
ISP Account ISP Account Create and manage ISP account information for PPPoE/PPTP
SSL Application Create SSL web application objects.
DHCPv6 Request Configure IPv6 DHCP request type and interface information.
System
Host Name Configure the system and domain name for the ZyWALL.
USB Storage Settings Configure the settings for the connected USB devices.
Date/Time Configure the current date, time, and time zone in the ZyWALL.
Session Control Limit the number of concurrent client NAT/firewall sessions.
VPN Gateway Configure IKE tunnels.
Concentrator Combine IPSec VPN con nections into a single secure network
Configuration
Provisioning
Global Setting Configure the ZyWALL’s SSL VPN settings that apply to all
Active-Passive
Mode
Group Create and manage groups of users.
Setting Manage default settings for all users, general settings for user
Address Group Create and manage groups of addresses.
Service Group Create and manage groups of services.
LDAP Configure the LDAP settings.
RADIUS Configure the RADIUS settings.
Method
Trusted Certificates Import and manage certificates from trusted sources.
Lease Configu r e IPv6 DHCP lease type and interface information.
Set who can retrieve VPN rule settings from the ZyWALL using the
ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client.
connections.
interface monitored by device HA.
Configure active-passive mode device HA.
sessions, and rules to force user authentication.
Create and manage ways of authenticating users.
interfaces.
28
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
Chapter 1 Introduction
Table 7 Configuration Menu Screens Summary (continued)
FOLDER OR LINK TAB FUNCTION
Console Speed Set the console speed.
DNS Configure the DNS server and address records for the ZyWALL.
WWW Service Control Configure HTTP, HTTPS, and general authentication.
Login Page Configure how the login and access user screens look.
SSH Configure SSH server and SSH service settings.
TELNET Configure telnet server settings for the ZyWALL.
FTP Configure FTP server settings.
SNMP Configure SNMP communities and services.
Language Select the Web Configurator language.
IPv6 Enable IPv6 globally on the ZyWALL here.
Log & Report
Email Daily
Report
Log Settings Configure the system log, e-mail logs, and remote syslog servers.
Configure where and how to send daily reports and what reports to
send.
Maintenance Menu
Use the maintenance menu screens to manage configuration and firmware files, run diagnostics,
and reboot or shut down the ZyWALL.
Table 8 Maintenance Menu Screens Summary
FOLDER
OR LINK
File
Manager
Diagnostics Diagnostic Collect diagnostic information.
Packet
Flow
Explore
Reboot Restart the ZyWALL.
Shutdown Turn off the ZyWALL.
TAB FUNCTION
Configuration File Manage and upload configuration files for the ZyWALL.
Firmware Package View the current firmware version and to upload firmware.
Shell Script Manage and run shell script files for the ZyWALL.
Packet Capture Capture packets for analysis.
Core Dump Connect a USB device to the ZyWALL and save the ZyWALL operating
System Log Connect a USB device to the ZyWALL and archive the ZyWALL system logs
Routing Status Check how the ZyWALL determines where to route a packet.
SNAT Status View a clear picture on how the ZyWALL converts a packet’s source IP
1.3.4 Tables and Lists
system kernel to it here.
to it here.
address and check the related settings.
Web Configurator tables and lists are flexible with several options for how to display their entries.
Click a column heading to sort the table’s entries according to that column’s criteria.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
29
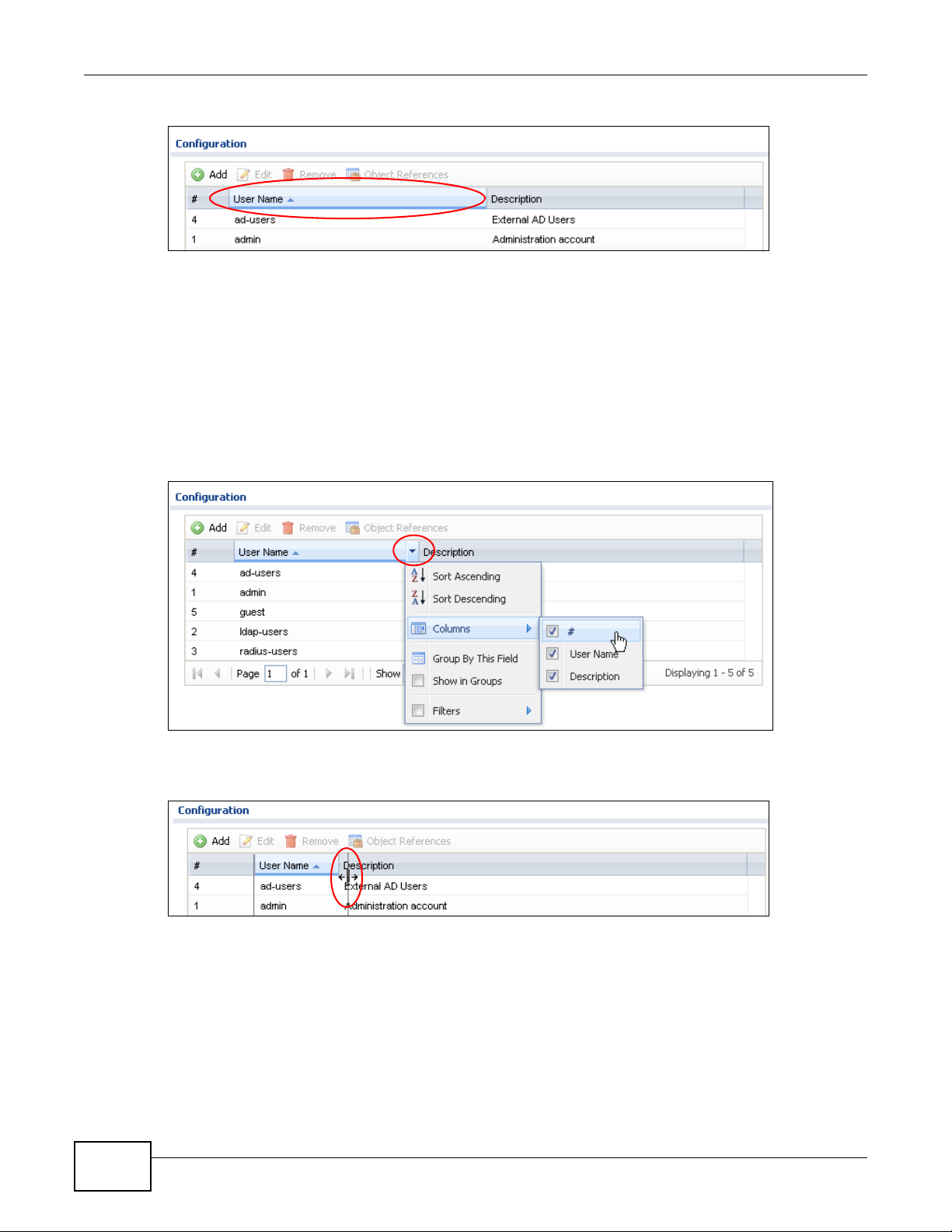
Chapter 1 Introduction
Figure 14 Sorting Table Entries by a Column’s Criteria
Click the down arrow next to a column heading for more options about how to display the entries.
The options available vary depending on the type of fields in the column. Here are some examples
of what you can do:
• Sort in ascending or descending (reverse) alphabetical order
• Select which columns to display
• Group entries by field
• Show entries in groups
• Filter by mathematical operators (<, >, or =) or searching for text
Figure 15 Common Table Column Options
30
Select a column heading cell’s right border and drag to re-size the column.
Figure 16 Resizing a Table Column
Select a column heading and drag and drop it to change the column order. A green check mark
displays next to the column’s title when you drag the column to a valid new location.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 1 Introduction
Figure 17 Moving Columns
Use the icons and fields at the bottom of the table to navigate to different pages of entries and
control how many entries display at a time.
Figure 18 Navigating Pages of Table Entries
The tables have icons for working with table entries. You can often use the [Shift] or [Ctrl] key to
select multiple entries to remove, activate, or deactivate.
Figure 19 Common Table Icons
Here are descriptions for the most common table icons.
Table 9 Common Table Icons
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Add Click this to create a new entry. For features where the entry’s position in the numbered list is
important (features where the ZyWALL applies the table’s entries in order like the firewall for
example), you can select an entry and click Add to create a new entry after the selected entry.
Edit Double-click an entry or select it and click Edit to open a screen where you can modify the
Remove To remove an entry, select it and click Remove. The ZyWALL confirms you want to remove it
Activate To turn on an entry, select it and click Activate.
Inactivate To turn off an entry, select it and click Inactivate.
Connect To connect an entry, select it and click Connect.
Disconnect To disconnect an entry, select it and click Disconnect.
Object
References
Move To change an entry’s position in a numbered list, select it and click Move to display a field to
entry’s settings. In some tables you can just click a table entry and edit it directly in the table.
For those types of tables small red triangles display for table entries with changes that you have
not yet applied.
before doing so.
Select an entry and click Object References to check which settings use the entry.
type a number for where you want to put that entry and press [ENTER] to move the entry to the
number that you typed. For example, if you type 6, the entry you are moving becomes number 6
and the previous entry 6 (if there is one) gets pushed up (or down) one.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
31

Chapter 1 Introduction
Working with Lists
When a list of available entries displays next to a list of selected entries, you can often just doubleclick an entry to move it from one list to the other. In some lists you can also use the [Shift] or
[Ctrl] key to select multiple entries, and then use the arrow button to move them to the other list.
32
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

CHAPTER 2
Installation Setup Wizard
2.1 Installation Setup Wi zard Screens
When you log into the Web Configurator for the first time or when you reset the ZyWALL to its
default configuration, the Installation Setup Wizard screen displays. This wizard helps you
configure Internet connection settings and activate subscription services. This chapter provides
information on configuring the Web Configurator's installation setup wizard . See the feature-specific
chapters in this User’s Guide for background information.
Figure 20 Installation Setup Wizard
• Click the double arrow in the upper right corner to display or hide the help.
• Click Go to Dashboard to skip the installation setup wizard or click Next to start configuring for
Internet access.
2.1.1 Internet Access Setup - WAN Interface
Use this screen to configure the WAN interface’s type of encapsulation and method of IP address
assignment.
The screens vary depending on the encapsulation type. Refer to information provided by your ISP
to know what to enter in each field. Leave a field blank if you don’t have that information.
Note: Enter the Internet access information exactly as your ISP gave it to you.
• Encapsulation: Choose the Ethernet option when the WAN port is used as a regular Ethernet.
Otherwise, choose PPPoE or PPTP for a dial-up connection according to the information from
your ISP.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide 33

Chapter 2 Installation Setup Wizard
• WAN Interface: This is the interface you are configuring for Internet access.
• Zone: This is the security zone to which this interface and Internet connection belong.
• IP Address Assignment: Select Auto if your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
Select Static if the ISP assigned a fixed IP address.
2.1.2 Internet Access: Ethernet
This screen is read-only if you set the previous screen’s IP Address Assignment field to Auto.
Use this screen to configure your IP address settings.
Note: Enter the Internet access information exactly as given to you by your ISP.
• Encapsulation: This displays the type of Internet connection you are configuring.
• First WAN Interface: This is the number of the interface that will connect with your ISP.
• Zone: This is the security zone to which this interface and Internet connection will belong.
• IP Address: Enter your (static) public IP address. Auto displays if you selected Auto as the IP
Address Assignment in the previous screen.
The following fields display if you selected static IP address assignment.
• IP Subnet Mask: Enter the subnet mask for this WAN connection's IP address.
• Gateway IP Address: Enter the IP address of the router through which this WAN connection
will send traffic (the default gateway).
• First / Second DNS Server: These fields display if you selected static IP address assignment.
The Domain Name System (DNS) maps a domain name to an IP address and vice versa. Enter a
DNS server's IP address(es). The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you
must know the IP address of a computer before you can access it. The ZyWALL uses these (in the
order you specify here) to resolve domain names for VPN, DDNS and the time server. Leave the
field as 0.0.0.0 if you do not want to configure DNS servers.
2.1.3 Internet Access: PPPoE
Note: Enter the Internet access information exactly as given to you by your ISP.
2.1.3.1 ISP Parameters
• T ype the PPPoE Se rvice Name from your service provider. PPPoE uses a service name to identify
and reach the PPPoE server. You can use alphanumeric and -_@$./ characters, and it can be up
to 64 characters long.
• Authentication Type - Select an authentication protocol for outgoing connection requests.
Options are:
• CHAP/PAP - Your ZyWALL accepts either CHAP or PAP when requested by the remote node.
• CHAP - Your ZyWALL accepts CHAP only.
• PAP - Your ZyWALL accepts PAP only.
• MSCHAP - Your ZyWALL accepts MSCHAP only.
• MSCHAP-V2 - Your ZyWALL accepts MSCHAP-V2 only.
•Type the User Name given to you by your ISP. Y ou can use alphanumeric and -_@$./ characters,
and it can be up to 31 characters long.
34
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

•Type the Password associated with the user name. Use up to 64 ASCII characters except the []
and ?. This field can be blank.
•Select Nailed-Up if you do not want the connection to time out. Otherwise, type the Idle
Timeout in seconds that elapses before the router automatically disconnects from the PPPoE
server.
2.1.3.2 WAN IP Address Assignments
• WAN Interface: This is the name of the interface that will connect with your ISP.
• Zone: This is the security zone to which this interface and Internet connection will belong.
• IP Address: Enter your (static) public IP address. Auto displays if you selected Auto as the IP
Address Assignment in the previous screen.
• First / Second DNS Server: These fields display if you selected static IP address assignment.
The Domain Name System (DNS) maps a domain name to an IP address and vice versa. Enter a
DNS server's IP address(es). The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you
must know the IP address of a computer before you can access it. The ZyWALL uses these (in the
order you specify here) to resolve domain names for VPN, DDNS and the time server. Leave the
field as 0.0.0.0 if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not configure a DNS server,
you must know the IP address of a machine in order to access it.
2.1.4 Internet Access: PPTP
Chapter 2 Installation Setup Wizard
Note: Enter the Internet access information exactly as given to you by your ISP.
2.1.5 ISP Parameters
• Authentication Type - Select an authentication protocol for outgoing calls. Options are:
• CHAP/PAP - Your ZyWALL accepts either CHAP or PAP when requested by the remote node.
• CHAP - Your ZyWALL accepts CHAP only.
• PAP - Your ZyWALL accepts PAP only.
• MSCHAP - Your ZyWALL accepts MSCHAP only.
• MSCHAP-V2 - Your ZyWALL accepts MSCHAP-V2 only.
•Type the User Name given to you by your ISP. Y ou can use alphanumeric and -_@$./ characters,
and it can be up to 31 characters long.
•Type the Password associated with the user name. Use up to 64 ASCII characters except the []
and ?. This field can be blank. Re-type your password in the next field to confirm it.
•Select Nailed-Up if you do not want the connection to time out. Otherwise, type the Idle
Timeout in seconds that elapses before the router automatically disconnects from the PPTP
server.
2.1.5.1 PPTP Configuration
• Base Interface: This identifies the Ethernet interface you configure to connect with a modem or
router.
•Type a Base IP Address (static) assigned to you by your ISP.
• Type the IP Subnet Mask assigned to you by your ISP (if given).
• Server IP: Type the IP address of the PPTP server.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
35

Chapter 2 Installation Setup Wizard
•Type a Connection ID or connection name. It must follow the “c:id” and “n:name” format. For
example, C:12 or N:My ISP. This field is optional and depends on the requirements of your
broadband modem or router. You can use alphanumeric and -_: characters, and it can be up to
31 characters long.
2.1.5.2 WAN IP Address Assignments
• First WAN Interface: This is the connection type on the interface you are configuring to
connect with your ISP.
• Zone This is the security zone to which this interface and Internet connection will belong.
• IP Address: Enter your (static) public IP address. Auto displays if you selected Auto as the IP
Address Assignment in the previous screen.
• First / Second DNS Server: These fields display if you selected static IP address assignment.
The Domain Name System (DNS) maps a domain name to an IP address and vice versa. Enter a
DNS server's IP address(es). The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you
must know the IP address of a computer before you can access it. The ZyWALL uses these (in the
order you specify here) to resolve domain names for VPN, DDNS and the time server. Leave the
field as 0.0.0.0 if you do not want to configure DNS servers.
2.1.6 Internet Access - Finish
You have set up your ZyWALL to access the Internet. A screen displays with your settings. If they
are not correct, click Back.
36
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

CHAPTER 3
Physical Ports
Interfaces
Zones
P7
ext-wlan
110
LAN1
lan1
LAN2
lan2
WAN
wan1 wan2
P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6
WLAN DMZ
dmz
opt
None
Physical Ports
Interfaces
P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6
ge1ge2 ge3
ge6
WLAN
ge4ge5
310
Zones
WAN
DMZ
LAN
P7 P8
ge8
None
ge7
Physical Ports
Interfaces
P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P6
ge1ge2
ge3
ge6
ge4ge5
1100
Zones
WAN
DMZ
LAN
P7 P8
ge8
None
ge7
Hardware Introduction
3.1 Default Zones, Interfaces, and Ports
The default configurations for zones, interfaces, and ports are as follows. References to interfaces
may be generic rather than the specific name used in your model. For example, this guide may use
“the WAN interface” rather than “wan1” or “wan2”, “ge2” or” ge3”.
An OPT (optional) Ethernet port can be configured as an additional WAN port, LAN, WLAN, or DMZ
port.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide 37

Chapter 3 Hardware Introduction
Note: Use an 8-wire Ethernet cable to run your Gigabit Ethernet at 1000 Mbps. Using a 4-
wire Ethernet cable limits your connection to 100 Mbps. Note that the connection
speed also depends on what the Ethernet device at the other end can support.
3.2 Stopping the ZyWALL
Always use Maintenance > Shutdown > Shutdown or the shutdown command before you turn
off the ZyWALL or remove the power. Not doing so can cause the firmware to become corrupt.
3.3 Rack-mounting
See Chapter 1 on page 18 for the ZyWALL models that can be rack mounted. Use the following
steps to mount the ZyWALL on an EIA standard size, 19-inch rack or in a wiring closet with other
equipment using a rack-mounting kit. Mak e sure the rack will safely support the combined weight of
all the equipment it contains and that the position of the ZyWALL does not make the rack unstable
or top-heavy. Take all necessary precautions to anchor the rack securely before installing the unit.
Note: Leave 10 cm of clearance at the sides and 20 cm in the rear.
Use a #2 Phillips screwdriver to install the screws.
Note: Failure to use the proper screws may damage the unit.
1 Align one bracket with the holes on one side of the ZyW ALL and secure it with the included bracket
screws (smaller than the rack-mounting screws).
2 Attach the other bracket in a similar fashion.
3 After attaching both mounting brackets, position the ZyWALL in the rack and up the bracket holes
with the rack holes. Secure the ZyWALL to the rack with the rack-mounting screws.
38
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

3.4 Wall-mounting
See Chapter 1 on page 18 for the ZyWALL models that can be wall-mounted. Do the following to
attach your ZyWALL to a wall.
Chapter 3 Hardware Introduction
1 Screw two screws with 6 mm ~ 8 mm (0.24" ~ 0.31") wide heads into the wall 150 mm apart (see
the figure in step 2). Do not screw the screws all the way in to the wall; leave a small gap between
the head of the screw and the wall.
The gap must be big enough for the screw heads to slide into the screw slots and the connection
cables to run down the back of the ZyWALL.
Note: Make sure the screws are securely fixed to the wall and strong enough to hold the
weight of the ZyWALL with the connection cables.
2 Use the holes on the bottom of the ZyWALL to hang the ZyWALL on the screws.
3.5 Front Panel LEDs
This section introduces the ZyWALL’s front panel LEDs.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
39

Chapter 3 Hardware Introduction
110
310
1100
Figure 21 ZyWALL Front Panel
The following tables describe the LEDs.
Table 10 Front Panel LEDs
LED COLOR STATUS DESCRIPTION
PWR Off The ZyWALL is turned off.
Green On The ZyWALL is turned on.
Red On There is a hardware component failure. Shut down the device, wait for a few
minutes and then restart the device (see Section 3.2 on page 38). If the LED
turns red again, then please contact your vendor.
SYS Green Off The ZyWALL is not ready or has failed.
On The ZyWALL is ready and running.
Blinking The ZyWALL is booting.
Red On The ZyWALL xd an error or has failed.
USB Green Off No device is con nected to the ZyWALL’s USB port or the connected device is
On A 3G USB card or USB storage device is connected to the USB port.
Orange On Connected to a 3G network through the connected 3G USB card.
P1, P2... Green Off There is no traffic on this port.
Blinking The ZyWALL is sending or receiving packets on this port.
Orange Off There is no connection on this port.
On This port has a successful link.
not supported by the ZyWALL.
40
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
3.5.1 Rear Panels
110
310
1100
The following graphic shows the rear panel of the ZyWALL.
Chapter 3 Hardware Introduction
Tab le 11 Rear Panel
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Console You can use the console port to manage the ZyWALL using CLI commands. You will be
prompted to enter your user name and password. See the Command Reference Guide for
more information about the CLI.
When configuring using the console port, you need a computer equipped with
communications software configured to the following parameters:
• Speed 115200 bps
•Data Bits 8
• Parity None
•Stop Bit 1
• Flow Control Off
CF Card Slot This feature is not supported at the time of writing.
Power Use the included power cord to connect the power socket to a power outlet. T urn the power
Lock Attach a loc k-and-cable from the Kensington lock (the small, metal-reinforced, oval hole)
Fan The fans are for cooling the ZyW ALL. Make sure th ey are not obstructed t o allow maximum
switch on if your ZyWALL has a power switch.
to a permanent object, such as a pole, to secure the ZyWALL in place.
ventilation.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
41

4.1 Quick Setup Overview
The Web Configurator's quick setup wizards help y o u configu re Intern et and VPN connection
settings. This chapter provides information on configuring the quick setup screens in the Web
Configurator. See the feature-specific chapters in this User’s Guide for background information.
In the Web Configur ator, click Configuration > Quick Setup to open the first Quick Setup
screen.
Figure 22 Quick Setup
CHAPTER 4
Quick Setup Wizards
•WAN Interface
Click this link to open a wizard to set up a WAN (Internet) connection. This wizard creates
matching ISP account settings in the ZyWALL if you use PPPoE or PPTP. See Section 4.2 on page
42.
•VPN SETUP
Use VPN Setup to configure a VPN (Virtual Private Network) rule for a secure connection to
another computer or network. Use VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning to set up a
VPN rule that can be retrieved with the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client. You only need to enter a user
name, password and the IP address of the ZyWALL in the Z yWALL IPSec VPN Client to get all VPN
settings automatically from the ZyWALL. See Section 4.3 on page 47.
4.2 WAN Interface Quick Setup
Click WAN Interface in the main Quick Setup screen to open the WAN Interface Quick Setup
Wizard Welcome screen. Use these screens to configure an interface to connect to the Internet.
Click Next.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide 42
Figure 23 WAN Interface Quick Setup Wizard
4.2.1 Choose an Ethernet Interface
Select the Ethernet interface that you want to configure for a WAN connection and click Next.
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Figure 24 Choose an Ethernet Interface
4.2.2 Select WAN Type
WAN Type Selection: Select the type of encapsulation this connection is to use. Choose Ethernet
when the WAN port is used as a regular Ethernet.
Otherwise, choose PPPoE or PPTP for a dial-up connection according to the information from your
ISP.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
43
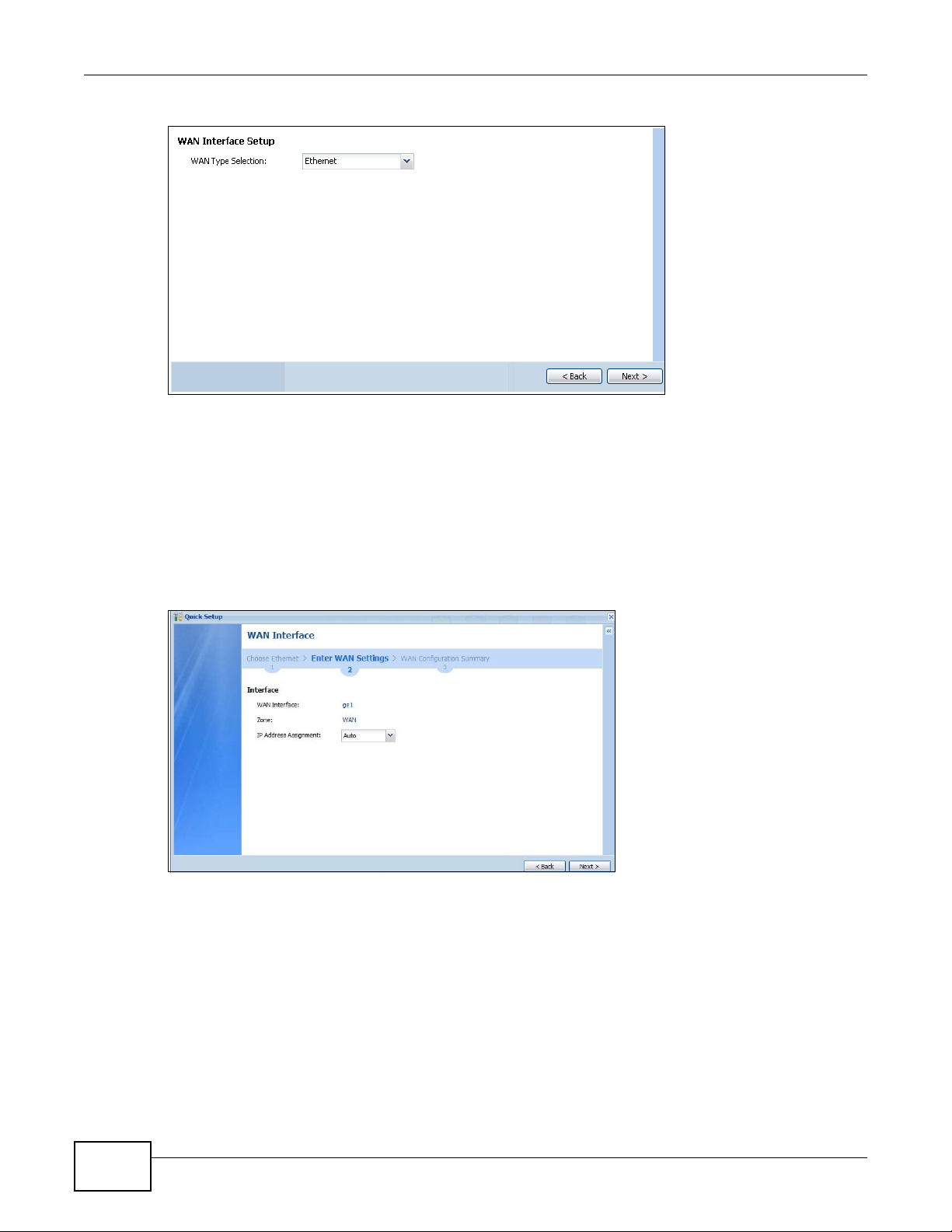
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Figure 25 WAN Interface Setup: Step 2
The screens vary depending on what encapsulation type you use. Refer to information provided by
your ISP to know what to enter in each field. Leave a field blank if you don’t have that information.
Note: Enter the Internet access information exactly as your ISP gave it to you.
4.2.3 Configure WAN Settings
Use this screen to select whether the interface should use a fixed or dynamic IP address.
Figure 26 WAN Interface Setup: Step 2
• WAN Interface: This is the interface you are configuring for Internet access.
• Zone: This is the security zone to which this interface and Internet connection belong.
• IP Address Assignment: Select Auto If your ISP did not assign you a fixed IP address.
Select Static if you have a fixed IP address.
4.2.4 WAN and ISP Connection Settings
Use this screen to configure the ISP and WAN interface settings. This screen is read-only if you set
the IP Address Assignment to Static.
Note: Enter the Internet access information exactly as your ISP gave it to you.
44
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Figure 27 WAN and ISP Connection Settings: (PPTP Shown)
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 12 WAN and ISP Connection Settings
LABEL DESCRIPTION
ISP Parameter This section appears if the interface uses a PPPoE or PPTP Internet connection.
Encapsulation This displays the type of Internet connection you are configuring.
Authentication
Type
User Name Type the user name given to you by your ISP. You can use alphanumeric and -_
Password Type the password associated with the user name above. Use up to 64 ASCII characters
Retype to
Confirm
Nailed-Up Select Nailed-Up if you do not want the connection to time out.
Idle Timeout Type the time in seconds that elapses before the router automatically disconnects from
PPTP Configuration This section only appears if the interface uses a PPPoE or PPTP Internet connection.
Base Interface This displays the identity of the Ethernet interface you configure to connect wit h a
Base IP Address Type the (static) IP address assigned to you by your ISP.
IP Subnet Mask Type the subnet mask assigned to you by your ISP (if given).
Use the drop-down list box to select an authentication protocol for outgoing calls.
Options are:
CHAP/PAP - Your Z yWALL accepts either CHAP or PAP when requested by this remote
node.
CHAP - Your ZyWALL accepts CHAP only.
PAP - Your ZyWALL accepts PAP only.
MSCHAP - Your ZyWALL accepts MSCHAP only.
MSCHAP-V2 - Your ZyWALL accepts MSCHAP-V2 only.
characters, and it can be up to 31 characters long.
except the [] and ?. This field can be blank.
Type your password again for confirmation.
the PPPoE server. 0 means no timeout.
modem or router.
@$./
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
45

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Table 12 WAN and ISP Connection Settings (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Server IP Type the IP address of the PPTP server.
Connection ID Enter the connection ID or connection name in this field. It must follow the "c:id" and
WAN Interface
Setup
WAN Interface This displays the identity of the interface you configure to connect with your ISP.
Zone This field displays to which security zone this interface and Internet connection will
IP Address This field is read-only when the WAN interface uses a dynamic IP address. If your WAN
First DNS
Server
Second DNS
Server
Back Click Back to return to the previous screen.
Next Click Next to continue.
"n:name" format. For example, C:12 or N:My ISP.
This field is optional and depends on the requirements of your DSL modem.
You can use alphanumeric and -_
belong.
interface uses a static IP address, enter it in this field.
These fields only display for an interface with a static IP address. Enter the DNS server
IP address(es) in the field(s) to the right.
Leave the field as 0.0.0.0 if you do not want to configure DNS servers. If you do not
configure a DNS server, you must know the IP address of a machine in order to access
it.
DNS (Domain Name System) is for mapping a domain name to its corresponding IP
address and vice versa. The DNS server is extremely important because without it, you
must know the IP address of a computer before you can access it. The ZyWALL uses a
system DNS server (in the order you specify here) to resolve domain names for VPN,
DDNS and the time server.
: characters, and it can be up to 31 characters long.
4.2.5 Quick Setup Interface Wizard: Summary
This screen displays the WAN interface’s settings.
Figure 28 Interface Wizard: Summary WAN (PPTP Shown)
46
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 13 Interface Wizard: Summary WAN
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Encapsulation This displays what encapsulation this interface uses to connect to the Internet.
Service Name This field only appears for a PPPoE interface. It displays the PPPoE service name specified
Server IP This field only appears for a PPTP interface. It displays the IP address of the PPTP server.
User Name This is the user name given to you by your ISP.
Nailed-Up If No displays the connection will not time out. Yes means the ZyWALL uses the idle
Idle Timeout This is how many seconds the connection can be idle before the router automatically
Connection ID If you specified a connection ID, it displays here.
WAN Interface This identifies the interface you configure to connect with your ISP.
Zone This field displays to which security zone this interface and Internet connection will belong.
IP Address
Assignment
First DNS Server
Second DNS
Server
Close Click Close to exit the wizard.
in the ISP account.
timeout.
disconnects from the PPPoE server. 0 means no timeout.
This field displays whether the WAN IP address is static or dynamic (Auto).
If the IP Address Assignment is Static, these fields display the DNS server IP
address(es).
4.3 VPN Setup Wizard
Click VPN Setup in the main Quick Setup screen to open the VPN Setup Wizard Welcome screen.
Figure 29 VPN Setup Wizard
4.3.1 Welcome
Use wizards to create Virtual Private Network (VPN) rules. After you complete the wizard, the Phase
1 rule settings appear in the VPN > IPSec VPN > VPN Gateway screen and the Phase 2 rule
settings appear in the VPN > IPSec VPN > VPN Connection screen.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
47

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
• VPN Setup configures a VPN tunnel for a secure connection to another computer or network.
• VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning sets up a VPN rule the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client
can retrieve. Just enter a user name, password and the IP address of the Z yWALL in the ZyWALL
IPSec VPN Client to get the VPN settings automatically from the ZyWALL.
Figure 30 VPN Wizard Welcome
4.3.2 VPN Setup Wizard: Wizard Type
Choose Express to create a VPN rule with the default phase 1 and phase 2 settings to connect to
another ZLD-based ZyWALL using a pre-shared key.
Choose Advanced to change the default settings and/or use certificates instead of a pre-shared
key to create a VPN rule to connect to another IPSec device.
Figure 31 VPN Setup Wizard: Wizard Type
48
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
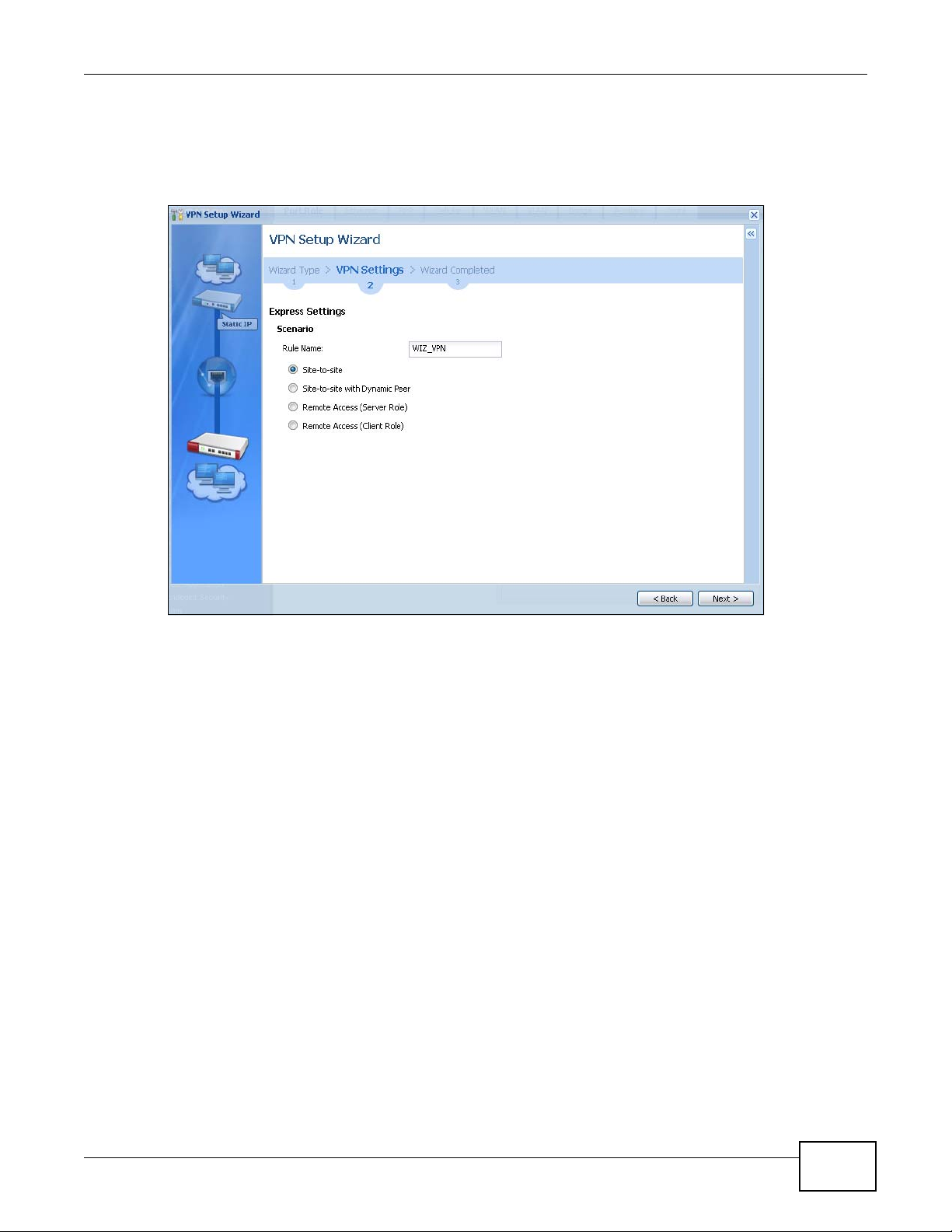
4.3.3 VPN Express Wizard - Scenario
Click the Express radio button as shown in Figure 31 on page 48 to display the following screen.
Figure 32 VPN Express Wizard: Scenario
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Rule Name: Type the name used to identify this VPN connection (and VPN gateway). You may use
1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores (_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a
number. This value is case-sensitive.
Select the scenario that best describes your intended VPN connection. The figure on the left of the
screen changes to match the scenario you select.
• Site-to-site - The remote IPSec device has a static IP address or a domain name. This ZyWALL
can initiate the VPN tunnel.
• Site-to-site with Dynamic Peer - The remote IPSec device has a dynamic IP address. Only the
remote IPSec device can initiate the VPN tunnel.
• Remote Access (Server Role) - Allow incoming connections from IPSec VPN clients. The
clients have dynamic IP addresses and are also known as dial-in users. Only the clients can
initiate the VPN tunnel.
• Remote Access (Client Role) - Connect to an IPSec server. This ZyWALL is the client (dial-in
user) and can initiate the VPN tunnel.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
49

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
4.3.4 VPN Express Wizard - Configuration
Figure 33 VPN Express Wizard: Configuration
• Secure Gateway: Any displays in this field if it is not configurable for the chosen scenario.
Otherwise, enter the WAN IP address or domain name of the remote IPSec device (secure
gateway) to identify the remote IPSec router by its IP address or a domain name. Use 0.0.0.0 if
the remote IPSec router has a dynamic WAN IP address.
• Pre-Shared Key: T ype the password. Both ends of the VPN tunnel must use the same password.
Use 8 to 31 case-sensitive ASCII characters or 8 to 31 pairs of hexadecimal (“0-9”, “A-F”)
characters. Proceed a hexadecimal key with “0x”. You will receive a PYLD_MALFORMED (payload
malformed) packet if the same pre-shared key is not used on both ends.
• Local Policy (IP/Mask): Type the IP address of a computer on your network that can use the
tunnel. You can also specify a subnet. This must match the remote IP address configured on the
remote IPSec device.
• Remote Policy (IP/Mask): Any displays in this field if it is not configurable for the chosen
scenario. Otherwise, type the IP address of a computer behind the remote IPSec device. You can
also specify a subnet. This must match the local IP address configured on the remote IPSec
device.
4.3.5 VPN Express Wizard - Summary
This screen provides a read-only summary of the VPN tunnel’s configuration and commands that
you can copy and paste into another ZLD-based ZyWALL’s command line interface to configure it.
50
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Figure 34 VPN Express Wizard: Summary
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
• Rule Name: Identifies the VPN gateway policy.
• Secure Gateway: IP address or domain name of the remote IPSec device. If this field displays
Any, only the remote IPSec device can initiate the VPN connection.
• Pre-Shared Key: VPN tunnel password. It identifies a communicating party during a phase 1
IKE negotiation.
• Local Policy: IP address and subnet mask of the computers on the network behind your ZyWALL
that can use the tunnel.
• Remote Policy: IP address and subnet mask of the computers on the network behind the
remote IPSec device that can use the tunnel. If this field displays Any, only the remote IPSec
device can initiate the VPN connection.
• Copy and paste the Configuration for Secure Gateway commands into another ZLD-based
ZyWALL’ s command line interface to configure it to serve as the other end of this VPN tunnel. Y ou
can also use a text editor to save these commands as a shell script file with a “.zysh” filename
extension. Use the file manager to run the script in order to configure the VPN connection. See
the commands reference guide for details on the commands displayed in this list.
4.3.6 VPN Express Wizard - Finish
Now the rule is configured on the ZyWALL. The Phase 1 rule settings appear in the VPN > IPSec
VPN > VPN Gateway screen and the Phase 2 rule settings appear in the VPN > IPSec VPN >
VPN Connection screen.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
51

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Figure 35 VPN Express Wizard: Finish
Click Close to exit the wizard.
4.3.7 VPN Advanced Wizard - Scenario
Click the Advanced radio button as shown in Figure 31 on page 48 to display the following screen.
52
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Figure 36 VPN Advanced Wizard: Scenario
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Rule Name: Type the name used to identify this VPN connection (and VPN gateway). You may use
1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores (_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a
number. This value is case-sensitive.
Select the scenario that best describes your intended VPN connection. The figure on the left of the
screen changes to match the scenario you select.
• Site-to-site - The remote IPSec device has a static IP address or a domain name. This ZyWALL
can initiate the VPN tunnel.
• Site-to-site with Dynamic Peer - The remote IPSec device has a dynamic IP address. Only the
remote IPSec device can initiate the VPN tunnel.
• Remote Access (Server Role) - Allow incoming connections from IPSec VPN clients. The
clients have dynamic IP addresses and are also known as dial-in users. Only the clients can
initiate the VPN tunnel.
• Remote Access (Client Role) - Connect to an IPSec server. This ZyWALL is the client (dial-in
user) and can initiate the VPN tunnel.
4.3.8 VPN Advanced Wizard - Phase 1 Settings
There are two phases to every IKE (Internet Key Exchange) negotiation – phase 1 (Authentication)
and phase 2 (Key Exchange). A phase 1 exchange establishes an IKE SA (Security Association).
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
53

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Figure 37 VPN Advanced Wizard: Phase 1 Settings
• Secure Gateway: Any displays in this field if it is not configurable for the chosen scenario.
Otherwise, enter the WAN IP address or domain name of the remote IPSec device (secure
gateway) to identify the remote IPSec device by its IP address or a domain name. Use 0.0.0.0 if
the remote IPSec device has a dynamic WAN IP address.
• My Address (interface): Select an interface from the drop-down list box to use on your
ZyWALL.
• Negotiation Mode: Select Main for identity protection. Select Aggressive to allow more
incoming connections from dynamic IP addresses to use separate passwords.
Note: Multiple SAs connecting through a secure gateway mus t have the same negotiation
mode.
• Encryption Algorithm: 3DES and AES use encryption. The longer the key, the higher the
security (this may affect throughput). Both sender and receiver must use the same secret key,
which can be used to encrypt and decrypt the message or to generate and verify a message
authentication code. The DES encryption algorithm uses a 56-bit key. Triple DES (3DES) is a
variation on DES that uses a 168-bit key. As a result, 3DES is more secure than DES. It also
requires more processing power, resulting in increased latency and decreased throughput.
AES128 uses a 128-bit key and is faster than 3DES. AES192 uses a 192-bit key, and AES256
uses a 256-bit key.
• Authentication Algorithm: MD5 gives minimal security and SHA512 gives the highest
security . MD5 (Message Digest 5) and SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) are hash algorithms used to
authenticate packet data. The stronger the algorithm the slower it is.
• Key Group: DH5 is more secure than DH1 or DH2 (although it may affect throughput). DH1
(default) refers to Diffie-Hellman Group 1 a 768 bit random number. DH2 refers to Diffie-Hellman
Group 2 a 1024 bit (1Kb) random number. DH5 refers to Diffie-Hellman Group 5 a 1536 bit
random number.
• SA Life Time: Set how often the ZyWALL renegotiates the IKE SA. A short SA life time increases
security, but renegotiation temporarily disconnects the VPN tunnel.
• NAT Traversal: Select this if the VPN tunnel must pass through NAT (there is a NAT router
between the IPSec devices).
Note: The remote IPSec device must also have NAT traversal enabled. See the help in the
main IPSec VPN screens for more information.
54
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

• Dead Peer Detection (DPD) has the ZyWALL make sure the remote IPSec device is there
before transmitting data through the IKE SA. If there has been no tr affic for at least 15 seconds,
the ZyWALL sends a message to the remote IPSec device. If it responds, the ZyWALL transmits
the data. If it does not respond, the ZyWALL shuts down the IKE SA.
• Authentication Method: Select Pre-Shared Key to use a password or Certificate to use one
of the ZyWALL’s certificates.
4.3.9 VPN Advanced Wizard - Phase 2
Phase 2 in an IKE uses the SA that was established in phase 1 to negotiate SAs for IPSec.
Figure 38 VPN Advanced Wizard: Step 4
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
• Active Protocol: ESP is compatible with NAT, AH is not.
• Encapsulation: Tunnel is compatible with NAT, Transport is not.
• Encryption Algorithm: 3DES and AES use encryption. The longer the AES key, the higher the
security (this may affect throughput). Null uses no encryption.
• Authentication Algorithm: MD5 gives minimal security and SHA512 gives the highest
security . MD5 (Message Digest 5) and SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) are hash algorithms used to
authenticate packet data. The stronger the algorithm the slower it is.
• SA Life Time: Set how often the ZyWALL renegotiates the IKE SA. A short SA life time increases
security, but renegotiation temporarily disconnects the VPN tunnel.
• Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS): Disabling PFS allows faster IPSec setup, but is less secure.
Select DH1, DH2 or DH5 to enable PFS. DH5 is more secure than DH1 or DH2 (although it may
affect throughput). DH1 refers to Diffie-Hellman Group 1 a 768 bit random number. DH2 refers to
Diffie-Hellman Group 2 a 1024 bit (1Kb) random number. DH5 refers to Diffie-Hellman Group 5 a
1536 bit random number (more secure, yet slower).
• Local Policy (IP/Mask): Type the IP address of a computer on your network. You can also
specify a subnet. This must match the remote IP address configured on the remote IPSec device.
• Remote Policy (IP/Mask): T ype the IP address of a computer behind the remote IPSec device.
You can also specify a subnet. This must match the local IP address configured on the remote
IPSec device.
• Nailed-Up: This displays for the site-to-site and remote access client role scenarios. Select this
to have the ZyWALL automatically renegotiate the IPSec SA when the SA life time expires.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
55

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
4.3.10 VPN Advanced Wizard - Summary
This is a read-only summary of the VPN tunnel settings.
Figure 39 VPN Advanced Wizard: Step 5
• Rule Name: Identifies the VPN connection (and the VPN gateway).
• Secure Gateway: IP address or domain name of the remote IPSec device.
• Pre-Shared Key: VPN tunnel password.
• Certificate: The certificate the ZyWALL uses to identify itself when setting up the VPN tunnel.
• Local Policy: IP address and subnet mask of the computers on the network behind your ZyWALL
that can use the tunnel.
• Remote Policy: IP address and subnet mask of the computers on the network behind the
remote IPSec device that can use the tunnel.
• Copy and paste the Configuration for Remote Gateway commands into another ZLD-based
ZyWALL’s command line interface.
• Click Save to save the VPN rule.
4.3.11 VPN Advanced Wizard - Finish
Now the rule is configured on the ZyWALL. The Phase 1 rule settings appear in the VPN > IPSec
VPN > VPN Gateway screen and the Phase 2 rule settings appear in the VPN > IPSec VPN >
VPN Connection screen.
56
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Figure 40 VPN Wizard: Finish
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Click Close to exit the wizard.
4.4 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Wizard: Wizard Type
Use VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning to set up a VPN rule that can be retrieved
with the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client.
VPN rules for the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client have certain restrictions. They must not contain the
following settings:
• AH active protocol
• NULL encryption
• SHA512 authentication
• A subnet or range remote policy
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
57
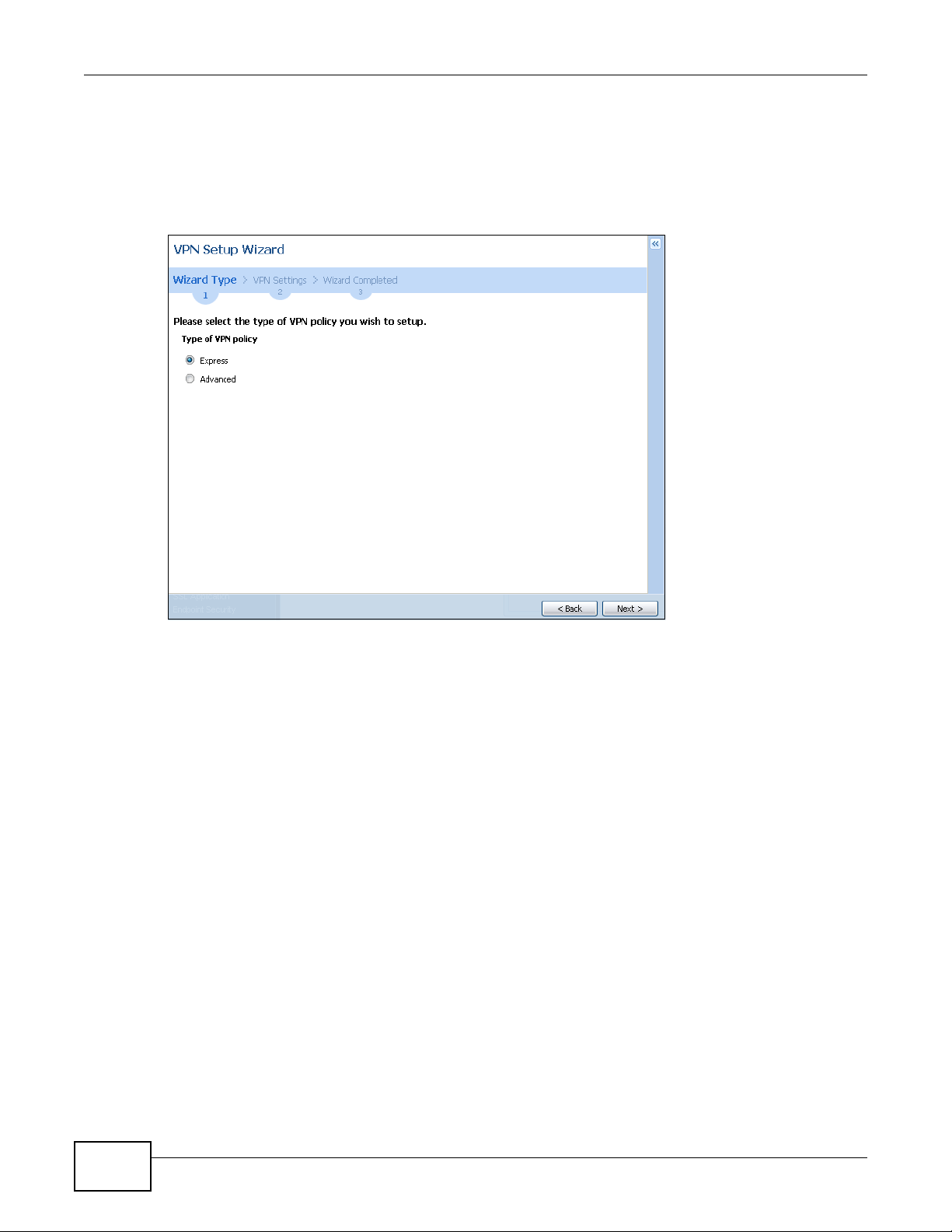
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Choose Express to create a VPN rule with the default phase 1 and phase 2 settings and to use a
pre-shared key.
Choose Advanced to change the default settings and/or use certificates instead of a pre-shared
key in the VPN rule.
Figure 41 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard: Wizard Type
4.4.1 Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard - VPN Settings
Click the Express radio button as shown in the previous screen to display the following screen.
58
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Figure 42 VPN for Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard: Settings Scenario
Rule Name: Type the name used to identify this VPN connection (and VPN gateway). You may use
1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores (_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a
number. This value is case-sensitive.
Application Scenario: Only the Remote Access (Server Role) is allowed in this wizard. It
allows incoming connections from the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client.
4.4.2 Configuration Provisioning VPN Express Wizard - Configuration
Click Next to continue the wizard.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
59

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Figure 43 VPN for Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard: Configuration
• Secure Gateway: Any displays in this field because it is not configurable in this wizard. It allows
incoming connections from the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client.
• Pre-Shared Key: T ype the password. Both ends of the VPN tunnel must use the same password.
Use 8 to 31 case-sensitive ASCII characters or 8 to 31 pairs of hexadecimal (“0-9”, “A-F”)
characters. Proceed a hexadecimal key with “0x”. You will receive a PYLD_MALFORMED (payload
malformed) packet if the same pre-shared key is not used on both ends.
• Local Policy (IP/Mask): Type the IP address of a computer on your network. You can also
specify a subnet. This must match the remote IP address configured on the remote IPSec device.
• Remote Policy (IP/Mask): Any displays in this field because it is not configurable in this
wizard.
4.4.3 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard Summary
This screen has a read-only summary of the VPN tunnel’s configuration and commands you can
copy and paste into another ZLD-based ZyWALL’s command line interface to configure it.
60
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Figure 44 VPN for Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard: Save
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
• Rule Name: Identifies the VPN gateway policy.
• Secure Gateway: Any displays in this field because it is not configurable in this wizard. It allows
incoming connections from the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client.
• Pre-Shared Key: VPN tunnel password. It identifies a communicating party during a phase 1
IKE negotiation.
• Local Policy: (Static) IP address and subnet mask of the computers on the network behind y our
ZyWALL that can be accessed using the tunnel.
• Remote Policy: Any displays in this field because it is not configurable in this wizard.
•The Configuration for Secure Gateway displays the configur ation that the ZyWALL IPSec VPN
Client will get from the ZyWALL.
4.4.4 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard - Finish
Now the rule is configured on the ZyWALL. The Phase 1 rule settings appear in the VPN > IPSec
VPN > VPN Gateway screen and the Phase 2 rule settings appear in the VPN > IPSec VPN >
VPN Connection screen. Enter the IP address of the ZyWALL in the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client to
get all these VPN settings automatically from the ZyWALL.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
61
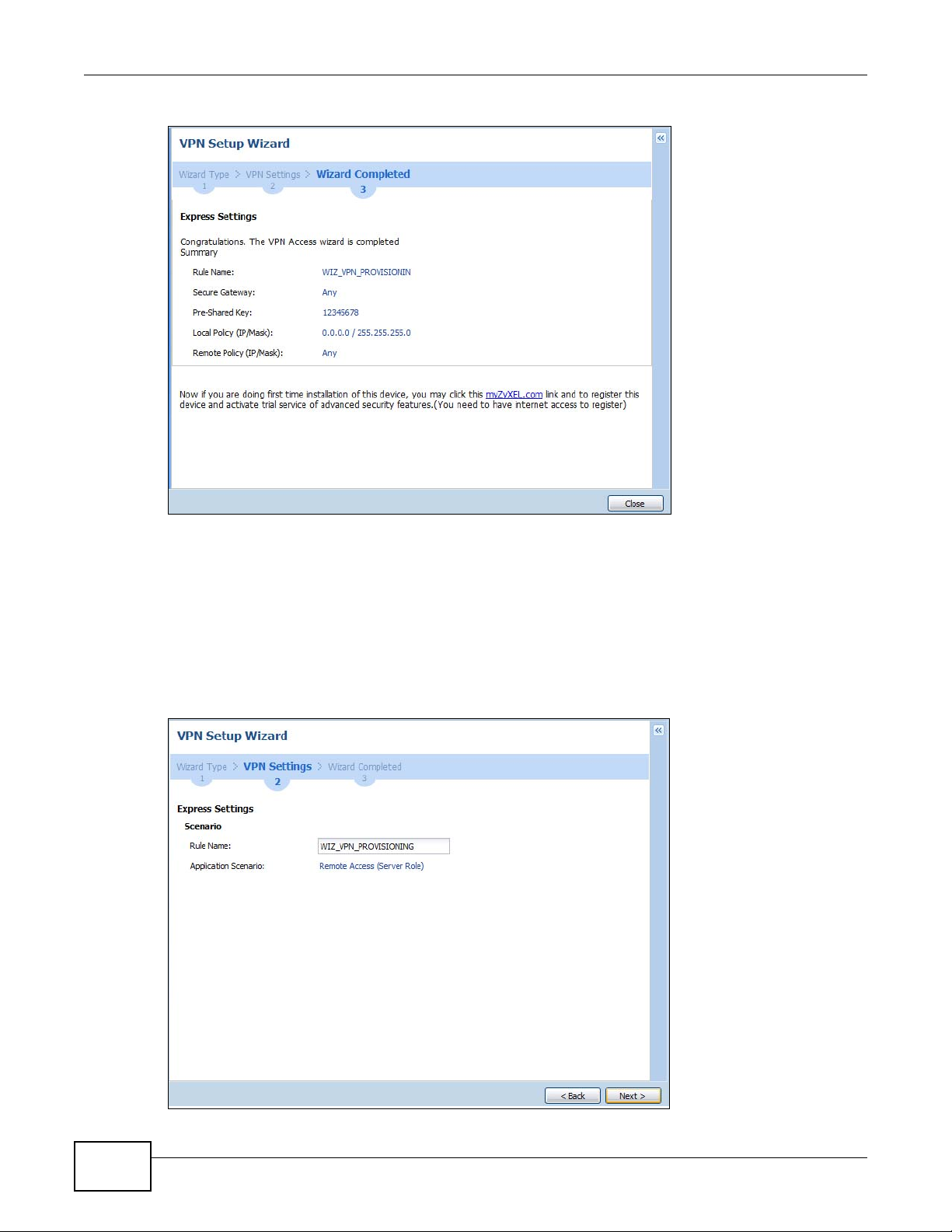
Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Figure 45 VPN for Configuration Provisioning Express Wizard: Finish
Click Close to exit the wizard.
4.4.5 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard Scenario
Click the Advanced radio button as shown in the screen shown in Figure 41 on page 58 to displa y
the following screen.
Figure 46 VPN for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard: Scenario Settings
62
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
Rule Name: Type the name used to identify this VPN connection (and VPN gateway). You may use
1-31 alphanumeric characters, underscores (_), or dashes (-), but the first character cannot be a
number. This value is case-sensitive.
Application Scenario: Only the Remote Access (Server Role) is allowed in this wizard. It
allows incoming connections from the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client.
Click Next to continue the wizard.
4.4.6 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard - Phase 1 Settings
There are two phases to every IKE (Internet Key Exchange) negotiation – phase 1 (Authentication)
and phase 2 (Key Exchange). A phase 1 exchange establishes an IKE SA (Security Association).
Figure 47 VPN for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard: Phase 1 Settings
• Secure Gateway: Any displays in this field because it is not configurable in this wizard. It allows
incoming connections from the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client.
• My Address (interface): Select an interface from the drop-down list box to use on your
ZyWALL.
• Negotiation Mode: Select Main for identity protection. Select Aggressive to allow more
incoming connections from dynamic IP addresses to use separate passwords.
Note: Multiple SAs connecting through a secure gateway mus t have the same negotiation
mode.
• Encryption Algorithm: 3DES and AES use encryption. The longer the key, the higher the
security (this may affect throughput). Both sender and receiver must know the same secret key,
which can be used to encrypt and decrypt the message or to generate and verify a message
authentication code. The DES encryption algorithm uses a 56-bit key. Triple DES (3DES) is a
variation on DES that uses a 168-bit key. As a result, 3DES is more secure than DES. It also
requires more processing power, resulting in increased latency and decreased throughput.
AES128 uses a 128-bit key and is faster than 3DES. AES192 uses a 192-bit key and AES256 uses
a 256-bit key.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
63

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
• Authentication Algorithm: MD5 (Message Digest 5) and SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) are
hash algorithms used to authenticate packet data. MD5 gives minimal security. SHA1 gives
higher security and SHA256 gives the highest security. The stronger the algorithm, the slower it
is.
• Key Group: DH5 is more secure than DH1 or DH2 (although it may affect throughput). DH1
(default) refers to Diffie-Hellman Group 1 a 768 bit random number. DH2 refers to Diffie-Hellman
Group 2 a 1024 bit (1Kb) random number. DH5 refers to Diffie-Hellman Group 5 a 1536 bit
random number.
• SA Life Time: Set how often the ZyWALL renegotiates the IKE SA. A short SA life time increases
security, but renegotiation temporarily disconnects the VPN tunnel.
• Authentication Method: Select Pre-Shared Key to use a password or Certificate to use one
of the ZyWALL’s certificates.
4.4.7 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard - Phase 2
Phase 2 in an IKE uses the SA that was established in phase 1 to negotiate SAs for IPSec.
Figure 48 VPN for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard: Phase 2
64
• Active Protocol: ESP is compatible with NAT. AH is not available in this wizard.
• Encapsulation: Tunnel is compatible with NAT, Transport is not.
• Encryption Algorithm: 3DES and AES use encryption. The longer the AES key, the higher the
security (this may affect throughput). Null uses no encryption.
• Authentication Algorithm: MD5 (Message Digest 5) and SHA (Secure Hash Algorithm) are
hash algorithms used to authenticate packet data. MD5 gives minimal security. SHA1 gives
higher security and SHA256 gives the highest security. The stronger the algorithm, the slower it
is.
• SA Life Time: Set how often the ZyWALL renegotiates the IKE SA. A short SA life time increases
security, but renegotiation temporarily disconnects the VPN tunnel.
• Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS): Disabling PFS allows faster IPSec setup, but is less secure.
Select DH1, DH2 or DH5 to enable PFS. DH5 is more secure than DH1 or DH2 (although it may
affect throughput). DH1 refers to Diffie-Hellman Group 1 a 768 bit random number. DH2 refers to
Diffie-Hellman Group 2 a 1024 bit (1Kb) random number. DH5 refers to Diffie-Hellman Group 5 a
1536 bit random number (more secure, yet slower).
• Local Policy (IP/Mask): Type the IP address of a computer on your network. You can also
specify a subnet. This must match the remote IP address configured on the remote IPSec device.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
• Remote Policy (IP/Mask): Any displays in this field because it is not configurable in this
wizard.
• Nailed-Up: This displays for the site-to-site and remote access client role scenarios. Select this
to have the ZyWALL automatically renegotiate the IPSec SA when the SA life time expires.
4.4.8 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard Summary
This is a read-only summary of the VPN tunnel settings.
Figure 49 VPN for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard: Summary
• Rule Name: Identifies the VPN connection (and the VPN gateway).
• Secure Gateway: Any displays in this field because it is not configurable in this wizard. It
allows incoming connections from the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client.
• Pre-Shared Key: VPN tunnel password.
• Certificate: The certificate the ZyWALL uses to identify itself when setting up the VPN tunnel.
• Local Policy: IP address and subnet mask of the computers on the network behind your ZyWALL
that can use the tunnel.
• Remote Policy: Any displays in this field because it is not configurable in this wizard.
•The Configuration for Secure Gateway displays the configur ation that the ZyWALL IPSec VPN
Client will get from the ZyWALL.
• Click Save to save the VPN rule.
4.4.9 VPN Settings for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard- Finish
Now the rule is configured on the ZyWALL. The Phase 1 rule settings appear in the VPN > IPSec
VPN > VPN Gateway screen and the Phase 2 rule settings appear in the VPN > IPSec VPN >
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
65

Chapter 4 Quick Setup Wizards
VPN Connection screen. Enter the IP address of the ZyWALL in the ZyWALL IPSec VPN Client to
get all these VPN settings automatically from the ZyWALL.
Figure 50 VPN for Configuration Provisioning Advanced Wizard: Finish
Click Close to exit the wizard.
66
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

5.1 Overview
Use the Dashboard screens to check status information about the ZyWALL.
5.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
Use the Dashboard screens for the following.
•Use the main Dashboard screen (see Section 5.2 on page 67) to see the ZyWALL’s general
device information, system status, system resource usage, licensed service status, and interface
status. You can also display other status screens for more information.
•Use the VPN status screen (see Section 5.2.4 on page 74) to look at the VPN tunnels that are
currently established.
•Use the DHCP Table screen (see Section 5.2.5 on page 75) to look at the IP addresses currently
assigned to DHCP clients and the IP addresses reserved for specific MAC addresses.
•Use the Current Users screen (see Section 5.2.6 on page 76) to look at a list of the users
currently logged into the ZyWALL.
CHAPTER 5
Dashboard
5.2 The Dashboard Screen
The Dashboard screen displays when you log into the ZyWALL or click Dashboard in the
navigation panel. The dashboard displays general device information, system status, system
resource usage, licensed service status, and interface status in widgets that you can re-arrange to
suit your needs. You can also collapse, refresh, and close individual widgets.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide 67

Chapter 5 Dashboard
A
B
C
D
E
Figure 51 Dashboard
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 14 Dashboard
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Widget Setting
(A)
Up Arrow (B) Click this to collapse a widget. It then becomes a down arrow . Click it again to enlarge the
Refresh Time
Setting (C)
Refresh Now (D) Click this to update the widget’s information immediately.
Close Widget (E) Click this to close the widget. Use Widget Setting to re-open it.
Virtual Device
Rear Panel Click this to view details about the ZyWALL’s rear panel. Hover your cursor over a
Front Panel Click this to view details about the status of the ZyWALL’s front panel LEDs and
Name This field displays the name of each interface.
Slot This field displays the name of each extension slot.
Use this link to open or close widgets by selecting/clearing the associated checkbox.
widget again.
Set the interval for refreshing the information displayed in the widget.
connected interface or slot to display status details.
connections. See Section 3.5 on page 39 for LED descriptions. An unconnected interface or
slot appears grayed out.
The following front and rear panel labels display when you hover your cursor over a
connected interface or slot.
68
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 5 Dashboard
Table 14 Dashboard (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device This field displays the name of the device connected to the USB port if one is connected.
Status This field displays the current status of each interface or device installed in a slot. The
possible values depend on what type of interface it is.
Inactive - The Ethernet interface is disabled.
Down - The Ethernet interface is enabled but not connected.
Speed / Duplex - The Ethernet interface is enabled and connected. This field displays the
port speed and duplex setting (Full or Half).
For cellular (3G) interfaces, see Section 7.5 on page 132 the Web Help for the status that
can appear.
Zone This field displays the zone to which the interface is currently assigned.
IP Address/
Mask
Device
Information
System
Name
Model Name This field displays the model name of this ZyWALL.
Serial
Number
MAC Address
Range
Firmware
Version
System Status
System
Uptime
Current
Date/Time
VPN Status Click th is to look at the VPN tunnels that are currently established. See Section 5.2.1 on
DHCP Table Click this to look at the IP addresses currently assigned to the ZyWALL’s DHCP clients and
Current Login
User
Number of
Login Users
This field displays the current IP address and subnet mask assigned to the interface. If the
interface is a member of an active virtual router, this field displays the IP address it is
currently using. This is either the static IP address of the interface (if it is the master) or
the management IP address (if it is a backup).
This identifies a device installed in one of the ZyWALL’s extension slots or USB ports.
This field displays the name used to identify the ZyWALL on any network. Click the icon to
open the screen where you can change it.
This field displays the serial number of this ZyWALL. The serial number is used for device
tracking and control.
This field displays the MAC addresses used by the ZyWALL. Each physical port has one
MAC address. The first MAC address is assigned to physical port 1, the second MAC
address is assigned to physical port 2, and so on.
This field displays the version number and date of the firmware the ZyWAL L is currently
running. Click the icon to open the screen where you can upload firmware.
This field displays how long the ZyWALL has been running since it last restarted or was
turned on.
This field displays the current date and time in the ZyWALL. The format is yyyy-mm-dd
hh:mm:ss.
page 72.
the IP addresses reserved for specific MAC addresses. See Section 5.2.5 on page 75.
This field displays the user name used to log in to the current session, the amount of
reauthentication time remain ing, and the amount of lease time remaining.
This field displays the number of users curre ntly logged in to the Z yW ALL. Click the icon to
pop-open a list of the users who are currently logged in to the ZyWALL.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
69

Chapter 5 Dashboard
Table 14 Dashboard (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Boot Status This field displays details about the ZyWALL’s startup state.
System
Resources
CPU Usage This field displays what percentage of the ZyWALL’s processing capability is currently being
Memory
Usage
Flash Usage This field displays what percentage of the ZyWALL’s onboard flash memory is currently
USB Storage
Usage
Active
Sessions
Extension Slot This section of t he screen displays the status of the extension card slot the USB ports.
Extension
Slot
Device This field displays the name of the device connected to the extension slot (or none if no
OK - The ZyWALL started up successfully.
Firmware update OK - A firmware update was successful.
Problematic configuration after firmware update - The application of the
configuration failed after a firmware upgrade.
System default configuration - The ZyWALL successfully applied the system default
configuration. This occurs when the ZyWALL starts for the first time or you intentionally
reset the ZyWALL to the system default settings.
Fallback to lastgood configuration - The ZyWALL was unable to apply the startupconfig.conf configuration file and fell back to the lastgood.conf configuration file.
Fallback to system default configuration - The ZyWALL was unable to apply the
lastgood.conf configuration file and fell back to the system default configuration file
(system-default.conf).
Booting in progress - The ZyWALL is still applying the system configuration.
used. Hover your cursor over this field to display the Show CPU Usage icon that takes
you to a chart of the ZyWALL’s recent CPU usage.
This field displays what percentage of the ZyWALL’s RAM is currently being used. Hover
your cursor over this field to display the Show Memory Usage icon that takes you to a
chart of the ZyWALL’s recent memory usage.
being used.
This field shows how much storage in the USB device connected to the ZyWALL is in use.
This field shows how many sessions, established and non-established, that pass through/
from/to/within the ZyWALL. Hover your cursor over this field to display icons. Click the
Detail icon to go to the Session Monitor screen to see details about the active s es si o ns .
Click the Show Active Sessions icon to display a chart of ZyWALL’s recent se ssion usage.
This field displays the name of each extension slot.
device is detected).
70
USB Flash Drive - Indicates a connected USB storage device and the drive’s storage
capacity.
Status For cellular (3G) interfaces, see Section 6.10 on page 96 the Web Help for the status that
can appear.
Ready - A USB storage device connected to the ZyWALL is ready for the ZyWALL to use.
Unused - The ZyWALL is unable to mount a USB storage device connected to the ZyWALL.
Interface Status
Summary
# This shows how many interfaces there are.
Name This field displays the name of each interface.
If an Ethernet interface does not have any physical ports associated with it, its entry is
displayed in light gray text. Click the Detail icon to go to a (more detailed) summary
screen of interface statistics.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 5 Dashboard
Table 14 Dashboard (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status This field displays the cu rrent status of ea ch interface. The possible values depend on what
type of interface it is.
For Ethernet interfaces:
Inactive - The Ethernet interface is disabled.
Down - The Ethernet interface does not have any physical ports associated with it or the
Ethernet interface is enabled but not connected.
Speed / Duplex - The Ethernet interface is enabled and connected. This field displays the
port speed and duplex setting (Full or Half).
For PPP interfaces:
Connected - The PPP interface is connected.
Disconnected - The PPP interface is not connected.
If the PPP interface is disabled, it does not appear in the list.
Zone This field displays the zone to which the interface is currently assigned.
IP Addr/
Netmask
This field displays the current IP address and subnet mask assigned to the interface. If the
IP address is 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0, the interface is disabled or did not receive an IP address and
subnet mask via DHCP.
If this interface is a member of an active virtual router, this field displays t he IP address it
is currently using. This is either the static IP address of the interface (if it is the master) or
the management IP address (if it is a backup).
Action Use this field to get or to update the IP address for the interface.
Click Renew to send a new DHCP request to a DHCP server.
Click the Connect icon to have the ZyWALL try to connect a PPPoE/PPTP interface. If the
interface cannot use one of these ways to get or to update its IP address, this field displays
n/a.
Click the Disconnect icon to stop a PPPoE/PPTP connection.
Top 5 Firewall
Rules that
blocked IPv4
(IPv6) Traffic
# This is the entry’s rank in the list of the most commonly triggered firewall rules.
Priority This is the position of the triggered firewall rule in the global rule list. The ordering of
From This shows the zone packets came from that the triggered firewall rule.
To This shows the zone packets went to that the triggered firewall rule.
Description This field displays the descriptive name (if any) of the triggered firewall rule.
Hits This field displays how many times the firewall rule was triggered.
Schedule This field displays the schedule object of the triggered firewall rule.
User This is the user name or user group name of the triggered firewall rule.
IPv4 (IPv6)
Source
IPv4 (IPv6)
Destination
Service This displays the service object of the triggered firewall rule.
Access This field displays whether the triggered firewall rule denied (silently discarded) or rejected
This section displays the most triggered five fir ewall rules that caused the ZyW ALL to block
.
firewall rules is important as rules are applied in sequence.
This displays the source IPv4 (IPv6) address object of the triggered firewall rule.
This displays the destination IPv4 (IPv6) address object of the triggered firewall rule.
the passage of packets of the triggered firewall rule.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
71

Chapter 5 Dashboard
Table 14 Dashboard (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Logs This field displays whether a log (and alert) was created for the triggered firewall rule.
The Latest Alert
Logs
# This is the entry’s rank in the list of alert logs.
Time This field displays the date and time the log was created.
Priority This field displays the severity of the log.
Category This field displays the type of log generated.
Message This field displays the actual log message.
Source This field displays the source address (if any) in the packet that generated the log.
Destination This field displays the destination address (if any) in the packet that generated the log.
Protocol This field displays the service protocol in the packet that generated the log.
Note This field displays descriptive information (if any) of the log.
These fields display recent logs generated by the ZyWALL.
5.2.1 The CPU Usage Screen
Use this screen to look at a chart of the ZyWALL’s recent CPU usage. To access this screen, click
CPU Usage in the dashboard.
Figure 52 Dashboard > CPU Usage
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 15 Dashboard > CPU Usage
LABEL DESCRIPTION
The y-axis represents the percentage of CPU usage.
The x-axis shows the time period over which the CPU usage occurred
Refresh Interval Enter how often you want this window to be automatically updated.
Refresh Click this to update the information in the window right away.
72
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

5.2.2 The Memory Usage Screen
Use this screen to look at a chart of the ZyWALL’s recent memory (RAM) usage. To access this
screen, click Memory Usage in the dashboard.
Figure 53 Dashboard > Memory Usage
Chapter 5 Dashboard
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 16 Dashboard > Memory Usage
LABEL DESCRIPTION
The y-axis represents the percentage of RAM usage.
The x-axis shows the time period over which the RAM usage occurred
Refresh Interval Enter how often you want this window to be automatically updated.
Refresh Click this to update the information in the window right away.
5.2.3 The Active Sessions Screen
Use this screen to look at a chart of the ZyWALL’s recent traffic session usage. To access this
screen, click Session Usage in the dashboard.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
73
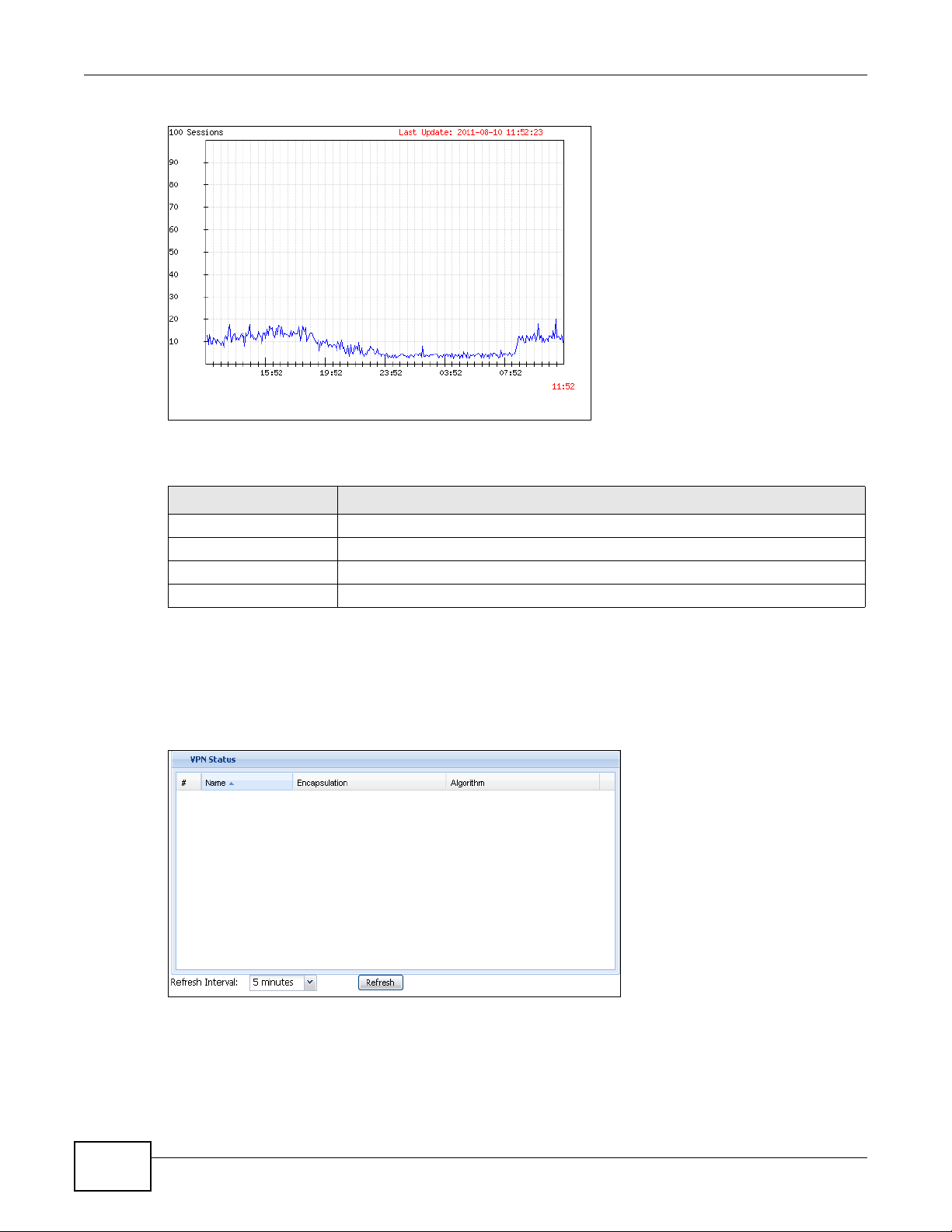
Chapter 5 Dashboard
Figure 54 Dashboard > Session Usage
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 17 Dashboard > Session Usage
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Sessions The y-axis represents the number of session.
Refresh Interval Enter how often you want this window to be automatically updated.
Refresh Click this to update the information in the window right away.
The x-axis shows the time period over which the session usage occurred
5.2.4 The VPN Status Screen
Use this screen to look at the VPN tunnels that are currently established. To access this screen, click
VPN Status in System Status in the dashboard.
Figure 55 Dashboard > System Status > VPN Status
74
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 18 Dashboard > VPN Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with a specific SA.
Name This field displays the name of the IPSec SA.
Encapsulation This field displays how the IPSec SA is encapsulated.
Algorithm This field displays the encryption and authentication algorithms used in the SA.
Refresh Interval Select how often you want this window to be updated automatically.
Refresh Click this to update the information in the window right away.
5.2.5 The DHCP Table Screen
Use this screen to look at the IP addresses currently assigned to DHCP clients and the IP addresses
reserved for specific MAC addresses. T o access this screen, click DHCP Table in System Status in
the dashboard.
Figure 56 Dashboard > System Status >DHCP Table
Chapter 5 Dashboard
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 19 Dashboard > DHCP Table
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with a specific entry.
Interface This field identifies the interface that assigned an IP address to a DHCP client.
IP Address This field displays the IP address currently assigned to a DHCP client or reserved for a specific
MAC address. Click the column’s heading cell to sort the table entries by IP address. Click the
heading cell again to reverse the sort order.
Host Name This field displays the name used to identify this device on the network (the computer name).
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address to which the IP address is currently assigned or for which
Description For a static DHCP entry, the host name or the description you configured shows here. This field
Reserve If this field is selected, this entry is a static DHCP entry. The IP address is reserved for the MAC
The ZyWALL learns these from the DHCP client requests. “None” shows here for a static DHCP
entry .
the IP address is reserved. Click the column’s heading cell to sort the table entries by MAC
address. Click the heading cell again to reverse the sort order.
is blank for dynamic DHCP entries.
address.
If this field is clear, this entry is a dynamic DHCP entry. The IP address is assigned to a DHCP
client.
T o create a static DHCP entry using an existing dynamic DHCP entry, select this field, and then
click Apply.
To remove a static DHCP entry, clear this field, and then click Apply.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
75
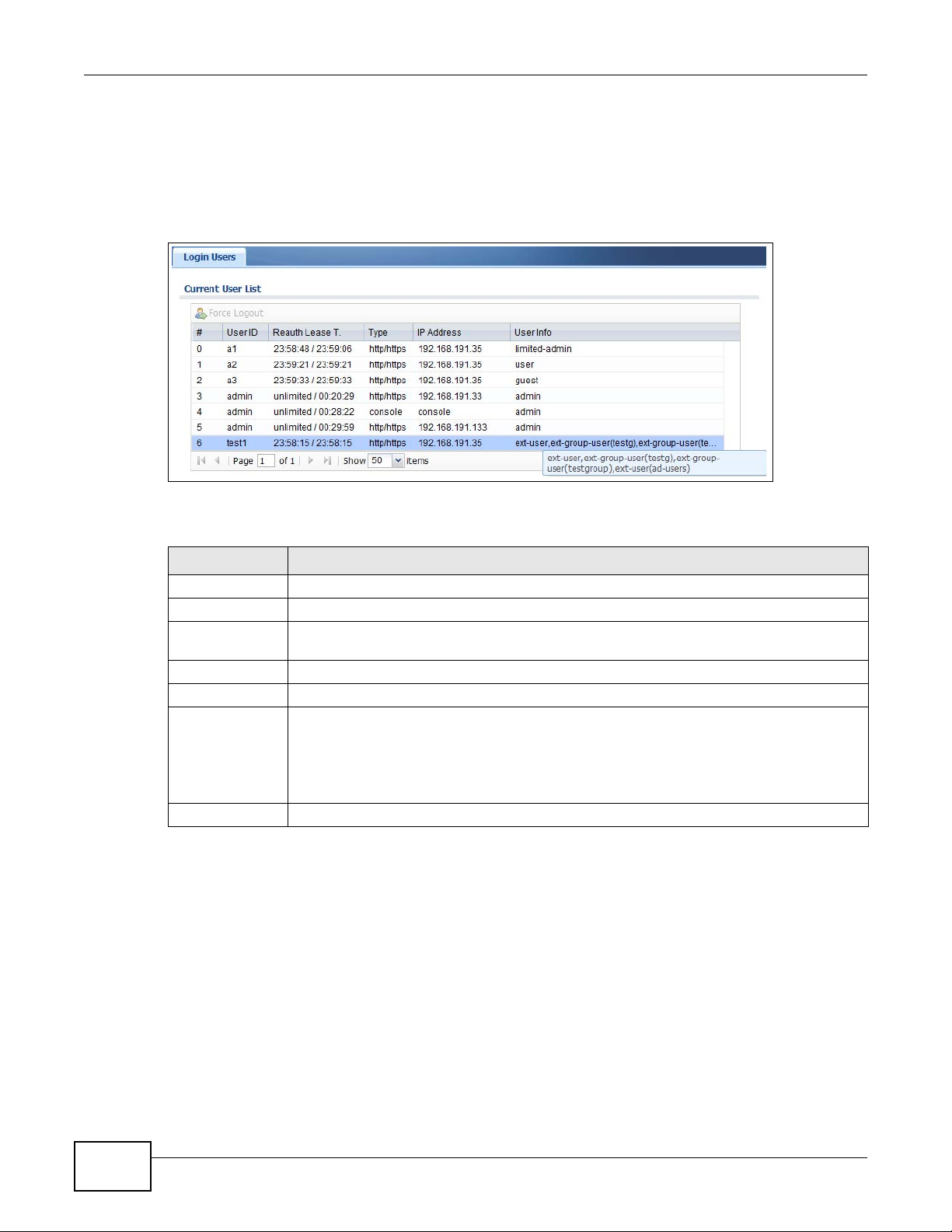
Chapter 5 Dashboard
5.2.6 The Number of Login Users Screen
Use this screen to look at a list of the users currently logged into the ZyW ALL. Users who close their
browsers without logging out are still shown as logged in here. To access this screen, click Number
of Login Users in System Status in the dashboard or Monitor > Login User.
Figure 57 Dashboard >
System Status > Number of Login Users
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 20 Dashboard > Number of Login Users
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This field is a sequential value and is not associated with any entry.
User ID This field displays the user name of each user who is currently logged in to the ZyWALL.
Reauth Lease T. This field displays the amount of reauthentication time remaining and the amount of lease
time remaining for each user. See Chapter 27 on page 361 for more information.
Type This field displays the way the user logged in to the ZyWALL.
IP address This field displays the IP address of the computer used to log in to the ZyWALL.
User Info This field displays the types of user accounts the ZyWALL uses. If the user type is ext-user
(external user), this field will show its external-group information when you move your
mouse over it.
76
If the external user matches two external-group objects, both external-group object
names will be shown.
Force Logout Click this icon to end a user’s session.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

PART II
Technical Reference
77

78

6.1 Overview
Use the Monitor screens to check status and statistics information.
6.1.1 What You Can Do in this Chapter
Use the Monitor screens for the following.
•Use the System Status > Port Statistics screen (see Section 6.2 on page 80) to look at packet
statistics for each physical port.
•Use the System Status > Port Statistics > Graph View screen (see Section 6.2 on page 80)
to look at a line graph of packet statistics for each physical port.
•Use the System Status > Interface Status screen (Section 6.3 on page 82) to see all of the
ZyWALL’s interfaces and their packet statistics.
•Use the System Status > Traffic Statistics screen (see Section 6.4 on page 86) to start or
stop data collection and view statistics.
•Use the System Status > Session Monitor screen (see Section 6.5 on page 89) to view
sessions by user or service.
•Use the System Status > DDNS Status screen (see Section 6.6 on page 91) to view the status
of the ZyWALL’s DDNS domain names.
•Use the System Status > IP/MAC Binding screen (Section 6.7 on page 91) to view a list of
devices that have received an IP address from ZyWALL interfaces with IP/MAC binding enabled.
•Use the System Status > Login Users screen (Section 6.8 on page 92) to look at a list of the
users currently logged into the ZyWALL.
•Use the System Status > Cellular Status screen (Section 6.9 on page 93) to check your 3G
connection status.
•Use the System Status > USB Storage screen (Section 6.10 on page 96) to view information
about a connected USB storage device.
•Use the VPN Monitor > IPSec screen (Section 6.11 on page 97) to display and manage active
IPSec SAs.
•Use the VPN Monitor > SSL screen (see Section 6.12 on page 99) to list the users currently
logged into the VPN SSL client portal. You can also log out individual users and delete related
session information.
•Use the VPN Monitor > L2TP over IPSec screen (see Section 6.13 on page 99) to display
and manage the ZyWALL’s connected L2TP VPN sessions.
•Use the Log (Section 6.14 on page 100) screen to view the ZyWALL’s current log messages. You
can change the way the log is displayed, you can e-mail the log, and you can also clear the log in
this screen.
CHAPTER 6
Monitor
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide 79
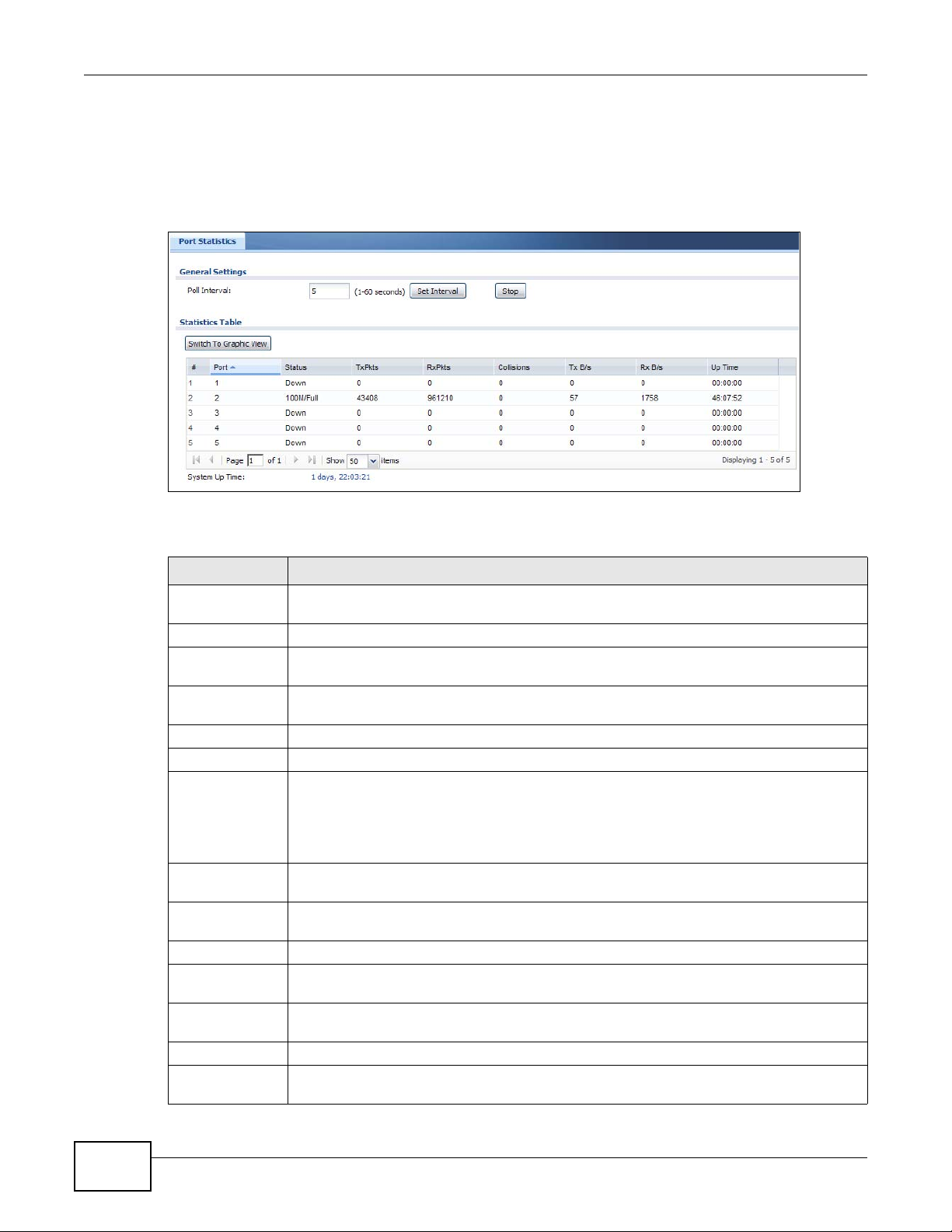
Chapter 6 Monitor
6.2 The Port Statistics Screen
Use this screen to look at packet statistics for each Gigabit Ethernet port. To access this screen,
click Monitor > System Status > Port Statistics.
Figure 58 Monitor > System Status > Port Statistics
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 21 Monitor > System Status > Port Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Poll Interval Enter how often you want this window to be updated automatically, and click Set
Set Interval Click this to set the Poll Interval the screen uses.
Stop Click this to stop the wi ndow from u pdating au tomaticall y. You can start it again by settin g
Switch to
Graphic View
# This field displays the port’s number in the list.
Port This field displays the physical port number.
Status This field displays the current status of the physical port.
TxPkts This field displays the number of packets transmitted from the ZyWALL on the physical
RxPkts This field displays the number of packets received by the ZyWALL on the physical port
Collisions This field displays the number of collisions on the physical port since it was last connected.
Tx B/s This field displays the transmission speed, in bytes per second, on the physical port in the
Rx B/s This field displays the reception speed, in bytes per second, on the physical port in the
Up Time This field displays how long the physical port has been connected.
System Up Time This field displays how long the ZyWALL has been running since it last restarted or was
Interval.
the Poll Interval and clicking Set Interval.
Click this to display the port statistics as a line graph.
Down - The physical port is not connected.
Speed / Duplex - The physical port is connected. This field displays the port speed and
duplex setting (Full or Half).
port since it was last connected.
since it was last connected.
one-second interval before the screen updated.
one-second interval before the screen updated.
turned on.
80
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

6.2.1 The Port Statistics Graph Screen
Use this screen to look at a line graph of packet statistics for each physical port. To access this
screen, click Port Statistics in the Status screen and then the Switch to Graphic View Button.
Figure 59 Monitor > System Status > Port Statistics > Switch to Graphic View
Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 22 Monitor > System Status > Port Statistics > Switch to Graphic View
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh Interval Enter how often you want this window to be automatically updated.
Refresh Now Click this to update the information in the window right away.
Port Selection Select the number of the physical port for which you want to display graphics.
Switch to Grid
View
bps The y-axis represents the speed of transmission or reception.
time The x-axis shows the time period over which the transmission or reception occurred
TX This line represents traffic transmitted from the ZyWALL on the physical port since it was
RX This line represents the tr affic receiv ed by the Z yWALL on th e physical port sinc e it was last
Last Update This field displays the date and time the information in the window was last updated.
System Up Time This field displays how long the ZyWALL has been running since it last restarted or was
Click this to display the port statistics as a table.
last connected.
connected.
turned on.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
81

Chapter 6 Monitor
6.3 Interface Status Screen
This screen lists all of the ZyWALL’s interfaces and gives packet statistics for them. Click Monitor >
System Status > Interface Status to access this screen.
82
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Figure 60 Monitor > System Status > Interface Status
Chapter 6 Monitor
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
83

Chapter 6 Monitor
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 23 Monitor > System Status > Interface Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface Status If an Ethernet interface does not have any physical ports associated with it, its entry is
Expand/Close Click this button to show or hide statistics for all the virtual interfaces on top of the
Name This field displays the name of each interface. If there is an Expand icon (plus-sign) next
Port This field displays the physical port number.
Status This field displays the current status of each interface. The possible values depend on what
displayed in light gray text.
Ethernet interfaces.
to the name, click this to look at the status of virtual interfaces on top of this interface.
type of interface it is.
For Ethernet interfaces:
Inactive - The Ethernet interface is disabled.
Down - The Ethernet interface is enabled but not connected.
Speed / Duplex - The Ethernet interface is enabled and connected. This field displays the
port speed and duplex setting (Full or Half).
For cellular (3G) interfaces, see Section 6.10 on page 96 the Web Help for the status that
can appear.
For virtual interfaces, this field always displays Up. If the virtual interface is disabled, it
does not appear in the list.
For VLAN and bridge interfaces, this field always displays Up. If the VLAN or bridge
interface is disabled, it does not appear in the list.
For PPP interfaces:
Connected - The PPP interface is connected.
Disconnected - The PPP interface is not connected.
If the PPP interface is disabled, it does not appear in the list.
Zone This field displays the zone to which the interface is assigned.
IP Addr/Netmask This field displays the current IP address and subnet mask assigned to the interface. If the
IP address and subnet mask are 0.0.0.0, the interface is disabled or did not receive an IP
address and subnet mask via DHCP.
If this interface is a member of an active virtual router, this field displays the IP address it
is currently using. This is either the static IP address of the interface (if it is the master) or
the management IP address (if it is a backup).
IP Assignment This field displays how the interface gets its IP address.
Static - This interface has a static IP address.
DHCP Client - This interface gets its IP address from a DHCP server.
Services This field lists which services the interface provides to the network. Examples include
Action Use this field to get or to update the IP address fo r the interface. Click Renew to send a
T unnel Interface
Status
Name This field displays the name of the interface.
DHCP relay, DHCP server, DDNS, RIP, and OSPF. This field displays n/a if the interface
does not provide any services to the network.
new DHCP request to a DHCP server. Click Connect to try to connect a PPPoE/PPTP
interface. If the interface cannot use one of these ways to get or to update its IP address,
this field displays n/a.
This displays the details of the ZyWALL’s configured tunnel interface s.
84
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 6 Monitor
Table 23 Monitor > System Status > Interface Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status The activate (light bulb) icon is lit when the entry is active and dimmed when the entry is
inactive.
Zone This field displays the zone to which the interface is assigned.
IP Address This is the IP address of the interface. If the interface is active (and connected), the
ZyWALL tunnels local traffic sent to this IP address to the Remote Gateway Address.
My Address This is the interface or IP address uses to identify itself to the remote gateway. The
Remote Gateway
Address
Mode This field displays the tunnel mode that you are using.
Action This field lists which services the interface provides to the network. This field displays n/a
IPv6 Interface
Status
Expand/Close Click this button to show or hide statistics for all the virtual interfaces on top of the
Name This field displays the name of each interface. If there is an Expand icon (plus-sign) next
Port This field displays the physical port number.
Status This field displays the current status of each interface. The possible values depend on what
ZyWALL uses this as the source for the packets it tunnels to the remote gateway.
This is the IP address or domain name of the remote gateway to which this interface
tunnels traffic.
if the interface does not provide any services to the network.
This section displays the status of the IPv6 interface. If an Ethernet interface does not
have any physical ports associated with it, its entry is displayed in light gray text.
Ethernet interfaces.
to the name, click this to look at the status of virtual interfaces on top of this interface.
type of interface it is.
For Ethernet interfaces:
Inactive - The Ethernet interface is disabled.
Down - The Ethernet interface is enabled but not connected.
Speed / Duplex - The Ethernet interface is enabled and connected. This field displays the
port speed and duplex setting (Full or Half).
For cellular (3G) interfaces, see Section 6.9 on page 93 the Web Help for the status that
can appear.
For virtual interfaces, this field always displays Up. If the virtual interface is disabled, it
does not appear in the list.
For VLAN and bridge interfaces, this field always displays Up. If the VLAN or bridge
interface is disabled, it does not appear in the list.
For PPP interfaces:
Connected - The PPP interface is connected.
Disconnected - The PPP interface is not connected.
If the PPP interface is disabled, it does not appear in the list.
HA Status This field displays the status of the interface in the virtual router.
Active - This interface is the master interface in the virtual router.
Stand-By - This interface is a backup interface in the virtual router.
Fault - This VRRP group is not functioning in the virtual router right now. For example, this
might happen if the interface is down.
n/a - Device HA is not active on the interface.
Zone This field displays the zone to which the interface is assigned.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
85

Chapter 6 Monitor
Table 23 Monitor > System Status > Interface Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
IP Address This field displays the current IPv6 address assigned to the interface. If the IPv6 address is
IP Assignment This field displays how the interface gets its IP address.
Services This field lists which services the interface provides to the network. Examples include
Action Use this field to get or to update the IP address fo r the interface. Click Renew to send a
Interface
Statistics
Refresh Click this button to update the information in the screen.
Expand/Close Click this button to show or hide statistics for all the virtual interfaces on top of the
Name This field displays the name of each interface. If there is a Expand icon (plus-sign) next to
Status This field displays the current status of the interface.
not displayed, the interface is disabled or did not receive an IPv6 address via DHCP.
If this interface is a member of an active virtual router, this field displays the IP address it
is currently using. This is either the static IP address of the interface (if it is the master) or
the management IP address (if it is a backup).
Static - This interface has a static IP address.
DHCP Client - This interface gets its IP address from a DHCP server.
DHCP relay, DHCP server, DDNS, RIP, and OSPF. This field displays n/a if the interface
does not provide any services to the network.
new DHCP request to a DHCP server. Click Connect to try to connect a PPPoE/PPTP
interface. If the interface cannot use one of these ways to get or to update its IP address,
this field displays n/a.
This table provides packet statistics for each interface.
Ethernet interfaces.
the name, click this to look at the statistics for virtual interfaces on top of this interface.
Down - The interface is not connected.
Speed / Duplex - The interface is connected. This field displays the port speed and
duplex setting (Full or Half).
This field displays Connected and the accumulated connection time (hh:mm:ss) when the
PPP interface is connected.
TxPkts This field displays the number of packets transmitted from the ZyWALL on the interface
since it was last connected.
RxPkts This field displays the number of packets received by the ZyWALL on the interface since it
was last connected.
Tx B/s This field displays the tr ansm ission speed, in bytes per second, on the interface in the one-
Rx B/s This field displays the reception speed, in bytes per second, on the interface in the one-
second interval before the screen updated.
second interval before the screen updated.
6.4 The Traffic Statistics Screen
Click Monitor > System Status > Traffic Statistics to display the Traffic Statistics screen. This
screen provides basic information about the following for example:
• Most-visited Web sites and the number of times each one was visited. This count may not be
accurate in some cases because the ZyWALL counts HTTP GET packets. Please see Table 24 on
page 87 for more information.
• Most-used protocols or service ports and the amount of traffic on each one
86
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 6 Monitor
• LAN IP with heaviest traffic and how much traffic has been sent to and from each one
You use the Traffic Statistics screen to tell the ZyWALL when to start and when to stop collecting
information for these reports. You cannot schedule data collection; you have to start and stop it
manually in the Traffic Statistics screen.
Figure 61 Monitor > System Status > Traffic Statistics
There is a limit on the number of records shown in the report. Please see Table 25 on page 89 for
more information. The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 24 Monitor > System Status > Traffic Statistics
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Data Collection
Collect Statistics Select this to have the ZyWALL collect data for the report. If the ZyWALL has already been
collecting data, the collection period displays to the right. The progress is not tracked here
real-time, but you can click the Refresh button to update it.
Apply Click Apply to save your changes back to the ZyWALL.
Reset Click Reset to return the screen to its last-saved settings.
Statistics
Interface Select the interface from which to collect information. You can collect information from
Ethernet, VLAN, bridge and PPPoE/PPTP interfaces.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
87

Chapter 6 Monitor
Table 24 Monitor > System Status > Traffic Statistics (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Traffic Type Select the type of report to display. Choices are:
Refresh Click this button to update the report display.
Flush Data Click this button to discard all of the screen’s statistics and update the report display.
# This field is the rank of each record. The IP addresses and users are sorted by the amount
IP Address/User This field displays the IP address or user in this record. The maximum number of IP
Direction This field indicates whether the IP address or user is sending or receiving traffic.
Host IP Address/User - displays the IP addresses or us ers with the most t raffic and h ow
much traffic has been sent to and from each one.
Service/Port - displays the most-used protocols or service ports and the amount of
traffic for each one.
Web Site Hits - displays the most-visited Web sites and how many times each one has
been visited.
Each type of report has different information in the report (below).
These fields are available when the Traffic Type is Host IP Address/User.
of traffic.
addresses or users in this report is indicated in Table 25 on page 89.
Ingress- traffic is coming from the IP address or user to the ZyWALL.
Egress - traffic is going from the ZyWALL to the IP address or user.
Amount This field displays how much traffic was sent or received from the indicated IP address or
user. If the Direction is Ingress, a red bar is displayed; if the Direction is Egress, a
blue bar is displayed. The unit of measure is bytes, Kbytes, Mbytes or Gbytes, depending
on the amount of traffic for the particular IP address or user. The count starts over at zero
if the number of bytes passes the byte count limit. See Table 25 on page 89.
These fields are available when the Traffic Type is Service/Port.
# This field is the rank of each record. The protocols and service ports are sorted by the
Service/Port This field displays the service and port in this record. The maximum number of services
Protocol This field indicates what protocol the service was using.
Direction This field indicates whether the indicated protocol or service port is sending or receiving
Amount This field displays how much traffic was sent or received from the indicated service / port.
# This field is the rank of each record. The domain names are sorted by the number of hits.
Web Site This field displays the domain names most often visited. The ZyWALL counts each page
Hits This field displays how many hits the Web site received. The ZyWALL counts hits by
amount of traffic.
and service ports in this report is indicated in Table 25 on page 89.
traffic.
Ingress - traffic is coming into the router through the interface
Egress - traffic is going out from the router through the interface
If the Direction is Ingress, a red bar is displayed; if the Direction is Egress, a blue bar
is displayed. The unit of measure is bytes, Kbytes, Mbytes, Gbytes, or Tbytes, depending
on the amount of traffic for the particular protocol or service port. The count starts over at
zero if the number of bytes passes the byte count limit. See Table 25 on page 89.
These fields are available when the Traffic Type is Web Site Hits.
viewed on a Web site as another hit. The maximum number of domain names in this report
is indicated in Table 25 on page 89.
counting HTTP GET packets. Many Web sites have HT TP GET references to other Web sites,
and the ZyWALL counts these as hits too. The count starts over at zero if the number of
hits passes the hit count limit. See Table 25 on page 89.
88
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

The following table displays the maximum number of records shown in the report, the byte count
limit, and the hit count limit.
Table 25 Maximum Values for Reports
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Maximum Number of Records 20
64
Byte Count Limit 2
Hit Count Limit 2
bytes; this is just less than 17 million terabytes.
64
hits; this is over 1.8 x 1019 hits.
6.5 The Session Monitor Screen
The Session Monitor screen displays all established sessions that pass through the ZyWALL for
debugging or statistical analysis. It is not possible to manage sessions in this screen. The following
information is displayed.
• User who started the session
• Protocol or service port used
• Source address
• Destination address
• Number of bytes received (so far)
• Number of bytes transmitted (so far)
• Duration (so far)
Chapter 6 Monitor
You can look at all established sessions that passed through the Z yW ALL by user, service, source IP
address, or destination IP address. You can also filter the information by user, protocol / service or
service group, source address, and/or destination address and view it by user.
Click Monitor > System Status > Session Monitor to display the following screen.
Figure 62 Monitor > System Status > Session Monitor
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
89

Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 26 Monitor > System Status > Session Monitor
LABEL DESCRIPTION
View Select how you want the established sessions that passed through the ZyWALL to be
Refresh Click this button to update the information on the screen. The screen also refreshes
User This field displays the user in each active session.
Service This field displays the protocol used in each active session.
Source This field displays the source IP address and port in each active session.
Destination This field displays the destination IP address and port in each active session.
Rx This field displays the amount of information received by the source in the active session.
Tx This field displays the amount of information transmitted by the source in the active
Duration This field displays the length of the active session in seconds.
displayed. Choices are:
sessions by users - display all active sessions grouped by user
sessions by services - display all active sessions grouped by service or protocol
sessions by source IP - display all active sessions grouped by source IP address
sessions by destination IP - display all active sessions grouped by destination IP
address
all sessions - filter the active sessions by the User, Service, Source Address, and
Destination Address, and display each session individually (sorted by user).
automatically when you open and close the screen.
The User, Service, Source Address, and Destination Address fields display if you view
all sessions. Select your desired filter criteria and click the Search button to filter the list
of sessions.
User This field displays when View is set to all sessions. Type the user whose sessions you
want to view. It is not possible to type part of the user name or use wildcards in this field;
you must enter the whole user name.
Service This field displays when View is set to all sessions. Select the service or service group
whose sessions you want to view. The ZyWALL identifies the service by comparing the
protocol and destination port of each packet to the protocol and port of each services that
is defined. (See Chapter 29 on page 380 for more information about services.)
Source This field displays when View is set to all sessions. Type the source IP address whose
sessions you want to view. You cannot include the source port.
Destination This field displays when View is set to all sessions. Type the destination IP address
Search This button displays when View is set to all sessions. Click this button to update the
whose sessions you want to view. You cannot include the destination port.
information on the screen using the filter criteria in the User, Service, Source Address,
and Destination Address fields.
If you are looking at the sessions by users (or all sessions) report, click +
display or hide details about a user’s sessions.
If you are looking at the sessions by services report, click + or - to display or hide
details about a protocol’s sessions.
If you are looking at the sessions by source IP report, click + or - to display or hide
details about a source IP address’s sessions.
If you are looking at the sessions by destination IP report, click + or - to display or
hide details about a destination IP address’s sessions.
session.
or - to
90
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

6.6 The DDNS Status Screen
The DDNS Status screen shows the status of the ZyW ALL’ s DDNS domain names. Click Monitor >
System Status > DDNS Status to open the following screen.
Figure 63 Monitor > System Status > DDNS Status
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 27 Monitor > System Status > DDNS Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Update Click this to have the ZyWALL update the profile to the DDNS server. The ZyWALL
attempts to resolve the IP address for the domain name.
Profile Name This field displays the descriptive profile name for this entry.
Domain Name This field displays each domain name the ZyWALL can route.
Effective IP This is the (resolved) IP address of the domain name.
Last Update Status This shows whether the last attempt to resolve the IP address for the domain name
was successful or not. Updating means the ZyWALL is currently attempting to
resolve the IP address for the domain name.
Last Update Time This shows when the last attempt to resolve the IP address for the domain name
occurred (in year-month-day hour:minute:second format).
Chapter 6 Monitor
6.7 IP/MAC Binding Monitor
Click Monitor > System Status > IP/MAC Binding to open the IP/MAC Binding Monitor
screen. This screen lists the devices that have received an IP address from ZyWALL interfaces with
IP/MAC binding enabled and have ever established a session with the ZyWALL. Devices that have
never established a session with the ZyWALL do not display in the list.
Figure 64 Monitor > System Status > IP/MAC Binding
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
91

Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 28 Monitor > System Status > IP/MAC Binding
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Interface Select a ZyWALL interface that has IP/MAC binding enabled to show to which devices
# This is the index number of an IP/MAC binding entry.
IP Address This is the IP address that the ZyWALL assigned to a device.
Host Name This field displays the name used to identify this device on the network (the computer
MAC Address This field displays the MAC address to which the IP address is currently assigned.
Last Access This is when the device last established a session with the ZyWALL through this
Refresh Click this button to update the information in the screen.
it has assigned an IP address.
name). The ZyWALL learns these from the DHCP client requests.
interface.
6.8 The Login Users Screen
Use this screen to look at a list of the users currently logged into the ZyWALL. T o access this screen,
click Monitor > System Status >
Login Users.
Figure 65 Monitor > System Status > Login Users
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 29 Monitor > System Status > Login Users
LABEL DESCRIPTION
# This field is a sequential value and is not associated with any entry.
User ID This field displays the user name of each user who is currently logged in to the
Reauth Lease T. This field displays the amount of reauthentication time remaining and the amount of
Type This field displays the way the user logged in to the ZyWALL.
IP Address This field displays the IP address of the computer used to log in to the ZyWALL.
ZyWALL.
lease time remaining for each user. See Chapter 27 on page 361.
92
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Table 29 Monitor > System Status > Login Users (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
User Info This field displays the types of user accounts the ZyWALL uses. If the user type is
ext-user (external user), this field will show its external-group information when you
move your mouse over it.
If the external user matches two external-group objects, both external-group object
names will be shown.
Force Logout Select a user ID and click this icon to end a user’s session.
Refresh Click this button to update the information in the screen.
6.9 Cellular Status Screen
This screen displays your 3G connection status. Click Monitor > System Status > Cellular
Status to display this screen.
Figure 66 Monitor > System Status > Cellular Status
Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 30 Monitor > System Status > Cellular Status
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Refresh Click this button to update the information in the screen.
More Information Click this to display more information on your 3G, such as the signal strength,
IMEA/ESN and IMSI. This is only available when the 3G device attached and
activated on your ZyWALL. Refer to Section 6.9.1 on page 95.
# This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with any interface.
Extension Slot This field displays where the entry’s cellular card is located.
Connected Device This field displays the model name of the cellular card.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
93

Chapter 6 Monitor
Table 30 Monitor > System Status > Cellular Status (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status No device - no 3G device is connected to the ZyWALL.
Service Provider This displays the name of your network service provider. This show s Limited
Cellular System This field displays what type of cellular network the 3G connection is using. The
Signal Quality This displays the strength of the signal. The signal strength mainly depends on the
No Service - no 3G network is available in the area; you cannot connect to the
Internet.
Limited Service - returned by the service provider in cases where the SIM card is
expired, the user failed to pay for the service and so on; you cannot connect to the
Internet.
Device detected - displays when you connect a 3G device.
Device error - a 3G device is connected but there is an error.
Probe device fail - the ZyWALL’s test of the 3G device failed.
Probe device ok - the ZyWALL’s test of the 3G device succeeded.
Init device fail - the ZyWALL was not able to initialize the 3G device.
Init device ok - the ZyWALL initialized the 3G card.
Check lock fail - the ZyWALL’s check of whether or not the 3G device is locked
failed.
Device locked - the 3G device is locked.
SIM error - there is a SIM card error on the 3G device.
SIM locked-PUK - the PUK is locked on the 3G device’s SIM card.
SIM locked-PIN - the PIN is locked on the 3G device’s SIM card.
Unlock PUK fail - Your attempt to unlock a WCDMA 3G device’s PUK failed
because you entered an incorrect PUK.
Unlock PIN fail - Your attempt to unlock a WCDMA 3G device’s PIN failed
because you entered an incorrect PIN.
Unlock device fail - Your attempt to unlock a CDMA2000 3G device failed
because you entered an incorrect device code.
Device unlocked - You entered the correct device code and unlocked a
CDMA2000 3G device.
Get dev-info fail - The ZyWALL cannot get cellular device information.
Get dev-info ok - The ZyWALL succeeded in retrieving 3G device information.
Searching network - The 3G device is searching for a network.
Get signal fail - The 3G device cannot get a signal from a network.
Network found - The 3G device found a network.
Apply config - The ZyWALL is applying your configuration to the 3G device.
Inactive - The 3G interface is disabled.
Active - The 3G interface is enabled.
Incorrect device - The connected 3G device is not compatible with the ZyWALL.
Correct device - The ZyWALL detected a compatible 3G device.
Set band fail - Applying your band selection was not successful.
Set band ok - The ZyWALL successfully applied your band selection.
Set profile fail - Applying your ISP settings was not successful.
Set profile ok - The ZyWALL successfully applied your ISP settings.
PPP fail - The ZyWALL failed to create a PPP connection for the cellular interface.
Need auth-password - You need to enter the password for the 3G card in the
cellular edit screen.
Device ready - The Z yW ALL success fully applied all of your configur ation and y ou
can use the 3G connection.
Service
example if the bill has not been paid or the account has expired.
network type varies depending on the 3G card you inserted and could be UMTS,
UMTS/HSDPA, GPRS or EDGE when you insert a GSM 3G card, or 1xRTT, EVDO
Rev.0 or EVDO Rev.A when you insert a CDMA 3G card.
antenna output power and the distance between your ZyWALL and the service
provider’s base station.
if the service provider has stopped service to the 3G SIM card. For
94
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
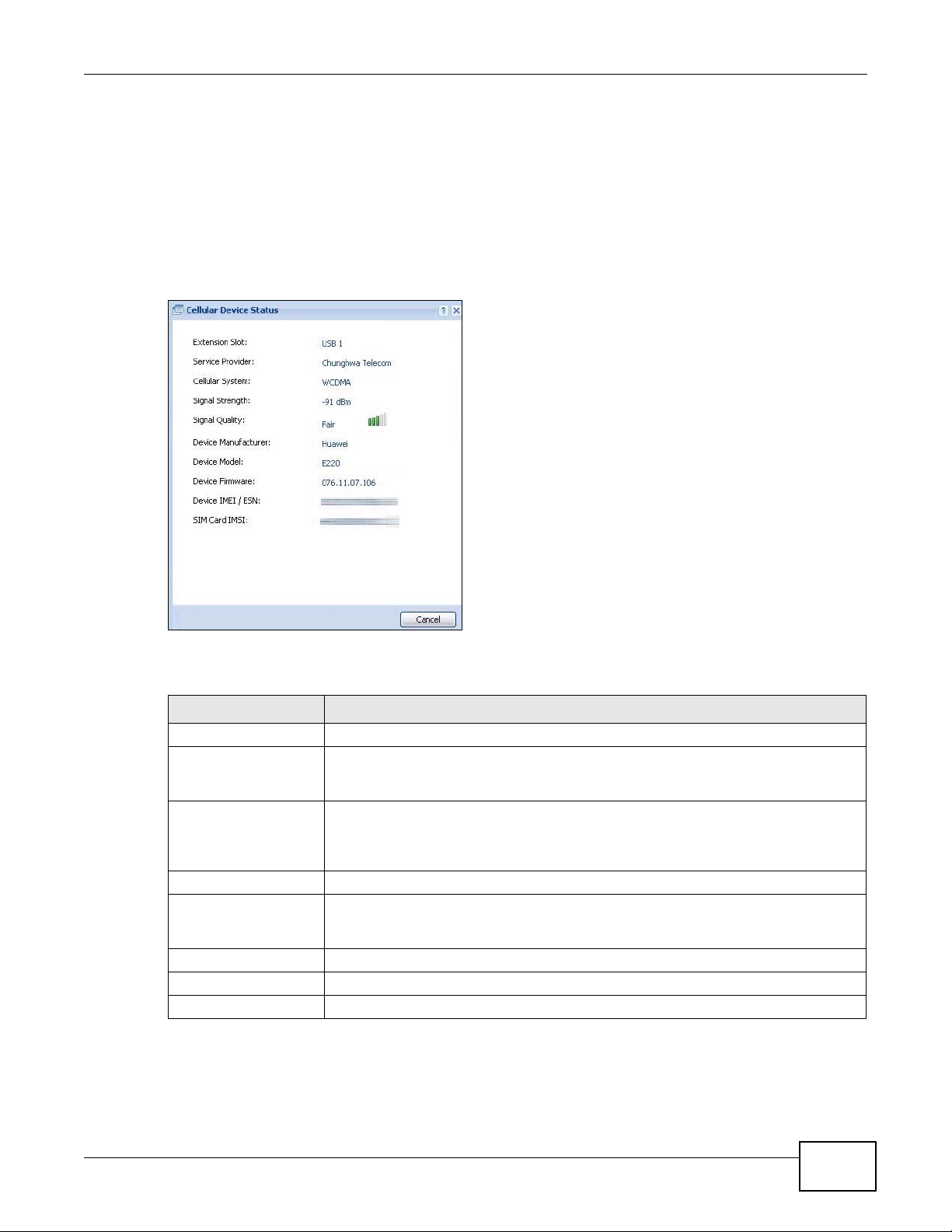
6.9.1 More Information
This screen displays more information on your 3G, such as the signal strength, IMEA/ESN and IMSI
that helps identify your 3G device and SIM card. Click Monitor > System Status > More
Information to display this screen.
Note: This screen is only available when the 3G device is attached to and activa ted on the
ZyWALL.
Figure 67 Monitor > System Status > More Information
Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 31 Monitor > System Status > More Information
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Extension Slot This field displays where the entry’s cellular card is located.
Service Provider This displays the name of your network service provider. This shows Limited
Service if the service provider has stopped service to the 3G SIM card. For example
if the bill has not been paid or the account has expired.
Cellular System This field displays what type of cel l u l ar network the 3G connection is using. The
network type varies depending on the 3G card you inserted and could be UMTS,
UMTS/HSDPA, GPRS or EDGE when you insert a GSM 3G card, or 1xRTT, EVDO
Rev.0 or EVDO Rev.A when you insert a CDMA 3G card.
Signal Strength This is the Signal Quality measured in dBm.
Signal Quality This displays the strength of the signal. The signal strength mainly depends on the
antenna output power and the distance between your ZyWALL and the service
provider’s base station.
Device Manufacturer This shows the name of the company that produced the 3G device.
Device Model This field displays the model name of the ce llular card.
Device Firmware This shows the software version of the 3G device.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
95
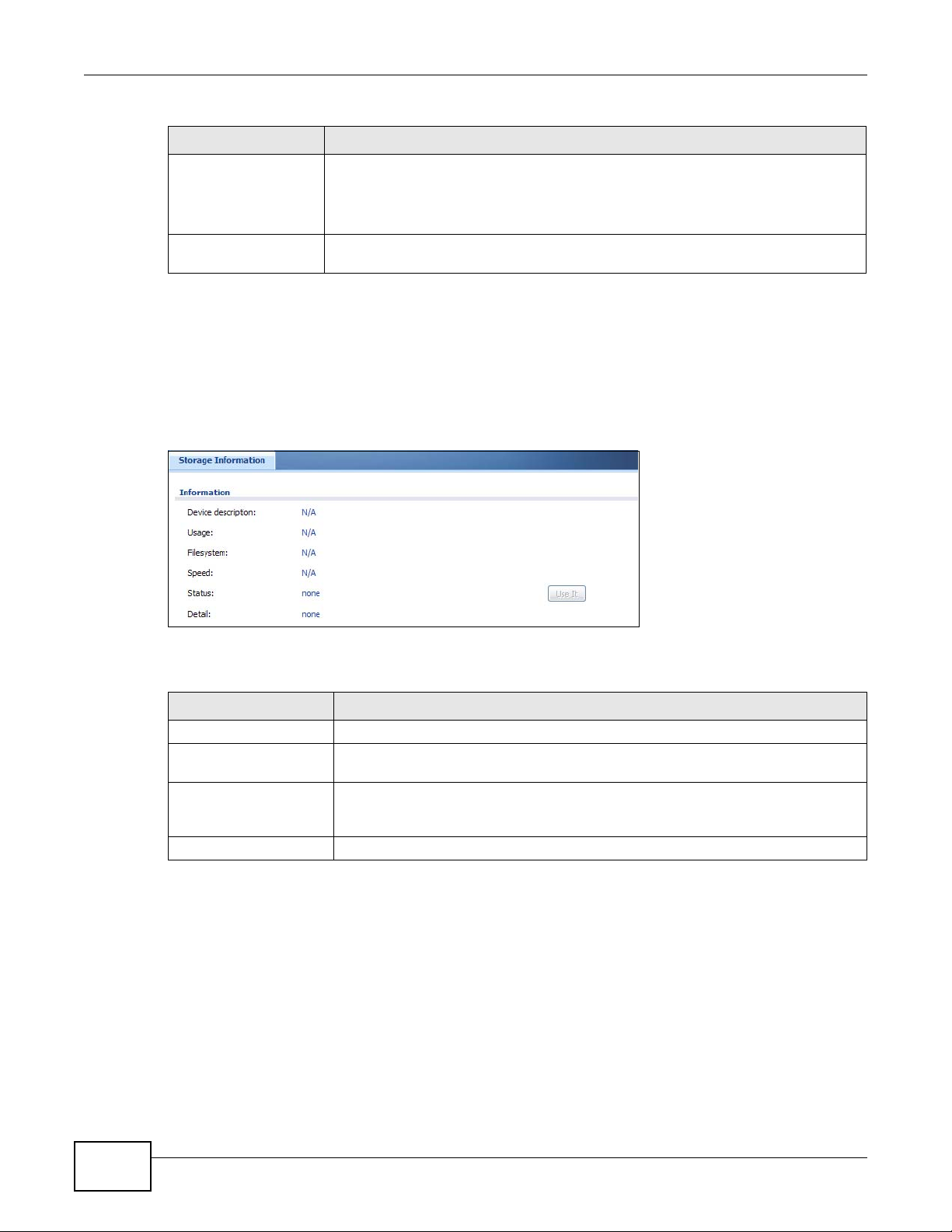
Chapter 6 Monitor
Table 31 Monitor > System Status > More Information (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device IMEI/ESN IMEI (International Mobile Equ ipm ent Identity) is a 15-digit code in decimal format
that identifies the 3G device.
ESN (Electronic Serial Number) is an 8-digit code in hexadecimal format that
identifies the 3G device.
SIM Card IMSI IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity) is a 15-digit code that identifies the
SIM card.
6.10 USB Storage Screen
This screen displays information about a connected USB storage device. Click Monitor > System
Status > USB Storage to display this screen.
Figure 68 Monitor > System Status > USB Storage
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 32 Monitor > System Status > USB Storage
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Device description This is a basic description of the type of USB device.
Usage This field displays how much of the USB storage device’s capacity is currently being
used out of its total capacity and what percentage that makes.
Filesystem This field displays what file system the USB storage device is formatted with. This
field displays Unknown if the file system of the USB storage device is not
supported by the ZyWALL, such as NTFS.
Speed This field displays the connection speed the USB storage device supports.
96
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

Chapter 6 Monitor
Table 32 Monitor > System Status > USB Storage (continued)
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Status Ready - you can have the ZyWALL use the USB storage device.
Click Remove Now to stop the ZyWA LL from usi ng the USB st or age device so y ou
can remove it.
Unused - the connected USB storage device was manually unmounted by using
the Remove Now button or for some reason the ZyWALL cannot mount it.
Click Use It to have the ZyWALL mount a connected USB storage device. This
button is grayed out if the file system is not supported (unknown) by the ZyWALL.
none - no USB storage device is connected.
Detail This field displays any other information the ZyWALL retrieves from the USB
storage device.
Deactivated - the use of a USB storage device is disabled (turned off) on the
ZyWALL.
OutofSpace - the available disk space is less than the disk space full threshold
(see Section 37.2 on page 433 for how to configure this threshold).
Mounting - the ZyWALL is mounting the USB storage device.
Removing - the ZyWALL is unmounting the USB storage device.
none - the USB device is operating normally or not connected.
6.11 The IPSec Monitor Screen
You can use the IPSec Monitor screen to display and to manage active IPSec To access this
screen, click Monitor > VPN Monitor > IPSec. The following screen appears. SAs. Click a
column’s heading cell to sort the table entries by that column’ s criteria. Click the heading cell again
to reverse the sort order.
Figure 69 Monitor > VPN Monitor > IPSec
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
97

Chapter 6 Monitor
Each field is described in the following table.
Table 33 Monitor > VPN Monitor > IPSec
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Name Enter the name of a IPSec SA here and click Search to find it (if it is associated).
Policy Enter the IP address(es) or names of the local and remote policies for an IPSec
Search Click this button to search for an IPSec SA that matches the information you
Disconnect Select an IPSec SA and click this button to disconnect it.
Total Connection This field displays the total number of associated IPSec SAs.
connection per page
Page x of x This is the number of the page of entries currently displayed and the total
# This field is a sequential value, and it is not associated with a specific SA.
Name This field displays the name of the IPSec SA.
Encapsulation This field displays how the IPSec SA is encapsulated.
Policy This field displays the content of the local and remote policies for this IPSec SA.
Algorithm This field displays the encryption and authentication algorithms used in the SA.
Up Time This field displays how many seconds the IPSec SA has been active. This field
Timeout This field displays how many seconds remain in the SA life time, before the
Inbound (Bytes) This field displays the amount of traffic that has gone through the IPSec SA from
Outbound (Bytes) This field displays the amount of traffic that has gone through the IPSec SA from
Refresh Click Refresh to update the information in the display.
You can use a keyword or regular expression. Use up to 30 alphanumeric and
_+-.()!$*^:?|{}[]<>/ characters. See Section 6.11.1 on page 98 for more
details.
SA and click Search to find it. You can use a keyword or regular expression. Use
up to 30 alphanumeric and _+-.()!$*^:?|{}[]<>/ characters. See Section
6.11.1 on page 98 for more details.
specified above.
Select how many entries you want to display on each page.
number of pages of entries. Type a page number to go to or use the arrows to
navigate the pages of entries.
The IP addresses, not the address objects, are displayed.
displays N/A if the IPSec SA uses manual keys.
ZyWALL automatically disconnects the IPSec SA. This field displays N/A if the
IPSec SA uses manual keys.
the remote IPSec router to the ZyWALL since the IPSec SA was established.
the ZyWALL to the remote IPSec router since the IPSec SA was established.
6.11.1 Regular Expressions in Searching IPSec SAs
A question mark (?) lets a single character in the VPN connection or policy name vary. For example,
use “a?c” (without the quotation marks) to specify abc, acc and so on.
Wildcards (*) let multiple VPN connection or policy names match the pattern. For example, use
“*abc” (without the quotation marks) to specify any VPN connection or policy name that ends with
“abc” . A VPN connection named “testabc” would match. There could be an y number (of any type) of
characters in front of the “abc” at the end and the VPN connection or policy name would still match.
A VPN connection or policy name named “testacc” for example would not match.
A * in the middle of a VPN connection or policy name has the ZyWALL check the beginning and end
and ignore the middle. For example, with “abc*123”, any VPN connection or policy name starting
with “abc” and ending in “123” matches, no matter how many characters are in between.
98
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide

The whole VPN connection or policy name has to match if you do not use a question mark or
asterisk.
6.12 The SSL Connection Monitor Screen
The ZyWALL keeps track of the users who are currently logged into the VPN SSL client Click
Monitor > VPN Monitor > SSL to display the user list.
portal. Use this screen to do the following:
• View a list of active SSL VPN connections.
• Log out individual users and delete related session information.
Once a user logs out, the corresponding entry is removed from the Connection Monitor screen.
Figure 70 Monitor > VPN Monitor > SSL
Chapter 6 Monitor
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 34 Monitor > VPN Monitor > SSL
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Disconnect Select a connection and click this button to terminate the user’s connection and
delete corresponding session information from the ZyWALL.
# This field displays the index number.
User This field displays the account user name used to establish this SSL VPN connection.
Access This field displays the name of the SSL VPN application the user is accessing.
Login Address This field displays the IP address the user used to establish this SSL VPN connection.
Connected Time This field displays the time this connection was established.
Inbound (Bytes) This field displays the number of bytes received by the ZyWALL on this connection.
Outbound (Bytes) This field displays the number of bytes transmitted by the ZyWALL on this
connection.
Refresh Click Refresh to update this screen.
6.13 The L2TP over IPSec Session Monitor Screen
Click Monitor > VPN Monitor > L2TP over IPSec to open the following screen. Use this screen
to display and manage the ZyWALL’s connected L2TP VPN sessions.
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
99

Chapter 6 Monitor
Figure 71 Monitor > VPN Monitor > L2TP over IPSec
The following table describes the fields in this screen.
Table 35 Monitor > VPN Monitor > L2TP over IPSec
LABEL DESCRIPTION
Disconnect Select a connection and click this button to disconnect it.
# This is the index number of a current L2TP VPN session.
User Name This field displays the remote user’s user name.
Hostname This field displays the name of the computer that has this L2TP VPN connection
Assigned IP This field displays the IP address that the ZyWALL assigned for the remote user’s
Public IP This field displays the public IP address that the remote user is using to connect to
Refresh Click Refresh to update this screen.
with the ZyWALL.
computer to use within the L2TP VPN tunnel.
the Internet.
6.14 Log Screen
Log messages are stored in two separate logs, one for regular log messages and one for debugging
messages. In the regular log, you can look at all the log messages by selecting All Logs, or you can
select a specific category of log messages (for example, firewall or user). You can also look at the
debugging log by selecting Debug Log. All debugging messages have the same priority.
To access this screen, click Monitor > Log. The log is displayed in the following screen.
Note: When a log reaches the maximum number of log messages, new log messages
automatically overwrite existing log messages, starting with the oldest existing log
message first.
• The maximum possible number of log messages in the ZyWALL varies by model.
Events that generate an alert (as well as a log message) display in red. Regular logs display in
black. Click a column’s heading cell to sort the table entries by that column’s criteria. Click the
heading cell again to reverse the sort order.
100
ZyWALL 110/310/1100 Series User’s Guide
 Loading...
Loading...