
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
UM012913-0407
Copyright ©2007 by ZiLOG, Inc. All rights reserved.
www.zilog.com

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
Safeguards
The following precaution must be taken care while working with the
devices mentioned in this document.
Caution:
Always use a grounding strap to prevent damage resulting from
electrostatic discharge (ESD).
UM012913-0407

Table of Contents
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Key Features of the development kit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .1
Hardware Specifications . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
eZ80L92 Development Board Revision History . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .2
eZ80Acclaim!
®
eZ80
Development Platform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .7
Physical Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .9
Operational Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
eZ80L92 Module Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .10
Application Module Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .20
I/O Functionality . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .23
Embedded Modem Socket Interface . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .27
eZ80
LEDs . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Push Buttons . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .33
Jumpers . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .34
Connectors . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .40
Console . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
Modem . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
2
I
C Devices . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .41
eZ80L92 Module. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Functional Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Physical Dimensions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .43
Operational Description . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
Ethernet Media Access Controller . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .46
eZ80L92 Module Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
Reset Generator . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .49
®
Development Platform Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .3
®
Development Platform Memory . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .30
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
iii
UM012913-0407 Table of Contents

iv
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
IrDA Transceiver . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 49
DC Characteristics . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Flash Loader Utility . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 52
Mounting the Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
Changing the Power Supply Plug . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 53
ZPAK II . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
ZDI Target Interface Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
JTAG . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
Application Modules . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 55
ZDS II. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 56
Troubleshooting . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Overview . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
Cannot Download Code . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
No Output on Console Port . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 57
IrDA Port Not Working . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Difference Between EMAC and IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
Media Access Control . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 58
IP Address . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 59
Schematic Diagrams . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
eZ80Acclaim
®
Development Platform . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 61
eZ80L92 Module . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 66
Appendix A . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
General Array Logic Equations . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
U10 Address Decoder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 75
U15 Address Decoder . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 77
Table of Contents UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
Introduction
The eZ80L92 Development Kit, PSI #eZ80L920210ZCO, provides a gen-
eral-purpose platform for evaluating the capabilities and operation of
ZiLOG’s eZ80L92 microprocessor. The eZ80L92 Development Kit fea-
tures two primary boards: the eZ80Acclaim!
the eZ80L92 Module. This arrangement provides a complete develop-
ment platform while using both the boards. It also provides a smaller-
sized reference platform with the eZ80L92 Module as a stand-alone
development tool.
Key Features of the Development Kit
The key features of the eZ80L92 Development Kit are:
User Manual
®
Development Platform and
1
•
eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform:
– Up to 2 MB fast SRAM (12 ns access time).
– Embedded Modem Socket with a U.S. Telephone Line Interface.
2
C EEPROM.
–I
2
C Configuration Register.
–I
– General-Purpose Port and Memory Headers.
– Supported by ZiLOG Developer Studio II and the eZ80
C-Compiler.
– LEDs, including a 7 x 5 LED matrix..
– Jumpers.
– Two RS232 connectors—Console, Modem.
– RS485 connector.
– ZiLOG Debug Interface (ZDI).
– JTAG Debug Interface.
– 9 V DC Power Connector.
– Telephone Jack.
UM012913-0407 Introduction
®

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
2
•
eZ80L92 Module:
– eZ80L92 microprocessor operating at 48 MHz
– 1 MB Flash Memory
– 512 KB SRAM
– 10 BaseT Ethernet Interface
– Real time clock with battery back-up
•
ZPAK II Debug Interface.
•
4-port 10 BaseT Ethernet hub.
•
eZ80L92 Development Kit Software and Documentation CD-ROM.
Hardware Specifications
Table 1 lists the specifications of the eZ80Acclaim!® Development Plat-
form.
Table 1. eZ80® Development Platform Hardware Specifications
Operating Temperature 20 ºC ±5 ºC
Operating Voltage 9 V DC
eZ80L92 Development Board Revision History
99C0858-001 Rev C or later:
10/20/03 - Updated layout and added reset fix.
05/30/06 - The following components are not populated on the board:
– U11: Triac, SCR Phone Line D0-214
– U26 and U27: IC RS485, XCVR, Low PWR, 8-SOIC
– C3 and C4: CAP 1000pF Ceramic Disc 1KV
– D1 and D3: Diode LED Amber 0805 SMT
– T1: Inductor Ferrite Bead, 2x15 Turns
Key Features of the Development Kit UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
– J1: Conn HDR/Pin 1x32 2mm socket
– J5: Conn HDR/Pin 1x2 2mm socket
– J9: Conn HDR/Pin 1x9 2mm socket
– P4: Conn RJ14 Jack 6-Pos 4-CKT
– P5: Conn 9-CKT Cir rt-angl PC Mount
eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Overview
3
The purpose of the eZ80L92 Development Kit is to provide the developer
®
with a set of tools for evaluating the features of the eZ80
family of
devices and to develop a new application before building application
hardware. The eZ80Acclaim!
accept a number of application-specific modules and Z8
®
Development Platform is designed to
®
and eZ80®
based add-on modules, including the eZ80L92 Module, which features an
EMAC, an IrDA transceiver, and the eZ80L92 microprocessor.
The eZ80L92 Development Kit features two primary boards: the
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform and the eZ80L92 Module. This
arrangement provides a complete development platform while using both
boards. It can also provide a smaller-sized reference platform with the
eZ80L92 Module as a stand-alone development tool.
The eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform can operate in stand-alone
mode with Flash memory, or interface via the ZPAK II emulator to a host
PC running ZiLOG Developer Studio II Integrated Development
Environment (ZDS II IDE) software. If the eZ80Acclaim!
demands Internet connectivity or a network connection, the eZ80
®
application
®
can
serve web pages over a TCP/IP network allowing easy system monitoring
and control, and effortless processor code updates.
The address bus, data bus, and all eZ80L92 Module control signals are
buffered on the eZ80Acclaim!
cient drive capability. A block diagram of the eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform to provide suffi-
®
Develop-
ment Platform and the eZ80L92 Module is shown in Figure 1.
UM012913-0407 eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Overview
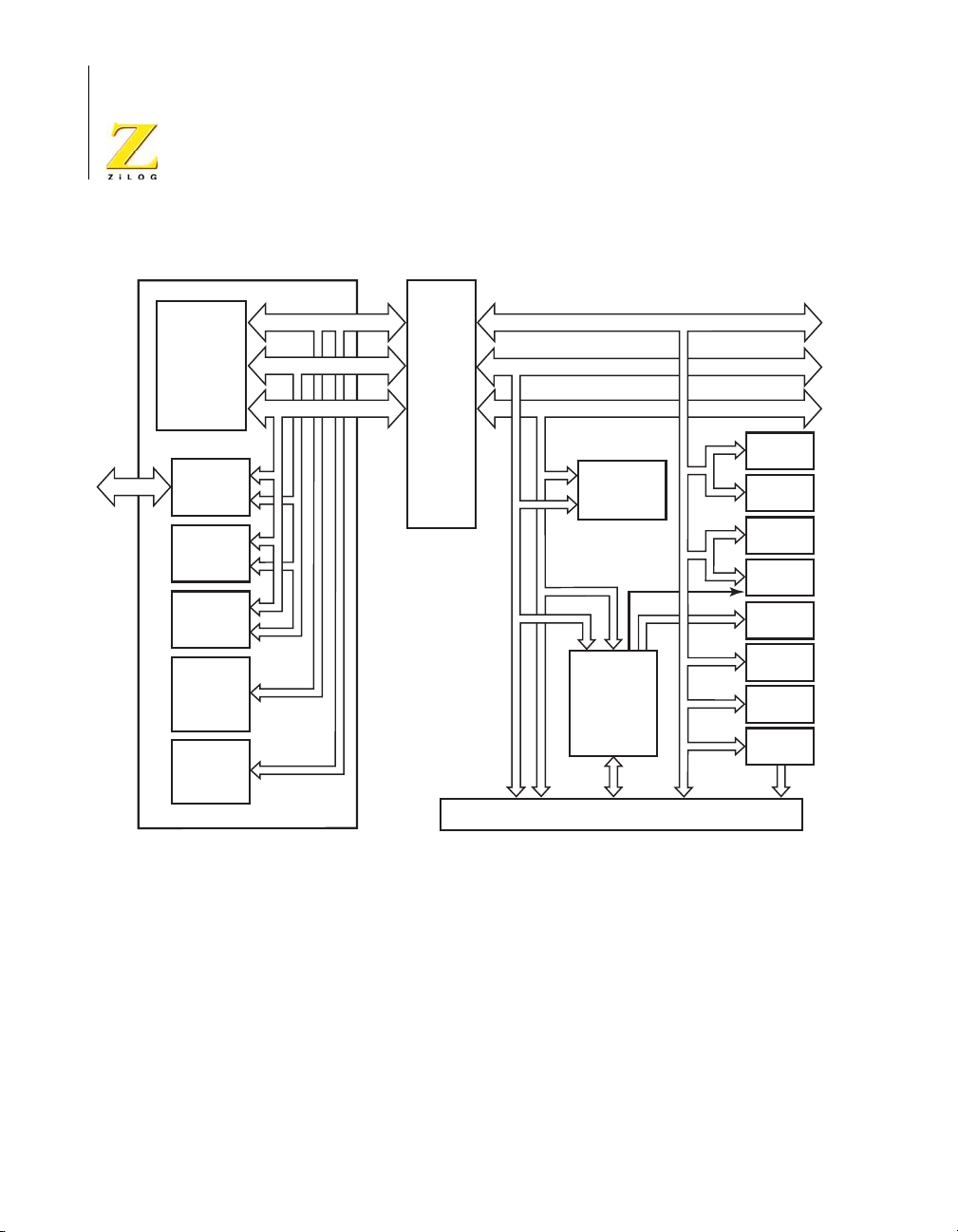
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
4
Ethernet
eZ80F92
eZ80L92
EMAC
Flash
(1 MB)
SRAM
(512 KB)
Battery &
Oscillator
for RTC
IrDA
Transceiver
Peripheral Device Signals
Address Bus
Data Bus
E-NET
Module
Interface
Peripheral Device Signals
Address Bus
Data Bus
SRAM
(512 KB
up to 2 MB)
GPIO
and
Address
Decoder
Application Module Headers
RS232-0
(Console)
RS485
RS232-1
(Modem)
Embedded
Modem
LED
(7x5 matrix)
Push-
buttons
2
I C
EEPROM
2
I C
Register
Figure 1. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Block Diagram with eZ80L92
Module
eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Overview UM012913-0407
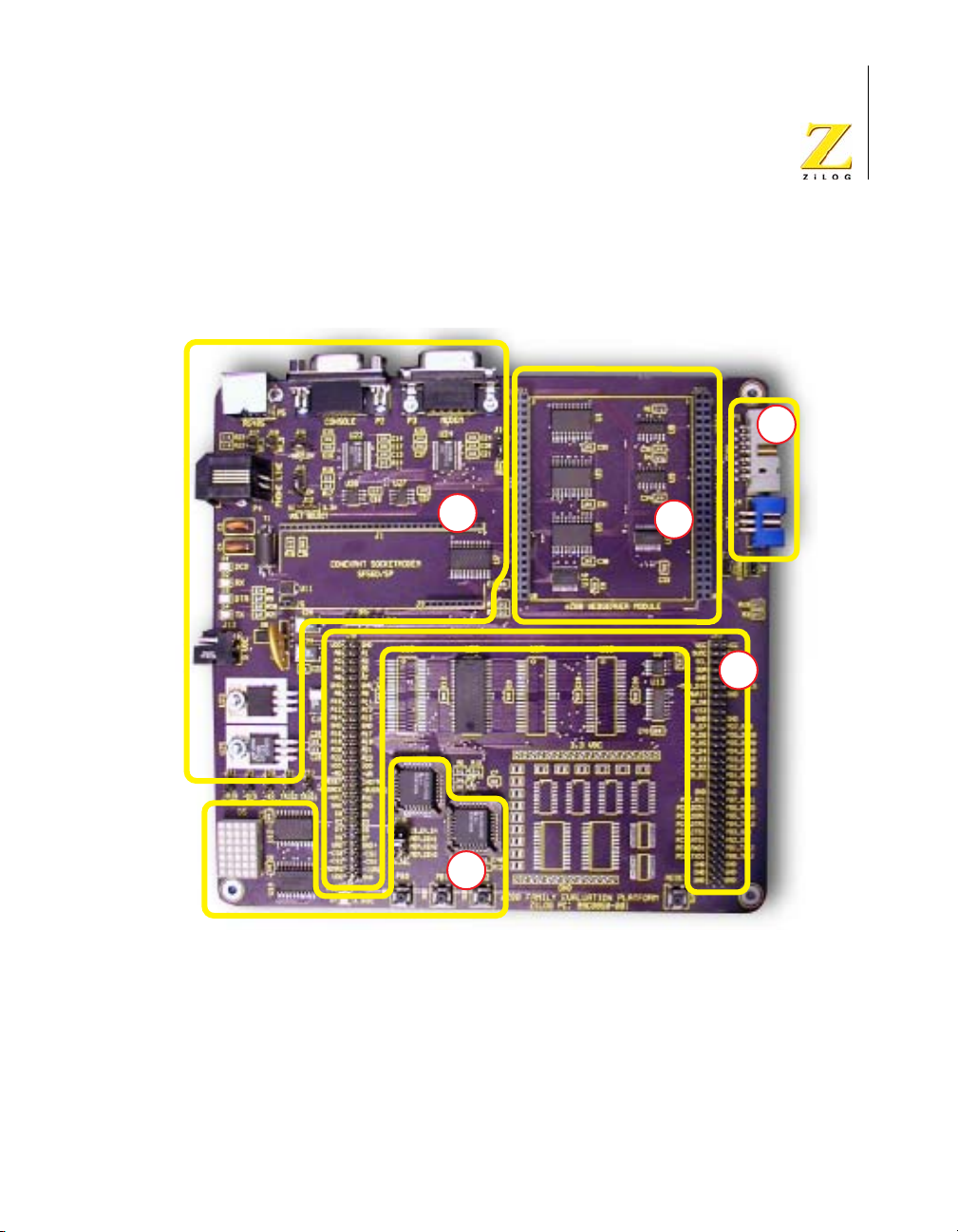
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
Figure 2 is a photographic representation of the eZ80Acclaim!® Develop-
ment Platform segmented into its key blocks.
C
5
Note: Key blocks A–E
A. Power and serial communications.
B.
eZ80L92 Module interface.
C. Debug interface.
Figure 2. The eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform
A
B
D
E
D. Application Module Interfaces.
E. General-Purpose Port and LED with Address
Decoder.
UM012913-0407 eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Overview
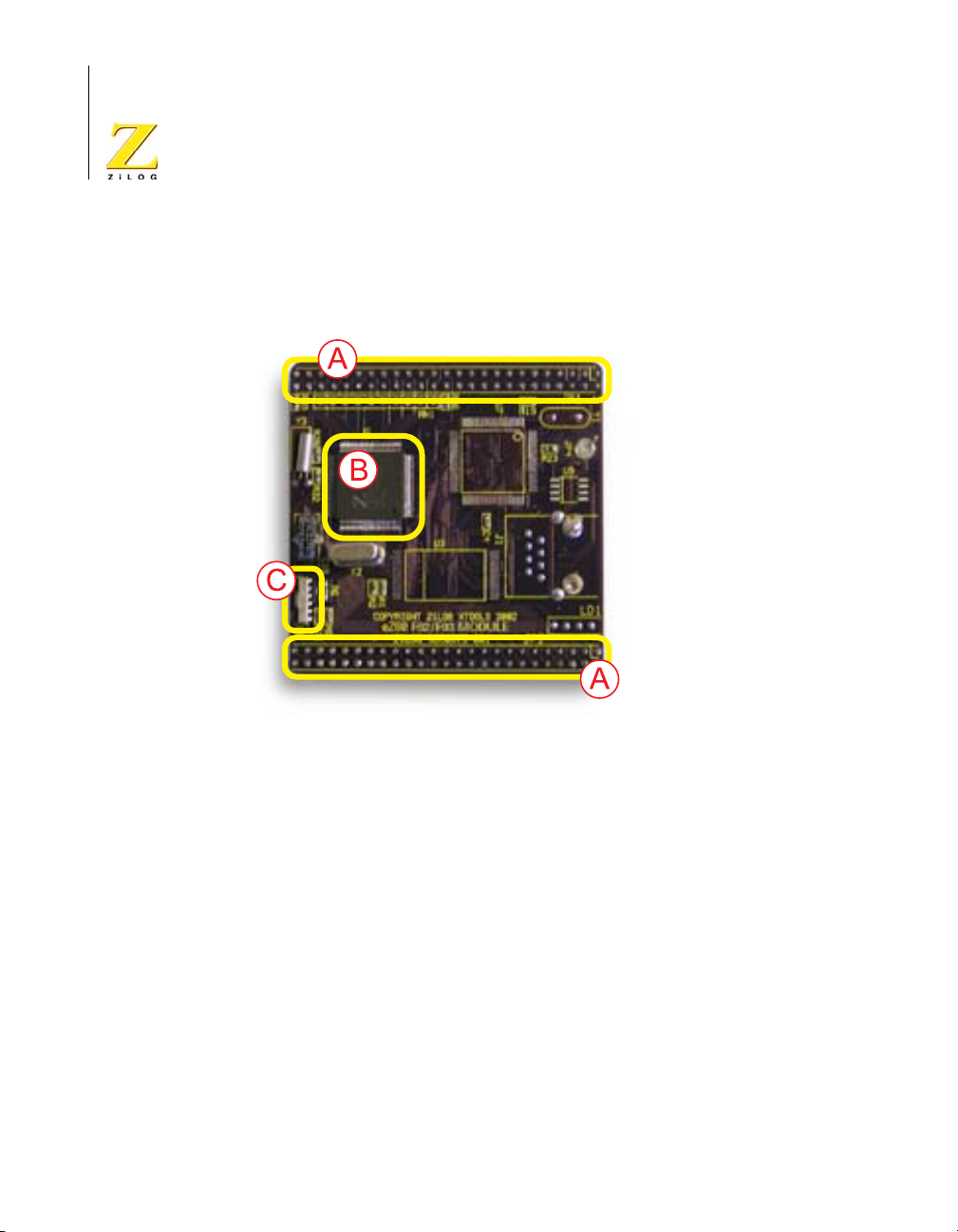
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
6
Figure 3 is a photographic representation of the eZ80L92 Module
segmented into its key blocks.
Note: Key blocks A–C.
A. eZ80L92 Module interfaces.
B. CPU and memory.
C. Ethernet connection.
D. IrDA transceiver.
Figure 3. The eZ80L92 Module
®
The structures of the eZ80Acclaim!
Development Platform and the
eZ80L92 Module are illustrated in the Schematic Diagrams from page 61.
eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Overview UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
eZ80® Development Platform
This chapter describes the eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform hardware, its key components and the interfaces, including detailed programmer interface information like memory maps, register definitions, and
interrupt usage.
Functional Description
The eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform consists of seven major hardware blocks. These blocks, listed below, are illustrated in Figure 4.
•
eZ80L92 Module interface (2 female headers).
•
Power supply for the eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform, the
eZ80L92 Module, and application modules.
User Manual
7
•
Application module interface (2 male headers).
•
General-Purpose Port and LED matrix.
•
RS232 serial communications ports.
•
Embedded modem interface.
•
I2C devices.
UM012913-0407 eZ80® Development Platform
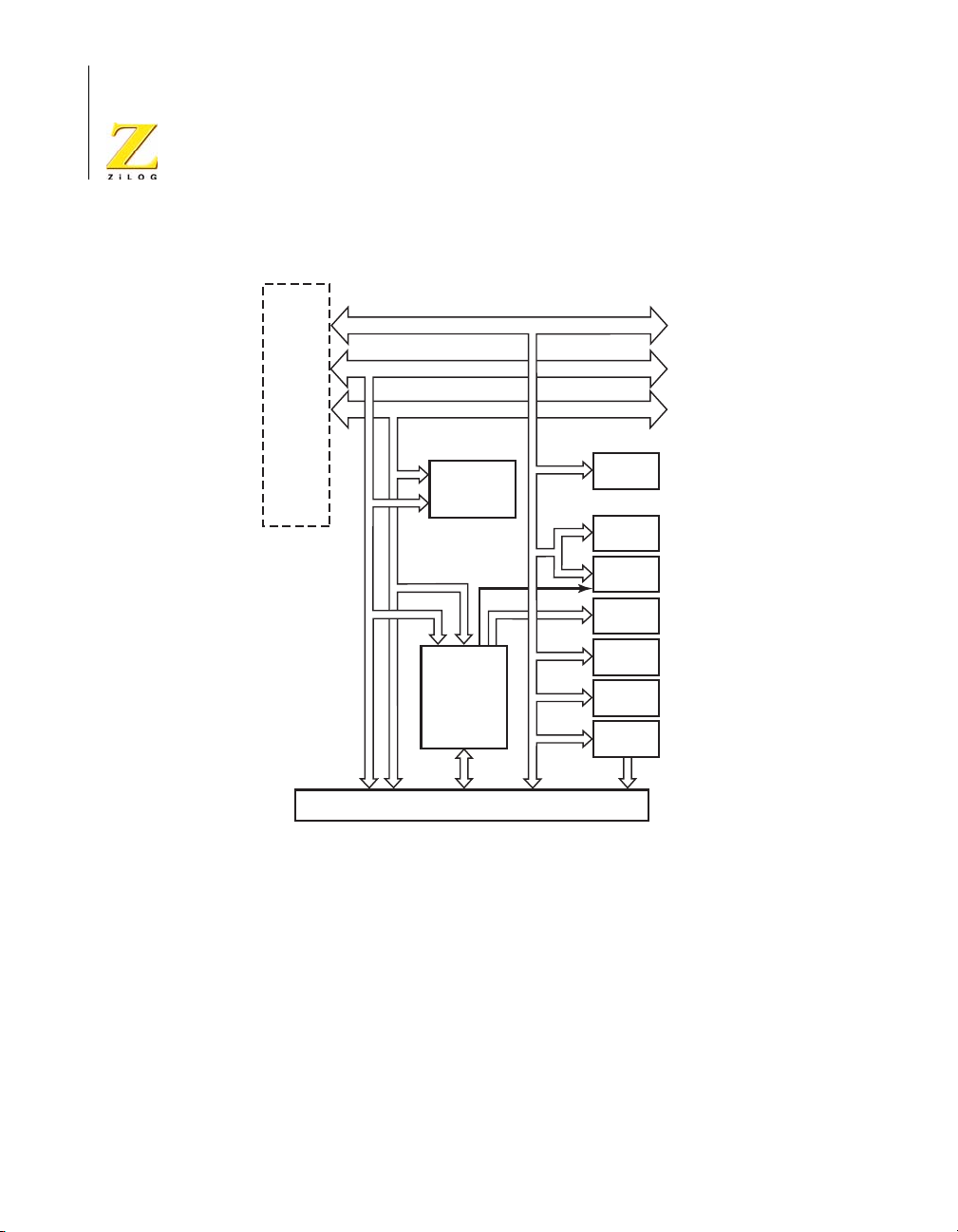
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
8
Peripheral Device Signals
E-NET
Module
Interface
Address Bus
Data Bus
SRAM
(512 KB
up to 2 MB)
GPIO
and
Address
Decoder
RS232-0
(Console)
RS232-1
(Modem)
Embedded
Modem
LED
(7x5 matrix)
Push-
buttons
2
I C
EEPROM
2
I C
Register
Application Module Headers
Figure 4. Basic eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Block Diagram
Functional Description UM012913-0407

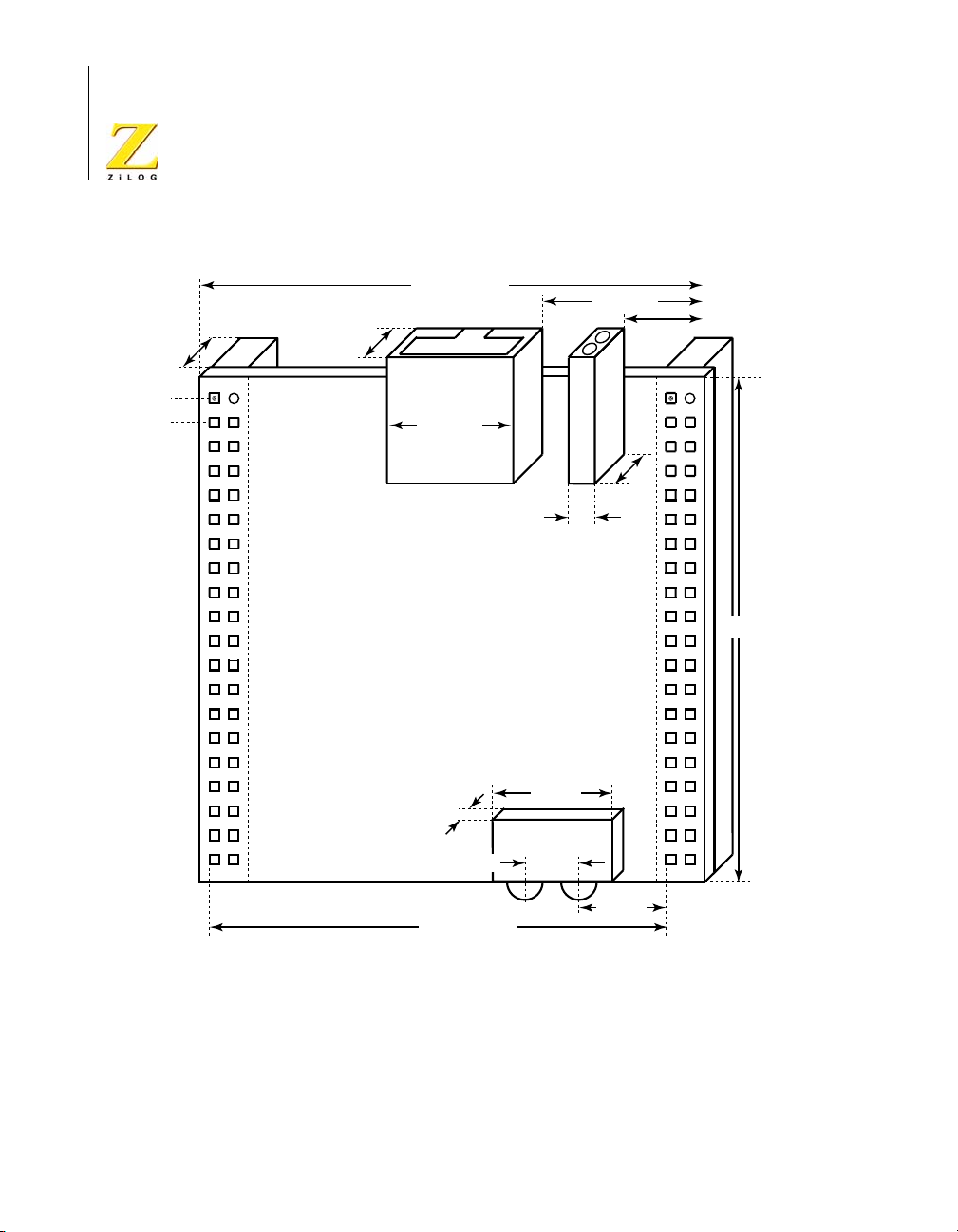
Physical Dimensions
The dimension of the eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform PCB is
177.8 mm x 182.9 mm. The overall height is 38.1 mm. See Figure 5.
43.2 mm
96.5 mm 55.9 mm
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
9
175.3 mm
114.3 mm
157.5 mm
167.6 mm
5.1 mm
165.1 mm
5.1 mm
Figure 5. Physical Dimensions of eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform
UM012913-0407 Functional Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
10
Operational Description
The eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform can accept any eZ80® corebased modules, provided that the module interfaces correctly to the
eZ80Acclaim!
eZ80Acclaim!
developer with a tool to evaluate the features of the eZ80L92 device and
to develop an application without building additional hardware.
eZ80L92 Module Interface
®
Development Platform. The purpose of the
®
Development Platform is to provide the application
The eZ80L92 Module interface provides easy connection of the eZ80L92
Module. It also provides easy connection for any eZ80
designed to this interface. This includes modules using future eZ80
devices and user-developed modules using current eZ80
®
based module
®
devices.
®
The eZ80L92 Module interface consists of two 50-pin receptacles, JP1
and JP2.
Peripheral Bus Connector
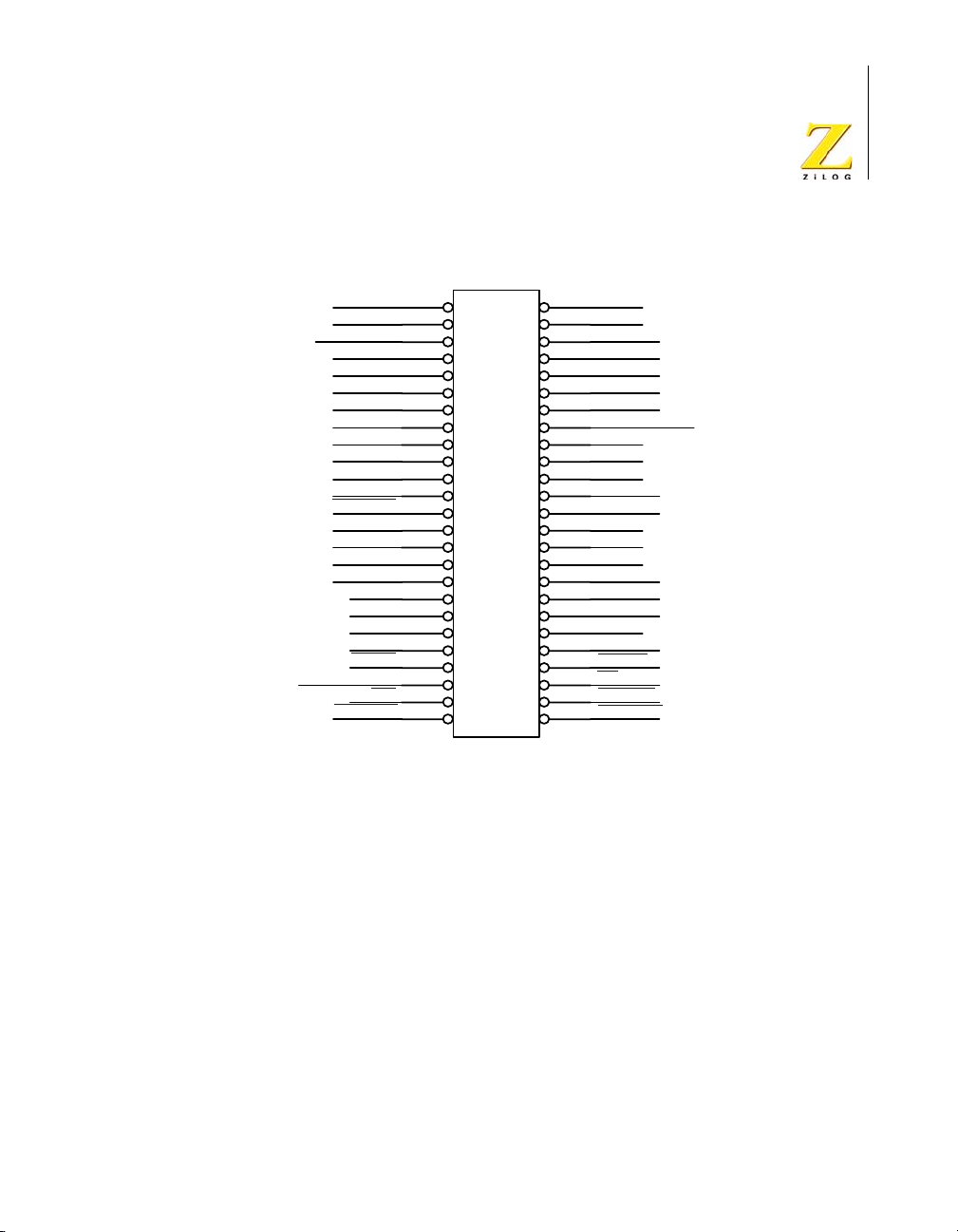
Figure 6 illustrates the pin layout of the Peripheral Bus Connector in the
®
50-pin header located at position JP1 on the eZ80Acclaim!
Develop-
ment Platform. Table 2 describes the pins and their functions.
Operational Description UM012913-0407
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
11
A6
A10
GND_EXT
A8
A13
A15
A18 A1 6
A19
A2
A11
A4
A5
DIS_ETH
A21
A22
CS0
CS2
D1
D3
D5
D7
MREQ
GND_EXT
WR
BUSACK
JP1
12
34
56
78
910
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
HEADER 25X2
IDC50
A0
A3
V3.3_EXT
A7
A9
A14
GND_EXT
A1
A12
A20
A17
DIS_FLASH
V3.3_EXT
A23
CS1
D0
D2
D4
GND_EXT
D6
IOREQ
RD
INSTRD
BUSREQ
Figure 6. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Peripheral Bus Connector Pin
Configuration—JP1
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
12
Table 2. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Peripheral Bus Connector
Identification—JP1
1
Pin No. Symbol Signal Direction Active Level eZ80L92 Signal
1 A6 Bidirectional Yes
2 A0 Bidirectional Yes
3 A10 Bidirectional Yes
4 A3 Bidirectional Yes
5GND
6V
DD
7 A8 Bidirectional Yes
8 A7 Bidirectional Yes
9 A13 Bidirectional Yes
10 A9 Bidirectional Yes
11 A15 Bidirectional Yes
12 A14 Bidirectional Yes
13 A18 Bidirectional Yes
14 A16 Bidirectional Yes
2
15 A19 Bidirectional Yes
Notes:
1. For the sake of simplicity in describing the interface, Power and Ground nets are omitted from
this table. The entire interface is represented in the eZ80L92 Module Schematics. see
eZ80L92 Module.
2. The Power and Ground nets are connected directly to the eZ80L92 device.
Additional note: external capacitive loads on RD
below 10 pF to satisfy the timing requirements for the eZ80
pulled to either V
to reduce noise sensitivity. To prevent EMI, the EZ80CLK output can be deactivated via software in
the eZ80L92’s Peripheral Power-Down Register.
or GND, depending on their inactive levels to reduce power consumption and
DD
Operational Description UM012913-0407
, WR, IORQ, MREQ, D0–D7 and A0–A23 should be
®
CPU. All unused inputs should be

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
13
Table 2. eZ80Acclaim!
Identification—JP1
®
Development Platform Peripheral Bus Connector
1
(Continued)
Pin No. Symbol Signal Direction Active Level eZ80L92 Signal
16 GND
17 A2 Bidirectional Yes
18 A1 Bidirectional Yes
19 A11 Bidirectional Yes
20 A12 Bidirectional Yes
21 A4 Bidirectional Yes
22 A20 Bidirectional Yes
23 A5 Bidirectional Yes
24 A17 Bidirectional Yes
25 DIS_ETH
26 EN_FLASH
Output Low No
Output Low No
27 A21 Bidirectional Yes
28 V
DD
29 A22 Bidirectional Yes
2
30 A23 Bidirectional Yes
Notes:
1. For the sake of simplicity in describing the interface, Power and Ground nets are omitted from
this table. The entire interface is represented in the eZ80L92 Module Schematics. see
eZ80L92 Module.
2. The Power and Ground nets are connected directly to the eZ80L92 device.
Additional note: external capacitive loads on RD
below 10 pF to satisfy the timing requirements for the eZ80
pulled to either V
to reduce noise sensitivity. To prevent EMI, the EZ80CLK output can be deactivated via software in
the eZ80L92’s Peripheral Power-Down Register.
or GND, depending on their inactive levels to reduce power consumption and
DD
UM012913-0407 Operational Description
, WR, IORQ, MREQ, D0–D7 and A0–A23 should be
®
CPU. All unused inputs should be

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
14
Table 2. eZ80Acclaim!
Identification—JP1
®
Development Platform Peripheral Bus Connector
1
(Continued)
Pin No. Symbol Signal Direction Active Level eZ80L92 Signal
31 CS0 Input Low Yes
32 CS1 Input Low Yes
33 CS2 Input Low Yes
34 D0 Bidirectional Yes
35 D1 Bidirectional Yes
36 D2 Bidirectional No
37 D3 Bidirectional Yes
38 D4 Bidirectional Yes
39 D5 Bidirectional Yes
40 GND
41 D7 Bidirectional Yes
42 D6 Bidirectional Yes
43 MREQ
Bidirectional Low Yes
2
44 IORQ
Bidirectional Low Yes
45 GND
Notes:
1. For the sake of simplicity in describing the interface, Power and Ground nets are omitted from
this table. The entire interface is represented in the eZ80L92 Module Schematics. see
eZ80L92 Module.
2. The Power and Ground nets are connected directly to the eZ80L92 device.
Additional note: external capacitive loads on RD
below 10 pF to satisfy the timing requirements for the eZ80
pulled to either V
to reduce noise sensitivity. To prevent EMI, the EZ80CLK output can be deactivated via software in
the eZ80L92’s Peripheral Power-Down Register.
or GND, depending on their inactive levels to reduce power consumption and
DD
Operational Description UM012913-0407
, WR, IORQ, MREQ, D0–D7 and A0–A23 should be
®
CPU. All unused inputs should be

Table 2. eZ80Acclaim!
Identification—JP1
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
®
Development Platform Peripheral Bus Connector
1
(Continued)
15
Pin No. Symbol Signal Direction Active Level eZ80L92 Signal
2
46 RD Bidirectional Low Yes
47 WR
48 INSTRD
49 BUSACK
50 BUSREQ
Notes:
1. For the sake of simplicity in describing the interface, Power and Ground nets are omitted from
this table. The entire interface is represented in the eZ80L92 Module Schematics. see
Bidirectional Low Yes
Input Low Yes
Input Pull-Up 10 KΩ; Low Yes
Output Pull-Up 10 KΩ; Low Yes
eZ80L92 Module.
2. The Power and Ground nets are connected directly to the eZ80L92 device.
Additional note: external capacitive loads on RD
below 10 pF to satisfy the timing requirements for the eZ80
pulled to either V
to reduce noise sensitivity. To prevent EMI, the EZ80CLK output can be deactivated via software in
the eZ80L92’s Peripheral Power-Down Register.
or GND, depending on their inactive levels to reduce power consumption and
DD
, WR, IORQ, MREQ, D0–D7 and A0–A23 should be
®
CPU. All unused inputs should be
UM012913-0407 Operational Description
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
16
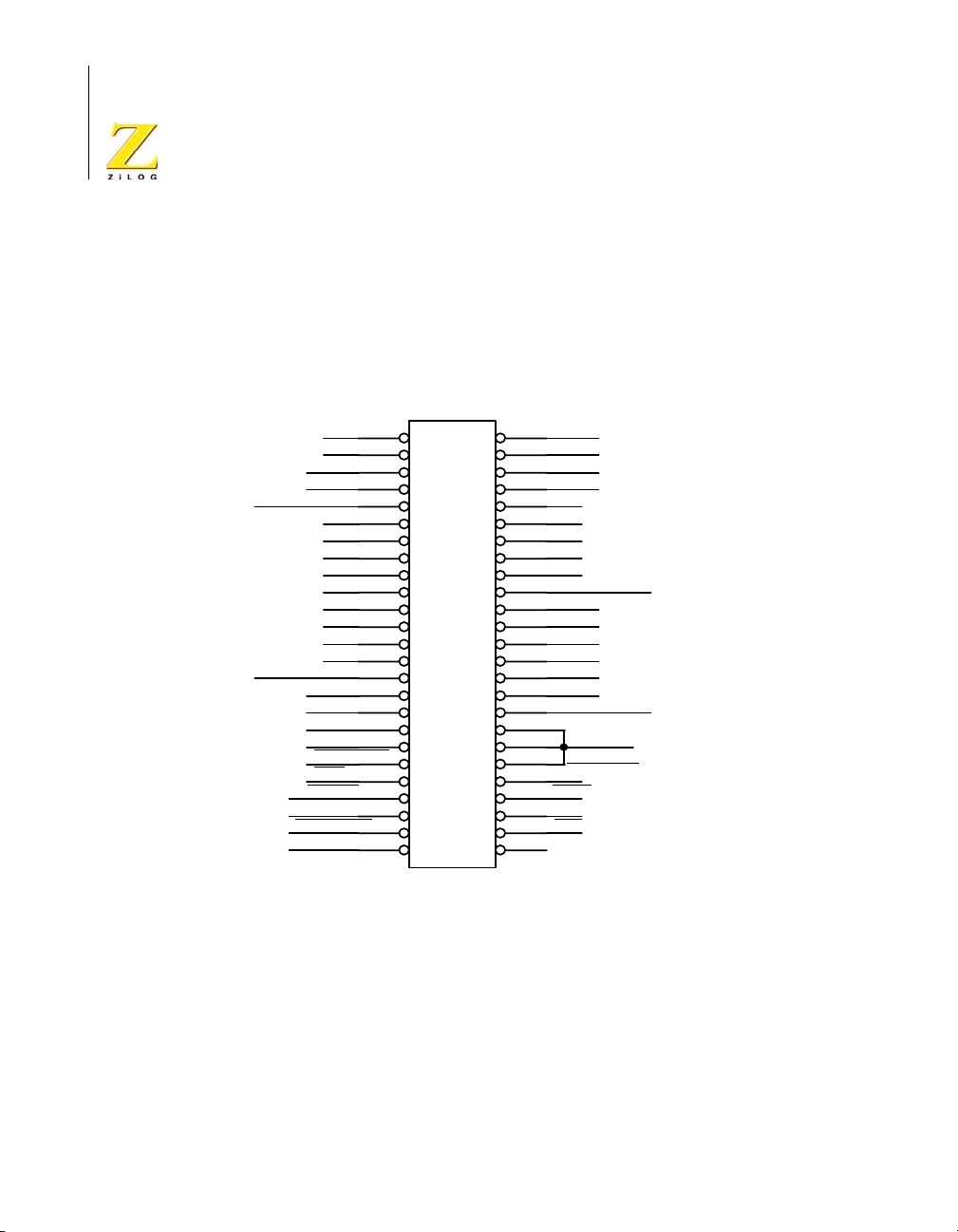
I/O Connector
Figure 7 illustrates the pin layout of the I/O Connector in the 50-pin
header located at position JP2 of the eZ80Acclaim!
form. Table 3 describes the pins and their functions.
®
Development Plat-
PB7
PB5
PB3
PB1
GND_EXT
PC6
PC4
PC2
PC0
PD6
PD5
PD3
PD1
GND_EXT
TCK TMS
RTC_VDD
IICSCL
IICSDA
FLASHWE
CS3
RESET
V3.3_EXT
HALT_SLP
V3.3_EXT
JP2
12
34
56
78
910
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
HEADER 25X2
IDC50
PB6
PB4
PB2
PB0
PC7
PC5
PC3
PC1
PD7
GND_EXT
PD4
PD2
PD0
TDITDO
TRIGOUT
EZ80CLK
GND_EXT
DIS_IRDA
WAIT
GND_EXT
NMI
Figure 7. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform I/O Connector Pin Configuration—
JP2
Operational Description UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
Table 3. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform I/O Connector Identification—JP21
17
Pin No. Symbol Signal Direction Active Level eZ80L92 Signal
1 PB7 Bidirectional Yes
2 PB6 Bidirectional Yes
3 PB5 Bidirectional Yes
4 PB4 Bidirectional Yes
5 PB3 Bidirectional Yes
6 PB2 Bidirectional Yes
7 PB1 Bidirectional Yes
8 PB0 Bidirectional Yes
9GND
10 PC7 Bidirectional Yes
11 PC6 Bidirectional Yes
12 PC5 Bidirectional Yes
13 PC4 Bidirectional Yes
14 PC3 Bidirectional Yes
15 PC2 Bidirectional Yes
2
16 PC1 Bidirectional Yes
17 PC0 Bidirectional Yes
18 PD7 Bidirectional Yes
19 PD6 Bidirectional
20 GND
Notes:
1. For the sake of simplicity in describing the interface, Power and Ground nets are omitted from
this table. The interface is represented in the eZ80L92 Module Schematics.
2. The Power and Ground nets are connected directly to the eZ80L92 device.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
18
Table 3. eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform I/O Connector Identification—JP21
Pin No. Symbol Signal Direction Active Level eZ80L92 Signal
21 PD5 Bidirectional Yes
22 PD4 Bidirectional Yes
23 PD3 Bidirectional Yes
24 PD2 Bidirectional Yes
25 PD1 Bidirectional Yes
26 PD0 Bidirectional Yes
27 TDO Input Yes
28 TDI/ZDA Output Yes
29 GND
30 TRIGOUT Input High
31 TCK/ZCL Output Yes
32 TMS Output High Yes
33 RTC_V
DD
34 EZ80CLK Input Yes
2
35 SCL Bidirectional Yes
36 GND
37 SDA Bidirectional Yes
38 GND
39 FlashWE
Output Low No
40 GND
Notes:
1. For the sake of simplicity in describing the interface, Power and Ground nets are omitted from
this table. The interface is represented in the eZ80L92 Module Schematics.
2. The Power and Ground nets are connected directly to the eZ80L92 device.
Operational Description UM012913-0407

Table 3. eZ80Acclaim!
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
®
Development Platform I/O Connector Identification—JP21
19
Pin No. Symbol Signal Direction Active Level eZ80L92 Signal
41 CS3 Input Low Yes
42 DIS_IrDA
43 RESET
44 WAIT
45 V
46 GND
47 HALT_SLP
48
49 V
50 Reserved
Notes:
1. For the sake of simplicity in describing the interface, Power and Ground nets are omitted from
this table. The interface is represented in the eZ80L92 Module Schematics.
2. The Power and Ground nets are connected directly to the eZ80L92 device.
DD
NMI
DD
Output Low No
Bidirectional Low Yes
Output Pull-Up 10 KΩ; Low Yes
Input Low Yes
Output Low Yes
2
Almost all the connectors’ signals are received directly from the CPU.
Four input signals, in particular, offer options to the application developer
by disabling certain functions of the eZ80L92 Module.
These four inputs signals are:
•
Disable Ethernet (DIS_ETH)
•
Enable Flash (EN_FLASH)
•
Flash Write Enable (FlashWE)
•
Disable IrDA (DIS_IrDA)
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
20
These four inputs are described below.
Disable Ethernet
When active Low, the DIS_ETH
responding to CPU requests. As a result, additional inputs, outputs, or
memory devices can be used in the CS3 address space. The logic that disables the Ethernet signal is listed in Appendix A on page 75.
Enable Flash
When active Low, the EN_FLASH
the eZ80L92 Module.
Flash Write Enable
When active Low, the FlashWE
the Flash boot block of the eZ80L92 Module.
output signal disables the EMAC from
input signal disables the Flash chip on
input signal enables Write operations on
Disable IrDA
When the DIS_IrDA
input signal is pulled Low, the IrDA transceiver,
located on the eZ80L92 Module is disabled. As a result, UART0 can be
used with the RS232 or the RS485 interfaces on the eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform.
Application Module Interface
An application module interface is provided to allow you to add an
application-specific module to the
ZiLOG’s Thermostat Application Module (not provided in the kit) is an
example application-specific module that demonstrates an HVAC control
system. Implementing an application module with the application module
interface requires that the
eZ80L92 Module
eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform, as the
the eZ80L92 microprocessor. To mount an application module, use the two
male headers J6 and J8.
Operational Description UM012913-0407
eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform.
also be mounted on the
eZ80L92 Module
contains

eZ80L92 Development Kit
Jumper J6 carries the general-purpose port and jumper J8 carries memory
and control signals. To design an application module, you must be
familiar with the architecture and features of the installed eZ80L92
Module. Table 4 and Table 5 list the signals and functions related to each
of these jumpers by pin. Power and ground signals are omitted for the
sake of simplicity.
Table 4. General-Purpose Port Connector J6*
Signal Pin No. Function Direction Notes
SCL 5 I
SDA 7 I
2
C Clock Bidirectional
2
C Data Bidirectional
User Manual
21
MOD_DIS
MWAIT
EM_D0 15 GPIO, Bit 0 Bidirectional
CS3
EM_D[7:1] 21,23,25,
Reserved 35
PC[7:0] 39,41,43,
Note: All signals are driven directly by the CPU.
9 Modem Disable Input If a shunt is installed between
13 WAIT signal for
the CPU
17 Chip Select 3 of
the CPU
GPIO, Bit [7:1] Bidirectional
27,29,31,
33
Port C, Bit [7:0] Bidirectional
45,47,49,
51,53
Input
Output This signal is also present on
pins 6 and 9, the modem
function on the eZ80Acclaim!
Development Platform is
disabled.
the J8.
®
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
22
Table 4. General-Purpose Port Connector J6* (Continued)
Signal Pin No. Function Direction Notes
ID_[2:0] 6,8,10 eZ80Acclaim!®
Output
Development
Platform ID
CON_DIS
12 Console Disable Input If a shunt is installed between
pins 12 and 14, the Console
function on the eZ80Acclaim!
Development Platform is
disabled.
Reserved 16,18
PD[7:0] 22,24,26,
Port D, Bit[7:0] Bidirectional
28,30,32,
34,36
PB[7:0] 40,42,44,
Port B, Bit[7:0] Bidirectional
46,48,50,
52,54
Note: All signals are driven directly by the CPU.
Table 5. CPU Bus Connector J8*
Signal Pin No. Function Direction
A[0:7] 3–10 Address Bus, Low Byte Output
®
A[8:15] 13–20 Address Bus, High Byte Output
A[16:23] 23–30 Address Bus, Upper Byte Output
RD
RESET
Note: All the signals except BUSACK and INSTRD are driven by low-voltage CMOS technology
(LVC) drivers.
33 READ Signal Output
35 Push Button Reset Output
Operational Description UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
Table 5. CPU Bus Connector J8* (Continued)
Signal Pin No. Function Direction
BUSACK 37 CPU Bus Acknowledge Signal Output
23
NMI
D[0:7] 43–50 Data Bus Bidirectional
CS[0:3]
MEMRQ
WR 34 WRITE Signal Output
INSTRD
BUSREQ
PHY 40 Clock output of the CPU Output
Note: All the signals except BUSACK and INSTRD are driven by low-voltage CMOS technology
(LVC) drivers.
39 Nonmaskable Interrupt Input
53–56 Chip Selects
57 Memory Request Output
36 Instruction Fetch Output
38 CPU Bus Request signal
I/O Functionality
The
eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform provides additional functional-
ity, featuring general-purpose port, an LED matrix, a modem reset, and two
user triggers. These functions are memory-mapped with an address decoder
based on the Generic Array Logic GAL22lV10D (U15) device manufactured by Lattice Semiconductor, and a bidirectional latch (U16). Additionally, U15 is used to decode addresses for access to the 7 x 5 LED matrix.
Table 6
the above functions. The register at address
lists the memory map addresses to registers that allow access to
800000h
controls generalpurpose port output control and LED anode register functions. The register
at address
modem reset, and user triggers. Address
800001h
controls the register functions for the LED cathode,
800002h
controls general-pur-
pose port data.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
24
Table 6. LED and Port Emulation Addresses
Address Register Function Access
800000h LED Anode/General-Purpose Port
800001h LED Cathode/Modem/Trig WR
800002h General-Purpose Port Data RD/WR
General-Purpose Port
The general-purpose port is emulated using GPIO Output Control
Register and the GPIO Data Register. If bit 7 in the GPIO Output Control
Register is 1, all the lines on the general-purpose port are configured as
inputs. If this bit is 0, all the lines on the general-purpose port are
configured as outputs. Table 7 lists the multiple functions of the register.
WR
Output Control
Table 7. LED Anode/General-Purpose Port Output Control Register
Bit No.
Function
Anode Col 1 X
Anode Col 2 X
Anode Col 3 X
Anode Col 4 X
Anode Col 5 X
Anode Col 6 X
GPIO Output X
76543210
The GPIO Data Register receives inputs or provides outputs for each of
the seven general-purpose port lines, depending on the configuration of
the port. See Table 8.
Operational Description UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
Table 8. General-Purpose Port Data Register
Function/Bit # 76543210
GPIO D0 X
GPIO D1 X
GPIO D2 X
GPIO D3 X
GPIO D4 X
GPIO D5 X
GPIO D6 X
GPIO D7 X
25
Caution:
Reading from the general-purpose port can damage the drivers used for
the general-purpose port and memory. The port can, however, be used for
writing data.
LED Matrix
The one 7 x 5 LED matrix device on the eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development
Platform is a memory-mapped device that can be used to display information, such as programmed alphanumeric characters. For example, the
LED display sample program that is shipped with this kit displays the
alphanumeric message:
eZ80
To illuminate any LED in the matrix, its respective anode bit must be set
to 1 and its corresponding cathode bit must be set to 0.
Bits 0–6 in Tabl e 7 are LED anode bits. They must be set High (1) and
their corresponding cathode bits, bits 0–4 in Table 9, must be set Low (0)
to illuminate each of the LED’s, respectively.
Bit 7 in Table 7 does not carry any significance within the LED matrix. It
is used for the general-purpose port as a control bit.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
26
Table 9 indicates the multiple register functions of the LED cathode,
modem, and triggers. This table shows the bit configuration for each cathode bit. Bits 5, 6, and 7 do not carry any significance within the LED
matrix. These three bits are control bits for the modem reset, Trig1, and
Trig2 functions, respectively.
Table 9. Bit Access to the LED Cathode, Modem, and Triggers
Function
Cathode Row 5 X
Cathode Row 4 X
Cathode Row 3 X
Cathode Row 2 X
Cathode Row 1 X
Modem RST X
Trig 1 X
Trig 2 X
Bit #
76543210
An LED display sample program is shipped with the eZ80L92
Development Kit. Refer to the eZ80L92 Development Kit Quick Start
Guide (QS0015) or to the Tutorial section in the ZiLOG Developer Studio
®
II—eZ80Acclaim!
User Manual (UM0144).
Modem Reset
The Modem Reset signal, MRESET, is used to reset an optional socket
modem. This signal is controlled by bit 5 in the register shown in
Table 9.
The MRESET signal is available at the embedded modem socket interface (J9, Pin 1).
Setting this bit Low places the optional socket modem into
a reset state. The user must pull this bit High again to enable the socket
modem. Reference the appropriate documentation for the socket modem to
reset timing requirements.
Operational Description UM012913-0407
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
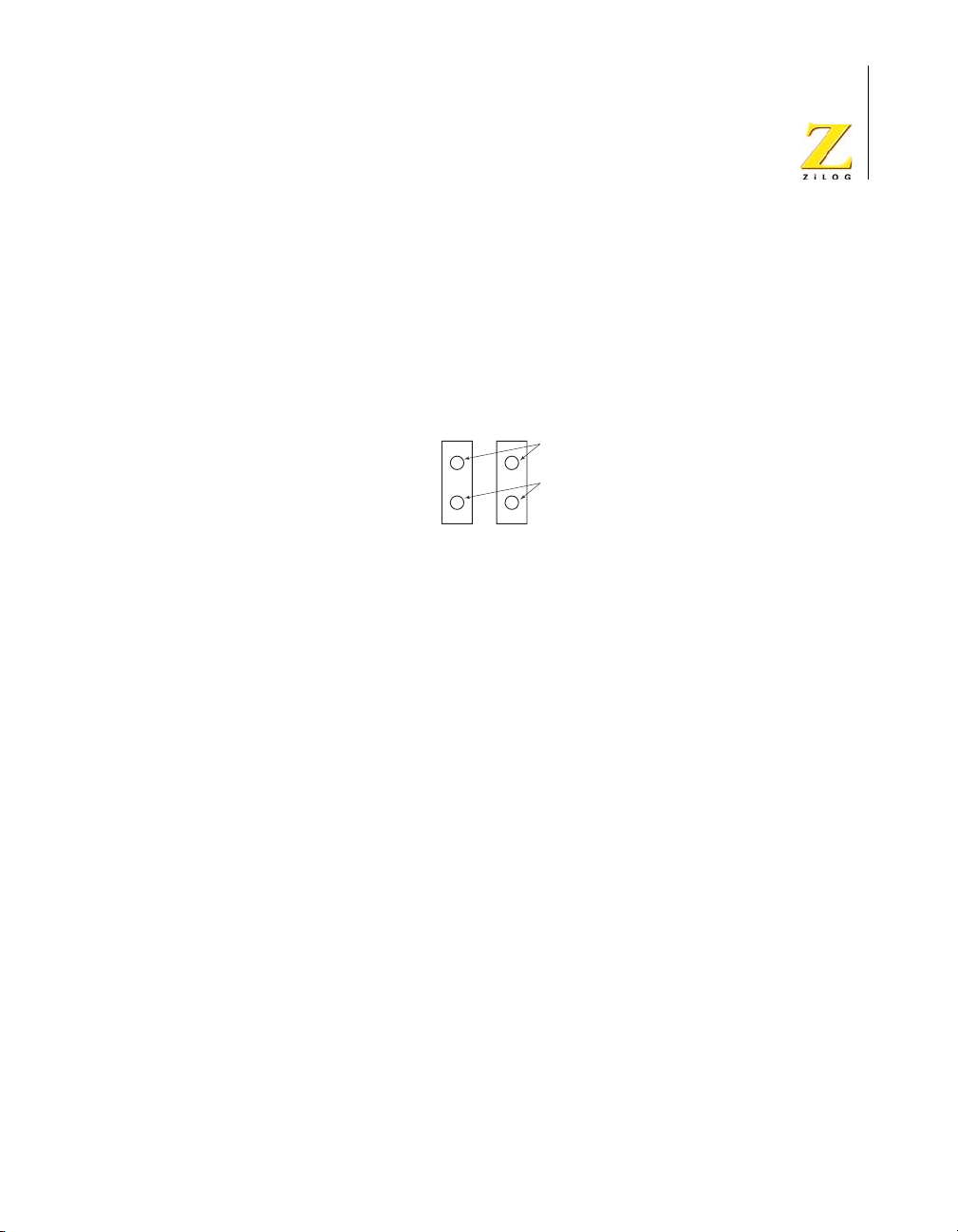
User Triggers
Two general-purpose trigger output pins are provided on the
®
eZ80Acclaim!
Development Platform. Labeled J21 (Trig2) and J22
(Trig1), these pins allow you to trigger external equipment to aid in the
debug of the system. See Figure 8 for trigger pin details.
J21
J22
Ground
Trigger output
Trig2
Trig1
Figure 8. Trigger Pins J21 and J22
27
Bit 6 and Bit 7 in Table 9 are the control bits for the user triggers. If either
bit is a 1, the corresponding Trig1 and Trig2 signals are driven High. If
either bit is 0, the corresponding Trig1 and Trig2 signals are driven Low.
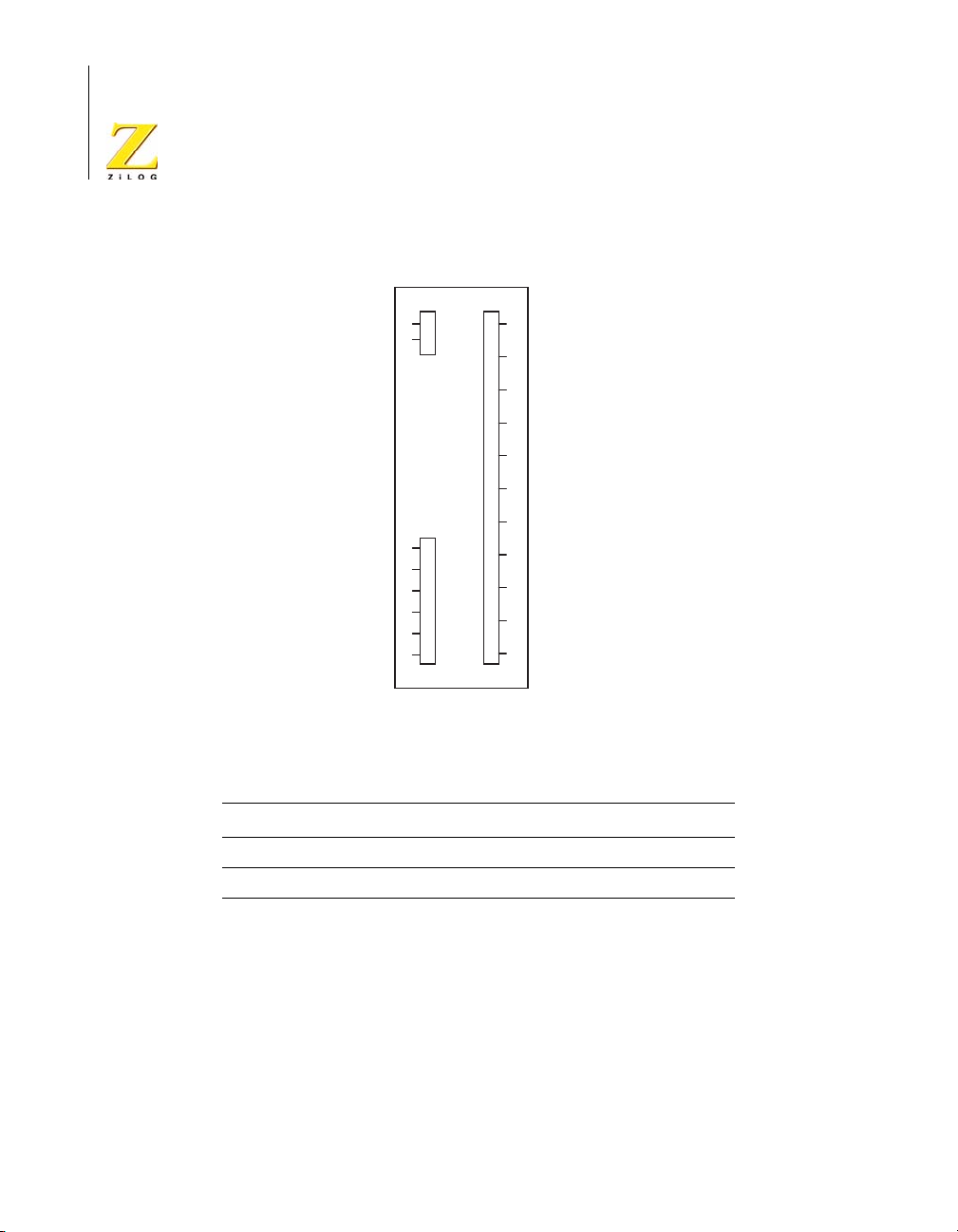
Embedded Modem Socket Interface
The eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform features a socket for an
optional 56K modem (a modem is not included in the kit).
Connectors J1, J5, and J9 provide connection capability. The modem
socket interface provided by these three connectors is shown in Figure 9.
Table 10 and Tabl e 1 2 identify the pins for each connector. The embedded
modem utilizes UART1, which is available via the Port C pins.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
28
J5
12
2
J9
1
3
6
7
8
9
J1
4
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
Figure 9. Embedded Modem Socket Interface—J1, J5, and J9
Table 10. Connector J5
Pin Symbol Description
1 M-TIP Telephone Line Interface—TIP.
2 M-RING Telephone Line Interface—RING.
Operational Description UM012913-0407

Table 11. Connector J9
Pin Symbol Description
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
29
1 MRESET
3 GND Ground.
6 D1 DCD indicator; can drive an LED anode without
7 D2 RxD indicator; can drive an LED anode without
8 D3 DTR indicator; can drive an LED anode without
9 D4 TxD indicator; can drive an LED anode without
Table 12. Connector J1
Pin Symbol Description
2MOD_DIS
4V
24 GND Ground.
25 PC4_DTR1 DTR interface; TTL levels.
CC
Reset, active Low, 50–100 ms. Closure to GND for
reset.
additional circuitry.
additional circuitry.
additional circuitry.
additional circuitry.
Modem disable, active Low.
+5 V DC or +3.3 V DC input.
26 PC6_DCD1 DCD interface; TTL levels.
27 PC3_CTS1 CTS interface; TTL levels.
28 PC5_DSR1 DSR interface; TTL levels.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
30
Table 12. Connector J1
29 PC7_RI1 Ring Indicator interface; TTL levels.
30 PC0_TXD1 TxD interface; TTL levels.
31 PC1_RXD1 RxD interface; TTL levels.
32 PC2_RTS1 RTS interface; TTL levels.
Components P4, T1, C3, C4, and U11 provide the phone line interface to
®
the modem. On the eZ80Acclaim!
Development Platform, LEDs D1,
D2, D3, and D4 function as status indicators for this optional modem.
The phone line connection for the modem is for the United States only.
Connecting the modem outside the U.S. requires modification.
The tested modem for this
eZ80L92 Development Kit
modem, part number SF56D/SP. Information about this modem and its interface is available in the SmartSCM SocketModem data sheet (Doc. No.
101522D) from
www.conexant.com
.
eZ80® Development Platform Memory
Memory space on the eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform consists of
onboard SRAM and additional footprints.
Onboard SRAM
®
The eZ80Acclaim!
U20. This SRAM provides the basic memory requirement for small applications development. This SRAM is in the address range
BFFFFFh.
Additional SRAM
The amount of eZ80Acclaim!
extended if required by adding SRAM devices. U19, U18, and U17 pro-
Development Platform features 512 KB SRAM at
®
Development Platform memory can be
is a Conexant socket
B80000h–
Operational Description UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
vides this capability. However, you should be aware that additional
SRAM must be installed in the following order:
31
1. U19, address range
B00000h–B7FFFFh
2. U18, address range A80000h–AFFFFFh
3. U17, address range A00000h–A7FFFFh
If SRAM memory is installed in a different order than the above
sequence, SRAM will not be contiguous unless the user is able to change
the address decoder, U10. Memory access decoding is performed by this
address decoder, implemented in the Generic Array Logic device,
GAL22LV10D (U10).
Flash Memory
The eZ80L92 Development Kit allows Flash memories between 1 MB
and 4 MB. The chips are housed in wide TSOP40 cases. Flash ROM
access times are 55–150 ns; typically 90 ns.
When accessing Flash memory, the eZ80L92 device should be configured
to operate in Intel bus mode to satisfy setup and hold times and to prevent
bus contention with a Write cycle that could possibly follow. For proper
CPU operation at 48 MHz, first set the bus mode control register
CS0_BMC (I/O address
register CS0_CTL (I/O address
F0h) to 82h, then set the Chip Select Control
AAh) to 08h. These settings select Intel
Bus Mode with two system clocks per bus cycle and zero wait states.
Memory Map
A memory map of the
ory and SRAM on the
are active Low. SRAM on the
eZ80® CPU is illustrated in
eZ80L92 Module
are addressed when CS0 and CS1
eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform is
Figure 10
. Flash mem-
addressed when CS2 is active Low.
Note:
UM012913-0407 Operational Description
The Ethernet controller located on the eZ80L92 Module, is mapped as an
I/O device at address
300h. It uses CS3.

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
32
FFFFFFh
DFFFFFh
SRAM Memory
up to 2 MB
C7FFFFh
C00000h
BFFFFFh
B80000h
E-NET Module
SRAM
Main Board
SRAM (512 KB)
CS1
Expansion SRAM Memory
up to 1.5 MB
80FFFFh
800000h
7FFFFFh
Expansion Module
Flash Memory up to 4 MB
400000h
3FFFFFh
Flash Memory
0FFFFFh
000000h
Up to 4 MB
1 MB on
E-NET Module
Up to 4 MB
CS2
CS0 (8 MB)
Figure 10. Memory Map of the eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform
and eZ80L92 Module
The LED matrix and the general-purpose port circuitry are mapped in the
address range
800000h–80ffffh. The CS2 chip select should be driven
Low to select the LED matrix or general-purpose port.
Operational Description UM012913-0407

LEDs
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
33
As stated earlier, LEDs D1, D2, D3, and D4 function as status indicators
for an optional modem. This section describes each LED and the LED
matrix device.
Data Carrier Detect
The Data Carrier Detect (DCD) signal at D1 indicates that a good carrier
signal is being received from the remote modem.
RX
The RX signal at D2 indicates that data is received from the modem.
Data Terminal Ready
The Data Terminal Ready (DTR) signal at D3 informs the modem that the
PC is ready.
TX
The TX signal at D4 indicates that data is transmitted to the modem.
Push Buttons
The eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform provides user controls in the
form of push buttons. These push buttons serve as input devices to the
eZ80L92 microprocessor. The programmer can use them for application
development. All push buttons are connected to the general-purpose port
pins.
PB0
The PB0 push button switch, SW1, is connected to bit 0 of the generalpurpose port. This switch can be used as the port input.
PB1
The PB1 push button switch, SW2, is connected to bit 1 of the generalpurpose port. This switch can be used as the port input.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
34
PB2
The PB2 push button switch, SW3, is connected to bit 2 of the generalpurpose port. This switch can be used as the port input.
RESET
The Reset push button switch, SW4, resets the eZ80
eZ80Acclaim!
Jumpers
The eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform provides a number of jumpers that are used to enable or disable functionality on the platform, enable
or disable optional features, or provide protection from inadvertent use.
Jumper J2
The J2 jumper connection enables/disables IrDA transceiver functionality. When the shunt is placed, IrDA communication is disabled. See
Table 13.
®
Development Platform.
®
CPU and the
Table 13. J2—DIS_IrDA
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
IN IrDA interface disabled UART0 is configured to work with the RS232 or the
RS485 interfaces.
OUT IrDA interface enabled The IrDA and UART0 interfaces on the eZ80L92
Module perform their functions.
Operational Description UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
Jumper J3
The J3 jumper connection controls the mode of the general-purpose port
and communication with the 7 x 5 LED. When the shunt is placed, the
general-purpose port is disabled. See Table 14 .
Table 14. J3—DIS_EM
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
User Manual
35
IN Application Module Hardware
Disabled
OUT Application Module Hardware
Enabled
Communication with 7 x 5 LED and Port
emulation circuit is disabled.
Communication with 7 x 5 LED and the
general-purpose port circuit is enabled.
Jumper J7
The J7 jumper connection controls Flash boot loader programming. When
the shunt is placed, overwriting of the Flash boot loader program is
enabled. See Table 15.
Table 15. J7—FlashWE
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
OUT The Flash boot sector of the
eZ80L92 Module is writeprotected.
IN The Flash boot sector of the
eZ80L92 Module is enabled for
writing or overwriting.
Flash boot sector of the eZ80L92 Module.
Flash boot sector of the eZ80L92 Module.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
36
Jumper J11
The J11 jumper connection controls access to the off-chip Flash memory
device. When the shunt is placed, access to this Flash device is enabled.
See Table 16.
Note:
The silk-screened label on the eZ80Acclaim!
jumper J11 is incorrect. Currently, it reads DIS_FLASH. The correct label
is EN_FLASH.
Table 16. J11—EN_FLASH (Off-Chip)*
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
IN All access to external Flash memory on
the eZ80L92 Module is enabled.
OUT All access to external Flash memory on
the eZ80L92 Module is disabled.
Note: As shipped from the factory, external Flash memory is not installed.
External Flash memory on the
eZ80L92 Module.
External Flash memory on the
eZ80L92 Module.
®
Development Platform for
Jumper J12
The J12 jumper connection controls the selection of a 5 V or 3 VDC power
supply to the embedded modem, if an embedded modem is used. See
Table 17.
Table 17. J12—Power Supply to an Embedded Modem
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
1–2 5 V DC is provided to power the embedded
modem.
2–3 3.3 V DC is provided to power the
embedded modem.
Operational Description UM012913-0407
Embedded modem.
Embedded modem.

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
Jumper J14
The J14 jumper connection controls the polarity of the Ring Indicator. See
Table 18.
Table 18. J14—RI
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
1–2 The Ring Indicator for UART1 is inverted. UART1.
2–3 The Ring Indicator for UART1 is not inverted. UART1.
Jumper J15
The J15 jumper connection controls the selection RS485 circuit along
with UART0. When the shunt is placed, the RS485 circuit is enabled. See
Table 19. RS485 functionality will be available for the future eZ80
devices.
37
®
Table 19. J15—RS485_1_EN*
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
IN The RS485 circuit is enabled on UART0.
The UART0 CONSOLE interface and IrDA are
disabled.
OUT The RS485 circuit is disabled on UART0. IrDA, UART0 CONSOLE
Note: *To enable the RS485 circuit, the corresponding IrDA/RS232 circuit must be disabled.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description
IrDA, UART0 CONSOLE
interface, RS485 interface.
interface, RS485 interface.

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
38
Jumper J16
The J16 jumper connection controls the selection of the RS485 circuit.
However, UART1 MODEM interface and the socket modem interface are
disabled if the RS485 circuit is enabled. When the shunt is placed, the
RS485 circuit is enabled. See Tab le 2 0 .
Table 20. J16—RS485_2_EN
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
IN The RS485 circuit is enabled on UART1. The
UART1 MODEM interface and the Socket
Modem interface are disabled.
OUT The RS485 circuit is disabled on UART1. UART1 MODEM interface,
UART1 MODEM interface,
Socket Modem Interface,
and RS485 interface.
Socket Modem Interface,
and RS485 interface.
Jumper J17
The J17 jumper connection controls the selection of the RS485 termination resistor circuit. When the shunt is placed, the RS485 termination
resistor circuit is enabled. See Tab l e 2 1 .
Table 21. J17—RT_1*
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
IN The Termination Resistor for RS485_1 is IN. RS485 interface.
OUT The Termination Resistor for RS485_1 is OUT. RS485 interface.
Note: *Before enabling the termination resistor, ensure that the device is located at the end of the
interface line.
Operational Description UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
Jumper J18
The J18 jumper connection controls the selection of the RS485 termination resistor circuit. When the shunt is placed, the RS485 termination
resistor circuit is enabled. See Tab l e 2 2 .
Table 22. J18—RT_2*
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
IN The Termination Resistor for RS485_2 is IN. RS485 interface.
OUT The Termination Resistor for RS485_2 is OUT. RS485 interface.
Note: *Before enabling the termination resistor, ensure that the device is located at the end of the
interface line.
39
Jumper J19
The J19 jumper connection selects the range of memory addresses for the
external chip select signal, CS_EX
, to the application module. See
Table 23.
Table 23. J19—EX_SEL
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
1–2 CS_EX
located in the address range 400000h–7FFFFFh.
3–4 CS_EX
located in the address range A00000h–A7FFFFh.
5–6 CS_EX
located in the address range A80000h–AFFFFFh.
7–8 CS_EX
located in the address range B00000h–B7FFFFh.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description
is decoded in the CS0 memory space and is
is decoded in the CS2 memory space and is
is decoded in the CS2 memory space and is
is decoded in the CS2 memory space and is
Application module
addressing.
Application module
addressing.
Application module
addressing.
Application module
addressing.

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
40
Jumper J20
The J20 jumper connection controls the selection of the external chip
select in the external application module. When the shunt is placed, the
external chip select signal, CS_EX
Table 24. J20—EX_FL_DIS
Shunt
Status Function Affected Device
IN The jumper for EX_FL_DIS is IN. The chip select on the application module
, is disabled. See Table 24.
is disabled.
OUT
The jumper for EX_FL_DIS is OUT.
Connectors
A number of connectors are available for connecting external devices
such as the ZPAK II emulator, PC serial ports, external modems, the console, and LAN/telephone lines.
J6 and J8 are the headers, or connectors, that provide pin-outs to connect
any external application module, such as ZiLOG’s Thermostat Application Module.
Connector J6
The J6 connector provides pin-outs to make use of GPIO functionality.
Connector J8
The J8 connector provides pin-outs to access memory and other control
signals.
The chip select on the application module
is enabled.
Operational Description UM012913-0407

Console
Connector P2 is the RS232 terminal, which can be used for observing the
console output. P2 can be connected to the HyperTerminal, if required.
Modem
Connector P3 provides a terminal for connecting an external modem, if
used with the eZ80L92 Development Kit. RS485 functionality will be
available in future eZ80
I2C Devices
The two I2C devices on the eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform are
the U2 EEPROM and the U13 Configuration register. The
EEPROM provides 16 KB memory. The Configuration register provides
access to control the configuration of an application-specific function at
the application module interface. Neither device is utilized by the
eZ80L92 Development Kit software. You are free to develop proprietary
software for these two devices. The addresses for accessing these devices
are listed in Table 25.
®
devices.
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
41
Table 25. I2C Addresses
Device/Bit # 7654321 0
EEPROM (U10)* 1 0 1 0 0 A1 A0 R/W
Configuration Register (U13) 1001110R/W
Note: *EEPROM address bit A0 and bit A1 are configured for 0s.
DC Characteristics
This section provides an estimate of the average current requirement
when different combinations of the application modules are plugged into
the eZ80Acclaim!
UM012913-0407 I2C Devices
®
Development Platform.

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
42
The receiver supply current is 90–150 µA and the transmitter supply
current is 260 mA, when the LED is active. The measurements of current
are shown in Table 26 are for your reference. These values can vary
depending on the type of application developed to run with the platform.
Table 26. DC Current Characteristics of the eZ80® Development Platform with
Different Module Loads
Current
Platform/Modules Configurations
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform
and eZ80L92 Module
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform,
eZ80L92 Module and Modem Module
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform,
eZ80L92 Module and Thermostat
Application Module
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform,
eZ80L92 Module, Modem Module, and
Thermostat Application Module
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform
and eZ80L92 Module
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform,
eZ80L92 Module and Modem Module
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform,
eZ80L92 Module and Thermostat
Application Module
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform,
eZ80L92 Module, Modem Module and
Thermostat Application Module
Requirement (mA) Status
173 When connected only to a
power supply, and when
no program is running.
174 When connected only to a
power supply, and when
no program is running.
195 When connected only to a
power supply, and when
no program is running.
203 When connected only to a
power supply, and when
no program is running.
325 When the LED demo is
running.
325 When the LED demo is
running.
350 When the LED demo is
running.
360 When the LED demo is
running.
DC Characteristics UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Module
This chapter describes the eZ80L92 Module hardware, its interfaces and
key components, including the CPU, Ethernet Media Access Control, and
memory.
Functional Description
The eZ80L92 Module is a compact, high-performance Ethernet module
specially designed for the rapid development and deployment of
embedded systems requiring control and Internet/Intranet connectivity via
Ethernet and/or IrDA. Additional devices such as serial ports, LED
matrices, general-purpose port, and I
connected to the
representing both of the boards is illustrated in Figure 1 on page 4.
eZ80Acclaim!
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
2
®
C devices are supported when
Development Platform. A block diagram
43
The eZ80L92 Module is developed to be a plug-in module to the
eZ80Acclaim!
vides a CPU, RAM, Flash memory, an IrDA transceiver, and an Ethernet
Media Access Controller (EMAC). This low-cost, expandable module is
powered by the eZ80L92 microprocessor, a member of ZiLOG’s eZ80
product family. The module also contains a battery and an oscillator in
support of the on-chip real time clock (RTC). The eZ80L92 Module can
also be used as a stand-alone development tool when provided with an
external power source.
®
Development Platform. This small-footprint module pro-
®
Physical Dimensions
The dimensions of the eZ80L92 Module PCB is 64 x 64 mm. With an
RJ-45 Ethernet connector, the overall height is 25 mm. See Figure 11.
UM012913-0407 eZ80L92 Module
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
44
8.3 mm
max.
2.54 mm
63.5 mm
13.7 mm
1
16.3 mm
LAN
Link
16 mm
8.5 mm
LEDs
1
RJ45
9 mm
3.5 mm
64 mm
Bus Connector
Top View
I/O Connector
9 mm
2.7 mm
6.2 mm
55.88 mm
IrDA
7 mm
Figure 11. Physical Dimensions of the eZ80L92 Module
Functional Description UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
Figure 12 illustrates the top layer silkscreen of the eZ80L92 Module.
45
Figure 12. Top Layer
UM012913-0407 Functional Description
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
46
Figure 13 illustrates the bottom layer silkscreen of the eZ80L92 Module.
Figure 13. Bottom Layer
Operational Description
The purpose of the eZ80L92 Module as a feature of the eZ80L92
Development Kit is to provide the application developer with a plug-in
tool to evaluate the EMAC, memory, IrDA, and other features of the
eZ80L92 device.
Ethernet Media Access Controller
The eZ80L92 Development Kit contains a CS8900A Ethernet Media
Access Controller (EMAC—controls MAC and PHY functions) which is
attached to the data/address bus (A0–A3, D0–D7, RD, and WR) of the
processor. This chip is connected to the processor’s CS3 Chip Select and
to the PD4 pins for interrupt purposes. Connection of pin PD6 and pin
Operational Description UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
PD7 for LANACT (wake-up from sleep) and SLEEP is optional and
resistor-selectable onboard (see below). Details about the internal registers of the CS8900A EMAC can be found on the Cirrus Logic website at
www.cirrus.com
.
Ethernet LEDs
There are two green LEDs, a Link LED and a LAN LED, that are located
adjacent to each other on the eZ80L92 Module. A steady LAN LED
indicates received link pulses from the 10 Base-T Ethernet. This LAN
LED should be ON if RX+ is connected to TX+ and RX– is connected to
TX–. A flashing Link LED indicates Traffic (RX or TX) on the LAN.
Ethernet Connector
The eZ80L92 Development Kit is equipped with an RJ-45 connector that
features integrated magnetics (transformer, common mode chokes). The
remaining pins on the onboard RJ-45 connector are not connected.
47
An RJ-45 loopback connector can be used to verify the correct operation
of the Receiver and the Transmitter. Pin assignments for the RJ-45
Ethernet connector are shown in Table 27.
Table 27. Ethernet Connector Pin Assignments
Pin Function
1 TX+
2 TX–
3 RX+
6 RX–
To connect the eZ80L92 Development Kit directly to another host (for
example, to a personal computer), a crossover cable must be used.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
48
The EMAC can be additionally protected by placing an ESD protection
array on the module at U9. This array can be either of the LCDA15C-6
(Semtech) or ESDA25B1 (ST Microelectronics) devices.
GPIO Pins for Enabling LAN Activity, Sleep, Interrupt
GPIO input bit PD4 serves as an active High interrupt input for the
EMAC’s INTRQ0 output.
GPIO output bit PD7 can be used to enter the EMAC into SLEEP mode.
When pulling SLEEP (PD7) Low after enabling HWStandbyE and
HWSleepE modes, the chip draws lower current, because only the
receiver is operating. A zero-Ohm resistor at position R14 on the
eZ80L92 Development Kit is required for this function.
If LAN activity is detected, the LANACT signal is pulled Low. The
LANACT is connected to GPIO input PD6 and can be used in interrupt
edge-detection mode to wake up and reinitialize the Ethernet chip.
A zero-Ohm resistor at position R15 on the module is required for this
function. In this case, the PD6 pin is not available for GPIO on the I/O
connector.
EMAC Ports
Chip Select CS3 is used for selecting the EMAC device. The base address
is user-selectable. The EMAC is connected as an 8-bit device.
EMAC Wait States
The CS8900A EMAC should be operated in Intel bus mode so that the
setup and hold times for the I/O access are met. For 48 MHz operation,
first set CS3_BMC (I/O address
system clock cycles per bus cycle) and then CS3_CTL (I/O Address
to
18h (0 wait states for I/O). For a 20.8 ns CPU Clock cycle time, the
F3h) to 84h (Intel bus mode with four
B3h)
READ and WRITE access time is:
2 x 4 x 20.8 ns–16 ns (for capacitive and chip delays) = 150 ns
Operational Description UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Module Memory
The eZ80L92 Module contains 512 KB SRAM and 1 MB Flash memory.
This addressing structure provides 1 MB of contiguous SRAM for
immediate use.
SRAM Memory
The eZ80L92 Module features 512 KB of fast SRAM. Access speed is
typically 12 ns or faster, allowing zero-wait-state operation at 48 MHz.
With the CPU at 48 MHz, onboard SRAM can be accessed with zero wait
states in eZ80 mode. CS1_CTL (chip select CS1) can be set to
wait states).
Flash Memory
The Flash Boot Loader, application code, and user configuration data are
held permanently in Flash memory. As an example, for 128 KB onboard
SRAM, 1 MB of ROM is required.
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
49
08h (no
Reset Generator
The onboard Reset Generator Chip is connected to the eZ80L92 Reset
input pin. It performs reliable Power-On Reset functions, generating a
reset pulse with a duration of 200 ms if the power supply drops below
2.93 V. This reset pulse ensures that the board always starts in a defined
condition. The RESET pin on the I/O connector reflects the status of the
RESET line. It is a bidirectional pin for resetting external peripheral components or for resetting the eZ80L92 Development Kit with a low-impedance output (for example, a 100-Ohm push button).
IrDA Transceiver
An onboard IrDA transceiver (ZiLOG ZHX1810) is connected to PD0
(TX), PD1 (RX), and PD2 (Shutdown, IR_SD). The IrDA transceiver is
of the LED type 870 nm Class 1.
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
50
The IrDA transceiver is accessible via the IrDA controller attached to
UART0 on the eZ80L92 device. The UART0 console and the IrDA transceiver cannot be used simultaneously.
To use the UART0 for console or to save power, the transceiver can be
disabled by the software or by an off-board signal when using the proper
jumper selection. The transceiver is disabled by setting PD2 (IR_SD)
High or by pulling the DIS_IRDA
shutdown feature is used for power savings. To enable the IrDA transceiver, DIS_IRDA
The eZ80L92 Module contains a ZiLOG IrDA transceiver that is connected to the UART0 port. This port can be used as a wireless connection
into the eZ80L92 Module. The UART0 can connect to a standard RS232
port, or it can be configured to control the IrDA transceiver; however, it
cannot do both at the same time. Only a few registers are required to configure the UART0 port to send and receive IrDA data.
pin on the I/O connector Low. The
is left floating and PD2 is set to Low.
The RxD and TxD signals on the transceiver perform the same functions
as a standard RS232 port. However, these signals are processed as IrDA
3/16 coding pulses (sometimes called IrDA encoder/decoder pulses).
When the IrDA function is enabled, the final output to the RxD and TxD
pins are routed through the 3/16 pulse generator.
Another signal that is used in the eZ80L92 Module’s IrDA system is
Shut_Down (SD). The SD pin is connected to PD2 on the eZ80L92 Module. The IrDA control software on the wireless device must enable this
pin to wake the IrDA transceiver. The SD pin must be set Low to enable
the IrDA transceiver. On the eZ80L92 Module, a two-input OR gate
allows an external pin to shut down the IrDA transceiver. Both pins must
be set Low to enable this function.
Figure 14 highlights the eZ80L92 Module IrDA hardware connections.
Operational Description UM012913-0407
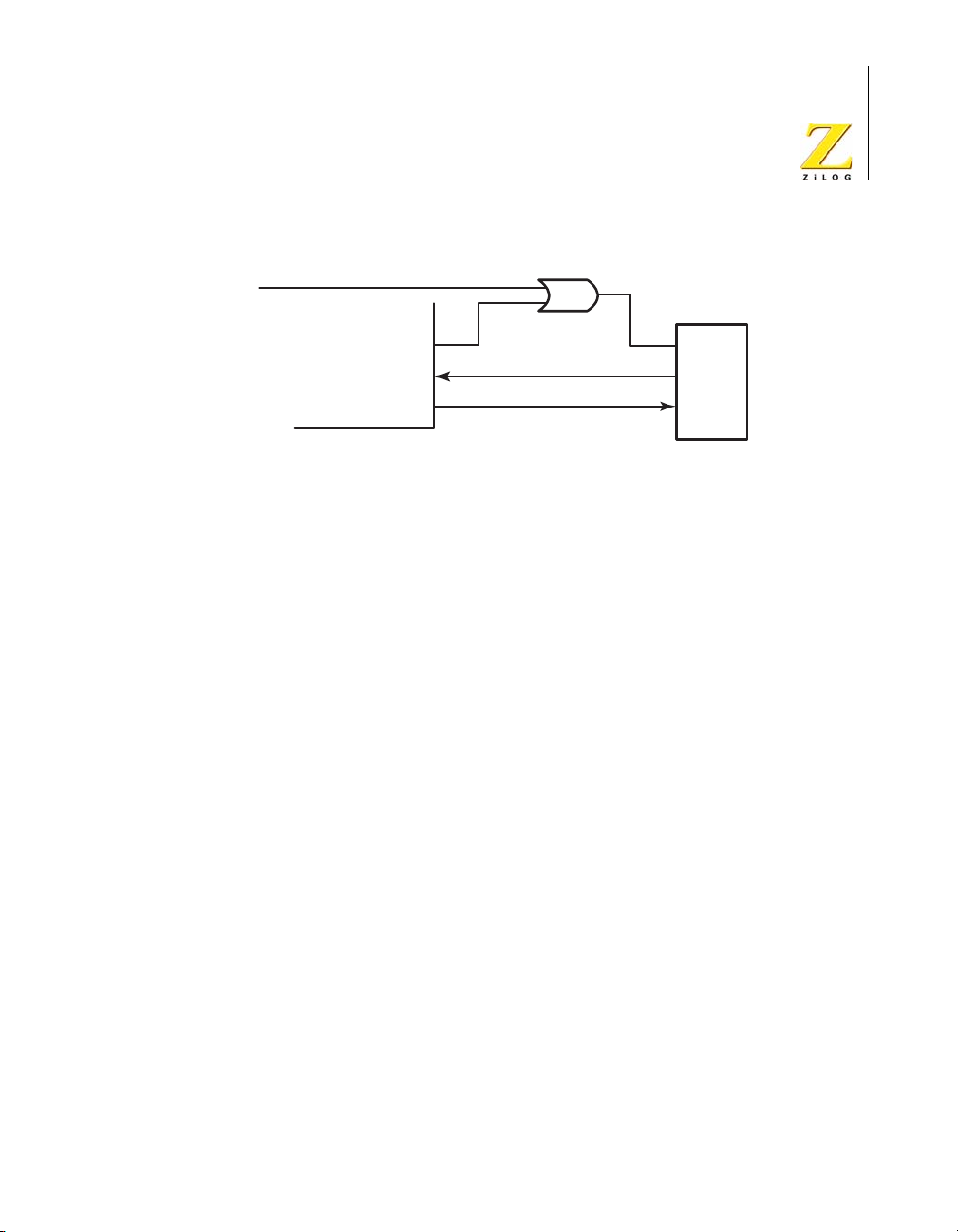
External Disable
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
51
IrDA
eZ80L92
Device
PD2(IR_SD)
PD1(RxD)
PD0(TxD)
Figure 14. IrDA Hardware Connections
SD
RD
TD
The eZ80L92 Module features an Infrared Encoder/Decoder register that
configures the IrDA function. This register is located at address
0BFh in
the internal I/O register map.
The Infrared Encoder/Decoder register contains three control bits. Bit 0
enables or disables the IrDA encoder/decoder block. Bit 1, if set, enables
received data to pass into the UART0 Receive FIFO data buffer. Bit 2 is a
test function that provides a loopback sequence from the TxD pin to the
RxD input.
Bit 1, the Receive Enable bit, is used to block data from filling up the
Receive FIFO when the eZ80L92 Module is transmitting data. Because
IrDA data passes through the air as a light source, transmitted data can
also be received. This Receive Enable bit prevents the data from being
received. After the eZ80L92 Module completes transmitting, this bit is
changed to allow for incoming messages.
The code below provides an example of how this function is enabled on
the eZ80L92 Module.
//Init_IRDA
// Make sure to first set PD 2 as a port bit, an ou tput a nd se t it L ow.
PD_ALT1 &= 0xFC; // PD0 = uart0tx, PD1 = uart0_rx
PD_ALT2 |= 0x03; // Enable alternate function
UART_LCTL0= 0x80; // Select dlab to access baud rate generator
UM012913-0407 Operational Description

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
52
BRG_DLRL0=0x2F; // Baud rate Masterclock/(16*baudrate)
BRG_DLRH0=0x00; // High byte of baud rate
UART_LCTL0=0x00; // Disable dlab
UART_FCTL0=0xC7; // Clear tx fifo, enable fifo
UART_LCTL0=0x03; // 8bit, N, 1 stop
IR_CTL = 0x03; // enable IRDA Encode/decode and Receive
// enable bit.
//IRDA_Xmit
IR_CTL = 0x01; //Disable receive
Putchar(0xb0); //Output a byte to the uart0 port.
DC Characteristics
As different combinations of application modules are loaded on the
eZ80Acclaim!
Table 26 on page 42 to reference current consumption values for different
module combinations.
A 0.1-Farad capacitor is provided on the eZ80L92 Module as a short-term
battery backup for the RTC (see eZ80L92 Module on page 66). The part
number of the capacitor made by Panasonic is EECS0HDV. The capacitor
is connected to RTC_VDD to provide power to the RTC when main
power to the chip is removed; it is also connected to the 3.3 V supply to
the chip for recharging. The RTC can operate down to 3.0 V; it requires
10 µA of current. The (keep alive) time this capacitor can supply power
to the RTC (from 3.3 V to 3.0 V), is approximately 3000 seconds, or 50
minutes.
Flash Loader Utility
The Flash Loader utility resides in the boot sector of Flash memory,
located on the eZ80L92 Module. The Flash Loader utility allows the
operation of the Boot Block utility or jumping to the application code.
Refer to the External Flash Loader Product User Guide (PUG0013) for
more details.
®
Development Platform, current requirements change, see
DC Characteristics UM012913-0407

Mounting the Module
While mounting the eZ80L92 Module onto the eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform, check its orientation to the platform to ensure a correct fit.
Pin 1 of JP1 on the eZ80L92 Module must align with pin 1 of JP1 on the
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Development Platform; Pin 1 of JP2 on the eZ80L92
Module must align with pin 1 of JP2 on the eZ80Acclaim!
Platform.
Changing the Power Supply Plug
The universal 9 V DC power supply offers three different plug
configurations and a tool that aids in removing one plug configuration to
insert another, as illustrated in Figure 15.
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
®
Development
53
Figure 15. 9 V DC Universal Power Supply Components
Follow the steps below to exchange one plug configuration for another:
1. Place the tip of the removal tool into the round hole at the top of the
current plug configuration.
2. Press to disengage the keeper tab and push the plug configuration out
of its slot.
UM012913-0407 Mounting the Module

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
54
3. Select the plug configuration appropriate to the location, and insert it
4. Push the new plug configuration down until it snaps into place, as
into the slot formerly occupied by the previous plug configuration.
illustrated in Figure 16.
Figure 16. Inserting a New Plug Configuration
Changing the Power Supply Plug UM012913-0407

ZPAK II
ZPAK II is a debug tool used to develop and debug hardware and
software. It is a networked device featuring an Ethernet interface and an
RS232 console port. ZPAK II is shipped with a pre-configured IP address
that can be changed to suit on a local network. For more information on
using and configuring ZPAK II, refer to the ZPAK II Debug Interface Tool
Product User Guide (PUG0015) and the eZ80L92 Development Kit Quick
Start Guide (QS0015).
ZDI Target Interface Module
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
55
The ZDI Target Interface Module provides a physical interface between
ZPAK II and the eZ80Acclaim!
ule supports ZDI functions. For more information on using the TIM module or ZDI, refer to the eZ80L92 Development Kit Quick Start Guide
(QS0015) and the eZ80L92 Module Product Specification (PS0170).
JTAG
Connector P1 is the JTAG connector on the eZ80Acclaim!® Development
Platform. JTAG will be supported in the future eZ80
Application Modules
ZiLOG offers the Thermostat Application module, which is used for
evaluating and developing process control and simple I/O applications.
The Thermostat Application module is equipped with an LCD display
that displays process control and other physical parameters. For more
information on Thermostat application, refer to the Java Thermostat
Demo Application Note (AN0104), available on www.zilog.com
®
Development Platform. The TIM mod-
®
products.
.
UM012913-0407 ZPAK II

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
56
ZDS II
ZiLOG Developer Studio II (ZDS II) Integrated Development
Environment is a complete stand-alone development environment. Based
on the Windows
faces, ZDS II integrates a language-sensitive editor, project manager, CCompiler, assembler, linker, librarian, and source-level symbolic debugger that supports the eZ80L92 microprocessor. For more information on
using and configuring ZDS II, refer to the ZiLOG Developer Studio II—
eZ80Acclaim!
®
Win 98SE/Win2000-SP4/WinXP Professional inter-
®
User Manual (UM0144).
ZDS II UM012913-0407

Troubleshooting
Overview
If a hardware failure is suspected, contact a local ZiLOG representative
for assistance. Before contacting ZiLOG Customer Support to submit a
problem report, follow the instructions below.
Cannot Download Code
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
57
If you are unable to download code to RAM using ZDS, ensure that you
press and release the Reset button on the eZ80Acclaim!
Platform before selecting
ZDS.
No Output on Console Port
The eZ80L92 Development Kit is shipped with a Flash Loader utility that
is loaded in the protected boot sector of Flash memory (U3). On power-up
of the eZ80Acclaim!
the eZ80L92 device on the module runs the code from the Flash memory
area. This code enables the Console port with settings of 57.6 kbps, 8, N,
1.
The Console checks the Receive buffer. If a space character is received on
the Console port, the Flash Loader utility is enabled and a boot message is
displayed on your connected device. If no message is displayed, check the
following:
•
Jumper J2 must be ON (IrDA is disabled).
•
On Connector J6, the jumper must be removed from pin 6 and pin 9
(con_dis and GND).
®
Development Platform and the eZ80L92 Module,
Debug
→
Reset
and then
®
Development
Debug → Go
in
UM012913-0407 Troubleshooting

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
58
IrDA Port Not Working
While using the IrDA transceiver on the eZ80L92 Module, ensure the
following hardware settings:
•
Jumper J2 must be OFF (to enable the control gate that drives the
IrDA device).
•
Set port pin PD2 Low. When this port pin and Jumper J2 are turned
OFF, the IrDA device is enabled.
•
Install a jumper on connector J6 across pins con_dis and GND to disable the console serial port driver.
Difference Between EMAC and IP Address
Media Access Control
Each Ethernet device interfaced with the network media (for example,
network adapter, port on a hub) contains a unique Media Access Control
(MAC) address, which is hard-coded into the hardware. An Ethernet
device addresses a host using a unique 48-bit address called its Ethernet
address or MAC address.
MAC addresses are usually represented as six colon-separated pairs of
hex digits, for example, 6:0:20:11:ac: 85. The first three bytes (for
example, 6-0-20) are the manufacturer’s code, which is used to identify
the manufacturer. The last three bytes are the unique station ID or serial
number for the interface. This station ID is unique and is associated with a
particular Ethernet device. The Data Link layers protocol-specific header
specifies the MAC address of the packets source and destination. When a
packet is sent to all hosts (broadcast), a special MAC address
(ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff) is used.
MAC address uniquely identifies each node in a network at the MAC
layer, the lowest network layer that directly interfaces with the physical
media (for example, twisted-pair wires).
IrDA Port Not Working UM012913-0407

On a local area network or other network, the MAC address is a
computer’s unique hardware number. (On an Ethernet LAN, the MAC
address is the same as an Ethernet address.) When connected to the
Internet, a computer (or host as the Internet protocol considers it), a
correspondence table relates the Internet Protocol (IP) address to the
computer's physical (MAC) address on the LAN.
IP Address
An IP address is a 32-bit number that identifies each sender or receiver of
information that is sent in packets across the Internet.
An IP address has two parts: the identifier of a particular network on the
Internet and an identifier of the particular device (which can be a server or
a workstation) within that network. On the Internet itself—that is between
the router that moves packets from one point to another along the route—
only the network part of the address is examined.
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
59
Relationship between IP Address and Physical Address
The machine or physical address used within an organization's local area
networks can be different than the Internet IP address. An example is the
48-bit Ethernet address. TCP/IP includes the Address Resolution Protocol
(ARP) that allows the administrator create a table that maps IP addresses
to physical addresses.
The Ethernet MAC address of the ZPAK II
While connecting the ZPAK II serial port to a PC running HyperTerminal,
hold the space bar and reset the ZPAK II.
When HyperTerminal prompts with
eZ80>
enter e to display the MAC address.
UM012913-0407 Difference Between EMAC and IP Address

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
60
Resolving IP Address/Subnet Mask Conflicts
For running demos properly, the ZPAK II IP address and subnet mask
must be properly configured. Follow the instructions provided in the
eZ80L92 Development Kit Quick Start Guide (QS0015) to set up and run
the demo on ZDS II.
Difference Between EMAC and IP Address UM012913-0407

e
Z80L92 D
Kit
5 4 3 2 1
evelopment
User Manual
Schematic Diagrams
eZ80Acclaim® Development Platform
Figure 17 through Figure 21 diagram the layout of the eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform.
GND
GND
_T5_O
GND
0_TXD1
GND
VDD
P
VDD
J4
12
34
56
Header 3x2
JP1
12
34
56
78
9
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
Header 25x2
JP2
12
34
56
78
9
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
Header 25x2
ZDI
INTERFAC
VDD
R4
10K
VDD
RX
TX
MA
0
MA
3
VDD
MA
7
MA
GND
VDD
GND
PC5_DSR1
PC3_CTS1
PC1_RXD1
PD7_RI0
GND
PD4_DTR0
PD2_RTS0
PD
GND
GND
TCK
TDI
D1
D3
MA14
MA16
MA
MA12
MA20
MA17
-DIS_FL
MA23
-M_CS
MD0
MD2
MD4
MD6
-M_IORQ
-M_RD
INSTRD
-BUSREQ
PB6_MISO
PB4
_T4_O
PB2_SS
PB0_T0_I
PC7_RI1
0_TXD0
TDI
TRIGOUT
TM
M_PHI
-DIS_IRDA
-M
WAIT
-NMI
R19
10K
DCD
21
DTR
21
9
1
S
21
21
10
10
E
PRSTn
D2
D4
1
-DIS_FL
VDD
M_T
IP
M_RING
-MRE
R8
R9
R20
R21
SET
MA0
MA1
MA2
MA3
MA4
MA5
MA6
MA7
MA8
MA9
MA10
MA11
MA12
MA13
MA14
MA15
R2
10K
MA16
MA17
MA18
MA19
MA20
MA21
MA22
MA23
GND
0
0
0
0
M_
TIP
M_RING
-MR
ESET
GND
2
4
6
8
11
13
15
17
1
19
2
4
6
8
11
13
15
17
1
19
2
4
6
8
11
13
15
17
1
19
U1
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
1OE
2OE
74LVC244A
U3
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
1OE
2OE
74LVC244A
U5
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
1OE
2OE
74LVC244A
1
2
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
18
Y1
16
Y2
14
Y3
12
Y4
9
Y5
7
Y6
5
Y7
3
Y8
20
VCC
10
GND
18
Y1
16
Y2
14
Y3
12
Y4
9
Y5
7
Y6
5
Y7
3
Y8
20
VCC
10
GND
18
Y1
16
Y2
14
Y3
12
Y4
9
Y5
7
Y6
5
Y7
3
Y8
20
VCC
10
GND
J5
HEADER 2
J9
HEADER 9
MODEM CONNECTORS
J1
HEADER 32
DO NOT USE J6_17 A
9V_DC
9VDC
SCL
SDA
-MOD_DIS
-MW
AIT
EM_D0
EM_D7
EM_D6
EM_D5
EM_D4
EM_D3
EM_D2
EM_D1
PC7_RI1
PC6_DCD1
PC5_DSR1
PC4_DTR1
PC3_CTS1
PC2_RTS1
PC1_RXD1
PC
0_TXD1
-BUSACK
-NMI
-RST
U8A
GND
TC7
-RD
-ME
-CS3
VDD
GND
GND
VDD
GND
-CS0
-CS2
MRQ
14
1
7
4LVT125
VCC
GND
GND
GND
-RESE
GND
VDD
23
ND J6_35
GND
A0
A2
A4
A6
A8
A10
A12
A14
A16
A18
A20
A22
T
D0
D2
D4
D6
VDD
R5
1K
J6
12
34
56
78
9
10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
51 52
53 54
55 56
57 58
59 60
Header 30x2
J8
12
34
56
78
9
10
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
51 52
53 54
55 56
57 58
59 60
Header 30x2
VDD
U9A
3
GND
TVCC_RESETn
ID_2
ID_1
ID_0
GND
GND
GND
PB7_MOSI
PB6_MISO
PB
5_T5_O
PB
4_T4_O
PB3_SCK
PB2_SS
PB1_T1_I
PB0_T0_I
A1
A3
A5
A7
A9
A11
A13
A15
A17
A19
A21
A23
PHI
GND
D1
D3
D5
D7
GND
147
TC74LVC08
TDI
TD
O
TCK
VDD
1
2
PD7_RI0
PD6_DCD0
PD5_DSR0
PD4_DTR0
PD3_CTS0
PD2_RTS0
PD1_RXD0
PD
PB2_SS
PB1_T1_I
PB0_T0_I
GND
GND
GND
VDD
GND
-CS1
-C
S_EX
-IORQ
ID_2
ID_1
ID_0
-CON_DIS
0_TXD0
-WR
INSTRD
-BUSREQ
PHI
-DIS_ETH
VDD
VDD
P1
12
34
56
78
9
11 12
13 14
con 7x2
MA6
MA10
MA8
MA13
MA15
MA18
MA19
MA2
MA11
MA4
MA5
-DIS_ETH
MA21
MA22
-M_CS0
-M_CS2
MD1
MD3
MD5
MD7
-M_MEMRQ
-M_WR
-BUSACK
R1
10K
PB7_MOSI
PB5
PB3_SCK
PB1_T1_I
PC6_DCD1
PC4_DTR1
PC2_RTS1
PC
PD6_DCD0
PD5_DSR0
PD3_CTS0
PD1_RXD0
TDO
TCK
RTC_VDD
SCL
SDA
-FLASHWE
R3
-M_CS3
10K
-RST
HALT_SL
VDD
GND
R24
10K
-RESE
T
GND
10
TMS
PRSTn
TRIGOUT
Figure 17. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Schematic Diagram, #1 of 5
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams
VDD
GND
VDD
GND
VDD
GND
A[23:0]
MODEM's
AGND
VCC
GND
PC4_DTR1
PC6_DCD1
PC3_CTS1
PC5_DSR1
PC7_RI1
PC
0_TXD1
PC1_RXD1
PC2_RTS1
A[23:0]
C30
0.1uF
C31
0.1uF
C33
0.1uF
-MOD_DIS
J2
HEADER 2
J7
HEADER 2
1
GND
2
-FLASHWE
1
GND
2
VCC
VDD
MD0
MD1
MD2
MD3
MD4
MD5
MD6
MD7
-M_RD
-L_RD
VCC
VDD
GND
GND
SCL
-DIS_IRDA
-M_CS0
-M_CS1
-M_CS2
-M_IORQ
-M_MEMRQ
-M_WR
-M_RD
-M_CS3
M_PHI
GND
J12
1
2
3
Header 3
U7
2
A0
B0
3
A1
B1
4
A2
B2
5
A3
B3
6
A4
B4
7
A5
B5
8
A6
B6
9
A7
B7
1
DIR
VCC
19
OE
GND
74LVC245/SO
VCC
VDD
GND
ZiLOG
910 E. Hamilton Avenue
Title
Schematic,
SizeDocument Number
B
Friday, October 10, 2003
Date:
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
A21
A22
A23
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
U2
U21
2
A1
3
A2
4
A3
5
A4
6
A5
7
A6
8
A7
9
A8
10
A9
11
A10Y9Y10
1
OE1
13
OE2
74LVC827/SO
18
17
16
15
14
13
12
11
20
10
GND
GND
1
2
6
7
VDD
A0
A1
SCL
WP
AT24C1
Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
Y5
Y6
Y7
Y8
VCC
GND
5
SDA
8
VCC
4
GND
3
NC
28
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
15
14
24
GND
12
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
C1
0.1uF
MD0
MD1
MD2
MD3
MD4
MD5
MD6
MD7
eZ80L92 Evaluation Board
96C
0858-001
Sheet
D[7:0]
-CS0
-CS1
-CS2
-IORQ
-ME
-WR
-RD
-CS3
PHI
VDD
SDA
VDD
MRQ
C34
0.1uF
D[7:0]
MD[7:0]
Connectors
of
14
61
Rev
C
Z80L92 D
Kit
5 4 3 2 1
R6
J11
VDD
TRIG1
TRIG2
VDD
GND
-EM_WR_OE
VDD
GND
2
1
2
1
10K
CT4
CT3
CT2
CT1
CT0
MD[7:0]
10K
-MRE
C6
0.1uF
-EX_FL_DIS
R7
SET
C5
0.1uF
MD7
MD6
MD5
MD4
MD3
MD2
MD1
MD0
-EM_WR
-EM_RD
-EM_WR_O
-MRE
E
AN6
-FL_DIS
-CS0
A23
A22
A21
A20
A19
A18
A17
A16
SET
AN0
AN1
AN5
-CS2
AN2
AN3
AN4
10
14
13
11
23
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
12
11
2
9
4
5
6
U16
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
LEAB
LEBA
OEAB
OEBA
CEAB
CEBA
74LCX543/
U10
3
I1
4
I2
5
I3
6
I4
7
I5
9
I6
10
I7
11
I8
12
I9
13
I10
16
I11
2
CLK/I0
22V10A/LCC
1 3107 8
22
B1
21
B2
20
B3
19
B4
18
B5
17
B6
16
B7
15
B8
24
VCC
12
GND
SO
VDD
I/O0
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
I/O4
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
I/O8
I/O9
VCC
GND
EM_D7
EM_D6
EM_D5
EM_D4
EM_D3
EM_D2
EM_D1
EM_D0
GND
M_
M_RING
SCL
SDA
GND
VDD
TIP
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 9
-CON_DIS
-DIS_0
-DIS_IRDA
R10
R11
10K
10K
P-757
C8
0.1uF
-EM_EN
VDD
GND
GND
-CS_EX_IN
-MEM_CEN1
-MEM_CEN2
-MEM_CEN3
-MEM_CEN4
-L_RD
-DIS_FL
C2
0.1uF
TRIG1
TRIG2
-MEM_CEN1
-MEM_CEN2
-MEM_CEN3
-MEM_CEN4
JP4
1
Pin2
JP5
1
Pin2
14
10
9 8
U8C
7
TC7
4LVT125
14
4
5 6
U8B
7
TC7
4LVT125
SW1
SW PUSHBUTTON
SW2
SW PUSHBUTTON
SW3
SW PUSHBUTTON
17
18
19
20
21
23
24
25
26
27
28
14
D5
LT
EM_D7
EM_D6
EM_D5
EM_D4
EM_D3
EM_D2
EM_D1
EM_D0
GND
GND
-EM_RD
-EM_WR
-CT_WR
-AN_WR
-CS3
A6
-FL_DIS
-EX_FL_DIS
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q7
VCC
Q0
Q1
Q2
Q3
Q4
Q5
Q6
Q7
VCC
-DIS_ETH
C7
0.1uF
VDD
J15
2
5
6
9
12
15
16
19
20
10
2
5
6
9
12
15
16
19
20
10
A[23:0]
D[7:0]
MD[7:0]
MD[7:0]
-CS0
-CS1
PHI
-RD
-WR
SDA
SCL
-CS2
-CS2
-CS3
-CS3
-ME
-IORQ
VDD
GND
J3
MRQ
2
1
-IORQ
-DIS_EM
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
D[7:0]
A20
A21
A22
A23
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
GND
-CS0
-CS1
PHI
-RD
-WR
SDA
SCL
VDD
GND
D[7:0]
VDD
R13
10K
-EM_EN
A0
A1
-RD
-WR
A2
A3
A4
A5 A7
U15
3
I1
4
I2
5
I3
6
I4
7
I5
9
I6
10
I7
11
I8
12
I9
13
I10
16
I11
2
CLK/I0
22V10A/LCC_0
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
-CT_WR
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
-AN_WR
I/O0
I/O1
I/O2
I/O3
I/O4
I/O5
I/O6
I/O7
I/O8
I/O9
VCC
GND
U12
3
D0
4
D1
7
D2
8
D3
13
D4
14
D5
17
D6
18
D7
11
CLK
1
OE
74HCT374
U14
3
D0
4
D1
7
D2
8
D3
13
D4
14
D5
17
D6
18
D7
11
CLK
1
OE
74HCT374
17
18
19
20
21
23
24
25
26
27
VDD
28
14
GND
Figure 18. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Schematic Diagram, #2 of 5
12
SIDACTOR P3100SB
U11
C3
0.001uF
GND
U13
SCL
SDA
OVERR
M_IN_A
M_IN_B
M_IN_C
M_IN_D
GND
PCA8550
R12
10K
Title
SizeDocument Number
B
Date:
VDD
N_MUX_O
MUX_SEL
M_OUT_A
M_OUT_B
M_OUT_C
M_OUT_D
GND
-CS_EX_IN
-MEM_CEN1
-MEM_CEN2
-MEM_CEN3
PB0_T0_I
PB1_T1_I
PB2_SS
Schematic,
Friday, October 10, 2003
e
WP
Ferrite Core
C4
0.001uF
16
15
14
13
12
11
10
14
12 11
U8D
7
TC7
J19
2
4
6
8
EX_
evelopment
T1
VDD
GND
GND
ID_2
ID_1
ID_0
13
4LVT125
1
3
5
7
SEL
eZ80L92 Evaluation Board
96
C0858-001
Sheet
User Manual
P4
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
RJ14
-DIS_1
-MOD_DIS
-C
S_EX
Logic
Rev
C
of
24
62
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams
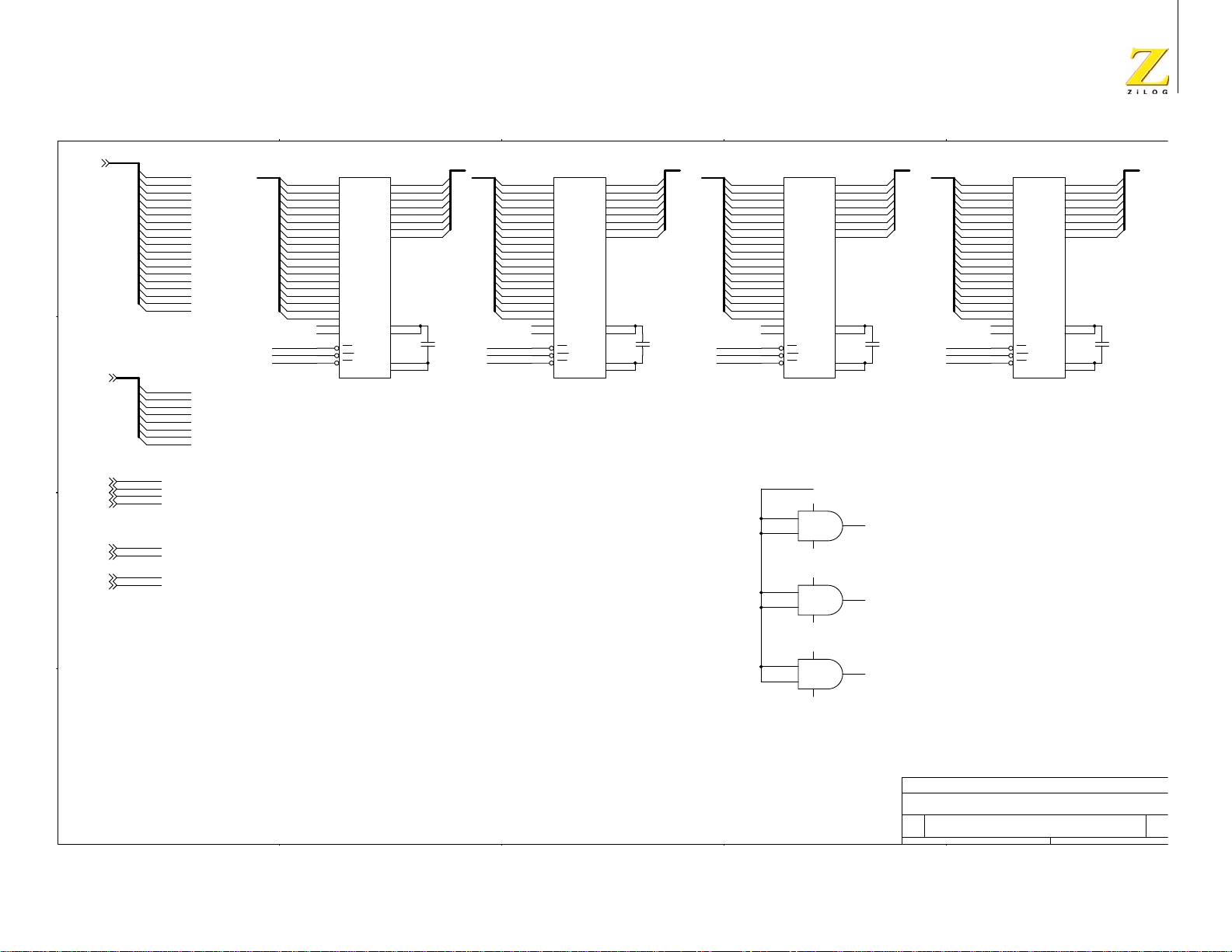
Z80L92 D
Kit
5 4 3 2 1
A[23:0]
A[23:0]
D[7:0]
D[7:0]
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
A[23:0]
-MEM_CEN1
-WR
-RD
1
2
3
4
5
14
15
16
17
18
20
21
22
23
24
32
33
34
35
19
36
6
13
31
U17
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
NC
NC
CE
WE
OE
AS7C34096
VDD0
VDD1
VSS0
VSS1
7
D0
8
D1
11
D2
12
D3
25
D4
26
D5
29
D6
30
D7
9
27
10
28
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
D[7:0]
A[23:0]
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
C9
0.1uF
GND GND GND GND
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
-MEM_CEN2
-WR
-RD
1
2
3
4
5
14
15
16
17
18
20
21
22
23
24
32
33
34
35
19
36
6
13
31
U18
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
NC
NC
CE
WE
OE
AS7C34096
VDD0
VDD1
VSS0
VSS1
7
D0
8
D1
11
D2
12
D3
25
D4
26
D5
29
D6
30
D7
9
27
10
28
D[7:0]
C10
0.1uF
A[23:0]
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
-MEM_CEN3
-WR -WR
-RD
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
1
2
3
4
5
14
15
16
17
18
20
21
22
23
24
32
33
34
35
19
36
6
13
31
U19
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
NC
NC
CE
WE
OE
AS7C34096
VDD0
VDD1
VSS0
VSS1
7
D0
8
D1
11
D2
12
D3
25
D4
26
D5
29
D6
30
D7
9
27
10
28
D[7:0]
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
VDDVDD
C11
0.1uF
A[23:0]
e
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
-MEM_CEN4
-RD
1
2
3
4
5
14
15
16
17
18
20
21
22
23
24
32
33
34
35
19
36
6
13
31
evelopment
U20
A0
D0
A1
D1
A2
D2
A3
D3
A4
D4
A5
D5
A6
D6
A7
D7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
NC
VDD0
NC
VDD1
CE
WE
OE
VSS0
VSS1
AS7C34096
User Manual
D[7:0]
D0
7
D1
8
D2
11
D3
12
D4
25
D5
26
D6
29
D7
30
VDDVDD
9
27
C12
0.1uF
10
28
63
-MEM_CEN1
-MEM_CEN2
-MEM_CEN3
-MEM_CEN4
-RD
-WR
VDD
GND
-MEM_CEN1
-MEM_CEN2
-MEM_CEN3
-MEM_CEN4
-RD
-WR
VDD
GND
GND
9
10
4
5
12
13
U9C
147
TC74LVC08
8
U9B
147
TC74LVC08
6
U9D
147
TC74LVC08
11
Figure 19. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Schematic Diagram, #3 of 5
Title
Schematic,
SizeDocument Number
B
Friday, October 10, 2003
Date:
eZ80L92 Evaluation Board
96
C0858-001
Sheet
Memory
Rev
C
of
34
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams

e
Z80L92 D
Kit
5 4 3 2 1
evelopment
User Manual
64
12345
RESET
C26
0.1
SW4
TXD0
CTS0
RXD0
RTS0
DCD1
DSR1
RXD1
TXD1
CTS1
DTR1
RI1
GND
F1
RXE16
0
J15
1
2
RS485_1_EN
1
2
3
4 5
1
2
3
4 5
J16
RS485_2_EN
D6
S26
U26
RO
RE
DE
DI
DS1487
U27
RO
RE
DE
DI
DS1487
C22
0.1
8
VCC
7
B
6
A
GND
8
VCC
7
B
6
A
GND
1
2
J13
2
3
1
PWR JACK
-RESET
P2
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
CONSOL
5
DB9 Female
P3
1
6
2
7
3
8
4
9
5
MODE
DB9 Male
M
E
PD1_RXD0
PD2_RTS0
PD
0_TXD0
PC1_RXD1
PC2_RTS1
PC
0_TXD1
U23
LM7805C/TO220/0.5A
1 3
IN
+
C23
22uF
R17
10K
VCC
GND
R18
10K
VCC
OUT
GND
2
C32
0.1uF
VDD
26
U22
28
C14
0.1
C15
0.1
PD
PC7_RI1
0_TXD0
PD2_RTS0
VDD
RI1_B
RI1_NB
-CON_DIS
R14
10K
PD3_CTS0
PD1_RXD0
GND
VDD
J14
1
2
3
Header 3
24
1
2
14
13
12
22
23
20
19
18
17
16
15
-MOD_DIS
R16
C1+
C1C2+
C2T1IN
T2IN
T3IN
FORCEOFF
FORCEON
R2OUTB
R1OUT
R2OUT
R3OUT
R4OUT
R5OUT
C25
0.1
PC
0_TXD1
PC4_DTR1
PC2_RTS1
10K
PC5_DSR1
PC3_CTS1
PC1_RXD1
PC6_DCD1
RI1_NB
C24
0.1
RI1_B
VCC
GND
25
T1OUT
T2OUT
T3OUT
INVALID
MAX324
V+
V-
R1IN
R2IN
R3IN
R4IN
R5IN
5CAI
28
24
1
2
14
13
12
22
23
20
19
18
17
16
15
27
3
9
10
11
21
4
5
6
7
8
VDD
U24
C1+
C1C2+
C2T1IN
T2IN
T3IN
FORCEOFF
FORCEON
R2OUTB
R1OUT
R2OUT
R3OUT
R4OUT
R5OUT
TXD0
RTS0
CTS0
RXD
C13
0.1uF
J10
HEADER 5
C17
C16
0.1uF
0.1uF
GND
0
C21
0.1
26
25
VCC
GND
T1OUT
T2OUT
T3OUT
INVALID
R1IN
R2IN
R3IN
R4IN
R5IN
MAX324
27
V+
3
V-
9
10
11
21
4
5
6
7
8
5CAI
C27
TXD1
DTR1
RTS1
0.1
DSR1
RI1
CTS1 RTS1
RXD
1
DCD1
Figure 20. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Schematic Diagram, #4 of 5
5V
C20
0.1
U25
3 2
VIN
1
GND
LT1086-3.3/TO
-DIS_0
J17
1
2
RT_
1
C18
0.1uF
J18
1
2
RT_
2
Title
Schematic,
SizeDocument Number
B
Friday, October 10, 2003
Date:
9VDC
9VDC
VCC
VCC
+
C19
22/10
VOUT
3.3V
+
220
R23
12
0
R22
12
0
C28
22/6.3
C29
0.1
GND
POWER & RS232
eZ80L92 Evaluation Board
96
C0858-001
Sheet
VDD
VDD
R15
68
0
21
D7
GREEN
3.3 O
K
GND
P4
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
con8
-DIS_1
Rev
C
of
44
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams

Z80L92 D
Kit
MATES WITH AMP = 749268-1
P1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
LENGTH = 5’
WIRES 28 AWG
Figure 21. eZ80Acclaim!® Development Platform Schematic Diagram, #5 of 5—RS-485 Cable
e
evelopment
User Manual
65
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams

Z80L92 D
Kit
eZ80L92 Module
Figure 22 through Figure 30 illustrate the layout of the eZ80L92 Module.
e
evelopment
User Manual
66
RAM
03
SRAM
ROM
04
NOR-Flash
Power
09
PowerSupply
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-RD
-WR
-CS1
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-RD
-WR
-CSFLASH
-RESFLASH
-FLASHWE
V3.3
GND
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-RD
-WR
-CS1
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-RD
-WR
-CSFLASH
-RESFLASH
-FLASHWE
V3.3
GND
02
05
CPU
eZ80
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-RD
-WR
Ethernet
CS8900A
-RESET
-IOREQ
-MREQ
-INSTRD
-WAIT
-HALT_SLP
-BUSREQ
-BUSACK
-NMI
CLK_OUT
RTC_VDD
IICSDA
IICSCL
PB[0..7]
PC[0..7]
PD[0..7]
-CS[0..3]
JTAG[1..4]
SD[0..7]
SA[0..3]
IOCHRDY
-ETHRD
-ETHWR
ETHIRQ
-SLEEP
-ACTIVE
-DIS_ETH
TDO
-IOREQ
-MREQ
-INSTRD
-WAIT
-HALT_SLP
-BUSREQ
-BUSACK
-NMI
CLK_OUT
RTC_VDD
IICSDA
IICSCL
PB[0..7]
PC[0..7]
PD[0..7]
-CS[0..3]
JTAG[1..4]
TDO
ETHIRQ
-SLEEP
-ACTIVE
-RESET
-RESET
-WAIT
SD[0..7]
SA[0..3]
IOCHRDY
-ETHRD
-ETHWR
Peripherals
07
Reset
Logic
06
CTR L-Logic
-RESET
-RESET
-W AIT
PD[0..7]
-CS[0..3]
SA[0..3]
SD[0..7]
IRDA_TXD
IRDA_RXD
IRDA_SD
A[0..23]
D[0..7]
D[0..7]
IRDA_TXD
IRDA_RXD
IRDA_SD
-DIS_FL
-DIS_IRDA
-CSFLASH
-RESFLASH
-ETHRD
-ETHWR
IOCHRDY
-WR
-WR
A[0..23]
ETHIRQ
-SLEEP
ETHIRQ
IRDA_TXD
IRDA_RXD
IRDA_SD
-RD
-RD
-SLEEP
-ACTIVE
-ACTIVE
IRDA_TXD
IRDA_RXD
IRDA_SD
-CSFLASH
-RESFLASH
-DIS_FL
-DIS_IRDA
-RESET
-FLASHWE
-IOREQ
-MREQ
-INSTRD
-WAIT
-HALT_SLP
-BUSREQ
-BUSACK
-NMI
CLK_OUT
RTC _VDD
IICSDA
IICSCL
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-WR
-RD
PB[0..7]
PC[0..7]
PD[0..7]
-CS[0..3]
JTAG[1..4]
TDO
V3.3
GND
08
Connector
Headers
-RESET
-FLASHWE
-IOREQ
-MREQ
-INSTRD
-WAIT
-HALT_SLP
-BUSREQ
-BUSACK
-NMI
CLK_OUT
RTC _VDD
IICSDA
IICSCL
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-WR
-RD
-DIS_FL
-DIS_IRDA
PB[0..7]
PC[0..7]
PD[0..7]
-CS[0..3]
JTAG[1..4]
TDO
-DIS_ETH
V3.3_EXT
GND_EXT
Figure 22. eZ80L92 Module Schematic Diagram, #1 of 9—Top Level
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams

Z80L92 D
Kit
eZ80=IIC-bus-master
IICSDA
IICSCL
CLK_OUT
PB[0..7]
PC[0..7]
PD[0..7]
-RESET
JTAG[1..4]
TDO
-RD
-WR
-IOREQ
-MREQ
-INSTRD
-HALT_SLP
-BUSREQ
-BUSACK
-NMI
A[0..23]
-CS[0..3]
D[0..7]
RTC_VDD
-WAIT
CLK_OUT
IICSDA
IICSCL
PB[0..7]
PC[0..7]
PD[0..7]
-RESET
JTAG[1..4]
TDO
-RD
-WR
-IOREQ
-MREQ
-INSTRD
-WAIT
-HALT_SLP
-BUSREQ
-BUSACK
-NMI
A[0..23]
-CS[0..3]
D[0..7]
RTC _VDD
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
A[0..23]
V3.3V3.3 V3.3
C21
1nF
IICSDA
IICSCL
CLK_OUT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
-CS[0..3]
C22
1nF
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
VDD
VSS
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
VDD
VSS
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
A20
100
994998
PHI
SCL
A21
A22
2634273228
A21
A22
C23
1nF
PB7
PB6
PB5
PB4
PB3
PB2
PB1
PB0
97
SDA
96
VSS
VDD
93
94
95
PB6/MISO
PB7/MOSI
PB5/T5_OUT
92
PB4/T4_OUT
89
90
91
PB2/SS
PB3/SCK
U8
878284
88
PB0/T0_IN
PB1/T1_IN
eZ80L92
TQFP100
CS2
-CS3
CS3
33
VDD
D0
D1
D2
VSS
D3
35
36
37
38
394740
D0D1D2D3D4D5D6
A23
A23
CS1
CS0
30
-CS0
-CS1
D[0..7]
31
-CS2
PLACE CAPS CLOSE
TO PINS
97,7,33,43
XOUT
86
VDD
XOUT
D4RDD5
XIN
85
41
XIN
D6
VSS
D7
42
D7
PC7
PC6
PC5
PC4
83
81
807279657829774576
PC7/RI1
PC5/DSR1
PC6/DCD1
PD1/RxD0/IR_RXD
IOREQ
VDD
VSS
46
43
44
-MREQ
-IOREQ
PC[0..7]PB[0..7]
PC3
PC2
PC1
PC0
PC0/TxD1
PC1/RxD1
PC3/CTS1
PC2/RTS1
PC4/DTR1
PD0/TxD0/IR_TXD
MREQ
PD7/RI0
PD6/DCD0
PD5/DSR0
PD4/DTR0
PD3/CTS0
PD2/RTS0/IR_SD
VDD
TDO
TDI (ZDA)
TRIGOUT
TCK (ZCL)
TMS
VSS
RTC_VDD
RTC_XOUT
RTC_XIN
VSS
VDD
HALT_SLP
BUSACK
BUSREQ
RESET
INSTRD
WAIT
WR
50
48
-INSTRD
-WAIT
-RD
-WR
NMI
PD7
75
PD6
74
PD5
73
PD4
PD3
71
PD2
70
PD1
69
PD0
68
67
TDO
66
TDI JTAG1
TRIGOUT JTAG2
64
TCK JTAG3
63
TMS JTAG4
62
61
RTC _VDD
60
RTC_XOUT
59
RTC_XIN
58
57
56
-HALT_SLP
55
-BUSACK
54
-BUSREQ
53
-NMI
52
-RESET
51
RTC _XOUT
RT C_XIN
(= JTAG0)
=
=
=
=
R32
220
XOUT
PD[0..7]
R29
10k
XIN
3.3H
JTAG[1..4]
Y3
32.768kHz
XTAL3
C24
18pF
L1
e
Y2
C16
15pF
RTC _VDD
C18
100nF
C20
18pF
evelopment
User Manual
48 MHz
HC49SM
1M
R27
C17
4.7pF
V3.3
R28
100
D1
TMM BAT 41
MINIMELF_AK
GoldCap
C19
0,1F
GOLDCAP_SD
VDD
VSS
V3.3
GND
C25
220pF
67
Figure 23. eZ80L92 Module Schematic Diagram, #2 of 9—100-Pin QFP eZ80L92 Device
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams

e
Z80L92 D
Kit
evelopment
User Manual
68
A[0..23]
-CS1
D[0..7]
-RD
-WR
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-CS1
-RD
-WR
A21/A22/A23
not used
here
A18
A0
A1
A2
A3
-CS1
D0
D1
D2
D3
-WR
A12
A6
A4
A17
U1
1
A0
2
A1
3
A2
4
A3
5
A4
6
CE
7
I/O0
8
I/O1
9
VDD
10
VSS
11
I/O2
12
I/O3
13
WE
14
A5
15
A6
16
A7
17
A8
18
A9
512kx8 SRAM
SOJ36.400
N.C.
A18
A17
A16
A15
OE
I/O7
I/O6
VSS
VDD
I/O5
I/O4
A14
A13
A12
A11
A10
N.C.
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
A8
A7
A5
A16
A15
A14
A13
-RD
D7
D6
D5
D4
A11
A10A9
A20
A19
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
RN1
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
4.7k
12
C7
100nF
V3.3
GND
14
11 10
U2E
74LVC04/SO
14
9 8
14
13 12
U2D
74LVC04/SO
U2F
74LVC04/SO
VDD
VSS
Figure 24. eZ80L92 Module Schematic Diagram, #3 of 9—36-Pin SRAM Device
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams

Z80L92 D
Kit
D[0..7]
e
evelopment
User Manual
69
A[0..23]
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-CSFLASH
-RD
-WR
-RESFLASH
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
A6
A7
A8
A9
A10
A11
A12
A13
A14
A15
A16
A17
A18
A19
36
40
13
37 38
Pin37=N.C.
for 4MbitFlashes
D[0..7]
A[0..23]
-CSFLASH
-RD
-WR
-RESFLASH
30
23
31
VDD
VSS
39
U3
8
A8
7
A9
A10
6
A11
5
A12
4
A13
3
A14
2
A15
1
A16
A17
A18
A19 N.C.
A22/A23
not used here
Intel-Type
DQ0A0
VDD
DQ1A1
DQ2A2
DQ3A3
DQ4A4
DQ5A5
DQ6A6
DQ7A7
CE
OE
WE
RP
WP
VPP
N.C.
VSS
MT28F008B3VG
TSOP40.20MM
2521
2620
2719
2818
3217
3316
3415
3514
22
24
9
10
12
11
29
-CSFLASH
-RD
-WR
-RESFLASH
-WP
VPP
A21
A20
D0DFLASH0
=
D1DFLASH1
=
D2DFLASH2
=
D3DFLASH3
=
D4DFLASH4
=
D5DFLASH5
=
D6DFLASH6
=
D7DFLASH7
=
0R
R2
A20/A21 used for
16/32Mbit-Flash
C8
100nF
14
U2A
12
74L VC04/SO
VDD
R1
10K
-FLASHWE
V3.3
VDD
VSS
GND
-FLASHWE
-FLASHWE
Note: Must be pulled ’low’
externally for programming.
Figure 25. eZ80L92 Module Schematic Diagram, #4 of 9—Flash Device
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams
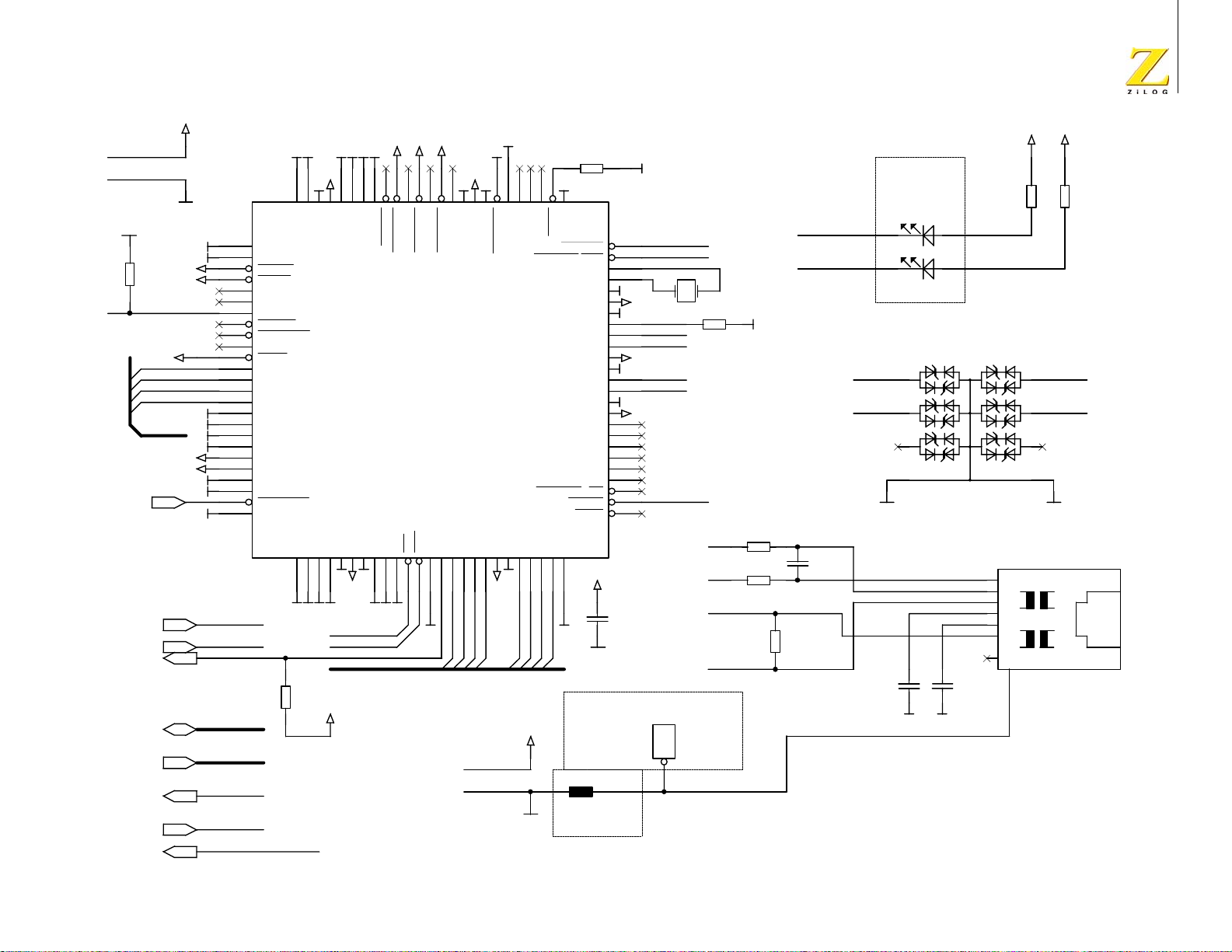
Z80L92 D
Kit
V3.3
e
evelopment
User Manual
70
VDD
VSS
GND
R22
4k7
ETHIRQ
SA0
SA1
SA2
SA3
SA[0..3]
-DIS_ETH
device addresses:
00300h bis 0030Fh
-ETHRD
-ETHWR
IOCHRDY
SD[0..7]
SA[0..3]
ETHIRQ
-SLEEP
-ACTIVE
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
SD11
SD9
SD8
MEMW
MEMR
INTRQ2
INTRQ1
INTRQ0
IOCS16
MEMCS16
INTRQ3
SHBE
SA0
SA1
SA2
SA3
SA4
SA5
SA6
SA7
SA8
SA9
SA10
SA11
REFRESH
SA12
-LANLED-ACTIVE
SD10
SA13
515253
R34
10k
0603
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
-ETHRD
-ETHWR -ETHWR
SD[0..7]
SA[0..3]
ETHIRQ
-SLEEP
=
DVSS
SA14
SA15
DVDD
SA16
54
555657
-ETHRD
SD13
SD12
DVSS
DVDD
SD[0..7]
15
16
17
18
SD15
SD14
CSOUT
DMACK0
DMARQ0
DMACK2
DMACK1
DMARQ1
DVSS
DMARQ2
U7
CS8900A-CQ3
TQFP100
SD0
IOW
AEN (TCK)
IOCHRDY
64
SD1
656667
SD0
SD1
SA17
DVSS
585960
SA18
SA19
IOR
616263
DVDD
SD2
SD2
VDD
VSS
DVSS
CHIPSEL
EEDATAIN
EEDATAOUT (TDO)
SD4
SD3
DVDD
DVSS
717273
68
69
70
SD3
SD4
V3.3
GND
R19
10k
138239340441542643744845946104711481249135014
AVSS
ELCS
EESK
EECS
LANLED
LINKLED/HC0
XTAL2
XTAL1
AVSS
AVDD
AVSS
RES
RXD-
RXD+
AVDD
AVSS
TXDTXD+
AVSS
AVDD
DO-
DO+
BSTATUS/HC1
SLEEP
TEST
SD5
SD6
SD7
RESET
74
75
SD5
SD6
SD7
through hole
solder pad
place
near
J1
L2
ferrite
tbd
don’t stuff
CI+
DI+
CI-
DI-
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
C13
100nF
-LANLED
-LINKLED
R23
RXD-
4k99/1%
RXD+
TXDTXD+
-SLEEP
int. Pull-Up
JP4
HEADER 1
SIP1
don’t
1
stuff
green
-LANLED
8R2
C12
560pF
8R2
-LINKLED
yellow
RD+
Y1
20.000 MHz
HC49SM
TXD-
R24
TXD+
R25
RXD- R D-
R26
100
RXD+
CASE
90 degree,
stacked
dual-LED
LD1B
LD1A
43
21
ESD protection array
U9
RD+
1
RD- TD-
2
3
4 5
GND GND
TD-
TD+
CTD
CRD
C14
100nF
C15
100nF
R20
220
0603
LCDA15C-6
SO8.150
1
1
2
2
3
3
4
4
5
5
6
6
8
8
TX+ <-> 1
TX- <-> 2
RX+ <-> 3
RX- <-> 6
R21
220
0603
TD+
8
7
6
J1
HFJ11-1041
HALOFASTJACK
Figure 26. eZ80L92 Module Schematic Diagram, #5 of 9—E-NET Module
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams
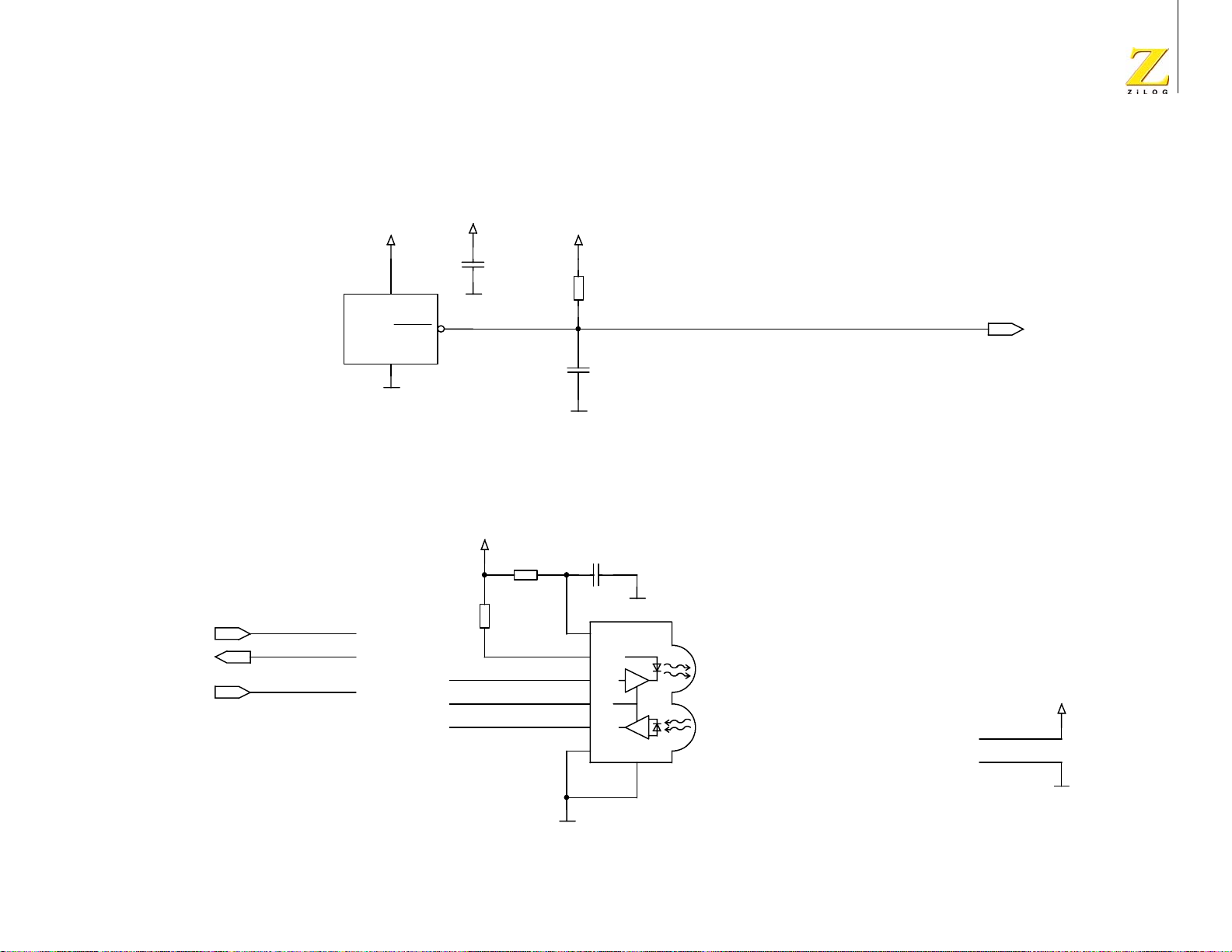
Z80L92 D
Kit
power supervisor
V3.3
U4
RESET
GND VDD
MAX6328UR29
1 3
SOT-23-L3
alternative:
Maxim
MAX6802UR29D3
C9
100nF
0603
2
open-drain
R3
2k2
0603
C10
10nF
0603
-RESET
e
evelopment
User Manual
71
-RESET
IR-transceiver
V3.3
R5
68R
R6
IRDA_TXD
IRDA_RXD
IRDA_SD
IRDA_TXD
IRDA_RXD
IRDA_SD
2R7, 0.25W
1206
(MMA 020 4)
IRDA_TXD
IRDA_SD
IRDA_RXD
Figure 27. eZ80L92 Module Schematic Diagram, #6 of 9—IrDA Reset
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams
C11
330nF
U5
5
VCC
1
LEDA
2
TXD
4
SD
3
RXD
6
GND
T
ZHX1810
0
V3.3
VDD
VSS
GND

e
Z80L92 D
Kit
evelopment
User Manual
72
A[0..23]
D[0..7]
-CS[0..3]
IICSDA
IICSCL
CLK_OUT
-DIS_FL
-DIS_IRDA
-FLASHWE
RTC_VDD
-DIS_ETH
PB[0..7]
PC[0..7]
PD[0..7]
-RESET
-RD
-WR
-IOREQ
-MREQ
-INSTRD
-WAIT
-HALT_SLP
-BUSREQ
-BUSACK
-NMI
JTAG[1..4]
TDO
A[0..23]
D[0..7]
-CS[0..3]
IICSDA IICSDA
IICSCL IICSCL
CLK_OUT
-DIS_FL
R7
4k7
R9
33
place near eZ80
R8
4k7
EZ80CLK
output (PHI)
-DIS_IRDA
-FLASHWE
RTC_VDD
PB[0..7]
PC[0..7]
PD[0..7]
-RESET
-RD
-WR
-IOREQ
-MREQ
-INSTRD
-HALT_SLP
-BUSREQ -BUSREQ
-BUSACK
-NMI
JTAG[1..4]
TDO
-W AIT-WAIT
V3.3
R10
2k2
0603
A6
A10
GND_EXT
A8
A13
A15
A18 A16
A19
A2
A11
A4
A5
DIS_ETH
A21
A22
-CS0
-CS2
D1
D3
D5
D7
-MREQ
GND_EXT
-WR
-BUSACK
R36
10K
R33
2k2
0603
R11
10k
JTAG1 TD I
=
(JTAG0 =)
JTAG2 TRIGOUT
JTAG3 TCK
JTAG4 TMS
TDO
=
=
=
JP1
12
34
56
78
910
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
HEADER 25X2
IDC50
R12
10k
A0
A3
V3.3_EXT
A7
A9
A14
GND_EXT
A1
A12
A20
A17
-DIS_FL
V3.3_EXT
A23
-CS1
D0
D2
D4
GND _EXT
D6
-IOREQ
-RD
-INSTRD
-BUSREQ
connector 2connector 1
PB7
PB5
PB3
PB1
GND_EXT
PC6
PC4
PC2
PC0
PD6
PD5
PD3
PD1
GND_EXT
TCK TMS
RTC _VDD
IICSCL
IICSDA
-FLASHWE
-RESET
V3.3_EXT
-HALT_SLP
V3.3_EXT
JP2
12
34
56
78
910
11 12
13 14
15 16
17 18
19 20
21 22
23 24
25 26
27 28
29 30
31 32
33 34
35 36
37 38
39 40
41 42
43 44
45 46
47 48
49 50
HEADER 25X2
IDC50
PB6
PB4
PB2
PB0
PC7
PC5
PC3
PC1
PD7
GND _EXT
PD4
PD2
PD0
TDITDO
TRIGOUT
EZ80CLK
GND_EXT
-DIS_IRDA-CS3
-W AIT
GND_EXT
-NMI
V3.3_EXT
GND_EXT
V3.3_EXT
GND_EXT
GND
R13
4k7
Figure 28. eZ80L92 Module Schematic Diagram, #7 of 9—Headers
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams
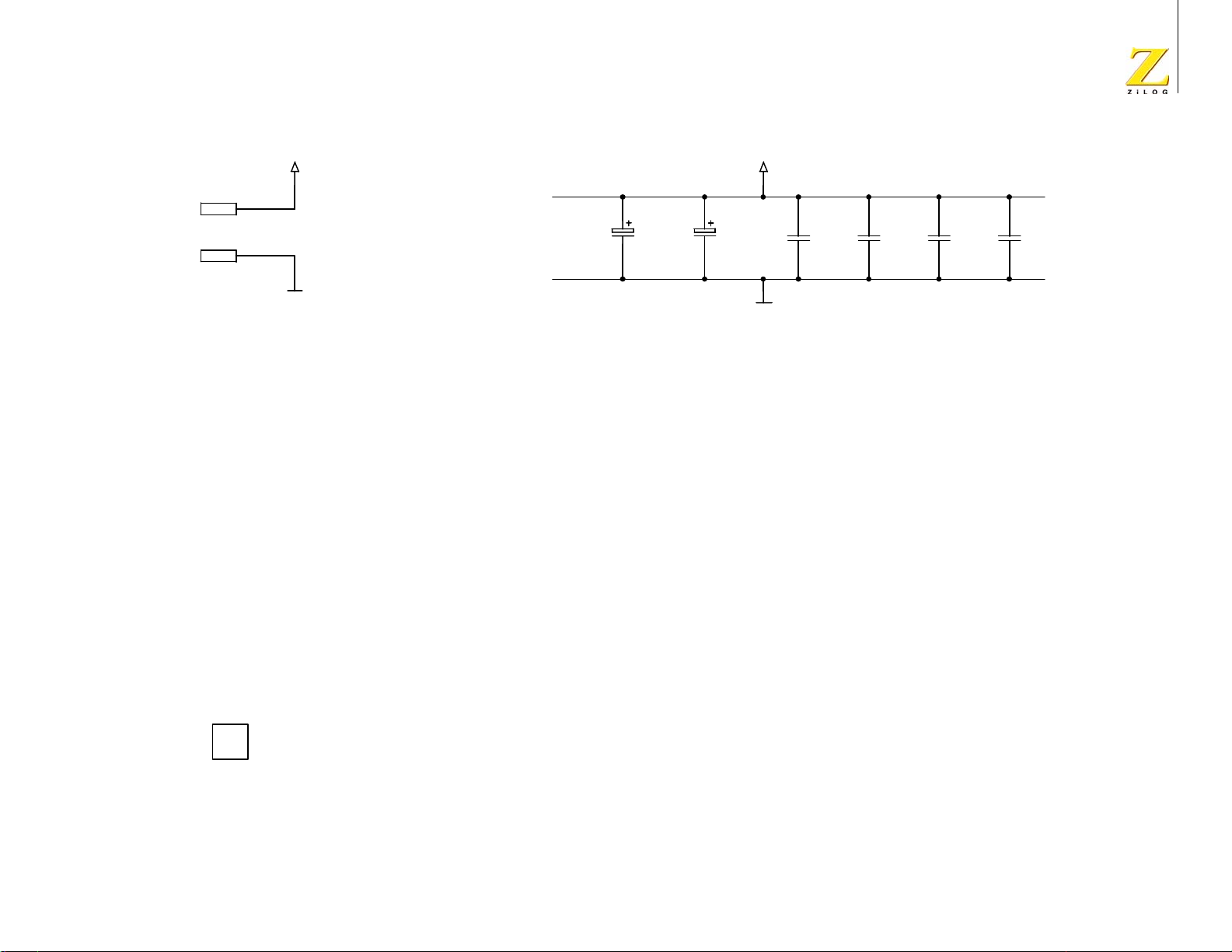
Z80L92 D
Kit
V3.3
GND
V3.3
GND
V3.3
GND
V3.3
GND
no power supply on board!
C1
47uF
TAJC
C2
47uF
TAJC
e
common power plane
C3
1nF
C4
100nF
C5
1nF
common ground plane
evelopment
User Manual
73
C6
100nF
Input: VDD(=V3.3) = 3.3V –5%
Power: Pmax = 1.6W
Ptyp = 0.4W
Current: Imax = 200mA (IrDA not in use)
Imax = 460mA (IrDA in use)
Ityp = 100mA
PCB1
E-NET Module Rev.B
98Cxxxx-xxx
Figure 29. eZ80L92 Module Schematic Diagram, #8 of 9—Power Supply
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams

e
Z80L92 D
Kit
evelopment
User Manual
74
D[0..7] SD[0..7]
A[0..23] SA[0..3]
PD[0..7]
-RESET
-DIS_FL
-DIS_IRDA
-RD
-WR
-CS[0..3]
-W AIT
PD[0..7]
-RESET
-W AIT
-DIS_FL
-DIS_IRDA
-RD
-WR
-CS[0..3]
only A0,A1,A2,A3
are used here
PD3 and PD5
not used here
-CS1 and-CS2
not used
-RD
-CS3 -CSETH
-WR
here
VDD
-DIS_FL
-DIS_IRDA
R30
10k
0603
3 4
R17
10k
0603
5 6
14
14
74LVC04/SO
U2B
DIS_FL
74LVC04/SO
U2C
DIS_IRDA
A[0..23] SA[0..3]
U6D
12
13
1
2
4
5
9
10
74LCX32
TSSOP14
U6A
74LCX32
TSSOP14
U6B
74LCX32
TSSOP14
U6C
74LCX32
TSSOP14
=
-CS0
IR_SDPD2
=
=
=
SA0A0
=
SA1A1
=
SA2A2
=
SA3A3
VDD
14
-ETHRD
11
PD7
PD6
=
R14
R15
don’t stuff
14
-ETHWR
3
14
6
14
8
-CSFLASH
IRDA_SD
V3.3
-W AIT
0R
0R
R35 0
=
=
=
SD[0..7]D[0..7]
SA[0..3]A[0..23]
-ETHRD
-ETHWR
ETHIRQPD4
-SLEEP
-ACTIVE
IRDA_TXDPD0
IRDA_RXDPD1
IRDA_SD
-RESFLASH-RESET
-CSFLASH
SD[0..7]D[0..7]
-ETHRD
-ETHWR
ETHIRQ
-SLEEP
-ACTIVE
IOCHRDY
IRDA_TXD
IRDA_RXD
IRDA_SD
-RESFLASH
-CSFLASH
VDD
VSS
GND
Figure 30. eZ80L92 Module Schematic Diagram, #9 of 9—Control Logic
UM012913-0407 Schematic Diagrams

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
Appendix A
General Array Logic Equations
Appendix A provides the equations for disabling the Ethernet signals
provided by the U10 and U15 General Array Logic (GAL) devices.
U10 Address Decoder
//`define idle 2'b00
//`define state1 2'b01
//`define state2 2'b11
//`define state3 2'b10
// FOR eZ80
// This PAL generates 4 memory chip selects
module l92_decod(
nCS_EX, //Enables Extension Module's Memory when Low
nFL_DIS, //when Low WEB Module Flash is disabled (nDIS_FL=0),
nCS0,
A7, //A23
A6, //A22
A5, //A21
A4, //A20
A3, //A19
A2, //A18
A1, //A17
A0, //A16
nCS2,
nEX_FL_DIS, //disables Flash on the expansion module, when Low
nEM_EN, //enables Development Platform LED and
nDIS_FL, //disables E-NET Module Flash when Low
nL_RD, //enables local data bus to be read by CPU
nmemen1,
®
Development Platform Rev B
//when High nDIS_FL depends upon state of nmemenX
//the general-purpose port.
75
UM012913-0407 Appendix A

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
76
nmemen2,
nmemen3,
nmemen4
);
input
nFL_DIS /* synthesis loc="P4"*/,
nCS0 /* synthesis loc="P5"*/,
nCS2 /* synthesis loc="P3"*/, //was 23
A7 /* synthesis loc="P6"*/,
A6 /* synthesis loc="P7"*/,
A5 /* synthesis loc="P9"*/,
A4 /* synthesis loc="P10"*/,
A3 /* synthesis loc="P11"*/,
A2 /* synthesis loc="P12"*/,
A1 /* synthesis loc="P13"*/,
A0 /* synthesis loc="P16"*/,
nEX_FL_DIS /* synthesis loc="P2"*/;
//input[7:0] A; upper part of Address Bus of L92
//A23=A7,A22=A6,A21=A5,A20=A4,A19=A3
//A18=A2,A17=A1,A16=A0
output
nCS_EX /* synthesis loc="P17"*/, //enables memory on the
//Expansion Module
nmemen1 /* synthesis loc="P18"*/, //enables memory on the
//Development Platform
nmemen2 /* synthesis loc="P19"*/,
nmemen3 /* synthesis loc="P20"*/,
nmemen4 /* synthesis loc="P21"*/,
nEM_EN /* synthesis loc="P24"*/, //enables LED and the
//general-purpose port.
nDIS_FL /* synthesis loc="P25"*/,
nL_RD /* synthesis loc="P23"*/
;
General Array Logic Equations UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
wire nCS_EX,
nmemen1,
nmemen2,
nmemen3,
nmemen4;
//wire MOD_DIS =
((nmemen1==0)|(nmemen2==0)|(nmemen3==0)|(nmemen4==0));//if any
//of the signals is Low,
//Flash on the Module will be
//disabled if nDIS_FL is High
wire nEXP_EN = ~((nCS0==0)&(A7==0)&(A6==1));//expansion module
//Flash enabled if this is 0
//wire nDIS_FL = (nFL_DIS) ? ~nEXP_EN : ~(nFL_DIS);
77
wire nDIS_FL = nFL_DIS & nEXP_EN; //if either of them is 0 Flash is
//disabled
assign nCS_EX = (nEX_FL_DIS) ? nEXP_EN : ~(nEX_FL_DIS);
assign nL_RD =
~((nmemen1==0)|(nmemen2==0)|(nmemen3==0)|(nmemen4==0)|(nEM_EN==0
)|(nCS_EX==0));
assign nmemen4 = ~((nCS2==0)&({A7,A6,A5,A4,A3}==5'h17));
assign nmemen3 = ~((nCS2==0)&({A7,A6,A5,A4,A3}==5'h16));
assign nmemen2 = ~((nCS2==0)&({A7,A6,A5,A4,A3}==5'h15));
assign nmemen1 = ~((nCS2==0)&({A7,A6,A5,A4,A3}==5'h14));
assign nEM_EN = ~((nCS2==0)&({A7,A6,A5,A4,A3,A2,A1,A0}==8'h80));
endmodule
U15 Address Decoder
`define anode 8'h00
`define cathode 8'h01
`define latch 8'h02
// FOR eZ80
UM012913-0407 General Array Logic Equations
®
Development Platform Rev B

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
78
// This PAL generates signals that control Expansion Module
// access, LED and the general-purpose port.
// This device is a GAL22LV10-5JC (5ns tpd) or equivalent with
// Package = 28 pin PLCC
//
//
module l92_em_pal(
nDIS_EM,
nEM_EN,
A0,
A1,
A2,
A3,
A4,
A5,
A6,
A7,
nRD,
nCS,
nWR,
nMEMRQ,
nIORQ,
nEM_RD,
nEM_WR,
nAN_WR,
nCT_WR,
nDIS_ETH
);
input nDIS_EM /* synthesis loc="P3"*/,
nEM_EN /* synthesis loc="P4"*/,
A0 /* synthesis loc="P5"*/,
A1 /* synthesis loc="P6"*/,
A2 /* synthesis loc="P10"*/,
A3 /* synthesis loc="P11"*/,
A4 /* synthesis loc="P12"*/,
General Array Logic Equations UM012913-0407

eZ80L92 Development Kit
A5 /* synthesis loc="P13"*/,
A6 /* synthesis loc="P27"*/,
A7 /* synthesis loc="P26"*/,
nIORQ /* synthesis loc="P2"*/,
nRD /* synthesis loc="P7"*/,
nCS /* synthesis loc="P25"*/, //CS3 for CS9800
nWR /* synthesis loc="P9"*/,
nMEMRQ /* synthesis loc="P16"*/;
output
nEM_RD /* synthesis loc="P17"*/,
nEM_WR /* synthesis loc="P18"*/,
nCT_WR /* synthesis loc="P19"*/,
nAN_WR /* synthesis loc="P20"*/,
nDIS_ETH /* synthesis loc="P21"*/;
User Manual
79
parameter anode=8'h00;
parameter cathode=8'h01;
parameter latch=8'h02;
wire [7:0] address={A7,A6,A5,A4,A3,A2,A1,A0};
assign nEM_WR =
~((nDIS_EM==1)&(nWR==0)&(nEM_EN==0)&(address==latch));
assign nEM_RD =
~((nDIS_EM==1)&(nRD==0)&(nEM_EN==0)&(address==latch));
assign nAN_WR =
~((nDIS_EM==1)&(nWR==0)&(nEM_EN==0)&(address==anode));
assign nCT_WR =
~((nDIS_EM==1)&(nWR==0)&(nEM_EN==0)&(address==cathode));
assign nDIS_ETH = ~(nCS);
endmodule
UM012913-0407 General Array Logic Equations

eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
80
General Array Logic Equations UM012913-0407

Customer Support
For answers to technical questions about the product, documentation,
or any other issues with ZiLOG’s offerings, please visit ZiLOG’s Knowledge Base at http://www.zilog.com/kb
For any comments, detail technical questions, or reporting problems,
please visit ZiLOG’s Technical Support at http://support.zilog.com
eZ80L92 Development Kit
User Manual
81
.
.
UM012913-0407

Warning:
DO NOT USE IN LIFE SUPPORT
LIFE SUPPORT POLICY
ZiLOG'S PRODUCTS ARE NOT AUTHORIZED FOR USE AS CRITICAL
COMPONENTS IN LIFE SUPPORT DEVICES OR SYSTEMS WITHOUT THE
EXPRESS PRIOR WRITTEN APPROVAL OF THE PRESIDENT AND GENERAL
COUNSEL OF ZiLOG CORPORATION.
As used herein
Life support devices or systems are devices which (a) are intended for surgical implant
into the body, or (b) support or sustain life and whose failure to perform when properly
used in accordance with instructions for use provided in the labeling can be reasonably
expected to result in a significant injury to the user. A critical component is any
component in a life support device or system whose failure to perform can be reasonably
expected to cause the failure of the life support device or system or to affect its safety or
effectiveness.
Document Disclaimer
©2007 by ZiLOG, Inc. All rights reserved. Information in this publication concerning the
devices, applications, or technology described is intended to suggest possible uses and
may be superseded. ZiLOG, INC. DOES NOT ASSUME LIABILITY FOR OR
PROVIDE A REPRESENTATION OF ACCURACY OF THE INFORMATION,
DEVICES, OR TECHNOLOGY DESCRIBED IN THIS DOCUMENT. ZiLOG ALSO
DOES NOT ASSUME LIABILITY FOR INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY
INFRINGEMENT RELATED IN ANY MANNER TO USE OF INFORMATION,
DEVICES, OR TECHNOLOGY DESCRIBED HEREIN OR OTHERWISE. The
information contained within this document has been verified according to the general
principles of electrical and mechanical engineering.
Z8, Z8 Encore!, eZ80, and eZ80Acclaim!, and Z8 Encore! XP are registered trademarks of ZiLOG, Inc. All
other product or service names are the property of their respective owners.
 Loading...
Loading...